- Skip Navigation
- Skip to contents

- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 46(2); 2022 > Article
-
ReviewMetabolic Risk/Epidemiology Not Control but Conquest: Strategies for the Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
-
Jinyoung Kim
 , Hyuk-Sang Kwon
, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2022;46(2):165-180.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0377
Published online: March 24, 2022
Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
-
Corresponding author: Hyuk-Sang Kwon
 Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, 10 63(yuksam)-ro, Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul 07345, Korea E-mail: drkwon@catholic.ac.kr
Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, 10 63(yuksam)-ro, Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul 07345, Korea E-mail: drkwon@catholic.ac.kr
Copyright © 2022 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- ABSTRACT
- INTRODUCTION
- CAN DIABETES BE CURED? DEFINITION OF REMISSION
- STRATEGIES FOR THE REMISSION OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
- HOW DOES DIABETES REMISSION OCCUR? PATHOPHYSIOLOGY FOR DIABETES REMISSION
- TIME IS OUTCOME? PREDICTORS OF DIABETES REMISSION
- DOES DIABETES REMISSION PERSIST? THE STORY AFTER REMISSION
- UNMET NEEDS
- CONCLUSIONS
- NOTES
- REFERENCES
ABSTRACT
- A durable normoglycemic state was observed in several studies that treated type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients through metabolic surgery, intensive therapeutic intervention, or significant lifestyle modification, and it was confirmed that the functional β-cell mass was also restored to a normal level. Therefore, expert consensus introduced the concept of remission as a common term to express this phenomenon in 2009. Throughout this article, we introduce the recently updated consensus statement on the remission of T2DM in 2021 and share our perspective on the remission of diabetes. There is a need for more research on remission in Korea as well as in Western countries. Remission appears to be prompted by proactive treatment for hyperglycemia and significant weight loss prior to irreversible β-cell changes. T2DM is not a diagnosis for vulnerable individuals to helplessly accept. We attempt to explain how remission of T2DM can be achieved through a personalized approach. It may be necessary to change the concept of T2DM towards that of an urgent condition that requires rapid intervention rather than a chronic, progressive disease. We must grasp this paradigm shift in our understanding of T2DM for the benefit of our patients as endocrine experts.
- Keywords: Consensus; Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Recovery of function
- Diabetes is classified into type 1 and type 2 according to classical dichotomy. Unlike type 1 diabetes mellitus, which is the predominant cause of decreased insulin secretion due to pancreatic damage related to autoimmunity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has multiple causes, such as genetic and environmental factors [1]. Although genetic predisposition plays a role in the onset of T2DM, most cases develop after middle age, and associations with diet, lifestyle, and weight gain have been confirmed [2]. A progressive decline in β-cell function is observed in most T2DM patients [3]. More drugs are required over time [4], and irreversible complications can arise [5].
- However, normalization of blood glucose levels can be achieved and sustained without therapeutic intervention in some patients [6], and this semipermanent improvement of diabetes is being observed more often with recently updated treatments [7,8]. A durable normoglycemic state was observed in a number of studies that treated T2DM patients through metabolic surgery, intensive therapeutic interventions or significant lifestyle modification [9-11]. It was confirmed that the functional β-cell mass was also restored to a normal level [12].
- Therefore, expert consensus introduced the concept of remission as a common term to express this phenomenon in 2009 [13]. Throughout this article, we introduce the recently updated consensus statement on the remission of T2DM in 2021 [14] and share our perspective on diabetes remission.
INTRODUCTION
- Defining remission of T2DM is difficult. Unlike diseases that sometimes resolve completely and are classified as disease status versus healthy, diabetes is defined by hyperglycemia based on constantly changing blood glucose levels in the body that may be affected in the short term by temporary events such as drug effects, pregnancy, and acute illnesses [15-17].
- Different expressions, such as cure, reversal, resolution, and remission, have been used in various studies to express “the occurrence of durable normoglycemia without antidiabetic medications,” which is confirmed after diabetes is diagnosed due to persistent hyperglycemia [18-20]. Therefore, a group of experts proposed expressing the state of postdiabetes as “remission” through a consensus meeting in 2009. In a consensus statement for 2021, the group explained that remission was adopted as a representative term to express the normalization of glycemic control according to the opinion that it can reflect the characteristics of susceptible individuals who may require continuous monitoring and support. The definitions and criteria for diabetic remission defined in 2009 and 2021 are presented in Table 1.
- In the initial consensus from 2009, partial remission and complete remission were diagnosed for prediabetes and normal blood glucose levels, respectively, and criteria subdivided into prolonged remission were presented when complete remission status was more than 5 years [13]. However, in the new consensus from 2021, remission was changed to a single diagnostic standard, and the classification of the period was removed considering the complexity and lack of evidence for the standards of blood glucose level and maintenance period [14].
- As a diagnostic criterion, it was recommended to measure the glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level 3 months after the discontinuation of drug treatment [21], and remission was confirmed if the HbA1c level was found to be less than 6.5%. In clinical situations where HbA1c may not reflect blood glucose levels, fasting glucose or the 2-hour postprandial glucose of oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) can be used according to the diagnostic criteria for diabetes, but OGTT was described as an undesirable method due to the variability and complexity of the test. Since continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has been recently applied, it is recommended to use the estimated HbA1c level (eA1c) or a glucose management indicator on CGM [22].
- This suggested definition is primarily based on expert opinion, and there is not much evidence on the frequency, durability, and long-term medical outcome of remission status. In particular, it is worth noting that remission does not mean complete resolution of diabetes, as the definition of diabetic remission includes temporary remission of hyperglycemia over several months. The remission of T2DM is an unknown field that requires continued attention.
CAN DIABETES BE CURED? DEFINITION OF REMISSION
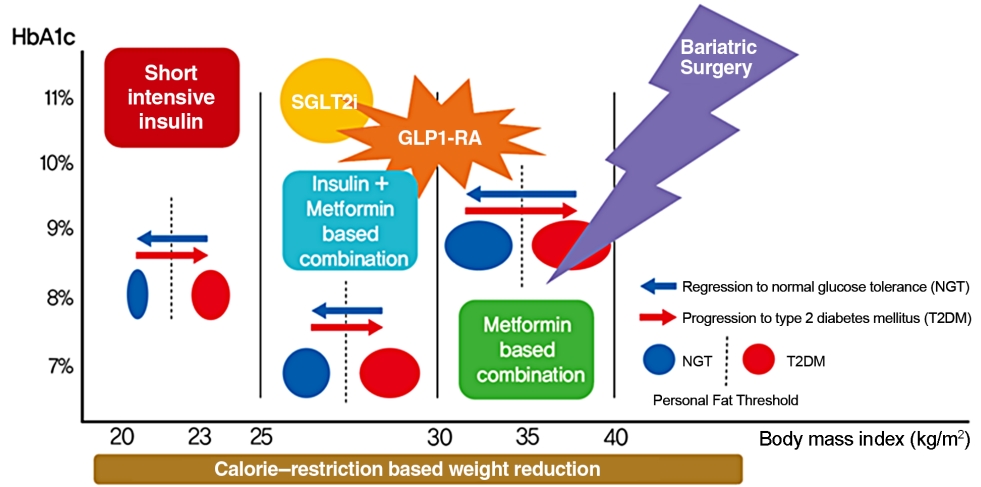
- The number of patients reaching remission was extremely low in the natural course of diabetes. In a cohort study of 25.6 million American adults who received standard medical therapy, 1.5% of patients reported normal glycemic control that could stop treatment, and prolonged normalization over 5 years was 0.007% [6]. However, it has been consistently reported that more than half of patients can achieve remission with recent treatment methods that induce active glycemic control and significant weight loss (Tables 2-4). New diabetes drugs with significant weight loss effects have recently been developed and are expected to help patients achieve remission of T2DM [23,24].
- Metabolic surgery for patients with morbid obesity
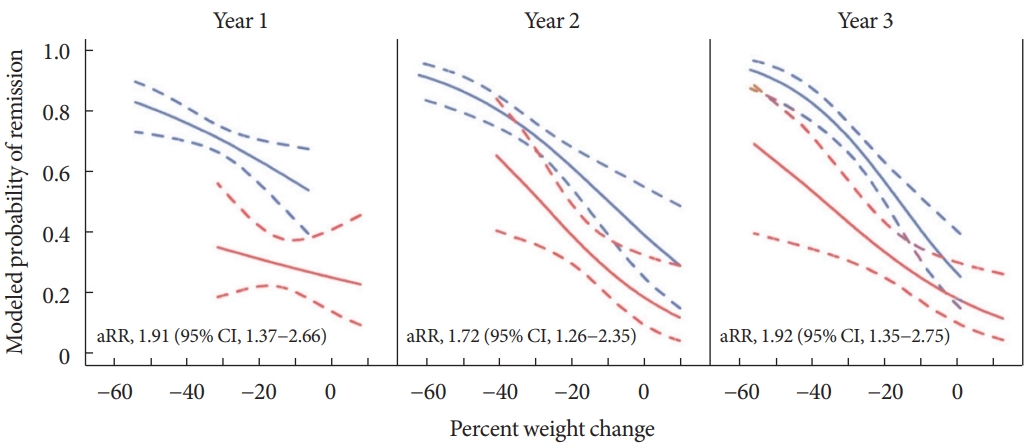
- Surgical intervention increases satiety and decreases absorption by physically narrowing the path through which ingested food passes. In addition to weight loss, this method is accompanied by favorable effects on glycemic control including the threshold increment of incretin hormones caused by changes in intestinal structure [25,26]. Metabolic surgery has various forms, such as adjustable gastric band, vertical sleeve gastrectomy, and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). The effect may be different depending on the surgical method [27-29]. Diabetic remission was associated with postoperative weight loss, but subjects receiving RYGB were twice as likely to have diabetes remission than laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) even after adjusting for weight change (Fig. 1).
- The first rationale for remission was presented through metabolic, or bariatric surgery [30], and has been confirmed in a number of randomized clinical trials (Table 2) [31-38]. In a previous meta-analysis of 4,070 patients that included 19 observational studies for metabolic surgery, the overall T2DM remission rate after the surgery reached 78% [39]. In addition, a meta-analysis of clinical trials showed that bariatric surgery had better outcomes than the nonsurgical option. The effectiveness of surgical intervention is quick and definite [40]. However, permanent structural changes did not guarantee eternal effects. In some patients, weight regain occurred, and the improvement glycemic control may worsen again [41]. Additionally, surgical intervention is an invasive procedure that includes general anesthesia and can result in acute complications, including death [42]. Chronic complications, such as malnutrition and mental illness, are also commonly observed [43-45].
- Therefore, experts recommend selective surgical treatment for patients with morbid obesity that cannot be easily controlled with routine pharmacologic approaches or patients with severe obesity with a body mass index higher than 30 to 35 kg/m2 [46,47]. Significant weight loss is necessary for fat loss of the visceral organs in terms of diabetes remission [48], and metabolic surgery may be an effective method that can induce sufficient and reliable weight loss for severely obese patients.
- Intensive insulin therapy for newly diagnosed patients with severe hyperglycemia
- Remission was observed in newly diagnosed patients with uncontrolled hyperglycemia following 2 to 3 weeks of intensive insulin therapy [49]. In subsequent studies, randomized clinical trials were performed to compare conventional treatment and different insulin treatment methods, and status was evaluated to determine whether remission was reached (Table 3, Fig. 2) [50-54]. Remission following intensive insulin therapy has been demonstrated to last more than 2 years, and it is believed that the shorter the time interval between diagnosis and intensive insulin therapy is, the greater the likelihood of remission [10]. β-cell conservation was also confirmed after intensive treatment early in the disease process [55,56]. Long-term effectiveness of glycemic control was observed in patients who received early combination therapy [57]. Improvement in β-cell function and long-term β-cell preservation was observed in patients treated with short-term intensive insulin therapy [58]. Therefore, early intervention for newly diagnosed T2DM patients is considered one of the strategies.
- The detrimental effects of hyperglycemia itself on β-cell function and insulin action are known [59], and it is established that the amount of time spent in hyperglycemic conditions increases the risk of complications [60-62]. Therefore, proactive treatment intensification has been proposed to minimize the cumulative effect of hyperglycemia. Since the pathogenesis of T2DM is complex, a synergistic effect between several drugs can be expected by using a combination therapy of drugs with various mechanisms. Early combined therapy can prevent delays in glycemic control due to clinical inertia that occurs during sequential intensification. The use of early combination therapy may be superior to reach optimal glycemic control quickly [63,64]. The significant impact of combination therapy in restoring β-cell function is receiving more attention with the development of new drugs [65].
- However, indiscreet use of the initial intensive treatment may result in overtreatment of patients with borderline blood glucose levels, who may have otherwise maintained adequate glycemic control with lifestyle modifications or monotherapy. Combination therapy is expensive [66], and may increase the likelihood of side effects from taking multiple drugs [67]. Elderly patients may require a minimal approach, considering the correlation between hypoglycemia risk and life expectancy. Therefore, a personalized approach is needed because sequential approaches starting with minimal agents could be effective in some patients [68,69].
- Intensive weight management with dietary calorie-restriction
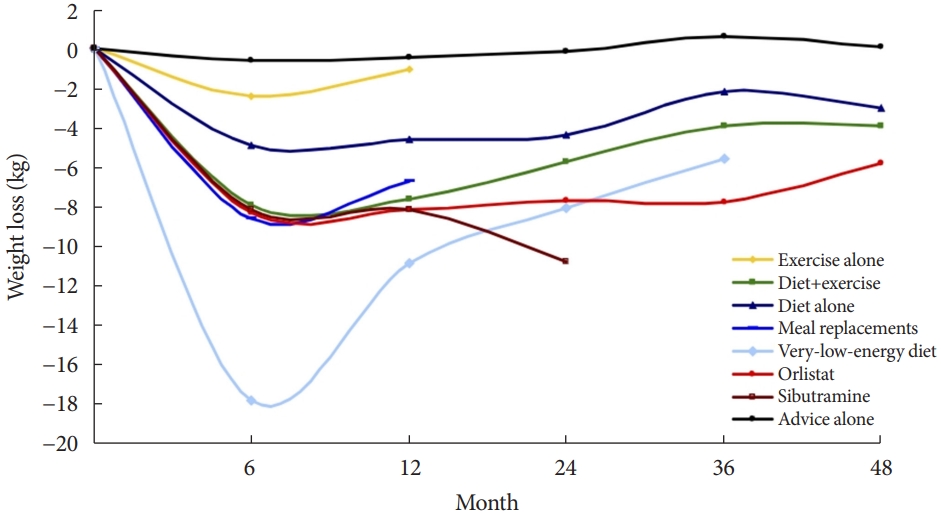
- As a basic method to improve blood glucose control and reduce pancreatic β-cell burden, a lifestyle that reduces calorie intake and increases physical activity is recommended for all diabetic patients [70]. Among lifestyle modification strategies, the favorable effect of caloric restriction on glycemic control could be the most effective strategy in terms of both weight control and glycemic control [71-73]. In the meta-analysis of various weight loss methods, the very-low-calorie diet (VLCD) showed the most significant weight loss effect (Fig. 3).
