
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Others
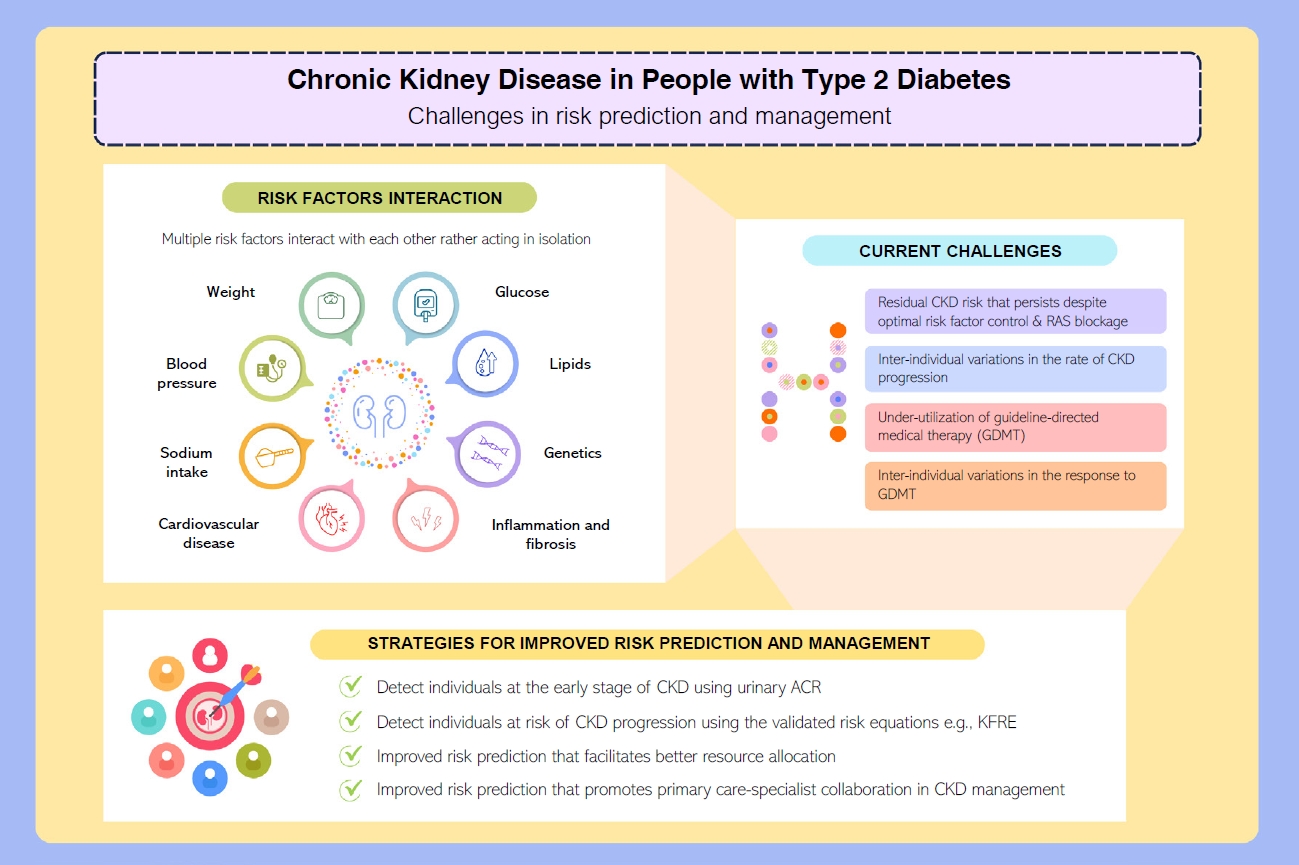
- Risk Prediction and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in People Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ying-Guat Ooi, Tharsini Sarvanandan, Nicholas Ken Yoong Hee, Quan-Hziung Lim, Sharmila S. Paramasivam, Jeyakantha Ratnasingam, Shireene R. Vethakkan, Soo-Kun Lim, Lee-Ling Lim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):196-207. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0244
- 1,838 View
- 350 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - People with type 2 diabetes mellitus have increased risk of chronic kidney disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Improved care delivery and implementation of guideline-directed medical therapy have contributed to the declining incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in high-income countries. By contrast, the global incidence of chronic kidney disease and associated mortality is either plateaued or increased, leading to escalating direct and indirect medical costs. Given limited resources, better risk stratification approaches to identify people at risk of rapid progression to end-stage kidney disease can reduce therapeutic inertia, facilitate timely interventions and identify the need for early nephrologist referral. Among people with chronic kidney disease G3a and beyond, the kidney failure risk equations (KFRE) have been externally validated and outperformed other risk prediction models. The KFRE can also guide the timing of preparation for kidney replacement therapy with improved healthcare resources planning and may prevent multiple complications and premature mortality among people with chronic kidney disease with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. The present review summarizes the evidence of KFRE to date and call for future research to validate and evaluate its impact on cardiovascular and mortality outcomes, as well as healthcare resource utilization in multiethnic populations and different healthcare settings.
- Drug/Regimen
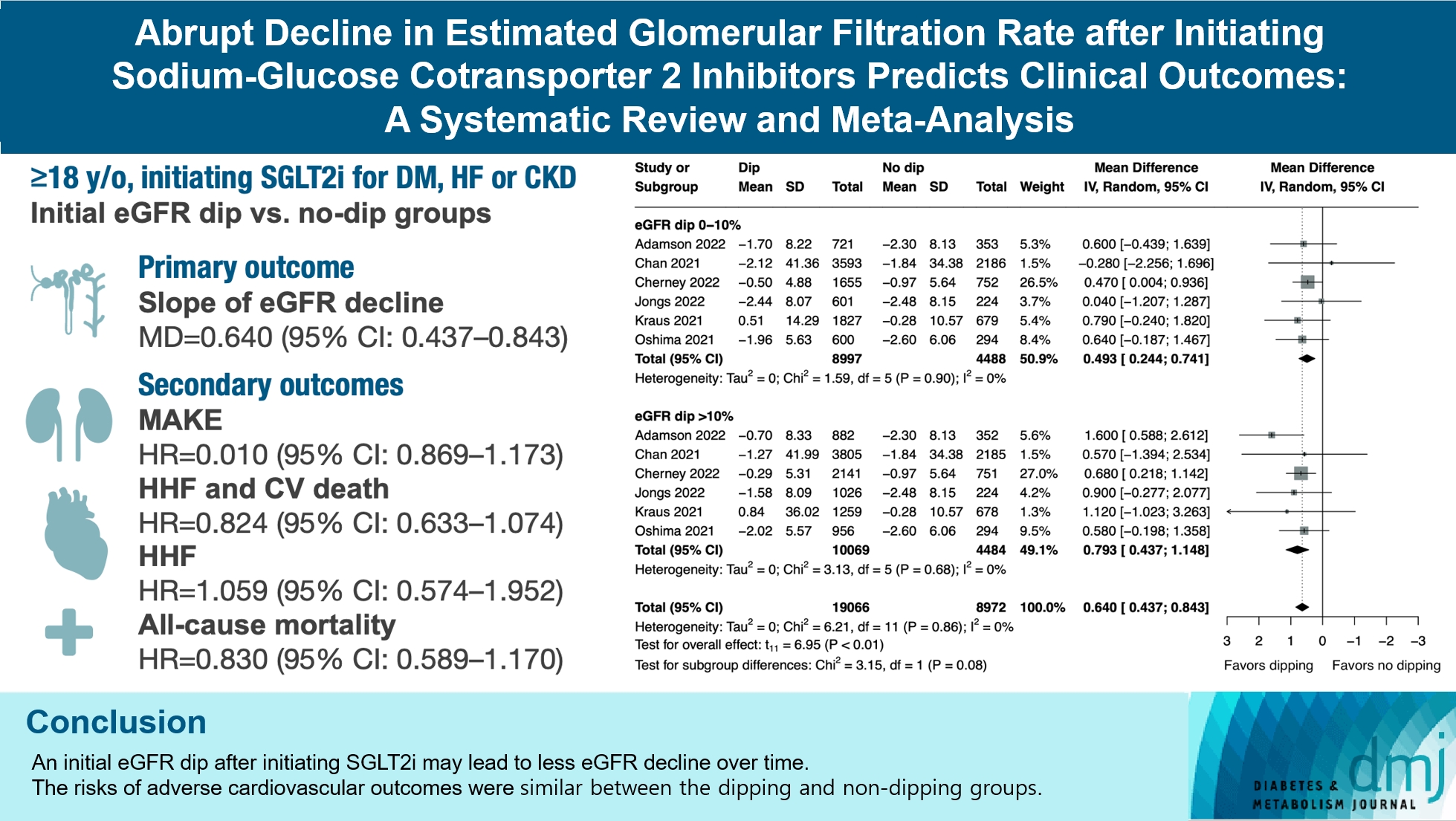
- Abrupt Decline in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate after Initiating Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Predicts Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Min-Hsiang Chuang, Yu-Shuo Tang, Jui-Yi Chen, Heng-Chih Pan, Hung-Wei Liao, Wen-Kai Chu, Chung-Yi Cheng, Vin-Cent Wu, Michael Heung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):242-252. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0201
- 1,501 View
- 202 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The initiation of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) typically leads to a reversible initial dip in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). The implications of this phenomenon on clinical outcomes are not well-defined.
Methods
We searched MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane Library from inception to March 23, 2023 to identify randomized controlled trials and cohort studies comparing kidney and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with and without initial eGFR dip after initiating SGLT2i. Pooled estimates were calculated using random-effect meta-analysis.
Results
We included seven studies in our analysis, which revealed that an initial eGFR dip following the initiation of SGLT2i was associated with less annual eGFR decline (mean difference, 0.64; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.437 to 0.843) regardless of baseline eGFR. The risk of major adverse kidney events was similar between the non-dipping and dipping groups but reduced in patients with a ≤10% eGFR dip (hazard ratio [HR], 0.915; 95% CI, 0.865 to 0.967). No significant differences were observed in the composite of hospitalized heart failure and cardiovascular death (HR, 0.824; 95% CI, 0.633 to 1.074), hospitalized heart failure (HR, 1.059; 95% CI, 0.574 to 1.952), or all-cause mortality (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.589 to 1.170). The risk of serious adverse events (AEs), discontinuation of SGLT2i due to AEs, kidney-related AEs, and volume depletion were similar between the two groups. Patients with >10% eGFR dip had increased risk of hyperkalemia compared to the non-dipping group.
Conclusion
Initial eGFR dip after initiating SGLT2i might be associated with less annual eGFR decline. There were no significant disparities in the risks of adverse cardiovascular outcomes between the dipping and non-dipping groups.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
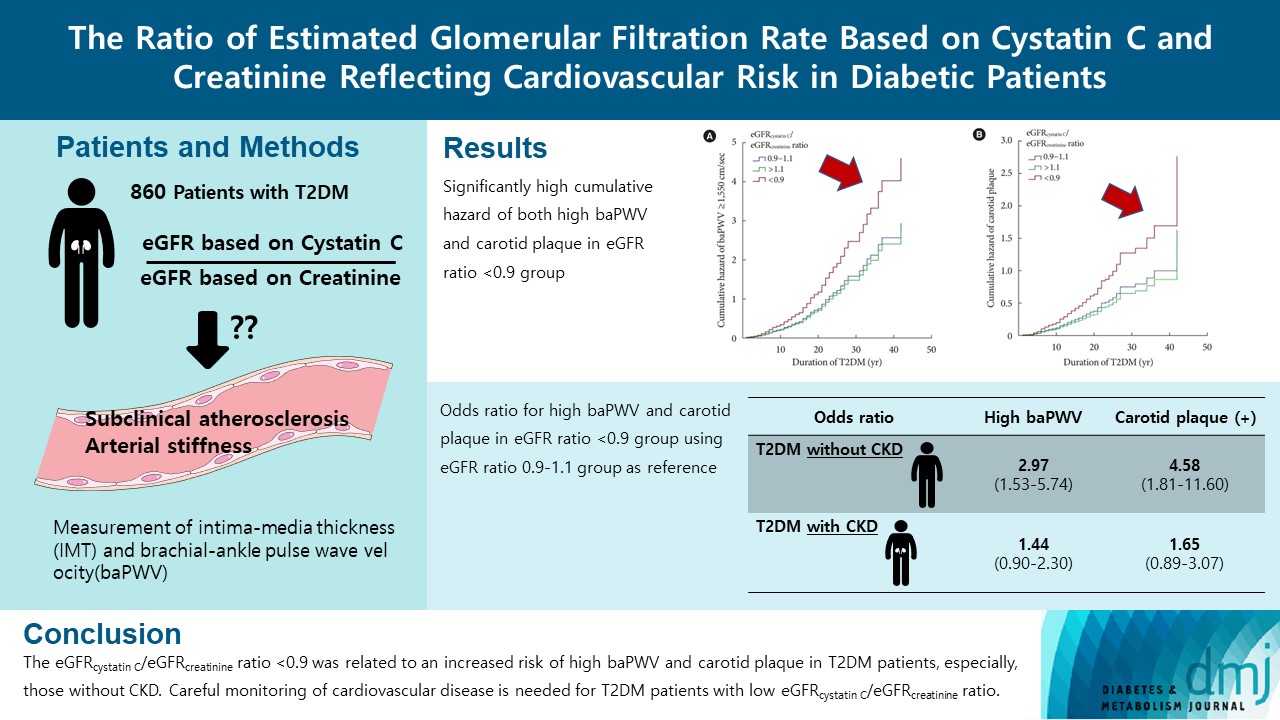
- The Ratio of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Based on Cystatin C and Creatinine Reflecting Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetic Patients
- Ah Reum Khang, Min Jin Lee, Dongwon Yi, Yang Ho Kang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):415-425. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0177
- 1,823 View
- 112 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The ratio of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) based on cystatin C and creatinine (eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio) is related to accumulating atherosclerosis-promoting proteins and increased mortality in several cohorts.
Methods
We assessed whether the eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio is a predictor of arterial stiffness and sub-clinical atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, who were followed up during 2008 to 2016. GFR was estimated using an equation based on cystatin C and creatinine.
Results
A total of 860 patients were stratified according to their eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio (i.e., <0.9, 0.9–1.1 [a reference group], and >1.1). Intima-media thickness was comparable among the groups; however, presence of carotid plaque was frequent in the <0.9 group (<0.9 group, 38.3%; 0.9–1.1 group, 21.6% vs. >1.1 group, 17.2%, P<0.001). Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) was faster in the <0.9 group (<0.9 group, 1,656.3±333.0 cm/sec; 0.9–1.1 group, 1,550.5±294.8 cm/sec vs. >1.1 group, 1,494.0±252.2 cm/sec, P<0.001). On comparing the <0.9 group with the 0.9–1.1 group, the multivariate-adjusted odds ratios of prevalence of high baPWV and carotid plaque were 2.54 (P=0.007) and 1.95 (P=0.042), respectively. Cox regression analysis demonstrated near or over 3-fold higher risks of the prevalence of high baPWV and carotid plaque in the <0.9 group without chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Conclusion
We concluded that eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio <0.9 was related to an increased risk of high baPWV and carotid plaque in T2DM patients, especially, those without CKD. Careful monitoring of cardiovascular disease is needed for T2DM patients with low eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress of Creatinine, Cystatin C, and Their Ratio in Renal Diseases
广智 杨
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(04): 976. CrossRef - Muscle mass, creatinine, cystatin C and selective glomerular hypofiltration syndromes
Linnea Malmgren, Anders Grubb
Clinical Kidney Journal.2023; 16(8): 1206. CrossRef - Investigating kidney function changes in young adults with COVID-19: Serum creatinine level, glomerular filtration rate, and biochemical profile analysis
Nikita Matyushin, Dmitriy Ermakov, Inna Vasileva, Roza Vakolyuk, Anastasiya Spaska
Electronic Journal of General Medicine.2023; 20(6): em547. CrossRef - Intraindividual difference in estimated GFR by creatinine and cystatin C, cognitive trajectories and motoric cognitive risk syndrome
Jinqi Wang, Yueruijing Liu, Rui Jin, Xiaoyu Zhao, Zhiyuan Wu, Ze Han, Zongkai Xu, Xiuhua Guo, Lixin Tao
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research Progress of Creatinine, Cystatin C, and Their Ratio in Renal Diseases
- Complications
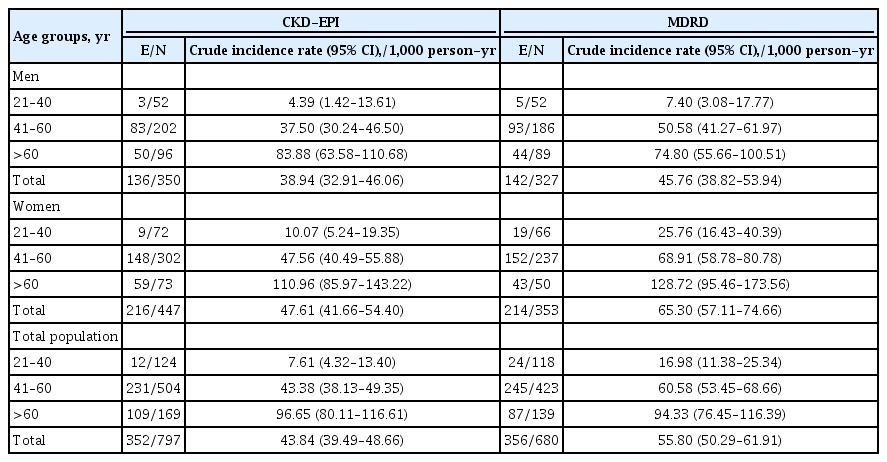
- High Incidence of Chronic Kidney Disease among Iranian Diabetic Adults: Using CKD-EPI and MDRD Equations for Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate
- Seyyed Saeed Moazzeni, Reyhane Hizomi Arani, Mitra Hasheminia, Maryam Tohidi, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):684-697. Published online March 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0109
- 5,823 View
- 157 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To investigate the population based incidence rate of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and its potential risk factors among Iranian diabetic adults during over 14 years of follow-up.
Methods
Two different equations (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration [CKD-EPI] and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease [MDRD]) were applied for the calculating the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Among a total of 1,374 diabetic Tehranian adults, 797 and 680 individuals were eligible for CKD-EPI and MDRD analyses, respectively. CKD was defined as eGFR lower than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for all potential risk factors.
Results
The incidence rates (95% CI) of CKD per 1,000 person-years were 43.84 (39.49 to 48.66) and 55.80 (50.29 to 61.91) based on CKD-EPI and MDRD equations, respectively. Being older, a history of cardiovascular disease, and having lower levels of eGFR were significant risk factors in both equations. Moreover, in CKD-EPI, using glucose-lowering medications and hypertension, and in MDRD, female sex and fasting plasma glucose ≥10 mmol/L were also independent risk factors. Regarding the discrimination index, CKD-EPI equation showed a higher range of C-index for the predicted probability of incident CKD in the full-adjusted model, compared to MDRD equation (0.75 [0.72 to 0.77] vs. 0.69 [0.66 to 0.72]).
Conclusion
We found an incidence rate of more than 4%/year for CKD development among our Iranian diabetic population. Compared to MDRD, it can be suggested that CKD-EPI equation can be a better choice to use for prediction models of incident CKD among the Iranian diabetic populations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of the Holy Quran Recitation on Inflammatory Markers in Hemodialysis Patients in Iran: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Maedeh Teimourzadeh, Hassan Babamohamadi, Maliheh Yarmohamadi, Raheb Ghorbani, Harold G. Koenig
Journal of Religion and Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of anemia and its associated factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a referral diabetic clinic in the north of Iran
Reyhane Hizomi Arani, Farima Fakhri, Mohammad Naeimi Tabiee, Fatemeh Talebi, Zahra Talebi, Negin Rashidi, Maryam Zahedi
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between fasting plasma glucose variability and incident eGFR decline: evidence from two cohort studies
Niloofar Deravi, Yasaman Sharifi, Fatemeh Koohi, Seyed Saeed Tamehri Zadeh, Soroush Masrouri, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Low LncRNA LUCAT1 Expression Assists in the Diagnosis of Chronic Heart Failure and Predicts Poor Prognosis
Jian Wang, Xujin Wu, Li Wang, Chengyong Zhao
International Heart Journal.2023; 64(3): 409. CrossRef - Comparison of eGFR formulas (CKD-EPI and MDRD) in patients with multiple myeloma
Osman ERİNÇ, Soner YEŞİLYURT, Meliha NALCACİ
Cukurova Medical Journal.2023; 48(2): 336. CrossRef - Comparison and evaluation of the 2009 and 2021 chronic kidney disease-epidemiological collaboration equations among Jordanian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Randa I. Farah, Abdulrahman Alhajahjeh, Oraib Al-farahid, Hana Abuzaid, Dana Hiasat, Rama Rayyan, Laith Bdier, Izzat AlAwwa, Kamel Ajlouni
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 61(2): 169. CrossRef - Effect of teaching health-promoting behaviors on the care burden of family caregivers of hemodialysis patients: a four-group clinical trial
Mehrdad Hayati, Razieh Bagherzadeh, Mehdi Mahmudpour, Fatemeh Heidari, Hakimeh Vahedparast
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of social and clinical factors on the diagnostic delay of chronic kidney disease: an evaluation study
Mousa Ghelichi-Ghojogh, Mohammad fararouei, Mozhgan Seif, Bahram Shahryari, Maryam Pakfetrat
International Urology and Nephrology.2022; 54(7): 1603. CrossRef - Chronic kidney disease and its health-related factors: a case-control study
Mousa Ghelichi-Ghojogh, Mohammad Fararouei, Mozhgan Seif, Maryam Pakfetrat
BMC Nephrology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence and risk factors of severe non‐proliferative/proliferative diabetic retinopathy: More than a decade follow up in the Tehran Lipids and Glucose Study
Mahsa Sardarinia, Samaneh Asgari, Reyhane Hizomi Arani, Fatemeh Eskandari, Fereidoun Azizi, Davood Khalili, Farzad Hadaegh
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(2): 317. CrossRef - Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 181. CrossRef - Prevalence of chronic kidney diseases and its determinants among Iranian adults: results of the first phase of Shahedieh cohort study
Ali Dehghani, Sadegh Alishavandi, Nader Nourimajalan, Hossein Fallahzadeh, Vahid Rahmanian
BMC Nephrology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Construct a classification decision tree model to select the optimal equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate and estimate it more accurately
Zhenliang Fan, Qiaorui Yang, Zhuohan Xu, Ke Sun, Mengfan Yang, Riping Yin, Dongxue Zhao, Junfen Fan, Hongzhen Ma, Yiwei Shen, Hong Xia
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease
Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(Suppl 2): S46. CrossRef - Prevalence and Associated Factors of Kidney Dysfunction in Patients with Hypertension and/or Diabetes Mellitus from a Primary Care Population in Northwest China
Mengyue Lin, Mulalibieke Heizhati, Lin Wang, Lin Gan, Mei Li, Wenbo Yang, Ling Yao, Zhongrong Wang, Zhikang Yang, Reyila Abudoyreyimu, Zihao Wu, Nanfang Li
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 7567. CrossRef
- The Effect of the Holy Quran Recitation on Inflammatory Markers in Hemodialysis Patients in Iran: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor for Renal Function Preservation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
- Tae Jung Oh, Ju-Young Moon, Kyu Yeon Hur, Seung Hyun Ko, Hyun Jung Kim, Taehee Kim, Dong Won Lee, Min Kyong Moon, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline, Korean Diabetes Association and Committee of the Cooperative Studies, Korean Society of Nephrology
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):489-497. Published online August 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0172
- 7,803 View
- 167 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
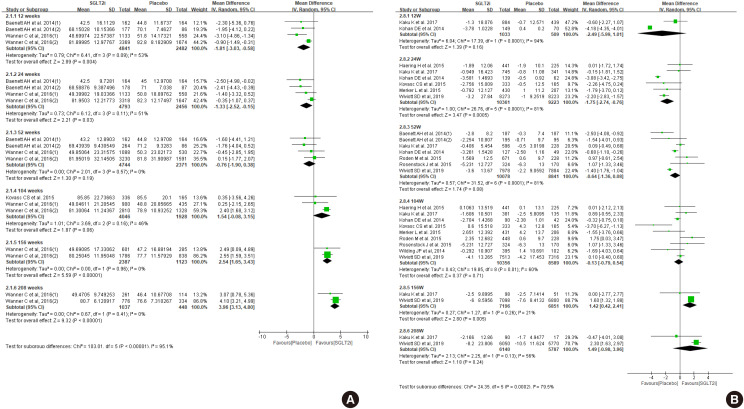
ePub Diabetes is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Therefore, prevention of renal dysfunction is an important treatment goal in the management of diabetes. The data of landmark cardiovascular outcome trials of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor showed profound reno-protective effects. The Korean Diabetes Association and the Korean Society of Nephrology reviewed clinical trials and performed meta-analysis to assess the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on the preservation of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). We limited the data of SGLT2 inhibitors which can be prescribed in Korea. Both eGFR value and its change from the baseline were significantly more preserved in the SGLT2 inhibitor treatment group compared to the control group after 156 weeks. However, some known adverse events were increased in SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, such as genital infection, diabetic ketoacidosis, and volume depletion. We recommend the long-term use SGLT2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) for attenuation of renal function decline. However, we cannot generalize our recommendation due to lack of long-term clinical trials testing reno-protective effects of every SGLT2 inhibitor in a broad range of patients with T2DM. This recommendation can be revised and updated after publication of several large-scale renal outcome trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 701. CrossRef
- Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
- Complication
- Soluble Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Levels Are Associated with Decreased Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Eun-Hee Cho, Sang-Wook Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):97-104. Published online October 8, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0030
- 4,231 View
- 52 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) is strongly expressed in the kidney, and soluble levels of this protein are used as a marker in various chronic inflammatory diseases, including diabetes, coronary artery disease, and cancer. This study examined the association between the serum soluble DPP-4 levels and renal function or cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods In this retrospective analysis, soluble DPP-4 levels were measured in preserved sera from 140 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who had participated in our previous coronary artery calcium (CAC) score study.
Results The mean±standard deviation soluble DPP-4 levels in our study sample were 645±152 ng/mL. Univariate analyses revealed significant correlations of soluble DPP-4 levels with the total cholesterol (
r =0.214,P =0.019) and serum creatinine levels (r =−0.315,P <0.001) and the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR; estimated using the modification of diet in renal disease equation) (r =0.303,P =0.001). The associations of soluble DPP-4 levels with serum creatinine and GFR remained significant after adjusting for age, body mass index, and duration of diabetes. However, no associations were observed between soluble DPP-4 levels and the body mass index, waist circumference, or CAC score.Conclusion These data suggest the potential use of serum soluble DPP-4 levels as a future biomarker of deteriorated renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sitagliptin Mitigates Diabetic Nephropathy in a Rat Model of Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes: Possible Role of PTP1B/JAK-STAT Pathway
Sarah M. AL-Qabbaa, Samaher I. Qaboli, Tahani K. Alshammari, Maha A. Alamin, Haya M. Alrajeh, Lama A. Almuthnabi, Rana R. Alotaibi, Asma S. Alonazi, Anfal F. Bin Dayel, Nawal M. Alrasheed, Nouf M. Alrasheed
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6532. CrossRef - Evaluation of the efficacy of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 enzyme and selenium element in people with kidney failure in Kirkuk governorate
Ibrahim Abdullah Ali Al-Jubouri, Nadia Ahmed Saleh Al-Jubouri
Materials Today: Proceedings.2022; 60: 795. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Effects of Incretin-Based Therapies: Integrating Mechanisms With Cardiovascular Outcome Trials
John R. Ussher, Amanda A. Greenwell, My-Anh Nguyen, Erin E. Mulvihill
Diabetes.2022; 71(2): 173. CrossRef - Computer-Aided Screening of Phytoconstituents from Ocimum tenuiflorum against Diabetes Mellitus Targeting DPP4 Inhibition: A Combination of Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, and Pharmacokinetics Approaches
Harshit Sajal, Shashank M. Patil, Ranjith Raj, Abdullah M. Shbeer, Mohammed Ageel, Ramith Ramu
Molecules.2022; 27(16): 5133. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - An update on the interaction between COVID-19, vaccines, and diabetic kidney disease
Yang Yang, Shubiao Zou, Gaosi Xu
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Lobeglitazone Versus Pioglitazone on Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(1): 171. CrossRef - Renoprotective Effects of DPP-4 Inhibitors
Daiji Kawanami, Yuichi Takashi, Hiroyuki Takahashi, Ryoko Motonaga, Makito Tanabe
Antioxidants.2021; 10(2): 246. CrossRef - Serum levels of soluble dipeptidyl peptidase-4 in type 2 diabetes are associated with severity of liver fibrosis evaluated by transient elastography (FibroScan) and the FAST (FibroScan-AST) score, a novel index of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with signif
Masaaki Sagara, Toshie Iijima, Masato Kase, Kanako Kato, Shintaro Sakurai, Takuya Tomaru, Teruo Jojima, Isao Usui, Yoshimasa Aso
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(5): 107885. CrossRef - Distinctive CD26 Expression on CD4 T-Cell Subsets
Oscar J. Cordero, Carlos Rafael-Vidal, Rubén Varela-Calviño, Cristina Calviño-Sampedro, Beatriz Malvar-Fernández, Samuel García, Juan E. Viñuela, José M. Pego-Reigosa
Biomolecules.2021; 11(10): 1446. CrossRef - The Long-Term Study of Urinary Biomarkers of Renal Injury in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Sebastián Montoro-Molina, Andrés Quesada, Francisco O’Valle, Natividad Martín Morales, María del Carmen de Gracia, Isabel Rodríguez-Gómez, Antonio Osuna, Rosemary Wangensteen, Félix Vargas
Kidney and Blood Pressure Research.2021; 46(4): 502. CrossRef - Serum Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 level is related to adiposity in type 1 diabetic adolescents
Amany Ibrahim, Shaimaa Salah, Mona Attia, Hanan Madani, Samah Ahmad, Noha Arafa, Hend Soliman
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(4): 609. CrossRef - Phase I study of YS110, a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody to CD26, in Japanese patients with advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma
Masayuki Takeda, Yuichiro Ohe, Hidehito Horinouchi, Toyoaki Hida, Junichi Shimizu, Takashi Seto, Kaname Nosaki, Takumi Kishimoto, Itaru Miyashita, Masayuki Yamada, Yutaro Kaneko, Chikao Morimoto, Kazuhiko Nakagawa
Lung Cancer.2019; 137: 64. CrossRef
- Sitagliptin Mitigates Diabetic Nephropathy in a Rat Model of Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes: Possible Role of PTP1B/JAK-STAT Pathway
- Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Levels in Comparison with Glomerular Filtration Rate for Evaluation of Renal Function in Patients with Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease
- Kwang-Sook Woo, Jae-Lim Choi, Bo-Ram Kim, Ji-Eun Kim, Won-Suk An, Jin-Yeong Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(4):307-313. Published online August 20, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.4.307
- 4,004 View
- 27 Download
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is a promising biomarker of acute kidney injury. There is a growing body of evidence suggesting that NGAL is also a marker of kidney disease and severity in chronic kidney disease (CKD). We studied the utility of urinary NGAL in more accurately predicting renal function in patients with diabetic CKD.
Methods We studied possible relationships between urinary NGAL, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and proteinuria in diabetic CKD patients and in healthy populations.
Results Urinary NGAL levels were significantly higher in CKD patients than in healthy controls (96.0 [2.7 to 975.2] ng/mL vs. 18.8 [1.3 to 81.9] ng/mL,
P =0.02), and the GFR was lower among CKD patients (49.3 [13.1 to 78.3] mL/min/1.73 m2 vs. 85.6 [72 to 106.7] mL/min/1.73 m2,P <0.0001). The urinary NGAL level showed a significant inverse correlation with GFR (r =-0.5634,P <0.0001). The correlation analyses between urinary protein level and urinary NGAL levels and GFR were as follows: urine protein and urinary NGAL (r =0.3009,P =0.0256), urine protein and GFR (r =-0.6245,P <0.0001), urine microalbumin and urinary NGAL (r =0.1794,P =0.2275), and urine microalbumin and GFR (r =-0.5190,P =0.0002).Conclusion From these results, we concluded that urinary NGAL is a reliable marker of renal function in diabetic CKD patients. However, urinary NGAL did not provide more accurate information regarding renal function than GFR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nanoparticle-antibody conjugate-based immunoassays for detection of CKD-associated biomarkers
Monika Chhillar, Deepak kukkar, Preeti Kukkar, Ki-Hyun Kim
TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry.2023; 158: 116857. CrossRef - Fecal and Urinary Adipokines as Disease Biomarkers
Hauke C. Tews, Tanja Elger, Thomas Grewal, Simon Weidlich, Francesco Vitali, Christa Buechler
Biomedicines.2023; 11(4): 1186. CrossRef - Application of SERS-based nanobiosensors to metabolite biomarkers of CKD
Deepak Kukkar, Monika Chhillar, Ki-Hyun Kim
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2023; 232: 115311. CrossRef - A New Clinical Utility for Tubular Markers to Identify Kidney Responders to Saxagliptin Treatment in Adults With Diabetic Nephropathy
Marwa Mohsen, Ahmed A. Elberry, Alaa Mohamed Rabea, Doaa Mahmoud Khalil, Mohamed E.A. Abdelrahim, Raghda R.S. Hussein
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2022; 46(2): 134. CrossRef - Serum Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin in Patients with Toxic Nephropathies. Prospective Study
Lyudmila A. Demidchik, Valentina V. Lee, Dmitriy A. Klyuyev, Ryszhan Y. Bakirova, Vilen B. Molotov-Luchanskiy, Yelena V. Pozdnyakova, Irina V. Beinikova, Semyon S. Bobyrev
Annals of the Russian academy of medical sciences.2021; 76(2): 142. CrossRef - Assessment of Renal Function Status in Steady-State Sickle Cell Anaemic Children Using Urine Human Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Albumin:Creatinine Ratio
Olatubosun Oladipupo Olawale, Abiodun Folasade Adekanmbi, Ayobola Abimbola Sonuga, Oyebola Oluwagbemiga Sonuga, Samuel Olufemi Akodu, Morufat Mojisola Ogundeyi
Medical Principles and Practice.2021; 30(6): 557. CrossRef - Association of neutrophil-gelatinase-associated lipocalin with microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study
Erhan Aslanhan, David Ojalvo, Ekmek Burak Özsenel, Sema Ucak Basat, Fatih Borlu
Cardiovascular Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 8(3): 82. CrossRef - MicroRNA as novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets in diabetic kidney disease: An update
Qinghua Cao, Xin‐Ming Chen, Chunling Huang, Carol A. Pollock
FASEB BioAdvances.2019; 1(6): 375. CrossRef - Potential serum biomarkers for early detection of diabetic nephropathy
Tarek Kamal Motawi, Nagwa Ibrahim Shehata, Mahmoud Mohamed ElNokeety, Yasmin Farid El-Emady
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 136: 150. CrossRef - Modern methods of diagnosing chronic kidney disease in patients with diabetes mellitus
Tatiana N. Markova, Viktoriia V. Sadovskaya, Marina Y. Bespyatova
Diabetes mellitus.2018; 20(6): 454. CrossRef - Evaluation value of neutrophil gelatinase‐associated lipocalin for the renal dysfunction of patients with chronic kidney disease: A meta‐analysis
Lulu Guo, Yaya Zhao, Zhenzhu Yong, Weihong Zhao
AGING MEDICINE.2018; 1(2): 185. CrossRef - Urinary Tubular Injury Biomarkers Are Associated With ESRD and Death in the REGARDS Study
Ruth F. Dubin, Suzanne Judd, Rebecca Scherzer, Michael Shlipak, David G. Warnock, Mary Cushman, Mark Sarnak, Chirag Parikh, Michael Bennett, Neil Powe, Carmen A. Peralta
Kidney International Reports.2018; 3(5): 1183. CrossRef - Add-on plasmonic patch as a universal fluorescence enhancer
Jingyi Luan, Jeremiah J. Morrissey, Zheyu Wang, Hamed Gholami Derami, Keng-Ku Liu, Sisi Cao, Qisheng Jiang, Congzhou Wang, Evan D. Kharasch, Rajesh R. Naik, Srikanth Singamaneni
Light: Science & Applications.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum NGAL and Cystatin C Comparison With Urinary Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio and Inflammatory Biomarkers as Early Predictors of Renal Dysfunction in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Marcelo R. Bacci, Ethel Z. Chehter, Ligia A. Azzalis, Beatriz Costa de Aguiar Alves, Fernando L.A. Fonseca
Kidney International Reports.2017; 2(2): 152. CrossRef - Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin to predict renal response after induction therapy in active lupus nephritis
Bancha Satirapoj, Chagriya Kitiyakara, Asada Leelahavanichkul, Yingyos Avihingsanon, Ouppatham Supasyndh
BMC Nephrology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) and Retinol-Binding Protein 4 (RBP4) in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Nephropathy
Mohamed H. Mahfouz, Adel M. Assiri, Mohammed H. Mukhtar
Biomarker Insights.2016; 11: BMI.S33191. CrossRef - Intra-abdominal Hypertension and Postoperative Kidney Dysfunction in Cardiac Surgery Patients
Michael A. Mazzeffi, Patrick Stafford, Karin Wallace, Wendy Bernstein, Seema Deshpande, Patrick Odonkor, Ashanpreet Grewal, Erik Strauss, Latoya Stubbs, James Gammie, Peter Rock
Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia.2016; 30(6): 1571. CrossRef - Effects of Therapy on Urine Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Nondiabetic Glomerular Diseases with Proteinuria
Amnuay Sirisopha, Somlak Vanavanan, Anchalee Chittamma, Bunyong Phakdeekitcharoen, Ammarin Thakkinstian, Amornpan Lertrit, Nuankanya Sathirapongsasuti, Chagriya Kitiyakara
International Journal of Nephrology.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Novel urinary biomarkers in pre-diabetic nephropathy
Vikas Garg, Manish Kumar, Himansu Sekhar Mahapatra, Anubhuti Chitkara, Adesh Kumar Gadpayle, Venketansan Sekhar
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology.2015; 19(5): 895. CrossRef - High expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in the kidney proximal tubules of diabetic rats
Fenghua Liu, Huayu Yang, Haiping Chen, Mi Zhang, Qing Ma
Advances in Medical Sciences.2015; 60(1): 133. CrossRef - Anti-albuminuric effects of spironolactone in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial
Sawako Kato, Shoichi Maruyama, Hirofumi Makino, Jun Wada, Daisuke Ogawa, Takashi Uzu, Hisazumi Araki, Daisuke Koya, Keizo Kanasaki, Yutaka Oiso, Motomitsu Goto, Akira Nishiyama, Hiroyuki Kobori, Enyu Imai, Masahiko Ando, Seiichi Matsuo
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology.2015; 19(6): 1098. CrossRef - The inflammation–lipocalin 2 axis may contribute to the development of chronic kidney disease
Atsushi Hashikata, Akiko Yamashita, Shigeki Suzuki, Shintaro Nagayasu, Takanori Shinjo, Ataru Taniguchi, Mitsuo Fukushima, Yoshikatsu Nakai, Kazuko Nin, Naoya Watanabe, Tomoichiro Asano, Yoshimitsu Abiko, Akifumi Kushiyama, Shoichiro Nagasaka, Fusanori Ni
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2014; 29(3): 611. CrossRef - Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin as a Marker of Tubular Damage in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with and without Albuminuria
Abeer A. Al-Refai, Safaa I. Tayel, Ahmed Ragheb, Ashraf G. Dala, Ahmed Zahran
Open Journal of Nephrology.2014; 04(01): 37. CrossRef - Importance of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Differential Diagnosis of Acute and Chronic Renal Failure
Seda Ozkan, Polat Durukan, Cemil Kavalci, Ali Duman, Mustafa Burak Sayhan, Omer Salt, Afsin Ipekci
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined biomarkers evaluation for diagnosing kidney injury in preeclampsia
Jing Xiao, Jianying Niu, Xianwu Ye, Qianqian Yu, Yong Gu
Hypertension in Pregnancy.2013; 32(4): 439. CrossRef
- Nanoparticle-antibody conjugate-based immunoassays for detection of CKD-associated biomarkers
- Clinical Significance of Decreased Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) without Albuminuria among Type 2 Diabetics.
- Ji Eun Lee, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee, Ji Sung Yoon
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(3):252-258. Published online June 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.3.252
- 2,326 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes is a predictor of development of clinical nephropathy and cardiovascular disease. But, it has been reported that reduced glomerular filtration rate (GFR) may occur in some normoalbuminuric diabetic patients. The aim of this study was to identify whether decreased GFR without microalbuminuria is to predict diabetic vascular complications. METHODS: Between January 1998 and February 2001, 73 patients with type 2 diabetes who visited Yeungnam university medical center were divided into 5 groups according to initial GFR ranges: group 1 (GFR < 30 mL/min), group 2 (30 < or = GFR < 60 mL/min), group 3 (60 < or = GFR < 90 mL/min), group 4 (90 < or = GFR < 125 mL/min), group 5 (125 mL/min < or = GFR). They were examined for microvascular and macrovascular complications initially and after 4 years. RESULTS: Decreased GFR had a negative correlation with age (r = -0.472, P = 0.001). Decreased GFR without microalbuminuria had a significant correlation with development of diabetic nephropathy (P = 0.016) after 4 years. There were no significant correlation with the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy, peripheral neuropathy, and macrovacular disease. But, our study showed that coronary artery disease had an increasing tendency with decreased GFR without statistical significance (P = 0.085). CONCLUSIONS: Our data suggest that reduced GFR, independent of albuminuria, may be an important predictor of diabetic nephropathy and coronary artery disease to some extent. So we recommend that not only the microalbuminuria, but also the decrease in GFR should be evaluated at the follow-up of patients with type 2 diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Screening and Management of Diabetic Nephropathy
Ji Sung Yoon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2013; 14(1): 19. CrossRef
- Screening and Management of Diabetic Nephropathy
- Changes of Glomerular Filtration Rate and Urinary Albumin Excretion Rate in NIDDM patients with Microalbuminuria.
- Hyo Jung Kim, Jung Min Koh, Eun Sug Shin, Yun Ey Chung, Young Il Kim, Chul Hee Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Sung Kwan Hong, Ki Up Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 1997;21(4):414-424. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,046 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
We previously suggested that micro-albuminuria in the presence of retinopathy may represent a state of real incipient diabetic nephropathy with declining glomerular filtration rate(GFR), while the meaning of microalbuminuria in the absence of retinopathy may be more heterogeneous. This study was performed to further test this hypothesis. METHODS: We prospectively followed up the changes in GFR and urinary albumin excretinn rate (UAE) in microalbuminuric NIDDM patients with or without diabetic retinopathy for 3.1 years. RESULTS: 1) Among 45 patients who completed the followup, 27 had retinopathy from the baseline(group A), while 18 patients did not have retinopathy throughout the study(group B). 2) UAE at baseline was not statistically different between the group A and group B. During follow-up, VAE remained stable in the group B patients(40.0 [20.5 ~ 158.0) to 60.0[20.2 ~ 231.0] ug/min, NS). On the other hand, UAE significantly increased in the group A patients(47.9[20.0~186.0] to 140.0[24.5~2862.0] ug/min, P <0.001). 3) Thirty percent of the group A patients(8/27) progressed to overt proteinuria, while 11%(2/18) of the group B patients developed overt proteinuria(NS). 4) GFR significantly decreased both in the group A (113.0+21.2 to 89.1+24.0 mL/min/1.73 m, P < 0,001) and in the group B patients(134.1+27.2 to 121.5+27.3 mL/min/1.73 m, P<0.01). However, the magnitude of change in GFR was significantly higher in the group A than in the group B patients(7.7+7.6 vs 3.9+4.2 mL/min/1.73 m /year, P <0.05), 5) Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that the presence of retinopathy was a independent risk factor for faster decline in GFR. CONCLUSION: It appears that clinical course is different in NIDDM patients with microalbuminuria, according to the presence or absence of diabetic retinopathy. Microalbuminuria in the presence of retinopathy predicts aggravation of albuminuria and decline in GFR. In contrast, the renal function in microalbuminuric NIDDM patients in the absence of retinopathy may remain stable for years.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





