
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Harnessing Metabolic Indices as a Predictive Tool for Cardiovascular Disease in a Korean Population without Known Major Cardiovascular Event
- Hyun-Jin Kim, Byung Sik Kim, Yonggu Lee, Sang Bong Ahn, Dong Wook Kim, Jeong-Hun Shin
- Received June 22, 2023 Accepted August 18, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0197 [Epub ahead of print]

- 931 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study evaluated the usefulness of indices for metabolic syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and insulin resistance (IR), as predictive tools for cardiovascular disease in middle-aged Korean adults.
Methods
The prospective data obtained from the Ansan-Ansung cohort database, excluding patients with major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE). The primary outcome was the incidence of MACCE during the follow-up period.
Results
A total of 9,337 patients were included in the analysis, of whom 1,130 (12.1%) experienced MACCE during a median follow-up period of 15.5 years. The metabolic syndrome severity Z-score, metabolic syndrome severity score, hepatic steatosis index, and NAFLD liver fat score were found to significantly predict MACCE at values above the cut-off point and in the second and third tertiles. Among these indices, the hazard ratios of the metabolic syndrome severity score and metabolic syndrome severity Z-score were the highest after adjusting for confounding factors. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of the 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) score for predicting MACCE was 0.716, and the metabolic syndrome severity Z-score had an AUC of 0.619.
Conclusion
The metabolic syndrome severity score is a highly reliable indicator and was closely associated with the 10-year ASCVD risk score in predicting MACCE in the general population. Given the specific characteristics and limitations of metabolic syndrome severity scores as well as the indices of NAFLD and IR, a more practical scoring system that considers these factors is essential to achieve greater accuracy in forecasting cardiovascular outcomes.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, and All-Cause Mortality according to Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level in the Elderly, a Nationwide Study
- You-Bin Lee, Minji Koo, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Jung A Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):722-732. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0225
- 6,993 View
- 331 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We assessed the myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and all-cause death risks during follow-up according to the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels among older adults.
Methods
The Korean National Health Insurance Service datasets (2002 to 2020) were used for this population-based cohort study. The hazards of MI, stroke, and all-cause mortality during follow-up were analyzed according to LDL-C level in individuals aged ≥65 years without baseline cardiovascular diseases (n=1,391,616).
Results
During a mean 7.55 years, 52,753 MIs developed; 84,224 strokes occurred over a mean 7.47 years. After a mean 8.50 years, 233,963 died. A decrease in LDL-C was associated with lower hazards of MI and stroke. The decreased hazard of stroke in lower LDL-C was more pronounced in statin users, and individuals with diabetes or obesity. The hazard of all-cause death during follow-up showed an inverted J-shaped pattern according to the LDL-C levels. However, the paradoxically increased hazard of mortality during follow-up in lower LDL-C was attenuated in statin users and individuals with diabetes, hypertension, or obesity. In statin users, lower LDL-C was associated with a decreased hazard of mortality during follow-up.
Conclusion
Among the elderly, lower LDL-C was associated with decreased risks of MI and stroke. Lower LDL-C achieved by statins in the elderly was associated with a decreased risk of all-cause death during follow-up, suggesting that LDL-C paradox for the premature death risk in the elderly should not be applied to statin users. Intensive statin therapy should not be hesitated for older adults with cardiovascular risk factors including diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combination of low- or moderate-intensity statin and ezetimibe vs. high-intensity statin monotherapy on primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and all-cause death: a propensity-matched nationwide cohort study
Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, You-Cheol Hwang
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol With All-cause and Cause-specific Mortality in Older Adults in China
Wenqing Ni, Yuebin Lv, Xueli Yuan, Yan Zhang, Hongmin Zhang, Yijing Zheng, Xiaoming Shi, Jian Xu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and all-cause or cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective study
Chin-Huan Chang, Shu-Tin Yeh, Seng-Wei Ooi, Chung-Yi Li, Hua-Fen Chen
PeerJ.2023; 11: e14609. CrossRef - ERCC1 polymorphism and its expression associated with ischemic stroke in Chinese population
Xiao-Dong Deng, Jian-Lin Ke, Tai-Yu Chen, Qin Gao, Zhuo-Lin Zhao, Wei Zhang, Huan Liu, Ming-Liang Xiang, Li-Zhen Wang, Ying Ma, Yun Liu
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 517. CrossRef - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 759. CrossRef
- Combination of low- or moderate-intensity statin and ezetimibe vs. high-intensity statin monotherapy on primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and all-cause death: a propensity-matched nationwide cohort study
- COVID-19
- Effects of Social Distancing on Diabetes Management in Older Adults during COVID-19 Pandemic
- Soo Myoung Shin, Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):765-772. Published online August 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0096
- 5,960 View
- 191 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
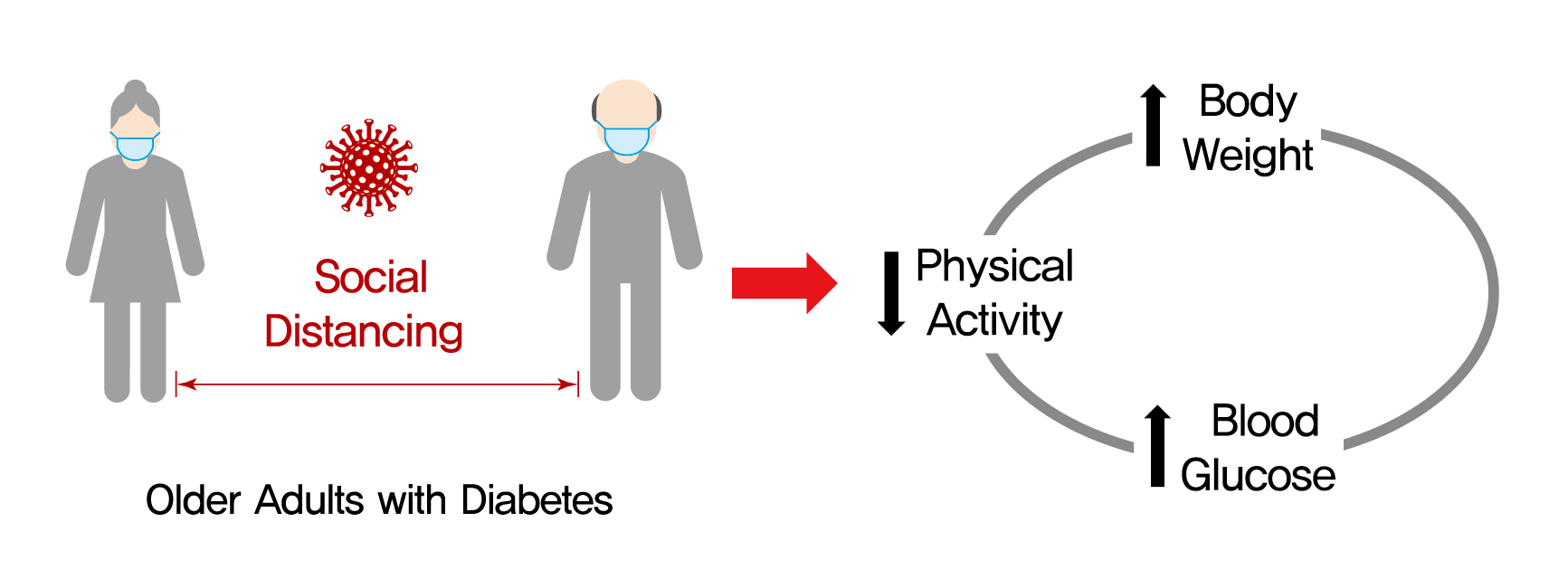
On March 22, 2020, intense social distancing (SD) was implemented in Korea to prevent the spread of coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19). This study examined the impact of SD on diabetes control in older adults with diabetes.
Methods
Adults aged 60 to 90 years with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were physically and mentally independent were recruited. Participants who had complete blood chemistry data from April to July 2019 (pre-SD era) and April to July 2020 (SD era) were enrolled. Data were obtained about physical activity, nutrition, sarcopenia, and psychological and mental health from questionnaires in April to July 2020. Calf circumference was measured.
Results
In total, 246 people (100 men, 146 women; mean age, 73.8±5.7 years) participated in this study. The levels of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c, 7.4%±1.0% vs. 7.1%±0.8%, P<0.001), fasting glucose (142.2±16.7 mg/dL vs. 132.0±27.7 mg/dL, P<0.001), and body weight (62.6±9.4 kg vs. 61.8±10.1 kg, P<0.01) were higher in the SD era than in the pre-SD era. Total physical activity was lower in the SD era (2,584.6±2,624.1 MET-min/week–1 vs. 1,987.3±2,295.0 MET-min/week–1, P<0.001). A larger increase in HbA1c level was associated with increased body weight and decreased physical activity.
Conclusion
SD had negative effects on diabetes management in older adults with diabetes. Fasting glucose and HbA1c levels and body weight increased during the SD era. Participants with reduced physical activity gained more weight and had higher blood glucose levels. Given that the COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing, health professionals and diabetes educators should monitor changes in lifestyle factors in older adults with diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preliminary efficacy of a technology-based physical activity intervention for older Korean adults during the COVID-19 pandemic
Soonhyung Kwon, Oejin Shin, Rosalba Hernandez
Educational Gerontology.2024; 50(1): 27. CrossRef - Obesity and weight change during the COVID‐19 pandemic in children and adults: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Laura N. Anderson, Yulika Yoshida‐Montezuma, Nora Dewart, Ezza Jalil, Jayati Khattar, Vanessa De Rubeis, Sarah Carsley, Lauren E. Griffith, Lawrence Mbuagbaw
Obesity Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in lifestyle-related behaviour during the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan: a questionnaire survey for examinees who underwent an annual health check-up
Miyako Kishimoto, Kayo Masuko, Sumie Yamamoto, Retsu Fujita, Shoko Nakamura, Masato Odawara, Mikio Zeniya
Journal of International Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycaemic monitoring and control among high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes in Australian general practice during COVID-19
Kirrilee Jane Barlow, Paul P Fahey, Evan Atlantis
Family Medicine and Community Health.2023; 11(3): e002271. CrossRef - Social isolation, loneliness and subsequent risk of major adverse cardiovascular events among individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yannis Yan Liang, Yilin Chen, Hongliang Feng, Huachen Xue, Yu Nie, Qi-Yong H Ai, Jiacheng Ma, Lulu Yang, Jihui Zhang, Sizhi Ai
General Psychiatry.2023; 36(6): e101153. CrossRef - Stress, Depression, and Unhealthy Behavior Changes among Patients with Diabetes during COVID-19 in Korea
Hae Ran Kim, Jeong-Soon Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(2): 303. CrossRef - Reply to comment on “Unexpected decline in glycated hemoglobin level after emergency COVID‐19 measures in three robust older Japanese women with prediabetes/mild type 2 diabetes”
Tazuo Okuno, Osamu Iritani, Kumie Kodera, Daisuke Hama, Asami Kane, Kozue Morigaki, Toshio Terai, Norie Maeno, Shigeto Morimoto
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2022; 22(7): 541. CrossRef - Anxiety, Distress and Stress among Patients with Diabetes during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Rubén A. García-Lara, José L. Gómez-Urquiza, María José Membrive-Jiménez, Almudena Velando-Soriano, Monserrat E. Granados-Bolivar, José L. Romero-Béjar, Nora Suleiman-Martos
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(9): 1412. CrossRef - Prevalence of Depression and Related Factors among Patients with Chronic Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Rubén A. García-Lara, Nora Suleiman-Martos, María J. Membrive-Jiménez, Victoria García-Morales, Miguel Quesada-Caballero, Isabel M. Guisado-Requena, José L. Gómez-Urquiza
Diagnostics.2022; 12(12): 3094. CrossRef
- Preliminary efficacy of a technology-based physical activity intervention for older Korean adults during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Drug/Regimen
- Effects of Teneligliptin on HbA1c levels, Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Time in Range and Glycemic Variability in Elderly Patients with T2DM (TEDDY Study)
- Ji Cheol Bae, Soo Heon Kwak, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Sunghwan Suh, Bok Jin Hyun, Ji Eun Cha, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):81-92. Published online June 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0016
- 7,564 View
- 431 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate the effects of teneligliptin on glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)-derived time in range, and glycemic variability in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Methods
This randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study was conducted in eight centers in Korea (clinical trial registration number: NCT03508323). Sixty-five participants aged ≥65 years, who were treatment-naïve or had been treated with stable doses of metformin, were randomized at a 1:1 ratio to receive 20 mg of teneligliptin (n=35) or placebo (n=30) for 12 weeks. The main endpoints were the changes in HbA1c levels from baseline to week 12, CGM metrics-derived time in range, and glycemic variability.
Results
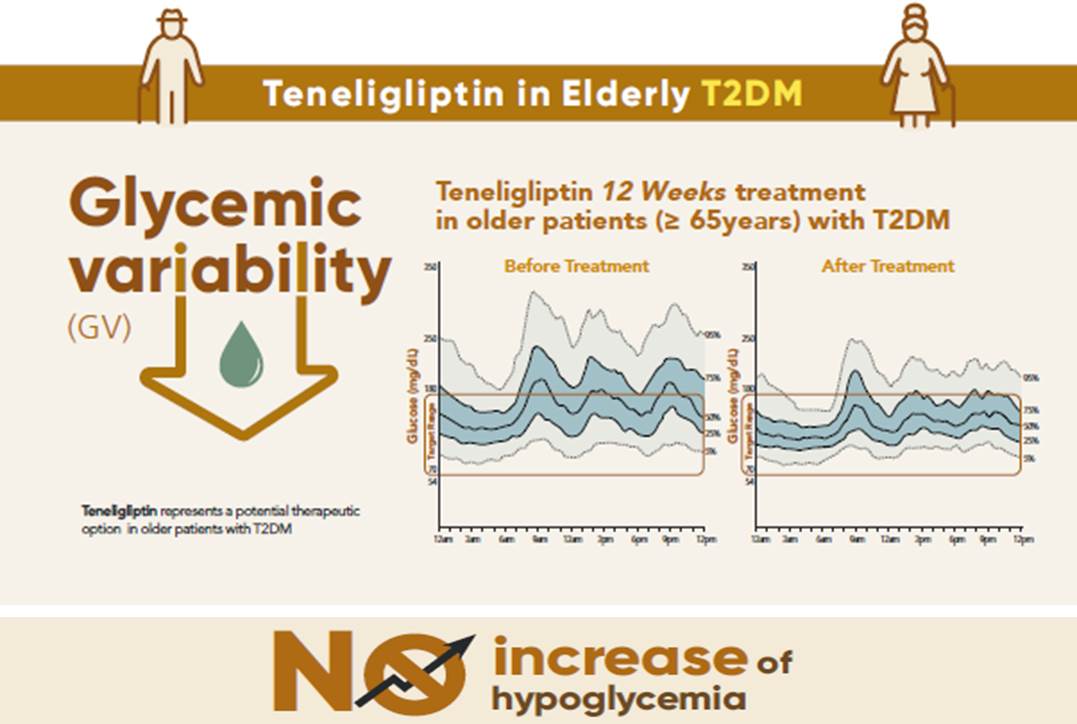
After 12 weeks, a significant reduction (by 0.84%) in HbA1c levels was observed in the teneligliptin group compared to that in the placebo group (by 0.08%), with a between-group least squares mean difference of –0.76% (95% confidence interval [CI], –1.08 to –0.44). The coefficient of variation, standard deviation, and mean amplitude of glycemic excursion significantly decreased in participants treated with teneligliptin as compared to those in the placebo group. Teneligliptin treatment significantly decreased the time spent above 180 or 250 mg/dL, respectively, without increasing the time spent below 70 mg/dL. The mean percentage of time for which glucose levels remained in the 70 to 180 mg/dL time in range (TIR70–180) at week 12 was 82.0%±16.0% in the teneligliptin group, and placebo-adjusted change in TIR70–180 from baseline was 13.3% (95% CI, 6.0 to 20.6).
Conclusion
Teneligliptin effectively reduced HbA1c levels, time spent above the target range, and glycemic variability, without increasing hypoglycemia in our study population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of teneligliptin and other gliptin-based regimens in addressing insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study
Harmanjit Singh, Ravi Rohilla, Shivani Jaswal, Mandeep Singla
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 19(1): 81. CrossRef - Potential approaches using teneligliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: current status and future prospects
Harmanjit Singh, Jasbir Singh, Ravneet Kaur Bhangu, Mandeep Singla, Jagjit Singh, Farideh Javid
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 16(1): 49. CrossRef - Mechanism of molecular interaction of sitagliptin with human DPP4 enzyme - New Insights
Michelangelo Bauwelz Gonzatti, José Edvar Monteiro Júnior, Antônio José Rocha, Jonathas Sales de Oliveira, Antônio José de Jesus Evangelista, Fátima Morgana Pio Fonseca, Vânia Marilande Ceccatto, Ariclécio Cunha de Oliveira, José Ednésio da Cruz Freire
Advances in Medical Sciences.2023; 68(2): 402. CrossRef - A prospective multicentre open label study to assess effect of Teneligliptin on glycemic control through parameters of time in range (TIR) Metric using continuous glucose monitoring (TOP-TIR study)
Banshi Saboo, Suhas Erande, A.G. Unnikrishnan
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(2): 102394. CrossRef - Association between Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors and Cardiometabolic Outcomes
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 49. CrossRef
- Comparison of teneligliptin and other gliptin-based regimens in addressing insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study
- Drug/Regimen
- Increasing Age Associated with Higher Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition Rate Is a Predictive Factor for Efficacy of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors
- Sangmo Hong, Chang Hee Jung, Song Han, Cheol-Young Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):63-70. Published online April 19, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0253

- 65,535 View
- 287 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
It is not known which type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients would most benefit from dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor treatment. We aimed to investigate the predictors of response to DPP-4 inhibitors considering degree of DPP-4 inhibition.
Methods
This study is a post hoc analysis of a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, phase III trial that compared the efficacy and safety of a DPP-4 inhibitor (gemigliptin vs. sitagliptin) in patients with T2DM. Subjects were classified into tertiles of T1 <65.26%, T2=65.26%–76.35%, and T3 ≥76.35% by DPP-4 inhibition. We analyzed the change from baseline in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) according to DPP-4 inhibition with multiple linear regression adjusting for age, ethnicity, body mass index, baseline HbA1c, and DPP-4 activity at baseline.
Results
The mean age was greater in the high tertile group compared with the low tertile group (T1: 49.8±8.3 vs. T2: 53.1±10.5 vs. T3: 55.3±9.5, P<0.001) of DPP-4 inhibition. Although HbA1c at baseline was not different among tertiles of DPP-4 inhibition (P=0.398), HbA1c after 24-week treatment was lower in the higher tertile compares to the lower tertile (T1: 7.30%±0.88% vs. T2: 7.12%±0.78% vs. T3: 7.00%±0.78%, P=0.021). In multiple regression analysis, DPP-4 enzyme inhibition rate was not a significant determent for HbA1c reduction due to age. In subgroup analysis by tertile of DPP-4 inhibition, age was the only significant predictor and only in the highest tertile (R2=0.281, B=–0.014, P=0.024).
Conclusion
This study showed that HbA1c reduction by DPP-4 inhibitor was associated with increasing age, and this association was linked with higher DPP-4 inhibition.
- Complications
- The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Seung Min Chung, Yin Young Lee, Eunyeong Ha, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee, Jian Hur, Kyung Soo Hong, Jong Geol Jang, Hyun Jung Jin, Eun Young Choi, Kyeong-Cheol Shin, Jin Hong Chung, Kwan Ho Lee, June Hong Ahn, Jun Sung Moon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):405-413. Published online May 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0105
- 10,200 View
- 143 Download
- 43 Web of Science
- 45 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background To determine the role of diabetes mellitus (DM) in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), we explored the clinical characteristics of patients with DM and compared risk factors such as age, glycemic control, and medications to those without DM.
Methods This was a retrospective cohort study of 117 confirmed patients with COVID-19 which conducted at a tertiary hospital in Daegu, South Korea. The primary outcome was defined as the severe and critical outcome (SCO), of which the composite outcomes of acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, intensive care unit care, and 28-day mortality. We analyzed what clinical features and glycemic control-related factors affect the prognosis of COVID-19 in the DM group.
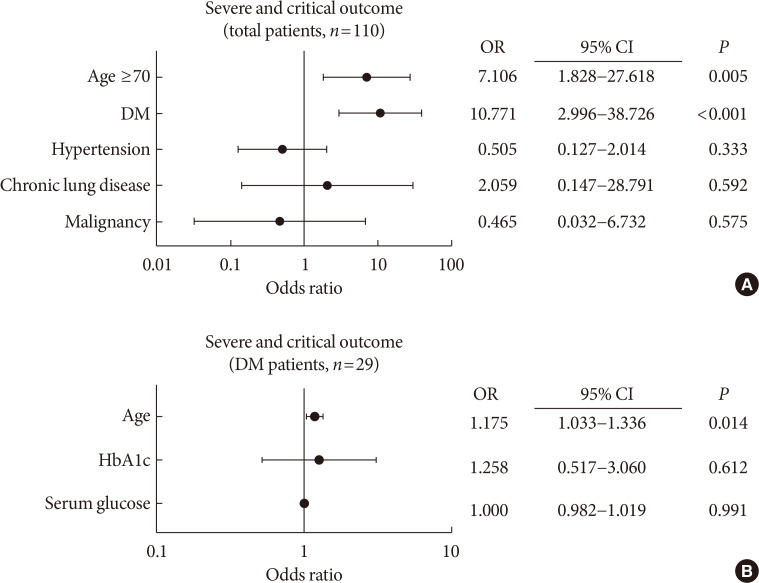
Results After exclusion, 110 participants were finally included. DM patients (
n =29) was older, and showed higher blood pressure compared to non-DM patients. DM group showed higher levels of inflammation-related biomarkers and severity score, and highly progressed to SCO. After adjustment with other risk factors, DM increased the risk of SCO (odds ratio [OR], 10.771;P <0.001). Among the DM patients, SCO was more prevalent in elderly patients of ≥70 years old and age was an independent risk factor for SCO in patients with DM (OR, 1.175;P =0.014), while glycemic control was not. The use of medication did not affect the SCO, but the renin-angiotensin system inhibitors showed protective effects against acute cardiac injury (OR, 0.048;P =0.045).Conclusion The COVID-19 patients with DM had higher severity and resulted in SCO. Intensive and aggressive monitoring of COVID-19 clinical outcomes in DM group, especially in elderly patients is warranted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Development Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination
Hyeyeon Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Mi Kyoung Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Severity of Symptoms and Mortality in Diabetic Patients with COVID- 19 Infection. Review
Zahraa ALBasry, Abeer Abdulhadi Rashid, Shaymaa Hasan Abbas
Al Mustansiriyah Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2023; 23(1): 91. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Alexander Lang, Nikoletta Christodoulou, Philipp Linnerz, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Manuela Neuenschwander, Janett Barbaresko, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2023; 66(8): 1395. CrossRef - COVID-19 and Cardiovascular Comorbidities
Dirk Müller-Wieland, Nikolaus Marx, Michael Dreher, Katharina Fritzen, Oliver Schnell
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(03): 178. CrossRef - Prevalence and impact of diabetes in hospitalized COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sian A. Bradley, Maciej Banach, Negman Alvarado, Ivica Smokovski, Sonu M. M. Bhaskar
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(2): 144. CrossRef - Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Adithan Ganesh, Michael D. Randall
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2022; 88(6): 2642. CrossRef - Cardioprotective effect of extracellular vesicles derived from ticagrelor-pretreated cardiomyocyte on hyperglycemic cardiomyocytes through alleviation of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Ceylan Verda Bitirim, Zeynep Busra Ozer, Dunya Aydos, Kardelen Genc, Seyma Demirsoy, Kamil Can Akcali, Belma Turan
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of diabetes on COVID‐19 mortality and hospital outcomes from a global perspective: An umbrella systematic review and meta‐analysis
Stavroula Kastora, Manisha Patel, Ben Carter, Mirela Delibegovic, Phyo Kyaw Myint
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycated Albumin and Glycated Albumin/HbA1c Predict the Progression of Coronavirus Disease 2019 from Mild to Severe Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Jeongseon Yoo, Youngah Choi, Shin Ae Park, Ji Yeon Seo, Chul Woo Ahn, Jaehyun Han
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2327. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors and COVID‐19: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis Revealing Critical Bias Across a Body of Observational Research
Jordan Loader, Frances C. Taylor, Erik Lampa, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship of age, sex and prothrombin time related to the severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta analysis
Audrey Fabianisa Mirza, Ceria Halim, Mutiara Indah Sari
F1000Research.2022; 11: 729. CrossRef - Evaluating the effect of COVID-19 on quality measures of patients with type 2 diabetes in two family nurse practitioner–owned clinics
Wendy L. Wright, Patricia A. White, Meredith Welsh, Kelly Cutting
Journal of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners.2022; 34(9): 1090. CrossRef - Early glycaemic variability increases 28-day mortality and prolongs intensive care unit stay in critically ill patients with pneumonia
Seong Ho Kim, Ji Young Kim, Eun Song Kim, Il Rae Park, Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Annals of Medicine.2022; 54(1): 2724. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory drugs and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: Current knowledge and potential effects on early SARS-CoV-2 infection
Iris Louise N. Cabbab, Rafael Vincent M. Manalo
Virus Research.2021; 291: 198190. CrossRef - The Effect of Prior Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor and Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Treatment on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Susceptibility and Outcome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jiuyang Xu, Yaqun Teng, Lianhan Shang, Xiaoying Gu, Guohui Fan, Yijun Chen, Ran Tian, Shuyang Zhang, Bin Cao
Clinical Infectious Diseases.2021; 72(11): e901. CrossRef - Diabetes predicts severity of COVID‐19 infection in a retrospective cohort: A mediatory role of the inflammatory biomarker C‐reactive protein
Huilin Koh, Angela Mei Chung Moh, Ester Yeoh, Yi Lin, Serena Kiat Mun Low, Say Tat Ooi, Seng Kiong Tan, Jaime Hui Xian Lin, Caroline Wei Shan Hoong
Journal of Medical Virology.2021; 93(5): 3023. CrossRef - Susceptibility for Some Infectious Diseases in Patients With Diabetes: The Key Role of Glycemia
Jesús Chávez-Reyes, Carlos E. Escárcega-González, Erika Chavira-Suárez, Angel León-Buitimea, Priscila Vázquez-León, José R. Morones-Ramírez, Carlos M. Villalón, Andrés Quintanar-Stephano, Bruno A. Marichal-Cancino
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes is most important cause for mortality in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Giovanni Corona, Alessandro Pizzocaro, Walter Vena, Giulia Rastrelli, Federico Semeraro, Andrea M Isidori, Rosario Pivonello, Andrea Salonia, Alessandra Sforza, Mario Maggi
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2021; 22(2): 275. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes: Analysis of the scientific production indexed in Scopus
Ibraín Enrique Corrales-Reyes, Frank Hernández-García, Christian R. Mejia
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(3): 765. CrossRef - Impact of diabetes mellitus on in-hospital mortality in adult patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Halla Kaminska, Lukasz Szarpak, Dariusz Kosior, Wojciech Wieczorek, Agnieszka Szarpak, Mahdi Al-Jeabory, Wladyslaw Gawel, Aleksandra Gasecka, Milosz J. Jaguszewski, Przemyslawa Jarosz-Chobot
Acta Diabetologica.2021; 58(8): 1101. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Manuela Neuenschwander, Alexander Lang, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2021; 64(7): 1480. CrossRef - Evolution of a Cohort of COVID-19 Infection Suspects Followed-Up from Primary Health Care
Valle Coronado-Vázquez, Maria del Valle Ramírez-Durán, Juan Gómez-Salgado, María Silvia Dorado-Rabaneda, Elena Benito-Alonso, Marina Holgado-Juan, Cristina Bronchalo-González
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(6): 459. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide 3.0 and 4.5 mg in patients aged younger than 65 and 65 years or older: Post hoc analysis of the AWARD‐11 trial
Juan P. Frias, Enzo Bonora, Luis Nevárez Ruiz, Stanley H. Hsia, Heike Jung, Sohini Raha, David A. Cox, M. Angelyn Bethel, Manige Konig
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(10): 2279. CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Primary Prevention and COVID‐19
Jordan Loader, Erik Lampa, Stefan Gustafsson, Thomas Cars, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive value of HbA1c for in-hospital adverse prognosis in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Zheng Zhu, Yaqian Mao, Gang Chen
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(6): 910. CrossRef - High Fibrosis-4 Index Is Related with Worse Clinical Outcome in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes Mellitus: A Multicenter Observational Study
Sung-Woo Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Jun Sung Moon, Mi Kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 800. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 757. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diabetes Associated Mortality in Patients with COVID-19
Puneeta Gupta, Meeta Gupta, Neena KAtoch, Ketan Garg, Bhawna Garg
International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes, Drug Treatment, and Mortality in COVID-19: A Multinational Retrospective Cohort Study
Jennifer E. Nyland, Nazia T. Raja-Khan, Kerstin Bettermann, Philippe A. Haouzi, Douglas L. Leslie, Jennifer L. Kraschnewski, Leslie J. Parent, Patricia Sue Grigson
Diabetes.2021; 70(12): 2903. CrossRef - Impact of Diabetes on COVID-19 Mortality and Hospital Outcomes, a Global Perspective: An ONTOP Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Stavroula Kastora, Manisha Patel, Ben Carter, Mirela Delibegovic, Phyo Kyaw Myint
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Response: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53)
Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 484. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus is Associated with Severe Infection and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Luxiang Shang, Mengjiao Shao, Qilong Guo, Jia Shi, Yang Zhao, Jiasuoer Xiaokereti, Baopeng Tang
Archives of Medical Research.2020; 51(7): 700. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Mortality Predictors of COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized at Nationally-Designated Treatment Hospitals
Seong-Su Moon, Kwan Lee, Jungi Park, Seongcheol Yun, Yun Sik Lee, Dong Seok Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Mortality Rate and Predictors of Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes
Dilaram Acharya, Kwan Lee, Dong Seok Lee, Yun Sik Lee, Seong-Su Moon
Healthcare.2020; 8(3): 338. CrossRef - Letter: The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:405–13)
So-Yeon Kim, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 621. CrossRef - Response: The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:405–13)
Seung Min Chung, June Hong Ahn, Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 625. CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Diabetes in Daegu, South Korea
Mi Kyung Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Sung-Woo Kim, Jun Sung Moon, Nan Hee Cho, Eugene Han, Ji Hong You, Ji Yeon Lee, Miri Hyun, Jae Seok Park, Yong Shik Kwon, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Ki Tae Kwon, Shin Yup Lee, Eon Ju Jeon, Jin-Woo Kim, Hyo-Lim Hong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Chi Yo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 602. CrossRef - Fasting Plasma Glucose Level Independently Predicts the Mortality of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection: A Multicenter, Retrospective Cohort Study
Min Cheol Chang, Jong-Moon Hwang, Jae-Han Jeon, Sang Gyu Kwak, Donghwi Park, Jun Sung Moon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(3): 595. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19
Jeong Hyun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 116. CrossRef - Management of Diabetes in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Prognosis and Practical Issues
Hye Soon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 120. CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Sun Joon Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Sung-Rae Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 737. CrossRef - Adverse impact of renin–angiotensin system blockade on the clinical course in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study
Jeong-Hoon Lim, Jang-Hee Cho, Yena Jeon, Ji Hye Kim, Ga Young Lee, Soojee Jeon, Hee Won Noh, Yong-Hoon Lee, Jaehee Lee, Hyun-Ha Chang, Hee-Yeon Jung, Ji-Young Choi, Sun-Hee Park, Chan-Duck Kim, Yong-Lim Kim, Shin-Woo Kim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes: The Epidemic and the Korean Diabetes Association Perspective
Junghyun Noh, Hyun-Ha Chang, In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 372. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19: Global and regional perspectives
In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon, Moon Kyu Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 166: 108303. CrossRef
- Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Development Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination
- Complications
- Higher Prevalence and Progression Rate of Chronic Kidney Disease in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Kyung-Soo Kim, Seok Won Park, Yong-Wook Cho, Soo-Kyung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):224-232. Published online May 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0065
- 5,255 View
- 73 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 33 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background To evaluate the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and progression rate to CKD in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods We investigated the medical records of 190 elderly patients (65 years or older) with T2DM from 2005 to 2011 in 6-month increments. Mean follow-up duration was 64.5 months. CKD was defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and/or the presence of albuminuria.
Results The mean age was 70.4 years and mean diabetes duration was 10.6 years. Among all the participants, 113 patients (59.5%) had CKD. The eGFR was significantly decreased between baseline (65.7±15.0 mL/min/1.73 m2) and the end of follow-up (52.7±17.5 mL/min/1.73 m2,
P <0.001). At the end of follow-up, the prevalence of eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 had increased by 61.6% (at baseline, 44.2%). Furthermore, in patients with eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2, the progression rate to more than CKD stage 3 was 39.6% at the end of follow-up; 30.2% of elderly diabetic patients had progressed to albuminuria from normoalbuminuria. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the time interval to worsening nephropathy was significantly shorter in elderly patients with diabetes duration ≥10 years than in those with diabetes duration <5 years (P =0.018).Conclusion CKD was commonly observed in older patients with T2DM, and the progression rate to CKD is also high. Consequently, it is important to identify and manage CKD as early as possible in elderly patients with T2DM, especially in those with diabetes duration ≥10 years.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing heatwave effects on disabled persons in South Korea
Yeji Kang, Ingul Baek, Jongchul Park
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of Risks of BMI and Health-Related Lifestyles on Kidney Function in the Prediabetic Japanese Population: A Prospective Cohort Study
Jou-Yin Chen, Shiqi Deng, Yukiko Wagatsuma
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(7): 5338. CrossRef - Hormonal imbalance in patients with chronic renal failure in the pre-dialysis and dialysis periods (part1)
I.P. Katerenchuk, S.T. Rustamyan, V.V. Talash, T.I. Yarmola
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(1): 65. CrossRef - The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
Dong-Hwa Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 484. CrossRef - Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Glycemia Risk Index and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee Hee Yoo, Ji Yoon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(10): 726. CrossRef - Global burden and influencing factors of chronic kidney disease due to type 2 diabetes in adults aged 20–59 years, 1990–2019
Dandan Xie, Tianpeng Ma, Haoliang Cui, Jing Li, Aihua Zhang, Zhifeng Sheng, Yiqiang Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Early Advanced Glycation End Product Accumulation Testing in the Diagnosis of Diabetes: A Health Risk Factor Analysis Using the Body Mass Index as a Moderator
Yi Zhang, Tian Jiang, Chao Liu, Honglin Hu, Fang Dai, Li Xia, Qiu Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Causal association pathways between fetuin-A and kidney function: a mediation analysis
Philip Etabee Bassey, Pawin Numthavaj, Sasivimol Rattanasiri, Piyamitr Sritara, Mark McEvoy, Boonsong Ongphiphadhanakul, Ammarin Thakkinstian
Journal of International Medical Research.2022; 50(4): 030006052210828. CrossRef - Advanced glycation end products and diabetes and other metabolic indicators
Tian Jiang, Yi Zhang, Fang Dai, Chao Liu, Honglin Hu, Qiu Zhang
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes management in people aged over seventy-five years: targets and treatment strategies
Theocharis Koufakis, Maria Grammatiki, Kalliopi Kotsa
Maturitas.2021; 143: 118. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Lobeglitazone Versus Pioglitazone on Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(1): 171. CrossRef - Chronic kidney disease progression in aged patients
Murat Tuğcu, Dilek Barutçu Ataş
International Urology and Nephrology.2021; 53(12): 2619. CrossRef - Factors determining the clinical significance of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the treatment of elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
I. V. Glinkina, A. V. Balashova, A. S. Shyman, A. V. Oderij, S. A. Khan, G. E. Runova, T. B. Morgunova, V. V. Fadeev
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2021; (7): 56. CrossRef - Effect of Oral carnosine supplementation on urinary TGF-β in diabetic nephropathy: a randomized controlled trial
Narongrit Siriwattanasit, Bancha Satirapoj, Ouppatham Supasyndh
BMC Nephrology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimation of the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in combination with diabetic kidney disease and identification of the associated factors in patients attending primary hospitals in Anhui Province, China
Li Xia, Lanlan Cheng, Tian Jiang, Chao Liu, Shiqi Zhang, Honglin Hu, Fang Dai, Qiu Zhang, Yunxia Lu
Journal of International Medical Research.2021; 49(10): 030006052110512. CrossRef - A STUDY TO EVALUATE THE EFFECT OF ANAEMIA IN TYPE-2 DIABETIC PATIENTS
Radhika Maheshwari, Divya J., J. Sahayaraj, Muthukrishnan R.
GLOBAL JOURNAL FOR RESEARCH ANALYSIS.2021; : 117. CrossRef - Metformin treatment for patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology consensus statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Metformin Treatment for Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 3. CrossRef - The prevalence of diabetic chronic kidney disease in adult Greek subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A series from hospital-based diabetes clinics
Ilias N. Migdalis, Nikolaos Papanas, Athanasios E. Raptis, Ioannis M. Ioannidis, Alexios E. Sotiropoulos, George D. Dimitriadis
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 166: 108243. CrossRef - Proteinuria Is Associated with Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in Non-Albuminuric Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jaehyun Bae, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 136. CrossRef - Renal status in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes
Kazunaga Takamatsu
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology.2020; 24(1): 53. CrossRef - The fat mass, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and chronic inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients
Tomáš Šálek, Alena Adamíková, Petr Ponížil
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin: Trigger and Target of Renal Functions
Ana F. Pina, Diego O. Borges, Maria João Meneses, Patrícia Branco, Rita Birne, Antonio Vilasi, Maria Paula Macedo
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Rate of kidney function decline and factors predicting progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with reduced kidney function: A nationwide retrospective cohort study
Wisit Kaewput, Charat Thongprayoon, Api Chewcharat, Ram Rangsin, Bancha Satirapoj, Chalermrat Kaewput, Picha Suwannahitatorn, Tarun Bathini, Michael A. Mao, Liam D. Cato, Andrew M. Harrison, Pradeep Vaitla, Wisit Cheungpasitporn
Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis.2020; 24(6): 677. CrossRef - Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Time in Range, Other Core Metrics, and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee Hee Yoo, Min Sun Choi, Jiyeon Ahn, Sung Woon Park, Yejin Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Sang-Man Jin, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2020; 22(10): 768. CrossRef - Comparison of Renal Effects of Ezetimibe–Statin Combination versus Statin Monotherapy: A Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis
Jaehyun Bae, Namki Hong, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(3): 798. CrossRef - Metformin Use and Risk of All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yao Hu, Min Lei, Guibao Ke, Xin Huang, Xuan Peng, Lihui Zhong, Ping Fu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Treatment with Cinacalcet in Hemodialysis Patients with Severe Secondary Hyperparathyroidism, Influences Bone Mineral Metabolism and Anemia Parameters
Maria Aktsiali, Theodora Papachrysanthou , Ioannis Griveas, Christos Andriopoulos, Panagiotis Sitaras, Ioannis K. Triantafyllopoulos , George I. Lambrou
Current Drug Therapy.2020; 15(3): 249. CrossRef - Gemigliptin Attenuates Renal Fibrosis Through Down-Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome
Jung Beom Seo, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Hye-In Woo, Yun-A Jung, Sungwoo Lee, Seunghyeong Lee, Mihyang Park, In-Kyu Lee, Gwon-Soo Jung, Keun-Gyu Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 830. CrossRef - Glucometabolic characteristics and higher vascular complication risk in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes with non-albumin proteinuria
Yongin Cho, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-soo Cha, Byung-wan Lee
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(8): 585. CrossRef - Assessment of kidney function and associated risk factors among type 2 diabetic patients
Moyad Jamal Shahwan, Nageeb Abdul galil Hassan, Rima Ahd Shaheen
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(4): 2661. CrossRef - Influence of diabetes mellitus on patients with lumbar spinal stenosis: A nationwide population-based study
Chang Kyu Lee, Sun Kyu Choi, Dong Ah Shin, Seong Yi, Yoon Ha, Keung Nyun Kim, Insoo Kim, Gregory W.J. Hawryluk
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(3): e0213858. CrossRef - Predictores de progresión de enfermedad renal en el paciente anciano
Manuel Heras Benito, Mª José Fernández Reyes Luis
Enfermería Nefrológica.2019; 22(1): 19. CrossRef
- Assessing heatwave effects on disabled persons in South Korea
- Appendicular Skeletal Muscle Mass and Insulin Resistance in an Elderly Korean Population: The Korean Social Life, Health and Aging Project-Health Examination Cohort
- Seung Won Lee, Yoosik Youm, Won Joon Lee, Wungrak Choi, Sang Hui Chu, Yeong-Ran Park, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(1):37-45. Published online February 16, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.1.37
- 4,911 View
- 56 Download
- 89 Web of Science
- 80 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Increasing evidence supports an association between age-related loss of muscle mass and insulin resistance. However, the association has not been fully investigated in the general population. Thus, we investigated the association between appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM) and insulin resistance in an elderly Korean population.
Methods This cross-sectional study included 158 men (mean age, 71.8) and 241 women (mean age, 70.6) from the Korean Social Life, Health and Aging Project, which started in 2011. In this study, ASM was measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis and was analyzed in three forms: ASM (kg), ASM/height2 (kg/m2), and ASM/weight (%). The homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was used as a measure of insulin resistance. The relationships between the ASM values and the HOMA-IR were investigated by multiple linear regression models.
Results The HOMA-IR was positively associated with ASM (β=0.43,
P <0.0001) and ASM/height2 (β=0.36,P <0.0001) when adjusted for sex and age. However, after additional adjustment for body weight, HOMA-IR was inversely associated with ASM (β=-0.43,P <0.001) and ASM/height2 (β=-0.30,P =0.001). Adjustment for other potential confounders did not change these associations. Conversely, HOMA-IR was consistently and inversely associated with ASM/weight before and after adjustment for other potential confounders.Conclusion Our results support the idea that lower skeletal muscle mass is independently associated with insulin resistance in older adults. When evaluating sarcopenia or muscle-related conditions in older adults, their whole body sizes also need to be considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fat Accumulation and Elevated Free Fatty Acid Are Associated With Age-Related Glucose Intolerance: Bunkyo Health Study
Hitoshi Naito, Hideyoshi Kaga, Yuki Someya, Hiroki Tabata, Saori Kakehi, Tsubasa Tajima, Naoaki Ito, Nozomu Yamasaki, Motonori Sato, Satoshi Kadowaki, Daisuke Sugimoto, Yuya Nishida, Ryuzo Kawamori, Hirotaka Watada, Yoshifumi Tamura
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Skeletal Muscle Evaluation in Patients With Acromegaly
Angelo Milioto, Giuliana Corica, Federica Nista, Luiz Eduardo Armondi Wildemberg, Federica Rossi, Bianca Bignotti, Mônica R Gadelha, Diego Ferone, Alberto Stefano Tagliafico, Federico Gatto
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle attenuation, not skeletal muscle index, is an independent prognostic factor for survival in gastric cancer patients with overweight and obesity
Cheng-Le Zhuang, Hao-Fan Wu, Hao-Jie Jiang, Feng-Min Zhang, Han-Ping Shi, Zhen Yu, Xian Shen, Xiao-Lei Chen, Su-Lin Wang
Nutrition.2024; 122: 112391. CrossRef - Association between soft drink consumption and carotid atherosclerosis in a large-scale adult population: The TCLSIH cohort study
Ge Meng, Tongfeng Liu, Sabina Rayamajhi, Amrish Thapa, Shunming Zhang, Xuena Wang, Hongmei Wu, Yeqing Gu, Qing Zhang, Li Liu, Shaomei Sun, Xing Wang, Ming Zhou, Qiyu Jia, Kun Song, Zhongze Fang, Kaijun Niu
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(11): 2209. CrossRef - Sarcopenia is Associated With Oncological Prognosis and the Incidence of Secondary Cancer in Patients With Middle/Lower Rectal Cancer
Shinya Abe, Hiroaki Nozawa, Kazuhito Sasaki, Koji Murono, Shigenobu Emoto, Yuichiro Yokoyama, Hiroyuki Matsuzaki, Yuzo Nagai, Yuichiro Yoshioka, Takahide Shinagawa, Hirofumi Sonoda, Soichiro Ishihara
Clinical Colorectal Cancer.2023; 22(1): 143. CrossRef - Association between body mass index and reversion to normoglycemia from impaired fasting glucose among Chinese adults: a 5-year cohort study
Yong Han, Haofei Hu, Zhiqiang Huang, Dehong Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in glycemic control and skeletal muscle mass indices after dapagliflozin treatment in individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Yuta Yoshimura, Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Hiroshi Okada, Maya Takegami, Hanako Nakajima, Tomoki Miyoshi, Takashi Yoshimura, Masahiro Yamazaki, Masahide Hamaguchi, Michiaki Fukui
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(10): 1175. CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose Index is Strongly Associated with a Fragility Fracture in Postmenopausal Elderly Females with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Osteoporosis: A 6-Year Follow-Up Study
Jiangmei Pan, Xiuxian Huang, Qiu Wang, Jingxia Sun, Zhenwei Zhai, Jiacheng Mo, Jianhao Huang, Wensheng Lu
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2023; Volume 18: 1841. CrossRef - Osteocalcin has a muscle-protective effect during weight loss in men without metabolic syndrome: a multicenter, prospective, observational study
Yi Xiang, Wenyi Lu, Xiaomeng Mao, Jing Zou, Jialu Wang, Renying Xu, Qingya Tang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dual effects of insulin resistance on mortality and function in non-diabetic older adults: findings from the Toledo Study of Healthy Aging
Leocadio Rodríguez-Mañas, Javier Angulo, José A. Carnicero, Mariam El Assar, Francisco J. García-García, Alan J. Sinclair
GeroScience.2022; 44(2): 1095. CrossRef - Metabolically unhealthy individuals, either with obesity or not, have a higher risk of critical coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes than metabolically healthy individuals without obesity
Nam Hoon Kim, Kyeong Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
Metabolism.2022; 128: 154894. CrossRef - Prevalence and associated risk of advanced colorectal neoplasia in adults with sarcopenia
Min Cheol Kim, Kyeong Ok Kim, Min Kyu Kang
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(2): 294. CrossRef - Relationship between creatinine to body weight ratios and diabetes mellitus: A Chinese cohort study
Zhuangsen Chen, Yang Zou, Fan Yang, Xiao han Ding, Changchun Cao, Haofei Hu, Xinyu Wang
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(3): 167. CrossRef - Weight Trajectory Since Birth, Current Body Composition, Dietary Intake, and Glucose Tolerance in Young Underweight Japanese Women
Mika Takeuchi, Mari Honda, Ayaka Tsuboi, Satomi Minato-Inokawa, Miki Kurata, Bin Wu, Tsutomu Kazumi, Keisuke Fukuo
Women's Health Reports.2022; 3(1): 215. CrossRef - Advances in Phenotyping Obesity and in Its Dietary and Pharmacological Treatment: A Narrative Review
Roberta Pujia, Maria Grazia Tarsitano, Franco Arturi, Antonino De Lorenzo, Andrea Lenzi, Arturo Pujia, Tiziana Montalcini
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Can Biological Drugs Diminish the Risk of Sarcopenia in Psoriatic Patients? A Systematic Review
Zuzanna Piętowska, Danuta Nowicka, Jacek Szepietowski
Life.2022; 12(3): 435. CrossRef - Association between total protein intake and low muscle mass in Korean adults
Youn Huh, Ki Young Son
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between height-corrected appendicular and regional skeletal muscle mass and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes
Yoshikazu Hirasawa, Yoshiyuki Hamamoto
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2022; 34(5): 353. CrossRef - Association between dietary inflammatory index score and muscle mass and strength in older adults: a study from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2002
Lingzhi Chen, Jingjing Ming, Tianyi Chen, James R. Hébert, Peng Sun, Li Zhang, Hongya Wang, Qingkuo Wu, Cancan Zhang, Nitin Shivappa, Bo Ban
European Journal of Nutrition.2022; 61(8): 4077. CrossRef - Effect of low skeletal muscle mass and sarcopenic obesity on chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Da Hea Seo, Young Ju Suh, Yongin Cho, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongha Seo, Seongbin Hong, Yong‐ho Lee, Young Ju Choi, Eunjig Lee, So Hun Kim
Obesity.2022; 30(10): 2034. CrossRef - Sex‐specific associations between gut microbiota and skeletal muscle mass in a population‐based study
Chul‐Hyun Park, Eun‐Ju Lee, Hyung‐Lae Kim, Yong‐Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Han‐Na Kim
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2022; 13(6): 2908. CrossRef - Impact of Low Skeletal Muscle Mass and Obesity on Hearing Loss in Asymptomatic Individuals: A Population-Based Study
Chul-Hyun Park, Kyung Jae Yoon, Yong-Taek Lee, Sung Min Jin, Sang Hyuk Lee, Tae Hwan Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 2022. CrossRef - Lower insulin level is associated with sarcopenia in community-dwelling frail and non-frail older adults
Yanxia Lu, Wee Shiong Lim, Xia Jin, Ma Schwe Zin Nyunt, Tamas Fulop, Qi Gao, Su Chi Lim, Anis Larbi, Tze Pin Ng
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle alterations are independently associated with significant fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Yun‐Cheng Hsieh, Sae Kyung Joo, Bo Kyung Koo, Han‐Chieh Lin, Won Kim
Liver International.2021; 41(3): 494. CrossRef - A high lean body mass is not protecting from type 2 diabetes in the presence of a high body fat mass
Simo K.J. Rehunen, Hannu Kautiainen, Päivi E. Korhonen, Johan G. Eriksson
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(6): 101219. CrossRef - Abdominal aortic calcification is associated with decline in handgrip strength in the U.S. adult population ≥40 years of age
Robinson Ramírez-Vélez, Antonio García-Hermoso, María Correa-Rodríguez, Felipe Lobelo, Katherine González-Ruiz, Mikel Izquierdo
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2021; 31(4): 1035. CrossRef - Association of metabolic syndrome with mobility in the older adults: a Korean nationwide representative cross-sectional study
Ki Young Son, Dong Wook Shin, Ji Eun Lee, Sang Hyuck Kim, Jae Moon Yun, Belong Cho
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Low skeletal muscle mass is associated with liver fibrosis in individuals with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Mohammad Shafi Kuchay, Narendra Singh Choudhary, Sakshi Gagneja, Anu Mathew, Tarannum Bano, Parjeet Kaur, Bajarang Bahadur, Manish Kumar Singh, Harmandeep Kaur Gill, Jasjeet Singh Wasir, Randhir Sud, Sunil Kumar Mishra
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(11): 3204. CrossRef - Association of obesity, visceral adiposity, and sarcopenia with an increased risk of metabolic syndrome: A retrospective study
Su Hwan Kim, Hyoun Woo Kang, Ji Bong Jeong, Dong Seok Lee, Dong-Won Ahn, Ji Won Kim, Byeong Gwan Kim, Kook Lae Lee, Sohee Oh, Soon Ho Yoon, Sang Joon Park, Mauro Lombardo
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0256083. CrossRef - Paradigm shift in gastrointestinal surgery − combating sarcopenia with prehabilitation: Multimodal review of clinical and scientific data
Frederick H Koh, Jason MW Chua, Joselyn LJ Tan, Fung-Joon Foo, Winson J Tan, Sharmini S Sivarajah, Leonard Ming Li Ho, Bin-Tean Teh, Min-Hoe Chew
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2021; 13(8): 734. CrossRef - Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy Induces Body Composition Changes in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Comparison between Oral Cavity and Non-Oral Cavity Cancer
Yu-Ching Lin, Hang Huong Ling, Pei-Hung Chang, Yi-Ping Pan, Cheng-Hsu Wang, Wen-Chi Chou, Fang-Ping Chen, Kun-Yun Yeh
Nutrients.2021; 13(9): 2969. CrossRef - Low Skeletal Muscle Mass Is Associated With the Presence, Incidence, and Progression of Coronary Artery Calcification
Ji Eun Jun, Min Sun Choi, Sung Woon Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyunga Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, In-Kyung Jeong, Mira Kang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Canadian Journal of Cardiology.2021; 37(9): 1480. CrossRef - Association between Adjusted Handgrip Strength and Metabolic Syndrome in Arab Men
Shaea Alkahtani
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(20): 10898. CrossRef - Association Between Low Muscle Mass and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosed Using Ultrasonography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging Derived Proton Density Fat Fraction, and Comprehensive NAFLD Score in Korea
Hun Ju Lee, Jae Seung Chang, Jhii Hyun Ahn, Moon Young Kim, Kyu-Sang Park, Yeon-Soon Ahn, Sang Baek Koh
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2021; 54(6): 412. CrossRef - Impact of Sarcopenia on the Risk of Erosive Esophagitis
Chan Mi Heo, Tae Jun Kim, Hyuk Lee, Jeung Hui Pyo, Yang Won Min, Byung-Hoon Min, Jun Haeng Lee, Hee Jung Son, Sun-Young Baek, Kyunga Kim, Seungho Ryu, Poong-Lyul Rhee, Jae J. Kim
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 75(3): 132. CrossRef - Handgrip Strength Among Korean Adolescents With Metabolic Syndrome in 2014–2015
Yunkoo Kang, Sowon Park, Seung Kim, Hong Koh
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2020; 23(2): 271. CrossRef - Creatinine‐to‐bodyweight ratio is a predictor of incident non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: A population‐based longitudinal study
Takuro Okamura, Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Masahide Hamaguchi, Akihiro Obora, Takao Kojima, Michiaki Fukui
Hepatology Research.2020; 50(1): 57. CrossRef - Physical performance and chronic kidney disease development in elderly adults: results from a nationwide cohort study
Young Su Joo, Jong Hyun Jhee, Hyung-Woo Kim, Seung Hyeok Han, Tae-Hyun Yoo, Shin-Wook Kang, Jung Tak Park
Aging.2020; 12(17): 17393. CrossRef - Decreased Appendicular Skeletal Muscle Mass is Associated with Poor Outcomes after ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Ryosuke Sato, Eiichi Akiyama, Masaaki Konishi, Yasushi Matsuzawa, Hiroyuki Suzuki, Chika Kawashima, Yuichiro Kimura, Kozo Okada, Nobuhiko Maejima, Noriaki Iwahashi, Kiyoshi Hibi, Masami Kosuge, Toshiaki Ebina, Stephan von Haehling, Stefan D. Anker, Kouich
Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis.2020; 27(12): 1278. CrossRef - Sarcopenia is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in men with type 2 diabetes
D.H. Seo, Y.-h. Lee, S.W. Park, Y.J. Choi, B.W. Huh, E. Lee, K.B. Huh, S.H. Kim, B.-S. Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism.2020; 46(5): 362. CrossRef - Associations of skeletal muscle mass with atherosclerosis and inflammatory markers in Korean adults
Soon-Kyu Yoon, Ha-Na Kim, Sang-Wook Song
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2020; 90: 104163. CrossRef - Lean body mass is not beneficial, but may be detrimental for glucose tolerance – Splitting body mass index according to body composition
Simo KJ Rehunen, Hannu Kautiainen, Päivi E Korhonen, Johan G Eriksson
Primary Care Diabetes.2020; 14(6): 747. CrossRef - Association between the Thigh Muscle and Insulin Resistance According to Body Mass Index in Middle-Aged Korean Adults
Ji Eun Heo, Jee-Seon Shim, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 446. CrossRef - Independent and combined associations of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle strength with metabolic syndrome in older adults: A cross-sectional study
Marcyo Câmara, Rodrigo Alberto Vieira Browne, Gabriel Costa Souto, Daniel Schwade, Ludmila Pereira Lucena Cabral, Geovani Araújo Dantas Macêdo, Luiz Fernando Farias-Junior, Fabíola Leite Gouveia, Telma Maria Araújo Moura Lemos, Kenio Costa Lima, Todd A. D
Experimental Gerontology.2020; 135: 110923. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and adverse health‐related outcomes: An umbrella review of meta‐analyses of observational studies
Lin Xia, Rui Zhao, Qianyi Wan, Yutao Wu, Yong Zhou, Yong Wang, Yaping Cui, Xiaoding Shen, Xiaoting Wu
Cancer Medicine.2020; 9(21): 7964. CrossRef - Impact of sarcopenia on the risk of advanced colorectal neoplasia
Ji Taek Hong, Tae Jun Kim, Jeung Hui Pyo, Eun Ran Kim, Sung Noh Hong, Young‐Ho Kim, Hyeon Seon Ahn, Insuk Sohn, Dong Kyung Chang
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2019; 34(1): 162. CrossRef - Evaluation of muscle mass in obesity, prediabetes and diabetes mellitus by different equations used for the measurement of muscle mass
Mustafa Reşat Dabak, Elif Sevinç, Sabah Tüzün, Emine Özel Gün
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(3): 2148. CrossRef - Effect of Insulin Resistance on BMD and Fracture Risk in Older Adults
Nicola Napoli, Caterina Conte, Claudio Pedone, Elsa S Strotmeyer, Kamil E Barbour, Dennis M Black, Elizabeth J Samelson, Ann V Schwartz
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 104(8): 3303. CrossRef - Can 24 weeks strength training reduce feelings of depression and increase neurotransmitter in elderly females?
Yun-Sik Kim, David Michael O'Sullivan, Sang-Keun Shin
Experimental Gerontology.2019; 115: 62. CrossRef - The Differential Association between Muscle Strength and Diabetes Mellitus According to the Presence or Absence of Obesity
Bo Kyung Koo
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2019; 28(1): 46. CrossRef - Sarcopenic obesity and overall mortality: Results from the application of novel models of body composition phenotypes to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2004
Carla Van Aller, Jose Lara, Blossom C.M. Stephan, Lorenzo Maria Donini, Steven Heymsfield, Peter T. Katzmarzyk, Jonathan C.K. Wells, Carla M. Prado, Mario Siervo
Clinical Nutrition.2019; 38(1): 264. CrossRef - Carbohydrate oxidation and glucose utilisation under hyperglycaemia in aged and young males during exercise at the same relative exercise intensity
James J. Malone, Minoo Bassami, Sarah C. Waldron, Iain T. Campbell, Andrew Hulton, Dominic Doran, Don P. MacLaren
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2019; 119(1): 235. CrossRef - Association of the muscle/fat mass ratio with insulin resistance in gestational diabetes mellitus
Shin Kawanabe, Yoshio Nagai, Yuta Nakamura, Ami Nishine, Tomoko Nakagawa, Yasushi Tanaka
Endocrine Journal.2019; 66(1): 75. CrossRef - Low muscle mass and inflammation among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Indonesia
Perdana Samekto Tyasnugroho Suyoto, Bianda Aulia
Diabetology International.2019; 10(3): 219. CrossRef - Association of low skeletal muscle mass with advanced liver fibrosis in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
Min Kyu Kang, Jung Gil Park, Heon Ju Lee, Min Cheol Kim
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2019; 34(9): 1633. CrossRef - Evaluation of skeletal muscle mass indices, assessed by bioelectrical impedance, as indicators of insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes
Yoshikazu Hirasawa, Ryosuke Matsuki, Toshihiko Ebisu, Takeshi Kurose, Yoshiyuki Hamamoto, Yutaka Seino
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2019; 31(2): 190. CrossRef - Polycystic ovary syndrome is a risk factor for sarcopenic obesity: a case control study
Laura E. McBreairty, Philip D. Chilibeck, Julianne J. Gordon, Donna R. Chizen, Gordon A. Zello
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of hyperglycaemia in the relationship between serum osteocalcin levels and relative skeletal muscle index
Yiting Xu, Xiaojing Ma, Yun Shen, Chengchen Gu, Junling Tang, Yuqian Bao
Clinical Nutrition.2019; 38(6): 2704. CrossRef - Relationship Between Relative Skeletal Muscle Mass and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 7‐Year Longitudinal Study
Gyuri Kim, Seung‐Eun Lee, You‐Bin Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Jiyeon Ahn, Ji Cheol Bae, Sang‐Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hwan Jee, Moon‐Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Hepatology.2018; 68(5): 1755. CrossRef - Relationships between 25(OH)D concentration, sarcopenia and HOMA-IR in postmenopausal Korean women
J. H. Lee, S. Kim, M. K. Kim, B. H. Yun, S. Cho, Y. S. Choi, B. S. Lee, S. K. Seo
Climacteric.2018; 21(1): 40. CrossRef - Is the Relationship between Depression and C Reactive Protein Level Moderated by Social Support in Elderly?-Korean Social Life, Health, and Aging Project (KSHAP)
Nam Wook Hur, Hyeon Chang Kim, Linda Waite, Yoosik Youm
Psychiatry Investigation.2018; 15(1): 24. CrossRef - Challenges in Treatment of Obesity in the Elderly
Ignacio Sajoux
Endocrinology&Metabolism International Journal.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediterranean diet, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) style diet, and metabolic health in U.S. adults
Yong-Moon Mark Park, Susan E. Steck, Teresa T. Fung, Jiajia Zhang, Linda J. Hazlett, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Anwar T. Merchant
Clinical Nutrition.2017; 36(5): 1301. CrossRef - Sarcopenia is an independent risk factor for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and significant fibrosis
Bo Kyung Koo, Donghee Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Jung Ho Kim, Mee Soo Chang, Byeong Gwan Kim, Kook Lae Lee, Won Kim
Journal of Hepatology.2017; 66(1): 123. CrossRef - Low muscle mass and risk of type 2 diabetes in middle-aged and older adults: findings from the KoGES
Jang Won Son, Seong Su Lee, Sung Rae Kim, Soon Jib Yoo, Bong Yun Cha, Ho Young Son, Nam H. Cho
Diabetologia.2017; 60(5): 865. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Insomnia among the Elderly in a Korean Rural Community
Woo Jung Kim, Won-tak Joo, Jiwon Baek, Sung Yun Sohn, Kee Namkoong, Yoosik Youm, Hyeon Chang Kim, Yeong-Ran Park, Sang Hui Chu, Eun Lee
Psychiatry Investigation.2017; 14(4): 400. CrossRef - Differential association between sarcopenia and metabolic phenotype in Korean young and older adults with and without obesity
You‐Cheol Hwang, In‐Jin Cho, In‐Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung
Obesity.2017; 25(1): 244. CrossRef - Association of physical activity on body composition, cardiometabolic risk factors, and prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the Korean population (from the fifth Korea national health and nutrition examination survey, 2008–2011)
Gwang-Sil Kim, Eui Im, Ji-Hyuck Rhee
BMC Public Health.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Low skeletal muscle mass is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults: the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hee Yeon Kim, Chang Wook Kim, Chung-Hwa Park, Jong Young Choi, Kyungdo Han, Anwar T Merchant, Yong-Moon Park
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2016; 15(1): 39. CrossRef - Frailty and sarcopenia as the basis for the phenotypic manifestation of chronic diseases in older adults
Javier Angulo, Mariam El Assar, Leocadio Rodríguez-Mañas
Molecular Aspects of Medicine.2016; 50: 1. CrossRef - Importance of Lean Muscle Maintenance to Improve Insulin Resistance by Body Weight Reduction in Female Patients with Obesity
Yaeko Fukushima, Satoshi Kurose, Hiromi Shinno, Ha Cao Thu, Nana Takao, Hiromi Tsutsumi, Yutaka Kimura
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(2): 147. CrossRef - Difference between old and young adults in contribution of β‐cell function and sarcopenia in developing diabetes mellitus
Bo Kyung Koo, Eun Roh, Ye Seul Yang, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2016; 7(2): 233. CrossRef - Association between serum triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and sarcopenia in elderly Korean males: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Tae-Ha Chung, Yu-Jin Kwon, Jae-Yong Shim, Yong-Jae Lee
Clinica Chimica Acta.2016; 463: 165. CrossRef - Association between leukocyte count and sarcopenia in postmenopausal women: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Tae-Ha Chung, Jae-Yong Shim, Yong-Jae Lee
Maturitas.2016; 84: 89. CrossRef - Low Relative Lean Mass is Associated with Increased Likelihood of Abdominal Aortic Calcification in Community-Dwelling Older Australians
Alexander J. Rodríguez, David Scott, Belal Khan, Nayab Khan, Allison Hodge, Dallas R. English, Graham G. Giles, Peter R. Ebeling
Calcified Tissue International.2016; 99(4): 340. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and the cardiometabolic syndrome: A narrative review
G. Bahat, B. İlhan
European Geriatric Medicine.2016; 7(3): 220. CrossRef - Decreased β-Cell Function Is Associated with Reduced Skeletal Muscle Mass in Japanese Subjects without Diabetes
Satoshi Sakai, Keiji Tanimoto, Ayumi Imbe, Yuiko Inaba, Kanako Shishikura, Yoshimi Tanimoto, Takahisa Ushiroyama, Jungo Terasaki, Toshiaki Hanafusa, Marta Letizia Hribal
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(9): e0162603. CrossRef - Differences among skeletal muscle mass indices derived from height-, weight-, and body mass index-adjusted models in assessing sarcopenia
Kyoung Min Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(4): 643. CrossRef - Low muscle mass is associated with metabolic syndrome only in nonobese young adults: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2010
Byung Chul Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Sae-Young Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Anwar T. Merchant, Hyeon Woo Yim, Won-Chul Lee, Yong Gyu Park, Yong-Moon Park
Nutrition Research.2015; 35(12): 1070. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Is Associated with Prevalence of Physician-Diagnosed Urinary Incontinence in Postmenopausal Non-Diabetic Adult Women: Data from the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Byung Il Yoon, Kyung-Do Han, Kyu Won Lee, Hyuk Sang Kwon, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Wan Sohn, Yong-Hyun Cho, U-Syn Ha, Tatsuo Shimosawa
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(11): e0141720. CrossRef
- Fat Accumulation and Elevated Free Fatty Acid Are Associated With Age-Related Glucose Intolerance: Bunkyo Health Study
- Factors Associated for Mild Cognitive Impairment in Older Korean Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yun Jeong Lee, Hye Mi Kang, Na Kyung Kim, Ju Yeon Yang, Jung Hyun Noh, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Dong-Jun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(2):150-157. Published online April 18, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.2.150
- 4,063 View
- 35 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study was to identify factors associated with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in older Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods A total of 226 older (age ≥65 years) adults without a history of cerebrovascular disease or dementia participated in this study. Cognitive function was assessed with the Montreal Cognitive Assessment-Korean version (MoCA-K). A MoCA-K score <23 was defined as MCI.
Results The prevalence of MCI was 32.7%. In a logistic regression analysis, age (≥74 years old vs. 65-68 years old; odds ratio [OR], 3.69; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.55 to 8.82;
P =0.003), educational background (college graduation vs. no school or elementary school graduation; OR, 0.16; 95% CI, 0.05 to 0.46;P =0.001), and systolic blood pressure (≥135 mm Hg vs. ≤120 mm Hg; OR, 3.25; 95% CI, 1.29 to 8.17;P =0.012) were associated with MCI.Conclusion More concentrated efforts focused on early detection and appropriate management of MCI may be required in older Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction model for mild cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes using the autonomic function test
Heeyoung Kang, Juhyeon Kim, Minkyeong Kim, Jin Hyun Kim, Gu Seob Roh, Soo Kyoung Kim
Neurological Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cognitive screening among older adults with diabetes across diverse clinic settings
Deepashree Gupta, Holly Wilhalme, Gabriela Sauder, Tannaz Moin
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 196: 110184. CrossRef - Occurrence of mild cognitive impairment with hyperinsulinaemia in Africans with advanced type 2 diabetes mellitus
J. Bashir, I.U. Yarube
IBRO Neuroscience Reports.2022; 12: 182. CrossRef - Risk factors for cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Brazil: a prospective observational study
Ana Cristina Ravazzani de Almeida Faria, Joceline Franco Dall’Agnol, Aline Maciel Gouveia, Clara Inácio de Paiva, Victoria Chechetto Segalla, Cristina Pellegrino Baena
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The TELE-DD project on treatment nonadherence in the population with type 2 diabetes and comorbid depression
Juan Francisco Roy, María Luisa Lozano del Hoyo, Fernando Urcola-Pardo, Alicia Monreal-Bartolomé, Diana Cecilia Gracia Ruiz, María Mercedes Gómez Borao, Ana Belén Artigas Alcázar, José Pedro Martínez Casbas, Alexandra Aceituno Casas, María Teresa Andaluz
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential roles of Glucagon-like peptide-1 and its analogues in cognitive impairment associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Zi-Wei Yu, Rong Liu, Xin Li, Ying Wang, Yu-Hong Fu, Hui-Yao Li, Yue Yuan, Xin-Yuan Gao
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development.2020; 190: 111294. CrossRef - Predictors of Quality of Life among Older People with Mild Cognitive Impairment Attending Urban Primary Care Clinics
Alexander Lourdes Samy, Shahrul Bahyah Kamaruzzaman, Saroja Krishnaswamy, Wah-Yun Low
Clinical Gerontologist.2020; 43(4): 441. CrossRef - Influence of the Mediterranean and Ketogenic Diets on Cognitive Status and Decline: A Narrative Review
Federica Vinciguerra, Marco Graziano, Maria Hagnäs, Lucia Frittitta, Andrea Tumminia
Nutrients.2020; 12(4): 1019. CrossRef -
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN CHANGES IN THE PSYCHOLOGICAL STATUS AND METABOLIC DISORDERS IN WOMEN WITH ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION, OBESITY AND LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION
N. M. Kyrychenko
Bulletin of Problems Biology and Medicine.2020; 4(2): 102. CrossRef - Insulin resistance is a risk factor for mild cognitive impairment in elderly adults with T2DM
Hongjun Zhao, Chenglong Wu, Xiaoping Zhang, Liping Wang, Jianhong Sun, Fuyuan Zhuge
Open Life Sciences.2019; 14(1): 255. CrossRef - Oral diabetes medication and risk of dementia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes
Ju Young Kim, Young Sook Ku, Hyun Jeong Kim, Nga Thi Trinh, Woorim Kim, Bomi Jeong, Tae Young Heo, Myung Koo Lee, Kyung Eun Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2019; 154: 116. CrossRef - Biomarkers for cognitive decline in patients with diabetes mellitus: evidence from clinical studies
Xue Zhao, Qing Han, You Lv, Lin Sun, Xiaokun Gang, Guixia Wang
Oncotarget.2018; 9(7): 7710. CrossRef - Low education and lack of spousal relationship are associated with dementia in older adults with diabetes mellitus in Nigeria
Abdulkareem J. Yusuf, Olusegun Baiyewu, Adamu G. Bakari, Sani B. Garko, Mohammed E.‐B. Jibril, Aishatu M. Suleiman, Haruna M. Muktar, Micheal A. Amedu
Psychogeriatrics.2018; 18(3): 216. CrossRef - Prevalence and risk factors of cognitive dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving care in a reference hospital in Cameroon: a cross-sectional study
Zainab I. Abba, Yannick Mboue-Djieka, Yacouba N. Mapoure, Cyrille Nkouonlack, Henry N. Luma, Simeon-Pierre Choukem
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2018; 38(2): 158. CrossRef - Cognitive impairment among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients at Jimma University Specialized Hospital, Southwest Ethiopia
Dagnew Baye, Desalegn Wolide Amare, Mossie Andualem
Journal of Public Health and Epidemiology.2017; 9(11): 300. CrossRef - Association of metabolic syndrome and 25‐hydroxyvitamin D with cognitive impairment among elderly Koreans
Eun Young Lee, Su Jin Lee, Kyoung Min Kim, Young Mi Yun, Bo Mi Song, Jong Eun Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim, Yumie Rhee, Yoosik Youm, Chang Oh Kim
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2017; 17(7): 1069. CrossRef - Serum uric acid and impaired cognitive function in community-dwelling elderly in Beijing
Shuangling Xiu, Zheng Zheng, Shaochen Guan, Jin Zhang, Jinghong Ma, Piu Chan
Neuroscience Letters.2017; 637: 182. CrossRef - Assessment of relationship on excess arsenic intake from drinking water and cognitive impairment in adults and elders in arsenicosis areas
Jiayong Liu, Yanhui Gao, Hongxu Liu, Jing Sun, Yang Liu, Junhua Wu, Dandan Li, Dianjun Sun
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health.2017; 220(2): 424. CrossRef - An Update on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus as a Risk Factor for Dementia
Wei Li, Edgar Huang
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2016; 53(2): 393. CrossRef - Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(5): 845. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with brain atrophy and hypometabolism in the ADNI cohort
Wei Li, Shannon L. Risacher, Edgar Huang, Andrew J. Saykin
Neurology.2016; 87(6): 595. CrossRef - Cardiovascular risk factors and cognitive decline in older people with type 2 diabetes
Insa Feinkohl, Markéta Keller, Christine M. Robertson, Joanne R. Morling, Stela McLachlan, Brian M. Frier, Ian J. Deary, Mark W. J. Strachan, Jackie F. Price
Diabetologia.2015; 58(7): 1637. CrossRef - Association between obesity and depression in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2; a study protocol
Eduardo De la Cruz-Cano, Carlos Alfonso Tovilla-Zarate, Emilio Reyes-Ramos, Thelma Beatriz Gonzalez-Castro, Isela Juarez-Castro, Maria Lilia López-Narváez, Ana Fresan
F1000Research.2015; 4: 7. CrossRef
- Prediction model for mild cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes using the autonomic function test
- Factors that Affect Medication Adherence in Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Kyung-Ae Park, Jung-Guk Kim, Bo-Wan Kim, Sin Kam, Keon-Yeop Kim, Sung-Woo Ha, Sung-Taek Hyun
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(1):55-65. Published online February 28, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.1.55
- 4,494 View
- 96 Download
- 35 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study was conducted to evaluate the factors affecting medication adherence in geriatric diabetic patients treated at private clinics and tertiary hospitals. We compared the factors affecting medication adherence between these two patient groups.
Methods We included 108 diabetic patients older than 65 years treated at one tertiary hospital and 157 patients older than 65 years treated at two private clinics. We conducted an interview survey based on the Health Belief Model, and used a questionnaire that included the self-efficacy variable. For the medication adherence, Morisky's self-report was used.
Results The medication adherence based on Morisky's self-report was significantly higher in tertiary hospital patients (61.1%) compared to private clinic patients (43.2%) (
P < 0.01). The results showed that drug storage and self-efficacy were factors affecting adherence to medication in tertiary hospital patients (P < 0.05). The adherence was high in cases of proper drug storage (odds ratio [OR], 5.401) and in cases with high self-efficacy (OR, 13.114). In private clinic patients, financial level (P < 0.05), recognition of the seriousness of diabetes complications (P < 0.05) and self-efficacy (P < 0.01) were associated with medication adherence. The medication adherence was significantly lower in patients whose financial state were moderate than those with lower (OR, 0.410), and medication adherence was significantly higher in patients who had higher perceived severity (OR, 2.936) and in patients with higher self-efficacy (OR, 4.040).Conclusion Different strategies should be used to increase medication adherence in geriatric diabetic patients, depending on institutions whether they are treated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medication use problems among older adults at a primary care: A narrative of literature review
Christina Christopher, Bhuvan KC, Sunil Shrestha, Ali Qais Blebil, Deepa Alex, Mohamed Izham Mohamed Ibrahim, Norhasimah Ismail
AGING MEDICINE.2022; 5(2): 126. CrossRef - Changes in Treatment Satisfaction Over 3 Years in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes After Initiating Second-line Treatment
Tomoya Mita, Naoto Katakami, Mitsuyoshi Takahara, Masaru Kawashima, Fumitaka Wada, Hiroki Akiyama, Naru Morita, Yoko Kidani, Toshitaka Yajima, Iichiro Shimomura, Hirotaka Watada
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): 2424. CrossRef - Associated factors with treatment adherence of patients diagnosed with chronic disease: Relationship with health literacy
Sabahat Coskun, Gulcan Bagcivan
Applied Nursing Research.2021; 57: 151368. CrossRef - The relationships among self-efficacy, health literacy, self-care and glycemic control in older people with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ariyanti Saleh, Wirda Wirda, Andi Masyitha Irwan, Aulia Insani Latif
Working with Older People.2021; 25(2): 164. CrossRef - Tip 2 Diyabetli Bireylerin Hastalık Yönetiminde Karşılaştıkları Engellerin Değerlendirilmesi
Şuheda ÜSTÜNDAĞ, Nuray DAYAPOĞLU
Adnan Menderes Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; 5(3): 514. CrossRef - Influence of Health Literacy on Medication Adherence Among Elderly Females With Type 2 Diabetes in Pakistan
Nadia Hussain, Amira S. A. Said, Zainab Khan
International Quarterly of Community Health Education.2020; 41(1): 35. CrossRef - Elucidating factors associated with non-adherence among Type 1 diabetes patients in primary care setting in Southeastern Brazil
Heverton Alves Peres, Leonardo Régis Leira Pereira, Edson Zangiacomine Martinez, Carlos Manuel Viana, Maria Cristina Foss de Freitas
Primary Care Diabetes.2020; 14(1): 85. CrossRef - Predictors of poor adherence to antidiabetic therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study insight from Ethiopia
Gebre Teklemariam Demoz, Shishay Wahdey, Degena Bahrey, Halefom Kahsay, Gebremariam Woldu, Yirga Legesse Niriayo, Andrew Collier
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of medication storage with diabetes control: A cross-sectional study from Saudi Arabia
Ali F. Altebainawi, Mubarak N. Alrashidi, Moaath K. Aljbreen, Muhammad Majid Aziz, Abdullah A. Alhifany, Mohamad Aljofan, Thamir M. Alshammari
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal.2020; 28(4): 452. CrossRef - Facteurs associés à la non-observance thérapeutique chez les diabétiques de type 2 : première enquête algérienne
M.Y. Achouri, M. Mammeri, Y. Sehanine, M.A. Selka, W.I. Ghomari, A. Lahmer, M. Hadj Habib
Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises.2019; 77(6): 506. CrossRef - Heart failure is associated with non-adherence to pharmacotherapy in elderly with type 2 diabetes mellitus in public health system Brazilians
Heverton Alves Peres, Leonardo Régis Leira Pereira, Edson Zangiacomini Martinez, Carlos Manuel Viana, Maria Cristina Foss-Freitas
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(2): 939. CrossRef - Medication Adherence and its Predictors in Type 2 Diabetic Patients Referring to Urban Primary Health Care Centers in Kerman City, Southeastern Iran
Lila Benrazavy, Ali Khalooei
Shiraz E-Medical Journal.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Adherence to Bisphosphonates among People Admitted to an Orthopaedic and Geriatric Ward at a University Hospital in Sweden
Linnea Abramsson, Maria Gustafsson
Pharmacy.2018; 6(1): 20. CrossRef - Evaluation of factors for therapeutic adherence in diabetic patients
G. Belhabib, M. Lahyani, A. Mhiri, O. Gloulou, J. Sahli, N. Chouchane
Le Pharmacien Hospitalier et Clinicien.2018; 53(2): 159. CrossRef - Évaluation des facteurs conditionnant l’observance thérapeutique chez le patient diabétique
G. Belhabib, M. Lahyani, A. Mhiri, O. Gloulou, J. Sahli, N. Chouchane
Le Pharmacien Hospitalier et Clinicien.2018; 53(2): 87. CrossRef - Factors associated with antidiabetic medication non-adherence in patients with incident comorbid depression
Carlotta Lunghi, Arsène Zongo, Jocelyne Moisan, Jean-Pierre Grégoire, Line Guénette
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(7): 1200. CrossRef - Psychosocial factors associated with adherence to non-insulin antidiabetes treatments
Line Guénette, Marie-Claude Breton, Laurence Guillaumie, Sophie Lauzier, Jean-Pierre Grégoire, Jocelyne Moisan
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(2): 335. CrossRef - Effects of pharmacist-led patient education on diabetes-related knowledge and medication adherence: A home-based study
Ee Pin Chow, Mohamed Azmi Hassali, Fahad Saleem, Hisham Aljadhey
Health Education Journal.2016; 75(4): 421. CrossRef - Adherence to diabetes medication: a systematic review
I. Krass, P. Schieback, T. Dhippayom
Diabetic Medicine.2015; 32(6): 725. CrossRef - Study on prevalence and factors influencing patient’s adherence to anti-diabetic medications in Urban Pondicherry
P. Stalin, Zile Singh, Anil J. Purty, Yogesh Sharma, Sherin Billy Abraham
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2015; 35(S2): 128. CrossRef - Adherence to anti diabetic medication among patients with diabetes in eastern Uganda; a cross sectional study
James Bagonza, Elizeus Rutebemberwa, William Bazeyo
BMC Health Services Research.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of social support on the relationship of depressive symptoms to medication adherence and self‐care activities in adults with type 2 diabetes
Chun‐Ja Kim, Elizabeth A. Schlenk, Dae Jung Kim, Moonsun Kim, Judith A. Erlen, Se‐Eun Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2015; 71(9): 2164. CrossRef - Adesão ao tratamento do diabetes mellitus e variáveis sociodemográficas, clinicas e de controle metabólico
Clarissa Cordeiro Alves Arrelias, Heloisa Turcatto Gimenes Faria, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira, Manoel Antônio dos Santos, Maria Lucia Zanetti
Acta Paulista de Enfermagem.2015; 28(4): 315. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Short Term Mobile Phone Text Reminders in Improving Compliance among Hypertensive Patients
Jung Ah Lee, Woo Sang Kim, Moon Jung Bae, Young-Sik Kim, Han Jin Oh, Sang Yeoup Lee, Chul-Min Kim, Dong Hyeok Shin, Seong-Ho Han, Kyung-Hwan Cho
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2014; 14(1): 1. CrossRef - Role of depressive symptoms and self‐efficacy of medication adherence in Korean patients after successful percutaneous coronary intervention
Youn‐Jung Son, Sun‐Hee Kim, Jin‐Hee Park
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2014; 20(6): 564. CrossRef - Non-adherence and Associated Factors among Type 2 Diabetic Patients at Jimma University Specialized Hospital, Southwest Ethiopia
Gebrehiwot Teklay, Jemal Hussien, Dawit Tesfaye
Journal of Medical Sciences.2013; 13(7): 578. CrossRef - Conocimientos, percepciones y actitudes que intervienen en la adherencia al tratamiento en pacientes ancianos polimedicados desde una perspectiva cualitativa
E. Crespillo-García, F. Rivas-Ruiz, E. Contreras Fernández, P. Castellano Muñoz, G. Suárez Alemán, E. Pérez-Trueba
Revista de Calidad Asistencial.2013; 28(1): 56. CrossRef - Positive Psychological Characteristics in Diabetes: A Review
Christopher M. Celano, Eleanor E. Beale, Shannon V. Moore, Deborah J. Wexler, Jeff C. Huffman
Current Diabetes Reports.2013; 13(6): 917. CrossRef - The Effect of a Clinic Based Incentive Program on Medication Adherence among Patients with Hypertension or Diabetes Mellitus in Incheon
Won Cheong, Jun Yim, Dae-Kyu Oh, Jeong-Soo Im, Kwang Pil Ko, Ie Byung Park
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(4): 427. CrossRef - Difficulty adhering to antidiabetic treatment: Factors associated with persistence and compliance
L. Guénette, J. Moisan, M.-C. Breton, C. Sirois, J.-P. Grégoire
Diabetes & Metabolism.2013; 39(3): 250. CrossRef - Impact of Cognitive Function and Self-efficacy on Medication Adherence of Elderly Patients with Chronic Disease
Kyung-Hee Ryu, Youn-Jung Son
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2013; 15(3): 107. CrossRef - Prevalence and correlates of self-reported medication non-adherence among older adults with coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus, and/or hypertension
Zachary A. Marcum, Yan Zheng, Subashan Perera, Elsa Strotmeyer, Anne B. Newman, Eleanor M. Simonsick, Ronald I. Shorr, Douglas C. Bauer, Julie M. Donohue, Joseph T. Hanlon
Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy.2013; 9(6): 817. CrossRef - Medication Adherence in Type 2 Diabetes: The ENTRED Study 2007, a French Population-Based Study
Michel Tiv, Jean-François Viel, Frédéric Mauny, Eveline Eschwège, Alain Weill, Cécile Fournier, Anne Fagot-Campagna, Alfred Penfornis, German Malaga
PLoS ONE.2012; 7(3): e32412. CrossRef - Construction of Explanatory Model for Medication Adherence in Older People with Chronic disease
Shin Hong Min, Jong Im Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(4): 463. CrossRef - The Effects of Tele-care Case Management Services for Medical Aid Beneficiaries
Yang Heui Ahn, Eui Sook Kim, Il Sun Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(3): 351. CrossRef
- Medication use problems among older adults at a primary care: A narrative of literature review
- Self-Reported Goals in Aged Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Hae Kyung Jin, Hyun Kyung Chung
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(5):439-447. Published online October 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.5.439
- 2,022 View
- 23 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) is a growing health problem of the elderly population. Diabetes education based on effective patient-provider communication plays a major role in treatment of type 2 DM. In this study, as an effort for making better communication, we examined how older patients with type 2 DM report their healthcare goals, what factors influencing their goals and control their self-care behaviors. METHODS: Subjects were thirty three patients with type 2 DM aged 65 and older. An interviewer conducted one-on-one interviews using open questions about 5 categories: concept of "health," purpose of DM management, causes of DM, practical aspects of DM management, and decision making related to DM management. Interviews were audiotaped, transcribed and two investigators independently reviewed. RESULTS: The majority of our sample (79%) expressed their management goals in a socio-functional language, rather than medical issues. They defined "Healthy" as a status of keeping daily life without any symptoms. Many subjects has not altered their diet habits (33%) and making no efforts to exercise (64%) due to physical and psychological limitations though almost all (91%) older patients recognized the importance of diet control and exercise. CONCLUSION: When introduce the goal of DM management, it would be better to use socio-functional terms in diabetes education of elderly patients with type 2 DM. To improve the self-care behaviors, it is essential to make efforts not only to give knowledge but also to find their physical and psychological limitations related to poor performances. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Van evidencebased medicine naar shared decision-making bij diabetes mellitus
L. D'Hoore, C. Verroken, I. Matthys, W. Van Biesen
Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient-important outcomes to inform shared decision making and goal setting for diabetes treatment
Kristin L. Rising, Alexzandra T. Gentsch, Geoffrey Mills, Marianna LaNoue, Amanda M.B. Doty, Amy Cunningham, Brendan G. Carr, Judd E. Hollander
Patient Education and Counseling.2021; 104(10): 2592. CrossRef - Efficacy of Chronic Disease Self-management Program in Older Korean Adults with Low and High Health Literacy
Su Hyun Kim, Chang Ho Youn
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(1): 42. CrossRef - Antioxidant and Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity of Strychnos nux-vomica Extracts
Jeung-Min Lee, Jae-Hee Park, Hae-Ryong Park, Eun-Ju Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2010; 39(9): 1243. CrossRef
- Van evidencebased medicine naar shared decision-making bij diabetes mellitus
- Effects of 'Ubiquitous Healthcare' on the Ability of Self-Management in Elderly Diabetic Patients.
- Sung Hoon Yu, Sun Hee Kim, So Yeon Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Yoon Seok Chang, Hak Jong Lee, Young Joo Park, Hak Chul Jang
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(1):58-64. Published online February 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.58
- 2,263 View
- 20 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The need for a new healthcare system is growing due to the paradigm shift from health supervision to health maintenance. Previously, we performed a pilot study that examined the effectiveness of a ubiquitous healthcare (U-healthcare) diabetes management program which consists of self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and mobile phone services for elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this study, we investigated the effect of a diabetes management program using U-healthcare based on the self-care skills of elderly patients with diabetes mellitus. METHODS: From July to October 2005, 17 patients were recruited and provided with a blood glucometer with the ZigBee module and a mobile phone. In addition, the patients' understanding of diabetes self-care skills was examined at the beginning and end of the study. At the end of the study, we determined the level of patient satisfaction regarding U-healthcare services. RESULTS: The patients' test scores on their understanding of diabetes mellitus improved from 57.2 +/- 20.7 to 72.7 +/- 13.4%. Specifically, patient knowledge of the basic principles for a proper diabetic diet (52.9% vs. 82.4%, P = 0.046), foods that influence blood sugar level (41.2% vs. 76.5%, P = 0.007) and the influence of beverage choice (41.2% vs. 64.7%, P = 0.007), all increased. In addition, a significant increase in knowledge of living standards regarding diabetes mellitus was observed (64.7% vs. 88.2%, P = 0.0032). CONCLUSION: We conclude that the U-healthcare incorporating SMBG could be promising, as it improves self-management skills of diabetes mellitus patients, as well as their understanding of the disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-management of Chronic Conditions Using mHealth Interventions in Korea: A Systematic Review
Jae Yoon Yi, Yujin Kim, Yoon-Min Cho, Hongsoo Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2018; 24(3): 187. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the Smart Care Service for Diabetes Management
Young-Soon Chung, Yongsuk Kim, Chang Hee Lee
Healthcare Informatics Research.2014; 20(4): 288. CrossRef - Ubiquitous Healthcare Service Has the Persistent Benefit on Glycemic Control and Body Weight in Older Adults With Diabetes
Seon Mee Kang, Min Joo Kim, Hwa Young Ahn, Ji Won Yoon, Min Kyong Moon, Hye Seung Jung, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak C. Jang
Diabetes Care.2012; 35(3): e19. CrossRef - Improved Glycemic Control Without Hypoglycemia in Elderly Diabetic Patients Using the Ubiquitous Healthcare Service, a New Medical Information System
Soo Lim, Seon Mee Kang, Hayley Shin, Hak Jong Lee, Ji Won Yoon, Sung Hoon Yu, So-Youn Kim, Soo Young Yoo, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Jun Oh Ryu, Hak C. Jang
Diabetes Care.2011; 34(2): 308. CrossRef - A Survey on Ubiquitous Healthcare Service Demand among Diabetic Patients
Soo Lim, So-Youn Kim, Jung Im Kim, Min Kyung Kwon, Sei Jin Min, Soo Young Yoo, Seon Mee Kang, Hong Il Kim, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Jun Oh Ryu, Hayley Shin, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(1): 50. CrossRef
- Self-management of Chronic Conditions Using mHealth Interventions in Korea: A Systematic Review

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





