- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 40(6); 2016 > Article
-
ReviewObesity and Metabolic Syndrome Metabolic Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Experience from Asia
-
Wei-Jei Lee1
 , Lwin Aung2
, Lwin Aung2 -
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2016;40(6):433-443.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.6.433
Published online: December 2, 2016
1Department of Surgery, Min-Sheng General Hospital, National Taiwan University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
2Department of Surgery, Ng Teng Fong General Hospital, Singapore.
- Corresponding author: Wei-Jei Lee. Department of Surgery, Min-Sheng General Hospital, National Taiwan University, No 168, Chin Kuo Road, Taoyuan, Taiwan. wjlee_obessurg_tw@yahoo.com.tw
• Received: September 2, 2016 • Accepted: October 25, 2016
Copyright © 2016 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- ABSTRACT
- INTRODUCTION
- HISTORY
- EFFICACY OF DIFFERENT METABOLIC PROCEDURES
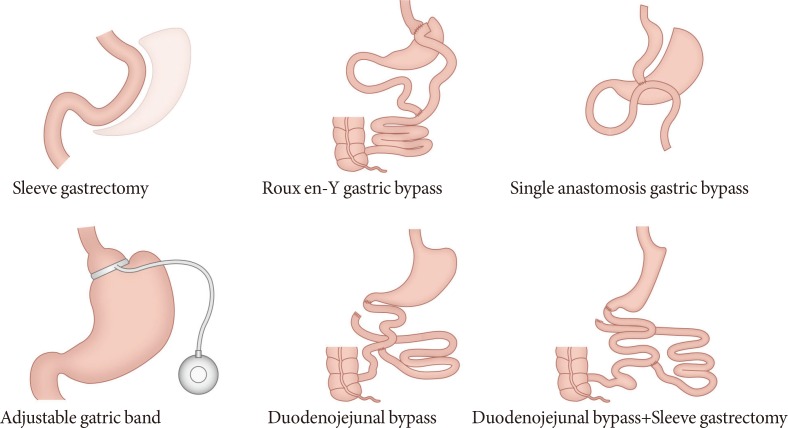
- NEW BARIATRIC/METABOLIC PROCEDURES
- EFFICACY OF METABOLIC SURGERY IN ASIANS IN CONTRAST TO NON-ASIAN POPULATION
- RANDOMIZED CONTROL TRIALS
- MECHANISM OF EFFECT
- OPERATIVE RISKS AND LONGTERM NUTRITIONAL EFFECTS
- PREDICTORS OF DIABETES REMISSION AND PATIENT SELECTION
- CONCLUSIONS
- NOTES
- REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Insulin resistance levels predicted metabolic improvement and weight loss after metabolic surgery in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes
Yaoquan Cao, Ping Luo, Haibo Tang, Pengzhou Li, Guohui Wang, Weizheng Li, Zhi Song, Zhihong Su, Xulong Sun, Xianhao Yi, Zhibing Fu, Beibei Cui, Shaihong Zhu, Liyong Zhu
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.2024; 20(1): 80. CrossRef - Long‐term outcomes of metabolic surgery in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes in Asia
Yu‐Min Huang, Yen‐Kuang Lin, Wei‐Jei Lee, Kyoung Yul Hur, Kazunori Kasama, Anton Kui Sing Cheng, Ming‐Hsien Lee, Simon Kin‐Hung Wong, Tien‐Chou Soong, Kuo‐Ting Lee, Davide Lomanto, Muffazal Lakdawala, Yen‐Hao Su, Weu Wang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(3): 742. CrossRef - Vertical sleeve gastrectomy induces distinctive transcriptomic responses in liver, fat and muscle
Chang Ho Ahn, Eun Hye Choi, Hyunjung Lee, Woochan Lee, Jong-Il Kim, Young Min Cho
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Remission Following Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients With a Body Mass Index of 27.5–32.5 kg/m2
Ping Luo, Yaoquan Cao, Pengzhou Li, Guohui Wang, Zhi Song, Weizheng Li, Zhihong Su, Hui Zhou, Xianhao Yi, Zhibing Fu, Xulong Sun, Haibo Tang, Beibei Cui, Qianqian Yu, Liyong Zhu, Shaihong Zhu
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pre- and postoperative respiratory muscle strength, body mass index and fasting glucose profile of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus submitted to metabolic surgery
Ariana de Melo Tosta, Marisa de Carvalho Borges, Élida Mara Carneiro da Silva, Alex Augusto da Silva, Eduardo Crema
Fisioterapia em Movimento.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes After Metabolic Surgery in Asians—a Meta-analysis
Danson Yeo, Charleen Yeo, Tze Yi Low, Saleem Ahmed, Sheena Phua, Aung Myint Oo, Jaideepraj Rao, Aaryan Koura, Kavita Venkataraman, Sanghvi Kaushal
Obesity Surgery.2019; 29(1): 114. CrossRef - Diabetes resolution after one anastomosis gastric bypass
Adam Abu-Abeid, Yonatan Lessing, Niv Pencovich, Danit Dayan, Joseph M. Klausner, Subhi Abu-Abeid
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.2018; 14(2): 181. CrossRef - Laparoscopic metabolic surgery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in Asia: a scoping review and evidence-based analysis
Zhiyong Dong, Sheikh Mohammed Shariful Islam, Ashley M. Yu, Rui Qu, Bingsheng Guan, Junchang Zhang, Zhao Hong, Cunchuang Wang
BMC Surgery.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Practice Recommendations for the Management of Obesity in the United Arab Emirates
Salahedeen Abusnana, Mohammad Fargaly, Shaima Hasan Alfardan, Fatema Hasan Al Hammadi, Alaaeldin Bashier, Ghaida Kaddaha, Barbara McGowan, Rita Nawar, Amena Sadiya
Obesity Facts.2018; 11(5): 413. CrossRef - Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy combined with single-anastomosis duodenal-jejunal bypass in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus of patients with body mass index higher than 27.5 kg/m2 but lower than 32.5 kg/m2
Ying-Xu Li, Deng-Hua Fang, Tian-Xi Liu
Medicine.2018; 97(31): e11537. CrossRef - Comparison of Great Curvature Plication with Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass (GCP-DJB) and Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) on Metabolic Indices and Gut Hormones in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rats
Nian-Cun Qiu, Wei Li, Miao-E Liu, Xiao-Xia Cen, Cheng-Xiang Shan, Wei Zhang, Qing Liu, Yang Wang, Ya-Ting Zhu, Ming Qiu
Obesity Surgery.2018; 28(12): 4014. CrossRef - Evolution of Diabetes Care in Hong Kong: From the Hong Kong Diabetes Register to JADE-PEARL Program to RAMP and PEP Program
Ivy H.Y. Ng, Kitty K.T. Cheung, Tiffany T.L. Yau, Elaine Chow, Risa Ozaki, Juliana C.N. Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(1): 17. CrossRef - Ethnicity Does Not Influence Glycemic Outcomes or Diabetes Remission After Sleeve Gastrectomy or Gastric Bypass in a Multiethnic Asian Cohort
Phong Ching Lee, Kwang Wei Tham, Sonali Ganguly, Hong Chang Tan, Alvin Kim Hock Eng, John B. Dixon
Obesity Surgery.2018; 28(6): 1511. CrossRef - Effects of GABAB receptor activation on spatial cognitive function and hippocampal neurones in rat models of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xiao-Jun Cai, Lei Wang, Chun-Mei Hu
Bioscience Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic surgery ameliorates cardiovascular risk in obese diabetic patients: Influence of different surgical procedures
Jih-Hua Wei, Ruey-Hsing Chou, Po-Hsun Huang, Wei-Jei Lee, Shu-Chun Chen, Shing-Jong Lin
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.2018; 14(12): 1832. CrossRef - Pulmonary function evaluation in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients submitted to metabolic surgery
Ariana de Melo Tosta, Marisa de Carvalho Borges, Élida Mara Carneiro da Silva, Tharsus Dias Takeuti, Júverson Alves Terra Júnior, Eduardo Crema
Fisioterapia em Movimento.2018;[Epub] CrossRef

 KDA
KDA
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite