
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse > Previous issues
Reviews
- Basic Research
- Regulation of Cellular Senescence in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: From Mechanisms to Clinical Applications
- Kanako Iwasaki, Cristian Abarca, Cristina Aguayo-Mazzucato
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):441-453. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0416

- 4,685 View
- 417 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Cellular senescence is accelerated by hyperglycemia through multiple pathways. Therefore, senescence is an important cellular mechanism to consider in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and an additional therapeutic target. The use of drugs that remove senescent cells has led to improvements in blood glucose levels and diabetic complications in animal studies. Although the removal of senescent cells is a promising approach for the treatment of T2DM, two main challenges limit its clinical application: the molecular basis of cellular senescence in each organ is yet to be understood, and the specific effect of removing senescent cells in each organ has to be determined. This review aims to discuss future applications of targeting senescence as a therapeutic option in T2DM and elucidate the characteristics of cellular senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotype in the tissues important for regulating glucose levels: pancreas, liver, adipocytes, and skeletal muscle.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Amide Alkaloids as Privileged Sources of Senomodulators for Therapeutic Purposes in Age-Related Diseases
Mazzarine Dotou, Aurore L’honoré, Roba Moumné, Chahrazade El Amri
Journal of Natural Products.2024; 87(3): 617. CrossRef - Study on the Pathogenesis of Cell Senescence in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver
丽媛 黄
Medical Diagnosis.2024; 14(01): 76. CrossRef - Senescent adipocytes and type 2 diabetes – current knowledge and perspective concepts
Weronika Kruczkowska, Julia Gałęziewska, Mateusz Kciuk, Adrianna Gielecińska, Elżbieta Płuciennik, Zbigniew Pasieka, Lin-Yong Zhao, Yi-Jin Yu, Damian Kołat, Żaneta Kałuzińska-Kołat
Biomolecular Concepts.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Long-Term Passage on Porcine SMCs’ Function and the Improvement of TGF-β1 on Porcine SMCs’ Secretory Function in Late Passage
Yan-Yan Zheng, Ze-Nan Hu, Zheng Liu, Yi-Chen Jiang, Ren-Peng Guo, Shi-Jie Ding, Guang-Hong Zhou
Foods.2023; 12(14): 2682. CrossRef - Exploring the Relationship between Cellular Senescence Markers and Aging-Related Diseases
怡 罗
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(08): 12298. CrossRef
- Amide Alkaloids as Privileged Sources of Senomodulators for Therapeutic Purposes in Age-Related Diseases
- Basic Research
- Rediscovering Primary Cilia in Pancreatic Islets
- Eun Young Lee, Jing W. Hughes
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):454-469. Published online April 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0442
- 2,588 View
- 240 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
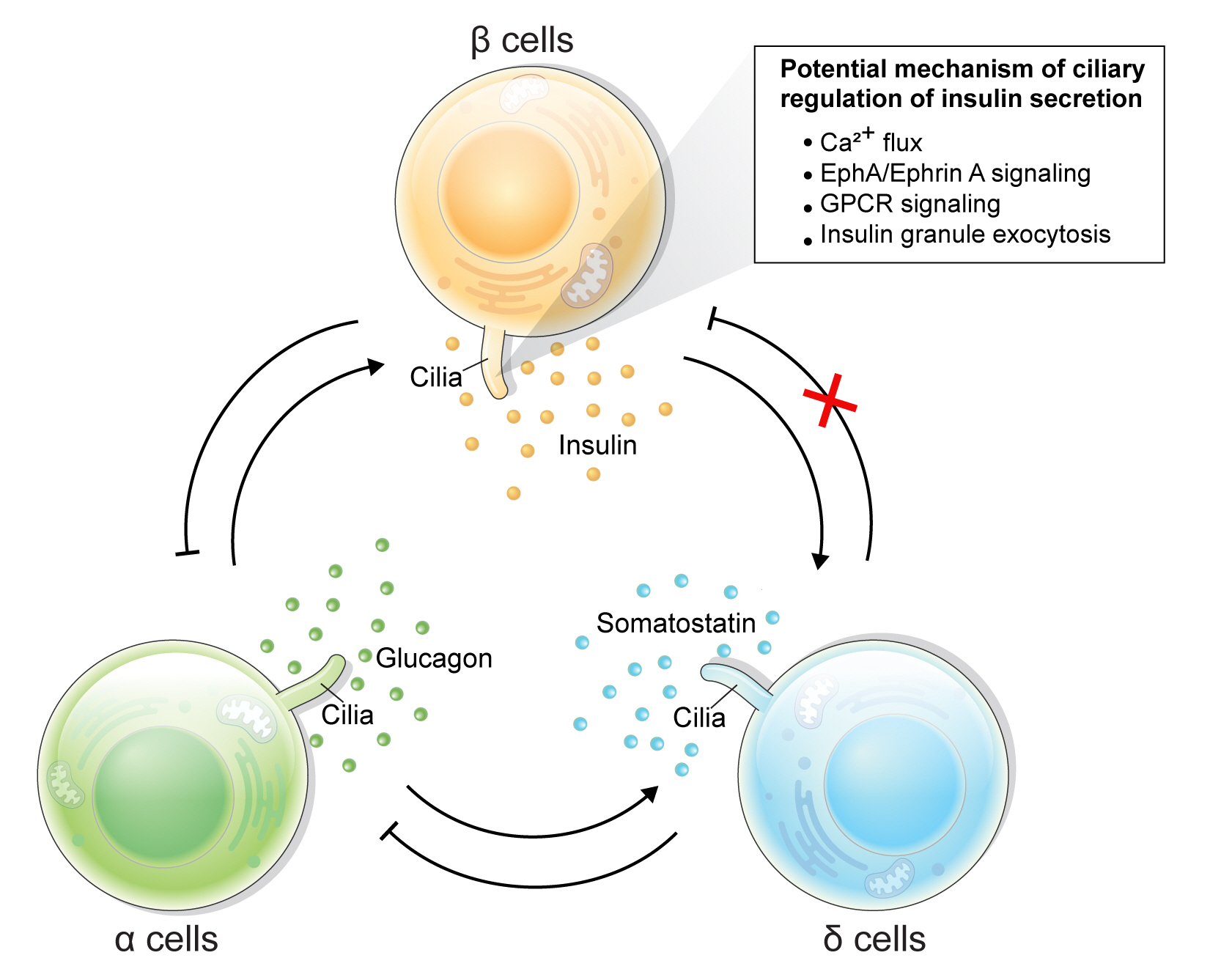
ePub - Primary cilia are microtubule-based sensory and signaling organelles on the surfaces of most eukaryotic cells. Despite their early description by microscopy studies, islet cilia had not been examined in the functional context until recent decades. In pancreatic islets as in other tissues, primary cilia facilitate crucial developmental and signaling pathways in response to extracellular stimuli. Many human developmental and genetic disorders are associated with ciliary dysfunction, some manifesting as obesity and diabetes. Understanding the basis for metabolic diseases in human ciliopathies has been aided by close examination of cilia action in pancreatic islets at cellular and molecular levels. In this article, we review the evidence for ciliary expression on islet cells, known roles of cilia in pancreas development and islet hormone secretion, and summarize metabolic manifestations of human ciliopathy syndromes. We discuss emerging data on primary cilia regulation of islet cell signaling and the structural basis of cilia-mediated cell crosstalk, and offer our interpretation on the role of cilia in glucose homeostasis and human diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beta cell primary cilia mediate somatostatin responsiveness via SSTR3
Samantha E. Adamson, Zipeng A. Li, Jing W. Hughes
Islets.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Beta cell primary cilia mediate somatostatin responsiveness via SSTR3
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- The Role of Echocardiography in Evaluating Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Sun Hwa Lee, Jae-Hyeong Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):470-483. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0036

- 2,721 View
- 293 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Patients with diabetes mellitus are highly susceptible to cardiovascular complications, which are directly correlated with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. In addition to coronary artery disease, there is growing awareness of the risk and prevalence of heart failure (HF) in patients with diabetes. Echocardiography is an essential diagnostic modality commonly performed in patients with symptoms suggestive of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), such as dyspnea or chest pain, to establish or rule out the cause of symptoms. Conventional echocardiographic parameters, such as left ventricular ejection fraction, are helpful not only for diagnosing CVD but also for determining severity, treatment strategy, prognosis, and response to treatment. Echocardiographic myocardial strain, a novel echocardiographic technique, enables the detection of early changes in ventricular dysfunction before HF symptoms develop. This article aims to review the role of echocardiography in evaluating CVD in patients with diabetes mellitus and how to use it in patients with suspected cardiac diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased Blood Pressure Variability Over a 16-Year Period Is Associated With Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in a Population-Based Cohort
Jae-Hyeong Park, Soon-Ki Ahn, Goo-Yeong Cho, Ki-Chul Sung, Seung Ku Lee, Seong Hwan Kim, Chol Shin
American Journal of Hypertension.2024; 37(3): 168. CrossRef - Biomarkers and subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes without clinical manifestations of cardiovascular diseases
T. G. Utina, D. U. Akasheva, D. V. Korsunsky, O. N. Dzhioeva, O. M. Drapkina
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2024; 23(1): 3914. CrossRef - Cardiovascular risk assessment in inflammatory bowel disease with coronary calcium score
Waqar Arif Rasool Chaudhry, Muhammad Ashfaq, Parvinder Kaur, Mahendra Kumar, Maria Faraz, Jahanzeb Malik, Amin Mehmoodi
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2024; 86(3): 1496. CrossRef
- Increased Blood Pressure Variability Over a 16-Year Period Is Associated With Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in a Population-Based Cohort
Editorial
- The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
- Dong-Hwa Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):484-486. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0165
- 1,378 View
- 106 Download
Original Articles
- Basic Research
- Pharmacologic Activation of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme II Alleviates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy in db/db Mice by Reducing Reactive Oxidative Stress
- Donghyun Kim, Wooju Jeong, Yumin Kim, Jibeom Lee, Sung Woo Cho, Chang-Myung Oh, Raekil Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):487-499. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0125
- 2,255 View
- 149 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
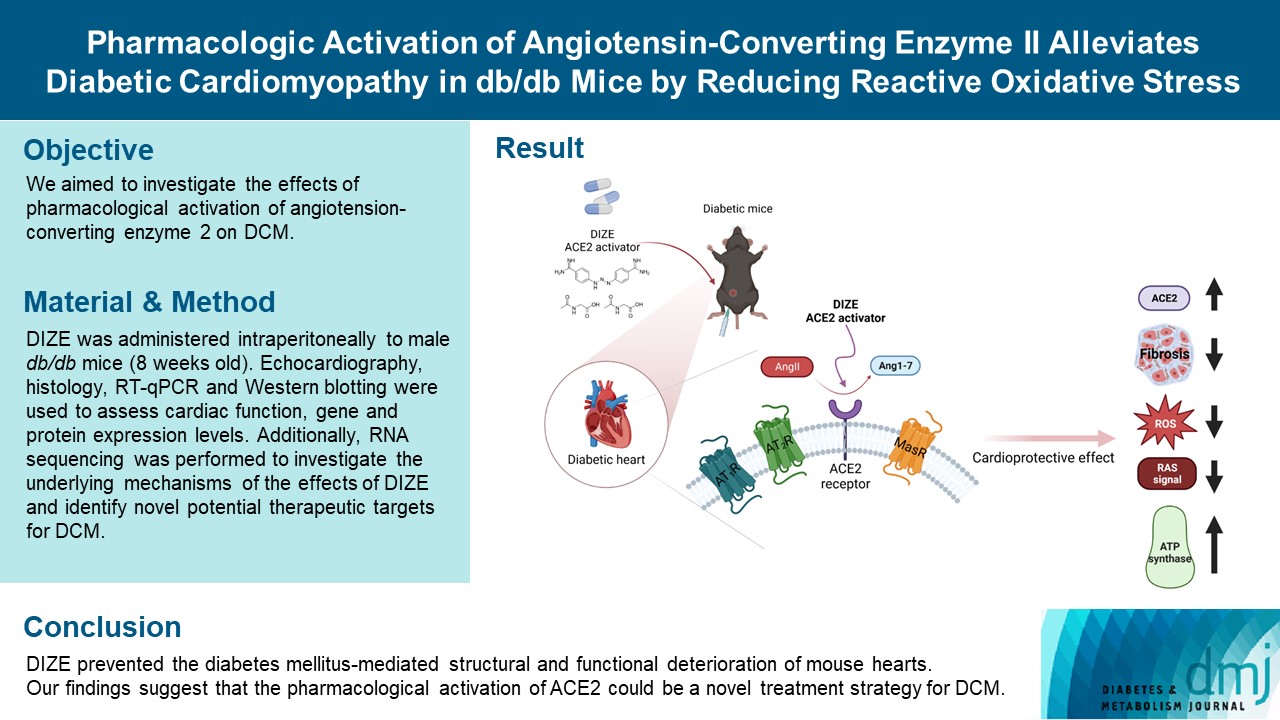
ePub - Background
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common chronic diseases worldwide, and cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in diabetic patients. Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a phenomenon characterized by a deterioration in cardiac function and structure, independent of vascular complications. Among many possible causes, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and angiotensin II have been proposed as major drivers of DCM development. In the current study, we aimed to investigate the effects of pharmacological activation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) on DCM.
Methods
The ACE2 activator diminazene aceturate (DIZE) was administered intraperitoneally to male db/db mice (8 weeks old) for 8 weeks. Transthoracic echocardiography was used to assess cardiac mass and function in mice. Cardiac structure and fibrotic changes were examined using histology and immunohistochemistry. Gene and protein expression levels were examined using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting, respectively. Additionally, RNA sequencing was performed to investigate the underlying mechanisms of the effects of DIZE and identify novel potential therapeutic targets for DCM.
Results
Echocardiography revealed that in DCM, the administration of DIZE significantly improved cardiac function as well as reduced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Transcriptome analysis revealed that DIZE treatment suppresses oxidative stress and several pathways related to cardiac hypertrophy.
Conclusion
DIZE prevented the diabetes mellitus-mediated structural and functional deterioration of mouse hearts. Our findings suggest that the pharmacological activation of ACE2 could be a novel treatment strategy for DCM.
- Basic Research
- Beneficial Effects of a Curcumin Derivative and Transforming Growth Factor-β Receptor I Inhibitor Combination on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Kyung Bong Ha, Eun Soo Lee, Na Won Park, Su Ho Jo, Soyeon Shim, Dae-Kee Kim, Chan Mug Ahn, Choon Hee Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):500-513. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0110
- 2,168 View
- 144 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
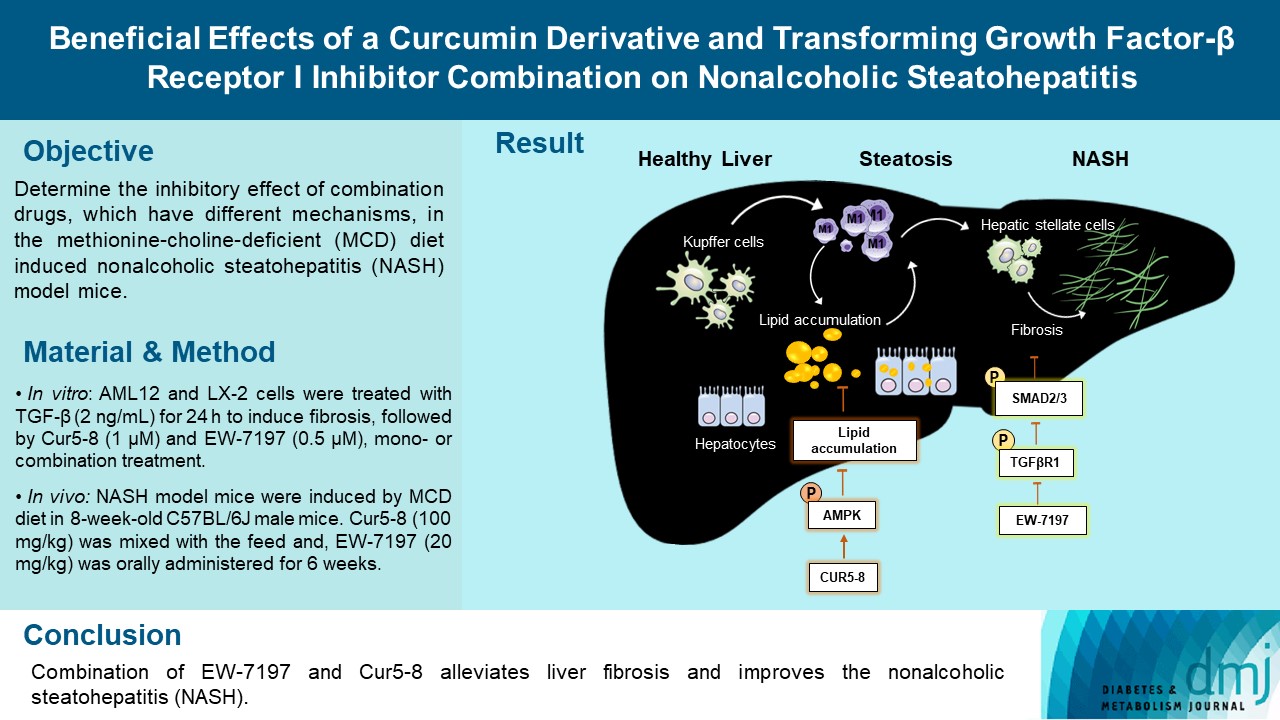
Curcumin 2005-8 (Cur5-8), a derivative of curcumin, improves fatty liver disease via AMP-activated protein kinase activation and autophagy regulation. EW-7197 (vactosertib) is a small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) receptor I and may scavenge reactive oxygen species and ameliorate fibrosis through the SMAD2/3 canonical pathway. This study aimed to determine whether co-administering these two drugs having different mechanisms is beneficial.
Methods
Hepatocellular fibrosis was induced in mouse hepatocytes (alpha mouse liver 12 [AML12]) and human hepatic stellate cells (LX-2) using TGF-β (2 ng/mL). The cells were then treated with Cur5-8 (1 μM), EW-7197 (0.5 μM), or both. In animal experiments were also conducted during which, methionine-choline deficient diet, Cur5-8 (100 mg/kg), and EW-7197 (20 mg/kg) were administered orally to 8-week-old C57BL/6J mice for 6 weeks.
Results
TGF-β-induced cell morphological changes were improved by EW-7197, and lipid accumulation was restored on the administration of EW-7197 in combination with Cur5-8. In a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-induced mouse model, 6 weeks of EW-7197 and Cur5-8 co-administration alleviated liver fibrosis and improved the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score.
Conclusion
Co-administering Cur5-8 and EW-7197 to NASH-induced mice and fibrotic hepatocytes reduced liver fibrosis and steatohepatitis while maintaining the advantages of both drugs. This is the first study to show the effect of the drug combination against NASH and NAFLD. Similar effects in other animal models will confirm its potential as a new therapeutic agent.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- The Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus according to Changes in Obesity Status in Late Middle-Aged Adults: A Nationwide Cohort Study of Korea
- Joon Ho Moon, Yeonhoon Jang, Tae Jung Oh, Se Young Jung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):514-522. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0159
- 2,058 View
- 133 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
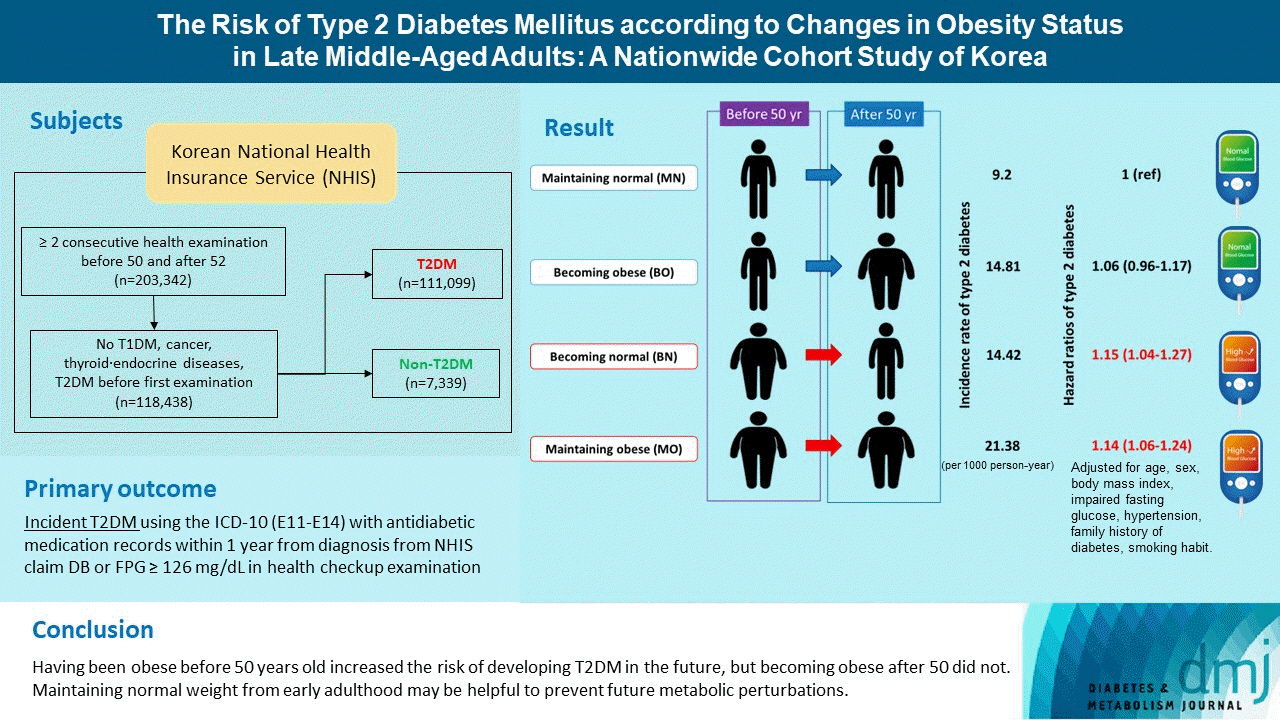
Although obesity is a well-known risk factor of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), there is scant data on discriminating the contribution of previous obesity and recent weight gain on developing T2DM.
