
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
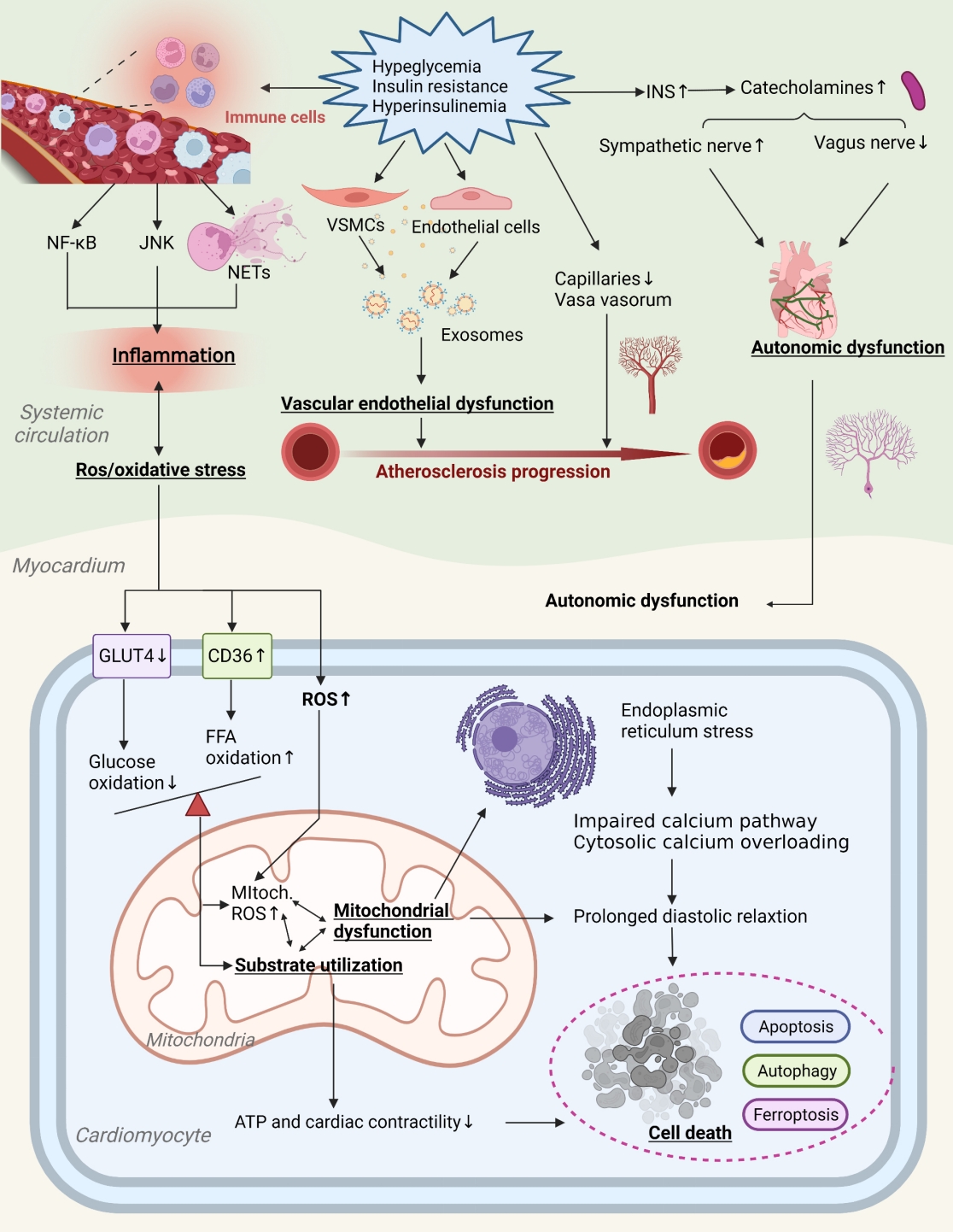
- Pathophysiology
- Primordial Drivers of Diabetes Heart Disease: Comprehensive Insights into Insulin Resistance
- Yajie Fan, Zhipeng Yan, Tingting Li, Aolin Li, Xinbiao Fan, Zhongwen Qi, Junping Zhang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):19-36. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0110
- 2,161 View
- 182 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Insulin resistance has been regarded as a hallmark of diabetes heart disease (DHD). Numerous studies have shown that insulin resistance can affect blood circulation and myocardium, which indirectly cause cardiac hypertrophy and ventricular remodeling, participating in the pathogenesis of DHD. Meanwhile, hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia associated with insulin resistance can directly impair the metabolism and function of the heart. Targeting insulin resistance is a potential therapeutic strategy for the prevention of DHD. Currently, the role of insulin resistance in the pathogenic development of DHD is still under active research, as the pathological roles involved are complex and not yet fully understood, and the related therapeutic approaches are not well developed. In this review, we describe insulin resistance and add recent advances in the major pathological and physiological changes and underlying mechanisms by which insulin resistance leads to myocardial remodeling and dysfunction in the diabetic heart, including exosomal dysfunction, ferroptosis, and epigenetic factors. In addition, we discuss potential therapeutic approaches to improve insulin resistance and accelerate the development of cardiovascular protection drugs.
