
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Basic Research
- Roles of Histone Deacetylase 4 in the Inflammatory and Metabolic Processes
- Hyunju Kang, Young-Ki Park, Ji-Young Lee, Minkyung Bae
- Received June 5, 2023 Accepted February 7, 2024 Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0174 [Epub ahead of print]

- 634 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4), a class IIa HDAC, has gained attention as a potential therapeutic target in treating inflammatory and metabolic processes based on its essential role in various biological pathways by deacetylating non-histone proteins, including transcription factors. The activity of HDAC4 is regulated at the transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational levels. The functions of HDAC4 are tissue-dependent in response to endogenous and exogenous factors and their substrates. In particular, the association of HDAC4 with non-histone targets, including transcription factors, such as myocyte enhancer factor 2, hypoxia-inducible factor, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, and forkhead box proteins, play a crucial role in regulating inflammatory and metabolic processes. This review summarizes the regulatory modes of HDAC4 activity and its functions in inflammation, insulin signaling and glucose metabolism, and cardiac muscle development.
- Basic research
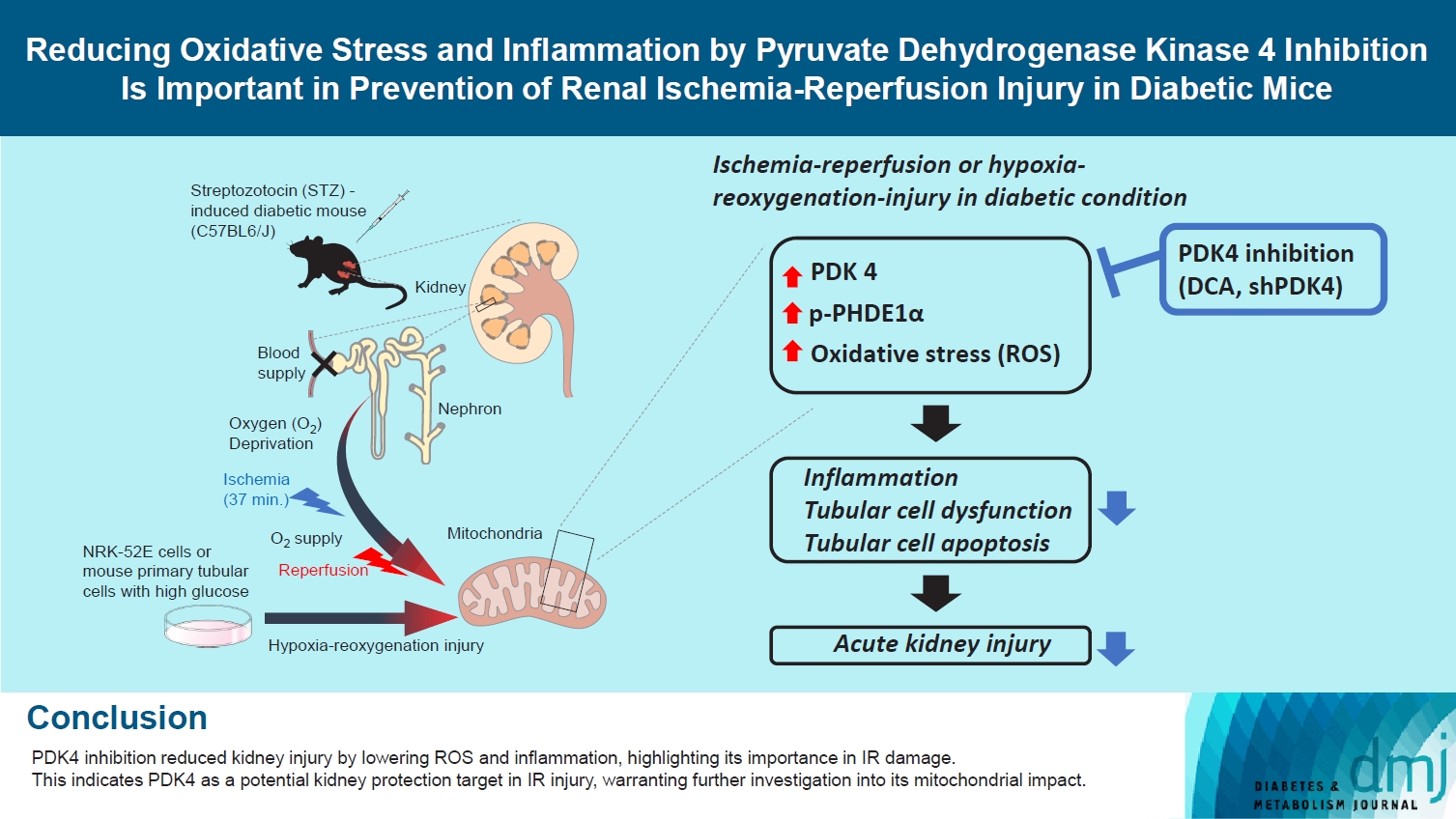
- Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4 Inhibition Is Important in Prevention of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Mice
- Ah Reum Khang, Dong Hun Kim, Min-Ji Kim, Chang Joo Oh, Jae-Han Jeon, Sung Hee Choi, In-Kyu Lee
- Received June 22, 2023 Accepted July 13, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0196 [Epub ahead of print]
- 776 View
- 75 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammation are reported to have a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury, a leading cause of acute kidney injury. The present study investigated the role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) in ROS production and inflammation following IR injury.
Methods
We used a streptozotocin-induced diabetic C57BL6/J mouse model, which was subjected to IR by clamping both renal pedicles. Cellular apoptosis and inflammatory markers were evaluated in NRK-52E cells and mouse primary tubular cells after hypoxia and reoxygenation using a hypoxia work station.
Results
Following IR injury in diabetic mice, the expression of PDK4, rather than the other PDK isoforms, was induced with a marked increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase E1α (PDHE1α) phosphorylation. This was accompanied by a pronounced ROS activation, as well as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) production. Notably, sodium dichloroacetate (DCA) attenuated renal IR injury-induced apoptosis which can be attributed to reducing PDK4 expression and PDHE1α phosphorylation levels. DCA or shPdk4 treatment reduced oxidative stress and decreased TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and MCP-1 production after IR or hypoxia-reoxygenation injury.
Conclusion
PDK4 inhibition alleviated renal injury with decreased ROS production and inflammation, supporting a critical role for PDK4 in IR mediated damage. This result indicates another potential target for reno-protection during IR injury; accordingly, the role of PDK4 inhibition needs to be comprehensively elucidated in terms of mitochondrial function during renal IR injury.
- Drug/Regimen
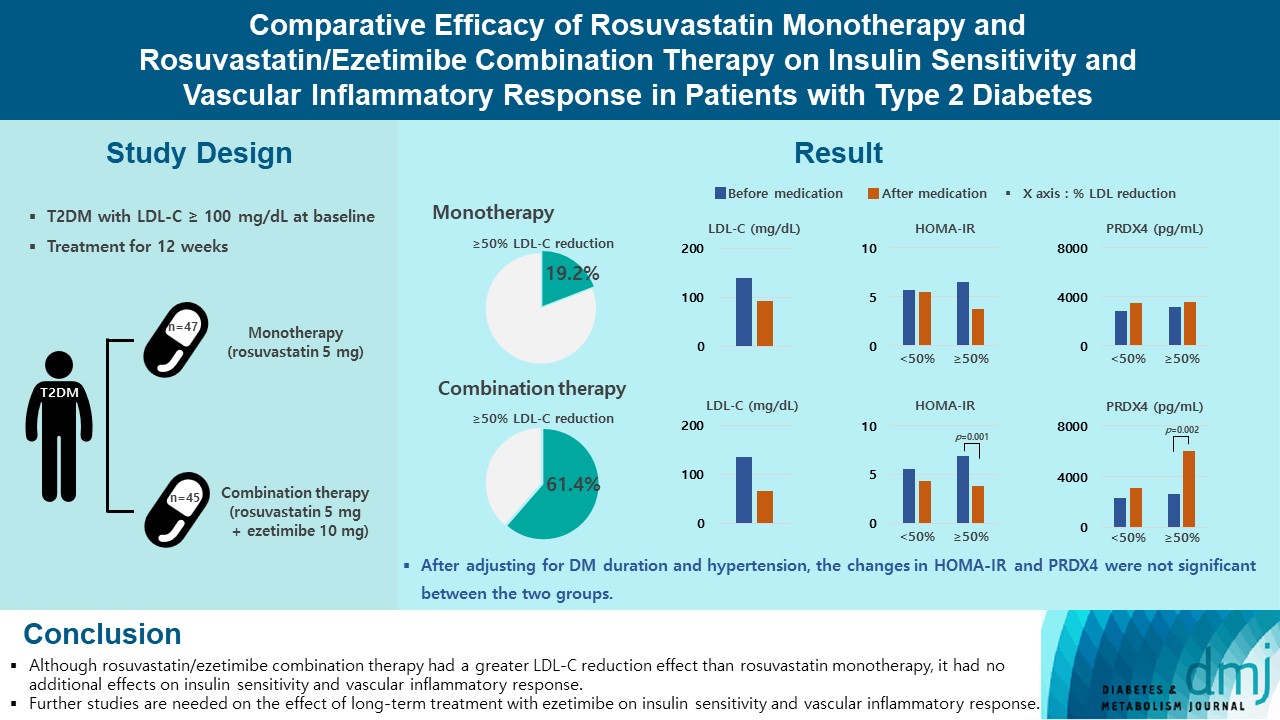
- Comparative Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy and Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination Therapy on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammatory Response in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Hye Han, Kyong Hye Joung, Jun Choul Lee, Ok Soon Kim, Sorim Choung, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Ju Hee Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Hyun Jin Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):112-121. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0402
- 2,018 View
- 222 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) induces endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, which are the main factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. The present study aimed to compare the effects of rosuvastatin monotherapy and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy on lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, and vascular inflammatory response in patients with T2DM.
Methods
A total of 101 patients with T2DM and dyslipidemia were randomized to either rosuvastatin monotherapy (5 mg/day, n=47) or rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy (5 mg/10 mg/day, n=45) and treated for 12 weeks. Serum lipids, glucose, insulin, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), and peroxiredoxin 4 (PRDX4) levels were determined before and after 12 weeks of treatment.
Results
The reduction in low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% from baseline after treatment was more in the combination therapy group. The serum sICAM-1 levels increased significantly in both groups, but there was no difference between the two groups. The significant changes in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and PRDX4 were confirmed only in the subgroup in which LDL-C was reduced by 50% or more in the combination therapy group. However, after adjusting for diabetes mellitus duration and hypertension, the changes in HOMA-IR and PRDX4 were not significant between the two groups.
Conclusion
Although rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy had a greater LDL-C reduction effect than rosuvastatin monotherapy, it had no additional effects on insulin sensitivity and vascular inflammatory response. Further studies are needed on the effect of long-term treatment with ezetimibe on insulin sensitivity and vascular inflammatory response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Roh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 55. CrossRef
- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Basic Research
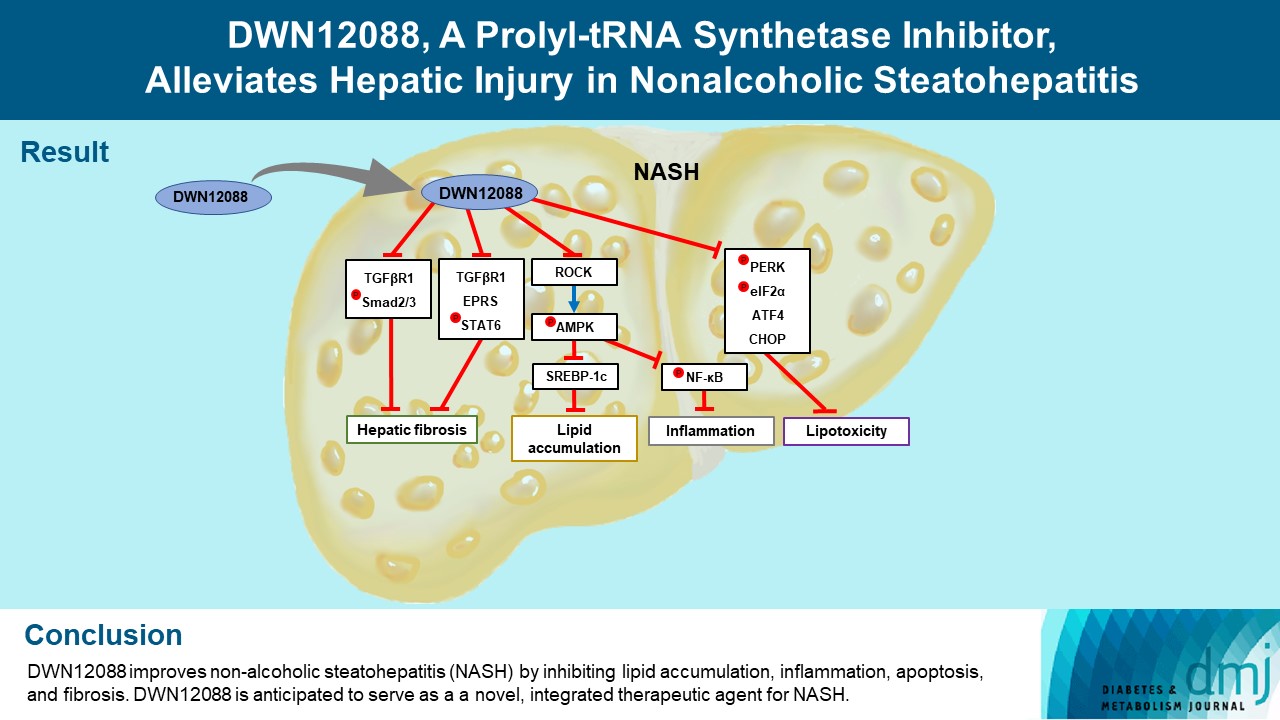
- DWN12088, A Prolyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitor, Alleviates Hepatic Injury in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Dong-Keon Lee, Su Ho Jo, Eun Soo Lee, Kyung Bong Ha, Na Won Park, Deok-Hoon Kong, Sang-In Park, Joon Seok Park, Choon Hee Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):97-111. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0367
- 1,749 View
- 180 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a liver disease caused by obesity that leads to hepatic lipoapoptosis, resulting in fibrosis and cirrhosis. However, the mechanism underlying NASH is largely unknown, and there is currently no effective therapeutic agent against it. DWN12088, an agent used for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, is a selective prolyl-tRNA synthetase (PRS) inhibitor that suppresses the synthesis of collagen. However, the mechanism underlying the hepatoprotective effect of DWN12088 is not clear. Therefore, we investigated the role of DWN12088 in NASH progression.
Methods
Mice were fed a chow diet or methionine-choline deficient (MCD)-diet, which was administered with DWN12088 or saline by oral gavage for 6 weeks. The effects of DWN12088 on NASH were evaluated by pathophysiological examinations, such as real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, immunoblotting, biochemical analysis, and immunohistochemistry. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of hepatic injury were assessed by in vitro cell culture.
Results
DWN12088 attenuated palmitic acid (PA)-induced lipid accumulation and lipoapoptosis by downregulating the Rho-kinase (ROCK)/AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK)/α subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2α)/activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4)/C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP) signaling cascades. PA increased but DWN12088 inhibited the phosphorylation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) p65 (Ser536, Ser276) and the expression of proinflammatory genes. Moreover, the DWN12088 inhibited transforming growth factor β (TGFβ)-induced pro-fibrotic gene expression by suppressing TGFβ receptor 1 (TGFβR1)/Smad2/3 and TGFβR1/glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase (EPRS)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) axis signaling. In the case of MCD-diet-induced NASH, DWN12088 reduced hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and lipoapoptosis and prevented the progression of fibrosis.
Conclusion
Our findings provide new insights about DWN12088, namely that it plays an important role in the overall improvement of NASH. Hence, DWN12088 shows great potential to be developed as a new integrated therapeutic agent for NASH.
- Basic Research
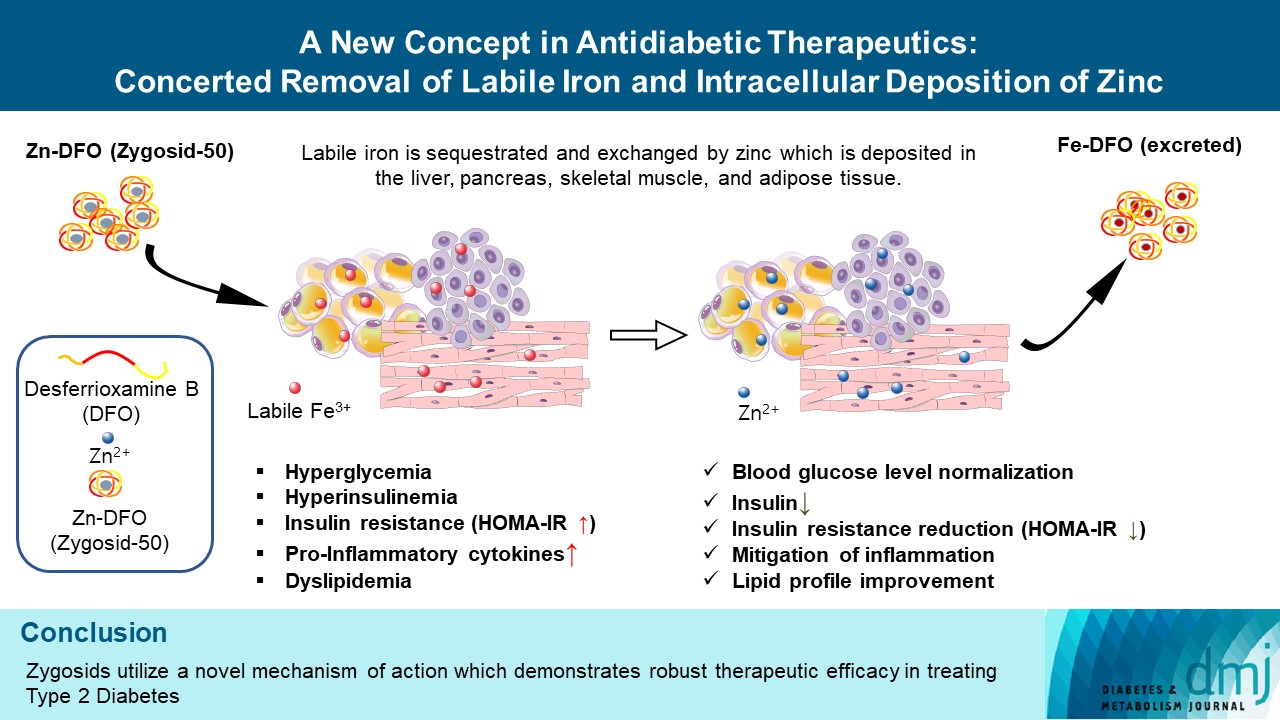
- A New Concept in Antidiabetic Therapeutics: A Concerted Removal of Labile Iron and Intracellular Deposition of Zinc
- Vladimir Vinokur, Eduard Berenshtein, Mordechai Chevion, Dror Chevion
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):59-71. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0292
- Retraction in: Diabetes Metab J 2024;48(2):325
- 1,565 View
- 178 Download
- Basic Research
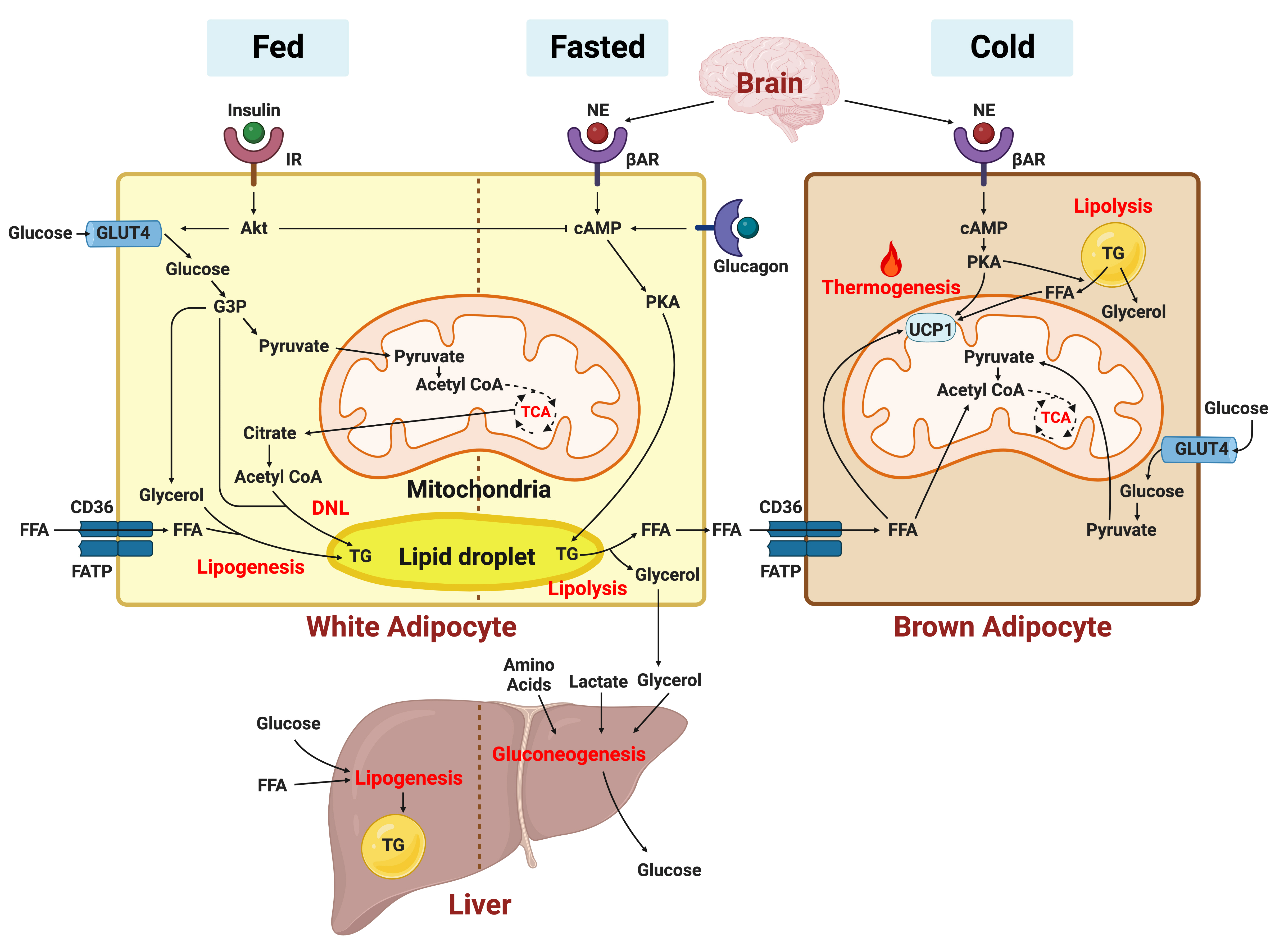
- Adipose Tissue and Metabolic Health
- Sung-Min An, Seung-Hee Cho, John C. Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):595-611. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0011
- 3,846 View
- 442 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - In this review, we provide a brief synopsis of the connections between adipose tissue and metabolic health and highlight some recent developments in understanding and exploiting adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue plays critical roles in the regulation of systemic glucose and lipid metabolism and secretes bioactive molecules possessing endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine functions. Dysfunctional adipose tissue has a detrimental impact on metabolic health and is intimately involved in key aspects of metabolic diseases such as insulin resistance, lipid overload, inflammation, and organelle stress. Differences in the distribution of fat depots and adipose characteristics relate to divergent degrees of metabolic dysfunction found in metabolically healthy and unhealthy obese individuals. Thermogenic adipocytes increase energy expenditure via mitochondrial uncoupling or adenosine triphosphate-consuming futile substrate cycles, while functioning as a metabolic sink and participating in crosstalk with other metabolic organs. Manipulation of adipose tissue provides a wealth of opportunities to intervene and combat the progression of associated metabolic diseases. We discuss current treatment modalities for obesity including incretin hormone analogs and touch upon emerging strategies with therapeutic potential including exosome-based therapy, pharmacological activation of brown and beige adipocyte thermogenesis, and administration or inhibition of adipocyte-derived factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pharmacological targets at the lysosomal autophagy–NLRP3 inflammasome crossroads
Srinivasa Reddy Bonam, Dylan Mastrippolito, Philippe Georgel, Sylviane Muller
Trends in Pharmacological Sciences.2024; 45(1): 81. CrossRef - Senescent adipocytes and type 2 diabetes – current knowledge and perspective concepts
Weronika Kruczkowska, Julia Gałęziewska, Mateusz Kciuk, Adrianna Gielecińska, Elżbieta Płuciennik, Zbigniew Pasieka, Lin-Yong Zhao, Yi-Jin Yu, Damian Kołat, Żaneta Kałuzińska-Kołat
Biomolecular Concepts.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Visceral Adipose Tissue: The Hidden Culprit for Type 2 Diabetes
Sneha Dhokte, Krzysztof Czaja
Nutrients.2024; 16(7): 1015. CrossRef - Beyond the Cold: Activating Brown Adipose Tissue as an Approach to Combat Obesity
Cristina Elena Negroiu, Iulia Tudorașcu, Cristina Maria Bezna, Sanziana Godeanu, Marina Diaconu, Raluca Danoiu, Suzana Danoiu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(7): 1973. CrossRef
- Pharmacological targets at the lysosomal autophagy–NLRP3 inflammasome crossroads
- Basic Research
- Multiple Roles of Sirtuin 6 in Adipose Tissue Inflammation
- Eun Ju Bae, Byung-Hyun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):164-172. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0270

- 3,745 View
- 229 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Adipose tissue (AT) inflammation is strongly associated with obesity-induced insulin resistance. When subjected to metabolic stress, adipocytes become inflamed and secrete a plethora of cytokines and chemokines, which recruit circulating immune cells to AT. Although sirtuin 6 (Sirt6) is known to control genomic stabilization, aging, and cellular metabolism, it is now understood to also play a pivotal role in the regulation of AT inflammation. Sirt6 protein levels are reduced in the AT of obese humans and animals and increased by weight loss. In this review, we summarize the potential mechanism of AT inflammation caused by impaired action of Sirt6 from the immune cells’ point of view. We first describe the properties and functions of immune cells in obese AT, with an emphasis on discrete macrophage subpopulations which are central to AT inflammation. We then highlight data that links Sirt6 to functional phenotypes of AT inflammation. Importantly, we discuss in detail the effects of Sirt6 deficiency in adipocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils on insulin resistance or AT browning. In our closing perspectives, we discuss emerging issues in this field that require further investigation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Increased Expression of Sirtuin 6 in the Prevention of Premature Aging Pathomechanisms
Adrianna Dzidek, Olga Czerwińska-Ledwig, Małgorzata Żychowska, Wanda Pilch, Anna Piotrowska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(11): 9655. CrossRef - Exploring the Influence of Age, Gender and Body Mass Index on Colorectal Cancer Location
Dorel Popovici, Cristian Stanisav, Sorin Saftescu, Serban Negru, Radu Dragomir, Daniel Ciurescu, Razvan Diaconescu
Medicina.2023; 59(8): 1399. CrossRef
- The Role of Increased Expression of Sirtuin 6 in the Prevention of Premature Aging Pathomechanisms
- Lifestyle
- Effectiveness of Resistance Exercise on Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
- Rubén Fernández-Rodríguez, Sonia Monedero-Carrasco, Bruno Bizzozero-Peroni, Miriam Garrido-Miguel, Arthur Eumann Mesas, Vicente Martínez-Vizcaíno
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):118-134. Published online April 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0007

- 9,809 View
- 310 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is related to increased inflammatory processes. The effects of resistance exercise on inflammatory biomarkers in T2DM are controversial. Our purpose was to determine the effectiveness of resistance exercise on inflammatory biomarkers in patients diagnosed with T2DM.
Methods
We searched four databases until September 2021. We included randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of the effects of resistance exercise on inflammatory biomarkers (C-reactive protein [CRP], tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6, and interleukin-10) in patients with T2DM. A random effects meta-analysis was conducted to determine the standardized mean difference (SMD) and the raw mean difference (MD) for CRP.
Results
Thirteen RCTs were included in the review, and 11 in the meta-analysis for CRP. Lower CRP levels were observed when resistance exercise was compared with the control groups (SMD=–0.20; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.37 to –0.02). When conducting the MD meta-analysis, resistance exercise showed a significant decrease in CRP of –0.59 mg/dL (95% CI, –0.88 to –0.30); otherwise, in the control groups, the CRP values increased 0.19 mg/dL (95% CI, 0.17 to 0.21).
Conclusion
Evidence supports resistance exercise as an effective strategy to manage systemic inflammation by decreasing CRP levels in patients with T2DM. The evidence is still inconclusive for other inflammatory biomarkers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Körperliche Aktivität und Trainingstherapie bei Typ-2-Diabetes – ein Update
Andreas M. Nieß, Ansgar Thiel
Diabetologie und Stoffwechsel.2024; 19(01): 38. CrossRef - Genetic predisposition, lifestyle inflammation score, food-based dietary inflammatory index, and the risk for incident diabetes: Findings from the KoGES data
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park, Bomi Park
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(3): 642. CrossRef - Associations of meeting 24-h movement guidelines and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults during the COVID-19 pandemic
S.W. Shin, Y. Choi, Y.H. Kang, J. Kim
Public Health.2024; 227: 187. CrossRef - Association of hypoglycemic events with cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Protocol for a dose-response meta-analysis
Min Ye, Ai Hong Yuan, Qi Qi Yang, Qun Wei Li, Fei Yue Li, Yan Wei, Muhammad Shahzad Aslam
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0296662. CrossRef - Exercise Interventions for the Prevention and Treatment of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Women with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review
Hongmei Li, Haiyun Liu, Boliang Wang, Xiao Jia, Jingjing Yu, Yurong Zhang, Die Sang, Yimin Zhang
Journal of Science in Sport and Exercise.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Additive impact of diabetes and sarcopenia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A longitudinal nationwide population-based study
Eyun Song, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Ahreum Jang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155678. CrossRef - Endothelial progenitor cell response to a multicomponent exercise training program in adults with cardiovascular risk factors
Suiane Cavalcante, Manuel Teixeira, Marisol Gouveia, Ana Duarte, Miriam Ferreira, Maria I. Simões, Maria Conceição, Mariana Costa, Ilda P. Ribeiro, Ana Cristina Gonçalves, José Oliveira, Fernando Ribeiro
German Journal of Exercise and Sport Research.2023; 53(2): 225. CrossRef - “Does Physical Exercise Promote Health Benefits for Diabetic Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic?”: A Systematic Review
Erivaldo de Souza, Daniela Meneses-Santos, Josué Cruz Santos, Felipe J. Aidar, Carla Roberta de Oliveira Carvalho, Jymmys Lopes dos Santos, Anderson Carlos Marçal
Sports.2023; 11(10): 192. CrossRef - Effect of exercise on inflammatory markers in postmenopausal women with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Liang Tan, Weihua Yan, Weilin Yang, Agata Kamionka, Mariusz Lipowski, Zijian Zhao, Gang Zhao
Experimental Gerontology.2023; 183: 112310. CrossRef - Resistance Training Improves Beta Cell Glucose Sensing and Survival in Diabetic Models
Gabriela Alves Bronczek, Gabriela Moreira Soares, Carine Marmentini, Antonio Carlos Boschero, José Maria Costa-Júnior
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(16): 9427. CrossRef
- Körperliche Aktivität und Trainingstherapie bei Typ-2-Diabetes – ein Update
- Complications
- Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):181-197. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0329
- 11,971 View
- 787 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 45 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Although diabetic kidney disease (DKD) remains the leading cause of end-stage kidney disease eventually requiring chronic kidney replacement therapy, the prevalence of DKD has failed to decline over the past 30 years. In order to reduce disease prevalence, extensive research has been ongoing to improve prediction of DKD onset and progression. Although the most commonly used markers of DKD are albuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate, their limitations have encouraged researchers to search for novel biomarkers that could improve risk stratification. Considering that DKD is a complex disease process that involves several pathophysiologic mechanisms such as hyperglycemia induced inflammation, oxidative stress, tubular damage, eventually leading to kidney damage and fibrosis, many novel biomarkers that capture one specific mechanism of the disease have been developed. Moreover, the increasing use of high-throughput omic approaches to analyze biological samples that include proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics has emerged as a strong tool in biomarker discovery. This review will first describe recent advances in the understanding of the pathophysiology of DKD, and second, describe the current clinical biomarkers for DKD, as well as the current status of multiple potential novel biomarkers with respect to protein biomarkers, proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of polyphenols in the management of diabetic complications
Jeevika Raina, Atika Firdous, Gurvinder Singh, Rajesh Kumar, Charanjit Kaur
Phytomedicine.2024; 122: 155155. CrossRef - Role of MCP-1 as an inflammatory biomarker in nephropathy
Yanlong Liu, Ke Xu, Yuhua Xiang, Boyan Ma, Hailong Li, Yuan Li, Yue Shi, Shuju Li, Yan Bai
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Urinary podocyte stress marker as a prognostic indicator for diabetic kidney disease
Lingfeng Zeng, Jack Kit-Chung Ng, Winston Wing-Shing Fung, Gordon Chun-Kau Chan, Kai-Ming Chow, Cheuk-Chun Szeto
BMC Nephrology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification and validation of immune and cuproptosis - related genes for diabetic nephropathy by WGCNA and machine learning
Yubing Chen, Lijuan Liao, Baoju Wang, Zhan Wu
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Specific Alternation of Gut Microbiota and the Role of Ruminococcus gnavus in the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy
Jinni Hong, Tingting Fu, Weizhen Liu, Yu Du, Junmin Bu, Guojian Wei, Miao Yu, Yanshan Lin, Cunyun Min, Datao Lin
Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2024; 34(3): 547. CrossRef - A Narrative Review of New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy
Aadhira Pillai, Darshna Fulmali
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bamboo leaf: A review of traditional medicinal property, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and purification technology
Yaqian Cheng, Siqi Wan, Linna Yao, Ding Lin, Tong Wu, Yongjian Chen, Ailian Zhang, Chenfei Lu
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2023; 306: 116166. CrossRef - Molecular Pathways of Diabetic Kidney Disease Inferred from Proteomics
Lan Wei, Yuanyuan Han, Chao Tu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 117. CrossRef - Omics and Artificial Intelligence in Kidney Diseases
Nadja Grobe, Josef Scheiber, Hanjie Zhang, Christian Garbe, Xiaoling Wang
Advances in Kidney Disease and Health.2023; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Intestinal microbiome diversity of diabetic and non-diabetic kidney disease: Current status and future perspective
Soumik Das, Ramanathan Gnanasambandan
Life Sciences.2023; 316: 121414. CrossRef - Pediatric Diabetic Nephropathy: Novel Insights from microRNAs
Francesca Lanzaro, Annalisa Barlabà, Angelica De Nigris, Federica Di Domenico, Valentina Verde, Emanuele Miraglia del Giudice, Anna Di Sessa
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(4): 1447. CrossRef - Novel Biomarkers of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Jorge Rico-Fontalvo, Gustavo Aroca-Martínez, Rodrigo Daza-Arnedo, José Cabrales, Tomás Rodríguez-Yanez, María Cardona-Blanco, Juan Montejo-Hernández, Dairo Rodelo Barrios, Jhonny Patiño-Patiño, Elber Osorio Rodríguez
Biomolecules.2023; 13(4): 633. CrossRef - Diabetic vascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies
Yiwen Li, Yanfei Liu, Shiwei Liu, Mengqi Gao, Wenting Wang, Keji Chen, Luqi Huang, Yue Liu
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic phenotypes and risk of end-stage kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Lijun Zhao, Yutong Zou, Yucheng Wu, Linli Cai, Yuancheng Zhao, Yiting Wang, Xiang Xiao, Qing Yang, Jia Yang, Honghong Ren, Nanwei Tong, Fang Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of a New RNA and Protein Integrated Biomarker Panel Associated with Kidney Function Impairment in DKD: Translational Implications
Alessandra Scamporrino, Stefania Di Mauro, Agnese Filippello, Grazia Di Marco, Antonino Di Pino, Roberto Scicali, Maurizio Di Marco, Emanuele Martorana, Roberta Malaguarnera, Francesco Purrello, Salvatore Piro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(11): 9412. CrossRef - Increased serum PCSK9 levels are associated with renal function impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Zhicai Feng, Xiangyu Liao, Hao Zhang, Juan Peng, Zhijun Huang, Bin Yi
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Serum Pyrodeath Re-lated Proteins and Renal Injury in Patients with Type 2 DKD
茹洁 马
Asian Case Reports in Emergency Medicine.2023; 11(02): 53. CrossRef - Loganin reduces diabetic kidney injury by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
Xiangri Kong, Yunyun Zhao, Xingye Wang, Yongjiang Yu, Ying Meng, Guanchi Yan, Miao Yu, Lihong Jiang, Wu Song, Bingmei Wang, Xiuge Wang
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2023; 382: 110640. CrossRef - Machine-learning algorithm-based prediction of a diagnostic model based on oxidative stress-related genes involved in immune infiltration in diabetic nephropathy patients
Heng-Mei Zhu, Na Liu, Dong-Xuan Sun, Liang Luo
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The roles of gut microbiota and its metabolites in diabetic nephropathy
Hui Zhao, Cheng-E Yang, Tian Liu, Ming-Xia Zhang, Yan Niu, Ming Wang, Jun Yu
Frontiers in Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High triglyceride levels increase the risk of diabetic microvascular complications: a cross-sectional study
Jiahang Li, Lei Shi, Guohong Zhao, Fei Sun, Zhenxing Nie, Zhongli Ge, Bin Gao, Yan Yang
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Nephrin Levels in Iraqi Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy
Raghda Hisham Aljorani, Eman Saadi Saleh , Khalaf Gata Hussein Al Mohammadawi
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2023; 5: 99. CrossRef - Diabetic Nephropathy: Significance of Determining Oxidative Stress and Opportunities for Antioxidant Therapies
Marina Darenskaya, Sergey Kolesnikov, Natalya Semenova, Lyubov Kolesnikova
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(15): 12378. CrossRef - Evaluation of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio, Low-Density Lipoprotein/Albumin Ratio, and Red Cell Distribution Width/Albumin Ratio in the Estimation of Proteinuria in Uncontrolled Diabetic Patients
Duygu Tutan, Murat Doğan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hedysarum polybotrys polysaccharide attenuates renal inflammatory infiltration and fibrosis in diabetic mice by inhibiting the HMGB1/RAGE/TLR4 pathway
Changqing Xu, Yanxu Cheng, Zongmei Liu, Xiaoyan Fu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Abdominal adipose tissue and type 2 diabetic kidney disease: adipose radiology assessment, impact, and mechanisms
Fei Lu, Jinlei Fan, Fangxuan Li, Lijing Liu, Zhiyu Chen, Ziyu Tian, Liping Zuo, Dexin Yu
Abdominal Radiology.2023; 49(2): 560. CrossRef - Inhibition of MD2 by natural product-drived JM-9 attenuates renal inflammation and diabetic nephropathy in mice
Minxiu Wang, Qianhui Zhang, Shuaijie Lou, Leiming Jin, Gaojun Wu, Wenqi Wu, Qidong Tang, Yi Wang, Xiaohong Long, Ping Huang, Wu Luo, Guang Liang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115660. CrossRef - Multifaceted relationship between diabetes and kidney diseases: Beyond diabetes
Pasquale Esposito, Daniela Picciotto, Francesca Cappadona, Francesca Costigliolo, Elisa Russo, Lucia Macciò, Francesca Viazzi
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(10): 1450. CrossRef - Mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein: a potential therapeutic target in renal disease
Meng Wu, Zhiyin Pei, Guangfeng Long, Hongbing Chen, Zhanjun Jia, Weiwei Xia
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Research progress on multiple cell death pathways of podocytes in diabetic kidney disease
Can Yang, Zhen Zhang, Jieting Liu, Peijian Chen, Jialing Li, Haiying Shu, Yanhui Chu, Luxin Li
Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative profiling of carboxylic compounds by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for revealing biomarkers of diabetic kidney disease
Rongrong Zhu, Yan Yuan, Rourou Qi, Jianying Liang, Yan Shi, Hongbo Weng
Journal of Chromatography B.2023; 1231: 123930. CrossRef - Jiangtang Decoction Ameliorates Diabetic Kidney Disease Through the Modulation of the Gut Microbiota
Jinni Hong, Tingting Fu, Weizhen Liu, Yu Du, Junmin Bu, Guojian Wei, Miao Yu, Yanshan Lin, Cunyun Min, Datao Lin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3707. CrossRef - GLP-1RA Combined with SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Meta Analysis
莹 郭
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(11): 18117. CrossRef - Potential application of Klotho as a prognostic biomarker for patients with diabetic kidney disease: a meta-analysis of clinical studies
Li Xia Yu, Min Yue Sha, Yue Chen, Fang Tan, Xi Liu, Shasha Li, Qi-Feng Liu
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals RAC1 Involvement in Macrophages Efferocytosis in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Yi Song, Yifan Liu, Feng Guo, Lin Zhao, Guijun Qin
Inflammation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Research progress of natural active compounds on improving podocyte function to reduce proteinuria in diabetic kidney disease
Le Gong, Rui Wang, Xinyu Wang, Jing Liu, Zhaodi Han, Qian Li, Yi Jin, Hui Liao
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of potential crosstalk genes and mechanisms between periodontitis and diabetic nephropathy through bioinformatic analysis
Huijuan Lu, Jia Sun, Jieqiong Sun
Medicine.2023; 102(52): e36802. CrossRef - Mitochondrial RNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Functional Impairment in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Stefania Di Mauro, Alessandra Scamporrino, Agnese Filippello, Maurizio Di Marco, Maria Teresa Di Martino, Francesca Scionti, Antonino Di Pino, Roberto Scicali, Roberta Malaguarnera, Francesco Purrello, Salvatore Piro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8198. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Partial Synthetic PPARƳ Derivative Ameliorates Aorta Injury in Experimental Diabetic Rats Mediated by Activation of miR-126-5p Pi3k/AKT/PDK 1/mTOR Expression
Yasmin M. Ahmed, Raha Orfali, Nada S. Abdelwahab, Hossam M. Hassan, Mostafa E. Rateb, Asmaa M. AboulMagd
Pharmaceuticals.2022; 15(10): 1175. CrossRef - Polydatin attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting YAP expression and nuclear translocation
Manlin He, Lan Feng, Yang Chen, Bin Gao, Yiwei Du, Lu Zhou, Fei Li, Hongbao Liu
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of diabetic nephropathy in the diabetes mellitus population: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
Sicheng Li, Huidi Xie, Yang Shi, Hongfang Liu
Medicine.2022; 101(42): e31232. CrossRef - Stratification of diabetic kidney diseases via data-independent acquisition proteomics–based analysis of human kidney tissue specimens
Qinghua Huang, Xianming Fei, Zhaoxian Zhong, Jieru Zhou, Jianguang Gong, Yuan Chen, Yiwen Li, Xiaohong Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel biomarkers and therapeutic approaches for diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy: Recent progress and future perspectives
Ziyan Xie, Xinhua Xiao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease
Susanne B. Nicholas, Amy K. Mottl
Nephrology Self-Assessment Program.2022; 21(5): 394. CrossRef
- Role of polyphenols in the management of diabetic complications
- Basic Research
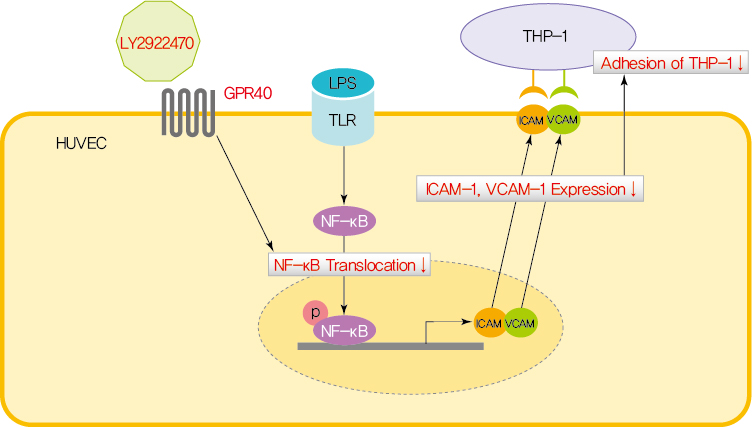
- GPR40 Agonism Modulates Inflammatory Reactions in Vascular Endothelial Cells
- Joo Won Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Hye Jin Yoo, Hwan-Jin Hwang, Sei Hyun Baik
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):506-511. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0092
- 4,730 View
- 229 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Endothelial dysfunction is strongly linked with inflammatory responses, which can impact cardiovascular disease. Recently, G protein-coupled receptor 40 (GPR40) has been investigated as a modulator of metabolic stress; however, the function of GPR40 in vascular endothelial cells has not been reported. We analyzed whether treatment of GPR40-specific agonists modulated the inflammatory responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Treatment with LY2922470, a GPR40 agonist, significantly reduced lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) phosphorylation and movement into the nucleus from the cytosol. However, treatment with another GPR40 agonist, TAK875, did not inhibit LPS-induced NF-κB activation. LPS treatment induced expression of adhesion molecules vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and attachment of THP-1 cells to HUVECs, which were all decreased by LY2922470 but not TAK875. Our results showed that ligand-dependent agonism of GPR40 is a promising therapeutic target for overcoming inflammatory reactions in the endothelium.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthetic GPR40/FFAR1 agonists: An exhaustive survey on the most recent chemical classes and their structure-activity relationships
Abhik Paul, Sourin Nahar, Pankaj Nahata, Arnab Sarkar, Avik Maji, Ajeya Samanta, Sanmoy Karmakar, Tapan Kumar Maity
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2024; 264: 115990. CrossRef - Metabolite-sensing GPCRs in rheumatoid arthritis
Xuezhi Yang, Wankang Zhang, Luping Wang, Yingjie Zhao, Wei Wei
Trends in Pharmacological Sciences.2024; 45(2): 118. CrossRef - GPR40 deficiency worsens metabolic syndrome‐associated periodontitis in mice
Yanchun Li, Zhongyang Lu, Cameron L. Kirkwood, Keith L. Kirkwood, Stephen A. Wank, Ai‐Jun Li, Maria F. Lopes‐Virella, Yan Huang
Journal of Periodontal Research.2023; 58(3): 575. CrossRef - Signaling pathways and intervention for therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Rong Cao, Huimin Tian, Yu Zhang, Geng Liu, Haixia Xu, Guocheng Rao, Yan Tian, Xianghui Fu
MedComm.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - G Protein-Coupled Receptor 40 Agonist LY2922470 Alleviates Ischemic-Stroke-Induced Acute Brain Injury and Functional Alterations in Mice
Yingyu Lu, Wanlu Zhou, Qinghua Cui, Chunmei Cui
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(15): 12244. CrossRef - AM1638, a GPR40-Full Agonist, Inhibited Palmitate- Induced ROS Production and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Enhancing HUVEC Viability in an NRF2-Dependent Manner
Hwan-Jin Hwang, Joo Won Kim, SukHwan Yun, Min Jeong Park, Eyun Song, Sooyeon Jang, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 760. CrossRef - Learn from failures and stay hopeful to GPR40, a GPCR target with robust efficacy, for therapy of metabolic disorders
Hong-Ping Guan, Yusheng Xiong
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Synthetic GPR40/FFAR1 agonists: An exhaustive survey on the most recent chemical classes and their structure-activity relationships
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
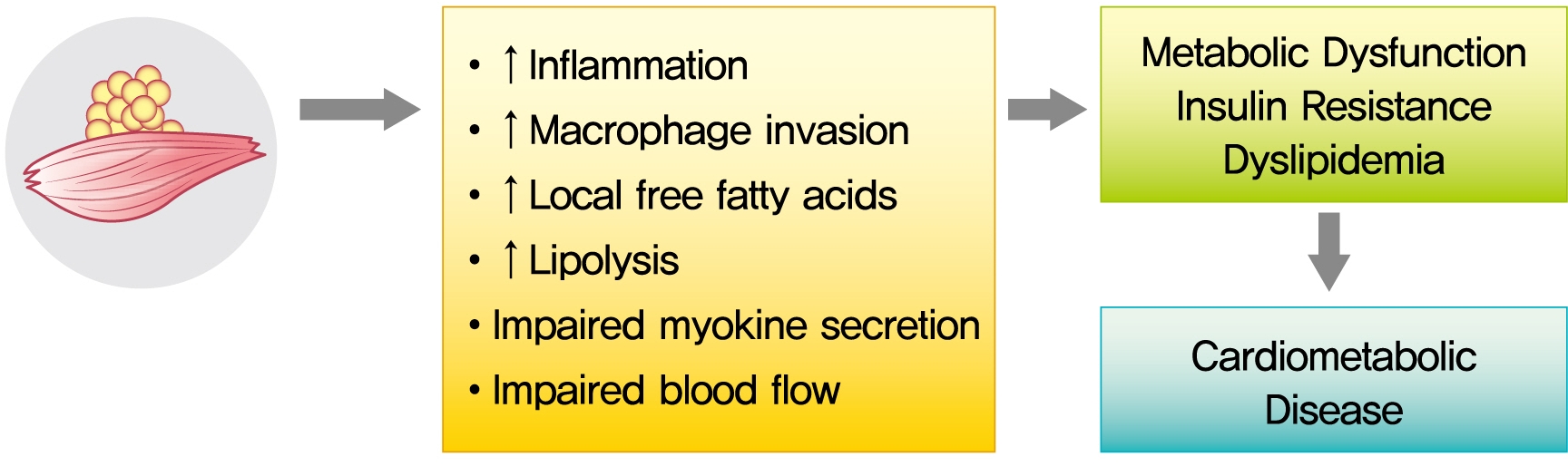
- Computed Tomography-Derived Myosteatosis and Metabolic Disorders
- Iva Miljkovic, Chantal A. Vella, Matthew Allison
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):482-491. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0277
- 6,210 View
- 236 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 44 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- The role of ectopic adipose tissue infiltration into skeletal muscle (i.e., myosteatosis) for metabolic disorders has received considerable and increasing attention in the last 10 years. The purpose of this review was to evaluate and summarize existing studies focusing on computed tomography (CT)-derived measures of myosteatosis and metabolic disorders. There is consistent evidence that CT-derived myosteatosis contributes to dysglycemia, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and inflammation, and, to some extent, dyslipidemia, independent of general obesity, visceral fat, and other relevant risk factors, suggesting that it may serve as a tool for metabolic risk prediction. Identification of which muscles should be examined, and the standardized CT protocols to be employed, are necessary to enhance the applicability of findings from epidemiologic studies of myosteatosis. Additional and longer longitudinal studies are necessary to confirm a role of myosteatosis in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, and examine these associations in a variety of muscles across multiple race/ethnic populations. Given the emerging role of myosteatosis in metabolic health, well-designed intervention studies are needed to investigate relevant lifestyle and pharmaceutical approaches.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Muscle Fat Content and Muscle Mass With Impaired Lung Function in Young Adults With Obesity: Evaluation With MRI
Xin Yu, Yan-Hao Huang, You-Zhen Feng, Zhong-Yuan Cheng, Cun-Chuan Wang, Xiang-Ran Cai
Academic Radiology.2024; 31(1): 9. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle alterations indicate poor prognosis in cirrhotic patients: a multicenter cohort study in China
Xin Zeng, Zhi-Wen Shi, Jia-Jun Yu, Li-Fen Wang, Chun-Yan Sun, Yuan-Yuan Luo, Pei-Mei Shi, Yong Lin, Yue-Xiang Chen, Jia Guo, Chun-Qing Zhang, Wei-Fen Xie
Hepatology International.2024; 18(2): 673. CrossRef - Subtype-specific Body Composition and Metabolic Risk in Patients With Primary Aldosteronism
Seung Shin Park, Chang Ho Ahn, Sang Wan Kim, Ji Won Yoon, Jung Hee Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(2): e788. CrossRef - Myosteatosis as a novel predictor of new‐onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation
Takahito Wakamiya, Takuya Fujimoto, Takahito Endo, Shun Nishioka, Naoki Yokoyama, Shimpei Yamashita, Kazuro Kikkawa, Yoji Hyodo, Takeshi Ishimura, Yasuo Kohjimoto, Isao Hara, Masato Fujisawa
International Journal of Urology.2024; 31(1): 39. CrossRef - Predictors of visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue and muscle density: The ShapeUp! Kids study
Gertraud Maskarinec, Yurii Shvetsov, Michael C. Wong, Devon Cataldi, Jonathan Bennett, Andrea K. Garber, Steven D. Buchthal, Steven B. Heymsfield, John A. Shepherd
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(3): 799. CrossRef - Association of daily carbohydrate intake with intermuscular adipose tissue in Korean individuals with obesity: a cross-sectional study
Ha-Neul Choi, Young-Seol Kim, Jung-Eun Yim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(1): 78. CrossRef - Myosteatosis is associated with poor survival after kidney transplantation: a large retrospective cohort validation
Jie Chen, Yue Li, Chengjie Li, Turun Song
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 49(4): 1210. CrossRef - Regenerative rehabilitation measures to restore tissue function after arsenic exposure
Adam A. Jasper, Kush H. Shah, Helmet Karim, Swathi Gujral, Iva Miljkovic, Caterina Rosano, Aaron Barchowsky, Amrita Sahu
Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering.2024; 30: 100529. CrossRef - Impact of CFTR modulator therapy on body composition as assessed by thoracic computed tomography: A follow-up study
Víctor Navas-Moreno, Fernando Sebastian-Valles, Víctor Rodríguez-Laval, Carolina Knott-Torcal, Mónica Marazuela, Nuria Sánchez de la Blanca, Jose Alfonso Arranz Martín, Rosa María Girón, Miguel Antonio Sampedro-Núñez
Nutrition.2024; 123: 112425. CrossRef - Myosteatosis predicts postoperative complications and long‐term survival in robotic gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A propensity score analysis
Pingan Ding, Jiaxiang Wu, Haotian Wu, Tongkun Li, Jiaxuan Yang, Li Yang, Honghai Guo, Yuan Tian, Peigang Yang, Lingjiao Meng, Qun Zhao
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A multifaceted and inclusive methodology for the detection of sarcopenia in patients undergoing bariatric surgery: an in-depth analysis of current evidence
Eunhye Seo, Yeongkeun Kwon, Ahmad ALRomi, Mohannad Eledreesi, Sungsoo Park
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Body Composition at CT and Risk of Future Disease
Michael A. Ohliger
Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between hypertension and myosteatosis evaluated by abdominal computed tomography
Han Na Jung, Yun Kyung Cho, Hwi Seung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Woo Je Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(4): 845. CrossRef - Muscle fat infiltration in chronic kidney disease: a marker related to muscle quality, muscle strength and sarcopenia
Carla Maria Avesani, Aline Miroski de Abreu, Heitor S. Ribeiro, Torkel B. Brismar, Peter Stenvinkel, Alice Sabatino, Bengt Lindholm
Journal of Nephrology.2023; 36(3): 895. CrossRef - Myosteatosis: a potential missing link between hypertension and metabolic disorder in the Asian population
Minyoung Lee, Sungha Park
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(6): 1603. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - Association between sarcopenic obesity and poor muscle quality based on muscle quality map and abdominal computed tomography
Yun Kyung Cho, Han Na Jung, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Joong‐Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Hong‐Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Obesity.2023; 31(6): 1547. CrossRef - Chest CT opportunistic biomarkers for phenotyping high-risk COVID-19 patients: a retrospective multicentre study
Anna Palmisano, Chiara Gnasso, Alberto Cereda, Davide Vignale, Riccardo Leone, Valeria Nicoletti, Simone Barbieri, Marco Toselli, Francesco Giannini, Marco Loffi, Gianluigi Patelli, Alberto Monello, Gianmarco Iannopollo, Davide Ippolito, Elisabetta Maria
European Radiology.2023; 33(11): 7756. CrossRef - Early menopause and premature ovarian insufficiency may increase the risk of sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Efstathios Divaris, Panagiotis Anagnostis, Nifon K. Gkekas, Evangelia Kouidi, Dimitrios G. Goulis
Maturitas.2023; 175: 107782. CrossRef - The Important Role of Intermuscular Adipose Tissue on Metabolic Changes Interconnecting Obesity, Ageing and Exercise: A Systematic Review
I Gusti Putu Suka Aryana, Ivana Beatrice Paulus, Sanjay Kalra, Dian Daniella, Raden Ayu Tuty Kuswardhani, Ketut Suastika, Sony Wibisono
European Endocrinology.2023; 19(1): 54. CrossRef - Increase in skeletal muscular adiposity and cognitive decline in a biracial cohort of older men and women
Caterina Rosano, Anne Newman, Adam Santanasto, Xiaonan Zhu, Bret Goodpaster, Iva Miljkovic
Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.2023; 71(9): 2759. CrossRef - Myosteatosis and bone marrow adiposity are not associated among postmenopausal women with fragility fractures
Sammy Badr, Héloïse Dapvril, Daniela Lombardo, Huda Khizindar, Claire Martin, Bernard Cortet, Anne Cotten, Julien Paccou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between trunk intramuscular adipose tissue content and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Japanese men
Noriko I. Tanaka, Masataka Suwa, Hisashi Maeda, Aya Tomita, Takayuki Imoto, Hiroshi Akima
Nutrition.2023; 113: 112083. CrossRef - Sarcopenic obesity and its relation with muscle quality and mortality in patients on chronic hemodialysis
Alice Sabatino, Carla Maria Avesani, Giuseppe Regolisti, Marianna Adinolfi, Giuseppe Benigno, Marco Delsante, Enrico Fiaccadori, Ilaria Gandolfini
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(8): 1359. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle adiposity is a novel risk factor for poor cognition in African Caribbean women
Adrianna I. Acevedo‐Fontánez, Ryan K. Cvejkus, Joseph M. Zmuda, Allison L. Kuipers, Emma Barinas‐Mitchell, Akira Sekikawa, Victor Wheeler, Caterina Rosano, Iva Miljkovic
Obesity.2023; 31(9): 2398. CrossRef - Obesity, Sarcopenia and Myosteatosis: Impact on Clinical Outcomes in the Operative Management of Crohn’s Disease
Mark Donnelly, Dorothee Driever, Éanna J Ryan, Jessie A Elliott, John Finnegan, Deirdre McNamara, Ian Murphy, Kevin C Conlon, Paul C Neary, Dara O Kavanagh, James M O’Riordan
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Meld-sarcopenia score and skeletal muscle density predicts short-term readmission of patients with hepatic encephalopathy
Shuo Yang, Lin Zhang, Qian Jin, Jian Wang, Danli Ma, Jie Gao, Rui Huang
European Journal of Radiology.2023; 169: 111178. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Adults
W. Guo, X. Zhao, D. Cheng, X. Liang, M. Miao, X. Li, J. Lu, N. Xu, Shuang Hu, Qun Zhang
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(11): 960. CrossRef - Association between relative muscle strength and hypertension in middle-aged and older Chinese adults
Jin-hua Luo, Tu-ming Zhang, Lin-lin Yang, Yu-ying Cai, Yu Yang
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynapenic Abdominal Obesity as a Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome in Individual 50 Years of Age or Older: English Longitudinal Study of Ageing
P.C. Ramírez, R. de Oliveira Máximo, D. Capra de Oliveira, A.F. de Souza, M. Marques Luiz, M. L. Bicigo Delinocente, A. Steptoe, C. de Oliveira, Tiago da Silva Alexandre
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(12): 1188. CrossRef - Editorial Comment to Myosteatosis as a novel predictor of urinary incontinence after robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy
Nobuhiro Haga, Naotaka Gunge, Hiroshi Matsuzaki, Yu Okabe, Takeshi Miyazaki
International Journal of Urology.2022; 29(1): 40. CrossRef - Ammonia and the Muscle: An Emerging Point of View on Hepatic Encephalopathy
Simone Di Cola, Silvia Nardelli, Lorenzo Ridola, Stefania Gioia, Oliviero Riggio, Manuela Merli
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(3): 611. CrossRef - Single skeletal muscle fiber mechanical properties: a muscle quality biomarker of human aging
Jae-Young Lim, Walter R. Frontera
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2022; 122(6): 1383. CrossRef - Sarcopenia in Patients with Cirrhosis after Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Placement
Jiacheng Liu, Jinqiang Ma, Chongtu Yang, Manman Chen, Qin Shi, Chen Zhou, Songjiang Huang, Yang Chen, Yingliang Wang, Tongqiang Li, Bin Xiong
Radiology.2022; 303(3): 711. CrossRef - Myosteatosis Significantly Predicts Persistent Dyspnea and Mobility Problems in COVID-19 Survivors
Rebecca De Lorenzo, Anna Palmisano, Antonio Esposito, Chiara Gnasso, Valeria Nicoletti, Riccardo Leone, Davide Vignale, Elisabetta Falbo, Marica Ferrante, Marta Cilla, Cristiano Magnaghi, Sabina Martinenghi, Giordano Vitali, Alessio Molfino, Patrizia Rove
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of myosteatosis in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Shaofang Feng, Huiwen Mu, Rong Hou, Yunxin Liu, Jianjun Zou, Zheng Zhao, Yubing Zhu
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2022; 27(7): 1127. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Strongly Associated With Hyperuricemia: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chinese Adults
Ningxin Chen, Tingting Han, Hongxia Liu, Jie Cao, Wenwen Liu, Didi Zuo, Ting Zhang, Xiucai Lan, Xian Jin, Yurong Weng, Yaomin Hu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in muscle health and nutrition: A toolkit for healthcare professionals
Carla M. Prado, Francesco Landi, Samuel T.H. Chew, Philip J. Atherton, Jeroen Molinger, Tobias Ruck, Maria Cristina Gonzalez
Clinical Nutrition.2022; 41(10): 2244. CrossRef - Factors related to trunk intramuscular adipose tissue content – A comparison of younger and older men
Funa Kitagawa, Madoka Ogawa, Akito Yoshiko, Yoshiharu Oshida, Teruhiko Koike, Hiroshi Akima, Noriko I. Tanaka
Experimental Gerontology.2022; 168: 111922. CrossRef - Association of myosteatosis with various body composition abnormalities and longer length of hospitalization in patients with decompensated cirrhosis
Xiaoyu Wang, Mingyu Sun, Yifan Li, Gaoyue Guo, Wanting Yang, Lihong Mao, Zihan Yu, Yangyang Hui, Xiaofei Fan, Binxin Cui, Kui Jiang, Chao Sun
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Peripheral bone structure, geometry, and strength and muscle density as derived from peripheral quantitative computed tomography and mortality among rural south Indian older adults
Guru Rajesh Jammy, Robert M. Boudreau, Iva Miljkovic, Pawan Kumar Sharma, Sudhakar Pesara Reddy, Susan L. Greenspan, Anne B. Newman, Jane A. Cauley, Bert B. Little
PLOS Global Public Health.2022; 2(10): e0000333. CrossRef - Muscle fat contents rather than muscle mass determines nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in patients with severe obesity
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Won Lee, Seungwan Ryu, Hye Soon Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Youngsung Suh
Obesity.2022; 30(12): 2440. CrossRef - Sex- and region-specific associations of skeletal muscle mass with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
Pei Xiao, Pu Liang, Panjun Gao, Jinyi Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging based body composition profiling and outcomes after oncologic liver surgery
Lorenzo Bernardi, Raffaello Roesel, Filippo Vagelli, Pietro Majno-Hurst, Alessandra Cristaudi
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of Muscle Fat Content and Muscle Mass With Impaired Lung Function in Young Adults With Obesity: Evaluation With MRI
- Type 1 Diabetes
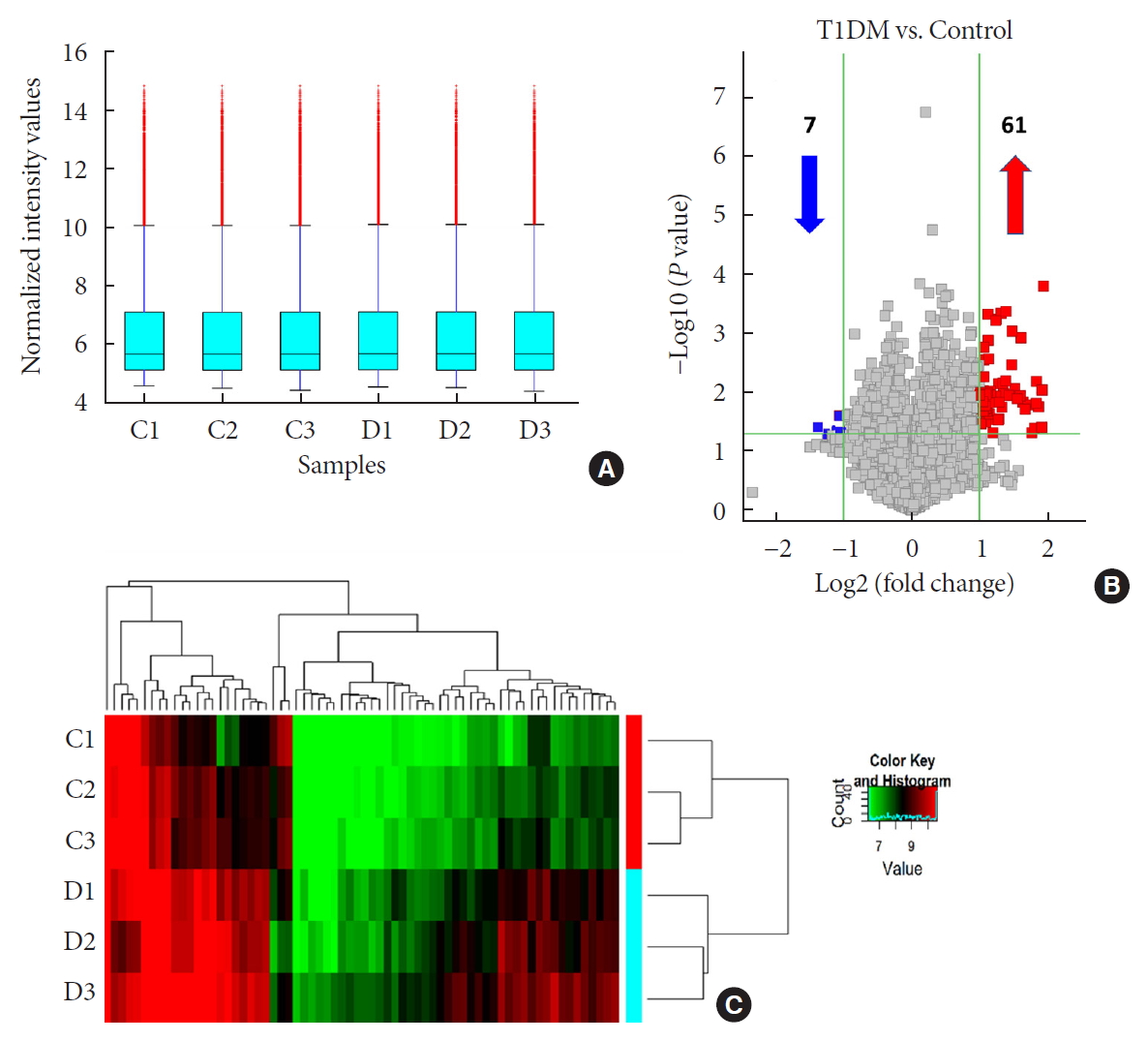
- Differential Profile of Plasma Circular RNAs in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yangyang Li, Ying Zhou, Minghui Zhao, Jing Zou, Yuxiao Zhu, Xuewen Yuan, Qianqi Liu, Hanqing Cai, Cong-Qiu Chu, Yu Liu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):854-865. Published online July 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0151
- 6,156 View
- 131 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background No currently available biomarkers or treatment regimens fully meet therapeutic needs of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Circular RNA (circRNA) is a recently identified class of stable noncoding RNA that have been documented as potential biomarkers for various diseases. Our objective was to identify and analyze plasma circRNAs altered in T1DM.
Methods We used microarray to screen differentially expressed plasma circRNAs in patients with new onset T1DM (
n =3) and age-/gender-matched healthy controls (n =3). Then, we selected six candidates with highest fold-change and validated them by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in independent human cohort samples (n =12). Bioinformatic tools were adopted to predict putative microRNAs (miRNAs) sponged by these validated circRNAs and their downstream messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses were performed to gain further insights into T1DM pathogenesis.Results We identified 68 differentially expressed circRNAs, with 61 and seven being up- and downregulated respectively. Four of the six selected candidates were successfully validated. Curations of their predicted interacting miRNAs revealed critical roles in inflammation and pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders. Functional relations were visualized by a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network. GO and KEGG analyses identified multiple inflammation-related processes that could be potentially associated with T1DM pathogenesis, including cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, inflammatory mediator regulation of transient receptor potential channels and leukocyte activation involved in immune response.
Conclusion Our study report, for the first time, a profile of differentially expressed plasma circRNAs in new onset T1DM. Further
in silico annotations and bioinformatics analyses supported future application of circRNAs as novel biomarkers of T1DM.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Non-coding RNAs and exosomal non-coding RNAs in diabetic retinopathy: A narrative review
Yuhong Zhong, Juan Xia, Li Liao, Mohammad Reza Momeni
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2024; 259: 128182. CrossRef - Circular RNAs: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for autoimmune diseases
Ren-Jie Zhao, Wan-Ying Zhang, Xing-Xing Fan
Heliyon.2024; 10(1): e23694. CrossRef - Research progress of circular RNA molecules in aging and age-related diseases
Zhidan Zhang, Yuling Huang, AYao Guo, Lina Yang
Ageing Research Reviews.2023; 87: 101913. CrossRef - CircRNAs and RNA-Binding Proteins Involved in the Pathogenesis of Cancers or Central Nervous System Disorders
Yuka Ikeda, Sae Morikawa, Moeka Nakashima, Sayuri Yoshikawa, Kurumi Taniguchi, Haruka Sawamura, Naoko Suga, Ai Tsuji, Satoru Matsuda
Non-Coding RNA.2023; 9(2): 23. CrossRef - Decrypting the circular RNAs does a favor for us: Understanding, diagnosing and treating diabetes mellitus and its complications
Zi Li, Yuanyuan Ren, Ziwei Lv, Man Li, Yujia Li, Xiaobin Fan, Yuyan Xiong, Lu Qian
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115744. CrossRef - Circular RNA PIP5K1A Promotes Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorders and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ge Song, YiQian Zhang, YiHua Jiang, Huan Zhang, Wen Gu, Xiu Xu, Jing Yao, ZhengFang Chen
Molecular Biotechnology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hsa_circRNA_405498 and hsa_circRNA_100033 Serve as Potential Biomarkers for Differential Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes
Ziwei Zhang, Shuoming Luo, Zilin Xiao, Wenfeng Yin, Xiajie Shi, Hongzhi Chen, Zhiguo Xie, Zhenqi Liu, Xia Li, Zhiguang Zhou
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Circular RNA PIP5K1A act as microRNA-552-3p sponge to regulates inflammation, oxidative damage in glucolipotoxicity-induced pancreatic INS-1 β-cells via Janus kinase 1
Lei Ren
Bioengineered.2022; 13(3): 5724. CrossRef - Circular RNAs in diabetes mellitus and its complications
Wenqi Fan, Haipeng Pang, Zhiguo Xie, Gan Huang, Zhiguang Zhou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus-Related circRNAs Regulate CD4+ T Cell Functions
Jianni Chen, Guanfei Jia, Xue Lv, Shufa Li, Christos K. Kontos
BioMed Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - An intriguing role of circular RNA in insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: the future perspectives
Monisha Prasad, Selvaraj Jayaraman, Vishnu Priya Veeraraghavan
Hypertension Research.2022; 45(11): 1843. CrossRef - Circular RNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy: Updates and Perspectives
Miao Liu, Junli Zhao
Aging and disease.2022; 13(5): 1365. CrossRef - CircRNAs: Key molecules in the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke
Zeyu Liu, Yanhong Zhou, Jian Xia
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 156: 113845. CrossRef - Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Promote the Transcription of Circular RNAs in Human Pancreatic β Cells
Simranjeet Kaur, Caroline Frørup, Aashiq H. Mirza, Tina Fløyel, Reza Yarani, Maikel L. Colli, Jesper Johannesen, Joachim Størling, Decio L. Eizirik, Flemming Pociot
Non-Coding RNA.2022; 8(5): 69. CrossRef - Differential Expression and Bioinformatics Analysis of Plasma-Derived Exosomal circRNA in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Haipeng Pang, Wenqi Fan, Xiajie Shi, Shuoming Luo, Yimeng Wang, Jian Lin, Yang Xiao, Xia Li, Gan Huang, Zhiguo Xie, Zhiguang Zhou, Jinhui Liu
Journal of Immunology Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Circular RNAs in diabetes and its complications: Current knowledge and future prospects
Wenfeng Yin, Ziwei Zhang, Zilin Xiao, Xia Li, Shuoming Luo, Zhiguang Zhou
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Circular RNA in autoimmune diseases: special emphasis on regulation mechanism in RA and SLE
Yurong Huang, Qiuyun Xue, Chenglong Cheng, Yuting Wang, Xiao Wang, Jun Chang, Chenggui Miao
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging roles of circular RNAs in systemic lupus erythematosus
Xin Wang, Rui Ma, Weimin Shi, Zhouwei Wu, Yuling Shi
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids.2021; 24: 212. CrossRef - Understanding Competitive Endogenous RNA Network Mechanism in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Using Computational and Bioinformatics Approaches
Xuanzi Yi, Xu Cheng
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 3865. CrossRef
- Non-coding RNAs and exosomal non-coding RNAs in diabetic retinopathy: A narrative review
- Complications
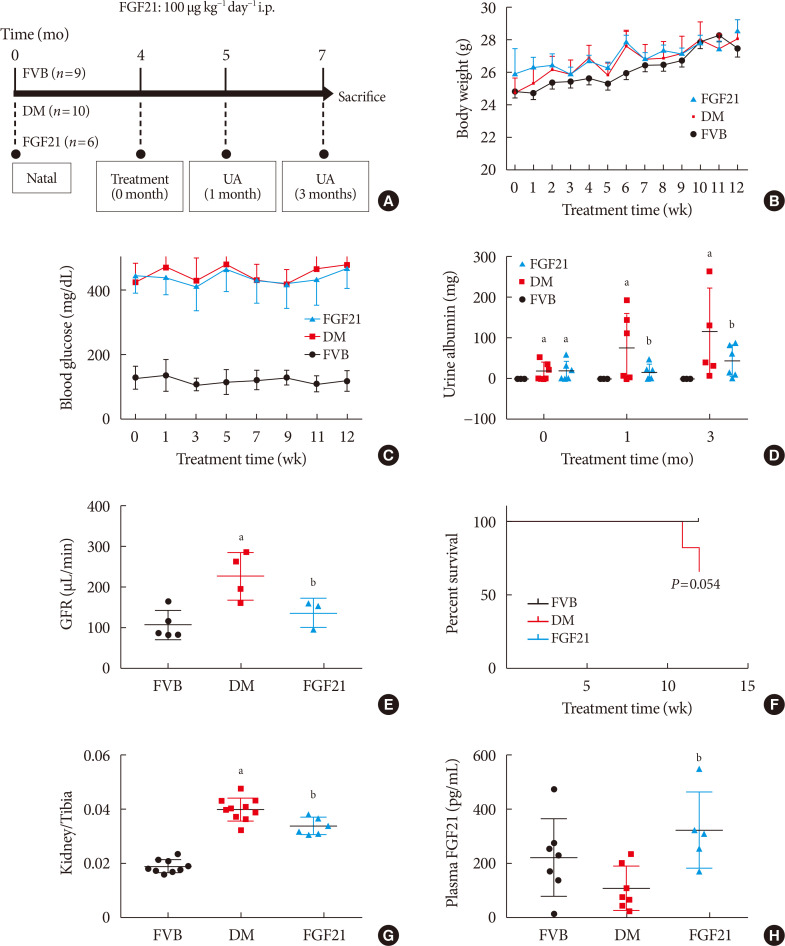
- Therapeutic Effects of Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 on Diabetic Nephropathy and the Possible Mechanism in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Mice
- Wenya Weng, Tingwen Ge, Yi Wang, Lulu He, Tinghao Liu, Wanning Wang, Zongyu Zheng, Lechu Yu, Chi Zhang, Xuemian Lu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):566-580. Published online May 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0089
- 5,910 View
- 102 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has been only reported to prevent type 1 diabetic nephropathy (DN) in the streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) mouse model. However, the FVB (Cg)-Tg (Cryaa-Tag, Ins2-CALM1) 26OVE/PneJ (OVE26) transgenic mouse is a widely recommended mouse model to recapture the most important features of T1DM nephropathy that often occurs in diabetic patients. In addition, most previous studies focused on exploring the preventive effect of FGF21 on the development of DN. However, in clinic, development of therapeutic strategy has much more realistic value compared with preventive strategy since the onset time of DN is difficult to be accurately predicted. Therefore, in the present study OVE26 mice were used to investigate the potential therapeutic effects of FGF21 on DN.
Methods Four-month-old female OVE26 mice were intraperitoneally treated with recombinant FGF21 at a dose of 100 µg/kg/day for 3 months. The diabetic and non-diabetic control mice were treated with phosphate-buffered saline at the same volume. Renal functions, pathological changes, inflammation, apoptosis, oxidative stress and fibrosis were examined in mice of all groups.
Results The results showed that severe renal dysfunction, morphological changes, inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis were observed in OVE26 mice. However, all the renal abnormalities above in OVE26 mice were significantly attenuated by 3-month FGF21 treatment associated with improvement of renal adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) expression.
Conclusion Therefore, this study demonstrated that FGF21 might exert therapeutic effects on DN through AMPK-SIRT1 pathway.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Wenhui Zhong, Yuheng Jiang, Huizhen Wang, Xiang Luo, Tao Zeng, Huimi Huang, Ling Xiao, Nan Jia, Aiqing Li
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119620. CrossRef - Urinary Excretion of Biomolecules Related to Cell Cycle, Proliferation, and Autophagy in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Anton I. Korbut, Vyacheslav V. Romanov, Vadim V. Klimontov
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 487. CrossRef - New developments in the biology of fibroblast growth factors
David M. Ornitz, Nobuyuki Itoh
WIREs Mechanisms of Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SIRT1–SIRT7 in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
Wenxiu Qi, Cheng Hu, Daqing Zhao, Xiangyan Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Fibrotic Diseases
Min-Qi Jia, Cha-Xiang Guan, Jia-Hao Tao, Yong Zhou, Liang-Jun Yan
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease increases the risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with biopsy-confirmed diabetic nephropathy: a propensity-matched cohort study
Yutong Zou, Lijun Zhao, Junlin Zhang, Yiting Wang, Yucheng Wu, Honghong Ren, Tingli Wang, Yuancheng Zhao, Huan Xu, Lin Li, Nanwei Tong, Fang Liu
Acta Diabetologica.2022; 60(2): 225. CrossRef - FGF21 and Chronic Kidney Disease
João Victor Salgado, Miguel Angelo Goes, Natalino Salgado Filho
Metabolism.2021; 118: 154738. CrossRef - The Multiple Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factor in Diabetic Nephropathy
Junyu Deng, Ye Liu, Yiqiu Liu, Wei Li, Xuqiang Nie
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 5273. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect and mechanism of combined use of FGF21 and insulin on diabetic nephropathy
Fanrui Meng, Yukai Cao, Mir Hassan Khoso, Kai Kang, Guiping Ren, Wei Xiao, Deshan Li
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2021; 713: 109063. CrossRef - FGF19 and FGF21 for the Treatment of NASH—Two Sides of the Same Coin? Differential and Overlapping Effects of FGF19 and FGF21 From Mice to Human
Emma Henriksson, Birgitte Andersen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - FGF21: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Related Metabolic Diseases
Erik J. Tillman, Tim Rolph
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Basic Research
- The Role of CD36 in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: β-Cell Dysfunction and Beyond
- Jun Sung Moon, Udayakumar Karunakaran, Elumalai Suma, Seung Min Chung, Kyu Chang Won
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):222-233. Published online April 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0053
- 7,509 View
- 168 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Impaired β-cell function is the key pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus, and chronic exposure of nutrient excess could lead to this tragedy. For preserving β-cell function, it is essential to understand the cause and mechanisms about the progression of β-cells failure. Glucotoxicity, lipotoxicity, and glucolipotoxicity have been suggested to be a major cause of β-cell dysfunction for decades, but not yet fully understood. Fatty acid translocase cluster determinant 36 (CD36), which is part of the free fatty acid (FFA) transporter system, has been identified in several tissues such as muscle, liver, and insulin-producing cells. Several studies have reported that induction of CD36 increases uptake of FFA in several cells, suggesting the functional interplay between glucose and FFA in terms of insulin secretion and oxidative metabolism. However, we do not currently know the regulating mechanism and physiological role of CD36 on glucolipotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells. Also, the downstream and upstream targets of CD36 related signaling have not been defined. In the present review, we will focus on the expression and function of CD36 related signaling in the pancreatic β-cells in response to hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia (ceramide) along with the clinical studies on the association between CD36 and metabolic disorders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nrf2 inhibition regulates intracellular lipid accumulation in mouse insulinoma cells and improves insulin secretory function
Alpana Mukhuty, Samanwita Mandal, Chandrani Fouzder, Snehasis Das, Dipanjan Chattopadhyay, Tanmay Majumdar, Rakesh Kundu
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2024; 581: 112112. CrossRef - CD36 gene variant rs1761667(G/A) as a biomarker in obese type 2 diabetes mellitus cases
Ashwin Kumar Shukla, Amreen Shamsad, Atar Singh Kushwah, Shalini Singh, Kauser Usman, Monisha Banerjee
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - CD36 regulates macrophage and endothelial cell activation and multinucleate giant cell formation in anti neutrophil cytoplasm antibody vasculitis
Xiang Zhang, Catherine King, Alexander Dowell, Paul Moss, Lorraine Harper, Dimitrios Chanouzas, Xiong-zhong Ruan, Alan David Salama
Clinical Immunology.2024; 260: 109914. CrossRef - The association of soluble cluster of differentiation 36 with metabolic diseases: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target
Yun Li, Yaxi Chen, Xiong Z. Ruan
Pediatric Discovery.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of candidate transport proteins in β‐cell long‐chain fatty acid uptake: Where are we now?
Christina Clavelo‐Farrow, Patricia Thomas
Diabetic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 in the pancreas and the impaired islet function in COVID-19 patients
Ningfei Ji, Mingshun Zhang, Liang Ren, Yunyun Wang, Bicheng Hu, Jie Xiang, Yingyun Gong, Chaojie Wu, Guoqiang Qu, Wenqiu Ding, Zhiqiang Yin, Shan Li, Zhengxia Wang, Lianzheng Zhou, Xueqin Chen, Yuan Ma, Jinhai Tang, Yun Liu, Liang Liu, Mao Huang
Emerging Microbes & Infections.2022; 11(1): 1115. CrossRef - Is imaging-based muscle quantity associated with risk of diabetes? A meta-analysis of cohort studies
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109939. CrossRef - Lipotoxicity in a Vicious Cycle of Pancreatic Beta Cell Exhaustion
Vladimir Grubelnik, Jan Zmazek, Matej Završnik, Marko Marhl
Biomedicines.2022; 10(7): 1627. CrossRef - Association of cluster determinant 36, scavenger receptor class B type 1, and major facilitator superfamily domain containing the 2a genetic polymorphism with serum lipid profile in aging population with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xixiang Wang, Xiaojun Ma, Jingjing Xu, Yujie Guo, Shaobo Zhou, Huiyan Yu, Linhong Yuan
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - CD36-Fatty Acid-Mediated Metastasis via the Bidirectional Interactions of Cancer Cells and Macrophages
Noorzaileen Eileena Zaidi, Nur Aima Hafiza Shazali, Thean-Chor Leow, Mohd Azuraidi Osman, Kamariah Ibrahim, Wan-Hee Cheng, Kok-Song Lai, Nik Mohd Afizan Nik Abd Rahman
Cells.2022; 11(22): 3556. CrossRef - The Past and Present Lives of the Intraocular Transmembrane Protein CD36
Rucui Yang, Qingping Liu, Mingzhi Zhang
Cells.2022; 12(1): 171. CrossRef - Implicating the effect of ketogenic diet as a preventive measure to obesity and diabetes mellitus
Sachin Kumar, Tapan Behl, Monika Sachdeva, Aayush Sehgal, Shilpa Kumari, Arun Kumar, Gagandeep Kaur, Harlokesh Narayan Yadav, Simona Bungau
Life Sciences.2021; 264: 118661. CrossRef - Contribution of rs3211938 polymorphism at CD36 to glucose levels, oxidized low-density lipoproteins, insulin resistance, and body mass index in Mexican mestizos with type-2 diabetes from western Mexico
Beatriz Teresita Martín-Márquez, Flavio Sandoval-Garcia, Mónica Vazquez-Del Mercado, Erika-Aurora Martínez-García, Fernanda-Isadora Corona-Meraz, Ana-Lilia Fletes-Rayas, Soraya-Amalí Zavaleta-Muñiz
Nutrición Hospitalaria.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigating the association of CD36 gene polymorphisms (rs1761667 and rs1527483) with T2DM and dyslipidemia: Statistical analysis, machine learning based prediction, and meta-analysis
Ma’mon M. Hatmal, Walhan Alshaer, Ismail S. Mahmoud, Mohammad A. I. Al-Hatamleh, Hamzeh J. Al-Ameer, Omar Abuyaman, Malek Zihlif, Rohimah Mohamud, Mais Darras, Mohammad Al Shhab, Rand Abu-Raideh, Hilweh Ismail, Ali Al-Hamadi, Ali Abdelhay, Kanhaiya Singh
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0257857. CrossRef - Misregulation of Wnt Signaling Pathways at the Plasma Membrane in Brain and Metabolic Diseases
Mustafa Karabicici, Yagmur Azbazdar, Evin Iscan, Gunes Ozhan
Membranes.2021; 11(11): 844. CrossRef
- Nrf2 inhibition regulates intracellular lipid accumulation in mouse insulinoma cells and improves insulin secretory function
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
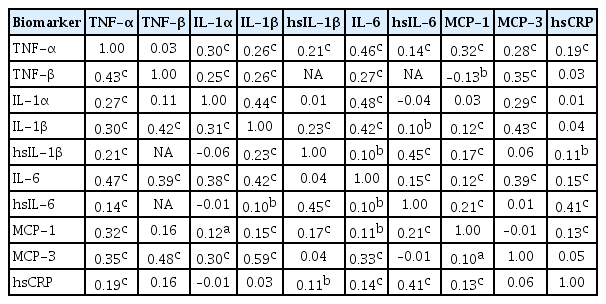
- Sex-, Age-, and Metabolic Disorder-Dependent Distributions of Selected Inflammatory Biomarkers among Community-Dwelling Adults
- So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):711-725. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0119
- 5,922 View
- 83 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Inflammatory cytokines are increasingly utilized to detect high-risk individuals for cardiometabolic diseases. However, with large population and assay methodological heterogeneity, no clear reference currently exists.
Methods Among participants of the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center cohort, of community-dwelling adults aged 30 to 64 without overt cardiovascular diseases, we presented distributions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and -β, interleukin (IL)-1α, -1β, and 6, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 and -3 and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) with and without non-detectable (ND) measurements using multiplex enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Then, we compared each markers by sex, age, and prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, using the Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test.
Results In general, there were inconsistencies in direction and magnitude of differences in distributions by sex, age, and prevalence of cardiometabolic disorders. Overall, the median and the 99th percentiles were higher in men than in women. Older participants had higher TNF-α, high sensitivity IL-6 (hsIL-6), MCP-1, hsCRP, TNF-β, and MCP-3 median, after excluding the NDs. Participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus had higher median for all assayed biomarkers, except for TNF-β, IL-1α, and MCP-3, in which the medians for both groups were 0.00 due to predominant NDs. Compared to normotensive group, participants with hypertension had higher TNF-α, hsIL-6, MCP-1, and hsCRP median. When stratifying by dyslipidemia prevalence, the comparison varied significantly depending on the treatment of NDs.
Conclusion Our findings provide sex-, age-, and disease-specific reference values to improve risk prediction and diagnostic performance for inflammatory diseases in both population- and clinic-based settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterizing CD8+ TEMRA Cells in CP/CPPS Patients: Insights from Targeted Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Functional Investigations
Fei Zhang, Qintao Ge, Jialin Meng, Jia Chen, Chaozhao Liang, Meng Zhang
ImmunoTargets and Therapy.2024; Volume 13: 111. CrossRef - Association between physical activity and inflammatory markers in community-dwelling, middle-aged adults
So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Justin Y. Jeon, Hyeon Chang Kim
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2021; 46(7): 828. CrossRef - The monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio: Sex-specific differences in the tuberculosis disease spectrum, diagnostic indices and defining normal ranges
Thomas S. Buttle, Claire Y. Hummerstone, Thippeswamy Billahalli, Richard J. B. Ward, Korina E. Barnes, Natalie J. Marshall, Viktoria C. Spong, Graham H. Bothamley, Selvakumar Subbian
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0247745. CrossRef
- Characterizing CD8+ TEMRA Cells in CP/CPPS Patients: Insights from Targeted Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Functional Investigations

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





