- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 45(1); 2021 > Article
-
ReviewComplications Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Current and Future
-
Tomotaka Yamazaki
 , Imari Mimura, Tetsuhiro Tanaka
, Imari Mimura, Tetsuhiro Tanaka , Masaomi Nangaku
, Masaomi Nangaku -
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2021;45(1):11-26.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0217
Published online: January 22, 2021
Division of Nephrology and Endocrinology, The University of Tokyo Graduate School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan
-
Corresponding author: Tetsuhiro Tanaka
 Division of Nephrology and Endocrinology, The University of Tokyo Graduate School of Medicine, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan E-mail: tetsu-tky@umin.ac.jp
Division of Nephrology and Endocrinology, The University of Tokyo Graduate School of Medicine, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan E-mail: tetsu-tky@umin.ac.jp
Copyright © 2021 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
- Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is the major cause of end-stage kidney disease. However, only renin-angiotensin system inhibitor with multidisciplinary treatments is effective for DKD. In 2019, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor showed efficacy against DKD in Canagliflozin and Renal Events in Diabetes with Established Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation (CREDENCE) trial, adding a new treatment option. However, the progression of DKD has not been completely controlled. The patients with transient exposure to hyperglycemia develop diabetic complications, including DKD, even after normalization of their blood glucose. Temporary hyperglycemia causes advanced glycation end product (AGE) accumulations and epigenetic changes as metabolic memory. The drugs that improve metabolic memory are awaited, and AGE inhibitors and histone modification inhibitors are the focus of clinical and basic research. In addition, incretin-related drugs showed a renoprotective ability in many clinical trials, and these trials with renal outcome as their primary endpoint are currently ongoing. Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors recently approved for renal anemia may be renoprotective since they improve tubulointerstitial hypoxia. Furthermore, NF-E2–related factor 2 activators improved the glomerular filtration rate of DKD patients in Bardoxolone Methyl Treatment: Renal Function in chronic kidney disease/Type 2 Diabetes (BEAM) trial and Phase II Study of Bardoxolone Methyl in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes (TSUBAKI) trial. Thus, following SGLT2 inhibitor, numerous novel drugs could be utilized in treating DKD. Future studies are expected to provide new insights.
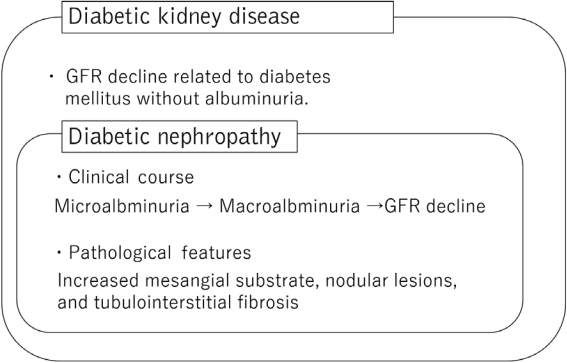
- Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is one of the major complications for diabetic patients and the most significant cause of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) [1]. Until now, chronic kidney disease (CKD) caused by diabetes mellitus is diagnosed as diabetic nephropathy, which begins with microalbuminuria, followed by macroalbuminuria and then gradual decline in kidney function, and is diagnosed pathologically by characteristic pathological findings, such as increased mesangial substrate, nodular lesions, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis [2]. However, in recent years, cases of impaired renal function without albuminuria have been reported [3,4]. In this background, a new disease concept called DKD was born. DKD is defined as CKD with diabetes being partially involved in the pathogenesis of kidney disease, encompassing the concept of classical diabetic nephropathy (Fig. 1) [5].
- The pathogenesis of DKD includes glomerular hypertension, change of renal hemodynamics, ischemia and hypoxia, oxidative stress, and upregulation of the renin-aldosterone system [6]. However, the full pathogenesis of the disease remains to be understood, and therapeutic targets have not been determined. Therefore, the treatment strategy for DKD remains the same with that of conventional diabetic nephropathy. Multi-disciplinary treatments, including blood glucose control, blood pressure and lipid control with renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAS) inhibitors, appropriate weight management, and guidance for diet and smoking cessation, are important. Aside from multidisciplinary treatments, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors were also added as a new drug of choice for DKD treatment in 2019, as the Canagliflozin and Renal Events in Diabetes with Established Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation (CREDENCE) study showed that SGLT2 inhibitors inhibited DKD progression [7]. However, even with the use of RAS and SGLT2 inhibitors, 5.27% (116/2,202) of patients continue to develop ESKD in the CREDENCE study.
- One of the important factors in DKD development is the phenomenon known as “metabolic memory.” Patients with past exposure to hyperglycemia have been known to develop complications, including DKD, even after treatment has normalized their blood glucose levels [8,9]. Past hyperglycemia is considered to have led to the accumulation of advanced glycation end product (AGE) and epigenetic genetic changes, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, which may have led to the progression of DKD as a cellular memory [10,11]. These DKD mechanisms have the potential as novel therapeutics for DKD. This paper outlines current and future therapies for DKD.
INTRODUCTION
- RAS inhibitor
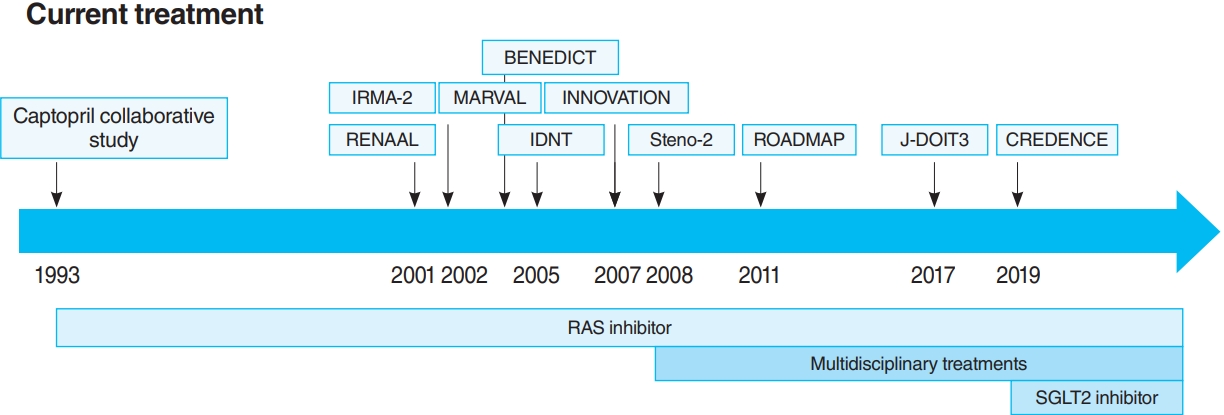
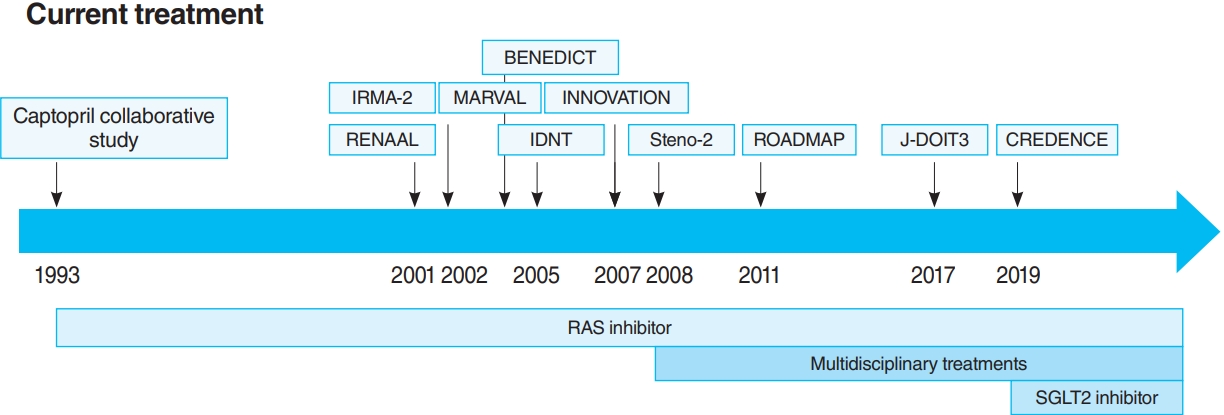
- The oldest and most preeminent drug for DKD treatment is the RAS inhibitor. Actually, RAS inhibitors have been shown to be effective in treating DKD in many clinical trials. In 1993, the Captopril Collaborative Study published by Lewis et al. [12] showed that captopril, angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor (ACE-I), inhibited the progression of nephropathy in patients with overt nephropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus (Fig. 2). In addition, angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) in diabetic patients with manifest nephropathy has been demonstrated in large randomized controlled trials (RCTs), such as the Reduction of Endpoints in NIDDM with the Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan (RENAAL) and Irbesartan in Diabetic nephropathy Trial (IDNT) [13,14]. Moreover, a number of reports on microalbuminuria among DKD patients have been noted. In the Irbesartan in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Microalbuminuria Study (IRMA-2), irbesartan was reported to inhibit the progression from microalbuminuria to overt proteinuria by approximately 70% [15]. The Incident to overt: Angiotensin II receptor blocker, Telmisartan, Investigation On type II diabetic Nephropathy (INNOVATION) study in Japan also reported telmisartan to inhibit the progression from microalbuminuria to overt proteinuria by approximately 60% compared to placebo [16]. Furthermore, Microalbuminuria reduction with valsartan (MARVAL), which compared an ARB with a calcium channel blocker, showed that only ARB was effective in lowering microalbuminuria, indicating that RAS inhibitors have an inhibitory effect on nephropathy and a blood pressure-lowering ability [17]. Large RCTs, Bergamo Nephrologic Diabetes Complications Trial (BENEDICT) and Randomized Olmesartan and Diabetes Microalbuminuria Prevention (ROADMAP), have also demonstrated that ARBs reduced the incidence of microalbuminuria among patients who did not present with microalbuminuria [18,19]. However, RAS inhibitors have also been reported to not be significantly effective in preventing the development of microalbuminuria among patients who are normotensive and without microalbuminuria [20]. Therefore, RAS inhibitors should be used in patients presenting with either hypertension or nephropathy.
- In this way, RAS inhibitors have been shown to be effective in all stages of DKD. The combination therapy of ACE-I and ARB was also studied in large randomized trials. Although some studies have shown combination therapy to be beneficial [21], the Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial (ONTARGET) reported a significant increase in worsening kidney function and mortality in the telmisartan-ramipril combination treatment group [22]. Furthermore, in the Veterans Affairs nephropathy in Diabetes (VA Nephron D) study, no significant difference was noted in the efficacy for DKD of the combination treatment group, and the increase in adverse events, such as hyperkalemia and acute kidney injury (AKI), has been reported [23]. Based on these results, the combination of ACE-I and ARB is not recommended.
- Overactivation of RAS causes intraglomerular hypertension due to constricted efferent arterioles, leading to increased proteinuria, mesangial cell proliferation, and activation of inflammatory responses and fibrotic factors [24,25]. Apart from the glomerular hypertension mechanism, angiotensin II is also known to cause cellular hypertrophy, accumulation of extracellular matrix and production of reactive oxygen species, and inflammatory changes by the production of cytokines, such as transforming growth factor (TGF)-β in glomerular cells [26,27]. Angiotensin II has also been reported to induce apoptosis of podocytes and decrease tubular interstitial microvessels and chronic hypoxia [28,29]. Moreover, aldosterone has been reported to cause increased expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and TGF-β, activation of macrophages, and endothelial cell damage by a different mechanism from glomerular hypertension [30]. RAS inhibitors inhibit DKD progression by suppressing these mechanisms caused by RAS overactivation.
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) has an antihypertensive effect by suppressing the action of aldosterone, the end product of RAS and has been reported to reduce proteinuria. For example, spironolactone was reported to be beneficial in decreasing albuminuria, inflammation, and fibrosis among DKD patients [31], and eplerenone was also reported to reduce albuminuria more than enalapril among systemic hypertension patients [32]. However, these drugs cause hyperkalemia in CKD patients and are contraindicated in patients with impaired renal function. In this context, new MRAs, finerenone and esaxerenone, have been developed, which are more selective for mineralocorticoid receptor, have no steroid structure, and have fewer complications than spironolactone and eplerenone. They have also been reported to reduce proteinuria among DKD patients [33,34]. In Japan, esaxerenone was approved for hypertension in 2019 and, unlike spironolactone and eplerenone, has been used for DKD patients with microalbuminuria and patients with moderate renal impairment. Furthermore, the large phase III studies, Finerenone in reducing Kidney Failure and Disease Progression in Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIDELIO-DKD) and Finerenone in Reducing Cardiovascular Mortality and Morbidity in Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIGARO-DKD), are evaluating, evaluate the efficacy and safety of finerenone in DKD patients, focusing on the composite primary endpoints of renal and cardiovascular functions [35,36].
- In this way, both large clinical trials and basic experiments have a solid evidence that RAS inhibitors, especially ACE-I and ARB, can treat DKD. However, although RAS inhibitors reduce proteinuria and slow the decline of glomerular filtration rate (GFR), they cannot suppress ESKD development completely. In addition, they increase the incidence of complications, such as AKI and hyperkalemia. Therefore, a new drug for DKD was expected to come out.
- Importance of multidisciplinary treatments
- For a long time, there were no drugs specific to DKD other than RAS inhibitors. In this context, some papers reported that multidisciplinary treatment, such as blood glucose control, blood pressure control with RAS inhibitor, lipid control, and lifestyle modifications, significantly reduced cardiovascular events in DKD patients and, as a secondary endpoint, suppressed renal events. The most famous trial that demonstrated the effectiveness of multidisciplinary treatment was the Steno-2 study (Fig. 2) [37]. The Steno-2 trial reported that multidisciplinary treatment not only reduced cardiovascular events among DKD patients but also retarded the progression of DKD itself. However, some problems with the Steno-2 study were noted, including the small number of participants and the much higher mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) than the current guideline targets even in the intensive-therapy group (HbA1c, 7.9%). From this background, Japan Diabetes Optimal Integrated Treatment Study for 3 major risk factors of cardiovascular disease (J-DOIT3) study was reported in 2017, which examined the efficacy of multifactor intensification therapy for the prevention of cardiovascular complications among Japanese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients (Fig. 2) [38, 39]. The J-DOIT3 study included 2,542 type 2 diabetes mellitus patients, with a target HbA1c level of 6.2% in the intensive treatment group. Similar to the Steno-2 study, J-DOIT3 showed a nonsignificant reduction in cardiovascular events and an inhibitory effect on DKD progression in the multidisciplinary treatment group.
- SGLT2 inhibitor
- SGLT2, which is a cotransporter, transports sodium and glucose in 1:1 ratio using Na-K ATPase-mediated sodium concentration gradient on the proximal tubular basement membrane. SGLT2 inhibitors inhibit proximal tubular glucose reabsorption and promote urinary glucose excretion, resulting in hypoglycemia. Empagliflozin Cardiovascular Outcome Event Trial in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients (EMPA-REG OUTCOME), published in 2015, showed that empagliflozin significantly reduces cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease [40], and a post hoc analysis of renal outcomes showed that empagliflozin significantly reduced the progression of nephropathy [41]. Aside from empagliflozin, the results of the Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study (CANVAS) Program in canagliflozin [42] and the Multicenter Trial to Evaluate the Effect of Dapagliflozin on the Incidence of Cardiovascular Events (DECLARETIMI58) study in dapagliflozin [43], as well as the systematic review and meta-analysis of these three studies, demonstrated similar cardiovascular and kidney protective effects [44]. However, all the large trials validated the primary endpoint to be cardiovascular events and included patients with a low risk for kidney disease, which has resulted in a low number of kidney events. CREDENCE study was conducted in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients who developed overt albuminuria (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] 30 to 90 mL/min/1.73 m2, albuminuria 300 to 5,000 mg/gCr), the primary outcome of which being kidney disease events (Fig. 2) [7]. CREDENCE trial achieved prespecified efficacy criteria in July 2018, which was stopped early, demonstrating the efficacy of SGTL2 inhibitors for DKD in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
- The renoprotective effect mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibitor are not fully understood, the most important of which are the correction of glomerular hyperfiltration and improvement of kidney hypoxia. Glomerular hyperfiltration is known to be responsible for the risk of the appearance of new albuminuria and a decrease in eGFR [45]. SGLT2 inhibitors are thought to have a renoprotective effect by increasing Na reaching the macula densa cells of the distal tubules, thereby correcting the dilation of afferent arterioles and glomerular hyperfiltration by the tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF). They are also thought to have the potential in improving hypoxia in the kidney. A rat model of diabetic nephropathy has been reported to show that oxygen consumption in proximal tubular cells was approximately doubled and that treatment with phlorizin, an SGLT1/2 inhibitor, reduced Na-K ATPase activity, inhibited the increase in oxygen consumption, and improved renal cortex oxygenation [46]. SGLT2 inhibitors are also known to cause a mild increase of ketones in the blood. Compared to glucose and fatty acids, ketone bodies can produce more ATP with small amounts of oxygen, contributing to the improvement of kidney hypoxia [47]. Blocking the intracellular influx of glucose in the proximal tubules reduces mitochondrial damage, leading to anti-inflammatory and antifibrosis results via inhibition of oxidative stress [48]. Furthermore, a comprehensive search for glycolytic and tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle metabolites in the kidney by imaging mass spectrometry revealed the inhibition by SGLT2 inhibitor treatment of the accumulation of TCA intermediate metabolites and the reduction of oxidative stress in the glomerulus [49].
- The advantages of SGLT2 inhibitor for the treatment of DKD include its efficacy when combined with RAS inhibitor and its ability to treat DKD independently of the hypoglycemic effect. Therefore, it is possible that SGLT2 inhibitor may be effective in the treatment of other CKD forms. A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Dapagliflozin on Renal Outcomes and Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease (DAPA-CKD) study, a phase III study of dapagliflozin, reported that dapagliflozin was effective in patients with CKD, with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus [50]. Furthermore, the Study of Heart and Kidney Protection with empagliflozin (EMPA-KIDNEY) study, a phase III study of empagliflozin, are currently underway for the application of SGLT2 inhibitors for CKD other than DKD, the result of which is expected to be published in the near future. However, the combination therapy with RAS and SGLT2 inhibitor is still only effective in slowing the increase in GFR, with a hope for development of new therapies.
CURRENT TREATMENT
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin II receptor blocker
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist
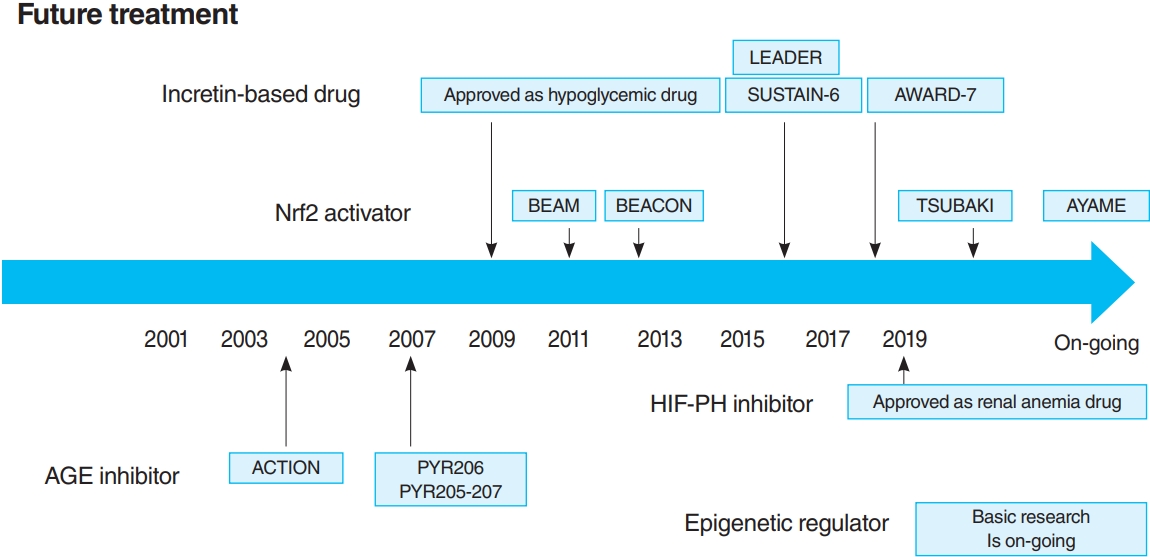
- NF-E2–related factor 2 activator
- Although current treatments, such as RAS inhibitor and SGLT2 inhibitor, can only slow the decline of GFR, NF-E2–related factor 2 (Nrf2) activator is a novel drug with the potential to improve the GFR of DKD patients [51]. Bardoxolone methyl is a drug that activates Nrf2, which is a transcription factor responsible for the defense response to oxidative stress. Under unstressed conditions, Nrf2 is ubiquitinated and degraded by the proteasome through the action of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), whereas under oxidative stress, Keap1 undergoes various chemical modifications, which reduce its affinity for Nrf2 and inhibit its degradation. Nrf2, which has escaped degradation by Keap1, enters the nucleus to form heterodimers with small Maf proteins and binds to antioxidant responsive elements (ARE) for the enhancement of the expression of downstream genes involved in antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities [52]. Bardoxolone methyl binds to Keap1 and undergoes a conformational change to promote Nrf2 dissociation, allowing Nrf2 to migrate into the nucleus, and exert antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects [53].
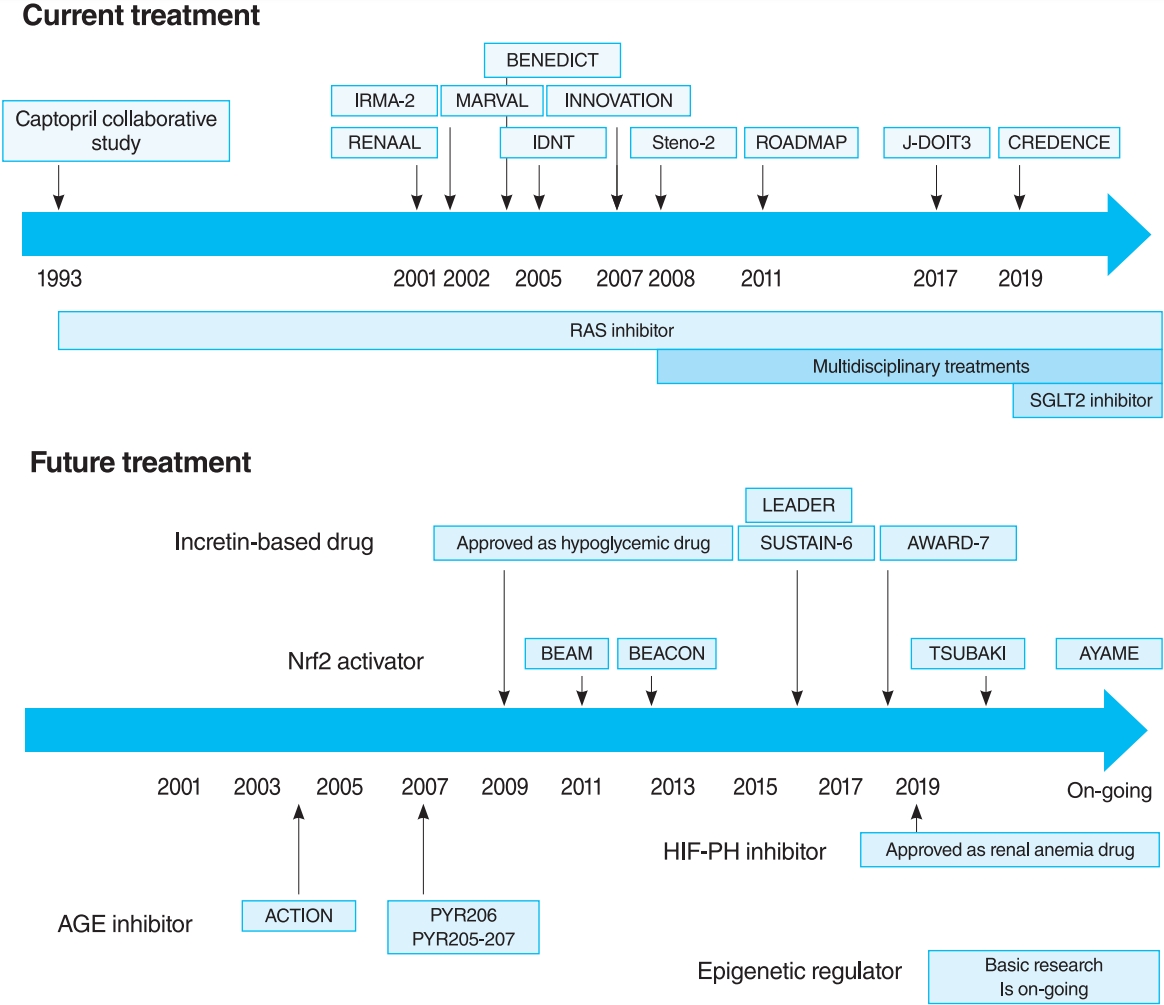
- In 2011, the result of 52-Week Bardoxolone Methyl Treatment: Renal Function in chronic kidney disease/Type 2 Diabetes (BEAM) study, a phase II placebo-controlled trial in DKD patients, was published (Fig. 3) [54]. The BEAM study subjects had DKD with type 2 diabetes mellitus and 20 to 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 eGFR and were randomized into the placebo or bardoxolone methyl group. The bardoxolone methyl group showed a significantly greater increase in eGFR than the placebo group, which persisted for up to 52 weeks, making bardoxolone methyl the major focus for DKD treatment. The Bardoxolone Methyl Evaluation in Patients with CKD and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: the Occurrence of Renal Events (BEACON) study is a larger phase III placebo-controlled study than BEAM, which was conducted to provide further evidence of the renoprotective effects of bardoxolone methyl (Fig. 3) [55]. The subjects had DKD with an eGFR of 15 to 30 mL/min/1.73 m2. This study included patients with a more advanced renal impairment than those in the BEAM study. These patients were randomized into placebo or bardoxolone methyl (20 mg/day) group. However, the significantly increased rates of heart failure-related hospitalizations and deaths in the bardoxolone methyl group were observed, resulting in early termination of the study (after 9 months of observation). Despite the early termination, a significant increase in the eGFR levels of the bardoxolone methyl group was still noted. In addition, a post hoc analysis of the BEACON study showed two risk factors for developing heart failure: brain natriuretic peptides (BNPs) ≥200 pg/mL and a history of hospitalization due to heart failure [56]. For patients without these two factors, the incidence of heart failure in the bardoxolone methyl and placebo groups was very low (2%). With this background, the Phase II Study of Bardoxolone Methyl in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes (TSUBAKI) trial was conducted in Japan (Fig. 3) [57], which included patients with G3-4 DKD without heart failure risk factors such as BNP ≥200 pg/mL or a history of hospitalization for heart failure. The bardoxolone methyl group had a significant increase in GFR of 6.6 mL/min/1.73 m2 over the placebo group, and the G4 DKD patients showed no signs of heart failure, suggesting that bardoxolone methyl may be a breakthrough agent for improving eGFR in DKD among patients other than those at high risk for heart failure. A Phase 3 Study of Bardoxolone Methyl in Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease (AYAME) trial is a phase III multicenter, placebo-controlled study in Japan last May 2018 (Fig. 3). Similar to the TSUBAKI study, it will evaluate the efficacy of bardoxolone methyl for DKD. The study is currently underway with a target date of March 2022 and is expected to provide stronger evidence of the renoprotective effect of bardoxolone methyl on DKD.
- Presently, the renoprotective effect mechanism of bardoxolone methyl is not fully understood. Nrf2 increases target genes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and NAD(P)H quinone reductase (NQO1), which are detoxifying enzymes, glutathione synthase, heme oxygenase (HO-1), thioredoxin, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase, which are antioxidant enzymes, and inhibits he inflammatory response of macrophages and the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB). These effects may possibly be protective against oxidative stress and chronic inflammation that underlie the progression of DKD. Indeed, diabetic patients have an elevated urinary 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), an indicator of oxidative stress, which correlates with renal complications [58]. In rats, bardoxolone methyl inhibits angiotensin II-stimulated mesangium contraction [59]. It also stabilizes vascular endothelial cell homeostasis by upregulating nitric oxide synthase (NOS) expression [60]. Furthermore, bardoxolone methyl may ameliorate tubular interstitial damage and inhibit the accumulation of extracellular substrates by suppressing TGF-β [61].
- The role of Nrf2 and Keap1 in various models of renal damage has also been investigated by using knockout mice. Nrf2 knockout mice are known to develop lupus nephritis-like autoimmune nephritis after approximately 60 weeks of age, with a deteriorating kidney function [62]. Conversely, Keap1 knockout mice, which degrade Nrf2, were expected to acquire resistance to renal damage by activating Nrf2, but all of them died within 21 weeks of birth due to the hyperkeratinization of the esophagus and other factors [63]. Therefore, for Keap1, studies have been performed in knockdown and conditional knockdown mice, and, in ischemia-reperfusion and nephrotic syndrome models. In NEP25 mice, an improvement in renal damage and an increase in antioxidant factors by Nrf2 activation were noted [64,65]. These experiments in genetically modified mice also show that bardoxolone methyl has a renoprotective effect in activating Nrf2 by suppressing Keap1.
- Nrf2 activator has the potential to improve GFR in DKD patients with no high risk for heart failure. However, Nrf2 activator resulted in an increased albuminuria in both BEAM and BEACON studies. Whether this increase is related to glomerular hyperfiltration, which is the pathogenesis of DKD, needs to be examined.
- Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor
- Regardless of the cause of CKD, irreversible kidney damage is known to progress as CKD progresses beyond a certain point, and the vicious cycle of tubular interstitial hypoxia is thought to be the final common pathway for this progression [66]. In the course of CKD progression, a reduction or loss of blood flow in peritubular capillaries (PTC) is seen from a very early experimental stage. For example, in a rat model of bilateral ischemia-reperfusion injury, a decrease in PTCs has been observed at week 4, and in a mouse model of ischemia-reperfusion injury, fluorescent microangiography has demonstrated a decrease in the perfused area of PTCs at 8 weeks [67]. In addition, the exposure of tubular cells to hypoxia due to reduced blood flow in PTCs leads to the induction of tubular cell apoptosis and cytokines, such as TGF-β, which in turn activate interstitial fibroblasts and increase the production of extracellular matrix, resulting in tubulointerstitial fibrosis progression. Tubulointerstitial fibrosis itself has also been reported to reduce the ability to diffuse oxygen between tubular cells and PTCs [68], creating a vicious cycle, which is thought to be the mechanism of CKD progression. In addition, the vicious cycle of hypoxia also progressed by increased oxygen demand in the nephron caused by hyperfiltration due to a decreased residual glomerular count, decreased NO production and mitochondrial uncoupling due to oxidative stress, and decreased oxygen-carrying capacity due to renal anemia.
- Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) is a key transcription factor in the response to hypoxia. HIF prolyl hydroxylase (HIF-PH) inhibitors impede the degradation of HIF-α by suppressing HIF-PH, which is responsible for its oxygen-dependent degradation, stabilizing its expression and activating it. HIF activation may have a renoprotective effect by ameliorating this vicious cycle of chronic hypoxia, which has been previously tested in numerous experimental animal models. The long-term observation of ischemia-reperfusion injury (AKI-to-CKD transition model) was reported to reduce renal fibrosis by the administration of HIF-PH inhibitor [69]. In addition, a number of experimental CKD models have demonstrated a reduction in tubular interstitial damage due to HIF activation, including Thy-1 nephritis rats, 5/6 nephrectomy rats, and streptozocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus rats. The activation of HIF has been reported to suppress tubular cell apoptosis in Thy-1 nephritis and 5/6 nephrectomy [70,71], whereas its suppression in ischemia-reperfusion models has been reported to increase NF-κB expression and induce inflammation [72], suggesting HIF’s possible renoprotective effect by suppressing cell death and having an anti-inflammatory effect. HIF has also been reported to promote cell regeneration and proliferation; for example, it is known to induce the expression of stromal derived factor-1 and recruit progenitor cells to damaged tissues [73]. Indeed, in five out of six nephrectomized rats, the activation of HIF was effective in preserving PTC [71]. However, with regard to its effects on cell regeneration and proliferation, HIF activation was also reported to induce p27, which represses the cell cycle [74], resulting in tubular cell proliferation of the ischemia-reperfusion injury model [72]. Therefore, whether HIF is protective of tubular cell regeneration remains a debatable point. In this way, HIF has a renoprotective effect in many models of CKD. However, a study on long-term HIF activators in a 5/6 nephrectomy model resulted in worsened renal fibrosis in the long-term (2 to 12 weeks) group [75].
- Thus, the long-term effects of HIF-PH inhibition or HIF activation on CKD are likely to be influenced by multiple factors, including primary disease and disease stage, and need to be investigated in ongoing clinical trials and further basic experiments. However, it is notable that a HIF-PH inhibitor significantly reduced albuminuria and glomerular inflammation in a type 2 diabetes mellitus mouse model [76]. As HIF-PH inhibitors have been approved for renal anemia in CKD not yet on dialysis, clinical trials are required to investigate efficacy as CKD treatment, including DKD, in the future (Fig. 3).
- Incretin-based drugs (glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors)
- Incretin, which is secreted from the gastrointestinal tract after food intake, promotes insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells as blood glucose rises, creating a hypoglycemic effect, and is composed of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Various extrapancreatic effects of incretin are observed because its receptors are expressed not only in the pancreas but also in the small intestine, kidney, heart, and central nervous system [77]. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) is capable of degrading GLP-1 and GIP. GLP-1 levels are reported to be low in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients [78], and DPP4 expression is reported to be elevated in kidney biopsy specimens from DKD patients [79].
- A recent RCT reported the multiple effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists and DPP4 inhibitors, including renoprotective and hypoglycemic effects. In the Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome Results (LEADER) trial [80,81] and the preapproval Trial to Evaluate Cardiovascular and Other Long-term Outcomes with Semaglutide in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes (SUSTAIN-6) [82], combined renal events (the development of overt albuminuria, serum creatinine doubling and eGFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m2, renal replacement therapy, and kidney disease-related death) were decreased in the GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment group (Fig. 3). However, this reduction was largely due to a reduction in the development of overt albuminuria, with no differences in other parameters (serum creatinine doubling, eGFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m2, and renal replacement therapy). Furthermore, the Exenatide Study of Cardiovascular Event Lowering (EXSCEL) study and the Evaluation of Lixisenatide in Acute Coronary Syndrome (ELIXA) trial showed a similar reduction in the development of overt albuminuria, but did not inhibit eGFR reduction [83,84]. In dulaglutide versus insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate-to-severe chronic kidney disease (AWARD-7) trial, which compared dulaglutide and insulin glargine, even though the glycemic and blood pressure control was comparable in both groups, a decrease in albuminuria as well as a decrease in the rate of eGFR reduction in the dulaglutide group was noted (Fig. 3) [85].
- In this way, many RCTs have shown that incretin-based drugs can reduce albuminuria of DKD patients, but there is still controversy on the reduction of the GFR decrease. However, albuminuria is known to be strongly associated with the GFR decrease in DKD, and so, incretin-based drugs are likely to be effective in DKD by reducing albuminuria. In addition, incretin-based drugs are already used for diabetic patients as hypoglycemic agents, and further evidence of their efficacy for DKD is expected to emerge in the future.
- AGE inhibitor
- AGE is a product of nonenzymatic protein and nucleic acid glycation [86]. It is induced by high blood sugar and oxidative stress and causes damage to various organs. Indeed, AGE accumulation has been reported to correlate with DKD progression in human kidney samples [87,88]. AGE, both directly and through its receptor, receptor of advanced glycation end products (RAGE), causes increased oxidative stress, NF-κB–mediated induction of inflammation, and promotion of fibrosis through the induction of TGF-β [89,90]. The experiments in rats reported that AGE caused DKD symptoms in the kidneys of healthy rats, such as glomerular hypertrophy, mesangial expansion, glomerular basement membrane thickening, glomerular sclerosis, and albuminuria [91]. RAGE overexpression in diabetic mice was reported to worsen DKD histological changes and renal dysfunction progression [92]; conversely, RAGE inhibitor was reported to inhibit DKD progression in rats [93]. In addition, the majority of AGE is eliminated from the kidney [94]. Therefore, the progression of DKD due to AGE forms a vicious cycle.