- Others
- Change Profiles and Functional Targets of MicroRNAs in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Obesity
- Guanhua Lu, Huanhuan Gao, Zhiyong Dong, Shuwen Jiang, Ruixiang Hu, Cunchuan Wang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):559-570. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0226
- 1,702 View
- 76 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) exert an essential contribution to obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study aimed to investigate the differences of miRNAs in the presence and absence of T2DM in patients with obesity, as well as before and after bariatric surgery in T2DM patients with obesity. Characterization of the common changes in both was further analyzed.
Methods
We enrolled 15 patients with obesity but without T2DM and 15 patients with both obesity and T2DM. Their preoperative clinical data and serum samples were collected, as well as 1 month after bariatric surgery. The serum samples were analyzed by miRNA sequencing, and the miRNAs profiles and target genes characteristics were compared.
Results
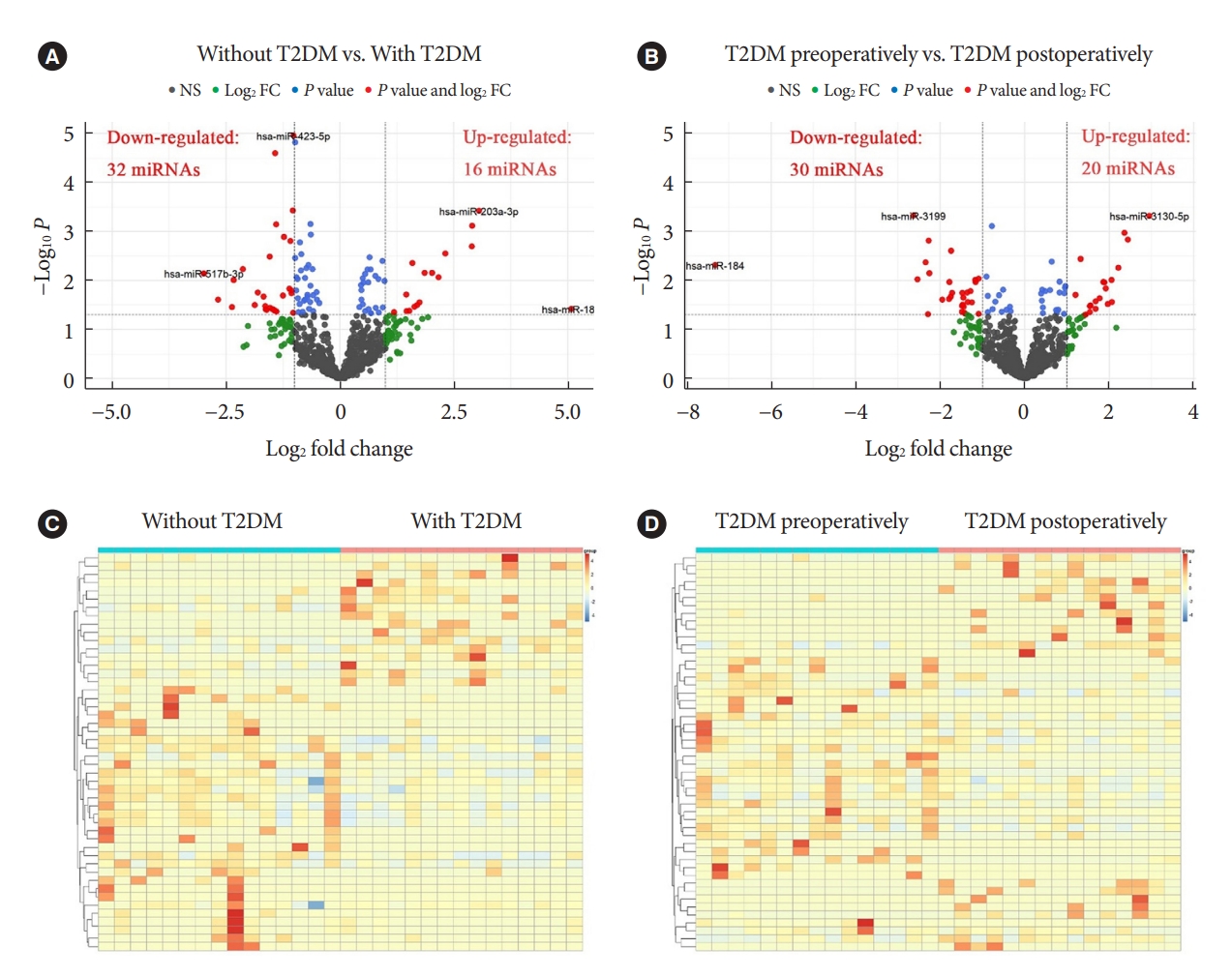
Patients with T2DM had 16 up-regulated and 32 down-regulated miRNAs compared to patients without T2DM. Improvement in metabolic metrics after bariatric surgery of T2DM patients with obesity was correlated with changes in miRNAs, as evidenced by the upregulation of 20 miRNAs and the downregulation of 30 miRNAs. Analysis of the two miRNAs profiles identified seven intersecting miRNAs that showed opposite changes. The target genes of these seven miRNAs were substantially enriched in terms or pathways associated with T2DM.
Conclusion