Methods
We analyzed the Korean National Health Insurance Service-Health Screening Cohort data from 2002 to 2015 where Korean residents underwent biennial health checkups. Participants were classified into four groups according to their obesity status (body mass index [BMI] ≥25 kg/m2) before and after turning 50 years old: maintaining normal (MN), becoming obese (BO), becoming normal (BN), and maintaining obese (MO). Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to estimate the risk of T2DM factoring in the covariates age, sex, BMI, presence of impaired fasting glucose or hypertension, family history of diabetes, and smoking status.
Results
A total of 118,438 participants (mean age, 52.5±1.1 years; men, 45.2%) were prospectively evaluated for incident T2DM. A total of 7,339 (6.2%) participants were diagnosed with T2DM during a follow-up period of 4.8±2.6 years. Incidence rates of T2DM per 1,000 person-year were 9.20 in MN, 14.81 in BO, 14.42 in BN, 21.38 in MO. After factoring in covariates, participants in the groups BN (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.15; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04 to 1.27) and MO (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.06 to 1.24) were at increased risk of developing T2DM compared to MN, whereas BO (hazard ratio, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.96 to 1.17) was not.
Conclusion
Having been obese before 50 years old increased the risk of developing T2DM in the future, but becoming obese after 50 did not. Therefore, it is important to maintain normal weight from early adulthood to prevent future metabolic perturbations.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
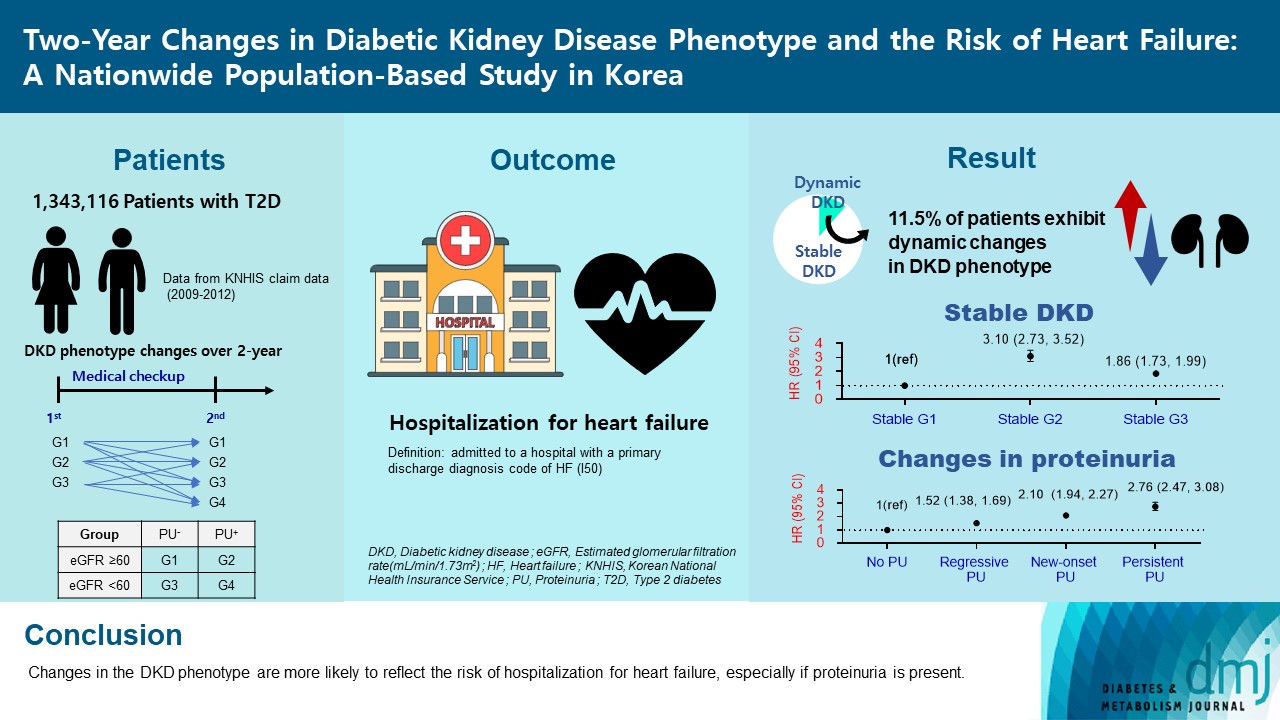
- Two-Year Changes in Diabetic Kidney Disease Phenotype and the Risk of Heart Failure: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in Korea
- Seung Eun Lee, Juhwan Yoo, Han Seok Choi, Kyungdo Han, Kyoung-Ah Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):523-534. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0096
- 1,712 View
- 100 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a risk factor for hospitalization for heart failure (HHF). DKD could be classified into four phenotypes by estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, normal vs. low) and proteinuria (PU, negative vs. positive). Also, the phenotype often changes dynamically. This study examined HHF risk according to the DKD phenotype changes across 2-year assessments.
Methods
The study included 1,343,116 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database after excluding a very high-risk phenotype (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) at baseline, who underwent two cycles of medical checkups between 2009 and 2014. From the baseline and 2-year eGFR and PU results, participants were divided into 10 DKD phenotypic change categories.
Results
During an average of 6.5 years of follow-up, 7,874 subjects developed HHF. The cumulative incidence of HHF from index date was highest in the eGFRlowPU– phenotype, followed by eGFRnorPU+ and eGFRnorPU–. Changes in DKD phenotype differently affect HHF risk. When the persistent eGFRnorPU– category was the reference, hazard ratios for HHF were 3.10 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.73 to 3.52) in persistent eGFRnorPU+ and 1.86 (95% CI, 1.73 to 1.99) in persistent eGFRlowPU–. Among altered phenotypes, the category converted to eGFRlowPU+ showed the highest risk. In the normal eGFR category at the second examination, those who converted from PU– to PU+ showed a higher risk of HHF than those who converted from PU+ to PU–.
Conclusion
Changes in DKD phenotype, particularly with the presence of PU, are more likely to reflect the risk of HHF, compared with DKD phenotype based on a single time point in patients with T2DM.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
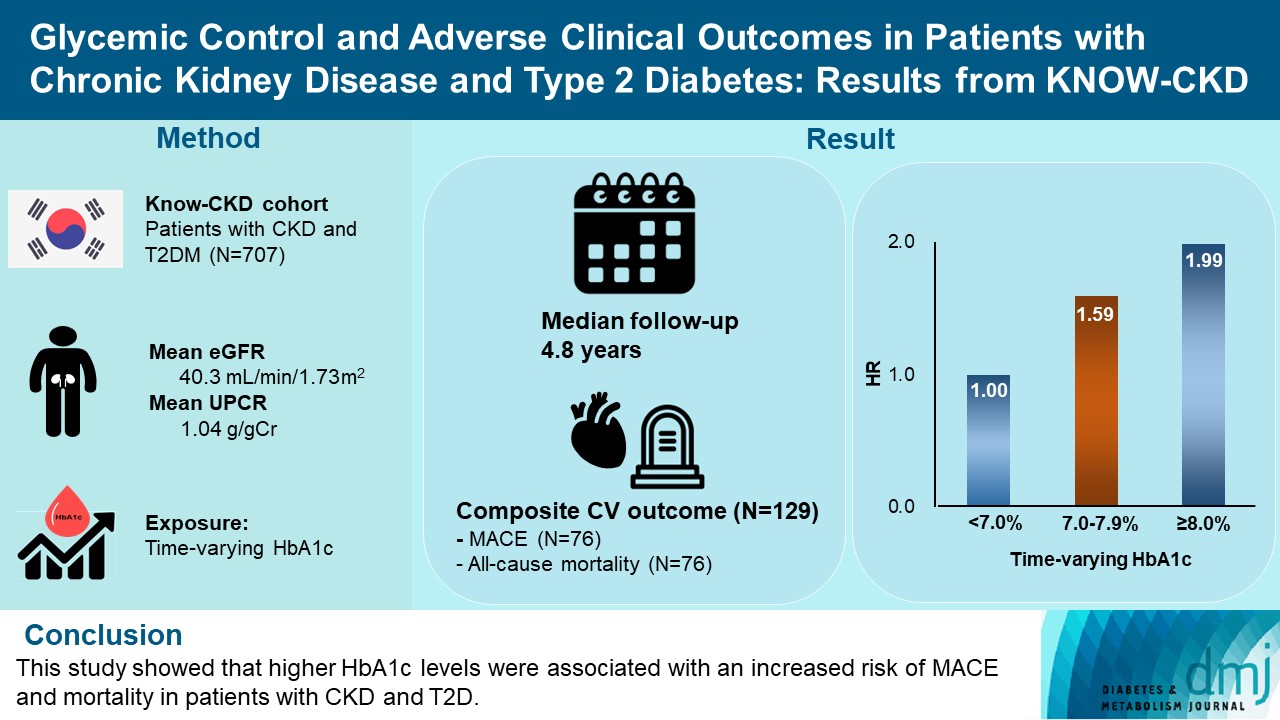
- Glycemic Control and Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from KNOW-CKD
- Ga Young Heo, Hee Byung Koh, Hyung Woo Kim, Jung Tak Park, Tae-Hyun Yoo, Shin-Wook Kang, Jayoun Kim, Soo Wan Kim, Yeong Hoon Kim, Su Ah Sung, Kook-Hwan Oh, Seung Hyeok Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):535-546. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0112
- 2,650 View
- 162 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The optimal level of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) to prevent adverse clinical outcomes is unknown in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
We analyzed 707 patients with CKD G1-G5 without kidney replacement therapy and T2DM from the KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcome in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease (KNOW-CKD), a nationwide prospective cohort study. The main predictor was time-varying HbA1c level at each visit. The primary outcome was a composite of development of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) or all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included the individual endpoint of MACEs, all-cause mortality, and CKD progression. CKD progression was defined as a ≥50% decline in the estimated glomerular filtration rate from baseline or the onset of end-stage kidney disease.
Results
During a median follow-up of 4.8 years, the primary outcome occurred in 129 (18.2%) patients. In time-varying Cox model, the adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) for the primary outcome were 1.59 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 2.49) and 1.99 (95% CI, 1.24 to 3.19) for HbA1c levels of 7.0%–7.9% and ≥8.0%, respectively, compared with <7.0%. Additional analysis of baseline HbA1c levels yielded a similar graded association. In secondary outcome analyses, the aHRs for the corresponding HbA1c categories were 2.17 (95% CI, 1.20 to 3.95) and 2.26 (95% CI, 1.17 to 4.37) for MACE, and 1.36 (95% CI, 0.68 to 2.72) and 2.08 (95% CI, 1.06 to 4.05) for all-cause mortality. However, the risk of CKD progression did not differ between the three groups.
Conclusion
This study showed that higher HbA1c levels were associated with an increased risk of MACE and mortality in patients with CKD and T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
Dong-Hwa Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 484. CrossRef - Prevalence and predictors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients worldwide, systematic review and meta-analysis
Eneyew Talie Fenta, Habitu Birhan Eshetu, Natnael Kebede, Eyob Ketema Bogale, Amare Zewdie, Tadele Derbew Kassie, Tadele Fentabil Anagaw, Elyas Melaku Mazengia, Sintayehu Shiferaw Gelaw
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Bayesian network meta-analysis
Miao Zhu, Ruifang Guan, Guo Ma
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
- Lifestyle
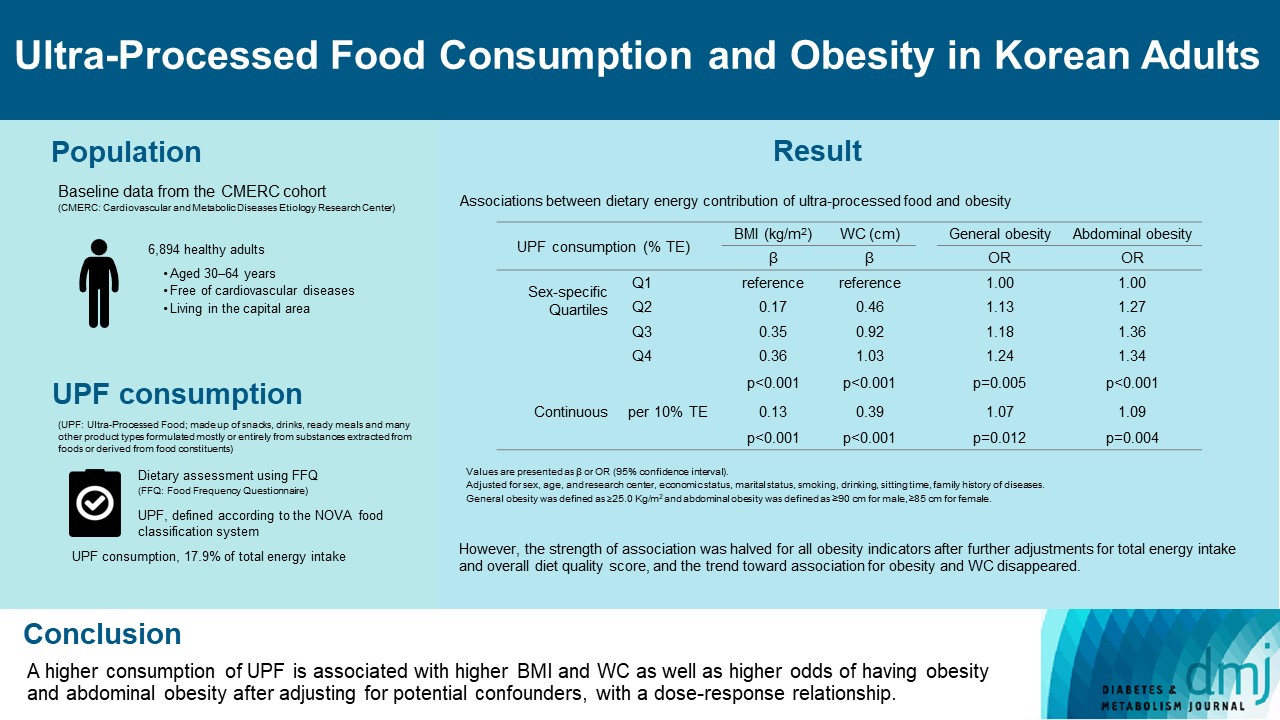
- Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Obesity in Korean Adults
- Jee-Seon Shim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):547-558. Published online April 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0026
- 2,850 View
- 139 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the association between consumption of ultra-processed foods (UPF) and obesity in Korean adults.
Methods
We included the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center cohort study baseline data of adults aged 30 to 64 years who completed a validated food frequency questionnaire. UPF was defined using the NOVA food classification. Multivariable linear and logistic regression analyses were performed to assess the association of dietary energy contribution of UPF with obesity indicators (body mass index [BMI], obesity, waist circumference [WC], and abdominal obesity).
Results
Consumption of UPF accounted for 17.9% of total energy intake and obesity and abdominal obesity prevalence was 35.4% and 30.2%, respectively. Compared with those in the lowest quartile of UPF consumption, adults in the highest quartile had greater BMI (β=0.36; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.15 to 0.56), WC (β=1.03; 95% CI, 0.46 to 1.60), higher odds of having obesity (odds ratio [OR], 1.24; 95% CI, 1.07 to 1.45), and abdominal obesity (OR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.14 to 1.57), after adjusting for sociodemographic characteristics, health-related behaviors, and family history of diseases. Dose-response associations between UPF consumption and obesity indicators were consistently found (all P trend <0.01). However, the strength of association was halved for all obesity indicators after further adjustments for total energy intake and overall diet quality score, and the trend toward association for obesity and WC disappeared.
Conclusion
Our finding supports the evidence that consumption of UPF is positively associated with obesity among Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultra-processed food consumption and increased risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: A cross-sectional analysis of the KNHANES 2016–2020
Hansol Park, Youngmi Lee, Jinah Hwang, Yujin Lee
Nutrition.2024; 122: 112374. CrossRef - Diet quality partially mediates the association between ultraprocessed food consumption and adiposity indicators
Jee‐Seon Shim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim
Obesity.2023; 31(9): 2430. CrossRef - Development of a Semi-Quantitative Food-Frequency Questionnaire for Korean Adults with Obesity
Jina Chung, Seoeun Ahn, Hyojee Joung, Sangah Shin
Nutrients.2023; 15(22): 4848. CrossRef
- Ultra-processed food consumption and increased risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: A cross-sectional analysis of the KNHANES 2016–2020
- Others
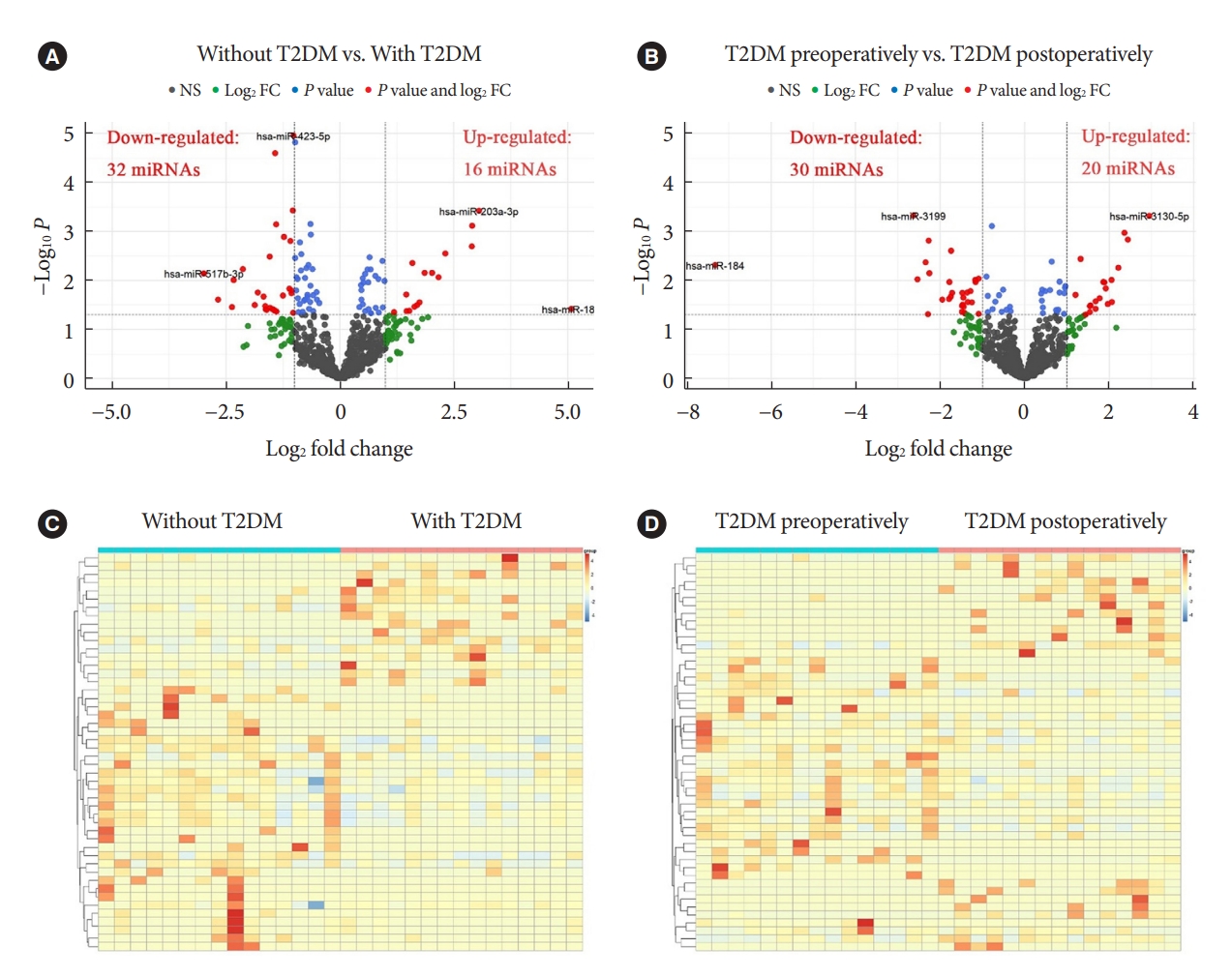
- Change Profiles and Functional Targets of MicroRNAs in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Obesity
- Guanhua Lu, Huanhuan Gao, Zhiyong Dong, Shuwen Jiang, Ruixiang Hu, Cunchuan Wang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):559-570. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0226
- 1,696 View
- 76 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) exert an essential contribution to obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study aimed to investigate the differences of miRNAs in the presence and absence of T2DM in patients with obesity, as well as before and after bariatric surgery in T2DM patients with obesity. Characterization of the common changes in both was further analyzed.
Methods
We enrolled 15 patients with obesity but without T2DM and 15 patients with both obesity and T2DM. Their preoperative clinical data and serum samples were collected, as well as 1 month after bariatric surgery. The serum samples were analyzed by miRNA sequencing, and the miRNAs profiles and target genes characteristics were compared.
Results
Patients with T2DM had 16 up-regulated and 32 down-regulated miRNAs compared to patients without T2DM. Improvement in metabolic metrics after bariatric surgery of T2DM patients with obesity was correlated with changes in miRNAs, as evidenced by the upregulation of 20 miRNAs and the downregulation of 30 miRNAs. Analysis of the two miRNAs profiles identified seven intersecting miRNAs that showed opposite changes. The target genes of these seven miRNAs were substantially enriched in terms or pathways associated with T2DM.
Conclusion
We determined the expression profiles of miRNAs in the obese population, with and without diabetes, before and after bariatric surgery. The miRNAs that intersected in the two comparisons were discovered. Both the miRNAs discovered and their target genes were closely associated with T2DM, demonstrating that they might be potential targets for the regulation of T2DM.
Letter
- Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy between Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:394-404)
- Jihee Ko, Sun Joon Moon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):571-572. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0164
- 977 View
- 65 Download
Response
- Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy between Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:394-404)
- Tzu-Yi Lin, Eugene Yu-Chuan Kang, Shih-Chieh Shao, Edward Chia-Cheng Lai, Yih-Shiou Hwang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):573-574. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0188
- 1,065 View
- 58 Download

 KDA
KDA


 First
First Prev
Prev





