
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Basic Research
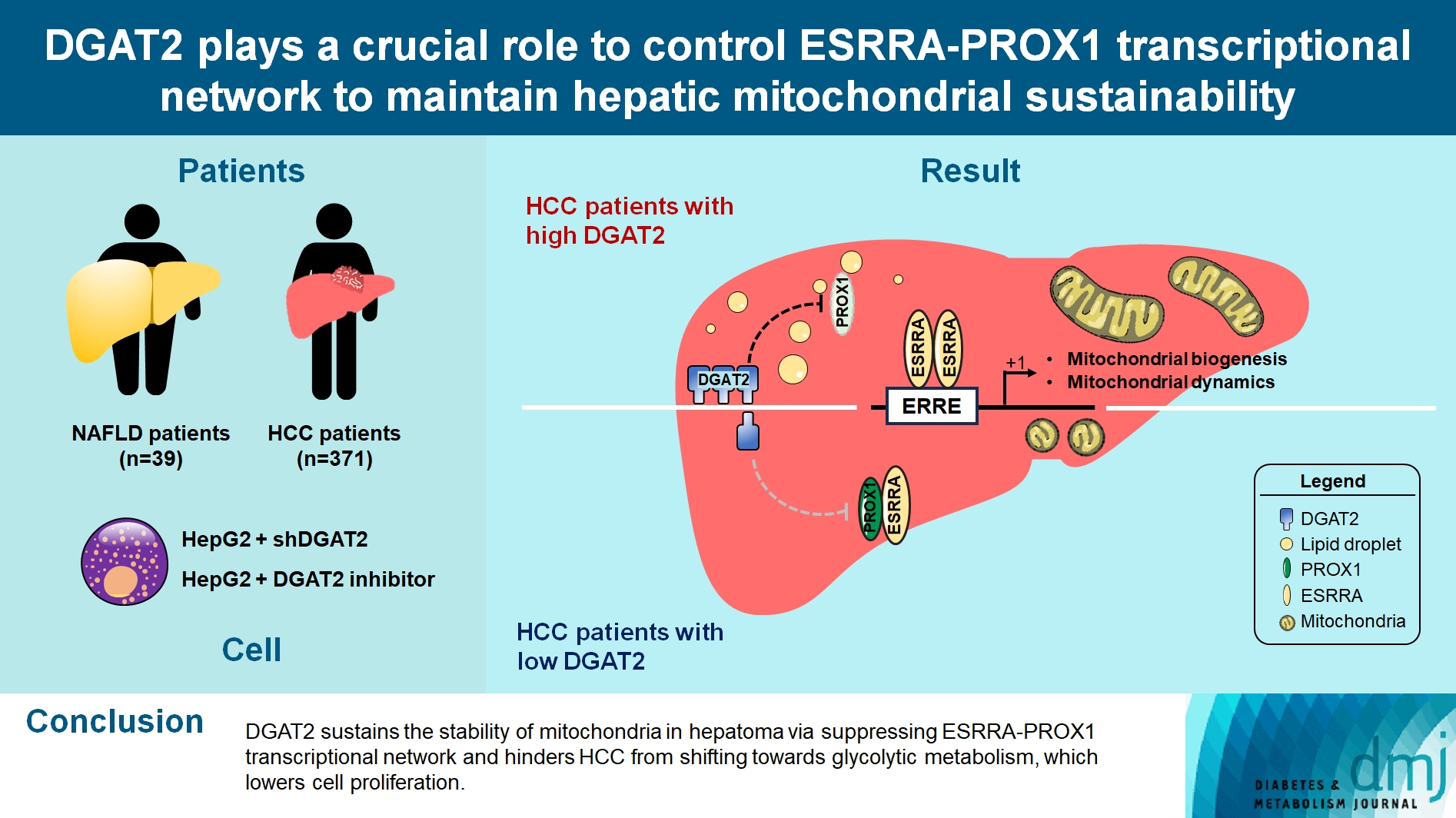
- DGAT2 Plays a Crucial Role to Control ESRRAPROX1 Transcriptional Network to Maintain Hepatic Mitochondrial Sustainability
- Yoseob Lee, Yeseong Hwang, Minki Kim, Hyeonuk Jeon, Seyeon Joo, Sungsoon Fang, Jae-Woo Kim
- Received October 13, 2023 Accepted December 11, 2023 Published online April 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0368 [Epub ahead of print]
- 402 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2) synthesizes triacylglycerol (TG) from diacylglycerol; therefore, DGAT2 is considered as a therapeutic target for steatosis. However, the consequence of inhibiting DGAT2 is not fully investigated due to side effects including lethality and lipotoxicity. In this article, we observed the role of DGAT2 in hepatocarcinoma.
Methods
The role of DGAT2 is analyzed via loss-of-function assay. DGAT2 knockdown (KD) and inhibitor treatment on HepG2 cell line was analyzed. Cumulative analysis of cell metabolism with bioinformatic data were assessed, and further compared with different cohorts of liver cancer patients and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients to elucidate how DGAT2 is regulating cancer metabolism.
Results
Mitochondrial function is suppressed in DGAT2 KD HepG2 cell along with the decreased lipid droplets. In the aspect of the cancer, DGAT2 KD upregulates cell proliferation. Analyzing transcriptome of NAFLD and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients highlights negatively correlating expression patterns of 73 lipid-associated genes including DGAT2. Cancer patients with the lower DGAT2 expression face lower survival rate. DGAT2 KD cell and patients’ transcriptome show downregulation in estrogen- related receptor alpha (ESRRA) via integrated system for motif activity response analysis (ISMARA), with increased dimerization with corepressor prospero homeobox 1 (PROX1).
Conclusion
DGAT2 sustains the stability of mitochondria in hepatoma via suppressing ESRRA-PROX1 transcriptional network and hinders HCC from shifting towards glycolytic metabolism, which lowers cell proliferation.
Review
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
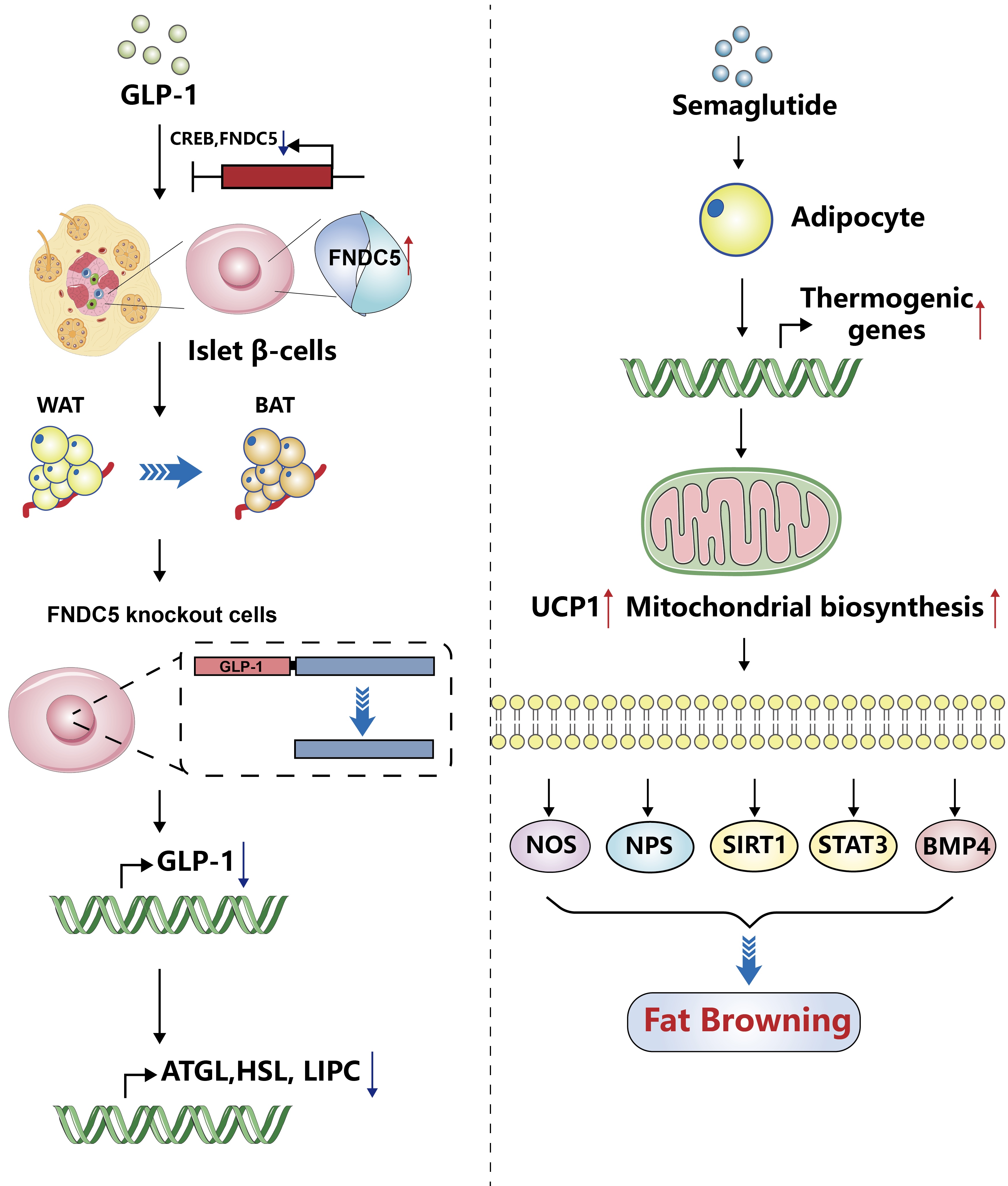
- Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: New Regulator in Lipid Metabolism
- Tong Bu, Ziyan Sun, Yi Pan, Xia Deng, Guoyue Yuan
- Received August 14, 2023 Accepted January 1, 2024 Published online April 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0277 [Epub ahead of print]
- 626 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30-amino acid peptide hormone that is mainly expressed in the intestine and hypothalamus. In recent years, basic and clinical studies have shown that GLP-1 is closely related to lipid metabolism, and it can participate in lipid metabolism by inhibiting fat synthesis, promoting fat differentiation, enhancing cholesterol metabolism, and promoting adipose browning. GLP-1 plays a key role in the occurrence and development of metabolic diseases such as obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and atherosclerosis by regulating lipid metabolism. It is expected to become a new target for the treatment of metabolic disorders. The effects of GLP-1 and dual agonists on lipid metabolism also provide a more complete treatment plan for metabolic diseases. This article reviews the recent research progress of GLP-1 in lipid metabolism.
Original Article
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
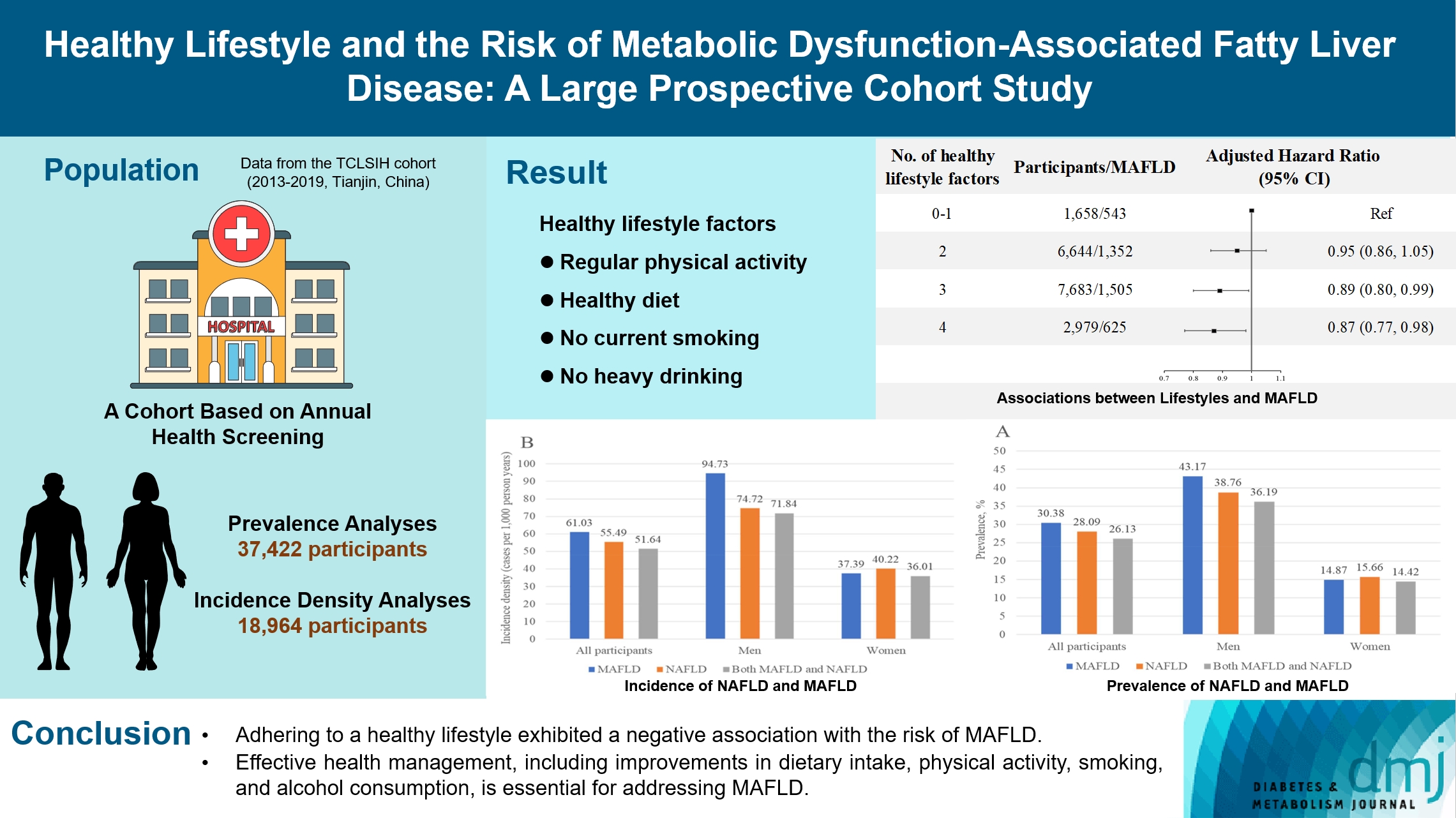
- Healthy Lifestyle and the Risk of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Large Prospective Cohort Study
- Qing Chang, Yixiao Zhang, Tingjing Zhang, Zuyun Liu, Limin Cao, Qing Zhang, Li Liu, Shaomei Sun, Xing Wang, Ming Zhou, Qiyu Jia, Kun Song, Yang Ding, Yuhong Zhao, Kaijun Niu, Yang Xia
- Received April 27, 2023 Accepted November 30, 2023 Published online March 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0133 [Epub ahead of print]
- 612 View
- 43 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The incidence density of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and the effect of a healthy lifestyle on the risk of MAFLD remain unknown. We evaluated the prevalence and incidence density of MAFLD and investigated the association between healthy lifestyle and the risk of MAFLD.
Methods
A cross-sectional analysis was conducted on 37,422 participants to explore the prevalence of MAFLD. A cohort analysis of 18,964 individuals was conducted to identify the incidence of MAFLD, as well as the association between healthy lifestyle and MAFLD. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to calculate the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) with adjustments for confounding factors.
Results
The prevalence of MAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and their comorbidities were 30.38%, 28.09%, and 26.13%, respectively. After approximately 70 thousand person-years of follow-up, the incidence densities of the three conditions were 61.03, 55.49, and 51.64 per 1,000 person-years, respectively. Adherence to an overall healthy lifestyle was associated with a 19% decreased risk of MAFLD (HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.72 to 0.92), and the effects were modified by baseline age, sex, and body mass index (BMI). Subgroup analyses revealed that younger participants, men, and those with a lower BMI experienced more significant beneficial effects from healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion
Our results highlight the beneficial effect of adherence to a healthy lifestyle on the prevention of MAFLD. Health management for improving dietary intake, physical activity, and smoking and drinking habits are critical to improving MAFLD.
Sulwon Lecture 2023
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
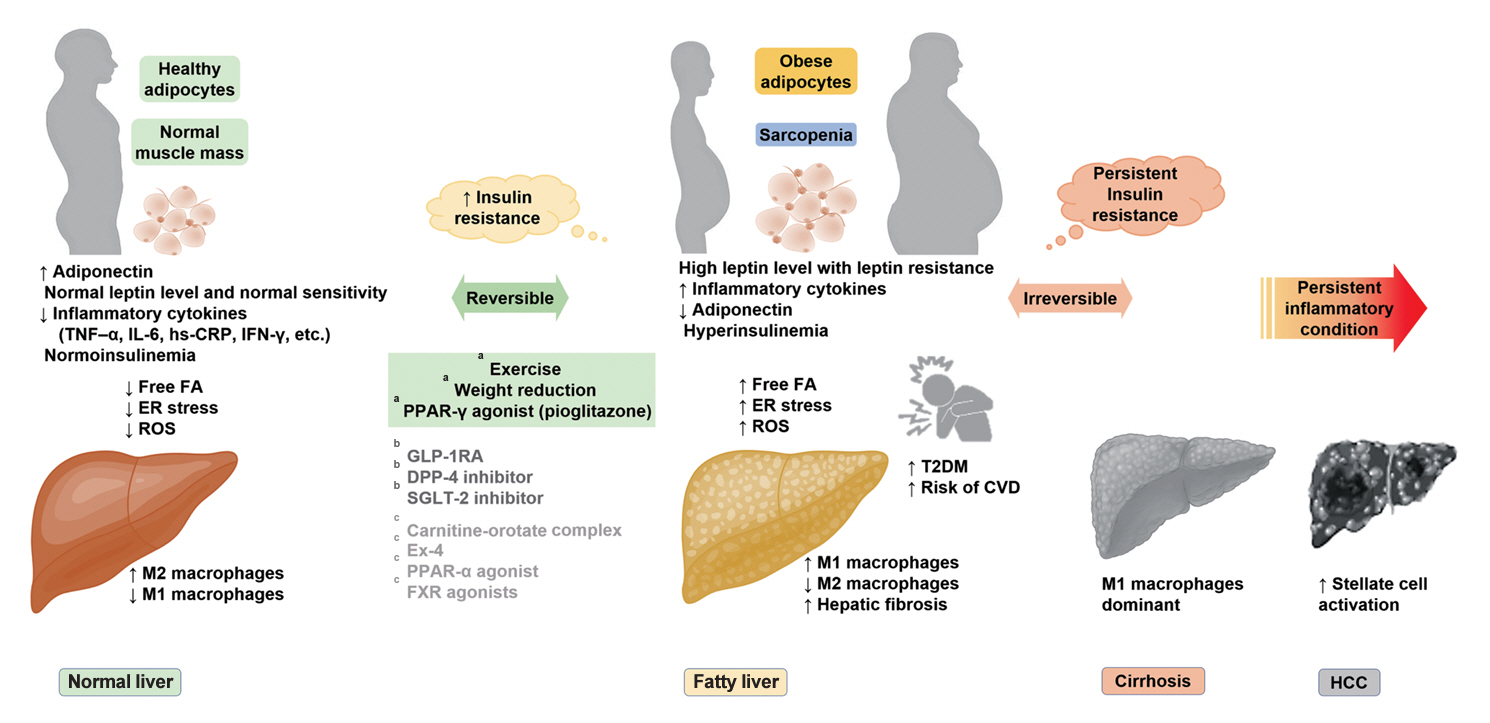
- Insulin Resistance, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Clinical and Experimental Perspective
- Inha Jung, Dae-Jeong Koo, Won-Young Lee
- Received October 4, 2023 Accepted December 26, 2024 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0350 [Epub ahead of print]
- 1,013 View
- 60 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - It has been generally accepted that insulin resistance (IR) and reduced insulin secretory capacity are the basic pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In addition to genetic factors, the persistence of systemic inflammation caused by obesity and the associated threat of lipotoxicity increase the risk of T2DM. In particular, the main cause of IR is obesity and subjects with T2DM have a higher body mass index (BMI) than normal subjects according to recent studies. The prevalence of T2DM with IR has increased with increasing BMI during the past three decades. According to recent studies, homeostatic model assessment of IR was increased compared to that of the 1990s. Rising prevalence of obesity in Korea have contributed to the development of IR, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and T2DM and cutting this vicious cycle is important. My colleagues and I have investigated this pathogenic mechanism on this theme through clinical and experimental studies over 20 years and herein, I would like to summarize some of our studies with deep gratitude for receiving the prestigious 2023 Sulwon Award.
Original Articles
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Glycemic Control Is Associated with Histological Findings of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Teruki Miyake, Shinya Furukawa, Bunzo Matsuura, Osamu Yoshida, Masumi Miyazaki, Akihito Shiomi, Ayumi Kanamoto, Hironobu Nakaguchi, Yoshiko Nakamura, Yusuke Imai, Mitsuhito Koizumi, Takao Watanabe, Yasunori Yamamoto, Yohei Koizumi, Yoshio Tokumoto, Masashi Hirooka, Teru Kumagi, Eiji Takesita, Yoshio Ikeda, Masanori Abe, Yoichi Hiasa
- Received June 24, 2023 Accepted September 21, 2023 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0200 [Epub ahead of print]

- 938 View
- 40 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Poor lifestyle habits may worsen nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), with progression to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis. This study investigated the association between glycemic control status and hepatic histological findings to elucidate the effect of glycemic control on NAFLD.
Methods
This observational study included 331 patients diagnosed with NAFLD by liver biopsy. Effects of the glycemic control status on histological findings of NAFLD were evaluated by comparing the following four glycemic status groups defined by the glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level at the time of NAFLD diagnosis: ≤5.4%, 5.5%–6.4%, 6.5%–7.4%, and ≥7.5%.
Results
Compared with the lowest HbA1c group (≤5.4%), the higher HbA1c groups (5.5%–6.4%, 6.5%–7.4%, and ≥7.5%) were associated with advanced liver fibrosis and high NAFLD activity score (NAS). On multivariate analysis, an HbA1c level of 6.5%– 7.4% group was significantly associated with advanced fibrosis compared with the lowest HbA1c group after adjusting for age, sex, hemoglobin, alanine aminotransferase, and creatinine levels. When further controlling for body mass index and uric acid, total cholesterol, and triglyceride levels, the higher HbA1c groups were significantly associated with advanced fibrosis compared with the lowest HbA1c group. On the other hand, compared with the lowest HbA1c group, the higher HbA1c groups were also associated with a high NAS in both multivariate analyses.
Conclusion
Glycemic control is associated with NAFLD exacerbation, with even a mild deterioration in glycemic control, especially a HbA1c level of 6.5%–7.4%, contributing to NAFLD progression. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combined effect of histological findings and diabetes mellitus on liver‐related events in patients with metabolic dysfunction‐associated steatotic liver disease
Akihito Shiomi, Teruki Miyake, Shinya Furukawa, Bunzo Matsuura, Osamu Yoshida, Takao Watanabe, Ayumi Kanamoto, Masumi Miyazaki, Hironobu Nakaguchi, Yoshio Tokumoto, Masashi Hirooka, Masanori Abe, Yoichi Hiasa
Hepatology Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Combined effect of histological findings and diabetes mellitus on liver‐related events in patients with metabolic dysfunction‐associated steatotic liver disease
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Harnessing Metabolic Indices as a Predictive Tool for Cardiovascular Disease in a Korean Population without Known Major Cardiovascular Event
- Hyun-Jin Kim, Byung Sik Kim, Yonggu Lee, Sang Bong Ahn, Dong Wook Kim, Jeong-Hun Shin
- Received June 22, 2023 Accepted August 18, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0197 [Epub ahead of print]

- 964 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study evaluated the usefulness of indices for metabolic syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and insulin resistance (IR), as predictive tools for cardiovascular disease in middle-aged Korean adults.
Methods
The prospective data obtained from the Ansan-Ansung cohort database, excluding patients with major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE). The primary outcome was the incidence of MACCE during the follow-up period.
Results
A total of 9,337 patients were included in the analysis, of whom 1,130 (12.1%) experienced MACCE during a median follow-up period of 15.5 years. The metabolic syndrome severity Z-score, metabolic syndrome severity score, hepatic steatosis index, and NAFLD liver fat score were found to significantly predict MACCE at values above the cut-off point and in the second and third tertiles. Among these indices, the hazard ratios of the metabolic syndrome severity score and metabolic syndrome severity Z-score were the highest after adjusting for confounding factors. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of the 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) score for predicting MACCE was 0.716, and the metabolic syndrome severity Z-score had an AUC of 0.619.
Conclusion
The metabolic syndrome severity score is a highly reliable indicator and was closely associated with the 10-year ASCVD risk score in predicting MACCE in the general population. Given the specific characteristics and limitations of metabolic syndrome severity scores as well as the indices of NAFLD and IR, a more practical scoring system that considers these factors is essential to achieve greater accuracy in forecasting cardiovascular outcomes.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
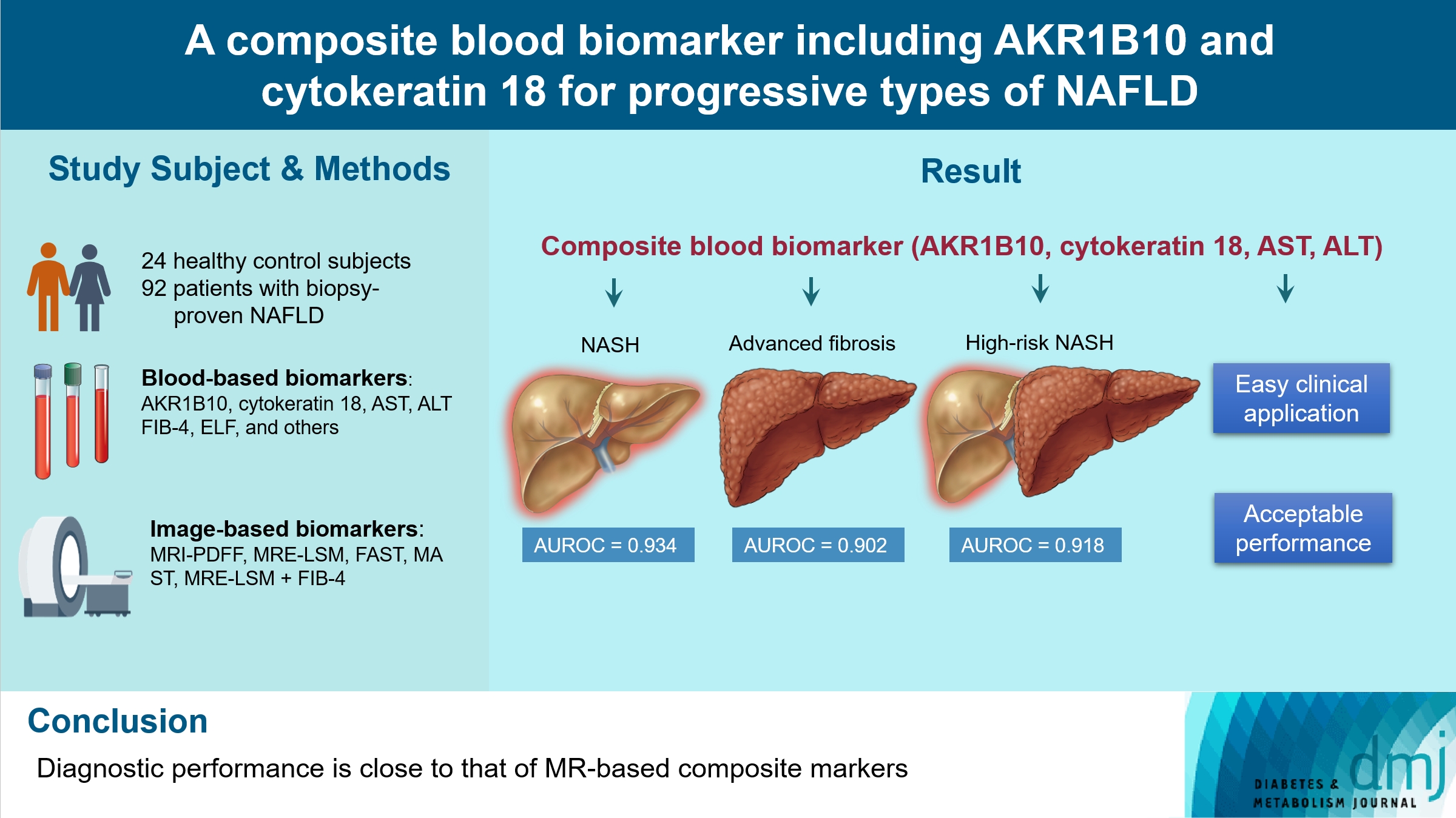
- A Composite Blood Biomarker Including AKR1B10 and Cytokeratin 18 for Progressive Types of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Seung Joon Choi, Sungjin Yoon, Kyoung-Kon Kim, Doojin Kim, Hye Eun Lee, Kwang Gi Kim, Seung Kak Shin, Ie Byung Park, Seong Min Kim, Dae Ho Lee
- Received June 18, 2023 Accepted August 16, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0189 [Epub ahead of print]
- 791 View
- 50 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate whether composite blood biomarkers including aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 (AKR1B10) and cytokeratin 18 (CK-18; a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [NASH] marker) have clinically applicable performance for the diagnosis of NASH, advanced liver fibrosis, and high-risk NASH (NASH+significant fibrosis).
Methods
A total of 116 subjects including healthy control subjects and patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) were analyzed to assess composite blood-based and imaging-based biomarkers either singly or in combination.
Results
A composite blood biomarker comprised of AKR1B10, CK-18, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) showed excellent performance for the diagnosis of, NASH, advanced fibrosis, and high-risk NASH, with area under the receiver operating characteristic curve values of 0.934 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.888 to 0.981), 0.902 (95% CI, 0.832 to 0.971), and 0.918 (95% CI, 0.862 to 0.974), respectively. However, the performance of this blood composite biomarker was inferior to that various magnetic resonance (MR)-based composite biomarkers, such as proton density fat fraction/MR elastography- liver stiffness measurement (MRE-LSM)/ALT/AST for NASH, MRE-LSM+fibrosis-4 index for advanced fibrosis, and the known MR imaging-AST (MAST) score for high-risk NASH.
Conclusion
Our blood composite biomarker can be useful to distinguish progressive forms of NAFLD as an initial noninvasive test when MR-based tools are not available.
- Basic Research
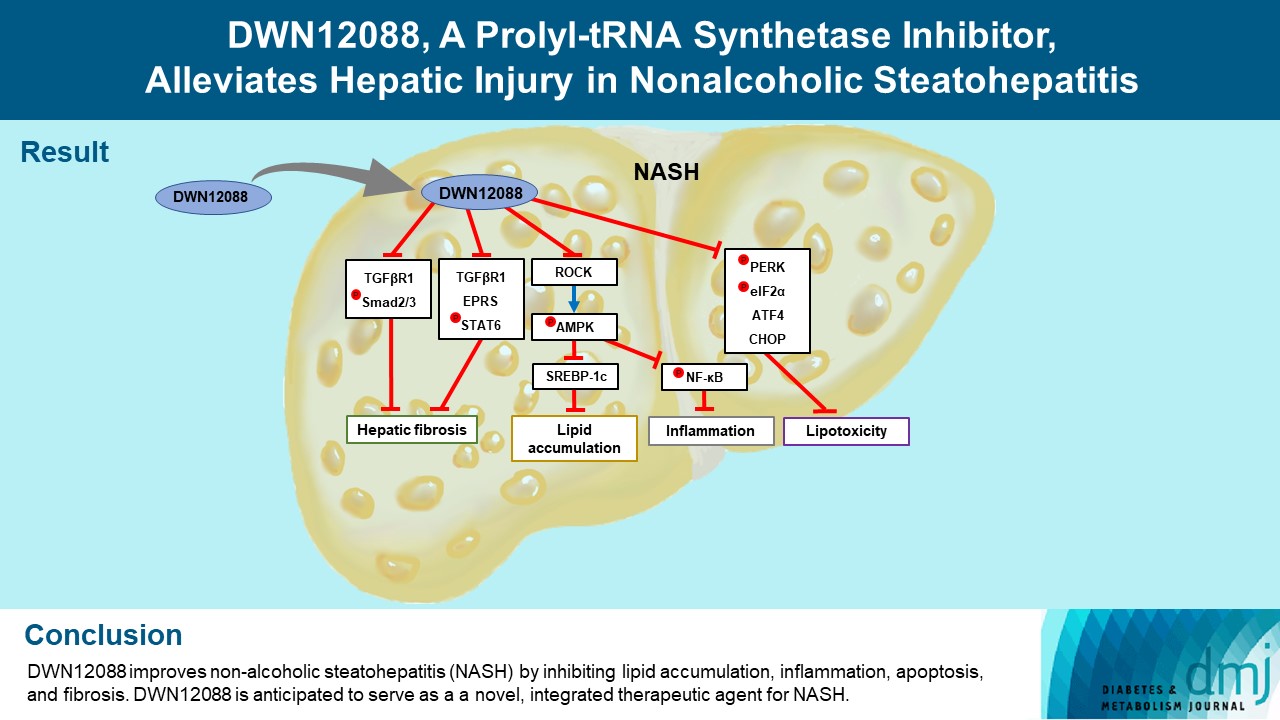
- DWN12088, A Prolyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitor, Alleviates Hepatic Injury in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Dong-Keon Lee, Su Ho Jo, Eun Soo Lee, Kyung Bong Ha, Na Won Park, Deok-Hoon Kong, Sang-In Park, Joon Seok Park, Choon Hee Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):97-111. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0367
- 1,811 View
- 181 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a liver disease caused by obesity that leads to hepatic lipoapoptosis, resulting in fibrosis and cirrhosis. However, the mechanism underlying NASH is largely unknown, and there is currently no effective therapeutic agent against it. DWN12088, an agent used for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, is a selective prolyl-tRNA synthetase (PRS) inhibitor that suppresses the synthesis of collagen. However, the mechanism underlying the hepatoprotective effect of DWN12088 is not clear. Therefore, we investigated the role of DWN12088 in NASH progression.
Methods
Mice were fed a chow diet or methionine-choline deficient (MCD)-diet, which was administered with DWN12088 or saline by oral gavage for 6 weeks. The effects of DWN12088 on NASH were evaluated by pathophysiological examinations, such as real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, immunoblotting, biochemical analysis, and immunohistochemistry. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of hepatic injury were assessed by in vitro cell culture.
Results
DWN12088 attenuated palmitic acid (PA)-induced lipid accumulation and lipoapoptosis by downregulating the Rho-kinase (ROCK)/AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK)/α subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2α)/activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4)/C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP) signaling cascades. PA increased but DWN12088 inhibited the phosphorylation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) p65 (Ser536, Ser276) and the expression of proinflammatory genes. Moreover, the DWN12088 inhibited transforming growth factor β (TGFβ)-induced pro-fibrotic gene expression by suppressing TGFβ receptor 1 (TGFβR1)/Smad2/3 and TGFβR1/glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase (EPRS)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) axis signaling. In the case of MCD-diet-induced NASH, DWN12088 reduced hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and lipoapoptosis and prevented the progression of fibrosis.
Conclusion
Our findings provide new insights about DWN12088, namely that it plays an important role in the overall improvement of NASH. Hence, DWN12088 shows great potential to be developed as a new integrated therapeutic agent for NASH.
- Basic Research
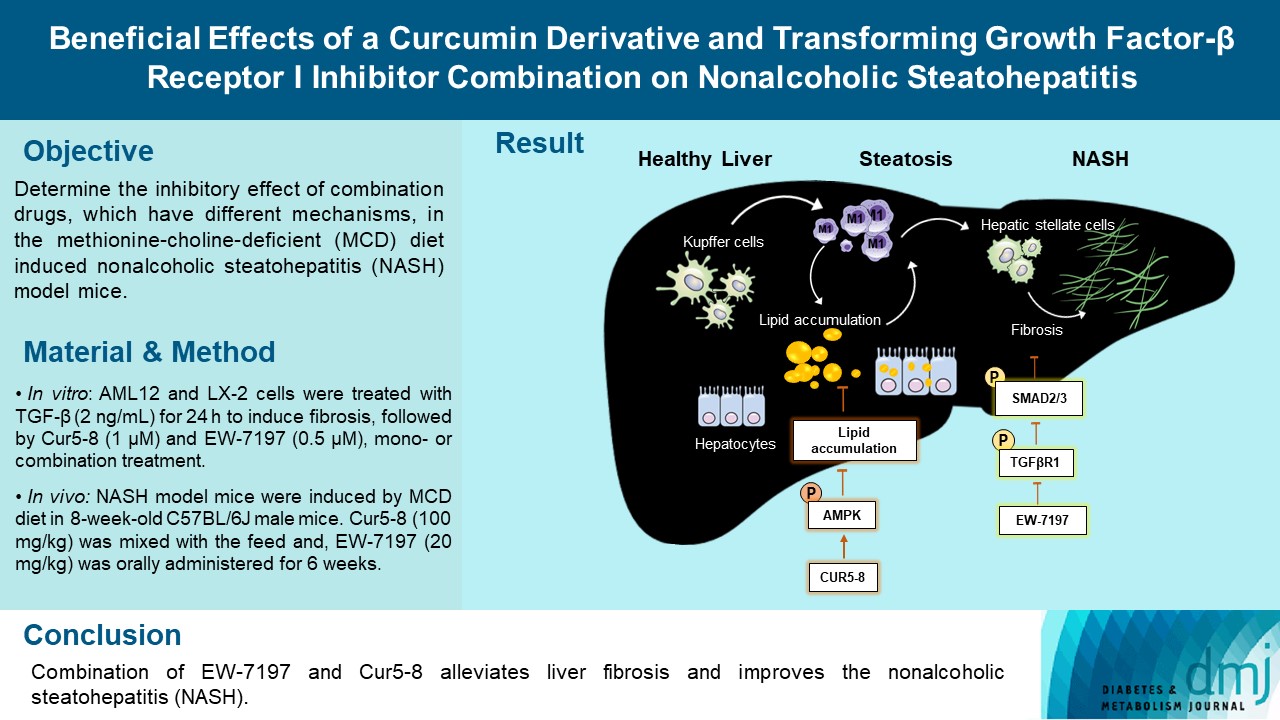
- Beneficial Effects of a Curcumin Derivative and Transforming Growth Factor-β Receptor I Inhibitor Combination on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Kyung Bong Ha, Eun Soo Lee, Na Won Park, Su Ho Jo, Soyeon Shim, Dae-Kee Kim, Chan Mug Ahn, Choon Hee Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):500-513. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0110
- 2,223 View
- 145 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Curcumin 2005-8 (Cur5-8), a derivative of curcumin, improves fatty liver disease via AMP-activated protein kinase activation and autophagy regulation. EW-7197 (vactosertib) is a small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) receptor I and may scavenge reactive oxygen species and ameliorate fibrosis through the SMAD2/3 canonical pathway. This study aimed to determine whether co-administering these two drugs having different mechanisms is beneficial.
Methods
Hepatocellular fibrosis was induced in mouse hepatocytes (alpha mouse liver 12 [AML12]) and human hepatic stellate cells (LX-2) using TGF-β (2 ng/mL). The cells were then treated with Cur5-8 (1 μM), EW-7197 (0.5 μM), or both. In animal experiments were also conducted during which, methionine-choline deficient diet, Cur5-8 (100 mg/kg), and EW-7197 (20 mg/kg) were administered orally to 8-week-old C57BL/6J mice for 6 weeks.
Results
TGF-β-induced cell morphological changes were improved by EW-7197, and lipid accumulation was restored on the administration of EW-7197 in combination with Cur5-8. In a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-induced mouse model, 6 weeks of EW-7197 and Cur5-8 co-administration alleviated liver fibrosis and improved the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score.
Conclusion
Co-administering Cur5-8 and EW-7197 to NASH-induced mice and fibrotic hepatocytes reduced liver fibrosis and steatohepatitis while maintaining the advantages of both drugs. This is the first study to show the effect of the drug combination against NASH and NAFLD. Similar effects in other animal models will confirm its potential as a new therapeutic agent.
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
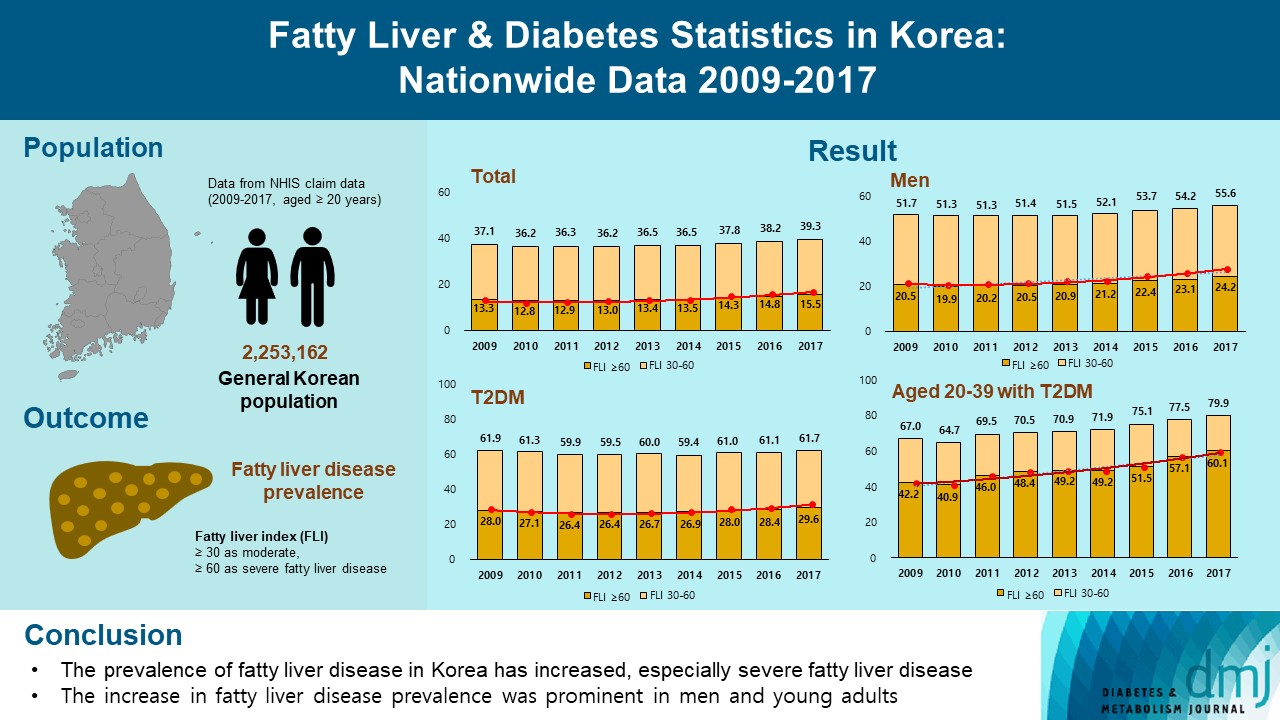
- Fatty Liver & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2009 to 2017
- Eugene Han, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-ho Lee, Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Cheol-Young Park, on Behalf of Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):347-355. Published online March 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0444
- 3,590 View
- 208 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the changes of fatty liver disease prevalence in general Korean population.
Methods
This study analyzed data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service from 2009 to 2017 that included individuals aged 20 years or older who had undergone a medical health examination. Fatty liver disease was assessed using the fatty liver index (FLI). The disease severity was defined by FLI cutoff, ≥30 as moderate, and ≥60 as severe fatty liver disease.
Results
The prevalence of Korean adults aged 20 years or over with fatty liver disease (FLI ≥60) increased from 13.3% in 2009 to 15.5% in 2017 (P for trend <0.001). The increase in fatty liver disease prevalence was prominent in men (from 20.5% to 24.2%) and the young age (20 to 39 years) group (from 12.8% to 16.4%) (P for interaction <0.001). The prevalence of fatty liver disease was the highest in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM, 29.6%) population compared to that of prediabetes or normoglycemia (10.0% and 21.8%) in 2017. The prevalence of fatty liver disease had statistically increased in individuals with T2DM and prediabetes (P for trend <0.001). Its prevalence increased more steeply in the young-aged population with T2DM, from 42.2% in 2009 to 60.1% in 2017. When applying a lower FLI cutoff (≥30) similar results were observed.
Conclusion
The prevalence of fatty liver disease in the Korean population has increased. Individuals who are young, male, and have T2DM are vulnerable to fatty liver disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Longitudinal changes in fatty liver index are associated with risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A nationwide cohort study in Korea
Min Gu Kang, Chang Hun Lee, Chen Shen, Jong Seung Kim, Ji Hyun Park
Journal of Hepatology.2024; 80(5): e216. CrossRef - Repeated detection of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease increases the incidence risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Jin Hwa Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Mee Kyoung Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 180. CrossRef - Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Eugene Han, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Sang Hoon Ahn, Yong-ho Lee, Seung Up Kim
Metabolism.2024; 152: 155789. CrossRef - Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMJ.2024; : e076388. CrossRef - Hepatic Fibrosis and Cancer: The Silent Threats of Metabolic Syndrome
Scott L. Friedman
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 161. CrossRef - Reply to G. Wang et al
Joo-Hyun Park, Jung Yong Hong, Kyungdo Han
Journal of Clinical Oncology.2023; 41(32): 5070. CrossRef - The Role of the Fatty Liver Index (FLI) in the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review
Teodora Biciusca, Sorina Ionelia Stan, Mara Amalia Balteanu, Ramona Cioboata, Alice Elena Ghenea, Suzana Danoiu, Ana-Maria Bumbea, Viorel Biciusca
Diagnostics.2023; 13(21): 3316. CrossRef - Lean or Non-obese Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Are They Really Lean?
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 980. CrossRef - Approach to Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Ji Cheol Bae
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 107. CrossRef
- Longitudinal changes in fatty liver index are associated with risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A nationwide cohort study in Korea
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
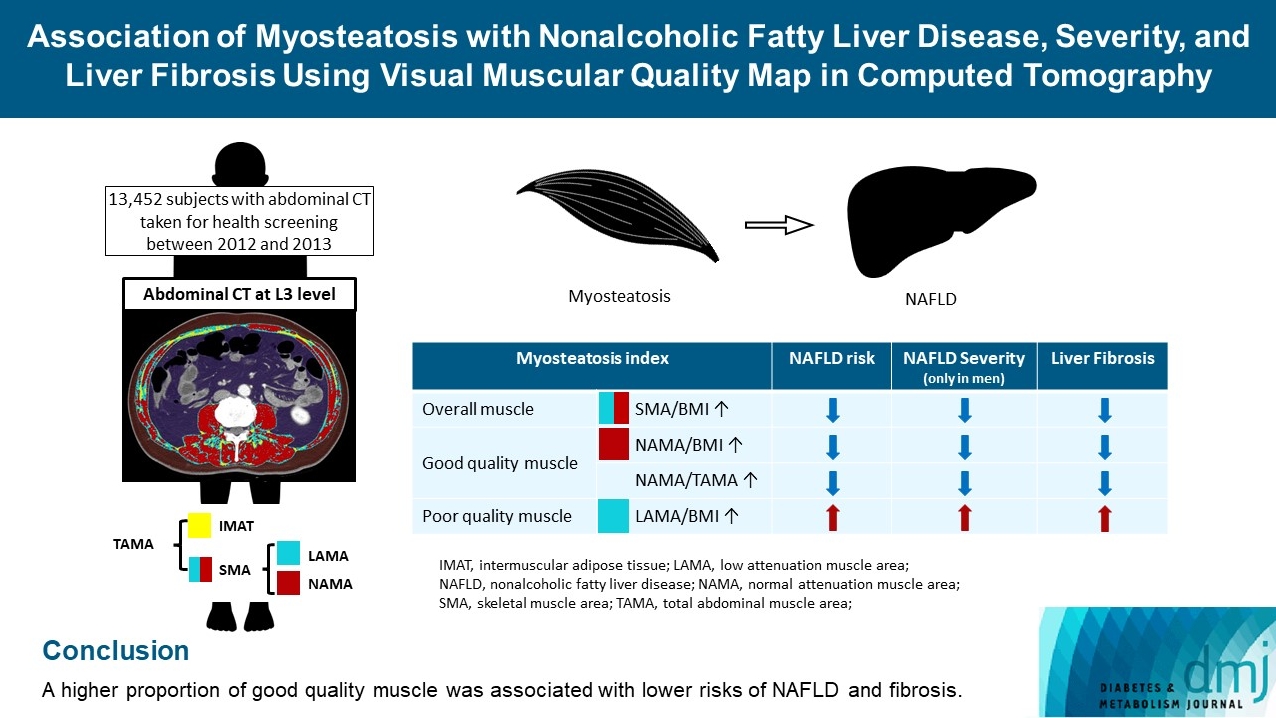
- Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography
- Hwi Seung Kim, Jiwoo Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, In Young Bae, Woo Je Lee, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):104-117. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0081
- 3,272 View
- 176 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The association of myosteatosis measured using visual muscular quality map in computed tomography (CT) with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), its severity, and fibrosis was analyzed in a large population.
Methods
Subjects (n=13,452) with abdominal CT between 2012 and 2013 were measured total abdominal muscle area (TAMA) at L3 level. TAMA was segmented into intramuscular adipose tissue and skeletal muscle area (SMA), which was further classified into normal attenuation muscle area (NAMA) and low attenuation muscle area (LAMA). The following variables were adopted as indicators of myosteatosis: SMA/body mass index (BMI), NAMA/BMI, NAMA/TAMA, and LAMA/BMI. NAFLD and its severity were assessed by ultrasonography, and liver fibrosis was measured by calculating the NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) and fibrosis-4 index (FIB-4) scores.
Results
According to multiple logistic regression analyses, as quartiles of SMA/BMI, NAMA/BMI, and NAMA/TAMA increased, the odds ratios (ORs) for NAFLD decreased in each sex (P for trend <0.001 for all). The ORs of moderate/severe NAFLD were significantly higher in the Q1 group than in the Q4 group for SMA/BMI, NAMA/BMI, and NAMA/TAMA in men. The ORs of intermediate/high liver fibrosis scores assessed by NFS and FIB-4 scores increased linearly with decreasing quartiles for SMA/BMI, NAMA/BMI, and NAMA/TAMA in each sex (P for trend <0.001 for all). Conversely, the risk for NAFLD and fibrosis were positively associated with LAMA/BMI quartiles in each sex (P for trend <0.001 for all).
Conclusion
A higher proportion of good quality muscle was associated with lower risks of NAFLD and fibrosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:104-17)
Hwi Seung Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 304. CrossRef - Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:104-17)
Eun Roh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 301. CrossRef - Sarcopenia, a condition shared by various diseases: can we alleviate or delay the progression?
Giovanni Tarantino, Gaia Sinatti, Vincenzo Citro, Silvano Santini, Clara Balsano
Internal and Emergency Medicine.2023; 18(7): 1887. CrossRef - Association of Visceral Fat Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Obesity
Hong-Kyu Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Hana Park, Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Jaewon Choe
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Current view of the surgical anatomy of the anterolateral abdominal wall muscles and their aponeuroses
A.V. Pavlov, A.S. Baranova, A.V. Fedoseyev, A.I. Vvedensky, G.S. Lazutina, N.V. Ovchinnikova, I.V. Bakharev
Operativnaya khirurgiya i klinicheskaya anatomiya (Pirogovskii nauchnyi zhurnal).2023; 7(3): 44. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Adults
W. Guo, X. Zhao, D. Cheng, X. Liang, M. Miao, X. Li, J. Lu, N. Xu, Shuang Hu, Qun Zhang
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(11): 960. CrossRef
- Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:104-17)
- Complications
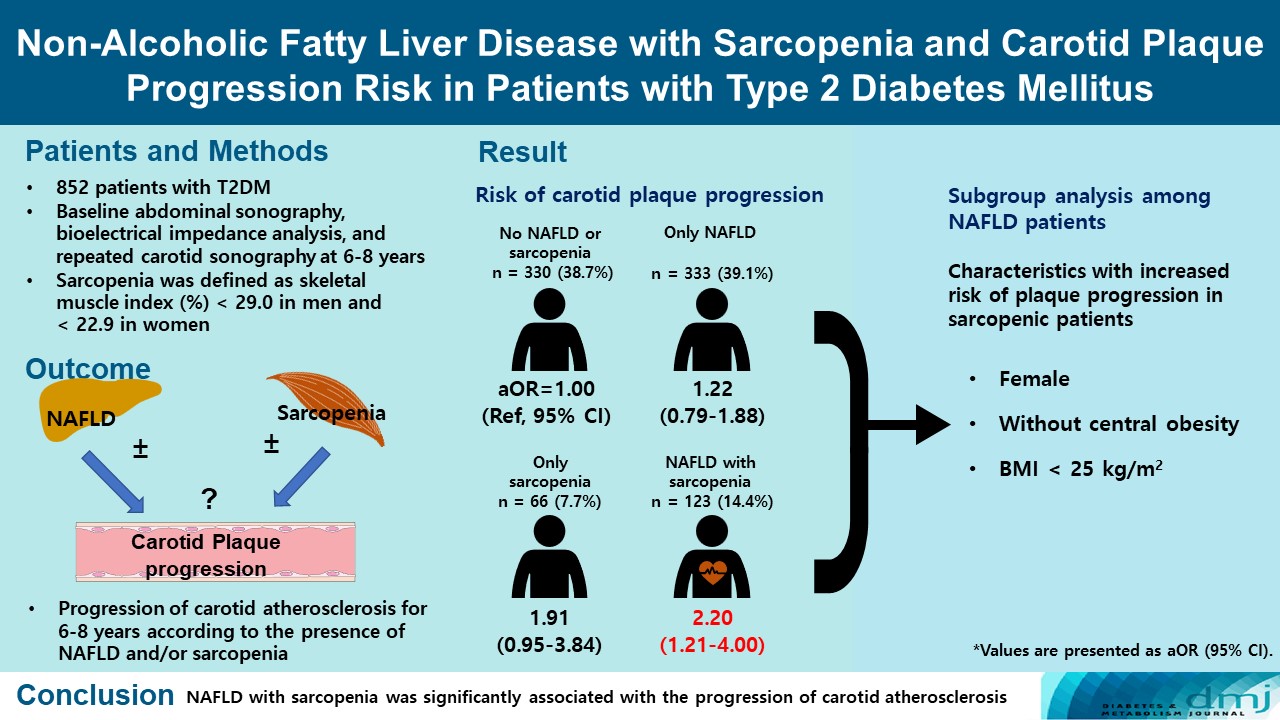
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Sarcopenia and Carotid Plaque Progression Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yongin Cho, Hye-Sun Park, Byung Wook Huh, Yong-ho Lee, Seong Ha Seo, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):232-241. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0355
- 3,640 View
- 223 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate whether non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with or without sarcopenia is associated with progression of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
We investigated 852 T2DM patients who underwent abdominal ultrasonography, bioelectrical impedance analysis, and carotid artery ultrasonography at baseline and repeated carotid ultrasonography after 6 to 8 years. NAFLD was confirmed by abdominal ultrasonography, and sarcopenia was defined as a sex-specific skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) value <2 standard deviations below the mean for healthy young adults. SMI was calculated by dividing the sum of appendicular skeletal mass by body weight. We investigated the association between NAFLD with or without sarcopenia and the progression of carotid atherosclerosis.
Results
Of the 852 patients, 333 (39.1%) were classified as NAFLD without sarcopenia, 66 (7.7%) were classified as sarcopenia without NAFLD, and 123 (14.4%) had NAFLD with sarcopenia at baseline. After 6 to 8 years, patients with both NAFLD and sarcopenia had a higher risk of atherosclerosis progression (adjusted odds ratio, 2.20; P<0.009) than controls without NAFLD and sarcopenia. When a subgroup analysis was performed on only patients with NAFLD, female sex, absence of central obesity, and non-obesity were significant factors related to increased risk of plaque progression risk in sarcopenic patients.
Conclusion
NAFLD with sarcopenia was significantly associated with the progression of carotid atherosclerosis in T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and sarcopenia: A double whammy
Aditya Viswanath, Sherouk Fouda, Cornelius James Fernandez, Joseph M Pappachan
World Journal of Hepatology.2024; 16(2): 152. CrossRef - Prevalence and outcome of sarcopenia in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Suprabhat Giri, Prajna Anirvan, Sumaswi Angadi, Ankita Singh, Anurag Lavekar
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and carotid media‐intima thickness: A systematic review and a meta‐analysis
Manouchehr Khoshbaten, Sepideh H. Maleki, Sara Hadad, Amrit Baral, Ana V. Rocha, Laxmi Poudel, Alireza Abdshah
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes and sarcopenia
Yu. G. Samoilova, M. V. Matveeva, E. A. Khoroshunova, D. V. Podchinenova, L. L. Maksimova, G. G. Gorbach, A. B. Trivozhenko, V. A. Avkhimenko
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2023; 23(1): 3655. CrossRef
- Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and sarcopenia: A double whammy
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
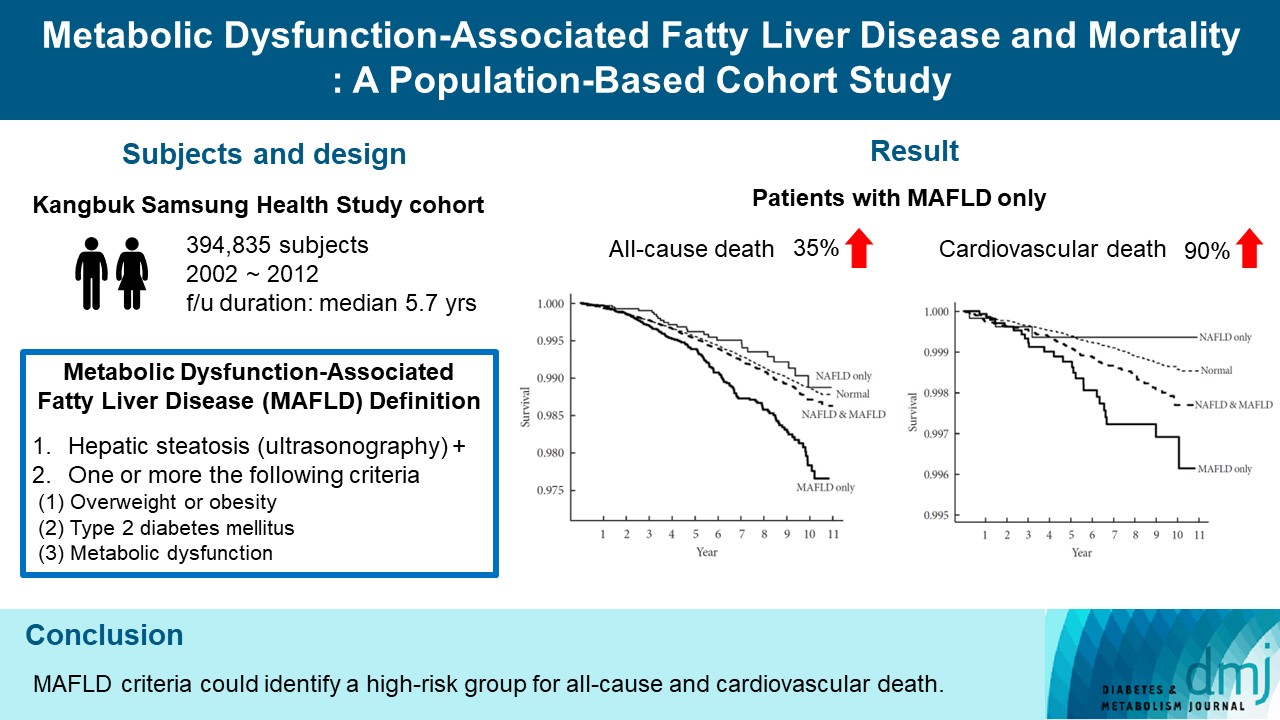
- Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
- Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):220-231. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0327
- 65,535 View
- 282 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated whether metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is associated with an elevated risk of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality using a large-scale health examination cohort.
Methods
A total of 394,835 subjects in the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study cohort were enrolled from 2002 to 2012. Participants were categorized by the presence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and MAFLD as follows: normal subjects; patients with both NAFLD and MAFLD; patients with NAFLD only; and patients with MAFLD only. Cox proportional hazards models were used to analyze the risk of mortality.
Results
During a median 5.7 years of follow-up, 20.69% was patients with both NAFLD and MAFLD, 1.51% was patients with NAFLD only, and 4.29% was patients with MAFLD only. All-cause and cardiovascular death was higher in patients with MAFLD than those without MAFLD (P<0.001, respectively). In patients with MAFLD only, the hazard ratio (HR) of all-cause and cardiovascular death was 1.35 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.13 to 1.60) and 1.90 (95% CI, 1.26 to 2.88) after adjusting for age, which lost its statistical significance by multivariable adjustments. Compared to patients with less than two components of metabolic dysfunction, patients with more than two components of metabolic dysfunction were a higher risk of cardiovascular death (HR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.25 to 3.38) and only women with more than two components of metabolic dysfunction were a higher risk of all-cause death (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.02 to 2.03).
Conclusion
MAFLD criteria could identify a high-risk group for all-cause and cardiovascular death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Eugene Han, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Sang Hoon Ahn, Yong-ho Lee, Seung Up Kim
Metabolism.2024; 152: 155789. CrossRef - Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMJ.2024; : e076388. CrossRef - Sex differences in mortality and liver‐related events in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Huimin Zhou, Haiyan Chen, Hanxiao Lu, Bo Wu, Shuo Zhang, Yuanlong Gu, Guangwen Zhou, Jie Xiang, Jun Yang
Liver International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between dietary carbohydrate to fiber ratio and metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease in adults: evidence from the NHANES 2017–2020
Zhenmin Liu, Taiyong Fang
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Outcomes Between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis
Ghazala S Virk, Jaahnavi Vajje, Nausheen K Virk, Raam Mannam, Wajeeh Rehman, Naglaa G Ghobriel , Irfan-ud-din Mian, Muhammad Usama
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in prevalence and all-cause mortality of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease among adults in the past three decades: Results from the NHANES study
Zhi-Qin Xie, Hong-Xia Li, Bing-Kun Wang, Zhao-Ming Yang, Zi-Yu Zhang, Wen-Liang Tan, Wen-Xin Li, Qing-Bin Wang, Lei Yang, Hong-Kai Zhuang, Chen-Wei Tang, Chang-Zhen Shang, Ya-Jin Chen
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 110: 62. CrossRef - Comparing the Mortality Risk between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Han Na Jung, Chang Hee Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 198. CrossRef - Increased expression of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and O-GlcNAcylation in hepatocytes drives non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hye Jin Chun, Eun Ran Kim, Minyoung Lee, Da Hyun Choi, Soo Hyun Kim, Eugene Shin, Jin-Hong Kim, Jin Won Cho, Dai Hoon Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Metabolism.2023; 145: 155612. CrossRef - Current understanding and future perspectives on the impact of changing NAFLD to MAFLD on global epidemiology and clinical outcomes
Karl Vaz, Daniel Clayton-Chubb, Ammar Majeed, John Lubel, David Simmons, William Kemp, Stuart K. Roberts
Hepatology International.2023; 17(5): 1082. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Quality Control: Its Role in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
Soyeon Shin, Jaeyoung Kim, Ju Yeon Lee, Jun Kim, Chang-Myung Oh
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(4): 289. CrossRef
- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
- Basic Research
- Peroxisomal Fitness: A Potential Protective Mechanism of Fenofibrate against High Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice
- Songling Jiang, Md Jamal Uddin, Xiaoying Yu, Lingjuan Piao, Debra Dorotea, Goo Taeg Oh, Hunjoo Ha
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):829-842. Published online June 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0274
- 4,968 View
- 292 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been increasing in association with the epidemic of obesity and diabetes. Peroxisomes are single membrane-enclosed organelles that play a role in the metabolism of lipid and reactive oxygen species. The present study examined the role of peroxisomes in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced NAFLD using fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) agonist.
Methods
Eight-week-old male C57BL/6J mice were fed either a normal diet or HFD for 12 weeks, and fenofibrate (50 mg/kg/day) was orally administered along with the initiation of HFD.
Results
HFD-induced liver injury as measured by increased alanine aminotransferase, inflammation, oxidative stress, and lipid accumulation was effectively prevented by fenofibrate. Fenofibrate significantly increased the expression of peroxisomal genes and proteins involved in peroxisomal biogenesis and function. HFD-induced attenuation of peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation was also significantly restored by fenofibrate, demonstrating the functional significance of peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation. In Ppara deficient mice, fenofibrate failed to maintain peroxisomal biogenesis and function in HFD-induced liver injury.
Conclusion
The present data highlight the importance of PPARα-mediated peroxisomal fitness in the protective effect of fenofibrate against NAFLD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pharmacological potential of ginseng and ginsenosides in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Young-Su Yi
Journal of Ginseng Research.2024; 48(2): 122. CrossRef - Fenofibrate alleviates NAFLD by enhancing the PPARα/PGC-1α signaling pathway coupling mitochondrial function
Xuemei Wang, Jieying Wang, Cao Ying, Yuan Xing, Xuan Su, Ke Men
BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 184. CrossRef - Current Therapeutical Approaches Targeting Lipid Metabolism in NAFLD
Manuela Vitulo, Elisa Gnodi, Giulia Rosini, Raffaella Meneveri, Roberto Giovannoni, Donatella Barisani
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(16): 12748. CrossRef - PPARα agonist fenofibrate prevents postoperative cognitive dysfunction by enhancing fatty acid oxidation in mice
Tiantian Liu, Xinlu Chen, Ziqi Wei, Xue Han, Yujia Liu, Zhengliang Ma, Tianjiao Xia, Xiaoping Gu
Translational Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fenofibrate enhances lipid deposition via modulating PPARγ, SREBP-1c, and gut microbiota in ob/ob mice fed a high-fat diet
Ying Zhang, Xiu-Bin Jia, Yun-Chao Liu, Wen-Qian Yu, Yan-Hong Si, Shou-Dong Guo
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Pharmacological potential of ginseng and ginsenosides in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Review
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Lifestyle Interventions for Non-Obese Patients Both with, and at Risk, of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Xin-Lei Zhang, Ting-Yao Wang, Giovanni Targher, Christopher D. Byrne, Ming-Hua Zheng
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):391-401. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0048

- 5,303 View
- 274 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease occurring in non-obese subjects (the so-called non-obese NAFLD) is a highly prevalent but neglected liver condition, which is closely associated with metabolic disorders and suboptimal lifestyles. Landmark studies have shown that lifestyle interventions are potentially beneficial in decreasing the risk of developing non-obese NAFLD and in ameliorating NAFLD in non-obese individuals with pre-existing NAFLD. Lifestyle interventions usually refer to changes in eating habits and physical activity, both of which have a powerful effect on non-obese NAFLD and on risk factors for non-obese NAFLD. However, to date, patients and health-care professionals have a poor awareness and understanding of non-obese NAFLD and the beneficial effects of lifestyle interventions in this patient population. The aim of this narrative review is to briefly discuss the evidence for the effects of lifestyle changes and what changes are needed amongst medical personnel and other stakeholders in order to raise awareness of non-obese NAFLD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triglycerides Mediate the Influence of Body Mass Index on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Non-Obese Chinese Population with Normal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels
Xixi Han, Jingwen Kong, Hemin Zhang, Yuan Zhao, Yafeng Zheng, Chao Wei
Obesity Facts.2024; 17(2): 191. CrossRef - Patients with NAFLD exhibit more advanced fibrosis in liver biopsy than patients with other chronic liver diseases
Lydia Rohr, Peter Lemmer, Marie Henning, Andrea Tannapfel, Theodor Baars, Paul Manka, Ali Canbay, Jan-Peter Sowa
Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie.2023; 61(01): 29. CrossRef - Performance of Simple Fibrosis Score in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with and without Type 2 Diabetes
Seung Min Chung, Min Kyu Kang, Jun Sung Moon, Jung Gil Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 277. CrossRef - An international multidisciplinary consensus statement on MAFLD and the risk of CVD
Xiao-Dong Zhou, Giovanni Targher, Christopher D. Byrne, Virend Somers, Seung Up Kim, C. Anwar A. Chahal, Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, Jingjing Cai, Michael D. Shapiro, Mohammed Eslam, Philippe Gabriel Steg, Ki-Chul Sung, Anoop Misra, Jian-Jun Li, Carlos Brotons,
Hepatology International.2023; 17(4): 773. CrossRef - Lean or Non-obese Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Are They Really Lean?
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 980. CrossRef - Sex-Based Differences and Risk Factors for Comorbid Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Bipolar Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study
Ying Wang, Yiyi Liu, Xun Zhang, Qing Wu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3533. CrossRef - Benefits of Physical Exercise as Approach to Prevention and Reversion of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents with Obesity
Valeria Calcaterra, Vittoria Magenes, Matteo Vandoni, Clarissa Berardo, Luca Marin, Alice Bianchi, Erika Cordaro, Giustino Silvestro, Dario Silvestri, Vittoria Carnevale Pellino, Cristina Cereda, Gianvincenzo Zuccotti
Children.2022; 9(8): 1174. CrossRef - The effects of supplementation of probiotics, prebiotics, or synbiotics on patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Wenmin Xing, Wenyan Gao, Xiaoling Lv, Zhenlei Zhao, Genxiang Mao, Xiaoyan Dong, Zuyong Zhang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Triglycerides Mediate the Influence of Body Mass Index on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Non-Obese Chinese Population with Normal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