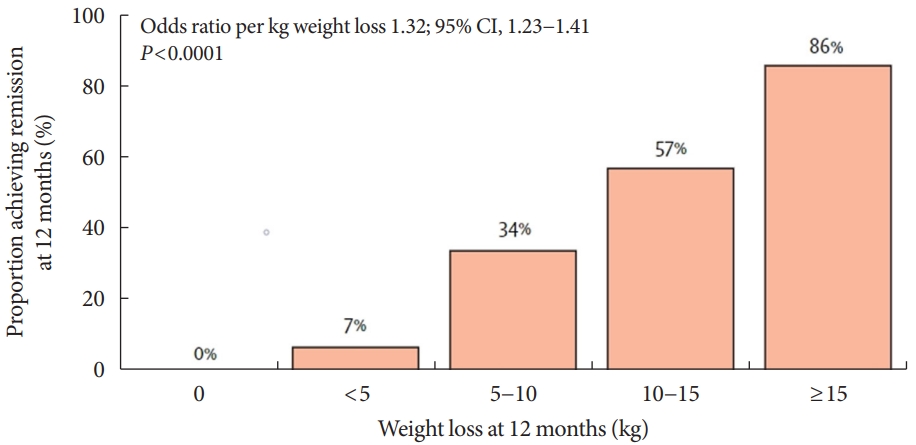
- VLCD refers to a diet that contains 800 kcal or less per day with a relatively high protein-to-calorie ratio and with essential micronutrients. This diet is usually served in liquid form for 3 to 4 months [74]. Researchers considered the VLCD protocol as a therapeutic approach for obese diabetic patients [75]. Recent studies have also evaluated diabetes remission in these patients (Table 4) [76-79]. Lean et al. [78] combined VLCD with routine primary care and confirmed remission in 46% of study subjects. In the study subject group, the greater the weight loss was, the higher the remission rate, which is shown in Fig. 4.
- Although VLCD is generally a safe method, it is recommended that it be performed under medical supervision. Fatigue and gastrointestinal disturbances may occur in the early stages [80,81], and sudden death with arrhythmia has been reported, although it is rare [82]. Currently, VLCD is not recommended for individuals with normal weight [83]. Previous researchers have suggested that preoperative VLCD application to patients with severe obesity planning metabolic surgery can reduce perioperative complications and maximize the effectiveness of surgery [84].
- Development and clinical applications of new drugs
- Recently, developed diabetes drugs have a unique mechanism, causing significant weight loss. For instance, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors act on the proximal convoluted tubule of the kidney to decrease glucose resorption in a way that induces glycosuria, and they have a glucose-lowering effect regardless of insulin secretion or insulin sensitivity [85]. This class of drugs can reduce weight and visceral fat because it is associated with urinary glucose excretion that causes caloric loss [86]. In a clinical trial using SGLT2 inhibitors in addition to basal insulin and metformin as an intensive intervention, the intervention group with SGLT2 inhibitors achieved more remission than compared to the conventional group (24.7% vs. 16.9%), and reduced the risk of diabetes recurrence by 43% [23].
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP1) is a type of incretin hormone that acts in the intestines and inhibits glucagon secretion; various types of GLP1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs) have been developed and used [87]. Liraglutide, a type of GLP1-RA, has been studied to help preserve pancreatic β-cell function when used in early T2DM [88]. Recently, tirzepatide with higher potency has been developed and approved; it is a drug that exhibits dual action in both types of incretins, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and GLP1 [89]. The drug resulted in a remission rate of 66% to 81%, depending on the drug dose over 52 weeks of use in a clinical study [90]. These drugs can produce rare hypoglycemic events and a large weight loss effect [91,92]. Therefore, we may consider these new medications rather than aggressive methods with known medical risks such as surgery, early intensive insulin therapy, and VLCD. However, as these drugs are relatively new methods, clear evidence for diabetes remission is lacking. Further studies are needed on the effects of new drugs on diabetes remission.
- In addition, these newly developed drugs are unavailable for a small number of patients. SGLT2 inhibitors cannot be used for patients with chronic kidney disease, and it has been reported that they may cause ketoacidosis in more patients than conventional drugs [93]. Since GLP1-RAs and tirzepatide are injections, a psychological burden of patients is expected, and side effects such as local reactions at the injection site have been reported. Some patients discontinued the use of the drug due to gastrointestinal symptoms [94]. Moreover, these new drugs are expensive. Therefore, an approach that selects patients who may particularly benefit from this intervention may be necessary.
STRATEGIES FOR THE REMISSION OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
- Dedifferentiation as a mechanism for degenerative changes in insulin-secreting β-cells
- Predispositions that make individuals more susceptible to diabetes include genetic factors [95], the nutritional status of the prenatal period [96], and the environment in the early years of life [97]. β-Cells proliferate and secrete more insulin to adapt to the body’s increasing insulin requirements depending on the degree of weight gain [98]. However, β-cell failure eventually shows a progressive deterioration in which the drug demand gradually increases because of chronic hyperglycemia and overload related to weight gain [99]. Previously, it was explained that β-cells undergo apoptosis and progressively die in the worsening course of diabetes. However, as the concept of dedifferentiation is proposed and studies to support it are presented, it will become the basis for strategies to revitalize β-cells and restore function [100,101].
- Hypothesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus as an intestinal disease
- Rubino, a surgeon who specializes in metabolic surgery, describes diabetes as an operable intestinal disease, and he has paid attention to the improvement of diabetes and its mechanism after bariatric surgery [102]. Glycemic control improves rapidly within days of bariatric surgery, which occurs too quickly to account for weight loss alone [103]. Therefore, the structural change in the intestine was suggested as a mechanism for the improvement of blood glucose control. The change caused by food bypassing the proximal part of the small intestine is called the foregut hypothesis, and the change caused by food rapidly reaching the distal end of the small intestine is called the hindgut hypothesis [104]. The intestinal hormone—incretins play a major role in these changes, and the enteroinsular axis was first proposed in 1969 by Unger and Eisentraut [105] as a mechanism for the association between diabetes and intestinal hormones. They studied gut hormones secreted from intestines that are stimulated by food, particularly by carbohydrates and affect insulin secretion [106]. As a significant hormone associated with diabetes, in particular, GLP1 and GIP are two incretins thought to have a significant effect. Agonists for these hormones have also been developed as diabetes drugs and have shown significant effects, and remission studies for these drugs need to be continued.
- Twin cycle hypothesis and personal fat threshold
- Weight loss and consequent visceral fat loss are key for the remission of diabetes [107]. Some researchers have focused on the pathological role of fatty liver in T2DM in terms of energy balance and metabolic disturbances [108,109]. Fatty liver disease is caused by the storage of extra fat and improves in the early stage of weight loss [110]. Fat reduction according to weight loss varies depending on the body part, and it was reported that 16% of weight loss was accompanied by a 30% intra-abdominal fat reduction and 65% intrahepatic triglyceride loss [111,112]. In 2008, Taylor [20] proposed the twin cycle hypothesis, which posits that T2DM occurs because of a vicious cycle of fat accumulation in the liver and pancreas. Chronic excess energy causes fatty liver and an increase in lipids in systemic circulation if the liver overflows with fat. Fatty liver reduces insulin production and sensitivity and thus leads to a vicious cycle [113]. Finally, fat accumulates in the pancreas, leading to decreased β-cell function. He also proposed the concept of a personal fat threshold to explain the development of diabetes in individuals with relatively low body weight, which is supported by genetic studies associated with the capacity for subcutaneous fat storage [114,115]. Even in prediabetic patients who are of normal weight or slightly overweight who are not obese, weight loss may be helpful to prevent diabetes, which supports the personal fat threshold hypothesis [116].
HOW DOES DIABETES REMISSION OCCUR? PATHOPHYSIOLOGY FOR DIABETES REMISSION
- Because the induction of remission results in relatively drastic changes in the body, selecting the target group and timing of intervention can be crucial points of discussion. Since some individuals have reached remission status after metabolic surgery, an assessment tool has been developed to predict the outcomes of these patients before surgery, and these models are primarily based on whether β-cell function is conserved (c-peptide), the degree to control of diabetes (HbA1c), the severity of diabetes (number of antidiabetic drugs and insulin use), and the duration of diabetes [117-122]. To increase the predictive power, a method that considers the demographics, surgical methods, and comorbidities has also been proposed [123], and recently, attempts have been made to make predictions easier through biochemical biomarkers [124].
- In studies based on metabolic surgery and VLCD, it was reported that younger patients were more likely to reach remission [125]. In addition, the study that enrolled younger patients [77] reported higher remission rates (remission rate at 1 year: 61% vs. 46%) than the study [78] involving relatively older patients (average age of study subjects: 41.9 years vs. 52.9 years). However, in a cohort study in which patients received conventional medical therapy, remission was reported to have a higher prevalence in elderly patients. The remission in the total population was 1.5% [6], whereas the remission in the study targeting the population over 65 years old was 5% [126]. Although weight-based intervention appears to be more effective for patients at a younger age, diabetes in older adults may be more likely to “disappear” in terms of genetic susceptibility and exposure to drugs that can cause diabetes.
- If diabetes is present for a long period of time, patients’ metabolic profiles are less likely to respond to weight changes [125]. The duration of diabetes was an important predictor of remission, which has been consistently reported in several studies [6,117,119,122,127,128]. Most patients treated with multiple antidiabetic drugs could not achieve remission even after significant weight loss following bariatric surgery due to irreversible β-cell damage [129]. In particular, insulin treatment appears to be significant in relation to the severity of diabetes and the degree of preservation of β-cell function [6,118,120-122].
- In summary, factors such as the degree of glycemic control, whether insulin is needed and disease characteristics such as the duration of illness are considered to be significant factors rather than patient factors such as the patient’s age, sex, or BMI. In particular, the most important factor to reach remission may be early intervention for newly diagnosed diabetic patients. As with all diseases, early screening and active early treatment are thought to help improve the prognosis for diabetes.
TIME IS OUTCOME? PREDICTORS OF DIABETES REMISSION
- Individuals who have previously been diagnosed with diabetes are more susceptible to diabetes than other individuals and have a higher risk of relapse. Researchers believe that weight loss and maintenance are key to maintaining remission of T2DM [115,130]. Sometimes the body resists changes following significant weight loss, and weight is easily regained [131]. To form and maintain a healthy lifestyle and to maintain longterm remission of diabetes, the patient’s own will is important, but the cooperation and support of family members, partners, acquaintances, and members of society is essential [132].
- In addition, hyperglycemia appears to continue to affect the body even after it has improved, as the long-term consequences for hyperglycemic conditions, are referred to as the “metabolic memory” or “legacy effect” [133]. This effect is mainly associated with microvascular complications rather than effects on macrovascular complications or survival [134]. It is thought that individuals liberated from hyperglycemia will require continuous surveillance for recurrence and complications even after remission is confirmed.
DOES DIABETES REMISSION PERSIST? THE STORY AFTER REMISSION
- Validation of remission definitions
- The current definition of remission was determined by expert opinion based on the diagnostic criteria for diabetes, and new criteria (including the duration of maintaining remission) or different glucose standards may have to be considered. It may be necessary to lower the cutoff to reduce the risk of recurrence. The consensus of 2021 states that CGM-derived data can be used, but only the eA1c level is presented among the values. The data could be considered a novel metric, such as time in range (TIR), in the evaluation of remission.
- Postdiabetes surveillance
- The consensus recommends that patients with a history of diabetes after remission should undergo testing for glycemic status and complications related to diabetes at 1-year intervals. This is based on reported metabolic memory that is the lasting effect of previous hyperglycemic status despite improved glycemic control [135,136]. Through study of the long-term medical outcomes of patients following remission, how the monitoring cycle should be carried out and which procedures should be used to check for complications can be the subject of additional discussion.
- Social intervention
- With regard to the increase in the incidence of T2DM along with the prevalence of obesity, obesity may be not only a personal problem but also a social burden [137]. Therefore, obesity and related diseases are clearly fields that require intervention from the perspective of public health [138]. From the viewpoint of reducing the incidence of diabetes and the burden of medical expenses, the chronic disease management model for diabetes needs to be changed to a social intervention model for obesity [112], such as one that includes health campaigns for the general population and sugar taxes on food [139,140].
- Studies for Korean ethnicity
- T2DM occurs at an earlier age in Asian populations than in other races. The Asian population shows reduced insulin secretion, low weight tendencies, and many complications [141]. In terms of remission evaluation according to each treatment method, there are relatively few studies conducted in the Asian population, especially for Koreans. Therefore, there is a need for more research on remission in Korea as well as in Western countries.
UNMET NEEDS
- Remission appears to be induced by intensive glycemic control and significant lifestyle change prior to irreversible β-cell changes [142,143]. By implementing short-term intensive insulin therapy in patients with uncontrolled hyperglycemia at an early stage of the disease, β-cell function improves, and remission of T2DM can be secured for a considerable period. In patients who are overweight at the initial stage of diagnosis, remission can be reached in more than half of patients if significant weight loss is induced by methods such as metabolic surgery or VLCD. New drugs, such SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP1-RAs, have a weight loss effect, so they can help to achieve this remission goal in a safer way (Fig. 5). Intensive glycemic control in T2DM increases the likelihood of remission at the earlier stage of the disease and helps to reduce the complications associated with T2DM even if remission is not achieved [144,145]. However, we should be wary of the side effects that accompany these methods, which cause dramatic changes in the body. From the perspective of long-term survival, it is necessary to pay attention to the risk of hypoglycemia in elderly patients, and additional research is needed on the long-term medical outcomes of diabetic remission [146,147]. Patients who have previously been diagnosed with diabetes are exposed to the risks of diabetes-related complications, even in patients who have improved and confirmed remission. Support and continuous medical supervision from family members, friends and medical staff are essential so that they can maintain a healthy lifestyle and screen for comorbidities associated with diabetes. T2DM is not a fate for individuals to helplessly accept. We have discussed the remission of T2DM, which can be achieved through a personalized approach. It may be necessary to change the concept of T2DM towards that of an urgent condition that requires rapid intervention rather than a chronic, progressive disease. We must grasp this paradigm shift in our understanding of T2DM for the benefit of our patients as endocrine experts.
CONCLUSIONS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
FUNDING
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2021R1A2C2013890).
NOTES
-
Acknowledgements
- We thank the copyright holders who gave permission to the figures of this article.


| 2009 [13] | 2021 [14] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Partial remission | Remission | ||
| Hyperglycemia below diagnostic thresholds for diabetes | A return of glycosylated hemoglobin to <6.5% (<48 mmol/mol) that occurs spontaneously or following an intervention and that persists for at least 3 months | ||
| At least 1 year’s duration | |||
| No active pharmacologic therapy or ongoing procedures | |||
| Complete remission | |||
| Normal glycemic measures | Alternative criteria | ||
| At least 1 year’s duration | Fasting plasma glucose <126 mg/dL (<7.0 mmol/L) | ||
| No active pharmacologic therapy or ongoing procedures | Estimated glycosylated hemoglobin <6.5% calculated from continuous glucose monitoring values | ||
| Prolonged remission | |||
| Complete remission of at least 5 years’ duration | |||
| Patients | Type | Number | Follow-up, yr | Weight-loss | End-point | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dixon et al. [31] | T2DM within 2 years BMI 30–40 kg/m2 | AGB vs. conventional therapy | 30 vs. 30 | 2 | 20.7% vs. 1.4% | HbA1c <6.2% | 73% vs. 13% |
| Ding et al. [32] | T2DM BMI 30–45 kg/m2 | AGB vs. ILMI | 23 vs. 22 | 1 | 13.5 kg vs. 8.5 kg | HbA1c <6.5%a | 33% vs. 23% |
| Courcoulas et al. [33] | T2DM BMI 30–40 kg/m2 | RYGB vs. AGB vs. ILMI | 21 vs. 20 vs. 20 | 1 | 27.0% vs. 17.3% vs. 10.2% | HbA1c <5.7% | 27% vs. 23% vs. 0% |
| Schauer et al. [34] | T2DM BMI 27–43 kg/m2 | RYGB vs. SG vs. ILMI | 50 vs. 50 vs. 50 | 1 | 29.4 kg vs. 25.1 kg vs. 5.4 kg | HbA1c <6.0% | 42% vs. 37% vs. 12% |
| Ikramuddin et al. [35] | T2DM BMI 30–40 kg/m2 | RYGB vs. ILMI | 60 vs. 60 | 1 | 26.1% vs. 7.9% | HbA1c <7.0% | 49% vs. 19% |
| Halperin et al. [36] | T2DM within 1 year BMI 30–42 kg/m2 | RYGB vs. ILMI | 19 vs. 19 | 1 | 5.1 kg vs. 1.4 kg | HbA1c <6.5% | 58% vs. 16% |
| Cummings et al. [37] | T2DM BMI 30–45 kg/m2 | RYGB vs. ILMI | 23 vs. 20 | 1 | 25.8% vs. 6.4% | HbA1c <6.0% | 60% vs. 6% |
| Mingrone et al. [38] | T2DM over 5 years BMI over 35 kg/m2 | BPD vs. RYGB vs. ILMI | 20 vs. 20 vs. 20 | 2 | 33.8% vs. 33.3% vs. 4.7% | HbA1c <6.5% | 95% vs. 75% vs. 0% |
| Patients | Type | Number | Follow-up | End-point | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ilkova et al. [50] | Newly diagnosed T2DM | CSII for 2 weeks | 13 | 6 months | FPG <7.8 mmol/L or PPG <10.0 mmol/L | 69% |
| Li et al. [51] | Newly diagnosed T2DM | CSII for 2 weeks | 138 | 2-year | FPG <7.0 mmol/L or PPG <10.0 mmol/L | 42% |
| Weng et al. [52] | Newly diagnosed T2DM | CSII vs. MDI vs. OHA for 2 weeks | 124 vs. 113 vs. 94 | 1-year | FPG <6.1 mmol/L or PPG < 8.0 mmol/L | 51% vs. 45% vs. 27% |
| Chen et al. [53] | Newly diagnosed T2DM | CSII for 2 weeks | 118 | 1-year | FPG <7.0 mmol/L or PPG <10.0 mmol/L | 55% |
