
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Harnessing Metabolic Indices as a Predictive Tool for Cardiovascular Disease in a Korean Population without Known Major Cardiovascular Event
- Hyun-Jin Kim, Byung Sik Kim, Yonggu Lee, Sang Bong Ahn, Dong Wook Kim, Jeong-Hun Shin
- Received June 22, 2023 Accepted August 18, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0197 [Epub ahead of print]

- 934 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study evaluated the usefulness of indices for metabolic syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and insulin resistance (IR), as predictive tools for cardiovascular disease in middle-aged Korean adults.
Methods
The prospective data obtained from the Ansan-Ansung cohort database, excluding patients with major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE). The primary outcome was the incidence of MACCE during the follow-up period.
Results
A total of 9,337 patients were included in the analysis, of whom 1,130 (12.1%) experienced MACCE during a median follow-up period of 15.5 years. The metabolic syndrome severity Z-score, metabolic syndrome severity score, hepatic steatosis index, and NAFLD liver fat score were found to significantly predict MACCE at values above the cut-off point and in the second and third tertiles. Among these indices, the hazard ratios of the metabolic syndrome severity score and metabolic syndrome severity Z-score were the highest after adjusting for confounding factors. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of the 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) score for predicting MACCE was 0.716, and the metabolic syndrome severity Z-score had an AUC of 0.619.
Conclusion
The metabolic syndrome severity score is a highly reliable indicator and was closely associated with the 10-year ASCVD risk score in predicting MACCE in the general population. Given the specific characteristics and limitations of metabolic syndrome severity scores as well as the indices of NAFLD and IR, a more practical scoring system that considers these factors is essential to achieve greater accuracy in forecasting cardiovascular outcomes.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
- Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):220-231. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0327
- 65,535 View
- 282 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated whether metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is associated with an elevated risk of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality using a large-scale health examination cohort.
Methods
A total of 394,835 subjects in the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study cohort were enrolled from 2002 to 2012. Participants were categorized by the presence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and MAFLD as follows: normal subjects; patients with both NAFLD and MAFLD; patients with NAFLD only; and patients with MAFLD only. Cox proportional hazards models were used to analyze the risk of mortality.
Results
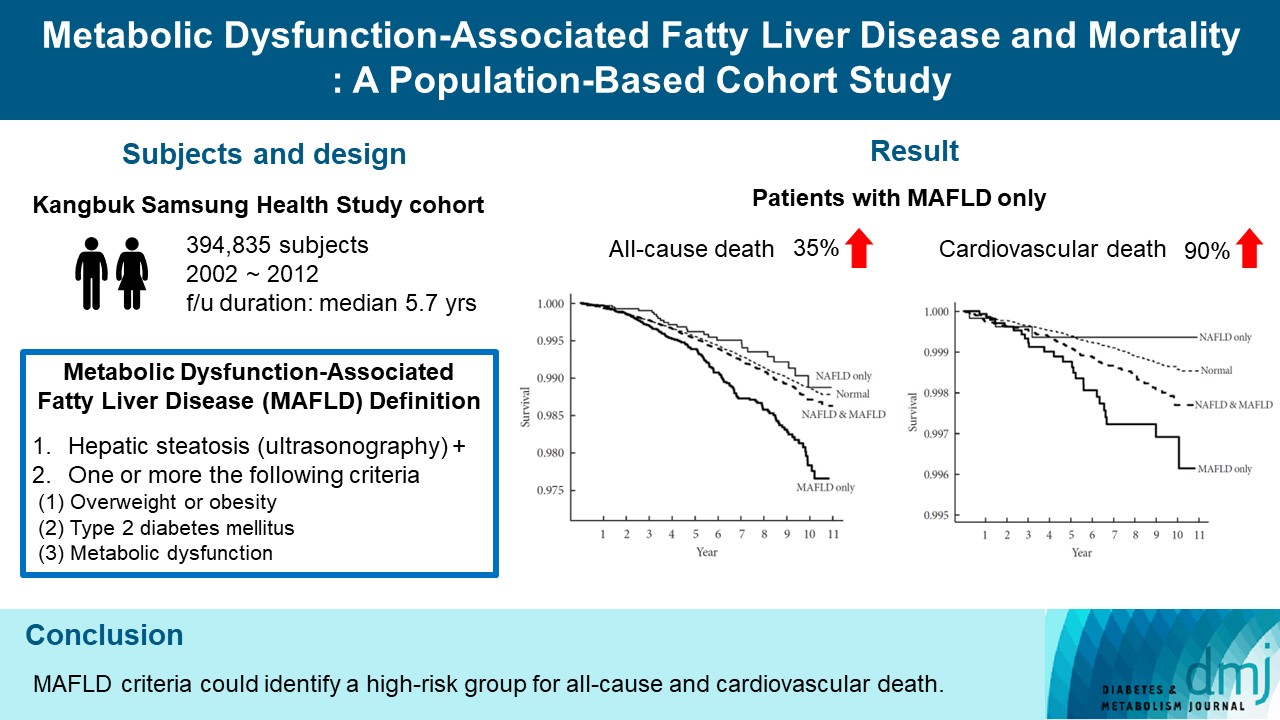
During a median 5.7 years of follow-up, 20.69% was patients with both NAFLD and MAFLD, 1.51% was patients with NAFLD only, and 4.29% was patients with MAFLD only. All-cause and cardiovascular death was higher in patients with MAFLD than those without MAFLD (P<0.001, respectively). In patients with MAFLD only, the hazard ratio (HR) of all-cause and cardiovascular death was 1.35 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.13 to 1.60) and 1.90 (95% CI, 1.26 to 2.88) after adjusting for age, which lost its statistical significance by multivariable adjustments. Compared to patients with less than two components of metabolic dysfunction, patients with more than two components of metabolic dysfunction were a higher risk of cardiovascular death (HR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.25 to 3.38) and only women with more than two components of metabolic dysfunction were a higher risk of all-cause death (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.02 to 2.03).
Conclusion
MAFLD criteria could identify a high-risk group for all-cause and cardiovascular death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Eugene Han, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Sang Hoon Ahn, Yong-ho Lee, Seung Up Kim
Metabolism.2024; 152: 155789. CrossRef - Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMJ.2024; : e076388. CrossRef - Sex differences in mortality and liver‐related events in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Huimin Zhou, Haiyan Chen, Hanxiao Lu, Bo Wu, Shuo Zhang, Yuanlong Gu, Guangwen Zhou, Jie Xiang, Jun Yang
Liver International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between dietary carbohydrate to fiber ratio and metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease in adults: evidence from the NHANES 2017–2020
Zhenmin Liu, Taiyong Fang
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Outcomes Between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis
Ghazala S Virk, Jaahnavi Vajje, Nausheen K Virk, Raam Mannam, Wajeeh Rehman, Naglaa G Ghobriel , Irfan-ud-din Mian, Muhammad Usama
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in prevalence and all-cause mortality of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease among adults in the past three decades: Results from the NHANES study
Zhi-Qin Xie, Hong-Xia Li, Bing-Kun Wang, Zhao-Ming Yang, Zi-Yu Zhang, Wen-Liang Tan, Wen-Xin Li, Qing-Bin Wang, Lei Yang, Hong-Kai Zhuang, Chen-Wei Tang, Chang-Zhen Shang, Ya-Jin Chen
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 110: 62. CrossRef - Comparing the Mortality Risk between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Han Na Jung, Chang Hee Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 198. CrossRef - Increased expression of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and O-GlcNAcylation in hepatocytes drives non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hye Jin Chun, Eun Ran Kim, Minyoung Lee, Da Hyun Choi, Soo Hyun Kim, Eugene Shin, Jin-Hong Kim, Jin Won Cho, Dai Hoon Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Metabolism.2023; 145: 155612. CrossRef - Current understanding and future perspectives on the impact of changing NAFLD to MAFLD on global epidemiology and clinical outcomes
Karl Vaz, Daniel Clayton-Chubb, Ammar Majeed, John Lubel, David Simmons, William Kemp, Stuart K. Roberts
Hepatology International.2023; 17(5): 1082. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Quality Control: Its Role in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
Soyeon Shin, Jaeyoung Kim, Ju Yeon Lee, Jun Kim, Chang-Myung Oh
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(4): 289. CrossRef
- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Synergistic Interaction between Hyperuricemia and Abdominal Obesity as a Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome Components in Korean Population
- Min Jin Lee, Ah Reum Khang, Yang Ho Kang, Mi Sook Yun, Dongwon Yi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):756-766. Published online January 20, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0166
- 4,879 View
- 252 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The present study investigated the role of synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity as a risk factor for the components of metabolic syndrome.
Methods
We performed a cross-sectional study using the data of 16,094 individuals from the seventh Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016 to 2018). The adjusted odds ratios of metabolic syndrome and its components were analyzed by multivariate logistic regression analysis. The presence of synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity was evaluated by calculating the additive scales—the relative excess risk due to interaction, attributable proportion due to interaction, and synergy index (SI).
Results
There was a synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity in hypertriglyceridemia (men: SI, 1.39; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 1.98; women: SI, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.02 to 2.69), and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (men: SI, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.41 to 2.91; women: SI, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.05 to 2.95). There was no significant synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity for the risk of high blood pressure (men: SI, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.85 to 1.77; women: SI, 1.53; 95% CI, 0.79 to 2.97), and hyperglycemia (men: SI, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.72 to 1.47; women: SI, 1.39; 95% CI, 0.75 to 2.57).
Conclusion
Hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity synergistically increased the risk of hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL-C in both sexes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and factors associated with overweight, obesity and central obesity among adults in Shenmu City, Shaanxi Province, China
Mingxia Liu, Chunjiao Jia, Yaoda Hu, Juan Liu, Lizhen Liu, Shengli Sun, Haiying Wang, Yonglin Liu
Preventive Medicine Reports.2024; 40: 102673. CrossRef - Synergistic interaction between hyperlipidemia and obesity as a risk factor for stress urinary incontinence in Americans
Fangyi Zhu, Mao Chen, Ya Xiao, Xiaoyu Huang, Liying Chen, Li Hong
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of cognitive function in the relationship between surrogate markers of visceral fat and depressive symptoms in general middle-aged and elderly population: A nationwide population-based study
Na Zhang, Jianqian Chao, Xueyu Wu, Hongling Chen, Min Bao
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 338: 581. CrossRef - Biodegradation of Uric Acid by Bacillus paramycoides-YC02
Xiaoyu Cao, Jingyuan Cai, Yu Zhang, Chao Liu, Meijie Song, Qianqian Xu, Yang Liu, Hai Yan
Microorganisms.2023; 11(8): 1989. CrossRef - A predictive model for hyperuricemia among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Urumqi, China
Palizhati Abudureyimu, Yuesheng Pang, Lirun Huang, Qianqian Luo, Xiaozheng Zhang, Yifan Xu, Liang Jiang, Patamu Mohemaiti
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary Ferulic Acid Ameliorates Metabolism Syndrome-Associated Hyperuricemia in Rats via Regulating Uric Acid Synthesis, Glycolipid Metabolism, and Hepatic Injury
Nanhai Zhang, Jingxuan Zhou, Lei Zhao, Ou Wang, Liebing Zhang, Feng Zhou
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prevalence and factors associated with overweight, obesity and central obesity among adults in Shenmu City, Shaanxi Province, China
- Pathophysiology
- Insulin Resistance: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies
- Shin-Hae Lee, Shi-Young Park, Cheol Soo Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):15-37. Published online December 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0280
- 30,363 View
- 2,655 Download
- 158 Web of Science
- 191 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
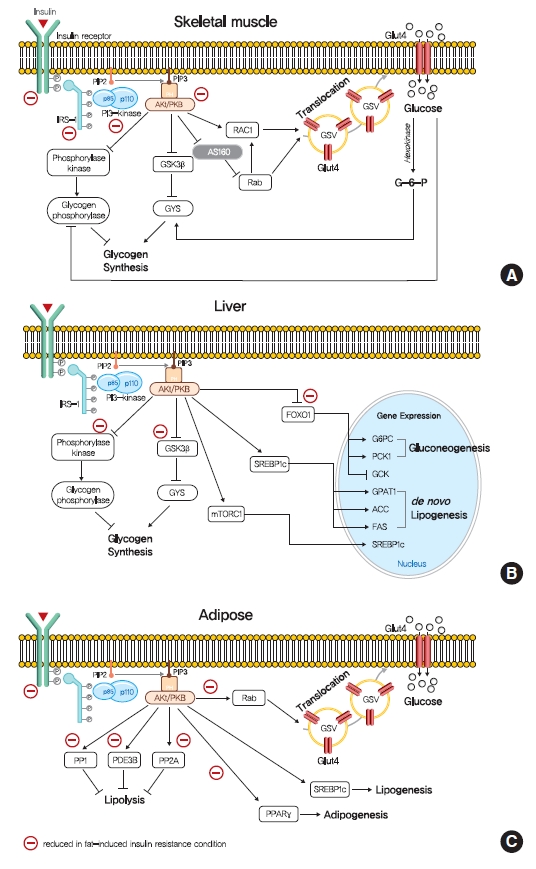
ePub - Insulin resistance is the pivotal pathogenic component of many metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes mellitus, and is defined as a state of reduced responsiveness of insulin-targeting tissues to physiological levels of insulin. Although the underlying mechanism of insulin resistance is not fully understood, several credible theories have been proposed. In this review, we summarize the functions of insulin in glucose metabolism in typical metabolic tissues and describe the mechanisms proposed to underlie insulin resistance, that is, ectopic lipid accumulation in liver and skeletal muscle, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and inflammation. In addition, we suggest potential therapeutic strategies for addressing insulin resistance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetic Encephalopathy: Role of Oxidative and Nitrosative Factors in Type 2 Diabetes
Debashree Mazumdar, Santosh Singh
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry.2024; 39(1): 3. CrossRef - Materials and structure of polysaccharide-based delivery carriers for oral insulin: A review
Xinran Wang, Hongnan Sun, Taihua Mu
Carbohydrate Polymers.2024; 323: 121364. CrossRef - β-Thalassemia and Diabetes Mellitus: Current State and Future
Directions
Jalal Taneera, Eglal Mahgoub, Reem Qannita, Ayah Alalami, Ola Al Shehadat, Mona Youssef, Ayah Dib, Alaa Al Hajji, Amani Al Hajji, Fatheya Al-Khaja, Hany Dewedar, Mawieh Hamad
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2024; 56(04): 272. CrossRef - Mulberry leaf multi-components exert hypoglycemic effects through regulation of the PI-3K/Akt insulin signaling pathway in type 2 diabetic rats
Yue Zhang, Liang Li, Tao Chai, Han Xu, Hong-yan Du, Yan Jiang
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2024; 319: 117307. CrossRef - Thyroid cancer and insulin resistance
Gabriela Brenta, Fernando Di Fermo
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024; 25(1): 19. CrossRef - Comparative profiling of gut microbiota and metabolome in diet-induced obese and insulin-resistant C57BL/6J mice
Hobby Aggarwal, Jyoti Gautam, Deepika Kumari, Sonu Kumar Gupta, Sneh Bajpai, Kartikey Chaturvedi, Yashwant Kumar, Madhu Dikshit
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119643. CrossRef - CD248 promotes insulin resistance by binding to the insulin receptor and dampening its insulin-induced autophosphorylation
Patricia O. Benedet, Nooshin S. Safikhan, Maria J. Pereira, Bryan M. Lum, José Diego Botezelli, Cheng-Hsiang Kuo, Hua-Lin Wu, Barbara P. Craddock, W. Todd Miller, Jan W. Eriksson, Jessica T.Y. Yue, Edward M. Conway
eBioMedicine.2024; 99: 104906. CrossRef - The Antiobesity Effects and Potential Mechanisms of Theaflavins
Yi Fang, Jun Wang, Yu Cao, Wenrui Liu, Lianxiang Duan, Jing Hu, Jinghua Peng
Journal of Medicinal Food.2024; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - The role of zinc finger proteins in the fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation
Bolun Li, Shibo Liu, Ze He, En Luo, Hanghang Liu
The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology.2024; 167: 106507. CrossRef - Gentianella turkestanorum (Gand.) Holub, a Chinese Herbal Medicine that can Alleviate T2DM in Db/db Mice, and its Active Mechanism of Action
Ying Wei, Jiaxin Sun, Liya Su, Tunhai Xu
Pharmacognosy Magazine.2024; 20(2): 646. CrossRef - Hyperglycemia affects axial signs in patients with Parkinson’s disease through mechanisms of insulin resistance or non-insulin resistance
Ruidan Wang, Zhaohui Jin, Qiaoxia Zhen, Lin Qi, Cui Liu, Ping Wang, Yonghong Liu, Jinping Fang, Yanjun Liu, Yuan Su, Yixuan Wang, Detao Meng, Hongjiao Yan, Yi Zhen, Zhenzhen Li, Boyan Fang
Neurological Sciences.2024; 45(5): 2011. CrossRef - Insulin resistance: Risk factors, diagnostic approaches and mathematical models for clinical practice, epidemiological studies, and beyond
Janusz Krzymien, Piotr Ladyzynski
Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; 44(1): 55. CrossRef - Effects of silybin supplementation on growth performance, serum indexes and liver transcriptome of Peking ducks
Ziyue Zhang, Bozhi Shi, Xueze Lv, Yingchao Dong, Lei Li, Zhaofei Xia
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Consuming Beverages Sweetened with Fructose, Glucose, High-Fructose Corn Syrup, Sucrose, or Aspartame on OGTT-Derived Indices of Insulin Sensitivity in Young Adults
Bettina Hieronimus, Valentina Medici, Vivien Lee, Marinelle V. Nunez, Desiree M. Sigala, Andrew A. Bremer, Chad L. Cox, Nancy L. Keim, Jean-Marc Schwarz, Giovanni Pacini, Andrea Tura, Peter J. Havel, Kimber L. Stanhope
Nutrients.2024; 16(1): 151. CrossRef - Association Between Insulin Resistance Markers and Poor Prognosis in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke After Intravenous Thrombolysis
Haimei Liu, Denglu Liu, Peng Zuo
The Neurologist.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Interplay of Angiotensin Peptides, Vasopressin, and Insulin in the Heart: Experimental and Clinical Evidence of Altered Interactions in Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus
Ewa Szczepanska-Sadowska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 1310. CrossRef - High-Density Lipoprotein Is Located Alongside Insulin in the Islets of Langerhans of Normal and Rodent Models of Diabetes
Sahar Mohsin, Haba Elabadlah, Mariam K. Alotaiba, Suhail AlAmry, Shamma J. Almehairbi, Maha M. K. Harara, Aisha M. H. Almuhsin, Saeed Tariq, Frank Christopher Howarth, Ernest A. Adeghate
Nutrients.2024; 16(2): 313. CrossRef - Sweet triterpenoid glycoside from Cyclocarya paliurus ameliorates obesity-induced insulin resistance through inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammatory pathway
Jie Li, Junyu He, Haibo He, Xiao Wang, Shuran Zhang, Yumin He, Jihong Zhang, Chengfu Yuan, HongWu Wang, Daoxiang Xu, Chaowang Pan, Huifan Yu, Kun Zou
Current Research in Food Science.2024; 8: 100677. CrossRef - Effect of supplementation with probiotics or synbiotics on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
TingRui Chen, Jing Wang, ZeKun Liu, Fei Gao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus progression in β-thalassaemia major patients: The impact of iron overload
Eglal Omer Mahgoub, Reem Qannita, Ayah Alalami, Ola Al Shehadat, Rabah Al Mahmoud, Ayah Dib, Alaa Al Hajji, Amani Al Hajji, Fatheya Al Khaja, Hany Dewedar, Mawieh Hamad, Jalal Taneera
Advances in Biomedical and Health Sciences.2024; 3(1): 5. CrossRef - Dietary Tomato Pectin Attenuates Hepatic Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in High-Fat-Diet Mice by Regulating the PI3K/AKT Pathway
Jing Sun, Kongyan Wu, Pan Wang, Yubin Wang, Dan Wang, Wenting Zhao, Yuanyuan Zhao, Chunhong Zhang, Xiaoyan Zhao
Foods.2024; 13(3): 444. CrossRef - Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. and Cuscuta chinensis Lam. extract relieves insulin resistance via PI3K/Akt signalling in diabetic Drosophila
Yinghong Li, Ye Xu, Biwei Zhang, Zhigang Wang, Leilei Ma, Longyu Sun, Xiuping Wang, Yimin Lin, Ji-an Li, Chenxi Wu
Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ketogenic diet ameliorates high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mouse skeletal muscle by alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress
Qin Ma, Lincheng Jiang, Yuehua You, Hongbing Ni, Li Ma, Xiaojing Lin, Zhuyun Wang, Weiyan Yan, Xiaoqiu Xiao, Xinyu Li, Jibin Li
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2024; 702: 149559. CrossRef - Brain insulin resistance and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review
Luis Jesuino de Oliveira Andrade, Luís Matos de Oliveira, Alcina Maria Vinhaes Bittencourt, Letícia Góes de Carvalho Lourenço, Gabriela Correia Matos de Oliveira
Dementia & Neuropsychologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Poorly controlled glycemia and worse beta cell function associate with higher resting and total energy expenditure in adults with obesity and type 2 diabetes: A doubly labeled water study
Kate Lillegard, John A. Del Castillo, Heidi J. Silver
Clinical Nutrition.2024; 43(3): 729. CrossRef - Gut microbiota in insulin resistance: a bibliometric analysis
Weiwei Tian, Li Liu, Ruirui Wang, Yunyun Quan, Bihua Tang, Dongmei Yu, Lei Zhang, Hua Hua, Junning Zhao
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of the triglyceride glucose index with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a general population of Iranian adults
Ghazaal Alavi Tabatabaei, Noushin Mohammadifard, Hamed Rafiee, Fatemeh Nouri, Asieh Maghami mehr, Jamshid Najafian, Masoumeh Sadeghi, Maryam Boshtam, Hamidreza Roohafza, Fahimeh Haghighatdoost, Marzieh Taheri, Nizal Sarrafzadegan
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Cells Associated with Insulin Resistance
Leszek Szablewski
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 2397. CrossRef - Evaluación de la resistencia a la insulina mediante el índice HOMA: un enfoque comparativo entre mujeres premenopáusicas y posmenopáusicas
Carlos Fernando Yauli Flores, Ericka Jazmín Tubón Luisa
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología.2024; 4: 729. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers
Leszek Szablewski
Current Oncology.2024; 31(2): 998. CrossRef - Muscle strength and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic-associated fatty liver disease
Xuan-Yu Hao, Kai Zhang, Xing-Yong Huang, Fei Yang, Si-Yu Sun
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(7): 636. CrossRef - Outcomes With Finerenone in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes by Baseline Insulin Resistance
Thomas Ebert, Stefan D. Anker, Luis M. Ruilope, Paola Fioretto, Vivian Fonseca, Guillermo E. Umpierrez, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Robert Lawatscheck, Charlie Scott, Katja Rohwedder, Peter Rossing
Diabetes Care.2024; 47(3): 362. CrossRef - Influence of Obesity and Insulin Resistance on the Reproductive Outcome of Iraqi Women Undergoing Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
Sundus Ali Dawood, Hayder Ali Lafta Mossa, Mufeeda Ali Jwad
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2024; 6(1): 179. CrossRef - Metabolic memory: mechanisms and diseases
Hao Dong, Yuezhang Sun, Lulingxiao Nie, Aimin Cui, Pengfei Zhao, Wai Keung Leung, Qi Wang
