
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Basic Research
- Mitochondrial Stress and Mitokines: Therapeutic Perspectives for the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases
- Benyuan Zhang, Joon Young Chang, Min Hee Lee, Sang-Hyeon Ju, Hyon-Seung Yi, Minho Shong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):1-18. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0115

- 2,035 View
- 255 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Mitochondrial stress and the dysregulated mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) are linked to various diseases, including metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer. Mitokines, signaling molecules released by mitochondrial stress response and UPRmt, are crucial mediators of inter-organ communication and influence systemic metabolic and physiological processes. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of mitokines, including their regulation by exercise and lifestyle interventions and their implications for various diseases. The endocrine actions of mitokines related to mitochondrial stress and adaptations are highlighted, specifically the broad functions of fibroblast growth factor 21 and growth differentiation factor 15, as well as their specific actions in regulating inter-tissue communication and metabolic homeostasis. Finally, we discuss the potential of physiological and genetic interventions to reduce the hazards associated with dysregulated mitokine signaling and preserve an equilibrium in mitochondrial stress-induced responses. This review provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying mitochondrial regulation of health and disease by exploring mitokine interactions and their regulation, which will facilitate the development of targeted therapies and personalized interventions to improve health outcomes and quality of life.
- Basic Research
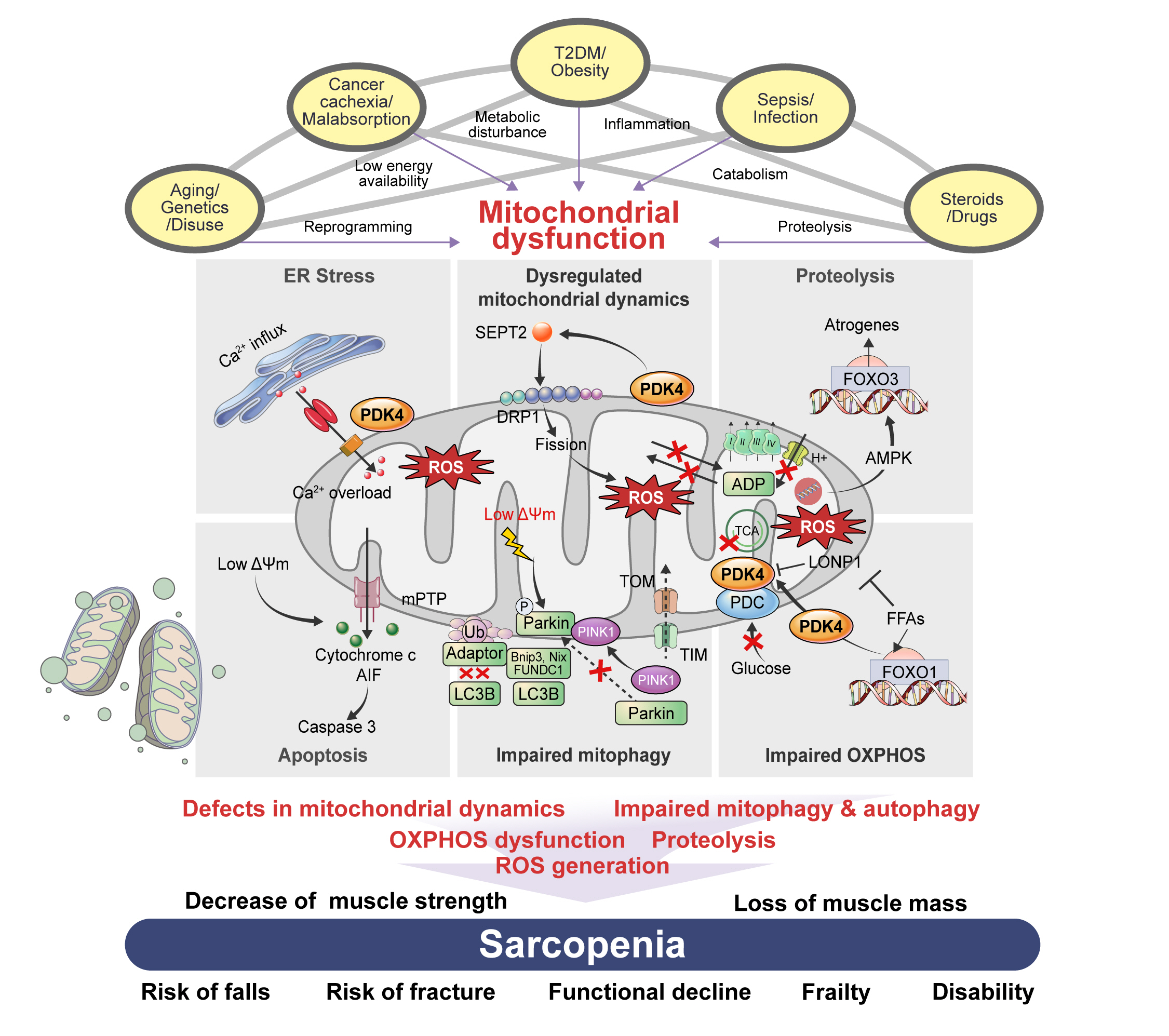
- The Link between Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Sarcopenia: An Update Focusing on the Role of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4
- Min-Ji Kim, Ibotombi Singh Sinam, Zerwa Siddique, Jae-Han Jeon, In-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):153-163. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0305
- 4,858 View
- 367 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Sarcopenia, defined as a progressive loss of muscle mass and function, is typified by mitochondrial dysfunction and loss of mitochondrial resilience. Sarcopenia is associated not only with aging, but also with various metabolic diseases characterized by mitochondrial dyshomeostasis. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases (PDKs) are mitochondrial enzymes that inhibit the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which controls pyruvate entry into the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the subsequent adenosine triphosphate production required for normal cellular activities. PDK4 is upregulated in mitochondrial dysfunction-related metabolic diseases, especially pathologic muscle conditions associated with enhanced muscle proteolysis and aberrant myogenesis. Increases in PDK4 are associated with perturbation of mitochondria-associated membranes and mitochondrial quality control, which are emerging as a central mechanism in the pathogenesis of metabolic disease-associated muscle atrophy. Here, we review how mitochondrial dysfunction affects sarcopenia, focusing on the role of PDK4 in mitochondrial homeostasis. We discuss the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of PDK4 on mitochondrial dysfunction in sarcopenia and show that targeting mitochondria could be a therapeutic target for treating sarcopenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis, activatory effects, molecular docking and ADME studies as rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase activators of ureido phenyl substituted 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives
Mustafa Oğuzhan Kaya, Tuna Demirci, Ümit Çalışır, Oğuzhan Özdemir, Yeşim Kaya, Mustafa Arslan
Research on Chemical Intermediates.2024; 50(1): 437. CrossRef - Unraveling the causes of sarcopenia: Roles of neuromuscular junction impairment and mitochondrial dysfunction
Yanmei Miao, Leiyu Xie, Jiamei Song, Xing Cai, Jinghe Yang, Xinglong Ma, Shaolin Chen, Peng Xie
Physiological Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic clues to aging: exploring the role of circulating metabolites in frailty, sarcopenia and vascular aging related traits and diseases
Zonghao Qian, Yuzhen Huang, Yucong Zhang, Ni Yang, Ziwei Fang, Cuntai Zhang, Le Zhang
Frontiers in Genetics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4 Protects Cardiomyocytes from lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mitochondrial Damage by Reducing Lactate Accumulation
Tangtian Chen, Qiumin Xie, Bin Tan, Qin Yi, Han Xiang, Rui Wang, Qin Zhou, Bolin He, Jie Tian, Jing Zhu, Hao Xu
Inflammation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of resistance training plus enriched probiotic supplement on sestrin2, oxidative stress, and mitophagy markers in elderly male Wistar rats
Majid Mohabbat, Hamid Arazi
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Neuroprotective Effects and Therapeutic Potential of Dichloroacetate: Targeting Metabolic Disorders in Nervous System Diseases
Yue Zhang, Meiyan Sun, Hongxiang Zhao, Zhengyan Wang, Yanan Shi, Jianxin Dong, Kaifang Wang, Xi Wang, Xingyue Li, Haiyan Qi, Xiaoyong Zhao
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2023; Volume 18: 7559. CrossRef
- Synthesis, activatory effects, molecular docking and ADME studies as rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase activators of ureido phenyl substituted 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives
- Basic Research
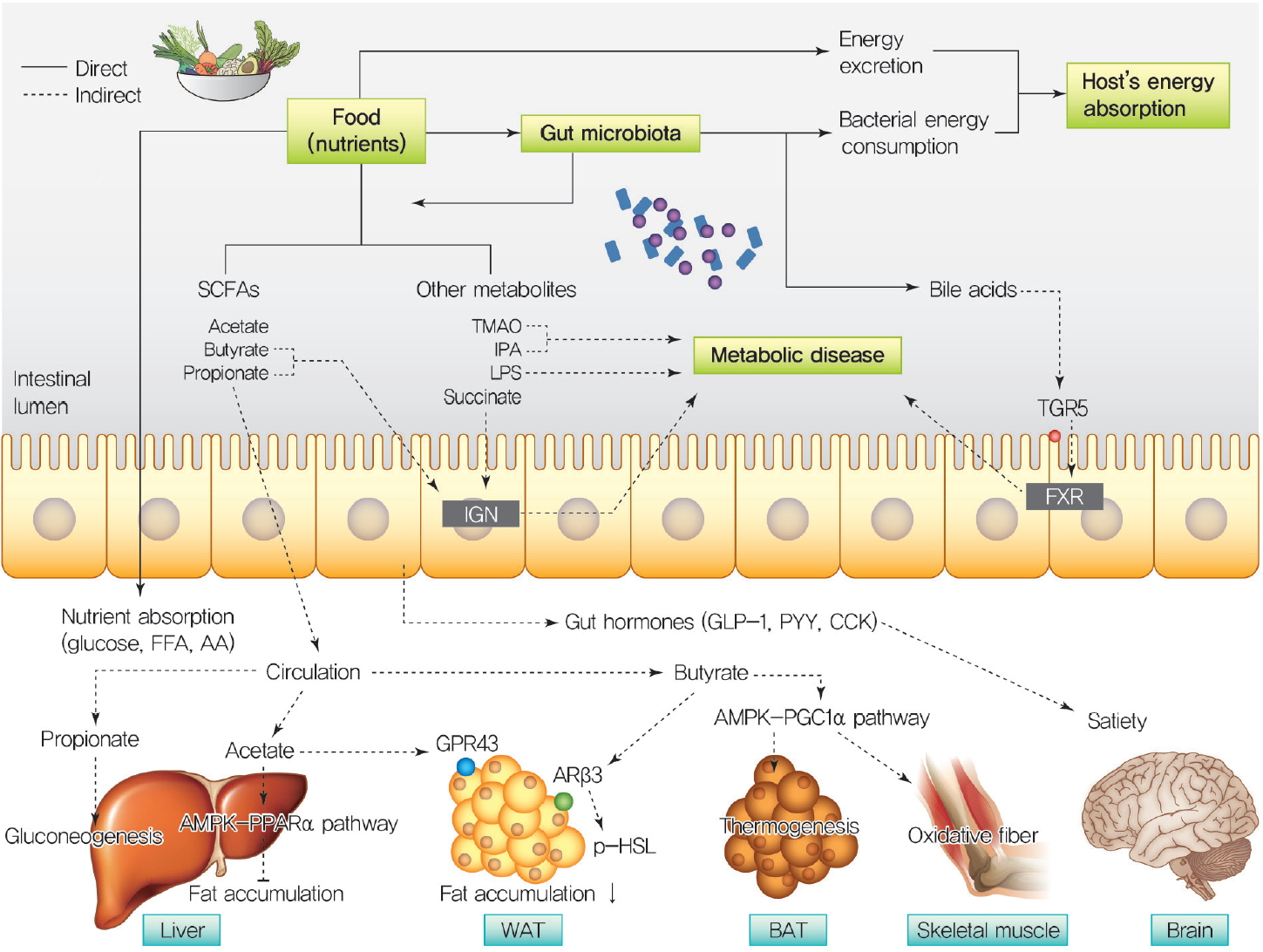
- Revisiting the Bacterial Phylum Composition in Metabolic Diseases Focused on Host Energy Metabolism
- Yeonmi Lee, Hui-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):658-667. Published online July 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0220
- 9,007 View
- 131 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Over a hundred billion bacteria are found in human intestines. This has emerged as an environmental factor in metabolic diseases, such as obesity and related diseases. The majority of these bacteria belong to two dominant phyla,
Bacteroidetes andFirmicutes . Since the ratio ofFirmicutes toBacteroidetes increases in people with obesity and in various animal models, it has been assumed that phylum composition causes the increase in occurrence of metabolic diseases over the past decade. However, this assumption has been challenged by recent studies that have found even an opposite association of phylum composition within metabolic diseases. Moreover, the gut microbiota affects host energy metabolism in various ways including production of metabolites and interaction with host intestinal cells to regulate signaling pathways that affect energy metabolism. However, the direct effect of gut bacteria on host energy intake, such as energy consumption by the bacteria itself and its effects on intestinal energy absorption, has been underestimated. This review aims to discuss whether increased ratio ofFirmicutes toBacteroidetes is associated with the development of metabolic diseases, and whether energy competition between the bacteria and host is a missing part of the mechanism linking gut microbiota to metabolic diseases.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Behavior, intestinal health, and growth of small sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus in different color morphs
Peng Ding, Yushi Yu, Zihe Zhao, Xiang Li, Xiajing Wang, Huiyan Wang, Xiyuan Huang, Jun Ding, Chong Zhao
Marine Environmental Research.2024; 193: 106300. CrossRef - Traditional Chinese Medicine formula Dai-Zong-Fang alleviating hepatic steatosis in db/db mice via gut microbiota modulation
Li-Wei Zhang, Li-Li Zhu, Xiao-Yun Zhu, Shou-Qiang Fu, Xi-Ming Liu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Repeated inoculation with rumen fluid accelerates the rumen bacterial transition with no benefit on production performance in postpartum Holstein dairy cows
Fanlin Kong, Feiran Wang, Yijia Zhang, Shuo Wang, Wei Wang, Shengli Li
Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of oncogenic signatures in the inflammatory colon of C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet
Huawei Zeng, Bryan D. Safratowich, Wen-Hsing Cheng, Michael R. Bukowski
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2023; 111: 109188. CrossRef - Evaluation of the gut microbiome alterations in healthy rats after dietary exposure to different synthetic ZnO nanoparticles
Xinyi Zhu, Henghui Li, Liuzhu Zhou, Huijun Jiang, Minghui Ji, Jin Chen
Life Sciences.2023; 312: 121250. CrossRef - Microplastic-induced gut microbiota and serum metabolic disruption in Sprague-Dawley rats
Nan Zhao, Meirong Zhao, Hangbiao Jin
Environmental Pollution.2023; 320: 121071. CrossRef - Effects of neutral polysaccharide from Platycodon grandiflorum on high-fat diet-induced obesity via the regulation of gut microbiota and metabolites
Jing Song, Qin liu, Mengqi Hao, Xiaohu Zhai, Juan Chen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolite interactions between host and microbiota during health and disease: Which feeds the other?
Yan Zhang, Rui Chen, DuoDuo Zhang, Shuang Qi, Yan Liu
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 160: 114295. CrossRef - Connecting Gut Microbial Diversity with Plasma Metabolome and Fecal Bile Acid Changes Induced by the Antibiotics Tobramycin and Colistin Sulfate
Aishwarya Murali, Varun Giri, Franziska Maria Zickgraf, Philipp Ternes, Hunter James Cameron, Saskia Sperber, Volker Haake, Peter Driemert, Hennicke Kamp, Dorothee Funk-Weyer, Shana J. Sturla, Ivonne M.C.M. Rietjens, Bennard van Ravenzwaay
Chemical Research in Toxicology.2023; 36(4): 598. CrossRef - Short-Term Alternate Feeding between Terrestrially Sourced Oil- and Fish Oil-Based Diets Modulates the Intestinal Microecology of Juvenile Turbot
Xiuhua Ma, Yaoyao Kong, Houguo Xu, Qingzhu Bi, Mengqing Liang, Kangsen Mai, Yanjiao Zhang
Biology.2023; 12(5): 650. CrossRef - Effects and action mechanisms of lotus leaf (Nelumbo nucifera) ethanol extract on gut microbes and obesity in high-fat diet-fed rats
Zhang Yanan, Ma Lu, Zhang Lu, Huo Jinhai, Wang Weiming
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of coffee with different roasting degrees on obesity and related metabolic disorders
Claudia I. Gamboa-Gómez, Laura J. Barragán-Zúñiga, Fernando Guerrero-Romero, Gerardo Martínez-Aguilar, José Luis Gónzalez, Almendra A. Valenzuela-Ramírez, Juan A. Rojas-Contreras, Monica Anese, Maribel Cervantes Flores, Marilisa Alongi
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 111: 105889. CrossRef - Gut Microbiota and Bacterial Translocation in the Pathogenesis of Liver Fibrosis
Roman Maslennikov, Elena Poluektova, Oxana Zolnikova, Alla Sedova, Anastasia Kurbatova, Yulia Shulpekova, Natyia Dzhakhaya, Svetlana Kardasheva, Maria Nadinskaia, Elena Bueverova, Vladimir Nechaev, Anna Karchevskaya, Vladimir Ivashkin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(22): 16502. CrossRef - Eugenol, A Major Component of Clove Oil, Attenuates Adiposity, and Modulates Gut Microbiota in High‐Fat Diet‐Fed Mice
Mengjie Li, Yuhan Zhao, Yanan Wang, Ruixuan Geng, Jingjing Fang, Seong‐Gook Kang, Kunlun Huang, Tao Tong
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Heimao tea polysaccharides ameliorate obesity by enhancing gut microbiota-dependent adipocytes thermogenesis in mice fed with high fat diet
Yu Wang, Ting Li, Yueyue Liu, Chengcheng Yang, Lei Liu, Xiangnan Zhang, Xingbin Yang
Food & Function.2022; 13(24): 13014. CrossRef - The Interplay of Sex Steroids, the Immune Response, and the Intestinal Microbiota
Fernanda Pace, Paula I. Watnick
Trends in Microbiology.2021; 29(9): 849. CrossRef - Heat stress on microbiota composition, barrier integrity, and
nutrient transport in gut, production performance, and its amelioration in farm
animals
Amlan Kumar Patra, Indrajit Kar
Journal of Animal Science and Technology.2021; 63(2): 211. CrossRef - Mechanisms linking gut microbial metabolites to insulin resistance
Hye Rim Jang, Hui-Young Lee
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(6): 730. CrossRef - The impact of gut microbiota metabolites on cellular bioenergetics and cardiometabolic health
Lenka Tomasova, Marian Grman, Karol Ondrias, Marcin Ufnal
Nutrition & Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Behavior, intestinal health, and growth of small sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus in different color morphs
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
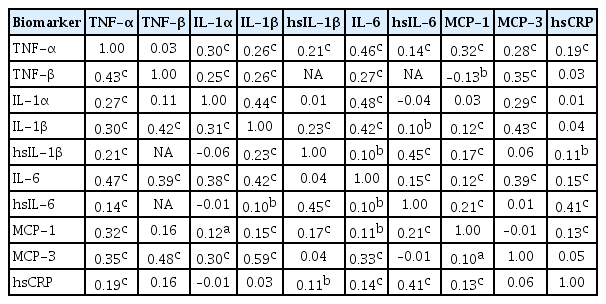
- Sex-, Age-, and Metabolic Disorder-Dependent Distributions of Selected Inflammatory Biomarkers among Community-Dwelling Adults
- So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):711-725. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0119
- 5,920 View
- 83 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Inflammatory cytokines are increasingly utilized to detect high-risk individuals for cardiometabolic diseases. However, with large population and assay methodological heterogeneity, no clear reference currently exists.
Methods Among participants of the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center cohort, of community-dwelling adults aged 30 to 64 without overt cardiovascular diseases, we presented distributions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and -β, interleukin (IL)-1α, -1β, and 6, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 and -3 and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) with and without non-detectable (ND) measurements using multiplex enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Then, we compared each markers by sex, age, and prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, using the Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test.
Results In general, there were inconsistencies in direction and magnitude of differences in distributions by sex, age, and prevalence of cardiometabolic disorders. Overall, the median and the 99th percentiles were higher in men than in women. Older participants had higher TNF-α, high sensitivity IL-6 (hsIL-6), MCP-1, hsCRP, TNF-β, and MCP-3 median, after excluding the NDs. Participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus had higher median for all assayed biomarkers, except for TNF-β, IL-1α, and MCP-3, in which the medians for both groups were 0.00 due to predominant NDs. Compared to normotensive group, participants with hypertension had higher TNF-α, hsIL-6, MCP-1, and hsCRP median. When stratifying by dyslipidemia prevalence, the comparison varied significantly depending on the treatment of NDs.
Conclusion Our findings provide sex-, age-, and disease-specific reference values to improve risk prediction and diagnostic performance for inflammatory diseases in both population- and clinic-based settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterizing CD8+ TEMRA Cells in CP/CPPS Patients: Insights from Targeted Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Functional Investigations
Fei Zhang, Qintao Ge, Jialin Meng, Jia Chen, Chaozhao Liang, Meng Zhang
ImmunoTargets and Therapy.2024; Volume 13: 111. CrossRef - Association between physical activity and inflammatory markers in community-dwelling, middle-aged adults
So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Justin Y. Jeon, Hyeon Chang Kim
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2021; 46(7): 828. CrossRef - The monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio: Sex-specific differences in the tuberculosis disease spectrum, diagnostic indices and defining normal ranges
Thomas S. Buttle, Claire Y. Hummerstone, Thippeswamy Billahalli, Richard J. B. Ward, Korina E. Barnes, Natalie J. Marshall, Viktoria C. Spong, Graham H. Bothamley, Selvakumar Subbian
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0247745. CrossRef
- Characterizing CD8+ TEMRA Cells in CP/CPPS Patients: Insights from Targeted Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Functional Investigations
- Pathophysiology
- Regulation of Systemic Glucose Homeostasis by T Helper Type 2 Cytokines
- Yea Eun Kang, Hyun Jin Kim, Minho Shong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):549-559. Published online October 24, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0157
- 6,724 View
- 93 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Obesity results in an inflammatory microenvironment in adipose tissue, leading to the deterioration of tissue protective mechanisms. Although recent studies suggested the importance of type 2 immunity in an anti-inflammatory microenvironment in adipose tissue, the regulatory effects of T helper 2 (Th2) cytokines on systemic metabolic regulation are not fully understood. Recently, we identified the roles of the Th2 cytokine (interleukin 4 [IL-4] and IL-13)-induced adipokine, growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15), in adipose tissue in regulating systemic glucose metabolism via signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) activation. Moreover, we showed that mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation is required to maintain these macrophage-regulating autocrine and paracrine signaling pathways via Th2 cytokine-induced secretion of GDF15. In this review, we discuss how the type 2 immune response and Th2 cytokines regulate metabolism in adipose tissue. Specifically, we review the systemic regulatory roles of Th2 cytokines in metabolic disease and the role of mitochondria in maintenance of type 2 responses in adipose tissue homeostasis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Orchestration of the Adipose Tissue Immune Landscape by Adipocytes
David Bradley, Tuo Deng, Dharti Shantaram, Willa A. Hsueh
Annual Review of Physiology.2024; 86(1): 199. CrossRef - Growth and differentiation factor-15: A link between inflammaging and cardiovascular disease
Balázs Bence Nyárády, Loretta Zsuzsa Kiss, Zsolt Bagyura, Béla Merkely, Edit Dósa, Orsolya Láng, László Kőhidai, Éva Pállinger
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 174: 116475. CrossRef - Evaluation of Mitochondrial Function in Blood Samples Shows Distinct Patterns in Subjects with Thyroid Carcinoma from Those with Hyperplasia
Julia Bernal-Tirapo, María Teresa Bayo Jiménez, Pedro Yuste-García, Isabel Cordova, Ana Peñas, Francisco-Javier García-Borda, Cesar Quintela, Ignacio Prieto, Cristina Sánchez-Ramos, Eduardo Ferrero-Herrero, María Monsalve
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6453. CrossRef - A Supportive Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Insulin-Producing Langerhans Islets with a Specific Emphasis on The Secretome
Ronit Vogt Sionov, Ronit Ahdut-HaCohen
Biomedicines.2023; 11(9): 2558. CrossRef - Gdf15 deletion exacerbates acute lung injuries induced by intratracheal inoculation of aerosolized ricin in mice
Mengyun Deng, Duo Su, Nan Xiao, Zhipeng Zhang, Yifeng Wang, Fuliang Zong, Sha Li, Jinglin Wang, Dongsheng Zhou, Yuee Zhao, Huiying Yang
Toxicology.2022; 469: 153135. CrossRef - Role of PPAR Receptor and Ligands in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Hematologic Malignancies
Jian Wu, Min Zhang, Allison Faircloth
Hemato.2022; 3(3): 422. CrossRef - Macrophage and Adipocyte Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Obesity-Induced Metabolic Diseases
Liwen Wang, Jie Hu, Haiyan Zhou
The World Journal of Men's Health.2021; 39(4): 606. CrossRef - Th2 Cytokines Increase the Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in the Liver
Seul-Gi Kang, Seong-Eun Lee, Min-Jeong Choi, Joon-Young Chang, Jung-Tae Kim, Ben-Yuan Zhang, Yea-Eun Kang, Ju-Hee Lee, Hyon-Seung Yi, Minho Shong
Cells.2021; 10(6): 1298. CrossRef - Growth/Differentiation Factor-15 (GDF-15): From Biomarker to Novel Targetable Immune Checkpoint
Jörg Wischhusen, Ignacio Melero, Wolf Herman Fridman
Frontiers in Immunology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcriptional, Epigenetic and Metabolic Programming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages
Irina Larionova, Elena Kazakova, Marina Patysheva, Julia Kzhyshkowska
Cancers.2020; 12(6): 1411. CrossRef
- Orchestration of the Adipose Tissue Immune Landscape by Adipocytes
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes: Part II: Treatment
- Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Yong Jin Kim, Dae Ho Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Cheol-Young Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):127-143. Published online April 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0034
- 7,673 View
- 140 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 35 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and diabetes are common metabolic disorders that are often comorbid conditions. Among many proposed treatments, weight reduction is the only approved option for NAFLD to date. However, it is not easy to maintain weight loss by lifestyle modification alone; pharmacological treatments are helpful in this regard. Although many drugs have been investigated, pioglitazone could be a first-line therapy in patients with NAFLD and diabetes. Many more drugs are currently being developed and investigated, and it is likely that combination strategies will be used for future treatment of NAFLD and diabetes. Attention should be paid to the management of NAFLD and diabetes and efforts should be made to intervene early and individualize treatment of NAFLD in patients with diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMJ.2024; : e076388. CrossRef - Research Progress of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
强江 郭
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(03): 561. CrossRef - Liver and cardiovascular disease outcomes in metabolic syndrome and diabetic populations: Bi-directional opportunities to multiply preventive strategies
Alhussain Yasin, Madison Nguyen, Angad Sidhu, Priyanka Majety, Jared Spitz, Amon Asgharpour, Mohammad S. Siddiqui, Laurence S. Sperling, Arshed A. Quyyumi, Anurag Mehta
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 211: 111650. CrossRef - Effect of aerobic training with silymarin consumption on glycemic indices and liver enzymes in men with type 2 diabetes
Keyvan Ghalandari, Mojtaba Shabani, Ali Khajehlandi, Amin Mohammadi
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2023; 129(1): 76. CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 220. CrossRef - Comparative antihypertensive efficacy of combinations of azilsartan medoxomil or olmesartan medoxomil with amlodipine in patients with arterial hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
I. А. Lukonin, V. V. Skibitsky, A. V. Fendrikova, A. V. Skibitsky, I. A. Antipov
South Russian Journal of Therapeutic Practice.2023; 4(1): 68. CrossRef - An Ethyl Acetate Extract of Eryngium carlinae Inflorescences Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Liver of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Cristian M. Trejo-Hurtado, Cinthia I. Landa-Moreno, Jenaro Lemus-de la Cruz, Donovan J. Peña-Montes, Rocío Montoya-Pérez, Rafael Salgado-Garciglia, Salvador Manzo-Avalos, Christian Cortés-Rojo, Juan Luis Monribot-Villanueva, José Antonio Guerrero-Analco,
Antioxidants.2023; 12(6): 1235. CrossRef - Pharmacogenetics of glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Iu.G. Samoilova, A.E. Stankova, M.V. Matveeva, O.E. Vaizova, D.V. Podchinenova, D.A. Kudlay, T.A. Filippova, I.R. Grishkevich
Profilakticheskaya meditsina.2023; 26(12): 95. CrossRef - Obesity is an important determinant of severity in newly defined metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
Ji Hye Huh, Kwang Joon Kim, Seung Up Kim, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2022; 21(3): 241. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index is a simple and easy‐to‐calculate marker associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung‐Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2022; 30(6): 1279. CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - Pharmacological Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Antidiabetic Agents
Kyung-Soo Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(2): 83. CrossRef - Efficacy and mechanism of Jiedu Tongluo Tiaogan Formula in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus combined with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Study protocol for a parallel-armed, randomized controlled trial
Jinghan Xu, Chunli Piao, Yue Qu, Tianjiao Liu, Yuting Peng, Qi Li, Xiaohua Zhao, Pei Li, Xuemin Wu, Yawen Fan, Binqin Chen, Jie Yang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intestinal microbiota in the treatment of metabolically associated fatty liver disease
Ji-Shuai Wang, Jin-Chun Liu
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(31): 11240. CrossRef - Efficiency of combined antihypertensive pharmacotherapy in patients with arterial hypertension, combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
I. A. Lukonin, V. V. Skibitsky, A. V. Fendrikova, I. I. Pavlyuchenko, K. Yu. Lazarev, F. A. Kovalenko
Systemic Hypertension.2022; 19(1): 31. CrossRef - Diosgenin Ameliorated Type II Diabetes-Associated Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Inhibiting De Novo Lipogenesis and Improving Fatty Acid Oxidation and Mitochondrial Function in Rats
Yujie Zhong, Zhiman Li, Ruyi Jin, Yanpeng Yao, Silan He, Min Lei, Xin Wang, Chao Shi, Li Gao, Xiaoli Peng
Nutrients.2022; 14(23): 4994. CrossRef - Pluchea indica Leaf Extract Alleviates Dyslipidemia and Hepatic Steatosis by Modifying the Expression of Lipid Metabolism-Related Genes in Rats Fed a High Fat-High Fructose Diet
Patcharin Singdam, Jarinyaporn Naowaboot, Laddawan Senggunprai, Kampeebhorn Boonloh, Patchareewan Pannangpetch
Preventive Nutrition and Food Science.2022; 27(4): 384. CrossRef - NAFLDin type 2 diabetes mellitus: Still many challenging questions
Simona Cernea, Itamar Raz
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Umbilical Cord-Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Improves Insulin Resistance in C2C12 Cell
Kyung-Soo Kim, Yeon Kyung Choi, Mi Jin Kim, Jung Wook Hwang, Kyunghoon Min, Sang Youn Jung, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Soo Choi, Yong-Wook Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 260. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Lobeglitazone Versus Pioglitazone on Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(1): 171. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment
Sook Jung Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(1): 38. CrossRef - Patient Management in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
A. E. Bagriy, A. D. Zubov, M. V. Khomenko, E. S. Mikhailichenko, E. A. Pylaeva, N. A. Khaustova, E. V. Bryukhovetskaya
Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology.2021; 31(2): 14. CrossRef - NAFLD and its link with diabetes: Why we should be worried
Louise Cremonesini, Emma Harkin
Independent Nurse.2021; 2021(8): 20. CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 698. CrossRef - Fatty liver index and development of cardiovascular disease in Koreans without pre-existing myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke: a large population-based study
Jun Hyung Kim, Jin Sil Moon, Seok Joon Byun, Jun Hyeok Lee, Dae Ryong Kang, Ki Chul Sung, Jang Young Kim, Ji Hye Huh
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel antisense inhibition of diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial
Rohit Loomba, Erin Morgan, Lynnetta Watts, Shuting Xia, Lisa A Hannan, Richard S Geary, Brenda F Baker, Sanjay Bhanot
The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 5(9): 829. CrossRef - Hepatic fibrosis is associated with total proteinuria in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes
Eugene Han, Yongin Cho, Kyung-won Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-wan Lee
Medicine.2020; 99(33): e21038. CrossRef - Metabolic liver disease in diabetes – From mechanisms to clinical trials
Bedair Dewidar, Sabine Kahl, Kalliopi Pafili, Michael Roden
Metabolism.2020; 111: 154299. CrossRef - Managing NAFLD in Type 2 Diabetes: The Effect of Lifestyle Interventions, a Narrative Review
Siôn A. Parry, Leanne Hodson
Advances in Therapy.2020; 37(4): 1381. CrossRef -
Diabetes and Metabolism Journal in 2020: Good to Great
In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 1. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
Byung-Wan Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Cheol-Young Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Nan-Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Bong-Soo Cha, Dae Ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 382. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of hepatic insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and potential treatment strategies
Chang-hua Zhang, Bu-gao Zhou, Jun-qing Sheng, Yang Chen, Ying-qian Cao, Chen Chen
Pharmacological Research.2020; 159: 104984. CrossRef - Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 430. CrossRef - Effects of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials
Baodi Xing, Yuhang Zhao, Bingzi Dong, Yue Zhou, Wenshan Lv, Wenjuan Zhao
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2020; 11(5): 1238. CrossRef - Empaglifozin mitigates NAFLD in high-fat-fed mice by alleviating insulin resistance, lipogenesis and ER stress
Tamiris Ingrid Petito-da-Silva, Vanessa Souza-Mello, Sandra Barbosa-da-Silva
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2019; 498: 110539. CrossRef
- Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Early Assessment of the Risk for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Can Fasting Parameters of Glucose Metabolism Contribute to Risk Prediction?
- Veronica Falcone, Grammata Kotzaeridi, Melanie Hanne Breil, Ingo Rosicky, Tina Stopp, Gülen Yerlikaya-Schatten, Michael Feichtinger, Wolfgang Eppel, Peter Husslein, Andrea Tura, Christian S. Göbl
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):785-793. Published online March 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0218
- 7,999 View
- 80 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background An early identification of the risk groups might be beneficial in reducing morbidities in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Therefore, this study aimed to assess the biochemical predictors of glycemic conditions, in addition to fasting indices of glucose disposal, to predict the development of GDM in later stage and the need of glucose-lowering medication.
Methods A total of 574 pregnant females (103 with GDM and 471 with normal glucose tolerance [NGT]) were included. A metabolic characterization was performed before 15+6 weeks of gestation by assessing fasting plasma glucose (FPG), fasting insulin (FI), fasting C-peptide (FCP), and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c). Thereafter, the patients were followed-up until the delivery.
Results Females with NGT had lower levels of FPG, FI, FCP, or HbA1c at the early stage of pregnancy, and therefore, showed an improved insulin action as compared to that in females who developed GDM. Higher fasting levels of FPG and FCP were associated with a higher risk of developing GDM. Moreover, the predictive accuracy of this metabolic profiling was also good to distinguish the patients who required glucose-lowering medications. Indices of glucose disposal based on C-peptide improved the predictive accuracy compared to that based on insulin. A modified quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKIc) showed the best differentiation in terms of predicting GDM (area under the receiver operating characteristics curve [ROC-AUC], 72.1%) or need for pharmacotherapy (ROC-AUC, 83.7%).
Conclusion Fasting measurements of glucose and C-peptide as well as the surrogate indices of glycemic condition could be used for stratifying pregnant females with higher risk of GDM at the beginning of pregnancy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maternal fasting serum C-peptide concentrations in the first and second trimesters and subsequent risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A nested case-control study among Chinese women
Chuanyu Zhao, Haiyan Liu, Yuzhi Deng, Hanbin Wu, Shuo Wang, Xinyi Lyu, Jueming Lei, Haishan Yang, Meina Hu, Yinzhu Zhao, Xu Ma, Xiaoxuan Zou, Ying Yang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111111. CrossRef - Future clinical prospects of C-peptide testing in the early diagnosis of gestational diabetes
Charalampos Milionis, Ioannis Ilias, Anastasia Lekkou, Evangelia Venaki, Eftychia Koukkou
World Journal of Experimental Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Early prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus using maternal demographic and clinical risk factors
Yanqi Wu, Paul Hamelmann, Myrthe van der Ven, Sima Asvadi, M. Beatrijs van der Hout-van der Jagt, S. Guid Oei, Massimo Mischi, Jan Bergmans, Xi Long
BMC Research Notes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestationsdiabetes (GDM) (Update 2023)
Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, Yvonne Winhofer, Herbert Kiss, Veronica Falcone, Angelika Berger, Monika Lechleitner, Raimund Weitgasser, Jürgen Harreiter
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2023; 135(S1): 115. CrossRef - MIDO GDM: an innovative artificial intelligence-based prediction model for the development of gestational diabetes in Mexican women
Héctor Gallardo-Rincón, María Jesús Ríos-Blancas, Janinne Ortega-Montiel, Alejandra Montoya, Luis Alberto Martinez-Juarez, Julieta Lomelín-Gascón, Rodrigo Saucedo-Martínez, Ricardo Mújica-Rosales, Victoria Galicia-Hernández, Linda Morales-Juárez, Lucía Ma
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Progress in the Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by the Combined Detection of Fasting Blood Glucose and Hemoglobin in Early Pregnancy
欢欢 赵
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(06): 9980. CrossRef - HOMA‐IR as a risk factor of gestational diabetes mellitus and a novel simple surrogate index in early pregnancy
Shuoning Song, Yuemei Zhang, Xiaolin Qiao, Yanbei Duo, Jiyu Xu, Zhenyao Peng, Jing Zhang, Yan Chen, Xiaorui Nie, Qiujin Sun, Xianchun Yang, Zechun Lu, Shixuan Liu, Tianyi Zhao, Tao Yuan, Yong Fu, Yingyue Dong, Weigang Zhao, Wei Sun, Ailing Wang
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2022; 157(3): 694. CrossRef - The diagnostic value of glycosylated hemoglobin for gestational diabetes mellitus in Asian populations: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Jiani Zhang, Fan Zhou, Tingting Xu, Jinfeng Xu, Yaqian Li, Li Lin, Qi Cao, Xiaodong Wang
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2022; 48(4): 902. CrossRef - Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 140. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnant Women with Beta-Thalassemia Minor: A Matched Case-Control Study
Veronica Falcone, Florian Heinzl, Bianca Karla Itariu, Theresa Reischer, Stephanie Springer, Dana Anaïs Muin, Petra Pateisky, Philipp Foessleitner, Johannes Ott, Alex Farr, Klara Rosta
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(7): 2050. CrossRef - Maternal metabolic factors and the association with gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Nahal Habibi, Aya Mousa, Chau Thien Tay, Mahnaz Bahri Khomami, Rhiannon K. Patten, Prabha H. Andraweera, Molla Wassie, Jared Vandersluys, Ali Aflatounian, Tina Bianco‐Miotto, Shao J. Zhou, Jessica A. Grieger
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact Of Prepregnancy Overweight And Obesity On Treatment Modality And Pregnancy Outcome In Women With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Tina Linder, Anna Eder, Cécile Monod, Ingo Rosicky, Daniel Eppel, Katharina Redling, Franziska Geissler, Evelyn A. Huhn, Irene Hösli, Christian S. Göbl
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of potential gene markers in gestational diabetes mellitus
Weichun Tang, Xiaoyu Wang, Liping Chen, Yiling Lu, Xinyi Kang
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between early-pregnancy serum C-peptide and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a nested case–control study among Chinese women
Xue Yang, Yi Ye, Yi Wang, Ping Wu, Qi Lu, Yan Liu, Jiaying Yuan, Xingyue Song, Shijiao Yan, Xiaorong Qi, Yi-Xin Wang, Ying Wen, Gang Liu, Chuanzhu Lv, Chun-Xia Yang, An Pan, Jianli Zhang, Xiong-Fei Pan
Nutrition & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Predictors of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in IVF-Conceived Pregnancies
Ayla Coussa, Hayder A. Hasan, Thomas M. Barber
Endocrine Practice.2021; 27(6): 579. CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef - Early Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Strategies and Clinical Implications
Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Lakshmi Nagendra, Aishwarya Krishnamurthy, Om J. Lakhani, Nitin Kapoor, Bharti Kalra, Sanjay Kalra
Medical Sciences.2021; 9(4): 59. CrossRef - Early markers of gestational diabetes mellitus
Vedrana Ivić, Jasenka Wagner, Andrijana Müller, Lada Zibar, Marta Kadivnik, Barbara Viljetić, Jelena Omazić
Biochemia medica.2021; 31(3): 416. CrossRef - Response: Early Assessment of the Risk for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Can Fasting Parameters of Glucose Metabolism Contribute to Risk Prediction? (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:785–93)
Christian S. Göbl, Andrea Tura
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 209. CrossRef - First-trimester fasting glycemia as a predictor of gestational diabetes (GDM) and adverse pregnancy outcomes
G. Sesmilo, P. Prats, S. Garcia, I. Rodríguez, A. Rodríguez-Melcón, I. Berges, B. Serra
Acta Diabetologica.2020; 57(6): 697. CrossRef - Letter: Early Assessment of the Risk for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Can Fasting Parameters of Glucose Metabolism Contribute to Risk Prediction? (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:785–93)
Ye Seul Yang, Hye Seung Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 199. CrossRef - Auch schon im 1. Trimenon ist Nüchternglukose Prädiktor für Gestationsdiabetes
Jens Stupin
Info Diabetologie.2020; 14(2): 14. CrossRef - Comparison of Machine Learning Methods and Conventional Logistic Regressions for Predicting Gestational Diabetes Using Routine Clinical Data: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Yunzhen Ye, Yu Xiong, Qiongjie Zhou, Jiangnan Wu, Xiaotian Li, Xirong Xiao
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Predictive Power of Unconjugated Estriol in Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes: A Cohort Study
Azam Amirian, Nourossadat Kariman, Mehdi Hedayati, Nasrin Borumandnia, Zohre Sheikhan
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Maternal fasting serum C-peptide concentrations in the first and second trimesters and subsequent risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A nested case-control study among Chinese women

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





