- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 37(4); 2013 > Article
-
Original ArticleObesity and Metabolic Syndrome The Role of Skeletal Muscle in Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2013;37(4):278-285.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.4.278
Published online: August 14, 2013
Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Hyoung Woo Lee. Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine1, 70 Hyeonchung-ro, Nam-gu, Daegu 705-717, Korea. helee@ynu.ac.kr
- *Jun Sung Moon and Ji Sung Yoon contributed equally to this study as first authors.
Copyright © 2013 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is closely correlated with abnormal accumulation of visceral fat, but the role of skeletal muscle remains unclear. The aim of this study was to elucidate the role of skeletal muscle in development of NAFLD.
-
Methods
- Among 11,116 subjects (6,242 males), we examined the effects of skeletal muscle mass and visceral fat area (VFA, by bioelectric impedance analysis) on NAFLD using by the fatty liver index (FLI).
-
Results
- Of the total subjects (9,565 total, 5,293 males) included, 1,848 were classified as having NALFD (FLI ≥60). Body mass index, lipid profile, fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, prevalence of type 2 diabetes (DM), hypertension (HTN), and metabolic syndrome were higher in males than females, but FLI showed no significant difference. The low FLI group showed the lowest VFA and highest skeletal muscle mass of all the groups. Skeletal muscle to visceral fat ratio (SVR) and skeletal muscle index had inverse correlations with FLI, when adjusted for age and gender. In multivariate regression analysis, SVR was negatively associated with FLI. Among SVR quartiles, the highest quartile showed very low risk of NAFLD when adjusted for age, gender, lipid profile, DM, HTN, and high sensitivity C-reactive protein from the lowest quartiles (odds ratio, 0.037; 95% confidence interval, 0.029 to 0.049).
-
Conclusion
- Skeletal muscle mass was inversely associated with visceral fat area, and higher skeletal muscle mass may have a beneficial effect in preventing NAFLD. These results suggest that further studies are needed to ameliorate or slow the progression of sarcopenia.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), characterized by an abnormal accumulation of fat in hepatocytes, is recognized as the most prevalent chronic liver disease in the general population [1], and is increasing rapidly in both Western countries and Asian countries such as Korea [2]. NAFLD is well known to be share the common pathophysiological mechanism of insulin resistance with obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes [3]. Regarding insulin resistance, the association between NAFLD and visceral fat is well established [4,5]. Koda et al. [6] suggested that visceral fat, not subcutaneous fat, was the most important factor for the development of hepatic steatosis. In addition, many studies have reported that NAFLD could be a risk factor for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease [7]. Thus, it is considered to be not only a simple hepatic disease but also a hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome [8].
- The fatty liver index (FLI) is a simple parameter for the determination of fatty liver, which is easily obtained from body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), triglyceride (TG), and γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT) levels [9]. For high diagnostic accuracy in detecting fatty liver, these parameters were recently validated in large population studies [10,11]. Moreover, higher FLI scores are correlated with an elevated risk for diabetes [12], early carotid atherosclerosis [10], coronary artery disease [13], and all-cause mortality [11].
- Skeletal muscle plays an important role in insulin sensitivity as a primary tissue contributing to whole body insulin-mediated glucose uptake [14]. Several findings reported that low skeletal muscle mass is associated with obesity, metabolic syndrome, and dysglycemia [15-17], and the reverse was shown in large populations, with higher muscle mass associated with better insulin resistance and a lower risk of developing diabetes [15]. However, little is known about the relationships between visceral fat and the role of skeletal muscle as a risk factor in NAFLD. The aims of this study are: 1) to determine whether visceral fat is related to FLI; 2) to evaluate the relationship between visceral fat and skeletal muscle mass; and 3) to determine whether skeletal muscle affects the development of NAFLD diagnosed by FLI in Korean subjects.
INTRODUCTION
- Study population
- We reviewed medical records of 11,116 subjects (6,242 males, 4,874 females; mean age, 47.2±10.2 [males] and 46.7±10.9 [females] years) who underwent a health examination at the Yeungnam University Health Promotion Center, Daegu, South Korea between January 2009 and December 2011. We excluded 778 patients who had positive serologic viral hepatitis (hepatitis B surface antigen or anti-hepatitis C virus antibody) and 773 subjects with excessive alcohol consumption (≥20 g/day). After exclusion, there remained 9,565 subjects (5,293 males, 4,272 females). The criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes recommended by the American Diabetes Association [18] were: 1) hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) ≥6.5%; and 2) fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L). Adopting International Diabetes Federation (IDF) criteria, metabolic syndrome in South Korean adults was defined by central obesity (waist circumference ≥90 cm for men and ≥85 cm for women) plus two of the following four factors: serum TG ≥150 mg/dL, high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) ≤40 mg/dL for men and ≤50 mg/dL for women, systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥130 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥85 mm Hg, and FPG ≥100 mg/dL [19]. Participants who had antihypertensive medication or were newly diagnosed (SBP ≥140 mm Hg or DBP ≥90 mm Hg) were classified as hypertension group. All patients gave informed consent, and this in turn was approved by the local ethics committee. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Yeungnam University Hospital (YUH-12-0463-O91).
- Clinical and laboratory assays
- Blood samples were obtained from each individual after a 12-hour overnight fast. Measurement of FPG, bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), GGT, blood urea nitrogen, and creatinine used the hexokinase method (AU 5400 Autoanalyser; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Total cholesterol (TC) was measured using enzyme colorimetry (Kyowa Medex Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), TG was measured using the glycerol elimination method, and HDL-C and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) were measured using direct enzymatic assays (Kyowa Medex Co., Ltd.). HbA1c and microalbuminuria assays were performed using the HLC-723G7 high performance liquid chromatography system (Tosoh, Tokyo, Japan).
- Surrogate marker of fatty liver
- For determination of nonalcoholic fatty liver, we used a surrogate marker, the FLI [9]. The index uses an algorithm based on BMI, WC, serum TG level, and GGT. It has been validated against hepatic ultrasonography (US) in the general population and has been proven accurate in detecting fatty liver (accuracy, 0.84; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.81 to 0.87) [9,13]. When FLI is greater than or equal to 60 (FLI ≥60), the probability of having a fatty liver is >78%, and if FLI is <20, the likelihood not to have fatty liver is greater than 91%. A validation of FLI against magnetic resonance spectroscopy demonstrated the presence of hepatic fat (range, 8.6% to 24.0%) in subjects with FLI ≥60 and the absence of hepatic fat in those FLI <20 [13]. Therefore, we categorized our study group into three groups: 1) the low FLI group, FLI <20; 2) the intermediate group, 20≥FLI<60; and 3) the high FLI group, FLI ≥60.
- Body composition determined by bioelectric impedance analysis
- Waist circumference was measured at the midpoint between the lower border of the rib cage and the iliac crest. We analyzed body composition of all subjects using the Inbody 720 (Biospace, Seoul, Korea), a multifrequency impedance body composition analyzer. The Inbody 720 uses an eight-point tactile electrode method, measuring resistance at five specific frequencies (1, 50, 250, 500 kHz, and 1 MHz) and reactance at three specific frequencies (5, 50, and 250 kHz). We obtained readings for skeletal muscle mass (SMM, kg) and visceral fat area (VFA, cm2). The SMM to VFA ratio (SVR, g/cm2) was calculated as a new index of risk factor for fatty liver by dividing the SMM (g) by VFA (cm2). Skeletal muscle index (SMI) was expressed as percent, dividing the SMM (kg) by total body weight (kg).
- Statistical analysis
- Quantitative data were expressed as mean±standard deviation, and categorical data were expressed as percentages. The t-tests were used to compare continuous variables, and a χ2 test was used for categorical variables. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) tests were performed to compare continuous variables among FLI groups. Associations between FLI and continuous variables were evaluated by simple and multiple regression analyses. Correlations (Pearson correlation coefficient) and multiple linear regression analyses were also performed. All data analyses were performed using SPSS software for Windows version 14.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
METHODS
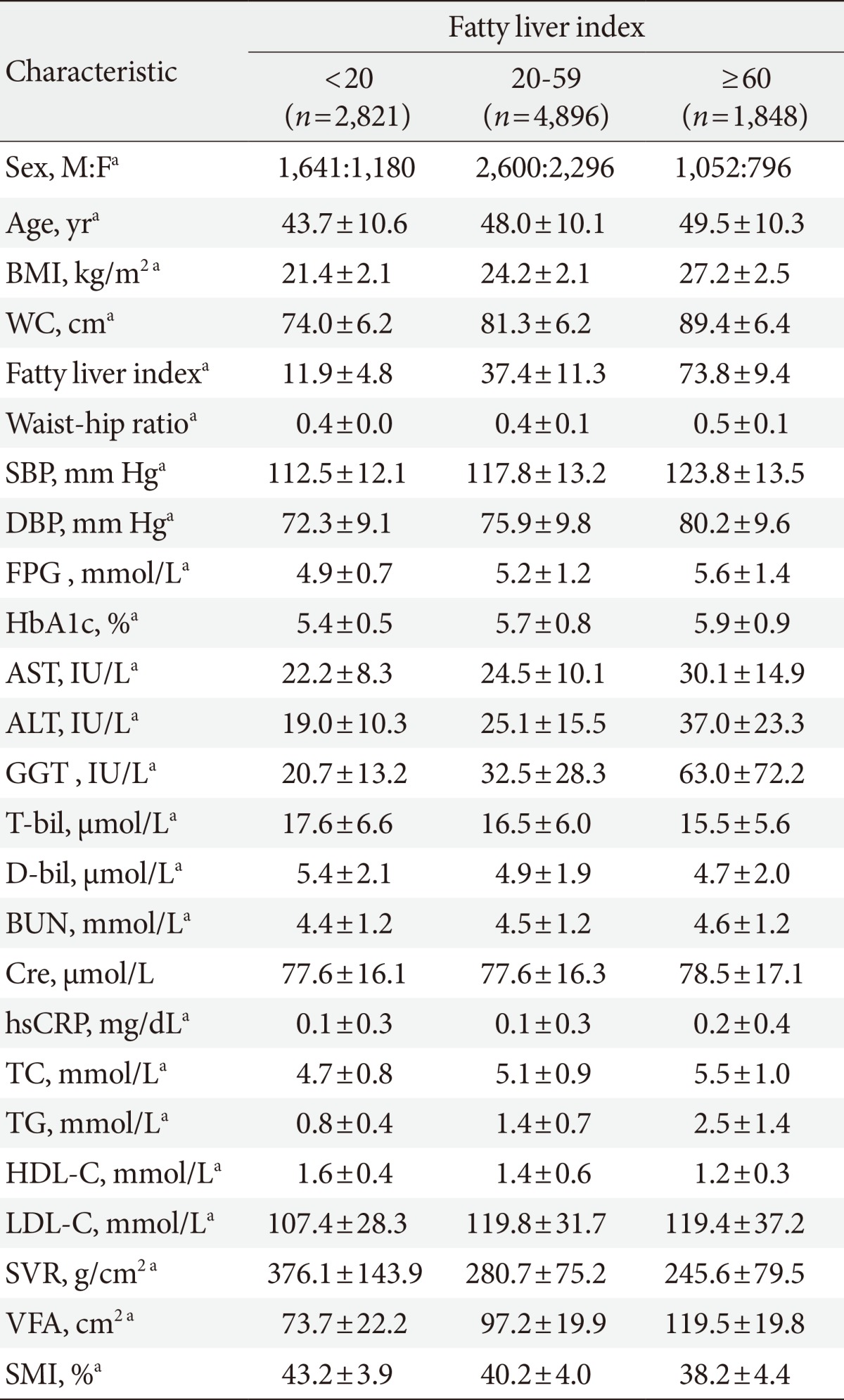
- The baseline characteristics of the subjects are shown in Supplementary Table 1. The mean age of males and females were 47.2 and 46.7 years, respectively. Anthropometric values including BMI and WC were significantly higher in males than females. While blood pressure (SBP, DPB), FPG, HbA1c, AST, ALT, GGT, TC, TG, LDL-C, and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) were also higher in the male group, FLI was not significantly different between the male and female groups. The male group showed a higher prevalence of metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and hypertension than the female group. Higher VFA and indexes of skeletal muscle (SMI, SVR, and skeletal muscle-to-total body fat ratio) were identified in the male group, but body fat mass was higher in the female group in bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA).
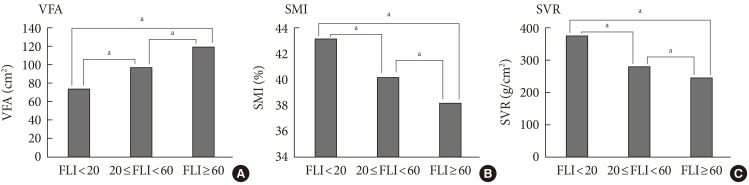
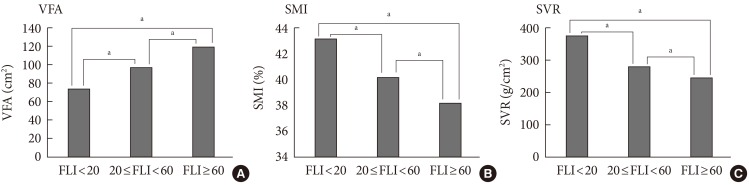
- We examined the anthropometric and clinical parameters using the FLI. Table 1 shows that biochemical parameters such as FPG, HbA1c, AST, ALT, TC, LDL-C, and hsCRP increased in the high FLI group compare with other groups, while bilirubin and HDL-C decreased. Compared with the low FLI group (FLI <20) by ANOVA, increased VFA and decreased SMI and SVR were observed in both the high FLI group (FLI ≥60) and the intermediated group (20≤FL<60). There was also an inverse correlation between SMM and VFA in the low FLI group (Fig. 1).
- The correlations between several metabolic parameters including FLI and indexes of body composition, such as SMI, SVR, and VFA, are shown in Table 2. Adjusted for age and gender, SMI and SVR correlated negatively with BMI (r=-0.60, r=-0.43, respectively) and FLI (r=-0.56, r=-0.41, respectively), while VFA had a strong positive correlation with FLI (r=0.73).
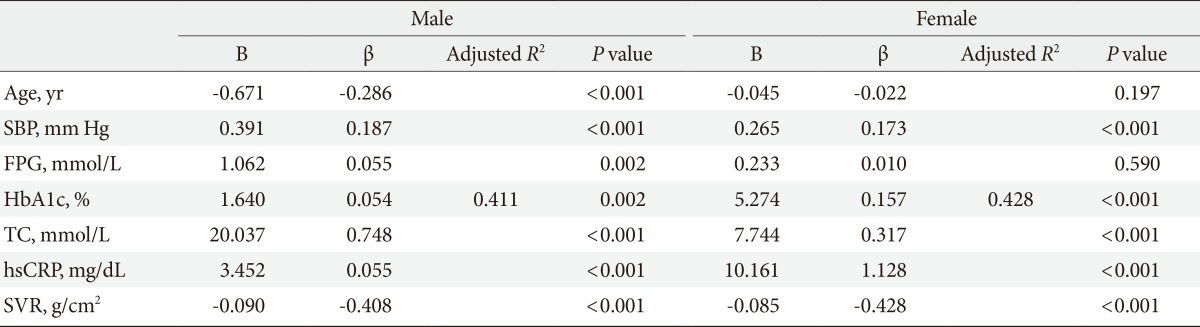
- In simple linear regression analysis (Supplementary Table 2), SVR (males, B=-0.076, β=-0.347; females, B=-0.114, β=-0.569) was shown to significantly affect FLI as a negative factor in both genders. Table 3 shows that in multiple regression analysis, a similar result was obtained, indicating that SVR was an independent factor in FLI and had an inverse correlation (males, B=-0.090, β=-0.408; females, B=-0.085, β=-0.428).
- Table 4 displays the odds ratio between NAFLD and SVR. For evaluation of SVR impact on fatty liver, we determined FLD as FLI above 60 and then examined the odds ratio by multiple logistic regression analysis. Among the quartiles, the highest SVR quartile (Q4) had a lower incidence of NAFLD and the odds was 0.038 (95% CI, 0.030 to 0.048) after adjustment for age and gender. In addition, after adjusting for lipid profile, diabetes, hypertension, and hsCRP, we determined that higher quartiles from the lowest quartile group showed a significantly lower odds ratio (Q2, 0.212; Q3, 0.129; Q4, 0.037).
RESULTS
- In the present study, we found that skeletal muscle and visceral fat contributed to NAFLD. First, the FLI increased in proportion to a rise in VFA and it was consistent with well-established relationships between abdominal obesity and NAFLD. Second, there was an inverse correlation between SMM and VFA. Finally, higher SMM, which is adjusted by visceral fat, was associated with low incidence of NAFLD.
- Little is known about how skeletal muscle works on abnormal fat accumulation in internal organs, especially the liver. The role of skeletal muscle has been studied, but is limited to disability and functional activity with aging. However, concerns are growing in the context of insulin resistance. Intuitively, an increase of SMM is expected to give a higher basal metabolic rate and greater energy expenditure, which may in turn lead to reduced weight, including visceral fat and FLD. Recent studies demonstrated that myokines secreted by skeletal muscle prevent systemic inflammation and insulin resistance through antagonizing the proinflammatory and metabolic effect of adipocytes [20]. Even a modest increase in muscle mass was able to prevent not only atherogenesis in prone mice, but also diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance [21]. Large population studies also have been used to characterize metabolic parameters associated with insulin, Srikanthan and Karlamangla [15] showed that higher muscle mass was related with better insulin sensitivity and lower risk of prevalence of transitional/prediabetes or overt diabetes. Physical activity also interrelates with skeletal muscle, even if they are not exactly the same parameters, and higher levels of habitual physical activity are related with a lower intrahepatic fat content [22]. Thus, skeletal muscle has a beneficial effect on the risk of metabolic and cardiovascular disease.
- Despite diverse clinical views on the definition of sarcopenia [23], decreased muscle mass is generally accepted as another risk factor of metabolic and cardiovascular disease in the context of insulin resistance. Lu et al. [24] confirmed that sarcopenia as well as obesity affect the development of metabolic syndrome. Kim et al. [16] reported that type 2 diabetes was independently associated with sarcopenia, which was defined using the SMI (%) in Korean patients. Srikanthan et al. [17] reported that sarcopenia might be an early predictor of diabetes susceptibility independent of obesity in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Study III study.
- In the present study, the FLI was lower in the group having higher SMM, and simultaneously, the group with NAFLD (FLI ≥60) had lower SMI and higher VFA when compare with the lower FLI group. The lowest SVR quartile group also showed the highest risk of NAFLD. These results are consistent with prior findings and further show that the incidence of NAFLD increases with decreased muscle mass relative to visceral fat (SVR). Thus, skeletal muscle could play a significant role in the development of NAFLD and our results support a favorable role for skeletal muscle in insulin resistance.
- We identified an inverse correlation between skeletal muscle and visceral fat. Prior studies showed abdominal obesity negatively affects muscle strength and contributes to the progression of sarcopenia [25], as proinflammatory cytokines and leptin which are secreted by adipocytes stimulate skeletal muscle catabolism and accelerate sarcopenia [26]. Given an increase in fat mass, particularly not subcutaneous but visceral fat, adipocytes overproduce proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor α, and C-reactive protein [27]. IL-6, a pleiotropic cytokine produced by different tissues and organs, is known to have dual effects on muscle. IL-6 is principally defined as a proinflammatory cytokine, which increases muscle wasting when systemic levels are elevated chronically under persistent inflammatory conditions, cancer, and other chronic disease states. Simultaneously, IL-6 is also one of the few genuine myokines that are produced by and act on skeletal muscle. Muscle induced IL-6 has beneficial effects in muscle growth, regeneration, and regulation of energy metabolism, but its action is transient and short-term [28]. Although the exact mechanisms are not fully understand, we found that skeletal muscle and visceral fat may influence each other in opposition and both strongly contribute to NAFLD. However, we did not directly measure the inflammatory cytokines.
- Age-related body composition changes are well documented, and both a progressive increase in fat mass and loss of muscle mass occur even when there are no significant changes in BMI [29]. The change of body composition, especially mass and distribution of fat tissue normally peaks at about age 65 years in men and later in women [30]. We hypothesize that the risk of FLD may increase with aging. However, the result was contrary to what we expected in multiple regression analysis. Even if not significant in women, it is thought to be caused by the relative young age combined with the high BMI of subjects in this study. According to the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, the incidence of obesity differed by sex and age in South Korea. The prevalence of obesity (defined by BMI) in men peaks in their 30s (42.3%), next in their 40s (41.2%), and decreases with age. In contrast, the proportion of obese women gradually rises with age (19% in their 30s, 26.7% in their 40s, and highest in their 60s, at 43.3%) [31]. Because participants in this study were in their mid-40s, with above average BMI for the Korean population (defined as overweight by BMI ≥23), obesity may affect their FLI more than age-related changes. Further studies are needed to define the relationship between age and FLD.
- Among the methods that assess liver fat accumulation, liver biopsy is the gold standard for evaluating hepatic steatosis and its changes by disease severity. But this procedure is difficult to apply to all patients due to limitations, including its invasiveness, cost, and potential life-threatening complications. Although liver ultrasonography has been used the most widely, low specificity, high cost, and bias of results by the examiner are barriers to use in large populations. Similar shortcomings were observed in other radiologic tests such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy [32]. Therefore, several methods have been developed for objective assessment of fatty liver, and FLI has been proposed and validated in the general population [10,11]. It can be inferred that factors for calculating the FLI, such as WC, BMI, TG, and GGT, are closely associated with insulin resistance. FLI additionally has advantages in large population studies for providing high accuracy and less error by the examiner. This index showed good predictive value for detection of fatty liver and was validated in studies with the Korean population [33,34]. There are reasons why we used FLI for this study. However, in spite of its many benefits, there are some disadvantages. This surrogate marker does not reflect a histological change of fatty infiltration, and was reported to be a poor predictor of significant steatosis in obese patients (BMI ≥28 kg/m2) [35]. It needs to be validated with various ethnic groups, including Asians, and calibrated for the Asian population because of different definitions of obesity (BMI).
- This study has several limitations. First, we did not include the analysis of physical activity. A recent study has shown that exercise reduces the risk of NAFLD and decreases liver enzymes, independent of obesity [36]. Consistent with this study, low physical activity in NAFLD patients was also reported [37]. Because physical activity is closely related to muscle mass, our findings might not be irrelevant, but the cross-sectional design of this study makes it difficult to infer causality between skeletal muscle, visceral fat, and FLD. Second, this study has selection bias because subjects were health check-up participants in a single center. Third, we used the BIA method to measure muscle mass. Though dual energy X-ray absorptiometry or CT were currently gold standard tests for evaluating SMM [38], these methods were limited to epidemiologic studies in terms of cost and time. BIA showed good correlation with the dual energy X-ray absorptiometry method and was also validated in studies of Asians including the Korean population [36,39]. However, overestimation of pathological states such as heart or renal failure may depend on the relationship between body composition and body water content. To minimize overestimation, all participants were required to fast for 8 hours and individuals with renal failure were excluded. Finally, findings from this study can be applied only to Asian populations, but not to other ethnic groups.
- In conclusion, VFA is closely correlated with NAFLD diagnosed by FLI. There is an inverse correlation between SMM and VFA. High SMM and low VFA, that is high SVR, is associated with low incidence of NAFLD. These results suggest that body composition, including skeletal muscle, may be more important than simple abdominal obesity in the development of FLD, and concerns about reducing or at least slowing the onset of sarcopenia are needed for prevention.
DISCUSSION
- 1. Byrne CD. Dorothy Hodgkin Lecture 2012: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, insulin resistance and ectopic fat: a new problem in diabetes management. Diabet Med 2012;29:1098-1107. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Park SH. Current status of liver disease in Korea: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Korean J Hepatol 2009;15(Suppl 6):S34-S39. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Utzschneider KM, Kahn SE. Review: the role of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:4753-4761. PubMed
- 4. Stranges S, Dorn JM, Muti P, Freudenheim JL, Farinaro E, Russell M, Nochajski TH, Trevisan M. Body fat distribution, relative weight, and liver enzyme levels: a population-based study. Hepatology 2004;39:754-763. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Eguchi Y, Eguchi T, Mizuta T, Ide Y, Yasutake T, Iwakiri R, Hisatomi A, Ozaki I, Yamamoto K, Kitajima Y, Kawaguchi Y, Kuroki S, Ono N. Visceral fat accumulation and insulin resistance are important factors in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol 2006;41:462-469. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Koda M, Kawakami M, Murawaki Y, Senda M. The impact of visceral fat in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. J Gastroenterol 2007;42:897-903. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Kim D, Choi SY, Park EH, Lee W, Kang JH, Kim W, Kim YJ, Yoon JH, Jeong SH, Lee DH, Lee HS, Larson J, Therneau TM, Kim WR. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with coronary artery calcification. Hepatology 2012;56:605-613. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, Tomassetti S, Bugianesi E, Lenzi M, McCullough AJ, Natale S, Forlani G, Melchionda N. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 2001;50:1844-1850. PubMed
- 9. Bedogni G, Bellentani S, Miglioli L, Masutti F, Passalacqua M, Castiglione A, Tiribelli C. The Fatty Liver Index: a simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol 2006;6:33ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 10. Kozakova M, Palombo C, Eng MP, Dekker J, Flyvbjerg A, Mitrakou A, Gastaldelli A, Ferrannini E. RISC Investigators. Fatty liver index, gamma-glutamyltransferase, and early carotid plaques. Hepatology 2012;55:1406-1415. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Calori G, Lattuada G, Ragogna F, Garancini MP, Crosignani P, Villa M, Bosi E, Ruotolo G, Piemonti L, Perseghin G. Fatty liver index and mortality: the Cremona study in the 15th year of follow-up. Hepatology 2011;54:145-152. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Balkau B, Lange C, Vol S, Fumeron F, Bonnet F. Group Study D.E.S.I.R. Nine-year incident diabetes is predicted by fatty liver indices: the French D.E.S.I.R. study. BMC Gastroenterol 2010;10:56ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 13. Gastaldelli A, Kozakova M, Hojlund K, Flyvbjerg A, Favuzzi A, Mitrakou A, Balkau B. RISC Investigators. Fatty liver is associated with insulin resistance, risk of coronary heart disease, and early atherosclerosis in a large European population. Hepatology 2009;49:1537-1544. ArticlePubMed
- 14. DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC, Ferrannini E. Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care 1992;15:318-368. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Srikanthan P, Karlamangla AS. Relative muscle mass is inversely associated with insulin resistance and prediabetes: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:2898-2903. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Kim TN, Park MS, Yang SJ, Yoo HJ, Kang HJ, Song W, Seo JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Baik SH, Choi DS, Choi KM. Prevalence and determinant factors of sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS). Diabetes Care 2010;33:1497-1499. PubMedPMC
- 17. Srikanthan P, Hevener AL, Karlamangla AS. Sarcopenia exacerbates obesity-associated insulin resistance and dysglycemia:findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III. PLoS One 2010;5:e10805ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2012. Diabetes Care 2012;35(Suppl 1):S11-S63. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J. IDF Epidemiology Task Force Consensus Group. The metabolic syndrome: a new worldwide definition. Lancet 2005;366:1059-1062. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Walsh K. Adipokines, myokines and cardiovascular disease. Circ J 2009;73:13-18. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Izumiya Y, Hopkins T, Morris C, Sato K, Zeng L, Viereck J, Hamilton JA, Ouchi N, LeBrasseur NK, Walsh K. Fast/Glycolytic muscle fiber growth reduces fat mass and improves metabolic parameters in obese mice. Cell Metab 2008;7:159-172. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Perseghin G, Lattuada G, De Cobelli F, Ragogna F, Ntali G, Esposito A, Belloni E, Canu T, Terruzzi I, Scifo P, Del Maschio A, Luzi L. Habitual physical activity is associated with intrahepatic fat content in humans. Diabetes Care 2007;30:683-688. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Brotto M. Lessons from the FNIH-NIA-FDA sarcopenia consensus summit. IBMS Bonekey 2012;9:210ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Lu CW, Yang KC, Chang HH, Lee LT, Chen CY, Huang KC. Sarcopenic obesity is closely associated with metabolic syndrome. Obes Res Clin Pract 2013;7:e301-e307.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Schrager MA, Metter EJ, Simonsick E, Ble A, Bandinelli S, Lauretani F, Ferrucci L. Sarcopenic obesity and inflammation in the InCHIANTI study. J Appl Physiol 2007;102:919-925. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Reuben DB, Judd-Hamilton L, Harris TB, Seeman TE. MacArthur Studies of Successful Aging. The associations between physical activity and inflammatory markers in high-functioning older persons: MacArthur Studies of Successful Aging. J Am Geriatr Soc 2003;51:1125-1130. ArticlePubMed
- 27. van der Poorten D, Milner KL, Hui J, Hodge A, Trenell MI, Kench JG, London R, Peduto T, Chisholm DJ, George J. Visceral fat: a key mediator of steatohepatitis in metabolic liver disease. Hepatology 2008;48:449-457. ArticlePubMed
- 28. Munoz-Canoves P, Scheele C, Pedersen BK, Serrano AL. Interleukin-6 myokine signaling in skeletal muscle: a double-edged sword? FEBS J Epub 2013 May 13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/febs.12338.
- 29. Newman AB, Lee JS, Visser M, Goodpaster BH, Kritchevsky SB, Tylavsky FA, Nevitt M, Harris TB. Weight change and the conservation of lean mass in old age: the Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;82:872-878. ArticlePubMed
- 30. Prentice AM, Jebb SA. Beyond body mass index. Obes Rev 2001;2:141-147. ArticlePubMed
- 31. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea health statistics 2010: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-1). Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2011.
- 32. Festi D, Schiumerini R, Marzi L, Di Biase AR, Mandolesi D, Montrone L, Scaioli E, Bonato G, Marchesini-Reggiani G, Colecchia A. Review article: the diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease -- availability and accuracy of non-invasive methods. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2013;37:392-400. ArticlePubMed
- 33. Kim JH, Kwon SY, Lee SW, Lee CH. Validation of fatty liver index and lipid accumulation product for predicting fatty liver in Korean population. Liver Int 2011;31:1600-1601. ArticlePubMed
- 34. Jung CH, Lee WJ, Hwang JY, Yu JH, Shin MS, Lee MJ, Jang JE, Leem J, Park JY, Kim HK. Assessment of the fatty liver index as an indicator of hepatic steatosis for predicting incident diabetes independently of insulin resistance in a Korean population. Diabet Med 2013;30:428-435. ArticlePubMed
- 35. Borman MA, Ladak F, Crotty P, Pollett A, Kirsch R, Pomier-Layrargues G, Beaton M, Duarte-Rojo A, Elkashab M, Myers RP. The Fatty Liver Index has limited utility for the detection and quantification of hepatic steatosis in obese patients. Hepatol Int 2013;7:592-599.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 36. Bae JC, Suh S, Park SE, Rhee EJ, Park CY, Oh KW, Park SW, Kim SW, Hur KY, Kim JH, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim KW, Lee WY. Regular exercise is associated with a reduction in the risk of NAFLD and decreased liver enzymes in individuals with NAFLD independent of obesity in Korean adults. PLoS One 2012;7:e46819ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Gerber L, Otgonsuren M, Mishra A, Escheik C, Birerdinc A, Stepanova M, Younossi ZM. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with low level of physical activity: a population-based study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012;36:772-781. ArticlePubMed
- 38. Haderslev KV, Haderslev PH, Staun M. Accuracy of body composition measurements by dual energy x-ray absorptiometry in underweight patients with chronic intestinal disease and in lean subjects. Dyn Med 2005;4:1ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Rush EC, Chandu V, Plank LD. Prediction of fat-free mass by bioimpedance analysis in migrant Asian Indian men and women: a cross validation study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006;30:1125-1131. ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Data are presented as the mean±standard deviation.
M, male; F, female; BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; GGT, γ-glutamyl transferase; T-bil, total bilirubin; D-bil, direct bilirubin; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; Cre, creatinine; hsCRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; SVR, skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio; VFA, visceral fat area; SMI, skeletal muscle index.
aP<0.001, for trend in analysis of variance analysis.
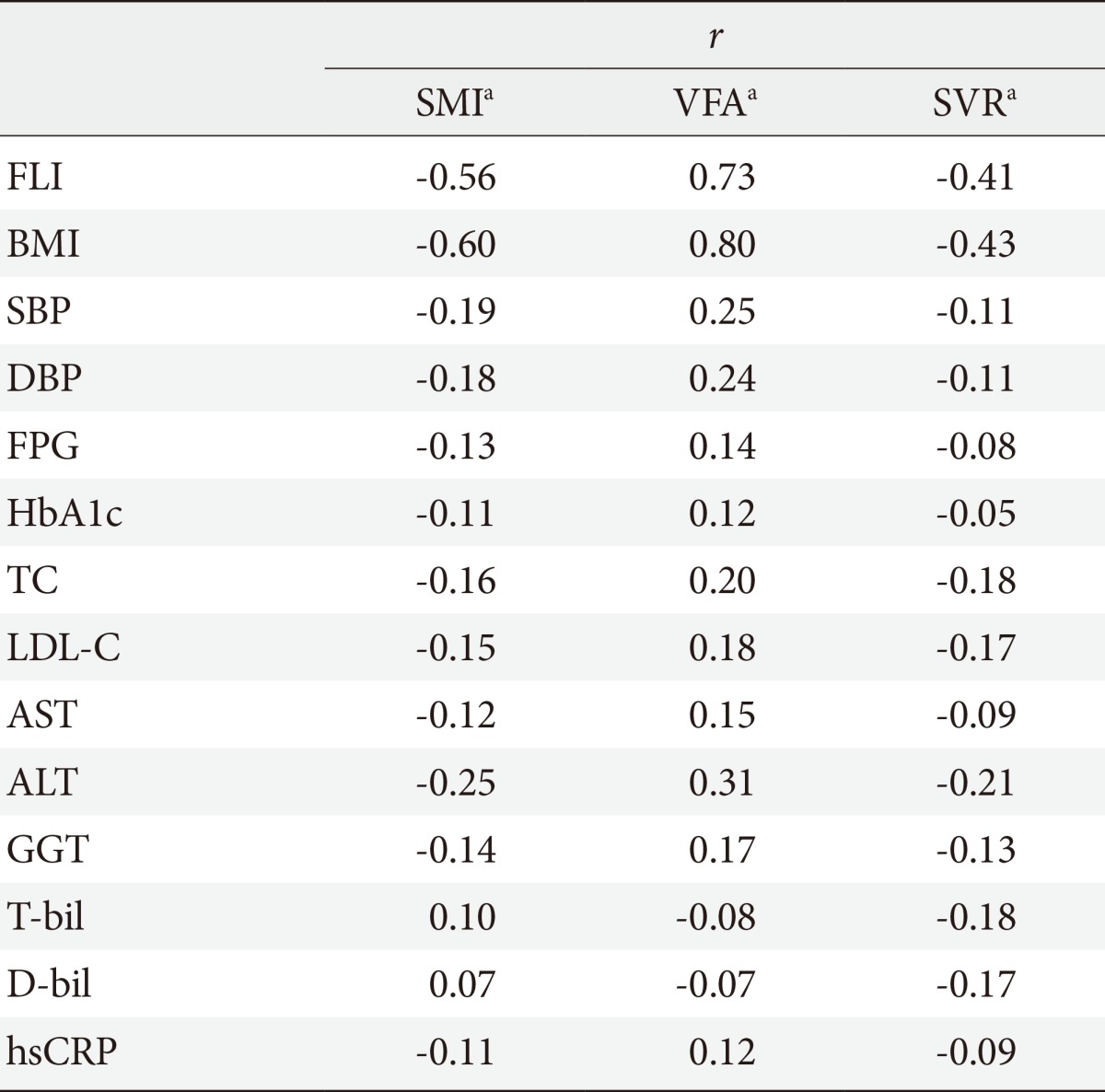
Correlation coefficients (r) and P values calculated using the Pearson partial correlation analysis.
SMI, skeletal muscle index; VFA, visceral fat area; SVR, skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio; FLI, fatty liver index; BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; TC, total cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; GGT, γ-glutamyl transferase; T-bil, total bilirubin; D-bil, direct bilirubin; hsCRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein.
aAdjusted for age and gender; all variables P<0.001.
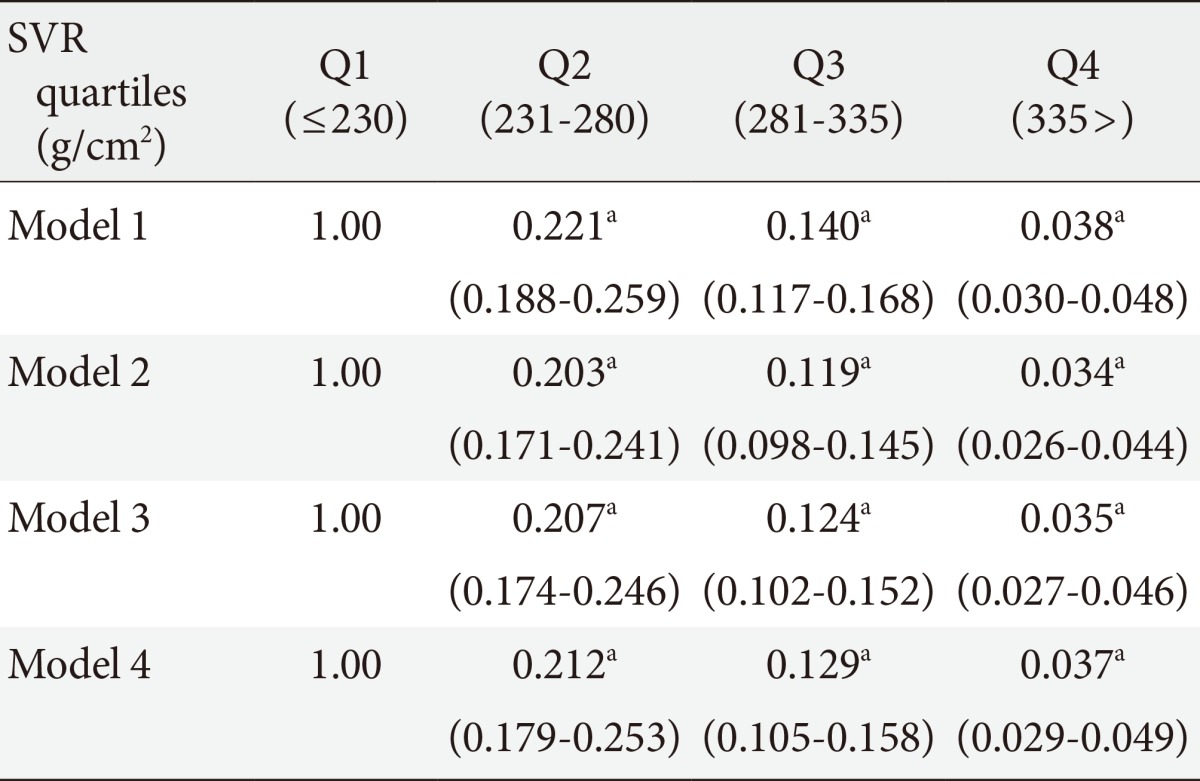
Model 1: adjusted for age and gender. Model 2: Model 1 and adjusted for total cholesterol and low density lipoprotein cholesterol. Model 3: Model 2 and adjusted for diabetes and hypertension. Model 4: Model 3 and adjusted for high sensitivity C-reactive protein.
SVR, skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio.
aP<0.001.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Effects of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease on sarcopenia: evidence from genetic methods
Jiaqin Yuan, Jinglin Zhang, Qiang Luo, Lipeng Peng
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages Intake on Sarcopenic Obesity, Visceral Obesity, and Sarcopenia in Lebanese Patients with MASLD: A Case-Control Study
Maha Hoteit, Myriam Dagher, Nikolaos Tzenios, Najat Al Kaaki, Ghadir Rkein, Abdul Rahman Chahine, Yonna Sacre, Samer Hotayt, Rami Matar, Mahmoud Hallal, Micheal Maitar, Bilal Hotayt
Healthcare.2024; 12(5): 591. CrossRef - Increased visceral fat area to skeletal muscle mass ratio is positively associated with the risk of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in a Chinese population
Chenbing Liu, Nan Li, Di Sheng, Yahong Shao, Lihong Qiu, Chao Shen, Zhong Liu
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Using hyperhomocysteinemia and body composition to predict the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in healthcare workers
Xiaoyan Hao, Honghai He, Liyuan Tao, Peng Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Criteria and Prognostic Relevance of Sarcopenia in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease—A Systematic Review
Claudia-Gabriela Potcovaru, Petruța Violeta Filip, Oana-Maria Neagu, Laura Sorina Diaconu, Teodor Salmen, Delia Cinteză, Anca Pantea Stoian, Florin Bobirca, Mihai Berteanu, Corina Pop
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4713. CrossRef - Association between Muscle Mass Deficits and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Adults with Body Mass Index Less than 23 kg/m2
Mi Young Lee, Hee Jeong Choi, Han Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2023; 13(3): 171. CrossRef - Sex influences the association between appendicular skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Gang Li, Rafael S. Rios, Xin-Xin Wang, Yue Yu, Kenneth I. Zheng, Ou-Yang Huang, Liang-Jie Tang, Hong-Lei Ma, Yi Jin, Giovanni Targher, Christopher D. Byrne, Xiao-Yan Pan, Ming-Hua Zheng
British Journal of Nutrition.2022; 127(11): 1613. CrossRef - 2019 Global NAFLD Prevalence: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Michael H. Le, Yee Hui Yeo, Xiaohe Li, Jie Li, Biyao Zou, Yuankai Wu, Qing Ye, Daniel Q. Huang, Changqing Zhao, Jie Zhang, Chenxi Liu, Na Chang, Feng Xing, Shiping Yan, Zi Hui Wan, Natasha Sook Yee Tang, Maeda Mayumi, Xinting Liu, Chuanli Liu, Fajuan Rui,
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 20(12): 2809. CrossRef - Impact of Sarcopenia and Myosteatosis in Non-Cirrhotic Stages of Liver Diseases: Similarities and Differences across Aetiologies and Possible Therapeutic Strategies
Annalisa Cespiati, Marica Meroni, Rosa Lombardi, Giovanna Oberti, Paola Dongiovanni, Anna Ludovica Fracanzani
Biomedicines.2022; 10(1): 182. CrossRef - Impact of Sarcopenia on the Severity of the Liver Damage in Patients With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Vittoria Zambon Azevedo, Cristina Alina Silaghi, Thomas Maurel, Horatiu Silaghi, Vlad Ratziu, Raluca Pais
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fatty Liver Index and Skeletal Muscle Density
Julie A. Pasco, Sophia X. Sui, Emma C. West, Kara B. Anderson, Pamela Rufus-Membere, Monica C. Tembo, Natalie K. Hyde, Lana J. Williams, Zoe S. J. Liu, Mark A. Kotowicz
Calcified Tissue International.2022; 110(6): 649. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio as a predictor of NAFLD in lean and overweight men and women with effect modification by sex
Yoosun Cho, Yoosoo Chang, Seungho Ryu, Hyun‐Suk Jung, Chan‐won Kim, Hyungseok Oh, Mi Kyung Kim, Won Sohn, Hocheol Shin, Sarah H. Wild, Christopher D. Byrne
Hepatology Communications.2022; 6(9): 2238. CrossRef - Association of Low Skeletal Muscle Mass with the Phenotype of Lean Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Jun-Hyeon Byeon, Min-Kyu Kang, Min-Cheol Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(5): 850. CrossRef - Muscle strength, but not body mass index, is associated with mortality in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
Phunchai Charatcharoenwitthaya, Khemajira Karaketklang, Wichai Aekplakorn
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2022; 13(5): 2393. CrossRef - Effect of progressive resistance training with weight loss compared with weight loss alone on the fatty liver index in older adults with type 2 diabetes: secondary analysis of a 12-month randomized controlled trial
Christine L Freer, Elena S George, Sze-Yen Tan, Gavin Abbott, David W Dunstan, Robin M Daly
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(5): e002950. CrossRef - Muscle Krüppel-like factor 15 regulates lipid flux and systemic metabolic homeostasis
Liyan Fan, David R. Sweet, Domenick A. Prosdocimo, Vinesh Vinayachandran, Ernest R. Chan, Rongli Zhang, Olga Ilkayeva, Yuan Lu, Komal S. Keerthy, Chloe E. Booth, Christopher B. Newgard, Mukesh K. Jain
Journal of Clinical Investigation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - “Bioelectrical impedance analysis in managing sarcopenic obesity in NAFLD”
David J. Hanna, Scott T. Jamieson, Christine S. Lee, Christopher A. Pluskota, Nicole J. Bressler, Peter N. Benotti, Sandeep Khurana, David D. K. Rolston, Christopher D. Still
Obesity Science & Practice.2021; 7(5): 629. CrossRef - Decreased Muscle-to-Fat Mass Ratio Is Associated with Low Muscular Fitness and High Alanine Aminotransferase in Children and Adolescent Boys in Organized Sports Clubs
Kai Ushio, Yukio Mikami, Hiromune Obayashi, Hironori Fujishita, Kouki Fukuhara, Tetsuhiko Sakamitsu, Kazuhiko Hirata, Yasunari Ikuta, Hiroaki Kimura, Nobuo Adachi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(11): 2272. CrossRef - Association of Skeletal Muscle and Adipose Tissue Distribution with Histologic Severity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver
Min-Kyu Kang, Jung-Hun Baek, Young-Oh Kweon, Won-Young Tak, Se-Young Jang, Yu-Rim Lee, Keun Hur, Gyeonghwa Kim, Hye-Won Lee, Man-Hoon Han, Joon-Hyuk Choi, Soo-Young Park, Jung-Gil Park
Diagnostics.2021; 11(6): 1061. CrossRef - Association of Body Composition and Sarcopenia with NASH in Obese Patients
Sophia Marie-Therese Schmitz, Lena Schooren, Andreas Kroh, Alexander Koch, Christine Stier, Ulf Peter Neumann, Tom Florian Ulmer, Patrick Hamid Alizai
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(15): 3445. CrossRef - Patchouli alcohol ameliorates skeletal muscle insulin resistance and NAFLD via AMPK/SIRT1-mediated suppression of inflammation
Do Hyeon Pyun, Tae Jin Kim, Seung Yeon Park, Hyun Jung Lee, A.M. Abd El-Aty, Ji Hoon Jeong, Tae Woo Jung
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2021; 538: 111464. CrossRef - Hepatic Steatosis Contributes to the Development of Muscle Atrophy via Inter-Organ Crosstalk
Kenneth Pasmans, Michiel E. Adriaens, Peter Olinga, Ramon Langen, Sander S. Rensen, Frank G. Schaap, Steven W. M. Olde Damink, Florian Caiment, Luc J. C. van Loon, Ellen E. Blaak, Ruth C. R. Meex
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle mass and cellular membrane integrity assessment in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Iasmin dos Santos Barreto, Raquel Oliveira dos Santos, Raquel Rocha, Claudineia de Souza, Naiade Almeida, Luiza Valois Vieira, Rafael Leiróz, Manoel Sarno, Carla Daltro, Helma Pinchemel Cotrim
Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira.2021; 67(9): 1233. CrossRef - A significant association of non-obese non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with sarcopenic obesity
Kazuhiro Kashiwagi, Michiyo Takayama, Kayoko Fukuhara, Ryoko Shimizu-Hirota, Po-Sung Chu, Nobuhiro Nakamoto, Nagamu Inoue, Yasushi Iwao, Takanori Kanai
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2020; 38: 86. CrossRef - Improvement in Menopause-Associated Hepatic Lipid Metabolic Disorders by Herbal Formula HPC03 on Ovariectomized Rats
BoYoon Chang, Dae Sung Kim, SungYeon Kim
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Sarcopenia is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in men with type 2 diabetes
D.H. Seo, Y.-h. Lee, S.W. Park, Y.J. Choi, B.W. Huh, E. Lee, K.B. Huh, S.H. Kim, B.-S. Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism.2020; 46(5): 362. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and sarcopenia: pathophysiological connections and therapeutic implications
Tiziana Fernández-Mincone, Felipe Contreras-Briceño, Maximiliano Espinosa-Ramírez, Patricio García-Valdés, Antonio López-Fuenzalida, Arnoldo Riquelme, Juan Pablo Arab, Daniel Cabrera, Marco Arrese, Francisco Barrera
Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 14(12): 1141. CrossRef - Association between Atrial Fibrillation and Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Min Kyu Kang, Jung Gil Park, Min Cheol Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2020; 61(10): 860. CrossRef - Relative fat mass at baseline and its early change may be a predictor of incident nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Hwi Young Kim, Su Jung Baik, Hye Ah Lee, Byoung Kwon Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Tae Hun Kim, Kwon Yoo
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Fisetin Alleviates Hepatic and Adipocyte Fibrosis and Insulin Resistance in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Myung-Sook Choi, Ji-Young Choi, Eun-Young Kwon
Journal of Medicinal Food.2020; 23(10): 1019. CrossRef - Relationship between relative skeletal muscle mass and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Changzhou Cai, Xin Song, Yishu Chen, Xueyang Chen, Chaohui Yu
Hepatology International.2020; 14(1): 115. CrossRef - Sarcopenia Is a New Risk Factor of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Min Kyu Kang, Kyeong Ok Kim, Min Cheol Kim, Jung Gil Park, Byung Ik Jang
Digestive Diseases.2020; 38(6): 507. CrossRef - Relationship between Muscle Mass/Strength and Hepatic Fat Content in Post-Menopausal Women
Yajie Zhang, Dajiang Lu, Renwei Wang, Weijie Fu, Shengnian Zhang
Medicina.2019; 55(10): 629. CrossRef - Lower hand grip strength in older adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a nationwide population-based study
Beom-Jun Kim, Seong Hee Ahn, Seung Hun Lee, Seongbin Hong, Mark W. Hamrick, Carlos M. Isales, Jung-Min Koh
Aging.2019; 11(13): 4547. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Nonobese Subjects of African Origin Has Atypical Metabolic Characteristics
Debbie S Thompson, Ingrid A Tennant, Deanne P Soares, Clive Osmond, Chris D Byrne, Terrence E Forrester, Michael S Boyne
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2019; 3(11): 2051. CrossRef - Sarcopenia in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: is it a clinically significant entity?
C. H. De Fré, M. A. De Fré, W. J. Kwanten, B. J. Op de Beeck, L. F. Van Gaal, S. M. Francque
Obesity Reviews.2019; 20(2): 353. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in The Rotterdam Study: About Muscle Mass, Sarcopenia, Fat Mass, and Fat Distribution
Louise Johanna Maria Alferink, Katerina Trajanoska, Nicole Stephanie Erler, Josje Dorothea Schoufour, Robert Jacobus de Knegt, M. Arfan Ikram, Harry Leonardus Antonius Janssen, Oscar H. Franco, Herold J. Metselaar, Fernando Rivadeneira, Sarwa Darwish Mura
Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.2019; 34(7): 1254. CrossRef - Sarcopenia Is Significantly Associated with Presence and Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Goh Eun Chung, Min Joo Kim, Jeong Yoon Yim, Joo Sung Kim, Ji Won Yoon
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2019; 28(2): 129. CrossRef - Association of low skeletal muscle mass with advanced liver fibrosis in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
Min Kyu Kang, Jung Gil Park, Heon Ju Lee, Min Cheol Kim
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2019; 34(9): 1633. CrossRef - Whole‐body vibration for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 6‐month prospective study
Sechang Oh, Natsumi Oshida, Noriko Someya, Tsuyoshi Maruyama, Tomonori Isobe, Yoshikazu Okamoto, Taeho Kim, Bokun Kim, Junichi Shoda
Physiological Reports.2019; 7(9): e14062. CrossRef - L-Lysine Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8 Mice
Tomonori SATO, Nao MURAMATSU, Yoshiaki ITO, Yoshio YAMAMOTO, Takashi NAGASAWA
Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology.2018; 64(3): 192. CrossRef - Short-term treatment with metformin reduces hepatic lipid accumulation but induces liver inflammation in obese mice
Alexandre Abilio de Souza Teixeira, Camila O. Souza, Luana A. Biondo, Loreana Sanches Silveira, Edson A. Lima, Helena A. Batatinha, Adriane Pereira Araujo, Michele Joana Alves, Sandro Massao Hirabara, Rui Curi, José Cesar Rosa Neto
Inflammopharmacology.2018; 26(4): 1103. CrossRef - Vitamin D and Related Deficiencies, Sarcopenia and Visceral Obesity in Obese People with NAFLD
Mihaela Petrova
Gastroenterology & Hepatology: Open Access.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Grip Strength Moderates the Association between Anthropometric and Body Composition Indicators and Liver Fat in Youth with an Excess of Adiposity
Robinson Ramírez-Vélez, Mikel Izquierdo, Jorge Correa-Bautista, Alejandra Tordecilla-Sanders, María Correa-Rodríguez, Jacqueline Schmidt Rio-Valle, Emilio González-Jiménez, Katherine González-Ruíz
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2018; 7(10): 347. CrossRef - Longitudinal Changes in Muscle Mass and Strength, and Bone Mass in Older Adults: Gender-Specific Associations Between Muscle and Bone Losses
Kyoung Min Kim, Soo Lim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Jae Young Lim, Ki Woong Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang
The Journals of Gerontology: Series A.2018; 73(8): 1062. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease connections with fat-free tissues: A focus on bone and skeletal muscle
Eleonora Poggiogalle, Lorenzo Maria Donini, Andrea Lenzi, Claudio Chiesa, Lucia Pacifico
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2017; 23(10): 1747. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Is there a relationship? A systematic review
Cristiane V Tovo, Sabrina A Fernandes, Caroline Buss, Angelo A de Mattos
World Journal of Hepatology.2017; 9(6): 326. CrossRef - Multiple molecular targets in the liver, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in ginger-elicited amelioration of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Chunxia Wang, Robert Batey, Johji Yamahara, Yuhao Li
Journal of Functional Foods.2017; 36: 43. CrossRef - Importance of Lean Muscle Maintenance to Improve Insulin Resistance by Body Weight Reduction in Female Patients with Obesity
Yaeko Fukushima, Satoshi Kurose, Hiromi Shinno, Ha Cao Thu, Nana Takao, Hiromi Tsutsumi, Yutaka Kimura
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(2): 147. CrossRef - Fatty Liver Index Associates with Relative Sarcopenia and GH/ IGF- 1 Status in Obese Subjects
Eleonora Poggiogalle, Carla Lubrano, Lucio Gnessi, Stefania Mariani, Andrea Lenzi, Lorenzo Maria Donini, Rasheed Ahmad
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(1): e0145811. CrossRef - The relationship between hepatic steatosis and skeletal muscle mass index in men with type 2 diabetes
Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Takafumi Osaka, Takuya Fukuda, Muhei Tanaka, Masahiro Yamazaki, Michiaki Fukui
Endocrine Journal.2016; 63(10): 877. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and the cardiometabolic syndrome: A narrative review
G. Bahat, B. İlhan
European Geriatric Medicine.2016; 7(3): 220. CrossRef - Low skeletal muscle mass is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults: the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hee Yeon Kim, Chang Wook Kim, Chung-Hwa Park, Jong Young Choi, Kyungdo Han, Anwar T Merchant, Yong-Moon Park
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2016; 15(1): 39. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk: Pathophysiological mechanisms and implications
Sven M. Francque, Denise van der Graaff, Wilhelmus J. Kwanten
Journal of Hepatology.2016; 65(2): 425. CrossRef - Differences among skeletal muscle mass indices derived from height-, weight-, and body mass index-adjusted models in assessing sarcopenia
Kyoung Min Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(4): 643. CrossRef - Relationship between grip strength and newly diagnosed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a large-scale adult population
Ge Meng, Hongmei Wu, Liyun Fang, Chunlei Li, Fei Yu, Qing Zhang, Li Liu, Huanmin Du, Hongbin Shi, Yang Xia, Xiaoyan Guo, Xing Liu, Xue Bao, Qian Su, Yeqing Gu, Huijun Yang, Bin Yu, Yuntang Wu, Zhong Sun, Kaijun Niu
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Volume-dependent effect of supervised exercise training on fatty liver and visceral adiposity index in subjects with type 2 diabetes The Italian Diabetes Exercise Study (IDES)
Stefano Balducci, Patrizia Cardelli, Luca Pugliese, Valeria D’Errico, Jonida Haxhi, Elena Alessi, Carla Iacobini, Stefano Menini, Lucilla Bollanti, Francesco G. Conti, Antonio Nicolucci, Giuseppe Pugliese
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2015; 109(2): 355. CrossRef - Sarcopenia is a risk factor for elevated aminotransferase in men independently of body mass index, dietary habits, and physical activity
Ki Deok Yoo, Dae Won Jun, Kang Nyeong Lee, Hang Lak Lee, Oh Young Lee, Byung Chul Yoon, Ho Soon Choi
Digestive and Liver Disease.2015; 47(4): 303. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite