
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
- Pioglitazone as Add-on THERAPY in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Inadequately Controlled with Dapagliflozin and Metformin: Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- Ji Hye Heo, Kyung Ah Han, Jun Hwa Hong, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Jae Myung Yu, Hye Seung Jung, Bong-Soo Cha
- Received September 1, 2023 Accepted October 25, 2023 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0314 [Epub ahead of print]
- 1,226 View
- 121 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study assessed the efficacy and safety of triple therapy with pioglitazone 15 mg add-on versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) inadequately controlled with metformin and dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this multicenter, double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study, patients with T2DM with an inadequate response to treatment with metformin (≥1,000 mg/day) plus dapagliflozin (10 mg/day) were randomized to receive additional pioglitazone 15 mg/day (n=125) or placebo (n=125) for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels from baseline to week 24 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05101135).
Results
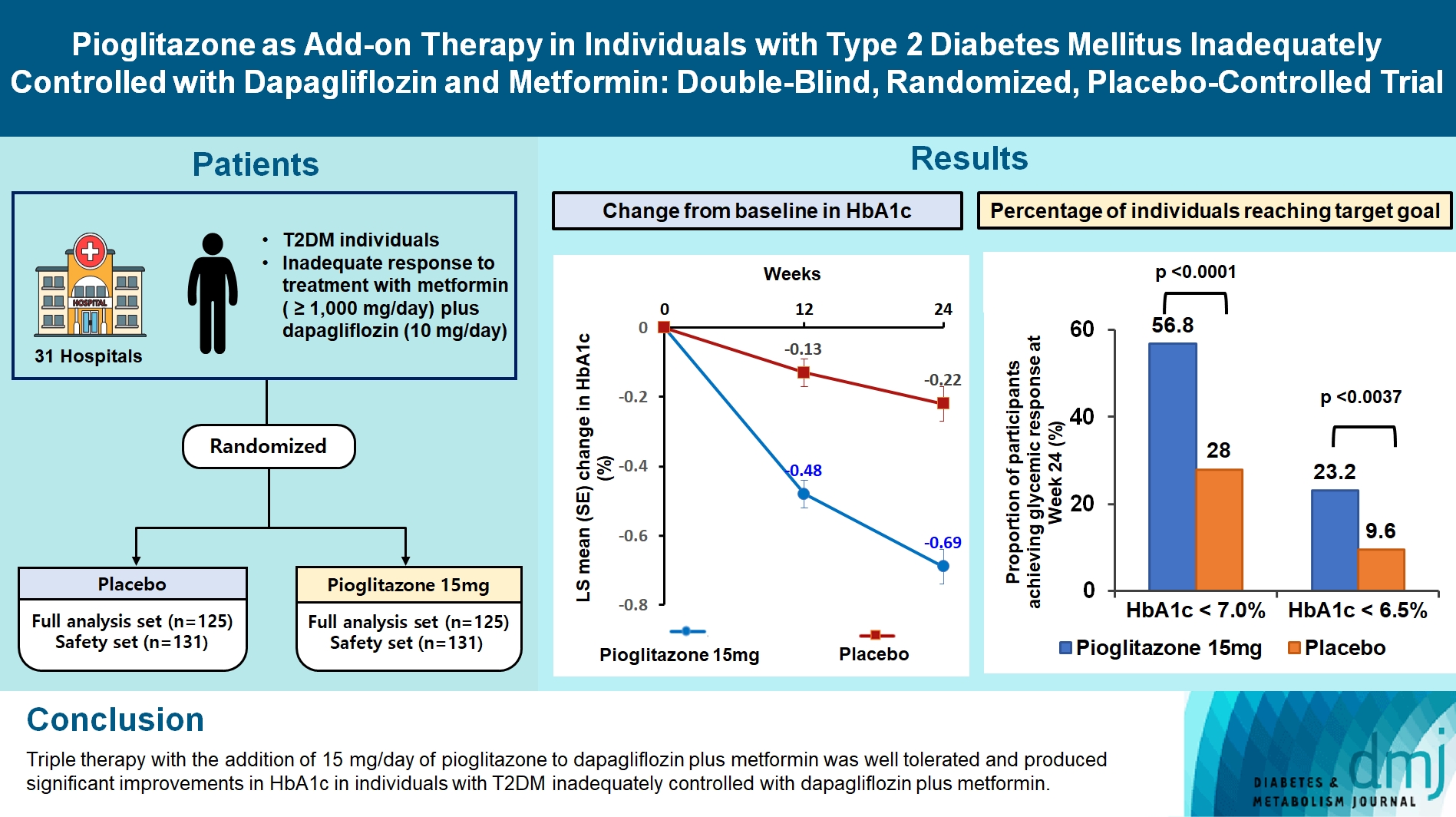
At week 24, the adjusted mean change from baseline in HbA1c level compared with placebo was significantly greater with pioglitazone treatment (–0.47%; 95% confidence interval, –0.61 to –0.33; P<0.0001). A greater proportion of patients achieved HbA1c <7% or <6.5% at week 24 with pioglitazone compared to placebo as add-on to 10 mg dapagliflozin and metformin (56.8% vs. 28% for HbA1c <7%, and 23.2% vs. 9.6% for HbA1c <6.5%; P<0.0001 for all). The addition of pioglitazone also significantly improved triglyceride, highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol levels, and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance levels, while placebo did not. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events was similar between the groups, and the incidence of fluid retention-related side effects by pioglitazone was low (1.5%).
Conclusion
Triple therapy with the addition of 15 mg/day of pioglitazone to dapagliflozin plus metformin was well tolerated and produced significant improvements in HbA1c in patients with T2DM inadequately controlled with dapagliflozin plus metformin.
- Drug/Regimen
- Abrupt Decline in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate after Initiating Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Predicts Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Min-Hsiang Chuang, Yu-Shuo Tang, Jui-Yi Chen, Heng-Chih Pan, Hung-Wei Liao, Wen-Kai Chu, Chung-Yi Cheng, Vin-Cent Wu, Michael Heung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):242-252. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0201
- 1,557 View
- 207 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The initiation of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) typically leads to a reversible initial dip in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). The implications of this phenomenon on clinical outcomes are not well-defined.
Methods
We searched MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane Library from inception to March 23, 2023 to identify randomized controlled trials and cohort studies comparing kidney and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with and without initial eGFR dip after initiating SGLT2i. Pooled estimates were calculated using random-effect meta-analysis.
Results
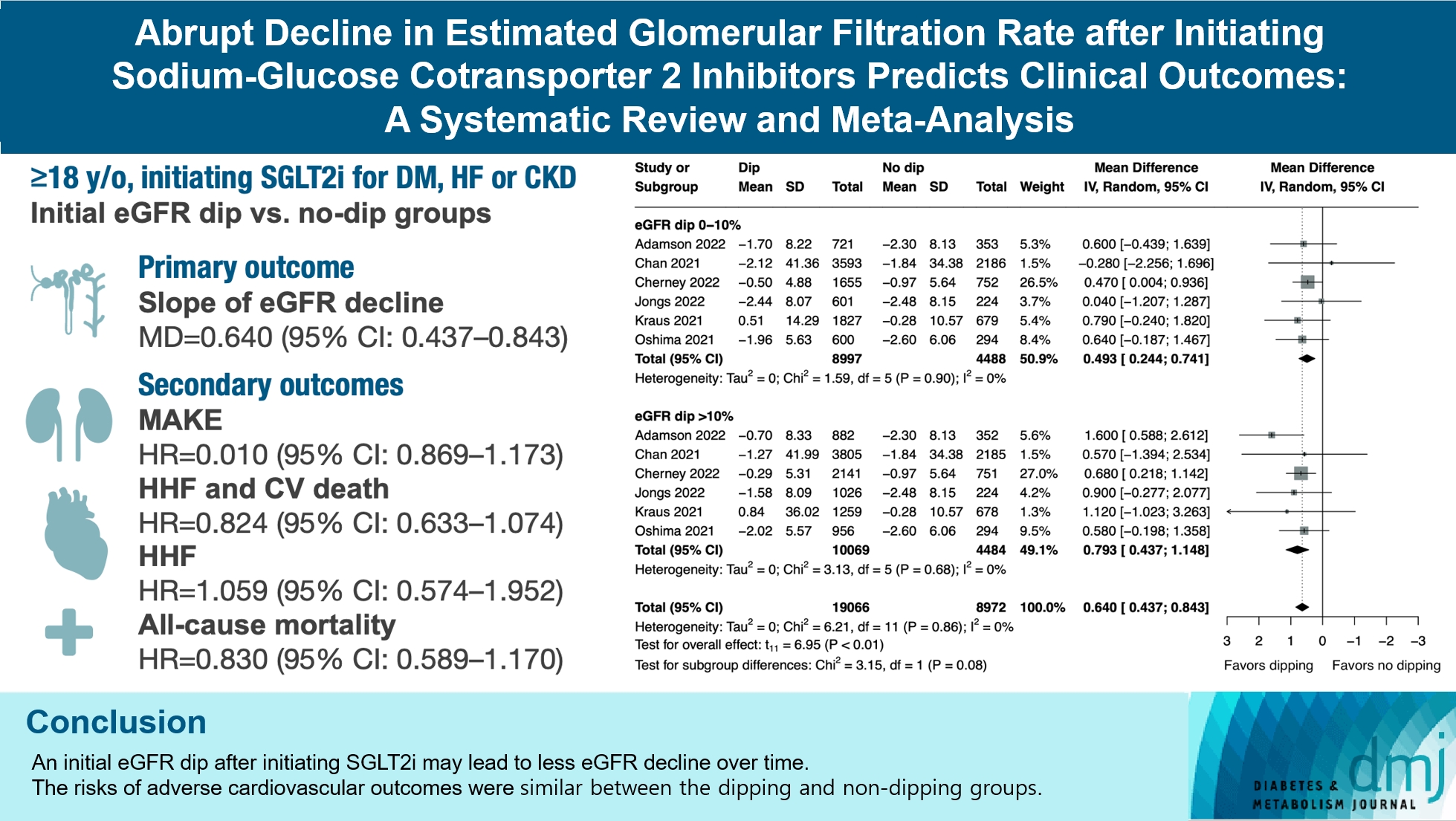
We included seven studies in our analysis, which revealed that an initial eGFR dip following the initiation of SGLT2i was associated with less annual eGFR decline (mean difference, 0.64; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.437 to 0.843) regardless of baseline eGFR. The risk of major adverse kidney events was similar between the non-dipping and dipping groups but reduced in patients with a ≤10% eGFR dip (hazard ratio [HR], 0.915; 95% CI, 0.865 to 0.967). No significant differences were observed in the composite of hospitalized heart failure and cardiovascular death (HR, 0.824; 95% CI, 0.633 to 1.074), hospitalized heart failure (HR, 1.059; 95% CI, 0.574 to 1.952), or all-cause mortality (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.589 to 1.170). The risk of serious adverse events (AEs), discontinuation of SGLT2i due to AEs, kidney-related AEs, and volume depletion were similar between the two groups. Patients with >10% eGFR dip had increased risk of hyperkalemia compared to the non-dipping group.
Conclusion
Initial eGFR dip after initiating SGLT2i might be associated with less annual eGFR decline. There were no significant disparities in the risks of adverse cardiovascular outcomes between the dipping and non-dipping groups.
- Drug/Regimen
- Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Young-Hwan Park, Minji Sohn, So Yeon Lee, Soo Lim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):253-264. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0128
- 1,751 View
- 280 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated the long-term efficacy and safety of initial triple therapy using metformin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
We enrolled 170 drug-naïve patients with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level >7.5% who had started triple therapy (metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin). Glycemic, metabolic, and urinary parameters were measured for 24 months.
Results
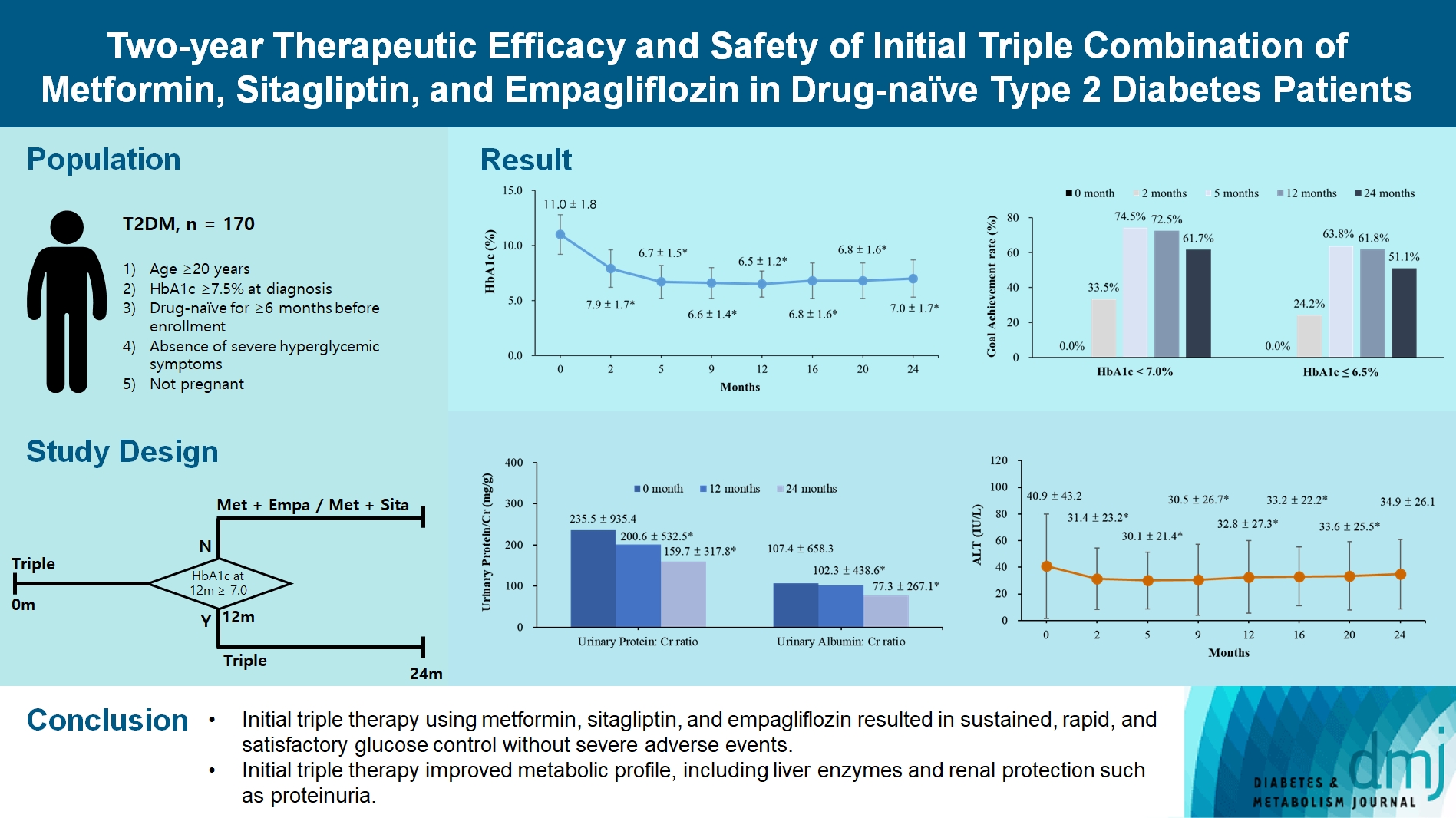
After 24 months, HbA1c level decreased significantly from 11.0%±1.8% to 7.0%±1.7%. At 12 and 24 months, the rates of achievement of the glycemic target goal (HbA1c <7.0%) were 72.5% and 61.7%, respectively, and homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function and insulin resistance indices improved. Whole-body fat percentage decreased by 1.08%, and whole-body muscle percentage increased by 0.97% after 24 months. Fatty liver indices and albuminuria improved significantly. The concentration of ketone bodies was elevated at the baseline but decreased after 24 months. There were no serious adverse events, including ketoacidosis.
Conclusion
Initial triple combination therapy with metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin led to achievement of the glycemic target goal, which was maintained for 24 months without severe hypoglycemia but with improved metabolic function and albuminuria. This combination therapy may be a good strategy for drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Drug/Regimen
- Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy between Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists
- Tzu-Yi Lin, Eugene Yu-Chuan Kang, Shih-Chieh Shao, Edward Chia-Cheng Lai, Sunir J. Garg, Kuan-Jen Chen, Je-Ho Kang, Wei-Chi Wu, Chi-Chun Lai, Yih-Shiou Hwang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):394-404. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0221
- 6,573 View
- 273 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To compare risk of diabetic retinopathy (DR) between patients taking sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) and those taking glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs) in routine care.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study emulating a target trial included patient data from the multi-institutional Chang Gung Research Database in Taiwan. Totally, 33,021 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using SGLT2is and GLP1-RAs between 2016 and 2019 were identified. 3,249 patients were excluded due to missing demographics, age <40 years, prior use of any study drug, a diagnosis of retinal disorders, a history of receiving vitreoretinal procedure, no baseline glycosylated hemoglobin, or no follow-up data. Baseline characteristics were balanced using inverse probability of treatment weighting with propensity scores. DR diagnoses and vitreoretinal interventions served as the primary outcomes. Occurrence of proliferative DR and DR receiving vitreoretinal interventions were regarded as vision-threatening DR.
Results
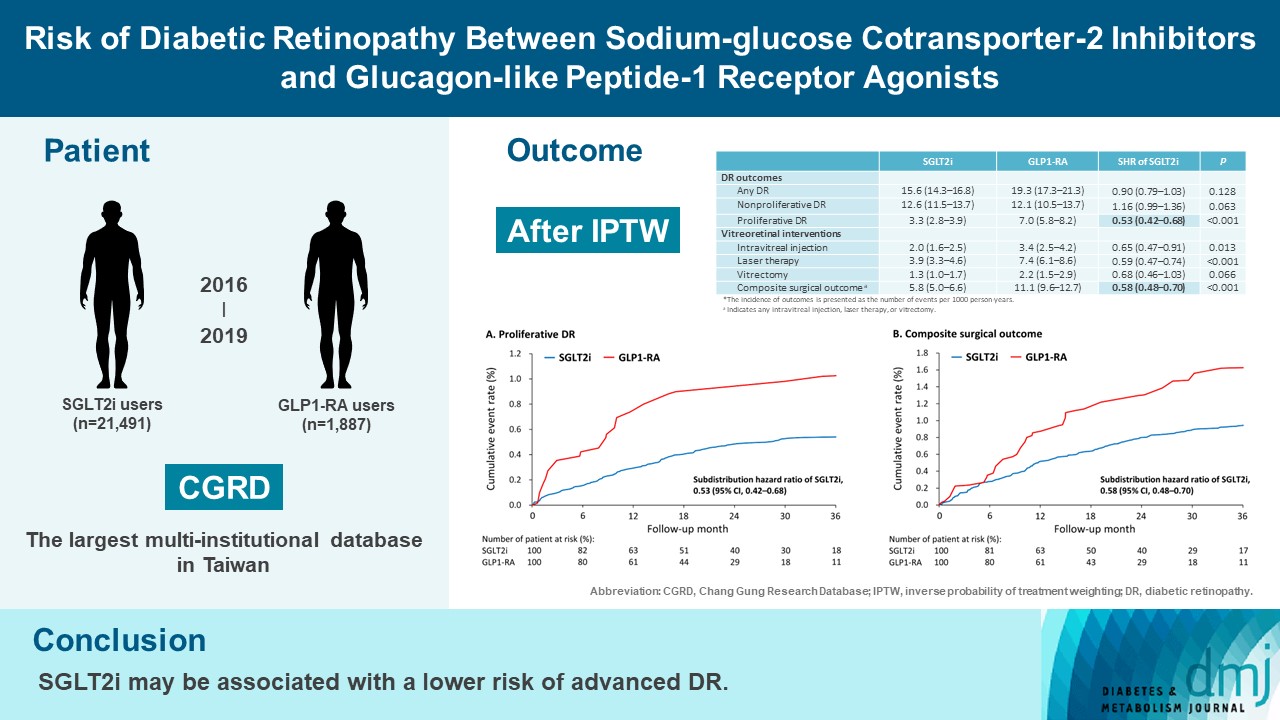
There were 21,491 SGLT2i and 1,887 GLP1-RA users included for the analysis. Patients receiving SGLT2is and GLP-1 RAs exhibited comparable rate of any DR (subdistribution hazard ratio [SHR], 0.90; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.79 to 1.03), whereas the rate of proliferative DR (SHR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.42 to 0.68) was significantly lower in the SGLT2i group. Also, SGLT2i users showed significantly reduced risk of composite surgical outcome (SHR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.48 to 0.70).
Conclusion
Compared to those taking GLP1-RAs, patients receiving SGLT2is had a lower risk of proliferative DR and vitreoretinal interventions, although the rate of any DR was comparable between the SGLT2i and GLP1-RA groups. Thus, SGLT2is may be associated with a lower risk of vision-threatening DR but not DR development. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incretin‐based drugs and the risk of diabetic retinopathy among individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of observational studies
Samuel Igweokpala, Naheemot Olaoluwa Sule, Antonios Douros, Oriana H. Y. Yu, Kristian B. Filion
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 721. CrossRef - Association of sodium–glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitors and the risk of retinal vascular occlusion: A real‐world retrospective cohort study in Taiwan
Tzu‐Yi Lin, Eugene Yu‐Chuan Kang, Shih‐Chieh Shao, Edward Chia‐Cheng Lai, Nan‐Kai Wang, Sunir J. Garg, Kuan‐Jen Chen, Je‐Ho Kang, Wei‐Chi Wu, Chi‐Chun Lai, Yih‐Shiou Hwang
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of rotator cuff tear and rotator cuff repair surgery comparison between sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonists: A real-world study
Yu-Chi Su, Pei-Chun Hsieh, Edward Chia-Cheng Lai, Yu-Ching Lin
Diabetes & Metabolism.2024; 50(2): 101522. CrossRef - Optimising renal risk parameters in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Perspectives from a retinal viewpoint
Sarita Jacob, George I. Varughese
Clinical Medicine.2024; 24(2): 100031. CrossRef - Risk of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema with sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: a real-world data study from a global federated database
Aikaterini Eleftheriadou, David Riley, Sizheng S. Zhao, Philip Austin, Gema Hernández, Gregory Y. H. Lip, Timothy L. Jackson, John P. H. Wilding, Uazman Alam
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of GLP-1 Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors on Diabetic Retinopathy Progression: An Aggregated Electronic Health Record Data Study
Karen M. Wai, Kapil Mishra, Euna Koo, Cassie Ann Ludwig, Ravi Parikh, Prithvi Mruthyunjaya, Ehsan Rahimy
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy between Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:394-404)
Tzu-Yi Lin, Eugene Yu-Chuan Kang, Shih-Chieh Shao, Edward Chia-Cheng Lai, Yih-Shiou Hwang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 573. CrossRef - Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy between Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:394-404)
Jihee Ko, Sun Joon Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 571. CrossRef - Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Risk of Retinopathy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Fu-Shun Yen, James Cheng-Chung Wei, Teng-Shun Yu, Yu-Tung Hung, Chih-Cheng Hsu, Chii-Min Hwu
JAMA Network Open.2023; 6(12): e2348431. CrossRef
- Incretin‐based drugs and the risk of diabetic retinopathy among individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of observational studies
- Drug Regimen
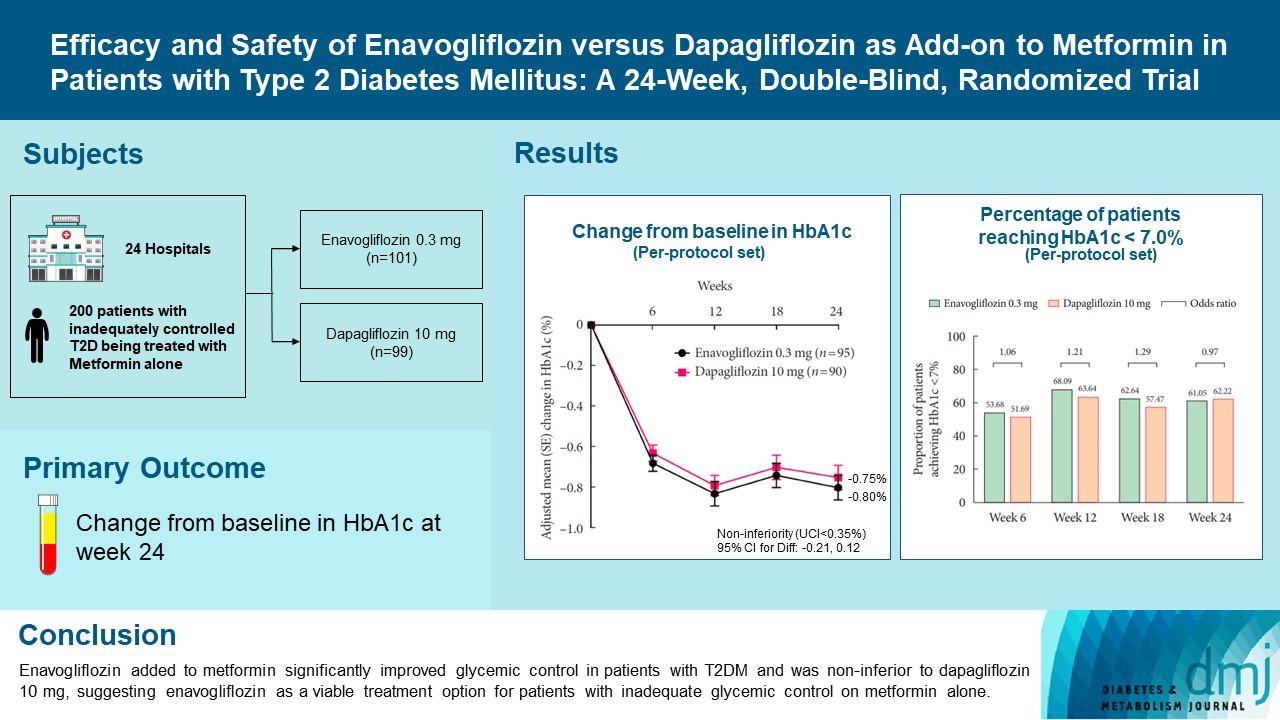
- Efficacy and Safety of Enavogliflozin versus Dapagliflozin as Add-on to Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial
- Kyung Ah Han, Yong Hyun Kim, Doo Man Kim, Byung Wan Lee, Suk Chon, Tae Seo Sohn, In Kyung Jeong, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, Jae Jin Nah, Hwa Rang Song, Seong In Cho, Seung-Ah Cho, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):796-807. Published online February 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0315
- 40,065 View
- 572 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Enavogliflozin is a novel sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor currently under clinical development. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin as an add-on to metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) against dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this multicenter, double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study, 200 patients were randomized to receive enavogliflozin 0.3 mg/day (n=101) or dapagliflozin 10 mg/day (n=99) in addition to ongoing metformin therapy for 24 weeks. The primary objective of the study was to prove the non-inferiority of enavogliflozin to dapagliflozin in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) change at week 24 (non-inferiority margin of 0.35%) (Clinical trial registration number: NCT04634500).
Results
Adjusted mean change of HbA1c at week 24 was –0.80% with enavogliflozin and –0.75% with dapagliflozin (difference, –0.04%; 95% confidence interval, –0.21% to 0.12%). Percentages of patients achieving HbA1c <7.0% were 61% and 62%, respectively. Adjusted mean change of fasting plasma glucose at week 24 was –32.53 and –29.14 mg/dL. An increase in urine glucose-creatinine ratio (60.48 vs. 44.94, P<0.0001) and decrease in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (–1.85 vs. –1.31, P=0.0041) were significantly greater with enavogliflozin than dapagliflozin at week 24. Beneficial effects of enavogliflozin on body weight (–3.77 kg vs. –3.58 kg) and blood pressure (systolic/diastolic, –5.93/–5.41 mm Hg vs. –6.57/–4.26 mm Hg) were comparable with those of dapagliflozin, and both drugs were safe and well-tolerated.
Conclusion
Enavogliflozin added to metformin significantly improved glycemic control in patients with T2DM and was non-inferior to dapagliflozin 10 mg, suggesting enavogliflozin as a viable treatment option for patients with inadequate glycemic control on metformin alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
Young Sang Lyu, Sangmo Hong, Si Eun Lee, Bo Young Cho, Cheol-Young Park
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A 52‐week efficacy and safety study of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin as an add‐on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: ENHANCE‐M extension study
Tae Seo Sohn, Kyung‐Ah Han, Yonghyun Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee, Suk Chon, In‐Kyung Jeong, Eun‐Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, JaeJin Na, Jae Min Cho, Seong In Cho, Wan Huh, Kun‐Ho Yoon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of renal function on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of enavogliflozin, a potent and selective sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes
Sae Im Jeong, Mu Seong Ban, Jun‐Gi Hwang, Min‐Kyu Park, Soo Lim, Sejoong Kim, Soon Kil Kwon, Yoonjin Kim, Jae Min Cho, Jae Jin Na, Wan Huh, Jae‐Yong Chung
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of novel sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor enavogliflozin in type-2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, B.G. Harish, Beatrice Anne, Lakshmi Nagendra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(8): 102816. CrossRef - Characteristics of the Latest Therapeutic Agent for Diabetes
Nuri Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 148. CrossRef - Prospects of using sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)
Iryna Kostitska, Nadia Protas, Liliia Petrovska
Diabetes Obesity Metabolic Syndrome.2023; (5): 8. CrossRef - Navigating the Future of Diabetes Treatment with New Drugs: Focusing on the Possibilities and Prospects of Enavogliflozin
Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 769. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
- Pathophysiology
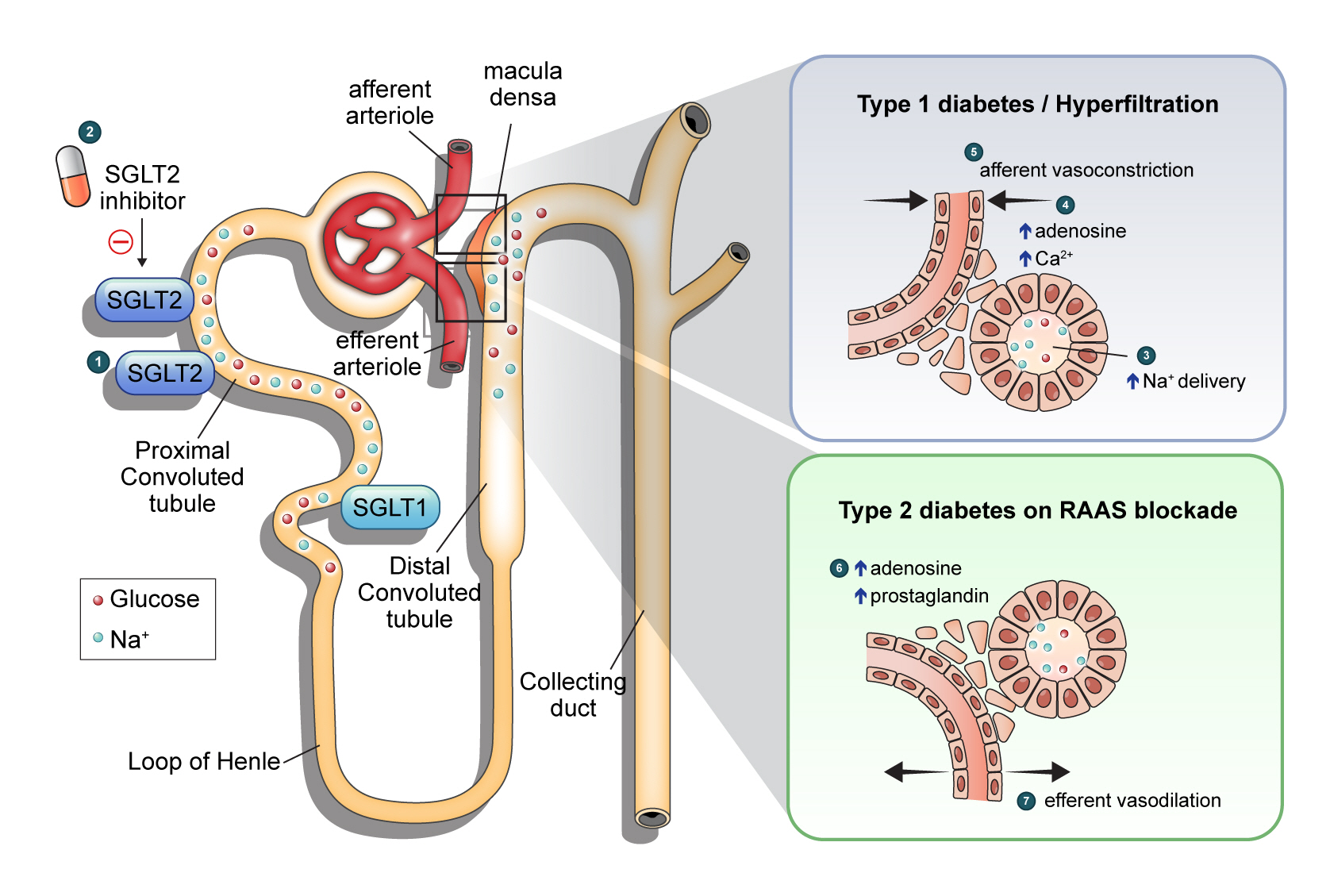
- Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
- Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):543-551. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0209
- 6,425 View
- 675 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a prevalent renal complication of diabetes mellitus that ultimately develops into end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) when not managed appropriately. Substantial risk of ESKD remains even with intensive management of hyperglycemia and risk factors of DKD and timely use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors reduce hyperglycemia primarily by inhibiting glucose and sodium reabsorption in the renal proximal tubule. Currently, their effects expand to prevent or delay cardiovascular and renal adverse events, even in those without diabetes. In dedicated renal outcome trials, SGLT2 inhibitors significantly reduced the risk of composite renal adverse events, including the development of ESKD or renal replacement therapy, which led to the positioning of SGLT2 inhibitors as the mainstay of chronic kidney disease management. Multiple mechanisms of action of SGLT2 inhibitors, including hemodynamic, metabolic, and anti-inflammatory effects, have been proposed. Restoration of tubuloglomerular feedback is a plausible explanation for the alteration in renal hemodynamics induced by SGLT2 inhibition and for the associated renal benefit. This review discusses the clinical rationale and mechanism related to the protection SGLT2 inhibitors exert on the kidney, focusing on renal hemodynamic effects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Using intravoxel incoherent motion imaging to evaluate uric acid-induced renal injury and efficacy after treatment
Zhong-Yuan Cheng, Shang-Ao Gong, Ping-Kang Chen, Zong-Chao Yu, Chen Qiu, Ji-Xin Lin, Jia-Bin Mo, Long Qian, You-Zhen Feng, Xiang-Ran Cai
British Journal of Radiology.2024; 97(1153): 274. CrossRef - Rethinking eGFR Comparisons in SGLT2 Inhibitor Research
Yuzuru Ohshiro
Journal of the American College of Cardiology.2024; 83(9): e87. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibitors and Diabetes: Where Does It Come from and Where Does It Go?
Ji Yoon Kim, Sin Gon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(1): 9. CrossRef - Cardiorenal outcomes and mortality after sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor initiation in type 2 diabetes patients with percutaneous coronary intervention history
Jin Hwa Kim, Young Sang Lyu, BongSeong Kim, Mee Kyung Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Baseline eGFR, albuminuria and renal outcomes in patients with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment: an updated meta-analysis
Yunke Ma, Chu Lin, Xiaoling Cai, Suiyuan Hu, Xingyun Zhu, Fang Lv, Wenjia Yang, Linong Ji
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(3): 435. CrossRef - Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on renal risk factors in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Mengnan Li, Jian Zhang, Guimei Yang, Jiaxin Zhang, Minmin Han, Yi Zhang, Yunfeng Liu
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 79(6): 859. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Exposure–Response Analysis of the Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Dapagliflozin and Empagliflozin on Kidney Hemodynamics in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Sjoukje van der Hoek, Jeroen V. Koomen, Erik J. M. van Bommel, Charlotte M. Mosterd, Rosalie A. Scholtes, Anne C. Hesp, Jasper Stevens, Daniel H. van Raalte, Hiddo J. L. Heerspink
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(5): 747. CrossRef - Osteopontin as a Biomarker in Chronic Kidney Disease
Satyesh K. Sinha, Michael Mellody, Maria Beatriz Carpio, Robert Damoiseaux, Susanne B. Nicholas
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1356. CrossRef - Increased expression of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and O-GlcNAcylation in hepatocytes drives non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hye Jin Chun, Eun Ran Kim, Minyoung Lee, Da Hyun Choi, Soo Hyun Kim, Eugene Shin, Jin-Hong Kim, Jin Won Cho, Dai Hoon Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Metabolism.2023; 145: 155612. CrossRef - Synthesis and biological profile of benzoxazolone derivatives
Parteek Prasher, Tanisqa Mall, Mousmee Sharma
Archiv der Pharmazie.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - SGLT2 inhibitors prevent LPS-induced M1 macrophage polarization and alleviate inflammatory bowel disease by downregulating NHE1 expression
Ye Jin Kim, Jonghwa Jin, Dong-Ho Kim, Daehoon Kim, You Mie Lee, Jun-Kyu Byun, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
Inflammation Research.2023; 72(10-11): 1981. CrossRef
- Using intravoxel incoherent motion imaging to evaluate uric acid-induced renal injury and efficacy after treatment
- Drug/Regimen
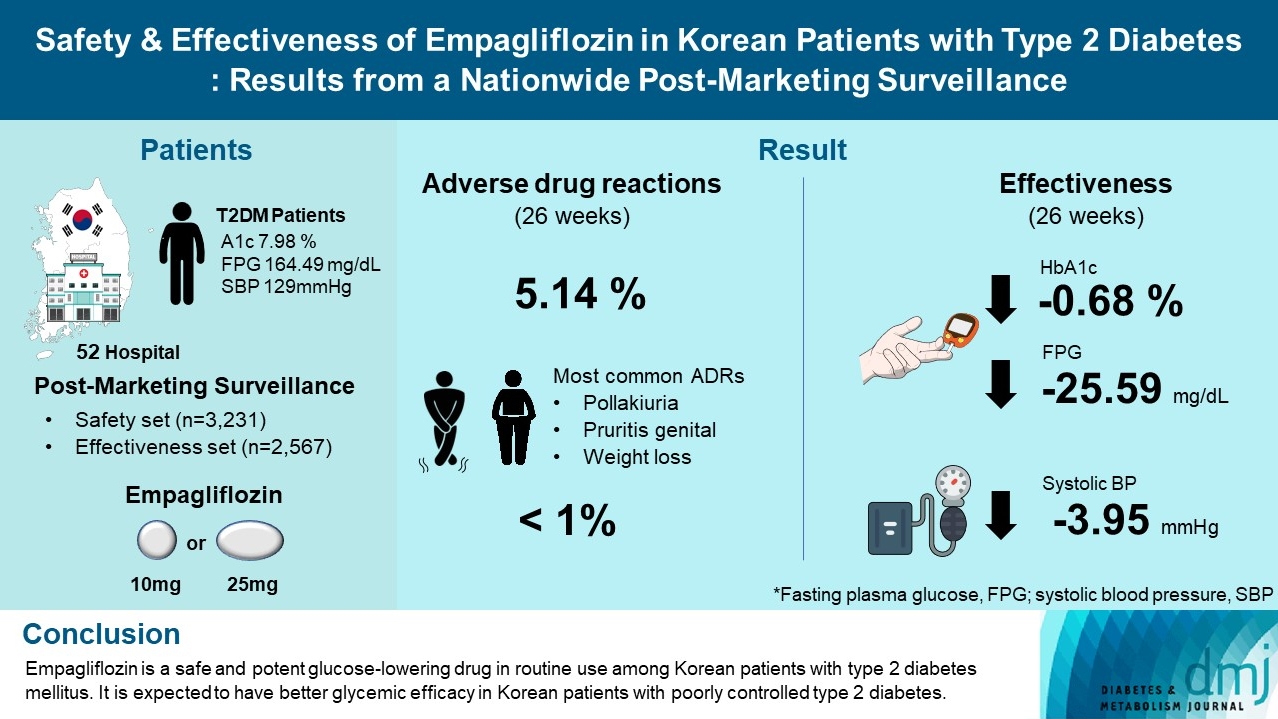
- Safety and Effectiveness of Empagliflozin in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Nationwide Post-Marketing Surveillance
- Jun Sung Moon, Nam Hoon Kim, Jin Oh Na, Jae Hyoung Cho, In-Kyung Jeong, Soon Hee Lee, Ji-Oh Mok, Nan Hee Kim, Dong Jin Chung, Jinhong Cho, Dong Woo Lee, Sun Woo Lee, Kyu Chang Won
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):82-91. Published online June 20, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0356
- 5,979 View
- 295 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of empagliflozin in routine clinical settings, we collected and assessed the clinical profiles of Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
This was a post-marketing surveillance study of empagliflozin 10 and 25 mg. Information on adverse events and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) was collected as safety data sets. Available effectiveness outcomes, including glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level, fasting plasma glucose, body weight, and blood pressure, were assessed.
Results
The incidence rate of ADRs was 5.14% in the safety dataset (n=3,231). Pollakiuria, pruritis genital, and weight loss were the most common ADRs. ADRs of special interest accounted for only 1.18%, and there were no serious events that led to mortality or hospitalization. In the effectiveness data set (n=2,567), empagliflozin significantly reduced the mean HbA1c level and body weight during the study period by –0.68%±1.39% and –1.91±3.37 kg (both P<0.0001), respectively. In addition, shorter disease duration, absence of dyslipidemia, and higher baseline HbA1c levels were identified as the clinical features characteristic of a “responder” to empagliflozin therapy.
Conclusion
Empagliflozin is a safe and potent glucose-lowering drug in routine use among Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is expected to have better glycemic efficacy in Korean patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of Empagliflozin in Bangladeshi Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (EFFISAEM Study)
Mohammad Saifuddin, Ajit Kumar Paul, Sultana Marufa Shefin, Md. Jahangir Alam, Shahjada Selim, Sunjida Islam, Tanjina Hossain, Sadiqa Tuqan, Nusrat Sultana, Marufa Mustari, Ramen Chandra Basak, Kazi Ali Aftab, Indrajit Prasad, Mohammad Rafiq Uddin, Shoma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Two Empagliflozin Formulations in Healthy Korean Subjects
Xu Jiang, Sungyeun Bae, Deok Yong Yoon, Shin Jung Park, Jaeseong Oh, Joo-Youn Cho, Kyung-Sang Yu
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2023; Volume 17: 2137. CrossRef - Comparative safety of different sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Chun Xing Li, Li Yan Liu, Chen Xiao Zhang, Xu Hua Geng, Si Meng Gu, Yu Qiao Wang, Hua Liu, Qing Xie, Shuo Liang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of Empagliflozin in Bangladeshi Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (EFFISAEM Study)
- Drug/Regimen
- Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
- Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):701-712. Published online June 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0002

- 4,934 View
- 319 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate prescription trends and clinical factors of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) use according to the presence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or heart failure (HF) in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Prescription patterns of SGLT2i use between 2015 and 2019 were determined using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database of claims.
Results
Of all patients with T2DM (n=4,736,493), the annual prescription rate of SGLT2i increased every year in patients with ASCVD (from 2.2% to 10.7%) or HF (from 2.0% to 11.1%). After the first hospitalization for ASCVD (n=518,572), 13.7% (n=71,259) of patients initiated SGLT2i with a median of 10.6 months. After hospitalization for HF (n=372,853), 11.2% (n=41,717) of patients initiated SGLT2i after a median of 8.8 months. In multivariate regression for hospitalization, older age (per 10 years, odds ratio [OR], 0.57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.56 to 0.57), lower household income (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.92 to 0.95), rural residents (OR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.93 to 0.97), and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) users (OR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.81 to 0.84) were associated with lesser initiation of SGLT2i in ASCVD. Additionally, female gender (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.95 to 0.99) was associated with lesser initiation of SGLT2i in HF.
Conclusion
The prescription rate of SGLT2i increased gradually up to 2019 but was suboptimal in patients with ASCVD or HF. After the first hospitalization for ASCVD or HF, older age, female gender, low household income, rural residents, and DPP-4i users were less likely to initiate SGLT2i. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024; 15(3): 285. CrossRef - Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Hospital Readmissions for Fluid Overload among Individuals with Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease: Risk Factors and Multivariable Prediction Models
Jiashen Cai, Dorothy Huang, Hanis Binte Abdul Kadir, Zhihua Huang, Li Choo Ng, Andrew Ang, Ngiap Chuan Tan, Yong Mong Bee, Wei Yi Tay, Chieh Suai Tan, Cynthia C. Lim
Nephron.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Prescribing patterns of SGLT-2 inhibitors for patients with heart failure: A two-center analysis
Teja Chakrala, Roshni O. Prakash, Justin Kim, Hanzhi Gao, Umar Ghaffar, Jaymin Patel, Alex Parker, Bhagwan Dass
American Heart Journal Plus: Cardiology Research and Practice.2023; 28: 100286. CrossRef - Risk of developing chronic kidney disease in young-onset Type 2 diabetes in Korea
Joonyub Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae Hyoung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Yeoree Yang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of SGLT2 inhibitors with DPP-4 inhibitors combined with metformin in patients with acute myocardial infarction and diabetes mellitus
Young Sang Lyu, Seok Oh, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Myung Ho Jeong
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 759. CrossRef
- Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
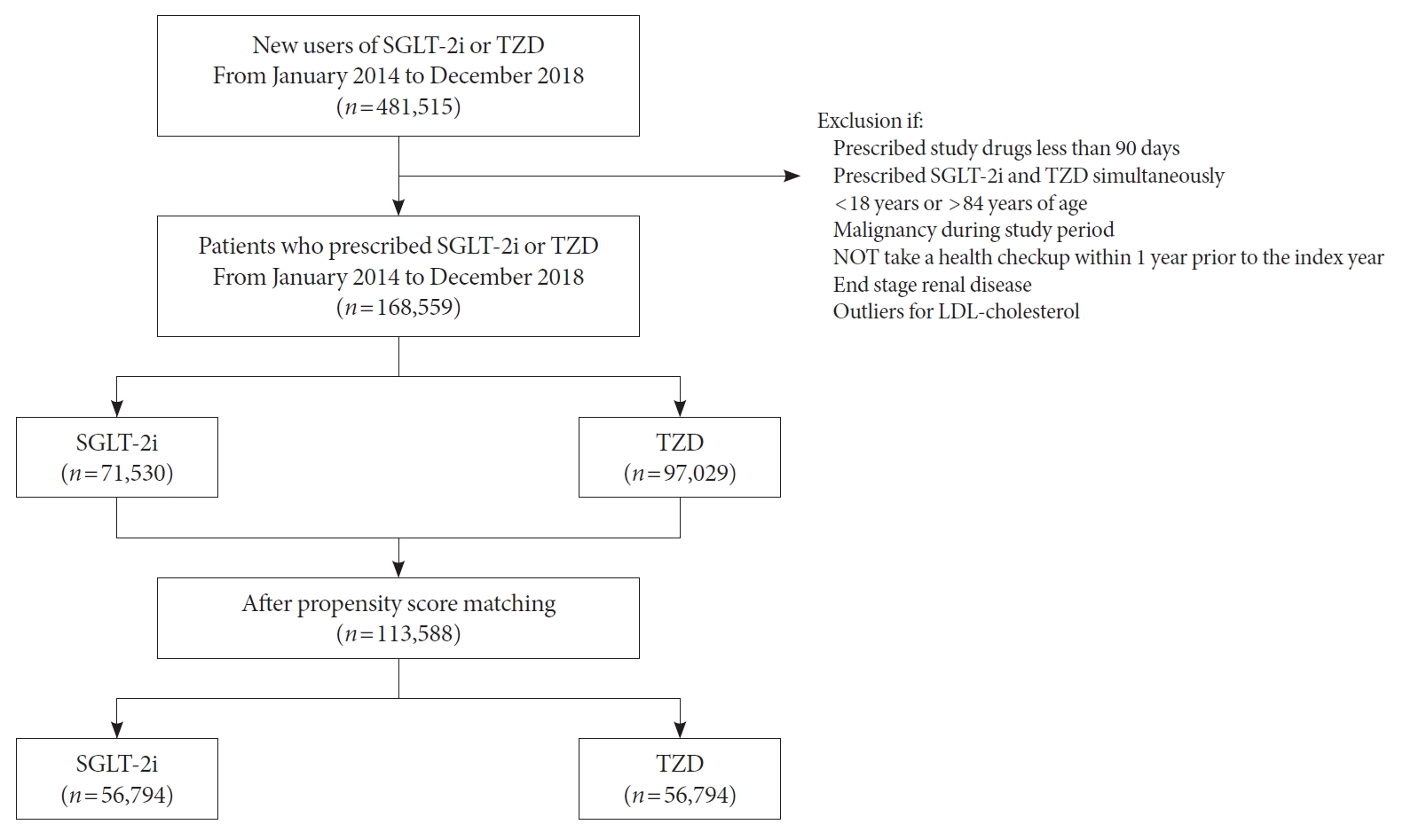
- Comparative Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor and Thiazolidinedione Treatment on Risk of Stroke among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Seung Eun Lee, Hyewon Nam, Han Seok Choi, Hoseob Kim, Dae-Sung Kyoung, Kyoung-Ah Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):567-577. Published online February 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0160
- 5,450 View
- 360 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Although cardiovascular outcome trials using sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) showed a reduction in risk of 3-point major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), they did not demonstrate beneficial effects on stroke risk. Additionally, meta-analysis showed SGLT-2i potentially had an adverse effect on stroke risk. Contrarily, pioglitazone, a type of thiazolidinedione (TZD), has been shown to reduce recurrent stroke risk. Thus, we aimed to compare the effect of SGLT-2i and TZD on the risk of stroke in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
Methods
Using the Korean National Health Insurance Service data, we compared a 1:1 propensity score-matched cohort of patients who used SGLT-2i or TZD from January 2014 to December 2018. The primary outcome was stroke. The secondary outcomes were myocardial infarction (MI), cardiovascular death, 3-point MACE, and heart failure (HF).
Results
After propensity-matching, each group included 56,794 patients. Baseline characteristics were well balanced. During the follow-up, 862 patients were newly hospitalized for stroke. The incidence rate of stroke was 4.11 and 4.22 per 1,000 person-years for the TZD and SGLT-2i groups respectively. The hazard ratio (HR) of stroke was 1.054 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.904 to 1.229) in the SGLT-2i group compared to the TZD group. There was no difference in the risk of MI, cardiovascular death, 3-point MACE between groups. Hospitalization for HF was significantly decreased in SGLT-2i-treated patients (HR, 0.645; 95% CI, 0.466 to 0.893). Results were consistent regardless of prior cardiovascular disease.
Conclusion
In this real-world data, the risk of stroke was comparable in T2DM patients treated with SGLT-2i or TZD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Similar incidence of stroke with SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in real-world cohort studies among patients with type 2 diabetes
André J. Scheen
Diabetes Epidemiology and Management.2024; 13: 100179. CrossRef - Lobeglitazone, a novel thiazolidinedione, for secondary prevention in patients with ischemic stroke: a nationwide nested case-control study
Joonsang Yoo, Jimin Jeon, Minyoul Baik, Jinkwon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Do SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists modulate differently the risk of stroke ? Discordance between randomised controlled trials and observational studies
André J. Scheen
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(5): 101474. CrossRef
- Similar incidence of stroke with SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in real-world cohort studies among patients with type 2 diabetes
- Drug/Regimen
- Clinical Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Study
- Hwi Seung Kim, Taekwan Yoon, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):658-662. Published online November 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0232
- 65,535 View
- 387 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) are novel anti-diabetic drugs whose glucose-lowering effect and cardiovascular and renal benefits were evidenced in clinical trials. We investigated the real-world efficacy and safety of the combination of SGLT2i and GLP-1RA in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea. The medical records of 104 patients who maintained the combination for at least 1 year were retrospectively reviewed. The change in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) after 6 months and 1 year of treatment was evaluated. The mean age was 51 years, and 41% were female. The mean baseline HbA1c, body mass index, and duration of diabetes were 9.0%, 28.8 kg/m2, and 11.7 years, respectively. Compared with baseline, the HbA1c decreased by 1.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.27 to 1.74; P<0.001) after 6 months and by 1.4% (95% CI, 1.19 to 1.70; P<0.001) after 1 year. Over 1 year, the bodyweight change was −2.8 kg (95% CI, −4.21 to −1.47; P<0.001). The combination of SGLT2i and GLP-1RA is effective and tolerable in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in real-world practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness and safety of the combination of sodium–glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Aftab Ahmad, Hani Sabbour
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hormonal Gut–Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3384. CrossRef - All‐cause mortality and cardiovascular outcomes with sodium‐glucose Co‐transporter 2 inhibitors, glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists and with combination therapy in people with type 2 diabetes
David R. Riley, Hani Essa, Philip Austin, Frank Preston, Isatu Kargbo, Gema Hernández Ibarburu, Ramandeep Ghuman, Daniel J. Cuthbertson, Gregory Y. H. Lip, Uazman Alam
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(10): 2897. CrossRef - The Efficacy and Safety of the Combination Therapy With GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Chen Li, Jie Luo, Mingyan Jiang, Keke Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Study (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46: 658-62)
Hwi Seung Kim, Woo Je Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 665. CrossRef - Clinical Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Study (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46: 658-62)
Tomoyuki Kawada
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 663. CrossRef - Durability of glucose-lowering effect of dulaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A real-world data study
Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Myung Jin Kim, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effectiveness and safety of the combination of sodium–glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- Basic Research
-
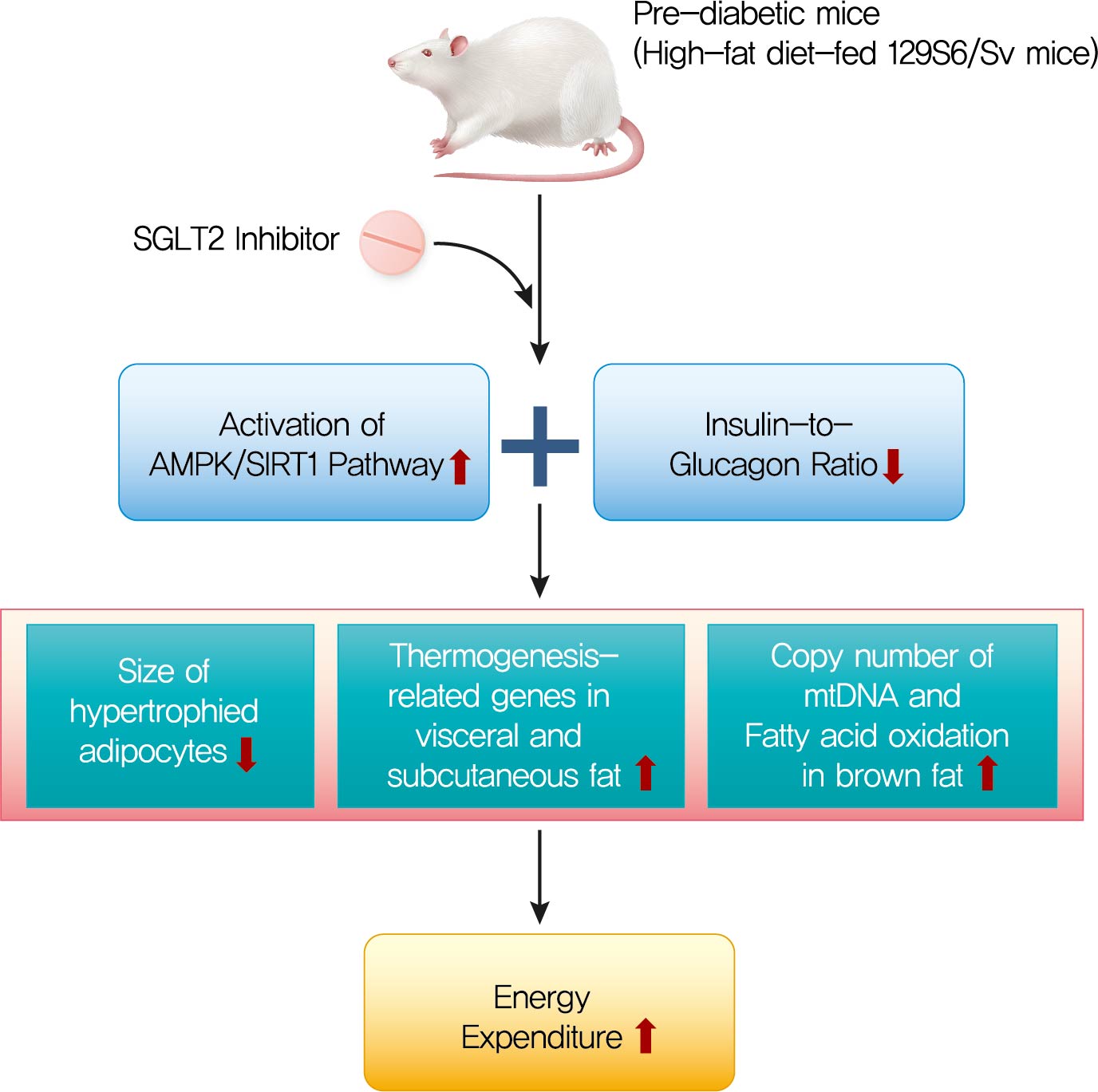
- Ipragliflozin, an SGLT2 Inhibitor, Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Changes by Upregulating Energy Expenditure through Activation of the AMPK/ SIRT1 Pathway
- Ji-Yeon Lee, Minyoung Lee, Ji Young Lee, Jaehyun Bae, Eugene Shin, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):921-932. Published online February 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0187
- 8,479 View
- 410 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are a new class of antidiabetic drugs that exhibit multiple extraglycemic effects. However, there are conflicting results regarding the effects of SGLT2 inhibition on energy expenditure and thermogenesis. Therefore, we investigated the effect of ipragliflozin (a selective SGLT2 inhibitor) on energy metabolism.
Methods
Six-week-old male 129S6/Sv mice with a high propensity for adipose tissue browning were randomly assigned to three groups: normal chow control, 60% high-fat diet (HFD)-fed control, and 60% HFD-fed ipragliflozin-treated groups. The administration of diet and medication was continued for 16 weeks.
Results
The HFD-fed mice became obese and developed hepatic steatosis and adipose tissue hypertrophy, but their random glucose levels were within the normal ranges; these features are similar to the metabolic features of a prediabetic condition. Ipragliflozin treatment markedly attenuated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis and reduced the size of hypertrophied adipocytes to that of smaller adipocytes. In the ipragliflozin treatment group, uncoupling protein 1 (Ucp1) and other thermogenesis-related genes were significantly upregulated in the visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue, and fatty acid oxidation was increased in the brown adipose tissue. These effects were associated with a significant reduction in the insulin-to-glucagon ratio and the activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) pathway in the liver and adipose tissue.
Conclusion
SGLT2 inhibition by ipragliflozin showed beneficial metabolic effects in 129S6/Sv mice with HFD-induced obesity that mimics prediabetic conditions. Our data suggest that SGLT2 inhibitors, through their upregulation of energy expenditure, may have therapeutic potential in prediabetic obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SGLT2 inhibitors and AMPK: The road to cellular housekeeping?
Nasser Safaie, Shahab Masoumi, Shaban Alizadeh, Pourya Mirzajanzadeh, Hamid Reza Nejabati, Mobasher Hajiabbasi, Vahid Alivirdiloo, Neda Chobdari Basmenji, Aysan Derakhshi Radvar, Ziba Majidi, Yousef Faridvand
Cell Biochemistry and Function.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanisms of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure and Their Clinical Value
Yafei Xie, Yujie Wei, Dan Li, Jie Pu, Hong Ding, Xiaowei Zhang
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology.2023; 81(1): 4. CrossRef - Current Treatment Options, Including Diet, Exercise, and Medications
Mazen Noureddin, Manal F. Abdelmalek
Clinics in Liver Disease.2023; 27(2): 397. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibitors and Kidney Diseases: A Clinical Perspective
Panagiotis Theofilis, Rigas G. Kalaitzidis
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 30(23): 2595. CrossRef - Treatment of obesity-related diabetes: significance of thermogenic adipose tissue and targetable receptors
Ruping Pan, Jiadai Liu, Yong Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunomodulatory Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors—Targeting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Aging
Ema Schönberger, Vjera Mihaljević, Kristina Steiner, Sandra Šarić, Tomislav Kurevija, Ljiljana Trtica Majnarić, Ines Bilić Ćurčić, Silvija Canecki-Varžić
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(17): 6671. CrossRef - SGLT‐2 inhibitors enhance the effect of metformin to ameliorate hormonal changes and inflammatory markers in a rat PCOS model
Manal Moustafa Mahmoud, Laila Ahmed Rashed, Somia Abdulatif Soliman, Safaa Mostafa Sayed, Omneya Kamel, Samaa Samir Kamar, Rania El Sayed Hussien
Physiological Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resting energy expenditure based on equation estimation can predict renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and biopsy-proven diabetic kidney disease
Xiang Xiao, Shuming Ji, Junlin Zhang, Deying Kang, Fang Liu
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium-glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Pathological Myocardial
Hypertrophy
Zhicheng Gao, Jiaqi Bao, Yilan Hu, Junjie Tu, Lifang Ye, Lihong Wang
Current Drug Targets.2023; 24(13): 1009. CrossRef - SIRT1 mediates the inhibitory effect of Dapagliflozin on EndMT by inhibiting the acetylation of endothelium Notch1
Weijie Wang, Yilan Li, Yanxiu Zhang, Tao Ye, Kui Wang, Shuijie Li, Yao Zhang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Direct cardio-protection of Dapagliflozin against obesity-related cardiomyopathy via NHE1/MAPK signaling
Ke Lin, Na Yang, Wu Luo, Jin-fu Qian, Wei-wei Zhu, Shi-ju Ye, Chen-xin Yuan, Di-yun Xu, Guang Liang, Wei-jian Huang, Pei-ren Shan
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2022; 43(10): 2624. CrossRef - Pleiotropic effects of SGLT2 inhibitors and heart failure outcomes
Panagiotis Theofilis, Marios Sagris, Evangelos Oikonomou, Alexios S. Antonopoulos, Gerasimos Siasos, Kostas Tsioufis, Dimitris Tousoulis
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 188: 109927. CrossRef - Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in the Regulation of Inflammatory Processes in Animal Models
Sandra Feijóo-Bandín, Alana Aragón-Herrera, Manuel Otero-Santiago, Laura Anido-Varela, Sandra Moraña-Fernández, Estefanía Tarazón, Esther Roselló-Lletí, Manuel Portolés, Oreste Gualillo, José Ramón González-Juanatey, Francisca Lago
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5634. CrossRef - Potential molecular mechanism of action of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in the prevention and management of diabetic retinopathy
Lia Meuthia Zaini, Arief S Kartasasmita, Tjahjono D Gondhowiardjo, Maimun Syukri, Ronny Lesmana
Expert Review of Ophthalmology.2022; 17(3): 199. CrossRef - New insights and advances of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in heart failure
Juexing Li, Lei Zhou, Hui Gong
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Critical Reanalysis of the Mechanisms Underlying the Cardiorenal Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors and Reaffirmation of the Nutrient Deprivation Signaling/Autophagy Hypothesis
Milton Packer
Circulation.2022; 146(18): 1383. CrossRef - Nutraceutical activation of Sirt1: a review
James J DiNicolantonio, Mark F McCarty, James H O'Keefe
Open Heart.2022; 9(2): e002171. CrossRef - Dapagliflozin Restores Impaired Autophagy and Suppresses Inflammation in High Glucose-Treated HK-2 Cells
Jing Xu, Munehiro Kitada, Yoshio Ogura, Haijie Liu, Daisuke Koya
Cells.2021; 10(6): 1457. CrossRef - Could Sodium/Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibitors Have Antiarrhythmic Potential in Atrial Fibrillation? Literature Review and Future Considerations
Dimitrios A. Vrachatis, Konstantinos A. Papathanasiou, Konstantinos E. Iliodromitis, Sotiria G. Giotaki, Charalampos Kossyvakis, Konstantinos Raisakis, Andreas Kaoukis, Vaia Lambadiari, Dimitrios Avramides, Bernhard Reimers, Giulio G. Stefanini, Michael C
Drugs.2021; 81(12): 1381. CrossRef - Differential Pathophysiological Mechanisms in Heart Failure With a Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction in Diabetes
Milton Packer
JACC: Heart Failure.2021; 9(8): 535. CrossRef - Ketone bodies: from enemy to friend and guardian angel
Hubert Kolb, Kerstin Kempf, Martin Röhling, Martina Lenzen-Schulte, Nanette C. Schloot, Stephan Martin
BMC Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- SGLT2 inhibitors and AMPK: The road to cellular housekeeping?
- Complications
- Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Current and Future
- Tomotaka Yamazaki, Imari Mimura, Tetsuhiro Tanaka, Masaomi Nangaku
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):11-26. Published online January 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0217
- 19,291 View
- 1,328 Download
- 92 Web of Science
- 92 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is the major cause of end-stage kidney disease. However, only renin-angiotensin system inhibitor with multidisciplinary treatments is effective for DKD. In 2019, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor showed efficacy against DKD in Canagliflozin and Renal Events in Diabetes with Established Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation (CREDENCE) trial, adding a new treatment option. However, the progression of DKD has not been completely controlled. The patients with transient exposure to hyperglycemia develop diabetic complications, including DKD, even after normalization of their blood glucose. Temporary hyperglycemia causes advanced glycation end product (AGE) accumulations and epigenetic changes as metabolic memory. The drugs that improve metabolic memory are awaited, and AGE inhibitors and histone modification inhibitors are the focus of clinical and basic research. In addition, incretin-related drugs showed a renoprotective ability in many clinical trials, and these trials with renal outcome as their primary endpoint are currently ongoing. Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors recently approved for renal anemia may be renoprotective since they improve tubulointerstitial hypoxia. Furthermore, NF-E2–related factor 2 activators improved the glomerular filtration rate of DKD patients in Bardoxolone Methyl Treatment: Renal Function in chronic kidney disease/Type 2 Diabetes (BEAM) trial and Phase II Study of Bardoxolone Methyl in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes (TSUBAKI) trial. Thus, following SGLT2 inhibitor, numerous novel drugs could be utilized in treating DKD. Future studies are expected to provide new insights.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical value of serum MMP-3 in chronic kidney disease
Yulin Fu, Cheng Song, Yuan Qin, Tianyu Zheng, Xiumei Zhou, Xueqin Zhao, Jian Zou, Biao Huang
Clinica Chimica Acta.2024; 553: 117725. CrossRef - β2-Adrenergic receptor agonists as a treatment for diabetic kidney disease
Ehtesham Arif, Danira Medunjanin, Ashish Solanki, Xiaofeng Zuo, Yanhui Su, Yujing Dang, Brennan Winkler, Kasey Lerner, Ahmed I. Kamal, Oleg Palygin, Marc-Andre Cornier, Bethany J. Wolf, Kelly J. Hunt, Joshua H. Lipschutz
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2024; 326(1): F20. CrossRef - β2-Adrenergic receptor agonists: a new treatment for diabetic kidney disease?
Zhiwen Liu, Zheng Dong
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2024; 326(1): F1. CrossRef - Urinary exosomal microRNA-145-5p and microRNA-27a-3p act as noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease
Lu-Lu Han, Sheng-Hai Wang, Ming-Yan Yao, Hong Zhou
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(1): 92. CrossRef - Placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against diabetic kidney disease by upregulating autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
Honghong Liu, Jiao Wang, Guanru Yue, Jixiong Xu
Renal Failure.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of serum Nrf2 protein levels with disease activity and renal impairment in lupus nephritis
Jicui Li, Qiaoyan Guo, Xianping Wei, Yuexin Zhu, Manyu Luo, Ping Luo
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Qidan Tangshen Granule on diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Hua Yang, Shisi Xia, Yilei Cong, Xinyu Yang, Jie Min, Tengfei Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111128. CrossRef - Comparison of conventional mathematical model and machine learning model based on recent advances in mathematical models for predicting diabetic kidney disease
Yingda Sheng, Caimei Zhang, Jing Huang, Dan Wang, Qian Xiao, Haocheng Zhang, Xiaoqin Ha
DIGITAL HEALTH.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Experimental Verification to Reveal the Mitophagy-Associated Mechanism of Tangshen Formula in the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy
Yinfeng Chen, Xiaying Wang, Jie Min, Jie Zheng, Xuanli Tang, Xiaoling Zhu, Dongrong Yu, De Jin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 739. CrossRef - Senolytic combination of dasatinib and quercetin protects against diabetic kidney disease by activating autophagy to alleviate podocyte dedifferentiation via the Notch pathway
Xinwang Zhu, Congxiao Zhang, Linlin Liu, Li Xu, Li Yao
International Journal of Molecular Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Decreased risk of renal cell carcinoma in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sodium glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitors
Chun‐Huei Chiu, Wei‐Yao Wang, Hung‐Yi Chen, Pei‐Lun Liao, Gwo‐Ping Jong, Tsung‐Yuan Yang
Cancer Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - System Biology Approaches for Systemic Diseases: Emphasis on Type II Diabetes Mellitus and Allied Metabolism
Mohan Das, Moumita Chakraborty, Promi Das, Sayantan Santra, Abhishek Mukherjee, Sarobi Das, Krisztian Banyai, Souvik Roy, Lopamudra Choudhury, Rudrak Gupta, Tama Dey, Dibya Das, Anirbandeep Bose, Balasubramanian Ganesh, Rintu Banerjee
Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology.2024; : 103176. CrossRef - Beneficial effects of ginsenosides on diabetic nephropathy: A systematical review and meta-analysis of preclinical evidence
Xiao-Mei Chen, Gui-Xuan Lin, Xue Wang, Hong-Yan Ma, Ru-Shang Wang, Shu-Mei Wang, Dan Tang
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2023; 302: 115860. CrossRef - Waist circumference and end‐stage renal disease based on glycaemic status: National Health Insurance Service data 2009–2018
Yun Kyung Cho, Ji Hye Huh, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Kyung‐do Han, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung‐Hee Ihm
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(1): 585. CrossRef - A Narrative Review of New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy
Aadhira Pillai, Darshna Fulmali
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Shenkang recipe alleviates renal aging in diabetic kidney disease by interfering with the lysine-specific demethylase KDM6B to modulate the PPAR-γ signaling pathway
Anna Zuo, Jiarun Xie, Junqiao Shao, Shuyu Li, Haoyu Lin, Shaoting Wang, Wei Sun, Jinjin Xia, Weiqiang Jiang, Jia Sun, Ming Wang
Pharmacological Research - Modern Chinese Medicine.2023; 6: 100216. CrossRef - miR-223-3p mediates the diabetic kidney disease progression by targeting IL6ST/STAT3 pathway
Ping Tang, Yushan Xu, Jingrong Zhang, Juanli Nan, Ruxian Zhong, Jingmei Luo, Dazhi Xu, Shaoqing Shi, Lihua Zhang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2023; 648: 50. CrossRef - miR‐124‐3p improves mitochondrial function of renal tubular epithelial cells in db/db mice
Luqun Liang, Chunxin Wo, Yao Yuan, Hongjuan Cao, Wanlin Tan, Xingcheng Zhou, Dan Wang, Rongyu Chen, Mingjun Shi, Fan Zhang, Ying Xiao, Lingling Liu, Yuxia Zhou, Tian Zhang, Yuanyuan Wang, Bing Guo
The FASEB Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Prolyl-Hydroxylase and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Low-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome-Related Anemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Report of Three Cases
Satoshi Yamasaki, Takahiko Horiuchi
Hematology Reports.2023; 15(1): 180. CrossRef - Diagnostic significance of hsa_circ_0000146 and hsa_circ_0000072 biomarkers for Diabetic Kidney Disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Amul Badr, Omayma Elkholy, Mona Said, Sally Fahim, Mohamed El-Khatib, Dina Sabry, Radwa Gaber
Journal of Medical Biochemistry.2023; 42(2): 239. CrossRef - The emerging insight into E3 ligases as the potential therapeutic target for diabetic kidney disease
Vivek Akhouri, Syamantak Majumder, Anil Bhanudas Gaikwad
Life Sciences.2023; 321: 121643. CrossRef - Klotho’s impact on diabetic nephropathy and its emerging connection to diabetic retinopathy
Anqi Tang, Yu Zhang, Ling Wu, Yong Lin, Lizeyu Lv, Liangbin Zhao, Bojun Xu, Youqun Huang, Mingquan Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences and Clinical Significance of Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 and Vasohibin-1 (VASH-1) Levels in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy and Different Renal Injuries
Hui Liu, Dongyan Wang, Jingnan Tang, Linlin Yu, Shanshan Su
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1085. CrossRef - Medial Arterial Calcification and the Risk of Amputation of Diabetic Foot Ulcer in Patients With Diabetic Kidney Disease
Joon Myeong So, Ji Ho Park, Jin Gyeong Kim, Il Rae Park, Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Chul Hyun Park, Woo-Sung Yun, Tae-Gon Kim, Woong Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Heparanase-2 protein and peptides have a protective effect on experimental glomerulonephritis and diabetic nephropathy
Baranca Buijsers, Marjolein Garsen, Mark de Graaf, Marinka Bakker-van Bebber, Chunming Guo, Xue Li, Johan van der Vlag
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis on the renal functional status in patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease
Z.Ya. Кotsiubiichuk, O.S. Khukhlina, А.А. Аntoniv, O.Ye. Mandryk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(2): 100. CrossRef - Roles of extracellular vesicles in ageing-related chronic kidney disease: Demon or angel
Siqi Yin, Zixuan Zhou, Peiwen Fu, Chaoying Jin, Peipei Wu, Cheng Ji, Yunjie Shan, Linru Shi, Min Xu, Hui Qian
Pharmacological Research.2023; 193: 106795. CrossRef - Role of Natural and Synthetic Compounds in Modulating NRF2/KEAP1 Signaling Pathway in Prostate Cancer
Giovanni Tossetta, Sonia Fantone, Daniela Marzioni, Roberta Mazzucchelli
Cancers.2023; 15(11): 3037. CrossRef - Risk factors for heart, cerebrovascular, and kidney diseases: evaluation of potential side effects of medications to control hypertension, hyperglycemia, and hypercholesterolemia
Kazumitsu Nawata
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Rationale and design of a prospective, clinical study of kidney biopsies in people with type 2 diabetes and severely increased albuminuria (the PRIMETIME 2 study)
Marie Møller, Rikke Borg, Iain Bressendorff, Lisbeth N Fink, Eva Gravesen, Karina Haar Jensen, Torben Hansen, Dorrit Krustrup, Frederik Persson, Peter Rossing, Frederikke E Sembach, Anne C B Thuesen, Ditte Hansen
BMJ Open.2023; 13(6): e072216. CrossRef - Oral Chinese patent medicines for diabetic kidney disease: An overview of systematic reviews
Xue Xue, Ke-ying Li, Shang-zhi Liu, Jia-xuan Li, Xin-yan Jin, Xue-han Liu, La-mei Lin, Xin-rong Zou, Chun-li Lu, Fang-fang Zhao, Jian-ping Liu, Xiao-qin Wang
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2023; 61: 102269. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Proteinuric Kidney Disease/Nephrotic Syndrome: Lessons from Knockout/Transgenic Mouse Models
Ryosuke Saiki, Kan Katayama, Kaoru Dohi
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1803. CrossRef - Epigenetic regulation of angiogenesis and ischemic response by long noncoding RNA LEENE in diabetes
Imari Mimura, Masaomi Nangaku
Kidney International.2023; 104(6): 1048. CrossRef - Advances in the pharmacological study of Chinese herbal medicine to alleviate diabetic nephropathy by improving mitochondrial oxidative stress
Ming Chen, Yao Chen, Wenhui Zhu, Xiaoming Yan, Jing Xiao, Peiqing Zhang, Peng Liu, Ping Li
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115088. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone Therapy in Patients with Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
FNU Jyotsna, Kamran Mahfooz, Tirath Patel, FNU Parshant, Fnu Simran, Fnu Harsha, Fnu Neha, Dev Jyotishna, Dipesh Mishra, Sirjana Subedi, Mahima Khatri, Satesh Kumar, Giustino Varrassi
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular implications of glycosaminoglycans in diabetes pharmacotherapy
Tanya Waseem, Madiha Ahmed, Tausif Ahmed Rajput, Mustafeez Mujtaba Babar
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 247: 125821. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: More than Just Glucose Regulation
Jasna Klen, Vita Dolžan
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(7): 1995. CrossRef - CUL3 induces mitochondrial dysfunction via MRPL12 ubiquitination in renal tubular epithelial cells
Xingzhao Ji, Xiaoli Yang, Xia Gu, Lingju Chu, Shengnan Sun, Jian Sun, Peng Song, Qian Mu, Ying Wang, Xiaoming Sun, Dun Su, Tong Su, Shaoshuai Hou, Yao Lu, Chen Ma, Mingqiang Liu, Tianyi Zhang, Weiying Zhang, Yi Liu, Qiang Wan
The FEBS Journal.2023; 290(22): 5340. CrossRef - HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
Chuanqiang Zhou, Min Wu, Gaolun Liu, Li Zhou
Open Life Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of the Potential of Nuclear Factor [Erythroid-Derived 2]-like 2 Activation in Autoimmune Diseases
Ilker Ates, Ayşe Didem Yılmaz, Brigitta Buttari, Marzia Arese, Luciano Saso, Sibel Suzen
Brain Sciences.2023; 13(11): 1532. CrossRef - Astragalus membranaceus and Salvia miltiorrhiza ameliorate diabetic kidney disease via the “gut-kidney axis”
Zhen Shen, Tao Cui, Yao Liu, Shuai Wu, Cong Han, Jie Li
Phytomedicine.2023; 121: 155129. CrossRef - The relevance of the non-invasive biomarkers lncRNA GAS5/miR-21 ceRNA regulatory network in the early identification of diabetes and diabetic nephropathy
He Sun, Tong Chen, Xin Li, Yonghong Zhu, Shuang Zhang, Ping He, Yali Peng, Qiuling Fan
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Activation of acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 mediates kidney injury in diabetic nephropathy
Jian Lu, Xue Qi Li, Pei Pei Chen, Jia Xiu Zhang, Liang Liu, Gui Hua Wang, Xiao Qi Liu, Ting Ting Jiang, Meng Ying Wang, Wen Tao Liu, Xiong Zhong Ruan, Kun Ling Ma
JCI Insight.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - SET7, a lysine-specific methyl transferase: An intriguing epigenetic target to combat diabetic nephropathy
Samarth Dwivedi, Atharva Chavan, Atish T. Paul
Drug Discovery Today.2023; 28(10): 103754. CrossRef - Dznep, a histone modification inhibitor, inhibits HIF1α binding to TIMP2 gene and suppresses TIMP2 expression under hypoxia
Tomotaka Yamazaki, Imari Mimura, Yu Kurata, Tetsuhiro Tanaka, Masaomi Nangaku
Physiological Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - GLP-1RAs inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway to regulate mouse renal podocyte pyroptosis
Xiang Li, Xiao Jiang, Mei Jiang, Zhi-feng Wang, Tao Zhao, Si-ming Cao, Qiu-Mei Li
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 61(2): 225. CrossRef - Highly Sensitive, Portable Detection System for Multiplex Chemiluminescence Analysis
Yannan Yu, Wei Nie, Kaiqin Chu, Xi Wei, Zachary J. Smith
Analytical Chemistry.2023; 95(39): 14762. CrossRef - From normal population to prediabetes and diabetes: study of influencing factors and prediction models
Di Gong, Xiaohong Chen, Lin Yang, Yongjian Zhang, Qianqian Zhong, Jing Liu, Chen Yan, Yongjiang Cai, Weihua Yang, Jiantao Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Monitoring through Urine Analysis Using ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and Machine Learning
Sajid Farooq, Denise Maria Zezell
Chemosensors.2023; 11(11): 565. CrossRef - Treatment and practical considerations of diabetic kidney disease
Yara Bilen, Allaa Almoushref, Kenda Alkwatli, Omar Osman, Ali Mehdi, Hanny Sawaf
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Metabolomics and Traditional Chinese Medicine for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment
Jing Li, Na Zhu, Yaqiong Wang, Yanlei Bao, Feng Xu, Fengjuan Liu, Xuefeng Zhou
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 4269. CrossRef - Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and incident diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, Min Sun Choi, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 184: 109181. CrossRef - Lipidomic Analysis Reveals the Protection Mechanism of GLP-1 Analogue Dulaglutide on High-Fat Diet-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease in Mice
Martin Ho Yin Yeung, Ka Long Leung, Lai Yuen Choi, Jung Sun Yoo, Susan Yung, Pui-Kin So, Chi-Ming Wong
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - GLP-1 receptor agonists in diabetic kidney disease: current evidence and future directions
Ji Hee Yu, So Young Park, Da Young Lee, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(2): 136. CrossRef - Evolving Type 2 diabetes management focuses on clinical outcomes
Caroline Fenton, Connie Kang
Drugs & Therapy Perspectives.2022; 38(4): 165. CrossRef - Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 181. CrossRef - Critical shear stress of red blood cells as a novel integrated biomarker for screening chronic kidney diseases in cases of type 2 diabetes
Il Rae Park, Jimi Choi, Eun Young Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Sehyun Shin, Sin Gon Kim, Kyu Chang Won
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2022; 81(4): 293. CrossRef - Inhibition of ChREBP ubiquitination via the ROS/Akt-dependent downregulation of Smurf2 contributes to lysophosphatidic acid-induced fibrosis in renal mesangial cells
Donghee Kim, Ga-Young Nam, Eunhui Seo, Hee-Sook Jun
Journal of Biomedical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Pathophysiological Basis of Diabetic Kidney Protection by Inhibition of SGLT2 and SGLT1
Yuji Oe, Volker Vallon
Kidney and Dialysis.2022; 2(2): 349. CrossRef - Dapagliflozin for the treatment of chronic kidney disease
Yu Kurata, Masaomi Nangaku
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 17(4): 275. CrossRef - Repurposing drugs for highly prevalent diseases: pentoxifylline, an old drug and a new opportunity for diabetic kidney disease
Javier Donate-Correa, María Dolores Sanchez-Niño, Ainhoa González-Luis, Carla Ferri, Alberto Martín-Olivera, Ernesto Martín-Núñez, Beatriz Fernandez-Fernandez, Víctor G Tagua, Carmen Mora-Fernández, Alberto Ortiz, Juan F Navarro-González
Clinical Kidney Journal.2022; 15(12): 2200. CrossRef - Cyproheptadine, a SET7/9 inhibitor, reduces hyperglycaemia-induced ER stress alleviating inflammation and fibrosis in renal tubular epithelial cells
Himanshu Sankrityayan, Ajinath Kale, Vishwadeep Shelke, Anil Bhanudas Gaikwad
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Pan-Src kinase inhibitor treatment attenuates diabetic kidney injury via inhibition of Fyn kinase-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress
Debra Dorotea, Songling Jiang, Eun Seon Pak, Jung Beom Son, Hwan Geun Choi, Sung-Min Ahn, Hunjoo Ha
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2022; 54(8): 1086. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Effect of once-weekly dulaglutide on renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease
Sungmin Kim, Jung Nam An, Young Rim Song, Sung Gyun Kim, Hyung Seok Lee, AJin Cho, Jwa-Kyung Kim, Tomislav Bulum
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0273004. CrossRef - Oxidative Stress and NRF2/KEAP1/ARE Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD): New Perspectives
Daniela Maria Tanase, Evelina Maria Gosav, Madalina Ioana Anton, Mariana Floria, Petronela Nicoleta Seritean Isac, Loredana Liliana Hurjui, Claudia Cristina Tarniceriu, Claudia Florida Costea, Manuela Ciocoiu, Ciprian Rezus
Biomolecules.2022; 12(9): 1227. CrossRef - Preventive and healing effect of high dosing grape seed flour on CKD patients of various stages and aetiologies
Wiem Bejaoui, Mohamed Mahmoudi, Kamel Charradi, Monia Abbes-Belhadj, Habib Boukhalfa, Mossadok Ben-Attia, Ferid Limam, Ezzedine Aouani
Biomarkers.2022; 27(8): 795. CrossRef - Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) in type 2 diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to therapeutics
Miyesaier Abudureyimu, Xuanming Luo, Xiang Wang, James R Sowers, Wenshuo Wang, Junbo Ge, Jun Ren, Yingmei Zhang, Wei-Ping Jia
Journal of Molecular Cell Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in the Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Diabetic Kidney Diseases
Wei Huang, Yi-Yuan Chen, Zi-Qi Li, Fang-Fang He, Chun Zhang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(18): 10882. CrossRef - Serum isthmin-1 levels are positively and independently correlated with albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chuan Wang, Mingyue Xu, Ruiying Feng, Lei Zhang, Xiaofei Yin, Ruoqi Feng, Kai Liang, Jinbo Liu
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(5): e002972. CrossRef - hucMSC-sEVs-Derived 14-3-3ζ Serves as a Bridge between YAP and Autophagy in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Siqi Yin, Wanzhu Liu, Cheng Ji, Yuan Zhu, Yunjie Shan, Zixuan Zhou, Wenya Chen, Leilei Zhang, Zixuan Sun, Wenqin Zhou, Hui Qian, Chaoliang Tang
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Adenosine receptors as emerging therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease
Eun Seon Pak, Jin Joo Cha, Dae Ryong Cha, Keizo Kanasaki, Hunjoo Ha
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(Suppl 2): S74. CrossRef - REDD1 Ablation Attenuates the Development of Renal Complications in Diabetic Mice
Siddharth Sunilkumar, Esma I. Yerlikaya, Allyson L. Toro, William P. Miller, Han Chen, Kebin Hu, Scot R. Kimball, Michael D. Dennis
Diabetes.2022; 71(11): 2412. CrossRef - The Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha in Renal Disease
Huixia Liu, Yujuan Li, Jing Xiong
Molecules.2022; 27(21): 7318. CrossRef - Resistant Starch as a Dietary Intervention to Limit the Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Anna M. Drake, Melinda T. Coughlan, Claus T. Christophersen, Matthew Snelson
Nutrients.2022; 14(21): 4547. CrossRef - Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
Yan Yuan, Yuanxia Liu, Mengyao Sun, Huijing Ye, Yuchen Feng, Zhenzhen Liu, Lingyu Pan, Hongbo Weng
Open Life Sciences.2022; 17(1): 1451. CrossRef - Single-cell multiomics reveals the complexity of TGFβ signalling to chromatin in iPSC-derived kidney organoids
Jessica L. Davis, Ciaran Kennedy, Shane Clerkin, Niall J. Treacy, Thomas Dodd, Catherine Moss, Alison Murphy, Derek P. Brazil, Gerard Cagney, Dermot F. Brougham, Rabi Murad, Darren Finlay, Kristiina Vuori, John Crean
Communications Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidized Albumin: Evaluation of Oxidative Stress as a Marker for the Progression of Kidney Disease
Hiroshi Watanabe
Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.2022; 45(12): 1728. CrossRef - Whether Renal Pathology Is an Independent Predictor for End-Stage Renal Disease in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients with Nephrotic Range Proteinuria: A Biopsy-Based Study
Tingli Wang, Junlin Zhang, Yiting Wang, Lijun Zhao, Yucheng Wu, Honghong Ren, Yutong Zou, Rui Zhang, Huan Xu, Zhonglin Chai, Mark Cooper, Jie Zhang, Fang Liu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(1): 88. CrossRef - What’s New in the Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Recent Advances
Kimio Watanabe, Emiko Sato, Eikan Mishima, Mariko Miyazaki, Tetsuhiro Tanaka
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 24(1): 570. CrossRef - Clinical efficacy and safety of astragalus injection combined with ACEI/ARB in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Zhiyue Zhu, Qi Zhang, Le Liu, Pengjie Bao, Shilin Liu, Chaoqun Song, Wenbo Yang, Zheng Nan
Medicine.2022; 101(49): e31490. CrossRef - Cudrania tricuspidata Root Extract Prevents Methylglyoxal-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Regulation of the PKC-NOX4 Pathway in Human Kidney Cells
Donghee Kim, Jayeon Cheon, Haelim Yoon, Hee-Sook Jun, Evangelia Dounousi
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Pleiotropic Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors: Renoprotective Mechanisms beyond Glycemic Control
Tomoaki Takata, Hajime Isomoto
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4374. CrossRef - HIF-α Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors and Their Implications for Biomedicine: A Comprehensive Review
Kiichi Hirota
Biomedicines.2021; 9(5): 468. CrossRef - Nephropathie bei Diabetes
Roland E. Schmieder
CardioVasc.2021; 21(3): 31. CrossRef - Clinical Predictors of Nondiabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Diabetes: A Single-Center Study
Francesco Fontana, Rossella Perrone, Francesco Giaroni, Gaetano Alfano, Silvia Giovanella, Giulia Ligabue, Riccardo Magistroni, Gianni Cappelli, Udeme Ekrikpo
International Journal of Nephrology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Activated Histone Acetyltransferase p300/CBP-Related Signalling Pathways Mediate Up-Regulation of NADPH Oxidase, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Diabetic Kidney
Alexandra-Gela Lazar, Mihaela-Loredana Vlad, Adrian Manea, Maya Simionescu, Simona-Adriana Manea
Antioxidants.2021; 10(9): 1356. CrossRef - Plasma and urine biomarkers in chronic kidney disease: closer to clinical application
Azadeh Zabetian, Steven G. Coca
Current Opinion in Nephrology & Hypertension.2021; 30(6): 531. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect and mechanism of combined use of FGF21 and insulin on diabetic nephropathy
Fanrui Meng, Yukai Cao, Mir Hassan Khoso, Kai Kang, Guiping Ren, Wei Xiao, Deshan Li
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2021; 713: 109063. CrossRef - Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Daiji Kawanami, Yuichi Takashi, Yoshimi Muta, Naoki Oda, Dai Nagata, Hiroyuki Takahashi, Makito Tanabe
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcription Factor ChREBP Mediates High Glucose-Evoked Increase in HIF-1α Content in Epithelial Cells of Renal Proximal Tubules
Aleksandra Owczarek, Katarzyna B. Gieczewska, Robert Jarzyna, Zuzanna Frydzinska, Katarzyna Winiarska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(24): 13299. CrossRef - The effect of modern hypoglycemic therapy on the course of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
V.I. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2021; 17(8): 624. CrossRef
- Clinical value of serum MMP-3 in chronic kidney disease
- Drug/Regimen
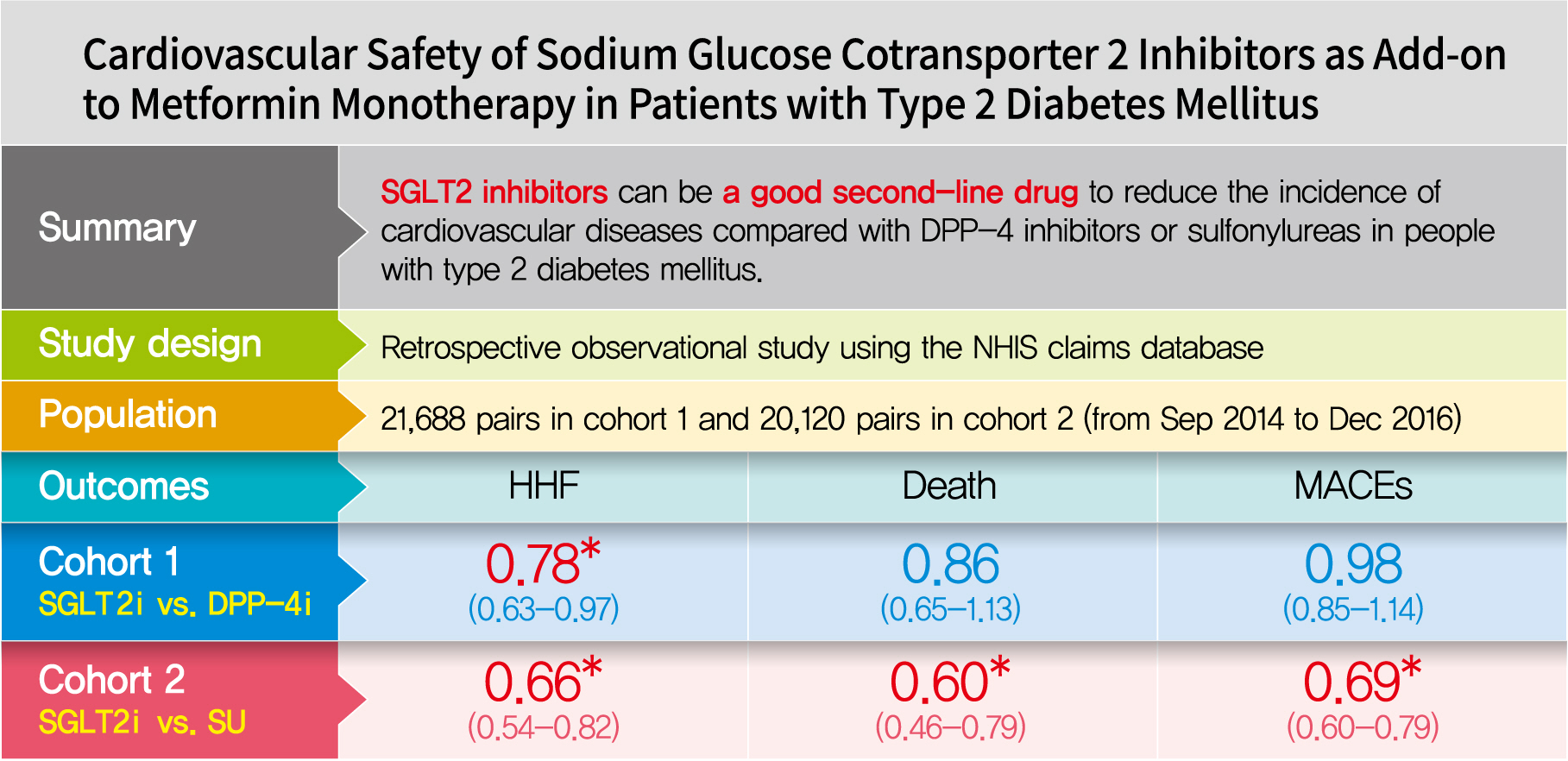
- Cardiovascular Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors as Add-on to Metformin Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ja Young Jeon, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):505-514. Published online October 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0057
- 7,921 View
- 341 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Using real-world data, cardiovascular safety was investigated in metformin users newly starting sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors compared with other glucose-lowering drugs in Korea.
Methods
This was a retrospective observational study using the National Health Insurance Service claims database in Korea. The study period was from September 2014 to December 2016. The study included subjects who were newly prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors or other glucose-lowering drugs while on metformin monotherapy; cohort 1 was composed of new users of SGLT2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors and cohort 2 included new users of SGLT2 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas. To balance the patient characteristics, propensity score matching was performed at a 1:1 ratio. Cardiovascular outcomes included hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), all-cause mortality, HHF plus all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and modified major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs).
Results
After propensity score matching, each cohort group was well balanced at baseline (21,688 pairs in cohort 1 and 20,120 pairs in cohort 2). As the second-line treatment, use of SGLT2 inhibitors was associated with a lower risk of HHF and HHF plus all-cause mortality compared with DPP-4 inhibitors. In addition, use of SGLT2 inhibitors versus sulfonylurea as add-on therapy to metformin was associated with decreased risks of HHF, all-cause mortality, HHF plus all-cause mortality, MI, stroke, and modified MACEs.
Conclusion
SGLT2 inhibitors can be a good second-line drug to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular diseases compared with DPP-4 inhibitors or sulfonylureas in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Advances in Research on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Targets and Therapeutic Agents
Jingqian Su, Yingsheng Luo, Shan Hu, Lu Tang, Songying Ouyang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13381. CrossRef - Cardioprotective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas in addition to metformin: A nationwide cohort study of patients with type 2 diabetes
Jui Wang, Hon-Yen Wu, Kuo-Liong Chien
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(3): 101299. CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ja Young Jeon, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(4): 614. CrossRef - The Impact of Novel Anti-Diabetic Medications on CV Outcomes: A New Therapeutic Horizon for Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Cardiac Patients
Israel Mazin, Fernando Chernomordik, Paul Fefer, Shlomi Matetzky, Roy Beigel
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(7): 1904. CrossRef - Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Inhibitors on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and Hospitalization for Heart Failure in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Atrial Fibrillation
Chang Hee Kwon, Ye-Jee Kim, Min-Ju Kim, Myung-Jin Cha, Min Soo Cho, Gi-Byoung Nam, Kee-Joon Choi, Jun Kim
The American Journal of Cardiology.2022; 178: 35. CrossRef - Using real-world data for supporting regulatory decision making: Comparison of cardiovascular and safety outcomes of an empagliflozin randomized clinical trial versus real-world data
Ha Young Jang, In-Wha Kim, Jung Mi Oh
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular Safety of SGLT2 Inhibitors Compared to DPP4 Inhibitors and Sulfonylureas as the Second-Line of Therapy in T2DM Using Large, Real-World Clinical Data in Korea
Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 502. CrossRef - The effect of sodium‐glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors on mortality and heart failure in randomized trials versus observational studies
Jesper Krogh, Carsten Hjorthøj, Søren L. Kristensen, Christian Selmer, Steen B. Haugaard
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes treated with SGLT-2 inhibitors versus DPP-4 inhibitors. An Italian real-world study in the context of other observational studies
Enrico Longato, Benedetta Maria Bonora, Barbara Di Camillo, Giovanni Sparacino, Lara Tramontan, Angelo Avogaro, Gian Paolo Fadini
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 179: 109024. CrossRef
- Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor for Renal Function Preservation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
- Tae Jung Oh, Ju-Young Moon, Kyu Yeon Hur, Seung Hyun Ko, Hyun Jung Kim, Taehee Kim, Dong Won Lee, Min Kyong Moon, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline, Korean Diabetes Association and Committee of the Cooperative Studies, Korean Society of Nephrology
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):489-497. Published online August 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0172
- 7,814 View
- 167 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Diabetes is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Therefore, prevention of renal dysfunction is an important treatment goal in the management of diabetes. The data of landmark cardiovascular outcome trials of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor showed profound reno-protective effects. The Korean Diabetes Association and the Korean Society of Nephrology reviewed clinical trials and performed meta-analysis to assess the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on the preservation of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). We limited the data of SGLT2 inhibitors which can be prescribed in Korea. Both eGFR value and its change from the baseline were significantly more preserved in the SGLT2 inhibitor treatment group compared to the control group after 156 weeks. However, some known adverse events were increased in SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, such as genital infection, diabetic ketoacidosis, and volume depletion. We recommend the long-term use SGLT2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) for attenuation of renal function decline. However, we cannot generalize our recommendation due to lack of long-term clinical trials testing reno-protective effects of every SGLT2 inhibitor in a broad range of patients with T2DM. This recommendation can be revised and updated after publication of several large-scale renal outcome trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 701. CrossRef
- Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
- Drug/Regimen
- Effect of Dapagliflozin as an Add-on Therapy to Insulin on the Glycemic Variability in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (DIVE): A Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Randomized Study
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Kyung-Wan Min, Byung-Wan Lee, In-Kyung Jeong, Soon-Jib Yoo, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):339-348. Published online May 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0203

- 8,297 View
- 332 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
Background Glycemic variability is associated with the development of diabetic complications and hypoglycemia. However, the effect of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on glycemic variability is controversial. We aimed to examine the effect of dapagliflozin as an add-on therapy to insulin on the glycemic variability assessed using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods In this multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized study, 84 subjects received 10 mg of dapagliflozin (
n =41) or the placebo (n =43) for 12 weeks. CGM was performed before and after treatment to compare the changes in glycemic variability measures (standard deviation [SD], mean amplitude of glycemic excursions [MAGEs]).Results At week 12, significant reductions in glycosylated hemoglobin (−0.74%±0.66% vs. 0.01%±0.65%,
P <0.001), glycated albumin (−3.94%±2.55% vs. −0.67%±2.48%,P <0.001), and CGM-derived mean glucose (−41.6±39.2 mg/dL vs. 1.1±46.2 mg/dL,P <0.001) levels were observed in the dapagliflozin group compared with the placebo group. SD and MAGE were significantly decreased in the dapagliflozin group, but not in the placebo group. However, the difference in ΔSD and ΔMAGE failed to reach statistical significance between two groups. No significant differences in the incidence of safety endpoints were observed between the two groups.Conclusion Dapagliflozin effectively decreased glucose levels, but not glucose variability, after 12 weeks of treatment in participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving insulin treatment. The role of SGLT2 inhibitors in glycemic variability warrants further investigations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Selective sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in the improvement of hemoglobin and hematocrit in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis
Yuanyuan Luo, Ruojing Bai, Wei Zhang, Guijun Qin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring Profiles and Health Outcomes After Dapagliflozin Plus Saxagliptin vs Insulin Glargine
Donald C Simonson, Marcia A Testa, Ella Ekholm, Maxwell Su, Tina Vilsbøll, Serge A Jabbour, Marcus Lind
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of empagliflozin on insulin needs in patients with heart failure and diabetes: An EMPEROR‐Pooled analysis
Khawaja M. Talha, Jennifer Green, Gerasimos Filippatos, Stuart Pocock, Faiez Zannad, Martina Brueckmann, Elke Schueler, Anne Pernille Ofstad, João Pedro Ferreira, Stefan D. Anker, Javed Butler, Julio Rosenstock, Milton Packer
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Urinary Tract Infection in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Dapagliflozin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Zhigui Zheng, Dongyuan He, Jianguo Chen, Xiaohui Xie, Yunan Lu, Binbin Wu, Xinxin Jiang
Clinical Drug Investigation.2023; 43(4): 209. CrossRef - Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors and Metformin on Inflammatory and Prognostic
Biomarkers in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Yang Cao, Ning Liang, Ting Liu, Jingai Fang, Xiaodong Zhang
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2023; 23(4): 530. CrossRef - What is Glycaemic Variability and which Pharmacological Treatment Options are Effective? A Narrative Review
Juan Miguel Huertas Cañas, Maria Alejandra Gomez Gutierrez, Andres Bedoya Ossa
European Endocrinology.2023; 19(2): 4. CrossRef - La variabilité glycémique : un facteur de risque singulier à conjuguer au pluriel
Louis Monnier, Claude Colette, Fabrice Bonnet, David Owens
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2022; 16(1): 15. CrossRef - Association between Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors and Cardiometabolic Outcomes
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 49. CrossRef - Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on serum urate levels in patients with and without diabetes: a systematic review and meta-regression of 43 randomized controlled trials
Alicia Swee Yan Yip, Shariel Leong, Yao Hao Teo, Yao Neng Teo, Nicholas L. X. Syn, Ray Meng See, Caitlin Fern Wee, Elliot Yeung Chong, Chi-Hang Lee, Mark Y. Chan, Tiong-Cheng Yeo, Raymond C. C. Wong, Ping Chai, Ching-Hui Sia
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2022; 13: 204062232210835. CrossRef - Hypoglycemic agents and glycemic variability in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
SuA Oh, Sujata Purja, Hocheol Shin, Minji Kim, Eunyoung Kim
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(3): 147916412211068. CrossRef - The Clinical Effect of Dapagliflozin in Patients with Angiographically Confirmed Coronary Artery Disease and Concomitant Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yana Yu. Dzhun, Yevhen Yu. Marushko, Yanina A. Saienko, Nadiya M. Rudenko, Borys M. Mankovsky
Ukrainian Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery.2022; 30(3): 35. CrossRef - Stress-Induced Hyperglycaemia in Non-Diabetic Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: From Molecular Mechanisms to New Therapeutic Perspectives
Alessandro Bellis, Ciro Mauro, Emanuele Barbato, Antonio Ceriello, Antonio Cittadini, Carmine Morisco
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(2): 775. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability Impacted by SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP 1 Agonists in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Heeyoung Lee, Se-eun Park, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(18): 4078. CrossRef - Effect of Dapagliflozin on Glycemic Variability in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes under Insulin Glargine Combined with Other Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs
Menghui Luo, Xiaocen Kong, Huiying Wang, Xiaofang Zhai, Tingting Cai, Bo Ding, Yun Hu, Ting Jing, Xiaofei Su, Huiqin Li, Jianhua Ma, Yoshifumi Saisho
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 828. CrossRef
- Selective sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in the improvement of hemoglobin and hematocrit in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





