
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Psychotic Disorders and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases, and All-Cause Mortality: A Population-Based Matched Cohort Study
- You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):122-133. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0431
- 1,105 View
- 144 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
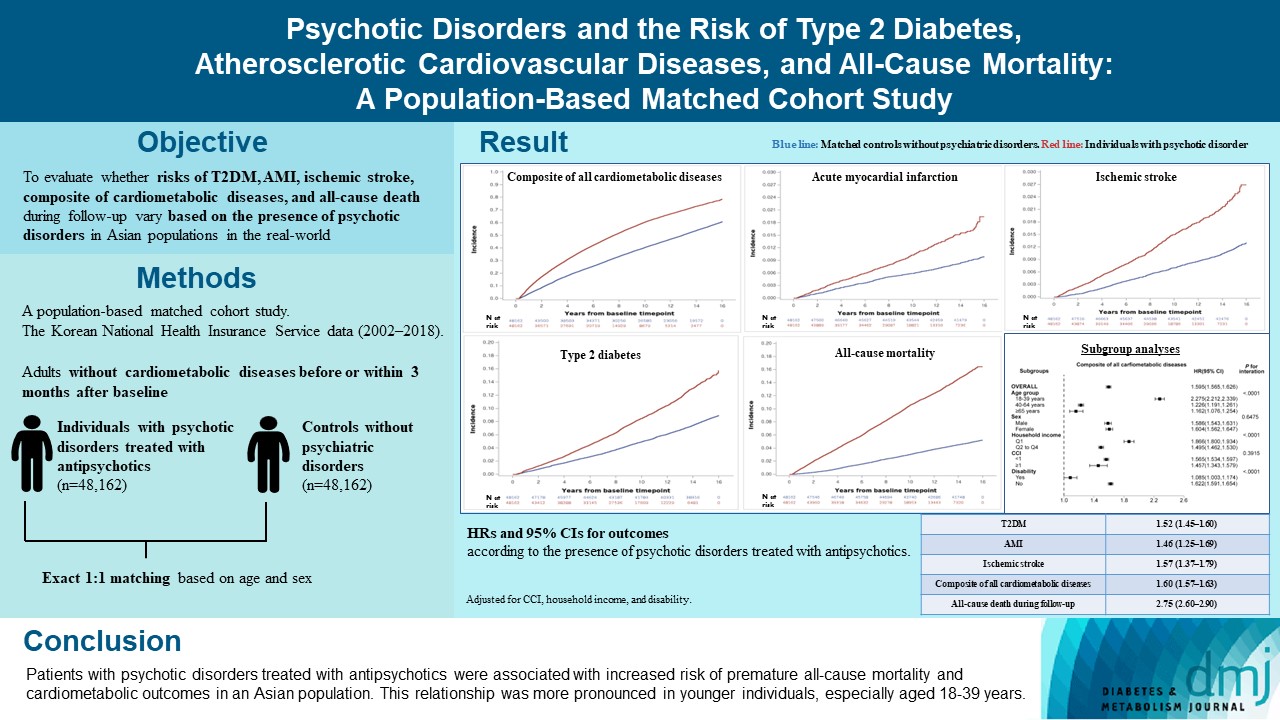
The effects of psychotic disorders on cardiometabolic diseases and premature death need to be determined in Asian populations.
Methods
In this population-based matched cohort study, the Korean National Health Insurance Service database (2002 to 2018) was used. The risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), acute myocardial infarction (AMI), ischemic stroke, composite of all cardiometabolic diseases, and all-cause death during follow-up was compared between individuals with psychotic disorders treated with antipsychotics (n=48,162) and 1:1 matched controls without psychiatric disorders among adults without cardiometabolic diseases before or within 3 months after baseline.