We determined the expression profiles of miRNAs in the obese population, with and without diabetes, before and after bariatric surgery. The miRNAs that intersected in the two comparisons were discovered. Both the miRNAs discovered and their target genes were closely associated with T2DM, demonstrating that they might be potential targets for the regulation of T2DM.
- Basic Research
- Long Non-Coding RNA TUG1 Attenuates Insulin Resistance in Mice with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus via Regulation of the MicroRNA-328-3p/SREBP-2/ERK Axis
- Xuwen Tang, Qingxin Qin, Wenjing Xu, Xuezhen Zhang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):267-286. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0216

- 2,848 View
- 188 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been illustrated to contribute to the development of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). In the present study, we aimed to elucidate how lncRNA taurine upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) influences insulin resistance (IR) in a high-fat diet (HFD)-induced mouse model of GDM.
Methods
We initially developed a mouse model of HFD-induced GDM, from which islet tissues were collected for RNA and protein extraction. Interactions among lncRNA TUG1/microRNA (miR)-328-3p/sterol regulatory element binding protein 2 (SREBP-2) were assessed by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Fasting blood glucose (FBG), fasting insulin (FINS), homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), HOMA pancreatic β-cell function (HOMA-β), insulin sensitivity index for oral glucose tolerance tests (ISOGTT) and insulinogenic index (IGI) levels in mouse serum were measured through conducting gain- and loss-of-function experiments.
Results
Abundant expression of miR-328 and deficient expression of lncRNA TUG1 and SREBP-2 were characterized in the islet tissues of mice with HFD-induced GDM. LncRNA TUG1 competitively bound to miR-328-3p, which specifically targeted SREBP-2. Either depletion of miR-328-3p or restoration of lncRNA TUG1 and SREBP-2 reduced the FBG, FINS, HOMA-β, and HOMA-IR levels while increasing ISOGTT and IGI levels, promoting the expression of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway-related genes, and inhibiting apoptosis of islet cells in GDM mice. Upregulation miR-328-3p reversed the alleviative effects of SREBP-2 and lncRNA TUG1 on IR.
Conclusion
Our study provides evidence that the lncRNA TUG1 may prevent IR following GDM through competitively binding to miR-328-3p and promoting the SREBP-2-mediated ERK signaling pathway inactivation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes and diabetic associative diseases: An overview of epigenetic regulations of TUG1
Mohammed Ageeli Hakami
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2024; 31(5): 103976. CrossRef - Effect of Tinospora cordifolia on gestational diabetes mellitus and its complications
Ritu Rani, Havagiray Chitme, Avinash Kumar Sharma
Women & Health.2023; 63(5): 359. CrossRef - Therapeutic Effect of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd) Extracts on Letrozole-Induced Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and its Complications in Murine Model
Ritu Rani, Avinash Kumar Sharma, Havagiray R Chitme
Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of ncRNA regulatory mechanisms in diseases—case on gestational diabetes
Dong Gao, Liping Ren, Yu-Duo Hao, Nalini Schaduangrat, Xiao-Wei Liu, Shi-Shi Yuan, Yu-He Yang, Yan Wang, Watshara Shoombuatong, Hui Ding
Briefings in Bioinformatics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - lncRNA TUG1 as potential novel biomarker for prognosis of cardiovascular diseases
Habib Haybar, Narjes Sadat Sadati, Daryush Purrahman, Mohammad Reza Mahmoudian-Sani, Najmaldin Saki
Epigenomics.2023; 15(23): 1273. CrossRef
- Diabetes and diabetic associative diseases: An overview of epigenetic regulations of TUG1
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Differential Profile of Plasma Circular RNAs in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yangyang Li, Ying Zhou, Minghui Zhao, Jing Zou, Yuxiao Zhu, Xuewen Yuan, Qianqi Liu, Hanqing Cai, Cong-Qiu Chu, Yu Liu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):854-865. Published online July 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0151
- 6,156 View
- 131 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background No currently available biomarkers or treatment regimens fully meet therapeutic needs of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Circular RNA (circRNA) is a recently identified class of stable noncoding RNA that have been documented as potential biomarkers for various diseases. Our objective was to identify and analyze plasma circRNAs altered in T1DM.
Methods We used microarray to screen differentially expressed plasma circRNAs in patients with new onset T1DM (
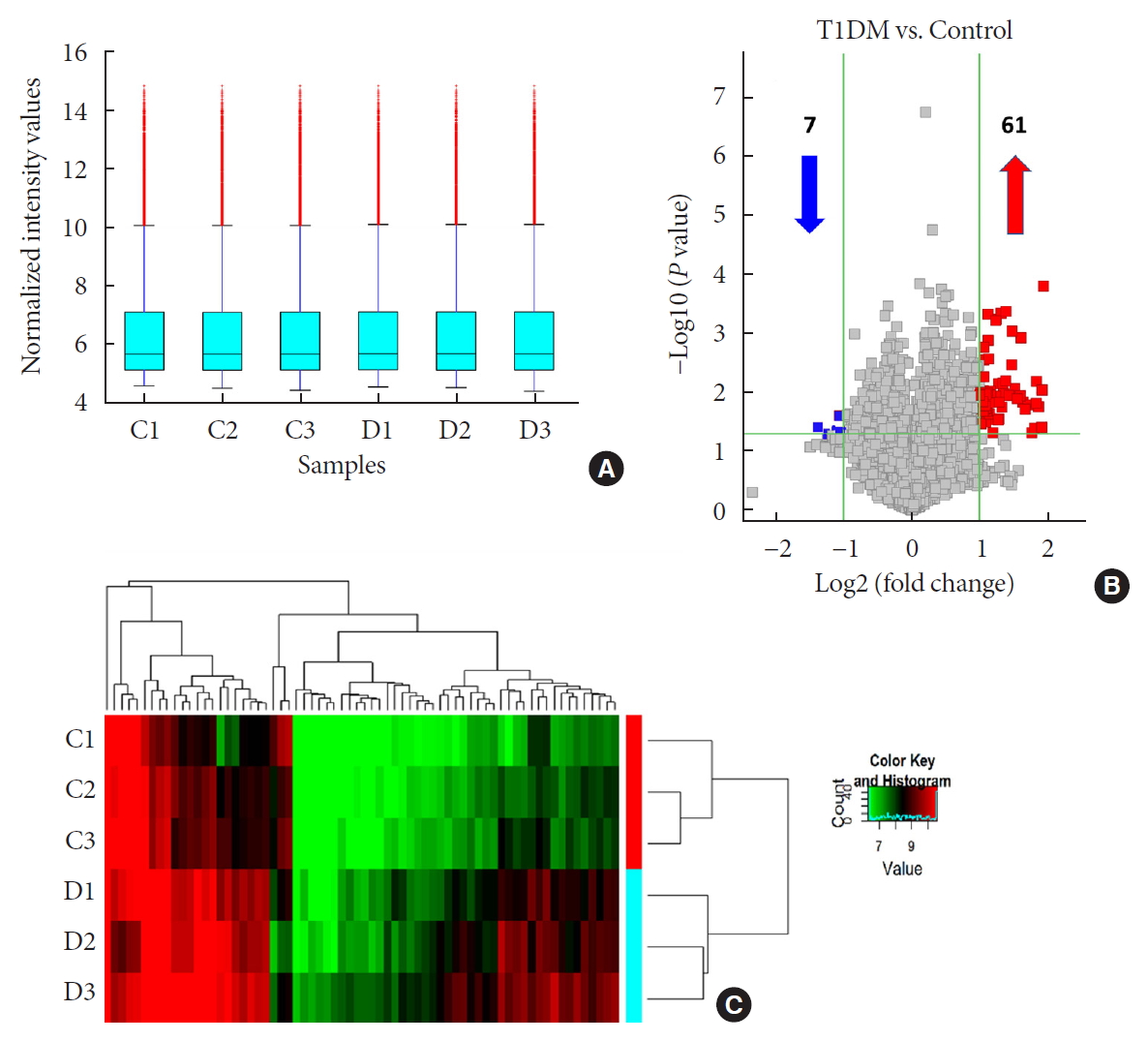
n =3) and age-/gender-matched healthy controls (n =3). Then, we selected six candidates with highest fold-change and validated them by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in independent human cohort samples (n =12). Bioinformatic tools were adopted to predict putative microRNAs (miRNAs) sponged by these validated circRNAs and their downstream messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses were performed to gain further insights into T1DM pathogenesis.Results We identified 68 differentially expressed circRNAs, with 61 and seven being up- and downregulated respectively. Four of the six selected candidates were successfully validated. Curations of their predicted interacting miRNAs revealed critical roles in inflammation and pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders. Functional relations were visualized by a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network. GO and KEGG analyses identified multiple inflammation-related processes that could be potentially associated with T1DM pathogenesis, including cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, inflammatory mediator regulation of transient receptor potential channels and leukocyte activation involved in immune response.
Conclusion Our study report, for the first time, a profile of differentially expressed plasma circRNAs in new onset T1DM. Further
in silico annotations and bioinformatics analyses supported future application of circRNAs as novel biomarkers of T1DM.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Non-coding RNAs and exosomal non-coding RNAs in diabetic retinopathy: A narrative review
Yuhong Zhong, Juan Xia, Li Liao, Mohammad Reza Momeni
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2024; 259: 128182. CrossRef - Circular RNAs: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for autoimmune diseases
Ren-Jie Zhao, Wan-Ying Zhang, Xing-Xing Fan
Heliyon.2024; 10(1): e23694. CrossRef - Research progress of circular RNA molecules in aging and age-related diseases
Zhidan Zhang, Yuling Huang, AYao Guo, Lina Yang
Ageing Research Reviews.2023; 87: 101913. CrossRef - CircRNAs and RNA-Binding Proteins Involved in the Pathogenesis of Cancers or Central Nervous System Disorders
Yuka Ikeda, Sae Morikawa, Moeka Nakashima, Sayuri Yoshikawa, Kurumi Taniguchi, Haruka Sawamura, Naoko Suga, Ai Tsuji, Satoru Matsuda
Non-Coding RNA.2023; 9(2): 23. CrossRef - Decrypting the circular RNAs does a favor for us: Understanding, diagnosing and treating diabetes mellitus and its complications
Zi Li, Yuanyuan Ren, Ziwei Lv, Man Li, Yujia Li, Xiaobin Fan, Yuyan Xiong, Lu Qian
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115744. CrossRef - Circular RNA PIP5K1A Promotes Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorders and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ge Song, YiQian Zhang, YiHua Jiang, Huan Zhang, Wen Gu, Xiu Xu, Jing Yao, ZhengFang Chen
Molecular Biotechnology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hsa_circRNA_405498 and hsa_circRNA_100033 Serve as Potential Biomarkers for Differential Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes
Ziwei Zhang, Shuoming Luo, Zilin Xiao, Wenfeng Yin, Xiajie Shi, Hongzhi Chen, Zhiguo Xie, Zhenqi Liu, Xia Li, Zhiguang Zhou
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Circular RNA PIP5K1A act as microRNA-552-3p sponge to regulates inflammation, oxidative damage in glucolipotoxicity-induced pancreatic INS-1 β-cells via Janus kinase 1
Lei Ren
Bioengineered.2022; 13(3): 5724. CrossRef - Circular RNAs in diabetes mellitus and its complications
Wenqi Fan, Haipeng Pang, Zhiguo Xie, Gan Huang, Zhiguang Zhou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus-Related circRNAs Regulate CD4+ T Cell Functions
Jianni Chen, Guanfei Jia, Xue Lv, Shufa Li, Christos K. Kontos
BioMed Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - An intriguing role of circular RNA in insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: the future perspectives
Monisha Prasad, Selvaraj Jayaraman, Vishnu Priya Veeraraghavan
Hypertension Research.2022; 45(11): 1843. CrossRef - Circular RNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy: Updates and Perspectives
Miao Liu, Junli Zhao
Aging and disease.2022; 13(5): 1365. CrossRef - CircRNAs: Key molecules in the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke
Zeyu Liu, Yanhong Zhou, Jian Xia
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 156: 113845. CrossRef - Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Promote the Transcription of Circular RNAs in Human Pancreatic β Cells
Simranjeet Kaur, Caroline Frørup, Aashiq H. Mirza, Tina Fløyel, Reza Yarani, Maikel L. Colli, Jesper Johannesen, Joachim Størling, Decio L. Eizirik, Flemming Pociot
Non-Coding RNA.2022; 8(5): 69. CrossRef - Differential Expression and Bioinformatics Analysis of Plasma-Derived Exosomal circRNA in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Haipeng Pang, Wenqi Fan, Xiajie Shi, Shuoming Luo, Yimeng Wang, Jian Lin, Yang Xiao, Xia Li, Gan Huang, Zhiguo Xie, Zhiguang Zhou, Jinhui Liu
Journal of Immunology Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Circular RNAs in diabetes and its complications: Current knowledge and future prospects
Wenfeng Yin, Ziwei Zhang, Zilin Xiao, Xia Li, Shuoming Luo, Zhiguang Zhou
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Circular RNA in autoimmune diseases: special emphasis on regulation mechanism in RA and SLE
Yurong Huang, Qiuyun Xue, Chenglong Cheng, Yuting Wang, Xiao Wang, Jun Chang, Chenggui Miao
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging roles of circular RNAs in systemic lupus erythematosus
Xin Wang, Rui Ma, Weimin Shi, Zhouwei Wu, Yuling Shi
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids.2021; 24: 212. CrossRef - Understanding Competitive Endogenous RNA Network Mechanism in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Using Computational and Bioinformatics Approaches
Xuanzi Yi, Xu Cheng
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 3865. CrossRef
- Non-coding RNAs and exosomal non-coding RNAs in diabetic retinopathy: A narrative review
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Three Months Monitored Metabolic Fitness Modulates Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Diabetic Patients
- Ilenia Cirilli, Sonia Silvestri, Fabio Marcheggiani, Fabiola Olivieri, Roberta Galeazzi, Roberto Antonicelli, Rina Recchioni, Fiorella Marcheselli, Tiziana Bacchetti, Luca Tiano, Patrick Orlando
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):893-897. Published online June 27, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0254
- 3,903 View
- 46 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Cardiovascular diseases represent the leading cause of death and moderate physical exercise is associated with a reduction in cardiovascular risk. The aim of the study was to evaluate the correlation between the amount of exercise recorded daily by a wearable gravitometer for 3 months and selected biochemical and clinical parameters. Nineteen sedentary type 2 diabetics were recruited and distributed into three homogenous groups, low, medium, and high exercise, according to the level of physical exercise monitored and expressed as MOVEs. Data showed an inverse correlation between MOVEs and oxidative stress indexes and a significant improvement in paraoxonase-1 activities and endothelial functionality. Decrease of visceral/total adipose tissue ratio, systolic blood pressure and a down-regulation of the inflammatory microRNA-146a in high exercise group were observed. Finally, a decrease of glycosylated hemoglobin and an up-regulation of the angiogenic microRNA-130a in medium exercise one was obtained. In this study, precise daily monitoring permitted to underline the importance of the amount of physical activity to counteract some cardiovascular risk factors persisting in diabetes. Finally, it identifies new microRNA biomarkers for future investigation on the same topic.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emerging roles of microRNAs as diagnostics and potential therapeutic interest in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Dharmsheel Shrivastav, Desh Deepak Singh
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(3): 525. CrossRef - Effects of Seven Weeks of Combined Physical Training on High-Density Lipoprotein Functionality in Overweight/Obese Subjects
Tiziana Bacchetti, Camilla Morresi, Gianna Ferretti, Anders Larsson, Torbjörn Åkerfeldt, Michael Svensson
Metabolites.2023; 13(10): 1068. CrossRef - Physical Exercise Protects Against Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases
Juan Gao, Xue Pan, Guoping Li, Emeli Chatterjee, Junjie Xiao
Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research.2022; 15(3): 604. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise Training on the Paracrine Function of Circulating Angiogenic Cells
William S. Evans, Ryan M. Sapp, Katherine I. Kim, James M. Heilman, James Hagberg, Steven J. Prior
International Journal of Sports Medicine.2021; 42(12): 1047. CrossRef - Chronic and Transient Hyperglycemia Induces Changes in the Expression Patterns of IL6 and ADIPOQ Genes and Their Associated Epigenetic Modifications in Differentiating Human Visceral Adipocytes
Adam Wróblewski, Justyna Strycharz, Ewa Świderska, Aneta Balcerczyk, Janusz Szemraj, Józef Drzewoski, Agnieszka Śliwińska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(13): 6964. CrossRef - The Potential Role of MicroRNA in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 54. CrossRef
- Emerging roles of microRNAs as diagnostics and potential therapeutic interest in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Technology/Device
- Role of MicroRNA-34a in Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
- In-Hwa Park, Yi-Sun Song, Hyun-Woo Joo, Guang-Yin Shen, Jin-Hee Seong, Na-Kyoung Shin, Young Jong Cho, Yonggu Lee, Jeong Hun Shin, Young-Hyo Lim, Hyuck Kim, Kyung-Soo Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):173-185. Published online April 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0211
- 5,503 View
- 75 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Recent studies have shown that microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in the process of cardiomyocyte apoptosis. We have previously reported that granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) ameliorated diastolic dysfunction and attenuated cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a rat model of diabetic cardiomyopathy. In this study, we hypothesized a regulatory role of cardiac miRNAs in the mechanism of the anti-apoptotic effect of G-CSF in a diabetic cardiomyopathy rat model.
Methods Rats were given a high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin injection and then randomly allocated to receive treatment with either G-CSF or saline. H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes were cultured under a high glucose (HG) condition to induce diabetic cardiomyopathy
in vitro . We examined the extent of apoptosis, miRNA expression, and miRNA target genes in the myocardium and H9c2 cells.Results G-CSF treatment significantly decreased apoptosis and reduced miR-34a expression in diabetic myocardium and H9c2 cells under the HG condition. G-CSF treatment also significantly increased B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) protein expression as a target for miR-34a. In addition, transfection with an miR-34a mimic significantly increased apoptosis and decreased Bcl-2 luciferase activity in H9c2 cells.
Conclusion Our results indicate that G-CSF might have an anti-apoptotic effect through down-regulation of miR-34a in a diabetic cardiomyopathy rat model.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The study of the mechanism of non-coding RNA regulation of programmed cell death in diabetic cardiomyopathy
Bingrui Zhang, Hua Wu, Jingwen Zhang, Cong Cong, Lin Zhang
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-coding RNAs in the pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Elisabeth A. Jalink, Amber W. Schonk, Reinier A. Boon, Rio P. Juni
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynamic interplay of microRNA in diseases and therapeutic
Neha Kargutkar, Priya Hariharan, Anita Nadkarni
Clinical Genetics.2023; 103(3): 268. CrossRef - LGR5+ Intestinal Stem Cells Display Sex-Dependent Radiosensitivity
Ryan C. Zitter, Rishi Man Chugh, Payel Bhanja, Bruce F. Kimler, Subhrajit Saha
Cells.2023; 13(1): 46. CrossRef - Female Mice are More Resistant to the Mixed-Field (67% Neutron + 33% Gamma) Radiation-Induced Injury in Bone Marrow and Small Intestine than Male Mice due to Sustained Increases in G-CSF and the Bcl-2/Bax Ratio and Lower miR-34a and MAPK Activation
Juliann G. Kiang, Georgetta Cannon, Matthew G. Olson, Joan T. Smith, Marsha N. Anderson, Min Zhai, M. Victoria Umali, Kevin Ho, Connie Ho, Wanchang Cui, Mang Xiao
Radiation Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential Role of Natural Plant Medicine Cyclocarya paliurus in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Han Wang, Cheng Tang, Zezheng Gao, Yishan Huang, Boxun Zhang, Jiahua Wei, Linhua Zhao, Xiaolin Tong, Yong Xu
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Ghrelin, a novel therapy, corrects cytokine and NF-κB-AKT-MAPK network and mitigates intestinal injury induced by combined radiation and skin-wound trauma
Juliann G. Kiang, Joan T. Smith, Georgetta Cannon, Marsha N. Anderson, Connie Ho, Min Zhai, Wanchang Cui, Mang Xiao
Cell & Bioscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of biomarkers in liver following Solanum melongena green calyx administration in diabetic rats
Shiva Roshankhah, Ahmad Shabanizadeh, Amir Abdolmaleki, Mohammad Reza Gholami, Mohammad Reza Salahshoor
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2020; 19(2): 1115. CrossRef - Diabetic cardiomyopathy: definition, diagnosis criteria, treatment directions and prevention of heart failure
N. A. Koziolova, P. G. Karavaev, A. S. Veklich
South Russian Journal of Therapeutic Practice.2020; 1(2): 93. CrossRef - The Potential Role of MicroRNA in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 54. CrossRef
- The study of the mechanism of non-coding RNA regulation of programmed cell death in diabetic cardiomyopathy

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





