- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 46(2); 2022 > Article
-
Original ArticleMetabolic Risk/Epidemiology Iron Overload and the Risk of Diabetes in the General Population: Results of the Chinese Health and Nutrition Survey Cohort Study
-
He Gao
 , Jinying Yang, Wenfei Pan, Min Yang
, Jinying Yang, Wenfei Pan, Min Yang
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2022;46(2):307-318.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0287
Published online: March 7, 2022
Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Zhejiang University School of Public Health, and Center of Clinical Big Data and Analytics of The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
-
Corresponding author: Min Yang
 Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Zhejiang University School of Public Health, 866 Yu-hang-tang Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310058, China E-mail: ymin36@zju.edu.cn
Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Zhejiang University School of Public Health, 866 Yu-hang-tang Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310058, China E-mail: ymin36@zju.edu.cn
Copyright © 2022 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- Recent studies have found that there are significant associations between body iron status and the development of diabetes. In the present study, we aimed to analyze the association among iron overload (IO), insulin resistance (IR), and diabetes in Chinese adults, and to explore the sex difference.
-
Methods
- Men and women (age >19 years) who participated in the Chinese Health and Nutrition Survey and did not have diabetes at baseline were followed between 2009 and 2015 (n=5,779). Over a mean of 6 years, 75 participants were diagnosed with incident diabetes. Logistic regression was used to assess the risk factors associated with IO. Cox proportional hazard regression was used to estimate the risk of incident diabetes and to determine whether the risk differed among subgroups. Causal mediation analysis (CMA) was used to explore the mechanism linking IO and diabetes.
-
Results
- According to sex-stratified multivariable-adjusted Cox proportional hazards regression, IO increased the risk of incident diabetes. Women with IO had a higher risk of diabetes than men. Subgroup analysis with respect to age showed that the association between IO and diabetes was stronger in older women and younger men (P<0.001). CMA showed that liver injury (alanine transaminase) and lipid metabolism abnormalities (triglyceride, apolipoprotein B) contributed to the association between IO and diabetes.
-
Conclusion
- IO is associated with diabetes and this association is sex-specific. IO may indirectly induce IR via liver injury and lipid metabolism abnormalities, resulting in diabetes.
- Iron overload (IO) is usually an excess of iron in the body that cannot be eliminated by physiological mechanisms. IO usually manifests as high ferritin (FET) and transferrin (TRF) saturation. IO can cause serious problems (such as liver fibrosis and heart failure), but it is often overlooked because of a lack of specific symptoms and slow progression of the disease. Recent epidemiologic studies have shown a high incidence of IO in apparently healthy people, especially in the Asia-Pacific region and Africa, which does not have a genetic explanation [1-4]. For most patients diagnosed with IO, the treatment is relatively simple and clear; however, if IO is not treated, fatal organ toxicity will occur. Therefore, screening and diagnosis of IO is necessary in the general population.
- Hereditary hemochromatosis was initially discovered to be associated with the development of diabetes [5]. Subsequently, some studies found that systemic iron status is also strongly associated with the development of multiple types of diabetes and their complications in the general population [4,6]. Numerous studies have also revealed that a much milder state of IO, owing to excessive dietary iron intake or a number of other factors, is also a risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus and gestational diabetes [5,7,8]. Nevertheless, the complete pathological mechanisms are not fully understood.
- Many experimental studies have been conducted to explore the possible effects and mechanisms of IO in diabetes. Potential explanations behind the association between IO and development of diabetes include: (1) excess iron can increase production of reactive oxygen species and liver steatosis; (2) IO can lead to abnormal metabolism of glucose and lipids; and (3) elevated iron levels can trigger β-cell compensation mechanisms and lead to functional failure [8-10]. However, some of these possible mechanisms have not been examined using human data.
- Levels of circulating FET vary considerably depending on sex and menopause, suggesting that there may be a sex-dependent relationship between FET and diabetes risk; however, this remains controversial [11-13]. A cross-sectional study of the China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS) showed that elevated concentrations of FET were related to a higher risk of diabetes among men but not among women [14]. In another study, higher levels of FET were associated with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in both sexes [15]. Menopause may also be an important factor in this association. It is necessary to explore sex differences and the influence of menopause on this association in a Chinese population.
- In this study, we aimed to investigate the epidemiology of IO and risk factors for its occurrence in a general Chinese population. We also aimed to identify the association between IO and diabetes according to sex. Mediation analysis was used to explore the potential mediators involved in the association.
INTRODUCTION
- Study population
- The CHNS is an ongoing open-cohort study that was approved by the Ministry of Health and is administered by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CCDC), and the China-Japan Friendship Hospital (CJFH). Fifteen provinces and municipal cities in China (Beijing, Chongqing, Guangxi, Guizhou, Heilongjiang, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, Liaoning, Shanxi, Shandong, Shanghai, Yunnan, and Zhejiang) are participating in the survey, and these vary in their geography, economic development, availability of public resources, and population health status. A multistage, random cluster process was used to draw the samples surveyed in each of the provinces. The survey has been conducted in 10 waves up to now: in 1989, 1991, 1993, 1997, 2000, 2004, 2006, 2009, 2011, and 2015. The participants gave their written informed consent before being included. The survey uses a questionnaire to collect information regarding the community, family, personal, dietary, and other social economic and health factors. The investigators were well trained before the survey commenced and all the procedures strictly observed the protocol written by the CHNS project team from the CJFH, Ministry of Health [16].
- In this study, we used the data of participants in three waves of the CHNS conducted between 2009 and 2015; only 2009 blood data were available. In the 2009 wave of the CHNS, 8,607 adult participants were recruited. We defined people of >19 years old as adult, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) age group definition [17]. Participants with a history of myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke were excluded. MI or stroke related to inflammation may have a higher FET lever and the cause is complicated, which may just be a phenomenon accompanying the disease and cannot properly reflect the iron storage in the body. On the other hand, people suffering from MI and stroke tend to change their lifestyle including diet and behavior [18]. We excluded participants with incomplete baseline data (physical examination, dietary assessment, fasting blood glucose, and behavioral status). We also excluded participants who had diabetes prior to the study and who had unknown diabetes statuses before or during the study. Ultimately, data from a total of 5,779 adults were analyzed.
- This survey was approved by Institutional Review Boards at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill (Chapel Hill, NC), and the National Institute of Nutrition and Food Safety, China Center for Disease Control and Prevention (Beijing, China), and each participant provided written informed consent. Further details of the study population, survey design, sample, data collection, and quality control procedures are available at http://content.digital.nhs.uk/npid and https://www.cpc.unc.edu/projects/china.
- Physical examination and behavioral survey
- Height and body mass were measured by trained investigators, following a standard protocol that is recommended by the WHO. Height was measured to the nearest 0.1 cm without shoes, and body mass was measured to the nearest 0.1 kg in lightweight clothing [19,20]. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as body mass in kg divided by height in meters, squared. Systolic and diastolic blood pressures were measured three times and the mean values were analyzed. Smoking status and alcohol intake status were collected using a structured questionnaire and were categorized as yes or no in the analyses.
- Dietary assessment
- Three consecutive 24-hour records for individuals and a food inventory for each household were made over the same 3-day periods and were combined to determine dietary intake [20,21]. All the participants were interviewed to determine their food consumption both away from home and at home on a 24-hour recall basis. Household food was weighed and the change in the inventory from the start to the end of each day was calculated. The consumption of food according to individual and household data was compared for each individual, and if significant discrepancies were found, the household and individual measurements in question were repeated to resolve these discrepancies. The Chinese Food Composition Table was used for food composition analysis [22].
- Fasting blood measurements
- Participants were asked to fast for at least 8 hours overnight before venipuncture. Blood samples were collected into three tubes by certified technicians under strict quality control by the CJFH. The sample collected in one 4-mL ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) tube was used for routine analyses on site, a second sample in a 4-mL separation gel tube was used for biochemical tests in a local laboratory, and a third sample collected in the same type of tube was frozen and transported to the central laboratory of the CJFH in Beijing (medical laboratory accreditation certificate ISO 15189:2007) for further biochemical analyses, immunological testing, and storage.
- Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) was measured in provincial laboratories; these met all the requirements for accurate measurement. Glucose concentration was analyzed using a Hitachi 7600 analyzer and glucose oxidase phenol 4-aminoantipyrine peroxidase kits (GOD-PAP, Randox, County Antrim, UK) [14]. The hemoglobin concentration in whole blood was measured using a Beckman Coulter LH750 (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA). Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), triglyceride (TG), and total cholesterol (TC) concentrations were measured enzymatically using a Hitachi 7600 automated analyzer (Kyowa, Japan) [19]. Total protein concentration was determined using the biuret method on a Hitachi 7600 automated analyzer (Randox). Apolipoprotein A (Apo-A), apolipoprotein B (Apo-B), and lipoprotein (a) concentrations were measured using the immunoturbidimetric method using a Hitachi 7600 automated analyzer. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (HSCRP) concentrations was measured using the immunoturbidimetric method on a Hitachi 7600 automated analyzer (Denka Seiken Co. Ltd., Niigata, Japan) [23]. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity and albumin concentration were measured using the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry (IFCC) enzyme and bromocresol green methods, respectively, on a Hitachi 7600 automated analyzer. Insulin (INS) and FET concentrations were analyzed radioimmunologically on a gamma counter (XH-6020, North Institute of Bio-Tech, Beijing, China) and TRF concentration was measured using the nephelometry method (B-type natriuretic peptide assay; Siemens, München, Germany). Only the results of blood tests in 2009 were available and were finally included in our analysis.
- Definitions of variables and diseases
- Iron deficiency (ID), anemia, and iron deficiency anemia (IDA) were defined in accordance with the WHO thresholds [24]. IDA was defined as the existence of both anemia and ID, and the threshold was adjusted for pregnancy status and altitude. IO was defined as a FET concentration >300 μg/L for adult men and >200 μg/L for adult women [25]. Insulin resistance (IR) was defined as a fasting INS concentration ≥12 mU/L [26,27]. The menopause was defined in this study as women of age equal to or greater than 52years old [28]. Diabetes was identified using the self-reported questionnaire with a tick box response to the question: “Have you ever been diagnosed with diabetes by a doctor?” (yes/no) [19].
- Statistical analysis
- Continuous variables are expressed as mean±standard deviation or median (interquartile range) and differences between participants with and without IO were identified using the unpaired t-test or the Kruskal-Wallis test. Categorical variables are expressed as percentages and data were compared using Fisher’s exact test.
- We used binary logistic regression to explore the underlying variables at baseline that were associated with IO, and the data were adjusted for 13 independent variables including age, physical examination findings, and biological, behavioral, and dietary factors. In order to avoid high correlations between the variables, we have used variance inflation factor to test multicollinearity.
- Cox proportional hazards models were used to calculate the hazard ratio (HR) for incident diabetes, comparing participants without (reference standard) to participants with IO. To avoid an effect of sex difference in diabetes prevalence, we decided a priori to stratify the models according to sex [29,30]. The formula ([β0]−[βn])/(β0)×100 was used to describe which groups of covariates were associated with a disparity in incident diabetes between the groups. We used multiple models to explore the relationships between each risk factor group and incident diabetes [29]. In model 1, only age was adjusted for, and in subsequent models, we added each risk factor group to the previous model in order, beginning with the biological factors (model 2) and ending with the behavioral factors (model 5). The final adjusted model (model 5) included all the risk factor groups. In a second modeling approach, we estimated the percentage reduction in the β estimates for each set of covariates from the base model, without adjusting for other sets of covariables. The proportional hazards assumption was tested, and no violations of this assumption were identified.
- Causal mediation analysis (CMA) was used to determine the effect of IO on the development of diabetes and identify possible mediators of the relationship. ALT, TG, and TC were ln-transformed because of their skewed distributions. Subgroup analysis was conducted according to age and BMI group. We excluded some variables because of possible collinearity among some of the covariates. A two-tailed P value of <0.05 was considered to represent statistical significance. R version 3.6.2 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) was used for all the analyses.
METHODS
- We excluded 203 participants who had MI and stroke and 1,403 participants who were unable to provide baseline data for at least one risk factor of interest. We also excluded 199 participants who had diabetes at baseline, 960 participants who were lost to follow-up at baseline, and 63 participants whose diabetes status was undetermined. In total, 5,779 participants were included in the analysis. A flow chart for the participants is shown in Supplementary Fig. 1. A comparison of the baseline characteristics of the included and excluded participants is presented as Supplementary Table 1.
- Baseline characteristics of all the participants
- Baseline characteristics of the 5,779 participants were classified on the basis of their iron status and sex, shown in Table 1. A total of 3,131 (54.18%) women and 2,648 (45.82%) men were included, with mean age 50.94 years. Of these participants, 20.76% (1,200) had abnormal iron status, with 9.22% (533) having ID and 11.54% (667) having IO, the numbers of participants with IO were 215 and 452 in women and men respectively. At the baseline examination, more men (20.58%) than women (7.37%) had IO and the mean age of women with IO was higher than that of men with IO. Although some of these indexes were still within the normal range, participants with IO tended to have higher BMI, HbA1c, HS-CRP, glucose, TG, TC, ALT, and Apo-B than those without IO (P<0.001). In addition, IR was more prevalent in participants with IO. Women with IO have shown the slightly elevated level of mean INS, and men have shown the normal level of mean INS. With respect to dietary factors, there were no differences in the macronutrient or energy intake between participants with and without IO. Behavioral factors did not significantly differ with respect to IO, except that men with IO drank more alcohol.
- Relationships of biological, dietary, and behavioral factors with IO
- We further explored baseline characteristics that were associated with IO using a logistic regression model. In this model, categorical data, including IR, smoking, and alcohol intake and continuous data including age, HS-CRP, TG, Apo-B, ALT, carbohydrate, protein, fat, BMI, and systolic pressure were analyzed at baseline. For women, old age, TG, Apo-B, and ALT were associated with the development of IO, whereas for men, old age, HS-CRP, TG, Apo-B, ALT, BMI, and alcohol intake were associated with the development of IO (Table 2).
- Relationship between IO and incident diabetes
- Over the mean 6 years of follow-up (29,428 person-years), 75 participants developed diabetes. Table 3 shows the HRs for diabetes and the percent reductions in β estimates for each model. IO was significantly associated with incident diabetes, but this association was shown to be affected by sex using the models stratified according to sex. In the basic model, women with IO had a much higher risk of developing diabetes than men with IO (HR, 4.74; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.29 to 9.79 vs. HR, 3.28; 95% CI, 1.66 to 6.46). In model 2, we adjusted for the biological factors (HS-CRP, TG, TC, Apo-B, ALT, IR, LDL-C) and found the disparity in diabetes HR estimates for IO disappeared in men (HR, 2.13; 95% CI, 0.99 to 4.57). After further adjustment for dietary, physical, and behavioral factors, the HR estimates for diabetes in men were further reduced whereas the estimates for women remained significant (P<0.05). Whether in men or women, adjustment for the biological factors was associated with the largest percentage reduction in β estimates (25.64% for women and 36.48% for men). The physical examination findings were associated with the second largest percentage reduction in β estimates in both sexes (Table 3).
- Risk factors mediating the relationship between IO and IR
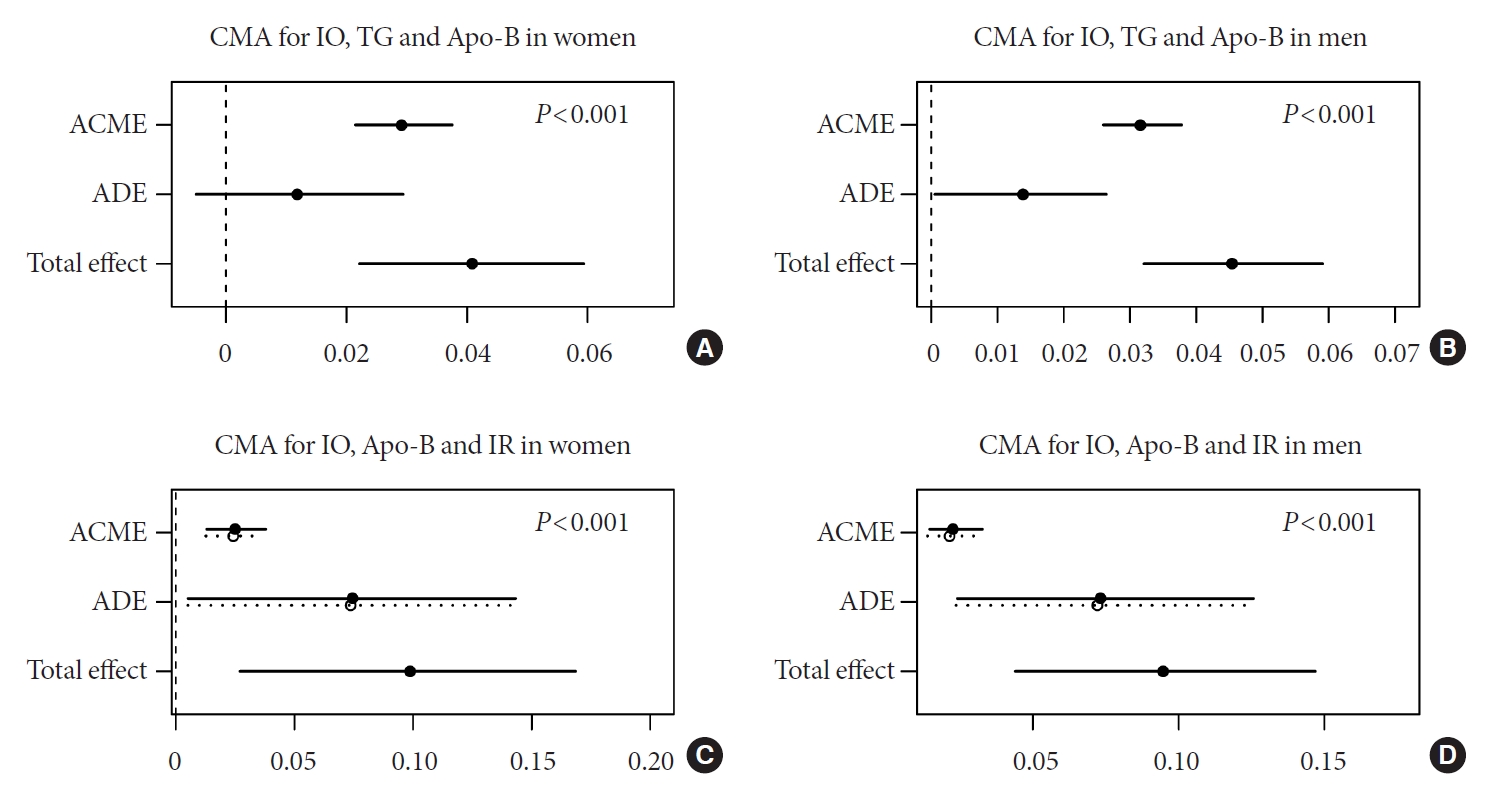
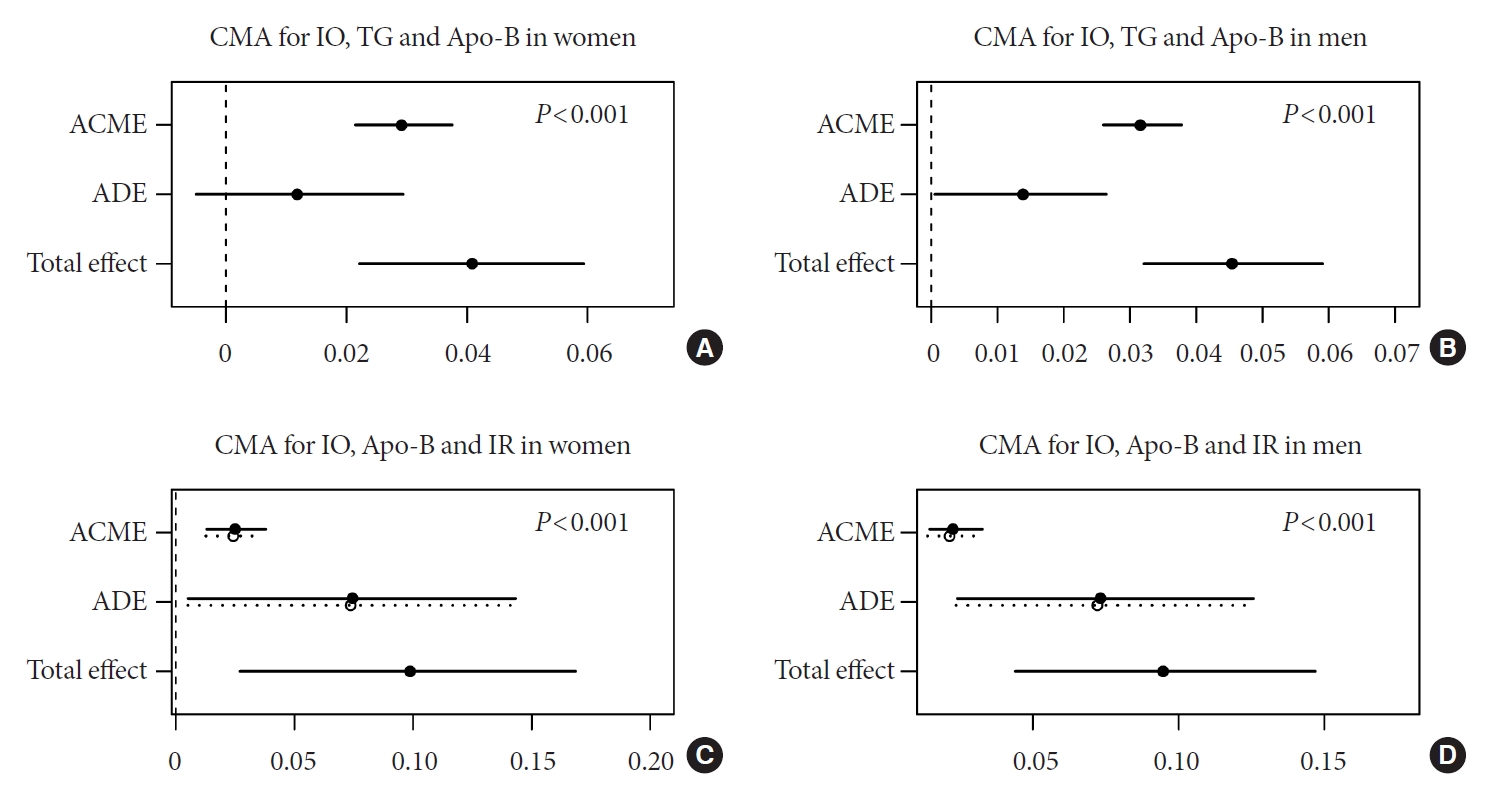
- The effects of IO on IR could be accounted for completely by ALT in women (Fig. 1A) and partially in men (Fig. 1B). ALT also acted as a partial mediator for the differences in TG metabolism (Fig. 1C and D). We found the significant completely mediation effect of TG in the association between IO and Apo-B metabolism (P<0.05) (Fig. 2A and B). In addition, Apo-B showed a partial mediation effect on IR (Fig. 2C and D). These results applied to both men and women, although the indirect effects were generally more pronounced in men than women (Supplementary Table 2).
- Subgroup analyses of the association between IO and incident diabetes
- The incidence of diabetes did not significantly differ between young women or old men with IO and those without. However, in women, age ≥52 years was significantly associated with the risk of incident diabetes; this association was the opposite in men: age <52 years was significantly associated with the risk of incident diabetes. In BMI subgroup analysis, there was a stronger association between IO and diabetes among participants with higher BMI after adjusting for age and HS-CRP. Women with BMI <24 showed a stronger association between IO and diabetes, but this was not the case in men (Table 4).
RESULTS
- In this study, we showed that IO indirectly affects the development of IR, which may cause incident diabetes and be mediated via liver damage and altered lipid metabolism. After adjustment for biological variables, our data suggest that the risk of incident diabetes associated with IO in men and women could be reduced by 25% to 35%. Reducing BMI was the second most effective method, and both biological variables and BMI were much more effective than adjusting smoking or dietary habits.
- The prevalence of IO in the general population exceeded our expectations; more than one-tenth of adults in our study had IO. Previously, researchers focused on IO prevention and treatment in hereditary hemochromatosis or red blood cell transfusion. However, attention should also be given to the general population. In comparison with participants without IO at baseline, those with IO displayed more evidence of IR, liver injury, and altered lipid metabolism. Participants with IO had higher ALT activity and TG and Apo-B concentrations, even though the values were within the normal ranges. The logistic regression model also showed these indexes were significantly associated with IO. Valenzuela et al. [9] found that excess hepatic iron storage promotes liver steatosis, increases plasma transaminase activity, and induces oxidative stress. Recent research has shown high FET concentration is associated with higher prevalences of dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes mellitus, and that these associations are mediated through this pathway [19,31]. In view of IO’s burden of disease, physicians should be aware of the presence of IO in the general population. We should also pay attention to the small increases in biochemical markers that are related to liver injury and lipid metabolism, even if they are within the normal range, especially in individuals with IO.
- Several previous studies have shown that excess iron may cause organ-specific oxidative stress, leading to IR and abnormal lipid metabolism [7,19,31]. However, Clara Podmore et al. [15] suggested the causal role of iron was not clear in development of IR and diabetes, which needed to be clarified. Animal study showed IO may contribute to liver injury, which may result in endoplasmic reticulum stress and IR [9,32]. High INS concentration, which is associated with IR, inhibits fatty acid oxidation and increases TG synthesis by activating insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 [33]. However, high concentrations of TG can increase Apo-B concentrations, which can induce endoplasmic reticulum stress and hepatic IR [34,35]. Others have also demonstrated that FET directly binds Apo-B via heminmediated binding [36]. In our study, the results of logistic regression did not suggest a direct causal association between IO and IR. However, in further mediation analysis, we found that ALT, TG, and Apo-B may mediate the induction of IR via IO; this process is summarized in Supplementary Fig. 2. To some extent, IO may indirectly promote IR, which is consistent with the results of previous studies. These findings suggest that IO is associated with liver injury and abnormal lipid metabolism. Such liver damage may lead to IR, and abnormal lipid metabolism may further aggravate IR. This may be part of the explanation of why people with IO are prone to develop diabetes.
- Another notable finding was the sex differences in the outputs of the Cox proportional hazards models and CMA. In the EPIC-Potsdam study, high FET concentration was still associated with diabetes after adjustment for HS-CRP, γ-glutamyl transferase, ALT, adiponectin, HDL-C, and TG [7]. However, in the present study, the risk of diabetes associated with IO remained in women but disappeared in men after adjustment for biological factors. We speculate sex hormones may explain this difference. Similar to previous studies [15], we found a stronger association between IO and diabetes in leaner participants. However, this association only presents in women whose BMI <18.5 (data not shown). Stratification of the participants according to age illustrated this difference: post-menopausal women (>52 years) showed a significant relationship between IO and the risk of incident diabetes, but the opposite trend was identified in men. Owing to menopause, it is difficult for excess iron to be excreted in older women. Furthermore, there is evidence that estrogen counteracts iron mediated oxidative stress and that androgens stimulate the hematopoietic system and can even be used to treat anemia [37,38]. Several previous studies have also shown that a high FET concentration and marked iron deposition are associated with hypogonadism [39]. Taking these findings together, it is reasonable to believe that sex hormones affect iron metabolism. In addition, our results show old women are more likely to develop diabetes and that protein intake is associated with IO in women but not in men. Therefore, although women are more susceptible to ID, IO is a neglected but potentially significant problem in older women, who should be careful with their dietary protein intake.
- The findings of our study contribute to the existing knowledge regarding the relationship between IO and diabetes. First, we found that IO has a high prevalence in a general Chinese population. Second, we found a significant association between IO and diabetes in this prospective study. Third, we found that the relationship between IO and diabetes is more pronounced in postmenopausal women and young men. We also explored the potential roles of liver injury and abnormal lipid metabolism in the development of diabetes.
- There are several limitations in this study. The study participants were all Chinese adults; this limits the generalizability of the study findings. Another drawback is the limited availability of fasting blood samples. Because of this, we were unable to assess the oxidative stress and sex hormone concentrations in the participants. We can’t exclude participants with clinically diagnosed Hereditary hemochromatosis, though according to the extremely low incidence of hereditary hemochromatosis in China, this is unlikely to make a substantial impact on the results. Additionally, diabetes was recorded on the basis of physician-diagnosed self-reporting rather than on oral glucose tolerance testing, which may cause underestimation of morbidity.
- In conclusion, this prospective cohort study provided strong evidence to support a positive association between IO and diabetes, which was more pronounced in post-menopausal women and young men. Liver injury and abnormal lipid metabolism partially mediates this association. Further studies are required to clarify the underlying molecular mechanisms.
DISCUSSION
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Fig. 1.
Supplementary Fig. 2.
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: M.Y., H.G.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: H.G., J.Y., M.Y.
Drafting the work or revising: H.G., J.Y., W.P., M.Y.
Final approval of the manuscript: H.G., J.Y., W.P., M.Y.
-
FUNDING
This study was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LGF18H260003) and Beijing Municipal Functional Peptide Engineering Research Center Foundation (2018).
NOTES
-
Acknowledgements
- This research uses data from China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS). We thank the National Institute of Nutrition and Food Safety, China Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Carolina Population Center, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the NIH (R01-HD30880, DK056350, and R01-HD38700) and the Fogarty International Center, NIH for financial support for the CHNS data collection and analysis files from 1989 to 2006 and both parties plus the China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Ministry of Health for support for CHNS 2009 and future surveys.
- We thank Zidong Chen, and Mark Cleasby PhD from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac) for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.

Values are presented as mean±standard deviation, median (interquartile range), or number (%).
SMD, standard mean difference; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; INS, insulin; IR, insulin resistance; HS-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; FET, ferritin; TRF, transferrin; Apo, apolipoprotein; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LP-A, lipoprotein (a); TG, triglyceride; TC, total cholesterol; ALB, albumin; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; TP, total protein.
| HRs by model |
Women |
Men |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IO HR (95% CI) | Reduction in β, %b | P value | IO HR (95% CI) | Reduction in β, %b | P value | ||
| Baseline risk factor adjustment (method 1) | |||||||
| Model 1: age | 4.74 (2.29–9.79) | Reference | <0.001 | 3.28 (1.66–6.46) | Reference | 0.001 | |
| Model 2: model 1+biologicalc | 3.18 (1.56–6.48) | 25.64 | 0.001 | 2.13 (0.99–4.57) | 36.48 | 0.053 | |
| Model 3: model 2+dietd | 3.47 (1.69–7.14) | 20.05 | 0.001 | 2.11 (0.98–4.52) | 37.15 | 0.055 | |
| Model 4: model 3+physical examinationse | 3.34 (1.55–7.2) | 22.56 | 0.002 | 1.85 (0.86–3.97) | 48.19 | 0.114 | |
| Model 5: model 4+behavioralf | 3.35 (1.54–7.26) | 22.37 | 0.002 | 1.91 (0.88–4.13) | 45.49 | 0.100 | |
| Baseline risk factor adjustment (method 2) | |||||||
| Model 1+biologicalc | 3.18 (1.56–6.48) | 25.64 | 0.001 | 2.13 (0.99–4.57) | 36.48 | 0.053 | |
| Model 1+dietd | 4.95 (2.36–10.36) | –2.76 | <0.001 | 3.16 (1.6–6.25) | 3.03 | 0.001 | |
| Model 1+physical examinationse | 4.18 (1.97–8.88) | 8.03 | <0.001 | 2.31 (1.18–4.55) | 29.32 | 0.015 | |
| Model 1+behavioralf | 4.72 (2.28–9.77) | 0.32 | <0.001 | 3.32 (1.69–6.54) | –1.18 | 0.001 | |
HR, hazard ratio; IO, iron overload; CI, confidence interval.
a The model was adjusted for baseline risk factors,
b Percent reduction in β estimate ([β0–βn]/[β0]×100). β0 indicates an age adjusted reference model. βn indicates the remaining models, ln HR=β,
c Biological factors: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, triglyceride, total cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, alanine aminotransferase, insulin resistance, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol,
d Diet factors: carbohydrate intake, fat intake, protein intake,
e Physical examinations factors: body mass index, systolic pressure,
f Behavioral factors: smoking status, alcohol status.
|
Women |
Men |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Hazard ratio | 95% CI | P value | Case | Hazard ratio | 95% CI | P value | |
| IO by age, yra | ||||||||
| <52 | 1,593 | 5.23 | 0.43–62.95 | 0.093 | 1,326 | 7.13 | 2.35–21.63 | <0.001 |
| ≥52 | 1,538 | 4.47 | 2.13–9.36 | <0.001 | 1,322 | 1.28 | 0.36–4.49 | 0.705 |
| IO by BMI, kg/m2b | ||||||||
| <24 | 1,884 | 4.77 | 1.27–17.92 | 0.021 | 1,604 | 1.02 | 0.13–7.85 | 0.985 |
| 24≤ and <28 | 933 | 4.55 | 0.90–23.11 | 0.068 | 815 | 1.70 | 0.51–5.70 | 0.393 |
| ≥28 | 314 | 4.09 | 1.38–12.15 | 0.011 | 229 | 4.46 | 1.26–15.75 | 0.020 |
- 1. Eshak ES, Iso H, Maruyama K, Muraki I, Tamakoshi A. Associations between dietary intakes of iron, copper and zinc with risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a large population-based prospective cohort study. Clin Nutr 2018;37:667-74.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Ikuta K, Hatayama M, Addo L, Toki Y, Sasaki K, Tatsumi Y, et al. Iron overload patients with unknown etiology from national survey in Japan. Int J Hematol 2017;105:353-60.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Wood MJ, Skoien R, Powell LW. The global burden of iron overload. Hepatol Int 2009;3:434-44.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. McElduff A. Iron: how much is too much? Diabetologia 2017;60:237-9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Simcox JA, McClain DA. Iron and diabetes risk. Cell Metab 2013;17:329-41.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Swaminathan S, Fonseca VA, Alam MG, Shah SV. The role of iron in diabetes and its complications. Diabetes Care 2007;30:1926-33.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Montonen J, Boeing H, Steffen A, Lehmann R, Fritsche A, Joost HG, et al. Body iron stores and risk of type 2 diabetes: results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Potsdam study. Diabetologia 2012;55:2613-21.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Backe MB, Moen IW, Ellervik C, Hansen JB, MandrupPoulsen T. Iron regulation of pancreatic beta-cell functions and oxidative stress. Annu Rev Nutr 2016;36:241-73.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Valenzuela R, Rincon-Cervera MA, Echeverria F, Barrera C, Espinosa A, Hernandez-Rodas MC, et al. Iron-induced prooxidant and pro-lipogenic responses in relation to impaired synthesis and accretion of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in rat hepatic and extrahepatic tissues. Nutrition 2018;45:49-58.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Silva M, Silva ME, de Paula H, Carneiro CM, Pedrosa ML. Iron overload alters glucose homeostasis, causes liver steatosis, and increases serum triacylglycerols in rats. Nutr Res 2008;28:391-8.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Jiang L, Wang K, Lo K, Zhong Y, Yang A, Fang X, et al. Sex-specific association of circulating ferritin level and risk of type 2 diabetes: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019;104:4539-51.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Lee BK, Kim Y, Kim YI. Association of serum ferritin with metabolic syndrome and diabetes mellitus in the South Korean general population according to the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008. Metabolism 2011;60:1416-24.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Huth C, Beuerle S, Zierer A, Heier M, Herder C, Kaiser T, et al. Biomarkers of iron metabolism are independently associated with impaired glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes: the KORA F4 study. Eur J Endocrinol 2015;173:643-53.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Han LL, Wang YX, Li J, Zhang XL, Bian C, Wang H, et al. Gender differences in associations of serum ferritin and diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity in the China Health and Nutrition Survey. Mol Nutr Food Res 2014;58:2189-95.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Podmore C, Meidtner K, Schulze MB, Scott RA, Ramond A, Butterworth AS, et al. Association of multiple biomarkers of iron metabolism and type 2 diabetes: the EPIC-InterAct study. Diabetes Care 2016;39:572-81.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Zhang B, Zhai FY, Du SF, Popkin BM. The China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1989-2011. Obes Rev 2014;15 Suppl 1:2-7.PubMed
- 17. World Health Organization. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV Infection: recommendations for a public health approach. 2nd ed. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. Chapter, Definition of key terms; p13-6 [cited 2021 Aug 31]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK374295.
- 18. He J, Fang A, Yu S, Shen X, Li K. Dietary nonheme, heme, and total iron intake and the risk of diabetes in adults: results from the China Health and Nutrition Survey. Diabetes Care 2020;43:776-84.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 19. Yu L, Yan J, Zhang Q, Lin H, Zhu L, Liu Q, et al. Association between serum ferritin and blood lipids: influence of diabetes and hs-CRP levels. J Diabetes Res 2020;2020:4138696.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 20. Xu X, Byles JE, Shi Z, Hall JJ. Evaluation of older Chinese people’s macronutrient intake status: results from the China Health and Nutrition Survey. Br J Nutr 2015;113:159-71.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Batis C, Sotres-Alvarez D, Gordon-Larsen P, Mendez MA, Adair L, Popkin B. Longitudinal analysis of dietary patterns in Chinese adults from 1991 to 2009. Br J Nutr 2014;111:1441-51.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Zhan Y, Chen R, Zheng W, Guo C, Lu L, Ji X, et al. Association between serum magnesium and anemia: China health and nutrition survey. Biol Trace Elem Res 2014;159:39-45.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Li X, He T, Yu K, Lu Q, Alkasir R, Guo G, et al. Markers of iron status are associated with risk of hyperuricemia among Chinese adults: nationwide population-based study. Nutrients 2018;10:191.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. WHO/UNICEF/UNU. Iron deficiency anaemia assessment, prevention and control. A guide for programme managers. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2001. p. 33.
- 25. StatPearls. Treasure Island. StatPearls Publishing; 2020. Chapter, Iron overload [cited 2021 Aug 31]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526131.Article
- 26. Ascaso JF, Pardo S, Real JT, Lorente RI, Priego A, Carmena R. Diagnosing insulin resistance by simple quantitative methods in subjects with normal glucose metabolism. Diabetes Care 2003;26:3320-5.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. McAuley KA, Williams SM, Mann JI, Walker RJ, Lewis-Barned NJ, Temple LA, et al. Diagnosing insulin resistance in the general population. Diabetes Care 2001;24:460-4.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Takahashi TA, Johnson KM. Menopause. Med Clin North Am 2015;99:521-34.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Bancks MP, Kershaw K, Carson AP, Gordon-Larsen P, Schreiner PJ, Carnethon MR. Association of modifiable risk factors in young adulthood with racial disparity in incident type 2 diabetes during middle adulthood. JAMA 2017;318:2457-65.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Khan NA, Wang H, Anand S, Jin Y, Campbell NR, Pilote L, et al. Ethnicity and sex affect diabetes incidence and outcomes. Diabetes Care 2011;34:96-101.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Pitchika A, Schipf S, Nauck M, Dorr M, Lerch MM, Felix SB, et al. Associations of iron markers with type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome: results from the prospective SHIP study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2020;163:108149.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Jahng JW, Alsaadi RM, Palanivel R, Song E, Hipolito VE, Sung HK, et al. Iron overload inhibits late stage autophagic flux leading to insulin resistance. EMBO Rep 2019;20:e47911.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 33. Weickert MO, Pfeiffer AF. Signalling mechanisms linking hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia 2006;49:1732-41.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 34. Hevi S, Chuck SL. Ferritins can regulate the secretion of apolipoprotein B. J Biol Chem 2003;278:31924-9.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Su Q, Tsai J, Xu E, Qiu W, Bereczki E, Santha M, et al. Apolipoprotein B100 acts as a molecular link between lipid-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and hepatic insulin resistance. Hepatology 2009;50:77-84.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Seki T, Kunichika T, Watanabe K, Orino K. Apolipoprotein B binds ferritin by hemin-mediated binding: evidence of direct binding of apolipoprotein B and ferritin to hemin. Biometals 2008;21:61-9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 37. Das SK, Patel VB, Basu R, Wang W, DesAulniers J, Kassiri Z, et al. Females are protected from iron-overload cardiomyopathy independent of iron metabolism: key role of oxidative stress. J Am Heart Assoc 2017;6:e003456.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Shahani S, Braga-Basaria M, Maggio M, Basaria S. Androgens and erythropoiesis: past and present. J Endocrinol Invest 2009;32:704-16.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 39. Yang JH, Chou CH, Yang WS, Ho HN, Yang YS, Chen MJ. Iron stores and obesity are negatively associated with ovarian volume and anti-Mullerian hormone levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 2015;54:686-92.PubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Quantitative susceptibility mapping for iron monitoring of multiple subcortical nuclei in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sana Mohammadi, Sadegh Ghaderi, Fatemeh Sayehmiri, Mobina Fathi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Ferritin Concentrations in the General Population: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Anthropometric, Metabolic, and Dietary Correlates
Cara Övermöhle, Sabina Waniek, Gerald Rimbach, Katharina Susanne Weber, Wolfgang Lieb
The Journal of Nutrition.2023; 153(5): 1524. CrossRef - Association of Body Iron Metabolism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women of Childbearing Age: Results from the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015)
Jie Feng, Xiaoyun Shan, Lijuan Wang, Jiaxi Lu, Yang Cao, Lichen Yang
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1935. CrossRef - Iron overload induces islet β cell ferroptosis by activating ASK1/P-P38/CHOP signaling pathway
Ling Deng, Man-Qiu Mo, Jinling Zhong, Zhengming Li, Guoqiao Li, Yuzhen Liang
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15206. CrossRef - The role of ferroptosis in metabolic diseases
Ling Xie, Bin Fang, Chun Zhang
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2023; 1870(6): 119480. CrossRef - Epidemiological and transcriptome data identify potential key genes involved in iron overload for type 2 diabetes
Xuekui Liu, Xiu Hong, Shiqiang Jiang, Rui Li, Qian Lv, Jie Wang, Xiuli Wang, Manqing Yang, Houfa Geng, Yang Li
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum iron and liver transaminases based on a large adult women population
Andong He, Zhuoping Zhou, Lili Huang, Ka Cheuk Yip, Jing Chen, Ruiling Yan, Ruiman Li
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum ferritin and uric acid levels and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the Chinese population
Fangli Zhou, Xiaoli He, Dan Liu, Yan Ye, Haoming Tian, Li Tian
PeerJ.2023; 11: e16267. CrossRef - The Role of Iron Overload in Diabetic Cognitive Impairment: A Review
Ji-Ren An, Qing-Feng Wang, Gui-Yan Sun, Jia-Nan Su, Jun-Tong Liu, Chi Zhang, Li Wang, Dan Teng, Yu-Feng Yang, Yan Shi
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3235. CrossRef - The Association Between METS-IR and Serum Ferritin Level in United States Female: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on NHANES
Han Hao, Yan Chen, Ji Xiaojuan, Zhang Siqi, Chu Hailiang, Sun Xiaoxing, Wang Qikai, Xing Mingquan, Feng Jiangzhou, Ge Hongfeng
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress on Relationship Between Iron Overload and Lower Limb Arterial Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Zhongjing Wang, Shu Fang, Sheng Ding, Qin Tan, Xuyan Zhang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 2259. CrossRef - Iron deficiency in cardiac surgical patients
L Hof, O Old, A.U. Steinbicker, P Meybohm, S Choorapoikayil, K Zacharowski
Acta Anaesthesiologica Belgica.2022; 73(4): 235. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite