
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Alogliptin-Pioglitazone Combination for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Poorly Controlled with Metformin: A Multicenter, Double-Blind Randomized Trial
- Ji-Yeon Park, Joonyub Lee, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kyung Wan Min, Kyung Ah Han, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soo Lim, Young-Hyun Kim, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Mook Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, the Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) study investigators
- Received August 7, 2023 Accepted November 30, 2023 Published online April 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0259 [Epub ahead of print]

- 198 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Guidelines for switching to triple combination therapy directly after monotherapy failure are limited. This study investigated the efficacy, long-term sustainability, and safety of either mono or dual add-on therapy using alogliptin and pioglitazone for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who did not achieve their target glycemic range with metformin monotherapy.
Methods
The Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) was a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial. A total of 214 participants were randomized to receive alogliptin+pioglitazone (Alo+Pio group, n=70), alogliptin (Alo group, n=75), or pioglitazone (Pio group, n=69). The primary outcome was the difference in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels between the three groups at baseline to 24 weeks. For durability, the achievement of HbA1c levels <7% and <6.5% was compared in each group. The number of adverse events was investigated for safety.
Results
After 24 weeks of treatment, the change of HbA1c in the Alo+Pio, Alo, and Pio groups were –1.38%±0.08%, –1.03%±0.08%, and –0.84%±0.08%, respectively. The Alo+Pio group had significantly lower HbA1c levels than the other groups (P=0.0063, P<0.0001) and had a higher proportion of patients with target HbA1c achievement. In addition, insulin sensitivity and β-cell function, lipid profiles, and other metabolic indicators were also improved. There were no significant safety issues in patients treated with triple combination therapy.
Conclusion
Early combination triple therapy showed better efficacy and durability than the single add-on (dual) therapy. Therefore, combination therapy with metformin, alogliptin, and pioglitazone is a valuable early treatment option for T2DM poorly controlled with metformin monotherapy.
- Drug Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extension
- Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):808-817. Published online September 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0387
- 2,576 View
- 281 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
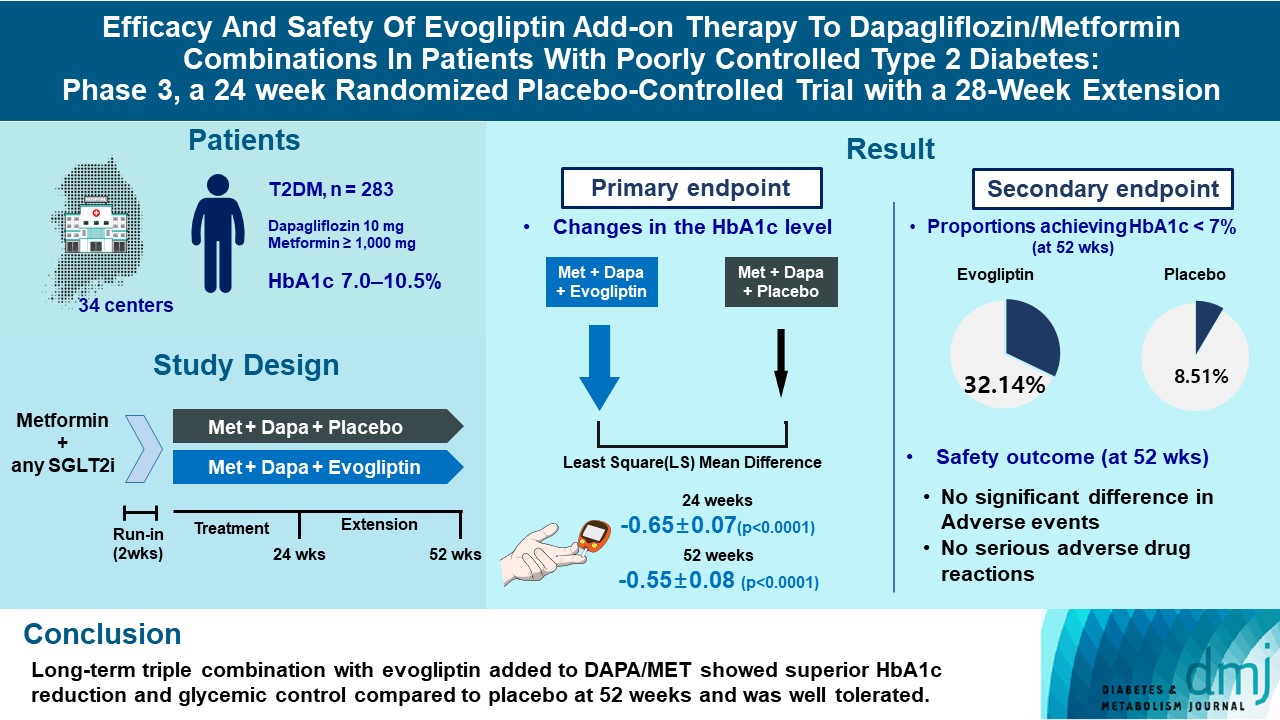
This study investigates the long-term efficacy and safety of evogliptin add-on therapy in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) previously received dapagliflozin and metformin (DAPA/MET) combination.
Methods
In this multicenter randomized placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, patients with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels 7.0% to 10.5% (n=283) previously used DAPA 10 mg plus MET (≥1,000 mg) were randomly assigned to the evogliptin 5 mg once daily or placebo group (1:1). The primary endpoint was the difference in the HbA1c level from baseline at week 24, and exploratory endpoints included the efficacy and safety of evogliptin over 52 weeks (trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04170998).
Results
Evogliptin add-on to DAPA/MET therapy was superior in HbA1c reduction compared to placebo at weeks 24 and 52 (least square [LS] mean difference, –0.65% and –0.55%; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.79 to –0.51 and –0.71 to –0.39; P<0.0001). The proportion of patients achieving HbA1c <7% was higher in the triple combination group at week 52 (32.14% vs. 8.51% in placebo; odds ratio, 5.62; P<0.0001). Evogliptin significantly reduced the fasting glucose levels and mean daily glucose levels with improvement in homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function (LS mean difference, 9.04; 95% CI, 1.86 to 16.21; P=0.0138). Adverse events were similar between the groups, and no serious adverse drug reactions were reported in the evogliptin group.
Conclusion
Long-term triple combination with evogliptin added to DAPA/MET showed superior HbA1c reduction and glycemic control compared to placebo at 52 weeks and was well tolerated.
- Drug Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Enavogliflozin versus Dapagliflozin as Add-on to Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial
- Kyung Ah Han, Yong Hyun Kim, Doo Man Kim, Byung Wan Lee, Suk Chon, Tae Seo Sohn, In Kyung Jeong, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, Jae Jin Nah, Hwa Rang Song, Seong In Cho, Seung-Ah Cho, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):796-807. Published online February 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0315
- 40,043 View
- 572 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
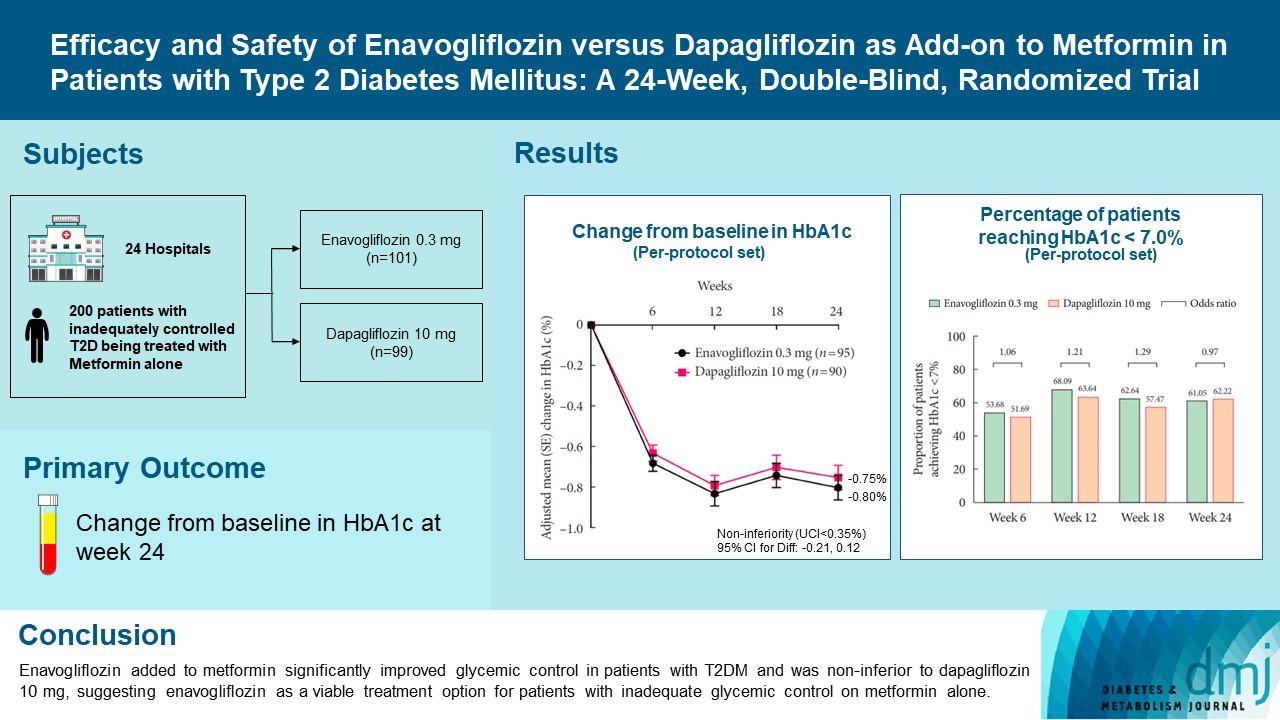
Enavogliflozin is a novel sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor currently under clinical development. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin as an add-on to metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) against dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this multicenter, double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study, 200 patients were randomized to receive enavogliflozin 0.3 mg/day (n=101) or dapagliflozin 10 mg/day (n=99) in addition to ongoing metformin therapy for 24 weeks. The primary objective of the study was to prove the non-inferiority of enavogliflozin to dapagliflozin in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) change at week 24 (non-inferiority margin of 0.35%) (Clinical trial registration number: NCT04634500).
Results
Adjusted mean change of HbA1c at week 24 was –0.80% with enavogliflozin and –0.75% with dapagliflozin (difference, –0.04%; 95% confidence interval, –0.21% to 0.12%). Percentages of patients achieving HbA1c <7.0% were 61% and 62%, respectively. Adjusted mean change of fasting plasma glucose at week 24 was –32.53 and –29.14 mg/dL. An increase in urine glucose-creatinine ratio (60.48 vs. 44.94, P<0.0001) and decrease in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (–1.85 vs. –1.31, P=0.0041) were significantly greater with enavogliflozin than dapagliflozin at week 24. Beneficial effects of enavogliflozin on body weight (–3.77 kg vs. –3.58 kg) and blood pressure (systolic/diastolic, –5.93/–5.41 mm Hg vs. –6.57/–4.26 mm Hg) were comparable with those of dapagliflozin, and both drugs were safe and well-tolerated.
Conclusion
Enavogliflozin added to metformin significantly improved glycemic control in patients with T2DM and was non-inferior to dapagliflozin 10 mg, suggesting enavogliflozin as a viable treatment option for patients with inadequate glycemic control on metformin alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
Young Sang Lyu, Sangmo Hong, Si Eun Lee, Bo Young Cho, Cheol-Young Park
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A 52‐week efficacy and safety study of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin as an add‐on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: ENHANCE‐M extension study
Tae Seo Sohn, Kyung‐Ah Han, Yonghyun Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee, Suk Chon, In‐Kyung Jeong, Eun‐Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, JaeJin Na, Jae Min Cho, Seong In Cho, Wan Huh, Kun‐Ho Yoon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of renal function on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of enavogliflozin, a potent and selective sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes
Sae Im Jeong, Mu Seong Ban, Jun‐Gi Hwang, Min‐Kyu Park, Soo Lim, Sejoong Kim, Soon Kil Kwon, Yoonjin Kim, Jae Min Cho, Jae Jin Na, Wan Huh, Jae‐Yong Chung
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of novel sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor enavogliflozin in type-2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, B.G. Harish, Beatrice Anne, Lakshmi Nagendra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(8): 102816. CrossRef - Characteristics of the Latest Therapeutic Agent for Diabetes
Nuri Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 148. CrossRef - Prospects of using sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)
Iryna Kostitska, Nadia Protas, Liliia Petrovska
Diabetes Obesity Metabolic Syndrome.2023; (5): 8. CrossRef - Navigating the Future of Diabetes Treatment with New Drugs: Focusing on the Possibilities and Prospects of Enavogliflozin
Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 769. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
- Drug/Regimen
- Long-Term Glycaemic Durability of Early Combination Therapy Strategy versus Metformin Monotherapy in Korean Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Soon-Jib Yoo, Sang-Ah Chang, Tae Seo Sohn, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Jong Min Lee, Sungdae Moon, Pieter Proot, Päivi M Paldánius, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):954-959. Published online November 12, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0173
- 55,052 View
- 367 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
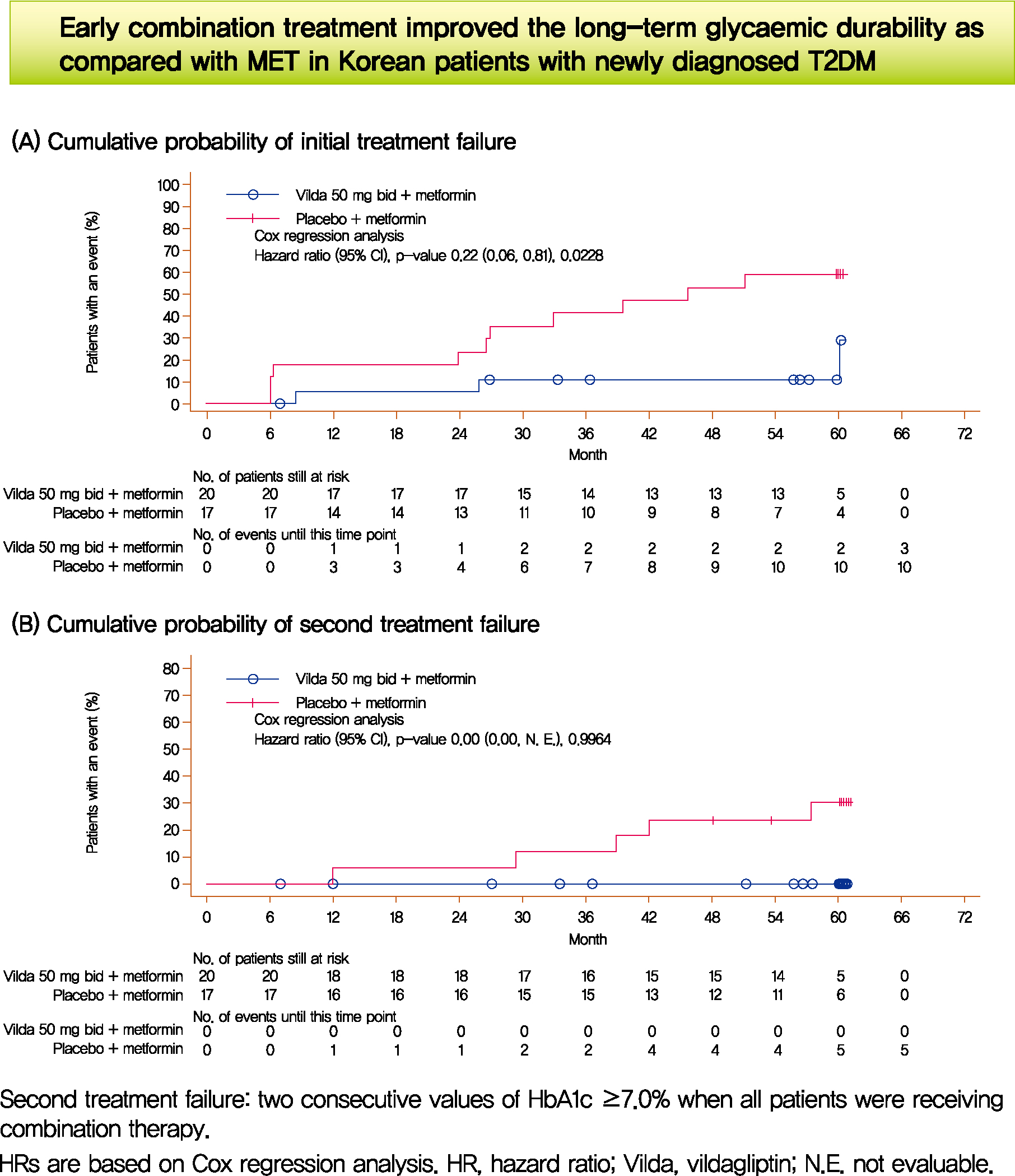
- We assessed the glycaemic durability with early combination (EC; vildagliptin+metformin [MET], n=22) versus MET monotherapy (n=17), among newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) enrolled (between 2012 and 2014) in the VERIFY study from Korea (n=39). Primary endpoint was time to initial treatment failure (TF) (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] ≥7.0% at two consecutive scheduled visits after randomization [end of period 1]). Time to second TF was assessed when both groups were receiving and failing on the combination (end of period 2). With EC the risk of initial TF significantly reduced by 78% compared to MET (n=3 [15%] vs. n=10 [58.7%], P=0.0228). No secondary TF occurred in EC group versus five patients (29.4%) in MET. Patients receiving EC treatment achieved consistently lower HbA1c levels. Both treatment approaches were well tolerated with no hypoglycaemic events. In Korean patients with newly diagnosed T2DM, EC treatment significantly and consistently improved the long-term glycaemic durability as compared with MET.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 461. CrossRef
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Drug/Regimen
- Evaluating the Evidence behind the Novel Strategy of Early Combination from Vision to Implementation
- Päivi Maria Paldánius
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):785-801. Published online September 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0179
- 7,109 View
- 287 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a complex and progressive chronic disease characterised by elevating hyperglycaemia and associated need to gradually intensify therapy in order to achieve and maintain glycaemic control. Treating hyperglycaemia with sequential therapy is proposed to allow holistic assessment of the efficacy and risk-to-benefit ratio of each added component. However, there is an array of evidence supporting the scientific rationale for using synergistic, earlier, modern drug combinations to achieve glycaemic goals, delay the deterioration of glycaemic control, and, therefore, potentially preserve or slow down the declining β-cell function. Additionally, implementation of early combination(s) may lead to opportunities to combat clinical inertia and other hurdles to optimised disease management outcomes. This review aims to discuss the latest empirical evidence for long-term clinical benefits of this novel strategy of early combination in people with newly diagnosed T2DM versus the current widely-implemented treatment paradigm, which focuses on control of hyperglycaemia using lifestyle interventions followed by sequentially intensified (mostly metformin-based) monotherapy. The recent reported Vildagliptin Efficacy in combination with metfoRmin For earlY treatment of T2DM (VERIFY) study results have provided significant new evidence confirming long-term glycaemic durability and tolerability of a specific early combination in the management of newly diagnosed, treatment-naïve patients worldwide. These results have also contributed to changes in clinical treatment guidelines and standards of care while clinical implementation and individualised treatment decisions based on VERIFY results might face barriers beyond the existing scientific evidence.
- Drug/Regimen
- Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats
- Sun Hee Kim, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):842-853. Published online May 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0190
- 6,146 View
- 177 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Metformin is widely marketed medication for the treatment of diabetes, but its pharmacological effect on diabetic peripheral neuropathy remains unclear. In this study, the effect of metformin on peripheral nerves in diabetic rats was investigated using diverse neuronal parameters of nerve fibers.
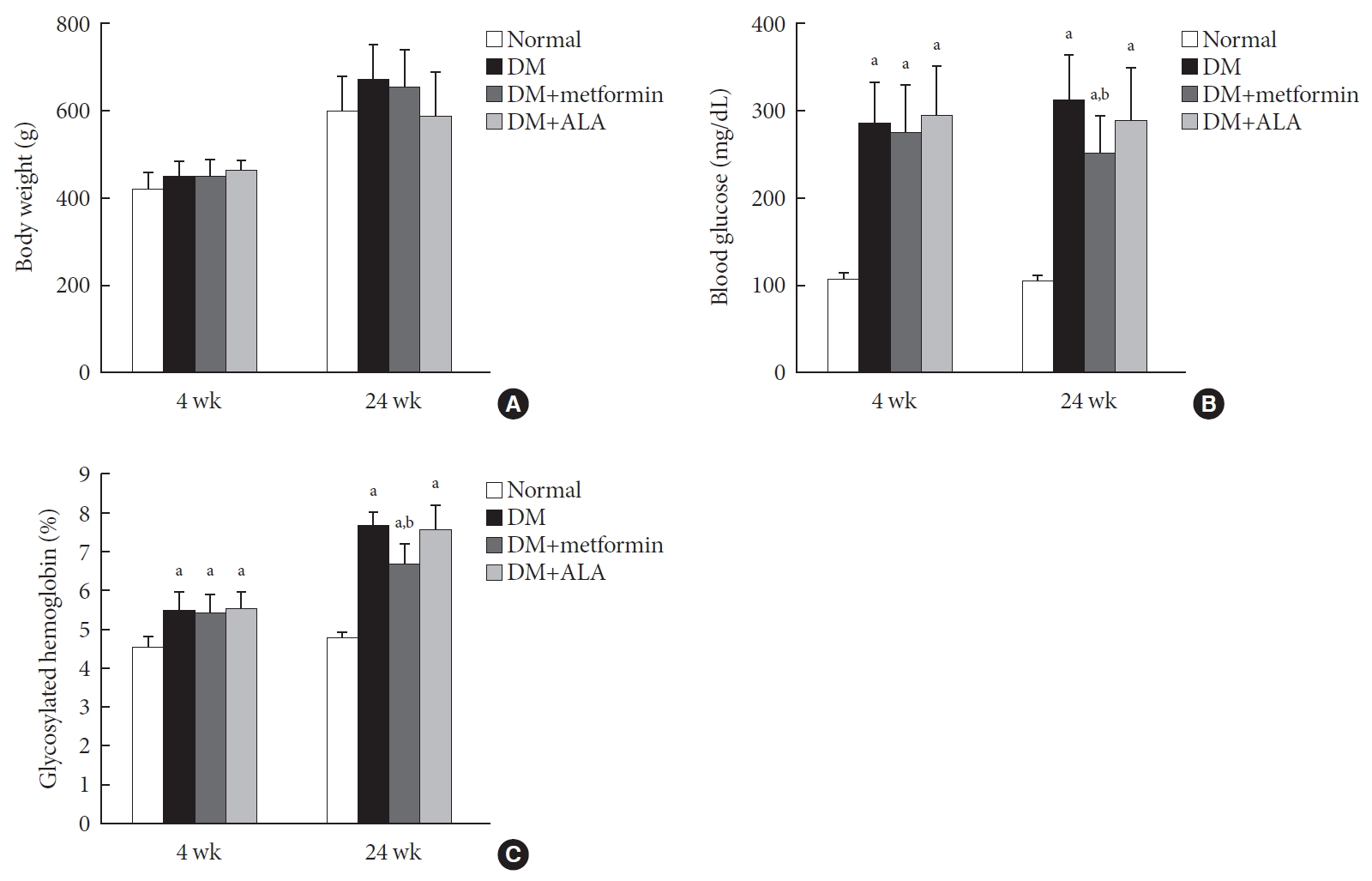
Methods Rats were assigned to one of four groups (
n =7 to 10 per group): normal, diabetes mellitus (DM), DM+metformin (100 mg/kg), and DM+alpha lipoic acid (ALA, 100 mg/kg). DM was induced by streptozotocin/high-fat diet (STZ/HFD). After 12 weeks, the sensory thresholds to mechanical and heat stimuli were assessed. Repeated sensory tests, immunofluorescence microscopic comparison of peripheral nerves, and biochemical blood analysis were performed after 24 weeks.Results Both DM+metformin and DM+ALA groups showed similar trends to diverse sensory tests at 24 weeks compared to DM group although the degree of change were different according to the stimulated senses. There was no significant difference in the comparison of the intraepidermal nerve fiber density (IENFD) of peripheral nerves between the DM+metformin and DM+ALA groups (11.83±0.07 fibers/mm vs. 12.37±1.82 fibers/mm, respectively). Both groups showed preserved IENFD significantly compared with DM group (8.46±1.98 fibers/mm,
P <0.05). Sciatic nerve morphology of the experimental animals showed a similar trend to the IENFD, with respect to axonal diameter, myelin sheath thickness, and myelinated fiber diameter.Conclusion Metformin has beneficial pharmacological effects on the preservation of peripheral nerves in diabetic rats and its effects are comparable to those of ALA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metformin improves diabetic neuropathy by reducing inflammation through up-regulating the expression of miR-146a and suppressing oxidative stress
Fengmin Liu, Fangqin You, Lihang Yang, Siyun Wang, Diya Xie
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2024; : 108737. CrossRef - Effect of Metformin on the Functional and Electrophysiological Recovery of Crush Injury-Induced Facial Nerve Paralysis in Diabetic Rats
Kyung Hoon Sun, Cheol Hee Choi, Gwang-Won Cho, Chul Ho Jang
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(9): 1317. CrossRef - Is metformin neuroprotective against diabetes mellitus-induced neurodegeneration? An updated graphical review of molecular basis
Fatemeh Karami, Hamidreza Jamaati, Natalie Coleman-Fuller, Maryam Shokrian Zeini, A. Wallace Hayes, Mina Gholami, Mahsa Salehirad, Mohammad Darabi, Majid Motaghinejad
Pharmacological Reports.2023; 75(3): 511. CrossRef - Early Diagnosis through Estimation of Inflammatory Biomarkers and the Neuroprotective Role of Metformin in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Laxmi Sri, Prabhakar Orsu
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Nanotechnology(IJPSN).2023; 16(2): 6427. CrossRef - Bidirectional association between diabetic peripheral neuropathy and vitamin B12 deficiency: Two longitudinal 9-year follow-up studies using a national sample cohort
Heung Yong Jin, Kyung Ae Lee, Yu Ji Kim, In Sun Gwak, Tae Sun Park, Sang Woo Yeom, Jong Seung Kim
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(5): 436. CrossRef - An overview of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Diagnosis and treatment advancements
Jonathan M. Hagedorn, Alyson M. Engle, Tony K. George, Jay Karri, Newaj Abdullah, Erik Ovrom, Jhon E. Bocanegra-Becerra, Ryan S. D'Souza
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 188: 109928. CrossRef - The role of MicroRNA networks in tissue-specific direct and indirect effects of metformin and its application
Qinzhi Yang, Gang Wang, Dan Fang, Xiaojun Gao, Yu Liang, Liqun Wang, Jianbo Wu, Min Zeng, Mao Luo
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 151: 113130. CrossRef - Is metformin a possible treatment for diabetic neuropathy?
