
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse > Previous issues
Reviews
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Effect of Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets and Intermittent Fasting on Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Hypertension Management: Consensus Statement of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, Korean Diabetes Association, and Korean Society of Hypertension
- Jong Han Choi, Yoon Jeong Cho, Hyun-Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Suk Chon, Jee-Hyun Kang, Kyoung-Kon Kim, Eun Mi Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Ga Eun Nam, Kwang Il Kim, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity (KSSO), Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines and Committee of Food and Nutrition, Korean Diabetes Association (KDA), Policy Committee of Korean Society of Hypertension (KSH), Policy Development Committee of National Academy of Medicine of Korea (NAMOK)
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):355-376. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0038
- 11,006 View
- 588 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
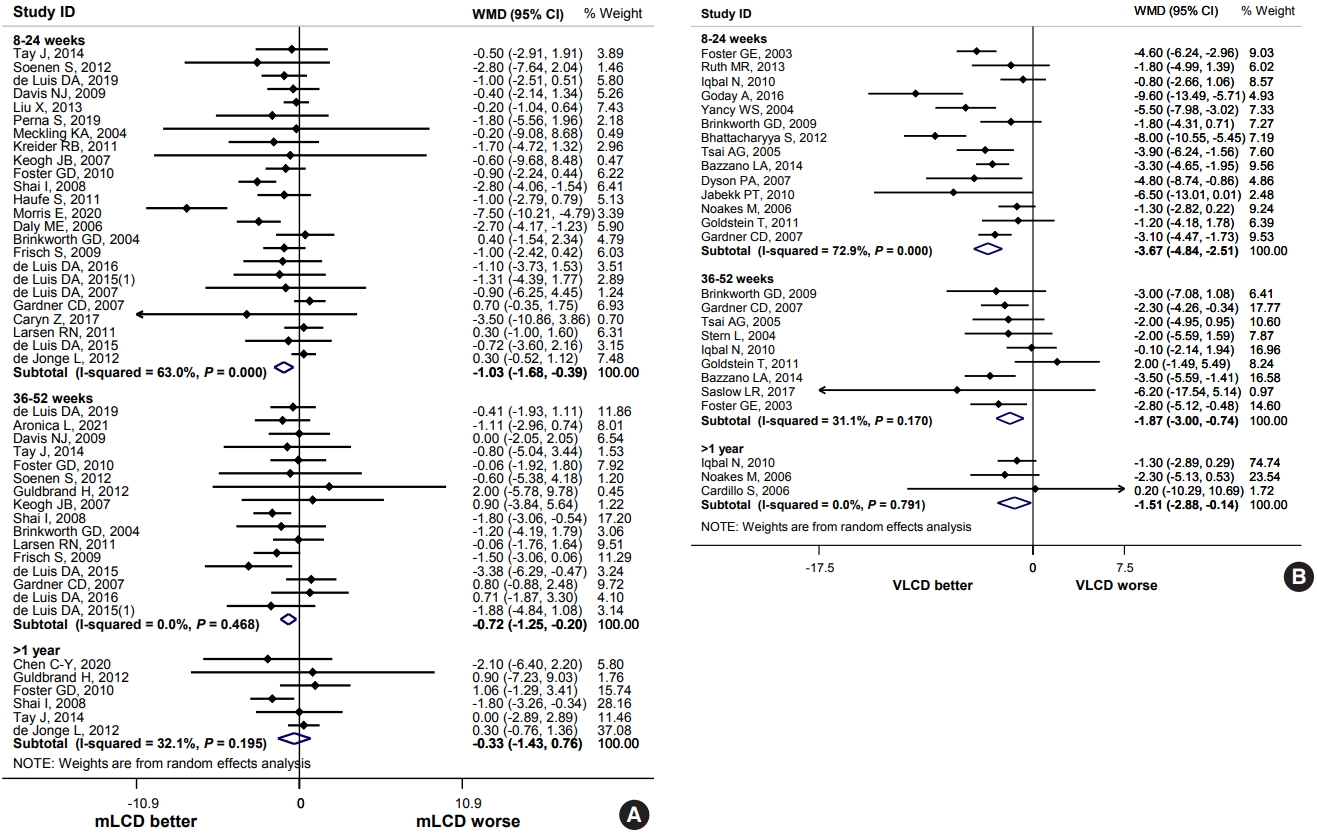
ePub - Carbohydrate-restricted diets and intermittent fasting (IF) have been rapidly gaining interest among the general population and patients with cardiometabolic disease, such as overweight or obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. However, there are limited expert recommendations for these dietary regimens. This study aimed to evaluate the level of scientific evidence on the benefits and harms of carbohydrate-restricted diets and IF to make responsible recommendations. A meta-analysis and systematic literature review of 66 articles on 50 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of carbohydrate-restricted diets and 10 articles on eight RCTs of IF was performed. Based on the analysis, the following recommendations are suggested. In adults with overweight or obesity, a moderately-low carbohydrate or low carbohydrate diet (mLCD) can be considered as a dietary regimen for weight reduction. In adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus, mLCD can be considered as a dietary regimen for improving glycemic control and reducing body weight. In contrast, a very-low carbohydrate diet (VLCD) and IF are recommended against in patients with diabetes. Furthermore, no recommendations are suggested for VLCD and IF in adults with overweight or obesity, and carbohydrate-restricted diets and IF in patients with hypertension. Here, we describe the results of our analysis and the evidence for these recommendations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic changes with intermittent fasting
Maria G. Lange, Alice A. Coffey, Paul C. Coleman, Thomas M. Barber, Thijs Van Rens, Oyinlola Oyebode, Sally Abbott, Petra Hanson
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2024; 37(1): 256. CrossRef - Papel do Jejum Intermitente e da Dieta Restrita em Carboidratos na Prevenção de Doenças Cardiovasculares em Pacientes Pré-Diabéticos
Mohamed Khalfallah, Basma Elnagar, Shaimaa S. Soliman, Ahmad Eissa, Amany Allaithy
Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Medical nutrition therapy for diabetes mellitus
Suk Chon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 421. CrossRef - Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis development in a patient with type 2 diabetes receiving a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor and a carbohydrate-restricted diet
Gwanpyo Koh, Jisun Bang, Soyeon Yoo, Sang Ah Lee
Journal of Medicine and Life Science.2023; 20(3): 126. CrossRef - Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hyperte
Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 377. CrossRef - The Related Metabolic Diseases and Treatments of Obesity
Ming Yang, Shuai Liu, Chunye Zhang
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1616. CrossRef - Updated Meta-Analysis of Studies from 2011 to 2021 Comparing the Effectiveness of Intermittent Energy Restriction and Continuous Energy Restriction
Kyoung-Kon Kim, Jee-Hyun Kang, Eun Mi Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(3): 230. CrossRef
- Metabolic changes with intermittent fasting
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hypertension
- Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):377-390. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0051
- 4,945 View
- 249 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
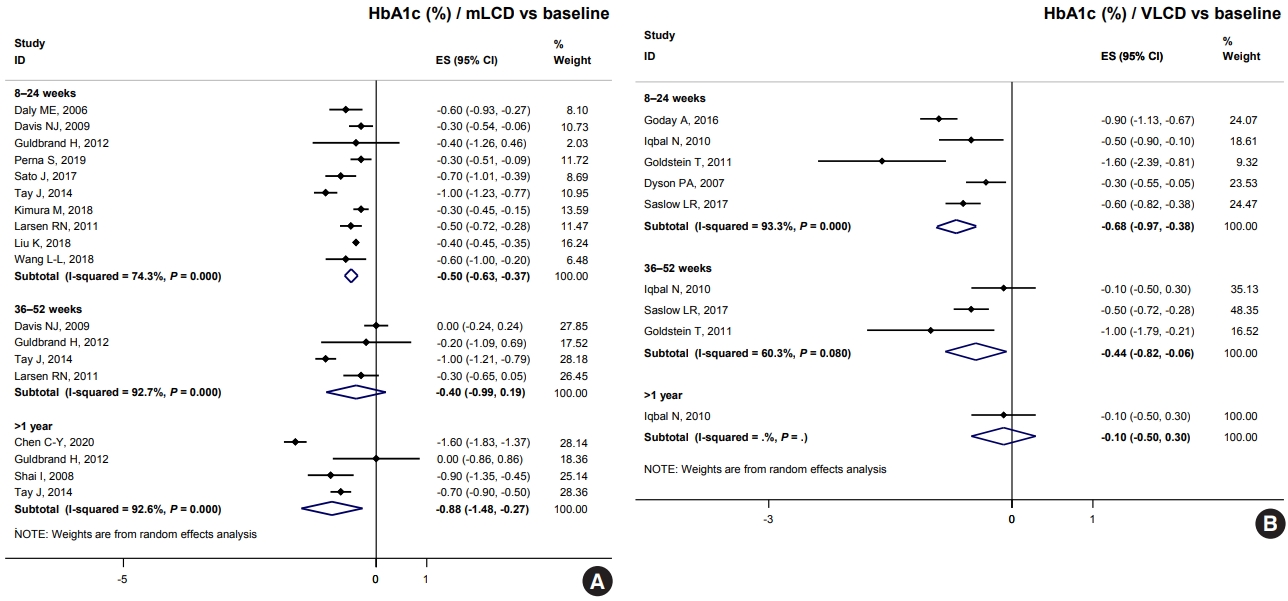
ePub - The Joint Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association, the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and the Korean Society of Hypertension announced a consensus statement on carbohydrate-restricted diets and intermittent fasting, representing an emerging and popular dietary pattern. In this statement, we recommend moderately-low-carbohydrate or low-carbohydrate diets, not a very-low-carbohydrate diet, for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. These diets can be considered a dietary regimen to improve glycemic control and reduce body weight in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. This review provides the detailed results of a meta-analysis and systematic literature review on the potential harms and benefits of carbohydrate-restricted diets in patients with diabetes. We expect that this review will help experts and patients by fostering an in-depth understanding and appropriate application of carbohydrate-restricted diets in the comprehensive management of diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of convenience meal-type foods designed for diabetes in the management of metabolic syndrome based on a 3-week trial
Do Gyeong Lee, In Gyeong Kang, Tae Seok Kim, Yun Ahn, Sang Yun Lee, Hye Jin Ahn, Yoo Kyoung Park
Nutrition.2024; 118: 112287. CrossRef - Long-Term Results of a Digital Diabetes Self-Management and Education Support Program Among Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Ashley Berthoumieux, Sarah Linke, Melinda Merry, Alison Megliola, Jessie Juusola, Jenna Napoleone
The Science of Diabetes Self-Management and Care.2024; 50(1): 19. CrossRef - Medical nutrition therapy for diabetes mellitus
Suk Chon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 421. CrossRef
- Efficacy of convenience meal-type foods designed for diabetes in the management of metabolic syndrome based on a 3-week trial
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Lifestyle Interventions for Non-Obese Patients Both with, and at Risk, of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Xin-Lei Zhang, Ting-Yao Wang, Giovanni Targher, Christopher D. Byrne, Ming-Hua Zheng
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):391-401. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0048

- 5,251 View
- 274 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease occurring in non-obese subjects (the so-called non-obese NAFLD) is a highly prevalent but neglected liver condition, which is closely associated with metabolic disorders and suboptimal lifestyles. Landmark studies have shown that lifestyle interventions are potentially beneficial in decreasing the risk of developing non-obese NAFLD and in ameliorating NAFLD in non-obese individuals with pre-existing NAFLD. Lifestyle interventions usually refer to changes in eating habits and physical activity, both of which have a powerful effect on non-obese NAFLD and on risk factors for non-obese NAFLD. However, to date, patients and health-care professionals have a poor awareness and understanding of non-obese NAFLD and the beneficial effects of lifestyle interventions in this patient population. The aim of this narrative review is to briefly discuss the evidence for the effects of lifestyle changes and what changes are needed amongst medical personnel and other stakeholders in order to raise awareness of non-obese NAFLD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triglycerides Mediate the Influence of Body Mass Index on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Non-Obese Chinese Population with Normal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels
Xixi Han, Jingwen Kong, Hemin Zhang, Yuan Zhao, Yafeng Zheng, Chao Wei
Obesity Facts.2024; 17(2): 191. CrossRef - Patients with NAFLD exhibit more advanced fibrosis in liver biopsy than patients with other chronic liver diseases
Lydia Rohr, Peter Lemmer, Marie Henning, Andrea Tannapfel, Theodor Baars, Paul Manka, Ali Canbay, Jan-Peter Sowa
Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie.2023; 61(01): 29. CrossRef - Performance of Simple Fibrosis Score in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with and without Type 2 Diabetes
Seung Min Chung, Min Kyu Kang, Jun Sung Moon, Jung Gil Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 277. CrossRef - An international multidisciplinary consensus statement on MAFLD and the risk of CVD
Xiao-Dong Zhou, Giovanni Targher, Christopher D. Byrne, Virend Somers, Seung Up Kim, C. Anwar A. Chahal, Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, Jingjing Cai, Michael D. Shapiro, Mohammed Eslam, Philippe Gabriel Steg, Ki-Chul Sung, Anoop Misra, Jian-Jun Li, Carlos Brotons,
Hepatology International.2023; 17(4): 773. CrossRef - Lean or Non-obese Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Are They Really Lean?
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 980. CrossRef - Sex-Based Differences and Risk Factors for Comorbid Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Bipolar Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study
Ying Wang, Yiyi Liu, Xun Zhang, Qing Wu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3533. CrossRef - Benefits of Physical Exercise as Approach to Prevention and Reversion of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents with Obesity
Valeria Calcaterra, Vittoria Magenes, Matteo Vandoni, Clarissa Berardo, Luca Marin, Alice Bianchi, Erika Cordaro, Giustino Silvestro, Dario Silvestri, Vittoria Carnevale Pellino, Cristina Cereda, Gianvincenzo Zuccotti
Children.2022; 9(8): 1174. CrossRef - The effects of supplementation of probiotics, prebiotics, or synbiotics on patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Wenmin Xing, Wenyan Gao, Xiaoling Lv, Zhenlei Zhao, Genxiang Mao, Xiaoyan Dong, Zuyong Zhang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Triglycerides Mediate the Influence of Body Mass Index on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Non-Obese Chinese Population with Normal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels
Sulwon Lecture 2021
- Basic Research
- Exercise, Mitohormesis, and Mitochondrial ORF of the 12S rRNA Type-C (MOTS-c)
- Tae Kwan Yoon, Chan Hee Lee, Obin Kwon, Min-Seon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):402-413. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0092
- 5,350 View
- 238 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
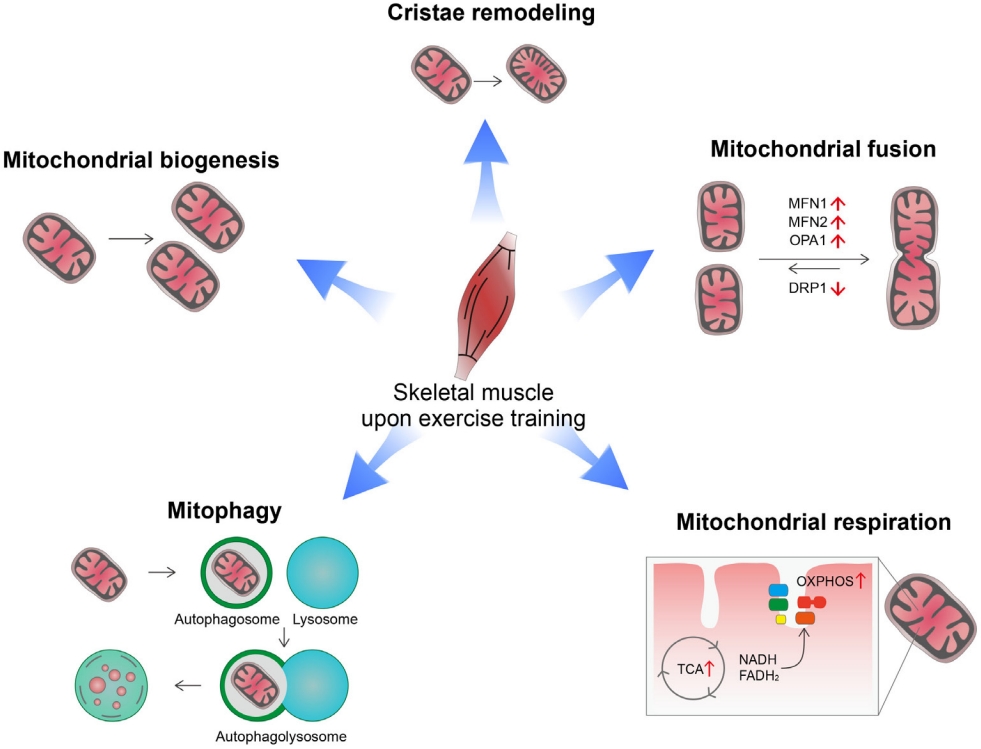
ePub - Low levels of mitochondrial stress are beneficial for organismal health and survival through a process known as mitohormesis. Mitohormetic responses occur during or after exercise and may mediate some salutary effects of exercise on metabolism. Exercise-related mitohormesis involves reactive oxygen species production, mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt), and release of mitochondria-derived peptides (MDPs). MDPs are a group of small peptides encoded by mitochondrial DNA with beneficial metabolic effects. Among MDPs, mitochondrial ORF of the 12S rRNA type-c (MOTS-c) is the most associated with exercise. MOTS-c expression levels increase in skeletal muscles, systemic circulation, and the hypothalamus upon exercise. Systemic MOTS-c administration increases exercise performance by boosting skeletal muscle stress responses and by enhancing metabolic adaptation to exercise. Exogenous MOTS-c also stimulates thermogenesis in subcutaneous white adipose tissues, thereby enhancing energy expenditure and contributing to the anti-obesity effects of exercise training. This review briefly summarizes the mitohormetic mechanisms of exercise with an emphasis on MOTS-c.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial-derived peptides: Antidiabetic functions and evolutionary perspectives
Satadeepa Kal, Sumana Mahata, Suborno Jati, Sushil K. Mahata
Peptides.2024; 172: 171147. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Low-Grade Mitochondrial Stress on Metabolic Diseases and Aging
Se Hee Min, Gil Myoung Kang, Jae Woo Park, Min-Seon Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2024; 65(2): 55. CrossRef - Roles of Myokines and Muscle-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Musculoskeletal Deterioration under Disuse Conditions
Jie Zhang, Yunfang Gao, Jiangwei Yan
Metabolites.2024; 14(2): 88. CrossRef - Antifragility and antiinflammaging: Can they play a role for a healthy longevity?
Fabiola Olivieri, Francesco Prattichizzo, Fabrizia Lattanzio, Anna Rita Bonfigli, Liana Spazzafumo
Ageing Research Reviews.2023; 84: 101836. CrossRef - MOTS-c: A promising mitochondrial-derived peptide for therapeutic exploitation
Yuejun Zheng, Zilin Wei, Tianhui Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - MOTS-c: A potential anti-pulmonary fibrosis factor derived by mitochondria
Zewei Zhang, Dongmei Chen, Kaili Du, Yaping Huang, Xingzhe Li, Quwen Li, Xiaoting Lv
Mitochondrion.2023; 71: 76. CrossRef - Mitochondrial-Encoded Peptide MOTS-c, Diabetes, and Aging-Related Diseases
Byung Soo Kong, Changhan Lee, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 315. CrossRef - MOTS-c Serum Concentration Positively Correlates with Lower-Body Muscle Strength and Is Not Related to Maximal Oxygen Uptake—A Preliminary Study
Remigiusz Domin, Michał Pytka, Mikołaj Żołyński, Jan Niziński, Marcin Rucinski, Przemysław Guzik, Jacek Zieliński, Marek Ruchała
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(19): 14951. CrossRef - Unique Properties of Apicomplexan Mitochondria
Ian M. Lamb, Ijeoma C. Okoye, Michael W. Mather, Akhil B. Vaidya
Annual Review of Microbiology.2023; 77(1): 541. CrossRef
- Mitochondrial-derived peptides: Antidiabetic functions and evolutionary perspectives
Editorial
- Implication of Sex Differences in Visceral Fat for the Assessment of Incidence Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Sang Hyeon Ju, Hyon-Seung Yi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):414-416. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0089
- 2,737 View
- 154 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction of high visceral adipose tissue for sex‐specific community residents in Taiwan
Yu‐Hsuan Chang, Chin‐Sung Chang, Chieh‐Yu Liu, Yin‐Fan Chang, Shiow‐Ching Shun
Nursing & Health Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Visceral fat and attribute-based medicine in chronic kidney disease
Hiroshi Kataoka, Kosaku Nitta, Junichi Hoshino
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The predictive significance of lipid accumulation products for future diabetes in a non-diabetic population from a gender perspective: an analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics
Jiajun Qiu, Maobin Kuang, Yang Zou, Ruijuan Yang, Qing Shangguan, Dingyang Liu, Guotai Sheng, Wei Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prediction of high visceral adipose tissue for sex‐specific community residents in Taiwan
Original Articles
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
- Jae Hyun Bae, Kyung-Do Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ye Seul Yang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Mook Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyu Chang Won, on Behalf of the Committee of Media-Public Relation of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):417-426. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0106

- 13,722 View
- 1,655 Download
- 76 Web of Science
- 99 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and management of diabetes mellitus, risk-factor control, and comorbidities among Korean adults.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey to assess the prevalence, treatment, risk factors, comorbidities, and self-management behaviors of diabetes mellitus from 2019 to 2020. We also analyzed data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service to evaluate the use of antidiabetic medications in people with diabetes mellitus from 2002 through 2018.
Results
Among Korean adults aged 30 years or older, the estimated prevalence of diabetes mellitus was 16.7% in 2020. From 2019 through 2020, 65.8% of adults with diabetes mellitus were aware of the disease and treated with antidiabetic medications. The percentage of adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) <6.5% was 24.5% despite the increased use of new antidiabetic medications. We found that adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved all three goals of HbA1c <6.5%, blood pressure (BP) <140/85 mm Hg, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL were 9.7%. The percentage of self-management behaviors was lower in men than women. Excess energy intake was observed in 16.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus among Korean adults remained high. Only 9.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved all glycemic, BP, and lipid controls from 2019 to 2020. Continuous evaluation of national diabetes statistics and a national effort to increase awareness of diabetes mellitus and improve comprehensive diabetes care are needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Jinyoung Kim, Bongseong Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 567. CrossRef - Changes in Fatty Liver Disease and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Young Korean Adults
Kye-Yeung Park, Hwan-Sik Hwang, Kyungdo Han, Hoon-Ki Park
American Journal of Preventive Medicine.2024; 66(4): 717. CrossRef - Widening disparities in the national prevalence of diabetes mellitus for people with disabilities in South Korea
I. Hwang, S.Y. Kim, Y.Y. Kim, J.H. Park
Public Health.2024; 226: 173. CrossRef - Questionnaire-Based Survey of Diabetes Self-Care Activities and Barriers among Young Korean Adults with Early-Onset Diabetes
Ji In Park, Sang-Wook Kim, Il Sung Nam-Goong, Kee-Ho Song, Ji Hee Yu, Ji Yun Jeong, Eun-Hee Cho
Yonsei Medical Journal.2024; 65(1): 42. CrossRef - Patients with diabetes in regions with population decline and likelihood of receiving diabetes management education and screenings for related complications in Korea
Yeong Jun Ju, Woorim Kim, Kyujin Chang, Tae Hoon Lee, Soon Young Lee
Preventive Medicine.2024; 178: 107793. CrossRef - Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung‐Do Han, Eun‐Jung Rhee, Won‐Young Lee
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2024; 15(2): 671. CrossRef - Gastroparesis might not be uncommon in patients with diabetes mellitus in a real-world clinical setting: a cohort study
Jeongmin Lee, Hye Lim Park, Su Young Park, Chul-Hyun Lim, Min-Hee Kim, Jung Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Jung-Hwan Oh
BMC Gastroenterology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to impaired fasting glucose and gastrointestinal cancer risk: A nationwide cohort study
Byeong Yun Ahn, Bokyung Kim, Sanghyun Park, Sang Gyun Kim, Kyungdo Han, Soo‐Jeong Cho
Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidimensional behavioral factors for diabetes management among middle-aged adults: a population-based study
Hyerang Kim, Heesook Son
Journal of Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Once-Daily Sitagliptin as Metformin Add-on in a Korean Population with Type 2 Diabetes
Byung-Wan Lee, Young Min Cho, Sin Gon Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Soo Lim, Amine Dahaoui, Jin Sook Jeong, Hyo Jin Lim, Jae Myung Yu
Diabetes Therapy.2024; 15(2): 547. CrossRef - Association between dietary selenium intake and severe abdominal aortic calcification in the United States: a cross-sectional study
Weiwei Dong, Xiaobai Liu, Lu Ma, Zhiyong Yang, Chunyan Ma
Food & Function.2024; 15(3): 1575. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to hypertriglyceridemia and risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Min-Kyung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jong-Dai Kim, Moon Jung Kim, Byungpyo Kim, Jung Heo, Jiyeon Ahn, Seo-Young Sohn, Jae-Hyuk Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111109. CrossRef - Recent evidence on target blood pressure in patients with hypertension
Hack-Lyoung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 17. CrossRef - Status and trends in epidemiologic characteristics of diabetic end-stage renal disease: an analysis of the 2021 Korean Renal Data System
Kyeong Min Kim, Seon A Jeong, Tae Hyun Ban, Yu Ah Hong, Seun Deuk Hwang, Sun Ryoung Choi, Hajeong Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Su Hyun Kim, Tae Hee Kim, Ho-Seok Koo, Chang-Yun Yoon, Kiwon Kim, Seon Ho Ahn, Yong Kyun Kim, Hye Eun Yoon
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 43(1): 20. CrossRef -
In silico
exploration of the potential inhibitory activities of in-house and ZINC database lead compounds against alpha-glucosidase using structure-based virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation approach
Zuhier A. Awan, Haider Ali Khan, Alam Jamal, Sulaiman Shams, Guojun Zheng, Abdul Wadood, Muhammad Shahab, Mohammad Imran Khan, Abdulaziz A. Kalantan
Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Mobile Applications for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Scoping Review
Jung Lim Lee, Youngji Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 368. CrossRef - Current status of remote collaborative care for hypertension in medically underserved areas
Seo Yeon Baik, Kyoung Min Kim, Hakyoung Park, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 33. CrossRef - Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMJ.2024; : e076388. CrossRef - Comparison of metabolic and neurological comorbidities in Asian patients with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis
Hee Joo Yang, Mi Young Lee, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Chang Jin Jung, Woo Jin Lee, Chong Hyun Won, Mi Woo Lee, Joon Min Jung, Sung Eun Chang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer risk according to fasting blood glucose trajectories: a population-based cohort study
Thi Minh Thu Khong, Thi Tra Bui, Hee-Yeon Kang, Jinhee Lee, Eunjung Park, Jin-Kyoung Oh
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2024; 12(1): e003696. CrossRef - Participation experience in self-care program for type 2 diabetes: A mixed-methods study
Mihwan Kim, Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - Fasting GLP-1 Levels and Albuminuria Are Negatively Associated in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Cheol-Won Jang, Tae Yang Yu, Jin Woo Jeong, Se Eun Ha, Rajan Singh, Moon Young Lee, Seungil Ro
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(3): 280. CrossRef - The clinical relevance of a polygenic risk score for type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Korean population
Na Yeon Kim, Haekyung Lee, Sehee Kim, Ye-Jee Kim, Hyunsuk Lee, Junhyeong Lee, Soo Heon Kwak, Seunggeun Lee
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic traits and colorectal cancer survival in a cohort of South Korean patients: A Mendelian randomization analysis
So Yon Jun, Sooyoung Cho, Min Jung Kim, Ji Won Park, Seung‐Bum Ryoo, Seung Yong Jeong, Kyu Joo Park, Aesun Shin
Cancer Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Real-World Outcomes of Individualized Targeted Therapy with Insulin Glargine 300 Units/mL in Insulin-Naïve Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes: TOBE Study
Eun-Gyoung Hong, Kyung-Wan Min, Jung Soo Lim, Kyu-Jeung Ahn, Chul Woo Ahn, Jae-Myung Yu, Hye Soon Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Won Kim, Dong Han Kim, Hak Chul Jang
Advances in Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of complicated, untreated and uncontrolled diabetes and pre‐diabetes on treatment outcome among patients with pulmonary tuberculosis
Kyung Hoon Kim, Hyung Woo Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Yeonhee Park, Sung Soo Jung, Jin Woo Kim, Jee Youn Oh, Heayon Lee, Sung Kyoung Kim, Sun‐Hyung Kim, Jiwon Lyu, Yousang Ko, Sun Jung Kwon, Yun‐Jeong Jeong, Do Jin Kim, Hyeon‐Kyoung Koo, Yangjin Jegal, Sun Young
Respirology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of dietary behavior and intake related to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes aged 30 years or older in Korea: Utilizing the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Jin-Ah Seok, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(2): 239. CrossRef - Management of Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Jin Hwa Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(1): 4. CrossRef - Baseline glycated albumin level and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Healthy individuals: a retrospective longitudinal observation in Korea
Kang-Su Shin, Min-Seung Park, Mi Yeon Lee, Eun Hye Cho, Hee-Yeon Woo, Hyosoon Park, Min-Jung Kwon
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation.2024; : 1. CrossRef - The Potential Role of Presepsin in Predicting Severe Infection in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Eun Yeong Ha, Il Rae Park, Seung Min Chung, Young Nam Roh, Chul Hyun Park, Tae-Gon Kim, Woong Kim, Jun Sung Moon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(8): 2311. CrossRef - Myotonic dystrophy type 1 in South Korea: a comprehensive analysis of cancer and comorbidity risks
Incheol Seo, Jin-Mo Park
Neurological Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 426. CrossRef - Diabetes screening in South Korea: a new estimate of the number needed to screen to detect diabetes
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyung Ae Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(1): 93. CrossRef - Sex differences in the impact of diabetes mellitus on tuberculosis recurrence: a retrospective national cohort study
Dararat Eksombatchai, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2023; 127: 1. CrossRef - Response to Letter to the Editor From Han and Xu: “Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes”
Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(4): e58. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in catholic priests compared with general public
Youngmi Eun, Sun Myeong Ock, Se-Hong Kim, Ju Hye Chung, Se Jin Park, Churlmin Kim, Min-Kyun Im, Kyung-do Han
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(5): 655. CrossRef - Blood pressure control and its associated factors in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes
Anan S Jarab, Walid Al-Qerem, Salam Alqudah, Shrouq R Abu Heshmeh, Tareq L Mukattash, Karem H Alzoubi
Electronic Journal of General Medicine.2023; 20(3): em477. CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of diabetes mellitus among patients with tuberculosis in South Korea from 2011 to 2018: a nationwide cohort study
Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Jeong Mi Seo, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
BMJ Open.2023; 13(3): e069642. CrossRef - The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 38. CrossRef - Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 211. CrossRef - Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 201. CrossRef - Evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin in healthy subjects
Heeyoung Kim, Choon Ok Kim, Hyeonsoo Park, Min Soo Park, Dasohm Kim, Taegon Hong, Yesong Shin, Byung Hak Jin
Translational and Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 31(1): 59. CrossRef - Vascular and metabolic effects of ipragliflozin versus sitagliptin (IVS) in type 2 diabetes treated with sulphonylurea and metformin: IVS study
Seon Mee Kang, Han Mi Yun, Minji Sohn, Soo Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(7): 1922. CrossRef - Diabetes and Skin Disease
Jungah Lim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 29. CrossRef - Revisiting the Diabetes Crisis in Korea: Call for Urgent Action
Jun Sung Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between Sleep Duration and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Healthy Subjects: A 14-Year Longitudinal Cohort Study
Jin ha Jang, Wonjin Kim, Jin Sil Moon, Eun Roh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm, Ji Hye Huh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(8): 2899. CrossRef - Exercise Frequency Reduction Is Associated With Higher Risk of Infection in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Nationally Representative Cohort Study
Yohwan Lim, Hye Jun Kim, Sung Soo Yoon, Sang Jun Lee, Myeong Hoon Lee, Hyewon Park, Sun Jae Park, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Consuming Heat-Treated Dodamssal Brown Rice Containing Resistant Starch on Glucose Metabolism in Humans
Jiyoung Park, Sea-Kwan Oh, Miae Doo, Hyun-Jung Chung, Hyun-Jin Park, Hyejin Chun
Nutrients.2023; 15(10): 2248. CrossRef - Opening the Precision Diabetes Care through Digital Healthcare
Joonyub Lee, Jin Yu, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 307. CrossRef - Fatty Liver & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2009 to 2017
Eugene Han, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-ho Lee, Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 347. CrossRef - Trends in the Quality of Primary Care and Acute Care in Korea From 2008 to 2020: A Cross-sectional Study
Yeong Geun Gwon, Seung Jin Han, Kyoung Hoon Kim
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(3): 248. CrossRef - Development and Validation of Multiple Equations for Low-Density Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein B in Korean Patients Visiting Local Clinics and Hospitals
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Nutrients.2023; 15(12): 2786. CrossRef - The role of retinal vessel geometry as an indicator of systemic arterial stiffness assessed by cardio-ankle vascular index
Dae Joong Ma, Heesun Lee, Ji Min Choi, Hyo Eun Park, Su-Yeon Choi, Hyuk Jin Choi
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and depression among Korean midlife women: a cross-sectional analysis study
You Lee Yang, Eun-Ok Im, Yunmi Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of updated cardiovascular health metrics, including sleep health, with incident diabetes and cardiovascular events in older adults with prediabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Seung Jin Han
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110820. CrossRef - Paradigm Shift in Management of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Glucocentric versus Organ Protection
Jong Chul Won
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 59. CrossRef - Medical nutrition therapy for diabetes mellitus
Suk Chon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 421. CrossRef - Prevalence and treatment status of diabetes mellitus in Korea
Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 404. CrossRef - The impact of diabetes status on total and site-specific cancer risk in the elderly population: A nationwide cohort study
Kyuho Kim, Bongseong Kim, Hyunho Kim, Hyung Soon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110866. CrossRef - Response to comments of Lai et al. “Proposal of one option for patient-centered, heterogeneous selection of antidiabetic drug”
Sunyoung Kim, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110864. CrossRef - Association of Dental Diseases and Oral Hygiene Care With the Risk of Heart Failure in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Youn Huh, Jung Eun Yoo, Sang‐Hyun Park, Kyungdo Han, Seon Mee Kim, Hye Soon Park, Kyung Hwan Cho, Jin‐Soo Ahn, Sang Ho Jun, Ga Eun Nam
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bidirectional associations between periodontal disease and systemic diseases: a nationwide population-based study in Korea
Salma Nabila, Jaesung Choi, Ji-Eun Kim, Seokyung Hahn, In-Kyung Hwang, Tae-Il Kim, Hee-Kyung Park, Ji-Yeob Choi
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Effectiveness of the National Diabetes Quality Assessment Program in South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Serim Kwon, Gui Ok Kim, Bo Yeon Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(9): 1700. CrossRef - Refined Diagnostic Protocol for Diabetic Polyneuropathy: Paving the Way for Timely Detection
Byung-Mo Oh
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2023; 47(4): 234. CrossRef - Analysis of difference in body fluid composition and dietary intake between Korean adults with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yu-Gyeong Kim, Ha-Neul Choi, Jung-Eun Yim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 377. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus in the Elderly Adults in Korea: Based on Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019 to 2020
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Kyuho Kim, Jae-Hyun Bae, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Nan-Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 643. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between initial continuity of care status and diabetes-related health outcomes in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide retrospective cohort study in South Korea
Hyun Woo Jung, Woo-Ri Lee
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(6): 600. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of the fibrosis-4 index and the NAFLD fibrosis score for screening at-risk individuals in a health check-up setting
Huiyul Park, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Jonghyun Lee, Hye-Lin Kim, Seon Cho, Eun-Hee Nah, Dae Won Jun
Hepatology Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 522. CrossRef - Comparative Risk of Type 2 Diabetes after Gastrectomy and Endoscopic Resection for Gastric Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Yeongkeun Kwon, Jin-Won Kwon, Jiyun Kim, Dohyang Kim, Jinseub Hwang, Jane Ha, Shin-Hoo Park, Sungsoo Park
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2023; 237(6): 902. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extensio
Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 808. CrossRef - Association between diabetes mellitus and cause of death in patients with tuberculosis: A Korean nationwide cohort study
Se Hyun Kwak, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang, Frederick Quinn
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(12): e0295556. CrossRef - Strategies to Maintain the Remission of Diabetes Following Metabolic Surgery
Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Journal of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.2023; 12(2): 26. CrossRef - Anti-Diabetic Medications and Osteoporosis
Kyongyoung Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 173. CrossRef - The associations between changes in hepatic steatosis and heart failure and mortality: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Hasung Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Current status of obesity treatment in Korea: based on the 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guidelines for obesity management
Eun-Jung Rhee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(7): 388. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef - Analysis of the Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Renal Function in Middle-Aged Patients with Diabetes
Yoonjin Park, Su Jung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11832. CrossRef - The Degree of Glycemic Control for the First Three Months Determines the Next Seven Years
Nami Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun-Jin Kim, Kwang-il Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 667. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - Education for Insulin Injection in Elderly Diabetic Patients
Gi Yeon Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(3): 201. CrossRef - Recent Updates on Phytoconstituent Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors: An Approach towards the Treatment of Type Two Diabetes
Hamdy Kashtoh, Kwang-Hyun Baek
Plants.2022; 11(20): 2722. CrossRef - Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus in Korea
Soon Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(10): 640. CrossRef - Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 819. CrossRef - Oldies but Goodies: Thiazolidinedione as an Insulin Sensitizer with Cardioprotection
Eun-Hee Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 827. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Acceptance Action in the Relationship between Diabetes Distress and Self-stigma among Old Adults with Diabetes in South Korea
Hyesun Kim, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(4): 446. CrossRef
- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
- COVID-19
- Association of Metabolic Syndrome with COVID-19 in the Republic of Korea
- Woo-Hwi Jeon, Jeong-Yeon Seon, So-Youn Park, In-Hwan Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):427-438. Published online November 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0105
- 4,423 View
- 242 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
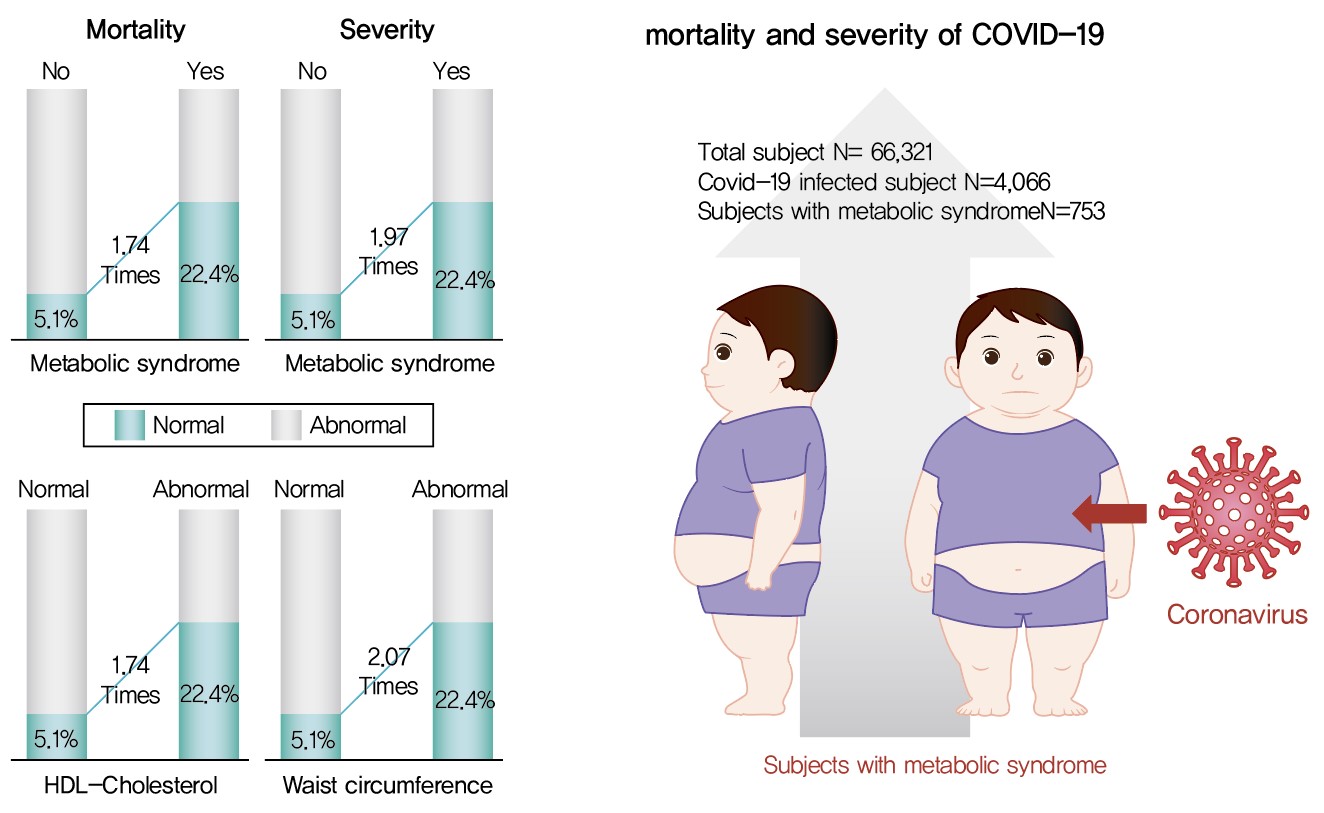
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is reportedly a crucial risk factor for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Since the epidemiological studies that examine this association are few and include small samples, we investigated the relationship between MetS and COVID-19 severity and death using a larger sample in the Republic of Korea.
Methods
We analyzed 66,321 patients, 4,066 of whom had COVID-19. We used chi-square tests to examine patients’ characteristics. We performed logistic regression analysis to analyze differences in COVID-19 infection and clinical outcomes according to the presence of MetS.
Results
Although MetS was not significantly associated with COVID-19 risk, acquiring MetS was significantly associated with the risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 1.97; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.34 to 2.91; P=0.001). The mortality risk was significantly higher in COVID-19 patients with MetS (OR, 1.74; 95% CI, 1.17 to 2.59; P=0.006). Patients with abnormal waist circumference were approximately 2.07 times more likely to develop severe COVID-19 (P<0.001), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels were significantly associated with COVID-19; the mortality risk due to COVID-19 was 1.74 times higher in men with an HDL-C level of <40 mg/dL and in women with an HDL-C level of <50 mg/dL (P=0.012).
Conclusion
COVID-19 is likely associated with severity and death in patients with MetS or in patients with MetS risk factors. Therefore, patients with MetS or those with abnormal waist circumference and HDL-C levels need to be treated with caution. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Heterogeneity in familial clustering of metabolic syndrome components in the multiethnic GENNID study
Jia Y. Wan, Deborah Goodman, Sukh Makhnoon, Trina M. Norden‐Krichmar, Baolin Wu, Karen L. Edwards
Obesity.2024; 32(1): 176. CrossRef - Associated Factors with Changes of Metabolic Abnormalities among General Population in COVID-19 Pandemic
Eunjoo Kwon, Eun-Hee Nah, Suyoung Kim, Seon Cho, Hyeran Park
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(2): 55. CrossRef - Association between metabolic syndrome and mortality in patients with COVID-19: A nationwide cohort study
Hyo Jin Park, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyungdo Han, Jean Shin, Yoojeong Lee, Yujin Chang, Kyeyeung Park, Yoon Jeong Cho, Youn Seon Choi, Seon Mee Kim, Ga Eun Nam
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2022; 16(6): 484. CrossRef
- Heterogeneity in familial clustering of metabolic syndrome components in the multiethnic GENNID study
- Drug/Regimen
- Comparison of Prevailing Insulin Regimens at Different Time Periods in Hospitalized Patients: A Real-World Experience from a Tertiary Hospital
- Sun Joon Moon, Hun Jee Choe, Soo Heon Kwak, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):439-450. Published online October 20, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0065

- 65,535 View
- 268 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Prevailing insulin regimens for glycemic control in hospitalized patients have changed over time. We aimed to determine whether the current basal-bolus insulin (BBI) regimen is superior to the previous insulin regimen, mainly comprising split-mixed insulin therapy.
Methods
This was a single tertiary center, retrospective observational study that included non-critically ill patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were treated with split-mixed insulin regimens from 2004 to 2007 (period 1) and with BBI from 2008 to 2018 (period 2). Patients from each period were analyzed after propensity score matching. The mean difference in glucose levels and the achievement of fasting and preprandial glycemic targets by day 6 of admission were assessed. The total daily insulin dose, incidence of hypoglycemia, and length of hospital stay were also evaluated.
Results
Among 244 patients from each period, both fasting glucose (estimated mean±standard error, 147.4±3.1 mg/dL vs. 129.4±3.2 mg/dL, P<0.001, day 6) and preprandial glucose (177.7±2.8 mg/dL vs. 152.8±2.8 mg/dL, P<0.001, day 6) were lower in period 2 than in period 1. By day 6 of hospital admission, 42.6% and 67.2% of patients achieved a preprandial glycemic target of <140 mg/dL in periods 1 and 2, respectively (relative risk, 2.00; 95% confidence interval, 1.54 to 2.59), without an increased incidence of hypoglycemia. Length of stay was shorter in period 2 (10.23±0.26 days vs. 8.70±0.26 days, P<0.001).
Conclusion
BBI improved glycemic control in a more efficacious manner than a split-mixed insulin regimen without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia in a hospital setting.
- Type 1 Diabetes
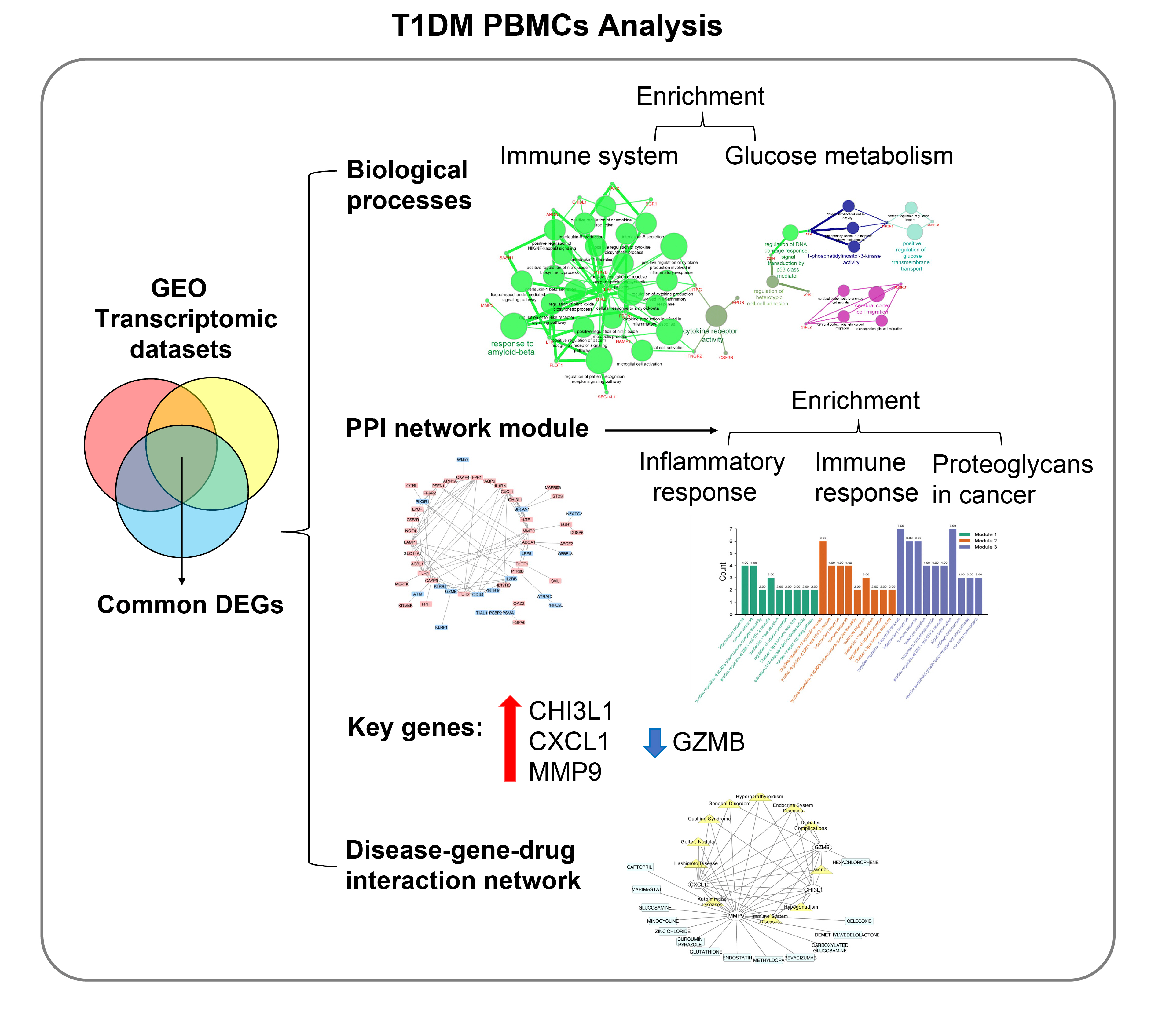
- Identification of Key Genes and Pathways in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis
- Xing Li, Mingyu Liao, Jiangheng Guan, Ling Zhou, Rufei Shen, Min Long, Jiaqing Shao
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):451-463. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0018
- 6,974 View
- 292 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The onset and progression of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is closely related to autoimmunity. Effective monitoring of the immune system and developing targeted therapies are frontier fields in T1DM treatment. Currently, the most available tissue that reflects the immune system is peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Thus, the aim of this study was to identify key PBMC biomarkers of T1DM.
Methods
Common differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets GSE9006, GSE72377, and GSE55098, and PBMC mRNA expression in T1DM patients was compared with that in healthy participants by GEO2R. Gene Ontology, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analyses of DEGs were performed using the Cytoscape, DAVID, and STRING databases. The vital hub genes were validated by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction using clinical samples. The disease-gene-drug interaction network was built using the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD) and Drug Gene Interaction Database (DGIdb).
Results
We found that various biological functions or pathways related to the immune system and glucose metabolism changed in PBMCs from T1DM patients. In the PPI network, the DEGs of module 1 were significantly enriched in processes including inflammatory and immune responses and in pathways of proteoglycans in cancer. Moreover, we focused on four vital hub genes, namely, chitinase-3-like protein 1 (CHI3L1), C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1 (CXCL1), matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP9), and granzyme B (GZMB), and confirmed them in clinical PBMC samples. Furthermore, the disease-gene-drug interaction network revealed the potential of key genes as reference markers in T1DM.
Conclusion
These results provide new insight into T1DM pathogenesis and novel biomarkers that could be widely representative reference indicators or potential therapeutic targets for clinical applications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Single-cell and transcriptomic analyses reveal the influence of diabetes on ovarian cancer
Zhihao Zhao, Qilin Wang, Fang Zhao, Junnan Ma, Xue Sui, Hyok Chol Choe, Peng Chen, Xue Gao, Lin Zhang
BMC Genomics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioinformatics analysis identifies TGF-β signaling pathway-associated molecular subtypes and gene signature in diabetic foot
Guanggang Du, Jie Chen, Xuezhu Zhu, Zongdong Zhu
iScience.2024; 27(3): 109094. CrossRef - Identification of Comorbidities, Genomic Associations, and Molecular Mechanisms for COVID-19 Using Bioinformatics Approaches
Shudeb Babu Sen Omit, Salma Akhter, Humayan Kabir Rana, A. R. M. Mahamudul Hasan Rana, Nitun Kumar Podder, Mahmudul Islam Rakib, Ashadun Nobi, Ali Imran
BioMed Research International.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Advanced Delivery Strategies for Immunotherapy in Type I Diabetes Mellitus
Mingshu Huang, Weixing Chen, Min Wang, Yisheng Huang, Hongyu Liu, Yue Ming, Yuanxin Chen, Zhengming Tang, Bo Jia
BioDrugs.2023; 37(3): 331. CrossRef - Identification of the key genes of tuberculosis and construction of a diagnostic model via weighted gene co-expression network analysis
Baiying Li, Lifang Sun, Yaping Sun, Libo Zhen, Qi Qi, Ting Mo, Huijie Wang, Meihua Qiu, Qingshan Cai
Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy.2023; 29(11): 1046. CrossRef - Probing biological network in concurrent carcinomas and Type-2 diabetes for potential biomarker screening: An advanced computational paradigm
Abdullah Al Marzan, Shatila Shahi, Md Sakil Arman, Md Zafrul Hasan, Ajit Ghosh
Advances in Biomarker Sciences and Technology.2023; 5: 89. CrossRef - Transcriptional analysis of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen
Jing Wei, Fangzheng Guo, Yamin Song, Kun Xu, Feiyang Lin, Kangsheng Li, Baiqing Li, Zhongqing Qian, Xiaojing Wang, Hongtao Wang, Tao Xu
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Combining bioinformatics and machine learning algorithms to identify and analyze shared biomarkers and pathways in COVID-19 convalescence and diabetes mellitus
Jinru Shen, Yaolou Wang, Xijin Deng, Si Ri Gu Leng Sana
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcriptome analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Zhaoxiang Wang, Li Zhang, Fengyan Tang, Zhongming Yang, Mengzhu Wang, Jue Jia, Dong Wang, Ling Yang, Shao Zhong, Guoyue Yuan
Endocrine.2022; 78(2): 270. CrossRef
- Single-cell and transcriptomic analyses reveal the influence of diabetes on ovarian cancer
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
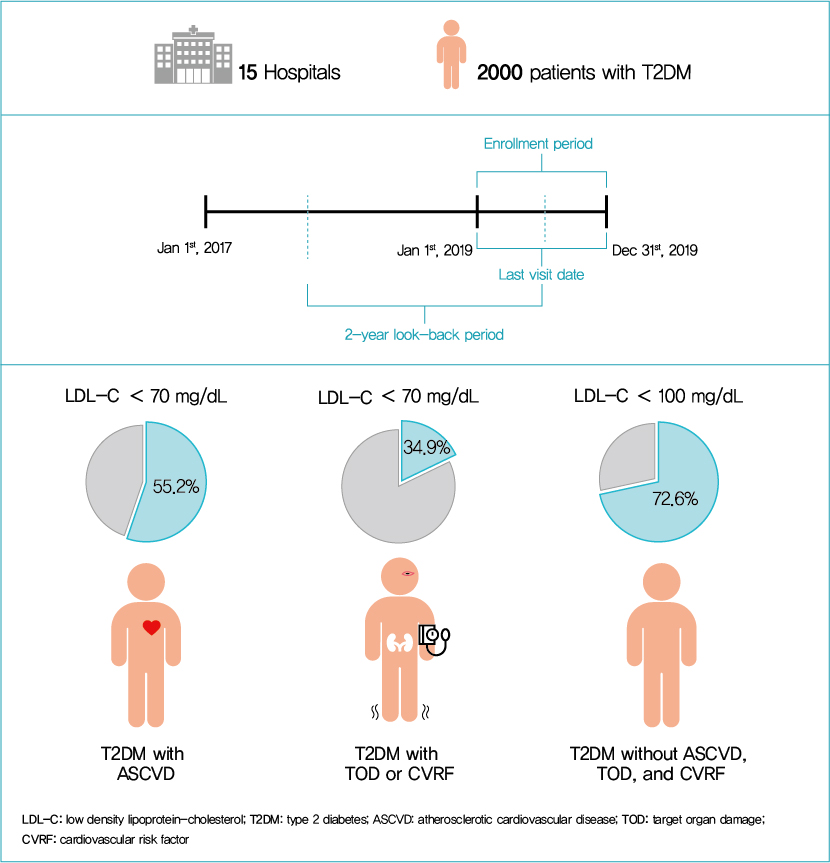
- Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):464-475. Published online March 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0088
- 6,928 View
- 347 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We evaluated the achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) according to up-to-date Korean Diabetes Association (KDA), European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS), and American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study collected electronic medical record data from patients with T2DM (≥20 years) managed by endocrinologists from 15 hospitals in Korea (January to December 2019). Patients were categorized according to guidelines to assess LDL-C target achievement. KDA (2019): Very High-I (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD]) <70 mg/dL; Very High-II (target organ damage [TOD], or cardiovascular risk factors [CVRFs]) <70 mg/dL; high (others) <100 mg/dL. ESC/EAS (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD): <55 mg/dL; Very High-II (TOD or ≥3-CVRF) <55 mg/dL; high (diabetes ≥10 years without TOD plus any CVRF) <70 mg/dL; moderate (diabetes <10 years without CVRF) <100 mg/dL. ADA (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD); Very High-II (age ≥40+ TOD, or any CVRF), for high intensity statin or statin combined with ezetimibe.
Results
Among 2,000 T2DM patients (mean age 62.6 years; male 55.9%; mean glycosylated hemoglobin 7.2%) ASCVD prevalence was 24.7%. Of 1,455 (72.8%) patients treated with statins, 73.9% received monotherapy. According to KDA guidelines, LDL-C target achievement rates were 55.2% in Very High-I and 34.9% in Very High-II patients. With ESC/EAS guidelines, target attainment rates were 26.6% in Very High-I, 15.7% in Very High-II, and 25.9% in high risk patients. Based on ADA guidelines, most patients (78.9%) were very-high risk; however, only 15.5% received high-intensity statin or combination therapy.
Conclusion
According to current dyslipidemia management guidelines, LDL-C goal achievement remains suboptimal in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Hidetaka Hamasaki
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299035. CrossRef - Distinct effects of rosuvastatin and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe on senescence markers of CD8+ T cells in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
Sang-Hyeon Ju, Joung Youl Lim, Minchul Song, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef
- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
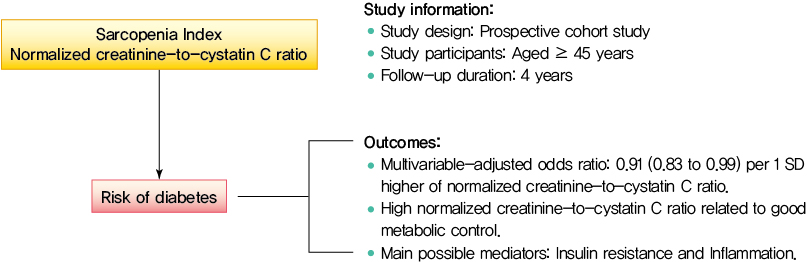
- Normalized Creatinine-to-Cystatin C Ratio and Risk of Diabetes in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
- Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Bo Xie, Yang Yuan, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):476-485. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0074
- 4,718 View
- 204 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio is recently suggested to be a surrogate marker for sarcopenia. However, little is known about its association with diabetes. This study aimed to fill in this gap based on a large-scale prospective cohort.
Methods
A population-based representative sample of 5,055 participants aged ≥45 years from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study was enrolled between 2011 and 2012 and followed at least once during the subsequent surveys at 2013, 2015, or 2018. Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio was calculated and normalized by body weight. Incident diabetes was ascertained by plasma glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, self-reported history, or use of anti-diabetic drugs. Logistic regression analysis and mediation analysis were employed.
Results
During follow-up, 634 participants developed diabetes. The risk of diabetes was gradually and significantly decreased with increased normalized creatinine–cystatin C ratio. The multivariable-adjusted odds ratio for diabetes was 0.91 (95% confidence interval, 0.83 to 0.99) per 1 standard deviation higher of normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio, and this relationship remained significant after controlling for muscle strength. The risk reduction in diabetes was significantly larger in participants with normal-weight and high normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio compared with those with overweight/obesity and high normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio (Pinteraction=0.01). Insulin resistance and inflammation appeared to be key mediators accounting for the observed relationship between normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio and risk of diabetes, with their mediating effect being 93.1% and 22.0%, respectively.
Conclusion
High normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio is associated with reduced risk of diabetes in middle-aged and older adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Muscle Quality in Relation to Prediabetes Phenotypes: A Population-Based Study With Mediation Analysis
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Xiaoying Zhou, Jinshui Xu, Zilin Sun, Haijian Guo, Tongzhi Wu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1151. CrossRef - Sex‐specific associations between skeletal muscle mass and incident diabetes: A population‐based cohort study
Dan Liu, Nan Li, Yiling Zhou, Miye Wang, Peige Song, Changzheng Yuan, Qingyang Shi, Hui Chen, Kaixin Zhou, Huan Wang, Tao Li, Xiong‐Fei Pan, Haoming Tian, Sheyu Li
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(3): 820. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus Should Be Considered While Analysing Sarcopenia-Related Biomarkers
Justyna Rentflejsz, Zyta Beata Wojszel
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(4): 1107. CrossRef - Associations of muscle mass and strength with new-onset diabetes among middle-aged and older adults: evidence from the China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS)
Yun-Yun He, Mei-Ling Jin, Xiang-Yang Fang, Xiao-Juan Wang
Acta Diabetologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The serum creatinine to cystatin C to waist circumference ratios predicts risk for type 2 diabetes: A Chinese cohort study
Yinfei Chen, Weiheng Wen, Zhiliang Mai, Ming Wang, Hong Chen, Jia Sun
Journal of Diabetes.2023; 15(10): 808. CrossRef - Associations of sarcopenia with peak expiratory flow among community-dwelling elderly population: based on the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS)
Yun-Yun He, Mei-Ling Jin, Jing Chang, Xiao-Juan Wang
European Geriatric Medicine.2023; 15(1): 95. CrossRef - Additive impact of diabetes and sarcopenia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A longitudinal nationwide population-based study
Eyun Song, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Ahreum Jang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155678. CrossRef
- Muscle Quality in Relation to Prediabetes Phenotypes: A Population-Based Study With Mediation Analysis
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Sex Differences of Visceral Fat Area and Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Fat Ratio for the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
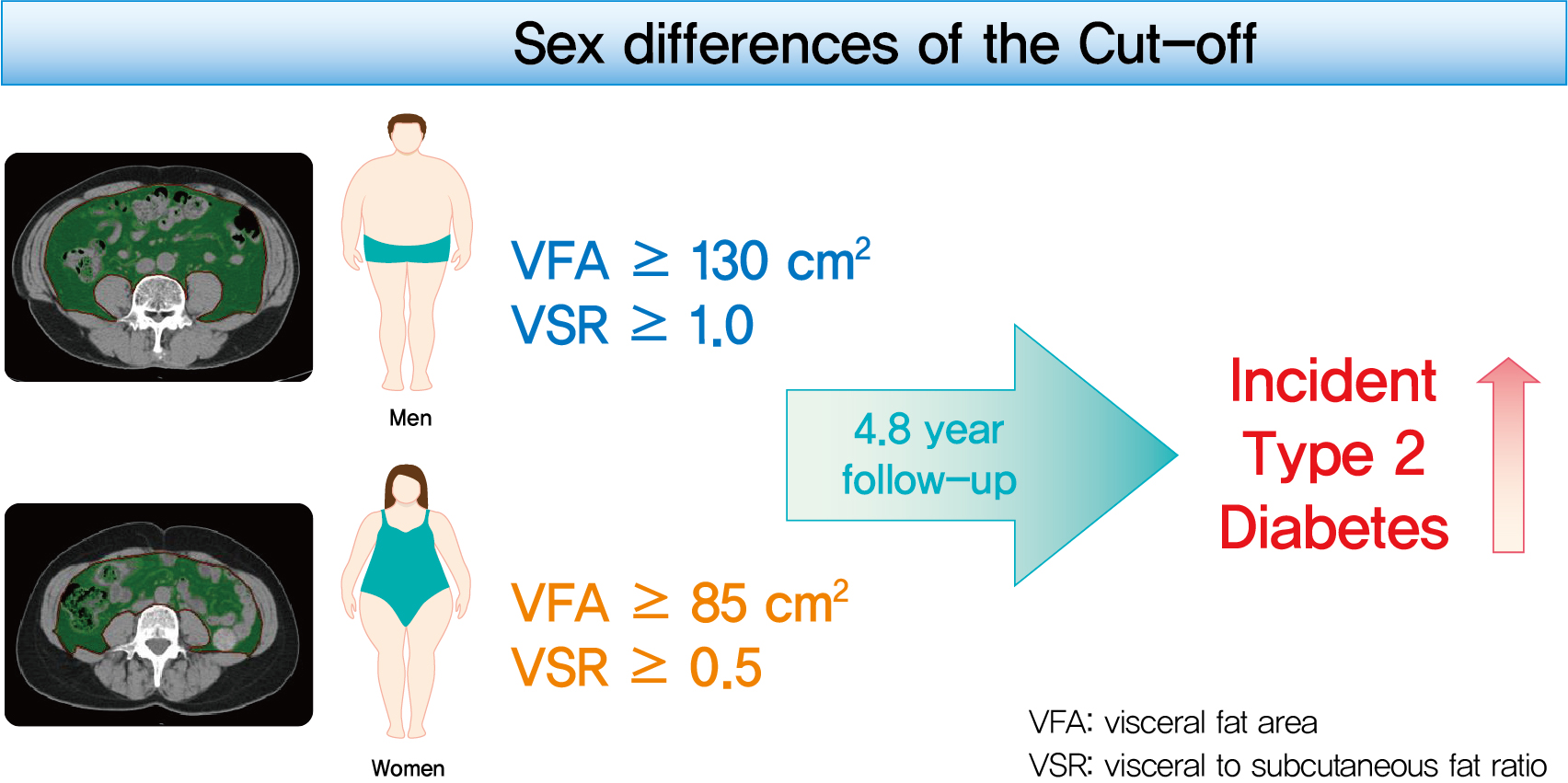
- Eun Hee Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Min Jung Lee, Sung-Jin Bae, Jaewon Choe, Chang Hee Jung, Chul-Hee Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):486-498. Published online November 18, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0095
- 9,227 View
- 363 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to determine the optimal cut-off values of visceral fat area (VFA) and visceral-to-subcutaneous fat ratio (VSR) for predicting incident type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
A total of 10,882 individuals (6,835 men; 4,047 women) free of T2DM at baseline aged between 30 and 79 years who underwent abdominal computed tomography scan between 2012 and 2013 as a part of routine health check-ups were included and followed. VFA, subcutaneous fat area, and VSR on L3 vertebral level were measured at baseline.
Results
During a median follow-up of 4.8 years, 730 (8.1% for men; 4.3% for women) incident cases of T2DM were identified. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that the optimal cut-off values of VFA and VSR for predicting incident T2DM were 130.03 cm2 and 1.08 in men, respectively, and 85.7 cm2 and 0.48 in women, respectively. Regardless of sex, higher VFA and VSR were significantly associated with a higher risk of incident T2DM. Compared with the lowest quartiles of VFA and VSR, the highest quartiles had adjusted odds ratios of 2.62 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.73 to 3.97) and 1.55 (95% CI, 1.14 to 2.11) in men, respectively, and 32.49 (95% CI, 7.42 to 142.02) and 11.07 (95% CI, 3.89 to 31.50) in women, respectively.
Conclusion
Higher VFA and VSR at baseline were independent risk factors for the development of T2DM. Sex-specific reference values for visceral fat obesity (VFA ≥130 cm2 or VSR ≥1.0 in men; VFA ≥85 cm2 or VSR ≥0.5 in women) are proposed for the prediction of incident T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Severity of adipose tissue dysfunction is associated with progression of pre-diabetes to type 2 diabetes: the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
Mohammad Jalali, Zahra Bahadoran, Parvin Mirmiran, Fereidoun Azizi, Farhad Hosseinpanah
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Should insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), insulin secretion (HOMA-β), and visceral fat area be considered for improving the performance of diabetes risk prediction models
Huan Hu, Tohru Nakagawa, Toru Honda, Shuichiro Yamamoto, Tetsuya Mizoue
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2024; 12(1): e003680. CrossRef - Adipose organ dysfunction and type 2 diabetes: Role of nitric oxide
Zahra Bahadoran, Parvin Mirmiran, Asghar Ghasemi
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 221: 116043. CrossRef - Prediction of high visceral adipose tissue for sex‐specific community residents in Taiwan
Yu‐Hsuan Chang, Chin‐Sung Chang, Chieh‐Yu Liu, Yin‐Fan Chang, Shiow‐Ching Shun
Nursing & Health Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Guidelines for obesity clinic consultations in primary healthcare clinics
Jee-Hyun Kang, Kyoung-Kon Kim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2024; 67(4): 240. CrossRef - Correlation between fat-to-muscle mass ratio and cognitive impairment in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study
Fan Wu, Yanlan Liu, Chenying Lin, Nahal Haghbin, Longfei Xia, Yaoshuang Li, Tong Chen, Huina Qiu, Weiran Jiang, Jingbo Li, Jingna Lin
BMC Geriatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Body Composition and Metabolic Dysfunction Really Matter for the Achievement of Better Outcomes in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
Mauricio A. Cuello, Fernán Gómez, Ignacio Wichmann, Felipe Suárez, Sumie Kato, Elisa Orlandini, Jorge Brañes, Carolina Ibañez
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1156. CrossRef - MEDICINAL BIOMAGNETISM FOR THE TREATMENT OF OBESITY
Ana Vergínia Campagnollo Bueno, Michelli Gonçalves Seneda, Ângela Mara Rambo, Ana Clara Campagnolo Gonçalves Toledo, Caroline Cabral de Azevedo, Adriane Viapiana Bossa
Health and Society.2023; 3(01): 411. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome in a national population-based cohort of young adults and sex-specific risk for type 2 diabetes
Min-Kyung Lee, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Seo Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Oak-Kee Hong, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The correlation between visceral fat/subcutaneous fat area ratio and monocyte/high-density lipoprotein ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and albuminuria
Haiyan Lin, Jun Zhu, Chen Zheng, Xiaoming Xu, Shandong Ye
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(11): 108521. CrossRef - Effects of the abdominal fat distribution on the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and thyroid hormones among Korean adult males
Hyun-Jin Kim, Byungmi Kim, Seyoung Kim, Hyuktae Kwon, Jae Moon Yun, Belong Cho, Jin-Ho Park
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Visceral Fat Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Obesity
Hong-Kyu Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Hana Park, Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Jaewon Choe
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Visceral adipose tissue reference data computed for GE HealthCare DXA from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data set
Jonathan P. Bennett, Brandon K. Quon, Bo Fan, En Liu, Leila Kazemi, Rosa C. Villegas‐Valle, Raj Ahgun, Xian‐pin Wu, Hou‐De Zhou, Ying Lu, John A. Shepherd
Obesity.2023; 31(12): 2947. CrossRef - Comparison of bioelectrical body and visceral fat indices and anthropometric measures in relation to type 2 diabetes by sex among Chinese adults, a cross-sectional study
Jiangshan He, Binbin Zhang, Yaqi Fan, Yuxue Wang, Mianzhi Zhang, Chunjun Li, Li Zhang, Pei Guo, Minying Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The predictive significance of lipid accumulation products for future diabetes in a non-diabetic population from a gender perspective: an analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics
Jiajun Qiu, Maobin Kuang, Yang Zou, Ruijuan Yang, Qing Shangguan, Dingyang Liu, Guotai Sheng, Wei Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cellular interplay between cardiomyocytes and non-myocytes in diabetic cardiomyopathy
Ren Jie Phang, Rebecca H. Ritchie, Derek J. Hausenloy, Jarmon G. Lees, Shiang Y. Lim
Cardiovascular Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Implication of Sex Differences in Visceral Fat for the Assessment of Incidence Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sang Hyeon Ju, Hyon-Seung Yi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 414. CrossRef - Visceral fat area and body fat percentage measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis correlate with glycometabolism
Shuying Li, Shaoping Li, Jie Ding, Weihong Zhou
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Demographic Specific Abdominal Fat Composition and Distribution Trends in US Adults from 2011 to 2018
Furong Xu, Jacob E. Earp, Bryan J. Blissmer, Ingrid E. Lofgren, Matthew J. Delmonico, Geoffrey W. Greene
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(19): 12103. CrossRef - Visceral Obesity Is a More Important Factor for Colorectal Adenomas than Skeletal Muscle or Body Fat
Ji Yeon Seo, Yoo Min Han, Su Jin Chung, Seon Hee Lim, Jung Ho Bae, Goh Eun Chung
Cancers.2022; 14(21): 5256. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Visceral Obesity and Related Diseases
佳佳 魏
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(12): 11686. CrossRef - Gender differences in the ideal cutoffs of visceral fat area for predicting MAFLD in China
Pingping Yu, Huachao Yang, Xiaoya Qi, Ruixue Bai, Shouqin Zhang, Jianping Gong, Ying Mei, Peng Hu
Lipids in Health and Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Severity of adipose tissue dysfunction is associated with progression of pre-diabetes to type 2 diabetes: the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
Short Communications
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Influence of Pre-Pregnancy Underweight Body Mass Index on Fetal Abdominal Circumference, Estimated Weight, and Pregnancy Outcomes in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Minji Kim, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Suk-Joo Choi, Soo-Young Oh, Cheong-Rae Roh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):499-505. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0059

- 5,014 View
- 201 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This study aimed to determine the influence of pre-pregnancy body mass index on pregnancy outcomes in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), comparing underweight patients with GDM with normal weight patients with GDM. Maternal baseline characteristics, ultrasonographic results, and pregnancy and neonatal outcomes were reviewed in 946 women with GDM with singleton pregnancies. Underweight patients with GDM showed a benign course in most aspects during pregnancy, except for developing a higher risk of giving birth to small for gestational age neonates. Underweight women with GDM required less insulin treatment, had a higher rate of vaginal delivery, and had a lower rate of cesarean delivery. In addition, their neonates were more likely to have fetal abdominal circumference and estimated fetal weight below the 10th percentile both at the time of GDM diagnosis and before delivery. Notably, their risk for preeclampsia and macrosomia were lower. Collectively, our data suggest that underweight women with GDM may require a different approach in terms of diagnosis and management throughout their pregnancy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Challenges in the management of gestational diabetes mellitus in anorexia nervosa
Rija Siddiqui, Carrie J McAdams
Psychiatry Research Case Reports.2024; 3(1): 100215. CrossRef - Obesity Is Associated With Higher Risk of Adverse Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes Than Supervised Gestational Diabetes
Namju Seo, You Min Lee, Ye-jin Kim, Ji-hee Sung, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Suk-Joo Choi, Cheong-Rae Roh, Soo-young Oh
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal pre-pregnancy obesity modifies the association between first-trimester thyroid hormone sensitivity and gestational Diabetes Mellitus: a retrospective study from Northern China
Honglin Sun, Yibo Zhou, Jia Liu, Ying Wang, Guang Wang
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Challenges in the management of gestational diabetes mellitus in anorexia nervosa
- Basic Research
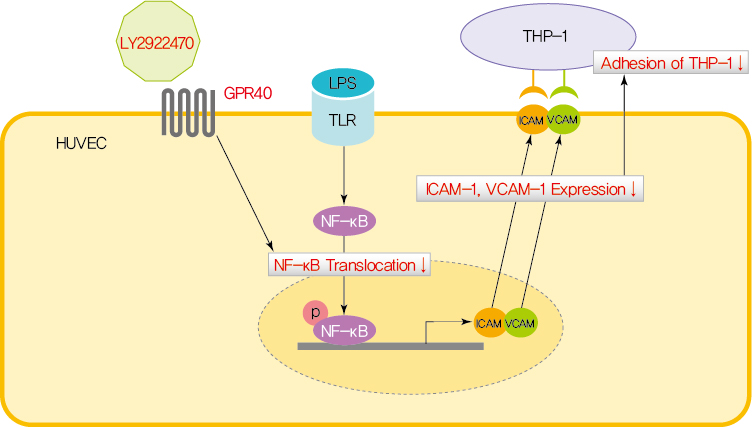
- GPR40 Agonism Modulates Inflammatory Reactions in Vascular Endothelial Cells
- Joo Won Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Hye Jin Yoo, Hwan-Jin Hwang, Sei Hyun Baik
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):506-511. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0092
- 4,726 View
- 229 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Endothelial dysfunction is strongly linked with inflammatory responses, which can impact cardiovascular disease. Recently, G protein-coupled receptor 40 (GPR40) has been investigated as a modulator of metabolic stress; however, the function of GPR40 in vascular endothelial cells has not been reported. We analyzed whether treatment of GPR40-specific agonists modulated the inflammatory responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Treatment with LY2922470, a GPR40 agonist, significantly reduced lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) phosphorylation and movement into the nucleus from the cytosol. However, treatment with another GPR40 agonist, TAK875, did not inhibit LPS-induced NF-κB activation. LPS treatment induced expression of adhesion molecules vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and attachment of THP-1 cells to HUVECs, which were all decreased by LY2922470 but not TAK875. Our results showed that ligand-dependent agonism of GPR40 is a promising therapeutic target for overcoming inflammatory reactions in the endothelium.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthetic GPR40/FFAR1 agonists: An exhaustive survey on the most recent chemical classes and their structure-activity relationships
Abhik Paul, Sourin Nahar, Pankaj Nahata, Arnab Sarkar, Avik Maji, Ajeya Samanta, Sanmoy Karmakar, Tapan Kumar Maity
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2024; 264: 115990. CrossRef - Metabolite-sensing GPCRs in rheumatoid arthritis
Xuezhi Yang, Wankang Zhang, Luping Wang, Yingjie Zhao, Wei Wei
Trends in Pharmacological Sciences.2024; 45(2): 118. CrossRef - GPR40 deficiency worsens metabolic syndrome‐associated periodontitis in mice
Yanchun Li, Zhongyang Lu, Cameron L. Kirkwood, Keith L. Kirkwood, Stephen A. Wank, Ai‐Jun Li, Maria F. Lopes‐Virella, Yan Huang
Journal of Periodontal Research.2023; 58(3): 575. CrossRef - Signaling pathways and intervention for therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Rong Cao, Huimin Tian, Yu Zhang, Geng Liu, Haixia Xu, Guocheng Rao, Yan Tian, Xianghui Fu
MedComm.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - G Protein-Coupled Receptor 40 Agonist LY2922470 Alleviates Ischemic-Stroke-Induced Acute Brain Injury and Functional Alterations in Mice
Yingyu Lu, Wanlu Zhou, Qinghua Cui, Chunmei Cui
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(15): 12244. CrossRef - AM1638, a GPR40-Full Agonist, Inhibited Palmitate- Induced ROS Production and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Enhancing HUVEC Viability in an NRF2-Dependent Manner
Hwan-Jin Hwang, Joo Won Kim, SukHwan Yun, Min Jeong Park, Eyun Song, Sooyeon Jang, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 760. CrossRef - Learn from failures and stay hopeful to GPR40, a GPCR target with robust efficacy, for therapy of metabolic disorders
Hong-Ping Guan, Yusheng Xiong
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Synthetic GPR40/FFAR1 agonists: An exhaustive survey on the most recent chemical classes and their structure-activity relationships
Letter
- Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microvascular Complications in Chinese Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:93-103)
- Gyuri Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):512-514. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0134
- 2,703 View
- 119 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) Analysis of Lipids, Proteins, DNA Oxidative Damage, and Antioxidant Defense in Plasma and Erythrocytes of Young Reproductive-Age Men with Early Stages of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) Nephropathy in the Irkutsk Reg
Marina Darenskaya, Elena Chugunova, Sergey Kolesnikov, Natalya Semenova, Isay Michalevich, Olga Nikitina, Anastasya Lesnaya, Lyubov Kolesnikova
Metabolites.2022; 12(12): 1282. CrossRef - Recent advances and potentiality of postbiotics in the food industry: Composition, inactivation methods, current applications in metabolic syndrome, and future trends
Yujie Zhong, Tao Wang, Ruilin Luo, Jiayu Liu, Ruyi Jin, Xiaoli Peng
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; : 1. CrossRef
- Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) Analysis of Lipids, Proteins, DNA Oxidative Damage, and Antioxidant Defense in Plasma and Erythrocytes of Young Reproductive-Age Men with Early Stages of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) Nephropathy in the Irkutsk Reg

 KDA
KDA


 First
First Prev
Prev