Results
In this cohort, 53,683 composite cases of all cardiometabolic diseases (during median 7.38 years), 899 AMI, and 1,216 ischemic stroke cases (during median 14.14 years), 7,686 T2DM cases (during median 13.26 years), and 7,092 deaths (during median 14.23 years) occurred. The risk of all outcomes was higher in subjects with psychotic disorders than matched controls (adjusted hazard ratios [95% confidence intervals]: 1.522 [1.446 to 1.602] for T2DM; 1.455 [1.251 to 1.693] for AMI; 1.568 [1.373 to 1.790] for ischemic stroke; 1.595 [1.565 to 1.626] for composite of all cardiometabolic diseases; and 2.747 [2.599 to 2.904] for all-cause mortality) during follow-up. Similar patterns of associations were maintained in subgroup analyses but more prominent in younger individuals (P for interaction <0.0001) when categorized as those aged 18–39, 40–64, or ≥65 years.
Conclusion
Patients with psychotic disorders treated with antipsychotics were associated with increased risk of premature allcause mortality and cardiometabolic outcomes in an Asian population. This relationship was more pronounced in younger individuals, especially aged 18 to 39 years.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Metabolic Syndrome Severity Score for Predicting Cardiovascular Events: A Nationwide Population-Based Study from Korea
- Yo Nam Jang, Jun Hyeok Lee, Jin Sil Moon, Dae Ryong Kang, Seong Yong Park, Jerim Cho, Jang-Young Kim, Ji Hye Huh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):569-577. Published online January 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0103
- 6,522 View
- 225 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
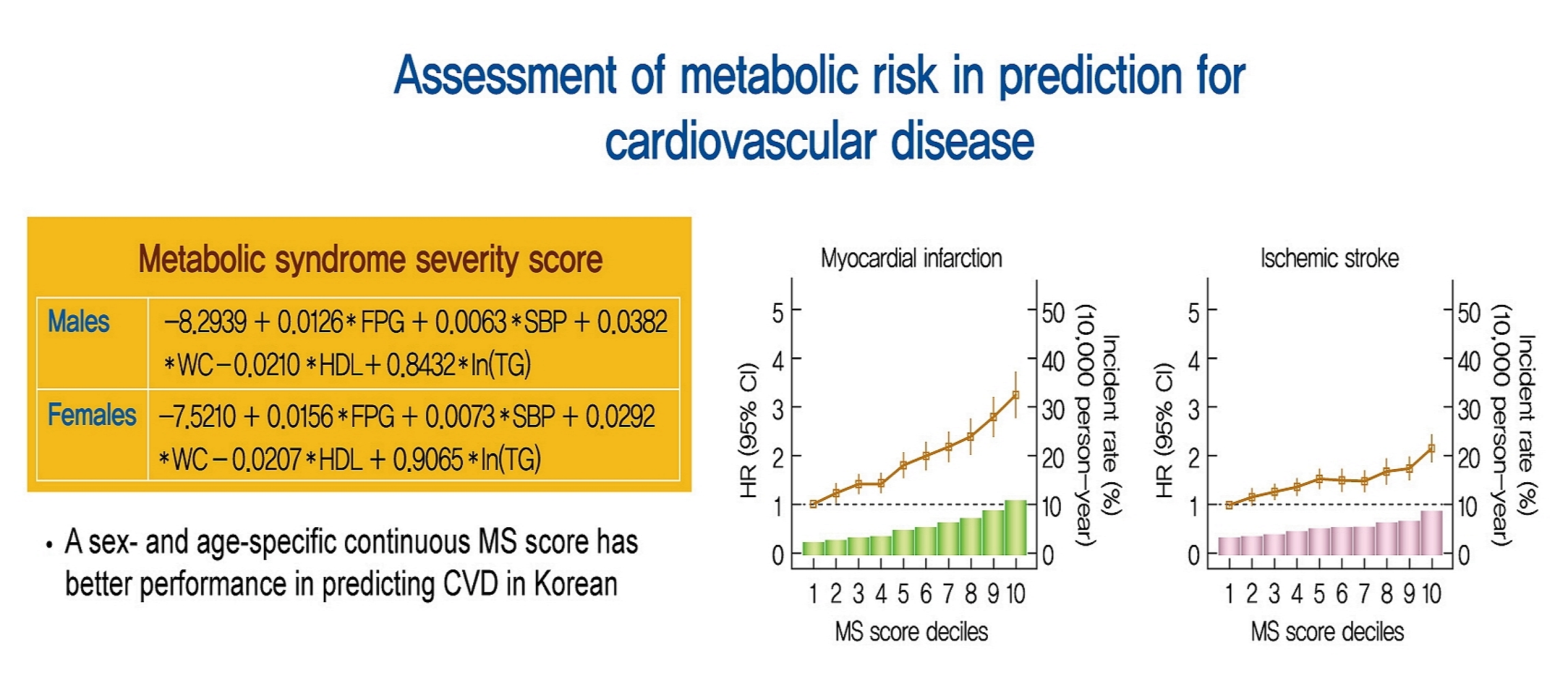
Recently, a metabolic syndrome severity score (MS score) using a dataset of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys has been developed. We aimed to determine whether the newly developed score is a significant predictor of cardiovascular (CV) events among the Korean population.
Methods
From the Korean National Health Insurance System, 2,541,364 (aged 40 to 59 years) subjects with no history of CV events (ischemic stroke or myocardial infarction [MI]), who underwent health examinations from 2009 to 2011 and were followed up until 2014 to 2017, were identified. Cox proportional hazard model was employed to investigate the association between MS score and CV events. Model performance of MS score for predicting CV events was compared to that of conventional metabolic syndrome diagnostic criteria (Adult Treatment Program III [ATP-III]) using the Akaike information criterion and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
Results
Over a median follow-up of 6 years, 15,762 cases of CV events were reported. MS score at baseline showed a linear association with incident CV events. In the multivariable-adjusted model, the hazard ratios (95% confidence intervals) comparing the highest versus lowest quartiles of MS score were 1.48 (1.36 to 1.60) for MI and 1.89 (1.74 to 2.05) for stroke. Model fitness and performance of the MS score in predicting CV events were superior to those of ATP-III.
Conclusion
The newly developed age- and sex-specific continuous MS score for the Korean population is an independent predictor of ischemic stroke and MI in Korean middle-aged adults even after adjusting for confounding factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic syndrome awareness in the general Korean population: results from a nationwide survey
Hyun-Jin Kim, Mi-Seung Shin, Kyung-Hee Kim, Mi-Hyang Jung, Dong-Hyuk Cho, Ju-Hee Lee, Kwang Kon Koh
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 39(2): 272. CrossRef - BMI-based metabolic syndrome severity score and arterial stiffness in a cohort Chinese study
Miao Wang, Chi Wang, Maoxiang Zhao, Shouling Wu, Hao Xue, Hongbin Liu
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between metabolic syndrome severity score and cardiovascular disease: results from a longitudinal cohort study on Chinese adults
Jing-jing Lin, Pin-yuan Dai, Jie Zhang, Yun-qi Guan, Wei-wei Gong, Min Yu, Le Fang, Ru-ying Hu, Qing-fang He, Na Li, Li-xin Wang, Ming-bin Liang, Jie-ming Zhong
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Omics biomarkers and an approach for their practical implementation to delineate health status for personalized nutrition strategies
Jaap Keijer, Xavier Escoté, Sebastià Galmés, Andreu Palou-March, Francisca Serra, Mona Adnan Aldubayan, Kristina Pigsborg, Faidon Magkos, Ella J. Baker, Philip C. Calder, Joanna Góralska, Urszula Razny, Malgorzata Malczewska-Malec, David Suñol, Mar Galofr
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Development and validation of a continuous metabolic syndrome severity score in the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
Mohammadjavad Honarvar, Safdar Masoumi, Ladan Mehran, Davood Khalili, Atieh Amouzegar, Fereidoun Azizi
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of metabolic syndrome, its severity with cognitive impairment among hemodialysis patients
Yuqi Yang, Qian Li, Yanjun Long, Jing Yuan, Yan Zha
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin serum levels and its association with clinical profile and carotid intima-media thickness in psoriasis: a cross-sectional study
Sofia Makishi Schlenker, Sofia Inez Munhoz, André Rochinski Busanello, Matheus Guedes Sanches, Barbara Stadler Kahlow, Renato Nisihara, Thelma Larocca Skare
Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia.2023; 98(6): 799. CrossRef - Cholecystectomy Increases the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in the Korean Population
Ji Hye Huh, Kyong Joo Lee, Yun Kyung Cho, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung-do Han, Dong Hee Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm
Annals of Surgery.2023; 278(2): e264. CrossRef - Cardiorespiratory Endurance is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Severity in Men
V. V. Sverchkov, E. V. Bykov
Journal Biomed.2023; 19(2): 61. CrossRef - Effect of a Wearable Device–Based Physical Activity Intervention in North Korean Refugees: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Kyoung Jin Kim, Kyeong Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jinhee Seo, Jung-Been Lee, Jae Hyun Bae, Nam Hoon Kim, Hee Young Kim, Soo-Kyung Lee, Sin Gon Kim
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2023; 25: e45975. CrossRef - Independent association between age- and sex-specific metabolic syndrome severity score and cardiovascular disease and mortality
Mohammadjavad Honarvar, Ladan Mehran, Safdar Masoumi, Sadaf Agahi, Shayesteh Khalili, Fereidoun Azizi, Atieh Amouzegar
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in Adults Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study Including More Than 4 Million Individuals From South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Sang Wook Park, Tae-Hwa Go, Dae Ryong Kang, Sang-Hak Lee, Jang-Young Kim
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-Glucose Index for the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study of 298,652 Individuals Receiving a Health Check-Up in China
Mingfei Jiang, Xiaoran Li, Huan Wu, Fan Su, Lei Cao, Xia Ren, Jian Hu, Grace Tatenda, Mingjia Cheng, Yufeng Wen, Hou De Zhou
International Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Changes in body composition, body balance, metabolic parameters and eating behavior among overweight and obese women due to adherence to the Pilates exercise program
Hyun Ju Kim, Jihyun Park, Mi Ri Ha, Ye Jin Kim, Chaerin Kim, Oh Yoen Kim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(6): 642. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Severity Score, Comparable to Serum Creatinine, Could Predict the Occurrence of End-Stage Kidney Disease in Patients with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis
Pil Gyu Park, Jung Yoon Pyo, Sung Soo Ahn, Jason Jungsik Song, Yong-Beom Park, Ji Hye Huh, Sang-Won Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(24): 5744. CrossRef
- Metabolic syndrome awareness in the general Korean population: results from a nationwide survey
- Drug/Regimen
- Cardiovascular Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors as Add-on to Metformin Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ja Young Jeon, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):505-514. Published online October 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0057
- 7,919 View
- 341 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
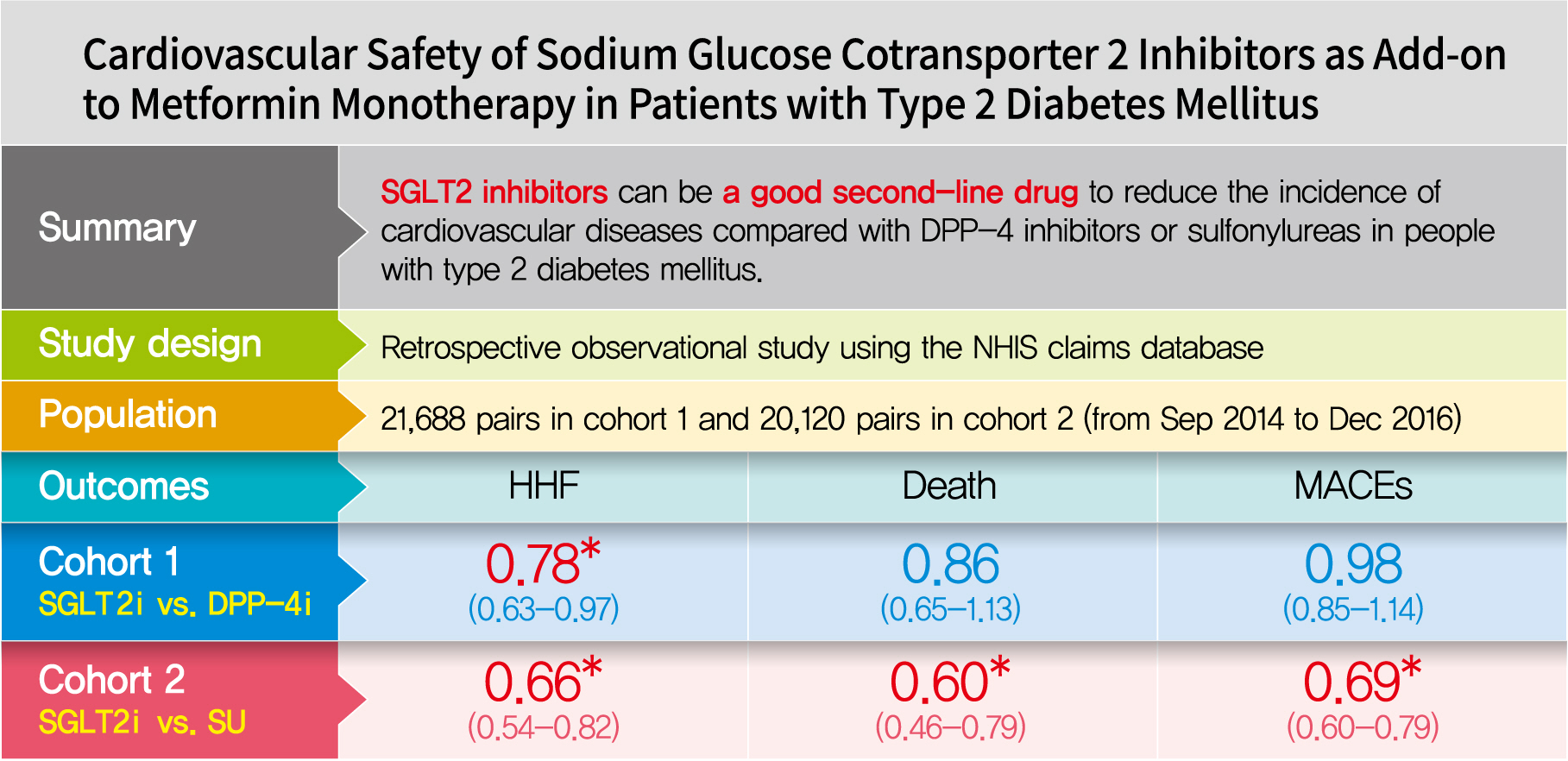
Using real-world data, cardiovascular safety was investigated in metformin users newly starting sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors compared with other glucose-lowering drugs in Korea.
Methods
This was a retrospective observational study using the National Health Insurance Service claims database in Korea. The study period was from September 2014 to December 2016. The study included subjects who were newly prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors or other glucose-lowering drugs while on metformin monotherapy; cohort 1 was composed of new users of SGLT2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors and cohort 2 included new users of SGLT2 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas. To balance the patient characteristics, propensity score matching was performed at a 1:1 ratio. Cardiovascular outcomes included hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), all-cause mortality, HHF plus all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and modified major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs).
Results
After propensity score matching, each cohort group was well balanced at baseline (21,688 pairs in cohort 1 and 20,120 pairs in cohort 2). As the second-line treatment, use of SGLT2 inhibitors was associated with a lower risk of HHF and HHF plus all-cause mortality compared with DPP-4 inhibitors. In addition, use of SGLT2 inhibitors versus sulfonylurea as add-on therapy to metformin was associated with decreased risks of HHF, all-cause mortality, HHF plus all-cause mortality, MI, stroke, and modified MACEs.
Conclusion
SGLT2 inhibitors can be a good second-line drug to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular diseases compared with DPP-4 inhibitors or sulfonylureas in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Advances in Research on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Targets and Therapeutic Agents
Jingqian Su, Yingsheng Luo, Shan Hu, Lu Tang, Songying Ouyang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13381. CrossRef - Cardioprotective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas in addition to metformin: A nationwide cohort study of patients with type 2 diabetes
Jui Wang, Hon-Yen Wu, Kuo-Liong Chien
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(3): 101299. CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ja Young Jeon, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(4): 614. CrossRef - The Impact of Novel Anti-Diabetic Medications on CV Outcomes: A New Therapeutic Horizon for Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Cardiac Patients
Israel Mazin, Fernando Chernomordik, Paul Fefer, Shlomi Matetzky, Roy Beigel
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(7): 1904. CrossRef - Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Inhibitors on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and Hospitalization for Heart Failure in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Atrial Fibrillation
Chang Hee Kwon, Ye-Jee Kim, Min-Ju Kim, Myung-Jin Cha, Min Soo Cho, Gi-Byoung Nam, Kee-Joon Choi, Jun Kim
The American Journal of Cardiology.2022; 178: 35. CrossRef - Using real-world data for supporting regulatory decision making: Comparison of cardiovascular and safety outcomes of an empagliflozin randomized clinical trial versus real-world data
Ha Young Jang, In-Wha Kim, Jung Mi Oh
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular Safety of SGLT2 Inhibitors Compared to DPP4 Inhibitors and Sulfonylureas as the Second-Line of Therapy in T2DM Using Large, Real-World Clinical Data in Korea
Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 502. CrossRef - The effect of sodium‐glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors on mortality and heart failure in randomized trials versus observational studies
Jesper Krogh, Carsten Hjorthøj, Søren L. Kristensen, Christian Selmer, Steen B. Haugaard
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes treated with SGLT-2 inhibitors versus DPP-4 inhibitors. An Italian real-world study in the context of other observational studies
Enrico Longato, Benedetta Maria Bonora, Barbara Di Camillo, Giovanni Sparacino, Lara Tramontan, Angelo Avogaro, Gian Paolo Fadini
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 179: 109024. CrossRef
- Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
- Cardiovascular risk/Epidemiology
- Clinical Impact of Dysglycemia in Patients with an Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Jae-Wook Chung, Yeong-Seon Park, Jeong-Eon Seo, Yeseul Son, Cheol-Woo Oh, Chan-Hee Lee, Jong-Ho Nam, Jung-Hee Lee, Jang-Won Son, Ung Kim, Jong-Seon Park, Kyu-Chang Won, Dong-Gu Shin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):270-274. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0164

- 5,661 View
- 119 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
This study aimed to determine the impact of dysglycemia on myocardial injury and cardiac dysfunction in acute myocardial infarctions (AMIs). From 2005 to 2016, a total of 1,593 patients with AMIs who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention were enrolled. The patients were classified into five groups according to the admission glucose level: ≤80, 81 to 140, 141 to 200, 201 to 260, and ≥261 mg/dL. The clinical and echocardiographic parameters and 30-day mortality were analyzed. The peak troponin I and white blood cell levels had a positive linear relationship to the admission glucose level. The left ventricular ejection fraction had an inverted
U -shape trend, and the E/E' ratio wasU -shaped based on euglycemia. The 30-day mortality also increased as the admission glucose increased, and the cut-off value for predicting the mortality was 202.5 mg/dL. Dysglycemia, especially hyperglycemia, appears to be associated with myocardial injury and could be another adjunctive parameter for predicting mortality in patients with AMIs.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in Adults Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study Including More Than 4 Million Individuals From South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Sang Wook Park, Tae-Hwa Go, Dae Ryong Kang, Sang-Hak Lee, Jang-Young Kim
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of admission hyperglycemia and all-cause mortality in acute myocardial infarction with percutaneous coronary intervention: A dose–response meta-analysis
Shao-Yong Cheng, Hao Wang, Shi-Hua Lin, Jin-Hui Wen, Ling-Ling Ma, Xiao-Ce Dai
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fenofibrate add-on to statin treatment is associated with low all-cause death and cardiovascular disease in the general population with high triglyceride levels
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155327. CrossRef - Basic types of the first-day glycemia in acute myocardial infarction: Prognostic, diagnostic, threshold and target glycemia
Goran Koracevic, Milan Djordjevic
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(3): 614. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Dysglycemia in Patients with an Acute Myocardial Infarction (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:270-4)
Bo-Yeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 787. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Dysglycemia in Patients with an Acute Myocardial Infarction (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:270-4)
Chan-Hee Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 791. CrossRef - The Effects of Glucose Lowering Agents on the Secondary Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 977. CrossRef - Effect of Admission Hyperglycemia on Short-Term Prognosis of Patients with Non-ST Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome without Diabetes Mellitus
Wei Liu, Zhijuan Li, Shiying Xing, Yanwei Xu, Gaetano Santulli
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in Adults Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study Including More Than 4 Million Individuals From South Korea
- Others
- Hemorheologic Alterations in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Presented with an Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Kyu-Hwan Park, Ung Kim, Kang-Un Choi, Jong-Ho Nam, Jung-Hee Lee, Chan-Hee Lee, Jang-Won Son, Jong-Seon Park, Dong-Gu Shin, Kyu-Chang Won, Jun Sung Moon, Yu Kyung Kim, Jang-Soo Suh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):155-163. Published online March 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.155
- 4,270 View
- 41 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Hemorheologic indices are known to be related to vascular complications in variable clinical settings. However, little is known about the associations between hemorheologic parameters and acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the changes of hemorheologic environment inside of blood using hemorheologic parameters, especially the elongation index (EI) and critical shear stress (CSS) in diabetics with versus without AMI.
Methods A total of 195 patients with T2DM were enrolled. Patients were divided into the study group with AMI (AMI+,
n =77) and control group (AMI−,n =118) who had no history of coronary artery disease. Hemorheologic parameters such as EI and CSS were measured and compared between the two groups.Results The EI was lower (30.44%±1.77% in AMI+ and 31.47%±1.48% in AMI−,
P <0.001) but the level of CSS was higher (316.13±108.20 mPa in AMI+ and 286.80±85.34 mPa in AMI−,P =0.040) in the AMI+. The CSS was significantly related to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (R 2=0.497,P <0.001) and use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (R 2=0.574,P =0.048).Conclusion Diabetics with AMI resulted in adverse hemorheologic changes with lower EI and higher CSS compared to diabetic subjects without AMI. Evaluation of the hemorheologic parameters may provide valuable supplementary information for managing patients with AMI and T2DM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Alpha-SNAP (M105I) mutation promotes neuronal differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells through overactivation of AMPK
Felipe A. Bustamante-Barrientos, Maxs Méndez-Ruette, Luis Molina, Tania Koning, Pamela Ehrenfeld, Carlos B. González, Ursula Wyneken, Roberto Henzi, Luis Federico Bátiz
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Red Cell Distribution Width and Elongation Index in a Cohort of Patients With Juvenile Acute Myocardial Infarction
Gregorio Caimi, Rosalia Lo Presti, Egle Corrado, Maria Montana, Melania Carlisi
Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Zinc improved erythrocyte deformability and aggregation in patients with beta-thalassemia: An in vitro study
Mukaddes Sinan, Ozlem Yalcin, Zeynep Karakas, Evrim Goksel, Nesrin Zeynep Ertan
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2023; 85(1): 1. CrossRef - Improved Erythrocyte Deformability Induced by Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Minkook Son, Ye Sung Lee, A Ram Hong, Jee Hee Yoon, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sung Yang
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy.2022; 36(1): 59. CrossRef - Change of RBC Deformability During Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Yu Kyung Kim, Jae Min Lee
Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.2022; 44(2): e329. CrossRef - Hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit and red blood cell count predict major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia
Martine Paquette, Sophie Bernard, Alexis Baass
Atherosclerosis.2021; 335: 41. CrossRef - Erythrocyte deformability reduction in various pediatric hematologic diseases
Yu Kyung Kim, Young Tae Lim, Jang Soo Suh, Jeong Ok Hah, Jae Min Lee
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2020; 75(3): 361. CrossRef - Fasting Plasma Glucose Variability and Gastric Cancer Risk in Individuals Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
So-hyeon Hong, Eunjin Noh, Jinsil Kim, Soon Young Hwang, Jun A. Kim, You-Bin Lee, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology.2020; 11(9): e00221. CrossRef - Use of RBC deformability index as an early marker of diabetic nephropathy
Sang Bae Lee, Yu-Sik Kim, Jung Hye Kim, Kahui Park, Ji Sun Nam, Shinae Kang, Jong Suk Park, Sehyun Shin, Chul Woo Ahn
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2019; 72(1): 75. CrossRef - Haemorheological and haemostatic alterations in coeliac disease and inflammatory bowel disease in comparison with non-coeliac, non-IBD subjects (HERMES): a case–control study protocol
Zsolt Szakács, Beáta Csiszár, Péter Kenyeres, Patrícia Sarlós, Bálint Erőss, Alizadeh Hussain, Ágnes Nagy, Balázs Kőszegi, Ibolya Veczák, Nelli Farkas, Emőke Bódis, Katalin Márta, Andrea Szentesi, Margit Tőkés-Füzesi, Tímea Berki, Áron Vincze, Kálmán Tóth
BMJ Open.2019; 9(3): e026315. CrossRef - Potential Diagnostic Hemorheological Indexes for Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Hoyoon Lee, Wonwhi Na, Sang Bae Lee, Chul Woo Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Kyu Chang Won, Sehyun Shin
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - PREVALENCE AND FORECASTING OF ALIMENTARY RISK FACTORS AMONG PATIENTS WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
A. V. Ivanenko, R. S. Goloschapov-Aksenov, Dmitry I. Kicha
Hygiene and sanitation.2019; 98(8): 873. CrossRef
- Alpha-SNAP (M105I) mutation promotes neuronal differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells through overactivation of AMPK
- An Autopsy Case of Diabetes Mellitus with Extensive Atherosclerotic Complication.
- Seok Hyung Kim, Jeong Wook Seo, In Ae Park, Seong Hoe Park, Eui Keun Ham, Hyun Soon Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2000;24(1):97-101. Published online January 1, 2001
- 872 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
A variety of circulatory abnormalities including atherosclerosis is a major complication of diabetes mellitus. In contrast to Western countries, incidence of extensive atherosclerotic complication is thought to be very low in Korean diabetic patients. METHODS: Recently, we have experienced an autopsy case of 66-year-old male with type 2 diabetes mellitus having severe atherosclerosis in major arteriss. RESULTS: Autopsy examination revealed severe ulcerative atherosclerosis in aorta and atheromatous embolization in numerous small and medium sized arteries of lung, kidney, liver, and intestine. Multiple old infarcts were noticed in myocardium and brain. In addition, severe diabetic nephropathy and pyelonephritis were also observed in kidneys. CONCLUSION: The cause of death in this case is assumed to be myocaridial infarction associated with obstruction of coronary arteries. This case suggests that incidence of extensive atherosclerosis in Korean diabetic patients may not be rare, if autopsy examination are performed more thoroughly on these patients.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