Juechun Wei, Yanling Wei, Meiyan Huang, Peng Wang, Shushan Jia
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(10): 658. CrossRef - Metformin as a potential therapeutic for neurological disease: mobilizing AMPK to repair the nervous system
Sarah Demaré, Asha Kothari, Nigel A. Calcutt, Paul Fernyhough
Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics.2021; 21(1): 45. CrossRef - Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53)
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 125. CrossRef - Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53)
Sun Hee Kim, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 127. CrossRef - Impacts of statin and metformin on neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Korean Health Insurance data
Hong Ki Min, Se Hee Kim, Jong Han Choi, Kyomin Choi, Hae-Rim Kim, Sang-Heon Lee
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(33): 10198. CrossRef
- Metformin improves diabetic neuropathy by reducing inflammation through up-regulating the expression of miR-146a and suppressing oxidative stress
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Metformin Treatment for Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
- Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):3-10. Published online February 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0004
- 9,462 View
- 332 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
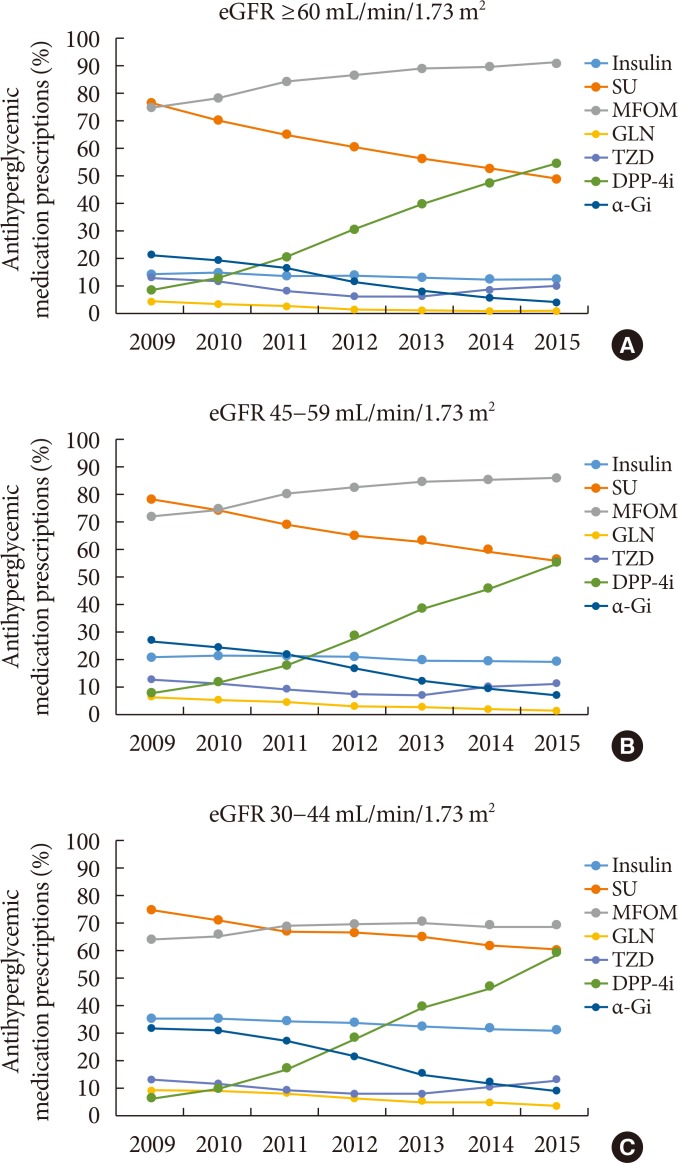
PubReader The safety of metformin use for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and advanced kidney disease is controversial, and more recent guidelines have suggested that metformin be used cautiously in this group until more definitive evidence concerning its safety is available. The Korean Diabetes Association and the Korean Society of Nephrology have agreed on consensus statements concerning metformin use for patients with T2DM and renal dysfunction, particularly when these patients undergo imaging studies using iodinated contrast media (ICM). Metformin can be used safely when the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is ≥45 mL/min/1.73 m2. If the eGFR is between 30 and 44 mL/min/1.73 m2, metformin treatment should not be started. If metformin is already in use, a daily dose of ≤1,000 mg is recommended. Metformin is contraindicated when the eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2. Renal function should be evaluated prior to any ICM-related procedures. During procedures involving intravenous administration of ICM, metformin should be discontinued starting the day of the procedures and up to 48 hours post-procedures if the eGFR is <60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Distribution and elimination kinetics of midazolam and metabolites after post-resuscitation care: a prospective observational study
Wonjoon Jeong, Jung Sunwoo, Yeonho You, Jung Soo Park, Jin Hong Min, Yong Nam In, Hong Joon Ahn, So Young Jeon, Jang Hee Hong, Ji Hye Song, Hyein Kang, My Tuyen Thi Nguyen, Jaehan Kim, Changshin Kang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction of glycosylated hemoglobin level in patients with cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus with respect to anti-diabetic medication
Alisher Ikramov, Shakhnoza Mukhtarova, Raisa Trigulova, Dilnoza Alimova, Saodat Abdullaeva
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of vitamin B12 deficiency in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus — A primary-care retrospective cohort study
Andrew Kien Han Wee, Rehena Sultana
BMC Primary Care.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors for post-contrast acute kidney injury in patients sequentially administered iodine- and gadolinium-based contrast media on the same visit to the emergency department: a retrospective study
Changshin Kang, Soo Hyun Han, Jung Soo Park, Dae Eun Choi
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 42(3): 358. CrossRef - Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus in patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemia
Mohammad E. Khamseh, Mojtaba Malek, Nahid Hashemi-madani, Fariba Ghassemi, Neda Rahimian, Amir Ziaee, Mohammad Reza Foroughi-Gilvaee, Pooya Faranoush, Negin Sadighnia, Ali Elahinia, Mohammad Reza Rezvany, Mohammad Faranoush
Iranian Journal of Blood and Cancer.2023; 15(4): 293. CrossRef - Continuous use of metformin in patients receiving contrast medium: what is the evidence? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Ting-Wan Kao, Kuo-Hua Lee, Wing P. Chan, Kang-Chih Fan, Che-Wei Liu, Yu-Chen Huang
European Radiology.2022; 32(5): 3045. CrossRef - Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease: The Past, Present, and Future
Filipe Ferrari, Rafael S. Scheffel, Vítor M. Martins, Raul D. Santos, Ricardo Stein
American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs.2022; 22(4): 363. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Lobeglitazone Versus Pioglitazone on Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(1): 171. CrossRef - Treatment Patterns of Type 2 Diabetes Assessed Using a Common Data Model Based on Electronic Health Records of 2000–2019
Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Yu Ji Kim, Yong-Jin Im, Eun-Young Kim, Tae Sun Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:698-707)
Eugene Han, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 972. CrossRef - KRCP's past and future path
Tae-Hyun Yoo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 39(3): 233. CrossRef - Metformin Use and Risk of All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yao Hu, Min Lei, Guibao Ke, Xin Huang, Xuan Peng, Lihui Zhong, Ping Fu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacotherapy for patients with diabetes mellitus
Joon Ho Moon, Soo Lim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2020; 63(12): 766. CrossRef
- Distribution and elimination kinetics of midazolam and metabolites after post-resuscitation care: a prospective observational study
- Pathophysiology
- Metformin Ameliorates Lipotoxic β-Cell Dysfunction through a Concentration-Dependent Dual Mechanism of Action
- Hong Il Kim, Ji Seon Lee, Byung Kook Kwak, Won Min Hwang, Min Joo Kim, Young-Bum Kim, Sung Soo Chung, Kyong Soo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):854-866. Published online June 27, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0179
- 6,651 View
- 115 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Chronic exposure to elevated levels of free fatty acids contributes to pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. Although it is well known that metformin induces cellular energy depletion and a concomitant activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) through inhibition of the respiratory chain, previous studies have shown inconsistent results with regard to the action of metformin on pancreatic β-cells. We therefore examined the effects of metformin on pancreatic β-cells under lipotoxic stress.
Methods NIT-1 cells and mouse islets were exposed to palmitate and treated with 0.05 and 0.5 mM metformin. Cell viability, glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, cellular adenosine triphosphate, reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and Rho kinase (ROCK) activities were measured. The phosphorylation of AMPK was evaluated by Western blot analysis and mRNA levels of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress markers and NADPH oxidase (NOX) were measured by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis.
Results We found that metformin has protective effects on palmitate-induced β-cell dysfunction. Metformin at a concentration of 0.05 mM inhibits NOX and suppresses the palmitate-induced elevation of ER stress markers and ROS levels in a AMPK-independent manner, whereas 0.5 mM metformin inhibits ROCK activity and activates AMPK.
Conclusion This study suggests that the action of metformin on β-cell lipotoxicity was implemented by different molecular pathways depending on its concentration. Metformin at a usual therapeutic dose is supposed to alleviate lipotoxic β-cell dysfunction through inhibition of oxidative stress and ER stress.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metformin enhances METTL14-Mediated m6A methylation to alleviate NIT-1 cells apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide
Si-min Zhou, Xin-ming Yao, Yi Cheng, Yu-jie Xing, Yue Sun, Qiang Hua, Shu-jun Wan, Xiang-jian Meng
Heliyon.2024; 10(2): e24432. CrossRef - Reduced Expression Level of Protein PhosphatasePPM1EServes to Maintain Insulin Secretion in Type 2 Diabetes
Sevda Gheibi, Luis Rodrigo Cataldo, Alexander Hamilton, Mi Huang, Sebastian Kalamajski, Malin Fex, Hindrik Mulder
Diabetes.2023; 72(4): 455. CrossRef - Metformin restores prohormone processing enzymes and normalizes aberrations in secretion of proinsulin and insulin in palmitate‐exposed human islets
Quan Wen, Azazul Islam Chowdhury, Banu Aydin, Mudhir Shekha, Rasmus Stenlid, Anders Forslund, Peter Bergsten
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(12): 3757. CrossRef - Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with stem cells and antidiabetic drugs: a dualistic and future-focused approach
Priyamvada Amol Arte, Kanchanlata Tungare, Mustansir Bhori, Renitta Jobby, Jyotirmoi Aich
Human Cell.2023; 37(1): 54. CrossRef - Metformin disrupts insulin secretion, causes proapoptotic and oxidative effects in rat pancreatic beta‐cells in vitro
Maíra M.R. Valle, Eloisa Aparecida Vilas‐Boas, Camila F. Lucena, Simone A. Teixeira, Marcelo N. Muscara, Angelo R. Carpinelli
Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Protection by metformin against severe Covid-19: An in-depth mechanistic analysis
Nicolas Wiernsperger, Abdallah Al-Salameh, Bertrand Cariou, Jean-Daniel Lalau
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(4): 101359. CrossRef - Insight Into Rho Kinase Isoforms in Obesity and Energy Homeostasis
Lei Wei, Jianjian Shi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Overexpression of miR-297b-5p Promotes Metformin-Mediated Protection Against Stearic Acid-Induced Senescence by Targeting Igf1r
Qingrui Zhao, Shenghan Su, Yuqing Lin, Xuebei Li, Lingfeng Dan, Yunjin Zhang, Chunxiao Yang, Xiaohan Li, Yimeng Dong, Chenchen Geng, Changhao Sun, Xia Chu, Huimin Lu
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metformin Dysregulates the Unfolded Protein Response and the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway in Endometrial Cancer Cells through an AMPK-Independent Mechanism
Domenico Conza, Paola Mirra, Gaetano Calì, Luigi Insabato, Francesca Fiory, Francesco Beguinot, Luca Ulianich
Cells.2021; 10(5): 1067. CrossRef - NADPH Oxidase (NOX) Targeting in Diabetes: A Special Emphasis on Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction
Suma Elumalai, Udayakumar Karunakaran, Jun-Sung Moon, Kyu-Chang Won
Cells.2021; 10(7): 1573. CrossRef - Metformin use and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a nationwide cohort study
Min Ho Kim, Hyung Jung Oh, Soon Hyo Kwon, Jin Seok Jeon, Hyunjin Noh, Dong Cheol Han, Hyoungnae Kim, Dong-Ryeol Ryu
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 40(4): 660. CrossRef - Different Effects of Metformin and A769662 on Sodium Iodate-Induced Cytotoxicity in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells: Distinct Actions on Mitochondrial Fission and Respiration
Chi-Ming Chan, Ponarulselvam Sekar, Duen-Yi Huang, Shu-Hao Hsu, Wan-Wan Lin
Antioxidants.2020; 9(11): 1057. CrossRef - Metformin Reduces Lipotoxicity-Induced Meta-Inflammation in β-Cells through the Activation of GPR40-PLC-IP3 Pathway
Ximei Shen, Beibei Fan, Xin Hu, Liufen Luo, Yuanli Yan, Liyong Yang
Journal of Diabetes Research.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef
- Metformin enhances METTL14-Mediated m6A methylation to alleviate NIT-1 cells apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Additional Effect of Dietary Fiber in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Metformin and Sulfonylurea: An Open-Label, Pilot Trial
- Seung-Eun Lee, Yongbin Choi, Ji Eun Jun, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Gwang Pyo Ko, Moon-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):422-431. Published online April 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0090
- 5,789 View
- 77 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Metformin, sulfonylurea, and dietary fiber are known to affect gut microbiota in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This open and single-arm pilot trial investigated the effects of the additional use of fiber on glycemic parameters, insulin, incretins, and microbiota in patients with T2DM who had been treated with metformin and sulfonylurea.
Methods Participants took fiber for 4 weeks and stopped for the next 4 weeks. Glycemic parameters, insulin, incretins during mixed-meal tolerance test (MMTT), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) level, and fecal microbiota were analyzed at weeks 0, 4, and 8. The first tertile of difference in glucose area under the curve during MMTT between weeks 0 and 4 was defined as ‘responders’ and the third as ‘nonresponders,’ respectively.
Results In all 10 participants, the peak incretin levels during MMTT were higher and LPS were lower at week 4 as compared with at baseline. While the insulin sensitivity of the ‘responders’ increased at week 4, that of the ‘nonresponders’ showed opposite results. However, the results were not statistically significant. In all participants, metabolically unfavorable microbiota decreased at week 4 and were restored at week 8. At baseline, metabolically hostile bacteria were more abundant in the ‘nonresponders.’ In ‘responders,’
Roseburia intestinalis increased at week 4.Conclusion While dietary fiber did not induce additional changes in glycemic parameters, it showed a trend of improvement in insulin sensitivity in ‘responders.’ Even if patients are already receiving diabetes treatment, the additional administration of fiber can lead to additional benefits in the treatment of diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of prebiotics on gastrointestinal side effects of metformin in youth: A pilot randomized control trial in youth-onset type 2 diabetes
Sydney A. Dixon, Sidharth Mishra, Katrina B. Dietsche, Shalini Jain, Lilian Mabundo, Michael Stagliano, Andrea Krenek, Amber Courville, Shanna Yang, Sara A. Turner, Abby G. Meyers, Doris E. Estrada, Hariom Yadav, Stephanie T. Chung
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of dietary, surgical, and pharmacological interventions on gut microbiota in individuals with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review
Patricia M. Bock, Andreza F. Martins, Rafaela Ramalho, Gabriela H. Telo, Gabriel Leivas, Clara K. Maraschin, Beatriz D. Schaan
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109944. CrossRef - Assessment of the safety and probiotic properties of Roseburia intestinalis: A potential “Next Generation Probiotic”
Chao Zhang, Kejia Ma, Kai Nie, Minzi Deng, Weiwei Luo, Xing Wu, Yujun Huang, Xiaoyan Wang
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Prebiotics and Oral Anti-Diabetic Agents on Gut Microbiome in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials
Omorogieva Ojo, Xiaohua Wang, Osarhumwese Osaretin Ojo, Joanne Brooke, Yiqing Jiang, Qingqing Dong, Trevor Thompson
Nutrients.2022; 14(23): 5139. CrossRef - The Effect of Dietary Interventions on Chronic Inflammatory Diseases in Relation to the Microbiome: A Systematic Review
Carlijn A. Wagenaar, Marieke van de Put, Michelle Bisschops, Wendy Walrabenstein, Catharina S. de Jonge, Hilde Herrema, Dirkjan van Schaardenburg
Nutrients.2021; 13(9): 3208. CrossRef - The Role of Dietary Fibre in Modulating Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials
Omorogieva Ojo, Qian-Qian Feng, Osarhumwese Osaretin Ojo, Xiao-Hua Wang
Nutrients.2020; 12(11): 3239. CrossRef - High Fiber and Beta Carotene from Sweet Potatoes and Pumpkin Improve Insulin Resistance by Inhibition of Sterol Regulatory Binding Protein 1c in Liver of Hypertriglyceridemic Rats
Sunarti Sunarti, Umar Santoso, Abrory Agus Cahya Pramana, Emy Huriyati, Dianandha Septiana Rubi
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2020; 8(A): 898. CrossRef
- The effects of prebiotics on gastrointestinal side effects of metformin in youth: A pilot randomized control trial in youth-onset type 2 diabetes
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Effects of Dapagliflozin on Endothelial Function, Renal Injury Markers, and Glycemic Control in Drug-Naïve Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Sung Hye Kong, Bo Kyung Koo, Min Kyong Moon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):711-717. Published online March 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0208
- 3,593 View
- 58 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The study aimed to evaluate the effects of dapagliflozin and metformin on vascular endothelial function and renal injury markers.
Methods This prospective, randomized, open-label, crossover study included drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, who were randomized to receive 8 weeks of initial treatment using metformin or dapagliflozin and crossed over for another 8 weeks of treatment after a 1-week washout period. Systemic endothelial function was evaluated via the reactive hyperemic index (RHI).
Results The 22 participants included 10 males (45.5%) and had a median age of 58 years. The RHI values were not significantly changed during both 8-week treatment periods and there was no significant difference between the treatments. Relative to the metformin group, 8 weeks of dapagliflozin treatment produced significantly higher median
N -acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase levels (10.0 ng/mL [interquartile range (IQR), 6.8 to 12.1 ng/mL] vs. 5.6 ng/mL [IQR, 3.8 to 8.0 ng/mL],P =0.013). Only the dapagliflozin group exhibited improved homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance and body weight, while serum ketone and β-hydroxybutyrate levels increased.Conclusion Dapagliflozin treatment did not affect systemic endothelial function or renal injury markers except
N -acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dapagliflozin protects the kidney in a non-diabetic model of cardiorenal syndrome
Konrad Urbanek, Donato Cappetta, Gabriella Bellocchio, Maria Antonietta Coppola, Paola Imbrici, Marialucia Telesca, Maria Donniacuo, Maria Antonietta Riemma, Elena Mele, Eleonora Cianflone, Silvio Naviglio, Elena Conte, Giulia Maria Camerino, Marco Mele,
Pharmacological Research.2023; 188: 106659. CrossRef - Novel use of structural equation modelling to examine diet and metabolic traits associated with microvascular endothelial dysfunction in middle-aged Chinese males: a cross-sectional study
Rujia Miao, Renhe Yu, Hui Zhou, Lei Liu, Ting Peng, Jiangang Wang
BMJ Open.2023; 13(9): e073357. CrossRef - Endothelial Dysfunction and Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction—An Updated Review of the Literature
Mariarosaria De Luca, Giulia Crisci, Giuseppe Armentaro, Sebastiano Cicco, Giovanni Talerico, Emanuele Bobbio, Lorena Lanzafame, Christopher G. Green, Abbie G. McLellan, Radek Debiec, Paolo Caferra, Roberto Scicali, Antonio Cannatà, Muhammad Zubair Israr,
Life.2023; 14(1): 30. CrossRef - Renoprotection by Dapagliflozin in a Non-Diabetic Model of Cardiorenal Syndrome
Konrad Urbanek, Donato Cappetta, Gabriella Bellocchio, Maria Antonietta Coppola, Paola Imbrici, Marialucia Telesca, Maria Donniacuo, Maria Antonietta Riemma, Eleonora Cianflone, Silvio Naviglio, Elena Conte, Giulia Maria Camerino, Marco Mele, Mariarosaria
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dapagliflozin increases the lean-to total mass ratio in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Vaneza Lira W. Wolf, Ikaro Breder, Luiz Sérgio F. de Carvalho, Alexandre A. S. Soares, Riobaldo M. Cintra, Joaquim Barreto, Daniel B. Munhoz, Sheila T. Kimura-Medorima, Wilson Nadruz, Gil Guerra-Júnior, Thiago Quinaglia, Elza Muscelli, Andrei C. Sposito
Nutrition & Diabetes.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Ion Homeostasis and Oxidative Stress associated Mechanisms in Heart Failure
Gloria M. Gager, Dirk von Lewinski, Harald Sourij, Bernd Jilma, Ceren Eyileten, Krzysztof Filipiak, Martin Hülsmann, Jacek Kubica, Marek Postula, Jolanta M. Siller-Matula
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 143: 112169. CrossRef - Association of Circulating Ketone Bodies With Functional Outcomes After ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Marie-Sophie L.Y. de Koning, B. Daan Westenbrink, Solmaz Assa, Erwin Garcia, Margery A. Connelly, Dirk J. van Veldhuisen, Robin P.F. Dullaart, Erik Lipsic, Pim van der Harst
Journal of the American College of Cardiology.2021; 78(14): 1421. CrossRef - Prognostic value of arterial stiffness measurements in cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and its complications: The potential role of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitors
Dimitrios Patoulias, Christodoulos Papadopoulos, Konstantinos Stavropoulos, Ioanna Zografou, Michael Doumas, Asterios Karagiannis
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2020; 22(4): 562. CrossRef - Rationale for the Early Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Yehuda Handelsman
Advances in Therapy.2019; 36(10): 2567. CrossRef - Letter: Effects of Dapagliflozin on Endothelial Function, Renal Injury Markers, and Glycemic Control in Drug-Naïve Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2019:43:711–7)
Dimitrios Patoulias, Michael Doumas
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 906. CrossRef - Response: Effects of Dapagliflozin on Endothelial Function, Renal Injury Markers, and Glycemic Control in Drug-Naïve Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2019:43:711–7)
Sung Hye Kong, Bo Kyung Koo, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 913. CrossRef
- Dapagliflozin protects the kidney in a non-diabetic model of cardiorenal syndrome
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Acarbose Add-on Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Metformin and Sitagliptin Failure: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
- Hae Kyung Yang, Seung-Hwan Lee, Juyoung Shin, Yoon-Hee Choi, Yu-Bae Ahn, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Jung Rhee, Kyung Wan Min, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):287-301. Published online December 20, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0054
- 5,876 View
- 104 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We evaluated the efficacy and safety of acarbose add-on therapy in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who are inadequately controlled with metformin and sitagliptin.
Methods A total of 165 subjects were randomized to metformin and sitagliptin (Met+Sita,
n =65), metformin, sitagliptin, and acarbose (Met+Sita+Acarb,n =66) and sitagliptin and acarbose (Sita+Acarb, exploratory assessment,n =34) therapy in five institutions in Korea. After 16 weeks of acarbose add-on or metformin-switch therapy, a triple combination therapy was maintained from week 16 to 24.Results The add-on of acarbose (Met+Sita+Acarb group) demonstrated a 0.44%±0.08% (
P <0.001 vs. baseline) decrease in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) at week 16, while changes in HbA1c were insignificant in the Met+Sita group (−0.09%±0.10%,P =0.113). After 8 weeks of triple combination therapy, HbA1c levels were comparable between Met+Sita and Met+Sita+Acarb group (7.66%±0.13% vs. 7.47%±0.12%,P =0.321). Acarbose add-on therapy demonstrated suppressed glucagon secretion (area under the curve of glucagon, 4,726.17±415.80 ng·min/L vs. 3,314.38±191.63 ng·min/L,P =0.004) in the absence of excess insulin secretion during the meal tolerance tests at week 16 versus baseline. The incidence of adverse or serious adverse events was similar between two groups.Conclusion In conclusion, a 16-week acarbose add-on therapy to metformin and sitagliptin, effectively lowered HbA1c without significant adverse events. Acarbose might be a good choice as a third-line therapy in addition to metformin and sitagliptin in Korean subjects with T2DM who have predominant postprandial hyperglycemia and a high carbohydrate intake.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of acarbose on inflammatory cytokines and adipokines in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Ali Mohammadian, Sahand Tehrani Fateh, Mahlagha Nikbaf-Shandiz, Fatemeh Gholami, Niloufar Rasaei, Hossein Bahari, Samira Rastgoo, Reza Bagheri, Farideh Shiraseb, Omid Asbaghi
Inflammopharmacology.2024; 32(1): 355. CrossRef - An Update on Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibiting Peptides
Sachithanantham Annapoorani Sivaraman, Varatharajan Sabareesh
Current Protein & Peptide Science.2024; 25(4): 267. CrossRef - Deciphering Molecular Aspects of Potential α-Glucosidase Inhibitors within Aspergillus terreus: A Computational Odyssey of Molecular Docking-Coupled Dynamics Simulations and Pharmacokinetic Profiling
Sameh S. Elhady, Noha M. Alshobaki, Mahmoud A. Elfaky, Abdulrahman E. Koshak, Majed Alharbi, Reda F. A. Abdelhameed, Khaled M. Darwish
Metabolites.2023; 13(8): 942. CrossRef - Change of metformin concentrations in the liver as a pharmacological target site of metformin after long-term combined treatment with ginseng berry extract
Choong Whan Lee, Byoung Hoon You, Sreymom Yim, Seung Yon Han, Hee-Sung Chae, Mingoo Bae, Seo-Yeon Kim, Jeong-Eun Yu, Jieun Jung, Piseth Nhoek, Hojun Kim, Han Seok Choi, Young-Won Chin, Hyun Woo Kim, Young Hee Choi
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
Fatma Haddad, Ghadeer Dokmak, Maryam Bader, Rafik Karaman
Life.2023; 13(4): 1012. CrossRef - The effects of acarbose treatment on cardiovascular risk factors in impaired glucose tolerance and diabetic patients: a systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Mohammad Zamani, Mahlagha Nikbaf-Shandiz, Yasaman Aali, Niloufar Rasaei, Mahtab Zarei, Farideh Shiraseb, Omid Asbaghi
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of acarbose on lipid profiles in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Mohsen Yousefi, Sahand Tehrani Fateh, Mahlagha Nikbaf-Shandiz, Fatemeh Gholami, Samira Rastgoo, Reza Bagher, Alireza Khadem, Farideh Shiraseb, Omid Asbaghi
BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A systematic review, meta-analysis, dose-response, and meta-regression of the effects of acarbose intake on glycemic markers in adults
Sina Raissi Dehkordi, Naseh Pahlavani, Mahlagha Nikbaf-Shandiz, Reza Bagheri, Niloufar Rasaei, Melika Darzi, Samira Rastgoo, Hossein Bahari, Farideh Shiraseb, Omid Asbaghi
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibitory activity of xanthoangelol isolated from Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei Koidzumi) towards α-glucosidase and dipeptidyl peptidase-IV: in silico and in vitro studies
Diah Lia Aulifa, I Ketut Adnyana, Sukrasno Sukrasno, Jutti Levita
Heliyon.2022; 8(5): e09501. CrossRef - Design, synthesis, and in silico studies of benzimidazole bearing phenoxyacetamide derivatives as α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitors
Nahal Shayegan, Aida Iraji, Nasim Bakhshi, Ali Moazzam, Mohammad Ali Faramarzi, Somayeh Mojtabavi, Seyyed Mehrdad Mostafavi Pour, Maliheh Barazandeh Tehrani, Bagher Larijani, Zahra Rezaei, Pardis Yousefi, Mehdi Khoshneviszadeh, Mohammad Mahdavi
Journal of Molecular Structure.2022; 1268: 133650. CrossRef - American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: Developing a Diabetes Mellitus Comprehensive Care Plan—2022 Update
Lawrence Blonde, Guillermo E. Umpierrez, S. Sethu Reddy, Janet B. McGill, Sarah L. Berga, Michael Bush, Suchitra Chandrasekaran, Ralph A. DeFronzo, Daniel Einhorn, Rodolfo J. Galindo, Thomas W. Gardner, Rajesh Garg, W. Timothy Garvey, Irl B. Hirsch, Danie
Endocrine Practice.2022; 28(10): 923. CrossRef - Combination of Bawang Dayak Extract and Acarbose against Male White Rat Glucose Levels
Aditya Maulana Perdana Putra, Ratih Pratiwi Sari, Siska Musiam
Borneo Journal of Pharmacy.2021; 4(2): 84. CrossRef - Natural α-Glucosidase and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors: A Source of Scaffold Molecules for Synthesis of New Multitarget Antidiabetic Drugs
Massimo Genovese, Ilaria Nesi, Anna Caselli, Paolo Paoli
Molecules.2021; 26(16): 4818. CrossRef - Impact of Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions on Antiglycoxidant and α-Glucosidase Inhibition Capacities of Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside
Didier Fraisse, Alexis Bred, Catherine Felgines, François Senejoux
Antioxidants.2021; 10(11): 1670. CrossRef
- The effect of acarbose on inflammatory cytokines and adipokines in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Tae Jung Oh, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Wan Min, Hyun Shik Son, Moon Kyu Lee, Kun Ho Yoon, Young Duk Song, Joong Yeol Park, In Kyung Jeong, Bong Soo Cha, Yong Seong Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, In Joo Kim, Doo Man Kim, Sung Rae Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Jeong Hyung Park, In Kyu Lee, Tae Sun Park, Sung Hee Choi, Sung Woo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):276-286. Published online December 7, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0051
- 7,048 View
- 98 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Combination of metformin to reduce the fasting plasma glucose level and an α-glucosidase inhibitor to decrease the postprandial glucose level is expected to generate a complementary effect. We compared the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination of voglibose plus metformin (vogmet) with metformin monotherapy in drug-naïve newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods A total of 187 eligible patients aged 20 to 70 years, with a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level of 7.0% to 11.0%, were randomized into either vogmet or metformin treatments for 24 weeks. A change in the HbA1c level from baseline was measured at week 24.
Results The reduction in the levels of HbA1c was −1.62%±0.07% in the vogmet group and −1.31%±0.07% in the metformin group (
P =0.003), and significantly more vogmet-treated patients achieved the target HbA1c levels of <6.5% (P =0.002) or <7% (P =0.039). Glycemic variability was also significantly improved with vogmet treatment, estimated by M-values (P =0.004). Gastrointestinal adverse events and hypoglycemia (%) were numerically lower in the vogmet-treated group. Moreover, a significant weight loss was observed with vogmet treatment compared with metformin (−1.63 kg vs. −0.86 kg,P =0.039).Conclusion Vogmet is a safe antihyperglycemic agent that controls blood glucose level effectively, yields weight loss, and is superior to metformin in terms of various key glycemic parameters without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phytochemical analysis and antihyperglycemic activity of Castilleja arvensis
Mónica Aideé Díaz-Román, Juan José Acevedo-Fernández, Gabriela Ávila-Villarreal, Elizabeth Negrete-León, A. Berenice Aguilar-Guadarrama
Fitoterapia.2024; 174: 105839. CrossRef - YAP/TAZ axis was involved in the effects of metformin on breast cancer
Yu Xu, Hongke Cai, Yuanfeng Xiong, Li Tang, Longjiang Li, Li Zhang, Yi Shen, Yongqiang Yang, Ling Lin, Jiayi Huang
Journal of Chemotherapy.2023; 35(7): 627. CrossRef - Diabetes remission: Myth or reality?
Ashok Kumar, ShubhaLaxmi Margekar, Ravi Kumar
Indian Journal of Medical Specialities.2023; 14(1): 3. CrossRef - Analysis of Reports Sent to the Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System and Published Literature Regarding the Safety of Metformin in the Elderly
Beatriz Esteves, Cristina Monteiro, Ana Paula Coelho Duarte
Healthcare.2023; 11(15): 2197. CrossRef - Rapid prediction method of α-Glycosidase inhibitory activity of Coreopsis tinctoria extract from different habitats by near infrared spectroscopy
Xiaogang He, Xiang Han, Jiaping Yu, Yulong Feng, Ganghui Chu
Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy.2022; 268: 120601. CrossRef - Insulin autoimmune syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes: A report of two cases
Y. Shin, T.J. Oh, S.H. Choi, H.C. Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(1): 101115. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study
Jun Sung Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Sang Soo Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Jeong Mi Kim, Min Hee Jang, Kyung Ae Lee, Ju Hyung Lee, Seung Min Chung, Young Sang Lyu, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jung Eun Jang, Tae Nyun Kim, Sung Woo Kim, Eonju Jeon, Nan Hee Cho, Mi-Kyung Ki
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 675. CrossRef - Quantifying Remission Probability in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sanjay Kalra, Ganapathi Bantwal, Nitin Kapoor, Rakesh Sahay, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Beatrice Anne, Raju A Gopal, Sunil Kota, Ashok Kumar, Ameya Joshi, Debmalya Sanyal, Mangesh Tiwaskar, Ashok Kumar Das
Clinics and Practice.2021; 11(4): 850. CrossRef - The effect of voglibose on metabolic profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Peyman Nowrouzi-Sohrabi, Reza Tabrizi, Shahla Rezaei, Fatemeh Jafari, Kamran Hessami, Mehdi Abedi, Mohammad Jalali, Pedram Keshavarzi, Saeed Shahabi, Ali Asghar Kolahi, Kristin Carson-Chahhoud, Amirhossein Sahebkar, Saeid Safiri
Pharmacological Research.2020; 159: 104988. CrossRef - Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Voglibose In Vitro and In Vivo
Mahesh Raj Nepal, Mi Jeong Kang, Geon Ho Kim, Dong Ho Cha, Ju-Hyun Kim, Tae Cheon Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 908. CrossRef - Response: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes metab J 2019;43;276-86)
Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 547. CrossRef - Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43;276-86)
Hannah Seok, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 545. CrossRef
- Phytochemical analysis and antihyperglycemic activity of Castilleja arvensis
- Clinical Diabetes and Therapeutics
- Hospital-Based Korean Diabetes Prevention Study: A Prospective, Multi-Center, Randomized, Open-Label Controlled Study
- Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Jeong-Taek Woo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):49-58. Published online November 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0033
- 5,305 View
- 131 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) continues to increase, and the disease burden is the highest of any medical condition in Korea. However, large-scale clinical studies have not yet conducted to establish the basis for diabetes prevention in Korea.
Methods The hospital-based Korean Diabetes Prevention Study (H-KDPS) is a prospective, multi-center, randomized, open-label controlled study conducted at university hospitals for the purpose of gathering data to help in efforts to prevent type 2 DM. Ten university hospitals are participating, and 744 subjects will be recruited. The subjects are randomly assigned to the standard care group, lifestyle modification group, or metformin group, and their clinical course will be observed for 36 months.
Results All intervention methodologies were developed, validated, and approved by Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) multi-disciplinary team members. The standard control group will engage in individual education based on the current KDA guidelines, and the lifestyle modification group will participate in a professionally guided healthcare intervention aiming for ≥5% weight loss. The metformin group will begin dosing at 250 mg/day, increasing to a maximum of 1,000 mg/day. The primary endpoint of this study is the cumulative incidence of DM during the 3 years after randomization.
Conclusion The H-KDPS study is the first large-scale clinical study to establish evidence-based interventions for the prevention of type 2 DM in Koreans. The evidence gathered by this study will be useful for enhancing the health of Koreans and improving the stability of the Korean healthcare system (Trial registration: CRIS KCT0002260, NCT02981121).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimating insulin sensitivity and β-cell function from the oral glucose tolerance test: validation of a new insulin sensitivity and secretion (ISS) model
Joon Ha, Stephanie T. Chung, Max Springer, Joon Young Kim, Phil Chen, Aaryan Chhabra, Melanie G. Cree, Cecilia Diniz Behn, Anne E. Sumner, Silva A. Arslanian, Arthur S. Sherman
American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 326(4): E454. CrossRef - Development and Adaptability of Smartphone-based Dietary Coaching Program for Patients Undergoing Diabetes and Prediabetes with Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device
Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Mi Ryu, Minkyeong Kang, Jiwon Park, Yeh Chan Ahn, Yang Seok Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 36. CrossRef - Improving Machine Learning Diabetes Prediction Models for the Utmost Clinical Effectiveness
Juyoung Shin, Joonyub Lee, Taehoon Ko, Kanghyuck Lee, Yera Choi, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(11): 1899. CrossRef - Impaired fasting glucose levels in overweight or obese subjects for screening of type 2 diabetes in Korea
Jin-Hee Lee, Suk Chon, Seon-Ah Cha, Sun-Young Lim, Kook-Rye Kim, Jae-Seung Yun, Sang Youl Rhee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Yu-Bae Ahn, Jeong-Taek Woo, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(2): 382. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Based Diabetes Prediction System Using a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort
Sang Youl Rhee, Ji Min Sung, Sunhee Kim, In-Jeong Cho, Sang-Eun Lee, Hyuk-Jae Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 515. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 461. CrossRef - Short-Term Effects of the Internet-Based Korea Diabetes Prevention Study: 6-Month Results of a Community-Based Randomized Controlled Trial
Jin-Hee Lee, Sun-Young Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Chan-Jung Han, Ah Reum Jung, Kook-Rye Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 960. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Seung-Hyun Ko
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 244. CrossRef - Optimal fasting plasma glucose and haemoglobin A1c levels for screening of prediabetes and diabetes according to 2‐hour plasma glucose in a high‐risk population: The Korean Diabetes Prevention Study
Seon‐Ah Cha, Suk Chon, Jae‐Seung Yun, Sang Youl Rhee, Sun‐Young Lim, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Yu‐Bae Ahn, Seung‐Hyun Ko, Jeong‐Taek Woo, Jin‐Hee Lee
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - How was the Diabetes Metabolism Journal added to MEDLINE?
Hye Jin Yoo
Science Editing.2020; 7(2): 201. CrossRef - Commercial Postural Devices: A Review
Nicole Kah Mun Yoong, Jordan Perring, Ralph Jasper Mobbs
Sensors.2019; 19(23): 5128. CrossRef - Changes in Metabolic Profile Over Time: Impact on the Risk of Diabetes
Yunjung Cho, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 407. CrossRef - Metformin for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in persons at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kasper S Madsen, Yuan Chi, Maria-Inti Metzendorf, Bernd Richter, Bianca Hemmingsen
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Estimating insulin sensitivity and β-cell function from the oral glucose tolerance test: validation of a new insulin sensitivity and secretion (ISS) model
- Others
- Synthesis of a New Zinc-Mixed Ligand Complex and Evaluation of Its Antidiabetic Properties in High Fat Diet: Low Dose Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats
- Muruganantham Koothappan, Roshana Devi Vellai, Iyyam Pillai Subramanian, Sorimuthu Pillai Subramanian
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):244-248. Published online April 24, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0002
- 3,682 View
- 49 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Due to the multifactorial and multisystemic nature of diabetes mellitus, it is often treated with a combination of therapeutic agents having different mode of action. Earlier, we have synthesized several organozinc complexes and evaluated their safety and antidiabetic properties in experimental type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). More recently, we have synthesized a metformin-3-hydroxyflavone complex and studied its antidiabetic efficacy in experimental rats. In the present study, a new zinc-mixed ligand (metformin-3-hydroxyflavone) was synthesized, characterized by spectral studies and its antidiabetic properties was evaluated in HFD fed—low dose streptozotocin induced T2DM in rats. The hypoglycemic efficacy of the complex was evaluated through oral glucose tolerance test, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, quantitative insulin sensitivity check index and by determining the status of important biochemical parameters. Oral administration of the complex at a concentration of 10 mg/kg body weight/rat/day for 30 days significantly improved the glucose homeostasis. The complex possesses significant antidiabetic properties relatively at a less concentration than metformin-3-hydroxyflavone complex in ameliorating hyperglycemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metformin compounds: A review on the importance and the possible applications
A H Ismail, Z S Al-Garawi, K Al-Shamari, A T Salman
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2021; 1853(1): 012060. CrossRef - A Review on Natural Products and Herbs Used in the Management of Diabetes
Deepshikha Patle, Manish Vyas, Gopal L. Khatik
Current Diabetes Reviews.2021; 17(2): 186. CrossRef - The role of activation of KАTP channels on hydrogen sulfide induced renoprotective effect on diabetic nephropathy
Eman A. Elbassuoni, Neven M. Аziz, Wagdу N. Habeeb
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2020; 235(6): 5223. CrossRef - A comprehensive review on zinc(II) complexes as anti-diabetic agents: The advances, scientific gaps and prospects
Chika Ifeanyi Chukwuma, Samson S. Mashele, Kenneth C. Eze, Godfrey R. Matowane, Shahidul Md. Islam, Susanna L. Bonnet, Anwar E.M. Noreljaleel, Limpho M. Ramorobi
Pharmacological Research.2020; 155: 104744. CrossRef
- Metformin compounds: A review on the importance and the possible applications
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(5):349-356. Published online October 19, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.349
- 5,644 View
- 70 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
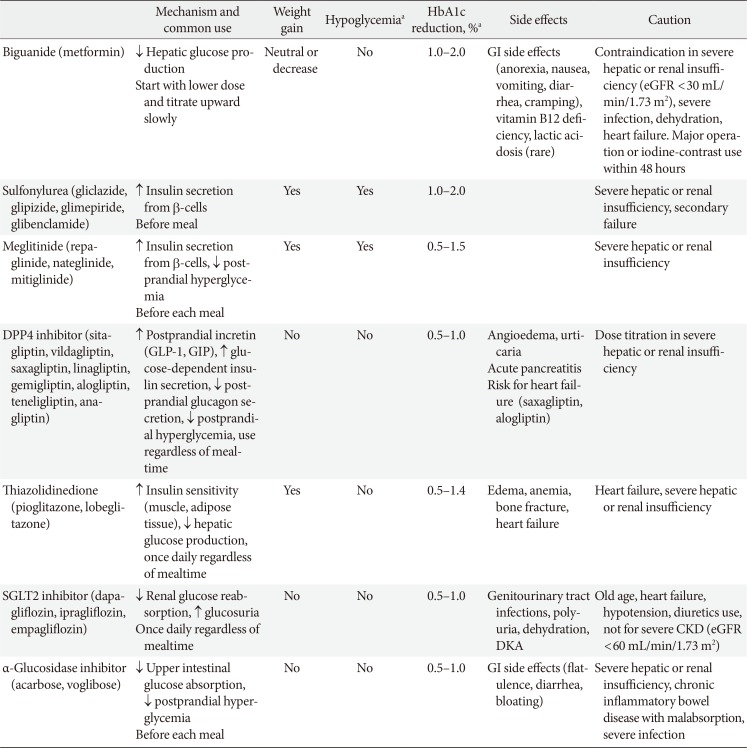
PubReader In order to improve the quality of life and to prevent chronic complications related to diabetes mellitus, intensive lifestyle modification and proper medication are needed from the early stage of diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). When using the first medication for diabetic patients, the appropriate treatment should be selected considering the clinical characteristics of the patient, efficacy of the drug, side effects, and cost. In general, the use of metformin as the first treatment for oral hypoglycemic monotherapy is recommended because of its excellent blood glucose-lowering effect, relatively low side effects, long-term proven safety, low risk of hypoglycemia, and low weight gain. If metformin is difficult to use as a first-line treatment, other appropriate medications should be selected in view of the clinical situation. If the goal of achieving glycemic control is not achieved by monotherapy, a combination therapy with different mechanisms of action should be initiated promptly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetic Patients with COVID-19 Complications: Insights into Prevalence,
Prognosis, Combination Medications, and Underlying Mechanisms
Pranay Wal, Jyotsana Dwivedi, Ankita Wal, Shivangi Kushwaha
Current Diabetes Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Increasing Individual Target Glucose Levels to Prevent Hypoglycemia in Patients with Diabetes
Juyoung Shin, Hyunah Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, Churlmin Kim, Whan-Seok Choi
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2021; 42(4): 269. CrossRef - Synthesis, antidiabetic activity and molecular docking study of rhodanine-substitued spirooxindole pyrrolidine derivatives as novel α-amylase inhibitors
Amani Toumi, Sarra Boudriga, Khaled Hamden, Mansour Sobeh, Mohammed Cheurfa, Moheddine Askri, Michael Knorr, Carsten Strohmann, Lukas Brieger
Bioorganic Chemistry.2021; 106: 104507. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Combination Therapy in Diabetic Neuropathy and Nephropathy
Harmeet Kaur, Arvinder Kaur, Pankaj Kumar Prashar, Anamika Gautam, Ankita Sood, Sachin Kumar Singh, Monica Gulati, Narendra Kumar Pandey, Bimlesh Kumar
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2021; : 3471. CrossRef - Type II diabetes mellitus: a review on recent drug based therapeutics
Santwana Padhi, Amit Kumar Nayak, Anindita Behera
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 131: 110708. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects of gemigliptin and dapagliflozin on glycaemic variability in type 2 diabetes: A randomized, open‐label, active‐controlled, 12‐week study (STABLE II study)
Soo Heon Kwak, You‐Cheol Hwang, Jong Chul Won, Ji Cheol Bae, Hyun Jin Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Eun Young Lee, Subin Lee, Sang‐Yong Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(2): 173. CrossRef - Metabolomics approach to identify the active substances influencing the antidiabetic activity of Lagerstroemia species
Mun-Ock Kim, Su Ui Lee, Heung Joo Yuk, Hyun-Jae Jang, Jae-Won Lee, Eun-Bin Kwon, Jin-Hyub Paik, SangHo Choi, Adek Nizar, Tran The Bach, Kongmany Sydara, Hang Jin, So-Yeun Woo, Sei-Ryang Oh, Hyung Won Ryu
Journal of Functional Foods.2020; 64: 103684. CrossRef - Cardiometabolic diseases and active aging - polypharmacy in control
Adriana Nancy Medeiros dos Santos, Dulcineia Rebecca Cappelletti Nogueira, Beatriz Aparecida Ozello Gutierrez, Rosa Yuka Sato Chubaci, Caroline Ribeiro de Borja Oliveira
Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-Diabetic Nephropathy Activities of Polysaccharides Obtained from Termitornyces albuminosus via Regulation of NF-κB Signaling in db/db Mice
Chang Yang, Qi Feng, Huan Liao, Xinlei Yu, Yang Liu, Di Wang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(20): 5205. CrossRef - Specific PERK inhibitors enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes
Min Joo Kim, Mi Na Kim, Se Hee Min, Dong-Sik Ham, Ji-Won Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
Metabolism.2019; 97: 87. CrossRef - A randomized, open‐label, multicentre, parallel‐controlled study comparing the efficacy and safety of biphasic insulin aspart 30 plus metformin with biphasic insulin aspart 30 monotherapy for type 2 diabetes patients inadequately controlled with oral anti
Lixin Guo, Li Chen, Baocheng Chang, Liyong Yang, Yu Liu, Bo Feng
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2018; 20(12): 2740. CrossRef - Monotherapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Sang Youl Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(1): 15. CrossRef
- Diabetic Patients with COVID-19 Complications: Insights into Prevalence,
Prognosis, Combination Medications, and Underlying Mechanisms

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