| Chon et al. [54] | Newly diagnosed T2DM | MDI vs. OHA for 12 weeks | 50 vs. 47 | 2-year | HbA1c <7% | 47% vs. 23% |
| Patients | Type | Number | Follow-up | Weight-loss | End-point | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lim et al. [76] | T2DM within 4 years BMI 25–45 kg/m2 | VLCD vs. ILMI for 8 weeks | 11 vs. 8 | 2 months | 13.1 kg | FPG <126 mg/dL | 100% |
| Steven et al. [77] | T2DM within 4 years vs. T2DM over 8 years BMI 27–45 kg/m2 | VLCD for 8 weeks | 15 vs. 14 | 2 months | 14.5 kg vs. 13.9 kg | HbA1c <6.5% | 87% vs. 50% |
| Lean et al. [78] | T2DM within 6 years BMI 27–45 kg/m2 | VLCD vs. ILMI for 3–5 months | 149 vs. 149 | 1 year | 10 kg vs. 1 kg | HbA1c <6.5% | 46% vs. 4% |
| Taheri et al. [79] | T2DM within 5 years BMI more than 27 kg/m2 | VLCD vs. ILMI for 12 weeks | 70 vs. 70 | 1 year | 12 kg vs. 4 kg | HbA1c <6.5% | 61% vs. 12% |
- 1. American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes: 2021. Diabetes Care 2021;44(Suppl 1):S15-33.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Schulz LO, Bennett PH, Ravussin E, Kidd JR, Kidd KK, Esparza J, et al. Effects of traditional and western environments on prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians in Mexico and the U.S. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1866-71.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Cnop M, Vidal J, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM, Carr DB, Schraw T, et al. Progressive loss of beta-cell function leads to worsening glucose tolerance in first-degree relatives of subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007;30:677-82.PubMed
- 4. Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA 1999;281:2005-12.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Ramlo-Halsted BA, Edelman SV. The natural history of type 2 diabetes. Implications for clinical practice. Prim Care 1999;26:771-89.PubMed
- 6. Karter AJ, Nundy S, Parker MM, Moffet HH, Huang ES. Incidence of remission in adults with type 2 diabetes: the diabetes & aging study. Diabetes Care 2014;37:3188-95.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 7. Wood GC, Gerhard GS, Benotti P, Petrick AT, Gabrielsen JD, Strodel WE, et al. Preoperative use of incretins is associated with increased diabetes remission after RYGB surgery among patients taking insulin: a retrospective cohort analysis. Ann Surg 2015;261:125-8.PubMed
- 8. Sachs S, Bastidas-Ponce A, Tritschler S, Bakhti M, Bottcher A, Sanchez-Garrido MA, et al. Targeted pharmacological therapy restores β-cell function for diabetes remission. Nat Metab 2020;2:192-209.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Sjostrom L, Lindroos AK, Peltonen M, Torgerson J, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med 2004;351:2683-93.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Kramer CK, Zinman B, Retnakaran R. Short-term intensive insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2013;1:28-34.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Gregg EW, Chen H, Wagenknecht LE, Clark JM, Delahanty LM, Bantle J, et al. Association of an intensive lifestyle intervention with remission of type 2 diabetes. JAMA 2012;308:2489-96.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Zhyzhneuskaya SV, Al-Mrabeh A, Peters C, Barnes A, Aribisala B, Hollingsworth KG, et al. Time course of normalization of functional β-cell capacity in the diabetes remission clinical trial after weight loss in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020;43:813-20.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Buse JB, Caprio S, Cefalu WT, Ceriello A, Del Prato S, Inzucchi SE, et al. How do we define cure of diabetes? Diabetes Care 2009;32:2133-5.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Riddle MC, Cefalu WT, Evans PH, Gerstein HC, Nauck MA, Oh WK, et al. Consensus report: definition and interpretation of remission in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021;44:2438-44.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Mizock BA. Alterations in carbohydrate metabolism during stress: a review of the literature. Am J Med 1995;98:75-84.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Hwang JL, Weiss RE. Steroid-induced diabetes: a clinical and molecular approach to understanding and treatment. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2014;30:96-102.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Buchanan TA, Xiang AH. Gestational diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 2005;115:485-91.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Tayek JA. Is weight loss a cure for type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Care 2002;25:397-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Cummings DE, Overduin J, Foster-Schubert KE. Gastric bypass for obesity: mechanisms of weight loss and diabetes resolution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89:2608-15.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Taylor R. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes: tracing the reverse route from cure to cause. Diabetologia 2008;51:1781-9.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Hanas R, John G; International HBA1c Consensus Committee. 2010 Consensus statement on the worldwide standardization of the hemoglobin A1C measurement. Diabetes Care 2010;33:1903-4.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 22. Bergenstal RM, Beck RW, Close KL, Grunberger G, Sacks DB, Kowalski A, et al. Glucose management indicator (GMI): a new term for estimating A1C from continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 2018;41:2275-80.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. McInnes N, Hall S, Sultan F, Aronson R, Hramiak I, Harris S, et al. Remission of type 2 diabetes following a short-term intervention with insulin glargine, metformin, and dapagliflozin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2020;105:dgaa248.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Miras AD, Perez-Pevida B, Aldhwayan M, Kamocka A, McGlone ER, Al-Najim W, et al. Adjunctive liraglutide treatment in patients with persistent or recurrent type 2 diabetes after metabolic surgery (GRAVITAS): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2019;7:549-59.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Ferrannini E, Mingrone G. Impact of different bariatric surgical procedures on insulin action and beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009;32:514-20.PubMedPMC
- 26. Nannipieri M, Baldi S, Mari A, Colligiani D, Guarino D, Camastra S, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: mechanisms of diabetes remission and role of gut hormones. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013;98:4391-9.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Sjostrom L, Narbro K, Sjostrom CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H, et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med 2007;357:741-52.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Purnell JQ, Dewey EN, Laferrere B, Selzer F, Flum DR, Mitchell JE, et al. Diabetes remission status during seven-year follow-up of the longitudinal assessment of bariatric surgery study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2021;106:774-88.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 29. Purnell JQ, Selzer F, Wahed AS, Pender J, Pories W, Pomp A, et al. Type 2 diabetes remission rates after laparoscopic gastric bypass and gastric banding: results of the longitudinal assessment of bariatric surgery study. Diabetes Care 2016;39:1101-7.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 30. Pories WJ, Caro JF, Flickinger EG, Meelheim HD, Swanson MS. The control of diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) in the morbidly obese with the Greenville Gastric Bypass. Ann Surg 1987;206:316-23.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Dixon JB, O’Brien PE, Playfair J, Chapman L, Schachter LM, Skinner S, et al. Adjustable gastric banding and conventional therapy for type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008;299:316-23.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Ding SA, Simonson DC, Wewalka M, Halperin F, Foster K, Goebel-Fabbri A, et al. Adjustable gastric band surgery or medical management in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015;100:2546-56.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Courcoulas AP, Goodpaster BH, Eagleton JK, Belle SH, Kalarchian MA, Lang W, et al. Surgical vs medical treatments for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg 2014;149:707-15.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, Brethauer SA, Kirwan JP, Pothier CE, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med 2012;366:1567-76.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Ikramuddin S, Korner J, Lee WJ, Connett JE, Inabnet WB, Billington CJ, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs intensive medical management for the control of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia: the Diabetes Surgery Study randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013;309:2240-9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Halperin F, Ding SA, Simonson DC, Panosian J, Goebel-Fabbri A, Wewalka M, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery or lifestyle with intensive medical management in patients with type 2 diabetes: feasibility and 1-year results of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg 2014;149:716-26.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Cummings DE, Arterburn DE, Westbrook EO, Kuzma JN, Stewart SD, Chan CP, et al. Gastric bypass surgery vs intensive lifestyle and medical intervention for type 2 diabetes: the CROSSROADS randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2016;59:945-53.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 38. Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, Guidone C, Iaconelli A, Leccesi L, et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2012;366:1577-85.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, Banel D, Jensen MD, Pories WJ, et al. Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med 2009 122:248-56. e5.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Yu J, Zhou X, Li L, Li S, Tan J, Li Y, et al. The long-term effects of bariatric surgery for type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and non-randomized evidence. Obes Surg 2015;25:143-58.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 41. Heber D, Greenway FL, Kaplan LM, Livingston E, Salvador J, Still C, et al. Endocrine and nutritional management of the post-bariatric surgery patient: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010;95:4823-43.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 42. Smith MD, Patterson E, Wahed AS, Belle SH, Berk PD, Courcoulas AP, et al. Thirty-day mortality after bariatric surgery: independently adjudicated causes of death in the longitudinal assessment of bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 2011;21:1687-92.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 43. Lupoli R, Lembo E, Saldalamacchia G, Avola CK, Angrisani L, Capaldo B. Bariatric surgery and long-term nutritional issues. World J Diabetes 2017;8:464-74.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Morgan DJ, Ho KM, Platell C. Incidence and determinants of mental health service use after bariatric surgery. JAMA Psychiatry 2020;77:60-7.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Omalu BI, Ives DG, Buhari AM, Lindner JL, Schauer PR, Wecht CH, et al. Death rates and causes of death after bariatric surgery for Pennsylvania residents, 1995 to 2004. Arch Surg 2007 142:923-8. discussion 929.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Kasama K, Mui W, Lee WJ, Lakdawala M, Naitoh T, Seki Y, et al. IFSO-APC consensus statements 2011. Obes Surg 2012;22:677-84.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 47. American Diabetes Association. 7. Obesity management for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes: 2018. Diabetes Care 2018;41(Suppl 1):S65-72.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 48. Ryan DH, Yockey SR. Weight loss and improvement in comorbidity: differences at 5%, 10%, 15%, and over. Curr Obes Rep 2017;6:187-94.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 49. Ryan EA, Imes S, Wallace C. Short-term intensive insulin therapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004;27:1028-32.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 50. Ilkova H, Glaser B, Tunckale A, Bagriacik N, Cerasi E. Induction of long-term glycemic control in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients by transient intensive insulin treatment. Diabetes Care 1997;20:1353-6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 51. Li Y, Xu W, Liao Z, Yao B, Chen X, Huang Z, et al. Induction of long-term glycemic control in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients is associated with improvement of beta-cell function. Diabetes Care 2004;27:2597-602.PubMed
- 52. Weng J, Li Y, Xu W, Shi L, Zhang Q, Zhu D, et al. Effect of intensive insulin therapy on beta-cell function and glycaemic control in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a multicentre randomised parallel-group trial. Lancet 2008;371:1753-60.PubMed
- 53. Chen A, Huang Z, Wan X, Deng W, Wu J, Li L, et al. Attitudes toward diabetes affect maintenance of drug-free remission in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes after short-term continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion treatment. Diabetes Care 2012;35:474-81.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 54. Chon S, Rhee SY, Ahn KJ, Baik SH, Park Y, Nam MS, et al. Long-term effects on glycaemic control and β-cell preservation of early intensive treatment in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a multicentre randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 2018;20:1121-30.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 55. Hu Y, Li L, Xu Y, Yu T, Tong G, Huang H, et al. Short-term intensive therapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes partially restores both insulin sensitivity and β-cell function in subjects with long-term remission. Diabetes Care 2011;34:1848-53.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 56. Harrison LB, Adams-Huet B, Raskin P, Lingvay I. β-Cell function preservation after 3.5 years of intensive diabetes therapy. Diabetes Care 2012;35:1406-12.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 57. Matthews DR, Paldanius PM, Proot P, Chiang Y, Stumvoll M, Del Prato S, et al. Glycaemic durability of an early combination therapy with vildagliptin and metformin versus sequential metformin monotherapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (VERIFY): a 5-year, multicentre, randomised, doubleblind trial. Lancet 2019;394:1519-29.ArticlePubMed
- 58. Chen HS, Wu TE, Jap TS, Hsiao LC, Lee SH, Lin HD. Beneficial effects of insulin on glycemic control and beta-cell function in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes with severe hyperglycemia after short-term intensive insulin therapy. Diabetes Care 2008;31:1927-32.PubMedPMC
- 59. Leahy JL, Cooper HE, Deal DA, Weir GC. Chronic hyperglycemia is associated with impaired glucose influence on insulin secretion. A study in normal rats using chronic in vivo glucose infusions. J Clin Invest 1986;77:908-15.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 60. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, et al. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ 2000;321:405-12.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 61. ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2560-72.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Riddle MC. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in the management of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial. Circulation 2010;122:844-6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 63. Nichols GA, Koo YH, Shah SN. Delay of insulin addition to oral combination therapy despite inadequate glycemic control: delay of insulin therapy. J Gen Intern Med 2007;22:453-8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 64. Khunti K, Wolden ML, Thorsted BL, Andersen M, Davies MJ. Clinical inertia in people with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study of more than 80,000 people. Diabetes Care 2013;36:3411-7.PubMedPMC
- 65. De Jesus DF, Kulkarni RN. More is better: combinatorial therapy to restore β-cell function in diabetes. Nat Metab 2020;2:130-1.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 66. Khazrai YM, Buzzetti R, Del Prato S, Cahn A, Raz I, Pozzilli P. The addition of E (Empowerment and Economics) to the ABCD algorithm in diabetes care. J Diabetes Complications 2015;29:599-606.ArticlePubMed
- 67. Lipska KJ, Krumholz H, Soones T, Lee SJ. Polypharmacy in the aging patient: a review of glycemic control in older adults with type 2 diabetes. JAMA 2016;315:1034-45.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes: 2021. Diabetes Care 2021;44(Suppl 1):S111-24.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 69. American Diabetes Association. 12. Older adults: standards of medical care in diabetes: 2021. Diabetes Care 2021;44(Suppl 1):S168-79.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 70. American Diabetes Association. 4. Lifestyle management. Diabetes Care 2017;40(Suppl 1):S33-43.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 71. Henry RR, Scheaffer L, Olefsky JM. Glycemic effects of intensive caloric restriction and isocaloric refeeding in noninsulindependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1985;61:917-25.ArticlePubMed
- 72. Franz MJ, VanWormer JJ, Crain AL, Boucher JL, Histon T, Caplan W, et al. Weight-loss outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of weight-loss clinical trials with a minimum 1-year follow-up. J Am Diet Assoc 2007;107:1755-67.ArticlePubMed
- 73. Spiegelman BM, Flier JS. Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell 2001;104:531-43.ArticlePubMed
- 74. Very low-calorie diets. National task force on the prevention and treatment of obesity, national institutes of health. JAMA 1993;270:967-74.PubMed
- 75. Sellahewa L, Khan C, Lakkunarajah S, Idris I. A systematic review of evidence on the use of very low calorie diets in people with diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev 2017;13:35-46.ArticlePubMed
- 76. Lim EL, Hollingsworth KG, Aribisala BS, Chen MJ, Mathers JC, Taylor R. Reversal of type 2 diabetes: normalisation of beta cell function in association with decreased pancreas and liver triacylglycerol. Diabetologia 2011;54:2506-14.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 77. Steven S, Taylor R. Restoring normoglycaemia by use of a very low calorie diet in long- and short-duration type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 2015;32:1149-55.ArticlePubMed
- 78. Lean ME, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, Brosnahan N, Thom G, McCombie L, et al. Primary care-led weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes (DiRECT): an open-label, clusterrandomised trial. Lancet 2018;391:541-51.ArticlePubMed
- 79. Taheri S, Zaghloul H, Chagoury O, Elhadad S, Ahmed SH, El Khatib N, et al. Effect of intensive lifestyle intervention on bodyweight and glycaemia in early type 2 diabetes (DIADEM-I): an open-label, parallel-group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2020;8:477-89.ArticlePubMed
- 80. Astrup A, Vrist E, Quaade F. Dietary fibre added to very low calorie diet reduces hunger and alleviates constipation. Int J Obes 1990;14:105-12.
- 81. Andersen T. Liver and gallbladder disease before and after very-low-calorie diets. Am J Clin Nutr 1992;56(1 Suppl):235S-9S.ArticlePubMed
- 82. Sours HE, Frattali VP, Brand CD, Feldman RA, Forbes AL, Swanson RC, et al. Sudden death associated with very low calorie weight reduction regimens. Am J Clin Nutr 1981;34:453-61.ArticlePubMed
- 83. Tsai AG, Wadden TA. The evolution of very-low-calorie diets: an update and meta-analysis. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2006;14:1283-93.ArticlePubMed
- 84. Thorell A, MacCormick AD, Awad S, Reynolds N, Roulin D, Demartines N, et al. Guidelines for perioperative care in bariatric surgery: enhanced recovery after surgery (eras) society recommendations. World J Surg 2016;40:2065-83.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 85. Ferrannini E. Sodium-glucose co-transporters and their inhibition: clinical physiology. Cell Metab 2017;26:27-38.ArticlePubMed
- 86. Kuchay MS, Krishan S, Mishra SK, Farooqui KJ, Singh MK, Wasir JS, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on liver fat in patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled trial (E-LIFT trial). Diabetes Care 2018;41:1801-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 87. Nauck M. Incretin therapies: highlighting common features and differences in the modes of action of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Diabetes Obes Metab 2016;18:203-16.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 88. Retnakaran R, Kramer CK, Choi H, Swaminathan B, Zinman B. Liraglutide and the preservation of pancreatic β-cell function in early type 2 diabetes: the LIBRA trial. Diabetes Care 2014;37:3270-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 89. Thomas MK, Nikooienejad A, Bray R, Cui X, Wilson J, Duffin K, et al. Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide improves beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2021;106:388-96.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 90. Del Prato S, Kahn SE, Pavo I, Weerakkody GJ, Yang Z, Doupis J, et al. Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes and increased cardiovascular risk (SURPASS-4): a randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021;398:1811-24.PubMed
- 91. Wilding JP, Batterham RL, Calanna S, Davies M, Van Gaal LF, Lingvay I, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med 2021;384:989.ArticlePubMed
- 92. Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, Greenway F, Halpern A, Krempf M, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N Engl J Med 2015;373:11-22.ArticlePubMed
- 93. Douros A, Lix LM, Fralick M, Dell’Aniello S, Shah BR, Ronksley PE, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and the risk for diabetic ketoacidosis: a multicenter cohort study. Ann Intern Med 2020;173:417-25.PubMed
- 94. Filippatos TD, Panagiotopoulou TV, Elisaf MS. Adverse effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Rev Diabet Stud 2014;11:202-30.ArticlePubMed
- 95. Pal A, McCarthy MI. The genetics of type 2 diabetes and its clinical relevance. Clin Genet 2013;83:297-306.ArticlePubMed
- 96. Poulsen P, Vaag AA, Kyvik KO, Moller Jensen D, Beck-Nielsen H. Low birth weight is associated with NIDDM in discordant monozygotic and dizygotic twin pairs. Diabetologia 1997;40:439-46.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 97. Gunderson EP, Hurston SR, Ning X, Lo JC, Crites Y, Walton D, et al. Lactation and progression to type 2 diabetes mellitus after gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med 2015;163:889-98.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 98. Weir GC, Laybutt DR, Kaneto H, Bonner-Weir S, Sharma A. Beta-cell adaptation and decompensation during the progression of diabetes. Diabetes 2001;50 Suppl 1:S154-9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 99. Alejandro EU, Gregg B, Blandino-Rosano M, Cras-Meneur C, Bernal-Mizrachi E. Natural history of β-cell adaptation and failure in type 2 diabetes. Mol Aspects Med 2015;42:19-41.ArticlePubMed
- 100. Talchai C, Xuan S, Lin HV, Sussel L, Accili D. Pancreatic β cell dedifferentiation as a mechanism of diabetic β cell failure. Cell 2012;150:1223-34.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 101. Cinti F, Bouchi R, Kim-Muller JY, Ohmura Y, Sandoval PR, Masini M, et al. Evidence of β-cell dedifferentiation in human type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016;101:1044-54.ArticlePubMed
- 102. Rubino F. Is type 2 diabetes an operable intestinal disease? A provocative yet reasonable hypothesis. Diabetes Care 2008;31 Suppl 2:S290-6.PubMed
- 103. Rubino F. Bariatric surgery: effects on glucose homeostasis. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2006;9:497-507.ArticlePubMed
- 104. Knop FK. Resolution of type 2 diabetes following gastric bypass surgery: involvement of gut-derived glucagon and glucagonotropic signalling? Diabetologia 2009;52:2270-6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 105. Unger RH, Eisentraut AM. Entero-insular axis. Arch Intern Med 1969;123:261-6.ArticlePubMed
- 106. Creutzfeldt W. The incretin concept today. Diabetologia 1979;16:75-85.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 107. Taylor R. Type 2 diabetes: etiology and reversibility. Diabetes Care 2013;36:1047-55.PubMedPMC
- 108. Taylor R, Al-Mrabeh A, Zhyzhneuskaya S, Peters C, Barnes AC, Aribisala BS, et al. Remission of human type 2 diabetes requires decrease in liver and pancreas fat content but is dependent upon capacity for β cell recovery. Cell Metab 2018;28:547-56.e3.ArticlePubMed
- 109. Eslam M, Sanyal AJ, George J; International Consensus Panel. MAFLD: a consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2020 158:1999-2014. e1.ArticlePubMed
- 110. Fabbrini E, Sullivan S, Klein S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: biochemical, metabolic, and clinical implications. Hepatology 2010;51:679-89.ArticlePubMed
- 111. Magkos F, Fraterrigo G, Yoshino J, Luecking C, Kirbach K, Kelly SC, et al. Effects of moderate and subsequent progressive weight loss on metabolic function and adipose tissue biology in humans with obesity. Cell Metab 2016;23:591-601.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 112. Ryan DH. Energy balance and weight loss for diabetes remission. Diabetes Spectr 2020;33:117-24.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 113. Shibata M, Kihara Y, Taguchi M, Tashiro M, Otsuki M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes in middle-aged Japanese men. Diabetes Care 2007;30:2940-4.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 114. Taylor R, Holman RR. Normal weight individuals who develop type 2 diabetes: the personal fat threshold. Clin Sci (Lond) 2015;128:405-10.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 115. Taylor R, Al-Mrabeh A, Sattar N. Understanding the mechanisms of reversal of type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2019;7:726-36.ArticlePubMed
- 116. Kim ES, Jeong JS, Han K, Kim MK, Lee SH, Park YM, et al. Impact of weight changes on the incidence of diabetes mellitus: a Korean nationwide cohort study. Sci Rep 2018;8:3735.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 117. Lee WJ, Hur KY, Lakadawala M, Kasama K, Wong SK, Chen SC, et al. Predicting success of metabolic surgery: age, body mass index, C-peptide, and duration score. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2013;9:379-84.ArticlePubMed
- 118. Still CD, Wood GC, Benotti P, Petrick AT, Gabrielsen J, Strodel WE, et al. Preoperative prediction of type 2 diabetes remission after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014;2:38-45.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 119. Aron-Wisnewsky J, Sokolovska N, Liu Y, Comaneshter DS, Vinker S, Pecht T, et al. The advanced-DiaRem score improves prediction of diabetes remission 1 year post-Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Diabetologia 2017;60:1892-902.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 120. Aminian A, Brethauer SA, Andalib A, Nowacki AS, Jimenez A, Corcelles R, et al. Individualized metabolic surgery score: procedure selection based on diabetes severity. Ann Surg 2017;266:650-7.PubMed
