
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
- Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):184-195. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0168
- 2,482 View
- 351 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
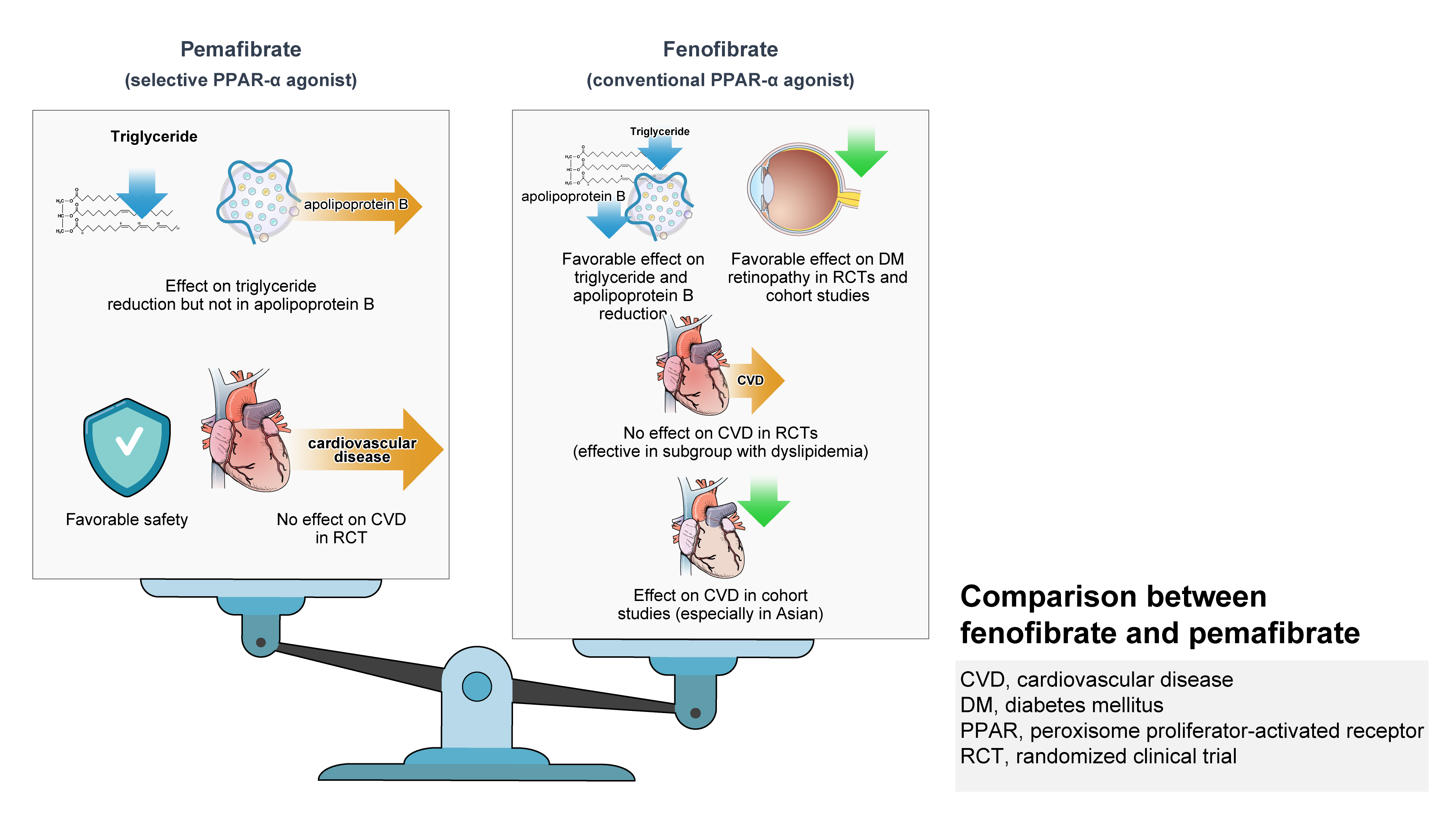
ePub - Hypertriglyceridemia and decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) persist despite statin therapy, contributing to residual atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk. Asian subjects are metabolically more susceptible to hypertriglyceridemia than other ethnicities. Fenofibrate regulates hypertriglyceridemia, raises HDL-C levels, and is a recommended treatment for dyslipidemia. However, data on fenofibrate use across different Asian regions are limited. This narrative review summarizes the efficacy and safety data of fenofibrate in Asian subjects with dyslipidemia and related comorbidities (diabetes, metabolic syndrome, diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic nephropathy). Long-term fenofibrate use resulted in fewer cardiovascular (CV) events and reduced the composite of heart failure hospitalizations or CV mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Fenofibrate plays a significant role in improving irisin resistance and microalbuminuria, inhibiting inflammatory responses, and reducing retinopathy incidence. Fenofibrate plus statin combination significantly reduced composite CV events risk in patients with metabolic syndrome and demonstrated decreased triglyceride and increased HDL-C levels with an acceptable safety profile in those with high CV or ASCVD risk. Nevertheless, care is necessary with fenofibrate use due to possible hepatic and renal toxicities in vulnerable individuals. Long-term trials and real-world studies are needed to confirm the clinical benefits of fenofibrate in the heterogeneous Asian population with dyslipidemia.
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
- Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong, on Behalf of the Committee of Public Relation of the Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):632-642. Published online August 2, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0135

- 3,187 View
- 324 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and status of dyslipidemia management among South Korean adults, as performed by the Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis under the name Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet 2022.
Methods
We analyzed the lipid profiles, age-standardized and crude prevalence, management status of hypercholesterolemia and dyslipidemia, and health behaviors among Korean adults aged ≥20 years, using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data between 2007 and 2020.
Results
In South Korea, the crude prevalence of hypercholesterolemia (total cholesterol ≥240 mg/dL or use of a lipid-lowering drug) in 2020 was 24%, and the age-standardized prevalence of hypercholesterolemia more than doubled from 2007 to 2020. The crude treatment rate was 55.2%, and the control rate was 47.7%. The crude prevalence of dyslipidemia—more than one out of three conditions (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≥160 or the use of a lipid-lowering drug, triglycerides ≥200, or high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [HDL-C] [men and women] <40 mg/dL)—was 40.2% between 2016 and 2020. However, it increased to 48.2% when the definition of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia in women changed from <40 to <50 mg/dL.
Conclusion
Although the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and dyslipidemia has steadily increased in South Korea, the treatment rate remains low. Therefore, continuous efforts are needed to manage dyslipidemia through cooperation between the national healthcare system, patients, and healthcare providers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oxidative Balance Score and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults without Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study-Health Examinees (KoGES-HEXA) Cohort
Mid-Eum Moon, Dong Hyuk Jung, Seok-Jae Heo, Byoungjin Park, Yong Jae Lee
Antioxidants.2024; 13(1): 107. CrossRef - Comparison of metabolic and neurological comorbidities in Asian patients with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis
Hee Joo Yang, Mi Young Lee, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Chang Jin Jung, Woo Jin Lee, Chong Hyun Won, Mi Woo Lee, Joon Min Jung, Sung Eun Chang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adding Apolipoprotein B Testing on the Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the Korean Adult Population
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Metabolites.2024; 14(3): 169. CrossRef - Exploring Utilization and Establishing Reference Intervals for the Apolipoprotein B Test in the Korean Population
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Diagnostics.2023; 13(20): 3194. CrossRef
- Oxidative Balance Score and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults without Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study-Health Examinees (KoGES-HEXA) Cohort
- Complications
- Dyslipidemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Updated Overview
- Sang Heon Suh, Soo Wan Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):612-629. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0067
- 3,165 View
- 413 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
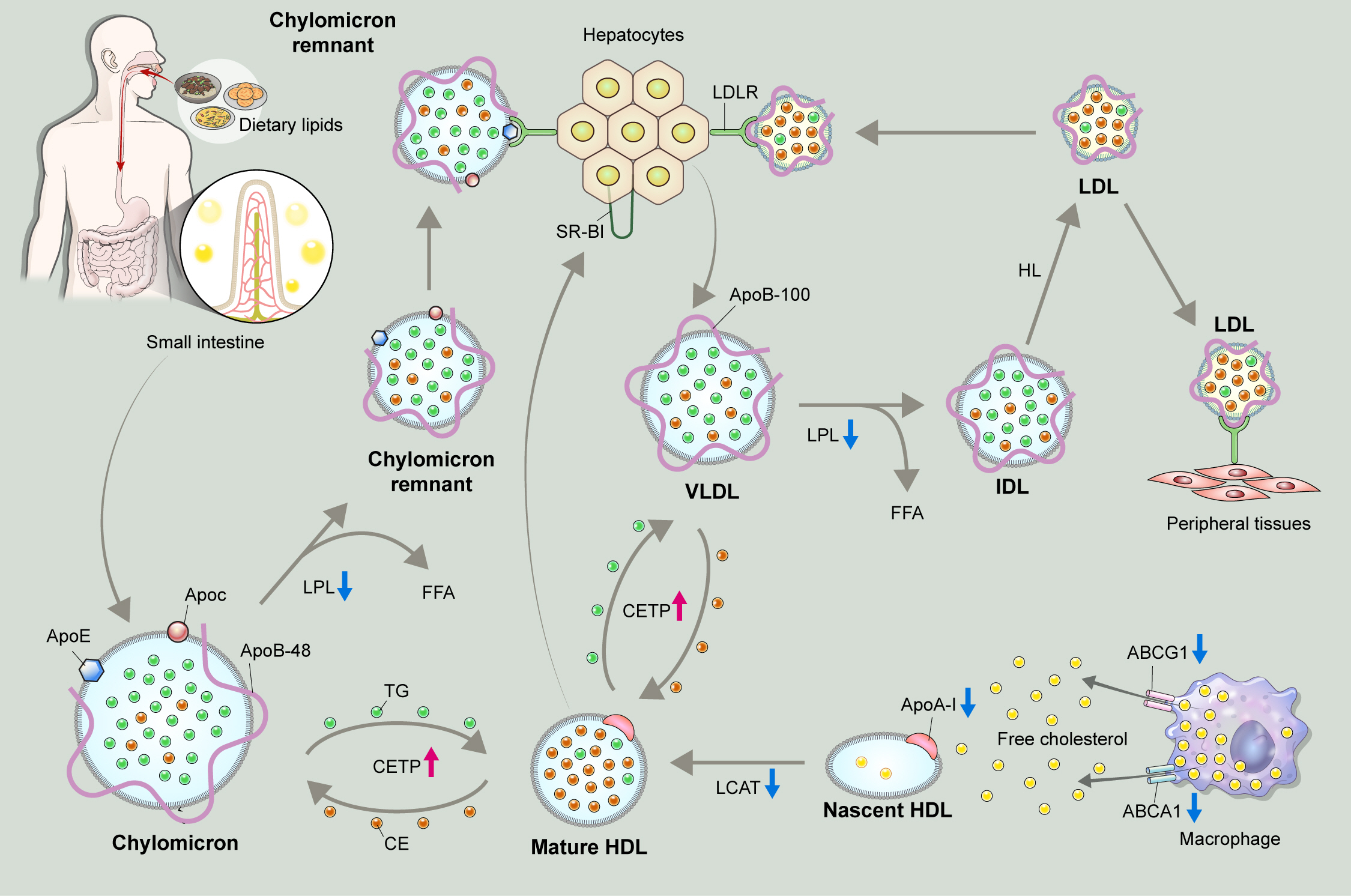
ePub - Dyslipidemia is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor. Whereas the recommendations for the treatment target of dyslipidemia in the general population are being more and more rigorous, the 2013 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes clinical practice guideline for lipid management in chronic kidney disease (CKD) presented a relatively conservative approach with respect to the indication of lipid lowering therapy and therapeutic monitoring among the patients with CKD. This may be largely attributed to the lack of high-quality evidence derived from CKD population, among whom the overall feature of dyslipidemia is considerably distinctive to that of general population. In this review article, we cover the characteristic features of dyslipidemia and impact of dyslipidemia on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CKD. We also review the current evidence on lipid lowering therapy to modify the risk of cardiovascular events in this population. We finally discuss the association between dyslipidemia and CKD progression and the potential strategy to delay the progression of CKD in relation to lipid lowering therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Statin Therapy and Lipid Indices in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic
Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Control Trials
Jafar Karami, Bahman Razi, Danyal Imani, Saeed Aslani, Mahdi Pakjoo, Mahdieh Fasihi, Keyhan Mohammadi, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2024; 30(5): 362. CrossRef
- Statin Therapy and Lipid Indices in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic
Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Control Trials
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Cardiovascular Outcomes according to Comorbidities and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong, on Behalf of the Committee of Practice Guideline of Korean Lipid and Atheroscelerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):45-58. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0344
- 3,009 View
- 263 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
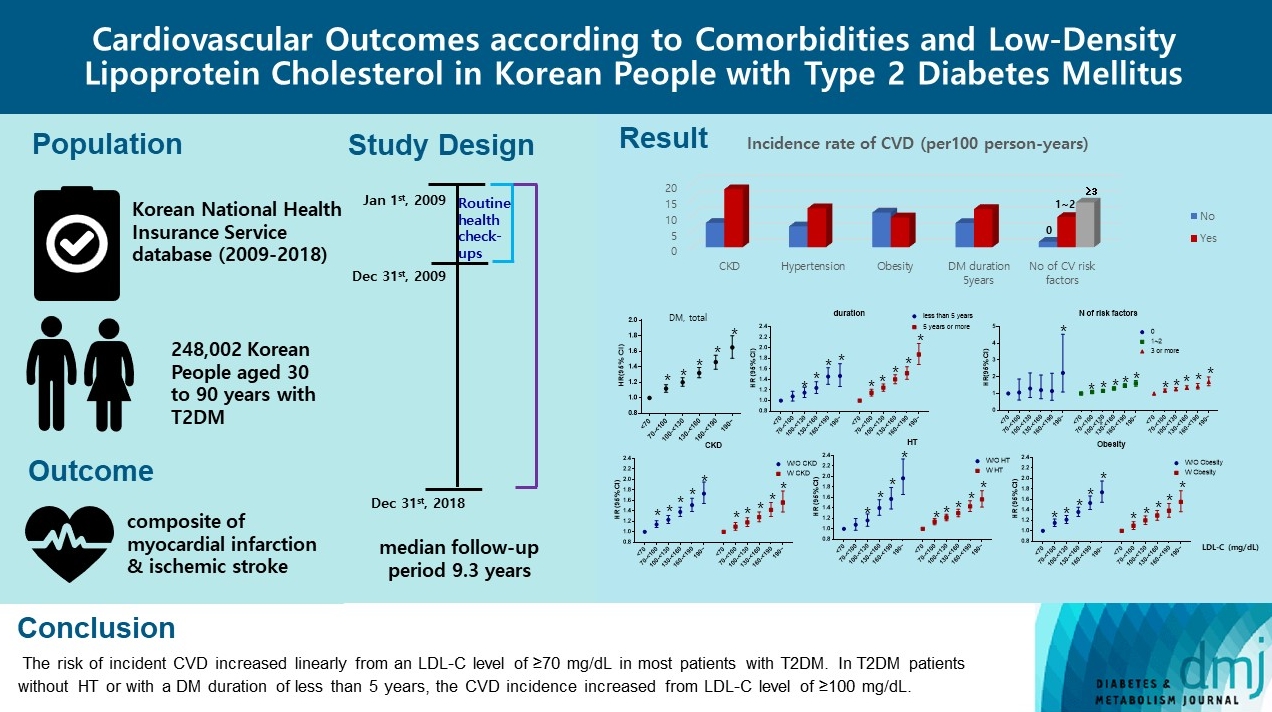
There are no clear data to support the cardiovascular (CV) risk categories and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) treatment goals in Korean people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We evaluated the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) according to comorbidities and suggested LDL-C treatment goals in Korean people with T2DM in nationwide cohort data.
Methods
Using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database, 248,002 people aged 30 to 90 years with T2DM who underwent routine health check-ups during 2009 were included. Subjects with previous CVD were excluded from the study. The primary outcome was incident CVD, defined as a composite of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke during the follow-up period from 2009 to 2018.
Results
The mean age of the study participants was 59.6±10.9 years, and median follow-up period was 9.3 years. CVD incidence increased in the order of DM duration of 5 years or more (12.04/1,000 person-years), hypertension (HT) (12.27/1,000 personyears), three or more CV risk factors (14.10/1,000 person-years), and chronic kidney disease (18.28/1,000 person-years). The risk of incident CVD increased linearly from an LDL-C level of ≥70 mg/dL in most patients with T2DM. In T2DM patients without HT or with a DM duration of less than 5 years, the CVD incidence increased from LDL-C level of ≥100 mg/dL.
Conclusion
For primary prevention of CVD in Korean adults with T2DM, it can be helpful to lower LDL-C targets when there are chronic kidney disease, HT, a long duration of diabetes mellitus, or three or more CV risk factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level for Primary Prevention in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ji Yoon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 42. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Significant Gap Between Guidelines and Practice in the Management of LDL Cholesterol: Insight From the Survey of the Korean Society of Myocardial Infarction
Sang Yeub Lee, Kyung Hoon Cho, Jang Hoon Lee, Young Joon Hong, Jin yong Hwang, Myung Ho Jeong, Weon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
- Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon, on Behalf of Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline, Korean Diabetes Association and Clinical Practice Guideline Committee, Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):1-9. Published online January 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0448
- 3,623 View
- 379 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
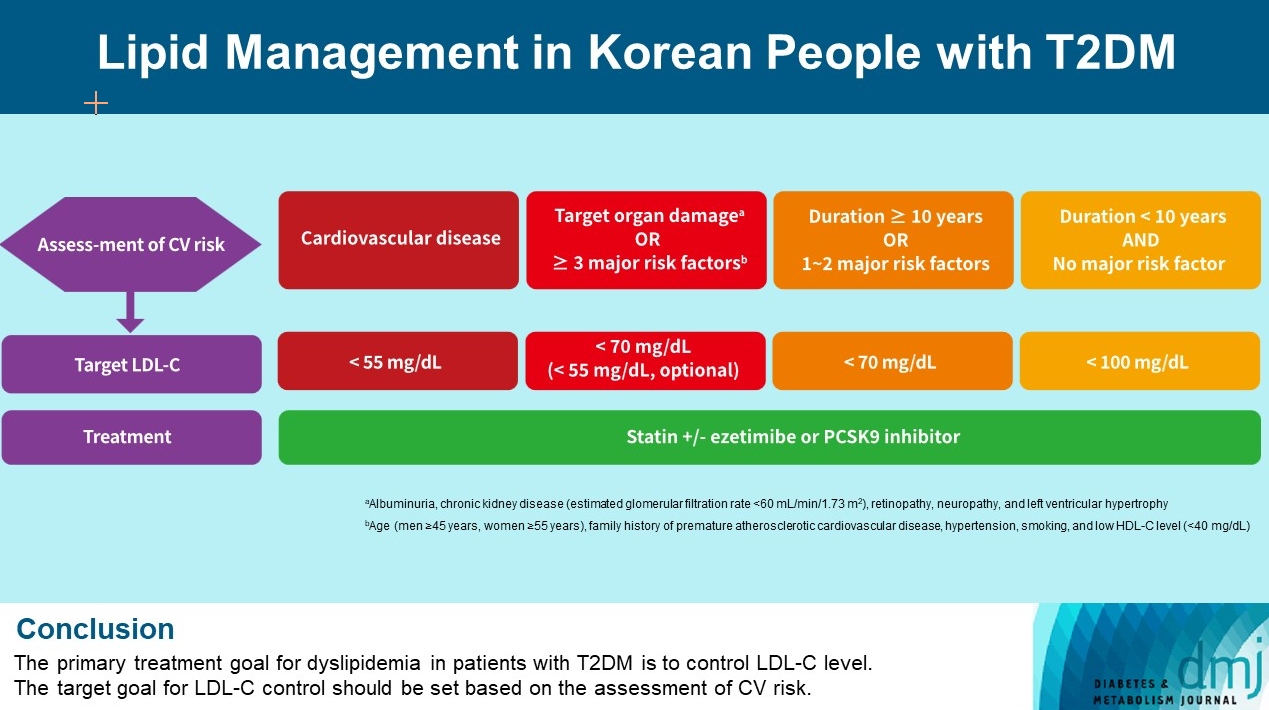
ePub - Dyslipidemia in patients with diabetes is an important treatment target as a modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Although the primary treatment goal for dyslipidemia is to control low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), achieving this goal remains suboptimal according to recent studies. It is important to set the target goal for LDL-C control based on an accurate risk assessment for CVD. Here, we summarize the latest evidence on lipid management in patients with diabetes and present a consensus of the Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis on the treatment goals of LDL-C according to the duration of diabetes, presence of CVD, target organ damage, or major cardiovascular risk factors. In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and CVD, an LDL-C goal of <55 mg/dL and a reduction in LDL-C level by 50% or more from the baseline is recommended. For the primary prevention of CVD in patients with T2DM with a duration of diabetes ≥10 years, major cardiovascular risk factors, or target organ damage, an LDL-C goal of <70 mg/dL is recommended. In patients with T2DM with a duration of diabetes <10 years and no major cardiovascular risk factors, an LDL-C goal of <100 mg/dL is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy.2024; 10(2): 118. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Statin Discontinuation in Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2024; 13(1): 41. CrossRef - Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 184. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 632. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(3): 237. CrossRef
- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
- Drug/Regimen
- New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
- Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):517-532. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0198
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2022;46(5):817
- 10,050 View
- 865 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
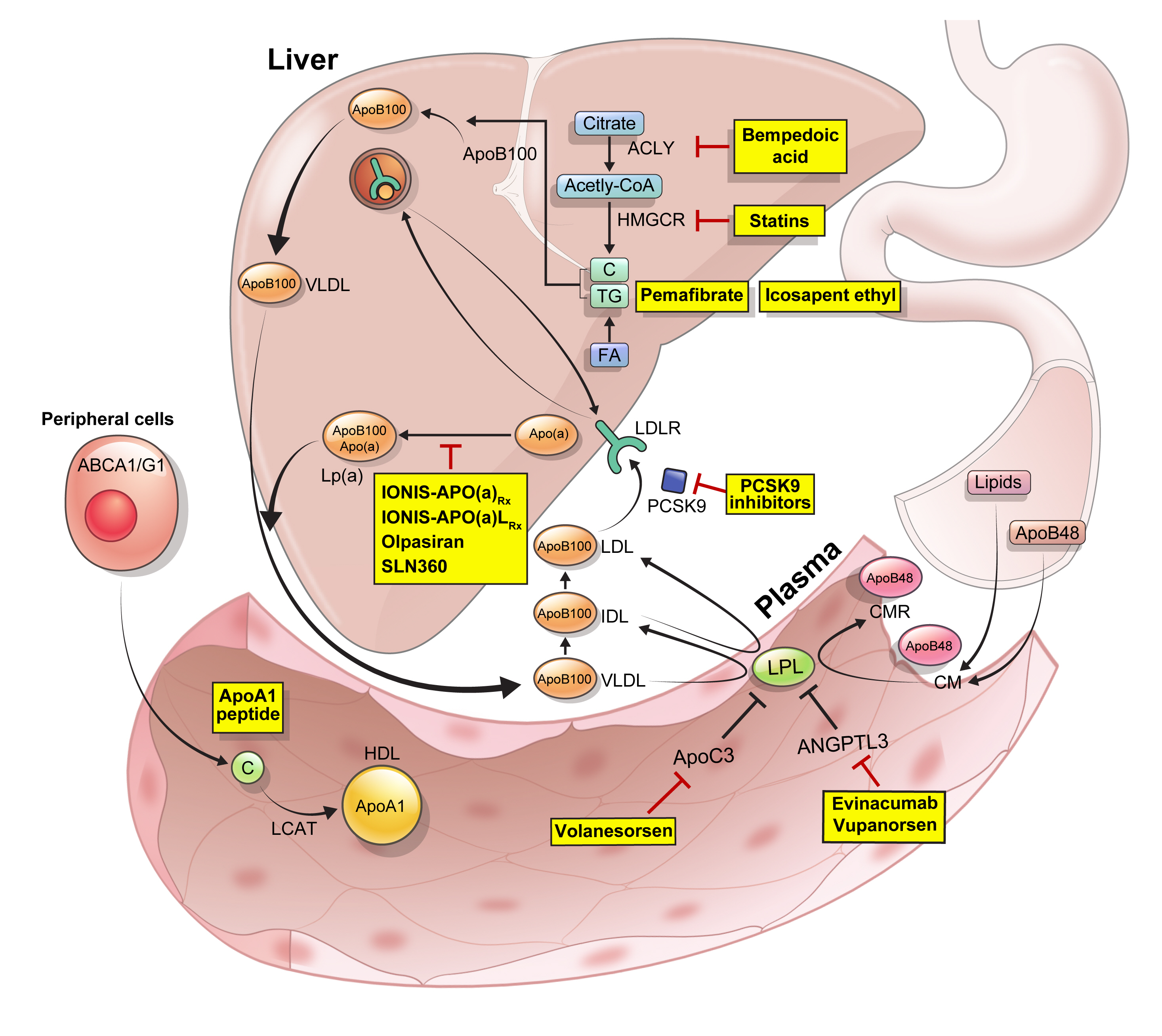
ePub - Statins are the cornerstone of the prevention and treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). However, even under optimal statin therapy, a significant residual ASCVD risk remains. Therefore, there has been an unmet clinical need for novel lipid-lowering agents that can target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and other atherogenic particles. During the past decade, several drugs have been developed for the treatment of dyslipidemia. Inclisiran, a small interfering RNA that targets proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9), shows comparable effects to that of PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies. Bempedoic acid, an ATP citrate lyase inhibitor, is a valuable treatment option for the patients with statin intolerance. Pemafibrate, the first selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha modulator, showed a favorable benefit-risk balance in phase 2 trial, but the large clinical phase 3 trial (PROMINENT) was recently stopped for futility based on a late interim analysis. High dose icosapent ethyl, a modified eicosapentaenoic acid preparation, shows cardiovascular benefits. Evinacumab, an angiopoietin-like 3 (ANGPTL3) monoclonal antibody, reduces plasma LDL-C levels in patients with refractory hypercholesterolemia. Novel antisense oligonucleotides targeting apolipoprotein C3 (apoC3), ANGPTL3, and lipoprotein(a) have significantly attenuated the levels of their target molecules with beneficial effects on associated dyslipidemias. Apolipoprotein A1 (apoA1) is considered as a potential treatment to exploit the athero-protective effects of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), but solid clinical evidence is necessary. In this review, we discuss the mode of action and clinical outcomes of these novel lipid-lowering agents beyond statins.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of adherence in patients with chronic diseases
Michel Burnier
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 119: 1. CrossRef - Bempedoic acid: new evidence and recommendations on use
Kristina Paponja, Ivan Pećin, Željko Reiner, Maciej Banach
Current Opinion in Lipidology.2024; 35(1): 41. CrossRef - Genetic insights into repurposing statins for hyperthyroidism prevention: a drug-target Mendelian randomization study
Anqi Huang, Xinyi Wu, Jiaqi Lin, Chiju Wei, Wencan Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting host-specific metabolic pathways—opportunities and challenges for anti-infective therapy
Monika I. Konaklieva, Balbina J. Plotkin
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) and Atherosclerosis: Does Hypolipidemic Treatment Have an Effect?
Petros Adamidis, Despoina Pantazi, Iraklis Moschonas, Evangelos Liberopoulos, Alexandros Tselepis
Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease.2024; 11(3): 72. CrossRef - Modulating effects of crocin on lipids and lipoproteins: Mechanisms and potential benefits
Habib Yaribeygi, Mina Maleki, Farin Rashid-Farrokhi, Payman Raise Abdullahi, Mohammad Amin Hemmati, Tannaz Jamialahmadi, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e28837. CrossRef - Assessing the Benefits of Lifestyle Influences on Cardiovascu-lar Health After Acute Coronary Syndrome
Marius Rus, Claudia Elena Stanis, Paula Marian, Lilliana Oana Pobirci, Loredana Ioana Banszki, Veronica Huplea, Gheorghe Adrian Osiceanu, Bianca-Maria Pop, Gabriela Dogaru, Felicia Liana Andronie-Cioara
Balneo and PRM Research Journal.2024; 15(Vol.15, no): 660. CrossRef - Liver cancer cells as the model for developing liver-targeted RNAi therapeutics
Beibei Hou, Linhui Qin, Linfeng Huang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2023; 644: 85. CrossRef - Insights into Causal Cardiovascular Risk Factors from Mendelian Randomization
C. M. Schooling, J. V. Zhao
Current Cardiology Reports.2023; 25(2): 67. CrossRef - Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside and anethole ameliorate lipid abnormalities, oxidative injury, hypercholesterolemia, heart, and liver conditions
Sana Noreen, Habib‐ur Rehman, Tabussam Tufail, Huma Badar Ul Ain, Chinaza Godswill Awuchi
Food Science & Nutrition.2023; 11(6): 2620. CrossRef - Colesterol remanente, riesgo vascular y prevención de la arteriosclerosis
Xavier Pintó, Marta Fanlo, Virginia Esteve, Jesús Millán, Agustín Blanco, Mariano Blasco, José Luís Díaz Díaz, Ángel Díaz Rodríguez, Alipio Mangas, Vicente Pascual, Juan Pedro Botet, Pablo Pérez Martínez
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis.2023; 35(4): 206. CrossRef - Evolving Management of Low‐Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol: A Personalized Approach to Preventing Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Across the Risk Continuum
Michael J. Wilkinson, Norman E. Lepor, Erin D. Michos
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The cell origins of foam cell and lipid metabolism regulated by mechanical stress in atherosclerosis
Zhi Ouyang, Jian Zhong, Junyi Shen, Ye Zeng
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-Rich Lipoprotein Metabolism: Key Regulators of Their Flux
Alejandro Gugliucci
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(13): 4399. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol, vascular risk, and prevention of atherosclerosis
Xavier Pintó, Marta Fanlo, Virginia Esteve, Jesús Millán
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis (English Edition).2023; 35(4): 206. CrossRef - Antibiotics and Lipid-Modifying Agents: Potential Drug–Drug Interactions and Their Clinical Implications
Marios Spanakis, Danny Alon-Ellenbogen, Petros Ioannou, Nikolaos Spernovasilis
Pharmacy.2023; 11(4): 130. CrossRef - Advances in Treatment of Dyslipidemia
Jill Dybiec, Wiktoria Baran, Bartłomiej Dąbek, Piotr Fularski, Ewelina Młynarska, Ewa Radzioch, Jacek Rysz, Beata Franczyk
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13288. CrossRef - Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α in Lipoprotein Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Elena Valeria Fuior, Evangelia Zvintzou, Theodosios Filippatos, Katerina Giannatou, Victoria Mparnia, Maya Simionescu, Anca Violeta Gafencu, Kyriakos E. Kypreos
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2696. CrossRef - Preparation, characterization and in vivo pharmacokinetic study of ginsenoside Rb1-PLGA nanoparticles
Lixin Du, Huiling Lu, Yifei Xiao, Zhihua Guo, Ya Li
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dysregulation of Cholesterol Homeostasis in Ovarian Cancer
Zahraa Qusairy, Anne Gangloff, Shuk On Annie Leung
Current Oncology.2023; 30(9): 8386. CrossRef - Riesgo residual. Conclusiones
Ángel Cequier, José Luis Zamorano
Revista Española de Cardiología Suplementos.2023; 23: 25. CrossRef - Causal effects of circulating lipids and lipid-lowering drugs on the risk of urinary stones: a Mendelian randomization study
Zilong Tan, Jing Hong, Aochuan Sun, Mengdi Ding, Jianwu Shen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of residual cardiovascular risk: trends and frontiers
Lin Wang, Sutong Wang, Chaoyuan Song, Yiding Yu, Yuehua Jiang, Yongcheng Wang, Xiao Li
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Understanding on the Genetic Basis of Key Metabolic Disorders: A Review
Kenneth Francis Rodrigues, Wilson Thau Lym Yong, Md. Safiul Alam Bhuiyan, Shafiquzzaman Siddiquee, Muhammad Dawood Shah, Balu Alagar Venmathi Maran
Biology.2022; 11(9): 1308. CrossRef - Lipoprotein Lipase: Is It a Magic Target for the Treatment of Hypertriglyceridemia
Joon Ho Moon, Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 575. CrossRef
- The role of adherence in patients with chronic diseases
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
- Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):464-475. Published online March 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0088
- 6,997 View
- 347 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We evaluated the achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) according to up-to-date Korean Diabetes Association (KDA), European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS), and American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines.
Methods
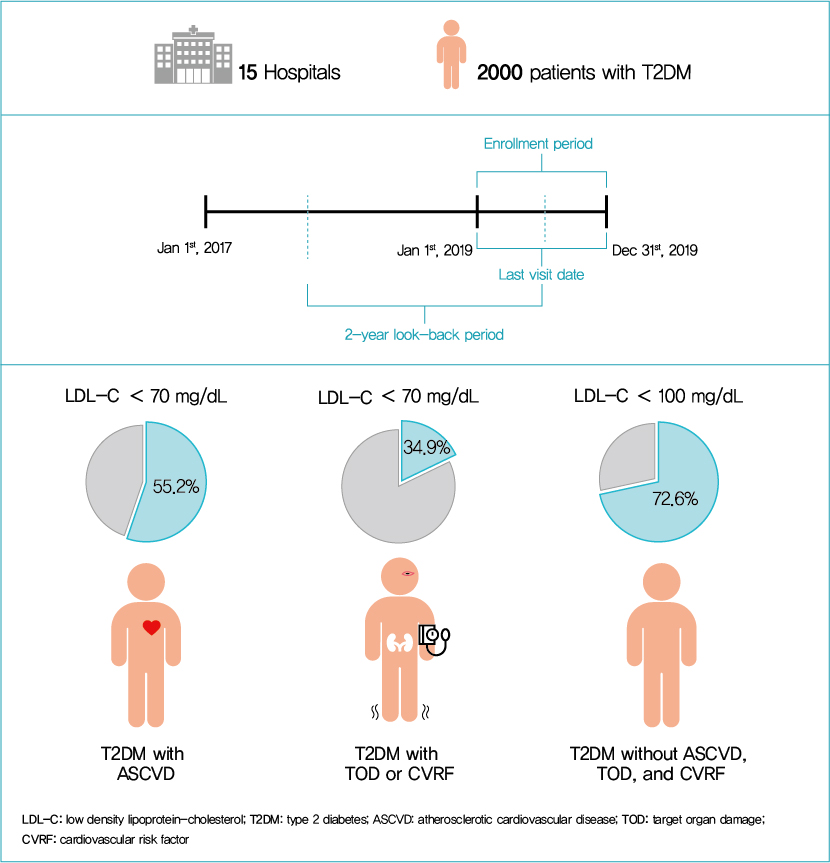
This retrospective cohort study collected electronic medical record data from patients with T2DM (≥20 years) managed by endocrinologists from 15 hospitals in Korea (January to December 2019). Patients were categorized according to guidelines to assess LDL-C target achievement. KDA (2019): Very High-I (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD]) <70 mg/dL; Very High-II (target organ damage [TOD], or cardiovascular risk factors [CVRFs]) <70 mg/dL; high (others) <100 mg/dL. ESC/EAS (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD): <55 mg/dL; Very High-II (TOD or ≥3-CVRF) <55 mg/dL; high (diabetes ≥10 years without TOD plus any CVRF) <70 mg/dL; moderate (diabetes <10 years without CVRF) <100 mg/dL. ADA (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD); Very High-II (age ≥40+ TOD, or any CVRF), for high intensity statin or statin combined with ezetimibe.
Results
Among 2,000 T2DM patients (mean age 62.6 years; male 55.9%; mean glycosylated hemoglobin 7.2%) ASCVD prevalence was 24.7%. Of 1,455 (72.8%) patients treated with statins, 73.9% received monotherapy. According to KDA guidelines, LDL-C target achievement rates were 55.2% in Very High-I and 34.9% in Very High-II patients. With ESC/EAS guidelines, target attainment rates were 26.6% in Very High-I, 15.7% in Very High-II, and 25.9% in high risk patients. Based on ADA guidelines, most patients (78.9%) were very-high risk; however, only 15.5% received high-intensity statin or combination therapy.
Conclusion
According to current dyslipidemia management guidelines, LDL-C goal achievement remains suboptimal in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Hidetaka Hamasaki
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299035. CrossRef - Distinct effects of rosuvastatin and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe on senescence markers of CD8+ T cells in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
Sang-Hyeon Ju, Joung Youl Lim, Minchul Song, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef
- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Computed Tomography-Derived Myosteatosis and Metabolic Disorders
- Iva Miljkovic, Chantal A. Vella, Matthew Allison
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):482-491. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0277
- 6,253 View
- 236 Download
- 42 Web of Science
- 44 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
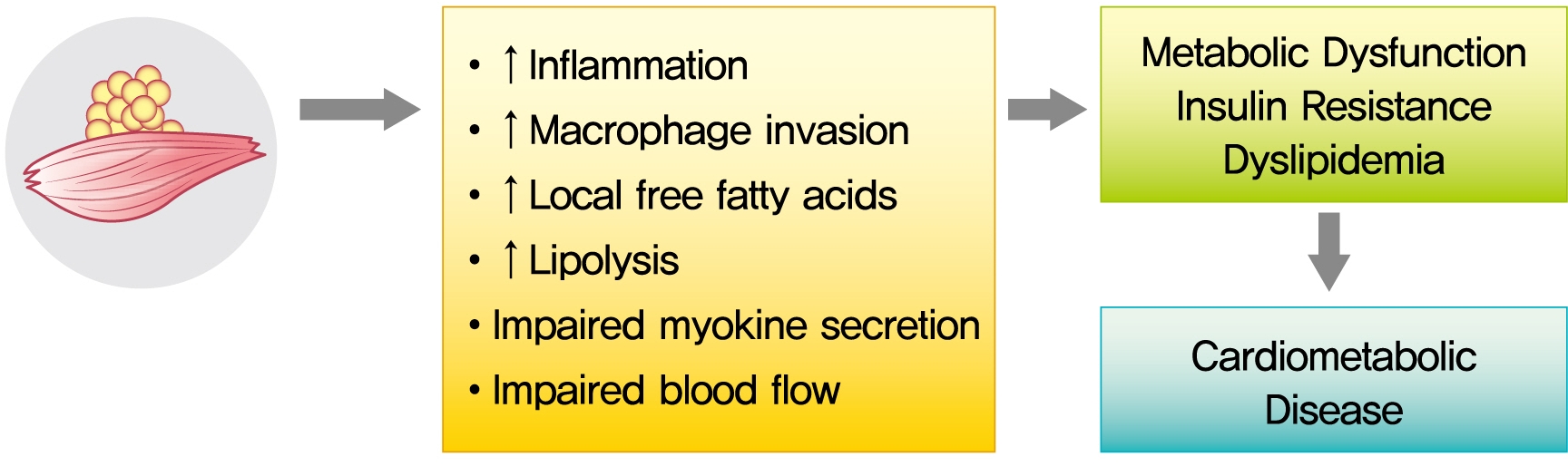
- The role of ectopic adipose tissue infiltration into skeletal muscle (i.e., myosteatosis) for metabolic disorders has received considerable and increasing attention in the last 10 years. The purpose of this review was to evaluate and summarize existing studies focusing on computed tomography (CT)-derived measures of myosteatosis and metabolic disorders. There is consistent evidence that CT-derived myosteatosis contributes to dysglycemia, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and inflammation, and, to some extent, dyslipidemia, independent of general obesity, visceral fat, and other relevant risk factors, suggesting that it may serve as a tool for metabolic risk prediction. Identification of which muscles should be examined, and the standardized CT protocols to be employed, are necessary to enhance the applicability of findings from epidemiologic studies of myosteatosis. Additional and longer longitudinal studies are necessary to confirm a role of myosteatosis in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, and examine these associations in a variety of muscles across multiple race/ethnic populations. Given the emerging role of myosteatosis in metabolic health, well-designed intervention studies are needed to investigate relevant lifestyle and pharmaceutical approaches.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Muscle Fat Content and Muscle Mass With Impaired Lung Function in Young Adults With Obesity: Evaluation With MRI
Xin Yu, Yan-Hao Huang, You-Zhen Feng, Zhong-Yuan Cheng, Cun-Chuan Wang, Xiang-Ran Cai
Academic Radiology.2024; 31(1): 9. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle alterations indicate poor prognosis in cirrhotic patients: a multicenter cohort study in China
Xin Zeng, Zhi-Wen Shi, Jia-Jun Yu, Li-Fen Wang, Chun-Yan Sun, Yuan-Yuan Luo, Pei-Mei Shi, Yong Lin, Yue-Xiang Chen, Jia Guo, Chun-Qing Zhang, Wei-Fen Xie
Hepatology International.2024; 18(2): 673. CrossRef - Subtype-specific Body Composition and Metabolic Risk in Patients With Primary Aldosteronism
Seung Shin Park, Chang Ho Ahn, Sang Wan Kim, Ji Won Yoon, Jung Hee Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(2): e788. CrossRef - Myosteatosis as a novel predictor of new‐onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation
Takahito Wakamiya, Takuya Fujimoto, Takahito Endo, Shun Nishioka, Naoki Yokoyama, Shimpei Yamashita, Kazuro Kikkawa, Yoji Hyodo, Takeshi Ishimura, Yasuo Kohjimoto, Isao Hara, Masato Fujisawa
International Journal of Urology.2024; 31(1): 39. CrossRef - Predictors of visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue and muscle density: The ShapeUp! Kids study
Gertraud Maskarinec, Yurii Shvetsov, Michael C. Wong, Devon Cataldi, Jonathan Bennett, Andrea K. Garber, Steven D. Buchthal, Steven B. Heymsfield, John A. Shepherd
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(3): 799. CrossRef - Association of daily carbohydrate intake with intermuscular adipose tissue in Korean individuals with obesity: a cross-sectional study
Ha-Neul Choi, Young-Seol Kim, Jung-Eun Yim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(1): 78. CrossRef - Myosteatosis is associated with poor survival after kidney transplantation: a large retrospective cohort validation
Jie Chen, Yue Li, Chengjie Li, Turun Song
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 49(4): 1210. CrossRef - Regenerative rehabilitation measures to restore tissue function after arsenic exposure
Adam A. Jasper, Kush H. Shah, Helmet Karim, Swathi Gujral, Iva Miljkovic, Caterina Rosano, Aaron Barchowsky, Amrita Sahu
Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering.2024; 30: 100529. CrossRef - Impact of CFTR modulator therapy on body composition as assessed by thoracic computed tomography: A follow-up study
Víctor Navas-Moreno, Fernando Sebastian-Valles, Víctor Rodríguez-Laval, Carolina Knott-Torcal, Mónica Marazuela, Nuria Sánchez de la Blanca, Jose Alfonso Arranz Martín, Rosa María Girón, Miguel Antonio Sampedro-Núñez
Nutrition.2024; 123: 112425. CrossRef - Myosteatosis predicts postoperative complications and long‐term survival in robotic gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A propensity score analysis
Pingan Ding, Jiaxiang Wu, Haotian Wu, Tongkun Li, Jiaxuan Yang, Li Yang, Honghai Guo, Yuan Tian, Peigang Yang, Lingjiao Meng, Qun Zhao
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A multifaceted and inclusive methodology for the detection of sarcopenia in patients undergoing bariatric surgery: an in-depth analysis of current evidence
Eunhye Seo, Yeongkeun Kwon, Ahmad ALRomi, Mohannad Eledreesi, Sungsoo Park
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Body Composition at CT and Risk of Future Disease
Michael A. Ohliger
Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between hypertension and myosteatosis evaluated by abdominal computed tomography
Han Na Jung, Yun Kyung Cho, Hwi Seung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Woo Je Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(4): 845. CrossRef - Muscle fat infiltration in chronic kidney disease: a marker related to muscle quality, muscle strength and sarcopenia
Carla Maria Avesani, Aline Miroski de Abreu, Heitor S. Ribeiro, Torkel B. Brismar, Peter Stenvinkel, Alice Sabatino, Bengt Lindholm
Journal of Nephrology.2023; 36(3): 895. CrossRef - Myosteatosis: a potential missing link between hypertension and metabolic disorder in the Asian population
Minyoung Lee, Sungha Park
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(6): 1603. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - Association between sarcopenic obesity and poor muscle quality based on muscle quality map and abdominal computed tomography
Yun Kyung Cho, Han Na Jung, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Joong‐Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Hong‐Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Obesity.2023; 31(6): 1547. CrossRef - Chest CT opportunistic biomarkers for phenotyping high-risk COVID-19 patients: a retrospective multicentre study
Anna Palmisano, Chiara Gnasso, Alberto Cereda, Davide Vignale, Riccardo Leone, Valeria Nicoletti, Simone Barbieri, Marco Toselli, Francesco Giannini, Marco Loffi, Gianluigi Patelli, Alberto Monello, Gianmarco Iannopollo, Davide Ippolito, Elisabetta Maria
European Radiology.2023; 33(11): 7756. CrossRef - Early menopause and premature ovarian insufficiency may increase the risk of sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Efstathios Divaris, Panagiotis Anagnostis, Nifon K. Gkekas, Evangelia Kouidi, Dimitrios G. Goulis
Maturitas.2023; 175: 107782. CrossRef - The Important Role of Intermuscular Adipose Tissue on Metabolic Changes Interconnecting Obesity, Ageing and Exercise: A Systematic Review
I Gusti Putu Suka Aryana, Ivana Beatrice Paulus, Sanjay Kalra, Dian Daniella, Raden Ayu Tuty Kuswardhani, Ketut Suastika, Sony Wibisono
European Endocrinology.2023; 19(1): 54. CrossRef - Increase in skeletal muscular adiposity and cognitive decline in a biracial cohort of older men and women
Caterina Rosano, Anne Newman, Adam Santanasto, Xiaonan Zhu, Bret Goodpaster, Iva Miljkovic
Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.2023; 71(9): 2759. CrossRef - Myosteatosis and bone marrow adiposity are not associated among postmenopausal women with fragility fractures
Sammy Badr, Héloïse Dapvril, Daniela Lombardo, Huda Khizindar, Claire Martin, Bernard Cortet, Anne Cotten, Julien Paccou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between trunk intramuscular adipose tissue content and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Japanese men
Noriko I. Tanaka, Masataka Suwa, Hisashi Maeda, Aya Tomita, Takayuki Imoto, Hiroshi Akima
Nutrition.2023; 113: 112083. CrossRef - Sarcopenic obesity and its relation with muscle quality and mortality in patients on chronic hemodialysis
Alice Sabatino, Carla Maria Avesani, Giuseppe Regolisti, Marianna Adinolfi, Giuseppe Benigno, Marco Delsante, Enrico Fiaccadori, Ilaria Gandolfini
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(8): 1359. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle adiposity is a novel risk factor for poor cognition in African Caribbean women
Adrianna I. Acevedo‐Fontánez, Ryan K. Cvejkus, Joseph M. Zmuda, Allison L. Kuipers, Emma Barinas‐Mitchell, Akira Sekikawa, Victor Wheeler, Caterina Rosano, Iva Miljkovic
Obesity.2023; 31(9): 2398. CrossRef - Obesity, Sarcopenia and Myosteatosis: Impact on Clinical Outcomes in the Operative Management of Crohn’s Disease
Mark Donnelly, Dorothee Driever, Éanna J Ryan, Jessie A Elliott, John Finnegan, Deirdre McNamara, Ian Murphy, Kevin C Conlon, Paul C Neary, Dara O Kavanagh, James M O’Riordan
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Meld-sarcopenia score and skeletal muscle density predicts short-term readmission of patients with hepatic encephalopathy
Shuo Yang, Lin Zhang, Qian Jin, Jian Wang, Danli Ma, Jie Gao, Rui Huang
European Journal of Radiology.2023; 169: 111178. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Adults
W. Guo, X. Zhao, D. Cheng, X. Liang, M. Miao, X. Li, J. Lu, N. Xu, Shuang Hu, Qun Zhang
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(11): 960. CrossRef - Association between relative muscle strength and hypertension in middle-aged and older Chinese adults
Jin-hua Luo, Tu-ming Zhang, Lin-lin Yang, Yu-ying Cai, Yu Yang
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynapenic Abdominal Obesity as a Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome in Individual 50 Years of Age or Older: English Longitudinal Study of Ageing
P.C. Ramírez, R. de Oliveira Máximo, D. Capra de Oliveira, A.F. de Souza, M. Marques Luiz, M. L. Bicigo Delinocente, A. Steptoe, C. de Oliveira, Tiago da Silva Alexandre
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(12): 1188. CrossRef - Editorial Comment to Myosteatosis as a novel predictor of urinary incontinence after robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy
Nobuhiro Haga, Naotaka Gunge, Hiroshi Matsuzaki, Yu Okabe, Takeshi Miyazaki
International Journal of Urology.2022; 29(1): 40. CrossRef - Ammonia and the Muscle: An Emerging Point of View on Hepatic Encephalopathy
Simone Di Cola, Silvia Nardelli, Lorenzo Ridola, Stefania Gioia, Oliviero Riggio, Manuela Merli
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(3): 611. CrossRef - Single skeletal muscle fiber mechanical properties: a muscle quality biomarker of human aging
Jae-Young Lim, Walter R. Frontera
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2022; 122(6): 1383. CrossRef - Sarcopenia in Patients with Cirrhosis after Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Placement
Jiacheng Liu, Jinqiang Ma, Chongtu Yang, Manman Chen, Qin Shi, Chen Zhou, Songjiang Huang, Yang Chen, Yingliang Wang, Tongqiang Li, Bin Xiong
Radiology.2022; 303(3): 711. CrossRef - Myosteatosis Significantly Predicts Persistent Dyspnea and Mobility Problems in COVID-19 Survivors
Rebecca De Lorenzo, Anna Palmisano, Antonio Esposito, Chiara Gnasso, Valeria Nicoletti, Riccardo Leone, Davide Vignale, Elisabetta Falbo, Marica Ferrante, Marta Cilla, Cristiano Magnaghi, Sabina Martinenghi, Giordano Vitali, Alessio Molfino, Patrizia Rove
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of myosteatosis in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Shaofang Feng, Huiwen Mu, Rong Hou, Yunxin Liu, Jianjun Zou, Zheng Zhao, Yubing Zhu
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2022; 27(7): 1127. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Strongly Associated With Hyperuricemia: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chinese Adults
Ningxin Chen, Tingting Han, Hongxia Liu, Jie Cao, Wenwen Liu, Didi Zuo, Ting Zhang, Xiucai Lan, Xian Jin, Yurong Weng, Yaomin Hu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in muscle health and nutrition: A toolkit for healthcare professionals
Carla M. Prado, Francesco Landi, Samuel T.H. Chew, Philip J. Atherton, Jeroen Molinger, Tobias Ruck, Maria Cristina Gonzalez
Clinical Nutrition.2022; 41(10): 2244. CrossRef - Factors related to trunk intramuscular adipose tissue content – A comparison of younger and older men
Funa Kitagawa, Madoka Ogawa, Akito Yoshiko, Yoshiharu Oshida, Teruhiko Koike, Hiroshi Akima, Noriko I. Tanaka
Experimental Gerontology.2022; 168: 111922. CrossRef - Association of myosteatosis with various body composition abnormalities and longer length of hospitalization in patients with decompensated cirrhosis
Xiaoyu Wang, Mingyu Sun, Yifan Li, Gaoyue Guo, Wanting Yang, Lihong Mao, Zihan Yu, Yangyang Hui, Xiaofei Fan, Binxin Cui, Kui Jiang, Chao Sun
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Peripheral bone structure, geometry, and strength and muscle density as derived from peripheral quantitative computed tomography and mortality among rural south Indian older adults
Guru Rajesh Jammy, Robert M. Boudreau, Iva Miljkovic, Pawan Kumar Sharma, Sudhakar Pesara Reddy, Susan L. Greenspan, Anne B. Newman, Jane A. Cauley, Bert B. Little
PLOS Global Public Health.2022; 2(10): e0000333. CrossRef - Muscle fat contents rather than muscle mass determines nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in patients with severe obesity
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Won Lee, Seungwan Ryu, Hye Soon Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Youngsung Suh
Obesity.2022; 30(12): 2440. CrossRef - Sex- and region-specific associations of skeletal muscle mass with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
Pei Xiao, Pu Liang, Panjun Gao, Jinyi Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging based body composition profiling and outcomes after oncologic liver surgery
Lorenzo Bernardi, Raffaello Roesel, Filippo Vagelli, Pietro Majno-Hurst, Alessandra Cristaudi
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of Muscle Fat Content and Muscle Mass With Impaired Lung Function in Young Adults With Obesity: Evaluation With MRI
- Drug/Regimen
- Fibrates Revisited: Potential Role in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
- Nam Hoon Kim, Sin Gon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):213-221. Published online April 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0001
- 7,686 View
- 312 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 42 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Fibrates, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α agonists, are potent lipid-modifying drugs. Their main effects are reduction of triglycerides and increase in high-density lipoprotein levels. Several randomized controlled trials have not demonstrated their benefits on cardiovascular risk reduction, especially as an “add on” to statin therapy. However, subsequent analyses by major clinical trials, meta-analyses, and real-world evidence have proposed their potential in specific patient populations with atherogenic dyslipidemia and metabolic syndrome. Here, we have reviewed and discussed the accumulated data on fibrates to understand their current status in cardiovascular risk management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy.2024; 10(2): 118. CrossRef - Role of PPARα in inflammatory response of C2C12 myotubes
Yuki Shimizu, Keiko Hamada, Tingting Guo, Chie Hasegawa, Yusuke Kuga, Katsushi Takeda, Takashi Yagi, Hiroyuki Koyama, Hiroshi Takagi, Daisuke Aotani, Hiromi Kataoka, Tomohiro Tanaka
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2024; 694: 149413. CrossRef - Obicetrapib: Reversing the Tide of CETP Inhibitor Disappointments
John J. P. Kastelein, Andrew Hsieh, Mary R. Dicklin, Marc Ditmarsch, Michael H. Davidson
Current Atherosclerosis Reports.2024; 26(2): 35. CrossRef - Metabolic Flexibility of the Heart: The Role of Fatty Acid Metabolism in Health, Heart Failure, and Cardiometabolic Diseases
Virginia Actis Dato, Stephan Lange, Yoshitake Cho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 1211. CrossRef - ApoB100 and Atherosclerosis: What’s New in the 21st Century?
Dimitris Kounatidis, Natalia G. Vallianou, Aikaterini Poulaki, Angelos Evangelopoulos, Fotis Panagopoulos, Theodora Stratigou, Eleni Geladari, Irene Karampela, Maria Dalamaga
Metabolites.2024; 14(2): 123. CrossRef - Follistatin-like 1 (FSTL1) levels as potential early biomarker of cardiovascular disease in a Mexican population
N. Ponce-Ruíz, J. F. Herrera-Moreno, A. E. Rojas-García, B. S. Barrón-Vivanco, C. A. González-Arias, Y. Y. Bernal-Hernández, L. Ortega-Cervantes, J. Ponce-Gallegos, J. A. Hernández-Nolasco, I. M. Medina-Díaz
Heart and Vessels.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 184. CrossRef - Coenzyme Q10 in atherosclerosis
Minjun Liao, Xueke He, Yangyang Zhou, Weiqiang Peng, Xiao-Mei Zhao, Miao Jiang
European Journal of Pharmacology.2024; 970: 176481. CrossRef - Onion Polyphenols as Multi-Target-Directed Ligands in MASLD: A Preliminary Molecular Docking Study
Maria Rosaria Paravati, Anna Caterina Procopio, Maja Milanović, Giuseppe Guido Maria Scarlata, Nataša Milošević, Maja Ružić, Nataša Milić, Ludovico Abenavoli
Nutrients.2024; 16(8): 1226. CrossRef - Present and Future of Dyslipidaemia Treatment—A Review
Iveta Merćep, Andro Vujević, Dominik Strikić, Ivana Radman, Ivan Pećin, Željko Reiner
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(18): 5839. CrossRef - VLDL receptor gene therapy for reducing atherogenic lipoproteins
Ronald M. Krauss, Jonathan T. Lu, Joseph J. Higgins, Cathryn M. Clary, Ray Tabibiazar
Molecular Metabolism.2023; 69: 101685. CrossRef - The emerging role of PPAR-alpha in breast cancer
Zhiwen Qian, Lingyan Chen, Jiayu Liu, Ying Jiang, Yan Zhang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 161: 114420. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives of peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor α agonists in cardiovascular health and disease
Yujie Pu, Chak Kwong Cheng, Hongsong Zhang, Jiang‐Yun Luo, Li Wang, Brian Tomlinson, Yu Huang
Medicinal Research Reviews.2023; 43(6): 2086. CrossRef - Macrophage angiotensin-converting enzyme reduces atherosclerosis by increasing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and fundamentally changing lipid metabolism
DuoYao Cao, Zakir Khan, Xiaomo Li, Suguru Saito, Ellen A Bernstein, Aaron R Victor, Faizan Ahmed, Aoi O Hoshi, Luciana C Veiras, Tomohiro Shibata, Mingtian Che, Lei Cai, Michifumi Yamashita, Ryan E Temel, Jorge F Giani, Daniel J Luthringer, Ajit S Divakar
Cardiovascular Research.2023; 119(9): 1825. CrossRef - Rapid flow synthesis of fenofibrate via scalable flash chemistry with in-line Li recovery
Sanket A. Kawale, Dong-Chang Kang, Gwang-Noh Ahn, Amirreza Mottafegh, Ji-Ho Kang, Gi-Su Na, Dong-Pyo Kim
Chemical Engineering Journal.2023; 477: 147033. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Safety of Fenofibrate in Routine Treatment of Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia and Metabolic Syndrome
Marat V. Ezhov, Gregory P. Arutyunov
Diseases.2023; 11(4): 140. CrossRef - Development of New Genome Editing Tools for the Treatment of Hyperlipidemia
Giulio Preta
Cells.2023; 12(20): 2466. CrossRef - Exploring the hypolipidemic effects of bergenin from Saxifraga melanocentra Franch: mechanistic insights and potential for hyperlipidemia treatment
Li Zhang, Yingying Tong, Yan Fang, Jinjin Pei, Qilan Wang, Gang Li
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and Dyslipidemia
Barbora Nussbaumerova, Hana Rosolova
Current Atherosclerosis Reports.2023; 25(12): 947. CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of residual cardiovascular risk: trends and frontiers
Lin Wang, Sutong Wang, Chaoyuan Song, Yiding Yu, Yuehua Jiang, Yongcheng Wang, Xiao Li
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia in Apoa5–/– mice results from reduced amounts of lipoprotein lipase in the capillary lumen
Ye Yang, Anne P. Beigneux, Wenxin Song, Le Phuong Nguyen, Hyesoo Jung, Yiping Tu, Thomas A. Weston, Caitlyn M. Tran, Katherine Xie, Rachel G. Yu, Anh P. Tran, Kazuya Miyashita, Katsuyuki Nakajima, Masami Murakami, Yan Q. Chen, Eugene Y. Zhen, Joonyoung R.
Journal of Clinical Investigation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood-Derived Lipid and Metabolite Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Research from Clinical Studies: A Recent Update
Dipali Kale, Amol Fatangare, Prasad Phapale, Albert Sickmann
Cells.2023; 12(24): 2796. CrossRef - Effective, disease-modifying, clinical approaches to patients with mild-to-moderate hypertriglyceridaemia
Gary F Lewis, Robert A Hegele
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2022; 10(2): 142. CrossRef - Effects of Alirocumab on Triglyceride Metabolism: A Fat-Tolerance Test and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study
Thomas Metzner, Deborah R. Leitner, Karin Mellitzer, Andrea Beck, Harald Sourij, Tatjana Stojakovic, Gernot Reishofer, Winfried März, Ulf Landmesser, Hubert Scharnagl, Hermann Toplak, Günther Silbernagel
Biomedicines.2022; 10(1): 193. CrossRef - Is there a role of lipid-lowering therapies in the management of fatty liver disease?
Ismini Tzanaki, Aris P Agouridis, Michael S Kostapanos
World Journal of Hepatology.2022; 14(1): 119. CrossRef - Therapeutic Strategies and Chemoprevention of Atherosclerosis: What Do We Know and Where Do We Go?
Ana Clara Aprotosoaie, Alexandru-Dan Costache, Irina-Iuliana Costache
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(4): 722. CrossRef - The Overlooked Transformation Mechanisms of VLCFAs: Peroxisomal β-Oxidation
Qinyue Lu, Weicheng Zong, Mingyixing Zhang, Zhi Chen, Zhangping Yang
Agriculture.2022; 12(7): 947. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 517. CrossRef - Novel Targets for a Combination of Mechanical Unloading with Pharmacotherapy in Advanced Heart Failure
Agata Jedrzejewska, Alicja Braczko, Ada Kawecka, Marcin Hellmann, Piotr Siondalski, Ewa Slominska, Barbara Kutryb-Zajac, Magdi H. Yacoub, Ryszard T. Smolenski
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 9886. CrossRef - Lipoprotein Lipase: Is It a Magic Target for the Treatment of Hypertriglyceridemia
Joon Ho Moon, Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 575. CrossRef - Fenofibrate add-on to statin treatment is associated with low all-cause death and cardiovascular disease in the general population with high triglyceride levels
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155327. CrossRef - Alterations of HDL’s to piHDL’s Proteome in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Diseases, and HDL-Targeted Therapies
Veronika Vyletelová, Mária Nováková, Ľudmila Pašková
Pharmaceuticals.2022; 15(10): 1278. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Risk Profile and Lipid Management in the Population-Based Cohort Study LATINO: 20 Years of Real-World Data
Cristina Gavina, Daniel Seabra Carvalho, Marisa Pardal, Marta Afonso-Silva, Diana Grangeia, Ricardo Jorge Dinis-Oliveira, Francisco Araújo, Tiago Taveira-Gomes
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(22): 6825. CrossRef - New and emerging lipid-lowering therapy
James M Backes, Daniel E Hilleman
Future Cardiology.2021; 17(8): 1407. CrossRef - Systemic PFOS and PFOA exposure and disturbed lipid homeostasis in humans: what do we know and what not?
Styliani Fragki, Hubert Dirven, Tony Fletcher, Bettina Grasl-Kraupp, Kristine Bjerve Gützkow, Ron Hoogenboom, Sander Kersten, Birgitte Lindeman, Jochem Louisse, Ad Peijnenburg, Aldert H. Piersma, Hans M. G. Princen, Maria Uhl, Joost Westerhout, Marco J. Z
Critical Reviews in Toxicology.2021; 51(2): 141. CrossRef -
A network pharmacology analysis on drug‐like compounds from
Ganoderma lucidum
for alleviation of atherosclerosis
Ki Kwang Oh, Md. Adnan, Dong Ha Cho
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Fenofibrate-Statin Combination Therapy in Patients With Inadequately Controlled Triglyceride Levels Despite Previous Statin Monotherapy: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, Phase IV Study
Myung Soo Park, Jong-Chan Youn, Eung Ju Kim, Ki Hoon Han, Sang Hak Lee, Sung Hea Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Sung Uk Kwon, Kyu-Hyung Ryu
Clinical Therapeutics.2021; 43(10): 1735. CrossRef - Prevalence of and Factors Associated With the Prescription of Fibrates Among Patients Receiving Lipid-Lowering Drugs in Germany
Louis Jacob, Roger-Axel Greiner, Mark Luedde, Karel Kostev
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology.2021; 78(6): 885. CrossRef - Challenging Issues in the Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Diabetes During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review of Current Literature
Leili Rahimi, Mojtaba Malek, Faramarz Ismail-Beigi, Mohammad E. Khamseh
Advances in Therapy.2020; 37(8): 3450. CrossRef - Treatment With Gemfibrozil Prevents the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease in Obese Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats
Corbin A. Shields, Bibek Poudel, Kasi C. McPherson, Andrea K. Brown, Ubong S. Ekperikpe, Evan Browning, Lamari Sutton, Denise C. Cornelius, Jan M. Williams
Frontiers in Physiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Renal and Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes
Amelia Charlton, Jessica Garzarella, Karin A. M. Jandeleit-Dahm, Jay C. Jha
Biology.2020; 10(1): 18. CrossRef
- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Pre-existing Depression among Newly Diagnosed Dyslipidemia Patients and Cardiovascular Disease Risk
- Jihoon Andrew Kim, Seulggie Choi, Daein Choi, Sang Min Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):307-315. Published online November 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0002
- 5,233 View
- 89 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Whether depression before diagnosis of dyslipidemia is associated with higher cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk among newly diagnosed dyslipidemia patients is yet unclear.
Methods The study population consisted of 72,235 newly diagnosed dyslipidemia patients during 2003 to 2012 from the National Health Insurance Service–Health Screening Cohort of South Korea. Newly diagnosed dyslipidemia patients were then detected for pre-existing depression within 3 years before dyslipidemia diagnosis. Starting from 2 years after the diagnosis date, patients were followed up for CVD until 2015. Adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for CVD were calculated by Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results Compared to dyslipidemia patients without depression, those with depression had higher risk for CVD (aHR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.09 to 1.41). Similarly, pre-existing depression was associated with increased risk for stroke (aHR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.06 to 1.53). The risk for CVD among depressed dyslipidemia patients for high (aHR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.06 to 1.90), medium (aHR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.91 to 1.52), and low (aHR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.05 to 1.50) statin compliance patients tended to be increased compared to patients without pre-existing dyslipidemia. The risk-elevating effect of depression on CVD tended to be preserved regardless of subgroups of smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity, and body mass index.
Conclusion Dyslipidemia patients with pre-existing depression had increased risk for CVD. Future studies that determine CVD risk after management of depression among dyslipidemia patients are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating effect of depression on the association between cardiovascular disease and the risk of all‐cause mortality: NHANES in 2005−2018
Xinxin Ma, Huan Zhang, Yuan Tian, Yaping Wang, Ling Liu, Lei Wang
Clinical Cardiology.2023; 46(11): 1380. CrossRef - Associations of sleep duration, daytime napping, and snoring with depression in rural China: a cross-sectional study
Xueyao Zhang, Guangxiao Li, Chuning Shi, Yingxian Sun
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between socioeconomic inequality and the global prevalence of anxiety and depressive disorders: an ecological study
Fatemeh Shahbazi, Marjan Shahbazi, Jalal Poorolajal
General Psychiatry.2022; 35(3): e100735. CrossRef - Impact of Alexithymia on the Lipid Profile in Major Depressed Individuals
Camille Point, Benjamin Wacquier, Marjorie Dosogne, Mohammed Al Faker, Hadrien Willame, Gwenolé Loas, Matthieu Hein, Philip W. Wertz
Journal of Lipids.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Association of Depression With Cardiovascular Diseases
Zain I Warriach, Sruti Patel, Fatima Khan, Gerardo F Ferrer
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fenofibrate add-on to statin treatment is associated with low all-cause death and cardiovascular disease in the general population with high triglyceride levels
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155327. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia prevalence and trends among adult mental disorder inpatients in Beijing, 2005–2018: A longitudinal observational study
Fude Yang, Qiuyue Ma, Botao Ma, Wenzhan Jing, Jue Liu, Moning Guo, Juan Li, Zhiren Wang, Min Liu
Asian Journal of Psychiatry.2021; 57: 102583. CrossRef - Non-HDL cholesterol level and depression among Canadian elderly—a cross-sectional analysis of the baseline data from the CLSA
Jian Liu, Surim Son, Mike Giancaterino, Chris P. Verschoor, Miya Narushima, David Moher
FACETS.2020; 5(1): 1006. CrossRef
- Mediating effect of depression on the association between cardiovascular disease and the risk of all‐cause mortality: NHANES in 2005−2018
- Epidemiology
- Association between Change in Alcohol Consumption and Metabolic Syndrome: Analysis from the Health Examinees Study
- Seulggie Choi, Kyuwoong Kim, Jong-Koo Lee, Ji-Yeob Choi, Aesun Shin, Sue Kyung Park, Daehee Kang, Sang Min Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):615-626. Published online April 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0128
- 5,449 View
- 86 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background The association between change in alcohol intake and metabolic syndrome is unclear.
Methods This retrospective cohort consisted of 41,368 males and females from the Health Examinees-GEM study. Participants were divided into non-drinkers (0.0 g/day), light drinkers (male: 0.1 to 19.9 g/day; female: 0.1 to 9.9 g/day), moderate drinkers (male: 20.0 to 39.9 g/day; female: 10.0 to 19.9 g/day), and heavy drinkers (male: ≥40.0 g/day; female: ≥20.0 g/day) for each of the initial and follow-up health examinations. Logistic regression analysis was used to determine the adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for developing metabolic syndrome according to the change in alcohol consumption between the initial and follow-up health examinations. Adjusted mean values for the change in waist circumference, fasting serum glucose (FSG), blood pressure, triglycerides, and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels were determined according to the change in alcohol consumption by linear regression analysis.
Results Compared to persistent light drinkers, those who increased alcohol intake to heavy levels had elevated risk of metabolic syndrome (aOR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.09 to 1.92). In contrast, heavy drinkers who became light drinkers had reduced risk of metabolic syndrome (aOR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.44 to 0.84) compared to persistent heavy drinkers. Increased alcohol consumption was associated with elevated adjusted mean values for waist circumference, FSG, blood pressure, triglycerides, and HDL-C levels (all
P <0.05). Reduction in alcohol intake was associated with decreased waist circumference, FSG, blood pressure, triglycerides, and HDL-C levels among initial heavy drinkers (allP <0.05).Conclusion Heavy drinkers who reduce alcohol consumption could benefit from reduced risk of metabolic syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inverse association between type 2 diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma in East Asian populations
Jinlong Huo, Yaxuan Xu, Xingqi Chen, Jie Yu, Lijin Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulation Mechanism and Potential Value of Active Substances in Spices in Alcohol–Liver–Intestine Axis Health
Jianyu Huang, Tao Huang, Jinjun Li
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3728. CrossRef - Impact of green space and built environment on metabolic syndrome: A systematic review with meta-analysis
Muhammad Mainuddin Patwary, Mohammad Javad Zare Sakhvidi, Sadia Ashraf, Payam Dadvand, Matthew H.E.M. Browning, Md Ashraful Alam, Michelle L. Bell, Peter James, Thomas Astell-Burt
Science of The Total Environment.2024; 923: 170977. CrossRef - Causal effects of sleep traits on metabolic syndrome and its components: a Mendelian randomization study
Yongli Yang, Long Wen, Xuezhong Shi, Chaojun Yang, Jingwen Fan, Yi Zhang, Guibin Shen, Huiping Zhou, Xiaocan Jia
Sleep and Breathing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of biochemical markers for diabetes prevention in the new decade
Marie Chan Sun, Marie A. S. Landinaff, Ruben Thoplan
Physical Sciences Reviews.2023; 8(11): 3767. CrossRef - Alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome: Clinical and epidemiological impact on liver disease
Fredrik Åberg, Christopher D. Byrne, Carlos J. Pirola, Ville Männistö, Silvia Sookoian
Journal of Hepatology.2023; 78(1): 191. CrossRef - Serum Nutritional Biomarkers and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in U.S. Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: The Results from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001–2006
Xinwei Peng, Jingjing Zhu, Henry S. Lynn, Xi Zhang
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 553. CrossRef - Evaluation and Treatment of Obesity and Its Comorbidities: 2022 Update of Clinical Practice Guidelines for Obesity by the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity
Kyoung-Kon Kim, Ji-Hee Haam, Bom Taeck Kim, Eun Mi Kim, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Eonju Jeon, Eungu Kang, Ga Eun Nam, Hye Yeon Koo, Jeong-Hyun Lim, Jo-Eun Jeong, Jong-Hee Kim, Jong Won Kim, Jung Ha Park, Jun Hwa Hong, Sang Eok Lee, Se Hee Min, Seung
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between alcohol consumption and risk of hyperuricaemia among adults: a large cross-sectional study in Chongqing, China
Siyu Chen, Rui Ding, Xiaojun Tang, Liling Chen, Qinwen Luo, Meng Xiao, Xianbin Ding, Bin Peng
BMJ Open.2023; 13(12): e074697. CrossRef - Lifestyle Factors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Urban Cambodia
Miharu Tamaoki, Ikumi Honda, Keisuke Nakanishi, Maki Nakajima, Sophathya Cheam, Manabu Okawada, Hisataka Sakakibara
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(17): 10481. CrossRef - Gender Differences of Health Behaviors in the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome for Middle-Aged Adults: A National Cross-Sectional Study in South Korea
Jaehee Yoon, Jeewuan Kim, Heesook Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3699. CrossRef - Association between alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome among Chinese adults
Yi Lin, Yan-Yan Ying, Si-Xuan Li, Si-Jia Wang, Qing-Hai Gong, Hui Li
Public Health Nutrition.2021; 24(14): 4582. CrossRef - Triglyceride-rich lipoprotein and LDL particle subfractions and their association with incident type 2 diabetes: the PREVEND study
Sara Sokooti, Jose L. Flores-Guerrero, Hiddo J. L. Heerspink, Margery A. Connelly, Stephan J. L. Bakker, Robin P. F. Dullaart
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inverse association between type 2 diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma in East Asian populations
- Complications
- Lipid Abnormalities in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Overt Nephropathy
- Sabitha Palazhy, Vijay Viswanathan
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(2):128-134. Published online January 11, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.2.128
- 3,730 View
- 51 Download
- 32 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetic nephropathy is a major complication of diabetes and an established risk factor for cardiovascular events. Lipid abnormalities occur in patients with diabetic nephropathy, which further increase their risk for cardiovascular events. We compared the degree of dyslipidemia among type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) subjects with and without nephropathy and analyzed the factors associated with nephropathy among them.
Methods In this retrospective study, T2DM patients with overt nephropathy were enrolled in the study group (
n =89) and without nephropathy were enrolled in the control group (n =92). Both groups were matched for age and duration of diabetes. Data on total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), urea and creatinine were collected from the case sheets. TG/HDL-C ratio, a surrogate marker for small, dense, LDL particles (sdLDL) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were calculated using equations. Multivariate analysis was done to determine the factors associated with eGFR.Results Dyslipidemia was present among 56.52% of control subjects and 75.28% of nephropathy subjects (
P =0.012). The percentage of subjects with atherogenic dyslipidemia (high TG+low HDL-C+sdLDL) was 14.13 among controls and 14.61 among nephropathy subjects. Though serum creatinine was not significantly different, mean eGFR value was significantly lower among nephropathy patients (P =0.002). Upon multivariate analysis, it was found that TC (P =0.007) and HDL-C (P =0.06) were associated with eGFR among our study subjects.Conclusion Our results show that dyslipidemia was highly prevalent among subjects with nephropathy. Regular screening for dyslipidemia may be beneficial in controlling the risk for adverse events among diabetic nephropathy patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on Pathogenesis and Early Biomarkers of Diabetic Kidney Disease
玉金 王
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(04): 703. CrossRef - Association of matrix metalloproteinase‐2 gene variants with diabetic nephropathy risk
Sameh Sarray, Laila Ben Lamine, Meriem Dallel, Intissar Ezzidi, Nejla Sellami, Amira Turki, Amgad Elbaz El‐Agroudy Moustafa, Nabil Mtiraoui
The Journal of Gene Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio with lipid abnormalities and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Sitaram Khadka, Gopal K. Yadav, Prativa Subedi, Kapil Amgain, Arun Sharma, Rinku Joshi
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2023; 85(9): 4329. CrossRef - Evaluation of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio, Low-Density Lipoprotein/Albumin Ratio, and Red Cell Distribution Width/Albumin Ratio in the Estimation of Proteinuria in Uncontrolled Diabetic Patients
Duygu Tutan, Murat Doğan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation between alternative insulin resistance indexes and diabetic kidney disease: a retrospective study
Xiaodie Mu, Aihua Wu, Huiyue Hu, Min Yang, Hua Zhou
Endocrine.2023; 84(1): 136. CrossRef - Asprosin in early detection of nephropathy in type2 diabetes mellitus
Ola Hussein Abed Alwahid, Talat Tariq Khalil, Mohamed Abed AL-Ridha Ismael
Medical Journal of Babylon.2023; 20(4): 689. CrossRef - Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol is a Potential Marker for Predicting Laser Treatment for Retinopathy in Diabetic Patients
Atsuko Nakayama, Hiroyuki Morita, Tatsuyuki Sato, Takuya Kawahara, Norifumi Takeda, Satoshi Kato, Hiroshi Itoh, Issei Komuro
Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis.2022; 29(5): 678. CrossRef - Estimation of Fluoride and Sirtuin1 in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy in Kolar District of Karnataka, India
Sai Deepika Ram Mohan, Kurpad N. Shashidhar, Raveesha Anjanappa, Muninarayana Chandrappa
Journal of Laboratory Physicians.2022; 14(01): 057. CrossRef - The Relationship of 25(OH)D3 with Diabetes Mellitus and the Mediation Effect of Lipid Profile in Chinese Rural Population of Henan Province
Mimi Zhang, Fei Yu, Yuan Xue, Lulu Song, Mengsi Du, Xing Li, Wenjie Li
Medicina.2022; 58(1): 85. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia and its associated factors among adult diabetes outpatients in West Shewa zone public hospitals, Ethiopia
Daba Abdissa, Delessa Hirpa
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Fenofibrate Formulations for the Treatment of Lipid Disorders: Past, Present, and Future
Thu Nhan Nguyen, Jeong-Sook Park
CardioMetabolic Syndrome Journal.2022; 2(2): 77. CrossRef - Assessment of level of care of diabetic patients with nephropathy in predialysis stage 4 in Tanta
AhmedA A Elmoghany, MohammedH El-Naggar, Ali El-Sherbiny, IngyA W Ibrahim
Tanta Medical Journal.2022; 50(4): 267. CrossRef - Prediction models and nomograms for 10‐year risk of end‐stage renal disease in Chinese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in primary care
Weinan Dong, Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Daniel Yee Tak Fong, Ruby Lai Ping Kwok, David Vai Kiong Chao, Kathryn Choon Beng Tan, Eric Ming Tung Hui, Wendy Wing Sze Tsui, King Hong Chan, Colman Siu Cheung Fung, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(4): 897. CrossRef - Matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene polymorphism (-1562 C/T) and its correlation with diabetic nephropathy
Kholoud Shalaby, Rania Bahriz, Nancy Mahsoub, Mohammed M. El-Arman, Ghada El-Said
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Antidiabetic and Nephroprotective Effects of Polysaccharide Extract from the Seaweed Caulerpa racemosa in High Fructose-Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Nephropathy
Meng Cao, Yan Li, Ademola C Famurewa, Opeyemi Joshua Olatunji
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 2121. CrossRef - A Study of Creatinine Level among Patients with Dyslipidemia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Multilayer Perceptron and Multiple Linear Regression
Farah Muna Mohamad Ghazali, Wan Muhamad Amir W Ahmad, Kumar Chandan Srivastava, Deepti Shrivastava, Nor Farid Mohd Noor, Nurul Farid Nizam Akbar, Nor A Aleng, Mohammad Azlida Alam
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S795. CrossRef - L-ergothioneine and its combination with metformin attenuates renal dysfunction in type-2 diabetic rat model by activating Nrf2 antioxidant pathway
Ayobami Dare, Mahendra L. Channa, Anand Nadar
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 141: 111921. CrossRef TLR4 Polymorphisms (896A>G and 1196C>T) Affect the Predisposition to Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Narges Khaghanzadeh, Nadereh Naderi, Nazanin Pournasrollah, Elahe Farahbakhsh, Masoumeh Kheirandish, Afshin Samiei
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 1015. CrossRef- The Hypoglycemic and Renal Protection Properties of Crocin via Oxidative Stress-Regulated NF-κB Signaling in db/db Mice
Ye Qiu, Xue Jiang, Danping Liu, Zichun Deng, Weiwei Hu, Zhiping Li, Yuxin Li
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid profiles and risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in CKD and diabetes: A nationwide population-based study
Yeonhee Lee, Sehoon Park, Soojin Lee, Yaerim Kim, Min Woo Kang, Semin Cho, Sanghyun Park, Kyungdo Han, Yong Chul Kim, Seoung Seok Han, Hajeong Lee, Jung Pyo Lee, Kwon Wook Joo, Chun Soo Lim, Yon Su Kim, Dong Ki Kim, Gregory Shearer
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(4): e0231328. CrossRef - Zingerone produces antidiabetic effects and attenuates diabetic nephropathy by reducing oxidative stress and overexpression of NF-κB, TNF-α, and COX-2 proteins in rats
Brahmjot Singh, Ajay Kumar, Hasandeep Singh, Sarabjit Kaur, Satwinderjeet Kaur, Harpal Singh Buttar, Saroj Arora, Balbir Singh
Journal of Functional Foods.2020; 74: 104199. CrossRef Prevalence and Associated Factors of Dyslipidemia Among Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Arabia
Riyadh A Alzaheb, Abdullah H Altemani
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4033. CrossRef- Aqueous leaf extract of Clinacanthus nutans improved metabolic indices and sorbitol‐related complications in type II diabetic rats (T2D)
Mustapha Umar Imam, Maznah Ismail, Annie George, Sasikala M. Chinnappan, Ashril Yusof
Food Science & Nutrition.2019; 7(4): 1482. CrossRef - Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Ameliorate Diabetic Nephropathy In Vivo and In Vitro by Inhibiting Advanced Glycation End Product-Activated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Nanquan Rao, Xiaotong Wang, Jing Xie, Jingzhi Li, Yue Zhai, Xiaoxia Li, Tengjiaozi Fang, Yuanyuan Wang, Yuming Zhao, Lihong Ge
Stem Cells International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - The Antidiabetic and Antinephritic Activities of Auricularia cornea (An Albino Mutant Strain) via Modulation of Oxidative Stress in the db/db Mice
Di Wang, Xue Jiang, Shanshan Teng, Yaqin Zhang, Yang Liu, Xiao Li, Yu Li
Frontiers in Immunology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Prevalence and Range of Major Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Iranian Diabetic Adults
Nazanin Alaei Faradonbeh, Fariborz Nikaeen, Mojtaba Akbari, Naser Almasi, Mehrbod Vakhshoori
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine.2019; 1(7): 517. CrossRef - Anti-Diabetic Nephropathy Activities of Polysaccharides Obtained from Termitornyces albuminosus via Regulation of NF-κB Signaling in db/db Mice
Chang Yang, Qi Feng, Huan Liao, Xinlei Yu, Yang Liu, Di Wang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(20): 5205. CrossRef - Resveratrol exhibits an effect on attenuating retina inflammatory condition and damage of diabetic retinopathy via PON1
Yuhua Chen, Jiao Meng, Hua Li, Hong Wei, Fangfang Bi, Shi Liu, Kai Tang, Haiyu Guo, Wei Liu
Experimental Eye Research.2019; 181: 356. CrossRef - Novel aspects of PCSK9 and lipoprotein receptors in renal disease-related dyslipidemia
Pragyi Shrestha, Bart van de Sluis, Robin P.F. Dullaart, Jacob van den Born
Cellular Signalling.2019; 55: 53. CrossRef - Plasma triglyceride levels and central obesity predict the development of kidney injury in Chinese community older adults
Yujie Cao, Guangshan Sun, Rui Liu, Ao Sun, Qian Zhang, Yang Li, Lele Wang, Xiangli Chao, Xiaojie Zhou, Sha Zhang, Ruping Chen
Renal Failure.2019; 41(1): 946. CrossRef - The Antidiabetic and Antinephritic Activities ofTuber melanosporumvia Modulation of Nrf2-Mediated Oxidative Stress in the db/db Mouse
Xue Jiang, Shanshan Teng, Xue Wang, Shan Li, Yaqin Zhang, Di Wang
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - “Diabetes and Metabolism Disorders Medicinal Plants: A Glance at the Past and a Look to the Future 2018”: Antihyperglycemic Activity ofHamelia patensJacq. Extracts
Catalina Rugerio-Escalona, Cynthia Ordaz-Pichardo, Elvia Becerra-Martinez, María del Carmen Cruz-López, Victor E. López-y-López, Aarón Mendieta-Moctezuma, Ignacio E. Maldonado-Mendoza, Fabiola E. Jiménez-Montejo
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Spatholobus suberectus Ameliorates Diabetes-Induced Renal Damage by Suppressing Advanced Glycation End Products in db/db Mice
Moon Do, Jinyoung Hur, Jiwon Choi, Yoonsook Kim, Ho-Young Park, Sang Ha
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(9): 2774. CrossRef - Effect of Fiber-Rich Snacks on C-Reactive Protein and Atherogenic Index in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Nartyr Sunarti, Sri Lestari Sulistyo Rini, Hemi Sinorita, Dini Ariani
Romanian Journal of Diabetes Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases.2018; 25(4): 357. CrossRef - Effect of Fiber-Rich Snacks on C-Reactive Protein and Atherogenic Index in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Sunarti, Sri Lestari Sulistyo Rini, Hemi Sinorita, Dini Ariani
Romanian Journal of Diabetes Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases.2018; 25(3): 271. CrossRef - Correlation between Cholesterol, Triglycerides, Calculated, and Measured Lipoproteins: Whether Calculated Small Density Lipoprotein Fraction Predicts Cardiovascular Risks
Sikandar Hayat Khan, Nadeem Fazal, Athar Abbas Gilani Shah, Syed Mohsin Manzoor, Naveed Asif, Aamir Ijaz, Najmusaqib Khan Niazi, Muhammad Yasir
Journal of Lipids.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef
- Research Progress on Pathogenesis and Early Biomarkers of Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Clinical Care/Education
- Efficacy of Moderate Intensity Statins in the Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Sung Hye Kong, Bo Kyung Koo, Min Kyong Moon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(1):23-30. Published online December 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.1.23
- 4,504 View
- 84 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background There has been evidences of ethnic differences in the low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) lowering effect of statin. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy of moderate-intensity statins in the treatment of dyslipidemia among Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods We analyzed a retrospective cohort that consisted of Korean patients with T2DM aged 40 to 75 years who had been prescribed any of the moderate-intensity statins (atorvastatin 10 or 20 mg, rosuvastatin 5 or 10 mg, pitavastatin 2 mg, or pravastatin 40 mg). Among them, only patients with baseline lipid profiles before starting statin treatment were selected, and changes in their lipid profiles before and 6 months after statin therapy were analyzed.
Results Following the first 6 months of therapy, the overall LDL-C reduction was −47.4% (interquartile range, −56.6% to −34.1%). In total, 92.1% of the participants achieved an LDL-C level of <100 mg/dL, 38.3% had a 30% to 50% reduction in their LDL-C levels, and 42.3% had a reduction in their LDL-C levels greater than 50%. The response rates of each drug for achieving a LDL-C level <100 mg/dL were 81.7%, 93.1%, 95.0%, 95.0%, 96.5%, and 91.7% for treatment with atorvastatin doses of 10 or 20 mg, rosuvastatin 5 or 10 mg, pitavastatin 2 mg, and pravastatin 40 mg, respectively.
Conclusion In conclusion, the use of moderate-intensity statins reduced LDL-C levels less than 100 mg/dL in most of the Korean patients studied with T2DM. The efficacies of those statins were higher than expected in about 42% of Korean patients with T2DM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of combining evolocumab with statin on carotid intraplaque neovascularization in patients with premature coronary artery disease (EPOCH)
Yanyan Han, Ling Ren, Xiang Fei, Jingjing Wang, Tao Chen, Jun Guo, Qi Wang
Atherosclerosis.2024; 391: 117471. CrossRef - Impact of Plasma Exposure of Statins and Their Metabolites With Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Chinese Patients With Coronary Artery Disease
Xiao-hong Zhou, Li-yun Cai, Wei-Hua Lai, Xue Bai, Yi-bin Liu, Qian Zhu, Guo-dong He, Ji-Yan Chen, Min Huang, Zhi-ling Zhou, Shi-long Zhong
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of High-Dose Atorvastatin in Moderate-to-High Cardiovascular Risk Postmenopausal Korean Women with Dyslipidemia
Jaecheol Moon, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Kyung-Wan Min, Hyun Ho Shin
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2020; 9(1): 162. CrossRef - Effects of lowest-dose vs. highest-dose pitavastatin on coronary neointimal hyperplasia at 12-month follow-up in type 2 diabetic patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: an optical coherence tomography analysis
Jung Wook Lim, Han Saem Jeong, Soon Jun Hong, Hyo Jeong Kim, Young Chan Kim, Bong Gyun Kang, Su Min Jeon, Jae Young Cho, Seung Hoon Lee, Hyung Joon Joo, Jae Hyoung Park, Cheol Woong Yu
Heart and Vessels.2019; 34(1): 62. CrossRef - Effect of Statin Therapy on Outcomes of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke and Atrial Fibrillation
Kang‐Ho Choi, Woo‐Keun Seo, Man‐Seok Park, Joon‐Tae Kim, Jong‐Won Chung, Oh Young Bang, Gyeong‐Moon Kim, Tae‐Jin Song, Bum Joon Kim, Sung Hyuk Heo, Jin‐Man Jung, Kyung‐Mi Oh, Chi Kyung Kim, Sungwook Yu, Kwang‐Yeol Park, Jeong‐Min Kim, Jong‐Ho Park, Jay Ch
Journal of the American Heart Association.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Moderate-intensity versus high-intensity statin therapy in Korean patients with angina undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents: A propensity-score matching analysis
Mahn-Won Park, Gyung-Min Park, Seungbong Han, Yujin Yang, Yong-Giun Kim, Jae-Hyung Roh, Hyun Woo Park, Jon Suh, Young-Rak Cho, Ki-Bum Won, Soe Hee Ann, Shin-Jae Kim, Dae-Won Kim, Sung Ho Her, Sang-Gon Lee, George C.M. Siontis
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(12): e0207889. CrossRef - Letter: Efficacy of Moderate Intensity Statins in the Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:23-30)
Jae-Han Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(2): 150. CrossRef - Response: Efficacy of Moderate Intensity Statins in the Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:23-30)
Sung Hye Kong, Bo Kyung Koo, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(2): 152. CrossRef
- Effect of combining evolocumab with statin on carotid intraplaque neovascularization in patients with premature coronary artery disease (EPOCH)
- Others
- Effect of Atorvastatin on Growth Differentiation Factor-15 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia
- Ji Min Kim, Min Kyung Back, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(1):70-78. Published online February 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.1.70
- 4,189 View
- 33 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Elevated serum levels of growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) are associated with type 2 diabetes. Therefore, the effects of atorvastatin on metabolic parameters and GDF-15 levels in patients with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia were evaluated.
Methods In this prospective randomized trial from February 2013 to March 2014, 50 consecutive type 2 diabetic patients with a low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels ≥100 mg/dL were enrolled. The patients were divided into two groups based on the amount of atorvastatin prescribed, 10 mg/day (
n =23) or 40 mg/day (n =27). The effect of atorvastatin on metabolic parameters, including lipid profiles and GDF-15 levels, at baseline and after 8 weeks of treatment were compared.Results The baseline metabolic parameters and GDF-15 levels were not significantly different between the two groups. After 8 weeks of treatment, the total cholesterol (TC) and LDL-C levels were significantly decreased in both groups. The mean changes in TC and LDL-C levels were more significant in the 40 mg atorvastatin group. The GDF-15 level was decreased in the 10 mg atorvastatin group, from 1,460.6±874.8 to 1,451.0±770.8 pg/mL, and was increased in the 40 mg atorvastatin group, from 1,271.6±801.0 to 1,341.4±855.2 pg/mL. However, the change in the GDF-15 level was not statistically significant in the 10 or 40 mg atorvastatin group (
P =0.665 andP =0.745, respectively).Conclusion The GDF-15 levels were not significantly changed after an 8-week treatment with atorvastatin in type 2 diabetic patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship of Growth differentiation factor-15 with renal damage and dyslipidemia in non-albuminuric and albuminuric Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hasan Esat Yücel, Bilal İlanbey
Medical Science and Discovery.2022; 9(6): 334. CrossRef - Comparative effectiveness of statins on non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol in people with diabetes and at risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and network meta-analysis
Alexander Hodkinson, Dialechti Tsimpida, Evangelos Kontopantelis, Martin K Rutter, Mamas A Mamas, Maria Panagioti
BMJ.2022; : e067731. CrossRef - The Cytokine Growth Differentiation Factor-15 and Skeletal Muscle Health: Portrait of an Emerging Widely Applicable Disease Biomarker
Boel De Paepe
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(21): 13180. CrossRef - Biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with psoriasis
Hannah Kaiser, Xing Wang, Amanda Kvist-Hansen, Martin Krakauer, Peter Michael Gørtz, Benjamin D. McCauley, Lone Skov, Christine Becker, Peter Riis Hansen
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Growth differentiation factor-15 regulates oxLDL-induced lipid homeostasis and autophagy in human macrophages
Kathrin Ackermann, Gabriel A. Bonaterra, Ralf Kinscherf, Anja Schwarz
Atherosclerosis.2019; 281: 128. CrossRef
- The relationship of Growth differentiation factor-15 with renal damage and dyslipidemia in non-albuminuric and albuminuric Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Interaction between Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: More than Diabetic Dyslipidemia
- Klaus G. Parhofer
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(5):353-362. Published online October 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.5.353
- 11,257 View
- 261 Download
- 241 Web of Science
- 237 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Glucose and lipid metabolism are linked to each other in many ways. The most important clinical manifestation of this interaction is diabetic dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated triglycerides, low high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and predominance of small-dense LDL particles. However, in the last decade we have learned that the interaction is much more complex. Hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL-C cannot only be the consequence but also the cause of a disturbed glucose metabolism. Furthermore, it is now well established that statins are associated with a small but significant increase in the risk for new onset diabetes. The underlying mechanisms are not completely understood but modulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG CoA)-reductase may play a central role as genetic data indicate that mutations resulting in lower HMG CoA-reductase activity are also associated with obesity, higher glucose concentrations and diabetes. Very interestingly, this statin induced increased risk for new onset type 2 diabetes is not detectable in subjects with familial hypercholesterolemia. Furthermore, patients with familial hypercholesterolemia seem to have a lower risk for type 2 diabetes, a phenomenon which seems to be dose-dependent (the higher the low density lipoprotein cholesterol, the lower the risk). Whether there is also an interaction between lipoprotein(a) and diabetes is still a matter of debate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Response surface methodology based development of an optimized polyherbal formulation and evaluation of its anti-diabetic and anti-obesity potential in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
Tanisha, Sunil Venkategowda, Mala Majumdar
Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine.2024; 14(1): 70. CrossRef - Combined untargeted and targeted lipidomics approaches reveal potential biomarkers in type 2 diabetes mellitus cynomolgus monkeys
Chao‐Yang Tian, Qun‐Hui Yang, Hai‐Zhou Lv, Feng Yue, Fei‐Fan Zhou
Journal of Medical Primatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Aging Hallmarks and Progression and Age-Related Diseases: A Landscape View of Research Advancement
Rumiana Tenchov, Janet M. Sasso, Xinmei Wang, Qiongqiong Angela Zhou
ACS Chemical Neuroscience.2024; 15(1): 1. CrossRef - Premorbid lipid levels and long-term risk of ALS—a population-based cohort study
Anders Myhre Vaage, Jūratė Šaltytė Benth, Haakon E. Meyer, Trygve Holmøy, Ola Nakken
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degeneration.2024; 25(3-4): 358. CrossRef - Astaxanthin as a metabolic regulator of glucose and lipid homeostasis
Alessandro Medoro, Mariano Intrieri, Daniela Passarella, Donald Craig Willcox, Sergio Davinelli, Giovanni Scapagnini
Journal of Functional Foods.2024; 112: 105937. CrossRef - Gum acacia dietary fiber: Significance in immunomodulation, inflammatory diseases, and cancer
Srikanth Barkeer, Ramesh Pothuraju, Pushkar Malakar, Tatiana Colombo Pimentel, Jawed A. Siddiqui, S. Asha Nair
Phytotherapy Research.2024; 38(3): 1509. CrossRef - Exploring clinical indicator variations in stroke patients with multiple risk factors: focus on hypertension and inflammatory reactions
Jiejie Guo, Mei Tian, Yongang Li, Yitong Guo, Ting Zhang, Xuan Liu, Jinze Shen, Lin Zhang, Yueqi Yu, Ling Cao, Haiyan Gu, Yanfang Li, Shiwei Duan, Qinwen Wang
European Journal of Medical Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Environmental Enrichments on Welfare and Hepatic Metabolic Regulation of Broiler Chickens
Seong W. Kang, Karen D. Christensen, Michael T. Kidd Jr., Sara K. Orlowski
Animals.2024; 14(4): 557. CrossRef - Serum Glycome as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Factor in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Ognjen Radojičić, Lucia Pažitná, Zorana Dobrijević, Paras Kundalia, Kristina Kianičková, Jaroslav Katrlík, Vesna Mandić Marković, Željko Miković, Olgica Nedić, Dragana Robajac
Biochemistry (Moscow).2024; 89(1): 148. CrossRef - Antidiabetic activity of methanolic extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn. fruit in alloxan-induced Swiss albino diabetic mice
Shahida Akter, Hanif Ali, Ali A. Shati, Mohammad Y. Alfaifi, Serag Eldin I. Elbehairi, R. Z. Sayyed, Tanzima Yeasmin
Open Agriculture.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Probiotic Limosilactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 Changes Foxp3 Deficiency-Induced Dyslipidemia and Chronic Hepatitis in Mice
Erini Nessim Kostandy, Ji Ho Suh, Xiangjun Tian, Beanna Okeugo, Erin Rubin, Sara Shirai, Meng Luo, Christopher M. Taylor, Kang Ho Kim, J. Marc Rhoads, Yuying Liu
Nutrients.2024; 16(4): 511. CrossRef - Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein 1: A Mediator for High-Fat Diet–Induced Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Glucose Intolerance in Fish
Zengqi Zhao, Xiaojun Xiang, Qiang Chen, Jianlong Du, Si Zhu, Xiang Xu, Yanan Shen, Shunlang Wen, Yueru Li, Wei Xu, Kangsen Mai, Qinghui Ai
The Journal of Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of METS-IR index with depressive symptoms in US adults: A cross-sectional study
Qi Huang, Denghong Wang, Shanshan Chen, Lei Tang, Chaoyang Ma
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 355: 355. CrossRef - Relationships of apolipoprotein E genotypes with a cluster of seven in persons with type 2 diabetes
Douglas E. Barre, Kazimiera A. Mizier-Barre, Odette Griscti, Kevin Hafez
Endocrine Regulations.2024; 58(1): 40. CrossRef - Normal fat intake with high MUFA content and an appropriate SFA/MUFA/PUFA ratio improved the health of rats
Yuhao Zhou, Ligang Yang, Chu Chu, Shiqing Chen, Danwei Yue, Yoong Jun Hao, Guiju Sun, Hui Xia
European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Pueraria lobata root extract alleviates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating the gut microbiota and associated metabolites
Xin Tang, Yongkang Zhou, Fei Liu, Botao Wang, Bingyong Mao, Qiuxiang Zhang, Jianxin Zhao, Wei Chen, Shumao Cui
Food Bioscience.2024; : 103746. CrossRef - The nutritional profile of chia seeds and sprouts: tailoring germination practices for enhancing health benefits-a comprehensive review
Manting Huang, Hui Xu, Qian Zhou, Jianbo Xiao, Yuting Su, Mingfu Wang
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Model-Assisted Uniformly Honest Inference for Optimal Treatment Regimes in High Dimension
Yunan Wu, Lan Wang, Haoda Fu
Journal of the American Statistical Association.2023; 118(541): 305. CrossRef - Associations of PFAS-related plasma metabolites with cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations
T. Schillemans, I.A. Bergdahl, K. Hanhineva, L. Shi, C. Donat-Vargas, J. Koponen, H. Kiviranta, R. Landberg, A. Åkesson, C. Brunius
Environmental Research.2023; 216: 114570. CrossRef - Physiological mechanisms of TLR4 in glucolipid metabolism regulation: Potential use in metabolic syndrome prevention
Feng Zeng, Jiawei Zheng, Li Shen, Daniela D. Herrera-Balandrano, Wuyang Huang, Zhongquan Sui
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(1): 38. CrossRef - Ferulic acid improves glucose homeostasis by modulation of key diabetogenic activities and restoration of pancreatic architecture in diabetic rats
Veronica F. Salau, Ochuko L. Erukainure, Kolawole O. Olofinsan, Vishal Bharuth, Omamuyovwi M. Ijomone, Md. Shahidul Islam
Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 37(2): 324. CrossRef - Research Progress of TyG Index and IR in Cognitive Impairment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
艳梅 刘
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(01): 415. CrossRef - Potential Therapies Targeting the Metabolic Reprogramming of Diabetes-Associated Breast Cancer
Hang Chee Erin Shum, Ke Wu, Jaydutt Vadgama, Yong Wu
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(1): 157. CrossRef - Identification of reversible and druggable pathways to improve beta-cell function and survival in Type 2 diabetes
Smithamol Sithara, Tamsyn Crowley, Ken Walder, Kathryn Aston-Mourney
Islets.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Imaging and Molecular Biology Reveal the Interplay between Lipid Metabolism and DHA-Induced Modulation of Redox Homeostasis in RPE Cells
Giada Bianchetti, Maria Elisabetta Clementi, Beatrice Sampaolese, Cassandra Serantoni, Alessio Abeltino, Marco De Spirito, Shlomo Sasson, Giuseppe Maulucci
Antioxidants.2023; 12(2): 339. CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Low-Dose Photodynamic Therapy Effects on Diabetic Wound Healing Using Raman Spectroscopy
Hala Zuhayri, Alice A. Samarinova, Alexey V. Borisov, David A. Lopez Guardado, Houssain Baalbaki, Natalya A. Krivova, Yury V. Kistenev
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(2): 595. CrossRef - Plasma lipidomic profiling reveals metabolic adaptations to pregnancy and signatures of cardiometabolic risk: a preconception and longitudinal cohort study
Li Chen, Sartaj Ahmad Mir, Anne K. Bendt, Esther W. L. Chua, Kothandaraman Narasimhan, Karen Mei-Ling Tan, See Ling Loy, Kok Hian Tan, Lynette P. Shek, Jerry Chan, Fabian Yap, Michael J. Meaney, Shiao-Yng Chan, Yap Seng Chong, Peter D. Gluckman, Johan G.
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of eugenol on lipid profile, oxidative stress, sex hormone, liver injury, ovarian failure, and expression of COX-2 and PPAR-α genes in a rat model of diabetes
Zahra Kokabiyan, Parichehreh Yaghmaei, Seyed Behnamedin Jameie, Zahra Hajebrahimi
Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 50(4): 3669. CrossRef - Role of ferroptosis in pregnancy related diseases and its therapeutic potential
Jinfeng Xu, Fan Zhou, Xiaodong Wang, Chunheng Mo
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Fasting Blood Glucose Levels on Blood Pressure Parameters among Older Adults with Prediabetes
Thapanee Roengrit, Ruchada Sri-Amad, Nawiya Huipao, Suphawadee Phababpha, Piyapong Prasertsri, Francesco Giallauria
The Scientific World Journal.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of saffron and fenugreek on lowering blood glucose: A systematic review with meta‐analysis
Alisson Guilherme da Silva Correia, Matheus Batista Alencar, Alexsia Nunes dos Santos, Dayanne Cristina Barreto da Paixão, Flávia Luryane Ferreira Sandes, Brenda Andrade, Yandra Castro, Joseilze Santos de Andrade
Phytotherapy Research.2023; 37(5): 2092. CrossRef - The roles of dietary lipids and lipidomics in gut-brain axis in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Duygu Ağagündüz, Mehmet Arif Icer, Ozge Yesildemir, Tevfik Koçak, Emine Kocyigit, Raffaele Capasso
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Canagliflozin protects diabetic cardiomyopathy by mitigating fibrosis and preserving the myocardial integrity with improved mitochondrial function
Deepika Dasari, Srashti Gopal Goyal, Anuhya Penmetsa, Dharmarajan Sriram, Arti Dhar
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 949: 175720. CrossRef - Dietary fat intakes, lipid profiles, adiposity, inflammation, and glucose in women and men in the Framingham Offspring Cohort
Ioanna Yiannakou, Mengjie Yuan, Xinyi Zhou, Martha R. Singer, Lynn L. Moore
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Neutrophil-to-high-density-lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio and mortality among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Ke Shi, Jie Hou, Qun Zhang, Yufei Bi, Xuanwei Zeng, Xianbo Wang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolic disorders induced by per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance mixtures in zebrafish larvae
Yingxin Liu, Shuai Liu, Jing Huang, Yu Liu, Qiyu Wang, Jinyuan Chen, Liwei Sun, Wenqing Tu
Environment International.2023; 176: 107977. CrossRef - Association between the insulin resistance marker TyG index and subsequent adverse long-term cardiovascular events in young and middle-aged US adults based on obesity status
Weihua Chen, Shan Ding, Jiabin Tu, Guitao Xiao, Kaihong Chen, Yanbin Zhang, Rongchong Huang, Ying Liao
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Uncovering Predictors of Lipid Goal Attainment in Type 2 Diabetes Outpatients Using Logic Learning Machine: Insights from the AMD Annals and AMD Artificial Intelligence Study Group
Davide Masi, Rita Zilich, Riccardo Candido, Annalisa Giancaterini, Giacomo Guaita, Marco Muselli, Paola Ponzani, Pierluigi Santin, Damiano Verda, Nicoletta Musacchio
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(12): 4095. CrossRef - Nutritive value, material reduction, biomass conversion rate, and survival of black solider fly larvae reared on palm kernel meal supplemented with fish pellets and fructose
Rudy Agung Nugroho, Retno Aryani, Esti Handayani Hardi, Hetty Manurung, Rudianto Rudianto, Nadhifa Aurellia Wirawan, Nadya Syalsabillah, Wibowo Nugroho Jati
International Journal of Tropical Insect Science.2023; 43(4): 1243. CrossRef - Novel Antidiabetic Agents and Their Effects on Lipid Profile: A Single Shot for Several Cardiovascular Targets
Francesco Piccirillo, Sara Mastroberardino, Annunziata Nusca, Lorenzo Frau, Lorenzo Guarino, Nicola Napoli, Gian Paolo Ussia, Francesco Grigioni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(12): 10164. CrossRef - Triglyceride-Glucose index as an alternative tool for identifying prediabetes and insulin resistance: A study on Bangladeshi adults
SumonRahman Chowdhury, AmamZonaed Siddiki, AB. M. Kamrul-Hasan
Bangladesh Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 2(2): 73. CrossRef - Inhibitory Investigations of Acyl-CoA Derivatives against Human Lipoxygenase Isozymes
Michelle Tran, Kevin Yang, Alisa Glukhova, Michael Holinstat, Theodore Holman
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 10941. CrossRef - Implications of vitamin D deficiency in systemic inflammation and cardiovascular health
Sanjay Kumar Dey, Shashank Kumar, Diksha Rani, Shashank Kumar Maurya, Pratibha Banerjee, Madhur Verma, Sabyasachi Senapati
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; : 1. CrossRef - The effects of pomegranate peel added bread on anthropometric measurements, metabolic and oxidative parameters in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study
Özlem Özpak Akkuş, Uğurcan Metin, Zeynep Çamlık
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(4): 698. CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose index, its modified indices, and triglyceride HDL-C ratio as predictor markers of insulin resistance in prediabetic individuals
RojeenRasheed Suleiman, SherwanFerman Salih, BarhavIssa Abdullah, IbrahimHasan Ibrahim, ZindanAzeez Saeed
Medical Journal of Babylon.2023; 20(2): 268. CrossRef - Differentially Expressed Genes in Response to a Squalene-Supplemented Diet Are Accurate Discriminants of Porcine Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Roubi Abuobeid, Luis V. Herrera-Marcos, Carmen Arnal, Seyed Hesamoddin Bidooki, Javier Sánchez-Marco, Roberto Lasheras, Joaquín C. Surra, María Jesús Rodríguez-Yoldi, Roberto Martínez-Beamonte, Jesús Osada
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(16): 12552. CrossRef - Do markers of adiposity and glycaemia mediate the association between low carbohydrate diet and cardiovascular risk factors: findings from the UK National Diet and Nutrition Survey (NDNS) 2008–2016
Cláudia Raulino Tramontt, Saad Mouti, Marjorie Lima Do Vale, Xunhan Li, Rajna Golubic, Sumantra Ray
BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health.2023; 6(2): 153. CrossRef - Association of HDL Subfraction Profile with the Progression of Insulin Resistance
Peter Piko, Tibor Jenei, Zsigmond Kosa, Janos Sandor, Nora Kovacs, Ildiko Seres, Gyorgy Paragh, Roza Adany
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13563. CrossRef - The Role of Lipids in the Regulation of Immune Responses
Chelsea Garcia, Catherine J. Andersen, Christopher N. Blesso
Nutrients.2023; 15(18): 3899. CrossRef - The Decrease in Serum Total Cholesterol and Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Concentrations With the Initiation of Hemodialysis Despite a Concomitant Increase in Serum Albumin Concentrations
Ramin Sam, Li Zhang, Delphine S Tuot, Rafia Chaudhry
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome: prospects for the use of angiopoetin-like proteins type 3 and 4 for the diagnosis of metabolic disorders
V. A. Aleksandrov
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; (16): 68. CrossRef - Spectral characterization and binding dynamics of bioactive compounds from Chlorella minutissima against α-glucosidase: An in vitro and in silico approach
Koushalya Selvaraju, Vasantharaja Raguraman, Harlokesh Narayan Yadav, P. Hariprasad, Anushree Malik
Algal Research.2023; 75: 103281. CrossRef - Cholesterol reprograms glucose and lipid metabolism to promote proliferation in colon cancer cells
Shyamananda Singh Mayengbam, Abhijeet Singh, Himanshi Yaduvanshi, Firoz Khan Bhati, Bhavana Deshmukh, Dipti Athavale, Pranay L. Ramteke, Manoj Kumar Bhat
Cancer & Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - To Boost or to Reset: The Role of Lactoferrin in Energy Metabolism
Giusi Ianiro, Antonella Niro, Luigi Rosa, Piera Valenti, Giovanni Musci, Antimo Cutone
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(21): 15925. CrossRef - Lipid Profile Paradox: Investigating Improved Lipid Levels in Diabetic Mellitus Patients with Foot Ulcer Infections—A Prospective Descriptive Study
Andrei Ardelean, Andreea-Adriana Neamtu, Diana-Federica Balta, Carmen Neamtu, Dan Goldis, Mihai Rosu, Alexandru Nesiu, Silviu Moldovan, Cristi Tarta, Bogdan Dan Totolici
Diagnostics.2023; 13(23): 3531. CrossRef - Geraniol reverses obesity by improving conversion of WAT to BAT in high fat diet induced obese rats by inhibiting HMGCoA reductase
Shushmita Chand, Alok Shiomurti Tripathi, Tabinda Hasan, Kavitha Ganesh, Mary Anne W. Cordero, Mohammad Yasir, Magdi E. A. Zaki, Pankaj Tripathi, Lucy Mohapatra, Rahul Kumar Maurya
Nutrition & Diabetes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipidomics Profiling of Metformin-Induced Changes in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Insights and Biomarker Potential
Muhammad Mujammami, Shereen M. Aleidi, Adriana Zardini Buzatto, Awad Alshahrani, Reem H. AlMalki, Hicham Benabdelkamel, Mohammed Al Dubayee, Liang Li, Ahmad Aljada, Anas M. Abdel Rahman
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(12): 1717. CrossRef - Combined Inositols, α-Lactalbumin, Gymnema Sylvestre and Zinc Improve the Lipid Metabolic Profile of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Alessandro Nani, Federico Bertuzzi, Elena Meneghini, Elena Mion, Basilio Pintaudi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(24): 7650. CrossRef - Determination of Diabetes-associated Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Risk Factors among Insulin and Non-insulin Dependent Diabetics
Ibrahim Abdulsada, Zain Alabdeen Obaid, Farah Almerza, Mays Alwaeli, Anmar Al-Elayawi, Taha Al-Dayyeni, Harir Al-Tuhafy
The Journal of Medical Research.2023; 9(6): 141. CrossRef - Angiopoietin-like protein 8 (betatrophin) inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in diabetic mice
Zhicong Zhao, Xia Deng, Jue Jia, Li Zhao, Chenxi Wang, Zhensheng Cai, Chang Guo, Ling Yang, Dong Wang, Suxian Ma, Jialiang Deng, Haoxiang Li, Libin Zhou, Zhigang Tu, Guoyue Yuan
Metabolism.2022; 126: 154921. CrossRef - Clinical significance of controlling nutritional status score (CONUT) in evaluating outcome of postoperative patients with gastric cancer
Qi Xiao, Xiaoqing Li, Baojun Duan, Xiaofan Li, Sida Liu, Boyu Xu, Shuai Shi, Jin Zhang, Haoyuan Qin, Xianglong Duan, Yansong Pu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioactive Compounds from Cardoon as Health Promoters in Metabolic Disorders
Luís R. Silva, Telma A. Jacinto, Paula Coutinho
Foods.2022; 11(3): 336. CrossRef - Protective effect of vanillic acid against diabetes and diabetic nephropathy by attenuating oxidative stress and upregulation of NF‐κB, TNF‐α and COX‐2 proteins in rats
Brahmjot Singh, Ajay Kumar, Hasandeep Singh, Sarabjit Kaur, Saroj Arora, Balbir Singh
Phytotherapy Research.2022; 36(3): 1338. CrossRef - Variability, Mean, and Baseline Values of Metabolic Parameters in Predicting Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Duong Duc Pham, Jaekyung Song, Yunwan Jeon, Ibrahimi Hajar, Chae Hun Leem
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(5): 1270. CrossRef - Glycemic Control and the Heart: The Tale of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Continues
Miriam Longo, Lorenzo Scappaticcio, Paolo Cirillo, Antonietta Maio, Raffaela Carotenuto, Maria Ida Maiorino, Giuseppe Bellastella, Katherine Esposito
Biomolecules.2022; 12(2): 272. CrossRef - Mechanisms of antidiabetic drugs and cholesterol efflux: A clinical perspective
Ali Ahmadi, Mariam Bagheri Ekta, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Drug Discovery Today.2022; 27(6): 1679. CrossRef - DO‐SRS imaging of diet regulated metabolic activities in Drosophila during aging processes
Yajuan Li, Wenxu Zhang, Anthony A. Fung, Lingyan Shi
Aging Cell.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The multifaceted role of cytochrome P450-Derived arachidonic acid metabolites in diabetes and diabetic cardiomyopathy
Fadumo Ahmed Isse, Ahmed A. El-Sherbeni, Ayman O. S. El-Kadi
Drug Metabolism Reviews.2022; 54(2): 141. CrossRef - Lipid traits and type 2 diabetes risk in African ancestry individuals: A Mendelian Randomization study
Opeyemi Soremekun, Ville Karhunen, Yiyan He, Skanda Rajasundaram, Bowen Liu, Apostolos Gkatzionis, Chisom Soremekun, Brenda Udosen, Hanan Musa, Sarah Silva, Christopher Kintu, Richard Mayanja, Mariam Nakabuye, Tafadzwa Machipisa, Amy Mason, Marijana Vujko
eBioMedicine.2022; 78: 103953. CrossRef - Poor Glycaemic Control and its Associated Factors among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Southern Part of Peninsular Malaysia: A Registry-based Study
Norizzati Amsah, Zaleha Md Isa, Zaid Kassim
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(E): 422. CrossRef - The Impact of Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Prostate Cancer
André P. Sousa, Raquel Costa, Marco G. Alves, Raquel Soares, Pilar Baylina, Rúben Fernandes
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal lipid profile in pregnancy and embryonic size: a population-based prospective cohort study
Dionne V. Gootjes, Anke G. Posthumus, Deveney F. Wols, Yolanda B. de Rijke, Jeanine E. Roeters Van Lennep, Eric A. P. Steegers
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Successful correction of hyperglycemia is critical for weight loss and a decrease in cardiovascular risk in obese patients
Jolanta Zalejska-Fiolka, Anna Birková, Beáta Hubková, Tomasz Wielkoszyński, Beáta Čižmárová, Beata Szlachta, Rafał Fiolka, Urszula Błaszczyk, Adam Wylęgała, Sławomir Kasperczyk, Alicja Grzanka, Mária Mareková, Michal Toborek
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2022; 106: 109021. CrossRef - Morus alba L. for Blood Sugar Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hye In Jeong, Soobin Jang, Kyeong Han Kim, Fernanda Tonelli
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Correlation between HbA1c and Triglyceride Level with Coronary Stenosis Degree in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Coronary Heart Disease
Laily Adninta, Indranila Samsuria, Edward Kurnia Setiawan Limijadi
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(B): 944. CrossRef - Growth trajectories in lipid profile and fasting blood sugar in prediabetic people over a 16- year follow-up and future risk of type2 diabetes mellitus: A latent growth modeling approach
Awat Feizi, Fahimeh Haghighatdoost, Parisa Zakeri, Ashraf Aminorroaya, Masoud Amini
Alexandria Journal of Medicine.2022; 58(1): 52. CrossRef - Whole grain rice: Updated understanding of starch digestibility and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism
Zihang Cheng, Dongling Qiao, Siming Zhao, Binjia Zhang, Qinlu Lin, Fengwei Xie
Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety.2022; 21(4): 3244. CrossRef - The Role of Triglyceride-HDL Ratio and Triglyceride-glucose Index in Estimating Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Özgür Altun, Semih Kalyon
Meandros Medical and Dental Journal.2022; 23(1): 74. CrossRef - Murine Falcor/LL35 lncRNA Contributes to Glucose and Lipid Metabolism In Vitro and In Vivo
Evgeniya Shcherbinina, Tatiana Abakumova, Daniil Bobrovskiy, Ilia Kurochkin, Ksenia Deinichenko, Elena Stekolshchikova, Nickolay Anikanov, Rustam Ziganshin, Pavel Melnikov, Ekaterina Khrameeva, Maria Logacheva, Timofei Zatsepin, Olga Sergeeva
Biomedicines.2022; 10(6): 1397. CrossRef - The Role of Changes in Cumulative Lipid Parameter Burden in the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cohort Study of People Aged 35–65 Years in Rural China
Qi Wang, Tao Xie, Ting Zhang, Yuanjia Deng, Yuying Zhang, Qingfeng Wu, Minghua Dong, Xiaoting Luo
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1831. CrossRef - Alternate-day fasting, a high-sucrose/caloric diet and praziquantel treatment influence biochemical and behavioral parameters during Schistosoma mansoni infection in male BALB/c mice
Luis F.C. dos Reis, Cláudio D. Cerdeira, Guilherme S. Gagliano, Ana B.T. de Figueiredo, Juliana H. Ferreira, Aline P. Castro, Raquel L.M. Souza, Marcos J. Marques
Experimental Parasitology.2022; 240: 108316. CrossRef - The value of Genus Acacia in arid and semi-arid environments for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases
Akhtar Atiya, Taghreed Majrashi, Safia Akhtar, Arshad Ali Khan, Afnan Mohammad Sultan Asiri, Hanan Jamaan Al-Zahrania, Raghad Sameer Alnami, Sara Abdulrahman Alsharif, Taef Amer, Zainah Abdullah Faiz, Shimaa Ahmad M AlYahya, Shahad Saeedhabtar
Phytomedicine Plus.2022; 2(3): 100315. CrossRef - Beneficial effects of monounsaturated fatty acid‐rich blended oils with an appropriate polyunsaturated/saturated fatty acid ratio and a low n‐6/n‐3 fatty acid ratio on the health of rats
Ligang Yang, Chao Yang, Chu Chu, Min Wan, Dengfeng Xu, Da Pan, Hui Xia, Shao Kang Wang, Guofang Shu, Shiqing Chen, Guiju Sun
Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.2022; 102(15): 7172. CrossRef - Hibiscus sabdariffa in Diabetes Prevention and Treatment—Does It Work? An Evidence-Based Review
Daniel Jamrozik, Weronika Borymska, Ilona Kaczmarczyk-Żebrowska
Foods.2022; 11(14): 2134. CrossRef - Statin therapy is not warranted for a person with high LDL-cholesterol on a low-carbohydrate diet
David M. Diamond, Benjamin T. Bikman, Paul Mason
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2022; 29(5): 497. CrossRef - Probiotic therapy, a novel and efficient adjuvant approach to improve glycemic status: An umbrella meta-analysis
Meysam Zarezadeh, Vali Musazadeh, Amir Hossein Faghfouri, Bahareh Sarmadi, Parsa Jamilian, Parmida Jamilian, Helda Tutunchi, Parvin Dehghan
Pharmacological Research.2022; 183: 106397. CrossRef - Amelioration of hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in a high-fat diet-fed mice by supplementation of a developed optimized polyherbal formulation
Tanisha, Sunil Venkategowda, Mala Majumdar
3 Biotech.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Daily Treatment of Mice with Type 2 Diabetes with Adropin for Four Weeks Improves Glucolipid Profile, Reduces Hepatic Lipid Content and Restores Elevated Hepatic Enzymes in Serum
Marek Skrzypski, Paweł A. Kołodziejski, Ewa Pruszyńska-Oszmałek, Tatiana Wojciechowicz, Paulina Janicka, Małgorzata Krążek, Emilian Małek, Mathias Z. Strowski, Krzysztof W. Nowak
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 9807. CrossRef - Comparison of the triglyceride glucose (TyG) index, triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio, and metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) associated with periodontitis in Korean adults
Yea-Chan Lee, Ji-Won Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2022; 13: 204062232211226. CrossRef - Coadministration of L‐alanine and L‐glutamine ameliorate blood glucose levels, biochemical indices and histological features in alloxan‐induced diabetic rats
Ifeanyi J. Ezeonwumelu, Abduljalil M. Mode, Umar F. Magaji, Nnamdi A. Nzoniwu, Muhamad H. Tangaza, Fatima I. Tanimu, Shamsudeen U. Dandare
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Laboratory data clustering in defining population cohorts: Case study on metabolic indicators
Ivan Pavicevic, Goran Miljus, Olgica Nedic
Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society.2022; 87(9): 1025. CrossRef - Effects of Psychotropic Medication on Somatic Sterol Biosynthesis of Adult Mice
Marta Balog, Allison C Anderson, Marija Heffer, Zeljka Korade, Karoly Mirnics
Biomolecules.2022; 12(10): 1535. CrossRef - The Correlation Between Angiopoietin-Like 3 and Metabolic Markers of Some Lipid and Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients at the First Diagnosis
Minh Hoang Thi, Chung Dang Thanh, Thuan Huynh Quang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 3329. CrossRef - Joint inference of physiological network and survival analysis identifies factors associated with aging rate
Anurag Sethi, Eugene Melamud
Cell Reports Methods.2022; 2(12): 100356. CrossRef - Disease activity and prognosis in Takayasu’s arteritis
Sema Kaymaz Tahra, Fatma Alibaz Öner
Ulusal Romatoloji Dergisi.2022; 14(3): 137. CrossRef - Antihyperlipidemic effect of the hydroalcoholic extract of Basidiomycete Pycnoporus sanguineus (Fr.) Murr. in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
Maiza Von Dentz, Gabriela Gambato, Andreza Ferrari, Roselei Claudete Fontana, Eliseu Rodrigues, Mirian Salvador, Marli Camassola, Matheus Parmegiani Jahn
Advances in Traditional Medicine.2021; 21(3): 453. CrossRef - Effect of short-chain chlorinated paraffins on metabolic profiling of male SD rats
Ningbo Geng, Yun Luo, Rong Cao, Xiaoyao Song, Fang Li, Feidi Wang, Yufeng Gong, Liguo Xing, Haijun Zhang, Jiping Chen
Science of The Total Environment.2021; 750: 141404. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia and its associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ahmed Tijani Bawah, Richard Darko, Albert Abaka-Yawson, Mohammed Mustapha Seini, Silas Kinanyok, Samuel Adusei
Journal of Public Health.2021; 29(4): 985. CrossRef - The reduction of lipid-sourced energy production caused by ATGL inhibition cannot be compensated by activation of HSL, autophagy, and utilization of other nutrients in fish
Si-Lan Han, Yan Liu, Samwel M. Limbu, Li-Qiao Chen, Mei-Ling Zhang, Zhen-Yu Du
Fish Physiology and Biochemistry.2021; 47(1): 173. CrossRef - Diabetes, Lipids, and CV Risk
Jan Škrha
Current Atherosclerosis Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum soluble epoxide hydrolase related oxylipins and major depression in patients with type 2 diabetes
Natasha Z. Anita, Nubaira Forkan, Radia Kamal, Michelle M. Nguyen, Di Yu, Chelsi Major-Orfao, Sophie K. Wong, Krista L. Lanctôt, Nathan Herrmann, Paul I. Oh, Baiju R. Shah, Jeremy Gilbert, Angela Assal, Ilana J. Halperin, Theresa L. Pedersen, Ameer Y. Tah
Psychoneuroendocrinology.2021; 126: 105149. CrossRef - The controversial role of glucose in the diabetic kidney
Rui Fernandes
Porto Biomedical Journal.2021; 6(1): e113. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the piperine-supplemented Curcuma longa L. in metabolic control of patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial
Joana Furtado de Figueiredo Neta, Vivian Saraiva Veras, Danilo Ferreira de Sousa, Maria da Conceição dos Santos Oliveira Cunha, Maria Veraci Oliveira Queiroz, José Claudio Garcia Lira Neto, Marta Maria Coelho Damasceno, Márcio Flávio Moura de Araújo, Robe
International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition.2021; 72(7): 968. CrossRef - Mechanisms and Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Diabetes
Ehete Bahiru, Ruth Hsiao, Daniel Phillipson, Karol E. Watson
Current Cardiology Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Changes of Cholesterol Profile at the Different Insulin Resistance Range in the Czech Republic
Vladimír Kron, Miroslav Verner, Pavel Smetana, Dagmar Horáková, Jan Šlégr, Filip Studnička, Damián Bušovský, Karel Martiník
Medicina.2021; 57(3): 249. CrossRef - Chronic Intake of Energy Drinks and Their Sugar Free Substitution Similarly Promotes Metabolic Syndrome
Liam T. Graneri, John C. L. Mamo, Zachary D’Alonzo, Virginie Lam, Ryusuke Takechi
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1202. CrossRef - Association of maternal lipid profile and gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 292 studies and 97,880 women
Jiamiao Hu, Clare L. Gillies, Shaoling Lin, Zoe A. Stewart, Sarah E. Melford, Keith R. Abrams, Philip N. Baker, Kamlesh Khunti, Bee K. Tan
EClinicalMedicine.2021; 34: 100830. CrossRef - THE ROLE OF TRIGLYCERIDE GLUCOSE INDEX AS PREDICTOR OF GLYCEMIC CONTROL IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Charchit Mehta, Vidyasagar C R, Raveesha A
GLOBAL JOURNAL FOR RESEARCH ANALYSIS.2021; : 106. CrossRef - Interaction of Adiponectin Genotypes and Insulin Resistance on the Occurrence of Taiwanese Metabolic Syndrome
Chun-Chieh Chen, Yu-Hsiang Wei, Chia-Chen Huang, Shin-Hui Hung, Zeng-Wei Wang, Ruey-Hong Wong, Daniel Diaz
BioMed Research International.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Synergistic effects of black ginseng and aged garlic extracts for the amelioration of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in mice
Guihun Jiang, Karna Ramachandraiah, Mian Anjum Murtaza, Lili Wang, Shanji Li, Kashif Ameer
Food Science & Nutrition.2021; 9(6): 3091. CrossRef - Does vitamin C supplementation exert profitable effects on serum lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes? A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis
Zahra Namkhah, Damoon Ashtary-Larky, Fatemeh Naeini, Cain C.T. Clark, Omid Asbaghi
Pharmacological Research.2021; 169: 105665. CrossRef - Particulate matter air pollutants and cardiovascular disease: Strategies for intervention
Ankit Aryal, Ashlyn C. Harmon, Tammy R. Dugas
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2021; 223: 107890. CrossRef - Identification of Docetaxel as a Potential Drug to Promote HDL Biogenesis
Hong Y. Choi, Isabelle Ruel, Jacques Genest
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diet Rich in Lard Promotes a Metabolic Environment Favorable to Trypanosoma cruzi Growth
Débora Maria Soares de Souza, Maria Cláudia Silva, Silvia Elvira Barros Farias, Ana Paula de J. Menezes, Cristiane Maria Milanezi, Karine de P. Lúcio, Nívia Carolina N. Paiva, Paula Melo de Abreu, Daniela Caldeira Costa, Kelerson Mauro de Castro Pinto, Gu
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and abdominal aortic calcification in adults: A cross-sectional study
Yuxiong Chen, Zhen'ge Chang, Yakun Zhao, Yanbo Liu, Jia Fu, Yongqiao Zhang, Yijie Liu, Zhongjie Fan
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2021; 31(7): 2068. CrossRef - Roles of microRNAs in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism disorders and their therapeutic potential
Sujay Paul, Luis Alberto Bravo Vázquez, Samantha Pérez Uribe, Luis Aarón Manzanero Cárdenas, María Fernanda Ruíz Aguilar, Samik Chakraborty, Ashutosh Sharma
Biochimie.2021; 187: 83. CrossRef - Meal-induced inflammation: postprandial insights from the Personalised REsponses to DIetary Composition Trial (PREDICT) study in 1000 participants
Mohsen Mazidi, Ana M Valdes, Jose M Ordovas, Wendy L Hall, Joan C Pujol, Jonathan Wolf, George Hadjigeorgiou, Nicola Segata, Naveed Sattar, Robert Koivula, Tim D Spector, Paul W Franks, Sarah E Berry
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2021; 114(3): 1028. CrossRef - Daidzein mitigates myocardial injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats
Ankit P. Laddha, Yogesh A. Kulkarni
Life Sciences.2021; 284: 119664. CrossRef - Impact of triglycerides and waist circumference on insulin resistance and β-cell function in non-diabetic first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes
Fahd Ahmed, Molham AL-Habori, Ebtesam Al-Zabedi, Riyadh Saif-Ali
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence, prescriptions, outcomes and costs of type 2 diabetes patients with or without prior coronary artery disease or stroke: a longitudinal 5-year claims-data analysis of over 7 million inhabitants
Aldo Pietro Maggioni, Letizia Dondi, Felicita Andreotti, Giulia Ronconi, Silvia Calabria, Carlo Piccinni, Antonella Pedrini, Imma Esposito, Nello Martini
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2021; 12: 204062232110263. CrossRef - Fatty acid desaturase 2 (FADS 2) rs174575 (C/G) polymorphism, circulating lipid levels and susceptibility to type-2 diabetes mellitus
Shilpa S. Shetty, N. Suchetha Kumari
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Chitosan Oligosaccharide Alleviates Abnormal Glucose Metabolism without Inhibition of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in a High-Fat Diet/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rat Model
Shing-Hwa Liu, Fan-Wen Chen, Meng-Tsan Chiang
Marine Drugs.2021; 19(7): 360. CrossRef - Diabetic dyslipidaemia
Subashini C. Thambiah, Leslie Charles Lai
Practical Laboratory Medicine.2021; 26: e00248. CrossRef - Characterization of PFOS toxicity on in-vivo and ex-vivo mouse pancreatic islets
Hin Ting Wan, Lok Yi Cheung, Ting Fung Chan, Marco Li, Keng Po Lai, Chris Kong Chu Wong
Environmental Pollution.2021; 289: 117857. CrossRef - Prevalence and Metabolic Predictors for Early Diagnosed Prediabetes in Women with Previous Gestational Diabetes: Observational Cohort Study
Aleksandra Z. Jotic, Milica M. Stoiljkovic, Tanja J. Milicic, Katarina S. Lalic, Ljiljana Z. Lukic, Marija V. Macesic, Jelena N. Stanarcic Gajovic, Mina M. Milovancevic, Miroslava G. Gojnic Dugalic, Veljko M. Jeremic, Nebojsa M. Lalic
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(10): 2691. CrossRef - PKM2‐TMEM33 axis regulates lipid homeostasis in cancer cells by controlling SCAP stability
Fabao Liu, Min Ma, Ang Gao, Fengfei Ma, Gui Ma, Peng Liu, Chenxi Jia, Yidan Wang, Kristine Donahue, Shengjie Zhang, Irene M Ong, Sunduz Keles, Lingjun Li, Wei Xu
The EMBO Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride/Glucose Index (TyG Index) as a marker of glucose status conversion among reproductive-aged women in Jakarta, Indonesia: The Bogor cohort study (2011–2016)
Iche A. Liberty, Nasrin Kodim, Ratu A.D. Sartika, Indang Trihandini, R.M. Suryadi Tjekyan, Zulkarnain, Masdalina Pane, Livy B. Pratisthita, Dicky L. Tahapary, Pradana Soewondo
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(6): 102280. CrossRef - Novel Serum and Urinary Metabolites Associated with Diabetic Retinopathy in Three Asian Cohorts
Debra Q. Y. Quek, Feng He, Rehena Sultana, Riswana Banu, Miao Li Chee, Simon Nusinovici, Sahil Thakur, Chaoxu Qian, Ching-Yu Cheng, Tien Y. Wong, Charumathi Sabanayagam
Metabolites.2021; 11(9): 614. CrossRef - Lychee Seed as a Potential Hypoglycemic Agent, and Exploration of its Underlying Mechanisms
Yuehong Zhang, De Jin, Xuedong An, Liyun Duan, Yingying Duan, Fengmei Lian
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Indole-3-Propionic Acid, a Gut-Derived Tryptophan Metabolite, Associates with Hepatic Fibrosis
Ratika Sehgal, Mariana Ilha, Maija Vaittinen, Dorota Kaminska, Ville Männistö, Vesa Kärjä, Marjo Tuomainen, Kati Hanhineva, Stefano Romeo, Päivi Pajukanta, Jussi Pihlajamäki, Vanessa D. de Mello
Nutrients.2021; 13(10): 3509. CrossRef - Impact of diabetes on the accuracy and speed of accessing information from episodic and working memory
Selene Cansino, Frine Torres-Trejo, Cinthya Estrada-Manilla, Eira Castellanos-Domínguez, Ana Zamora-Olivares, Silvia Ruiz Velasco, Jim Grange
Cogent Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of the triglyceride-glucose index and major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events in female patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents: A retrospective study
Su Zou, Yingjia Xu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 181: 109073. CrossRef - Adherence to Treatment and Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 4-Year Follow-up PTM Bogor Cohort Study, Indonesia
Silma Kaaffah, Pradana Soewondo, Woro Riyadina, Fransiskus Samuel Renaldi, Rani Sauriasari
Patient Preference and Adherence.2021; Volume 15: 2467. CrossRef - Evaluation of secondary electronic cigarette inhalation on lipid metabolism in C57BL/6J mice using indirect calorimetry
Dolly L. Crawford, Alexis R. Phillips, Taylor R. Williams
Metabolism Open.2021; 12: 100150. CrossRef - Momordica charantia leaf extract reduces hepatic lipid accumulation and diet-induced dyslipidemia in zebrafish through lipogenesis and beta-oxidation
Semon Wu, Cheng Huang, You-Ren Chen, Hsiu-Chen Huang, Wen-Cheng Huang, Yu-Heng Lai
Journal of Functional Foods.2021; 87: 104857. CrossRef - Genetic Determinants of Plasma Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels: Monogenicity, Polygenicity, and “Missing” Heritability
Jesús Maria Martín-Campos
Biomedicines.2021; 9(11): 1728. CrossRef - Effect of blood lipid variability on mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: a large single-center cohort study
Mu-Cyun Wang, Chia-Ing Li, Chiu-Shong Liu, Chih-Hsueh Lin, Shing-Yu Yang, Tsai-Chung Li, Cheng-Chieh Lin
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Phenotype correlations reveal the relationships of physiological systems underlying human ageing
Meng Hao, Hui Zhang, Zixin Hu, Xiaoyan Jiang, Qi Song, Xi Wang, Jiucun Wang, Zuyun Liu, Xiaofeng Wang, Yi Li, Li Jin
Aging Cell.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of dyslipidemia, diabetes and metabolic syndrome with serum ferritin levels: a middle eastern population-based cross-sectional study
Neyla S. Al Akl, Olfa Khalifa, Khaoula Errafii, Abdelilah Arredouani
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties of Yttrium Oxide Nanoparticles: New Insights into Alleviating Diabetes
Kim San Tang
Current Diabetes Reviews.2021; 17(4): 496. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Anti-Hypercholesterolemic and Antioxidant Activity of Mentha pulegium (L.) Aqueous Extract in Normal and Streptozotocin- Induced Diabetic Rats
Omar Farid, Mohamed Eddouks
The Natural Products Journal.2020; 10(3): 236. CrossRef - Hyperlipidemias in elderly patients: results from the Berlin Aging Study II (BASEII), a cross-sectional study
Adrian Rosada, Ursula Kassner, Felix Weidemann, Maximilian König, Nikolaus Buchmann, Elisabeth Steinhagen-Thiessen, Dominik Spira
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Distinct effects of virgin coconut oil supplementation on the glucose and lipid homeostasis in non-diabetic and alloxan-induced diabetic rats
Siniša Đurašević, Gorana Nikolić, Ivan Zaletel, Ilijana Grigorov, Lidija Memon, Dragana Mitić-Ćulafić, Predrag Vujović, Jelena Đorđević, Zoran Todorović
Journal of Functional Foods.2020; 64: 103601. CrossRef - Medium and long-term effects of low doses of Chlorpyrifos during the postnatal, preweaning developmental stage on sociability, dominance, gut microbiota and plasma metabolites
Cristian Perez-Fernandez, Miguel Morales-Navas, Luis Manuel Aguilera-Sáez, Ana Cristina Abreu, Laia Guardia-Escote, Ignacio Fernández, José Antonio Garrido-Cárdenas, María Teresa Colomina, Estela Giménez, Fernando Sánchez-Santed
Environmental Research.2020; 184: 109341. CrossRef - Fatty Acids and Sterol Rich Stem Back Extract of Shorea Roxburghii Attenuates Hyperglycemia, Hyperlipidemia, and Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Rats
Emmanuel Ayobami Makinde, Nisaudah Radenahmad, Raihan Uz Zaman, Opeyemi Joshua Olatunji
European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Poor Glycemic and Lipid Levels in Ambulatory Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Patients in Asmara, Eritrea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Oliver Okoth Achila, Millen Ghebretinsae, Abraham Kidane, Michael Simon, Shewit Makonen, Yohannes Rezene
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Postprandial Metabolism is Impaired in Overweight Normoglycemic Young Adults without Family History of Diabetes
A. Aneesh Kumar, Gopika Satheesh, Gadadharan Vijayakumar, Mahesh Chandran, Priya R. Prabhu, Leena Simon, Vellappillil Raman Kutty, Chandrasekharan C. Kartha, Abdul Jaleel
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - HDL inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells in vitro by activation of Smoothened
Mustafa Yalcinkaya, Anja Kerksiek, Katrin Gebert, Wijtske Annema, Rahel Sibler, Silvija Radosavljevic, Dieter Lütjohann, Lucia Rohrer, Arnold von Eckardstein
Journal of Lipid Research.2020; 61(4): 492. CrossRef - Beneficial effects of pomegranate peel extract on plasma lipid profile, fatty acids levels and blood pressure in patients with diabetes mellitus type-2: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
Milkica Grabež, Ranko Škrbić, Miloš P. Stojiljković, Vesna Rudić-Grujić, Marija Paunović, Aleksandra Arsić, Snježana Petrović, Vesna Vučić, Bosa Mirjanić-Azarić, Katarina Šavikin, Nebojša Menković, Teodora Janković, Nađa Vasiljević
Journal of Functional Foods.2020; 64: 103692. CrossRef - Validation of the antidiabetic potential of isolated and nanoemulsified endophytic fungal metabolite 2,4,6-triphenylaniline through AMPK activation pathway
Nathiya Ranganathan, Gayathri Mahalingam
Journal of Molecular Liquids.2020; 316: 113836. CrossRef - Metabolism updates: new directions, techniques, and exciting research that is broadening the horizons
Chrysoula Boutari, Eirini Bouzoni, Aditya Joshi, Konstantinos Stefanakis, Olivia M. Farr, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2020; 102: 154009. CrossRef - Anabolic SIRT4 Exerts Retrograde Control over TORC1 Signaling by Glutamine Sparing in the Mitochondria
Eisha Shaw, Manasi Talwadekar, Zeenat Rashida, Nitya Mohan, Aishwarya Acharya, Subhash Khatri, Sunil Laxman, Ullas Kolthur-Seetharam
Molecular and Cellular Biology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress ameliorates cardiovascular injury in a rat model of metabolic syndrome
Eman Radwan, Marwa H. Bakr, Salma Taha, Sally A. Sayed, Alshaimaa A. Farrag, Maha Ali
Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology.2020; 143: 15. CrossRef - Combination of Exercise and Vegetarian Diet: Relationship with High Density-Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Taiwanese Adults Based on MTHFR rs1801133 Polymorphism
Shu-Lin Chang, Oswald Ndi Nfor, Chien-Chang Ho, Kuan-Jung Lee, Wen-Yu Lu, Chia-Chi Lung, Disline Manli Tantoh, Shu-Yi Hsu, Ming-Chih Chou, Yung-Po Liaw
Nutrients.2020; 12(6): 1564. CrossRef - Relation of Decreased Circulating Sortilin Levels With Unfavorable Metabolic Profiles in Subjects With Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
İsmail Demir, Ozden Yildirim Akan, Aslı Guler, Giray Bozkaya, Behnaz Aslanipour, Mehmet Calan
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2020; 359(1): 8. CrossRef - Antidiabetic effect of Wedelia chinensis leaf extract in alloxan induced Swiss albino diabetic mice
Md. Wasim Bari, Md. Monirul Islam, Mahbuba Khatun, Mst Julia Sultana, Rabbi Ahmed, Ariful Islam, Md. Ismail Hossain, Md. Matiar Rahman, Mohammad Amirul Islam
Clinical Phytoscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - iNOS as a metabolic enzyme under stress conditions
Sarit Anavi, Oren Tirosh
Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2020; 146: 16. CrossRef - Ginsenoside Rg5 relieves type 2 diabetes by improving hepatic insulin resistance in db/db mice
Yange Wei, Haixia Yang, Chenhui Zhu, Jianjun Deng, Daidi Fan
Journal of Functional Foods.2020; 71: 104014. CrossRef - High-coverage plasma lipidomics reveals novel sex-specific lipidomic fingerprints of age and BMI: Evidence from two large population cohort studies
Habtamu B. Beyene, Gavriel Olshansky, Adam Alexander T. Smith, Corey Giles, Kevin Huynh, Michelle Cinel, Natalie A. Mellett, Gemma Cadby, Joseph Hung, Jennie Hui, John Beilby, Gerald F. Watts, Jonathan S. Shaw, Eric K. Moses, Dianna J. Magliano, Peter J.
PLOS Biology.2020; 18(9): e3000870. CrossRef - Lack of collagen XVIII leads to lipodystrophy and perturbs hepatic glucose and lipid homeostasis
Tiina Petäistö, David Vicente, Kari A. Mäkelä, Mikko A. Finnilä, Ilkka Miinalainen, Jarkko Koivunen, Valerio Izzi, Mari Aikio, Sanna‐Maria Karppinen, Raman Devarajan, Jerome Thevenot, Karl‐Heinz Herzig, Ritva Heljasvaara, Taina Pihlajaniemi
The Journal of Physiology.2020; 598(16): 3373. CrossRef - Adipose Tissue-Liver Cross Talk in the Control of Whole-Body Metabolism: Implications in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Vian Azzu, Michele Vacca, Samuel Virtue, Michael Allison, Antonio Vidal-Puig
Gastroenterology.2020; 158(7): 1899. CrossRef - Emulsion Droplet Crystallinity Attenuates Short-Term Satiety in Healthy Adult Males: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Crossover, Acute Meal Study
Samar Hamad, Surangi H Samar, Amanda Cuncins, Melissa Brown, Amanda J Wright
The Journal of Nutrition.2020; 150(9): 2295. CrossRef - Protective effect of hypoglycemic granule against diabetes‐induced liver injury by alleviating glycolipid metabolic disorder and oxidative stress
Xiaosong Yang, Pengjie Zhang, Feixue Zhang, Zhiqiang Ke, Qingjie Chen, Chao Liu
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2020; 121(5-6): 3221. CrossRef - Candidate Regulators of Dyslipidemia in Chromosome 1 Substitution Lines Using Liver Co-Expression Profiling Analysis
Fuyi Xu, Maochun Wang, Shixian Hu, Yuxun Zhou, John Collyer, Kai Li, Hongyan Xu, Junhua Xiao
Frontiers in Genetics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Early detection of type 2 diabetes mellitus using machine learning-based prediction models
Leon Kopitar, Primoz Kocbek, Leona Cilar, Aziz Sheikh, Gregor Stiglic
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-HDL-Cholesterin
Leonie Adam, Thomas Bobbert
Diabetes aktuell.2020; 18(06): 242. CrossRef - Berberine Suppresses Colonic Inflammation in Dextran Sulfate Sodium–Induced Murine Colitis Through Inhibition of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Activity
Lixiang Zhai, Tao Huang, Hai-tao Xiao, Pei-gen Wu, Cheng-yuan Lin, Zi-wan Ning, Ling Zhao, Hiu Yee Anna Kwan, Xian-jing Hu, Hoi Leong Xavier Wong, Xian-qian Li, Zhao-xiang Bian
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of High-Fiber Biscuits on Lipid and Anthropometric Profile of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
FATMAH
Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology.2020; 66(Supplement): S391. CrossRef - Acute Myocardial Infarction Hospitalizations between Cold and Hot Seasons in an Island across Tropical and Subtropical Climate Zones—A Population-Based Study
Min-Liang Chu, Chiao-Yu Shih, Tsung-Cheng Hsieh, Han-Lin Chen, Chih-Wei Lee, Jen-Che Hsieh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(15): 2769. CrossRef - Hydroxyurea alters hematological, biochemical and inflammatory biomarkers in Brazilian children with SCA: Investigating associations with βS haplotype and α-thalassemia
Sètondji Cocou Modeste Alexandre Yahouédéhou, Caroline Conceição da Guarda, Camylla Vilas Boas Figueiredo, Rayra Pereira Santiago, Suellen Pinheiro Carvalho, Luciana Magalhães Fiuza, Uche Samuel Ndidi, Rodrigo Mota Oliveira, Magda Oliveira Seixas Carvalho
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(7): e0218040. CrossRef - Developmental Dioxin Exposure Alters the Methylome of Adult Male Zebrafish Gonads
Camille Akemann, Danielle N. Meyer, Katherine Gurdziel, Tracie R. Baker
Frontiers in Genetics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - 1H NMR based serum metabolic profiling reveals differentiating biomarkers in patients with diabetes and diabetes-related complication
Atul Rawat, Gunjan Misra, Madhukar Saxena, Sukanya Tripathi, Durgesh Dubey, Sulekha Saxena, Avinash Aggarwal, Varsha Gupta, M.Y. Khan, Anand Prakash
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(1): 290. CrossRef - Dietary calcium affects body composition and lipid metabolism in rats
Haya Alomaim, Philip Griffin, Eleonora Swist, Louise J. Plouffe, Michelle Vandeloo, Isabelle Demonty, Ashok Kumar, Jesse Bertinato, Juan J. Loor
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(1): e0210760. CrossRef - TyG index a promising biomarker for glycemic control in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ekhlas Khalid Hameed
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(1): 560. CrossRef - The association between exposure to different aspects of shift work and metabolic risk factors in health care workers, and the role of chronotype
Bette Loef, Debbie van Baarle, Allard J. van der Beek, Piet K. Beekhof, Linda W. van Kerkhof, Karin I. Proper, David Gatfield
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(2): e0211557. CrossRef - CHANGES IN PENTRAXIN-3 LEVEL AND ITS INTERACTION
WITH METABOLIC INDICES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY
ARTERY DISEASE AND TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Pavlo G. Kravchun, Olga I. Kadykova, Dmitry G. Molotyagin
Wiadomości Lekarskie.2019; 72(2): 181. CrossRef - Glucose metabolic effects of oat noodles with different processing in type 2 diabetic mice
Lijuan Wang, Lili Wang, Nachuan Zhang, Mengli Li, Zaigui Li
Journal of Cereal Science.2019; 88: 125. CrossRef - Raffia palm (Raphia hookeri G. Mann & H. Wendl) wine modulates glucose homeostasis by enhancing insulin secretion and inhibiting redox imbalance in a rat model of diabetes induced by high fructose diet and streptozotocin
Ochuko L. Erukainure, Olajumoke A. Oyebode, Omamuyovwi M. Ijomone, Chika I. Chukwuma, Neil A. Koorbanally, Md. Shahidul Islam
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2019; 237: 159. CrossRef - The Relation of Impaired Fasting Glucose and HDL-Cholesterol by Gender and Body Mass Index
Soo-Hee Jin
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(1): 8. CrossRef - The Effects of Poncirus fructus on Insulin Resistance and the Macrophage-Mediated Inflammatory Response in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Mia Kim, Mi Hyeon Seol, Byung-Cheol Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(12): 2858. CrossRef - HDL-Cholesterol, Its Variability, and the Risk of Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Seung-Hwan Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kun-Ho Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 104(11): 5633. CrossRef - Cardiovascular organ damage in type 2 diabetes mellitus: the role of lipids and inflammation
Michaela Kozakova, Carmela Morizzo, Isabel Goncalves, Andrea Natali, Jan Nilsson, Carlo Palombo
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of poor glycemic control among adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Jimma University Medical Center, Jimma zone, south west Ethiopia: a case control study
Yitagesu Mamo, Fekede Bekele, Tadesse Nigussie, Ameha Zewudie
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Functional polymorphisms of the APOA1/C3/A4/A5-ZPR1-BUD13 gene cluster are associated with dyslipidemia in a sex-specific pattern
Wei Bai, Changgui Kou, Lili Zhang, Yueyue You, Weiying Yu, Wanqing Hua, Yuanyuan Li, Yaqin Yu, Tiancheng Zhao, Yanhua Wu
PeerJ.2019; 6: e6175. CrossRef - A pre-meal of whey proteins induces differential effects on glucose and lipid metabolism in subjects with the metabolic syndrome: a randomised cross-over trial
Ann Bjørnshave, Jens Juul Holst, Kjeld Hermansen
European Journal of Nutrition.2019; 58(2): 755. CrossRef - Aging and Hyperglycemia Intensify Dyslipidemia-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Rats: Assessment of Restorative Potentials of ALA and EPA + DHA
Pooja Acharya, Ramaprasad Ravichandra Talahalli
Inflammation.2019; 42(3): 946. CrossRef - Diabetes Type 2 in Neurologically Impaired Children and Adolescents Without Obesity: A New Emerging Entity?
Valeria Calcaterra, Hellas Cena, Annalisa De Silvestri, Vincenza Girgenti, Denisia Bommarito, Gloria Pelizzo
Frontiers in Neurology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Raman spectral signatures of urinary extracellular vesicles from diabetic patients and hyperglycemic endothelial cells as potential biomarkers in diabetes
Maciej Roman, Agnieszka Kamińska, Anna Drożdż, Mark Platt, Marek Kuźniewski, Maciej T. Małecki, Wojciech M. Kwiatek, Czesława Paluszkiewicz, Ewa Ł. Stępień
Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine.2019; 17: 137. CrossRef - Triglycerides and glucose index as an insulin resistance marker in a sample of healthy adults
Carlos J. Toro-Huamanchumo, Diego Urrunaga-Pastor, Mirella Guarnizo-Poma, Herbert Lazaro-Alcantara, Socorro Paico-Palacios, Betzi Pantoja-Torres, Vitalia del Carmen Ranilla-Seguin, Vicente A. Benites-Zapata
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(1): 272. CrossRef - Effects of curcumin on glycemic control and lipid profile in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Nalinee Poolsup, Naeti Suksomboon, Putu Dian Marani Kurnianta, Kulchalee Deawjaroen, Stephen L. Atkin
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(4): e0215840. CrossRef - Effects of different dietary regimes alone or in combination with standardized Aronia melanocarpa extract supplementation on lipid and fatty acids profiles in rats
Petar Milic, Jovana Jeremic, Vladimir Zivkovic, Ivan Srejovic, Nevena Jeremic, Jovana Bradic, Tamara Nikolic Turnic, Isidora Milosavljevic, Sergey Bolevich, Stefani Bolevich, Milica Labudovic Borovic, Aleksandra Arsic, Miroslav Mitrovic, Vladimir Jakovlje
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2019; 461(1-2): 141. CrossRef - Repression of Transcriptional Activity of Forkhead Box O1 by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Ameliorates Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetic Rats
Hyun Cho, Young Seok, Hae Lee, Minji Song, InKyeom Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(11): 3539. CrossRef - Gender and Age Stratified Analyses of Nutrient and Dietary Pattern Associations with Circulating Lipid Levels Identify Novel Gender and Age-Specific Correlations
Huifeng Jin, Jessie Nicodemus-Johnson
Nutrients.2018; 10(11): 1760. CrossRef - Effect of Gum Arabic (Acacia Senegal) supplementation on visceral adiposity index (VAI) and blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus as indicators of cardiovascular disease (CVD): a randomized and placebo-controlled clinical trial
Rasha Babiker, Khalifa Elmusharaf, Michael B. Keogh, Amal M. Saeed
Lipids in Health and Disease.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Silymarin prevents lipid accumulation in the liver of rats with type 2 diabetes via sirtuin1 and SREBP-1c
Nejat Kheiripour, Jamshid Karimi, Iraj Khodadadi, Heidar Tavilani, Mohammad Taghi Goodarzi, Mohammad Hashemnia
Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology.2018; 29(3): 301. CrossRef - Sex-specific relationship between visceral fat index and dyslipidemia in Chinese rural adults: The Henan Rural Cohort Study
Zhongyan Tian, Yuqian Li, Zhenxing Mao, Songcheng Yu, Yanhua Wang, Xiaotian Liu, Runqi Tu, Haiqing Zhang, Xinling Qian, Xia Zhang, Lulu Zhang, Jingzhi Zhao, Lei Yin, Chongjian Wang
Preventive Medicine.2018; 116: 104. CrossRef - The Lipid Side of Bone Marrow Adipocytes: How Tumor Cells Adapt and Survive in Bone
Jonathan D. Diedrich, Mackenzie K. Herroon, Erandi Rajagurubandara, Izabela Podgorski
Current Osteoporosis Reports.2018; 16(4): 443. CrossRef - Revisiting the Diabetes-Heart Failure Connection
Markus Wallner, Deborah M. Eaton, Dirk von Lewinski, Harald Sourij
Current Diabetes Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - DNA methylation markers associated with type 2 diabetes, fasting glucose and HbA1c levels: a systematic review and replication in a case–control sample of the Lifelines study
Eliza Walaszczyk, Mirjam Luijten, Annemieke M. W. Spijkerman, Marc J. Bonder, Helen L. Lutgers, Harold Snieder, Bruce H. R. Wolffenbuttel, Jana V. van Vliet-Ostaptchouk
Diabetologia.2018; 61(2): 354. CrossRef - Ozone modifies the metabolic and endocrine response to glucose: Reproduction of effects with the stress hormone corticosterone
Errol M. Thomson, Shinjini Pilon, Josée Guénette, Andrew Williams, Alison C. Holloway
Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology.2018; 342: 31. CrossRef - Mechanisms and treatment of heart failure in diabetes
Joseph Timmons, Miles Fisher
Practical Diabetes.2018; 35(4): 117. CrossRef - Cyclocarya paliurus Leaves Tea Improves Dyslipidemia in Diabetic Mice: A Lipidomics-Based Network Pharmacology Study
Lixiang Zhai, Zi-wan Ning, Tao Huang, Bo Wen, Cheng-hui Liao, Cheng-yuan Lin, Ling Zhao, Hai-tao Xiao, Zhao-xiang Bian
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Actions of metformin and statins on lipid and glucose metabolism and possible benefit of combination therapy
Mariël F. van Stee, Albert A. de Graaf, Albert K. Groen
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Body composition analysis, anthropometric indices and lipid profile markers as predictors for prediabetes
Vineetha K. Ramdas Nayak, Kirtana Raghurama Nayak, Sudha Vidyasagar, Asha Kamath, Xiao-Feng Yang
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(8): e0200775. CrossRef - Effect of statins on fasting glucose in non-diabetic individuals: nationwide population-based health examination in Korea
Jinkwon Kim, Hye Sun Lee, Kyung-Yul Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Antihyperlipidemic Activity ofArchidendron pauciflorumFruit Peel Extract in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetes Female Wistar Rats
Madihah, A. R Rahim, D. M Malini, W Hermawan
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2018; 166: 012015. CrossRef - Prolactin regulatory element-binding (PREB) protein regulates hepatic glucose homeostasis
Joo-Man Park, Mi-Young Kim, Tae-Hyun Kim, Dong-Kook Min, Ga Eul Yang, Yong-Ho Ahn
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2018; 1864(6): 2097. CrossRef - Abnormalities in the relationship of paraoxonase 1 with HDL and apolipoprotein A1 and their possible connection to HDL dysfunctionality in type 2 diabetes
Alena Viktorinova, Ingrid Jurkovicova, Lubomira Fabryova, Sona Kinova, Michal Koren, Anna Stecova, Klara Svitekova
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 140: 174. CrossRef - Dietary stearic acid regulates mitochondria in vivo in humans
Deniz Senyilmaz-Tiebe, Daniel H. Pfaff, Sam Virtue, Kathrin V. Schwarz, Thomas Fleming, Sandro Altamura, Martina U. Muckenthaler, Jürgen G. Okun, Antonio Vidal-Puig, Peter Nawroth, Aurelio A. Teleman
Nature Communications.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Update 2017 – Lipide
K. G. Parhofer
Der Diabetologe.2017; 13(5): 313. CrossRef - Adipokines and free fatty acids regulate insulin sensitivity by increasing microRNA-21 expression in human mature adipocytes
Nannan Zhang, Naijian Zhang, Leilei Song, Hui Xie, Chao Zhao, Sujuan Li, Wenxi Zhao, Yaping Zhao, Chunlin Gao, Guangfeng Xu
Molecular Medicine Reports.2017; 16(2): 2254. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of a combination of red yeast rice and olive extract in hypercholesterolemic patients with and without statin-associated myalgia
Christian Tshongo Muhindo, Sylvie A. Ahn, Michel F. Rousseau, Yvan Dierckxsens, Michel P. Hermans
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2017; 35: 140. CrossRef - Independent relationship between serum ferritin levels and dyslipidemia in Chinese adults: A population study
Jiang Li, Weimin Bao, Tie Zhang, Yun Zhou, Hui Yang, Hongbing Jia, Rui Wang, Yongtong Cao, Cheng Xiao, Cheng Hu
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(12): e0190310. CrossRef - A Synthetic-Biology-Inspired Therapeutic Strategy for Targeting and Treating Hepatogenous Diabetes
Shuai Xue, Jianli Yin, Jiawei Shao, Yuanhuan Yu, Linfeng Yang, Yidan Wang, Mingqi Xie, Martin Fussenegger, Haifeng Ye
Molecular Therapy.2017; 25(2): 443. CrossRef - Klinische Bedeutung des HDL-Cholesterins
W. März, M. E. Kleber, H. Scharnagl, T. Speer, S. Zewinger, A. Ritsch, K. G. Parhofer, A. von Eckardstein, U. Landmesser, U. Laufs
Herz.2017; 42(1): 58. CrossRef - Increase in resting heart rate over 2 years predicts incidence of diabetes: A 10-year prospective study
G. Kim, Y.-h. Lee, J.Y. Jeon, H. Bang, B.-W. Lee, E.S. Kang, I.-K. Lee, B.-S. Cha, C.S. Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2017; 43(1): 25. CrossRef - A Potential of Coleus Tuberosus Crackers Rich in Resistant Starch Type 3 Improves Glucose and Lipid Profile of Alloxan –Induced Diabetic Mice
Mutiara Nugraheni, Siti Hamidah, Rizqie Auliana
Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science Journal.2017; 5(3): 308. CrossRef - Liver-adipose tissue crosstalk: A key player in the pathogenesis of glucolipid metabolic disease
De-wei Ye, Xiang-lu Rong, Ai-min Xu, Jiao Guo
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine.2017; 23(6): 410. CrossRef - Dyslipidaemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Niki Katsiki, Nikolaos Tentolouris, Dimitri P. Mikhailidis
Current Opinion in Cardiology.2017; 32(4): 422. CrossRef - The PDK1 Inhibitor Dichloroacetate Controls Cholesterol Homeostasis Through the ERK5/MEF2 Pathway
Abrar Ul Haq Khan, Nerea Allende-Vega, Delphine Gitenay, Sabine Gerbal-Chaloin, Claire Gondeau, Dang-Nghiem Vo, Sana Belkahla, Stefania Orecchioni, Giovanna Talarico, Francesco Bertolini, Milica Bozic, Jose M. Valdivielso, Fabienne Bejjani, Isabelle Jarie
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Susceptibility background for type 2 diabetes in eleven Mexican Indigenous populations: HNF4A gene analysis
M. A. Granados-Silvestre, M. G. Ortiz-López, J. Granados, S. Canizales-Quinteros, Rosenda I. Peñaloza-Espinosa, C. Lechuga, V. Acuña-Alonzo, K. Sánchez-Pozos, M. Menjivar
Molecular Genetics and Genomics.2017; 292(6): 1209. CrossRef - Analysis of risk factors and their interactions in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross‐sectional survey in Guilin, China
Disha Zou, Yao Ye, Nina Zou, Jian Yu
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2017; 8(2): 188. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Metformin alone, in Combination with Insulin or Metformin Plus Insulin in Presence of Simvastatin in Libyan Diabetic Patients
Fathi M Sherif
Pharmacy & Pharmacology International Journal.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - HDL cholesterol: reappraisal of its clinical relevance
Winfried März, Marcus E. Kleber, Hubert Scharnagl, Timotheus Speer, Stephen Zewinger, Andreas Ritsch, Klaus G. Parhofer, Arnold von Eckardstein, Ulf Landmesser, Ulrich Laufs
Clinical Research in Cardiology.2017; 106(9): 663. CrossRef - Glucose and Lipid Dysmetabolism in a Rat Model of Prediabetes Induced by a High-Sucrose Diet
Ana Burgeiro, Manuela Cerqueira, Bárbara Varela-Rodríguez, Sara Nunes, Paula Neto, Frederico Pereira, Flávio Reis, Eugénia Carvalho
Nutrients.2017; 9(6): 638. CrossRef - Longitudinal trends in HbA1c and associations with comorbidity and all-cause mortality in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes: A cohort study
Miyang Luo, Wei Yen Lim, Chuen Seng Tan, Yilin Ning, Kee Seng Chia, Rob M. van Dam, Wern Ee Tang, Ngiap Chuan Tan, Richard Chen, E. Shyong Tai, Kavita Venkataraman
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2017; 133: 69. CrossRef - Plasma Periostin Levels Are Increased in Chinese Subjects with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes and Are Positively Correlated with Glucose and Lipid Parameters
Yuanyuan Luo, Hua Qu, Hang Wang, Huili Wei, Jing Wu, Yang Duan, Dan Liu, Huacong Deng
Mediators of Inflammation.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Comprehensive assessment of lipoprotein subfraction profiles according to glucose metabolism status, and association with insulin resistance in subjects with early-stage impaired glucose metabolism
Jie-Eun Lee, Se Hee Min, Dong-Hwa Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Kyoung Min Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim
International Journal of Cardiology.2016; 225: 327. CrossRef - Clinical benefits of pitavastatin: focus on patients with diabetes or at risk of developing diabetes
Vivencio Barrios, Carlos Escobar
Future Cardiology.2016; 12(4): 449. CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose index, a marker of insulin resistance, is associated with coronary artery stenosis in asymptomatic subjects with type 2 diabetes
Eun Young Lee, Hae Kyung Yang, Joonyub Lee, Borami Kang, Yeoree Yang, Seung-Hwan Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yu-Bae Ahn, Bong Yun Cha, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae Hyoung Cho
Lipids in Health and Disease.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Update: Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus
Cecilia C. Low Wang, Connie N. Hess, William R. Hiatt, Allison B. Goldfine
Circulation.2016; 133(24): 2459. CrossRef - Role of growth hormone-releasing hormone in dyslipidemia associated with experimental type 1 diabetes
Maritza J. Romero, Rudolf Lucas, Huijuan Dou, Supriya Sridhar, Istvan Czikora, Eby M. Mosieri, Ferenc G. Rick, Norman L. Block, Subbaramiah Sridhar, David Fulton, Neal L. Weintraub, Zsolt Bagi, Andrew V. Schally
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2016; 113(7): 1895. CrossRef - Lipid changes during basal insulin peglispro, insulin glargine, or NPH treatment in six IMAGINE trials
Henry Ginsberg, Bertrand Cariou, Trevor Orchard, Lei Chen, Junxiang Luo, Edward J. Bastyr, Juliana Bue‐Valleskey, Annette M. Chang, Tibor Ivanyi, Scott J. Jacober, Byron J. Hoogwerf
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2016; 18(11): 1089. CrossRef - PCSK9-Inhibitoren bei Hypercholesterinämie
K. G. Parhofer
Herz.2016; 41(3): 217. CrossRef - Risk assessment and management of post-transplant diabetes mellitus
Eugene Han, Myoung Soo Kim, Yu Seun Kim, Eun Seok Kang
Metabolism.2016; 65(10): 1559. CrossRef - The changes of subtypes in pediatric diabetes and their clinical and laboratory characteristics over the last 20 years
Eun Byul Kwon, Hae Sang Lee, Young Seok Shim, Hwal Rim Jeong, Jin Soon Hwang
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2016; 21(2): 81. CrossRef - 4-Hydroxyisoleucine: A Potential New Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mohammad Ishraq Zafar, Feng Gao
BioDrugs.2016; 30(4): 255. CrossRef
- Response surface methodology based development of an optimized polyherbal formulation and evaluation of its anti-diabetic and anti-obesity potential in high-fat diet-induced obese mice

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





