
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse > Previous issues
- Pathophysiology
- The Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Energy Metabolism
- Joon Young Chang, Hyun Jung Hong, Seul Gi Kang, Jung Tae Kim, Ben Yuan Zhang, Minho Shong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):363-371. Published online June 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0087
- 8,140 View
- 226 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) is receiving great interest beyond its role as an aging and disease-related biomarker. Recent discovery of its receptor, glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family receptor α-like (GFRAL), suggests a central role in appetite regulation. However, there is also considerable evidence that GDF15 may have peripheral activity through an as-of-yet undiscovered mode of action. This raises the question as to whether increased GDF15 induction during pathophysiologic conditions also suppresses appetite. The present review will briefly introduce the discovery of GDF15 and describe the different contexts under which GDF15 is induced, focusing on its induction during mitochondrial dysfunction. We will further discuss the metabolic role of GDF15 under various pathophysiological conditions and conclude with possible therapeutic applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Growth differentiation factor-15 is an IFN-γ regulated mediator of infection-induced weight loss and the hepatic FGF21 response
Jojo Reyes, Yanlin Zhao, Krushang Pandya, George S. Yap
Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.2024; 116: 24. CrossRef - Biomarkers of disability worsening in inactive primary progressive multiple sclerosis
Maria-Elizabeth Baeva, Isabelle Tottenham, Marcus Koch, Carlos Camara-Lemarroy
Journal of Neuroimmunology.2024; 387: 578268. CrossRef - Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Intermediates and Individual Ageing
Natalia Kurhaluk
Biomolecules.2024; 14(3): 260. CrossRef - A long‐acting GDF15 analog causes robust, sustained weight loss and reduction of food intake in an obese nonhuman primate model
Songmao Zheng, David Polidori, Yuanping Wang, Brian Geist, Xiefan Lin‐Schmidt, Jennifer L. Furman, Serena Nelson, Andrea R. Nawrocki, Simon A. Hinke
Clinical and Translational Science.2023; 16(8): 1431. CrossRef - GDF15 enhances body weight and adiposity reduction in obese mice by leveraging the leptin pathway
Samuel N. Breit, Rakesh Manandhar, Hong-Ping Zhang, Michelle Lee-Ng, David A. Brown, Vicky Wang-Wei Tsai
Cell Metabolism.2023; 35(8): 1341. CrossRef - Serum growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) is a biomarker of cardiac manifestations in children with COVID-19
Sally Raafat Ishak, Mona Mostafa El Ganzoury, Eman Mahmoud Fouda, Maha Ahmad Anwar, Amany Moustafa Kamal, Heba Mostafa Hamza, Nehad Ahmed Bakry
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding the molecular basis of anorexia and tissue wasting in cancer cachexia
Eunbyul Yeom, Kweon Yu
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2022; 54(4): 426. CrossRef - Investigating the combination of plasma amyloid-beta and geroscience biomarkers on the incidence of clinically meaningful cognitive decline in older adults
Wan-Hsuan Lu, Kelly Virecoulon Giudici, John E. Morley, Sophie Guyonnet, Angelo Parini, Geetika Aggarwal, Andrew D. Nguyen, Yan Li, Randall J. Bateman, Bruno Vellas, Philipe de Souto Barreto, Bruno Vellas, Sophie Guyonnet, Isabelle Carrié, Lauréane Brigit
GeroScience.2022; 44(3): 1489. CrossRef - The Potential Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in COVID-19: A Corollary Subjective Effect or Not?
Ahmad O. Babalghith, Hayder M. Al-kuraishy, Ali I. Al-Gareeb, Michel De Waard, Jean-Marc Sabatier, Hebatallah M. Saad, Gaber El-Saber Batiha
Diagnostics.2022; 12(9): 2051. CrossRef - Metformin and growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A hidden treasure
Hayder M. Al‐kuraishy, Ali I. Al‐Gareeb, Athanasios Alexiou, Marios Papadakis, Eman Hassan Nadwa, Sarah M. Albogami, Mohammed Alorabi, Hebatallah M. Saad, Gaber El‐Saber Batiha
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(12): 806. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise Intervention on Mitochondrial Stress Biomarkers in Metabolic Syndrome Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Jae Seung Chang, Jun Namkung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(5): 2242. CrossRef - Neurological & psychological aspects of Barth syndrome: Clinical manifestations and potential pathogenic mechanisms
Melissa Olivar-Villanueva, Mindong Ren, Colin K.L. Phoon
Mitochondrion.2021; 61: 188. CrossRef - The metabolic role of spermidine in obesity: Evidence from cells to community
Yanee Choksomngam, Sintip Pattanakuhar, Nipon Chattipakorn, Siriporn C. Chattipakorn
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2021; 15(4): 315. CrossRef - The Role of GDF15 as a Myomitokine
Kornelia Johann, Maximilian Kleinert, Susanne Klaus
Cells.2021; 10(11): 2990. CrossRef
- Growth differentiation factor-15 is an IFN-γ regulated mediator of infection-induced weight loss and the hepatic FGF21 response
- Complications
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes: The Epidemic and the Korean Diabetes Association Perspective
- Junghyun Noh, Hyun-Ha Chang, In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):372-381. Published online June 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0138
- 8,266 View
- 138 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Diabetes has been associated with more severe outcomes and higher mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients compare to morbidity and mortality in patients without diabetes. Several mechanisms may play a role in this greater morbidity and mortality, especially uncontrolled hyperglycemia, an impaired immune system, pre-existing proinflammatory states, multiple comorbidities, and dysregulated angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 signaling. Thus, the diabetes medical community emergently needs to know about COVID-19 and its effects on patients with diabetes, as they must take precautions to carefully manage these patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Korean Diabetes Association provides some guidance and practical recommendations for the management of diabetes during the pandemic. This report provides insight into the association between diabetes and COVID-19, proper management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19 and an official suggestion by the Korean Diabetes Association for managing the COVID-19 outbreak.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medical comorbidities as predictors of COVID-19 short-term mortality: A historical cohort study in Indonesia
RizaldyTaslim Pinzon, Vanessa Veronica
Tzu Chi Medical Journal.2023; 35(1): 53. CrossRef - A year of experience with COVID‐19 in patients with cancer: A nationwide study
Mina Khosravifar, Sogol Koolaji, Negar Rezaei, Ali Ghanbari, Seyedeh Melika Hashemi, Erfan Ghasemi, Ali Bitaraf, Ozra Tabatabaei‐Malazy, Nazila Rezaei, Sahar Mohammadi Fateh, Arezou Dilmaghani‐Marand, Rosa Haghshenas, Ameneh Kazemi, Erfan Pakatchian, Farz
Cancer Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of COPD on clinical and CT characteristics of COVID-19-associated pneumonia: single tertiary center experience
Yevgeniya Filippenko, Marianna Zagurovskaya, Aigul Abdrakhmanova, Saule Kassenova, Zhanar Zhakenova, Aizat Aimakhanova, Zhamilya Zholdybay
Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Being caught in the perfect storm of a diabetes epidemic and the COVID‐19 pandemic: What should we do for our patients?
Yunjung Cho, Kun‐Ho Yoon
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(3): 297. CrossRef - COVID-19 associated with diabetes and other noncommunicable diseases led to a global health crisis
Mark Thomaz Ugliara Barone, Belinda Ngongo, Simone Bega Harnik, Lucas Xavier de Oliveira, Dániel Végh, Patrícia Vieira de Luca, Hermelinda Cordeiro Pedrosa, Franco Giraudo, Roque Cardona-Hernandez, Nayanjeet Chaudhury, Luiz Menna-Barreto
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108587. CrossRef - Impact of COPD on COVID-19 prognosis: A nationwide population-based study in South Korea
Sang Chul Lee, Kang Ju Son, Chang Hoon Han, Seon Cheol Park, Ji Ye Jung
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19
Sang Youl Rhee, Jeongwoo Lee, Hyewon Nam, Dae-Sung Kyoung, Dong Wook Shin, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 251. CrossRef - Towards Telemedicine Adoption in Korea: 10 Practical Recommendations for Physicians
Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nutritional information access and dietary behavior among people with diabetes during Covid-19 pandemic
Yovita Puri Subardjo, Gumintang Ratna Ramadhan, Dika Betaditya, Muflihatus Syarifah, Nurafifah Fauziana Abidin
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2021; 746(1): 012027. CrossRef - Dissection of non-pharmaceutical interventions implemented by Iran, South Korea, and Turkey in the fight against COVID-19 pandemic
Mohammad Keykhaei, Sogol Koolaji, Esmaeil Mohammadi, Reyhaneh Kalantar, Sahar Saeedi Moghaddam, Arya Aminorroaya, Shaghayegh Zokaei, Sina Azadnajafabad, Negar Rezaei, Erfan Ghasemi, Nazila Rezaei, Rosa Haghshenas, Yosef Farzi, Sina Rashedi, Bagher Larijan
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(2): 1919. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Seung-Hyun Ko
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 244. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Mortality Predictors of COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized at Nationally-Designated Treatment Hospitals
Seong-Su Moon, Kwan Lee, Jungi Park, Seongcheol Yun, Yun Sik Lee, Dong Seok Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Response: The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:405–13)
Seung Min Chung, June Hong Ahn, Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 625. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19
Jeong Hyun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 116. CrossRef
- Medical comorbidities as predictors of COVID-19 short-term mortality: A historical cohort study in Indonesia
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Byung-Wan Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Cheol-Young Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Nan-Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Bong-Soo Cha, Dae Ho Lee, Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) Fatty Liver Research Group
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):382-401. Published online May 11, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0010
- 12,352 View
- 338 Download
- 42 Web of Science
- 42 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader This clinical practice position statement, a product of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association, proposes recommendations for the diagnosis, progression and/or severity assessment, management, and follow-up of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Patients with both T2DM and NAFLD have an increased risk of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis and a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetic complications compared to those without NAFLD. With regards to the evaluation of patients with T2DM and NAFLD, ultrasonography-based stepwise approaches using noninvasive biomarker models such as fibrosis-4 or the NAFLD fibrosis score as well as imaging studies such as vibration-controlled transient elastography with controlled attenuation parameter or magnetic resonance imaging-proton density fat fraction are recommended. After the diagnosis of NAFLD, the stage of fibrosis needs to be assessed appropriately. For management, weight reduction achieved by lifestyle modification has proven beneficial and is recommended in combination with antidiabetic agent(s). Evidence that some antidiabetic agents improve NAFLD/NASH with fibrosis in patients with T2DM is emerging. However, there are currently no definite pharmacologic treatments for NAFLD in patients with T2DM. For specific cases, bariatric surgery may be an option if indicated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A combined extract containing Schisandra chinensis (SCE) reduced hepatic triglyceride accumulation in rats fed a high-sucrose diet
Haneul Lee, Eun Young Kang, Joowon Lee, Yejin Kim, Sumin Kang, Hayoon Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim, Gyoungok Gang, Sang-gil Lee, Cao Lei, Gwang-woong Go
Food Science and Biotechnology.2024; 33(6): 1449. CrossRef - Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMJ.2024; : e076388. CrossRef - Risk Scores for Prediction of Major Cardiovascular Events in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A No Man’s Land?
Liliana Gheorghe, Roxana Nemteanu, Andreea Clim, Gina Eosefina Botnariu, Irina Iuliana Costache, Alina Plesa
Life.2023; 13(4): 857. CrossRef - Increased expression of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and O-GlcNAcylation in hepatocytes drives non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hye Jin Chun, Eun Ran Kim, Minyoung Lee, Da Hyun Choi, Soo Hyun Kim, Eugene Shin, Jin-Hong Kim, Jin Won Cho, Dai Hoon Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Metabolism.2023; 145: 155612. CrossRef - Association between fatty liver index and risk of end-stage renal disease stratified by kidney function in patients with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population-based study
Goh Eun Chung, Kyungdo Han, Kyu-Na Lee, Jung Ho Bae, Sun Young Yang, Su-Yeon Choi, Jeong Yoon Yim, Nam Ju Heo
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101454. CrossRef - Comparison of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and thiazolidinediones on treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A network meta-analysis
Min Jeong Park, Hayeon Kim, Myeong Gyu Kim, Kyungim Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(3): 693. CrossRef - Histological analysis of hypoglycemic agents on liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review
Qingxing Xie, Xiaohui Pan, Xinyue Zhang, Jinfang Ma, Ge Peng, Nanwei Tong
Chinese Medical Journal.2023; 136(16): 2014. CrossRef - Hepatotropc effects of glucose-lowering drugs: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in focus
E. V. Uzhakova, Z. E. Zshanko, E. N. Smirnova
Experimental and Clinical Gastroenterology.2023; (6): 121. CrossRef - Complementary effects of dapagliflozin and lobeglitazone on metabolism in a diet-induced obese mouse model
Yun Kyung Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Ji In Lee, Bo Yoon Choi, Hyen Chung Cho, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 957: 175946. CrossRef - Hepatic T-cell senescence and exhaustion are implicated in the progression of fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes and mouse model with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Byeong Chang Sim, Yea Eun Kang, Sun Kyoung You, Seong Eun Lee, Ha Thi Nga, Ho Yeop Lee, Thi Linh Nguyen, Ji Sun Moon, Jingwen Tian, Hyo Ju Jang, Jeong Eun Lee, Hyon-Seung Yi
Cell Death & Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Circ_0004535/miR-1827/CASP8 network involved in type 2 diabetes mellitus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Min Li, Ai Zeng, Xinle Tang, Hui Xu, Wei Xiong, Yanying Guo
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Stratification by obesity class, rather than age, can identify a higher percent of children at risk for non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic dysfunction
Aurelia Radulescu, Adam J. Dugan, Mary Killian, Suzanna L. Attia, Marialena Mouzaki, George J. Fuchs, Rohit Kohli, Henrietta Bada, Philip A. Kern, Samir Softic
Pediatric Obesity.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Renal Tubular Damage Marker, Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase, as a Predictive Marker of Hepatic Fibrosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hae Kyung Kim, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 104. CrossRef - Dulaglutide Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Activating FAM3A Signaling Pathway
Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 74. CrossRef - State-of-the-Art Overview of the Pharmacological Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Yongin Cho, Yong-ho Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 38. CrossRef - Ezetimibe combination therapy with statin for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an open-label randomized controlled trial (ESSENTIAL study)
Yongin Cho, Hyungjin Rhee, Young-eun Kim, Minyoung Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Jin-Young Choi, Yong-ho Lee
BMC Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity is an important determinant of severity in newly defined metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
Ji Hye Huh, Kwang Joon Kim, Seung Up Kim, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2022; 21(3): 241. CrossRef - Anti-Obesity and Anti-Hyperglycemic Effects of Meretrix lusoria Protamex Hydrolysate in ob/ob Mice
Min Ju Kim, Ramakrishna Chilakala, Hee Geun Jo, Seung-Jae Lee, Dong-Sung Lee, Sun Hee Cheong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(7): 4015. CrossRef - The associations of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis using fatty liver index and BARD score with cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Level and Risk of Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Ji-Yeon Park, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 272. CrossRef - SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
Jun Sung Moon, Jun Hwa Hong, Yong Jin Jung, Ele Ferrannini, Michael A. Nauck, Soo Lim
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 33(6): 424. CrossRef - Plasma Aldo-Keto Reductase Family 1 Member B10 as a Biomarker Performs Well in the Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis
Aron Park, Seung Joon Choi, Sungjin Park, Seong Min Kim, Hye Eun Lee, Minjae Joo, Kyoung Kon Kim, Doojin Kim, Dong Hae Chung, Jae Been Im, Jaehun Jung, Seung Kak Shin, Byung-Chul Oh, Cheolsoo Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Dae Ho Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(9): 5035. CrossRef - Chinese Herbal Medicine for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sihan Peng, Lu Liu, Ziyan Xie, Xiyu Zhang, Chunguang Xie, Sha Ye, Xiangeng Zhang, Xiaoli Liang, Hongyan Wang, Ya Liu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and sarcopenia is associated with the risk of albuminuria independent of insulin resistance, and obesity
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Seung-Soon Im, Byoung Kuk Jang, Hye Soon Kim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(8): 108253. CrossRef - Extra-Glycemic Effects of Anti-Diabetic Medications: Two Birds with One Stone?
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 415. CrossRef - Plasma Metabolomics and Machine Learning-Driven Novel Diagnostic Signature for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Moongi Ji, Yunju Jo, Seung Joon Choi, Seong Min Kim, Kyoung Kon Kim, Byung-Chul Oh, Dongryeol Ryu, Man-Jeong Paik, Dae Ho Lee
Biomedicines.2022; 10(7): 1669. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with early left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabeteS
Walaa Sheba, Eman Morsy, Salah Altahan, Mona Ayaad, Sameh A. Lashen
Alexandria Journal of Medicine.2022; 58(1): 117. CrossRef - The association between changes in hepatic steatosis and hepatic fibrosis with cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in patients with New-Onset type 2 Diabetes: A nationwide cohort study
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 194: 110191. CrossRef - Advanced Liver Fibrosis Is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:630-9)
Ji Hye Huh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 953. CrossRef - The association of fatty liver index and BARD score with all-cause and cause-specific mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a nationwide population-based study
Goh Eun Chung, Su-Min Jeong, Eun Ju Cho, Ji Won Yoon, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Yuri Cho, Kyu-na Lee, Dong Wook Shin, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Su Jong Yu
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-Albumin Proteinuria (NAP) as a Complementary Marker for Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD)
Jaehyun Bae, Young Jun Won, Byung-Wan Lee
Life.2021; 11(3): 224. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment
Sook Jung Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(1): 38. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Elizabeth E Powell, Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, Mary Rinella
The Lancet.2021; 397(10290): 2212. CrossRef - Allopurinol ameliorates high fructose diet induced hepatic steatosis in diabetic rats through modulation of lipid metabolism, inflammation, and ER stress pathway
In-Jin Cho, Da-Hee Oh, Jin Yoo, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho-Yeon Chung, Soung Won Jeong, Ju-Young Moon, Sang-Ho Lee, Sung-Jig Lim, In-Kyung Jeong
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient Management in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
A. E. Bagriy, A. D. Zubov, M. V. Khomenko, E. S. Mikhailichenko, E. A. Pylaeva, N. A. Khaustova, E. V. Bryukhovetskaya
Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology.2021; 31(2): 14. CrossRef - Liver Fibrosis Indices for the Prediction of Mortality in Korean Subjects: A 16-Year Prospective Cohort Study
Tae Jung Oh, Kyuho Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Nam H Cho, Hak Chul Jang
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Reduced Rank Regression-Derived Dietary Patterns Related to the Fatty Liver Index and Associations with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among Ghanaian Populations under Transition: The RODAM Study
Tracy Bonsu Osei, Anne-Marieke van Dijk, Sjoerd Dingerink, Felix Patience Chilunga, Erik Beune, Karlijn Anna Catharina Meeks, Silver Bahendeka, Matthias Bernd Schulze, Charles Agyemang, Mary Nicolaou, Adriaan Georgius Holleboom, Ina Danquah
Nutrients.2021; 13(11): 3679. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yuan Zhu, Jiao Xu, Dong Zhang, Xingyu Mu, Yi Shi, Shangtao Chen, Zengxiang Wu, Shuangqing Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Liver fibrosis indices are related to diabetic peripheral neuropathy in individuals with type 2 diabetes
Kyuho Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Hyen Chung Cho, Yun Kyung Lee, Chang Ho Ahn, Bo Kyung Koo, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Grapefruit Juice in terms of Interleukin 18 Gene Expression in Rats with Fatty Liver and Healthy Rats
Simin Bahmanpoor, Noosha Zia-Jahromi
journal of ilam university of medical sciences.2021; 29(4): 74. CrossRef
- A combined extract containing Schisandra chinensis (SCE) reduced hepatic triglyceride accumulation in rats fed a high-sucrose diet
- Smoking as a Target for Prevention of Diabetes
- Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):402-404. Published online June 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0126
- 4,619 View
- 67 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Smoking Status and the Risk of Hip Fracture in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Se-Won Lee, Jun-Young Heu, Ju-Yeong Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 679. CrossRef - The Global Burden of Type 2 Diabetes Attributable to Tobacco: A Secondary Analysis From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
Jianjun Bai, Fang Shi, Yudiyang Ma, Donghui Yang, Chuanhua Yu, Jinhong Cao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between Smoking Status and the Risk of Hip Fracture in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Complications
- The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Seung Min Chung, Yin Young Lee, Eunyeong Ha, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee, Jian Hur, Kyung Soo Hong, Jong Geol Jang, Hyun Jung Jin, Eun Young Choi, Kyeong-Cheol Shin, Jin Hong Chung, Kwan Ho Lee, June Hong Ahn, Jun Sung Moon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):405-413. Published online May 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0105
- 10,206 View
- 143 Download
- 43 Web of Science
- 45 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
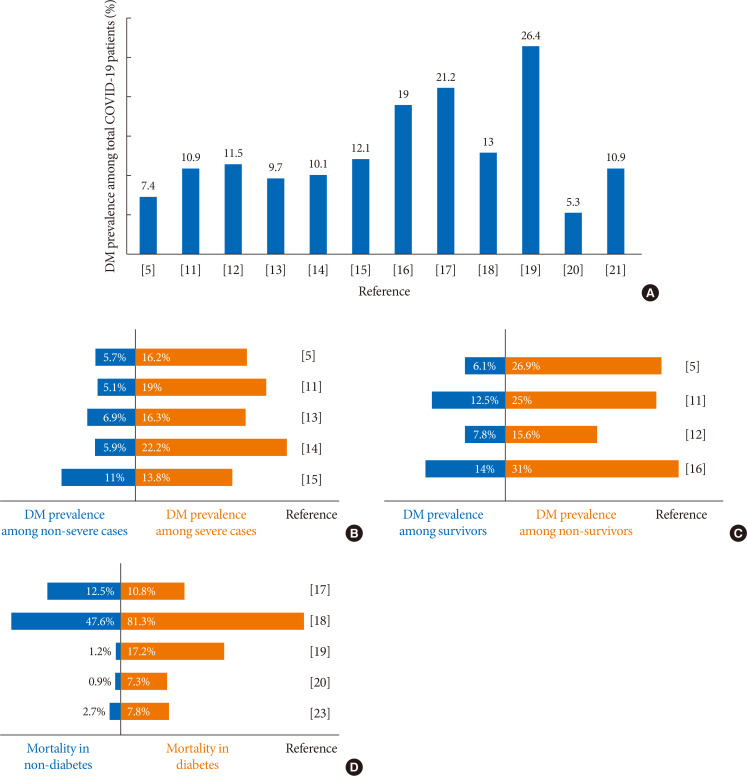
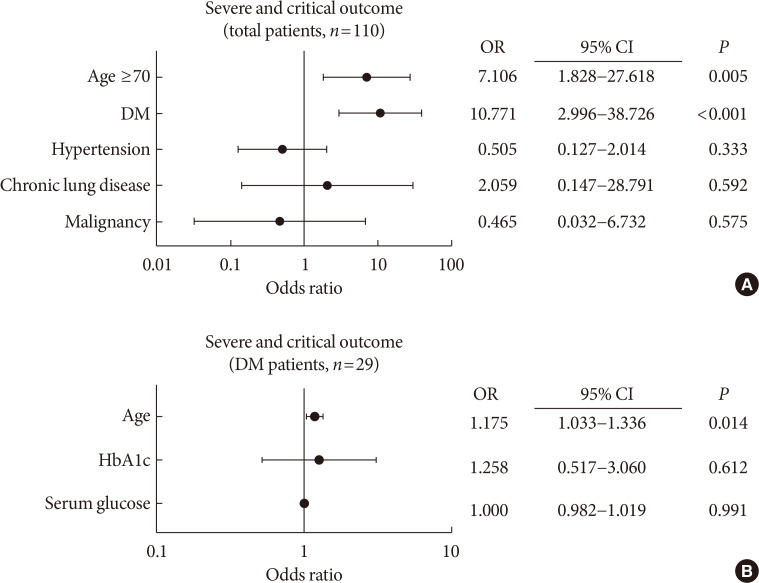
PubReader Background To determine the role of diabetes mellitus (DM) in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), we explored the clinical characteristics of patients with DM and compared risk factors such as age, glycemic control, and medications to those without DM.
Methods This was a retrospective cohort study of 117 confirmed patients with COVID-19 which conducted at a tertiary hospital in Daegu, South Korea. The primary outcome was defined as the severe and critical outcome (SCO), of which the composite outcomes of acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, intensive care unit care, and 28-day mortality. We analyzed what clinical features and glycemic control-related factors affect the prognosis of COVID-19 in the DM group.
Results After exclusion, 110 participants were finally included. DM patients (
n =29) was older, and showed higher blood pressure compared to non-DM patients. DM group showed higher levels of inflammation-related biomarkers and severity score, and highly progressed to SCO. After adjustment with other risk factors, DM increased the risk of SCO (odds ratio [OR], 10.771;P <0.001). Among the DM patients, SCO was more prevalent in elderly patients of ≥70 years old and age was an independent risk factor for SCO in patients with DM (OR, 1.175;P =0.014), while glycemic control was not. The use of medication did not affect the SCO, but the renin-angiotensin system inhibitors showed protective effects against acute cardiac injury (OR, 0.048;P =0.045).Conclusion The COVID-19 patients with DM had higher severity and resulted in SCO. Intensive and aggressive monitoring of COVID-19 clinical outcomes in DM group, especially in elderly patients is warranted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Development Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination
Hyeyeon Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Mi Kyoung Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Severity of Symptoms and Mortality in Diabetic Patients with COVID- 19 Infection. Review
Zahraa ALBasry, Abeer Abdulhadi Rashid, Shaymaa Hasan Abbas
Al Mustansiriyah Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2023; 23(1): 91. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Alexander Lang, Nikoletta Christodoulou, Philipp Linnerz, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Manuela Neuenschwander, Janett Barbaresko, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2023; 66(8): 1395. CrossRef - COVID-19 and Cardiovascular Comorbidities
Dirk Müller-Wieland, Nikolaus Marx, Michael Dreher, Katharina Fritzen, Oliver Schnell
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(03): 178. CrossRef - Prevalence and impact of diabetes in hospitalized COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sian A. Bradley, Maciej Banach, Negman Alvarado, Ivica Smokovski, Sonu M. M. Bhaskar
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(2): 144. CrossRef - Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Adithan Ganesh, Michael D. Randall
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2022; 88(6): 2642. CrossRef - Cardioprotective effect of extracellular vesicles derived from ticagrelor-pretreated cardiomyocyte on hyperglycemic cardiomyocytes through alleviation of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Ceylan Verda Bitirim, Zeynep Busra Ozer, Dunya Aydos, Kardelen Genc, Seyma Demirsoy, Kamil Can Akcali, Belma Turan
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of diabetes on COVID‐19 mortality and hospital outcomes from a global perspective: An umbrella systematic review and meta‐analysis
Stavroula Kastora, Manisha Patel, Ben Carter, Mirela Delibegovic, Phyo Kyaw Myint
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycated Albumin and Glycated Albumin/HbA1c Predict the Progression of Coronavirus Disease 2019 from Mild to Severe Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Jeongseon Yoo, Youngah Choi, Shin Ae Park, Ji Yeon Seo, Chul Woo Ahn, Jaehyun Han
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2327. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors and COVID‐19: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis Revealing Critical Bias Across a Body of Observational Research
Jordan Loader, Frances C. Taylor, Erik Lampa, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship of age, sex and prothrombin time related to the severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta analysis
Audrey Fabianisa Mirza, Ceria Halim, Mutiara Indah Sari
F1000Research.2022; 11: 729. CrossRef - Evaluating the effect of COVID-19 on quality measures of patients with type 2 diabetes in two family nurse practitioner–owned clinics
Wendy L. Wright, Patricia A. White, Meredith Welsh, Kelly Cutting
Journal of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners.2022; 34(9): 1090. CrossRef - Early glycaemic variability increases 28-day mortality and prolongs intensive care unit stay in critically ill patients with pneumonia
Seong Ho Kim, Ji Young Kim, Eun Song Kim, Il Rae Park, Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Annals of Medicine.2022; 54(1): 2724. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory drugs and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: Current knowledge and potential effects on early SARS-CoV-2 infection
Iris Louise N. Cabbab, Rafael Vincent M. Manalo
Virus Research.2021; 291: 198190. CrossRef - The Effect of Prior Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor and Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Treatment on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Susceptibility and Outcome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jiuyang Xu, Yaqun Teng, Lianhan Shang, Xiaoying Gu, Guohui Fan, Yijun Chen, Ran Tian, Shuyang Zhang, Bin Cao
Clinical Infectious Diseases.2021; 72(11): e901. CrossRef - Diabetes predicts severity of COVID‐19 infection in a retrospective cohort: A mediatory role of the inflammatory biomarker C‐reactive protein
Huilin Koh, Angela Mei Chung Moh, Ester Yeoh, Yi Lin, Serena Kiat Mun Low, Say Tat Ooi, Seng Kiong Tan, Jaime Hui Xian Lin, Caroline Wei Shan Hoong
Journal of Medical Virology.2021; 93(5): 3023. CrossRef - Susceptibility for Some Infectious Diseases in Patients With Diabetes: The Key Role of Glycemia
Jesús Chávez-Reyes, Carlos E. Escárcega-González, Erika Chavira-Suárez, Angel León-Buitimea, Priscila Vázquez-León, José R. Morones-Ramírez, Carlos M. Villalón, Andrés Quintanar-Stephano, Bruno A. Marichal-Cancino
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes is most important cause for mortality in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Giovanni Corona, Alessandro Pizzocaro, Walter Vena, Giulia Rastrelli, Federico Semeraro, Andrea M Isidori, Rosario Pivonello, Andrea Salonia, Alessandra Sforza, Mario Maggi
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2021; 22(2): 275. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes: Analysis of the scientific production indexed in Scopus
Ibraín Enrique Corrales-Reyes, Frank Hernández-García, Christian R. Mejia
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(3): 765. CrossRef - Impact of diabetes mellitus on in-hospital mortality in adult patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Halla Kaminska, Lukasz Szarpak, Dariusz Kosior, Wojciech Wieczorek, Agnieszka Szarpak, Mahdi Al-Jeabory, Wladyslaw Gawel, Aleksandra Gasecka, Milosz J. Jaguszewski, Przemyslawa Jarosz-Chobot
Acta Diabetologica.2021; 58(8): 1101. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Manuela Neuenschwander, Alexander Lang, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2021; 64(7): 1480. CrossRef - Evolution of a Cohort of COVID-19 Infection Suspects Followed-Up from Primary Health Care
Valle Coronado-Vázquez, Maria del Valle Ramírez-Durán, Juan Gómez-Salgado, María Silvia Dorado-Rabaneda, Elena Benito-Alonso, Marina Holgado-Juan, Cristina Bronchalo-González
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(6): 459. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide 3.0 and 4.5 mg in patients aged younger than 65 and 65 years or older: Post hoc analysis of the AWARD‐11 trial
Juan P. Frias, Enzo Bonora, Luis Nevárez Ruiz, Stanley H. Hsia, Heike Jung, Sohini Raha, David A. Cox, M. Angelyn Bethel, Manige Konig
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(10): 2279. CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Primary Prevention and COVID‐19
Jordan Loader, Erik Lampa, Stefan Gustafsson, Thomas Cars, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive value of HbA1c for in-hospital adverse prognosis in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Zheng Zhu, Yaqian Mao, Gang Chen
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(6): 910. CrossRef - High Fibrosis-4 Index Is Related with Worse Clinical Outcome in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes Mellitus: A Multicenter Observational Study
Sung-Woo Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Jun Sung Moon, Mi Kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 800. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 757. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diabetes Associated Mortality in Patients with COVID-19
Puneeta Gupta, Meeta Gupta, Neena KAtoch, Ketan Garg, Bhawna Garg
International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes, Drug Treatment, and Mortality in COVID-19: A Multinational Retrospective Cohort Study
Jennifer E. Nyland, Nazia T. Raja-Khan, Kerstin Bettermann, Philippe A. Haouzi, Douglas L. Leslie, Jennifer L. Kraschnewski, Leslie J. Parent, Patricia Sue Grigson
Diabetes.2021; 70(12): 2903. CrossRef - Impact of Diabetes on COVID-19 Mortality and Hospital Outcomes, a Global Perspective: An ONTOP Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Stavroula Kastora, Manisha Patel, Ben Carter, Mirela Delibegovic, Phyo Kyaw Myint
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Response: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53)
Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 484. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus is Associated with Severe Infection and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Luxiang Shang, Mengjiao Shao, Qilong Guo, Jia Shi, Yang Zhao, Jiasuoer Xiaokereti, Baopeng Tang
Archives of Medical Research.2020; 51(7): 700. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Mortality Predictors of COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized at Nationally-Designated Treatment Hospitals
Seong-Su Moon, Kwan Lee, Jungi Park, Seongcheol Yun, Yun Sik Lee, Dong Seok Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Mortality Rate and Predictors of Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes
Dilaram Acharya, Kwan Lee, Dong Seok Lee, Yun Sik Lee, Seong-Su Moon
Healthcare.2020; 8(3): 338. CrossRef - Letter: The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:405–13)
So-Yeon Kim, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 621. CrossRef - Response: The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:405–13)
Seung Min Chung, June Hong Ahn, Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 625. CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Diabetes in Daegu, South Korea
Mi Kyung Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Sung-Woo Kim, Jun Sung Moon, Nan Hee Cho, Eugene Han, Ji Hong You, Ji Yeon Lee, Miri Hyun, Jae Seok Park, Yong Shik Kwon, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Ki Tae Kwon, Shin Yup Lee, Eon Ju Jeon, Jin-Woo Kim, Hyo-Lim Hong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Chi Yo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 602. CrossRef - Fasting Plasma Glucose Level Independently Predicts the Mortality of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection: A Multicenter, Retrospective Cohort Study
Min Cheol Chang, Jong-Moon Hwang, Jae-Han Jeon, Sang Gyu Kwak, Donghwi Park, Jun Sung Moon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(3): 595. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19
Jeong Hyun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 116. CrossRef - Management of Diabetes in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Prognosis and Practical Issues
Hye Soon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 120. CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Sun Joon Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Sung-Rae Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 737. CrossRef - Adverse impact of renin–angiotensin system blockade on the clinical course in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study
Jeong-Hoon Lim, Jang-Hee Cho, Yena Jeon, Ji Hye Kim, Ga Young Lee, Soojee Jeon, Hee Won Noh, Yong-Hoon Lee, Jaehee Lee, Hyun-Ha Chang, Hee-Yeon Jung, Ji-Young Choi, Sun-Hee Park, Chan-Duck Kim, Yong-Lim Kim, Shin-Woo Kim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes: The Epidemic and the Korean Diabetes Association Perspective
Junghyun Noh, Hyun-Ha Chang, In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 372. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19: Global and regional perspectives
In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon, Moon Kyu Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 166: 108303. CrossRef
- Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Development Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Metabolic Health, Obesity, and the Risk of Developing Open-Angle Glaucoma: Metabolically Healthy Obese Patients versus Metabolically Unhealthy but Normal Weight Patients
- Younhea Jung, Kyungdo Han, Hae-Young L. Park, Seung Hoon Lee, Chan Kee Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):414-425. Published online December 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0048
- 6,828 View
- 122 Download
- 35 Web of Science
- 38 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study sought to investigate the associations between metabolic health status, obesity, and incidence of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG).
Methods In this nationwide, population-based, longitudinal prospective cohort study conducted using the Korean National Health Insurance System, we categorized all subjects based on presence and severity of metabolic syndrome and obesity. Insurance claims data were used to identify POAG development. Then, Cox regression was applied to calculate the hazard of developing POAG in people with various components of metabolic syndrome, obesity, or their combination.
Results Of the total 287,553 subjects, 4,970 (1.3%) developed POAG. High fasting glucose, blood pressure, and total cholesterol levels were all associated with increased risk of developing POAG. Regarding obesity level, people with body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2 were more likely to develop POAG than those with normal BMI. Also, people with greater number of metabolic syndrome components showed a greater POAG incidence. People who are metabolically unhealthy and obese (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 1.574; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.449 to 1.711) and those who are metabolically unhealthy nonobese (MUNO: adjusted HR, 1.521; 95% CI, 1.405 to 1.645) but not those who are metabolically healthy obese (MHO: adjusted HR, 1.019; 95% CI, 0.907 to 1.144) had an increased hazard of developing POAG compared with metabolically healthy nonobese (MHNO) subjects.
Conclusion Metabolic health status and obesity were significantly associated with increased risk of POAG incidence. MUNO subjects but not MHO subjects showed a higher risk of POAG development than did MHNO subjects, suggesting that metabolic status is more important than obesity in POAG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Association between the Gut Microbiota and Erectile Dysfunction
Tianle Zhu, Xi Liu, Peng Yang, Yukuai Ma, Pan Gao, Jingjing Gao, Hui Jiang, Xiansheng Zhang
The World Journal of Men's Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Potentially compromised systemic and local lactate metabolic balance in glaucoma, which could increase retinal glucose and glutamate concentrations
Mina Arai-Okuda, Yusuke Murai, Hidetaka Maeda, Akiyasu Kanamori, Takako Miki, Tomoko Naito, Kazunobu Sugihara, Michihiro Kono, Masaki Tanito, Hiromitsu Onoe, Kazuyuki Hirooka, Yoshiaki Kiuchi, Masakazu Shinohara, Sentaro Kusuhara, Sotaro Mori, Kaori Ueda,
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Glaucoma in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes
Siar Niazi, Filip Gnesin, Anna-Sophie Thein, Jens R. Andreasen, Anna Horwitz, Zaynab A. Mouhammad, Baker N. Jawad, Zia Niazi, Nelsan Pourhadi, Bochra Zareini, Amani Meaidi, Christian Torp-Pedersen, Miriam Kolko
Ophthalmology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Glycemic Traits and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Mendelian Randomization Study in the Japanese Population
Akiko Hanyuda, Atsushi Goto, Masahiro Nakatochi, Yoichi Sutoh, Akira Narita, Shiori Nakano, Ryoko Katagiri, Kenji Wakai, Naoyuki Takashima, Teruhide Koyama, Kokichi Arisawa, Issei Imoto, Yukihide Momozawa, Kozo Tanno, Atsushi Shimizu, Atsushi Hozawa, Keng
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2023; 245: 193. CrossRef - Microbiome Dysbiosis: A Pathological Mechanism at the Intersection of Obesity and Glaucoma
Salvatore Pezzino, Maria Sofia, Luigi Piero Greco, Giorgia Litrico, Giulia Filippello, Iacopo Sarvà, Gaetano La Greca, Saverio Latteri
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 1166. CrossRef - Phenotypic and Genetic Links between Body Fat Measurements and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Shi Song Rong, Xinting Yu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3925. CrossRef - Metabolic Health, Obesity, and Intraocular Pressure
Younhea Jung, Gyoung Nyun Kim, Eun Byeol Oh, Kyoung Ohn, Jung Il Moon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(5): 2066. CrossRef - Association between lifestyle habits and glaucoma incidence: a retrospective cohort study
Asahi Fujita, Yohei Hashimoto, Hiroki Matsui, Hideo Yasunaga, Makoto Aihara
Eye.2023; 37(16): 3470. CrossRef - Towards precision medicine in bariatric surgery prescription
Sofia S. Pereira, Marta Guimarães, Mariana P. Monteiro
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2023; 24(5): 961. CrossRef - Study of the relationship between serum lipid levels and primary open-angle glaucoma
Rajesh Subhash Joshi, Vaishnavi Hitesh Adatiya
Indian Journal of Ophthalmology.2023; 71(5): 1948. CrossRef - Primary open-angle glaucoma risk prediction with ABCA1 and LOC102723944 variants and their genotype–phenotype correlations in southern Chinese population
Zhenggen Wu, Chukai Huang, Yuqian Zheng, Xiang-Ling Yuan, Shaowan Chen, Yanxuan Xu, Li Jia Chen, Chi Pui Pang, Mingzhi Zhang, Tsz Kin Ng
Molecular Genetics and Genomics.2023; 298(6): 1343. CrossRef - Differences in Factors Associated With Glaucoma Progression With Lower Normal Intraocular Pressure in Superior and Inferior Halves of the Optic Nerve Head
Ryo Asaoka, Rei Sakata, Takeshi Yoshitomi, Aiko Iwase, Chota Matsumoto, Tomomi Higashide, Motohiro Shirakashi, Makoto Aihara, Kazuhisa Sugiyama, Makoto Araie
Translational Vision Science & Technology.2023; 12(8): 19. CrossRef - The association between obesity and glaucoma in older adults: evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Xiaohuan Zhao, Qiyu Bo, Junran Sun, Jieqiong Chen, Tong Li, Xiaoxu Huang, Minwen Zhou, Jing Wang, Wenjia Liu, Xiaodong Sun
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023034. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome as an independent risk factor for glaucoma: a nationally representative study
Jun-Hyuk Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Sung Jin Kim, Boyoung Joung
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors: Interaction Issues in Patients with Glaucoma and Arterial Hypertension. Review
S. I. Makogon, D. I. Ivanova, A. L. Onishchenko
Ophthalmology in Russia.2023; 20(4): 641. CrossRef - The role of the microbiota in glaucoma
Ling Huang, Yiwen Hong, Xiangyu Fu, Haishan Tan, Yongjiang Chen, Yujiao Wang, Danian Chen
Molecular Aspects of Medicine.2023; 94: 101221. CrossRef - Girl Power in Glaucoma: The Role of Estrogen in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
Kyrylo Fotesko, Bo Schneider Vohra Thomsen, Miriam Kolko, Rupali Vohra
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology.2022; 42(1): 41. CrossRef - Cholesterol and glaucoma: a systematic review and meta‐analysis
Laura Posch‐Pertl, Monja Michelitsch, Gernot Wagner, Brigitte Wildner, Günther Silbernagel, Gudrun Pregartner, Andreas Wedrich
Acta Ophthalmologica.2022; 100(2): 148. CrossRef - Non-drug interventions in glaucoma: Putative roles for lifestyle, diet and nutritional supplements
Foroogh Fahmideh, Nicoletta Marchesi, Annalisa Barbieri, Stefano Govoni, Alessia Pascale
Survey of Ophthalmology.2022; 67(3): 675. CrossRef - Relationship between Using Fibrate and Open-Angle Glaucoma in Hyperlipidemic Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Yung-En Tsai, Yi-Hao Chen, Chien-An Sun, Chi-Hsiang Chung, Wu-Chien Chien, Ke-Hung Chien
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(4): 2415. CrossRef - The Causal Association Between Obesity and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
Yi Lin, Xiaomin Zhu, Wangdu Luo, Bingcai Jiang, Qianyi Lin, Min Tang, Xiangji Li, Lin Xie
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Enzymatic activity of paraoxonase depending on polymorphism Q192R of the PON1 gene in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma
Yu.E. Filippova, T.N. Malishevskaya, S.A. Petrov, D.G. Gubin, A.S. Vlasova
Vestnik oftal'mologii.2022; 138(2): 58. CrossRef - Association of Metabolic Syndrome With Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension in a Midwest United States Population
Kristi Y. Wu, David O. Hodge, Launia J. White, Jacinta McDonald, Gavin W. Roddy
Journal of Glaucoma.2022; 31(6): e18. CrossRef - Metabolically Defined Body Size Phenotypes and Risk of Endometrial Cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)
Nathalie Kliemann, Romain Ould Ammar, Carine Biessy, Audrey Gicquiau, Verena Katzke, Rudolf Kaaks, Anne Tjønneland, Anja Olsen, Maria-Jose Sánchez, Marta Crous-Bou, Fabrizio Pasanisi, Sandar Tin Tin, Aurora Perez-Cornago, Dagfinn Aune, Sofia Christakoudi,
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2022; 31(7): 1359. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Management of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma in the United States: An Analysis of Real-World Evidence
Joseph S Imperato, Kelly H Zou, Jim Z Li, Tarek A Hassan
Patient Preference and Adherence.2022; Volume 16: 2213. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of Dyslipidemia and Blood Lipid Parameters on the Risk of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Guimei Huang, Jiayi Wang, Lei Li, Yuan Gao, Yijie Yan, Xi Lou
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Body shape and risk of glaucoma: A Mendelian randomization
Ruolan Yuan, Kangcheng Liu, Yingjun Cai, Fei He, Xiaoxiong Xiao, Jing Zou
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Systemic Comorbidities on Ocular Hypertension and Open-Angle Glaucoma, in a Population from Spain and Portugal
Carolina Garcia-Villanueva, Elena Milla, José M. Bolarin, José J. García-Medina, Javier Cruz-Espinosa, Javier Benítez-del-Castillo, José Salgado-Borges, Francisco J. Hernández-Martínez, Elena Bendala-Tufanisco, Irene Andrés-Blasco, Alex Gallego-Martinez,
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(19): 5649. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and its components are associated with non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy
Darrell Kohli, Kristi Y Wu, Launia J White, David O Hodge, John J Chen, Gavin W Roddy
BMJ Open Ophthalmology.2022; 7(1): e001111. CrossRef - Blood Pressure Measures and Incident Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Carmelo Macri, Christopher X. Wong, Samuel J. Tu, Robert Casson, Kuldev Singh, Sophia Y. Wang, Michelle T. Sun
Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science.2022; 63(13): 3. CrossRef - Relationship between anthropometric and biochemical changes of metabolic syndrome with retinal nerve fiber layer and macular thickness
Sze Hui New, Sue Ngein Leow, Suresh Kumar Vasudevan, Idayu Badilla Idris, Seng Fai Tang, Norshamsiah Md Din, Bang V Bui
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(2): e0246830. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and the aging retina
Gavin W. Roddy
Current Opinion in Ophthalmology.2021; 32(3): 280. CrossRef - Automated Detection of Glaucoma With Interpretable Machine Learning Using Clinical Data and Multimodal Retinal Images
Parmita Mehta, Christine A. Petersen, Joanne C. Wen, Michael R. Banitt, Philip P. Chen, Karine D. Bojikian, Catherine Egan, Su-In Lee, Magdalena Balazinska, Aaron Y. Lee, Ariel Rokem
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2021; 231: 154. CrossRef - Association of Hypertriglyceridemia and Incident Glaucoma in a Rural Chinese Population: The Handan Eye Study
Ye Zhang, Qing Zhang, Ravi Thomas, Si Zhen Li, Ning Li Wang
Translational Vision Science & Technology.2021; 10(8): 25. CrossRef - Risk of Glaucoma Associated with Components of Metabolic Disease in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Ya-Wen Chang, Fung-Chang Sung, Ya-Ling Tzeng, Chih-Hsin Mou, Peng-Tai Tien, Cheng-Wen Su, Yu-Kuei Teng
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 19(1): 305. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated With Ocular Hypertension and Glaucoma
Gavin W. Roddy
Journal of Glaucoma.2020; 29(9): 726. CrossRef - Association of dipping status of blood pressure, visual field defects, and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients with normotensive glaucoma
Seung Uk Lee, Han Su Park, Bong Joon Kim, Hyun Su Kim, Jung Ho Heo, Sung Il Im
Medicine.2020; 99(50): e23565. CrossRef - Ocular findings in metabolic syndrome: a review
Mário Lima-Fontes, Pedro Barata, Manuel Falcão, Ângela Carneiro
Porto Biomedical Journal.2020; 5(6): 104. CrossRef
- The Association between the Gut Microbiota and Erectile Dysfunction
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Association between Cigarette Smoking and New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus in 78,212 Koreans Using Self-Reported Questionnaire and Urine Cotinine
- Ji Hye Kim, Dae Chul Seo, Byung Jin Kim, Jeong Gyu Kang, Seung Jae Lee, Sung Ho Lee, Bum Soo Kim, Jin Ho Kang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):426-435. Published online November 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0068
- 6,662 View
- 94 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background No study has assessed association between cigarette smoking and new-onset diabetes mellitus (NODM) incidence using two different smoking classification systems: self-reported questionnaire and urine cotinine. The objective of this longitudinal study was to evaluate NODM risk using the above two systems in Korean adults.
Methods Among individuals enrolled in Kangbuk Samsung Health Study and Cohort Study who visited between 2011 and 2012 at baseline and 2014 at follow-up, 78,212 participants without baseline diabetes mellitus were followed up for a median of 27 months. Assessment of NODM incidence was made at the end of follow-up period. Cotinine-verified current smoking was having urinary cotinine ≥50 ng/mL.
Results Percentages of self-reported and cotinine-verified current smokers were 25.9% and 23.5%, respectively. Overall incidence of NODM was 1.5%. According to multivariate regression analyses, baseline self-reported current smoking (relative risk [RR], 1.33; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.07 to 1.65) and cotinine-verified current smoking (RR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.08 to 1.49) increased NODM risk compared to baseline self-reported never smoking and cotinine-verified current non-smoking. Higher daily amount and longer duration of smoking were also associated with increased NODM risk (
P for trends <0.05). In particular, self-reported current smokers who smoked ≥20 cigarettes/day (RR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.25 to 2.15) and ≥10 years (RR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.08 to 1.67) had the highest RRs for NODM. These results remained significant in males, although there was no gender interaction.Conclusion This longitudinal study showed that baseline self-reported and cotinine-verified current smoking were associated with increased risks of NODM, especially in males.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Variability in the association of smoking status with the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in the Korean population according to different definitions of smoking status: analysis based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2014-202
Yechan Kyung, Young Sook Park, Mi Hyeon Jin, Hae Jeong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Health Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Determination of Diabetes-associated Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Risk Factors among Insulin and Non-insulin Dependent Diabetics
Ibrahim Abdulsada, Zain Alabdeen Obaid, Farah Almerza, Mays Alwaeli, Anmar Al-Elayawi, Taha Al-Dayyeni, Harir Al-Tuhafy
The Journal of Medical Research.2023; 9(6): 141. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 351. CrossRef - Xenobiotics Delivered by Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems: Potential Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms on the Pathogenesis of Chronic Kidney Disease
Pablo Scharf, Felipe Rizzetto, Luana Filippi Xavier, Sandra Helena Poliselli Farsky
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(18): 10293. CrossRef - Cigarette Smoking Increases the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in
Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population-Based Cohort
Study
Chan Liu, Yanqin Wu, Wenjuan Duan, Wenming Xu
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(12): 793. CrossRef - Current status of health promotion in Korea
Soo Young Kim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(12): 776. CrossRef - Association between secondhand smoke exposure and diabetes mellitus in 131 724 Korean never smokers using self‐reported questionnaires and cotinine levels: Gender differences
Byung Jin Kim, Ji Hye Kim, Jeong Gyu Kang, Bum Soo Kim, Jin Ho Kang
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(1): 43. CrossRef - Changes in creatinine‐to‐cystatin C ratio over 4 years, risk of diabetes, and cardiometabolic control: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(12): 1025. CrossRef - Trends in the Socioeconomic Inequalities Related to Second-Hand Smoke Exposure as Verified by Urine Cotinine Levels Among Nonsmoking Adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2018
Seo Young Kang, Min Kyung Lim, Hong-Jun Cho
Nicotine & Tobacco Research.2021; 23(9): 1518. CrossRef - Letter: Association between Cigarette Smoking and New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus in 78,212 Koreans Using Self-Reported Questionnaire and Urine Cotinine (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:426–35)
Bo-Yeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 619. CrossRef - Response: Association between Cigarette Smoking and New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus in 78,212 Koreans Using Self-Reported Questionnaire and Urine Cotinine (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:426–35)
Ji Hye Kim, Byung Jin Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 623. CrossRef - Smoking as a Target for Prevention of Diabetes
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 402. CrossRef
- Variability in the association of smoking status with the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in the Korean population according to different definitions of smoking status: analysis based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2014-202
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Association between Higher Blood Pressure and Risk of Diabetes Mellitus in Middle-Aged and Elderly Chinese Adults
- Xue Yang, Jian Chen, An Pan, Jason H.Y. Wu, Fei Zhao, Yue Xie, Yi Wang, Yi Ye, Xiong-Fei Pan, Chun-Xia Yang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):436-445. Published online November 14, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0081
- 4,829 View
- 83 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background To examine the prospective association between higher blood pressure (BP) and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in middle-aged and elderly Chinese adults.
Methods A total of 9,642 middle-aged and elderly Chinese adults (≥45 years old; 47.30% men) without diabetes from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study were included for analyses. Participants were categorized into three groups: normal BP, prehypertension, and hypertension, according to the 2010 Chinese Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. The incidence of T2DM was determined by self-reported physician diagnosis during two follow-up surveys conducted in 2013 to 2014 and 2015 to 2016.
Results During the 4-year follow-up, 429 participants (4.45%) developed T2DM, including 3.51% of the men and 5.29% of the women. The incidence rates of T2DM were 2.57%, 3.75%, and 6.71% in the normal BP, prehypertension, and hypertension groups, respectively. After adjustment for age, sex, education level, residence, smoking status, alcohol consumption, body mass index, waist circumference, and dyslipidemia, both prehypertension (odds ratio [OR], 1.32; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.98 to 1.77) and hypertension (OR, 2.02; 95% CI, 1.54 to 2.64) were associated with increased risk of T2DM, compared to those with a normal BP. The ORs associated with T2DM were 1.08 (95% CI, 1.03 to 1.13) for an increase of 10 mm Hg in systolic BP and 1.06 (95% CI, 1.01 to 1.10) for an increase of 5 mm Hg in diastolic BP.
Conclusion Higher BP is a risk factor for T2DM in middle-aged and elderly Chines. It may be a potential target for diabetes prevention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Leveraging IgG N-glycosylation to infer the causality between T2D and hypertension
Haotian Wang, Yuan Li, Weijie Cao, Jie Zhang, Mingyang Cao, Xiaoni Meng, Di Liu, Youxin Wang
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Externalizing traits: Shared causalities for COVID-19 and Alzheimer's dementia using Mendelian randomization analysis
Haotian Wang, Mingyang Cao, Yingjun Xi, Weijie Cao, Xiaoyu Zhang, Xiaoni Meng, Deqiang Zheng, Lijuan Wu, Wei Wang, Di Liu, Youxin Wang, Shibu Yooseph
PNAS Nexus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Causal Paradigm Between Common Comorbidities of Cardiovascular and Metabolism-Related Diseases in Elderly: Evidence from Cross-Sectional and Mendelian Randomization Studies
Junwang Gu, Qi Wang, Xuanhui Wu, Han Zhang, Chunmei Wu, Wei Qiu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2953. CrossRef - Hypertension, Arterial Stiffness, and Diabetes: a Prospective Cohort Study
Xue Tian, Yingting Zuo, Shuohua Chen, Yijun Zhang, Xiaoli Zhang, Qin Xu, Shouling Wu, Anxin Wang
Hypertension.2022; 79(7): 1487. CrossRef - Integrated analysis of probability of type 2 diabetes mellitus with polymorphisms and methylation of SLC30A8 gene: a nested case-control study
Fulan Hu, Yanyan Zhang, Pei Qin, Yang Zhao, Dechen Liu, Qionggui Zhou, Gang Tian, Quanman Li, Chunmei Guo, Xiaoyan Wu, Ranran Qie, Shengbing Huang, Minghui Han, Yang Li, Dongsheng Hu, Ming Zhang
Journal of Human Genetics.2022; 67(11): 651. CrossRef - Understanding Frailty: Probabilistic Causality between Components and Their Relationship with Death through a Bayesian Network and Evidence Propagation
Ricardo Ramírez-Aldana, Juan Carlos Gomez-Verjan, Carmen García-Peña, Luis Miguel Gutiérrez-Robledo, Lorena Parra-Rodríguez
Electronics.2022; 11(19): 3001. CrossRef - Novel lipid indicators and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus among Chinese hypertensive patients: findings from the Guangzhou Heart Study
Hai Deng, Peng Hu, Huoxing Li, Huanning Zhou, Xiuyi Wu, Maohua Yuan, Xueru Duan, Miaochan Lao, Chuchu Wu, Murui Zheng, Xiang Qian Lao, Wenjing Zhao, Xudong Liu
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends and Comparisons of Blood Pressure and Fasting Plasma Glucose in Patients with Hypertension, Diabetes, and Comorbidity: 4-Year Follow-Up Data
Luxinyi Xu, Xiaotong Wen, Ying Yang, Dan Cui
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2022; Volume 15: 2221. CrossRef - Policyholder cluster divergence based differential premium in diabetes insurance
Benjiang Ma, Qing Tang, Yifang Qin, Muhammad Farhan Bashir
Managerial and Decision Economics.2021; 42(7): 1793. CrossRef - Association of hypertension and incident diabetes in Chinese adults: a retrospective cohort study using propensity-score matching
Yang Wu, Haofei Hu, Jinlin Cai, Runtian Chen, Xin Zuo, Heng Cheng, Dewen Yan
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Leveraging IgG N-glycosylation to infer the causality between T2D and hypertension
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Association between the Thigh Muscle and Insulin Resistance According to Body Mass Index in Middle-Aged Korean Adults
- Ji Eun Heo, Jee-Seon Shim, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):446-457. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0110
- 6,748 View
- 89 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We examined the associations between thigh muscle area (TMA) and insulin resistance (IR) according to body mass index (BMI) in middle-aged Korean general population.
Methods TMA was measured using quantitative computed tomography and corrected by body weight (TMA/Wt) in 1,263 men, 788 premenopausal women, and 1,476 postmenopausal women all aged 30 to 64 years. The tertiles of TMA/Wt were calculated separately for men and for premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was performed using fasting blood glucose and insulin levels, and increased IR was defined according to sex-specific, top quartiles of HOMA-IR. Associations between the TMA/Wt tertiles and increased IR according to the BMI categories (<25 and ≥25 kg/m2) were assessed using multivariable logistic regression analysis.
Results In men with higher BMIs, but not in those with lower BMIs, the presence of an increased IR had significantly higher odds ratios in the lower TMA/Wt tertiles, even after adjustment for visceral fat area. However, in premenopausal and postmenopausal women, there was no significant inverse association between TMA/Wt tertiles and increased IR, regardless of BMI category.
Conclusion Our findings suggest that the thigh muscle is inversely associated with IR in men, particularly in those with higher BMIs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of sleep apnea associated with higher blood pressure among Chinese and Korean Americans
Brittany N. Morey, Yuxi Shi, Soomin Ryu, Susan Redline, Ichiro Kawachi, Hye Won Park, Sunmin Lee
Ethnicity & Health.2024; 29(3): 295. CrossRef - Sex-specific equations to estimate body composition: Derivation and validation of diagnostic prediction models using UK Biobank
Yueqi Lu, Ying Shan, Liang Dai, Xiaosen Jiang, Congying Song, Bangwei Chen, Jingwen Zhang, Jing Li, Yue Zhang, Junjie Xu, Tao Li, Zuying Xiong, Yong Bai, Xiaoyan Huang
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(4): 511. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Relation to Body Composition, Insulin Resistance, and Islet Beta Cell Function in Newly Diagnosed Diabetic or Pre-Diabetic Patients
Minglei Ma, Tao Jiang, Zhen Wen, Dongxue Zhang, Lei Xiu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 723. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Sarcopenia and Carotid Plaque Progression Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yongin Cho, Hye-Sun Park, Byung Wook Huh, Yong-ho Lee, Seong Ha Seo, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 232. CrossRef - Prospective External Validation of an Algorithm Predicting Hourly
Basal Insulin Infusion Rates from Characteristics of Patients with Type 1
Diabetes Treated with Insulin Pumps
Jana S. Schmelzer, Melanie Kahle-Stephan, Juris J. Meier, Michael A. Nauck
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2023; 131(10): 539. CrossRef - Establishing reference values for percentage of appendicular skeletal muscle mass and their association with metabolic syndrome in Korean adolescents
Da Hye Lee, Sung-Chan Kang, Seung-Sik Hwang, Yun Jeong Lee, Hwa Young Kim, Seong Yong Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Jaehyun Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(4): 237. CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - Association between Lower-to-Upper Ratio of Appendicular Skeletal Muscle and Metabolic Syndrome
Hyun Eui Moon, Tae Sic Lee, Tae-Ha Chung
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(21): 6309. CrossRef
- Risk of sleep apnea associated with higher blood pressure among Chinese and Korean Americans
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Validation of Risk Prediction Models for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in a Prospective Korean Community-Based Cohort
- Jae Hyun Bae, Min Kyong Moon, Sohee Oh, Bo Kyung Koo, Nam Han Cho, Moon-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):458-469. Published online January 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0061
- 6,882 View
- 226 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background To investigate the performance of the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE) in a large, prospective, community-based cohort in Korea and to compare it with that of the Framingham Global Cardiovascular Disease Risk Score (FRS-CVD) and the Korean Risk Prediction Model (KRPM).
Methods In the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KOGES)-Ansan and Ansung study, we evaluated calibration and discrimination of the PCE for non-Hispanic whites (PCE-WH) and for African Americans (PCE-AA) and compared their predictive abilities with the FRS-CVD and the KRPM.
Results The present study included 7,932 individuals (3,778 men and 4,154 women). The PCE-WH and PCE-AA moderately overestimated the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) for men (6% and 13%, respectively) but underestimated the risk for women (−49% and −25%, respectively). The FRS-CVD overestimated ASCVD risk for men (91%) but provided a good risk prediction for women (3%). The KRPM underestimated ASCVD risk for men (−31%) and women (−31%). All the risk prediction models showed good discrimination in both men (C-statistic 0.730 to 0.735) and women (C-statistic 0.726 to 0.732). Recalibration of the PCE using data from the KOGES-Ansan and Ansung study substantially improved the predictive accuracy in men.
Conclusion In the KOGES-Ansan and Ansung study, the PCE overestimated ASCVD risk for men and underestimated the risk for women. The PCE-WH and the FRS-CVD provided an accurate prediction of ASCVD in men and women, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors for Infertility in Korean Women
Juyeon Lee, Chang-Woo Choo, Kyoung Yong Moon, Sang Woo Lyu, Hoon Kim, Joong Yeup Lee, Jung Ryeol Lee, Byung Chul Jee, Kyungjoo Hwang, Seok Hyun Kim, Sue K. Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating cardiovascular disease risk stratification using multiple-polygenic risk scores and pooled cohort equations: insights from a 17-year longitudinal Korean cohort study
Yi Seul Park, Hye-Mi Jang, Ji Hye Park, Bong-Jo Kim, Hyun-Young Park, Young Jin Kim
Frontiers in Genetics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Moderation of Weight Misperception on the Associations Between Obesity Indices and Estimated Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Kayoung Lee
International Journal of Behavioral Medicine.2023; 30(1): 89. CrossRef - Validation of the general Framingham Risk Score (FRS), SCORE2, revised PCE and WHO CVD risk scores in an Asian population
Sazzli Shahlan Kasim, Nurulain Ibrahim, Sorayya Malek, Khairul Shafiq Ibrahim, Muhammad Firdaus Aziz, Cheen Song, Yook Chin Chia, Anis Safura Ramli, Kazuaki Negishi, Nafiza Mat Nasir
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific.2023; 35: 100742. CrossRef - Principles of cardiovascular risk management in perimenopausal women with type 2 diabetes
F. O. Ushanova, T. Yu. Demidova, T. N. Korotkova
FOCUS. Endocrinology.2023; 4(2): 19. CrossRef - Prediction of the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in the Korean population
Sangwoo Park, Yong-Giun Kim, Soe Hee Ann, Young-Rak Cho, Shin-Jae Kim, Seungbong Han, Gyung-Min Park
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023052. CrossRef - Triglyceride-Glucose Index Predicts Future Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases: A 16-Year Follow-up in a Prospective, Community-Dwelling Cohort Study
Joon Ho Moon, Yongkang Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi, Nam H. Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 406. CrossRef - Validity of the models predicting 10-year risk of cardiovascular diseases in Asia: A systematic review and prediction model meta-analysis
Mahin Nomali, Davood Khalili, Mehdi Yaseri, Mohammad Ali Mansournia, Aryan Ayati, Hossein Navid, Saharnaz Nedjat, Hean Teik Ong
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0292396. CrossRef - Assessing the Validity of the Criteria for the Extreme Risk Category of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(1): 73. CrossRef - Mediation of Grip Strength on the Association Between Self-Rated Health and Estimated Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Kayoung Lee
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(6): 344. CrossRef - Implications of the heterogeneity between guideline recommendations for the use of low dose aspirin in primary prevention of cardiovascular disease
Xiao-Ying Li, Li Li, Sang-Hoon Na, Francesca Santilli, Zhongwei Shi, Michael Blaha
American Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 11: 100363. CrossRef - The Risk of Cardiovascular Disease According to Chewing Status Could Be Modulated by Healthy Diet in Middle-Aged Koreans
Hyejin Chun, Jongchul Oh, Miae Doo
Nutrients.2022; 14(18): 3849. CrossRef - Management of Cardiovascular Risk in Perimenopausal Women with Diabetes
Catherine Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 492. CrossRef - Comparative performance of the two pooled cohort equations for predicting atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Alessandra M. Campos-Staffico, David Cordwin, Venkatesh L. Murthy, Michael P. Dorsch, Jasmine A. Luzum
Atherosclerosis.2021; 334: 23. CrossRef - Usefulness of Relative Handgrip Strength as a Simple Indicator of Cardiovascular Risk in Middle-Aged Koreans
Won Bin Kim, Jun-Bean Park, Yong-Jin Kim
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2021; 362(5): 486. CrossRef
- Risk Factors for Infertility in Korean Women
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Impact of Diabetes Control on Subclinical Atherosclerosis: Analysis from Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography Registry
- Gyung-Min Park, Chang Hoon Lee, Seung-Whan Lee, Sung-Cheol Yun, Young-Hak Kim, Yong-Giun Kim, Ki-Bum Won, Soe Hee Ann, Shin-Jae Kim, Dong Hyun Yang, Joon-Won Kang, Tae-Hwan Lim, Eun Hee Koh, Woo Je Lee, Min-Seon Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Jaewon Choe, Sang-Gon Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):470-479. Published online November 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0073
- 8,680 View
- 69 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background There are limited data on the impact of diabetes control on the risk of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis.
Methods We analyzed 6,434 consecutive asymptomatic individuals without previous history of coronary artery disease who underwent coronary computed tomographic angiography (CCTA) (mean age, 53.7±7.6 years and 4,694 men [73.0%]). The degree and extent of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis were assessed by CCTA, and ≥50% diameter stenosis was defined as significant. A cardiac event was defined as a composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, or coronary revascularization. Study participants were categorized as normal (
n =5,319), controlled diabetes (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] <7%,n =747), or uncontrolled diabetes (HbA1c ≥7%,n =368), respectively.Results Compared with normal individuals, there were no statistically significant differences in the risk of for any atherosclerotic plaque (odds ratio [OR], 1.16; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.98 to 1.38;
P =0.086) and significant coronary artery stenosis (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.82 to 1.42;P =0.583) in controlled diabetic individuals. In contrast, uncontrolled diabetic individuals had consistently higher risks of any atherosclerotic plaque (OR, 2.16; 95% CI, 1.70 to 2.75;P <0.001) and significant coronary artery stenosis (OR, 3.34; 95% CI, 2.52 to 4.43;P <0.001) than normal individuals. During a follow-up of median 5.4 years, there was no significant difference in cardiac events between normal and controlled diabetic individuals (P =0.365). However, uncontrolled diabetes was associated with an increased risk of cardiac events compared with normal individuals (P <0.001) and controlled diabetic individuals (P =0.023).Conclusion Asymptomatic uncontrolled diabetes was associated with significant subclinical coronary atherosclerosis with subsequent high risk for cardiac events.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carotid Ultrasound Abnormalities of People Living With HIV in Kunming, China: Multiple Correspondence Analysis Approach to Identify Influencing Factors
Shuishui Pan, Haiyan Fu, Zhiqiong Ai, Chongxi Li, Jinsong Bai
International Journal of STD & AIDS.2023; 34(10): 710. CrossRef - Differential Impact of Degree of Hypertension on Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic Subjects With and Without Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun Woo Park, Sangyong Jo, Kyung Sun Park, Hyeji Lee, Young-Jee Jeon, Sangwoo Park, Soe Hee Ann, Yong-Giun Kim, Seong Hoon Choi, Woon Jung Kwon, Young-Rak Cho, Jon Suh, Gyung-Min Park
The American Journal of Cardiology.2023; 203: 343. CrossRef - Exosomal MALAT1 Derived from High Glucose-Treated Macrophages Up-Regulates Resistin Expression via miR-150-5p Downregulation
Kou-Gi Shyu, Bao-Wei Wang, Wei-Jen Fang, Chun-Ming Pan, Chiu-Mei Lin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(3): 1095. CrossRef - Comparison of Framingham risk score and pooled cohort equations for the prediction of coronary atherosclerosis in patients who meet the target LDL-C level of Korean dyslipidemia guideline
Su Bin Kim, Hae Won Jung
Medicine.2022; 101(47): e31816. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 368. CrossRef - Frequency and Significance of Right Bundle Branch Block and Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic Individuals
Hyeji Lee, Young-Jee Jeon, Byung Ju Kang, Tae Young Lee, Eun Ji Park, Sangwoo Park, Soe Hee Ann, Yong-Giun Kim, Yongjik Lee, Seong Hoon Choi, Gyung-Min Park
The American Journal of Cardiology.2021; 158: 30. CrossRef - The association between glucose-related variables and plaque morphology in patients with ST-segment elevated myocardial infarction
Jinxin Liu, Shanjie Wang, Can Cui, Hengxuan Cai, Rong Sun, Weili Pan, Shaohong Fang, Bo Yu
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Choosing Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: How to Reduce the Risk of Death
N. A. Koziolova, P. G. Karavaev, A. S. Veklich
Kardiologiia.2020; 60(4): 109. CrossRef
- Carotid Ultrasound Abnormalities of People Living With HIV in Kunming, China: Multiple Correspondence Analysis Approach to Identify Influencing Factors
- Letter: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53) - Ja Young Jeon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):480-481. Published online June 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0121
- 4,277 View
- 55 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
- Letter: Association between Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:267–76) - Sung Hoon Yu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):482-483. Published online June 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0123
- 4,067 View
- 55 Download
- Response: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53) - Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):484-485. Published online June 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0129
- [Original]
- 4,405 View
- 64 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in tissue-specific metabolic modulation by SARS-CoV-2
Alef Aragão Carneiro dos Santos, Luiz Eduardo Rodrigues, Amanda Lins Alecrim-Zeza, Liliane de Araújo Ferreira, Caio dos Santos Trettel, Gabriela Mandú Gimenes, Adelson Fernandes da Silva, Celso Pereira Batista Sousa-Filho, Tamires Duarte Afonso Serdan, Ad
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Behind the Higher COVID-19 Risk in Diabetes: A Critical Review
Amany Magdy Beshbishy, Victor B. Oti, Diaa E. Hussein, Ibrahim F. Rehan, Oluyomi S. Adeyemi, Nallely Rivero-Perez, Adrian Zaragoza-Bastida, Muhammad Ajmal Shah, Khaled Abouelezz, Helal F. Hetta, Natália Cruz-Martins, Gaber El-Saber Batiha
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital health services among patients with diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic: A scoping review
NiK D. Purnamayanti, AnggiL Wicaksana
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 25(2): 86. CrossRef
- Molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in tissue-specific metabolic modulation by SARS-CoV-2
- Response: Association between Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:267–76) - Hokyou Lee, Gyuri Kim, Yong-ho Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):486-487. Published online June 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0127
- [Original]
- 3,903 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease With Left Ventricular Diastolic Function and Cardiac Morphology
Dandan Peng, Zhenqiu Yu, Mingwei Wang, Junping Shi, Lei Sun, Yuanyuan Zhang, Wenbin Zhao, Chen Chen, Jiake Tang, Chunyi Wang, Jie Ni, Wen Wen, Jingjie Jiang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease With Left Ventricular Diastolic Function and Cardiac Morphology

 KDA
KDA


 First
First Prev
Prev