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of preoperative oral carbohydrates on insulin resistance in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled trial
Xiaohan Wang, Jingwen Zhuang, Jianxin Cheng, Zeyang Wang, Jingyi Sheng, Shanshan Guo, Rui Wang, Zhiping Wang
Langenbeck's Archives of Surgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Beta‐Cell Tipe1 Orchestrates Insulin Secretion and Cell Proliferation by Promoting Gαs/cAMP Signaling via USP5
Lu Ding, Yang Sun, Yan Liang, Jie Zhang, Zhendong Fu, Caiyue Ren, Pengfei Li, Wen Liu, Rong Xiao, Hao Wang, Zhaoying Zhang, Xuetian Yue, Chunyang Li, Zhuanchang Wu, Yuemin Feng, Xiaohong Liang, Chunhong Ma, Lifen Gao
Advanced Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome awareness in the general Korean population: results from a nationwide survey
Hyun-Jin Kim, Mi-Seung Shin, Kyung-Hee Kim, Mi-Hyang Jung, Dong-Hyuk Cho, Ju-Hee Lee, Kwang Kon Koh
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 39(2): 272. CrossRef - Pregnane X receptor knockout mitigates weight gain and hepatic metabolic dysregulation in female C57BL/6 J mice on a long-term high-fat diet
Lidya H. Gebreyesus, Sora Choi, Prince Neequaye, Mattia Mahmoud, Mia Mahmoud, Malvin Ofosu-Boateng, Elizabeth Twum, Daniel O. Nnamani, Lijin Wang, Nour Yadak, Sujoy Ghosh, Frank J. Gonzalez, Maxwell A. Gyamfi
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 173: 116341. CrossRef - TyG-GGT is a Reliable Non-Invasive Predictor of Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Overweight or Obese Individuals
Lei Jin, Jing Gu, Zhe Zhang, Cheng-Fei Du, Fei-Qi Xu, Xiao-Kun Huang, Zhen-Yu Gao, Ying Li, Li-Li Yu, Xin Zhang, Guo-Qing Ru, Jun-Wei Liu, Lei Liang, Xiao-Dong Sun, Zun-Qiang Xiao
Obesity Surgery.2024; 34(4): 1333. CrossRef - Excess homocysteine inhibits pancreatic β-cell secretory function by repressing Zbtb20 expression
Tianqi Ding, Bo Wen, Jian Chen, Wenbin Chu, Rong Fan, Xuewei Chen
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2024; 586: 112195. CrossRef - Testosterone therapy reduces insulin resistance in men with adult‐onset testosterone deficiency and metabolic syndrome. Results from the Moscow Study, a randomized controlled trial with an open‐label phase
Yuliya Tishova, Svetlana Kalinchenko, George Mskhalaya, Geoffrey Hackett, Mark Livingston, Carola König, Richard Strange, Michael Zitzmann, Amar Mann, Amro Maarouf, Sudarshan Ramachandran
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative contributing factors and the remission of diabetes after metabolic surgery: the mediating role of preoperative triglyceride
Lijuan Niu, Liqian Mu, Runda Wu, Shan Tong, Zhongqi Mao, Yi Yang, Jun Yin
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanisms of Action of Potentilla discolor Bunge in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification in Drosophila
Yinghong Li, Fanwu Wu, Jianbo Zhang, Ye Xu, Hong Chang, Yueyue Yu, Chunhua Jiang, Xiujuan Gao, Huijuan Liu, Zhen Chen, Chenxi Wu, Ji-An Li
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2024; Volume 18: 747. CrossRef - Diabetes and diabetic associative diseases: An overview of epigenetic regulations of TUG1
Mohammed Ageeli Hakami
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2024; 31(5): 103976. CrossRef - Sleep quality of patients with diabetes mellitus: association with anxiety trait and state
Lidiane Bernardes Faria Vilela, Larissa Cristina dos Santos Camargos, Guilherme Rocha Rodrigues, Adelzí Auto Alves Júnior, Renato Canevari Dutra da Silva, Elton Brás Camargo Júnior
Revista Gaúcha de Enfermagem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Qualidade do sono de pacientes com diabetes mellitus: associação com ansiedade traço e estado
Lidiane Bernardes Faria Vilela, Larissa Cristina dos Santos Camargos, Guilherme Rocha Rodrigues, Adelzí Auto Alves Júnior, Renato Canevari Dutra da Silva, Elton Brás Camargo Júnior
Revista Gaúcha de Enfermagem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of the triglyceride-glucose index with severity of coronary stenosis and in-hospital mortality in patients with acute ST elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention: a multicentre retrospective analysis cohort stud
Xin Lu, Xin Lin, Yingying Cai, Xiaoxiao Zhang, Haoyu Meng, Weiwei Chen, Peng Yu, Xiaohu Chen
BMJ Open.2024; 14(3): e081727. CrossRef - Effects of a Diabetic Microenvironment on Neurodegeneration: Special Focus on Neurological Cells
Vishal Chavda, Dhananjay Yadav, Snehal Patel, Minseok Song
Brain Sciences.2024; 14(3): 284. CrossRef - Mechanisms of body fat distribution and gluteal-femoral fat protection against metabolic disorders
Maha Alser, Khaled Naja, Mohamed A. Elrayess
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulation of lipid metabolism by E3 ubiquitin ligases in lipid-associated metabolic diseases
Yuanming Zou, Ying Zhang, Mohan Li, Kexin Cao, Chunyu Song, Zhaobo Zhang, Kexin Cai, Danxi Geng, Shuxian Chen, Yanjiao Wu, Naijin Zhang, Guozhe Sun, Jing Wang, Yixiao Zhang, Yingxian Sun
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2024; 265: 130961. CrossRef - METS-IR and all-cause mortality in Korean over 60 years old: Korean genome and epidemiology study-health examinees (KoGES-HEXA) cohorts
Ha Eun Ryu, Dong Hyuk Jung, Seok-Jae Heo, Byoungjin Park, Yong Jae Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of vitamin family members on insulin resistance and diabetes complications
Hong-Jin Chen, Min Wang, Ding-Min Zou, Gui-You Liang, Si-Yuan Yang
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(3): 568. CrossRef - Alleviative effects of the parthenolide derivative ACT001 on insulin resistance induced by sodium propionate combined with a high-fat diet and its potential mechanisms
Qian Yu, Xiang Zuo, Huijuan Bai, Shuhui Zhang, Jialu Luan, Qili Zhao, Xin Zhao, Xizeng Feng
European Journal of Pharmacology.2024; 971: 176529. CrossRef - The genetic causal relationship between type 2 diabetes, glycemic traits and venous thromboembolism, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study
Mingyi Yang, Xianjie Wan, Yani Su, Ke Xu, Pengfei Wen, Binfei Zhang, Lin Liu, Zhi Yang, Peng Xu
Thrombosis Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Transgenerational inheritance of insulin resistance in offspring of white rice-fed female fruit flies
Kehinde Ahmad Adeshina, Kasimu Ghandi Ibrahim, Murtala Bello Abubakar, Mustapha Umar Imam
Scientific African.2024; 24: e02208. CrossRef - PPARβ/δ as a promising molecular drug target for liver diseases: A focused review
Xin Meng, Lin Wang, Yan-Chao Du, Dong Cheng, Tao Zeng
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology.2024; 48(6): 102343. CrossRef - EPA and DHA Differentially Improve Insulin Resistance by Reducing Adipose Tissue Inflammation — Targeting GPR120/PPARγ Pathway
Xian Yang, Xudong Li, Manjiang Hu, Jie Huang, Siyan Yu, Huanting Zeng, Limei Mao
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2024; : 109648. CrossRef - The impact of diabetes mellitus on the development of psychiatric and neurological disorders
Olivia Kelly, Jillian Sullivan, Natalie Carris, Samantha Geci, Athena Martinez, Varvara Liashenko, James Colvin, Emily Misko, Gary Vanderlaan, He Liu, Prasad S. Dalvi
Brain Disorders.2024; 14: 100135. CrossRef - Oligonucleotide therapies for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Sixu Li, Feng Xiong, Songbo Zhang, Jinghua Liu, Guangping Gao, Jun Xie, Yi Wang
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids.2024; 35(2): 102184. CrossRef - The Contribution of Type 2 Diabetes to Parkinson’s Disease Aetiology
Samo Ribarič
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(8): 4358. CrossRef - Dose-response associations of triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and triglyceride–glucose index with arterial stiffness risk
Wenkai Zhang, Weifeng Huo, Huifang Hu, Tianze Li, Lijun Yuan, Jinli Zhang, Yifei Feng, Yuying Wu, Xueru Fu, Yamin Ke, Mengmeng Wang, Longkang Wang, Yaobing Chen, Yajuan Gao, Xi Li, Liang Sun, Jinyuan Pang, Zeqiang Zheng, Fulan Hu, Ming Zhang, Yu Liu, Dong
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Unraveling PCOS: Exploring its causes and diagnostic challenges
Mohd Altaf Dar, Mudasir Maqbool, Zulfkar Qadrie, Irfat Ara, Afshana Qadir
Open Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Diabetic
Retinopathy: A Meta-Analysis
Lanchu Yu, Bingqing Li
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Klotho and insulin resistance: Insights from a cross-sectional analysis
Laisha Yan, Xiaoyan Hu, Shanshan Wu, Shunying Zhao
Medicine.2024; 103(17): e37971. CrossRef - Research Progress of Correlation between Triglyceride Glucose Index and Kidney Disease
伊琳 黄
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(04): 2137. CrossRef - Oxygen-Dependent Aspects of Asprosin Action
V. V. Zinchuk, J. S. O. Al-Jebur
Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology.2024; 60(2): 818. CrossRef - Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance in Adult Patients with Acne: Association with Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Acne Severity
Ana Cecília Arcanjo Carneiro, Jozélio Freire de Carvalho, Daniel Coelho de Sá, Carlos Ewerton Maia Rodrigues
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2023; 21(2): 109. CrossRef - Metabolic and Genetic Association of Vitamin D with Calcium Signaling and Insulin Resistance
Najeebul Tarfeen, Khair Ul Nisa, Mir Bilal Ahmad, Ajaz Ahmad Waza, Bashir Ahmad Ganai
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry.2023; 38(4): 407. CrossRef - Tinosporaside from Tinospora cordifolia Encourages Skeletal Muscle Glucose Transport through Both PI-3-Kinase- and AMPK-Dependent Mechanisms
Akansha Mishra, Khushbu Sharma, Jyotsana Pandey, Kapil Dev, Sleman Kadan, Mahendra Sahai, Ishbal Ahmad, Arvind K. Srivastava, Akhilesh K. Tamrakar, Hilal Zaid, Rakesh Maurya
Molecules.2023; 28(2): 483. CrossRef - Pathophysiology of obesity and its associated diseases
Xin Jin, Tingting Qiu, Li Li, Rilei Yu, Xiguang Chen, Changgui Li, Christopher G. Proud, Tao Jiang
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B.2023; 13(6): 2403. CrossRef - Hypertension, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and p53 mutations negatively correlate with metastatic colorectal cancer patients’ survival
Alessandro Ottaiano, Mariachiara Santorsola, Luisa Circelli, Francesco Perri, Marco Cascella, Francesco Sabbatino, Maurizio Capuozzo, Vincenza Granata, Silvia Zappavigna, Angela Lombardi, Marianna Scrima, Nadia Petrillo, Monica Ianniello, Marika Casillo,
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose index and poor sleep patterns in non-diabetic adults: Evidence from NHANES 2005–2016
Chi-Feng Liu, Li-Wei Chien
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Polyphenol-Rich Extract of Fermented Chili Pepper Alleviates Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells via Regulating INSR, PTP1B, PPAR-γ, and AMPK Pathways
Tao Wang, Meiqi Li, Shengbao Cai, Linyan Zhou, Xiaosong Hu, Junjie Yi
Fermentation.2023; 9(2): 84. CrossRef - Effects of preoperative oral enzyme-hydrolyzed rice flour solution on gastric emptying and insulin resistance in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a prospective randomized controlled trial
Yang Yuan, Guangjun Shi, Huailong Chen, Mingshan Wang, Haofei Liu, Xiao Zhang, Bin Wang, Gaofeng Zhang, Lixin Sun
BMC Anesthesiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pathophysiology of polycystic ovary syndrome
Hiroshi Koike, Miyuki Harada, Akari Kusamoto, Zixin Xu, Tsurugi Tanaka, Nanoka Sakaguchi, Chisato Kunitomi, Jerilee M. K. Azhary, Nozomi Takahashi, Yoko Urata, Yutaka Osuga
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance (METS-IR) Predicts Cardiovascular Disease and Its Subtypes in Patients with Hypertension and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Wenbo Yang, Xintian Cai, Junli Hu, Wen Wen, Heizhati Mulalibieke, Xiaoguang Yao, Ling Yao, Qing Zhu, Jing Hong, Qin Luo, Shasha Liu, Nanfang Li
Clinical Epidemiology.2023; Volume 15: 177. CrossRef - Sperm DNA damage: The possible link between obesity and male infertility, an update of the current literature
Andrew Peel, Anmol Saini, Joshua C. Deluao, Nicole O. McPherson
Andrology.2023; 11(8): 1635. CrossRef - Glucose Homeostasis, Diabetes Mellitus, and Gender-Affirming Treatment
Charalampos Milionis, Ioannis Ilias, Evangelia Venaki, Eftychia Koukkou
Biomedicines.2023; 11(3): 670. CrossRef - From Metabolic Syndrome to Type 2 Diabetes in Youth
Dario Iafusco, Roberto Franceschi, Alice Maguolo, Salvatore Guercio Nuzio, Antonino Crinò, Maurizio Delvecchio, Lorenzo Iughetti, Claudio Maffeis, Valeria Calcaterra, Melania Manco
Children.2023; 10(3): 516. CrossRef - Kcnma1 is involved in mitochondrial homeostasis in diabetes‐related skeletal muscle atrophy
Shan‐Yan Gao, Yong‐Ping Liu, Ri Wen, Xin‐Mei Huang, Ping Li, Yu‐Hang Yang, Ni Yang, Tie‐Ning Zhang
The FASEB Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Capsaicin and Zinc Signalling Pathways as Promising Targets for Managing Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
Parisa Vahidi Ferdowsi, Kiran D. K. Ahuja, Jeffrey M. Beckett, Stephen Myers
Molecules.2023; 28(6): 2861. CrossRef - Mouse Models with SGLT2 Mutations: Toward Understanding the Role of SGLT2 beyond Glucose Reabsorption
Keiko Unno, Kyoko Taguchi, Yoshiichi Takagi, Tadashi Hase, Shinichi Meguro, Yoriyuki Nakamura
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6278. CrossRef - Association between triglyceride-glucose index and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with psoriatic arthritis
Wenhui Xie, Wei Bian, Zhibo Song, Xuerong Deng, Jiahao Qu, Zhuoli Zhang
Rheumatology.2023; 62(11): 3584. CrossRef - The relationship between HMGB1 and autophagy in the pathogenesis of diabetes and its complications
Kun Yang, Feng Cao, Weili Wang, Zhenyu Tian, Lu Yang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of long-term triglyceride-glucose index level and change with the risk of cardiometabolic diseases
Wenqi Xu, Haiyan Zhao, Lishu Gao, Lu Guo, Jianrong Liu, Haixia Li, Junyan Sun, Aijun Xing, Shuohua Chen, Shouling Wu, Yuntao Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - White Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: Pathophysiology and Emergent Measurements
Natalia Santillana, Camila Astudillo-Guerrero, Amanda D’Espessailles, Gonzalo Cruz
Nutrients.2023; 15(7): 1722. CrossRef - Soy protein compared with whey protein ameliorates insulin resistance by regulating lipid metabolism, AMPK/mTOR pathway and gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice
Andong Ji, Wei Chen, Chang Liu, Tianyu Zhang, Runjia Shi, Xinqi Wang, Huina Xu, Duo Li
Food & Function.2023; 14(12): 5752. CrossRef - Hepatic Insulin Resistance Model in the Male Wistar Rat Using Exogenous Insulin Glargine Administration
Victor Enrique Sarmiento-Ortega, Diana Moroni-González, Alfonso Diaz, Miguel Ángel García-González, Eduardo Brambila, Samuel Treviño
Metabolites.2023; 13(4): 572. CrossRef - Pathophysiological Effects of Contemporary Lifestyle on Evolutionary-Conserved Survival Mechanisms in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Jim Parker
Life.2023; 13(4): 1056. CrossRef - Metabolic dysfunction correction as a method of restoring the function of the reproductive system in women
G. E. Chernukha, V. A. Pronina
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; (5): 90. CrossRef - Associations between TyG-BMI and normal-high blood pressure values and hypertension: cross-sectional evidence from a non-diabetic population
Nan Peng, Maobin Kuang, Yi Peng, Hang Yu, Shuhua Zhang, Guobo Xie, Guotai Sheng, Yang Zou
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Inverse Correlation of Superoxide Dismutase and Catalase with Type 2 Diabetes among Rural Thais
Natnicha Promyos, Pornpimol Panprathip Phienluphon, Naruemon Wechjakwen, Jirayu Lainampetch, Pattaneeya Prangthip, Karunee Kwanbunjan
Nutrients.2023; 15(9): 2071. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - Oxygen-binding properties of blood in insulin resistance with different asprosin content
V.V. Zinchuk, J.S.O. Al-Jebur, N.V. Glutkina
Biomeditsinskaya Khimiya.2023; 69(2): 133. CrossRef - Associations between basal metabolic rate and insulin resistance in non-diabetic obese adults: Evidence from NHANES 2011–2018
Hai Guo, Dilihumaier Duolikun, Qiaoling Yao
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023; 43(6): 946. CrossRef - Biomarkers of Spinal Cord Injury in Patients Undergoing Complex Endovascular Aortic Repair Procedures—A Narrative Review of Current Literature
Anna Sotir, Johannes Klopf, Christine Brostjan, Christoph Neumayer, Wolf Eilenberg
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1317. CrossRef - The Hypoglycemic Activities and Underlying Mechanisms of Two Saponins‐Rich Components from Fried Ziziphus jujuba Mill. Kernel
Yi‐Meng Li, Ke‐xin Hao, Hong Xie, Jian‐Guo Jiang
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term outcomes and potential mechanisms of offspring exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia
Yi-Shang Yan, Chun Feng, Dan-Qing Yu, Shen Tian, Yin Zhou, Yi-Ting Huang, Yi-Ting Cai, Jian Chen, Miao-Miao Zhu, Min Jin
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Function of MondoA and ChREBP Nutrient—Sensing Factors in Metabolic Disease
Byungyong Ahn
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(10): 8811. CrossRef - An Update on the Molecular and Cellular Basis of Pharmacotherapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mohamed Omer Mahgoub, Ifrah Ismail Ali, Jennifer O. Adeghate, Kornélia Tekes, Huba Kalász, Ernest A. Adeghate
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(11): 9328. CrossRef - Study on the therapeutic effect and mechanism of Tangningtongluo Tablet on diabetic mice
Zengxiaorui Cai, Xiangka Hu, Liuming Gui, Mushuang Qi, Wanjun Zhu, Ying Ren, Shuyu Yang, Chunmei Dai
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(8): 108523. CrossRef - A Descriptive Review of the Action Mechanisms of Berberine, Quercetin and Silymarin on Insulin Resistance/Hyperinsulinemia and Cardiovascular Prevention
Paolo Bellavite, Serafino Fazio, Flora Affuso
Molecules.2023; 28(11): 4491. CrossRef - Relationships of neck circumference and abdominal obesity with insulin resistance considering relative handgrip strength in middle-aged and older individuals
Kayoung Lee
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2023; 114: 105097. CrossRef - Acute exposure to realistic concentrations of Bisphenol-A trigger health damage in fish: Blood parameters, gene expression, oxidative stress
Gustavo Axel Elizalde-Velázquez, Leobardo Manuel Gómez-Oliván, Selene Elizabeth Herrera-Vázquez, Karina Elisa Rosales-Pérez, Nely SanJuan-Reyes, Sandra García-Medina, Marcela Galar-Martínez
Aquatic Toxicology.2023; 261: 106610. CrossRef - Gαi‐coupled GPR41 activation increases Ca2+ influx in C2C12 cells and shows a therapeutic effect in diabetic animals
Do‐Hyung Lee, Kyung‐Sun Heo, Chang‐Seon Myung
Obesity.2023; 31(7): 1871. CrossRef - Physical inactivity induces insulin resistance in plantaris muscle through protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B activation in mice
Saori Kakehi, Yoshifumi Tamura, Shin-ichi Ikeda, Naoko Kaga, Hikari Taka, Yuya Nishida, Ryuzo Kawamori, Hirotaka Watada
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance: A Review of Complex Interlinks
Thomas M. Barber, Stefan Kabisch, Andreas F. H. Pfeiffer, Martin O. Weickert
Metabolites.2023; 13(6): 757. CrossRef - Metabolic Markers Associated with Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Induced by High-Fat Diet and Single Low Dose Streptozotocin in Rats
Maria Andonova, Petko Dzhelebov, Krastina Trifonova, Penka Yonkova, Nikola Kostadinov, Krasimira Nancheva, Veselin Ivanov, Krasimira Gospodinova, Nikola Nizamov, Ilia Tsachev, Chavdar Chernev
Veterinary Sciences.2023; 10(7): 431. CrossRef - Research Progress Into Adipose Tissue Macrophages and Insulin Resistance
M Fu, L Yang, H Wang, Y Chen, X Chen, Q Hu, H Sun
Physiological Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of aerobic exercises in prediabetes patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yifei Wang, Honglei Li, Dongxue Yang, Mengzhao Wang, Yanbai Han, Hongli Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of C-peptide with cardiometabolic parameters in women aged 25–44 years with different metabolic phenotypes
S. V. Mustafina, V. I. Alferova, L. V. Shcherbakova, E. V. Kashtanova, D. V. Denisova
Ateroscleroz.2023; 19(2): 115. CrossRef - Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Therapy as a new Treatment Option for Diabetes Mellitus
Agnieszka Mikłosz, Adrian Chabowski
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(8): 1889. CrossRef - Anthropometric Indices With Insulin Resistance in Obese Patients: A Literature Review
Khalid Khan, Anil Wanjari, Sourya Acharya, Sabiha Quazi
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Preventive and therapeutic effects of natural products and herbal extracts on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Yiming Cao, Xiaoxue Fang, Mingyang Sun, Yegang Zhang, Mengyao Shan, Xintian Lan, Difu Zhu, Haoming Luo
Phytotherapy Research.2023; 37(9): 3867. CrossRef - Tuina (Chinese massage) for insulin resistance and sensitivity: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis of animal and human studies
Zhixuan Zhao, Jun Yan, Yuxin Ding, Yingji Wang, Yan Li, Ricardo Ney Oliveira Cobucci
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(7): e0288414. CrossRef - Rubus chingii Hu relieved the polycystic ovary syndrome with enhanced insulin sensitivity through inhibiting TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling
Huizhen Li, Yongping Li, Ying Zhang, Li Tong, Yuping Sa, Wenping Sun
Gynecological Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Research Role of Triglyceride Glucose Index in Pre-Type 2 Diabetes
士博 徐
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(07): 11762. CrossRef - Underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of genistein in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and related complications
Tao Jiang, Yuhe Dong, Wanying Zhu, Tong Wu, Linyan Chen, Yuantong Cao, Xi Yu, Ye Peng, Ling Wang, Ying Xiao, Tian Zhong
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Gentiopicroside modulates glucose homeostasis in high-fat-diet and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice
Xing Wang, Dongmei Long, Xianghong Hu, Nan Guo
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Review of the Case Reports on Metformin, Sulfonylurea, and Thiazolidinedione Therapies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Elis Susilawati, Jutti Levita, Yasmiwar Susilawati, Sri Adi Sumiwi
Medical Sciences.2023; 11(3): 50. CrossRef - Effects of AIM2 and IFI16 on Infectious Diseases and Inflammation
Zhen Fan, Rui Chen, Wen Yin, Xiaomei Xie, Shan Wang, Chunbo Hao
Viral Immunology.2023; 36(7): 438. CrossRef - PREDICTING PROGRESSION TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A 3-YEAR FOLLOW-UP STUDY EXAMINING RISK FACTORS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES IN PATIENTS WITH PREDIABETES
Taras I. Griadil, Mykhaylo V. Bychko, Mykhaylo M. Hechko, Ksenia I. Chubirko, Ivan V. Chopey
Polski Merkuriusz Lekarski.2023; 51(3): 245. CrossRef - GABA Prevents Age-Related Sarcopenic Obesity in Mice with High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity
Heegu Jin, Hyun-Ji Oh, Boo-Yong Lee
Cells.2023; 12(17): 2146. CrossRef - Bio-Hacking Better Health—Leveraging Metabolic Biochemistry to Maximise Healthspan
Isabella D. Cooper, Yvoni Kyriakidou, Lucy Petagine, Kurtis Edwards, Bradley T. Elliott
Antioxidants.2023; 12(9): 1749. CrossRef - Hyperinsulinemia Impairs Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis of the Insulin Receptor and Activation of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Brain Endothelial Cells
Stephanie G. DiLucia, B. Jacob Kendrick, Catrina Sims-Robinson
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(19): 14670. CrossRef - Validation of a physiological type 2 diabetes model in human periodontal ligament stem cells
Dongqing Ai, Yuanyuan Yin, Xuyun Xia, Sihan Yang, Yu Sun, Jie Zhou, Han Qin, Xiaohui Xu, Jinlin Song
Oral Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Flavonoids from Lophatherum gracile Brongn. Ameliorate Liver Damages in High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice by Regulating PI3K/AKT and NF-Kappa B Pathways
Jian-Hua Zheng, Song-Xia Lin, Xiao-Yi Li, Chun-Yan Shen, Shao-Wei Zheng, Wen-Bin Chen, Walid Elfalleh
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Asprosin, a novel glucogenic adipokine implicated in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hongcui Diao, Xue Li, Yeqiu Xu, Xiuli Xing, Shuguang Pang
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(11): 108614. CrossRef - Impact of Fixed Combination of Metformin and Pioglitazone on Insulin Resistance of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Results of a Randomized Open-Label Study
Rui Sun, Lu Yuan, Yun Shen, Ziyang Shen, Bo Ding, Jianhua Ma
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2911. CrossRef - Integrating network analysis and experimental validation to reveal the mechanism of pinocembrin in alleviating high glucose and free fatty acid-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells
Kun Hu, Yongjin Sun, Jie Wang, Shaojun Wu, Jie Ren, Dan Su, Lidan Tang, Jinhong Gong, Hufeng Fang, Shan Xu, Hao Yang
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 110: 105879. CrossRef - A Literature Review and a Proposed Classification of the Relationships between Ovulatory Infertility and Lifestyle Factors Based on the Three Groups of Ovulation Disorders Classified by WHO
Magdalena Skowrońska, Michał Pawłowski, Robert Milewski
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(19): 6275. CrossRef - Targeting of insulin receptor endocytosis as a treatment to insulin resistance
Bryce Tim, Valentina L. Kouznetsova, Santosh Kesari, Igor F. Tsigelny
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(11): 108615. CrossRef - A U-shaped association between the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and the risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese men with normal glycemic levels: a population-based longitudinal cohort study
Bei Song, Kun Wang, Weilin Lu, Xiaofang Zhao, Tianci Yao, Ting Liu, Guangyu Gao, Haohui Fan, Chengyun Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of triglyceride-glucose index levels with gestational diabetes mellitus in the US pregnant women: a cross-sectional study
Yan Zeng, Li Yin, Xiaoping Yin, Danqing Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The protective role of resveratrol in diabetic wound healing
Minglei Bi, Yonghong Qin, Lerong Wang, Jin Zhang
Phytotherapy Research.2023; 37(11): 5193. CrossRef - Correlation between alternative insulin resistance indexes and diabetic kidney disease: a retrospective study
Xiaodie Mu, Aihua Wu, Huiyue Hu, Min Yang, Hua Zhou
Endocrine.2023; 84(1): 136. CrossRef - Enhancing Muscle Intracellular Ca2+ Homeostasis and Glucose Uptake: Passive Pulsatile Shear Stress Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes
Arkady Uryash, Jordan Umlas, Alfredo Mijares, Jose A. Adams, Jose R. Lopez
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2596. CrossRef - Review of Related Research on Type 2 Diabetes Related Macroangiopathy
珊珊 李
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(09): 15001. CrossRef - Association between lipoprotein(a) and insulin resistance in Chinese adults: results from the China health and nutrition survey
Heng Wang, Jia-Li Fan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between the Triglyceride–Glucose Index and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in patients with Atrial Fibrillation
Xiaozhong Li, Fenfang Zhan, Tian Peng, Zhen Xia, Juxiang Li
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resveratrol as a potential protective compound against skeletal muscle insulin resistance
Arash Bahramzadeh, Kosar Bolandnazar, Reza Meshkani
Heliyon.2023; 9(11): e21305. CrossRef - The Potential Role of C-Reactive Protein in Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Aging
Zheng Ding, Yuqiu Wei, Jing Peng, Siyu Wang, Guixi Chen, Jiazeng Sun
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2711. CrossRef - Obesity and Bone Mineral Density Protection Paradox in Chronic Kidney Disease: Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine as a Piece of the Puzzle?
Abdelaziz Ghanemi, Fabrice Mac-Way
Life.2023; 13(11): 2172. CrossRef - Correlation of Lipid Profile and Apolipoprotein B/A-I Ratio with Insulin Resistance in Non-Diabetes Mellitus Subjects
Andi Heriadi Palloge, Liong Boy Kurniawan, Yuyun Widyaningsih, Husaini Umar, Nurahmi Nurahmi, Andi Alfian Zainuddin
INDONESIAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY AND MEDICAL LABORATORY.2023; 30(1): 6. CrossRef - Endothelial progenitor cells as biomarkers of diabetes-related cardiovascular complications
Josefa Benítez-Camacho, Antonio Ballesteros, Lucía Beltrán-Camacho, Marta Rojas-Torres, Antonio Rosal-Vela, Margarita Jimenez-Palomares, Ismael Sanchez-Gomar, Mª Carmen Durán-Ruiz
Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of ginseng peptides on the hypoglycemic activity and gut microbiota of a type 2 diabetes mellitus mice model
Caijing Han, Xiaoting Kong, Xiaohong Xia, Xinyu Huang, Zhaojie Mao, Jiaxin Han, Fuyan Shi, Yaohui Liang, Anning Wang, Fengxiang Zhang
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 111: 105897. CrossRef - Effects of theasaponin E1 on the regulationglucose uptake of C2C12 myoblasts PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
Ming Zhang, Zhiyun Chen, Di Tian, Zaiqiao Li, Shaning Wang, Yujie Huo, Ling Song, Juan Lu, Jun Sheng, Xu Ji, Xiao Ma
CyTA - Journal of Food.2023; 21(1): 682. CrossRef - Efficacy and underlying mechanisms of berberine against lipid metabolic diseases: a review
Yajie Cai, Qiaoning Yang, Yanqiao Yu, Furong Yang, Ruina Bai, Xiaodi Fan
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipocyte-derived exosomal miR-22-3p modulated by circadian rhythm disruption regulates insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle cells
Haohao Zhang, Xiaoning Zhang, Saifei Wang, Lu Zheng, Hengru Guo, Yanqi Ren, Bo Qiao, Jing Wu, Di Zhao, Lijun Xu, Shengnan Ma, Xiao Hao, Yushan Yan
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2023; 299(12): 105476. CrossRef - Total Astragalus saponins can reverse type 2 diabetes mellitus-related intestinal dysbiosis and hepatic insulin resistance in vivo
Leilei Ma, Xiaojin La, Biwei Zhang, Wenxuan Xu, Chunyu Tian, Qianru Fu, Meng Wang, Chenxi Wu, Zhen Chen, Hong Chang, Ji-an Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Interplay between Vitamin D and Adipose Tissue: Implications for Adipogenesis and Adipose Tissue Function
Shiqi Lu, Zhen-Bo Cao
Nutrients.2023; 15(22): 4832. CrossRef - Alanine aminotransferase to high- density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is positively correlated with the occurrence of diabetes in the Chinese population: a population-based cohort study
Shiming He, Changhui Yu, Maobin Kuang, Jiajun Qiu, Ruijuan Yang, Shuhua Zhang, Guotai Sheng, Yang Zou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between the metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) index and urinary incontinence in the United States: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001–2018
Shangqi Cao, Linghao Meng, Lede Lin, Xu Hu, Xiang Li
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipose Tissue, Non-Communicable Diseases, and Physical Exercise: An Imperfect Triangle
Francisco A. Monsalve, Fernando Delgado-López, Barbra Fernández-Tapia, Daniel R. González
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(24): 17168. CrossRef - Risk of metabolic abnormalities in osteoarthritis: a new perspective to understand its pathological mechanisms
Guizheng Wei, Ke Lu, Muhammad Umar, Zhenglin Zhu, William W. Lu, John R. Speakman, Yan Chen, Liping Tong, Di Chen
Bone Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Sociodemographic Variables and Healthy Habits on the Values of Insulin Resistance Indicators in 386,924 Spanish Workers
Miguel Mestre Font, Carla Busquets-Cortés, José Ignacio Ramírez-Manent, Pilar Tomás-Gil, Hernán Paublini, Ángel Arturo López-González
Nutrients.2023; 15(24): 5122. CrossRef - Konjac flour-mediated gut microbiota alleviates insulin resistance and improves placental angiogenesis of obese sows
Deyuan Wu, Wenyu Xiong, Shuo Ma, Jinxi Luo, Hongxuan Ye, Shuangbo Huang, Fuyong Li, Xi’en Xiang, Qiling Chen, Binghui Gao, Jinping Deng, Yulong Yin, Chengquan Tan
AMB Express.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Physiological Adaptations to Life in Space: An Update
Isadora de Carvalho e Silva, Thais Russomano, Ricardo Alves Ferreira, Marli do Carmo Cupertino, Fabíola Alves Alcântara, Mauro Geller, Oswaldo Monteiro Del Cima, Rodrigo Siqueira-Batista
Journal of Aerospace Technology and Management.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood and Brain Metabolites after Cerebral Ischemia
Eva Baranovicova, Dagmar Kalenska, Peter Kaplan, Maria Kovalska, Zuzana Tatarkova, Jan Lehotsky
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(24): 17302. CrossRef - Key Therapeutic Targets to Treat Hyperglycemia-Induced Atherosclerosis Analyzed Using a Petri Net-Based Model
Agnieszka Rybarczyk, Dorota Formanowicz, Piotr Formanowicz
Metabolites.2023; 13(12): 1191. CrossRef - Exploration of the Mechanism of the Comorbidity Relationship between Alzheimer’s Disease and Diabetes Mellitus
涛 温
Medical Diagnosis.2023; 13(04): 440. CrossRef - Postbiyotikler ve İnsülin Direnci
Betül SARIDAĞ DEVRAN, Mendane SAKA
Van Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2023; 16(3): 268. CrossRef - The Anti-Diabetic Potential of Baicalin: Evidence from Rodent Studies
Tomasz Szkudelski, Katarzyna Szkudelska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 25(1): 431. CrossRef - Clinical application of Momordica charantia (Bitter Melon) for reducing blood sugar in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ashley Dahlquist, Dana Jandali, Mirielle C. Nauman, Jeremy J. Johnson, Sasho Stoleski
International Journal of Nutrition.2023; 7(4): 8. CrossRef - Alkaloids as Promising Agents for the Management of Insulin Resistance:
A Review
Ayoub Amssayef, Mohamed Eddouks
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2023; 29(39): 3123. CrossRef - Potential Mechanisms for How Long-Term Physical Activity May Reduce Insulin Resistance
Sindre Lee-Ødegård, Thomas Olsen, Frode Norheim, Christian Andre Drevon, Kåre Inge Birkeland
Metabolites.2022; 12(3): 208. CrossRef - Pathophysiological Link between Insulin Resistance and Adrenal Incidentalomas
Jordan A. Higgs, Alyssa P. Quinn, Kevin D. Seely, Zeke Richards, Shad P. Mortensen, Cody S. Crandall, Amanda E. Brooks
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4340. CrossRef - The Dose-Response Effects of Consuming High Fructose Corn Syrup-Sweetened Beverages on Hepatic Lipid Content and Insulin Sensitivity in Young Adults
Desiree M. Sigala, Bettina Hieronimus, Valentina Medici, Vivien Lee, Marinelle V. Nunez, Andrew A. Bremer, Chad L. Cox, Candice A. Price, Yanet Benyam, Yasser Abdelhafez, John P. McGahan, Nancy L. Keim, Michael I. Goran, Giovanni Pacini, Andrea Tura, Clau
Nutrients.2022; 14(8): 1648. CrossRef - Association of β-cell function and cognitive impairment in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism
Mengyi Guo, Jiaokun Jia, Jia Zhang, Mingyue Zhou, Anxin Wang, Shengyun Chen, Xingquan Zhao
BMC Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Insulin Resistance in Fueling NAFLD Pathogenesis: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Implications
Rossella Palma, Annamaria Pronio, Mario Romeo, Flavia Scognamiglio, Lorenzo Ventriglia, Vittorio Maria Ormando, Antonietta Lamazza, Stefano Pontone, Alessandro Federico, Marcello Dallio
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(13): 3649. CrossRef - Crosstalk between Schizophrenia and Metabolic Syndrome: The Role of Oxytocinergic Dysfunction
Kah Kheng Goh, Cynthia Yi-An Chen, Tzu-Hua Wu, Chun-Hsin Chen, Mong-Liang Lu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(13): 7092. CrossRef - TyG index is positively associated with risk of CHD and coronary atherosclerosis severity among NAFLD patients
Jianqi Zhao, Hongxuan Fan, Ting Wang, Bing Yu, Shaobin Mao, Xun Wang, Wenjing Zhang, Leigang Wang, Yao Zhang, Zhaoyu Ren, Bin Liang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association of Acute Phase Proteins in Stress and Inflammation-Induced T2D
Tammy Speelman, Lieke Dale, Ann Louw, Nicolette J. D. Verhoog
Cells.2022; 11(14): 2163. CrossRef - Probiotic Mechanisms Affecting Glucose Homeostasis: A Scoping Review
Maša Pintarič, Tomaž Langerholc
Life.2022; 12(8): 1187. CrossRef - Potential Molecular Targets of Oleanolic Acid in Insulin Resistance and Underlying Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review
Ángel Fernández-Aparicio, María Correa-Rodríguez, Jose M. Castellano, Jacqueline Schmidt-RioValle, Javier S. Perona, Emilio González-Jiménez
Antioxidants.2022; 11(8): 1517. CrossRef - Impact of Highly Saturated versus Unsaturated Fat Intake on Carbohydrate Metabolism and Vascular Reactivity in Rat
Youzan Ferdinand Djohan, Fabrice Raynaud, Karen Lambert, Jean-Paul Cristol, Charles Coudray, Christine Feillet-Coudray, Anne Virsolvy, Eric Badia, Néstor Gutiérrez-Méndez
Biochemistry Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Mitophagy: A potential therapeutic target for insulin resistance
Peng Ning, Xiaobo Jiang, Jing Yang, Jiaxing Zhang, Fan Yang, Hongyi Cao
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Higher neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with renal dysfunction and cardiac adverse remodeling in elderly with metabolic syndrome
Yuqi Zhu, Gang Li, Jari A. Laukkanen, Xing Song, Jing Zhang, Linping Wei, Xinrui Chen, Yufeng Li, Cheng Liu
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid droplet accumulation in β cells in patients with type 2 diabetes is associated with insulin resistance, hyperglycemia and β cell dysfunction involving decreased insulin granules
Tomomi Horii, Junji Kozawa, Yukari Fujita, Satoshi Kawata, Harutoshi Ozawa, Chisaki Ishibashi, Sho Yoneda, Takao Nammo, Jun-ichiro Miyagawa, Hidetoshi Eguchi, Iichiro Shimomura
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing the long non-coding RNA expression profiles of skeletal muscle and kidney tissues from patients with diabetes
Young-Kook Kim, Takahiro Nemoto
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0274794. CrossRef - The CCR2+ Monocyte Subsets Increase in Obese Boys but Not Girls with Abnormally High Carotid Intima-Media Thickness: A Pilot Study
María José Garcés-Hernández, Karen Pedraza-Escudero, Nayely Garibay-Nieto, Joselin Hernández-Ruiz, Jessica Lakshmi Prieto-Chávez, Lourdes Andrea Arriaga-Pizano, Eréndira Villanueva-Ortega, Galileo Escobedo, Aaron Noe Manjarrez-Reyna, Juan Carlos López-Alv
Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease.2022; 9(10): 330. CrossRef - Effect of honey bee venom on the histological changes of testes and hormonal disturbance in diabetic mice
Sattar J. J. AL-Shaeli, Talal Jabal Hussen, Ali M. Ethaeb
Veterinary World.2022; : 2357. CrossRef - Establishment and Validation of a New Predictive Model for Insulin Resistance based on 2 Chinese Cohorts: A Cross-Sectional Study
Shi Zhang, Xin-Cheng Wang, Jing Li, Xiao-He Wang, Yi Wang, Yan-Ju Zhang, Mei-Yang Du, Min-Ying Zhang, Jing-Na Lin, Chun-Jun Li, Aman Rajpal
International Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Zishen Pill alleviates diabetes in Db/db mice via activation of PI3K/AKT pathway in the liver
You Wu, Boju Sun, Xiaoyuan Guo, Lili Wu, Yaomu Hu, Lingling Qin, Tao Yang, Mei Li, Tianyu Qin, Miao Jiang, Tonghua Liu
Chinese Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Insulin and Pioglitazone on Protein Phosphatase 2A Interaction Partners in Primary Human Skeletal Muscle Cells Derived from Obese Insulin-Resistant Participants
Lana Alghanem, Xiangmin Zhang, Ruchi Jaiswal, Berhane Seyoum, Abdullah Mallisho, Zaher Msallaty, Zhengping Yi
ACS Omega.2022; 7(47): 42763. CrossRef - Dietary Plant Protein Intake Can Reduce Maternal Insulin Resistance during Pregnancy
Yuting Hong, Chen Yang, Jinjing Zhong, Yanmei Hou, Kui Xie, Linlin Wang
Nutrients.2022; 14(23): 5039. CrossRef - Preventive effect of probiotics supplementation on occurrence of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Azin Pakmehr, Hanieh-Sadat Ejtahed, Nooshin Shirzad, Mahboobeh Hemmatabadi, Sara Farhat, Bagher Larijani
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin resistance in ischemic stroke: Mechanisms and therapeutic approaches
Peng-Fei Ding, Hua-Sheng Zhang, Jie Wang, Yong-Yue Gao, Jian-Nan Mao, Chun-Hua Hang, Wei Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Long Noncoding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Insulin Resistance
Weili Yang, Yixiang Lyu, Rui Xiang, Jichun Yang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 16054. CrossRef - Predictability of HOMA-IR for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Early Pregnancy Based on Different First Trimester BMI Values
Yanbei Duo, Shuoning Song, Yuemei Zhang, Xiaolin Qiao, Jiyu Xu, Jing Zhang, Zhenyao Peng, Yan Chen, Xiaorui Nie, Qiujin Sun, Xianchun Yang, Ailing Wang, Wei Sun, Yong Fu, Yingyue Dong, Zechun Lu, Tao Yuan, Weigang Zhao
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 13(1): 60. CrossRef - MODERN CONCEPTS OF THE PATHOGENESIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
D.V. Kurkin, E.I. Morkovin, D.A. Bakulin, Yu.V. Gorbunova, A.V. Strygin, A.I. Robertus, I.E. Makarenko, V.B. Saparova, R.V. Drai, V.I. Petrov
Journal of Volgograd State Medical University.2022; 19(4): 34. CrossRef
- Diabetic Encephalopathy: Role of Oxidative and Nitrosative Factors in Type 2 Diabetes
- COVID-19
- Association of Metabolic Syndrome with COVID-19 in the Republic of Korea
- Woo-Hwi Jeon, Jeong-Yeon Seon, So-Youn Park, In-Hwan Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):427-438. Published online November 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0105
- 4,430 View
- 242 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is reportedly a crucial risk factor for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Since the epidemiological studies that examine this association are few and include small samples, we investigated the relationship between MetS and COVID-19 severity and death using a larger sample in the Republic of Korea.
Methods
We analyzed 66,321 patients, 4,066 of whom had COVID-19. We used chi-square tests to examine patients’ characteristics. We performed logistic regression analysis to analyze differences in COVID-19 infection and clinical outcomes according to the presence of MetS.
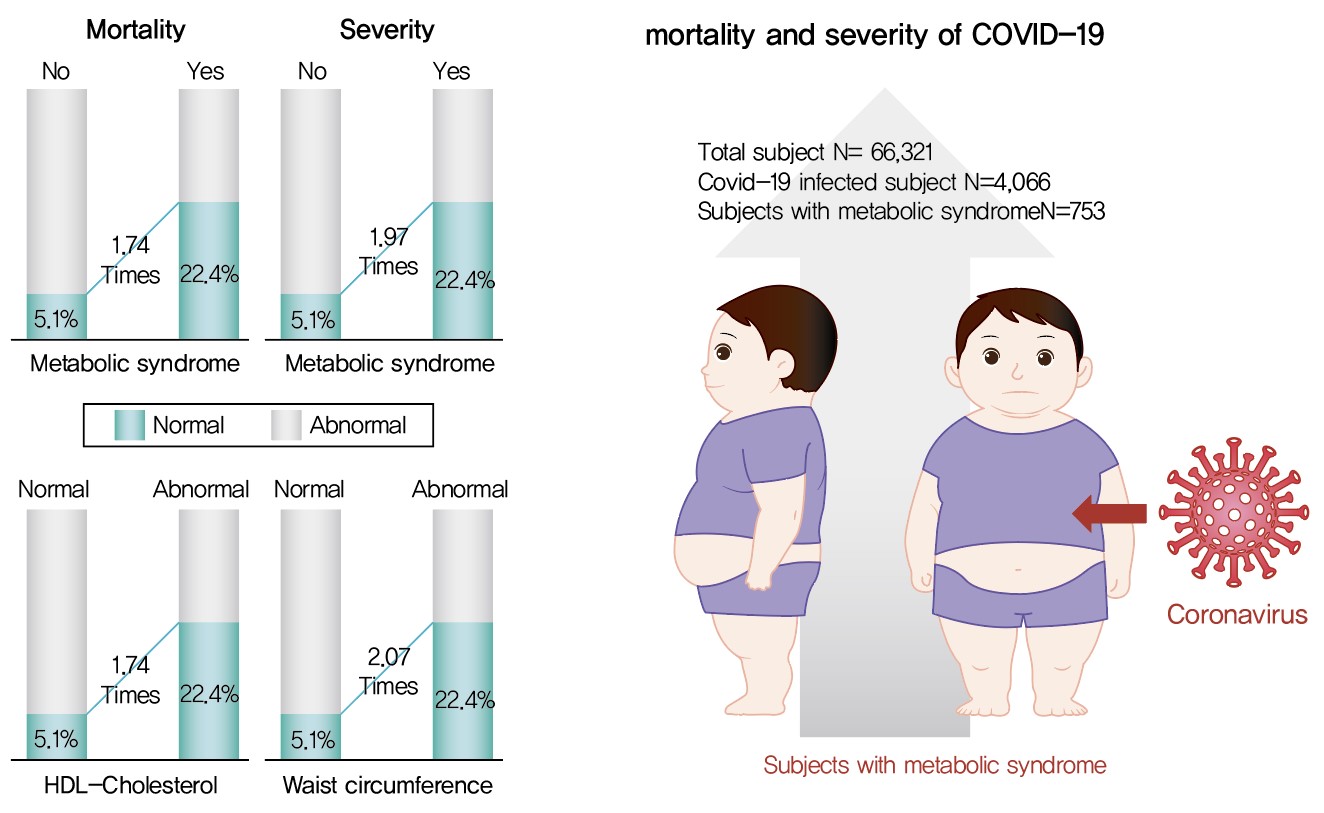
Results
Although MetS was not significantly associated with COVID-19 risk, acquiring MetS was significantly associated with the risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 1.97; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.34 to 2.91; P=0.001). The mortality risk was significantly higher in COVID-19 patients with MetS (OR, 1.74; 95% CI, 1.17 to 2.59; P=0.006). Patients with abnormal waist circumference were approximately 2.07 times more likely to develop severe COVID-19 (P<0.001), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels were significantly associated with COVID-19; the mortality risk due to COVID-19 was 1.74 times higher in men with an HDL-C level of <40 mg/dL and in women with an HDL-C level of <50 mg/dL (P=0.012).
Conclusion
COVID-19 is likely associated with severity and death in patients with MetS or in patients with MetS risk factors. Therefore, patients with MetS or those with abnormal waist circumference and HDL-C levels need to be treated with caution. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Heterogeneity in familial clustering of metabolic syndrome components in the multiethnic GENNID study
Jia Y. Wan, Deborah Goodman, Sukh Makhnoon, Trina M. Norden‐Krichmar, Baolin Wu, Karen L. Edwards
Obesity.2024; 32(1): 176. CrossRef - Associated Factors with Changes of Metabolic Abnormalities among General Population in COVID-19 Pandemic
Eunjoo Kwon, Eun-Hee Nah, Suyoung Kim, Seon Cho, Hyeran Park
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(2): 55. CrossRef - Association between metabolic syndrome and mortality in patients with COVID-19: A nationwide cohort study
Hyo Jin Park, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyungdo Han, Jean Shin, Yoojeong Lee, Yujin Chang, Kyeyeung Park, Yoon Jeong Cho, Youn Seon Choi, Seon Mee Kim, Ga Eun Nam
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2022; 16(6): 484. CrossRef
- Heterogeneity in familial clustering of metabolic syndrome components in the multiethnic GENNID study
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microvascular Complications in Chinese Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Qianwen Huang, Daizhi Yang, Hongrong Deng, Hua Liang, Xueying Zheng, Jinhua Yan, Wen Xu, Xiangwen Liu, Bin Yao, Sihui Luo, Jianping Weng
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):93-103. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0240
- 5,663 View
- 203 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Both type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and metabolic syndrome (MetS) are associated with an elevated risk of morbidity and mortality yet with increasing heterogeneity. This study primarily aimed to evaluate the prevalence of MetS among adult patients with T1DM in China and investigate its associated risk factors, and relationship with microvascular complications.
Methods
We included adult patients who had been enrolled in the Guangdong T1DM Translational Medicine Study conducted from June 2010 to June 2015. MetS was defined according to the updated National Cholesterol Education Program criterion. Logistic regression models were used to estimate the odds ratio (OR) for the association between MetS and the risk of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) and diabetic retinopathy (DR).
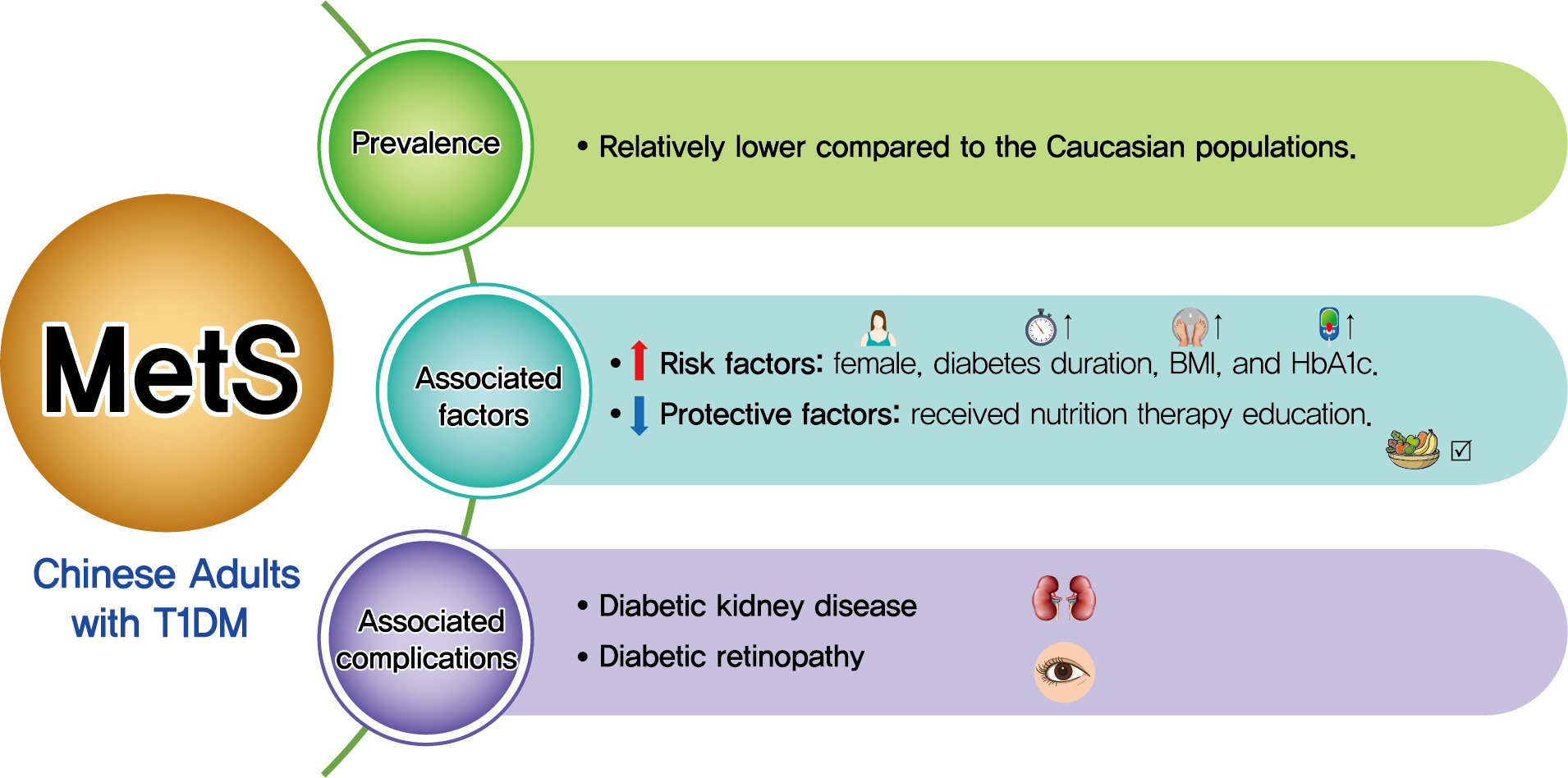
Results
Among the 569 eligible patients enrolled, the prevalence of MetS was 15.1%. While female gender, longer diabetes duration, higher body mass index, and glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) were risk factors associated with MetS (OR, 2.86, 1.04, 1.14, and 1.23, respectively), received nutrition therapy education was a protective factor (OR, 0.46). After adjustment for gender, age, diabetes duration, HbA1c, socioeconomic and lifestyle variables, MetS status was associated with an increased risk of DKD and DR (OR, 2.14 and 3.72, respectively; both P<0.05).
Conclusion
Although the prevalence of MetS in adult patients with T1DM in China was relatively low, patients with MetS were more likely to have DKD and DR. A comprehensive management including lifestyle modification might reduce their risk of microvascular complications in adults with T1DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Risk Factors Influence on Microvascular Complications in Patients With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Asad Riaz, Shoaib Asghar, Salman Shahid, Haider Tanvir, Muhammad Hamza Ejaz, Mamuna Akram
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Simplified integration of optimal self-management behaviors is associated with improved HbA1c in patients with type 1 diabetes
C. Deng, Y. Xie, F. Liu, X. Tang, L. Fan, X. Yang, Y. Chen, Z. Zhou, X. Li
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynamic Changes in Metabolic Status Are Associated With Risk of Ocular Motor Cranial Nerve Palsies
Daye Diana Choi, Kyung-Ah Park, Kyungdo Han, Sei Yeul Oh
Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of an age-sex-ethnicity-specific metabolic syndrome score in the Chinese adults
Shujuan Yang, Bin Yu, Wanqi Yu, Shaoqing Dai, Chuanteng Feng, Ying Shao, Xing Zhao, Xiaoqing Li, Tianjing He, Peng Jia
Nature Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Endotoxemia with Low-Grade Inflammation, Metabolic Syndrome and Distinct Response to Lipopolysaccharide in Type 1 Diabetes
Aleksejs Fedulovs, Leonora Pahirko, Kaspars Jekabsons, Liga Kunrade, Jānis Valeinis, Una Riekstina, Valdis Pīrāgs, Jelizaveta Sokolovska
Biomedicines.2023; 11(12): 3269. CrossRef - Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microvascular Complications in Chinese Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:93-103)
Qianwen Huang, Sihui Luo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 515. CrossRef - Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microvascular Complications in Chinese Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:93-103)
Gyuri Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 512. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome associated with higher glycemic variability in type 1 diabetes: A multicenter cross-sectional study in china
Keyu Guo, Liyin Zhang, Jianan Ye, Xiaohong Niu, Hongwei Jiang, Shenglian Gan, Jian Zhou, Lin Yang, Zhiguang Zhou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Risk Factors Influence on Microvascular Complications in Patients With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
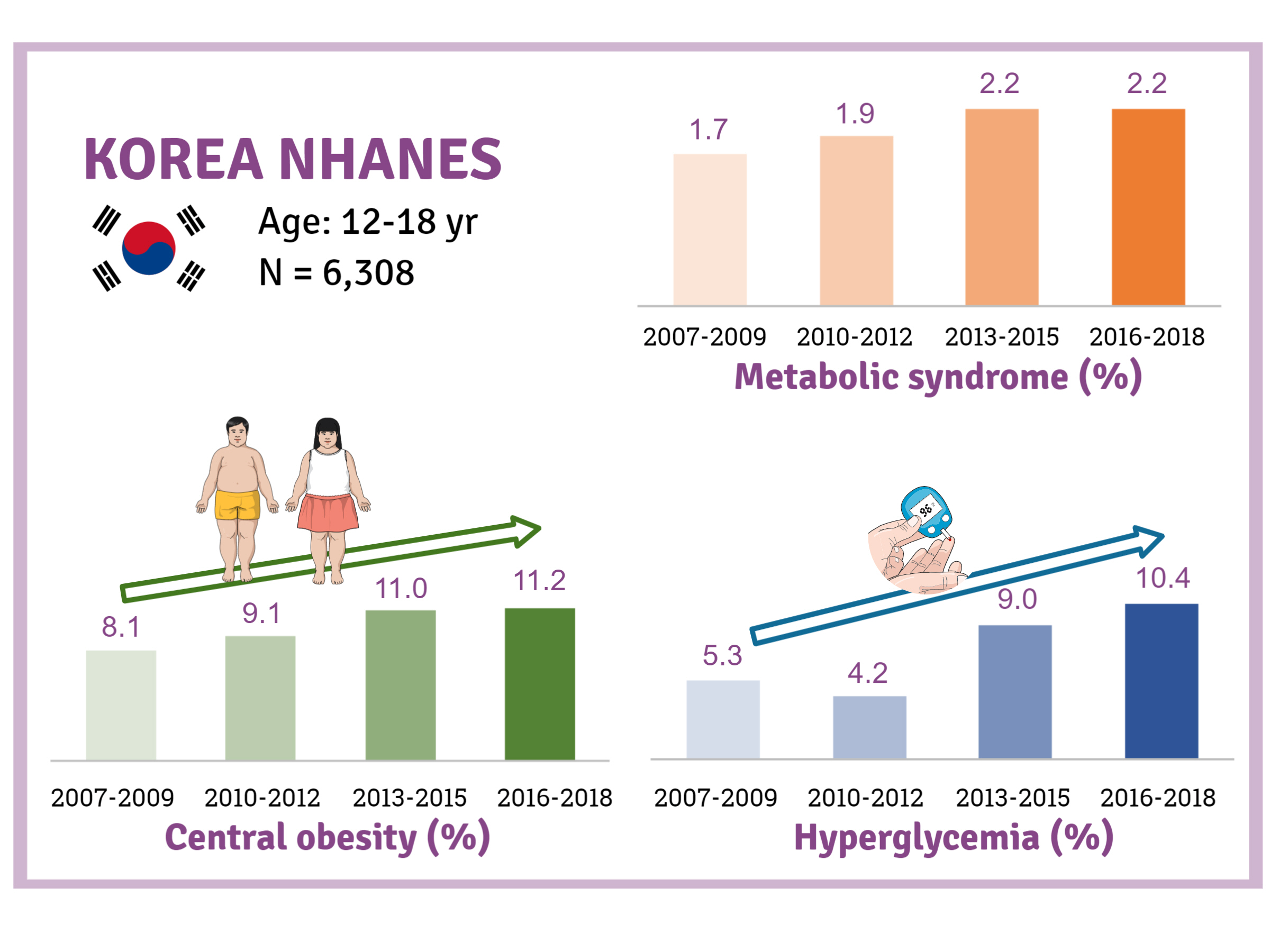
- Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018
- Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):880-889. Published online July 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0185
- 5,871 View
- 239 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
There is a lack of recent research on the changes in risk factors for metabolic syndrome (MetS) in the Asian pediatric population. We aimed to determine the 12-year trends in the prevalence of MetS and relevant lifestyle factors such as smoking, exercise, and calorie intake among Korean adolescents.
Methods
We investigated trends in MetS and lifestyle factors among 6,308 adolescents aged 12 to 18 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007 to 2018.
Results
The prevalence of MetS was stable from 2007 to 2018 (1.7% to 2.2%). There were significant increases in the prevalence of central obesity (from 8.1% to 11.2%, P=0.012) and hyperglycemia (from 5.3% to 10.4%, P<0.001) and decreases in hypo-high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterolemia (from 22.4% to 14.8%, P<0.001). Total calorie intake and calorie intake from fat significantly increased (P<0.001), whereas calorie intake from carbohydrates significantly decreased (P<0.001) during the study period. The proportions of tobacco smokers and regular walkers significantly decreased from 2007 to 2018. After controlling for all covariates, total calorie intake was positively correlated with waist circumference (P<0.05). HDL-cholesterol was negatively associated with carbohydrate consumption (P<0.01) and positively associated with fat consumption (P<0.001). Regular walking and regular strength training were associated with lower waist circumference (P<0.05). Smoking was associated with lower fasting glucose levels (P<0.01).
Conclusion
Although the prevalence rate of MetS is stable among Korean adolescents, the prevalence of central obesity and hyperglycemia has increased greatly in the recent decade. Public education on proper dietary intake and lifestyle modification is required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Overseas Deployment on Fatty Liver and Metabolic Diseases Among Korean Soldiers
Chang In Han, Jaejun Lee
Military Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impacts of dietary sphingomyelin supplementation on metabolic parameters of healthy adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Chen-Zi Li, Li-Mei Wu, Chen-Xi Zhu, Huan-Yu Du, Guo-Xun Chen, Fang Yang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Thyroid Function and Insulin Resistance Indices in Korean Adolescents: Findings from the 2014–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eunji Mun, Hye Ah Lee, Jung Eun Choi, Rosie Lee, Kyung Hee Kim, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2024; 11(3): 370. CrossRef - Ongoing increasing trends in central precocious puberty incidence among Korean boys and girls from 2008 to 2020
Sinyoung Kang, Mi Jung Park, Jung Min Kim, Jin-Sung Yuk, Shin-Hye Kim, Jun Mori
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0283510. CrossRef - The association between urinary cotinine level and metabolic syndrome profiles among adolescents: findings from the Ewha Birth and growth study
Hyunjin Park, Ui-Jeong Kim, Eun Jeong Choi, Seunghee Jun, Bomi Park, Hye Ah Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hyesook Park
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Based Speech Analysis System for Medical Support
Eui-Sun Kim, Dong Jin Shin, Sung Tae Cho, Kyung Jin Chung
International Neurourology Journal.2023; 27(2): 99. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Increase of Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents in Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the KNHANES
Jung Eun Choi, Hye Ah Lee, Sung Won Park, Jung Won Lee, Ji Hyen Lee, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2023; 10(7): 1105. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children and Adolescents
Ja Hyang Cho
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 103. CrossRef - Temporal Trends of the Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children and Adolescents between 2007 and 2020
Jieun Lee, Sung-Chan Kang, Obin Kwon, Seung-sik Hwang, Jin Soo Moon, Hyun Wook Chae, Jaehyun Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 170. CrossRef - Changes in the Number of Children and Adolescents with Complex Chronic Conditions and Medical Spending: Analyzing National Health Insurance Claims Data from 2011 to 2021
Jeong-Yoon Oh, Su-Jin Cho, Jin-Seon Jung, Jin-Suk Cho, Choon-Seon Park
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2023; 3(2): 155. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 349. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 351. CrossRef - Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hyperte
Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 377. CrossRef - Environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure in relation to metabolic syndrome in US adults
Xue Yang, Qingping Xue, Ying Wen, Yichao Huang, Yi Wang, Gaga Mahai, Tong Yan, Yanjun Liu, Tao Rong, Yixin Wang, Da Chen, Shuqin Zeng, Chun-Xia Yang, Xiong-Fei Pan
Science of The Total Environment.2022; 840: 156673. CrossRef - Commentary on "Single point insulin sensitivity estimator for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese adolescents"
Shin-Hye Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(3): 155. CrossRef
- Impact of Overseas Deployment on Fatty Liver and Metabolic Diseases Among Korean Soldiers
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Longitudinal Change in Myocardial Function and Clinical Parameters in Middle-Aged Subjects: A 3-Year Follow-up Study
- Dong-Hyuk Cho, Hyung Joon Joo, Mi-Na Kim, Hee-Dong Kim, Do-Sun Lim, Seong-Mi Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):719-729. Published online June 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0132
- 4,242 View
- 108 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is closely associated with the aging process. However, changes in metabolic conditions and cardiac function that occur in middle aged population remain unclear. We evaluated longitudinal changes in metabolic parameters and cardiac function during a 3-year period in subjects with suspected MetS.
Methods
We studied 191 participants with suspected MetS at baseline and after 3 years. Anthropometric parameters, including waist circumference (WC), and metabolic parameters, including fasting blood glucose and lipid profile were measured. Conventional echocardiography with two-dimensional speckle tracking was performed.
Results
Mean age was 56.2±4.4 years, and there were 97 women (50.8%). Men had increased WC and triglycerides (TG) (WC 91.2±6.8 cm vs. 84.0±8.0 cm, P<0.001; TG 184.4±116.3 mg/dL vs. 128.2±53.6 mg/dL, P<0.001), and reduced global longitudinal strain (GLS) (–15.4%±2.1% vs. –17.1%±2.0%, P<0.001) compared to women. After 3.4 years, values of WC and TG did not change in men but increased in women (all P<0.05). The absolute value of left ventricular (LV) GLS did not change in men but was reduced in women (P=0.011). Change in TG was independently associated with worsening of LV GLS only in women (standardized β, –0.309; 95% confidence interval, –0.130 to –0.009; P=0.025).
Conclusion
In middle aged population, a vulnerable period for metabolic disturbance, cardiac remodeling tended to progress, which was prominent in women. Progression of adiposity and dyslipidemia after menopause may accelerate subclinical cardiac remodeling in middle-aged women. Lifestyle modification and medical interventions may help prevent further cardiac dysfunction in these subjects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Positive additive interaction effects of age, sex, obesity, and metabolic syndrome on left ventricular dysfunction
Dan Zhou, Zhongwen Ye, Zhiqiang Nie, Chaolei Chen, Songyuan Luo, Mengqi Yan, Jiabin Wang, Yingqing Feng
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lung-Heart Outcomes and Mortality through the 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic in a Prospective Cohort of Breast Cancer Radiotherapy Patients
Vincent Vinh-Hung, Olena Gorobets, Nele Adriaenssens, Hilde Van Parijs, Guy Storme, Dirk Verellen, Nam P. Nguyen, Nicolas Magne, Mark De Ridder
Cancers.2022; 14(24): 6241. CrossRef
- Positive additive interaction effects of age, sex, obesity, and metabolic syndrome on left ventricular dysfunction
- Pathophysiology
- Hyperinsulinemia in Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer
- Anni M.Y. Zhang, Elizabeth A. Wellberg, Janel L. Kopp, James D. Johnson
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):285-311. Published online March 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0250
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2021;45(4):622
- 23,108 View
- 900 Download
- 81 Web of Science
- 88 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- The relative insufficiency of insulin secretion and/or insulin action causes diabetes. However, obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus can be associated with an absolute increase in circulating insulin, a state known as hyperinsulinemia. Studies are beginning to elucidate the cause-effect relationships between hyperinsulinemia and numerous consequences of metabolic dysfunctions. Here, we review recent evidence demonstrating that hyperinsulinemia may play a role in inflammation, aging and development of cancers. In this review, we will focus on the consequences and mechanisms of excess insulin production and action, placing recent findings that have challenged dogma in the context of the existing body of literature. Where relevant, we elaborate on the role of specific signal transduction components in the actions of insulin and consequences of chronic hyperinsulinemia. By discussing the involvement of hyperinsulinemia in various metabolic and other chronic diseases, we may identify more effective therapeutics or lifestyle interventions for preventing or treating obesity, diabetes and cancer. We also seek to identify pertinent questions that are ripe for future investigation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High adherence to Western dietary pattern increases breast cancer risk (an EPIC-Spain study)
Adela Castelló, Miguel Rodríguez-Barranco, Virginia Lope, Marcela Guevara, Sandra Colorado-Yohar, Ane Dorronsoro, José Ramón Quirós, Carlota Castro-Espin, Carmen Sayon-Orea, Carmen Santiuste, Pilar Amiano, Cristina Lasheras, María-José Sanchez, Marina Pol
Maturitas.2024; 179: 107868. CrossRef - Dietary Diabetes Risk Reduction Score (DDRRS) and Breast Cancer Risk: A Case-Control Study in Iran
Milad Mohammadzadeh, Alireza Bahrami, Fatemeh Abdi, Fatemeh Ghafouri-Taleghani, Amin Paydareh, Saba Jalali, Zeinab Heidari, Bahram Rashidkhani
Nutrition and Cancer.2024; 76(1): 106. CrossRef - White adipocyte dysfunction and obesity-associated pathologies in humans
Carolina E. Hagberg, Kirsty L. Spalding
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology.2024; 25(4): 270. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to impaired fasting glucose and gastrointestinal cancer risk: A nationwide cohort study
Byeong Yun Ahn, Bokyung Kim, Sanghyun Park, Sang Gyun Kim, Kyungdo Han, Soo‐Jeong Cho
Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Leptin receptor deficiency impedes metabolic surgery related-weight loss through inhibition of energy expenditure in db/db mice
Dan Tong, Jie Xiang, Wei Liu, Fang Sun, Lijuan Wang, Aidi Mou, Tingbing Cao, Qing Zhou, Mei You, Yingying Liao, Peng Gao, Daoyan Liu, Zongshi Lu, Zhiming Zhu
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and Cancer Rehabilitation for Functional Recovery and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Comprehensive Review
Lorenzo Lippi, Alessandro de Sire, Arianna Folli, Alessio Turco, Stefano Moalli, Marco Marcasciano, Antonio Ammendolia, Marco Invernizzi
Cancers.2024; 16(3): 521. CrossRef - Exploring the Role of Hyperinsulinemia in Obesity-Associated Tumor Development
Ericka Vélez-Bonet, Kristyn Gumpper-Fedus, Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate
Cancer Research.2024; 84(3): 351. CrossRef - Exploring Promising Therapies for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A ClinicalTrials.gov Analysis
Omar Hegazi, Samer Alalalmeh, Moyad Shahwan, Ammar Jairoun, Mansour Alourfi, Ghfran Bokhari, Abdullah Alkhattabi, Saeed Alsharif, Mohannad Aljehani, Abdulmalik Alsabban, Mohammad Almtrafi, Ysear Zakri, Abdullah AlMahmoud, Khalid Alghamdi, Ahmed Ashour, Na
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 545. CrossRef - Predictors of Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction in Obesity-Related Hypertension
Aqsa Mujaddadi, Saima Zaki, Majumi M Noohu, Irshad Husain Naqvi, Zubia Veqar
High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention.2024; 31(1): 77. CrossRef - The obesity-autophagy-cancer axis: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic perspectives
Amir Barzegar Behrooz, Marco Cordani, Alessandra Fiore, Massimo Donadelli, Joseph W. Gordon, Daniel J. Klionsky, Saeid Ghavami
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2024; 99: 24. CrossRef - Metformin’s role in lowering colorectal cancer risk among individuals with diabetes from the Southern Community Cohort Study
Thomas Lawler, Zoe L. Walts, Lauren Giurini, Mark Steinwandel, Loren Lipworth, Harvey J. Murff, Wei Zheng, Shaneda Warren Andersen
Cancer Epidemiology.2024; 90: 102566. CrossRef - Sex differences in insulin regulation of skeletal muscle glycogen synthase and changes during weight loss and exercise in adults
Alice S. Ryan, Guoyan Li, Shawna McMillin, Heidi K. Ortmeyer
Obesity.2024; 32(4): 667. CrossRef - Therapeutic Repurposing of Antidiabetic Drugs in Diabetes-associated
Comorbidities
Kalyani Pathak, Manash Pratim Pathak, Riya Saikia, Urvashee Gogoi, Ratna Jyoti Das, Pompy Patowary, Partha Pratim Kaishap, Smita Bordoloi, Jyotirmoy Das, Himangshu Sarma, Mohammad Zaki Ahmad, Aparoop Das
Current Drug Therapy.2024; 19(2): 178. CrossRef - The effect of metabolic syndrome on prognosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Wenjing Xiong, Liru Li, Xue Hui, Yue Liu, Hongbin Li, Yue Zhang, Shu Zhao
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Obesity-Related Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress on Cancer and Associated Molecular Targets
Joud AlBashtawi, Hend Al-Jaber, Sara Ahmed, Layla Al-Mansoori
Biomedicines.2024; 12(4): 793. CrossRef - Healthcare Management of an Obese Person
Syeda Rida Baqir, Shafaque Aslam Khan, Bushra Marium Zaman, Tahira Hamid Ali, Nazish Saeed Bangash, Muhammad Amjad Ali, Fatima Zaidi, Jahan Ara Farooq
DIET FACTOR (Journal of Nutritional and Food Sciences).2024; : 10. CrossRef - Associations between diabetes and cancer: A 10-year national population-based retrospective cohort study
Heléna Safadi, Ágnes Balogh, Judit Lám, Attila Nagy, Éva Belicza
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 211: 111665. CrossRef - Advances in “adiponcosis”: Insights in the inner mechanisms at the base of adipose and tumour tissues interplay
Cristina Pagano, Erika di Zazzo, Giorgio Avilia, Beatrice Savarese, Giovanna Navarra, Maria Chiara Proto, Donatella Fiore, Monica Rienzo, Patrizia Gazzerro, Chiara Laezza, Maurizio Bifulco
International Journal of Cancer.2023; 152(12): 2464. CrossRef - Influence of antidiabetic drugs on glucose metabolism and immune response in patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma receiving gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel as first-line treatment
Andrea Pretta, Pina Ziranu, Riccardo Giampieri, Clelia Donisi, Erika Cimbro, Dario Spanu, Eleonora Lai, Federica Pecci, Francesca Balconi, Alessio Lupi, Marta Pozzari, Mara Persano, Sara Murgia, Valeria Pusceddu, Marco Puzzoni, Rossana Berardi, Mario Scar
Digestive and Liver Disease.2023; 55(5): 655. CrossRef - Islet amyloid polypeptide does not suppress pancreatic cancer
Austin J. Taylor, Evgeniy Panzhinskiy, Paul C. Orban, Francis C. Lynn, David F. Schaeffer, James D. Johnson, Janel L. Kopp, C. Bruce Verchere
Molecular Metabolism.2023; 68: 101667. CrossRef - Pathophysiology of obesity and its associated diseases
Xin Jin, Tingting Qiu, Li Li, Rilei Yu, Xiguang Chen, Changgui Li, Christopher G. Proud, Tao Jiang
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B.2023; 13(6): 2403. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome as a risk factor for oncogenesis
M.A. Osadchuk, I.N. Vasilieva, V.V. Kozlov, O.I. Mitrokhina
Profilakticheskaya meditsina.2023; 26(1): 70. CrossRef - Polycystic ovary syndrome: Causes, symptoms, pathophysiology, and remedies
Ananya Chaudhuri
Obesity Medicine.2023; 39: 100480. CrossRef - Metformin and long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer
Morteza Gholami, Zeynab Nickhah Klashami, Pirooz Ebrahimi, Amir Ali Mahboobipour, Amir Salehi Farid, Aida Vahidi, Marziyeh Zoughi, Mojgan Asadi, Mahsa M. Amoli
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Host-Related Factors in the Interplay among Inflammation, Immunity and Dormancy in Breast Cancer Recurrence and Prognosis: An Overview for Clinicians
Lorenzo Ruggieri, Anna Moretti, Rossana Berardi, Maria Silvia Cona, Davide Dalu, Cecilia Villa, Davide Chizzoniti, Sheila Piva, Anna Gambaro, Nicla La Verde
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(5): 4974. CrossRef - Degree of obesity and gastrointestinal adverse reactions influence the weight loss effect of liraglutide in overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes
Fang Zhou, Lu Jiang, Jiamei Guo, Yuting Fan, Qin Pan, Tianlian Li, Xiaoshi Sun, Ping Li
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2023; 14: 204062232311615. CrossRef - Both early and late maternal age at childbirth is associated with increasing odds of central obesity in offspring
Hongyun Chen, Yinhua Feng, Changying Chen, Songcheng Yu
American Journal of Human Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated Physiology of the Exocrine and Endocrine Compartments in Pancreatic Diseases: Workshop Proceedings
Teresa L. Mastracci, Minoti Apte, Laufey T. Amundadottir, Alexandra Alvarsson, Steven Artandi, Melena D. Bellin, Ernesto Bernal-Mizrachi, Alejandro Caicedo, Martha Campbell-Thompson, Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate, Abdelfattah El Ouaamari, Kyle J. Gaulton, Andre
Diabetes.2023; 72(4): 433. CrossRef - Obesity-induced changes in cancer cells and their microenvironment: Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives to manage dysregulated lipid metabolism
Miriam Lee-Rueckert, Marina Canyelles, Mireia Tondo, Noemi Rotllan, Petri T. Kovanen, Vicenta Llorente-Cortes, Joan Carles Escolà-Gil
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2023; 93: 36. CrossRef - PIK3CA mutation in endometriotic epithelial cells promotes viperin-dependent inflammatory response to insulin
Mike R. Wilson, Shannon Harkins, Jake J. Reske, Rebecca A. Siwicki, Marie Adams, Victoria L. Bae-Jump, Jose M. Teixeira, Ronald L. Chandler
Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gut microbiome modified by bariatric surgery improves insulin sensitivity and correlates with increased brown fat activity and energy expenditure
Jitender Yadav, Tao Liang, Tairan Qin, Nayanan Nathan, Katherine J.P. Schwenger, Lauren Pickel, Li Xie, Helena Lei, Daniel A. Winer, Heather Maughan, Susan J. Robertson, Minna Woo, Wendy Lou, Kate Banks, Timothy Jackson, Allan Okrainec, Susy S. Hota, Susa
Cell Reports Medicine.2023; 4(5): 101051. CrossRef - Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes, Impaired Fasting Glucose, and Diabetes Risk in an Adult and Older North-Eastern Portuguese Population
Pedro M. Magalhães, José E. Teixeira, João P. Bragada, Carlos M. Duarte, José A. Bragada
Healthcare.2023; 11(12): 1712. CrossRef - Hyperinsulinemia Influences the Short-Term Efficiency of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy for Patients with Obesity and Insulin Resistance
Zilong Yue, Long Qian, Yan Jin, Yabin Xia, Hui Sha, Qin Wu, Kaifeng Hu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1745. CrossRef - Acetyl-11-Keto-Beta-Boswellic Acid Has Therapeutic Benefits for NAFLD Rat Models That Were Given a High Fructose Diet by Ameliorating Hepatic Inflammation and Lipid Metabolism
Reza Ataei Kachouei, Alireza Doagoo, Maral Jalilzadeh, Seyyed Hossein Khatami, Shima Rajaei, Ali Jahanbazi Jahan-Abad, Farzaneh Salmani, Roya Pakrad, Somayeh Mahmoodi Baram, Mitra Nourbakhsh, Mohammad-Amin Abdollahifar, Hojjat Allah Abbaszadeh, Shokoofeh
Inflammation.2023; 46(5): 1966. CrossRef - Cancer Risk and its Association With Diabetes Mellitus in Patients With Acromegaly: A Two Center-based Study
Zhe-Hao Xiao, Cheng Wang, Yong Wang, Shang-Kun Yuan, Cheng Huang, Ren-Fang Chen, Yong Li
Endocrine Practice.2023; 29(9): 699. CrossRef - Obesity, diabetes, and cancer: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and potential interventions
Leonardo de Andrade Mesquita, Laura Fink Wayerbacher, Gilberto Schwartsmann, Fernando Gerchman
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Stimulates IL-23 Expression in Human Adipocytes: A Possible Explanation for the Higher Prevalence of Psoriasis in Obesity
Angelo Di Vincenzo, Marnie Granzotto, Marika Crescenzi, Camilla Costa, Stefano Piaserico, Vincenzo Vindigni, Roberto Vettor, Marco Rossato
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1885. CrossRef - Immunometabolic aspects of chronic nonspecific inflammation in obesity
O. V. Skvortsova, N. B. Migacheva, E. G. Mikhailova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; (12): 75. CrossRef - The Reponic Classification of Insulin
Joshua Moen
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2023; 47(8): 680. CrossRef - Dietary Acid Load and Cancer Risk: A Review of the Uruguayan Experience
Alvaro Luis Ronco, Maximilian Andreas Storz
Nutrients.2023; 15(14): 3098. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes mellitus as growing aetiologies of hepatocellular carcinoma
Stephanie Talamantes, Michela Lisjak, Eduardo H. Gilglioni, Camilo J. Llamoza-Torres, Bruno Ramos-Molina, Esteban N. Gurzov
JHEP Reports.2023; 5(9): 100811. CrossRef - Alteration of Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated with the Decreased Risk of Colorectal Cancer
Eun Hyo Jin, Yoon Jin Choi, Joo Hyun Lim, Cheol Min Shin, Kyungdo Han, Dong Ho Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(15): 4889. CrossRef - Dietary interventions improve diabetic kidney disease, but not peripheral neuropathy, in a db/db mouse model of type 2 diabetes
Stephanie A. Eid, Phillipe D. O'Brien, Katharina H. Kretzler, Dae‐Gyu Jang, Faye E. Mendelson, John M. Hayes, Andrew Carter, Hongyu Zhang, Subramaniam Pennathur, Frank C. Brosius, Emily J. Koubek, Eva L. Feldman
The FASEB Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Decoding the role of leptin and adiponectin in obesity-related gastrointestinal cancer
Vanda Marques, Fabiola Arella, Marta B. Afonso, André A. Santos, Cecília M.P. Rodrigues
Clinical Science.2023; 137(15): 1095. CrossRef - Metformin Can Attenuate Beta-Cell Hypersecretion—Implications for Treatment of Children with Obesity
Quan Wen, Rasmus Stenlid, Azazul Islam Chowdhury, Iris Ciba, Banu Aydin, Sara Y. Cerenius, Hannes Manell, Anders Forslund, Peter Bergsten
Metabolites.2023; 13(8): 917. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of a Low Glycemic Index/Load Diet on Cardiometabolic, Glucometabolic, and Anthropometric Indices in Children with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ioustini Kalaitzopoulou, Xenophon Theodoridis, Evangelia Kotzakioulafi, Kleo Evripidou, Michail Chourdakis
Children.2023; 10(9): 1481. CrossRef - A review of the last decade: pancreatic cancer and type 2 diabetes
Jiaqi Wu, Liang Tang, Feng Zheng, Xun Chen, Lei Li
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Characteristics of Children and Adolescents with Hyperinsulinemia Undergoing Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: A Single-Center Retrospective Observational Study
Clelia Cipolla, Ilaria Lazzareschi, Antonietta Curatola, Claudia Lasorella, Lucia Celeste Pane, Linda Sessa, Giulia Rotunno, Donato Rigante, Giorgio Sodero
Diseases.2023; 11(3): 110. CrossRef - Hyperinsulinemia acts via acinar insulin receptors to initiate pancreatic cancer by increasing digestive enzyme production and inflammation
Anni M.Y. Zhang, Yi Han Xia, Jeffrey S.H. Lin, Ken H. Chu, Wei Chuan K. Wang, Titine J.J. Ruiter, Jenny C.C. Yang, Nan Chen, Justin Chhuor, Shilpa Patil, Haoning Howard Cen, Elizabeth J. Rideout, Vincent R. Richard, David F. Schaeffer, Rene P. Zahedi, Chr
Cell Metabolism.2023; 35(12): 2119. CrossRef - Dairy Intake Modifies the Level of the Bile Acid Precursor and Its Correlation with Serum Proteins Associated with Cholesterol Clearance in Subjects with Hyperinsulinemia
Atena Mahdavi, Jocelyn Trottier, Olivier Barbier, Michel Lebel, Iwona Rudkowska
Nutrients.2023; 15(22): 4707. CrossRef - Trapa Bispinosa Roxb. Inhibits the Insulin-Dependent AKT/WNK1 Pathway to Induce Autophagy in Mice with Type 2 Diabetes
Takahiro Suzuki, Takehito Sato, Kaori Masuhara, Mizuki Tokusanai, Hisako Akatsuka, Tomohiro Kashikawa, Yasuyuki Suzuki
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3095. CrossRef - Effects of Functional and Nutraceutical Foods in the Context of the Mediterranean Diet in Patients Diagnosed with Breast Cancer
Giovanna Flore, Andrea Deledda, Mauro Lombardo, Andrea Armani, Fernanda Velluzzi
Antioxidants.2023; 12(10): 1845. CrossRef - A systematic review exploring the mechanisms by which citrus bioflavonoid supplementation benefits blood glucose levels and metabolic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ankit Gupta, Abdulsatar Jamal, Dina A. Jamil, Hayder A. Al-Aubaidy
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(11): 102884. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and Gastric Cancer: Correlation and Potential Mechanisms
Li Wang, Zhe Zhang, Eusebio Chiefari
Journal of Diabetes Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - EXPLORATORY ANALYSIS OF DIETARY PATTERNS OF PATIENTS WITH GASTRIC ADENOCARCINOMA: A CASE-CONTROL STUDY IN CENTRAL BRAZIL
Silvana Barbosa SANTIAGO, Gabriela Rodrigues de SOUSA, Amanda Ferreira Paes Landim RAMOS, Gisele Aparecida FERNANDES, Maria Paula CURADO, Mônica Santiago BARBOSA
Arquivos de Gastroenterologia.2023; 60(4): 419. CrossRef - Risk of cancer in acromegaly patients: An updated meta-analysis and systematic review
Zhehao Xiao, Pingping Xiao, Yong Wang, Chen Fang, Yong Li, Alvaro Galli
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0285335. CrossRef - Long Follow-Up Times Weaken Observational Diet–Cancer Study Outcomes: Evidence from Studies of Meat and Cancer Risk
William B. Grant
Nutrients.2023; 16(1): 26. CrossRef - Serum Lipid Profiles and Cholesterol-Lowering Medication Use in Relation to Subsequent Risk of Colorectal Cancer in the UK Biobank Cohort
Fangcheng Yuan, Wanqing Wen, Guochong Jia, Jirong Long, Xiao-Ou Shu, Wei Zheng
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2023; 32(4): 524. CrossRef - Prevalence of diabetes mellitus among 80,193 gastrointestinal cancer patients in five European and three Asian countries
Christoph Roderburg, Sven H. Loosen, Laura Hoyer, Tom Luedde, Karel Kostev
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2022; 148(5): 1057. CrossRef - The Intricate Crosstalk Between Insulin and Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Review From Clinical to Molecular
Junyuan Deng, Yujie Guo, Jiali Du, Jichun Gu, Lei Kong, Boan Tao, Ji Li, Deliang Fu
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of hyperinsulinemia on pancreatic cancer development and the immune microenvironment revealed through single-cell transcriptomics
Anni M. Y. Zhang, Ken H. Chu, Brian F. Daly, Titine Ruiter, Yan Dou, Jenny C. C. Yang, Twan J. J. de Winter, Justin Chhuor, Su Wang, Stephane Flibotte, Yiwei Bernie Zhao, Xiaoke Hu, Hong Li, Elizabeth J. Rideout, David F. Schaeffer, James D. Johnson, Jane
Cancer & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ghrelin and Cancer: Examining the Roles of the Ghrelin Axis in Tumor Growth and Progression
Anuhya S. Kotta, Abigail S. Kelling, Karen A. Corleto, Yuxiang Sun, Erin D. Giles
Biomolecules.2022; 12(4): 483. CrossRef - Influence of obesity on reproductive health before andduring pregnancy
A. Konwisser, O. Korytko
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(8): 446. CrossRef - Research Status of the Correlation between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Occurrence and Development of Breast Cancer
聪 李
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(04): 3010. CrossRef - Effect of Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets and Intermittent Fasting on Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Hypertension Management: Consensus Statement of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, Korean Diabetes Association, and Korean Society of Hype
Jong Han Choi, Yoon Jeong Cho, Hyun-Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Suk Chon, Jee-Hyun Kang, Kyoung-Kon Kim, Eun Mi Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Ga Eun Nam, Kwang Il Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 355. CrossRef - Obesity and Pancreatic Cancer: Recent Progress in Epidemiology, Mechanisms and Bariatric Surgery
Shuhei Shinoda, Naohiko Nakamura, Brett Roach, David A. Bernlohr, Sayeed Ikramuddin, Masato Yamamoto
Biomedicines.2022; 10(6): 1284. CrossRef - Effect of carbohydrate-restricted diets and intermittent fasting on obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypertension management: consensus statement of the Korean Society for the Study of obesity, Korean Diabetes Association, and Korean Society of Hype
Jong Han Choi, Yoon Jeong Cho, Hyun-Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Suk Chon, Jee-Hyun Kang, Kyoung-Kon Kim, Eun Mi Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Ga Eun Nam, Kwang Il Kim
Clinical Hypertension.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D and Risk of Obesity-Related Cancers: Results from the SUN (‘Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra’) Project
Rodrigo Sánchez-Bayona, Maira Bes-Rastrollo, Cesar I. Fernández-Lázaro, Maite Bastyr, Ainhoa Madariaga, Juan J. Pons, Miguel A. Martínez-González, Estefanía Toledo
Nutrients.2022; 14(13): 2561. CrossRef - Metabolically Defined Body Size Phenotypes and Risk of Endometrial Cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)
Nathalie Kliemann, Romain Ould Ammar, Carine Biessy, Audrey Gicquiau, Verena Katzke, Rudolf Kaaks, Anne Tjønneland, Anja Olsen, Maria-Jose Sánchez, Marta Crous-Bou, Fabrizio Pasanisi, Sandar Tin Tin, Aurora Perez-Cornago, Dagfinn Aune, Sofia Christakoudi,
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2022; 31(7): 1359. CrossRef - Effect of Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets and Intermittent Fasting on Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Hypertension Management: Consensus Statement of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, Korean Diabetes Association, and Korean Society of Hype
Jong Han Choi, Yoon Jeong Cho, Hyun-Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Suk Chon, Jee-Hyun Kang, Kyoung-Kon Kim, Eun Mi Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Ga Eun Nam, Kwang Il Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(2): 100. CrossRef - Detangling the interrelations between MAFLD, insulin resistance, and key hormones
Shreya C. Pal, Mohammed Eslam, Nahum Mendez-Sanchez
Hormones.2022; 21(4): 573. CrossRef - Obesity, cancer risk, and time-restricted eating
Manasi Das, Nicholas J. G. Webster
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews.2022; 41(3): 697. CrossRef - Associations between early-life growth pattern and body size and follicular lymphoma risk and survival: a family-based case-control study
Michael K. Odutola, Marina T. van Leeuwen, Jennifer Turner, Fiona Bruinsma, John F. Seymour, H. Miles Prince, Samuel T. Milliken, Mark Hertzberg, Judith Trotman, Stephen S. Opat, Robert Lindeman, Fernando Roncolato, Emma Verner, Michael Harvey, Campbell T
Cancer Epidemiology.2022; 80: 102241. CrossRef - Differential expression of Ago2‐mediated microRNA signaling in adipose tissue is associated with food‐induced obesity
Hansi Zhang, Liang Qiao, Xiaoxuan Liu, Xiaojing Han, Jing Kang, Yanli Liu, Juntang Lin, Xin Yan
FEBS Open Bio.2022; 12(10): 1828. CrossRef - Proposal for standardizing normal insulin ranges in Brazilian patients and a new classification of metabolic syndrome
Pedro Renato Chocair, Precil Diego Miranda de Menezes Neves, Victor Augusto Hamamoto Sato, Sara Mohrbacher, Érico Souza Oliveira, Leonardo Victor Barbosa Pereira, Alessandra Martins Bales, Fagner Pereira da Silva, John A. Duley, Américo Lourenço Cuvello-N
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Two models of insulin resistance development and the strategy to combat age-related diseases: literature review
A. V. Martyushev-Poklad, D. S. Yankevich, M. V. Petrova, N. G. Savitskaya
Problems of Endocrinology.2022; 68(4): 59. CrossRef - In Vitro Mimicking of Obesity-Induced Biochemical Environment to Study Obesity Impacts on Cells and Tissues
Abdelaziz Ghanemi, Mayumi Yoshioka, Jonny St-Amand
Diseases.2022; 10(4): 76. CrossRef - Long‐term survival analysis of patients with stage IIIB‐IV non‐small cell lung cancer complicated by type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective propensity score matching analysis
Xuejiao Li, Haiyan Fang, Dongwei Zhang, Liming Xia, Xiang Wang, Jingping Yang, Shaohu Zhang, Ya Su, Yongfu Zhu
Thoracic Cancer.2022; 13(23): 3268. CrossRef - Diabetes and skin cancers: Risk factors, molecular mechanisms and impact on prognosis
Elena-Codruta Dobrică, Madalina Laura Banciu, Vincent Kipkorir, Mohammad Amin Khazeei Tabari, Madeleine Jemima Cox, L V Simhachalam Kutikuppala, Mihnea-Alexandru Găman
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(31): 11214. CrossRef - The role of the mTOR pathway in diabetic retinopathy
Fabio Casciano, Enrico Zauli, Erika Rimondi, Marco Mura, Maurizio Previati, Massimo Busin, Giorgio Zauli
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Hyperinsulinemia-induced microglial mitochondrial dynamic and metabolic alterations lead to neuroinflammation in vivo and in vitro
Xiaohan Yang, Yuan Xu, Wenting Gao, Li Wang, Xinnan Zhao, Gang Liu, Kai Fan, Shuang Liu, Huimin Hao, Siyan Qu, Renhou Dong, Xiaokai Ma, Jianmei Ma
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated Physiology of the Exocrine and Endocrine Compartments in Pancreatic Diseases
Teresa L. Mastracci, Minoti Apte, Laufey T. Amundadottir, Alexandra Alvarsson, Steven Artandi, Melena D. Bellin, Ernesto Bernal-Mizrachi, Alejandro Caicedo, Martha Campbell-Thompson, Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate, Abdelfattah El Ouaamari, Kyle J. Gaulton, Andre
Pancreas.2022; 51(9): 1061. CrossRef - Intestinal Microbiome Modified by Bariatric Surgery Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Correlates with Increased Brown Fat Activity and Energy Expenditure
jitender Yadav, Tao Liang, Tairan Qin, Nayanan N. Nathan, Katherine J.P Schwenger, Lauren Pickel, Li Xie, Helena Lei, Daniel A. Winer, Heather Maughan, Susan J. Robertson, Minna Woo, Wendy Y. W. Lou, Kate Banks, Timothy Jackson, Allan Okrainec, Susy S. Ho
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a report of two cases
Alison H. Affinati, Amisha Wallia, Roma Y. Gianchandani
Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Promises and pitfalls of beta cell–replacement therapies
Jelena Kolic, James D. Johnson
Nature Metabolism.2021; 3(8): 1036. CrossRef - Hiding unhealthy heart outcomes in a low-fat diet trial: the Women’s Health Initiative Randomized Controlled Dietary Modification Trial finds that postmenopausal women with established coronary heart disease were at increased risk of an adverse outcome if
Timothy David Noakes
Open Heart.2021; 8(2): e001680. CrossRef - On the causal relationships between hyperinsulinaemia, insulin resistance, obesity and dysglycaemia in type 2 diabetes
James D. Johnson
Diabetologia.2021; 64(10): 2138. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and cancer: a system of insulin-like growth factors
E. M. Frantsiyants, E. I. Surikova, I. V. Kaplieva, V. A. Bandovkina, I. V. Neskubina, E. A. Sheiko, M. I. Morozova, I. M. Kotieva
Problems of Endocrinology.2021; 67(5): 34. CrossRef
- High adherence to Western dietary pattern increases breast cancer risk (an EPIC-Spain study)
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Metabolic Syndrome Severity Score for Predicting Cardiovascular Events: A Nationwide Population-Based Study from Korea
- Yo Nam Jang, Jun Hyeok Lee, Jin Sil Moon, Dae Ryong Kang, Seong Yong Park, Jerim Cho, Jang-Young Kim, Ji Hye Huh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):569-577. Published online January 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0103
- 6,520 View
- 225 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Recently, a metabolic syndrome severity score (MS score) using a dataset of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys has been developed. We aimed to determine whether the newly developed score is a significant predictor of cardiovascular (CV) events among the Korean population.
Methods
From the Korean National Health Insurance System, 2,541,364 (aged 40 to 59 years) subjects with no history of CV events (ischemic stroke or myocardial infarction [MI]), who underwent health examinations from 2009 to 2011 and were followed up until 2014 to 2017, were identified. Cox proportional hazard model was employed to investigate the association between MS score and CV events. Model performance of MS score for predicting CV events was compared to that of conventional metabolic syndrome diagnostic criteria (Adult Treatment Program III [ATP-III]) using the Akaike information criterion and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
Results
Over a median follow-up of 6 years, 15,762 cases of CV events were reported. MS score at baseline showed a linear association with incident CV events. In the multivariable-adjusted model, the hazard ratios (95% confidence intervals) comparing the highest versus lowest quartiles of MS score were 1.48 (1.36 to 1.60) for MI and 1.89 (1.74 to 2.05) for stroke. Model fitness and performance of the MS score in predicting CV events were superior to those of ATP-III.
Conclusion
The newly developed age- and sex-specific continuous MS score for the Korean population is an independent predictor of ischemic stroke and MI in Korean middle-aged adults even after adjusting for confounding factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic syndrome awareness in the general Korean population: results from a nationwide survey
Hyun-Jin Kim, Mi-Seung Shin, Kyung-Hee Kim, Mi-Hyang Jung, Dong-Hyuk Cho, Ju-Hee Lee, Kwang Kon Koh
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 39(2): 272. CrossRef - BMI-based metabolic syndrome severity score and arterial stiffness in a cohort Chinese study
Miao Wang, Chi Wang, Maoxiang Zhao, Shouling Wu, Hao Xue, Hongbin Liu
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between metabolic syndrome severity score and cardiovascular disease: results from a longitudinal cohort study on Chinese adults
Jing-jing Lin, Pin-yuan Dai, Jie Zhang, Yun-qi Guan, Wei-wei Gong, Min Yu, Le Fang, Ru-ying Hu, Qing-fang He, Na Li, Li-xin Wang, Ming-bin Liang, Jie-ming Zhong
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Omics biomarkers and an approach for their practical implementation to delineate health status for personalized nutrition strategies
Jaap Keijer, Xavier Escoté, Sebastià Galmés, Andreu Palou-March, Francisca Serra, Mona Adnan Aldubayan, Kristina Pigsborg, Faidon Magkos, Ella J. Baker, Philip C. Calder, Joanna Góralska, Urszula Razny, Malgorzata Malczewska-Malec, David Suñol, Mar Galofr
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Development and validation of a continuous metabolic syndrome severity score in the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
Mohammadjavad Honarvar, Safdar Masoumi, Ladan Mehran, Davood Khalili, Atieh Amouzegar, Fereidoun Azizi
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of metabolic syndrome, its severity with cognitive impairment among hemodialysis patients
Yuqi Yang, Qian Li, Yanjun Long, Jing Yuan, Yan Zha
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin serum levels and its association with clinical profile and carotid intima-media thickness in psoriasis: a cross-sectional study
Sofia Makishi Schlenker, Sofia Inez Munhoz, André Rochinski Busanello, Matheus Guedes Sanches, Barbara Stadler Kahlow, Renato Nisihara, Thelma Larocca Skare
Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia.2023; 98(6): 799. CrossRef - Cholecystectomy Increases the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in the Korean Population
Ji Hye Huh, Kyong Joo Lee, Yun Kyung Cho, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung-do Han, Dong Hee Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm
Annals of Surgery.2023; 278(2): e264. CrossRef - Cardiorespiratory Endurance is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Severity in Men
V. V. Sverchkov, E. V. Bykov
Journal Biomed.2023; 19(2): 61. CrossRef - Effect of a Wearable Device–Based Physical Activity Intervention in North Korean Refugees: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Kyoung Jin Kim, Kyeong Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jinhee Seo, Jung-Been Lee, Jae Hyun Bae, Nam Hoon Kim, Hee Young Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee, Sin Gon Kim
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2023; 25: e45975. CrossRef - Independent association between age- and sex-specific metabolic syndrome severity score and cardiovascular disease and mortality
Mohammadjavad Honarvar, Ladan Mehran, Safdar Masoumi, Sadaf Agahi, Shayesteh Khalili, Fereidoun Azizi, Atieh Amouzegar
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in Adults Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study Including More Than 4 Million Individuals From South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Sang Wook Park, Tae-Hwa Go, Dae Ryong Kang, Sang-Hak Lee, Jang-Young Kim
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-Glucose Index for the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study of 298,652 Individuals Receiving a Health Check-Up in China
Mingfei Jiang, Xiaoran Li, Huan Wu, Fan Su, Lei Cao, Xia Ren, Jian Hu, Grace Tatenda, Mingjia Cheng, Yufeng Wen, Hou De Zhou
International Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Changes in body composition, body balance, metabolic parameters and eating behavior among overweight and obese women due to adherence to the Pilates exercise program
Hyun Ju Kim, Jihyun Park, Mi Ri Ha, Ye Jin Kim, Chaerin Kim, Oh Yoen Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(6): 642. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Severity Score, Comparable to Serum Creatinine, Could Predict the Occurrence of End-Stage Kidney Disease in Patients with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis
Pil Gyu Park, Jung Yoon Pyo, Sung Soo Ahn, Jason Jungsik Song, Yong-Beom Park, Ji Hye Huh, Sang-Won Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(24): 5744. CrossRef
- Metabolic syndrome awareness in the general Korean population: results from a nationwide survey
- Pathophysiology
- Relationships between Islet-Specific Autoantibody Titers and the Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Yiqian Zhang, Tong Yin, Xinlei Wang, Rongping Zhang, Jie Yuan, Yi Sun, Jing Zong, Shiwei Cui, Yunjuan Gu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):404-416. Published online July 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0239
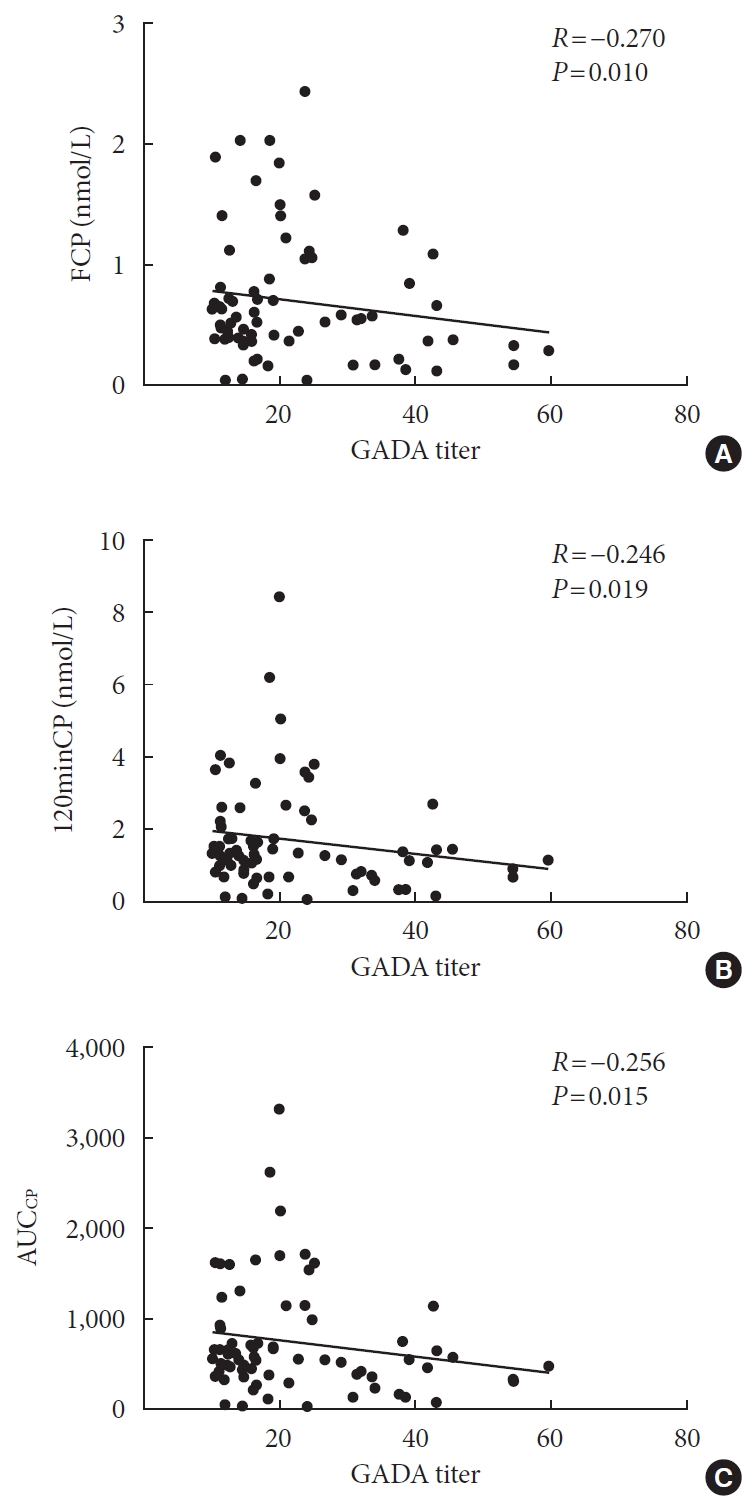
- 6,365 View
- 161 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Dysimmunity plays a key role in diabetes, especially type 1 diabetes mellitus. Islet-specific autoantibodies (ISAs) have been used as diagnostic markers for different phenotypic classifications of diabetes. This study was aimed to explore the relationships between ISA titers and the clinical characteristics of diabetic patients.
Methods A total of 509 diabetic patients admitted to Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism at the Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University were recruited. Anthropometric parameters, serum biochemical index, glycosylated hemoglobin, urinary microalbumin/creatinine ratio, ISAs, fat mass, and islet β-cell function were measured. Multiple linear regression analysis was performed to identify relationships between ISA titers and clinical characteristics.
Results Compared with autoantibody negative group, blood pressure, weight, total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), visceral fat mass, fasting C-peptide (FCP), 120 minutes C-peptide (120minCP) and area under C-peptide curve (AUCCP) of patients in either autoantibody positive or glutamate decarboxylase antibody (GADA) positive group were lower. Body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, triglycerides (TGs), body fat mass of patients in either autoantibody positive group were lower than autoantibody negative group. GADA titer negatively correlated with TC, LDL-C, FCP, 120minCP, and AUCCP. The islet cell antibody and insulin autoantibody titers both negatively correlated with body weight, BMI, TC, TG, and LDL-C. After adjusting confounders, multiple linear regression analysis showed that LDL-C and FCP negatively correlated with GADA titer.
Conclusion Diabetic patients with a high ISA titer, especially GADA titer, have worse islet β-cell function, but less abdominal obesity and fewer features of the metabolic syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between β-Cell Autoantibodies and Their Combination with Anthropometric and Metabolic Components and Microvascular Complications in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults
Tomislav Bulum, Marijana Vučić Lovrenčić, Jadranka Knežević Ćuća, Martina Tomić, Sandra Vučković-Rebrina, Lea Duvnjak
Biomedicines.2023; 11(9): 2561. CrossRef - RETRACTED ARTICLE: MiRNA-27a mediates insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 cells through the PPARγ
Yangming Zhuang, Ming Li
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 477(4): 1107. CrossRef - Correlation between Insulin Resistance and Microalbuminuria Creatinine Ratio in Postmenopausal Women
Han Na, Rong Wang, Hai-Long Zheng, Xiao-Pan Chen, Lin-Yang Zheng, Faustino R. Perez-Lopez
International Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - The longitudinal loss of islet autoantibody responses from diagnosis of type 1 diabetes occurs progressively over follow-up and is determined by low autoantibody titres, early-onset, and genetic variants
C L Williams, R Fareed, G L M Mortimer, R J Aitken, I V Wilson, G George, K M Gillespie, A J K Williams, Chitrabhanu Ballav, Atanu Dutta, Michelle Russell-Taylor, Rachel Besser, James Bursell, Shanthi Chandran, Sejal Patel, Anne Smith, Manohara Kenchaiah,
Clinical and Experimental Immunology.2022; 210(2): 151. CrossRef
- Relationship between β-Cell Autoantibodies and Their Combination with Anthropometric and Metabolic Components and Microvascular Complications in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults
- Drug/Regimen
- Fibrates Revisited: Potential Role in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
- Nam Hoon Kim, Sin Gon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):213-221. Published online April 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0001
- 7,657 View
- 310 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 42 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Fibrates, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α agonists, are potent lipid-modifying drugs. Their main effects are reduction of triglycerides and increase in high-density lipoprotein levels. Several randomized controlled trials have not demonstrated their benefits on cardiovascular risk reduction, especially as an “add on” to statin therapy. However, subsequent analyses by major clinical trials, meta-analyses, and real-world evidence have proposed their potential in specific patient populations with atherogenic dyslipidemia and metabolic syndrome. Here, we have reviewed and discussed the accumulated data on fibrates to understand their current status in cardiovascular risk management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy.2024; 10(2): 118. CrossRef - Role of PPARα in inflammatory response of C2C12 myotubes
Yuki Shimizu, Keiko Hamada, Tingting Guo, Chie Hasegawa, Yusuke Kuga, Katsushi Takeda, Takashi Yagi, Hiroyuki Koyama, Hiroshi Takagi, Daisuke Aotani, Hiromi Kataoka, Tomohiro Tanaka
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2024; 694: 149413. CrossRef - Obicetrapib: Reversing the Tide of CETP Inhibitor Disappointments
John J. P. Kastelein, Andrew Hsieh, Mary R. Dicklin, Marc Ditmarsch, Michael H. Davidson
Current Atherosclerosis Reports.2024; 26(2): 35. CrossRef - Metabolic Flexibility of the Heart: The Role of Fatty Acid Metabolism in Health, Heart Failure, and Cardiometabolic Diseases
Virginia Actis Dato, Stephan Lange, Yoshitake Cho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 1211. CrossRef - ApoB100 and Atherosclerosis: What’s New in the 21st Century?
Dimitris Kounatidis, Natalia G. Vallianou, Aikaterini Poulaki, Angelos Evangelopoulos, Fotis Panagopoulos, Theodora Stratigou, Eleni Geladari, Irene Karampela, Maria Dalamaga
Metabolites.2024; 14(2): 123. CrossRef - Follistatin-like 1 (FSTL1) levels as potential early biomarker of cardiovascular disease in a Mexican population
N. Ponce-Ruíz, J. F. Herrera-Moreno, A. E. Rojas-García, B. S. Barrón-Vivanco, C. A. González-Arias, Y. Y. Bernal-Hernández, L. Ortega-Cervantes, J. Ponce-Gallegos, J. A. Hernández-Nolasco, I. M. Medina-Díaz
Heart and Vessels.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 184. CrossRef - Coenzyme Q10 in atherosclerosis
Minjun Liao, Xueke He, Yangyang Zhou, Weiqiang Peng, Xiao-Mei Zhao, Miao Jiang
European Journal of Pharmacology.2024; 970: 176481. CrossRef - Onion Polyphenols as Multi-Target-Directed Ligands in MASLD: A Preliminary Molecular Docking Study
Maria Rosaria Paravati, Anna Caterina Procopio, Maja Milanović, Giuseppe Guido Maria Scarlata, Nataša Milošević, Maja Ružić, Nataša Milić, Ludovico Abenavoli
Nutrients.2024; 16(8): 1226. CrossRef - Present and Future of Dyslipidaemia Treatment—A Review
Iveta Merćep, Andro Vujević, Dominik Strikić, Ivana Radman, Ivan Pećin, Željko Reiner
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(18): 5839. CrossRef - VLDL receptor gene therapy for reducing atherogenic lipoproteins
Ronald M. Krauss, Jonathan T. Lu, Joseph J. Higgins, Cathryn M. Clary, Ray Tabibiazar
Molecular Metabolism.2023; 69: 101685. CrossRef - The emerging role of PPAR-alpha in breast cancer
Zhiwen Qian, Lingyan Chen, Jiayu Liu, Ying Jiang, Yan Zhang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 161: 114420. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives of peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor α agonists in cardiovascular health and disease
Yujie Pu, Chak Kwong Cheng, Hongsong Zhang, Jiang‐Yun Luo, Li Wang, Brian Tomlinson, Yu Huang
Medicinal Research Reviews.2023; 43(6): 2086. CrossRef - Macrophage angiotensin-converting enzyme reduces atherosclerosis by increasing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and fundamentally changing lipid metabolism
DuoYao Cao, Zakir Khan, Xiaomo Li, Suguru Saito, Ellen A Bernstein, Aaron R Victor, Faizan Ahmed, Aoi O Hoshi, Luciana C Veiras, Tomohiro Shibata, Mingtian Che, Lei Cai, Michifumi Yamashita, Ryan E Temel, Jorge F Giani, Daniel J Luthringer, Ajit S Divakar
Cardiovascular Research.2023; 119(9): 1825. CrossRef - Rapid flow synthesis of fenofibrate via scalable flash chemistry with in-line Li recovery
Sanket A. Kawale, Dong-Chang Kang, Gwang-Noh Ahn, Amirreza Mottafegh, Ji-Ho Kang, Gi-Su Na, Dong-Pyo Kim
Chemical Engineering Journal.2023; 477: 147033. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Safety of Fenofibrate in Routine Treatment of Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia and Metabolic Syndrome
Marat V. Ezhov, Gregory P. Arutyunov
Diseases.2023; 11(4): 140. CrossRef - Development of New Genome Editing Tools for the Treatment of Hyperlipidemia
Giulio Preta
Cells.2023; 12(20): 2466. CrossRef - Exploring the hypolipidemic effects of bergenin from Saxifraga melanocentra Franch: mechanistic insights and potential for hyperlipidemia treatment
Li Zhang, Yingying Tong, Yan Fang, Jinjin Pei, Qilan Wang, Gang Li
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and Dyslipidemia
Barbora Nussbaumerova, Hana Rosolova
Current Atherosclerosis Reports.2023; 25(12): 947. CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of residual cardiovascular risk: trends and frontiers
Lin Wang, Sutong Wang, Chaoyuan Song, Yiding Yu, Yuehua Jiang, Yongcheng Wang, Xiao Li
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia in Apoa5–/– mice results from reduced amounts of lipoprotein lipase in the capillary lumen
Ye Yang, Anne P. Beigneux, Wenxin Song, Le Phuong Nguyen, Hyesoo Jung, Yiping Tu, Thomas A. Weston, Caitlyn M. Tran, Katherine Xie, Rachel G. Yu, Anh P. Tran, Kazuya Miyashita, Katsuyuki Nakajima, Masami Murakami, Yan Q. Chen, Eugene Y. Zhen, Joonyoung R.
Journal of Clinical Investigation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood-Derived Lipid and Metabolite Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Research from Clinical Studies: A Recent Update
Dipali Kale, Amol Fatangare, Prasad Phapale, Albert Sickmann
Cells.2023; 12(24): 2796. CrossRef - Effective, disease-modifying, clinical approaches to patients with mild-to-moderate hypertriglyceridaemia
Gary F Lewis, Robert A Hegele
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2022; 10(2): 142. CrossRef - Effects of Alirocumab on Triglyceride Metabolism: A Fat-Tolerance Test and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study
Thomas Metzner, Deborah R. Leitner, Karin Mellitzer, Andrea Beck, Harald Sourij, Tatjana Stojakovic, Gernot Reishofer, Winfried März, Ulf Landmesser, Hubert Scharnagl, Hermann Toplak, Günther Silbernagel
Biomedicines.2022; 10(1): 193. CrossRef - Is there a role of lipid-lowering therapies in the management of fatty liver disease?
Ismini Tzanaki, Aris P Agouridis, Michael S Kostapanos
World Journal of Hepatology.2022; 14(1): 119. CrossRef - Therapeutic Strategies and Chemoprevention of Atherosclerosis: What Do We Know and Where Do We Go?
Ana Clara Aprotosoaie, Alexandru-Dan Costache, Irina-Iuliana Costache
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(4): 722. CrossRef - The Overlooked Transformation Mechanisms of VLCFAs: Peroxisomal β-Oxidation
Qinyue Lu, Weicheng Zong, Mingyixing Zhang, Zhi Chen, Zhangping Yang
Agriculture.2022; 12(7): 947. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 517. CrossRef - Novel Targets for a Combination of Mechanical Unloading with Pharmacotherapy in Advanced Heart Failure
Agata Jedrzejewska, Alicja Braczko, Ada Kawecka, Marcin Hellmann, Piotr Siondalski, Ewa Slominska, Barbara Kutryb-Zajac, Magdi H. Yacoub, Ryszard T. Smolenski
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 9886. CrossRef - Lipoprotein Lipase: Is It a Magic Target for the Treatment of Hypertriglyceridemia
Joon Ho Moon, Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 575. CrossRef - Fenofibrate add-on to statin treatment is associated with low all-cause death and cardiovascular disease in the general population with high triglyceride levels
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155327. CrossRef - Alterations of HDL’s to piHDL’s Proteome in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Diseases, and HDL-Targeted Therapies
Veronika Vyletelová, Mária Nováková, Ľudmila Pašková
Pharmaceuticals.2022; 15(10): 1278. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Risk Profile and Lipid Management in the Population-Based Cohort Study LATINO: 20 Years of Real-World Data
Cristina Gavina, Daniel Seabra Carvalho, Marisa Pardal, Marta Afonso-Silva, Diana Grangeia, Ricardo Jorge Dinis-Oliveira, Francisco Araújo, Tiago Taveira-Gomes
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(22): 6825. CrossRef - New and emerging lipid-lowering therapy
James M Backes, Daniel E Hilleman
Future Cardiology.2021; 17(8): 1407. CrossRef - Systemic PFOS and PFOA exposure and disturbed lipid homeostasis in humans: what do we know and what not?
Styliani Fragki, Hubert Dirven, Tony Fletcher, Bettina Grasl-Kraupp, Kristine Bjerve Gützkow, Ron Hoogenboom, Sander Kersten, Birgitte Lindeman, Jochem Louisse, Ad Peijnenburg, Aldert H. Piersma, Hans M. G. Princen, Maria Uhl, Joost Westerhout, Marco J. Z
Critical Reviews in Toxicology.2021; 51(2): 141. CrossRef -
A network pharmacology analysis on drug‐like compounds from
Ganoderma lucidum
for alleviation of atherosclerosis
Ki Kwang Oh, Md. Adnan, Dong Ha Cho
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Fenofibrate-Statin Combination Therapy in Patients With Inadequately Controlled Triglyceride Levels Despite Previous Statin Monotherapy: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, Phase IV Study
Myung Soo Park, Jong-Chan Youn, Eung Ju Kim, Ki Hoon Han, Sang Hak Lee, Sung Hea Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Sung Uk Kwon, Kyu-Hyung Ryu
Clinical Therapeutics.2021; 43(10): 1735. CrossRef - Prevalence of and Factors Associated With the Prescription of Fibrates Among Patients Receiving Lipid-Lowering Drugs in Germany
Louis Jacob, Roger-Axel Greiner, Mark Luedde, Karel Kostev
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology.2021; 78(6): 885. CrossRef - Challenging Issues in the Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Diabetes During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review of Current Literature
Leili Rahimi, Mojtaba Malek, Faramarz Ismail-Beigi, Mohammad E. Khamseh
Advances in Therapy.2020; 37(8): 3450. CrossRef - Treatment With Gemfibrozil Prevents the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease in Obese Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats
Corbin A. Shields, Bibek Poudel, Kasi C. McPherson, Andrea K. Brown, Ubong S. Ekperikpe, Evan Browning, Lamari Sutton, Denise C. Cornelius, Jan M. Williams
Frontiers in Physiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Renal and Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes
Amelia Charlton, Jessica Garzarella, Karin A. M. Jandeleit-Dahm, Jay C. Jha
Biology.2020; 10(1): 18. CrossRef
- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Insulin Resistance Increases Serum Immunoglobulin E Sensitization in Premenopausal Women
- Seung Eun Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Kyungdo Han, Eun Hee Koh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):175-182. Published online April 14, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0150
- 6,196 View
- 123 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
Background Although studies have shown that obesity is associated with aeroallergen sensitization (atopy), controversy still exists. We aimed to investigate the association between metabolic status, obesity, and atopy stratified by sex and menopausal status.
Methods A total of 1,700 adults from the 2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were classified into metabolically healthy nonobese (MHNO), metabolically unhealthy nonobese (MUNO), metabolically healthy obese (MHO), and metabolically unhealthy obese (MUO) by body mass index and insulin resistance. Atopy was defined as a positive response to at least one aeroallergen. Multiple regression analysis was used to evaluate the risk of immunoglobulin E (IgE) elevation or atopy in relation to the degree of metabolic abnormality and obesity.
Results In premenopausal women, total IgE was positively correlated with obesity and insulin resistance. MUNO participants had a higher risk of having elevated total IgE compared to MHNO participants (odds ratio [OR], 2.271; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.201 to 4.294), while MHO participants did not show a significant difference (OR, 1.435; 95% CI, 0.656 to 3.137) in premenopausal women. MUNO, but not MHO was also associated with atopy (OR, 2.157; 95% CI, 1.284 to 3.625). In men and postmenopausal women, there was no significant difference between metabolic status, obesity, and atopy among groups.
Conclusion Increased insulin resistance is associated with total IgE and atopy in premenopausal women but not in postmenopausal women or men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is There a Relationship between Insulin Resistance and Eosinophil, Inflammatory Parameters Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, C-Reactive Protein Values?
Meltem YİĞİT, Özgür OLUKMAN
Medical Records.2024; 6(1): 32. CrossRef
- Is There a Relationship between Insulin Resistance and Eosinophil, Inflammatory Parameters Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, C-Reactive Protein Values?
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Metabolic Health, Obesity, and the Risk of Developing Open-Angle Glaucoma: Metabolically Healthy Obese Patients versus Metabolically Unhealthy but Normal Weight Patients
- Younhea Jung, Kyungdo Han, Hae-Young L. Park, Seung Hoon Lee, Chan Kee Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):414-425. Published online December 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0048
- 6,824 View
- 122 Download
- 35 Web of Science
- 38 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study sought to investigate the associations between metabolic health status, obesity, and incidence of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG).
Methods In this nationwide, population-based, longitudinal prospective cohort study conducted using the Korean National Health Insurance System, we categorized all subjects based on presence and severity of metabolic syndrome and obesity. Insurance claims data were used to identify POAG development. Then, Cox regression was applied to calculate the hazard of developing POAG in people with various components of metabolic syndrome, obesity, or their combination.
Results Of the total 287,553 subjects, 4,970 (1.3%) developed POAG. High fasting glucose, blood pressure, and total cholesterol levels were all associated with increased risk of developing POAG. Regarding obesity level, people with body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2 were more likely to develop POAG than those with normal BMI. Also, people with greater number of metabolic syndrome components showed a greater POAG incidence. People who are metabolically unhealthy and obese (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 1.574; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.449 to 1.711) and those who are metabolically unhealthy nonobese (MUNO: adjusted HR, 1.521; 95% CI, 1.405 to 1.645) but not those who are metabolically healthy obese (MHO: adjusted HR, 1.019; 95% CI, 0.907 to 1.144) had an increased hazard of developing POAG compared with metabolically healthy nonobese (MHNO) subjects.
Conclusion Metabolic health status and obesity were significantly associated with increased risk of POAG incidence. MUNO subjects but not MHO subjects showed a higher risk of POAG development than did MHNO subjects, suggesting that metabolic status is more important than obesity in POAG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Association between the Gut Microbiota and Erectile Dysfunction
Tianle Zhu, Xi Liu, Peng Yang, Yukuai Ma, Pan Gao, Jingjing Gao, Hui Jiang, Xiansheng Zhang
The World Journal of Men's Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Potentially compromised systemic and local lactate metabolic balance in glaucoma, which could increase retinal glucose and glutamate concentrations
Mina Arai-Okuda, Yusuke Murai, Hidetaka Maeda, Akiyasu Kanamori, Takako Miki, Tomoko Naito, Kazunobu Sugihara, Michihiro Kono, Masaki Tanito, Hiromitsu Onoe, Kazuyuki Hirooka, Yoshiaki Kiuchi, Masakazu Shinohara, Sentaro Kusuhara, Sotaro Mori, Kaori Ueda,
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Glaucoma in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes
Siar Niazi, Filip Gnesin, Anna-Sophie Thein, Jens R. Andreasen, Anna Horwitz, Zaynab A. Mouhammad, Baker N. Jawad, Zia Niazi, Nelsan Pourhadi, Bochra Zareini, Amani Meaidi, Christian Torp-Pedersen, Miriam Kolko
Ophthalmology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Glycemic Traits and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Mendelian Randomization Study in the Japanese Population
Akiko Hanyuda, Atsushi Goto, Masahiro Nakatochi, Yoichi Sutoh, Akira Narita, Shiori Nakano, Ryoko Katagiri, Kenji Wakai, Naoyuki Takashima, Teruhide Koyama, Kokichi Arisawa, Issei Imoto, Yukihide Momozawa, Kozo Tanno, Atsushi Shimizu, Atsushi Hozawa, Keng
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2023; 245: 193. CrossRef - Microbiome Dysbiosis: A Pathological Mechanism at the Intersection of Obesity and Glaucoma
Salvatore Pezzino, Maria Sofia, Luigi Piero Greco, Giorgia Litrico, Giulia Filippello, Iacopo Sarvà, Gaetano La Greca, Saverio Latteri
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 1166. CrossRef - Phenotypic and Genetic Links between Body Fat Measurements and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Shi Song Rong, Xinting Yu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3925. CrossRef - Metabolic Health, Obesity, and Intraocular Pressure
Younhea Jung, Gyoung Nyun Kim, Eun Byeol Oh, Kyoung Ohn, Jung Il Moon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(5): 2066. CrossRef - Association between lifestyle habits and glaucoma incidence: a retrospective cohort study
Asahi Fujita, Yohei Hashimoto, Hiroki Matsui, Hideo Yasunaga, Makoto Aihara
Eye.2023; 37(16): 3470. CrossRef - Towards precision medicine in bariatric surgery prescription
Sofia S. Pereira, Marta Guimarães, Mariana P. Monteiro
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2023; 24(5): 961. CrossRef - Study of the relationship between serum lipid levels and primary open-angle glaucoma
Rajesh Subhash Joshi, Vaishnavi Hitesh Adatiya
Indian Journal of Ophthalmology.2023; 71(5): 1948. CrossRef - Primary open-angle glaucoma risk prediction with ABCA1 and LOC102723944 variants and their genotype–phenotype correlations in southern Chinese population
Zhenggen Wu, Chukai Huang, Yuqian Zheng, Xiang-Ling Yuan, Shaowan Chen, Yanxuan Xu, Li Jia Chen, Chi Pui Pang, Mingzhi Zhang, Tsz Kin Ng
Molecular Genetics and Genomics.2023; 298(6): 1343. CrossRef - Differences in Factors Associated With Glaucoma Progression With Lower Normal Intraocular Pressure in Superior and Inferior Halves of the Optic Nerve Head
Ryo Asaoka, Rei Sakata, Takeshi Yoshitomi, Aiko Iwase, Chota Matsumoto, Tomomi Higashide, Motohiro Shirakashi, Makoto Aihara, Kazuhisa Sugiyama, Makoto Araie
Translational Vision Science & Technology.2023; 12(8): 19. CrossRef - The association between obesity and glaucoma in older adults: evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Xiaohuan Zhao, Qiyu Bo, Junran Sun, Jieqiong Chen, Tong Li, Xiaoxu Huang, Minwen Zhou, Jing Wang, Wenjia Liu, Xiaodong Sun
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023034. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome as an independent risk factor for glaucoma: a nationally representative study
Jun-Hyuk Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Sung Jin Kim, Boyoung Joung
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors: Interaction Issues in Patients with Glaucoma and Arterial Hypertension. Review
S. I. Makogon, D. I. Ivanova, A. L. Onishchenko
Ophthalmology in Russia.2023; 20(4): 641. CrossRef - The role of the microbiota in glaucoma
Ling Huang, Yiwen Hong, Xiangyu Fu, Haishan Tan, Yongjiang Chen, Yujiao Wang, Danian Chen
Molecular Aspects of Medicine.2023; 94: 101221. CrossRef - Girl Power in Glaucoma: The Role of Estrogen in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
Kyrylo Fotesko, Bo Schneider Vohra Thomsen, Miriam Kolko, Rupali Vohra
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology.2022; 42(1): 41. CrossRef - Cholesterol and glaucoma: a systematic review and meta‐analysis
Laura Posch‐Pertl, Monja Michelitsch, Gernot Wagner, Brigitte Wildner, Günther Silbernagel, Gudrun Pregartner, Andreas Wedrich
Acta Ophthalmologica.2022; 100(2): 148. CrossRef - Non-drug interventions in glaucoma: Putative roles for lifestyle, diet and nutritional supplements
Foroogh Fahmideh, Nicoletta Marchesi, Annalisa Barbieri, Stefano Govoni, Alessia Pascale
Survey of Ophthalmology.2022; 67(3): 675. CrossRef - Relationship between Using Fibrate and Open-Angle Glaucoma in Hyperlipidemic Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Yung-En Tsai, Yi-Hao Chen, Chien-An Sun, Chi-Hsiang Chung, Wu-Chien Chien, Ke-Hung Chien
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(4): 2415. CrossRef - The Causal Association Between Obesity and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
Yi Lin, Xiaomin Zhu, Wangdu Luo, Bingcai Jiang, Qianyi Lin, Min Tang, Xiangji Li, Lin Xie
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Enzymatic activity of paraoxonase depending on polymorphism Q192R of the PON1 gene in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma
Yu.E. Filippova, T.N. Malishevskaya, S.A. Petrov, D.G. Gubin, A.S. Vlasova
Vestnik oftal'mologii.2022; 138(2): 58. CrossRef - Association of Metabolic Syndrome With Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension in a Midwest United States Population
Kristi Y. Wu, David O. Hodge, Launia J. White, Jacinta McDonald, Gavin W. Roddy
Journal of Glaucoma.2022; 31(6): e18. CrossRef - Metabolically Defined Body Size Phenotypes and Risk of Endometrial Cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)
Nathalie Kliemann, Romain Ould Ammar, Carine Biessy, Audrey Gicquiau, Verena Katzke, Rudolf Kaaks, Anne Tjønneland, Anja Olsen, Maria-Jose Sánchez, Marta Crous-Bou, Fabrizio Pasanisi, Sandar Tin Tin, Aurora Perez-Cornago, Dagfinn Aune, Sofia Christakoudi,
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2022; 31(7): 1359. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Management of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma in the United States: An Analysis of Real-World Evidence
Joseph S Imperato, Kelly H Zou, Jim Z Li, Tarek A Hassan
Patient Preference and Adherence.2022; Volume 16: 2213. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of Dyslipidemia and Blood Lipid Parameters on the Risk of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Guimei Huang, Jiayi Wang, Lei Li, Yuan Gao, Yijie Yan, Xi Lou
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Body shape and risk of glaucoma: A Mendelian randomization
Ruolan Yuan, Kangcheng Liu, Yingjun Cai, Fei He, Xiaoxiong Xiao, Jing Zou
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Systemic Comorbidities on Ocular Hypertension and Open-Angle Glaucoma, in a Population from Spain and Portugal
Carolina Garcia-Villanueva, Elena Milla, José M. Bolarin, José J. García-Medina, Javier Cruz-Espinosa, Javier Benítez-del-Castillo, José Salgado-Borges, Francisco J. Hernández-Martínez, Elena Bendala-Tufanisco, Irene Andrés-Blasco, Alex Gallego-Martinez,
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(19): 5649. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and its components are associated with non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy
Darrell Kohli, Kristi Y Wu, Launia J White, David O Hodge, John J Chen, Gavin W Roddy
BMJ Open Ophthalmology.2022; 7(1): e001111. CrossRef - Blood Pressure Measures and Incident Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Carmelo Macri, Christopher X. Wong, Samuel J. Tu, Robert Casson, Kuldev Singh, Sophia Y. Wang, Michelle T. Sun
Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science.2022; 63(13): 3. CrossRef - Relationship between anthropometric and biochemical changes of metabolic syndrome with retinal nerve fiber layer and macular thickness
Sze Hui New, Sue Ngein Leow, Suresh Kumar Vasudevan, Idayu Badilla Idris, Seng Fai Tang, Norshamsiah Md Din, Bang V Bui
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(2): e0246830. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and the aging retina
Gavin W. Roddy
Current Opinion in Ophthalmology.2021; 32(3): 280. CrossRef - Automated Detection of Glaucoma With Interpretable Machine Learning Using Clinical Data and Multimodal Retinal Images
Parmita Mehta, Christine A. Petersen, Joanne C. Wen, Michael R. Banitt, Philip P. Chen, Karine D. Bojikian, Catherine Egan, Su-In Lee, Magdalena Balazinska, Aaron Y. Lee, Ariel Rokem
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2021; 231: 154. CrossRef - Association of Hypertriglyceridemia and Incident Glaucoma in a Rural Chinese Population: The Handan Eye Study
Ye Zhang, Qing Zhang, Ravi Thomas, Si Zhen Li, Ning Li Wang
Translational Vision Science & Technology.2021; 10(8): 25. CrossRef - Risk of Glaucoma Associated with Components of Metabolic Disease in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Ya-Wen Chang, Fung-Chang Sung, Ya-Ling Tzeng, Chih-Hsin Mou, Peng-Tai Tien, Cheng-Wen Su, Yu-Kuei Teng
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 19(1): 305. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated With Ocular Hypertension and Glaucoma
Gavin W. Roddy
Journal of Glaucoma.2020; 29(9): 726. CrossRef - Association of dipping status of blood pressure, visual field defects, and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients with normotensive glaucoma
Seung Uk Lee, Han Su Park, Bong Joon Kim, Hyun Su Kim, Jung Ho Heo, Sung Il Im
Medicine.2020; 99(50): e23565. CrossRef - Ocular findings in metabolic syndrome: a review
Mário Lima-Fontes, Pedro Barata, Manuel Falcão, Ângela Carneiro
Porto Biomedical Journal.2020; 5(6): 104. CrossRef
- The Association between the Gut Microbiota and Erectile Dysfunction
- Epidemiology
- Association between Change in Alcohol Consumption and Metabolic Syndrome: Analysis from the Health Examinees Study
- Seulggie Choi, Kyuwoong Kim, Jong-Koo Lee, Ji-Yeob Choi, Aesun Shin, Sue Kyung Park, Daehee Kang, Sang Min Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):615-626. Published online April 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0128
- 5,423 View
- 86 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background The association between change in alcohol intake and metabolic syndrome is unclear.
Methods This retrospective cohort consisted of 41,368 males and females from the Health Examinees-GEM study. Participants were divided into non-drinkers (0.0 g/day), light drinkers (male: 0.1 to 19.9 g/day; female: 0.1 to 9.9 g/day), moderate drinkers (male: 20.0 to 39.9 g/day; female: 10.0 to 19.9 g/day), and heavy drinkers (male: ≥40.0 g/day; female: ≥20.0 g/day) for each of the initial and follow-up health examinations. Logistic regression analysis was used to determine the adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for developing metabolic syndrome according to the change in alcohol consumption between the initial and follow-up health examinations. Adjusted mean values for the change in waist circumference, fasting serum glucose (FSG), blood pressure, triglycerides, and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels were determined according to the change in alcohol consumption by linear regression analysis.
Results Compared to persistent light drinkers, those who increased alcohol intake to heavy levels had elevated risk of metabolic syndrome (aOR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.09 to 1.92). In contrast, heavy drinkers who became light drinkers had reduced risk of metabolic syndrome (aOR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.44 to 0.84) compared to persistent heavy drinkers. Increased alcohol consumption was associated with elevated adjusted mean values for waist circumference, FSG, blood pressure, triglycerides, and HDL-C levels (all
P <0.05). Reduction in alcohol intake was associated with decreased waist circumference, FSG, blood pressure, triglycerides, and HDL-C levels among initial heavy drinkers (allP <0.05).Conclusion Heavy drinkers who reduce alcohol consumption could benefit from reduced risk of metabolic syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inverse association between type 2 diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma in East Asian populations
Jinlong Huo, Yaxuan Xu, Xingqi Chen, Jie Yu, Lijin Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulation Mechanism and Potential Value of Active Substances in Spices in Alcohol–Liver–Intestine Axis Health
Jianyu Huang, Tao Huang, Jinjun Li
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3728. CrossRef - Impact of green space and built environment on metabolic syndrome: A systematic review with meta-analysis
Muhammad Mainuddin Patwary, Mohammad Javad Zare Sakhvidi, Sadia Ashraf, Payam Dadvand, Matthew H.E.M. Browning, Md Ashraful Alam, Michelle L. Bell, Peter James, Thomas Astell-Burt
Science of The Total Environment.2024; 923: 170977. CrossRef - Causal effects of sleep traits on metabolic syndrome and its components: a Mendelian randomization study
Yongli Yang, Long Wen, Xuezhong Shi, Chaojun Yang, Jingwen Fan, Yi Zhang, Guibin Shen, Huiping Zhou, Xiaocan Jia
Sleep and Breathing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of biochemical markers for diabetes prevention in the new decade
Marie Chan Sun, Marie A. S. Landinaff, Ruben Thoplan
Physical Sciences Reviews.2023; 8(11): 3767. CrossRef - Alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome: Clinical and epidemiological impact on liver disease
Fredrik Åberg, Christopher D. Byrne, Carlos J. Pirola, Ville Männistö, Silvia Sookoian
Journal of Hepatology.2023; 78(1): 191. CrossRef - Serum Nutritional Biomarkers and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in U.S. Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: The Results from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001–2006
Xinwei Peng, Jingjing Zhu, Henry S. Lynn, Xi Zhang
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 553. CrossRef - Evaluation and Treatment of Obesity and Its Comorbidities: 2022 Update of Clinical Practice Guidelines for Obesity by the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity
Kyoung-Kon Kim, Ji-Hee Haam, Bom Taeck Kim, Eun Mi Kim, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Eonju Jeon, Eungu Kang, Ga Eun Nam, Hye Yeon Koo, Jeong-Hyun Lim, Jo-Eun Jeong, Jong-Hee Kim, Jong Won Kim, Jung Ha Park, Jun Hwa Hong, Sang Eok Lee, Se Hee Min, Seung
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between alcohol consumption and risk of hyperuricaemia among adults: a large cross-sectional study in Chongqing, China
Siyu Chen, Rui Ding, Xiaojun Tang, Liling Chen, Qinwen Luo, Meng Xiao, Xianbin Ding, Bin Peng
BMJ Open.2023; 13(12): e074697. CrossRef - Lifestyle Factors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Urban Cambodia
Miharu Tamaoki, Ikumi Honda, Keisuke Nakanishi, Maki Nakajima, Sophathya Cheam, Manabu Okawada, Hisataka Sakakibara
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(17): 10481. CrossRef - Gender Differences of Health Behaviors in the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome for Middle-Aged Adults: A National Cross-Sectional Study in South Korea
Jaehee Yoon, Jeewuan Kim, Heesook Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3699. CrossRef - Association between alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome among Chinese adults
Yi Lin, Yan-Yan Ying, Si-Xuan Li, Si-Jia Wang, Qing-Hai Gong, Hui Li
Public Health Nutrition.2021; 24(14): 4582. CrossRef - Triglyceride-rich lipoprotein and LDL particle subfractions and their association with incident type 2 diabetes: the PREVEND study
Sara Sokooti, Jose L. Flores-Guerrero, Hiddo J. L. Heerspink, Margery A. Connelly, Stephan J. L. Bakker, Robin P. F. Dullaart
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inverse association between type 2 diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma in East Asian populations

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





