
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse > Previous issues
Reviews
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Not Control but Conquest: Strategies for the Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jinyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):165-180. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0377
- 8,753 View
- 508 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - A durable normoglycemic state was observed in several studies that treated type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients through metabolic surgery, intensive therapeutic intervention, or significant lifestyle modification, and it was confirmed that the functional β-cell mass was also restored to a normal level. Therefore, expert consensus introduced the concept of remission as a common term to express this phenomenon in 2009. Throughout this article, we introduce the recently updated consensus statement on the remission of T2DM in 2021 and share our perspective on the remission of diabetes. There is a need for more research on remission in Korea as well as in Western countries. Remission appears to be prompted by proactive treatment for hyperglycemia and significant weight loss prior to irreversible β-cell changes. T2DM is not a diagnosis for vulnerable individuals to helplessly accept. We attempt to explain how remission of T2DM can be achieved through a personalized approach. It may be necessary to change the concept of T2DM towards that of an urgent condition that requires rapid intervention rather than a chronic, progressive disease. We must grasp this paradigm shift in our understanding of T2DM for the benefit of our patients as endocrine experts.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Jinyoung Kim, Bongseong Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 567. CrossRef - Mechanisms and the strategy for remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Tien‐Jyun Chang
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(3): 351. CrossRef - Remission of type 2 diabetes: A critical appraisal
Michele Ricci, Juan José Mancebo-Sevilla, Lidia Cobos Palacios, Jaime Sanz-Cánovas, Almudena López-Sampalo, Halbert Hernández-Negrin, Miguel Angel Pérez-Velasco, Luis M. Pérez-Belmonte, Maria Rosa Bernal-López, Ricardo Gómez-Huelgas
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence and predictors of remission and relapse of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japan: Analysis of a nationwide patient registry (JDDM73)
Kazuya Fujihara, Laymon Khin, Koshiro Murai, Yurie Yamazaki, Kahori Tsuruoka, Noriko Yagyuda, Katsuya Yamazaki, Hiroshi Maegawa, Shiro Tanaka, Satoru Kodama, Hirohito Sone
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(8): 2227. CrossRef - Use of SGLT2 inhibitors after bariatric/metabolic surgery: Risk/benefit balance
André J. Scheen
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101453. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Type 2 Diabetes: Further Insights into the Power of Weight Loss and Exercise
Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(3): 302. CrossRef - Unlocking the Potential of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Remission
Prakriti Sharma, Swarupa Chakole
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Global research trends of diabetes remission: a bibliometric study
Xue Yang, Zhiwei He, Qilin Chen, Yu Chen, Guofang Chen, Chao Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gastrointestinal adverse events of tirzepatide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and trials sequential analysis
Keke Tong, Shuang Yin, Yunfeng Yu, Xinyu Yang, Gang Hu, Fei Zhang, Zhenjie Liu
Medicine.2023; 102(43): e35488. CrossRef - Optimal dose of tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
Yunfeng Yu, Gang Hu, Shuang Yin, Xinyu Yang, Manli Zhou, Weixiong Jian
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
- Complications
- Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):181-197. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0329
- 12,019 View
- 789 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 46 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Although diabetic kidney disease (DKD) remains the leading cause of end-stage kidney disease eventually requiring chronic kidney replacement therapy, the prevalence of DKD has failed to decline over the past 30 years. In order to reduce disease prevalence, extensive research has been ongoing to improve prediction of DKD onset and progression. Although the most commonly used markers of DKD are albuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate, their limitations have encouraged researchers to search for novel biomarkers that could improve risk stratification. Considering that DKD is a complex disease process that involves several pathophysiologic mechanisms such as hyperglycemia induced inflammation, oxidative stress, tubular damage, eventually leading to kidney damage and fibrosis, many novel biomarkers that capture one specific mechanism of the disease have been developed. Moreover, the increasing use of high-throughput omic approaches to analyze biological samples that include proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics has emerged as a strong tool in biomarker discovery. This review will first describe recent advances in the understanding of the pathophysiology of DKD, and second, describe the current clinical biomarkers for DKD, as well as the current status of multiple potential novel biomarkers with respect to protein biomarkers, proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of polyphenols in the management of diabetic complications
Jeevika Raina, Atika Firdous, Gurvinder Singh, Rajesh Kumar, Charanjit Kaur
Phytomedicine.2024; 122: 155155. CrossRef - Role of MCP-1 as an inflammatory biomarker in nephropathy
Yanlong Liu, Ke Xu, Yuhua Xiang, Boyan Ma, Hailong Li, Yuan Li, Yue Shi, Shuju Li, Yan Bai
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Urinary podocyte stress marker as a prognostic indicator for diabetic kidney disease
Lingfeng Zeng, Jack Kit-Chung Ng, Winston Wing-Shing Fung, Gordon Chun-Kau Chan, Kai-Ming Chow, Cheuk-Chun Szeto
BMC Nephrology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification and validation of immune and cuproptosis - related genes for diabetic nephropathy by WGCNA and machine learning
Yubing Chen, Lijuan Liao, Baoju Wang, Zhan Wu
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Specific Alternation of Gut Microbiota and the Role of Ruminococcus gnavus in the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy
Jinni Hong, Tingting Fu, Weizhen Liu, Yu Du, Junmin Bu, Guojian Wei, Miao Yu, Yanshan Lin, Cunyun Min, Datao Lin
Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2024; 34(3): 547. CrossRef - The Triglyceride-Glucose Index is Superior to Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance in predicting Metabolic Syndrome in an Adult Population in the United States
Beverley Adams-Huet, Rafael Zubirán, Alan T Remaley, Ishwarlal Jialal
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Narrative Review of New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy
Aadhira Pillai, Darshna Fulmali
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bamboo leaf: A review of traditional medicinal property, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and purification technology
Yaqian Cheng, Siqi Wan, Linna Yao, Ding Lin, Tong Wu, Yongjian Chen, Ailian Zhang, Chenfei Lu
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2023; 306: 116166. CrossRef - Molecular Pathways of Diabetic Kidney Disease Inferred from Proteomics
Lan Wei, Yuanyuan Han, Chao Tu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 117. CrossRef - Omics and Artificial Intelligence in Kidney Diseases
Nadja Grobe, Josef Scheiber, Hanjie Zhang, Christian Garbe, Xiaoling Wang
Advances in Kidney Disease and Health.2023; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Intestinal microbiome diversity of diabetic and non-diabetic kidney disease: Current status and future perspective
Soumik Das, Ramanathan Gnanasambandan
Life Sciences.2023; 316: 121414. CrossRef - Pediatric Diabetic Nephropathy: Novel Insights from microRNAs
Francesca Lanzaro, Annalisa Barlabà, Angelica De Nigris, Federica Di Domenico, Valentina Verde, Emanuele Miraglia del Giudice, Anna Di Sessa
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(4): 1447. CrossRef - Novel Biomarkers of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Jorge Rico-Fontalvo, Gustavo Aroca-Martínez, Rodrigo Daza-Arnedo, José Cabrales, Tomás Rodríguez-Yanez, María Cardona-Blanco, Juan Montejo-Hernández, Dairo Rodelo Barrios, Jhonny Patiño-Patiño, Elber Osorio Rodríguez
Biomolecules.2023; 13(4): 633. CrossRef - Diabetic vascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies
Yiwen Li, Yanfei Liu, Shiwei Liu, Mengqi Gao, Wenting Wang, Keji Chen, Luqi Huang, Yue Liu
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic phenotypes and risk of end-stage kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Lijun Zhao, Yutong Zou, Yucheng Wu, Linli Cai, Yuancheng Zhao, Yiting Wang, Xiang Xiao, Qing Yang, Jia Yang, Honghong Ren, Nanwei Tong, Fang Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of a New RNA and Protein Integrated Biomarker Panel Associated with Kidney Function Impairment in DKD: Translational Implications
Alessandra Scamporrino, Stefania Di Mauro, Agnese Filippello, Grazia Di Marco, Antonino Di Pino, Roberto Scicali, Maurizio Di Marco, Emanuele Martorana, Roberta Malaguarnera, Francesco Purrello, Salvatore Piro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(11): 9412. CrossRef - Increased serum PCSK9 levels are associated with renal function impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Zhicai Feng, Xiangyu Liao, Hao Zhang, Juan Peng, Zhijun Huang, Bin Yi
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Serum Pyrodeath Re-lated Proteins and Renal Injury in Patients with Type 2 DKD
茹洁 马
Asian Case Reports in Emergency Medicine.2023; 11(02): 53. CrossRef - Loganin reduces diabetic kidney injury by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
Xiangri Kong, Yunyun Zhao, Xingye Wang, Yongjiang Yu, Ying Meng, Guanchi Yan, Miao Yu, Lihong Jiang, Wu Song, Bingmei Wang, Xiuge Wang
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2023; 382: 110640. CrossRef - Machine-learning algorithm-based prediction of a diagnostic model based on oxidative stress-related genes involved in immune infiltration in diabetic nephropathy patients
Heng-Mei Zhu, Na Liu, Dong-Xuan Sun, Liang Luo
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The roles of gut microbiota and its metabolites in diabetic nephropathy
Hui Zhao, Cheng-E Yang, Tian Liu, Ming-Xia Zhang, Yan Niu, Ming Wang, Jun Yu
Frontiers in Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High triglyceride levels increase the risk of diabetic microvascular complications: a cross-sectional study
Jiahang Li, Lei Shi, Guohong Zhao, Fei Sun, Zhenxing Nie, Zhongli Ge, Bin Gao, Yan Yang
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Nephrin Levels in Iraqi Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy
Raghda Hisham Aljorani, Eman Saadi Saleh , Khalaf Gata Hussein Al Mohammadawi
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2023; 5: 99. CrossRef - Diabetic Nephropathy: Significance of Determining Oxidative Stress and Opportunities for Antioxidant Therapies
Marina Darenskaya, Sergey Kolesnikov, Natalya Semenova, Lyubov Kolesnikova
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(15): 12378. CrossRef - Evaluation of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio, Low-Density Lipoprotein/Albumin Ratio, and Red Cell Distribution Width/Albumin Ratio in the Estimation of Proteinuria in Uncontrolled Diabetic Patients
Duygu Tutan, Murat Doğan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hedysarum polybotrys polysaccharide attenuates renal inflammatory infiltration and fibrosis in diabetic mice by inhibiting the HMGB1/RAGE/TLR4 pathway
Changqing Xu, Yanxu Cheng, Zongmei Liu, Xiaoyan Fu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Abdominal adipose tissue and type 2 diabetic kidney disease: adipose radiology assessment, impact, and mechanisms
Fei Lu, Jinlei Fan, Fangxuan Li, Lijing Liu, Zhiyu Chen, Ziyu Tian, Liping Zuo, Dexin Yu
Abdominal Radiology.2023; 49(2): 560. CrossRef - Inhibition of MD2 by natural product-drived JM-9 attenuates renal inflammation and diabetic nephropathy in mice
Minxiu Wang, Qianhui Zhang, Shuaijie Lou, Leiming Jin, Gaojun Wu, Wenqi Wu, Qidong Tang, Yi Wang, Xiaohong Long, Ping Huang, Wu Luo, Guang Liang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115660. CrossRef - Multifaceted relationship between diabetes and kidney diseases: Beyond diabetes
Pasquale Esposito, Daniela Picciotto, Francesca Cappadona, Francesca Costigliolo, Elisa Russo, Lucia Macciò, Francesca Viazzi
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(10): 1450. CrossRef - Mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein: a potential therapeutic target in renal disease
Meng Wu, Zhiyin Pei, Guangfeng Long, Hongbing Chen, Zhanjun Jia, Weiwei Xia
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Research progress on multiple cell death pathways of podocytes in diabetic kidney disease
Can Yang, Zhen Zhang, Jieting Liu, Peijian Chen, Jialing Li, Haiying Shu, Yanhui Chu, Luxin Li
Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative profiling of carboxylic compounds by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for revealing biomarkers of diabetic kidney disease
Rongrong Zhu, Yan Yuan, Rourou Qi, Jianying Liang, Yan Shi, Hongbo Weng
Journal of Chromatography B.2023; 1231: 123930. CrossRef - Jiangtang Decoction Ameliorates Diabetic Kidney Disease Through the Modulation of the Gut Microbiota
Jinni Hong, Tingting Fu, Weizhen Liu, Yu Du, Junmin Bu, Guojian Wei, Miao Yu, Yanshan Lin, Cunyun Min, Datao Lin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3707. CrossRef - GLP-1RA Combined with SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Meta Analysis
莹 郭
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(11): 18117. CrossRef - Potential application of Klotho as a prognostic biomarker for patients with diabetic kidney disease: a meta-analysis of clinical studies
Li Xia Yu, Min Yue Sha, Yue Chen, Fang Tan, Xi Liu, Shasha Li, Qi-Feng Liu
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals RAC1 Involvement in Macrophages Efferocytosis in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Yi Song, Yifan Liu, Feng Guo, Lin Zhao, Guijun Qin
Inflammation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Research progress of natural active compounds on improving podocyte function to reduce proteinuria in diabetic kidney disease
Le Gong, Rui Wang, Xinyu Wang, Jing Liu, Zhaodi Han, Qian Li, Yi Jin, Hui Liao
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of potential crosstalk genes and mechanisms between periodontitis and diabetic nephropathy through bioinformatic analysis
Huijuan Lu, Jia Sun, Jieqiong Sun
Medicine.2023; 102(52): e36802. CrossRef - Mitochondrial RNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Functional Impairment in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Stefania Di Mauro, Alessandra Scamporrino, Agnese Filippello, Maurizio Di Marco, Maria Teresa Di Martino, Francesca Scionti, Antonino Di Pino, Roberto Scicali, Roberta Malaguarnera, Francesco Purrello, Salvatore Piro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8198. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Partial Synthetic PPARƳ Derivative Ameliorates Aorta Injury in Experimental Diabetic Rats Mediated by Activation of miR-126-5p Pi3k/AKT/PDK 1/mTOR Expression
Yasmin M. Ahmed, Raha Orfali, Nada S. Abdelwahab, Hossam M. Hassan, Mostafa E. Rateb, Asmaa M. AboulMagd
Pharmaceuticals.2022; 15(10): 1175. CrossRef - Polydatin attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting YAP expression and nuclear translocation
Manlin He, Lan Feng, Yang Chen, Bin Gao, Yiwei Du, Lu Zhou, Fei Li, Hongbao Liu
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of diabetic nephropathy in the diabetes mellitus population: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
Sicheng Li, Huidi Xie, Yang Shi, Hongfang Liu
Medicine.2022; 101(42): e31232. CrossRef - Stratification of diabetic kidney diseases via data-independent acquisition proteomics–based analysis of human kidney tissue specimens
Qinghua Huang, Xianming Fei, Zhaoxian Zhong, Jieru Zhou, Jianguang Gong, Yuan Chen, Yiwen Li, Xiaohong Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel biomarkers and therapeutic approaches for diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy: Recent progress and future perspectives
Ziyan Xie, Xinhua Xiao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease
Susanne B. Nicholas, Amy K. Mottl
Nephrology Self-Assessment Program.2022; 21(5): 394. CrossRef
- Role of polyphenols in the management of diabetic complications
- Complications
- Peripheral Neuropathy Phenotyping in Rat Models of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluating Uptake of the Neurodiab Guidelines and Identifying Future Directions
- Md Jakir Hossain, Michael D. Kendig, Meg E. Letton, Margaret J. Morris, Ria Arnold
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):198-221. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0347
- 5,206 View
- 225 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) affects over half of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, with an urgent need for effective pharmacotherapies. While many rat and mouse models of T2DM exist, the phenotyping of DPN has been challenging with inconsistencies across laboratories. To better characterize DPN in rodents, a consensus guideline was published in 2014 to accelerate the translation of preclinical findings. Here we review DPN phenotyping in rat models of T2DM against the ‘Neurodiab’ criteria to identify uptake of the guidelines and discuss how DPN phenotypes differ between models and according to diabetes duration and sex. A search of PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science databases identified 125 studies, categorised as either diet and/or chemically induced models or transgenic/spontaneous models of T2DM. The use of diet and chemically induced T2DM models has exceeded that of transgenic models in recent years, and the introduction of the Neurodiab guidelines has not appreciably increased the number of studies assessing all key DPN endpoints. Combined high-fat diet and low dose streptozotocin rat models are the most frequently used and well characterised. Overall, we recommend adherence to Neurodiab guidelines for creating better animal models of DPN to accelerate translation and drug development.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SIRT3 alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy by mediating the FoxO3a‐PINK1‐Parkin signaling pathway to activate mitophagy
Jing Yang, Zhuoying Yu, Ye Jiang, Zixian Zhang, Yue Tian, Jie Cai, Min Wei, Yanhan Lyu, Dongsheng Yang, Shixiong Shen, Guo‐Gang Xing, Min Li
CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Compound Qiying Granules alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis
Yan Hu, Chen Chen, Zhengting Liang, Tao Liu, Xiaoling Hu, Guanying Wang, Jinxia Hu, Xiaolin Xie, Zhiyan Liu
Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HCV affects KATP channels through GnT-IVa-mediated N-glycosylation of GLUT2 on the surface of pancreatic β-cells leading to impaired insulin secretion
Ben Niu, Lijing Ma, Lixuan Yao, Yating Zhang, Heng Su
Endocrine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multimodal Comparison of Diabetic Neuropathy in Aged Streptozotocin-Treated Sprague–Dawley and Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats
Annalisa Canta, Valentina A. Carozzi, Alessia Chiorazzi, Cristina Meregalli, Norberto Oggioni, Virginia Rodriguez-Menendez, Barbara Sala, Roberto Cosimo Melcangi, Silvia Giatti, Raffaella Lombardi, Roberto Bianchi, Paola Marmiroli, Guido Cavaletti
Biomedicines.2022; 11(1): 20. CrossRef
- SIRT3 alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy by mediating the FoxO3a‐PINK1‐Parkin signaling pathway to activate mitophagy
- Pathophysiology
- Glial and Vascular Cell Regulation of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Diabetes
- Xiaolong Li, Yan Cai, Zuo Zhang, Jiyin Zhou
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):222-238. Published online March 18, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0146
- 6,244 View
- 297 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - As a structural barrier, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is located at the interface between the brain parenchyma and blood, and modulates communication between the brain and blood microenvironment to maintain homeostasis. The BBB is composed of endothelial cells, basement membrane, pericytes, and astrocytic end feet. BBB impairment is a distinguishing and pathogenic factor in diabetic encephalopathy. Diabetes causes leakage of the BBB through downregulation of tight junction proteins, resulting in impaired functioning of endothelial cells, pericytes, astrocytes, microglia, nerve/glial antigen 2-glia, and oligodendrocytes. However, the temporal regulation, mechanisms of molecular and signaling pathways, and consequences of BBB impairment in diabetes are not well understood. Consequently, the efficacy of therapies diabetes targeting BBB leakage still lags behind the requirements. This review summarizes the recent research on the effects of diabetes on BBB composition and the potential roles of glial and vascular cells as therapeutic targets for BBB disruption in diabetic encephalopathy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gut microbiota and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a focus on the gut-brain axis
Yi Pan, Tong Bu, Xia Deng, Jue Jia, Guoyue Yuan
Endocrine.2024; 84(1): 1. CrossRef - Long-Term Exposure of Cultured Astrocytes to High Glucose Impact on Their LPS-Induced Activation
Ayna Abdyeva, Ekaterina Kurtova, Irina Savinkova, Maksim Galkov, Liubov Gorbacheva
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 1122. CrossRef - Role of autophagy in angiogenic potential of vascular pericytes
Soheil Zamen Milani, Aysa Rezabakhsh, Mohammad Karimipour, Leila Salimi, Narges Mardi, Maryam Taghavi Narmi, Fatemeh Sadeghsoltani, Ferzane Valioglu, Reza Rahbarghazi
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The NG2-glia is a potential target to maintain the integrity of neurovascular unit after acute ischemic stroke
Xiaoyan Hu, Panpan Geng, Xiaoyun Zhao, Qian Wang, Changqing Liu, Chun Guo, Wen Dong, Xinchun Jin
Neurobiology of Disease.2023; 180: 106076. CrossRef - Tight junction disruption and the pathogenesis of the chronic complications of diabetes mellitus: A narrative review
Ma Ludivina Robles-Osorio, Ernesto Sabath
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(7): 1013. CrossRef - Function and therapeutic value of astrocytes in diabetic cognitive impairment
Fanyu Meng, Jiafeng Fu, Lin Zhang, Mengqing Guo, Pengwei Zhuang, Qingsheng Yin, Yanjun Zhang
Neurochemistry International.2023; 169: 105591. CrossRef - Exploring the molecular targets for Type 2 diabetes-induced Alzheimer’s disease through bioinformatics analysis
Lin Gao, Chengyu Huang, Hui Li, Shidi Wu, Xiaoyan Zhou, Changjiang Ying
Epigenomics.2023; 15(11): 619. CrossRef - In vivo retinal imaging is associated with cognitive decline, blood-brain barrier disruption and neuroinflammation in type 2 diabetic mice
May Majimbi, Samuel McLenachan, Michael Nesbit, Fred K. Chen, Virginie Lam, John Mamo, Ryu Takechi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic microvascular disease in non-classical beds: the hidden impact beyond the retina, the kidney, and the peripheral nerves
Dídac Mauricio, Mònica Gratacòs, Josep Franch-Nadal
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcranial photobiomodulation improves insulin therapy in diabetic microglial reactivity and the brain drainage system
Shaojun Liu, Dongyu Li, Tingting Yu, Jingtan Zhu, Oxana Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, Dan Zhu
Communications Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - NG2‐glia crosstalk with microglia in health and disease
Zuo Zhang, Xiaolong Li, Hongli Zhou, Jiyin Zhou
CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics.2022; 28(11): 1663. CrossRef - Accelerated amyloid angiopathy and related vascular alterations in a mixed murine model of Alzheimer´s disease and type two diabetes
Maria Vargas-Soria, Juan Jose Ramos-Rodriguez, Angel del Marco, Carmen Hierro-Bujalance, Maria Jose Carranza-Naval, Maria Calvo-Rodriguez, Susanne J. van Veluw, Alan W. Stitt, Rafael Simó, Brian J. Bacskai, Carmen Infante-Garcia, Monica Garcia-Alloza
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Gut microbiota and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a focus on the gut-brain axis
- Others
- Links between Thyroid Disorders and Glucose Homeostasis
- Young Sil Eom, Jessica R. Wilson, Victor J. Bernet
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):239-256. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0013
- 10,917 View
- 635 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Thyroid disorders and diabetes mellitus often coexist and are closely related. Several studies have shown a higher prevalence of thyroid disorders in patients with diabetes mellitus and vice versa. Thyroid hormone affects glucose homeostasis by impacting pancreatic β-cell development and glucose metabolism through several organs such as the liver, gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, adipose tissue, skeletal muscles, and the central nervous system. The present review discusses the effect of thyroid hormone on glucose homeostasis. We also review the relationship between thyroid disease and diabetes mellitus: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, as well as guidelines for screening thyroid function with each disorder. Finally, we provide an overview of the effects of antidiabetic drugs on thyroid hormone and thyroid disorders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Linkage and association of rs3110045 and rs28499085 variants in the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor (TRHR) gene with the risk of familial type 2 diabetes
Rongling Wu, Claudia Gragnoli
Aspects of Molecular Medicine.2024; 3: 100037. CrossRef - Obesity and Obesity-Related Thyroid Dysfunction: Any Potential Role for the Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD)?
Sebastián Pablo Chapela, Alison Simancas-Racines, Florencia Ceriani, Andrés Luciano Nicolas Martinuzzi, María Paula Russo, Ana Karina Zambrano, Daniel Simancas-Racines, Ludovica Verde, Giovanna Muscogiuri, Christos S. Katsanos, Evelyn Frias-Toral, Luigi B
Current Nutrition Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and Pleiotropic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, Side Effects, and Sex-Related Differences
Guglielmina Froldi
Pharmaceuticals.2024; 17(4): 478. CrossRef - Thyroid Hormones and Diabetes in Euthyroid Hispanic/Latino Adults of Diverse Backgrounds: HCHS/SOL
Victoria Persky, Chibuzor Abasilim, Konstantina Tsintsifas, Tessa Day, Robert M Sargis, Martha Daviglus, Jianwen Cai, Sally Freels, Robert Kaplan, Carmen R Isasi, Amber Pirzada, Michelle L Meyer, Gregory A Talavera, Bharat Thyagarajan, Shivani Agarwal, No
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Managing Adults With Hypoglycemia
Christopher James Watson, Jonathan A. Edlow
Annals of Emergency Medicine.2023; 82(6): 705. CrossRef - Relationship of Glucose, C-peptide, Leptin, and BDNF in Maternal and Umbilical Vein Blood in Type-1 Diabetes
Josip Delmis, Slavko Oreskovic, Vesna Elvedji Gasparovic, Mirta Starcevic, Mislav Herman, Nada Dessardo, Vito Starcevic, Marina Ivanisevic
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 600. CrossRef - Isolated Maternal Hypothyroxinemia May be Associated with Insulin
Requirement in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Ömercan Topaloğlu, Mehmet Uzun, Seda Nur Topaloğlu, Ibrahim Sahin
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(04): 245. CrossRef - Association of urinary iodine concentration with prediabetes/diabetes in adults: Analysis of the NHANES 2005–2016
Jingmin Chen, Huanzhu Liang, Yuxuan Tan, Lin Wen, Ziang Guo, Jiyu Nie, Xiaoxiao Lin, Feng Huang, Jie Wang, Puyi Xing, Lihong Nie, Lihong Wang, Chunxia Jing
Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology.2023; 77: 127144. CrossRef - Central sensitivity to thyroid hormones is reduced in youths with overweight or obesity and impaired glucose tolerance
Procolo Di Bonito, Domenico Corica, Maria Rosaria Licenziati, Anna Di Sessa, Emanuele Miraglia del Giudice, Maria Felicia Faienza, Valeria Calcaterra, Francesca Franco, Giulio Maltoni, Giuliana Valerio, Malgorzata Wasniewska
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of thyroid stimulating hormone and time in range with risk of diabetic retinopathy in euthyroid type 2 diabetes
Yaxin Wang, Jingyi Lu, Jiaying Ni, Ming Wang, Yun Shen, Wei Lu, Wei Zhu, Yuqian Bao, Jian Zhou
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The circadian rhythm: an influential soundtrack in the diabetes story
Amirali Hariri, Mina Mirian, Ali Zarrabi, Mohammad Kohandel, Maryam Amini-Pozveh, Amir Reza Aref, Aliye Tabatabaee, Pranav Kumar Prabhakar, Ponnurengam Malliappan Sivakumar
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Folate deficiency may increase the risk for elevated TSH in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Lin Lin, Yushan Du, Guanyu Niu, Shuangbo Xia, Jufen Liu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - L- Thyroxine ameliorates renal function in thyroidectomized diabetic nephropathy rats through downregulation of TGF- β1, Ang II and ET-1 expression
Zeinab H. El-Said, Sherihan I. Gouda, Hebatallah A. Mahgoub, S El_desouky, Neven A. Ebrahim
Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2023; 10(1): 632. CrossRef - Thyroid dysfunction in children and adolescents affected by undernourished and overnourished eating disorders
Valeria Calcaterra, Vittoria Carlotta Magenes, Francesca Siccardo, Chiara Hruby, Martina Basso, Veronica Conte, Giulia Maggioni, Valentina Fabiano, Susanna Russo, Pierangelo Veggiotti, Gianvincenzo Zuccotti
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Preventive Effect of Molecular Iodine in Pancreatic Disorders from Hypothyroid Rabbits
Julia Rodríguez-Castelán, Evangelina Delgado-González, Esteban Rodríguez-Benítez, Francisco Castelán, Estela Cuevas-Romero, Brenda Anguiano, Michael C. Jeziorski, Carmen Aceves
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(19): 14903. CrossRef - Hypothyroidism increases angiotensinogen gene expression associated with vascular smooth muscle cells cholesterol metabolism dysfunction and aorta remodeling in Psammomys obesus
Samia Neggazi, Nadjiba Hamlat, Sihem Berdja, Saliha Boumaza, Leila Smail, Michel Beylot, Souhila Aouichat-Bouguerra
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Correlation Between Thyroid Parameters and the Ratios of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte and Platelet/Lymphocyte in Euthyroid Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Hui Chen, Jun-Qiang Ju, Xiao-Wu Qian, Zheng-Tai Zhu, Chun-Zhi Zhao, Zhe Liu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3763. CrossRef - Effects of high-intensity interval training program on pituartry function in basketball players: a randomized controlled trial
Recep Soslu, Abdullah Uysal, Meltem Devrilmez, İsmail Can Çuvalcıoğlu, Ali Ahmet Doğan, Sülbiye Karaburgu, Murat Taş
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Selenium and Selenoproteins at the Intersection of Type 2 Diabetes and Thyroid Pathophysiology
Francesca Gorini, Cristina Vassalle
Antioxidants.2022; 11(6): 1188. CrossRef - TSH levels within the normal range and risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality among individuals with diabetes
Ping Zhu, Guojuan Lao, Chuping Chen, Lihui Luo, Jing Gu, Jianmin Ran
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolite Changes during the Transition from Hyperthyroidism to Euthyroidism in Patients with Graves’ Disease
Ho Yeop Lee, Byeong Chang Sim, Ha Thi Nga, Ji Sun Moon, Jingwen Tian, Nguyen Thi Linh, Sang Hyeon Ju, Dong Wook Choi, Daiki Setoyama, Hyon-Seung Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 891. CrossRef
- Linkage and association of rs3110045 and rs28499085 variants in the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor (TRHR) gene with the risk of familial type 2 diabetes
Editorial
- Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors: Causative Factor or Epiphenomenon?
- Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):257-259. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0060
- 3,074 View
- 131 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef - Mean versus variability of lipid measurements over 6 years and incident cardiovascular events: More than a decade follow-up
Soroush Masrouri, Leila Cheraghi, Niloofar Deravi, Neda Cheraghloo, Maryam Tohidi, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Original Articles
- COVID-19
- Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on the Metabolic Control Parameters in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ifan Ali Wafa, Nando Reza Pratama, Nurizzah Farahiyah Sofia, Elsha Stephanie Anastasia, Tiffany Konstantin, Maharani Ayuputeri Wijaya, M. Rifqi Wiyono, Lilik Djuari, Hermina Novida
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):260-272. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0125
- 5,934 View
- 272 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Abrupt implementation of lockdowns during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic affected the management of diabetes mellitus in patients worldwide. Limited access to health facilities and lifestyle changes potentially affected metabolic parameters in patients at risk. We conducted a meta-analysis to determine any differences in the control of metabolic parameters in patients with diabetes, before and during lockdown.
Methods
We performed searches of five databases. Meta-analyses were carried out using random- or fixed-effect approaches to glycaemic control parameters as the primary outcome: glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), random blood glucose (RBG), fasting blood glucose (FBG), time-in-range (TIR), time-above-range (TAR), time-below-range (TBR). Mean difference (MD), confidence interval (CI), and P value were calculated. Lipid profile was a secondary outcome and is presented as a descriptive analysis.
Results
Twenty-one studies enrolling a total of 3,992 patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus (T1DM or T2DM) were included in the study. Patients with T1DM showed a significant improvement of TIR and TAR (MD=3.52% [95% CI, 0.29 to 6.74], I2=76%, P=0.03; MD=–3.36% [95% CI, –6.48 to –0.25], I2=75%, P=0.03), while FBG among patients with T2DM significantly worsened (MD=3.47 mg/dL [95% CI, 1.22 to 5.73], I2=0%, P<0.01). No significant difference was found in HbA1c, RBG, and TBR. Use of continuous glucose monitoring in T1DM facilitated good glycaemic control. Significant deterioration of lipid parameters during lockdown, particularly triglyceride, was observed.
Conclusion
Implementation of lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic did not worsen glycaemic control in patients with diabetes. Other metabolic parameters improved during lockdown, though lipid parameters, particularly triglyceride, worsened. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Disruption of diabetes and hypertension care during the COVID-19 pandemic and recovery approaches in the Latin America and Caribbean region: a scoping review protocol
Samira Barbara Jabakhanji, Oluwabunmi Ogungbe, Sonia Y Angell, Lawrence Appel, David Byrne, Roopa Mehta, John McCaffrey, Lori Rosman, Edward W Gregg, Kunihiro Matsushita
BMJ Open.2024; 14(1): e074443. CrossRef - Influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the achievement of guideline targets for HbA1c, blood pressure, and LDL cholesterol in people with diabetes in Japan
Shingo Kuwajima, Takahito Itoh, Tatsuya Sato, Shoya Ino, Satoru Shibata, Kouhei Ohno, Hiroyuki Hotta, Tomoaki Matsumoto, Hitoshi Ooiwa, Hirofumi Kubo, Takayuki Miki
Diabetology International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19: What We Learned From the Lockdown Experience
Catarina Almeida, André Ferreira, Daniela Duarte, Ana Filipa Viegas, André Santos, Alexandra Vaz, Edite Nascimento
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in body weight and glycemic control in association with COVID-19 Shutdown among 23,000 adults with type 2 diabetes
Emily Panza, Kevin E. Kip, Kripa Venkatakrishnan, Oscar C. Marroquin, Rena R. Wing
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(6): 787. CrossRef - The Impact of a Lockdown for the COVID-19 Pandemic on Seasonal HbA1c Variation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Yu-Cheng Cheng, Yu-Hsuan Li, Hsiu-Chen Liu, Chiann-Yi Hsu, Wan-Jen Chang, I-Te Lee, Chin-Li Lu
Life.2023; 13(3): 763. CrossRef - The Impact of Partial Lockdown During COVID-19 Pandemic on Metabolic Control in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ayşe Zülal TOKAÇ, Tuğde Buse UĞUR, Buse Ecem KURUGÖL, Sevilay ALİGÜLÜ, Osman HAYRAN
Journal of Biotechnology and Strategic Health Research.2023; 7(1): 67. CrossRef - Retrospective Study on the Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Northern Taiwan
Hsuan Huang, Hsiao-Ling Su, Chih-Hsung Huang, Yi-Hsin Lin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2539. CrossRef - RIPK1 and RIPK3 inhibitors: potential weapons against inflammation to treat diabetic complications
Dan Ke, Zhen Zhang, Jieting Liu, Peijian Chen, Yucen Dai, Xinhai Sun, Yanhui Chu, Luxin Li
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - “Does Physical Exercise Promote Health Benefits for Diabetic Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic?”: A Systematic Review
Erivaldo de Souza, Daniela Meneses-Santos, Josué Cruz Santos, Felipe J. Aidar, Carla Roberta de Oliveira Carvalho, Jymmys Lopes dos Santos, Anderson Carlos Marçal
Sports.2023; 11(10): 192. CrossRef - Impact of National Lockdown From COVID-19 Pandemic in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: An Observational Study
Nuntakorn Thongtang, Niracha Chanwimol, Lukana Preechasuk, Varisara Boonyuang, Pinyo Rattanaumpawan, Supawadee Likitmaskul, Apiradee Sriwijitkamol
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2022; 34(6-7): 708. CrossRef
- Disruption of diabetes and hypertension care during the COVID-19 pandemic and recovery approaches in the Latin America and Caribbean region: a scoping review protocol
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Performance of Diabetes and Kidney Disease Screening Scores in Contemporary United States and Korean Populations
- Liela Meng, Keun-Sang Kwon, Dae Jung Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Jeehyoung Kim, Abhijit V. Kshirsagar, Heejung Bang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):273-285. Published online September 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0054
- 65,535 View
- 239 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Risk assessment tools have been actively studied, and they summarize key predictors with relative weights/importance for a disease. Currently, standardized screening scores for type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and chronic kidney disease (CKD)—two key global health problems—are available in United States and Korea. We aimed to compare and evaluate screening scores for DM (or combined with prediabetes) and CKD, and assess the risk in contemporary United States and Korean populations.
Methods
Four (2×2) models were evaluated in the United States-National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 2015–2018) and Korea-NHANES (2016–2018)—8,928 and 16,209 adults. Weighted statistics were used to describe population characteristics. We used logistic regression for predictors in the models to assess associations with study outcomes (undiagnosed DM and CKD) and diagnostic measures for temporal and cross-validation.
Results
Korean adult population (mean age 47.5 years) appeared to be healthier than United States counterpart, in terms of DM and CKD risks and associated factors, with exceptions of undiagnosed DM, prediabetes and prehypertension. Models performed well in own country and external populations regarding predictor-outcome association and discrimination. Risk tests (high vs. low) showed area under the curve >0.75, sensitivity >84%, specificity >45%, positive predictive value >8%, and negative predictive value >99%. Discrimination was better for DM, compared to the combined outcome of DM and prediabetes, and excellent for CKD due to age.
Conclusion
Four easy-to-use screening scores for DM and CKD are well-validated in contemporary United States and Korean populations. Prevention of DM and CKD may serve as first-step in public health, with these self-assessment tools as basic tools to help health education and disparity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A meta‐analysis of diabetes risk prediction models applied to prediabetes screening
Yujin Liu, Sunrui Yu, Wenming Feng, Hangfeng Mo, Yuting Hua, Mei Zhang, Zhichao Zhu, Xiaoping Zhang, Zhen Wu, Lanzhen Zheng, Xiaoqiu Wu, Jiantong Shen, Wei Qiu, Jianlin Lou
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(5): 1593. CrossRef - Performance Analysis and Assessment of Type 2 Diabetes Screening Scores in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Norma Latif Fitriyani, Muhammad Syafrudin, Siti Maghfirotul Ulyah, Ganjar Alfian, Syifa Latif Qolbiyani, Chuan-Kai Yang, Jongtae Rhee, Muhammad Anshari
Mathematics.2023; 11(10): 2266. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Analysis of Chinese, Japanese, Korean, US-PIMA Indian, and Trinidadian Screening Scores for Diabetes Risk Assessment and Prediction
Norma Latif Fitriyani, Muhammad Syafrudin, Siti Maghfirotul Ulyah, Ganjar Alfian, Syifa Latif Qolbiyani, Muhammad Anshari
Mathematics.2022; 10(21): 4027. CrossRef
- A meta‐analysis of diabetes risk prediction models applied to prediabetes screening
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
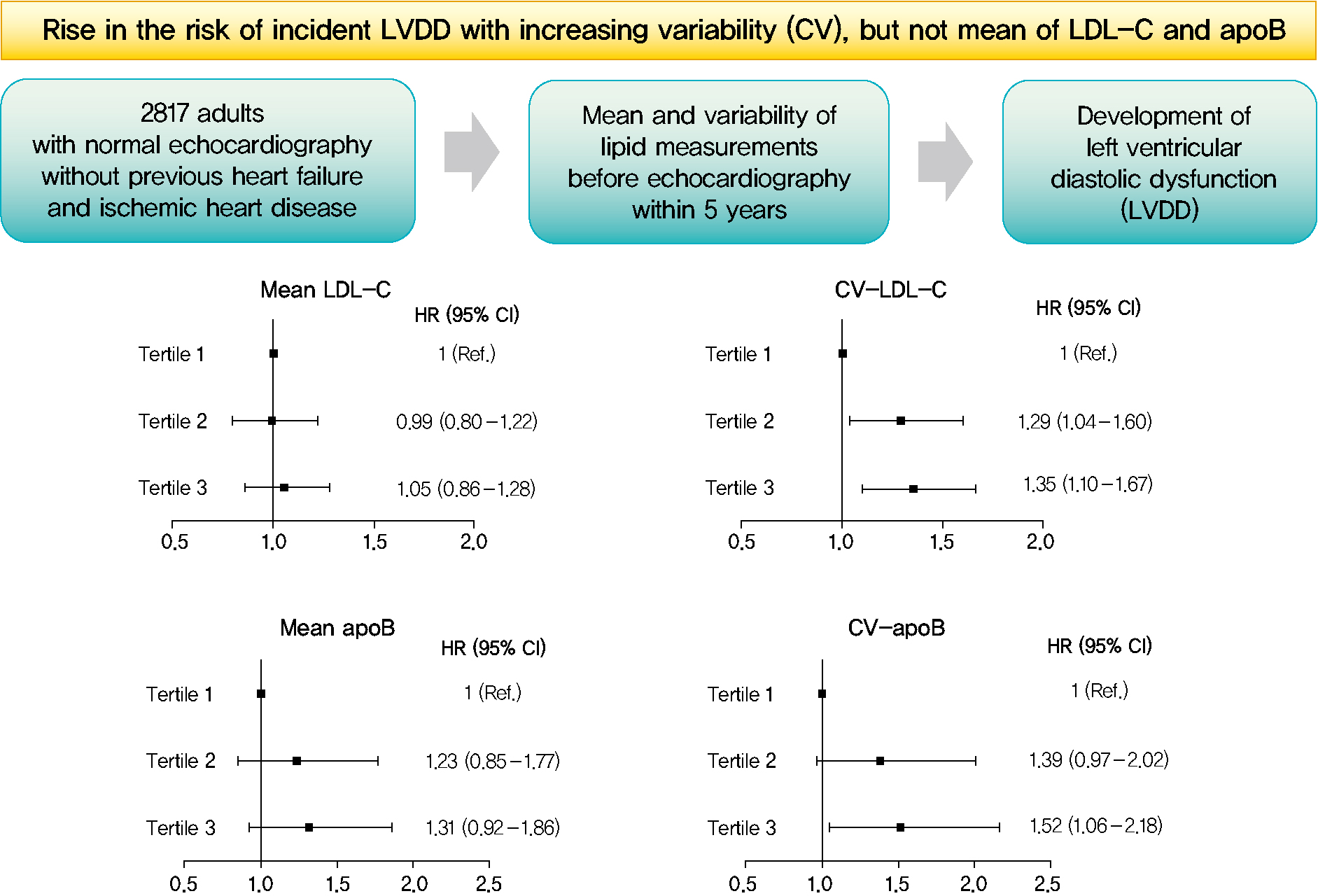
- Mean and Variability of Lipid Measurements and Risk for Development of Subclinical Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction
- Jiyun Park, Mira Kang, Jiyeon Ahn, Min Young Kim, Min Sun Choi, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Jeong Hoon Yang, Sang-Man Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):286-296. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0080
- 5,677 View
- 196 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Subclinical left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is an emerging consequence of increased insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia is one of the few correctable risk factors of LVDD. This study evaluated the role of mean and visit-to-visit variability of lipid measurements in risk of LVDD in a healthy population.
Methods
This was a 3.7-year (interquartile range, 2.1 to 4.9) longitudinal cohort study including 2,817 adults (median age 55 years) with left ventricular ejection fraction >50% who underwent an annual or biannual health screening between January 2008 and July 2016. The mean, standard deviation (SD), coefficient of variation (CV), variability independent of the mean (VIM), and average real variability of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), apolipoprotein B (apoB), non-HDL-C, and triglycerides were obtained from three to six measurements during the 5 years preceding the first echocardiogram.
Results
Among the 2,817 patients, 560 (19.9%) developed LVDD. The mean of no component of lipid measurements was associated with risk of LVDD. CV (hazard ratio [HR], 1.35; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.10 to 1.67), SD (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.57), and VIM (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.55) of LDL-C and all the variability parameters of apoB were significantly associated with development of LVDD. The association between CV-LDL and risk of LVDD did not have significant interaction with sex, increasing/decreasing trend at baseline, or use of stain and/or lipid-modifying agents.
Conclusion
The variability of LDL-C and apoB, rather than their mean, was associated with risk for LVDD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Separate and Joint Associations of Remnant Cholesterol Accumulation and Variability With Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Prospective Cohort Study
Jinqi Wang, Rui Jin, Xiaohan Jin, Zhiyuan Wu, Haiping Zhang, Ze Han, Zongkai Xu, Yueruijing Liu, Xiaoyu Zhao, Xiuhua Guo, Lixin Tao
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors: Causative Factor or Epiphenomenon?
Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 257. CrossRef
- Separate and Joint Associations of Remnant Cholesterol Accumulation and Variability With Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Prospective Cohort Study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
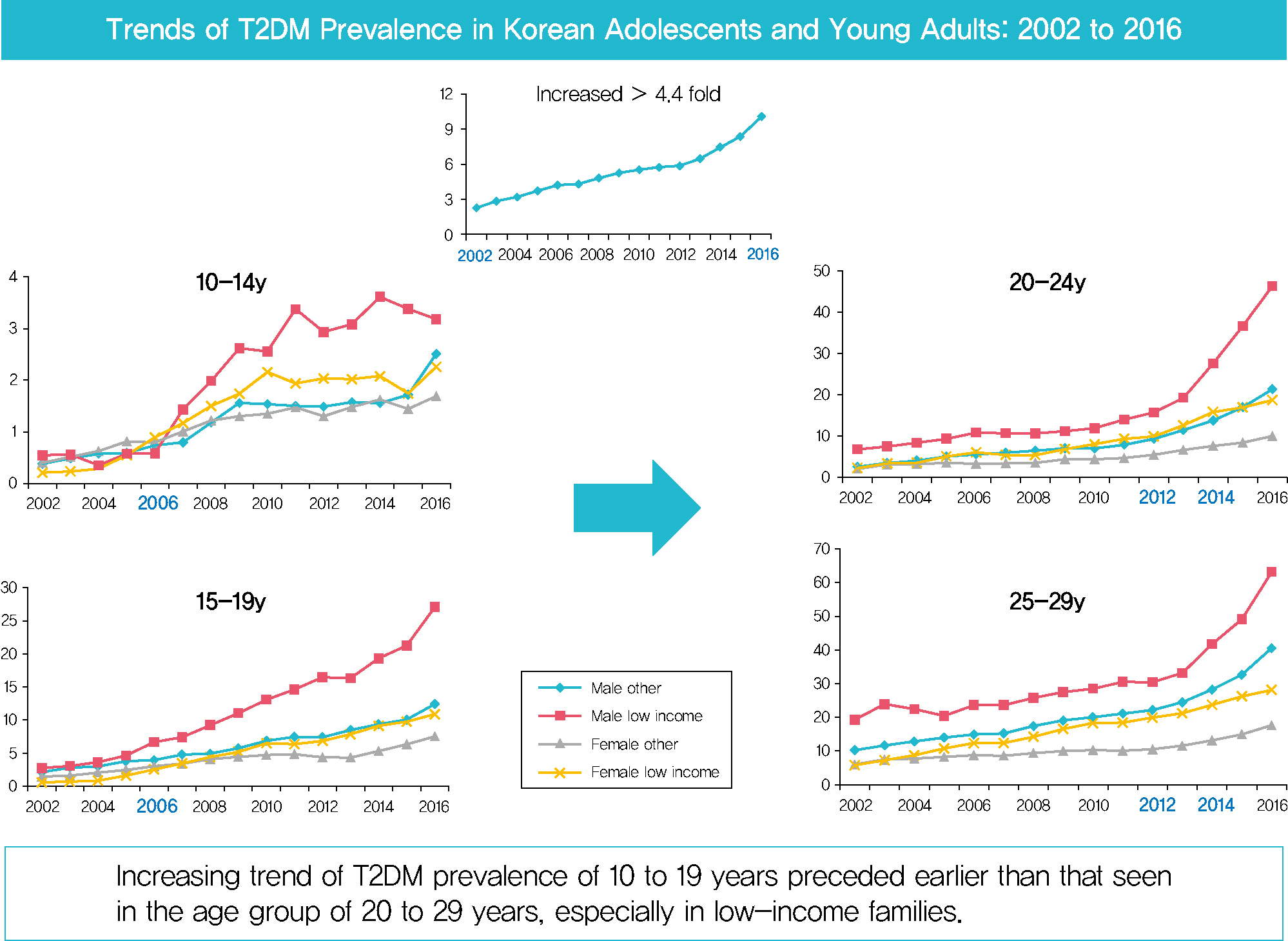
- Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among Korean Children, Adolescents, and Adults Younger than 30 Years: Changes from 2002 to 2016
- Yong Hee Hong, In-Hyuk Chung, Kyungdo Han, Sochung Chung, on Behalf of the Taskforce Team of the Obesity Fact Sheet of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):297-306. Published online October 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0038
- 9,313 View
- 343 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Despite the importance of and social concern regarding prevention of diabetes at younger ages, limited data are available. This study sought to analyze changes in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Koreans younger than 30 years according to sex, age, and level of income.
Methods
The dataset analyzed in this study was derived from health insurance claims recorded in the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database. Participants’ level of income was categorized as low (quintile 1, <20% of insurance premium) or others (quintile 2–5).
Results
In males and females, the prevalence of T2DM per 10,000 people steadily increased from 2.57 in 2002 to 11.41 in 2016, and from 1.96 in 2002 to 8.63 in 2016. The prevalence of T2DM in girls was higher in the age group of 5 to 14 years. Even though the prevalence was higher among those older than 20 years, the increase had started earlier, in the early 2000s, in younger age group. Adolescents aged 10 to 19 years in low-income families showed a remarkable increase in prevalence of T2DM, especially in boys.
Conclusion
The prevalence of T2DM in young Koreans increased more than 4.4-fold from 2002 to 2016, and the increase started in the early 2000s in younger age groups and in low-income families. This is the first study to examine the trend in prevalence of T2DM in children, adolescents, and young adults in Korea. Future studies and collaborations with social support systems to prevent T2DM at an early age group should be performed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
JungMin Choi, Soseul Sung, Sue K. Park, Seyong Park, Hyoyeong Kim, Myeong-Chan Cho, Bryan Williams, Hae-Young Lee
JACC: Asia.2024; 4(4): 265. CrossRef - Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and pathological characteristics of DKD patients with early-onset type 2 diabetes
Liang Wu, Yi-Yang Zhao, Meng-Rui Li, Dong-Yuan Chang, Ming-Hui Zhao, Min Chen
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(8): 108520. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes and Its Association With Psychiatric Disorders in Young Adults in South Korea
Min-Kyung Lee, Su-Young Lee, Seo-Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Hyuk Lee
JAMA Network Open.2023; 6(6): e2319132. CrossRef - Glycemic control and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents during the COVID-19 outbreak
Kyeong Eun Oh, Yu Jin Kim, Ye Rim Oh, Eungu Kang, Hyo-Kyoung Nam, Young-Jun Rhie, Kee-Hyoung Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(4): 275. CrossRef - Position Statement on the Appropriateness and Significance of Adding the Glycated Hemoglobin Test to the National Health Examination
Ji Hye Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Sangjoon Park, Kyunghoon Lee, Jun Goo Kang, Eu Jeong Ku, Su Kyoung Kwon, Won Jun Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Jang Won Son, Young Sil Eom, Kyung Ae Lee, Jeongrim Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Hwa Lee, Jung Hwa Jung, Hochan Cho, Da
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 178. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 349. CrossRef - Prevalence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous federal state in Germany, 2002-2020
C. Baechle, A. Stahl-Pehe, N. Prinz, T. Meissner, C. Kamrath, R.W. Holl, J. Rosenbauer
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 190: 109995. CrossRef - Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Youth
Hwa Young Kim, Jae Hyun Kim
The Ewha Medical Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting High-Risk for Diabetes among Korean Adolescents: An Analysis Using the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2020)
Kyung-Sook Bang, Sang-Youn Jang, Ji-Hye Choe
Children.2022; 9(8): 1249. CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 641. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef
- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Iron Overload and the Risk of Diabetes in the General Population: Results of the Chinese Health and Nutrition Survey Cohort Study
- He Gao, Jinying Yang, Wenfei Pan, Min Yang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):307-318. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0287
- 5,038 View
- 196 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Recent studies have found that there are significant associations between body iron status and the development of diabetes. In the present study, we aimed to analyze the association among iron overload (IO), insulin resistance (IR), and diabetes in Chinese adults, and to explore the sex difference.
Methods
Men and women (age >19 years) who participated in the Chinese Health and Nutrition Survey and did not have diabetes at baseline were followed between 2009 and 2015 (n=5,779). Over a mean of 6 years, 75 participants were diagnosed with incident diabetes. Logistic regression was used to assess the risk factors associated with IO. Cox proportional hazard regression was used to estimate the risk of incident diabetes and to determine whether the risk differed among subgroups. Causal mediation analysis (CMA) was used to explore the mechanism linking IO and diabetes.
Results
According to sex-stratified multivariable-adjusted Cox proportional hazards regression, IO increased the risk of incident diabetes. Women with IO had a higher risk of diabetes than men. Subgroup analysis with respect to age showed that the association between IO and diabetes was stronger in older women and younger men (P<0.001). CMA showed that liver injury (alanine transaminase) and lipid metabolism abnormalities (triglyceride, apolipoprotein B) contributed to the association between IO and diabetes.
Conclusion
IO is associated with diabetes and this association is sex-specific. IO may indirectly induce IR via liver injury and lipid metabolism abnormalities, resulting in diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative susceptibility mapping for iron monitoring of multiple subcortical nuclei in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sana Mohammadi, Sadegh Ghaderi, Fatemeh Sayehmiri, Mobina Fathi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Ferritin Concentrations in the General Population: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Anthropometric, Metabolic, and Dietary Correlates
Cara Övermöhle, Sabina Waniek, Gerald Rimbach, Katharina Susanne Weber, Wolfgang Lieb
The Journal of Nutrition.2023; 153(5): 1524. CrossRef - Association of Body Iron Metabolism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women of Childbearing Age: Results from the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015)
Jie Feng, Xiaoyun Shan, Lijuan Wang, Jiaxi Lu, Yang Cao, Lichen Yang
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1935. CrossRef - Iron overload induces islet β cell ferroptosis by activating ASK1/P-P38/CHOP signaling pathway
Ling Deng, Man-Qiu Mo, Jinling Zhong, Zhengming Li, Guoqiao Li, Yuzhen Liang
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15206. CrossRef - The role of ferroptosis in metabolic diseases
Ling Xie, Bin Fang, Chun Zhang
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2023; 1870(6): 119480. CrossRef - Epidemiological and transcriptome data identify potential key genes involved in iron overload for type 2 diabetes
Xuekui Liu, Xiu Hong, Shiqiang Jiang, Rui Li, Qian Lv, Jie Wang, Xiuli Wang, Manqing Yang, Houfa Geng, Yang Li
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum iron and liver transaminases based on a large adult women population
Andong He, Zhuoping Zhou, Lili Huang, Ka Cheuk Yip, Jing Chen, Ruiling Yan, Ruiman Li
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum ferritin and uric acid levels and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the Chinese population
Fangli Zhou, Xiaoli He, Dan Liu, Yan Ye, Haoming Tian, Li Tian
PeerJ.2023; 11: e16267. CrossRef - The Role of Iron Overload in Diabetic Cognitive Impairment: A Review
Ji-Ren An, Qing-Feng Wang, Gui-Yan Sun, Jia-Nan Su, Jun-Tong Liu, Chi Zhang, Li Wang, Dan Teng, Yu-Feng Yang, Yan Shi
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3235. CrossRef - The Association Between METS-IR and Serum Ferritin Level in United States Female: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on NHANES
Han Hao, Yan Chen, Ji Xiaojuan, Zhang Siqi, Chu Hailiang, Sun Xiaoxing, Wang Qikai, Xing Mingquan, Feng Jiangzhou, Ge Hongfeng
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress on Relationship Between Iron Overload and Lower Limb Arterial Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Zhongjing Wang, Shu Fang, Sheng Ding, Qin Tan, Xuyan Zhang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 2259. CrossRef - Iron deficiency in cardiac surgical patients
L Hof, O Old, A.U. Steinbicker, P Meybohm, S Choorapoikayil, K Zacharowski
Acta Anaesthesiologica Belgica.2022; 73(4): 235. CrossRef
- Quantitative susceptibility mapping for iron monitoring of multiple subcortical nuclei in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Complications
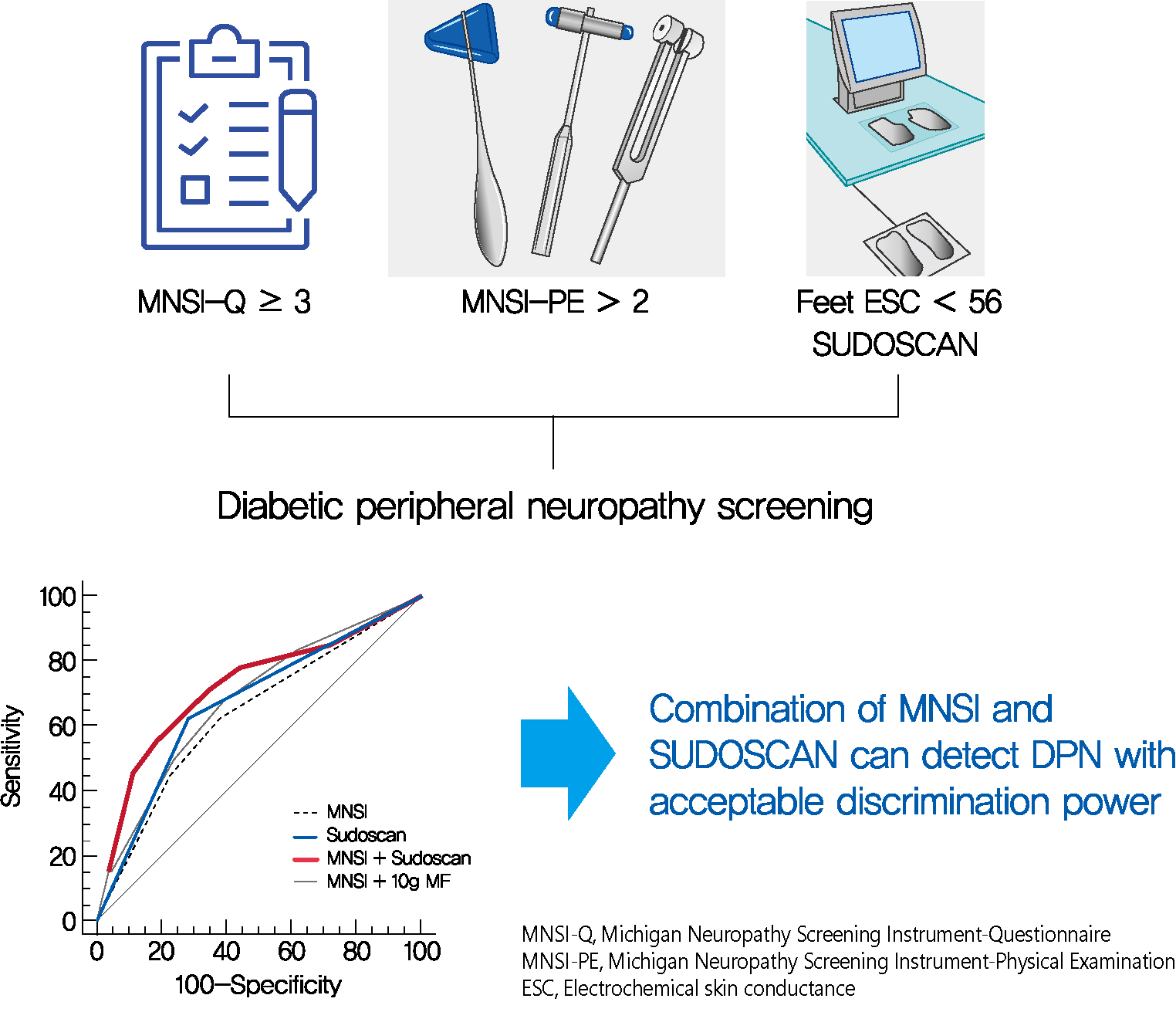
- SUDOSCAN in Combination with the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument Is an Effective Tool for Screening Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Tae Jung Oh, Yoojung Song, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):319-326. Published online September 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0014
- 5,825 View
- 314 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Screening for diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is important to prevent severe foot complication, but the detection rate of DPN is unsatisfactory. We investigated whether SUDOSCAN combined with Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI) could be an effective tool for screening for DPN in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in clinical practice.
Methods
We analysed the data for 144 people with T2DM without other cause of neuropathy. The presence of DPN was confirmed according to the Toronto Consensus criteria. Electrochemical skin conductance (ESC) of the feet was assessed using SUDOSCAN. We compared the discrimination power of following methods, MNSI only vs. SUDOSCAN only vs. MNSI plus SUDOSCAN vs. MNSI plus 10-g monofilament test.
Results
Confirmed DPN was detected in 27.8% of the participants. The optimal cut-off value of feet ESC to distinguish DPN was 56 μS. We made the DPN screening scores using the corresponding odds ratios for MNSI-Questionnaire, MNSI-Physical Examination, SUDOSCAN, and 10-g monofilament test. For distinguishing the presence of DPN, the MNSI plus SUDOSCAN model showed higher areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) than MNSI only model (0.717 vs. 0.638, P=0.011), and SUDOSCAN only model or MNSI plus 10-g monofilament test showed comparable AUC with MNSI only model.
Conclusion
The screening model for DPN that includes both MNSI and SUDOSCAN can detect DPN with acceptable discrimination power and it may be useful in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of sudomotor dysfunction with risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ming Wang, Niuniu Chen, Yaxin Wang, Jiaying Ni, Jingyi Lu, Weijing Zhao, Yating Cui, Ronghui Du, Wei Zhu, Jian Zhou
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus patients by predominantly increasing large-fiber lesions
Sijia Fei, Jingwen Fan, Jiaming Cao, Huan Chen, Xiaoxia Wang, Qi Pan
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111585. CrossRef - Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Diagnostic Options
Raffaele Galiero, Alfredo Caturano, Erica Vetrano, Domenico Beccia, Chiara Brin, Maria Alfano, Jessica Di Salvo, Raffaella Epifani, Alessia Piacevole, Giuseppina Tagliaferri, Maria Rocco, Ilaria Iadicicco, Giovanni Docimo, Luca Rinaldi, Celestino Sardu, T
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3554. CrossRef - Screening for diabetic peripheral neuropathy in resource-limited settings
Ken Munene Nkonge, Dennis Karani Nkonge, Teresa Njeri Nkonge
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The value of electrochemical skin conductance measurement by Sudoscan® for assessing autonomic dysfunction in peripheral neuropathies beyond diabetes
Jean-Pascal Lefaucheur
Neurophysiologie Clinique.2023; 53(2): 102859. CrossRef - Electrochemical skin conductances values and clinical factors affecting sudomotor dysfunction in patients with prediabetes, type 1 diabetes, and type 2 diabetes: A single center experience
Bedia Fulya Calikoglu, Selda Celik, Cemile Idiz, Elif Bagdemir, Halim Issever, Jean-Henri Calvet, Ilhan Satman
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(5): 499. CrossRef - Autonomic Nerve Function Tests in Patients with Diabetes
Heung Yong Jin, Tae Sun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 71. CrossRef - Validation of the Body Scan®, a new device to detect small fiber neuropathy by assessment of the sudomotor function: agreement with the Sudoscan®
Jean-Pierre Riveline, Roberto Mallone, Clarisse Tiercelin, Fetta Yaker, Laure Alexandre-Heymann, Lysa Khelifaoui, Florence Travert, Claire Fertichon, Jean-Baptiste Julla, Tiphaine Vidal-Trecan, Louis Potier, Jean-Francois Gautier, Etienne Larger, Jean-Pas
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Electrochemical Skin Conductance by Sudoscan in Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Liang-Te Chiu, Yu-Li Lin, Chih-Hsien Wang, Chii-Min Hwu, Hung-Hsiang Liou, Bang-Gee Hsu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(1): 187. CrossRef - The Presence of Clonal Hematopoiesis Is Negatively Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes
Tae Jung Oh, Han Song, Youngil Koh, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 243. CrossRef - Case report: Significant relief of linezolid-induced peripheral neuropathy in a pre-XDR-TB case after acupuncture treatment
Yuping Mo, Zhu Zhu, Jie Tan, Zhilin Liang, Jiahui Wu, Xingcheng Chen, Ming Hu, Peize Zhang, Guofang Deng, Liang Fu
Frontiers in Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of sudomotor alterations evaluated by Sudoscan in patients with recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Ana Cristina García-Ulloa, Paloma Almeda-Valdes, Teresa Enedina Cuatecontzi-Xochitiotzi, Jorge Alberto Ramírez-García, Michelle Díaz-Pineda, Fernanda Garnica-Carrillo, Alejandra González-Duarte, K M Venkat Narayan, Carlos Alberto Aguilar-Salinas, Sergio H
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(6): e003005. CrossRef
- Association of sudomotor dysfunction with risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Lifestyle
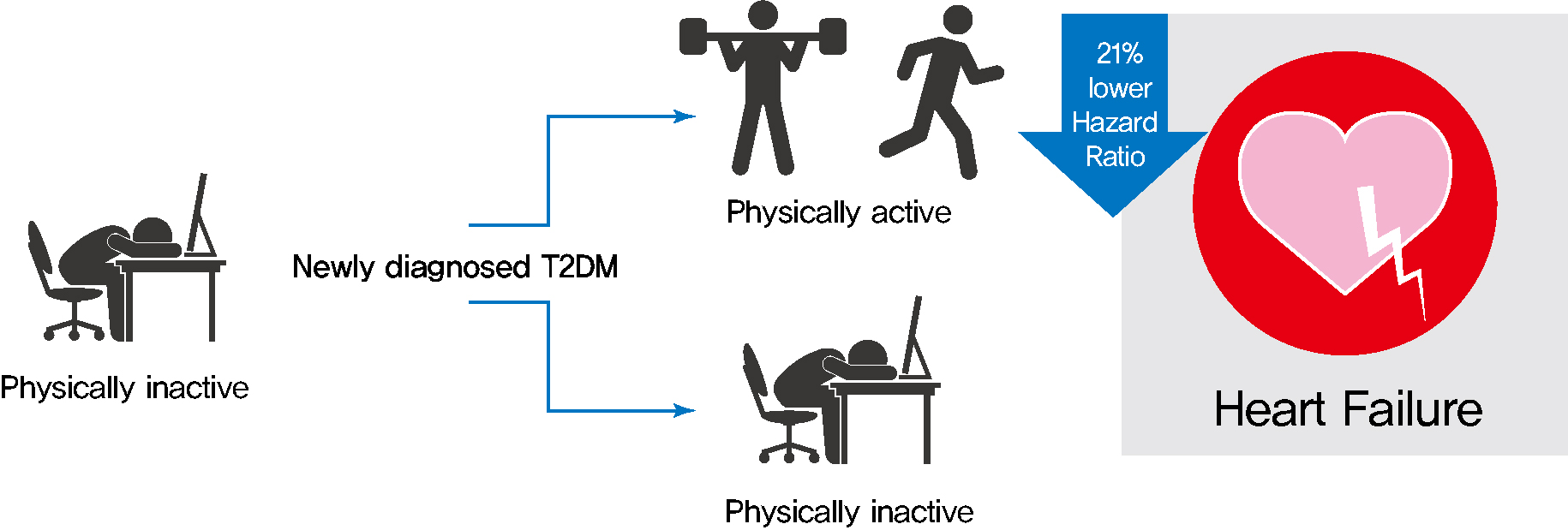
- Changes in Patterns of Physical Activity and Risk of Heart Failure in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):327-336. Published online November 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0046
- 5,397 View
- 210 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Exercise is recommended for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients to prevent cardiovascular disease. However, the effects of physical activity (PA) for reducing the risk of heart failure (HF) has yet to be elucidated. We aimed to assess the effect of changes in patterns of PA on incident HF, especially in newly diagnosed diabetic patients.
Methods
We examined health examination data and claims records of 294,528 participants from the Korean National Health Insurance Service who underwent health examinations between 2009 and 2012 and were newly diagnosed with T2DM. Participants were classified into the four groups according to changes in PA between before and after the diagnosis of T2DM: continuously inactive, inactive to active, active to inactive, and continuously active. The development of HF was analyzed until 2017.
Results
As compared with those who were continuously inactive, those who became physically active after diagnosis showed a reduced risk for HF (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.79; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.66 to 0.93). Those who were continuously active had the lowest risk for HF (aHR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.62 to 0.96). As compared with those who were inactive, those who exercised regularly, either performing vigorous or moderate PA, had a lower HF risk (aHR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.69 to 0.91).
Conclusion
Among individuals with newly diagnosed T2DM, the risk of HF was reduced in those with higher levels of PA after diagnosis was made. Our results suggest either increasing or maintaining the frequency of PA after the diagnosis of T2DM may lower the risk of HF. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations Between Physical Activity and the Risk of Hip Fracture Depending on Glycemic Status: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Kyoung Min Kim, Kyoung Jin Kim, Kyungdo Han, Yumie Rhee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1194. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Association of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and frailty in community-dwelling older adults
Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Eyun Song, Min Jeong Park, Hye Jin Yoo, Sei Hyun Baik, Miji Kim, Chang Won Won, Kyung Mook Choi
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The associations between changes in hepatic steatosis and heart failure and mortality: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Hasung Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Associations Between Physical Activity and the Risk of Hip Fracture Depending on Glycemic Status: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Basic Research
- DA-1241, a Novel GPR119 Agonist, Improves Hyperglycaemia by Inhibiting Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Enhancing Insulin Secretion in Diabetic Mice
- Youjin Kim, Si Woo Lee, Hyejin Wang, Ryeong-Hyeon Kim, Hyun Ki Park, Hangkyu Lee, Eun Seok Kang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):337-348. Published online January 21, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0056
- 5,530 View
- 276 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated the antidiabetic effects of DA-1241, a novel G protein-coupled receptor (GPR) 119 agonist, in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
DA-1241 was administrated to high-fat diet (HFD)-fed C57BL/6J mice for 12 weeks after hyperglycaemia developed. Oral/intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test and insulin tolerance test were performed. Serum insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) levels were measured during oral glucose tolerance test. Insulinoma cell line (INS-1E) cells and mouse islets were used to find whether DA-1241 directly stimulate insulin secretion in beta cell. HepG2 cells were used to evaluate the gluconeogenesis and autophagic process. Autophagic flux was evaluated by transfecting microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3-fused to green fluorescent protein and monomeric red fluorescent (mRFP-GFP-LC3) expression vector to HepG2 cells.
Results
Although DA-1241 treatment did not affect body weight gain and amount of food intake, fasting blood glucose level decreased along with increase in GLP-1 level. DA-1241 improved only oral glucose tolerance test and showed no effect in intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test. No significant effect was observed in insulin tolerance test. DA-1241 did not increase insulin secretion in INS-1E cell and mouse islets. DA-1241 reduced triglyceride content in the liver thereby improved fatty liver. Additionally, DA-1241 reduced gluconeogenic enzyme expression in HepG2 cells and mouse liver. DA-1241 reduced autophagic flow in HepG2 cells.
Conclusion
These findings suggested that DA-1241 augmented glucose-dependent insulin release via stimulation of GLP-1 secretion, and reduced hepatic gluconeogenesis, which might be associated with autophagic blockage, leading to improved glycaemic control. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- G protein-coupled receptors driven intestinal glucagon-like peptide-1 reprogramming for obesity: Hope or hype?
Mohan Patil, Ilaria Casari, Leon N. Warne, Marco Falasca
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 172: 116245. CrossRef - GPR119 agonists for type 2 diabetes: past failures and future hopes for preclinical and early phase candidates
Deanne H Hryciw, Rhiannon K Patten, Raymond J Rodgers, Joseph Proietto, Dana S Hutchinson, Andrew J McAinch
Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs.2024; 33(3): 183. CrossRef - Immunomodulation through Nutrition Should Be a Key Trend in Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Katarzyna Napiórkowska-Baran, Paweł Treichel, Marta Czarnowska, Magdalena Drozd, Kinga Koperska, Agata Węglarz, Oskar Schmidt, Samira Darwish, Bartłomiej Szymczak, Zbigniew Bartuzi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3769. CrossRef - Discovery of orally active sulfonylphenyl thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine derivatives as GPR119 agonists
Heecheol Kim, Minjung Kim, Kyujin Oh, Sohee Lee, Sunyoung Lim, Sangdon Lee, Young Hoon Kim, Kwee Hyun Suh, Kyung Hoon Min
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 258: 115584. CrossRef - Increased expression of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and O-GlcNAcylation in hepatocytes drives non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hye Jin Chun, Eun Ran Kim, Minyoung Lee, Da Hyun Choi, Soo Hyun Kim, Eugene Shin, Jin-Hong Kim, Jin Won Cho, Dai Hoon Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Metabolism.2023; 145: 155612. CrossRef - Human skin stem cell-derived hepatic cells as in vitro drug discovery model for insulin-driven de novo lipogenesis
Karolien Buyl, Martine Vrints, Ruani Fernando, Terry Desmae, Thomas Van Eeckhoutte, Mia Jans, Jan Van Der Schueren, Joost Boeckmans, Robim M. Rodrigues, Veerle De Boe, Vera Rogiers, Joery De Kock, Filip Beirinckx, Tamara Vanhaecke
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 957: 175989. CrossRef - GPR119 activation by DA-1241 alleviates hepatic and systemic inflammation in MASH mice through inhibition of NFκB signaling
Seung-Ho Lee, Hansu Park, Eun-Kyoung Yang, Bo Ram Lee, Il-Hoon Jung, Tae-Hyoung Kim, Moon Jung Goo, Yuna Chae, Mi-Kyung Kim
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 166: 115345. CrossRef - Characteristics of the Latest Therapeutic Agent for Diabetes
Nuri Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 148. CrossRef - DA-1241, a Novel GPR119 Agonist, Improves Hyperglycaemia by Inhibiting Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Enhancing Insulin Secretion in Diabetic Mice
Youjin Kim, Si Woo Lee, Hyejin Wang, Ryeong-Hyeon Kim, Hyun Ki Park, Hangkyu Lee, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 337. CrossRef - Autophagy Dysregulation in Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A New Therapeutic Target
Chun-Liang Chen, Yu-Cheng Lin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 10055. CrossRef
- G protein-coupled receptors driven intestinal glucagon-like peptide-1 reprogramming for obesity: Hope or hype?
Letter
- Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
- Dae Jung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):349-350. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0353
- 2,595 View
- 124 Download

 KDA
KDA


 First
First Prev
Prev