- A number of clinical trials have been conducted on AGE inhibitors, but their effectiveness remains controversial. For example, in pyridoxamine (PYR)-206 and PYR 205/207 studies, pyridoxamine reduced change from baseline in serum creatinine and urinary TGF-β1 excretion after 6 months of treatment in DKD patients (Fig. 3) [95]. The administration of thiamine was reported to reduce the albuminuria of DKD patients [96]. In the Aminoguanidine Clinical Trial in Overt Nephropathy (ACTION) trial of 690 DKD patients, aminoguanidine also reduced proteinuria and inhibited GFR decline (Fig. 3) [97]. On the contrary, the Aminoguanidine Clinical Trial in Overt Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy (ACTION II) trial in DKD patients was discontinued because aminoguanidine was not effective, causing additional side effects such as anemia, liver dysfunction, and vitamin B6 deficiency. When benfotiamine was administered to DKD patients, the albuminuria did not differ from the placebo group [98].
- AGE accumulation plays an important role in metabolic memory, and its inhibition is still an attractive treatment. Although some trials have not shown that AGE inhibitors are effective in treating DKD, there is still room for improvement as regards their optimal administration and sample sizes. Large RCT with optimal administration of AGE inhibitors is expected to prove their efficacy in DKD.
- Epigenetic regulator
- Epigenetics is a DNA sequence-independent regulatory mechanism of gene expression, involving DNA methylation, histone modification, and noncoding RNA. Epigenetic changes, even those caused by transient hyperglycemia or hypoxia, are known to be stored as cellular memory and progressively lead to irreversible renal damage [99]. In fact, vascular endothelial cells exposed to hyperglycemia have been reported to continue to increase oxidative stress and elicit inflammation even after normalization of blood glucose [100]. Furthermore, the aberrant DNA methylation in mesangial cells has been reported to be involved in the progression of diabetic nephropathy [101,102], and in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy, it, along with altered histone modifications in tubular cells, has been observed [103,104]. Thus, epigenetic genetic changes play an important role in DKD progression.
- With regard to DNA methylation, the promoter region of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) has been reported to be hypomethylated in whole blood cells and blood monocytes of DKD patients [105]. The knockout of TXNIP was reported to reduce renal damage in the DKD mouse model [106]. Therefore, this hypomethylation may possibly lead to advanced DKD progression. The hypomethylation of runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) and the increased expression of RUNX1 in tubular cells taken from human kidney biopsy samples [107] were also reported. With regard to histone modification, H3K9 acetylation (H3K9ac) is increased in the promoter region of the high glycated hemoglobin group, according to the report on the histone modification status of blood lymphocytes and monocytes from type 1 diabetes mellitus patients [108]. H3K9ac has been shown to be associated with the Nf-κB pathway, suggesting that increased H3K9ac may be involved in DKD progression by inflammation pathway [6]. Lipids are also known to induce SET7, an H3K4 methyltransferase, and promote the gene expression that causes glomerular hypertrophy and renal fibrosis [109]. The treatment of mesangial cells with losartan under hyperglycemic conditions was reported to reduce the increase of H3K9/14ac in the promoter regions of RAGE, PAI-1, and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) [110], indicating that AGE and epigenetics are interrelated to produce metabolic memory. HIF-1, a master regulator in the hypoxic response, induces histone-modifying enzymes, such as histone demethylases, including lysine demethylase (KDM) 3A, KDM3B, and KDM3C, to its binding sites, which alter chromatin structure and regulate gene expression [111]. For example, our group showed that a hypoxic stimulus to human umbilical venous endothelial cells caused HIF-1 to bind to the upstream site of glucose transporter 3 (GLUT3) transcriptional initiation point and induced KDM3A, one of the histone demethylases, to this site [112], which meant that hypoxia altered histone modifications and chromatin structures, resulting in the upregulation of gene expressions.
- Noncoding RNA is a generic term for RNA other than mRNA that is translated into proteins. It can regulate gene expressions by transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms and has various physiological functions. We found that aspartyl-tRNA synthetase antisense 1 (DARS-AS1), a long noncoding RNA, was induced by HIF1 in tubular cells under hypoxic conditions and that DARS-AS1 inhibited tubular cell apoptosis [113]. As regards DKD, the noncoding RNAs closely related to it include miRNA-21 and miRNA-29. miRNA-21 is highly expressed in the kidney and is known to be closely linked to TGF-β signaling [114,115]. In the blood and urine of transplant patients, peritoneal dialysis patients, and patients with immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy, it was reported to be strongly correlated with renal fibrosis [116-118]. On the contrary, miRNA-29 is considered an antifibrotic factor. Its expression is known to be reduced by TGF-β stimulation in tubular cells [119] and also reduced in unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) rats [120]. Thus, numerous miRNAs have been found to act as fibrotic and antifibrotic factors in DKD, but the mechanisms are extremely complex and require further basic research.
- Histone modification inhibitors are being studied as a potential treatment for these epigenetic changes. The histone deacetylase inhibitors, such as vorinostat, valproate, sodium butyrate, and trichostatin, have been reported to reduce proteinuria and improve oxidative stress, fibrosis, glomerular damage, and inflammation in the DKD rat model [121-125]. In addition, Dznep, an inhibitor of Ezh2, H3K27 methyltransferase, was reported to inhibit renal fibrosis in mice with UUO and AKI-to-CKD transition [126,127]. Our group showed that AKI damage caused an elevated level of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases 2 (TIMP2), which is considered a profibrotic gene, and that TIMP2 was downregulated by Dznep, which meant that TIMP2 was regulated epigenetically and that Dznep recovered this change. Therefore, Dznep can be a novel drug for renal fibrosis via the control of TIMP2. We are now researching on how Dznep regulates TIMP2 epigenetically. Moreover, the administration of MM-102, the inhibitor of myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1), H3K4 methyltransferase, also suppresses fibrosis in AKI-to-CKD transition mice after ischemia-reperfusion injury [128].
- CKD, including DKD, is known to be irreversible when it progresses beyond a certain point [60]. If the epigenetic changes in CKD can be elucidated, the potential to develop innovative drugs that can reverse CKD progression is seen. Current research on histone modification inhibitors strongly suggests this possibility. These histone modification inhibitors are expected to show efficacy in clinical trials for the treatment of CKD in the future.
FUTURE TREATMENT
- DKD is the most significant cause of ESKD, which requires renal replacement therapy. However, until recently, RAS inhibitor with multidisciplinary treatments has been the only available treatment option. In 2019, CREDENCE trial proved the efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors for DKD, adding a new treatment option. However, DKD does not completely inhibit the progression of the disease. Nrf2 activator is a novel drug that improves the kidney function in DKD patients. However, in the BEACON trial, it was discontinued as it caused heart failure; the Japanese TSUBAKI trial showed its effectiveness against DKD. HIF-PH inhibitor has been recently approved for renal anemia and has the potential to be effective against CKD and DKD by enhancing the biological response to hypoxia. Thus, it has the potential to be a breakthrough drug for DKD, like Nrf2 activator. Furthermore, by elucidating new mechanisms of metabolic memory caused by AGE and epigenetic changes in kidney, AGE and histone modification inhibitors are expected to become breakthroughs in DKD treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Imari Mimura and Tomotaka Yamazaki have no conflict of interest.
-
FUNDING
Masaomi Nangaku reports personal fees from Akebia, grants and personal fees from Astellas, personal fees from AstraZeneca, grants and personal fees from Bayer, grants and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from GSK, grants and personal fees from JT, grants and personal fees from Kyowa Kirin, grants and personal fees from Torii, grants and personal fees from Mitsubishi Tanabe, grants and personal fees from Ono, grants and personal fees from Chugai, grants and personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo, grants from Takeda. Tetsuhiro Tanaka has received honoraria from Kyowa-Kirin and Astellas, and research grant from JT.
NOTES
-
Acknowledgements
- None

- 1. Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, Chiang JL, de Boer IH, Goldstein-Fuchs J, et al. Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA Consensus Conference. Diabetes Care 2014;37:2864-83.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 2. Tervaert TW, Mooyaart AL, Amann K, Cohen AH, Cook HT, Drachenberg CB, et al. Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2010;21:556-63.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Yokoyama H, Sone H, Oishi M, Kawai K, Fukumoto Y, Kobayashi M, et al. Prevalence of albuminuria and renal insufficiency and associated clinical factors in type 2 diabetes: the Japan Diabetes Clinical Data Management study (JDDM15). Nephrol Dial Transplant 2009;24:1212-9.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Afkarian M, Zelnick LR, Hall YN, Heagerty PJ, Tuttle K, Weiss NS, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among us adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA 2016;316:602-10.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Hirakawa Y, Tanaka T, Nangaku M. Mechanisms of metabolic memory and renal hypoxia as a therapeutic target in diabetic kidney disease. J Diabetes Investig 2017;8:261-71.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 2001;414:813-20.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJ, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2019;380:2295-306.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth SM, Lachin JM, Orchard TJ, et al. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2643-53.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Chalmers J, Cooper ME. UKPDS and the legacy effect. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1618-20.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Ceriello A. Hypothesis: the “metabolic memory”, the new challenge of diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2009;86 Suppl 1:S2-6.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Reddy MA, Zhang E, Natarajan R. Epigenetic mechanisms in diabetic complications and metabolic memory. Diabetologia 2015;58:443-55.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, Rohde RD. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med 1993;329:1456-62.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2001;345:861-9.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Pohl MA, Blumenthal S, Cordonnier DJ, De Alvaro F, Deferrari G, Eisner G, et al. Independent and additive impact of blood pressure control and angiotensin II receptor blockade on renal outcomes in the irbesartan diabetic nephropathy trial: clinical implications and limitations. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005;16:3027-37.PubMed
- 15. Parving HH, Lehnert H, Brochner-Mortensen J, Gomis R, Andersen S, Arner P, et al. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2001;345:870-8.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Makino H, Haneda M, Babazono T, Moriya T, Ito S, Iwamoto Y, et al. Prevention of transition from incipient to overt nephropathy with telmisartan in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007;30:1577-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Viberti G, Wheeldon NM; MicroAlbuminuria Reduction With VALsartan (MARVAL) Study Investigators. Microalbuminuria reduction with valsartan in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a blood pressure-independent effect. Circulation 2002;106:672-8.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Ruggenenti P, Fassi A, Ilieva AP, Bruno S, Iliev IP, Brusegan V, et al. Preventing microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1941-51.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Haller H, Ito S, Izzo JL Jr, Januszewicz A, Katayama S, Menne J, et al. Olmesartan for the delay or prevention of microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2011;364:907-17.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Ali MK, Bullard KM, Saaddine JB, Cowie CC, Imperatore G, Gregg EW. Achievement of goals in U.S. diabetes care, 1999-2010. N Engl J Med 2013;368:1613-24.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Jacobsen P, Andersen S, Rossing K, Jensen BR, Parving HH. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system versus maximal recommended dose of ACE inhibition in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 2003;63:1874-80.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Mann JF, Schmieder RE, McQueen M, Dyal L, Schumacher H, Pogue J, et al. Renal outcomes with telmisartan, ramipril, or both, in people at high vascular risk (the ONTARGET study): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet 2008;372:547-53.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, Brophy M, Conner TA, Duckworth W, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2013;369:1892-903.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Patel S, Rauf A, Khan H, Abu-Izneid T. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS): the ubiquitous system for homeostasis and pathologies. Biomed Pharmacother 2017;94:317-25.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Koszegi S, Molnar A, Lenart L, Hodrea J, Balogh DB, Lakat T, et al. RAAS inhibitors directly reduce diabetes-induced renal fibrosis via growth factor inhibition. J Physiol 2019;597:193-209.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Kagami S, Border WA, Miller DE, Noble NA. Angiotensin II stimulates extracellular matrix protein synthesis through induction of transforming growth factor-beta expression in rat glomerular mesangial cells. J Clin Invest 1994;93:2431-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Reese S, Vidyasagar A, Jacobson L, Acun Z, Esnault S, Hullett D, et al. The Pin 1 inhibitor juglone attenuates kidney fibrogenesis via Pin 1-independent mechanisms in the unilateral ureteral occlusion model. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2010;3:1.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 28. Rincon-Choles H, Kasinath BS, Gorin Y, Abboud HE. Angiotensin II and growth factors in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl:2002;S8-11.Article
- 29. Kang JS, Lee SJ, Lee JH, Kim JH, Son SS, Cha SK, et al. Angiotensin II-mediated MYH9 downregulation causes structural and functional podocyte injury in diabetic kidney disease. Sci Rep 2019;9:7679.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 30. Barrera-Chimal J, Girerd S, Jaisser F. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and kidney diseases: pathophysiological basis. Kidney Int 2019;96:302-19.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Hou J, Xiong W, Cao L, Wen X, Li A. Spironolactone add-on for preventing or slowing the progression of diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis. Clin Ther 2015;37:2086-103.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Williams GH, Burgess E, Kolloch RE, Ruilope LM, Niegowska J, Kipnes MS, et al. Efficacy of eplerenone versus enalapril as monotherapy in systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol 2004;93:990-6.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Chan JC, Cooper ME, Gansevoort RT, Haller H, et al. Effect of finerenone on albuminuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2015;314:884-94.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Wan N, Rahman A, Nishiyama A. Esaxerenone, a novel nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor blocker (MRB) in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. J Hum Hypertens 2020 Jul 13 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-0377-6.Article
- 35. Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Anker SD, Pitt B, Ruilope LM, Nowack C, et al. Design and baseline characteristics of the finerenone in reducing kidney failure and disease progression in diabetic kidney disease trial. Am J Nephrol 2019;50:333-44.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 36. Ruilope LM, Agarwal R, Anker SD, Bakris GL, Filippatos G, Nowack C, et al. Design and baseline characteristics of the finerenone in reducing cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in diabetic kidney disease trial. Am J Nephrol 2019;50:345-56.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 37. Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:580-91.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Ueki K, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, Kato M, Okahata S, Katsuyama H, et al. Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (JDOIT3): an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2017;5:951-64.PubMed
- 39. Ueki K, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, Miyake K, Nangaku M, Ohashi Y, et al. Effect of multifactorial intervention on diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. SSRN 2019 Jun 21 . https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3409298.Article
- 40. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2117-28.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2016;375:323-34.ArticlePubMed
- 42. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2017;377:644-57.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2019;380:347-57.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Zelniker TA, Wiviott SD, Raz I, Im K, Goodrich EL, Bonaca MP, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet 2019;393:31-9.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Tonneijck L, Muskiet MH, Smits MM, van Bommel EJ, Heerspink HJ, van Raalte DH, et al. Glomerular hyperfiltration in diabetes: mechanisms, clinical significance, and treatment. J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;28:1023-39.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 46. Korner A, Eklof AC, Celsi G, Aperia A. Increased renal metabolism in diabetes. Mechanism and functional implications. Diabetes 1994;43:629-33.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Mudaliar S, Alloju S, Henry RR. Can a shift in fuel energetics explain the beneficial cardiorenal outcomes in the EMPAREG OUTCOME Study? A unifying hypothesis. Diabetes Care 2016;39:1115-22.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 48. Takagi S, Li J, Takagaki Y, Kitada M, Nitta K, Takasu T, et al. Ipragliflozin improves mitochondrial abnormalities in renal tubules induced by a high-fat diet. J Diabetes Investig 2018;9:1025-32.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 49. Tanaka S, Sugiura Y, Saito H, Sugahara M, Higashijima Y, Yamaguchi J, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition normalizes glucose metabolism and suppresses oxidative stress in the kidneys of diabetic mice. Kidney Int 2018;94:912-25.ArticlePubMed
- 50. Heerspink HJL, Stefansson BV, Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med 2020;383:1436-46.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Ito M, Tanaka T, Nangaku M. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 as a treatment target of kidney diseases. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2020;29:128-35.ArticlePubMed
- 52. Bryan HK, Olayanju A, Goldring CE, Park BK. The Nrf2 cell defence pathway: Keap1-dependent and -independent mechanisms of regulation. Biochem Pharmacol 2013;85:705-17.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Ruiz S, Pergola PE, Zager RA, Vaziri ND. Targeting the transcription factor Nrf2 to ameliorate oxidative stress and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2013;83:1029-41.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 54. Pergola PE, Raskin P, Toto RD, Meyer CJ, Huff JW, Grossman EB, et al. Bardoxolone methyl and kidney function in CKD with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2011;365:327-36.ArticlePubMed
- 55. de Zeeuw D, Akizawa T, Audhya P, Bakris GL, Chin M, Christ-Schmidt H, et al. Bardoxolone methyl in type 2 diabetes and stage 4 chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 2013;369:2492-503.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 56. Chin MP, Wrolstad D, Bakris GL, Chertow GM, de Zeeuw D, Goldsberry A, et al. Risk factors for heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and stage 4 chronic kidney disease treated with bardoxolone methyl. J Card Fail 2014;20:953-8.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Nangaku M, Kanda H, Takama H, Ichikawa T, Hase H, Akizawa T. randomized clinical trial on the effect of bardoxolone methyl on GFR in diabetic kidney disease patients (TSUBAKI Study). Kidney Int Rep 2020;5:879-90.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 58. Dandona P, Thusu K, Cook S, Snyder B, Makowski J, Armstrong D, et al. Oxidative damage to DNA in diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1996;347:444-5.ArticlePubMed
- 59. Ding Y, Stidham RD, Bumeister R, Trevino I, Winters A, Sprouse M, et al. The synthetic triterpenoid, RTA 405, increases the glomerular filtration rate and reduces angiotensin II-induced contraction of glomerular mesangial cells. Kidney Int 2013;83:845-54.ArticlePubMed
- 60. Heiss EH, Schachner D, Werner ER, Dirsch VM. Active NF-E2-related factor (Nrf2) contributes to keep endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) in the coupled state: role of reactive oxygen species (ROS), eNOS, and heme oxygenase (HO-1) levels. J Biol Chem 2009;284:31579-86.PubMedPMC
- 61. Zheng H, Whitman SA, Wu W, Wondrak GT, Wong PK, Fang D, et al. Therapeutic potential of Nrf2 activators in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2011;60:3055-66.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 62. Yoh K, Itoh K, Enomoto A, Hirayama A, Yamaguchi N, Kobayashi M, et al. Nrf2-deficient female mice develop lupuslike autoimmune nephritis. Kidney Int 2001;60:1343-53.PubMed
- 63. Wakabayashi N, Itoh K, Wakabayashi J, Motohashi H, Noda S, Takahashi S, et al. Keap1-null mutation leads to postnatal lethality due to constitutive Nrf2 activation. Nat Genet 2003;35:238-45.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 64. Nezu M, Souma T, Yu L, Suzuki T, Saigusa D, Ito S, et al. Transcription factor Nrf2 hyperactivation in early-phase renal ischemia-reperfusion injury prevents tubular damage progression. Kidney Int 2017;91:387-401.ArticlePubMed
- 65. Miyazaki Y, Shimizu A, Pastan I, Taguchi K, Naganuma E, Suzuki T, et al. Keap1 inhibition attenuates glomerulosclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2014;29:783-91.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 66. Nangaku M. Chronic hypoxia and tubulointerstitial injury: a final common pathway to end-stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006;17:17-25.PubMed
- 67. Kramann R, Tanaka M, Humphreys BD. Fluorescence microangiography for quantitative assessment of peritubular capillary changes after AKI in mice. J Am Soc Nephrol 2014;25:1924-31.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. Norman JT, Clark IM, Garcia PL. Hypoxia promotes fibrogenesis in human renal fibroblasts. Kidney Int 2000;58:2351-66.ArticlePubMed
- 69. Kapitsinou PP, Jaffe J, Michael M, Swan CE, Duffy KJ, Erickson-Miller CL, et al. Preischemic targeting of HIF prolyl hydroxylation inhibits fibrosis associated with acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2012;302:F1172-9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 70. Tanaka T, Matsumoto M, Inagi R, Miyata T, Kojima I, Ohse T, et al. Induction of protective genes by cobalt ameliorates tubulointerstitial injury in the progressive Thy1 nephritis. Kidney Int 2005;68:2714-25.ArticlePubMed
- 71. Tanaka T, Kojima I, Ohse T, Ingelfinger JR, Adler S, Fujita T, et al. Cobalt promotes angiogenesis via hypoxia-inducible factor and protects tubulointerstitium in the remnant kidney model. Lab Invest 2005;85:1292-307.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 72. Conde E, Gimenez-Moyano S, Martin-Gomez L, Rodriguez M, Ramos ME, Aguado-Fraile E, et al. HIF-1α induction during reperfusion avoids maladaptive repair after renal ischemia/reperfusion involving miR127-3p. Sci Rep 2017;7:41099.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 73. Ceradini DJ, Kulkarni AR, Callaghan MJ, Tepper OM, Bastidas N, Kleinman ME, et al. Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat Med 2004;10:858-64.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 74. Koshiji M, Huang LE. Dynamic balancing of the dual nature of HIF-1alpha for cell survival. Cell Cycle 2004;3:853-4.ArticlePubMed
- 75. Yu X, Fang Y, Ding X, Liu H, Zhu J, Zou J, et al. Transient hypoxia- inducible factor activation in rat renal ablation and reduced fibrosis with L-mimosine. Nephrology (Carlton) 2012;17:58-67.ArticlePubMed
- 76. Sugahara M, Tanaka S, Tanaka T, Saito H, Ishimoto Y, Wakashima T, et al. Prolyl hydroxylase domain inhibitor protects against metabolic disorders and associated kidney disease in obese type 2 diabetic mice. J Am Soc Nephrol 2020;31:560-77.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 77. Tanaka T, Higashijima Y, Wada T, Nangaku M. The potential for renoprotection with incretin-based drugs. Kidney Int 2014;86:701-11.ArticlePubMed
- 78. Lastya A, Saraswati MR, Suastika K. The low level of glucagonlike peptide-1 (glp-1) is a risk factor of type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Res Notes 2014;7:849.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 79. Sharkovska Y, Reichetzeder C, Alter M, Tsuprykov O, Bachmann S, Secher T, et al. Blood pressure and glucose independent renoprotective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition in a mouse model of type-2 diabetic nephropathy. J Hypertens 2014;32:2211-23.ArticlePubMed
- 80. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2016;375:311-22.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 81. Mann JFE, Orsted DD, Brown-Frandsen K, Marso SP, Poulter NR, Rasmussen S, et al. Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2017;377:839-48.ArticlePubMed
- 82. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jodar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2016;375:1834-44.ArticlePubMed
- 83. Holman RR, Bethel MA, Mentz RJ, Thompson VP, Lokhnygina Y, Buse JB, et al. Effects of once-weekly exenatide on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1228-39.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 84. Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, Dickstein K, Gerstein HC, Kober LV, et al. Lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2247-57.ArticlePubMed
- 85. Tuttle KR, Lakshmanan MC, Rayner B, Busch RS, Zimmermann AG, Woodward DB, et al. Dulaglutide versus insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate-to-severe chronic kidney disease (AWARD-7): a multicentre, openlabel, randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018;6:605-17.ArticlePubMed
- 86. Brownlee M, Vlassara H, Cerami A. Nonenzymatic glycosylation and the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Ann Intern Med 1984;101:527-37.ArticlePubMed
- 87. Mallipattu SK, Uribarri J. Advanced glycation end product accumulation: a new enemy to target in chronic kidney disease? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2014;23:547-54.PubMedPMC
- 88. Saulnier PJ, Wheelock KM, Howell S, Weil EJ, Tanamas SK, Knowler WC, et al. Advanced glycation end products predict loss of renal function and correlate with lesions of diabetic kidney disease in American Indians with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2016;65:3744-53.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 89. Fleming TH, Humpert PM, Nawroth PP, Bierhaus A. Reactive metabolites and AGE/RAGE-mediated cellular dysfunction affect the aging process: a mini-review. Gerontology 2011;57:435-43.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 90. Coughlan MT, Thorburn DR, Penfold SA, Laskowski A, Harcourt BE, Sourris KC, et al. RAGE-induced cytosolic ROS promote mitochondrial superoxide generation in diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 2009;20:742-52.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 91. Vlassara H, Striker LJ, Teichberg S, Fuh H, Li YM, Steffes M. Advanced glycation end products induce glomerular sclerosis and albuminuria in normal rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994;91:11704-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 92. Yamamoto Y, Kato I, Doi T, Yonekura H, Ohashi S, Takeuchi M, et al. Development and prevention of advanced diabetic nephropathy in RAGE-overexpressing mice. J Clin Invest 2001;108:261-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 93. Matsui T, Higashimoto Y, Nishino Y, Nakamura N, Fukami K, Yamagishi SI. RAGE-aptamer blocks the development and progression of experimental diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2017;66:1683-95.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 94. Miyata T, Ueda Y, Horie K, Nangaku M, Tanaka S, van Ypersele de Strihou C, et al. Renal catabolism of advanced glycation end products: the fate of pentosidine. Kidney Int 1998;53:416-22.ArticlePubMed
- 95. Williams ME, Bolton WK, Khalifah RG, Degenhardt TP, Schotzinger RJ, McGill JB. Effects of pyridoxamine in combined phase 2 studies of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy. Am J Nephrol 2007;27:605-14.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 96. Rabbani N, Alam SS, Riaz S, Larkin JR, Akhtar MW, Shafi T, et al. High-dose thiamine therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria: a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. Diabetologia 2009;52:208-12.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 97. Bolton WK, Cattran DC, Williams ME, Adler SG, Appel GB, Cartwright K, et al. Randomized trial of an inhibitor of formation of advanced glycation end products in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol 2004;24:32-40.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 98. Alkhalaf A, Klooster A, van Oeveren W, Achenbach U, Kleefstra N, Slingerland RJ, et al. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial on benfotiamine treatment in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care 2010;33:1598-601.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 99. Kato M, Natarajan R. Epigenetics and epigenomics in diabetic kidney disease and metabolic memory. Nat Rev Nephrol 2019;15:327-45.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 100. El-Osta A, Brasacchio D, Yao D, Pocai A, Jones PL, Roeder RG, et al. Transient high glucose causes persistent epigenetic changes and altered gene expression during subsequent normoglycemia. J Exp Med 2008;205:2409-17.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 101. Oba S, Ayuzawa N, Nishimoto M, Kawarazaki W, Ueda K, Hirohama D, et al. Aberrant DNA methylation of Tgfb1 in diabetic kidney mesangial cells. Sci Rep 2018;8:16338.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 102. Rosen ED, Kaestner KH, Natarajan R, Patti ME, Sallari R, Sander M, et al. Epigenetics and epigenomics: implications for diabetes and obesity. Diabetes 2018;67:1923-31.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 103. Marumo T, Yagi S, Kawarazaki W, Nishimoto M, Ayuzawa N, Watanabe A, et al. Diabetes induces aberrant DNA methylation in the proximal tubules of the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 2015;26:2388-97.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 104. Morgado-Pascual JL, Marchant V, Rodrigues-Diez R, Dolade N, Suarez-Alvarez B, Kerr B, et al. Epigenetic modification mechanisms involved in inflammation and fibrosis in renal pathology. Mediators Inflamm 2018;2018:2931049.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 105. Chen Z, Miao F, Paterson AD, Lachin JM, Zhang L, Schones DE, et al. Epigenomic profiling reveals an association between persistence of DNA methylation and metabolic memory in the DCCT/EDIC type 1 diabetes cohort. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;113:E3002-11.PubMedPMC
- 106. Shah A, Xia L, Masson EA, Gui C, Momen A, Shikatani EA, et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein deficiency protects against diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2015;26:2963-77.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 107. Ko YA, Mohtat D, Suzuki M, Park AS, Izquierdo MC, Han SY, et al. Cytosine methylation changes in enhancer regions of core pro-fibrotic genes characterize kidney fibrosis development. Genome Biol 2013;14:R108.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 108. Miao F, Chen Z, Genuth S, Paterson A, Zhang L, Wu X, et al. Evaluating the role of epigenetic histone modifications in the metabolic memory of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2014;63:1748-62.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 109. Yuan H, Reddy MA, Deshpande S, Jia Y, Park JT, Lanting LL, et al. Epigenetic histone modifications involved in profibrotic gene regulation by 12/15-lipoxygenase and its oxidized lipid products in diabetic nephropathy. Antioxid Redox Signal 2016;24:361-75.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 110. Reddy MA, Sumanth P, Lanting L, Yuan H, Wang M, Mar D, et al. Losartan reverses permissive epigenetic changes in renal glomeruli of diabetic db/db mice. Kidney Int 2014;85:362-73.ArticlePubMed
- 111. Mimura I, Tanaka T, Nangaku M. Novel therapeutic strategy with hypoxia- inducible factors via reversible epigenetic regulation mechanisms in progressive tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Semin Nephrol 2013;33:375-82.ArticlePubMed
- 112. Mimura I, Nangaku M, Kanki Y, Tsutsumi S, Inoue T, Kohro T, et al. Dynamic change of chromatin conformation in response to hypoxia enhances the expression of GLUT3 (SLC2A3) by cooperative interaction of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and KDM3A. Mol Cell Biol 2012;32:3018-32.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 113. Mimura I, Hirakawa Y, Kanki Y, Kushida N, Nakaki R, Suzuki Y, et al. Novel lnc RNA regulated by HIF-1 inhibits apoptotic cell death in the renal tubular epithelial cells under hypoxia. Physiol Rep 2017;5:e13203.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 114. Denby L, Baker AH. Targeting non-coding RNA for the therapy of renal disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2016;27:70-7.ArticlePubMed
- 115. Zhong X, Chung AC, Chen HY, Meng XM, Lan HY. Smad3- mediated upregulation of miR-21 promotes renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2011;22:1668-81.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 116. Wang G, Kwan BC, Lai FM, Chow KM, Li PK, Szeto CC. Urinary miR-21, miR-29, and miR-93: novel biomarkers of fibrosis. Am J Nephrol 2012;36:412-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 117. Lopez-Anton M, Lambie M, Lopez-Cabrera M, Schmitt CP, Ruiz-Carpio V, Bartosova M, et al. miR-21 promotes fibrogenesis in peritoneal dialysis. Am J Pathol 2017;187:1537-50.ArticlePubMed
- 118. Van der Hauwaert C, Savary G, Hennino MF, Pottier N, Glowacki F, Cauffiez C. Implication des microARN dans la fibrose rénale [MicroRNAs in kidney fibrosis]. Nephrol Ther 2015;11:474-82.PubMed
- 119. Qin W, Chung AC, Huang XR, Meng XM, Hui DS, Yu CM, et al. TGF-β/Smad3 signaling promotes renal fibrosis by inhibiting miR-29. J Am Soc Nephrol 2011;22:1462-74.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 120. Ramdas V, McBride M, Denby L, Baker AH. Canonical transforming growth factor-β signaling regulates disintegrin metalloprotease expression in experimental renal fibrosis via miR29. Am J Pathol 2013;183:1885-96.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 121. Sun XY, Qin HJ, Zhang Z, Xu Y, Yang XC, Zhao DM, et al. Valproate attenuates diabetic nephropathy through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Mol Med Rep 2016;13:661-8.ArticlePubMed
- 122. Khan S, Jena G, Tikoo K. Sodium valproate ameliorates diabetes-induced fibrosis and renal damage by the inhibition of histone deacetylases in diabetic rat. Exp Mol Pathol 2015;98:230-9.ArticlePubMed
- 123. Khan S, Jena G. Sodium butyrate, a HDAC inhibitor ameliorates eNOS, iNOS and TGF-β1-induced fibrogenesis, apoptosis and DNA damage in the kidney of juvenile diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol 2014;73:127-39.ArticlePubMed
- 124. Noh H, Oh EY, Seo JY, Yu MR, Kim YO, Ha H, et al. Histone deacetylase-2 is a key regulator of diabetes- and transforming growth factor-beta1-induced renal injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2009;297:F729-39.PubMed
- 125. Advani A, Huang Q, Thai K, Advani SL, White KE, Kelly DJ, et al. Long-term administration of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat attenuates renal injury in experimental diabetes through an endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent mechanism. Am J Pathol 2011;178:2205-14.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 126. Zhou X, Zang X, Ponnusamy M, Masucci MV, Tolbert E, Gong R, et al. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 inhibition attenuates renal fibrosis by maintaining smad7 and phosphatase and tensin homolog expression. J Am Soc Nephrol 2016;27:2092-108.ArticlePubMed
- 127. Mimura I, Hirakawa Y, Kanki Y, Nakaki R, Suzuki Y, Tanaka T, et al. Genome-wide analysis revealed that DZNep reduces tubulointerstitial fibrosis via down-regulation of pro-fibrotic genes. Sci Rep 2018;8:3779.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 128. Shimoda H, Doi S, Nakashima A, Sasaki K, Doi T, Masaki T. Inhibition of the H3K4 methyltransferase MLL1/WDR5 complex attenuates renal senescence in ischemia reperfusion mice by reduction of p16 INK4a. Kidney Int 2019;96:1162-75.PubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Clinical value of serum MMP-3 in chronic kidney disease
Yulin Fu, Cheng Song, Yuan Qin, Tianyu Zheng, Xiumei Zhou, Xueqin Zhao, Jian Zou, Biao Huang
Clinica Chimica Acta.2024; 553: 117725. CrossRef - β2-Adrenergic receptor agonists as a treatment for diabetic kidney disease
Ehtesham Arif, Danira Medunjanin, Ashish Solanki, Xiaofeng Zuo, Yanhui Su, Yujing Dang, Brennan Winkler, Kasey Lerner, Ahmed I. Kamal, Oleg Palygin, Marc-Andre Cornier, Bethany J. Wolf, Kelly J. Hunt, Joshua H. Lipschutz
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2024; 326(1): F20. CrossRef - β2-Adrenergic receptor agonists: a new treatment for diabetic kidney disease?
Zhiwen Liu, Zheng Dong
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2024; 326(1): F1. CrossRef - Urinary exosomal microRNA-145-5p and microRNA-27a-3p act as noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease
Lu-Lu Han, Sheng-Hai Wang, Ming-Yan Yao, Hong Zhou
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(1): 92. CrossRef - Placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against diabetic kidney disease by upregulating autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
Honghong Liu, Jiao Wang, Guanru Yue, Jixiong Xu
Renal Failure.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of serum Nrf2 protein levels with disease activity and renal impairment in lupus nephritis
Jicui Li, Qiaoyan Guo, Xianping Wei, Yuexin Zhu, Manyu Luo, Ping Luo
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Qidan Tangshen Granule on diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Hua Yang, Shisi Xia, Yilei Cong, Xinyu Yang, Jie Min, Tengfei Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111128. CrossRef - Comparison of conventional mathematical model and machine learning model based on recent advances in mathematical models for predicting diabetic kidney disease
Yingda Sheng, Caimei Zhang, Jing Huang, Dan Wang, Qian Xiao, Haocheng Zhang, Xiaoqin Ha
DIGITAL HEALTH.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Experimental Verification to Reveal the Mitophagy-Associated Mechanism of Tangshen Formula in the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy
Yinfeng Chen, Xiaying Wang, Jie Min, Jie Zheng, Xuanli Tang, Xiaoling Zhu, Dongrong Yu, De Jin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 739. CrossRef - Senolytic combination of dasatinib and quercetin protects against diabetic kidney disease by activating autophagy to alleviate podocyte dedifferentiation via the Notch pathway
Xinwang Zhu, Congxiao Zhang, Linlin Liu, Li Xu, Li Yao
International Journal of Molecular Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Decreased risk of renal cell carcinoma in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sodium glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitors
Chun‐Huei Chiu, Wei‐Yao Wang, Hung‐Yi Chen, Pei‐Lun Liao, Gwo‐Ping Jong, Tsung‐Yuan Yang
Cancer Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - System Biology Approaches for Systemic Diseases: Emphasis on Type II Diabetes Mellitus and Allied Metabolism
Mohan Das, Moumita Chakraborty, Promi Das, Sayantan Santra, Abhishek Mukherjee, Sarobi Das, Krisztian Banyai, Souvik Roy, Lopamudra Choudhury, Rudrak Gupta, Tama Dey, Dibya Das, Anirbandeep Bose, Balasubramanian Ganesh, Rintu Banerjee
Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology.2024; : 103176. CrossRef - Beneficial effects of ginsenosides on diabetic nephropathy: A systematical review and meta-analysis of preclinical evidence
Xiao-Mei Chen, Gui-Xuan Lin, Xue Wang, Hong-Yan Ma, Ru-Shang Wang, Shu-Mei Wang, Dan Tang
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2023; 302: 115860. CrossRef - Waist circumference and end‐stage renal disease based on glycaemic status: National Health Insurance Service data 2009–2018
Yun Kyung Cho, Ji Hye Huh, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Kyung‐do Han, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung‐Hee Ihm
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(1): 585. CrossRef - A Narrative Review of New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy
Aadhira Pillai, Darshna Fulmali
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Shenkang recipe alleviates renal aging in diabetic kidney disease by interfering with the lysine-specific demethylase KDM6B to modulate the PPAR-γ signaling pathway
Anna Zuo, Jiarun Xie, Junqiao Shao, Shuyu Li, Haoyu Lin, Shaoting Wang, Wei Sun, Jinjin Xia, Weiqiang Jiang, Jia Sun, Ming Wang
Pharmacological Research - Modern Chinese Medicine.2023; 6: 100216. CrossRef - miR-223-3p mediates the diabetic kidney disease progression by targeting IL6ST/STAT3 pathway
Ping Tang, Yushan Xu, Jingrong Zhang, Juanli Nan, Ruxian Zhong, Jingmei Luo, Dazhi Xu, Shaoqing Shi, Lihua Zhang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2023; 648: 50. CrossRef - miR‐124‐3p improves mitochondrial function of renal tubular epithelial cells in db/db mice
Luqun Liang, Chunxin Wo, Yao Yuan, Hongjuan Cao, Wanlin Tan, Xingcheng Zhou, Dan Wang, Rongyu Chen, Mingjun Shi, Fan Zhang, Ying Xiao, Lingling Liu, Yuxia Zhou, Tian Zhang, Yuanyuan Wang, Bing Guo
The FASEB Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Prolyl-Hydroxylase and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Low-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome-Related Anemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Report of Three Cases
Satoshi Yamasaki, Takahiko Horiuchi
Hematology Reports.2023; 15(1): 180. CrossRef - Diagnostic significance of hsa_circ_0000146 and hsa_circ_0000072 biomarkers for Diabetic Kidney Disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Amul Badr, Omayma Elkholy, Mona Said, Sally Fahim, Mohamed El-Khatib, Dina Sabry, Radwa Gaber
Journal of Medical Biochemistry.2023; 42(2): 239. CrossRef - The emerging insight into E3 ligases as the potential therapeutic target for diabetic kidney disease
Vivek Akhouri, Syamantak Majumder, Anil Bhanudas Gaikwad
Life Sciences.2023; 321: 121643. CrossRef - Klotho’s impact on diabetic nephropathy and its emerging connection to diabetic retinopathy
Anqi Tang, Yu Zhang, Ling Wu, Yong Lin, Lizeyu Lv, Liangbin Zhao, Bojun Xu, Youqun Huang, Mingquan Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences and Clinical Significance of Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 and Vasohibin-1 (VASH-1) Levels in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy and Different Renal Injuries
Hui Liu, Dongyan Wang, Jingnan Tang, Linlin Yu, Shanshan Su
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1085. CrossRef - Medial Arterial Calcification and the Risk of Amputation of Diabetic Foot Ulcer in Patients With Diabetic Kidney Disease
Joon Myeong So, Ji Ho Park, Jin Gyeong Kim, Il Rae Park, Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Chul Hyun Park, Woo-Sung Yun, Tae-Gon Kim, Woong Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Heparanase-2 protein and peptides have a protective effect on experimental glomerulonephritis and diabetic nephropathy
Baranca Buijsers, Marjolein Garsen, Mark de Graaf, Marinka Bakker-van Bebber, Chunming Guo, Xue Li, Johan van der Vlag
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis on the renal functional status in patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease
Z.Ya. Кotsiubiichuk, O.S. Khukhlina, А.А. Аntoniv, O.Ye. Mandryk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(2): 100. CrossRef - Roles of extracellular vesicles in ageing-related chronic kidney disease: Demon or angel
Siqi Yin, Zixuan Zhou, Peiwen Fu, Chaoying Jin, Peipei Wu, Cheng Ji, Yunjie Shan, Linru Shi, Min Xu, Hui Qian
Pharmacological Research.2023; 193: 106795. CrossRef - Role of Natural and Synthetic Compounds in Modulating NRF2/KEAP1 Signaling Pathway in Prostate Cancer
Giovanni Tossetta, Sonia Fantone, Daniela Marzioni, Roberta Mazzucchelli
Cancers.2023; 15(11): 3037. CrossRef - Risk factors for heart, cerebrovascular, and kidney diseases: evaluation of potential side effects of medications to control hypertension, hyperglycemia, and hypercholesterolemia
Kazumitsu Nawata
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Rationale and design of a prospective, clinical study of kidney biopsies in people with type 2 diabetes and severely increased albuminuria (the PRIMETIME 2 study)
Marie Møller, Rikke Borg, Iain Bressendorff, Lisbeth N Fink, Eva Gravesen, Karina Haar Jensen, Torben Hansen, Dorrit Krustrup, Frederik Persson, Peter Rossing, Frederikke E Sembach, Anne C B Thuesen, Ditte Hansen
BMJ Open.2023; 13(6): e072216. CrossRef - Oral Chinese patent medicines for diabetic kidney disease: An overview of systematic reviews
Xue Xue, Ke-ying Li, Shang-zhi Liu, Jia-xuan Li, Xin-yan Jin, Xue-han Liu, La-mei Lin, Xin-rong Zou, Chun-li Lu, Fang-fang Zhao, Jian-ping Liu, Xiao-qin Wang
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2023; 61: 102269. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Proteinuric Kidney Disease/Nephrotic Syndrome: Lessons from Knockout/Transgenic Mouse Models
Ryosuke Saiki, Kan Katayama, Kaoru Dohi
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1803. CrossRef - Epigenetic regulation of angiogenesis and ischemic response by long noncoding RNA LEENE in diabetes
Imari Mimura, Masaomi Nangaku
Kidney International.2023; 104(6): 1048. CrossRef - Advances in the pharmacological study of Chinese herbal medicine to alleviate diabetic nephropathy by improving mitochondrial oxidative stress
Ming Chen, Yao Chen, Wenhui Zhu, Xiaoming Yan, Jing Xiao, Peiqing Zhang, Peng Liu, Ping Li
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115088. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone Therapy in Patients with Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
FNU Jyotsna, Kamran Mahfooz, Tirath Patel, FNU Parshant, Fnu Simran, Fnu Harsha, Fnu Neha, Dev Jyotishna, Dipesh Mishra, Sirjana Subedi, Mahima Khatri, Satesh Kumar, Giustino Varrassi
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular implications of glycosaminoglycans in diabetes pharmacotherapy
Tanya Waseem, Madiha Ahmed, Tausif Ahmed Rajput, Mustafeez Mujtaba Babar
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 247: 125821. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: More than Just Glucose Regulation
Jasna Klen, Vita Dolžan
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(7): 1995. CrossRef - CUL3 induces mitochondrial dysfunction via MRPL12 ubiquitination in renal tubular epithelial cells
Xingzhao Ji, Xiaoli Yang, Xia Gu, Lingju Chu, Shengnan Sun, Jian Sun, Peng Song, Qian Mu, Ying Wang, Xiaoming Sun, Dun Su, Tong Su, Shaoshuai Hou, Yao Lu, Chen Ma, Mingqiang Liu, Tianyi Zhang, Weiying Zhang, Yi Liu, Qiang Wan
The FEBS Journal.2023; 290(22): 5340. CrossRef - HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
Chuanqiang Zhou, Min Wu, Gaolun Liu, Li Zhou
Open Life Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of the Potential of Nuclear Factor [Erythroid-Derived 2]-like 2 Activation in Autoimmune Diseases
Ilker Ates, Ayşe Didem Yılmaz, Brigitta Buttari, Marzia Arese, Luciano Saso, Sibel Suzen
Brain Sciences.2023; 13(11): 1532. CrossRef - Astragalus membranaceus and Salvia miltiorrhiza ameliorate diabetic kidney disease via the “gut-kidney axis”
Zhen Shen, Tao Cui, Yao Liu, Shuai Wu, Cong Han, Jie Li
Phytomedicine.2023; 121: 155129. CrossRef - The relevance of the non-invasive biomarkers lncRNA GAS5/miR-21 ceRNA regulatory network in the early identification of diabetes and diabetic nephropathy
He Sun, Tong Chen, Xin Li, Yonghong Zhu, Shuang Zhang, Ping He, Yali Peng, Qiuling Fan
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Activation of acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 mediates kidney injury in diabetic nephropathy
Jian Lu, Xue Qi Li, Pei Pei Chen, Jia Xiu Zhang, Liang Liu, Gui Hua Wang, Xiao Qi Liu, Ting Ting Jiang, Meng Ying Wang, Wen Tao Liu, Xiong Zhong Ruan, Kun Ling Ma
JCI Insight.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - SET7, a lysine-specific methyl transferase: An intriguing epigenetic target to combat diabetic nephropathy
Samarth Dwivedi, Atharva Chavan, Atish T. Paul
Drug Discovery Today.2023; 28(10): 103754. CrossRef - Dznep, a histone modification inhibitor, inhibits HIF1α binding to TIMP2 gene and suppresses TIMP2 expression under hypoxia
Tomotaka Yamazaki, Imari Mimura, Yu Kurata, Tetsuhiro Tanaka, Masaomi Nangaku
Physiological Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - GLP-1RAs inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway to regulate mouse renal podocyte pyroptosis
Xiang Li, Xiao Jiang, Mei Jiang, Zhi-feng Wang, Tao Zhao, Si-ming Cao, Qiu-Mei Li
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 61(2): 225. CrossRef - Highly Sensitive, Portable Detection System for Multiplex Chemiluminescence Analysis
Yannan Yu, Wei Nie, Kaiqin Chu, Xi Wei, Zachary J. Smith
Analytical Chemistry.2023; 95(39): 14762. CrossRef - From normal population to prediabetes and diabetes: study of influencing factors and prediction models
Di Gong, Xiaohong Chen, Lin Yang, Yongjian Zhang, Qianqian Zhong, Jing Liu, Chen Yan, Yongjiang Cai, Weihua Yang, Jiantao Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Monitoring through Urine Analysis Using ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and Machine Learning
Sajid Farooq, Denise Maria Zezell
Chemosensors.2023; 11(11): 565. CrossRef - Treatment and practical considerations of diabetic kidney disease
Yara Bilen, Allaa Almoushref, Kenda Alkwatli, Omar Osman, Ali Mehdi, Hanny Sawaf
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Metabolomics and Traditional Chinese Medicine for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment
Jing Li, Na Zhu, Yaqiong Wang, Yanlei Bao, Feng Xu, Fengjuan Liu, Xuefeng Zhou
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 4269. CrossRef - Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and incident diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, Min Sun Choi, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 184: 109181. CrossRef - Lipidomic Analysis Reveals the Protection Mechanism of GLP-1 Analogue Dulaglutide on High-Fat Diet-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease in Mice
Martin Ho Yin Yeung, Ka Long Leung, Lai Yuen Choi, Jung Sun Yoo, Susan Yung, Pui-Kin So, Chi-Ming Wong
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - GLP-1 receptor agonists in diabetic kidney disease: current evidence and future directions
Ji Hee Yu, So Young Park, Da Young Lee, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(2): 136. CrossRef - Evolving Type 2 diabetes management focuses on clinical outcomes
Caroline Fenton, Connie Kang
Drugs & Therapy Perspectives.2022; 38(4): 165. CrossRef - Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 181. CrossRef - Critical shear stress of red blood cells as a novel integrated biomarker for screening chronic kidney diseases in cases of type 2 diabetes
Il Rae Park, Jimi Choi, Eun Young Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Sehyun Shin, Sin Gon Kim, Kyu Chang Won
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2022; 81(4): 293. CrossRef - Inhibition of ChREBP ubiquitination via the ROS/Akt-dependent downregulation of Smurf2 contributes to lysophosphatidic acid-induced fibrosis in renal mesangial cells
Donghee Kim, Ga-Young Nam, Eunhui Seo, Hee-Sook Jun
Journal of Biomedical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Pathophysiological Basis of Diabetic Kidney Protection by Inhibition of SGLT2 and SGLT1
Yuji Oe, Volker Vallon
Kidney and Dialysis.2022; 2(2): 349. CrossRef - Dapagliflozin for the treatment of chronic kidney disease
Yu Kurata, Masaomi Nangaku
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 17(4): 275. CrossRef - Repurposing drugs for highly prevalent diseases: pentoxifylline, an old drug and a new opportunity for diabetic kidney disease
Javier Donate-Correa, María Dolores Sanchez-Niño, Ainhoa González-Luis, Carla Ferri, Alberto Martín-Olivera, Ernesto Martín-Núñez, Beatriz Fernandez-Fernandez, Víctor G Tagua, Carmen Mora-Fernández, Alberto Ortiz, Juan F Navarro-González
Clinical Kidney Journal.2022; 15(12): 2200. CrossRef - Cyproheptadine, a SET7/9 inhibitor, reduces hyperglycaemia-induced ER stress alleviating inflammation and fibrosis in renal tubular epithelial cells
Himanshu Sankrityayan, Ajinath Kale, Vishwadeep Shelke, Anil Bhanudas Gaikwad
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Pan-Src kinase inhibitor treatment attenuates diabetic kidney injury via inhibition of Fyn kinase-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress
Debra Dorotea, Songling Jiang, Eun Seon Pak, Jung Beom Son, Hwan Geun Choi, Sung-Min Ahn, Hunjoo Ha
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2022; 54(8): 1086. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Effect of once-weekly dulaglutide on renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease
Sungmin Kim, Jung Nam An, Young Rim Song, Sung Gyun Kim, Hyung Seok Lee, AJin Cho, Jwa-Kyung Kim, Tomislav Bulum
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0273004. CrossRef - Oxidative Stress and NRF2/KEAP1/ARE Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD): New Perspectives
Daniela Maria Tanase, Evelina Maria Gosav, Madalina Ioana Anton, Mariana Floria, Petronela Nicoleta Seritean Isac, Loredana Liliana Hurjui, Claudia Cristina Tarniceriu, Claudia Florida Costea, Manuela Ciocoiu, Ciprian Rezus
Biomolecules.2022; 12(9): 1227. CrossRef - Preventive and healing effect of high dosing grape seed flour on CKD patients of various stages and aetiologies
Wiem Bejaoui, Mohamed Mahmoudi, Kamel Charradi, Monia Abbes-Belhadj, Habib Boukhalfa, Mossadok Ben-Attia, Ferid Limam, Ezzedine Aouani
Biomarkers.2022; 27(8): 795. CrossRef - Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) in type 2 diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to therapeutics
Miyesaier Abudureyimu, Xuanming Luo, Xiang Wang, James R Sowers, Wenshuo Wang, Junbo Ge, Jun Ren, Yingmei Zhang, Wei-Ping Jia
Journal of Molecular Cell Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in the Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Diabetic Kidney Diseases
Wei Huang, Yi-Yuan Chen, Zi-Qi Li, Fang-Fang He, Chun Zhang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(18): 10882. CrossRef - Serum isthmin-1 levels are positively and independently correlated with albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chuan Wang, Mingyue Xu, Ruiying Feng, Lei Zhang, Xiaofei Yin, Ruoqi Feng, Kai Liang, Jinbo Liu
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(5): e002972. CrossRef - hucMSC-sEVs-Derived 14-3-3ζ Serves as a Bridge between YAP and Autophagy in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Siqi Yin, Wanzhu Liu, Cheng Ji, Yuan Zhu, Yunjie Shan, Zixuan Zhou, Wenya Chen, Leilei Zhang, Zixuan Sun, Wenqin Zhou, Hui Qian, Chaoliang Tang
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Adenosine receptors as emerging therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease
Eun Seon Pak, Jin Joo Cha, Dae Ryong Cha, Keizo Kanasaki, Hunjoo Ha
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(Suppl 2): S74. CrossRef - REDD1 Ablation Attenuates the Development of Renal Complications in Diabetic Mice
Siddharth Sunilkumar, Esma I. Yerlikaya, Allyson L. Toro, William P. Miller, Han Chen, Kebin Hu, Scot R. Kimball, Michael D. Dennis
Diabetes.2022; 71(11): 2412. CrossRef - The Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha in Renal Disease
Huixia Liu, Yujuan Li, Jing Xiong
Molecules.2022; 27(21): 7318. CrossRef - Resistant Starch as a Dietary Intervention to Limit the Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Anna M. Drake, Melinda T. Coughlan, Claus T. Christophersen, Matthew Snelson
Nutrients.2022; 14(21): 4547. CrossRef - Aggravated renal fibrosis is positively associated with the activation of HMGB1-TLR2/4 signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice
Yan Yuan, Yuanxia Liu, Mengyao Sun, Huijing Ye, Yuchen Feng, Zhenzhen Liu, Lingyu Pan, Hongbo Weng
Open Life Sciences.2022; 17(1): 1451. CrossRef - Single-cell multiomics reveals the complexity of TGFβ signalling to chromatin in iPSC-derived kidney organoids
Jessica L. Davis, Ciaran Kennedy, Shane Clerkin, Niall J. Treacy, Thomas Dodd, Catherine Moss, Alison Murphy, Derek P. Brazil, Gerard Cagney, Dermot F. Brougham, Rabi Murad, Darren Finlay, Kristiina Vuori, John Crean
Communications Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidized Albumin: Evaluation of Oxidative Stress as a Marker for the Progression of Kidney Disease
Hiroshi Watanabe
Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.2022; 45(12): 1728. CrossRef - Whether Renal Pathology Is an Independent Predictor for End-Stage Renal Disease in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients with Nephrotic Range Proteinuria: A Biopsy-Based Study
Tingli Wang, Junlin Zhang, Yiting Wang, Lijun Zhao, Yucheng Wu, Honghong Ren, Yutong Zou, Rui Zhang, Huan Xu, Zhonglin Chai, Mark Cooper, Jie Zhang, Fang Liu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(1): 88. CrossRef - What’s New in the Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Recent Advances
Kimio Watanabe, Emiko Sato, Eikan Mishima, Mariko Miyazaki, Tetsuhiro Tanaka
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 24(1): 570. CrossRef - Clinical efficacy and safety of astragalus injection combined with ACEI/ARB in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Zhiyue Zhu, Qi Zhang, Le Liu, Pengjie Bao, Shilin Liu, Chaoqun Song, Wenbo Yang, Zheng Nan
Medicine.2022; 101(49): e31490. CrossRef - Cudrania tricuspidata Root Extract Prevents Methylglyoxal-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Regulation of the PKC-NOX4 Pathway in Human Kidney Cells
Donghee Kim, Jayeon Cheon, Haelim Yoon, Hee-Sook Jun, Evangelia Dounousi
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Pleiotropic Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors: Renoprotective Mechanisms beyond Glycemic Control
Tomoaki Takata, Hajime Isomoto
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4374. CrossRef - HIF-α Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors and Their Implications for Biomedicine: A Comprehensive Review
Kiichi Hirota
Biomedicines.2021; 9(5): 468. CrossRef - Nephropathie bei Diabetes
Roland E. Schmieder
CardioVasc.2021; 21(3): 31. CrossRef - Clinical Predictors of Nondiabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Diabetes: A Single-Center Study
Francesco Fontana, Rossella Perrone, Francesco Giaroni, Gaetano Alfano, Silvia Giovanella, Giulia Ligabue, Riccardo Magistroni, Gianni Cappelli, Udeme Ekrikpo
International Journal of Nephrology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Activated Histone Acetyltransferase p300/CBP-Related Signalling Pathways Mediate Up-Regulation of NADPH Oxidase, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Diabetic Kidney
Alexandra-Gela Lazar, Mihaela-Loredana Vlad, Adrian Manea, Maya Simionescu, Simona-Adriana Manea
Antioxidants.2021; 10(9): 1356. CrossRef - Plasma and urine biomarkers in chronic kidney disease: closer to clinical application
Azadeh Zabetian, Steven G. Coca
Current Opinion in Nephrology & Hypertension.2021; 30(6): 531. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect and mechanism of combined use of FGF21 and insulin on diabetic nephropathy
Fanrui Meng, Yukai Cao, Mir Hassan Khoso, Kai Kang, Guiping Ren, Wei Xiao, Deshan Li
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2021; 713: 109063. CrossRef - Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Daiji Kawanami, Yuichi Takashi, Yoshimi Muta, Naoki Oda, Dai Nagata, Hiroyuki Takahashi, Makito Tanabe
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcription Factor ChREBP Mediates High Glucose-Evoked Increase in HIF-1α Content in Epithelial Cells of Renal Proximal Tubules
Aleksandra Owczarek, Katarzyna B. Gieczewska, Robert Jarzyna, Zuzanna Frydzinska, Katarzyna Winiarska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(24): 13299. CrossRef - The effect of modern hypoglycemic therapy on the course of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
V.I. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2021; 17(8): 624. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA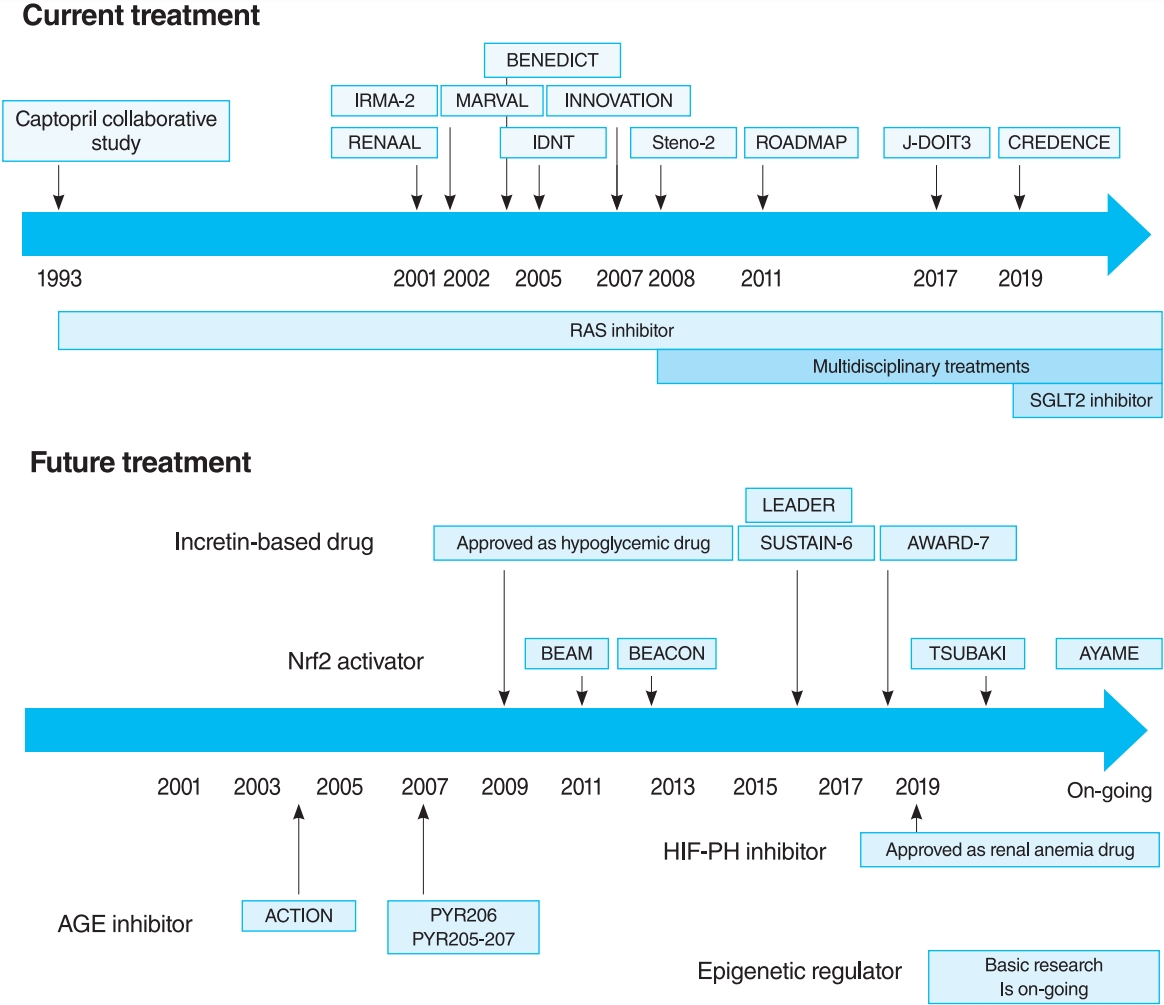
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite