
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Most view
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse > Most view
Most-read articles are from the articles published in 2023 during the last three month.
Reviews
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
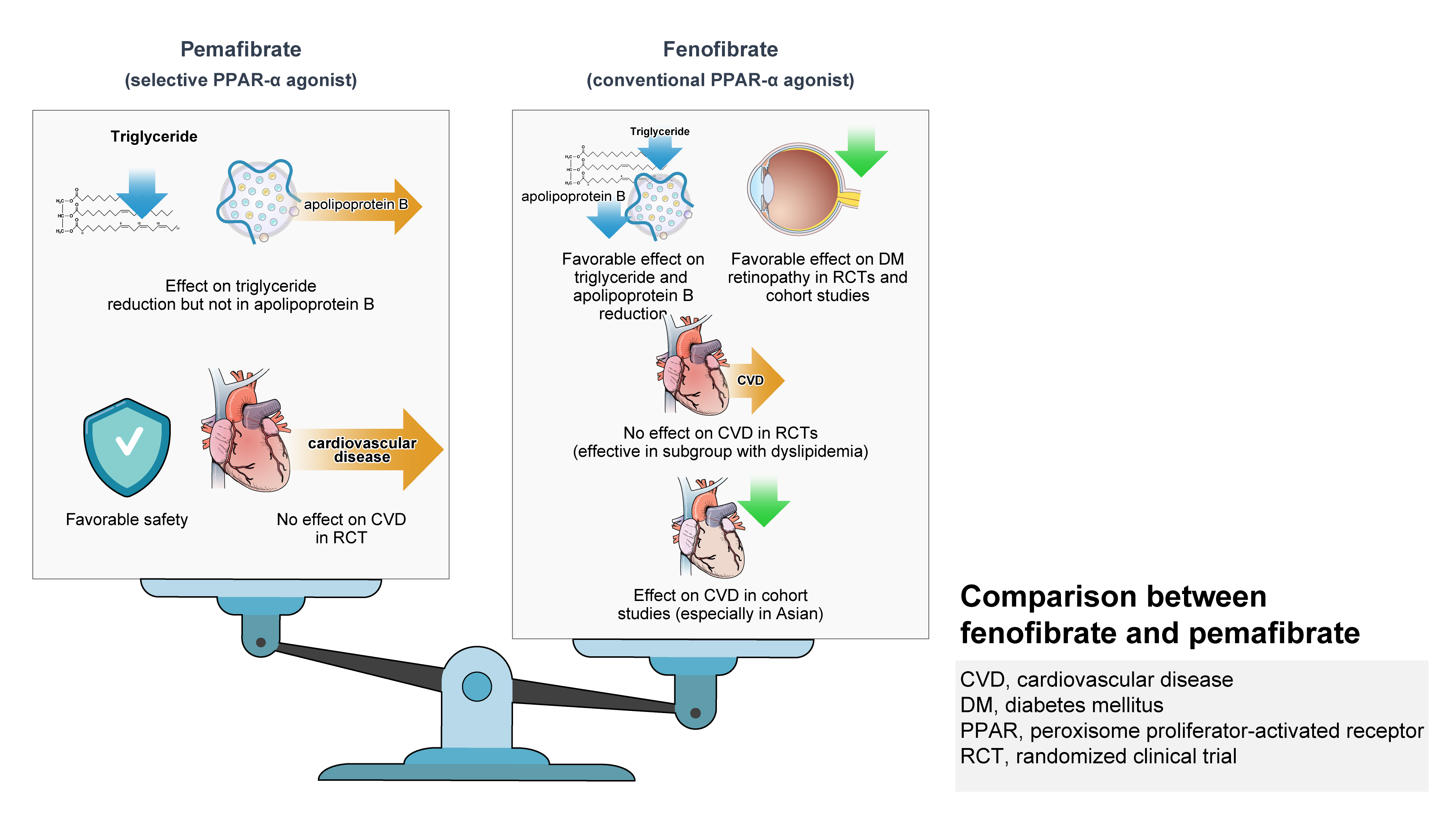
- Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
- Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):184-195. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0168
- 2,211 View
- 328 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Hypertriglyceridemia and decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) persist despite statin therapy, contributing to residual atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk. Asian subjects are metabolically more susceptible to hypertriglyceridemia than other ethnicities. Fenofibrate regulates hypertriglyceridemia, raises HDL-C levels, and is a recommended treatment for dyslipidemia. However, data on fenofibrate use across different Asian regions are limited. This narrative review summarizes the efficacy and safety data of fenofibrate in Asian subjects with dyslipidemia and related comorbidities (diabetes, metabolic syndrome, diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic nephropathy). Long-term fenofibrate use resulted in fewer cardiovascular (CV) events and reduced the composite of heart failure hospitalizations or CV mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Fenofibrate plays a significant role in improving irisin resistance and microalbuminuria, inhibiting inflammatory responses, and reducing retinopathy incidence. Fenofibrate plus statin combination significantly reduced composite CV events risk in patients with metabolic syndrome and demonstrated decreased triglyceride and increased HDL-C levels with an acceptable safety profile in those with high CV or ASCVD risk. Nevertheless, care is necessary with fenofibrate use due to possible hepatic and renal toxicities in vulnerable individuals. Long-term trials and real-world studies are needed to confirm the clinical benefits of fenofibrate in the heterogeneous Asian population with dyslipidemia.
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
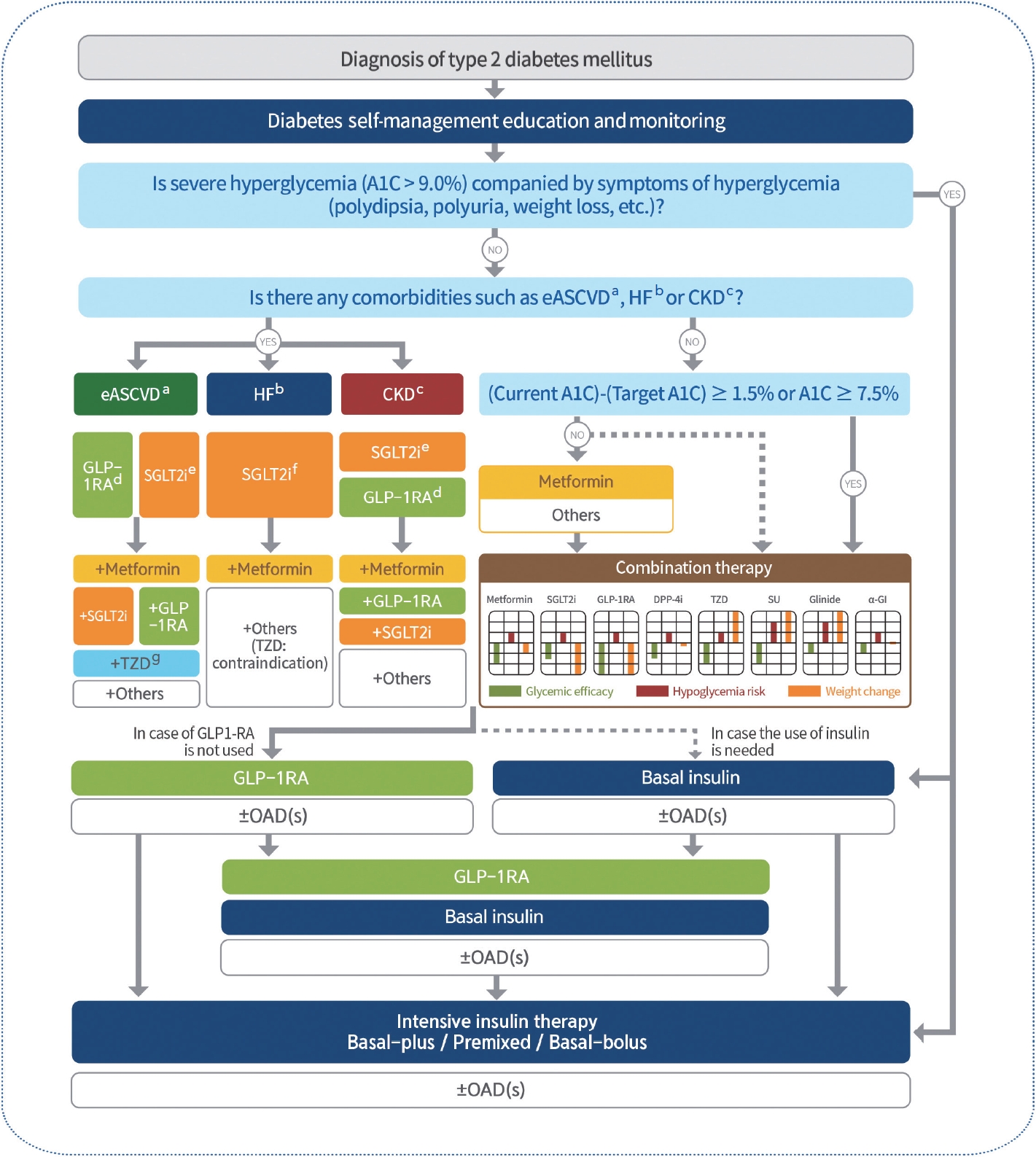
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae Jin Kim, Hyun Min Kim, Jung Hae Ko, Nam Hoon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Jeeyun Ahn, Tae Jung Oh, Soo-Kyung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Eugene Han, Sang-Man Jin, Won Suk Choi, Min Kyong Moon, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):575-594. Published online September 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0282
- 5,013 View
- 628 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - In May 2023, the Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Korean Diabetes Association published the revised clinical practice guidelines for Korean adults with diabetes and prediabetes. We incorporated the latest clinical research findings through a comprehensive systematic literature review and applied them in a manner suitable for the Korean population. These guidelines are designed for all healthcare providers nationwide, including physicians, diabetes experts, and certified diabetes educators who manage patients with diabetes or individuals at risk of developing diabetes. Based on recent changes in international guidelines and the results of a Korean epidemiological study, the recommended age for diabetes screening has been lowered. In collaboration with the relevant Korean medical societies, recently revised guidelines for managing hypertension and dyslipidemia in patients with diabetes have been incorporated into this guideline. An abridgment containing practical information on patient education and systematic management in the clinic was published separately.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Eugene Han, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Sang Hoon Ahn, Yong-ho Lee, Seung Up Kim
Metabolism.2024; 152: 155789. CrossRef - Letter by In-Kyung Jeong Regarding Article, Trends in Prevalence of Hypertriglyceridemia and Related Factors in Korean Adults: A Serial Cross-Sectional Study
In-Kyung Jeong
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2024; 13(1): 80. CrossRef - Association between cardiovascular disease risk and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in individuals with prediabetes: A retrospective cohort study
Myung Jin Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111125. CrossRef - Korea Hypertension Fact Sheet 2023: analysis of nationwide population-based data with a particular focus on hypertension in special populations
Hyeon Chang Kim, Hokyou Lee, Hyeok-Hee Lee, Dasom Son, Minsung Cho, Sojung Shin, Yeeun Seo, Eun-Jin kim, Song Vogue Ahn, Sun Ha Jee, Sungha Park, Hae-Young Lee, Min Ho Shin, Sang-Hyun Ihm, Seung Won Lee, Jong Ku Park, Il Suh, Tae-Yong Lee
Clinical Hypertension.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adding Apolipoprotein B Testing on the Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the Korean Adult Population
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Metabolites.2024; 14(3): 169. CrossRef - A self-powered and supercapacitive microneedle continuous glucose monitoring system with a wide range of glucose detection capabilities
Hye-Jun Kil, Jang Hyeon Kim, Kanghae Lee, Tae-Uk Kang, Ju-Hyun Yoo, Yong-ho Lee, Jin-Woo Park
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2024; 257: 116297. CrossRef - Cardiorenal outcomes and mortality after sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor initiation in type 2 diabetes patients with percutaneous coronary intervention history
Jin Hwa Kim, Young Sang Lyu, BongSeong Kim, Mee Kyung Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Recommendations for Pharmacological Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Junghyun Noh
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 127. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - A 33-Year-Old Man Presented with Abdominal Pain and Vomiting Starting a Day Ago
Jong Han Choi
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2023; 98(6): 289. CrossRef - Comorbidity Patterns and Management in Inpatients with Endocrine Diseases by Age Groups in South Korea: Nationwide Data
Sung-Soo Kim, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 14(1): 42. CrossRef
- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
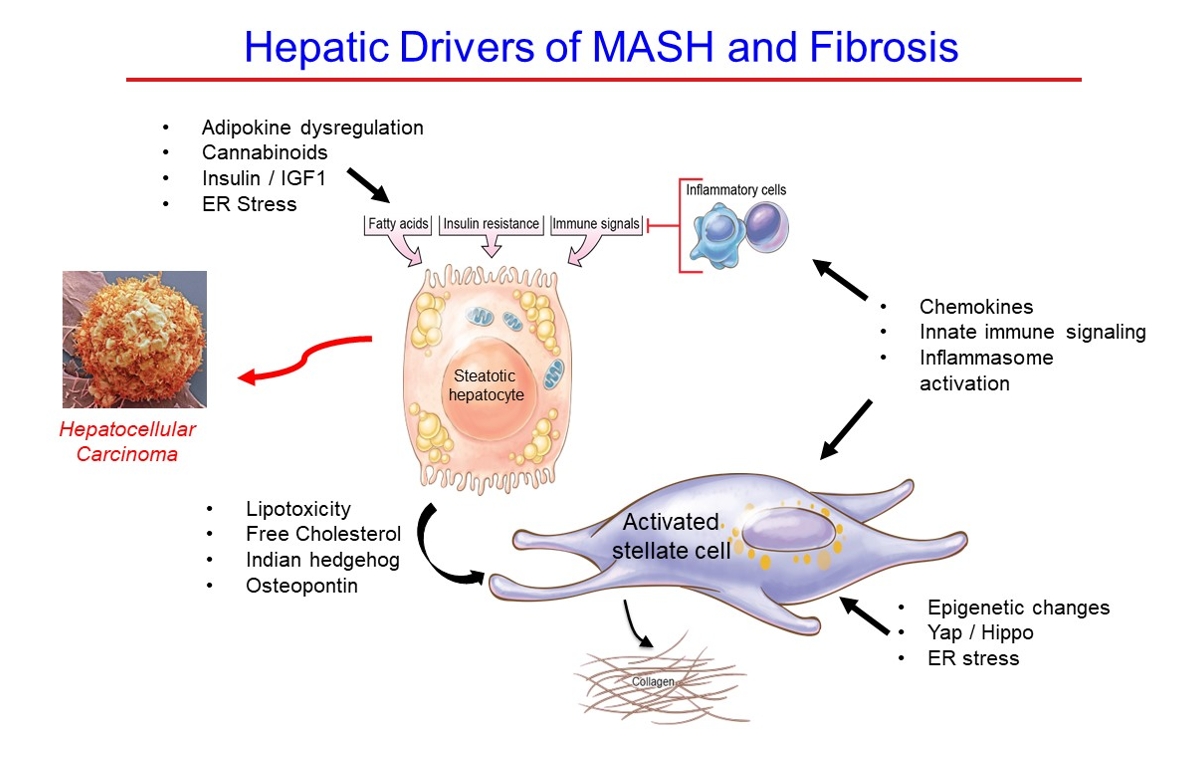
- Hepatic Fibrosis and Cancer: The Silent Threats of Metabolic Syndrome
- Scott L. Friedman
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):161-169. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0240
- 2,237 View
- 273 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic (fatty) liver disease (MASLD), previously termed non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, is a worldwide epidemic that can lead to hepatic inflammation, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The disease is typically a component of the metabolic syndrome that accompanies obesity, and is often overlooked because the liver manifestations are clinically silent until late-stage disease is present (i.e., cirrhosis). Moreover, Asian populations, including Koreans, have a higher fraction of patients who are lean, yet their illness has the same prognosis or worse than those who are obese. Nonetheless, ongoing injury can lead to hepatic inflammation and ballooning of hepatocytes as classic features. Over time, fibrosis develops following activation of hepatic stellate cells, the liver’s main fibrogenic cell type. The disease is usually more advanced in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, indicating that all diabetic patients should be screened for liver disease. Although there has been substantial progress in clarifying pathways of injury and fibrosis, there no approved therapies yet, but current research seeks to uncover the pathways driving hepatic inflammation and fibrosis, in hopes of identifying new therapeutic targets. Emerging molecular methods, especially single cell sequencing technologies, are revolutionizing our ability to clarify mechanisms underlying MASLD-associated fibrosis and HCC.
- Others
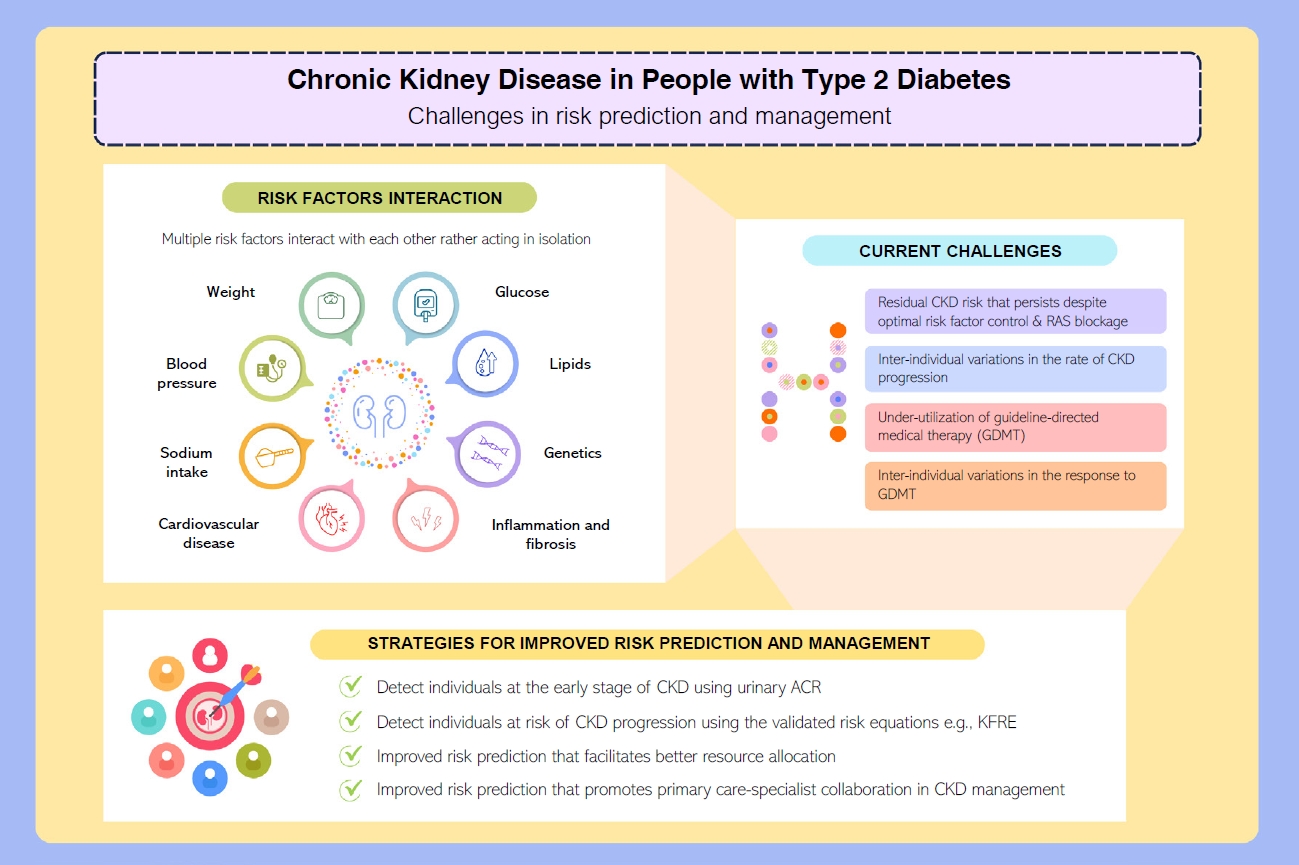
- Risk Prediction and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in People Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ying-Guat Ooi, Tharsini Sarvanandan, Nicholas Ken Yoong Hee, Quan-Hziung Lim, Sharmila S. Paramasivam, Jeyakantha Ratnasingam, Shireene R. Vethakkan, Soo-Kun Lim, Lee-Ling Lim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):196-207. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0244
- 1,838 View
- 350 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - People with type 2 diabetes mellitus have increased risk of chronic kidney disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Improved care delivery and implementation of guideline-directed medical therapy have contributed to the declining incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in high-income countries. By contrast, the global incidence of chronic kidney disease and associated mortality is either plateaued or increased, leading to escalating direct and indirect medical costs. Given limited resources, better risk stratification approaches to identify people at risk of rapid progression to end-stage kidney disease can reduce therapeutic inertia, facilitate timely interventions and identify the need for early nephrologist referral. Among people with chronic kidney disease G3a and beyond, the kidney failure risk equations (KFRE) have been externally validated and outperformed other risk prediction models. The KFRE can also guide the timing of preparation for kidney replacement therapy with improved healthcare resources planning and may prevent multiple complications and premature mortality among people with chronic kidney disease with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. The present review summarizes the evidence of KFRE to date and call for future research to validate and evaluate its impact on cardiovascular and mortality outcomes, as well as healthcare resource utilization in multiethnic populations and different healthcare settings.
- Pathophysiology
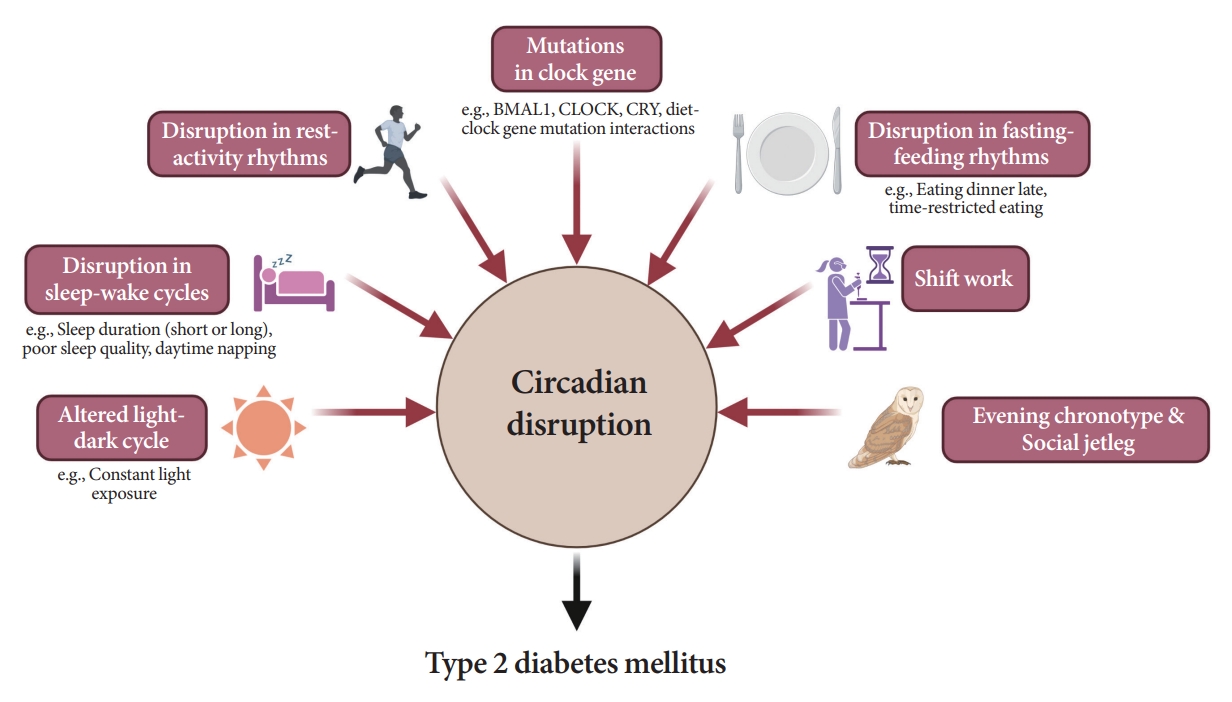
- Attention to Innate Circadian Rhythm and the Impact of Its Disruption on Diabetes
- Da Young Lee, Inha Jung, So Young Park, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Kyeong Jin Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):37-52. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0193
- 2,153 View
- 219 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Novel strategies are required to reduce the risk of developing diabetes and/or clinical outcomes and complications of diabetes. In this regard, the role of the circadian system may be a potential candidate for the prevention of diabetes. We reviewed evidence from animal, clinical, and epidemiological studies linking the circadian system to various aspects of the pathophysiology and clinical outcomes of diabetes. The circadian clock governs genetic, metabolic, hormonal, and behavioral signals in anticipation of cyclic 24-hour events through interactions between a “central clock” in the suprachiasmatic nucleus and “peripheral clocks” in the whole body. Currently, circadian rhythmicity in humans can be subjectively or objectively assessed by measuring melatonin and glucocorticoid levels, core body temperature, peripheral blood, oral mucosa, hair follicles, rest-activity cycles, sleep diaries, and circadian chronotypes. In this review, we summarized various circadian misalignments, such as altered light-dark, sleep-wake, rest-activity, fasting-feeding, shift work, evening chronotype, and social jetlag, as well as mutations in clock genes that could contribute to the development of diabetes and poor glycemic status in patients with diabetes. Targeting critical components of the circadian system could deliver potential candidates for the treatment and prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the future.
Original Article
- Drug/Regimen
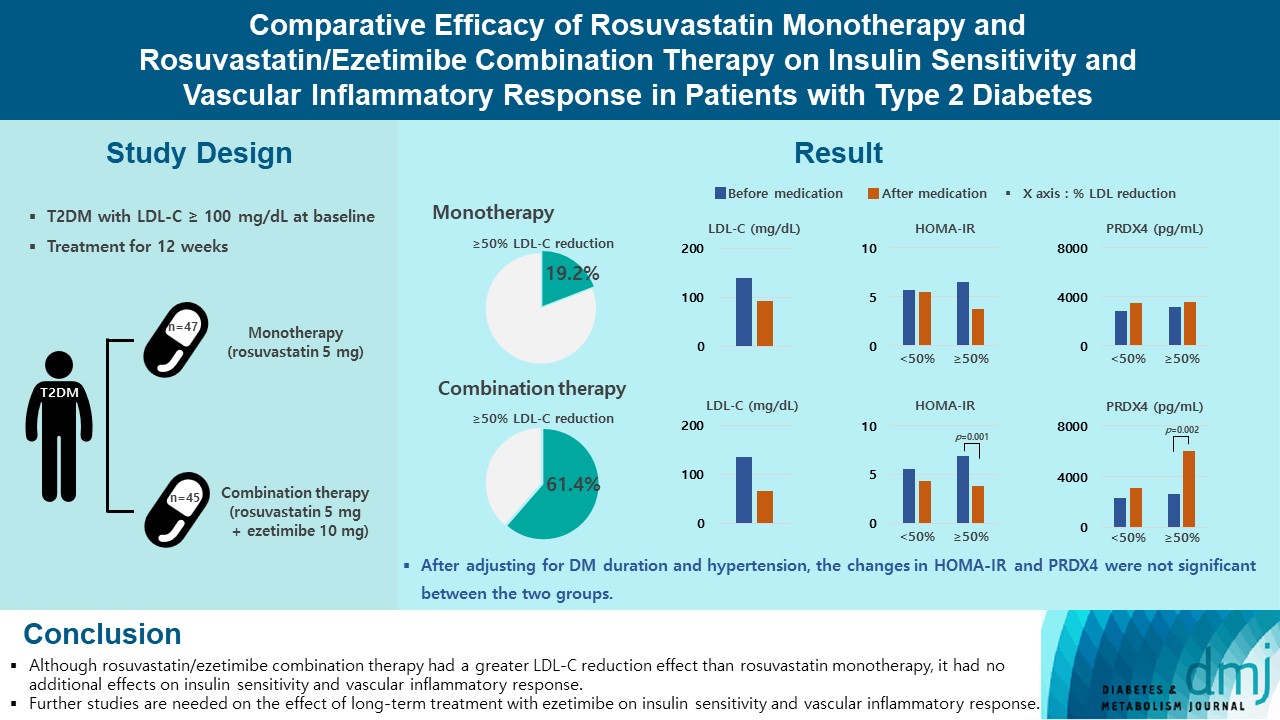
- Comparative Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy and Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination Therapy on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammatory Response in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Hye Han, Kyong Hye Joung, Jun Choul Lee, Ok Soon Kim, Sorim Choung, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Ju Hee Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Hyun Jin Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):112-121. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0402
- 1,997 View
- 221 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) induces endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, which are the main factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. The present study aimed to compare the effects of rosuvastatin monotherapy and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy on lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, and vascular inflammatory response in patients with T2DM.
Methods
A total of 101 patients with T2DM and dyslipidemia were randomized to either rosuvastatin monotherapy (5 mg/day, n=47) or rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy (5 mg/10 mg/day, n=45) and treated for 12 weeks. Serum lipids, glucose, insulin, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), and peroxiredoxin 4 (PRDX4) levels were determined before and after 12 weeks of treatment.
Results
The reduction in low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% from baseline after treatment was more in the combination therapy group. The serum sICAM-1 levels increased significantly in both groups, but there was no difference between the two groups. The significant changes in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and PRDX4 were confirmed only in the subgroup in which LDL-C was reduced by 50% or more in the combination therapy group. However, after adjusting for diabetes mellitus duration and hypertension, the changes in HOMA-IR and PRDX4 were not significant between the two groups.
Conclusion
Although rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy had a greater LDL-C reduction effect than rosuvastatin monotherapy, it had no additional effects on insulin sensitivity and vascular inflammatory response. Further studies are needed on the effect of long-term treatment with ezetimibe on insulin sensitivity and vascular inflammatory response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Roh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 55. CrossRef
- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Reviews
- Pathophysiology
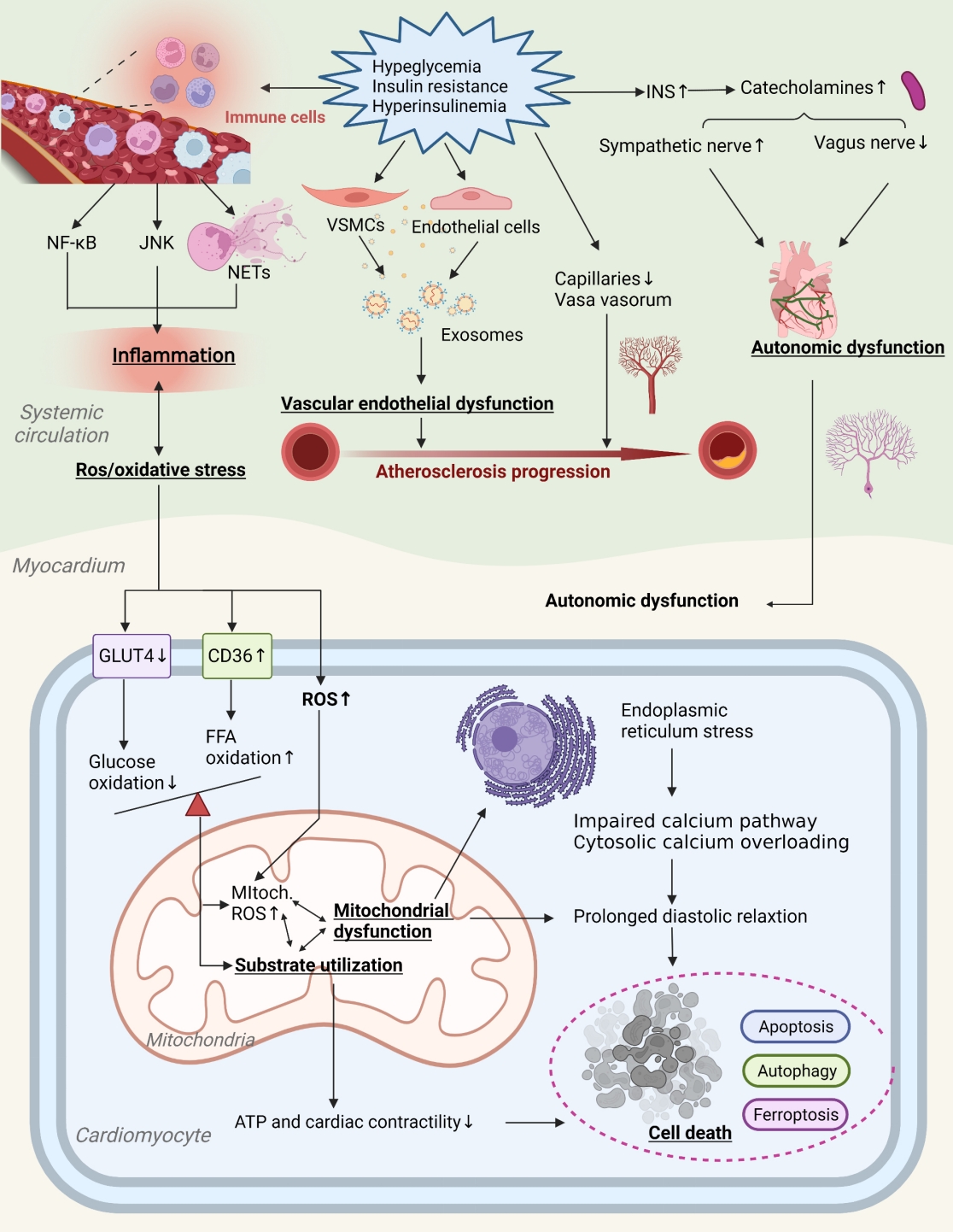
- Primordial Drivers of Diabetes Heart Disease: Comprehensive Insights into Insulin Resistance
- Yajie Fan, Zhipeng Yan, Tingting Li, Aolin Li, Xinbiao Fan, Zhongwen Qi, Junping Zhang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):19-36. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0110
- 2,153 View
- 182 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Insulin resistance has been regarded as a hallmark of diabetes heart disease (DHD). Numerous studies have shown that insulin resistance can affect blood circulation and myocardium, which indirectly cause cardiac hypertrophy and ventricular remodeling, participating in the pathogenesis of DHD. Meanwhile, hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia associated with insulin resistance can directly impair the metabolism and function of the heart. Targeting insulin resistance is a potential therapeutic strategy for the prevention of DHD. Currently, the role of insulin resistance in the pathogenic development of DHD is still under active research, as the pathological roles involved are complex and not yet fully understood, and the related therapeutic approaches are not well developed. In this review, we describe insulin resistance and add recent advances in the major pathological and physiological changes and underlying mechanisms by which insulin resistance leads to myocardial remodeling and dysfunction in the diabetic heart, including exosomal dysfunction, ferroptosis, and epigenetic factors. In addition, we discuss potential therapeutic approaches to improve insulin resistance and accelerate the development of cardiovascular protection drugs.
- Basic Research
- Mitochondrial Stress and Mitokines: Therapeutic Perspectives for the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases
- Benyuan Zhang, Joon Young Chang, Min Hee Lee, Sang-Hyeon Ju, Hyon-Seung Yi, Minho Shong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):1-18. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0115

- 2,028 View
- 255 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Mitochondrial stress and the dysregulated mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) are linked to various diseases, including metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer. Mitokines, signaling molecules released by mitochondrial stress response and UPRmt, are crucial mediators of inter-organ communication and influence systemic metabolic and physiological processes. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of mitokines, including their regulation by exercise and lifestyle interventions and their implications for various diseases. The endocrine actions of mitokines related to mitochondrial stress and adaptations are highlighted, specifically the broad functions of fibroblast growth factor 21 and growth differentiation factor 15, as well as their specific actions in regulating inter-tissue communication and metabolic homeostasis. Finally, we discuss the potential of physiological and genetic interventions to reduce the hazards associated with dysregulated mitokine signaling and preserve an equilibrium in mitochondrial stress-induced responses. This review provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying mitochondrial regulation of health and disease by exploring mitokine interactions and their regulation, which will facilitate the development of targeted therapies and personalized interventions to improve health outcomes and quality of life.
- Technology/Device
- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):27-41. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0271

- 6,231 View
- 384 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology has evolved over the past decade with the integration of various devices including insulin pumps, connected insulin pens (CIPs), automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, and virtual platforms. CGM has shown consistent benefits in glycemic outcomes in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) treated with insulin. Moreover, the combined effect of CGM and education have been shown to improve glycemic outcomes more than CGM alone. Now a CIP is the expected future technology that does not need to be worn all day like insulin pumps and helps to calculate insulin doses with a built-in bolus calculator. Although only a few clinical trials have assessed the effectiveness of CIPs, they consistently show benefits in glycemic outcomes by reducing missed doses of insulin and improving problematic adherence. AID systems and virtual platforms made it possible to achieve target glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetes while minimizing hypoglycemia, which has always been challenging in T1DM. Now fully automatic AID systems and tools for diabetes decisions based on artificial intelligence are in development. These advances in technology could reduce the burden associated with insulin treatment for diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Won Sang Yoo, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024; 26(4): 222. CrossRef - Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent advances in the precision control strategy of artificial pancreas
Wuyi Ming, Xudong Guo, Guojun Zhang, Yinxia Liu, Yongxin Wang, Hongmei Zhang, Haofang Liang, Yuan Yang
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital Health in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
Dorothy Avoke, Abdallah Elshafeey, Robert Weinstein, Chang H. Kim, Seth S. Martin
Endocrine Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic Outcomes During Early Use of the MiniMed™ 780G Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System with Guardian™ 4 Sensor
Toni L. Cordero, Zheng Dai, Arcelia Arrieta, Fang Niu, Melissa Vella, John Shin, Andrew S. Rhinehart, Jennifer McVean, Scott W. Lee, Robert H. Slover, Gregory P. Forlenza, Dorothy I. Shulman, Rodica Pop-Busui, James R. Thrasher, Mark S. Kipnes, Mark P. Ch
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(9): 652. CrossRef - Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - APSec1.0: Innovative Security Protocol Design with Formal Security Analysis for the Artificial Pancreas System
Jiyoon Kim, Jongmin Oh, Daehyeon Son, Hoseok Kwon, Philip Virgil Astillo, Ilsun You
Sensors.2023; 23(12): 5501. CrossRef - Advances and Development of Electronic Neural Interfaces
Xue Jiaxiang, Liu Zhixin
Journal of Computing and Natural Science.2023; : 147. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and Metabolic Control in a Cohort of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Coeliac Disease
Flavia Amaro, Maria Alessandra Saltarelli, Marina Primavera, Marina Cerruto, Stefano Tumini
Endocrines.2023; 4(3): 595. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemia Risk Index with Time in Range for Assessing Glycemic Quality
Ji Yoon Kim, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(12): 883. CrossRef - The Benefits Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Pregnancy
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 472. CrossRef - The Growing Challenge of Diabetes Management in an Aging Society
Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 630. CrossRef - Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos, Ranjit M. Anjana, Viswanathan Mohan, Charlotte Steenblock, Stefan R. Bornstein
Exploration of Endocrine and Metabolic Disease.2023; 1(1): 16. CrossRef - An Observational Pilot Study of a Tailored Environmental Monitoring and Alert System for Improved Management of Chronic Respiratory Diseases
Mohammed Alotaibi, Fady Alnajjar, Badr A Alsayed, Tareq Alhmiedat, Ashraf M Marei, Anas Bushnag, Luqman Ali
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 3799. CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef
- Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
- Complications
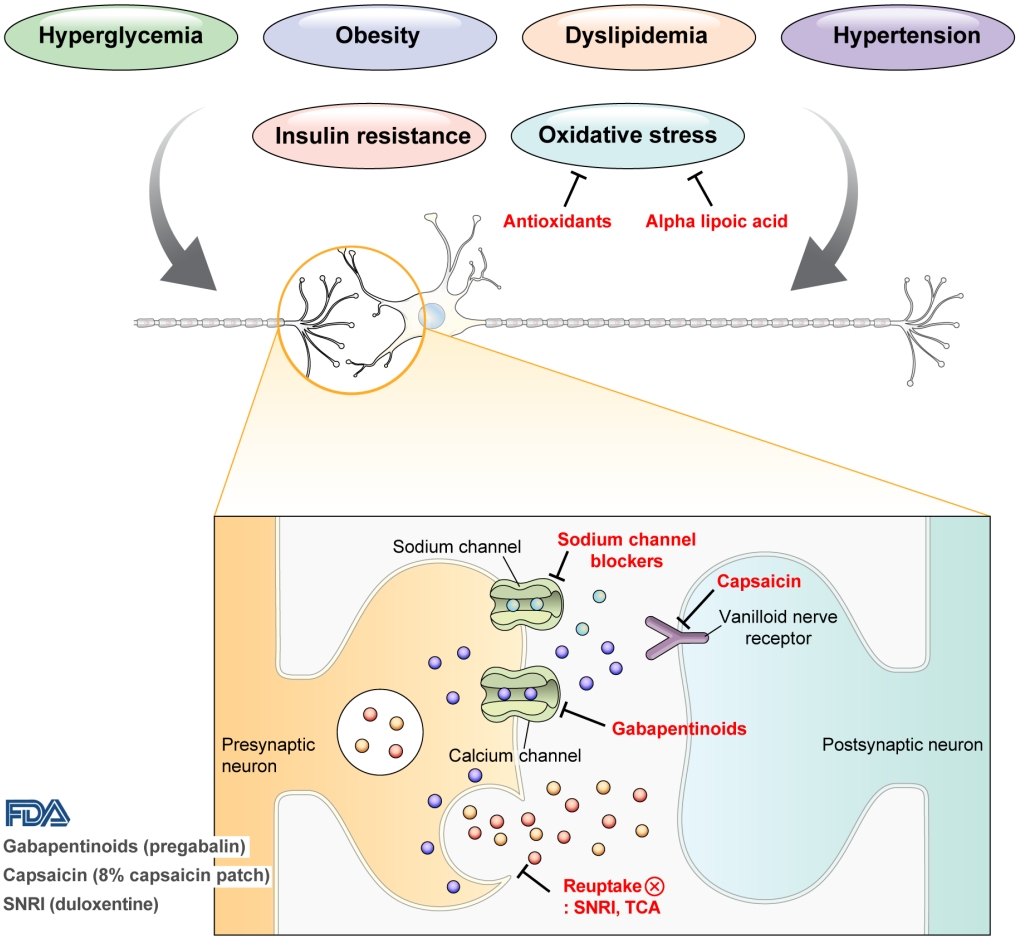
- Pharmacological and Nonpharmacological Treatments for Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Han Na Jang, Tae Jung Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):743-756. Published online September 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0018
- 3,904 View
- 546 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is one of the most prevalent chronic complications of diabetes. The lifetime prevalence of DPN is thought to be >50%, and 15%–25% of patients with diabetes experience neuropathic pain, referred to as “painful DPN.” Appropriate treatment of painful DPN is important because this pain contributes to a poor quality of life by causing sleep disturbance, anxiety, and depression. The basic principle for the management of painful DPN is to control hyperglycemia and other modifiable risk factors, but these may be insufficient for preventing or improving DPN. Because there is no promising diseasemodifying medication for DPN, the pain itself needs to be managed when treating painful DPN. Drugs for neuropathic pain, such as gabapentinoids, serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, alpha-lipoic acid, sodium channel blockers, and topical capsaicin, are used for the management of painful DPN. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved pregabalin, duloxetine, tapentadol, and the 8% capsaicin patch as drugs for the treatment of painful DPN. Recently, spinal cord stimulation using electrical stimulation is approved by the FDA for the treatment for painful DPN. This review describes the currently available pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatments for painful DPN.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- J-2156, a small molecule somatostatin type 4 receptor agonist, alleviated hindpaw hypersensitivity in the streptozotocin-induced rat model of painful diabetic neuropathy but with a 2-fold decrease in potency at an advanced stage in the model, mimicking mo
A. Kuo, M. Z. Imam, R. Li, L. Lin, A. Raboczyj, A. E. Bohmer, J. R. Nicholson, L. Corradini, M. T. Smith
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Chronic Wound–Related Pain Model
Kevin Woo
Clinics in Geriatric Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- J-2156, a small molecule somatostatin type 4 receptor agonist, alleviated hindpaw hypersensitivity in the streptozotocin-induced rat model of painful diabetic neuropathy but with a 2-fold decrease in potency at an advanced stage in the model, mimicking mo
Sulwon Lecture 2022
- Others
- Opening the Precision Diabetes Care through Digital Healthcare
- Joonyub Lee, Jin Yu, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):307-314. Published online March 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0386

- 5,223 View
- 247 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The national healthcare systems of every country in the world cannot sustain the rise in healthcare expenditure caused by chronic diseases and their complications. To sustain the national healthcare system, a novel system should be developed to improve the quality of care and minimize healthcare costs. For 20 years, our team developed patient-communicating digital healthcare platforms and proved their efficacy. National scale randomized control trials are underway to systematically measure the efficacy and economic benefits of this digital health care system. Precision medicine aims to maximize effectiveness of disease management by considering individual variability. Digital health technologies enable precision medicine at a reasonable cost that was not available before. The government launched the “National Integrated Bio-big Data Project” which will collect diverse health data from the participants. Individuals will share their health information to physicians or researchers at their will by gateway named “My-Healthway.’ Taken together, now we stand in front of the evolution of medical care, so-called “Precision medicine.” led by various kinds of technologies and a huge amount of health information exchange. We should lead these new trends as pioneers, not as followers, to establish and implement the best care for our patients that can help them to withstand their devastating diseases.
Reviews
- Basic Research
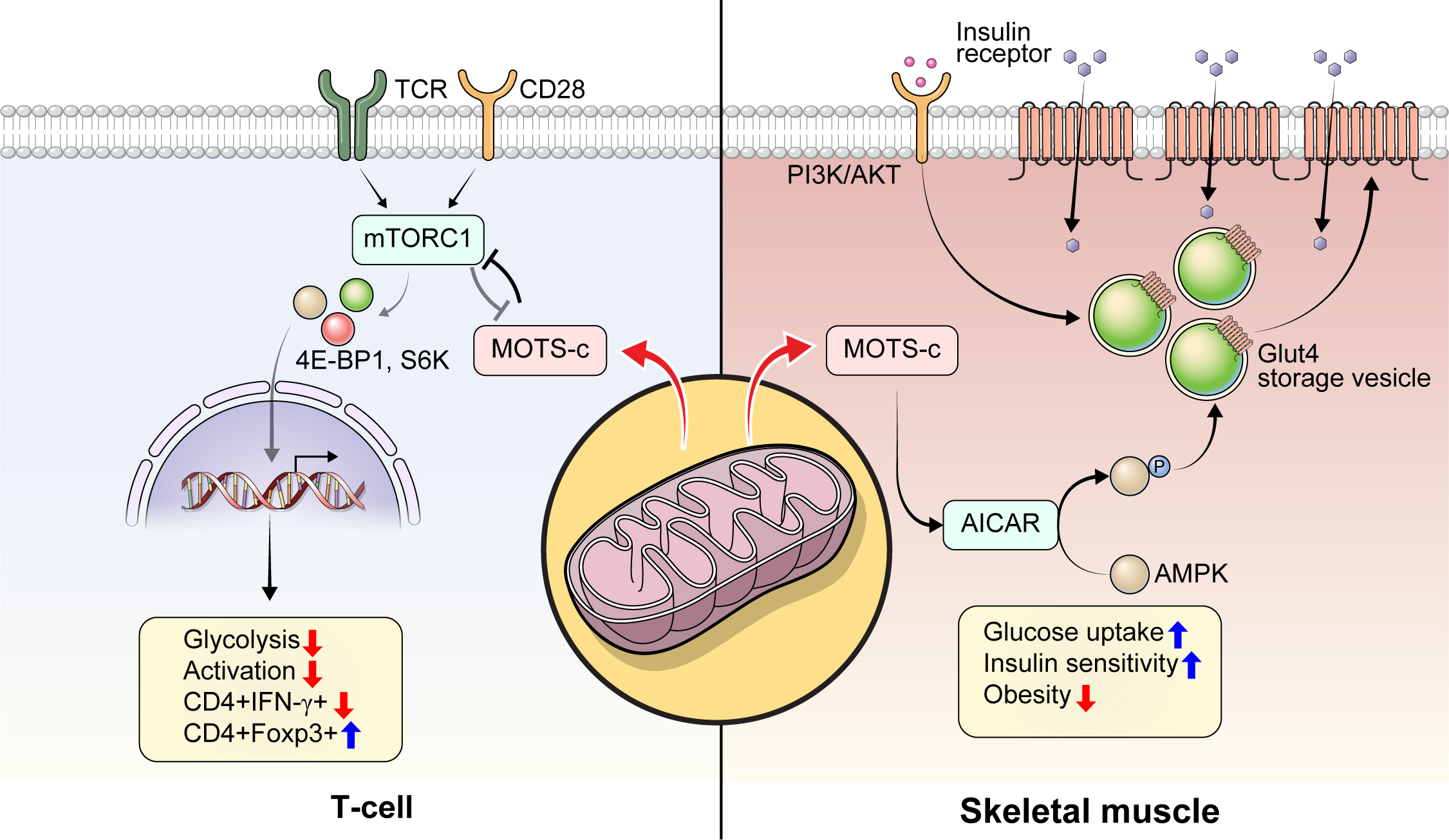
- Mitochondrial-Encoded Peptide MOTS-c, Diabetes, and Aging-Related Diseases
- Byung Soo Kong, Changhan Lee, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):315-324. Published online February 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0333
- 5,709 View
- 284 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Mitochondria are complex metabolic organelles with manifold pathophysiological implications in diabetes. Currently published mitochondrial-encoded peptides, which are expressed from the mitochondrial open reading frame of the 12S ribosomal RNA type-c (MOTS-c), 16S rRNA (humanin and short humanin like peptide 1-6 [SHLP1-6]), or small human mitochondrial open reading frame over serine tRNA (SHMOOSE) are associated with regulation of cellular metabolism and insulin action in age-related diseases, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus. This review focuses mainly on recent advances in MOTS-c research with regards to diabetes, including both type 1 and type 2. The emerging understanding of MOTS-c in diabetes may provide insight into the development of new therapies for diabetes and other age or senescence-related diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial-derived peptides: Antidiabetic functions and evolutionary perspectives
Satadeepa Kal, Sumana Mahata, Suborno Jati, Sushil K. Mahata
Peptides.2024; 172: 171147. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Stress and Mitokines: Therapeutic Perspectives for the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases
Benyuan Zhang, Joon Young Chang, Min Hee Lee, Sang-Hyeon Ju, Hyon-Seung Yi, Minho Shong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 1. CrossRef - Mitochondrial bioenergetics, metabolism, and beyond in pancreatic β-cells and diabetes
Alejandra María Rivera Nieves, Brian Michael Wauford, Accalia Fu
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mitochondrial-derived peptides: Antidiabetic functions and evolutionary perspectives
- Basic Research
- Adipose Tissue and Metabolic Health
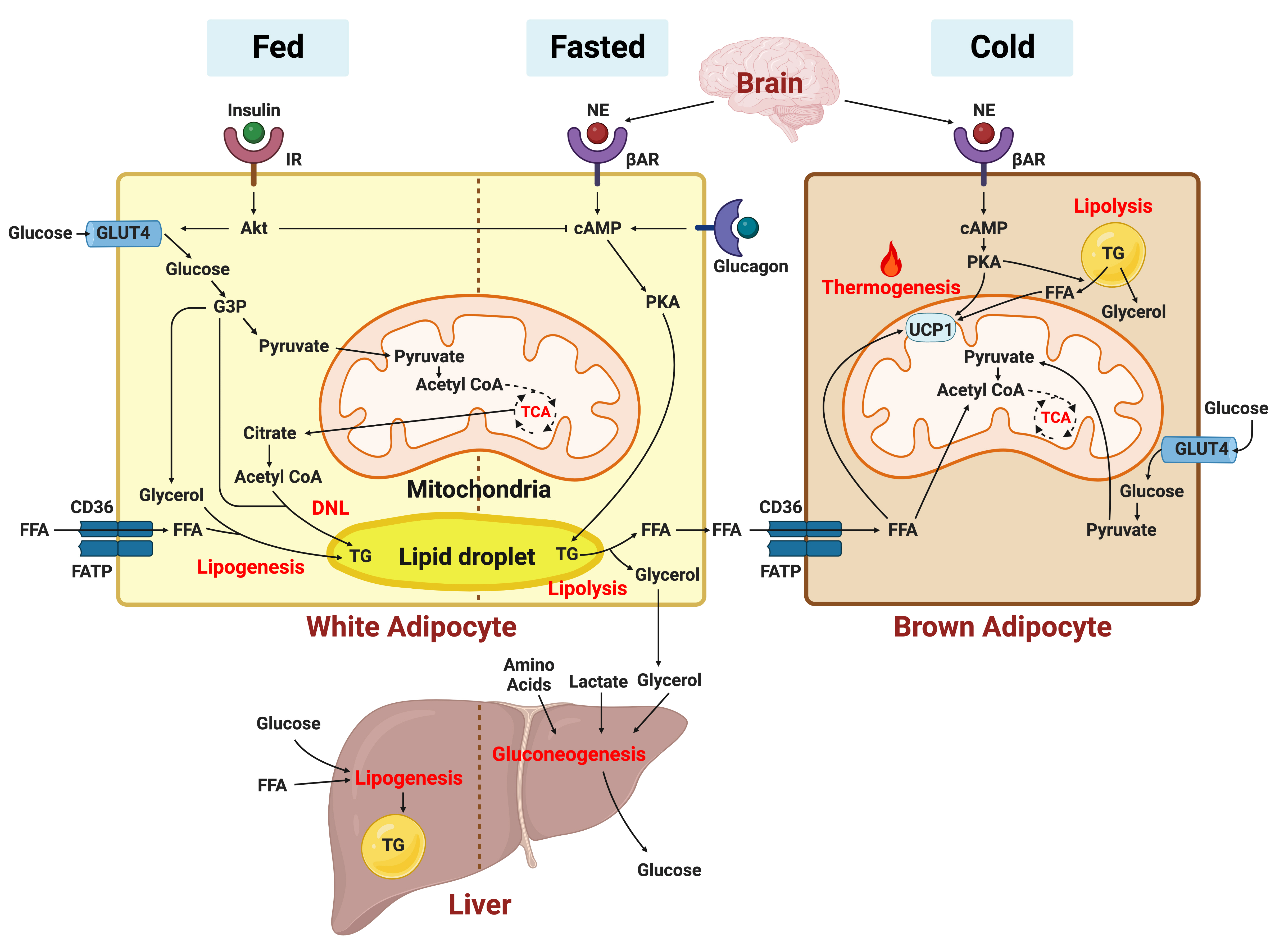
- Sung-Min An, Seung-Hee Cho, John C. Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):595-611. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0011
- 3,825 View
- 440 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - In this review, we provide a brief synopsis of the connections between adipose tissue and metabolic health and highlight some recent developments in understanding and exploiting adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue plays critical roles in the regulation of systemic glucose and lipid metabolism and secretes bioactive molecules possessing endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine functions. Dysfunctional adipose tissue has a detrimental impact on metabolic health and is intimately involved in key aspects of metabolic diseases such as insulin resistance, lipid overload, inflammation, and organelle stress. Differences in the distribution of fat depots and adipose characteristics relate to divergent degrees of metabolic dysfunction found in metabolically healthy and unhealthy obese individuals. Thermogenic adipocytes increase energy expenditure via mitochondrial uncoupling or adenosine triphosphate-consuming futile substrate cycles, while functioning as a metabolic sink and participating in crosstalk with other metabolic organs. Manipulation of adipose tissue provides a wealth of opportunities to intervene and combat the progression of associated metabolic diseases. We discuss current treatment modalities for obesity including incretin hormone analogs and touch upon emerging strategies with therapeutic potential including exosome-based therapy, pharmacological activation of brown and beige adipocyte thermogenesis, and administration or inhibition of adipocyte-derived factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pharmacological targets at the lysosomal autophagy–NLRP3 inflammasome crossroads
Srinivasa Reddy Bonam, Dylan Mastrippolito, Philippe Georgel, Sylviane Muller
Trends in Pharmacological Sciences.2024; 45(1): 81. CrossRef - Senescent adipocytes and type 2 diabetes – current knowledge and perspective concepts
Weronika Kruczkowska, Julia Gałęziewska, Mateusz Kciuk, Adrianna Gielecińska, Elżbieta Płuciennik, Zbigniew Pasieka, Lin-Yong Zhao, Yi-Jin Yu, Damian Kołat, Żaneta Kałuzińska-Kołat
Biomolecular Concepts.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Visceral Adipose Tissue: The Hidden Culprit for Type 2 Diabetes
Sneha Dhokte, Krzysztof Czaja
Nutrients.2024; 16(7): 1015. CrossRef - Beyond the Cold: Activating Brown Adipose Tissue as an Approach to Combat Obesity
Cristina Elena Negroiu, Iulia Tudorașcu, Cristina Maria Bezna, Sanziana Godeanu, Marina Diaconu, Raluca Danoiu, Suzana Danoiu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(7): 1973. CrossRef
- Pharmacological targets at the lysosomal autophagy–NLRP3 inflammasome crossroads
Original Articles
- Drug/Regimen
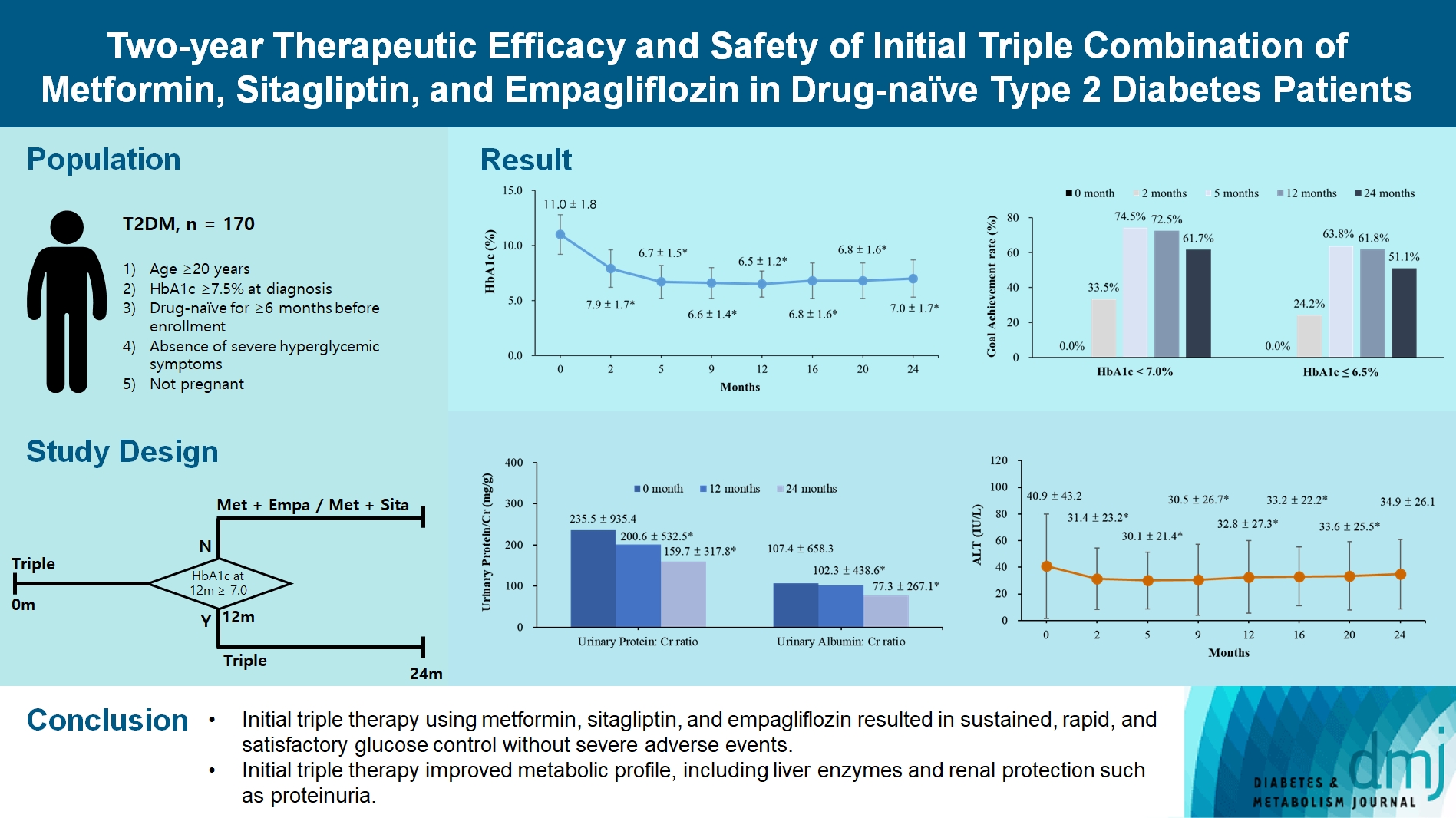
- Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Young-Hwan Park, Minji Sohn, So Yeon Lee, Soo Lim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):253-264. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0128
- 1,689 View
- 273 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated the long-term efficacy and safety of initial triple therapy using metformin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
We enrolled 170 drug-naïve patients with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level >7.5% who had started triple therapy (metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin). Glycemic, metabolic, and urinary parameters were measured for 24 months.
Results
After 24 months, HbA1c level decreased significantly from 11.0%±1.8% to 7.0%±1.7%. At 12 and 24 months, the rates of achievement of the glycemic target goal (HbA1c <7.0%) were 72.5% and 61.7%, respectively, and homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function and insulin resistance indices improved. Whole-body fat percentage decreased by 1.08%, and whole-body muscle percentage increased by 0.97% after 24 months. Fatty liver indices and albuminuria improved significantly. The concentration of ketone bodies was elevated at the baseline but decreased after 24 months. There were no serious adverse events, including ketoacidosis.
Conclusion
Initial triple combination therapy with metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin led to achievement of the glycemic target goal, which was maintained for 24 months without severe hypoglycemia but with improved metabolic function and albuminuria. This combination therapy may be a good strategy for drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Drug/Regimen
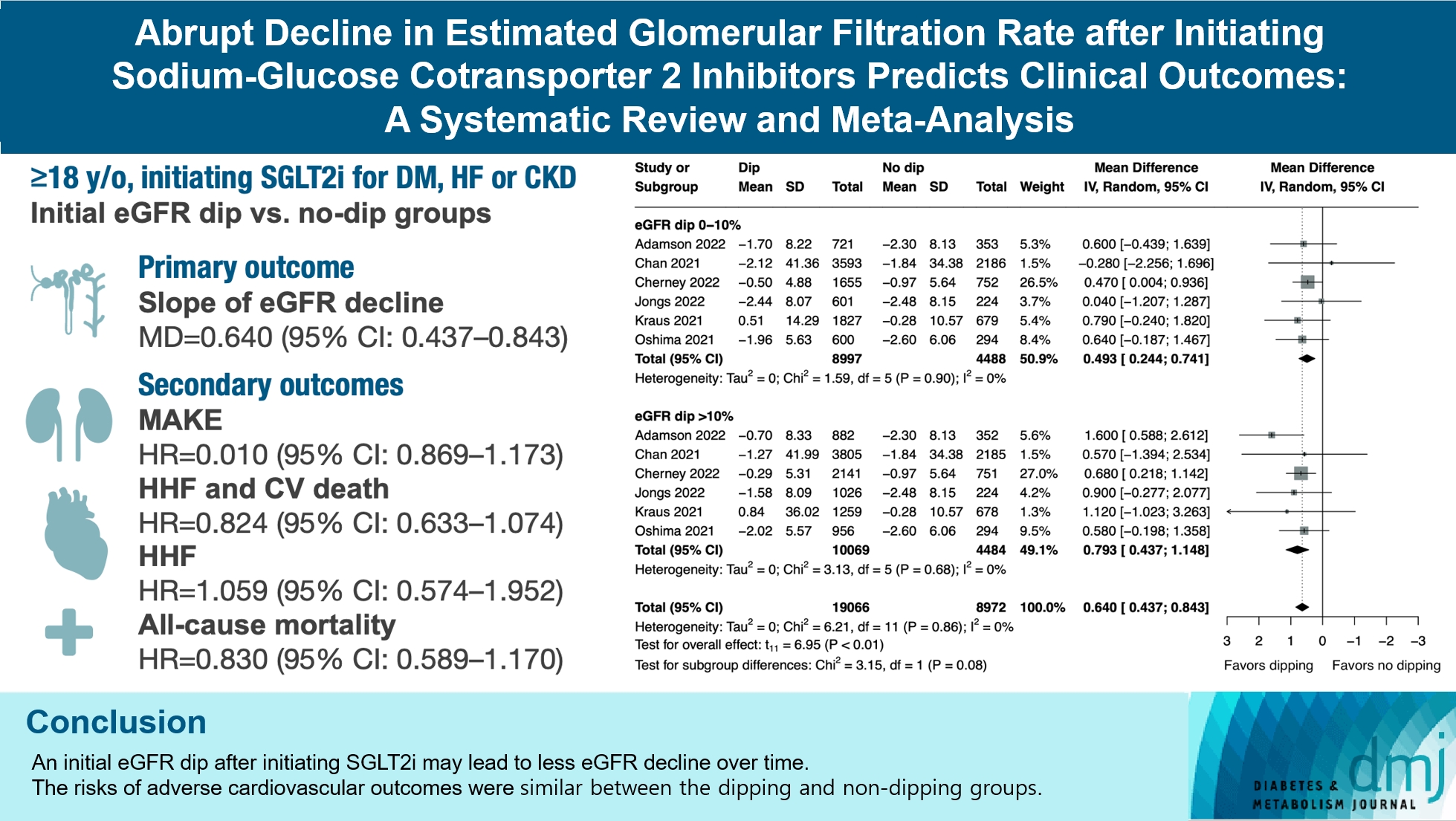
- Abrupt Decline in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate after Initiating Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Predicts Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Min-Hsiang Chuang, Yu-Shuo Tang, Jui-Yi Chen, Heng-Chih Pan, Hung-Wei Liao, Wen-Kai Chu, Chung-Yi Cheng, Vin-Cent Wu, Michael Heung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):242-252. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0201
- 1,501 View
- 202 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The initiation of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) typically leads to a reversible initial dip in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). The implications of this phenomenon on clinical outcomes are not well-defined.
Methods
We searched MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane Library from inception to March 23, 2023 to identify randomized controlled trials and cohort studies comparing kidney and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with and without initial eGFR dip after initiating SGLT2i. Pooled estimates were calculated using random-effect meta-analysis.
Results
We included seven studies in our analysis, which revealed that an initial eGFR dip following the initiation of SGLT2i was associated with less annual eGFR decline (mean difference, 0.64; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.437 to 0.843) regardless of baseline eGFR. The risk of major adverse kidney events was similar between the non-dipping and dipping groups but reduced in patients with a ≤10% eGFR dip (hazard ratio [HR], 0.915; 95% CI, 0.865 to 0.967). No significant differences were observed in the composite of hospitalized heart failure and cardiovascular death (HR, 0.824; 95% CI, 0.633 to 1.074), hospitalized heart failure (HR, 1.059; 95% CI, 0.574 to 1.952), or all-cause mortality (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.589 to 1.170). The risk of serious adverse events (AEs), discontinuation of SGLT2i due to AEs, kidney-related AEs, and volume depletion were similar between the two groups. Patients with >10% eGFR dip had increased risk of hyperkalemia compared to the non-dipping group.
Conclusion
Initial eGFR dip after initiating SGLT2i might be associated with less annual eGFR decline. There were no significant disparities in the risks of adverse cardiovascular outcomes between the dipping and non-dipping groups.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





