
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Differential Impact of Obesity on the Risk of Diabetes Development in Two Age Groups: Analysis from the National Health Screening Program
- Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Yang-Hyun Kim, Ga Eun Nam, Sang Hyun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):846-858. Published online August 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0242

- 1,232 View
- 143 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The effect of obesity on the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) in different age groups remains unclear. We assessed the impact of obesity on the development of DM for two age groups (40-year-old, middle age; 66-year-old, older adults) in the Korean population.
Methods
We analyzed Korean National Health Insurance Service data of 4,145,321 Korean adults with 40- and 66-year-old age without DM, between 2009 and 2014. Participants were followed up until 2017 or until the diagnosis of DM. We assessed the risk of DM based on the body mass index and waist circumference of the participants. Multiple confounding factors were adjusted.
Results
The median follow-up duration was 5.6 years. The association of general and abdominal obesity with the risk of DM development was stronger in the 40-year-old group (general obesity: hazard ratio [HR], 3.566, 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.512 to 3.622; abdominal obesity: HR, 3.231; 95% CI, 3.184 to 3.278) than in the 66-year-old group (general obesity: HR, 1.739; 95% CI, 1.719 to 1.759; abdominal obesity: HR, 1.799; 95% CI, 1.778 to 1.820). In the 66-year-old group, abdominal obesity had a stronger association with the development of DM as compared to general obesity. In the 40-year-old group, general obesity had a stronger association with the risk of DM development than abdominal obesity.
Conclusion
The influence of general and abdominal obesity on the development of DM differed according to age. In older adults, abdominal obesity had a stronger association with DM development than general obesity.
- Lifestyle
- Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Obesity in Korean Adults
- Jee-Seon Shim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):547-558. Published online April 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0026
- 2,917 View
- 140 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
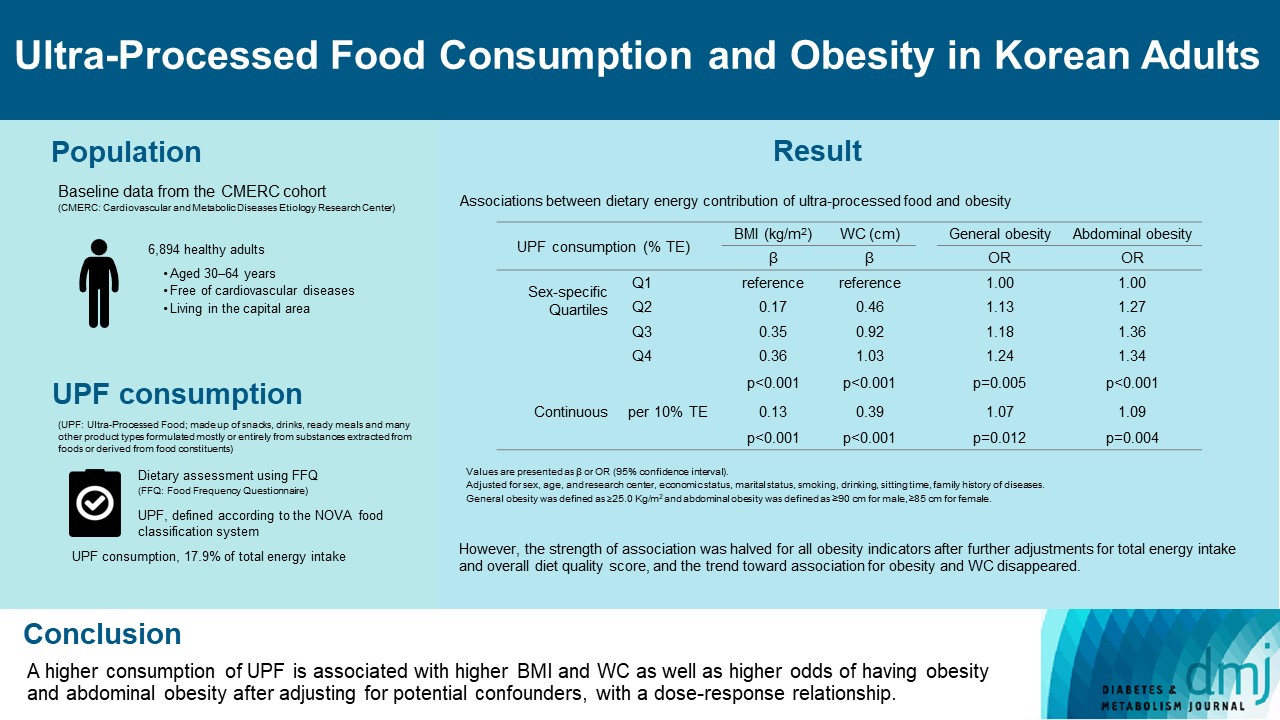
This study aimed to investigate the association between consumption of ultra-processed foods (UPF) and obesity in Korean adults.
Methods
We included the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center cohort study baseline data of adults aged 30 to 64 years who completed a validated food frequency questionnaire. UPF was defined using the NOVA food classification. Multivariable linear and logistic regression analyses were performed to assess the association of dietary energy contribution of UPF with obesity indicators (body mass index [BMI], obesity, waist circumference [WC], and abdominal obesity).
Results
Consumption of UPF accounted for 17.9% of total energy intake and obesity and abdominal obesity prevalence was 35.4% and 30.2%, respectively. Compared with those in the lowest quartile of UPF consumption, adults in the highest quartile had greater BMI (β=0.36; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.15 to 0.56), WC (β=1.03; 95% CI, 0.46 to 1.60), higher odds of having obesity (odds ratio [OR], 1.24; 95% CI, 1.07 to 1.45), and abdominal obesity (OR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.14 to 1.57), after adjusting for sociodemographic characteristics, health-related behaviors, and family history of diseases. Dose-response associations between UPF consumption and obesity indicators were consistently found (all P trend <0.01). However, the strength of association was halved for all obesity indicators after further adjustments for total energy intake and overall diet quality score, and the trend toward association for obesity and WC disappeared.
Conclusion
Our finding supports the evidence that consumption of UPF is positively associated with obesity among Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultra-processed food consumption and increased risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: A cross-sectional analysis of the KNHANES 2016–2020
Hansol Park, Youngmi Lee, Jinah Hwang, Yujin Lee
Nutrition.2024; 122: 112374. CrossRef - Diet quality partially mediates the association between ultraprocessed food consumption and adiposity indicators
Jee‐Seon Shim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim
Obesity.2023; 31(9): 2430. CrossRef - Development of a Semi-Quantitative Food-Frequency Questionnaire for Korean Adults with Obesity
Jina Chung, Seoeun Ahn, Hyojee Joung, Sangah Shin
Nutrients.2023; 15(22): 4848. CrossRef
- Ultra-processed food consumption and increased risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: A cross-sectional analysis of the KNHANES 2016–2020
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Novel Asian-Specific Visceral Adiposity Indices Are Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Korean Adults
- Jonghwa Jin, Hyein Woo, Youngeun Jang, Won-Ki Lee, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):426-436. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0099
- 2,547 View
- 128 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
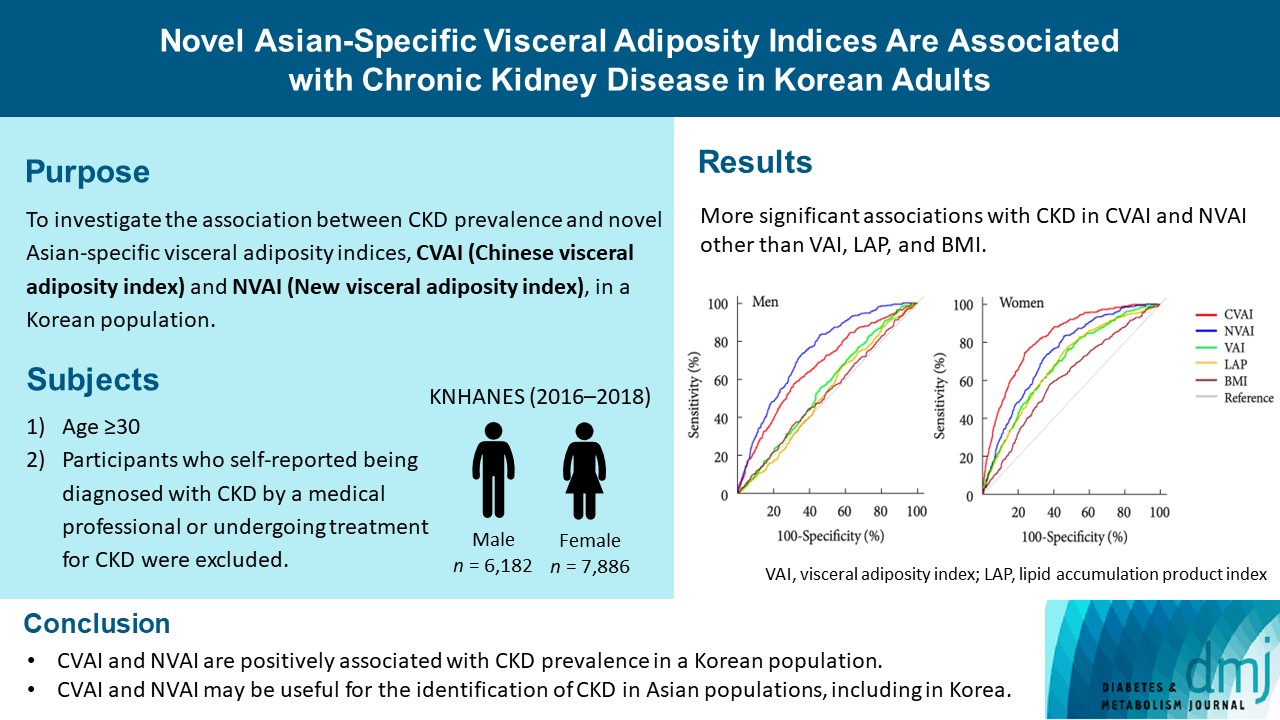
The Chinese visceral adiposity index (CVAI) and new visceral adiposity index (NVAI) are novel indices of visceral adiposity used to predict metabolic and cardiovascular diseases in Asian populations. However, the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have not been investigated. We aimed to characterize the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with the prevalence of CKD in Korean adults.
Methods
A total of 14,068 participants in the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (6,182 men and 7,886 women) were included. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were employed to compare the associations between indices of adiposity and CKD, and a logistic regression model was used to characterize the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with CKD prevalence.
Results
The areas under the ROC curves for CVAI and NVAI were significantly larger than for the other indices, including the visceral adiposity index and lipid accumulation product, in both men and women (all P<0.001). In addition, high CVAI or NVAI was significantly associated with a high CKD prevalence in both men (odds ratio [OR], 2.14; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.31 to 3.48 in CVAI and OR, 6.47; 95% CI, 2.91 to 14.38 in NVAI, P<0.05) and women (OR, 4.87; 95% CI, 1.85 to 12.79 in CVAI and OR, 3.03; 95% CI, 1.35 to 6.82 in NVAI, P<0.05); this association remained significant after adjustment for multiple confounding factors in men and women.
Conclusion
CVAI and NVAI are positively associated with CKD prevalence in a Korean population. CVAI and NVAI may be useful for the identification of CKD in Asian populations, including in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and risk of stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: evidence from a large national cohort study
Zenglei Zhang, Lin Zhao, Yiting Lu, Xu Meng, Xianliang Zhou
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and risk of stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: evidence from a large national cohort study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Synergistic Interaction between Hyperuricemia and Abdominal Obesity as a Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome Components in Korean Population
- Min Jin Lee, Ah Reum Khang, Yang Ho Kang, Mi Sook Yun, Dongwon Yi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):756-766. Published online January 20, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0166
- 4,945 View
- 253 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The present study investigated the role of synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity as a risk factor for the components of metabolic syndrome.
Methods
We performed a cross-sectional study using the data of 16,094 individuals from the seventh Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016 to 2018). The adjusted odds ratios of metabolic syndrome and its components were analyzed by multivariate logistic regression analysis. The presence of synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity was evaluated by calculating the additive scales—the relative excess risk due to interaction, attributable proportion due to interaction, and synergy index (SI).
Results
There was a synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity in hypertriglyceridemia (men: SI, 1.39; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 1.98; women: SI, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.02 to 2.69), and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (men: SI, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.41 to 2.91; women: SI, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.05 to 2.95). There was no significant synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity for the risk of high blood pressure (men: SI, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.85 to 1.77; women: SI, 1.53; 95% CI, 0.79 to 2.97), and hyperglycemia (men: SI, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.72 to 1.47; women: SI, 1.39; 95% CI, 0.75 to 2.57).
Conclusion
Hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity synergistically increased the risk of hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL-C in both sexes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and factors associated with overweight, obesity and central obesity among adults in Shenmu City, Shaanxi Province, China
Mingxia Liu, Chunjiao Jia, Yaoda Hu, Juan Liu, Lizhen Liu, Shengli Sun, Haiying Wang, Yonglin Liu
Preventive Medicine Reports.2024; 40: 102673. CrossRef - Synergistic interaction between hyperlipidemia and obesity as a risk factor for stress urinary incontinence in Americans
Fangyi Zhu, Mao Chen, Ya Xiao, Xiaoyu Huang, Liying Chen, Li Hong
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of cognitive function in the relationship between surrogate markers of visceral fat and depressive symptoms in general middle-aged and elderly population: A nationwide population-based study
Na Zhang, Jianqian Chao, Xueyu Wu, Hongling Chen, Min Bao
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 338: 581. CrossRef - Biodegradation of Uric Acid by Bacillus paramycoides-YC02
Xiaoyu Cao, Jingyuan Cai, Yu Zhang, Chao Liu, Meijie Song, Qianqian Xu, Yang Liu, Hai Yan
Microorganisms.2023; 11(8): 1989. CrossRef - A predictive model for hyperuricemia among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Urumqi, China
Palizhati Abudureyimu, Yuesheng Pang, Lirun Huang, Qianqian Luo, Xiaozheng Zhang, Yifan Xu, Liang Jiang, Patamu Mohemaiti
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary Ferulic Acid Ameliorates Metabolism Syndrome-Associated Hyperuricemia in Rats via Regulating Uric Acid Synthesis, Glycolipid Metabolism, and Hepatic Injury
Nanhai Zhang, Jingxuan Zhou, Lei Zhao, Ou Wang, Liebing Zhang, Feng Zhou
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prevalence and factors associated with overweight, obesity and central obesity among adults in Shenmu City, Shaanxi Province, China
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Sex Differences of Visceral Fat Area and Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Fat Ratio for the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Eun Hee Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Min Jung Lee, Sung-Jin Bae, Jaewon Choe, Chang Hee Jung, Chul-Hee Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):486-498. Published online November 18, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0095
- 9,402 View
- 367 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
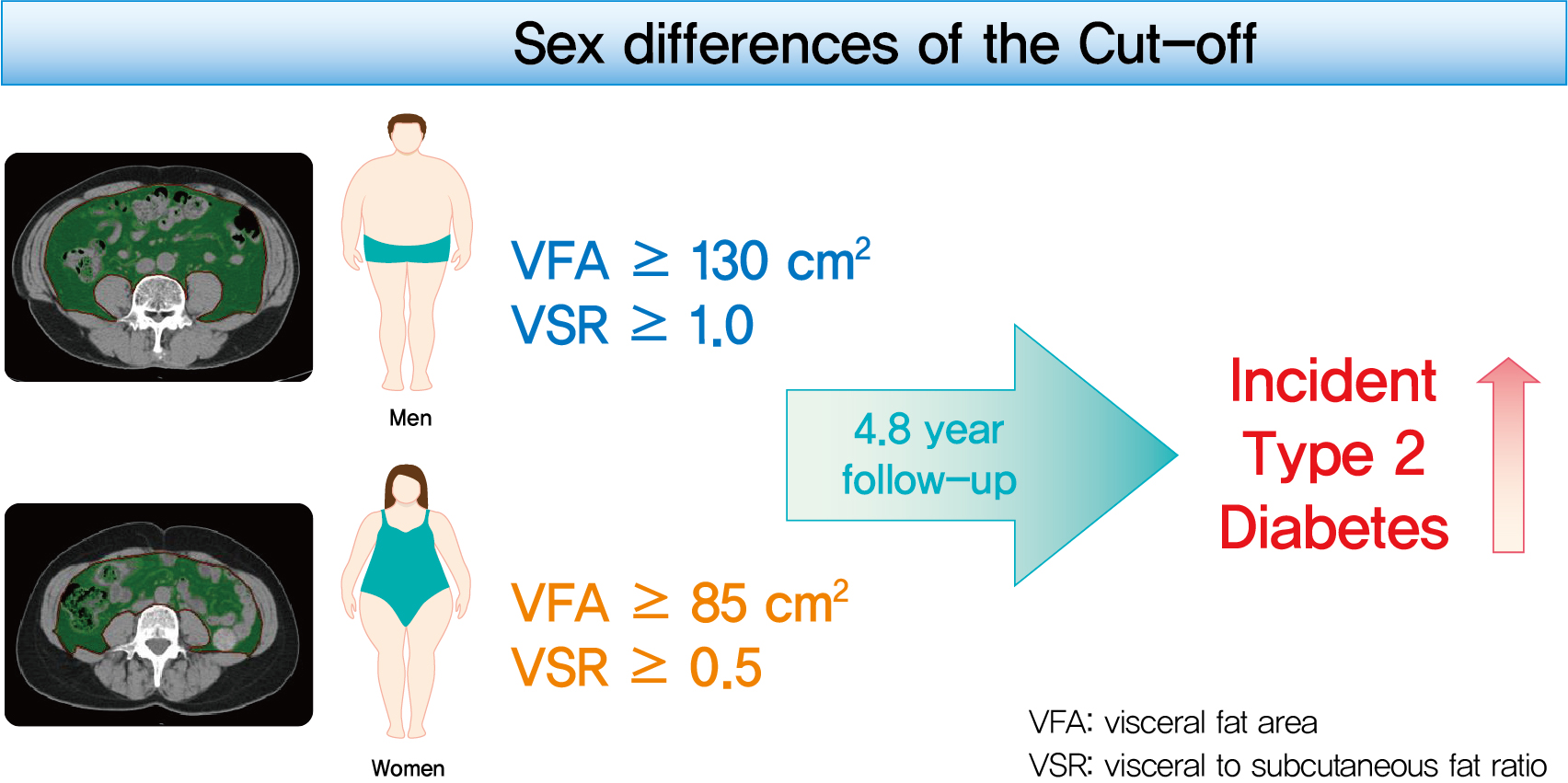
This study aimed to determine the optimal cut-off values of visceral fat area (VFA) and visceral-to-subcutaneous fat ratio (VSR) for predicting incident type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
A total of 10,882 individuals (6,835 men; 4,047 women) free of T2DM at baseline aged between 30 and 79 years who underwent abdominal computed tomography scan between 2012 and 2013 as a part of routine health check-ups were included and followed. VFA, subcutaneous fat area, and VSR on L3 vertebral level were measured at baseline.
Results
During a median follow-up of 4.8 years, 730 (8.1% for men; 4.3% for women) incident cases of T2DM were identified. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that the optimal cut-off values of VFA and VSR for predicting incident T2DM were 130.03 cm2 and 1.08 in men, respectively, and 85.7 cm2 and 0.48 in women, respectively. Regardless of sex, higher VFA and VSR were significantly associated with a higher risk of incident T2DM. Compared with the lowest quartiles of VFA and VSR, the highest quartiles had adjusted odds ratios of 2.62 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.73 to 3.97) and 1.55 (95% CI, 1.14 to 2.11) in men, respectively, and 32.49 (95% CI, 7.42 to 142.02) and 11.07 (95% CI, 3.89 to 31.50) in women, respectively.
Conclusion
Higher VFA and VSR at baseline were independent risk factors for the development of T2DM. Sex-specific reference values for visceral fat obesity (VFA ≥130 cm2 or VSR ≥1.0 in men; VFA ≥85 cm2 or VSR ≥0.5 in women) are proposed for the prediction of incident T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Severity of adipose tissue dysfunction is associated with progression of pre-diabetes to type 2 diabetes: the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
Mohammad Jalali, Zahra Bahadoran, Parvin Mirmiran, Fereidoun Azizi, Farhad Hosseinpanah
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Should insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), insulin secretion (HOMA-β), and visceral fat area be considered for improving the performance of diabetes risk prediction models
Huan Hu, Tohru Nakagawa, Toru Honda, Shuichiro Yamamoto, Tetsuya Mizoue
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2024; 12(1): e003680. CrossRef - Adipose organ dysfunction and type 2 diabetes: Role of nitric oxide
Zahra Bahadoran, Parvin Mirmiran, Asghar Ghasemi
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 221: 116043. CrossRef - Prediction of high visceral adipose tissue for sex‐specific community residents in Taiwan
Yu‐Hsuan Chang, Chin‐Sung Chang, Chieh‐Yu Liu, Yin‐Fan Chang, Shiow‐Ching Shun
Nursing & Health Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Guidelines for obesity clinic consultations in primary healthcare clinics
Jee-Hyun Kang, Kyoung-Kon Kim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2024; 67(4): 240. CrossRef - Correlation between fat-to-muscle mass ratio and cognitive impairment in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study
Fan Wu, Yanlan Liu, Chenying Lin, Nahal Haghbin, Longfei Xia, Yaoshuang Li, Tong Chen, Huina Qiu, Weiran Jiang, Jingbo Li, Jingna Lin
BMC Geriatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Body Composition and Metabolic Dysfunction Really Matter for the Achievement of Better Outcomes in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
Mauricio A. Cuello, Fernán Gómez, Ignacio Wichmann, Felipe Suárez, Sumie Kato, Elisa Orlandini, Jorge Brañes, Carolina Ibañez
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1156. CrossRef - MEDICINAL BIOMAGNETISM FOR THE TREATMENT OF OBESITY
Ana Vergínia Campagnollo Bueno, Michelli Gonçalves Seneda, Ângela Mara Rambo, Ana Clara Campagnolo Gonçalves Toledo, Caroline Cabral de Azevedo, Adriane Viapiana Bossa
Health and Society.2023; 3(01): 411. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome in a national population-based cohort of young adults and sex-specific risk for type 2 diabetes
Min-Kyung Lee, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Seo Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Oak-Kee Hong, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The correlation between visceral fat/subcutaneous fat area ratio and monocyte/high-density lipoprotein ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and albuminuria
Haiyan Lin, Jun Zhu, Chen Zheng, Xiaoming Xu, Shandong Ye
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(11): 108521. CrossRef - Effects of the abdominal fat distribution on the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and thyroid hormones among Korean adult males
Hyun-Jin Kim, Byungmi Kim, Seyoung Kim, Hyuktae Kwon, Jae Moon Yun, Belong Cho, Jin-Ho Park
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Visceral Fat Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Obesity
Hong-Kyu Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Hana Park, Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Jaewon Choe
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Visceral adipose tissue reference data computed for GE HealthCare DXA from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data set
Jonathan P. Bennett, Brandon K. Quon, Bo Fan, En Liu, Leila Kazemi, Rosa C. Villegas‐Valle, Raj Ahgun, Xian‐pin Wu, Hou‐De Zhou, Ying Lu, John A. Shepherd
Obesity.2023; 31(12): 2947. CrossRef - Comparison of bioelectrical body and visceral fat indices and anthropometric measures in relation to type 2 diabetes by sex among Chinese adults, a cross-sectional study
Jiangshan He, Binbin Zhang, Yaqi Fan, Yuxue Wang, Mianzhi Zhang, Chunjun Li, Li Zhang, Pei Guo, Minying Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The predictive significance of lipid accumulation products for future diabetes in a non-diabetic population from a gender perspective: an analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics
Jiajun Qiu, Maobin Kuang, Yang Zou, Ruijuan Yang, Qing Shangguan, Dingyang Liu, Guotai Sheng, Wei Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cellular interplay between cardiomyocytes and non-myocytes in diabetic cardiomyopathy
Ren Jie Phang, Rebecca H. Ritchie, Derek J. Hausenloy, Jarmon G. Lees, Shiang Y. Lim
Cardiovascular Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Implication of Sex Differences in Visceral Fat for the Assessment of Incidence Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sang Hyeon Ju, Hyon-Seung Yi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 414. CrossRef - Visceral fat area and body fat percentage measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis correlate with glycometabolism
Shuying Li, Shaoping Li, Jie Ding, Weihong Zhou
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Demographic Specific Abdominal Fat Composition and Distribution Trends in US Adults from 2011 to 2018
Furong Xu, Jacob E. Earp, Bryan J. Blissmer, Ingrid E. Lofgren, Matthew J. Delmonico, Geoffrey W. Greene
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(19): 12103. CrossRef - Visceral Obesity Is a More Important Factor for Colorectal Adenomas than Skeletal Muscle or Body Fat
Ji Yeon Seo, Yoo Min Han, Su Jin Chung, Seon Hee Lim, Jung Ho Bae, Goh Eun Chung
Cancers.2022; 14(21): 5256. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Visceral Obesity and Related Diseases
佳佳 魏
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(12): 11686. CrossRef - Gender differences in the ideal cutoffs of visceral fat area for predicting MAFLD in China
Pingping Yu, Huachao Yang, Xiaoya Qi, Ruixue Bai, Shouqin Zhang, Jianping Gong, Ying Mei, Peng Hu
Lipids in Health and Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Severity of adipose tissue dysfunction is associated with progression of pre-diabetes to type 2 diabetes: the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Clinical Significance of Body Fat Distribution in Coronary Artery Calcification Progression in Korean Population
- Heesun Lee, Hyo Eun Park, Ji Won Yoon, Su-Yeon Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):219-230. Published online October 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0161
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2021;45(6):974
- 6,550 View
- 257 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
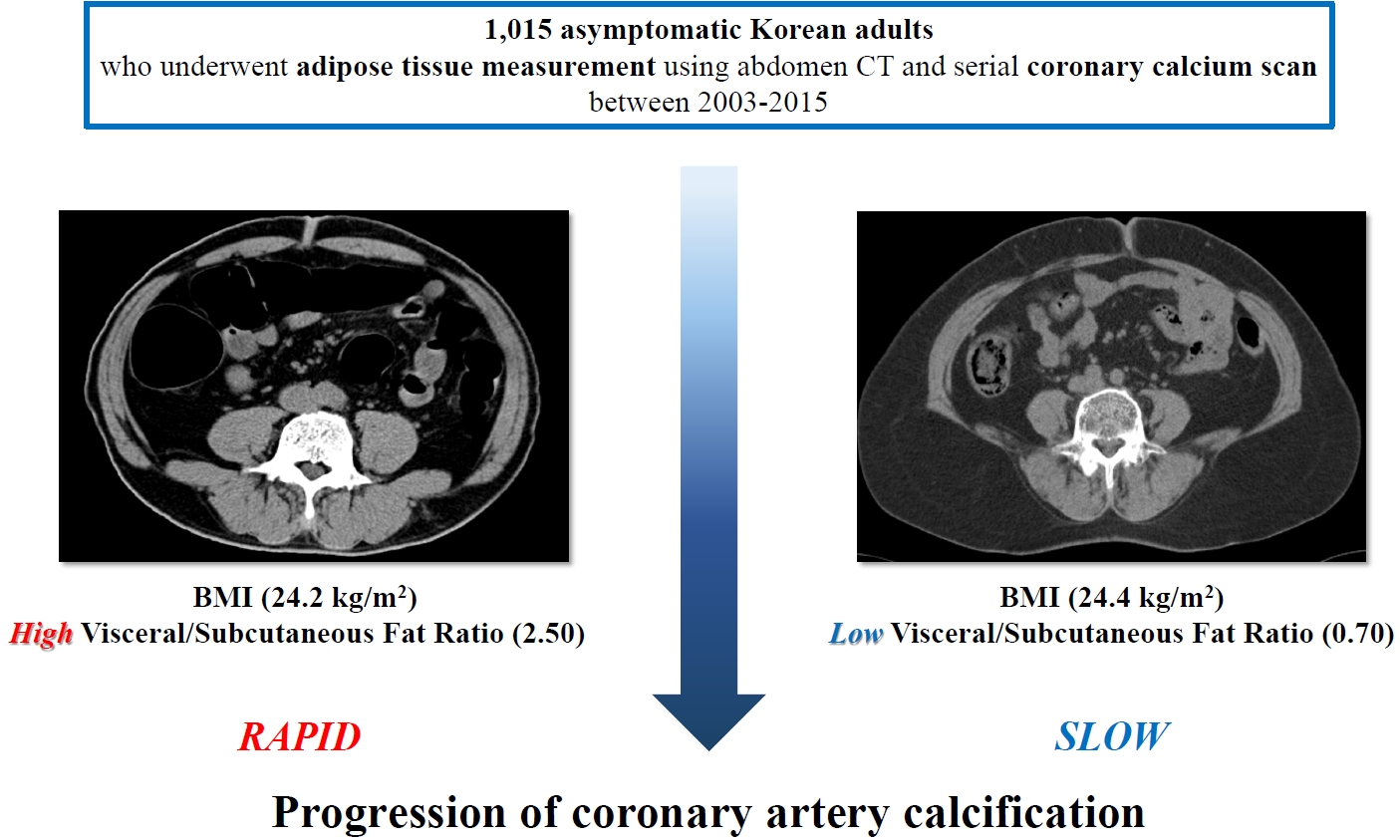
Although obesity differs according to ethnicity, it is globally established as a solid risk factor for cardiovascular disease. However, it is not fully understood how obesity parameters affect the progression of coronary artery calcification (CAC) in Korean population. We sought to evaluate the association of obesity-related parameters including visceral adipose tissue (VAT) measurement and CAC progression.
Methods
This retrospective observational cohort study investigated 1,015 asymptomatic Korean subjects who underwent serial CAC scoring by computed tomography (CT) with at least 1-year interval and adipose tissue measurement using non-contrast CT at baseline for a routine checkup between 2003 and 2015. CAC progression, the main outcome, was defined as a difference of ≥2.5 between the square roots of the baseline and follow-up CAC scores using Agatston units.
Results
During follow-up (median 39 months), 37.5% of subjects showed CAC progression of a total population (56.4 years, 80.6% male). Body mass index (BMI) ≥25 kg/m2, increasing waist circumferences (WC), and higher VAT/subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) area ratio were independently associated with CAC progression. Particularly, predominance of VAT over SAT at ≥30% showed the strongest prediction for CAC progression (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.20; P<0.001) and remained of prognostic value regardless of BMI or WC status. Further, it provided improved risk stratification of CAC progression beyond known prognosticators.
Conclusion
Predominant VAT area on CT is the strongest predictor of CAC progression regardless of BMI or WC in apparently healthy Korean population. Assessment of body fat distribution may be helpful to identify subjects at higher risk. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gender-specific abdominal fat distribution and insulin resistance associated with organophosphate esters and phthalate metabolites exposure
Xiaoliu Shi, Wanyue Wang, Jiafan Feng, Xiaochun Ma, Mengting Xu, Cui Wang
Environmental Pollution.2024; 349: 123959. CrossRef - The association between C-reactive protein and coronary artery calcification: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Amirhossein Tajani, Masoumeh Sadeghi, Navid Omidkhoda, Amir Hooshang Mohammadpour, Sara Samadi, Vahid Jomehzadeh
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Visceral adipose tissue is an independent predictor and mediator of the progression of coronary calcification: a prospective sub-analysis of the GEA study
Neftali Eduardo Antonio-Villa, Juan Gabriel Juárez-Rojas, Rosalinda Posadas-Sánchez, Juan Reyes-Barrera, Aida Medina-Urrutia
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning-based prediction for significant coronary artery stenosis on coronary computed tomography angiography in asymptomatic populations
Heesun Lee, Bong Gyun Kang, Jeonghee Jo, Hyo Eun Park, Sungroh Yoon, Su-Yeon Choi, Min Joo Kim
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between a novel non–insulin-based metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS‐IR) and coronary artery calcification
Zhenwei Wang, Xiaofang Hui, Xu Huang, Jingjie Li, Naifeng Liu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Abdominal Adipose Tissue Distribution and Risk of Endometrial Cancer: A Case-Control Study
Yuan Cheng, Zhongyu Wang, Xiaoxuan Jia, Rong Zhou, Jianliu Wang
Clinical Medicine Insights: Oncology.2022; 16: 117955492211407. CrossRef - Sex differences in cardiovascular risk may be related to sex differences in diet patterns: a narrative review
A. M. Tindall, V. A. Stallings
Annals of Human Biology.2021; 48(6): 517. CrossRef
- Gender-specific abdominal fat distribution and insulin resistance associated with organophosphate esters and phthalate metabolites exposure
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
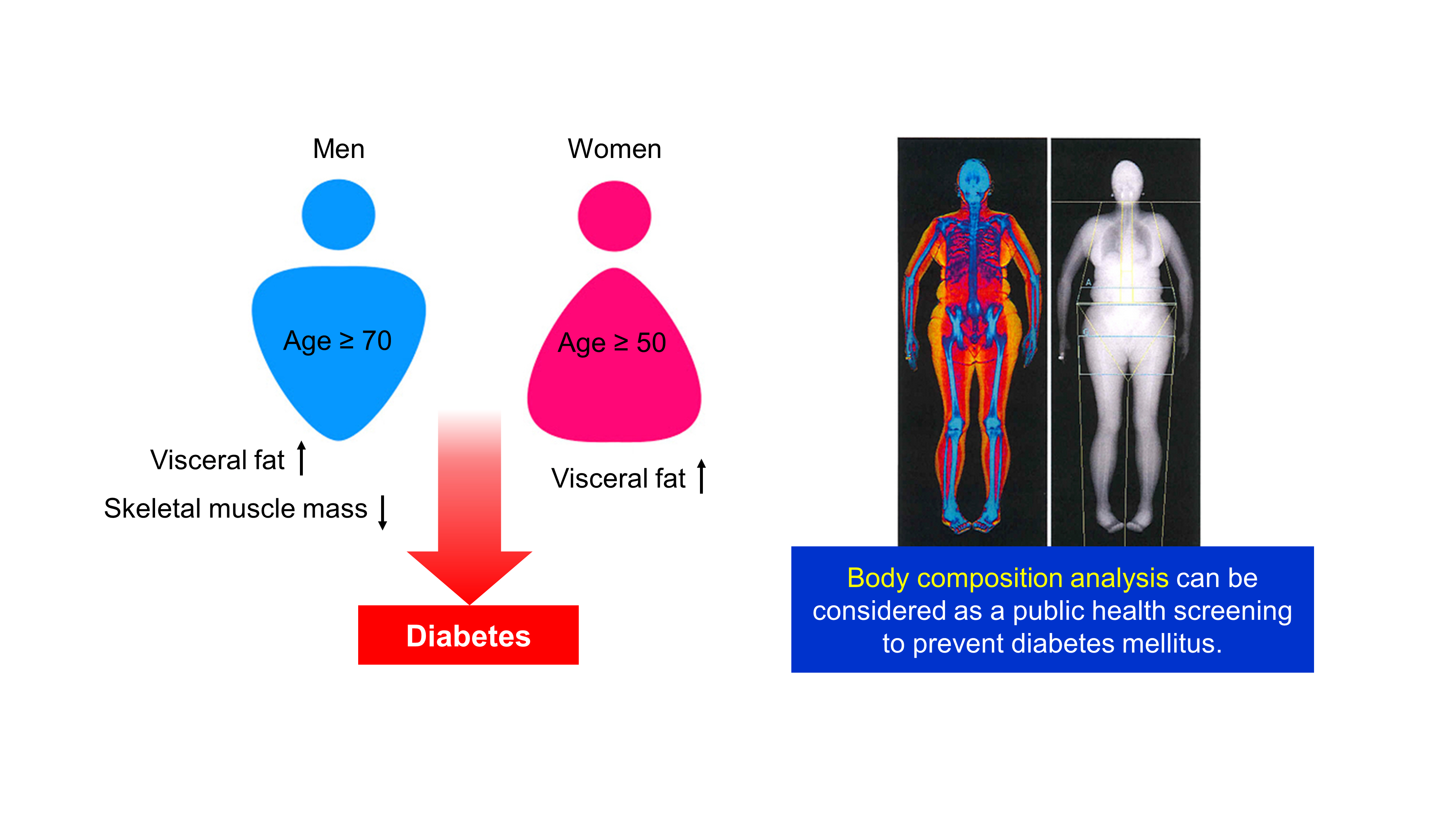
- Age- and Sex-Related Differential Associations between Body Composition and Diabetes Mellitus
- Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Jung A Kim, You-Bin Lee, So-hyeon Hong, Nam Hoon Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):183-194. Published online June 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0171
- 7,487 View
- 236 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
Background The age- and sex-related differences on the impacts of body composition on diabetes mellitus (DM) remain uncertain.
Methods The fourth and fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey included 15,586 subjects over 30 years of age who completed dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. We conducted a cross-sectional study to investigate whether muscle mass index (MMI), defined as appendicular skeletal muscle divided by body mass index (BMI), and fat mass index (FMI), defined as trunk fat mass divided by BMI, were differently associated with DM according to age and sex.
Results In multivariate logistic regression, the risk for DM significantly increased across quartiles of FMI in men aged ≥70. Meanwhile, MMI showed a protective association with DM in men of the same age. The odds ratios (ORs) for the highest quartile versus the lowest quartile of FMI and MMI were 3.116 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.405 to 6.914) and 0.295 (95% CI, 0.157 to 0.554), respectively. In women, the ORs of DM was significantly different across FMI quartiles in those over age 50. The highest quartile of FMI exhibited increased ORs of DM in subjects aged 50 to 69 (OR, 1.891; 95% CI, 1.229 to 2.908) and ≥70 (OR, 2.275; 95% CI, 1.103 to 4.69) compared to lowest quartile. However, MMI was not significantly associated with DM in women of all age groups.
Conclusion Both FMI and MMI were independent risk factors for DM in men aged 70 years or more. In women over 50 years, FMI was independently associated with DM. There was no significant association between MMI and DM in women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on Correlation between Body Composition Changes and Disease Pro-gression of Type 2 Diabetes
敏 张
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(03): 936. CrossRef - Low Skeletal Muscle Mass Accompanied by Abdominal Obesity Additively Increases the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, Seung-Eun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hwan Jee, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(5): 1173. CrossRef - Is imaging-based muscle quantity associated with risk of diabetes? A meta-analysis of cohort studies
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109939. CrossRef - Whole and segmental body composition changes during mid-follicular and mid-luteal phases of the menstrual cycle in recreationally active young women
Şükran Nazan Koşar, Yasemin Güzel, Mehmet Gören Köse, Ayşe Kin İşler, Tahir Hazır
Annals of Human Biology.2022; 49(2): 124. CrossRef - Body Composition and Diabetes
Hye Jin Yoo
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 238. CrossRef
- Research Progress on Correlation between Body Composition Changes and Disease Pro-gression of Type 2 Diabetes
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Intra-Abdominal Fat and High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Are Associated in a Non-Linear Pattern in Japanese-Americans
- Sun Ok Song, You-Cheol Hwang, Steven E. Kahn, Donna L. Leonetti, Wilfred Y. Fujimoto, Edward J. Boyko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):277-285. Published online March 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0008
- 4,697 View
- 63 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We describe the association between high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) concentration and computed tomography (CT)-measured fat depots.
Methods We examined the cross-sectional associations between HDL-C concentration and intra-abdominal (IAF), abdominal subcutaneous (SCF), and thigh fat (TF) areas in 641 Japanese-American men and women. IAF, SCF, and TF were measured by CT at the level of the umbilicus and mid-thigh. The associations between fat area measurements and HDL-C were examined using multivariate linear regression analysis adjusting for age, sex, diabetes family history, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and body mass index (BMI). Non-linearity was assessed using fractional polynomials.
Results Mean±standard deviation of HDL-C concentration and IAF in men and women were 1.30±0.34 mg/dL, 105±55.3 cm2, and 1.67±0.43 mg/dL, 74.4±46.6 cm2 and differed significantly by gender for both comparisons (
P <0.001). In univariate analysis, HDL-C concentration was significantly associated with CT-measured fat depots. In multivariate analysis, IAF was significantly and non-linearly associated with HDL-C concentration adjusted for age, sex, BMI, HOMA-IR, SCF, and TF (IAF: β=−0.1012, P<0.001; IAF2: β=0.0008,P <0.001). SCF was also negatively and linearly associated with HDL-C (β=−0.4919,P =0.001).Conclusion HDL-C does not linearly decline with increasing IAF in Japanese-Americans. A more complex pattern better fits this association.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of Serum Uric Acid to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio with Trunk Fat Mass and Visceral Fat Accumulation
Yansu Wang, Yiting Xu, Tingting Hu, Yunfeng Xiao, Yufei Wang, Xiaojing Ma, Haoyong Yu, Yuqian Bao
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 121. CrossRef - Obesity-related parameters in carriers of some BDNF genetic variants may depend on daily dietary macronutrients intake
Urszula Miksza, Edyta Adamska-Patruno, Witold Bauer, Joanna Fiedorczuk, Przemyslaw Czajkowski, Monika Moroz, Krzysztof Drygalski, Andrzej Ustymowicz, Elwira Tomkiewicz, Maria Gorska, Adam Kretowski
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Computed tomography-based investigation of the correlation of abdominal fat areas with metabolic syndrome
Kai-Yuan Cheng, Tsung-Hsien Yen, Jay Wu, Pei-Hsuan Li, Tian-Yu Shih
Journal of Radiological Science.2023; 48(1): 15. CrossRef - Lower High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Concentration Is Independently Associated with Greater Future Accumulation of Intra-Abdominal Fat
Sun Ok Song, You-Cheol Hwang, Han Uk Ryu, Steven E. Kahn, Donna L. Leonetti, Wilfred Y. Fujimoto, Edward J. Boyko
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 835. CrossRef
- Associations of Serum Uric Acid to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio with Trunk Fat Mass and Visceral Fat Accumulation
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Association of Soybean Food Intake and Cardiometabolic Syndrome in Korean Women: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007 to 2011)
- Sook-Hyun Jun, Woo-Kyoung Shin, Yookyung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):143-157. Published online December 2, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0078
- 5,769 View
- 68 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Soybean food consumption has been considered as a possible way to lower incidence of cardiometabolic syndrome (CMS) among Asians. However, results from studies investigating its efficacy on CMS in Asians have been inconsistent.
Methods We analyzed the association between soybean intake frequency and prevalence of CMS based on data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007 to 2011. Data of 9,287 women aged 20 to 64 years were analyzed. Food frequency questionnaire was used to assess soybean food consumption frequency. General linear model and multivariable logistic regression model were used to examine the association of soybean intake quintile with CMS and its risk factors. Least square means of metabolic factors mostly showed no significant relevance except liver indexes.
Results Compared to participants in the 1st quintile (<2 times/week of soybean food), odds ratios (OR) for CMS and abdominal obesity (AO) in the 4th quintile (8.5 times/week<soybean food≤17 times/week) were 0.73 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.57 to 0.95) and 0.72 (95% CI, 0.58 to 0.90), respectively. After excluding Tofu products, ORs of CMS, AO, high blood pressure, and hypertriglyceridemia were lower than those without excluding Tofu products. However, results still did not show significant inverse linear trend across frequency quintiles.
Conclusion Our findings suggest that soybean intake of 8.5 to 17 times/week was inversely associated with CMS in Korean women. The relation between soybean intake >17 times/week and CMS varied depending on soybean food items.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anti-obesogenic effects of plant natural products: A focus on Korean traditional foods
Gitishree Das, Luis Alfonso Jiménez Ortega, Sandra Gonçalves, J. Basilio Heredia, Maria de Lourdes Gomes Pereira, Anabela Romano, Han-Seung Shin, Jayanta Kumar Patra
Trends in Food Science & Technology.2024; : 104470. CrossRef - Sex differences in waist circumference obesity and eating speed: a cross-sectional study of Japanese people with normal body mass index
Yuri Yaguchi, Tsuneo Konta, Nahomi Imaeda, Chiho Goto, Yoshiyuki Ueno, Takamasa Kayama
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Dietary Patterns with Metabolic Syndrome in Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 7–17: The China National Nutrition and Health Surveillance of Children and Lactating Mothers in 2016–2017
Jia Shi, Hongyun Fang, Qiya Guo, Dongmei Yu, Lahong Ju, Xue Cheng, Wei Piao, Xiaoli Xu, Zizi Li, Di Mu, Liyun Zhao, Li He
Nutrients.2022; 14(17): 3524. CrossRef - What Is the Relationship between Antioxidant Efficacy, Functional Composition, and Genetic Characteristics in Comparing Soybean Resources by Year?
Han-Na Chu, Suji Lee, Xiaohan Wang, Chi-Do Wee, Hye-Myeong Yoon, Eun-Suk Jung, Mi-Kyung Seo, Yongseok Kwon, Kyeong-A Jang, Haeng-Ran Kim
Antioxidants.2022; 11(11): 2249. CrossRef - Longitudinal changes in adherence to the portfolio and DASH dietary patterns and cardiometabolic risk factors in the PREDIMED-Plus study
Andrea J. Glenn, Pablo Hernández-Alonso, Cyril W.C. Kendall, Miguel Ángel Martínez-González, Dolores Corella, Montserrat Fitó, J.Alfredo Martínez, Ángel M. Alonso-Gómez, Julia Wärnberg, Jesús Vioque, Dora Romaguera, José López-Miranda, Ramon Estruch, Fran
Clinical Nutrition.2021; 40(5): 2825. CrossRef - The Effects of Dietary Pattern on Metabolic Syndrome in Jiangsu Province of China: Based on a Nutrition and Diet Investigation Project in Jiangsu Province
Yuanyuan Wang, Yue Dai, Ting Tian, Jingxian Zhang, Wei Xie, Da Pan, Dengfeng Xu, Yifei Lu, Shaokang Wang, Hui Xia, Guiju Sun
Nutrients.2021; 13(12): 4451. CrossRef - Sex-Specific Energy Intakes and Physical Activity Levels According to the Presence of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Elderly People: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2018
Won-Sang Jung, Hun-Young Park, Sung-Woo Kim, Kiwon Lim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(15): 5416. CrossRef
- Anti-obesogenic effects of plant natural products: A focus on Korean traditional foods
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Comparison of Competitive Models of Metabolic Syndrome Using Structural Equation Modeling: A Confirmatory Factor Analysis
- Karimollah Hajian-Tilaki
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):433-441. Published online October 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0010
- 3,244 View
- 41 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The purpose of this study was to apply the structural equation modeling (SEM) to compare the fitness of different competing models (one, two, and three factors) of the metabolic syndrome (MetS) in Iranian adult population.
Methods Data are given on the cardiometabolic risk factors of 841 individuals with nondiabetic adults from a cross-sectional population-based study of glucose, lipids, and MetS in the north of Iran. The three conceptual hypothesized models (single factor, two correlated factors, and three correlated latent factors) were evaluated by using confirmatory factor analysis with the SEM approach. The summary statistics of correlation coefficients and the model summary fitting indexes were calculated.
Results The findings show that a single-factor model and a two-correlated factor model had a poorer summary fitting index compared with a three-correlated factor model. All fitting criteria met the conceptual hypothesized three-correlated factor model for both sexes. However, the correlation structure between the three underlying constructs designating the MetS was higher in women than in men.
Conclusion These results indicate the plausibility of the pathophysiology and etiology of MetS being multifactorial, rather than a single factor, in a nondiabetic Iranian adult population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Structural Equation Modelling for Predicting the Relative Contribution of Each Component in the Metabolic Syndrome Status Change
José E. Teixeira, José A. Bragada, João P. Bragada, Joana P. Coelho, Isabel G. Pinto, Luís P. Reis, Paula O. Fernandes, Jorge E. Morais, Pedro M. Magalhães
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3384. CrossRef - New risk score model for identifying individuals at risk for diabetes in southwest China
Liying Li, Ziqiong Wang, Muxin Zhang, Haiyan Ruan, Linxia Zhou, Xin Wei, Ye Zhu, Jiafu Wei, Sen He
Preventive Medicine Reports.2021; 24: 101618. CrossRef - Definition and early diagnosis of metabolic syndrome in children
Gunter Matthias Christian Flemming, Sarah Bussler, Antje Körner, Wieland Kiess
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 33(7): 821. CrossRef - Calcium-Sensing Receptor in Adipose Tissue: Possible Association with Obesity-Related Elevated Autophagy
Pamela Mattar, Sofía Sanhueza, Gabriela Yuri, Lautaro Briones, Claudio Perez-Leighton, Assaf Rudich, Sergio Lavandero, Mariana Cifuentes
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(20): 7617. CrossRef
- Structural Equation Modelling for Predicting the Relative Contribution of Each Component in the Metabolic Syndrome Status Change
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Proportion and Characteristics of the Subjects with Low Muscle Mass and Abdominal Obesity among the Newly Diagnosed and Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Jung A Kim, Soon Young Hwang, Hye Soo Chung, Nam Hoon Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):105-113. Published online September 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0036
- 4,938 View
- 70 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Sarcopenic obesity (SO) is a serious public health concern, few studies have examined the clinical implications of SO in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients. We evaluated the prevalence of the newly diagnosed, drug-naïve T2DM patients with low muscle mass with abdominal obesity and its association with insulin resistance and other diabetic complications.
Methods We classified 233 drug-naïve T2DM subjects into four groups according to abdominal obesity (waist circumference ≥90 cm in men and ≥85 cm in women) and low muscle mass status (appendicular skeletal muscle <7.0 kg/m2 for men and <5.4 kg/m2 for women).
Results The proportion of the subjects with low muscle mass and abdominal obesity among the newly diagnosed, drug-naïve T2DM patients was 8.2%. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) increased linearly according to body composition group from normal to abdominal obesity to both low muscle mass and abdominal obesity. The multiple logistic regression analysis indicated that subjects with low muscle mass and abdominal obesity (odds ratio [OR], 9.39; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.41 to 36.56) showed a higher risk for insulin resistance, defined as HOMA-IR ≥3, than those with abdominal obesity (OR, 5.36; 95% CI, 2.46 to 11.69), even after adjusting for other covariates. However, there were no differences in lipid profiles, microalbuminuria, or various surrogate markers for atherosclerosis among the four groups.
Conclusion Subjects with both low muscle mass and abdominal obesity had a higher risk of insulin resistance than those with low muscle mass or abdominal obesity only.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical observation on acupuncture for 80 patients with abdominal obesity in Germany: based on the theory of unblocking and regulating the Belt Vessel
Yuanyuan Li, Hang Xiong, Shuhui Ma, Jingzhang Dai
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science.2023; 21(2): 137. CrossRef - Waist circumference and end‐stage renal disease based on glycaemic status: National Health Insurance Service data 2009–2018
Yun Kyung Cho, Ji Hye Huh, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Kyung‐do Han, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung‐Hee Ihm
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(1): 585. CrossRef - Incidence of sarcopenic obesity in older patients with diabetes and association between sarcopenic obesity and higher-level functional capacity: evaluation based on a consensus statement
Satoshi Ida, Ryutaro Kaneko, Kanako Imataka, Kaoru Okubo, Kentaro Azuma, Kazuya Murata
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(6): 591. CrossRef - A Novel Anthropometric Parameter, Weight-Adjusted Waist Index Represents Sarcopenic Obesity in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Min Jeong Park, Soon Young Hwang, Nam Hoon Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in patients with diabetes and adverse outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yuan-yuan Zhou, Jin-feng Wang, Qian Yao, Qiu-feng Jian, Zhi-peng Luo
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2023; 58: 128. CrossRef - The Correlation Between Leg Muscle Mass Index and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Menggege Liu, Qing Zhang, Juan Liu, Huiling Bai, Ping Yang, Xinhua Ye, Xiaoqing Yuan
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 4169. CrossRef - Sarcopenic Obesity with Normal Body Size May Have Higher Insulin Resistance in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Tingting Han, Ting Yuan, Xinyue Liang, Ningxin Chen, Jia Song, Xin Zhao, Yurong Weng, Yaomin Hu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1197. CrossRef - Relationship between Visceral Adipose Index, Lipid Accumulation Product and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
停停 陈
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(04): 3350. CrossRef - Assessment of the relationship between prediabetes and low skeletal mass based on blood creatinine level
S. I. Ibragimova, G. O. Nuskabayeva, Z. N. Shalkharova, K. Zh. Sadykova, G. A. Junusbekova, M. Oran
Diabetes mellitus.2022; 25(3): 226. CrossRef - Changes in body composition and low blood urea nitrogen level related to an increase in the prevalence of fatty liver over 20 years: A cross‐sectional study
Yasushi Imamura, Seiichi Mawatari, Kohei Oda, Kotaro Kumagai, Yasunari Hiramine, Akiko Saishoji, Atsuko Kakihara, Mai Nakahara, Manei Oku, Kaori Hosoyamada, Shuji Kanmura, Akihiro Moriuchi, Hironori Miyahara, Akio ido
Hepatology Research.2021; 51(5): 570. CrossRef - Body Composition and Diabetes
Hye Jin Yoo
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 238. CrossRef - Reduced Skeletal Muscle Volume and Increased Skeletal Muscle Fat Deposition Characterize Diabetes in Individuals after Pancreatitis: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
Andre E. Modesto, Juyeon Ko, Charlotte E. Stuart, Sakina H. Bharmal, Jaelim Cho, Maxim S. Petrov
Diseases.2020; 8(3): 25. CrossRef - Low alanine aminotransferase levels predict low muscle strength in older patients with diabetes: A nationwide cross‐sectional study in Korea
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2020; 20(4): 271. CrossRef - Association between sarcopenic obesity and higher risk of type 2 diabetes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Dima Khadra, Leila Itani, Hana Tannir, Dima Kreidieh, Dana El Masri, Marwan El Ghoch
World Journal of Diabetes.2019; 10(5): 311. CrossRef
- Clinical observation on acupuncture for 80 patients with abdominal obesity in Germany: based on the theory of unblocking and regulating the Belt Vessel
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnant Korean Women Based on Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Thickness as Measured by Ultrasonography
- Sung Hee Yang, Changsoo Kim, Hyun Sook An, Hyun An, Jin Soo Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(6):486-491. Published online September 22, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.486
- 4,797 View
- 55 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study was performed to verify the correlation between abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness (ASFT) measured by ultrasonography (US) during the first trimester of pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) of the second trimester in Korean women and to establish a standard of ASFT for predicting GDM.
Methods A total of 333 singleton pregnant women participated in this study. Their ASFT was measured by US during the 10+6 to 13+6 weeks of pregnancy; then a GDM confirmatory test (100 g oral glucose tolerance test) was conducted during the 24 to 28 week period of pregnancy. Based on the GDM tests, comparative analyses of the ages of the subjects, pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), and weight gain during pregnancy were conducted.
Results The ages of the subjects and weight gains during pregnancy were not correlated to the GDM of the second trimester of pregnancy, but the pre-pregnancy BMIs (22±3.3 kg/m2) and the ASFT (1.9±0.5 cm) measurements between the control group and subjects during the first trimester of pregnancy were found to show significant differences (
P <0.001). The cut-off value of the ASFT for predicting GDM was determined to be 2.4 cm (area under the curve=0.90, sensitivity 75.61%, specificity 91.78%,P <0.001). The odds ratio was 2.91 (95% confidence interval, 1.07 to 7.92;P =0.034), which was higher than the 2.4 cm ASFT.Conclusion It was determined that ASFT as measured by US during the first trimester of pregnancy can be used to predict the risk of developing GDM during the second trimester of pregnancy and for prognosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness combined with a 50-g glucose challenge test at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy in predicting gestational diabetes mellitus
Süleyman Cemil Oğlak, Emine Zeynep Yılmaz, Mehmet Şükrü Budak
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Value of Maternal Upper Abdominal Ad-ipose Thickness in Predicting GDM in Early Pregnancy
娜娜 郭
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(03): 4702. CrossRef - Evaluating the Adipose Tissue Depth as a Predictor Factor for Gestational Diabetes in Later Pregnancy—A Systematic Review
Bianca-Margareta Salmen, Valeria-Anca Pietrosel, Cristiana-Elena Durdu, Teodor Salmen, Cosmina Theodora Diaconu, Ioana-Cristina Bica, Claudia Gabriela Potcovaru, Florentina Gherghiceanu, Roxana-Adriana Stoica, Anca Pantea Stoian
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1492. CrossRef - The Association Between Body Fat Index and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Prospective Cohort Study
Sawanya Benchahong, Prasert Sunsaneevithayakul, Dittakarn Boriboonhirunsarn
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasound evaluation of subcutaneous and visceral abdominal fat as a predictor of gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review
Fernanda Teixeira Benevides, Edward Araujo Júnior, Carla Soraya Costa Maia, Renan Magalhães Montenegro Junior, Francisco Herlânio Costa Carvalho
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine.2022; 35(11): 2216. CrossRef - The Early Sonographic Prediction of Gestational Diabetes in Women From India
Shivani Gupta, Arjun Gupta, C. P. Swarnakar, Monika Rathore, Ramesh Beniwal, Kiran Meena, Anita Simlot, Nidhi Gupta
Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography.2022; 38(1): 18. CrossRef - Can maternal abdominal fat thickness predict antenatal insulin therapy in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus?
Sedat Akgöl, Mehmet Şükrü Budak, Süleyman Cemil Oğlak, Fatma Ölmez, Mehmet Emin Dilek, Serhat Kartal
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2022; 48(3): 634. CrossRef - Prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus by different obesity indices
Zhimin Song, Yan Cheng, Tingting Li, Yongfang Fan, Qingying Zhang, Haidong Cheng
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between maternal adiposity measures and adverse maternal outcomes of pregnancy: Systematic review and meta‐analysis
Nicola Heslehurst, Lem Ngongalah, Theophile Bigirumurame, Giang Nguyen, Adefisayo Odeniyi, Angela Flynn, Vikki Smith, Lisa Crowe, Becky Skidmore, Laura Gaudet, Alexandre Simon, Louise Hayes
Obesity Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of body composition in early pregnancy with gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Fatemeh Alsadat Rahnemaei, Fatemeh Abdi, Reza Pakzad, Seyedeh Hajar Sharami, Fatemeh Mokhtari, Elham Kazemian, Rajakumar Anbazhagan
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0271068. CrossRef - Early Gestational Diabetes Detection Using Neural Network
Tanzina Rahman Hera, Md. Ashikur Rahman Khan, Nishu Nath
WSEAS TRANSACTIONS ON BIOLOGY AND BIOMEDICINE.2021; 18: 1. CrossRef - The association of general obesity, central obesity and visceral body fat with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sura M. Alwash, H. David McIntyre, Abdullah Mamun
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2021; 15(5): 425. CrossRef - Abdominal skin subcutaneous fat thickness over the gestational period in Korean pregnant women: a descriptive observational study
Moon Sook Hwang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(4): 318. CrossRef - Relationship between Maternal Central Obesity and the Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
Da Yao, Qing Chang, Qi-Jun Wu, Shan-Yan Gao, Huan Zhao, Ya-Shu Liu, Yu-Ting Jiang, Yu-Hong Zhao
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Maternal Adipose Tissue Expansion, A Missing Link in the Prediction of Birth Weight Centile
Eleanor M Jarvie, Frances M Stewart, Jane E Ramsay, E Ann Brown, Barbara J Meyer, Gunilla Olivecrona, Bruce A Griffin, Dilys J Freeman
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 105(3): e814. CrossRef - Ultrasound assessment of maternal adipose tissue during 1st trimester screening for aneuploidies and risk of developing gestational diabetes
Francesco D’Ambrosi, Gabriele Rossi, Chiara M. Soldavini, Matteo Di Maso, Ilma F. Carbone, Giulia E. Cetera, Enrico Colosi, Enrico Ferrazzi
Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica.2020; 99(5): 644. CrossRef - Vitamin D Deficiency at Mid-Pregnancy Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Postpartum Glucose Intolerance in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seok Won Park, Yong-Wook Cho, Soo-Kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 97. CrossRef - Fetal pancreatic hyperechogenicity may be an early ultrasonographic sign of gestational diabetes mellitus
Hatice Akkaya, Barış Büke, Gülsüm Uysal
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine.2020; 33(14): 2387. CrossRef The Body Composition in Early Pregnancy is Associated with the Risk of Development of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Late During the Second Trimester
Yanping Liu, Jing Liu, Yinjie Gao, Dan Zheng, Wei Pan, Min Nie, Liangkun Ma
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 2367. CrossRef- New Diagnostic Criteria for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Pregnancy Outcomes in Korea
Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 763. CrossRef - Inter and intra-reliability of ultrasonography for the measurement of abdominal subcutaneous & visceral adipose tissue thickness at 12 weeks gestation
Alexandra Cremona, Kevin Hayes, Clodagh S. O’Gorman, Ciara Ní Laighin, Khadijah I. Ismail, Alan E. Donnelly, Jill Hamilton, Amanda Cotter
BMC Medical Imaging.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness as a simple predictor for gestational diabetes mellitus
Mehmet Sukru Budak, Ilker Kahramanoglu, Salvatore Giovanni Vitale, Sedat Akgol, Mehmet Emin Dilek, Serhat Kartal, Salvatore Caruso, Bekir Kahveci, Mehmet Obut, Muhammed Hanifi Bademkiran, Antonio Cianci
Journal of Perinatal Medicine.2019; 47(6): 605. CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia and Waist Phenotype as Markers in the Prediction of Gestational Diabetes in Iraqi Women
Faris Anwer Rasheed, Raghad Hasan Mshattat, Ulfat Mohammad Alnakkash, Saad Abdulrahma
Research Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2018; 11(1): 25. CrossRef - The importance of treating mild hyperglycemia in pregnant women with diabetes
Kyung-Soo Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 33(6): 1079. CrossRef - Anthropometric and ultrasound measures of maternal adiposity in the first trimester of pregnancy
Narelle Kennedy, Ann Quinton, Michael John Peek, Valeria Lanzarone, Ron Benzie, Ralph Nanan
Australasian Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.2018; 21(3): 147. CrossRef - Simple Screening Using Ultrasonography for Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 438. CrossRef
- Abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness combined with a 50-g glucose challenge test at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy in predicting gestational diabetes mellitus
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Serum Calcium and the Risk of Incident Metabolic Syndrome: A 4.3-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study
- Jong Ha Baek, Sang-Man Jin, Ji Cheol Bae, Jae Hwan Jee, Tae Yang Yu, Soo Kyoung Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(1):60-68. Published online December 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.1.60
- 4,101 View
- 32 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background An association between serum calcium level and risk of metabolic syndrome (MetS) has been suggested in cross-sectional studies. This study aimed to evaluate the association between baseline serum calcium level and risk of incident MetS in a longitudinal study.
Methods We conducted a retrospective longitudinal study of 12,706 participants without MetS who participated in a health screening program, had normal range serum calcium level at baseline (mean age, 51 years), and were followed up for 4.3 years (18,925 person-years). The risk of developing MetS was analyzed according to the baseline serum calcium levels.
Results A total of 3,448 incident cases (27.1%) of MetS developed during the follow-up period. The hazard ratio (HR) for incident MetS did not increase with increasing tertile of serum calcium level in an age- and sex-matched model (
P for trend=0.915). The HRs (95% confidence interval [CI]) for incident MetS comparing the second and the third tertiles to the first tertile of baseline serum calcium level were 0.91 (95% CI, 0.84 to 0.99) and 0.85 (95% CI, 0.78 to 0.92) in a fully adjusted model, respectively (P for trend=0.001). A decreased risk of incident MetS in higher tertiles of serum calcium level was observed in subjects with central obesity and/or a metabolically unhealthy state at baseline.Conclusion There was no positive correlation between baseline serum calcium levels and incident risk of MetS in this longitudinal study. There was an association between higher serum calcium levels and decreased incident MetS in individuals with central obesity or two components of MetS at baseline.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Independent associations of serum calcium with or without albumin adjustment and serum phosphorus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: results from NHANES 1999-2018
Haolong Qi, Bin Wang, Lei Zhu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of the serum calcium level with metabolic syndrome and its components among adults in Taiwan
Jer-min Chen, Tai-yin Wu, Yi-fan Wu, Kuan-liang Kuo
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Elevated Chinese visceral adiposity index increases the risk of stroke in Chinese patients with metabolic syndrome
Zeyu Liu, Qin Huang, Bi Deng, Minping Wei, Xianjing Feng, Fang Yu, Jie Feng, Yang Du, Jian Xia
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metformin: Expanding the Scope of Application—Starting Earlier than Yesterday, Canceling Later
Yulia A. Kononova, Nikolai P. Likhonosov, Alina Yu. Babenko
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(4): 2363. CrossRef - Metformin in prediabetes: key mechanisms for the prevention of diabetes and cardiometabolic risks
A. Yu. Babenko
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (10): 96. CrossRef Calcium and Phosphate Levels are Among Other Factors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Normal Weight
Kamila Osadnik, Tadeusz Osadnik, Marcin Delijewski, Mateusz Lejawa, Martyna Fronczek, Rafał Reguła, Mariusz Gąsior, Natalia Pawlas
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 1281. CrossRef- Association between selected trace elements and body mass index and waist circumference: A cross sectional study
Mahnaz Zohal, Saeedeh Jam-Ashkezari, Nasim Namiranian, Amin Moosavi, Akram Ghadiri-Anari
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(2): 1293. CrossRef - Letter: Increased Serum Angiopoietin-Like 6 Ahead of Metabolic Syndrome in a Prospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:521-9)
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(5): 727. CrossRef - Genotype effects of glucokinase regulator on lipid profiles and glycemic status are modified by circulating calcium levels: results from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Oh Yoen Kim, So-Young Kwak, Hyunjung Lim, Min-Jeong Shin
Nutrition Research.2018; 60: 96. CrossRef
- Independent associations of serum calcium with or without albumin adjustment and serum phosphorus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: results from NHANES 1999-2018
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Association between Blood Mercury Level and Visceral Adiposity in Adults
- Jong Suk Park, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Ka He, Dae Jung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(2):113-120. Published online December 21, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.2.113
- 4,882 View
- 46 Download
- 38 Web of Science
- 39 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Few studies have examined the association between mercury exposure and obesity. The aim of this study is to investigate the association between blood mercury concentrations and indices of obesity in adults.
Methods A total of 200 healthy subjects, aged 30 to 64 years, who had no history of cardiovascular or malignant disease, were examined. Anthropometric and various biochemical profiles were measured. Visceral adipose tissue (VAT) was measured using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
Results All subjects were divided into three groups according to blood mercury concentrations. Compared with the subjects in the lowest tertile of mercury, those in the highest tertile were more likely to be male; were current alcohol drinkers and smokers; had a higher body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), and VAT; had higher levels of blood pressure, fasting glucose, and insulin resistance; and consumed more fish. The blood mercury concentration was significantly associated with anthropometric parameters, showing relationships with BMI, WC, and VAT. After adjusting for multiple risk factors, the odds ratios (ORs) for high mercury concentration was significantly higher in the highest VAT tertile than in the lowest VAT tertile (OR, 2.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.05 to 6.62;
P <0.05).Conclusion The blood mercury concentration was significantly associated with VAT in healthy adults. Further studies are warranted to confirm our findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exposure to Metal Mixtures and Overweight or Obesity Among Chinese Adults
Gaojie Fan, Qing Liu, Mingyang Wu, Jianing Bi, Xiya Qin, Qing Fang, Zhengce Wan, Yongman Lv, Youjie Wang, Lulu Song
Biological Trace Element Research.2023; 201(8): 3697. CrossRef - Methylmercury drives lipid droplet formation and adipokine expression during the late stages of adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells
Yasukazu Takanezawa, Yui Kashiwano, Ryosuke Nakamura, Yuka Ohshiro, Shimpei Uraguchi, Masako Kiyono
Toxicology.2023; 486: 153446. CrossRef - Expression Profiling of Adipogenic and Anti-Adipogenic MicroRNA Sequences following Methylmercury Exposure in Caenorhabditis elegans
Giancarlo Garofalo, Tyson Nielsen, Samuel Caito
Toxics.2023; 11(11): 934. CrossRef - Report of the Scientific Committee of the Spanish Agency for Food Safety and Nutrition (AESAN) on the available evidence in relation to the potential obesogenic activity of certain chemical compounds that may be present in foods
Ana María Rivas Velasco, Irene Bretón Lesmes, Araceli Díaz Perales, Ángel Gil Izquierdo, María José González Muñoz, Victoria Moreno Arribas, María del Puy Portillo Baquedano, Silvia Pichardo Sánchez
Food Risk Assess Europe.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lead, mercury, and cadmium exposures are associated with obesity but not with diabetes mellitus: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017
Min Kyong Moon, Inae Lee, Aram Lee, Hyunwoong Park, Min Joo Kim, Sunmi Kim, Yoon Hee Cho, Sooyeon Hong, Jiyoung Yoo, Gi Jeong Cheon, Kyungho Choi, Young Joo Park, Jeongim Park
Environmental Research.2022; 204: 111888. CrossRef - The Effect of Mixture of Heavy Metals on Obesity in Individuals ≥50 Years of Age
Hai Nguyen Duc, Hojin Oh, Min-Sun Kim
Biological Trace Element Research.2022; 200(8): 3554. CrossRef - MicroRNA Expression Influences Methylmercury-Induced Lipid Accumulation and Mitochondrial Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans
Tyson Nielsen, Nicole Crawford, Megan Martell, Belal Khalil, Farooq Imtiaz, Jennifer L. Newell-Caito, Samuel Caito
Chemical Research in Toxicology.2022; 35(1): 77. CrossRef - Relationship Between Serum Levels of Arsenic, Cadmium, and Mercury and Body Mass Index and Fasting Plasma Glucose in a Mexican Adult Population
Héctor Hernández-Mendoza, Héctor Edmundo Álvarez-Loredo, Elizabeth Teresita Romero-Guzmán, Darío Gaytán-Hernández, Consuelo Chang-Rueda, Israel Martínez-Navarro, Bertha Irene Juárez-Flores, María Judith Rios-Lugo
Biological Trace Element Research.2022; 200(12): 4916. CrossRef - Heavy metal-induced lipogenic gene aberration, lipid dysregulation and obesogenic effect: a review
Yang Zhou, Frank Peprah Addai, Xinshuang Zhang, Yuelin Liu, Yinfeng Wang, Feng Lin, Alex Tuffour, Jie Gu, Guangxiang Liu, Haifeng Shi
Environmental Chemistry Letters.2022; 20(3): 1611. CrossRef - Differential fat accumulation in early adulthood according to adolescent‐BMI and heavy metal exposure
Larissa Betanzos‐Robledo, Martha M. Téllez‐Rojo, Hector Lamadrid‐Figueroa, Ernesto Roldan‐Valadez, Karen E. Peterson, Erica C. Jansen, Nil Basu, Alejandra Cantoral
New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development.2022; 2022(181-182): 37. CrossRef - The Association of Mercury and ALT with Obesity in Korean Adults: Using Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 11 Years (KNHANES 2005, 2008~2017)
Sang Shin Pyo
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2022; 54(3): 192. CrossRef - Plasma titanium level is positively associated with metabolic syndrome: A survey in China’s heavy metal polluted regions
Miao Huang, Jingyuan Chen, Guangyu Yan, Yiping Yang, Dan Luo, Xiang Chen, Meian He, Hong Yuan, Zhijun Huang, Yao Lu
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.2021; 208: 111435. CrossRef - Relationship Between Elevated Hair Mercury Levels, Essential Element Status, and Metabolic Profile in Overweight and Obese Adults
Anatoly V. Skalny, Jung-Su Chang, Igor P. Bobrovnitsky, Philippe Yu Kopylov, Margarita G. Skalnaya, Shih-Yi Huang, Monica Maria Bastos Paoliello, Ekaterina S. Ivanova, Weu Wang, Alexey A. Tinkov
Biological Trace Element Research.2021; 199(8): 2874. CrossRef - Associations between metabolic syndrome and four heavy metals: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Ping Xu, Aiping Liu, Fengna Li, Alexey A. Tinkov, Longjian Liu, Ji-Chang Zhou
Environmental Pollution.2021; 273: 116480. CrossRef - Cadmium, lead and mercury in the blood of psoriatic and vitiligo patients and their possible associations with dietary habits
Marta Wacewicz-Muczyńska, Katarzyna Socha, Jolanta Soroczyńska, Marek Niczyporuk, Maria H. Borawska
Science of The Total Environment.2021; 757: 143967. CrossRef - Crude oil and public health issues in Niger Delta, Nigeria: Much ado about the inevitable
Orish Ebere Orisakwe
Environmental Research.2021; 194: 110725. CrossRef - Mercury in the human adrenal medulla could contribute to increased plasma noradrenaline in aging
Roger Pamphlett, Stephen Kum Jew, Philip A. Doble, David P. Bishop
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Multiple metal exposure and obesity: A prospective cohort study of adults living along the Yangtze River, China
Qi Zhong, Qi-rong Qin, Wan-jun Yang, Jia-liu He, Jin-liang Zhu, Zhen-yu Zhu, Fen Huang
Environmental Pollution.2021; 285: 117150. CrossRef - Association between Blood Mercury Levels and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Non-Obese Populations: The Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2012–2014
Yun-Jung Yang, Eun-Jung Yang, Kyongjin Park, Subin Oh, Taehyen Kim, Yeon-Pyo Hong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(12): 6412. CrossRef - Hair Lead, Aluminum, and Other Toxic Metals in Normal-Weight and Obese Patients with Coronary Heart Disease
Anatoly V. Skalny, Philippe Yu Kopylov, Monica M. B. Paoliello, Jung-Su Chang, Michael Aschner, Igor P. Bobrovnitsky, Jane C.-J. Chao, Jan Aaseth, Sergei N. Chebotarev, Alexey A. Tinkov
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 8195. CrossRef - Methylmercury chronic exposure affects the expression of DNA single-strand break repair genes, induces oxidative stress, and chromosomal abnormalities in young dyslipidemic APOE knockout mice
Cássia R. Roque, Letícia R. Sampaio, Mayumi N. Ito, Daniel V. Pinto, Juan S.R. Caminha, Paulo I.G. Nunes, Ramon S. Raposo, Flávia A. Santos, Cláudia C. Windmöller, Maria Elena Crespo-Lopez, Jacqueline I. Alvarez-Leite, Reinaldo B. Oriá, Ronald F. Pinheiro
Toxicology.2021; 464: 152992. CrossRef - Methylmercury-Induced Metabolic Alterations in Caenorhabditis elegans Are Diet-Dependent
Nicole Crawford, Megan Martell, Tyson Nielsen, Belal Khalil, Farooq Imtiaz, Etienne Nguidjo, Jennifer Newell-Caito, Julia Bornhorst, Tanja Schwerdtle, Samuel Caito
Toxics.2021; 9(11): 287. CrossRef - Antioxidant status in relation to heavy metals induced oxidative stress in patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
Manal Abudawood, Hajera Tabassum, Atheer H. Alanazi, Fatmah Almusallam, Feda Aljaser, Mir Naiman Ali, Naif D. Alenzi, Samyah T. Alanazi, Manal A. Alghamdi, Ghadah H. Altoum, Manar A. Alzeer, Majed O. Alotaibi, Arwa Abudawood, Hazem K. Ghneim, Lulu Abdulla
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Blood Mercury Levels with the Risks of Overweight and High Waist-to-Height Ratio in Children and Adolescents: Data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ky Young Cho
Children.2021; 8(12): 1087. CrossRef - The sex-specific effects of blood lead, mercury, and cadmium levels on hepatic steatosis and fibrosis: Korean nationwide cross-sectional study
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology.2020; 62: 126601. CrossRef - Elevated blood mercury level has a non-linear association with infertility in U.S. women: Data from the NHANES 2013–2016
Fangfang Zhu, Chi Chen, Yingxuan Zhang, Si Chen, Xian Huang, Jingwei Li, Yanxi Wang, Xiaorong Liu, Gaopi Deng, Jie Gao
Reproductive Toxicology.2020; 91: 53. CrossRef - Methylmercury Induces Metabolic Alterations in Caenorhabditis elegans: Role for C/EBP Transcription Factor
Samuel W Caito, Jennifer Newell-Caito, Megan Martell, Nicole Crawford, Michael Aschner
Toxicological Sciences.2020; 174(1): 112. CrossRef - Association of Fish Consumption and Mercury Exposure During Pregnancy With Metabolic Health and Inflammatory Biomarkers in Children
Nikos Stratakis, David V. Conti, Eva Borras, Eduardo Sabido, Theano Roumeliotaki, Eleni Papadopoulou, Lydiane Agier, Xavier Basagana, Mariona Bustamante, Maribel Casas, Shohreh F. Farzan, Serena Fossati, Juan R. Gonzalez, Regina Grazuleviciene, Barbara He
JAMA Network Open.2020; 3(3): e201007. CrossRef - Elemental Analysis of Aging Human Pituitary Glands Implicates Mercury as a Contributor to the Somatopause
Roger Pamphlett, Stephen Kum Jew, Philip A. Doble, David P. Bishop
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Mercury leads to features of polycystic ovary syndrome in rats
Eduardo Merlo, Ingridy R.G. Schereider, Maylla R. Simões, Dalton V. Vassallo, Jones B. Graceli
Toxicology Letters.2019; 312: 45. CrossRef - In utero exposure to mercury and childhood overweight or obesity: counteracting effect of maternal folate status
Guoying Wang, Jessica DiBari, Eric Bind, Andrew M. Steffens, Jhindan Mukherjee, Tami R. Bartell, David C. Bellinger, Xiumei Hong, Yuelong Ji, Mei-Cheng Wang, Marsha Wills-Karp, Tina L. Cheng, Xiaobin Wang
BMC Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Mercury Is Taken Up Selectively by Cells Involved in Joint, Bone, and Connective Tissue Disorders
Roger Pamphlett, Stephen Kum Jew
Frontiers in Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Cohort Profile: The Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center Cohort in Korea
Jee-Seon Shim, Bo Mi Song, Jung Hyun Lee, Seung Won Lee, Ji Hye Park, Dong Phil Choi, Myung Ha Lee, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungha Park, Won-Woo Lee, Yoosik Youm, Eui-Cheol Shin, Hyeon Chang Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2019; 60(8): 804. CrossRef - Chronic mercury at low doses impairs white adipose tissue plasticity
Danize Aparecida Rizzetti, Patricia Corrales, Janaina Trindade Piagette, José Antonio Uranga-Ocio, Gema Medina-Gomez, Franck Maciel Peçanha, Dalton Valentim Vassallo, Marta Miguel, Giulia Alessandra Wiggers
Toxicology.2019; 418: 41. CrossRef - Associations of cumulative exposure to heavy metal mixtures with obesity and its comorbidities among U.S. adults in NHANES 2003–2014
Xin Wang, Bhramar Mukherjee, Sung Kyun Park
Environment International.2018; 121: 683. CrossRef - Blood mercury concentration in relation to metabolic and weight phenotypes using the KNHANES 2011–2013 data
Kayoung Lee
International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health.2018; 91(2): 185. CrossRef - The association of total blood mercury levels and overweight among Korean adolescents: analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2010–2013
Yi-Yeon Shin, In-Kyung Ryu, Mi-Jung Park, Shin-Hye Kim
Korean Journal of Pediatrics.2018; 61(4): 121. CrossRef - Heavy Metal Exposure and Metabolic Syndrome: Evidence from Human and Model System Studies
Antonio Planchart, Adrian Green, Cathrine Hoyo, Carolyn J. Mattingly
Current Environmental Health Reports.2018; 5(1): 110. CrossRef - Association between Blood Mercury Level and Visceral Adiposity in Adults
Seong-Su Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(2): 96. CrossRef
- Exposure to Metal Mixtures and Overweight or Obesity Among Chinese Adults
- Optimal Waist Circumference Cutoff Value Based on Insulin Resistance and Visceral Obesity in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes
- Jung Soo Lim, Young Ju Choi, Soo-Kyung Kim, Byoung Wook Huh, Eun Jig Lee, Kap Bum Huh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(3):253-263. Published online April 24, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.3.253
- 4,317 View
- 28 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Visceral obesity is the most powerful contributor to the development of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and cardiovascular diseases. In light of visceral obesity, however, there is a paucity of data on the appropriate cutoff point of waist circumference (WC) in subjects with type 2 diabetes. The aim of this study was to investigate the optimal cutoff value for WC that signals insulin resistance (IR) and visceral obesity in Koreans with type 2 diabetes.
Methods We evaluated 4,252 patients with type 2 diabetes (male 2,220, female 2,032, mean age 57.24 years) who visited our clinic between January 2003 and June 2009. WC was measured at the midpoint between the lower rib and the iliac crest, and insulin sensitivity was assessed by the rate constant of plasma glucose disappearance (
Kitt %/min) using an insulin tolerance test. Visceral fat thickness was measured using ultrasonography. Statistical analysis was performed using receiver operating characteristic curve.Results The optimal cutoff points for WC for identifying the presence of IR and visceral obesity, as well as two or more metabolic components, were 87 cm for men and 81 cm for women. Moreover, these cutoff points had the highest predictive powers for the presence of visceral obesity. The MetS defined by new criteria correlated with the increased carotid intima-media thickness in female subjects.
Conclusion Our results suggest that the optimal cutoff values for WC in Koreans with type 2 diabetes should be reestablished based on IR and visceral obesity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Muscle Mass, Body Fat Mass, and Abdominal Circumstances with Insulin Resistance among Young Adult Population with Prediabetes Risk
Anindya Putri Adhisti, Siti Fatimah-Muis, Amalia Sukmadianti, Darmono S.S., Febe Christianto
The Indian Journal of Nutrition and Dietetics.2023; : 176. CrossRef - Brazil nut prevents oxidative DNA damage in type 2 diabetes patients
Tamires Pavei Macan, Thais Aquino de Amorim, Adriani Paganini Damiani, Ângela Caroline da Luz Beretta, Marina Lummertz Magenis, Thais Ceresér Vilela, João Paulo Teixeira, Vanessa Moraes de Andrade
Drug and Chemical Toxicology.2022; 45(3): 1066. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome and Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes: An Observational Patient Study
Dafina Ademi-Islami, Suzana Manxhuka-Kerliu, Dhurata Tarifa-Koroveshi, Rozafa Koliqi, Blerim Mujaj
Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical Research.2022; 16: 117822342210805. CrossRef - Performance of Two Novel Obesity Indicators for the Management of Metabolic Syndrome in Young Adults
Xiaoli Liu, Chunpeng Ma, Fuzai Yin, Rui Wang, Qiang Lu, Na Lu, Chunming Ma
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Differential effect of subcutaneous abdominal and visceral adipose tissue on cardiometabolic risk
Susan Sam
Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Three novel obese indicators perform better in monitoring management of metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes
Chun-Ming Ma, Na Lu, Rui Wang, Xiao-Li Liu, Qiang Lu, Fu-Zai Yin
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Body Weight Changes and Menstrual Irregularity: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010 to 2012
Kyung Min Ko, Kyungdo Han, Youn Jee Chung, Kun-Ho Yoon, Yong Gyu Park, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 248. CrossRef - The renal tubular damage marker urinary N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase may be more closely associated with early detection of atherosclerosis than the glomerular damage marker albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes
So Ra Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Sang-Guk Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between metabolic health, obesity phenotype and the risk of breast cancer
Yong‐Moon Mark Park, Alexandra J. White, Hazel B. Nichols, Katie M. O'Brien, Clarice R. Weinberg, Dale P. Sandler
International Journal of Cancer.2017; 140(12): 2657. CrossRef - Reappraisal of waist circumference cutoff value according to general obesity
Kyung-Soo Kim, Hyun-Ju Oh, Young Ju Choi, Byung Wook Huh, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seok Won Park, Eun Jig Lee, Yong-Wook Cho, Kap-Bum Huh
Nutrition & Metabolism.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between Muscle Mass, Body Fat Mass, and Abdominal Circumstances with Insulin Resistance among Young Adult Population with Prediabetes Risk

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