- 121. Pucci A, Tymoszuk U, Cheung WH, Makaronidis JM, Scholes S, Tharakan G, et al. Type 2 diabetes remission 2 years post Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: the role of the weight loss and comparison of DiaRem and DiaBetter scores. Diabet Med 2018;35:360-7.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 122. Still CD, Benotti P, Mirshahi T, Cook A, Wood GC. DiaRem2: incorporating duration of diabetes to improve prediction of diabetes remission after metabolic surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2019;15:717-24.ArticlePubMed
- 123. Guerron AD, Perez JE, Risoli T Jr, Lee HJ, Portenier D, Corsino L. Performance and improvement of the DiaRem score in diabetes remission prediction: a study with diverse procedure types. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2020;16:1531-42.ArticlePubMed
- 124. Kwee LC, Ilkayeva O, Muehlbauer MJ, Bihlmeyer N, Wolfe B, Purnell JQ, et al. Metabolites and diabetes remission after weight loss. Nutr Diabetes 2021;11:10.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 125. Steven S, Hollingsworth KG, Al-Mrabeh A, Avery L, Aribisala B, Caslake M, et al. Very low-calorie diet and 6 months of weight stability in type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological changes in responders and nonresponders. Diabetes Care 2016;39:808-15.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 126. Tangelloju S, Little BB, Esterhay RJ, Brock G, LaJoie AS. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) “remission” in non-bariatric patients 65 years and older. Front Public Health 2019;7:82.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 127. Ryan DH, Espeland MA, Foster GD, Haffner SM, Hubbard VS, Johnson KC, et al. Look AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes): design and methods for a clinical trial of weight loss for the prevention of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. Control Clin Trials 2003;24:610-28.ArticlePubMed
- 128. Thom G, Messow CM, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, Brosnahan N, McCombie L, et al. Predictors of type 2 diabetes remission in the Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial (DiRECT). Diabet Med 2021;38:e14395.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 129. Madsbad S, Dirksen C, Holst JJ. Mechanisms of changes in glucose metabolism and bodyweight after bariatric surgery. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014;2:152-64.ArticlePubMed
- 130. Lean ME, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, Brosnahan N, Thom G, McCombie L, et al. Durability of a primary care-led weight-management intervention for remission of type 2 diabetes: 2-year results of the DiRECT open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2019;7:344-355.ArticlePubMed
- 131. Sumithran P, Prendergast LA, Delbridge E, Purcell K, Shulkes A, Kriketos A, et al. Long-term persistence of hormonal adaptations to weight loss. N Engl J Med 2011;365:1597-604.ArticlePubMed
- 132. Taylor R, Barnes AC. Translating aetiological insight into sustainable management of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2018;61:273-83.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 133. Ceriello A, Ihnat MA, Thorpe JE. Clinical review 2: the “metabolic memory”: is more than just tight glucose control necessary to prevent diabetic complications? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:410-5.PubMed
- 134. Folz R, Laiteerapong N. The legacy effect in diabetes: are there long-term benefits? Diabetologia 2021;64:2131-7.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 135. Ihnat MA, Thorpe JE, Ceriello A. Hypothesis: the ‘metabolic memory’, the new challenge of diabetes. Diabet Med 2007;24:582-6.ArticlePubMed
- 136. Prattichizzo F, de Candia P, De Nigris V, Nicolucci A, Ceriello A. Legacy effect of intensive glucose control on major adverse cardiovascular outcome: systematic review and meta-analyses of trials according to different scenarios. Metabolism 2020;110:154308.ArticlePubMed
- 137. Oh SH, Ku H, Park KS. Prevalence and socioeconomic burden of diabetes mellitus in South Korean adults: a populationbased study using administrative data. BMC Public Health 2021;21:548.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 138. Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, et al. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet 2006;368:1681-8.ArticlePubMed
- 139. Atienza AA, King AC. Community-based health intervention trials: an overview of methodological issues. Epidemiol Rev 2002;24:72-9.ArticlePubMed
- 140. Brownell KD, Frieden TR. Ounces of prevention: the public policy case for taxes on sugared beverages. N Engl J Med 2009;360:1805-8.ArticlePubMed
- 141. Rhee EJ. Diabetes in Asians. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2015;30:263-9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 142. Kelly J, Karlsen M, Steinke G. Type 2 diabetes remission and lifestyle medicine: a position statement from the American College of Lifestyle Medicine. Am J Lifestyle Med 2020;14:406-19.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 143. Phillips LS, Ratner RE, Buse JB, Kahn SE. We can change the natural history of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2014;37:2668-76.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 144. Skyler JS, Bergenstal R, Bonow RO, Buse J, Deedwania P, Gale EA, et al. Intensive glycemic control and the prevention of cardiovascular events: implications of the ACCORD, ADVANCE, and VA diabetes trials: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and a scientific statement of the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association. Diabetes Care 2009;32:187-92.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 145. Zoungas S, Arima H, Gerstein HC, Holman RR, Woodward M, Reaven P, et al. Effects of intensive glucose control on microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a metaanalysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2017;5:431-7.ArticlePubMed
- 146. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group; Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2545-59.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 147. Reaven PD, Emanuele NV, Wiitala WL, Bahn GD, Reda DJ, McCarren M, et al. Intensive glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes: 15-year follow-up. N Engl J Med 2019;380:2215-24.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Jinyoung Kim, Bongseong Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 567. CrossRef - Mechanisms and the strategy for remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Tien‐Jyun Chang
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(3): 351. CrossRef - Remission of type 2 diabetes: A critical appraisal
Michele Ricci, Juan José Mancebo-Sevilla, Lidia Cobos Palacios, Jaime Sanz-Cánovas, Almudena López-Sampalo, Halbert Hernández-Negrin, Miguel Angel Pérez-Velasco, Luis M. Pérez-Belmonte, Maria Rosa Bernal-López, Ricardo Gómez-Huelgas
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence and predictors of remission and relapse of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japan: Analysis of a nationwide patient registry (JDDM73)
Kazuya Fujihara, Laymon Khin, Koshiro Murai, Yurie Yamazaki, Kahori Tsuruoka, Noriko Yagyuda, Katsuya Yamazaki, Hiroshi Maegawa, Shiro Tanaka, Satoru Kodama, Hirohito Sone
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(8): 2227. CrossRef - Use of SGLT2 inhibitors after bariatric/metabolic surgery: Risk/benefit balance
André J. Scheen
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101453. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Type 2 Diabetes: Further Insights into the Power of Weight Loss and Exercise
Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(3): 302. CrossRef - Unlocking the Potential of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Remission
Prakriti Sharma, Swarupa Chakole
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Global research trends of diabetes remission: a bibliometric study
Xue Yang, Zhiwei He, Qilin Chen, Yu Chen, Guofang Chen, Chao Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gastrointestinal adverse events of tirzepatide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and trials sequential analysis
Keke Tong, Shuang Yin, Yunfeng Yu, Xinyu Yang, Gang Hu, Fei Zhang, Zhenjie Liu
Medicine.2023; 102(43): e35488. CrossRef - Optimal dose of tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
Yunfeng Yu, Gang Hu, Shuang Yin, Xinyu Yang, Manli Zhou, Weixiong Jian
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite