- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 47(3); 2023 > Article
-
Original ArticleCOVID-19 Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data Analysis
-
Hye Jun Kim1,2,3
 , Sang Jun Lee1,2,3
, Sang Jun Lee1,2,3 , Soonok Sa1,2,3, Jung Ho Bae4, Gyuseon Song1,2,3, Chae Won Lee1,2,3, Ju Hee Kim1,2,3, Sung Ryul Shim1,2,3,5, Myunghee Hong1,2,3
, Soonok Sa1,2,3, Jung Ho Bae4, Gyuseon Song1,2,3, Chae Won Lee1,2,3, Ju Hee Kim1,2,3, Sung Ryul Shim1,2,3,5, Myunghee Hong1,2,3 , Hyun Wook Han1,2,3
, Hyun Wook Han1,2,3
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2023;47(3):356-365.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0129
Published online: March 6, 2022
1Department of Biomedical Informatics, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
2Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
3Institute for Biomedical Informatics, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
4Department of Internal Medicine and Healthcare Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital Healthcare System Gangnam Center, Seoul, Korea
5Department of Health and Medical Informatics, Kyungnam University College of Health Sciences, Changwon, Korea
-
Corresponding authors: Hyun Wook Han
 Department of Biomedical Informatics, Graduate School of Medicine, CHA University, 335 Pangyo-ro, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 13488, Korea E-mail: stepano7@gmail.com
Department of Biomedical Informatics, Graduate School of Medicine, CHA University, 335 Pangyo-ro, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 13488, Korea E-mail: stepano7@gmail.com -
Myunghee Hong
 Department of Biomedical Informatics, Graduate School of Medicine, CHA University, 335 Pangyo-ro, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 13488, Korea E-mail: mhhong99486@gmail.com
Department of Biomedical Informatics, Graduate School of Medicine, CHA University, 335 Pangyo-ro, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 13488, Korea E-mail: mhhong99486@gmail.com - * Hye Jun Kim and Sang Jun Lee contributed equally to this study as first authors.
Copyright © 2023 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- Little is known about the adverse events (AEs) associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
-
Methods
- This study used vaccine AE reporting system data to investigate severe AEs among vaccinated patients with T2DM. A natural language processing algorithm was applied to identify people with and without diabetes. After 1:3 matching, we collected data for 6,829 patients with T2DM and 20,487 healthy controls. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to calculate the odds ratio for severe AEs.
-
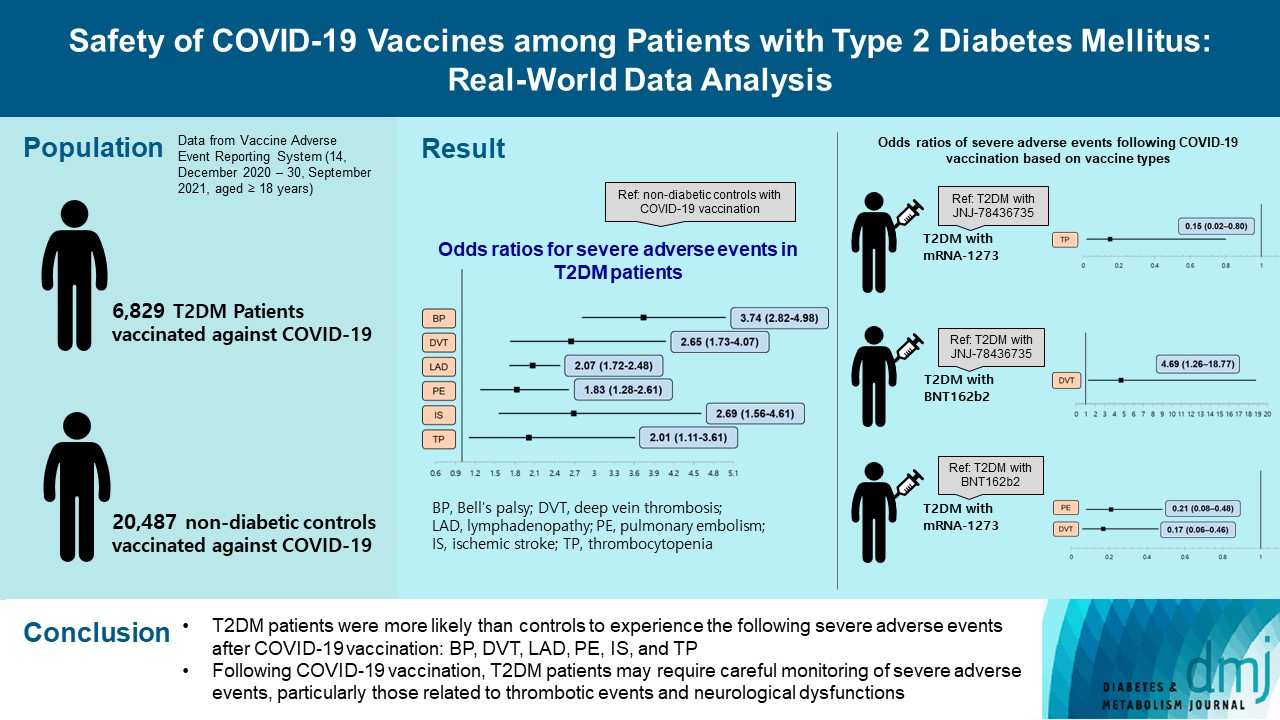
Results
- After COVID-19 vaccination, patients with T2DM were more likely to experience eight severe AEs than controls: cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, encephalitis myelitis encephalomyelitis, Bell’s palsy, lymphadenopathy, ischemic stroke, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), thrombocytopenia (TP), and pulmonary embolism (PE). Moreover, patients with T2DM vaccinated with BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 were more vulnerable to DVT and TP than those vaccinated with JNJ-78436735. Among patients with T2DM administered mRNA vaccines, mRNA-1273 was safer than BNT162b2 in terms of the risk of DVT and PE.
-
Conclusion
- Careful monitoring of severe AEs in patients with T2DM may be necessary, especially for those related to thrombotic events and neurological dysfunctions after COVID-19 vaccination.
- The outbreak of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in 2019 and its ramifications have spurred the development of vaccines [1]. Because of the urgency of this health crisis, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) rapidly approved vaccines on December 14, 2020: two mRNA vaccines (mRNA-1273, Moderna, Cambridge, MA, USA; and BNT162b2, Pfizer-BioNTech, New York, NY, USA) and one viral vector vaccine (JNJ-78436735, Janssen/Johnson and Johnson, Titusville, NJ, USA) [2,3]. Although the rapid dissemination of the COVID-19 vaccines has played an important role in minimizing the spread and damage of the virus, there are also considerable concerns about their safety [1]. Indeed, reported adverse events (AEs) after COVID-19 vaccination range from mild symptoms, such as pain at the injection site, fever, or headache, to severe symptoms, including death [4]. Phase 3 trials lacked sufficient follow-up time and had limited sample sizes and restrictive inclusion criteria. These issues may have hindered the detection of any serious AEs after COVID-19 vaccination [3].
- It has been widely reported that diabetes is undoubtedly associated with a poorer prognosis (or severe symptoms) after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection [5,6]. A meta-analysis demonstrated a higher mortality risk among patients with diabetes who contract COVID-19 [7]. Furthermore, a few cases of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE) [8], and Guillain–Barre syndrome [9] have been reported after COVID-19 vaccination. However, most of the studies on type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are case reports of AEs after COVID-19 vaccination, and few studies have considered the underlying disease of T2DM. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the risk of severe AEs after COVID-19 vaccine administration in patients with T2DM. The study also sought to investigate whether this risk varies with vaccine type.
INTRODUCTION
- This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the CHA Bundang Medical Center (CHAMC 2022 02 018). Written informed consent by the patients was waived due to a retrospective nature of our study. The guidelines for Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) were followed for this study (Supplementary Table 1).
- Data source
- This retrospective analysis was based on Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) data from 14 December 2020 to 30 September 2021. This data was used to analyze and describe AEs following the approval of COVID-19 vaccines for the United States population. The VAERS was developed in 1990 as a United States vaccine safety surveillance program by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the FDA. It collects information regarding AEs to serve as an early warning system for potential safety issues with United States-licensed vaccines. From vaccine recipients to healthcare providers and vaccine makers, everyone can openly report side effects on the VAERS [10]. Further information about the VAERS data is available at https://vaers.hhs.gov/data.html (accessed on December 14, 2021).
- Natural language processing
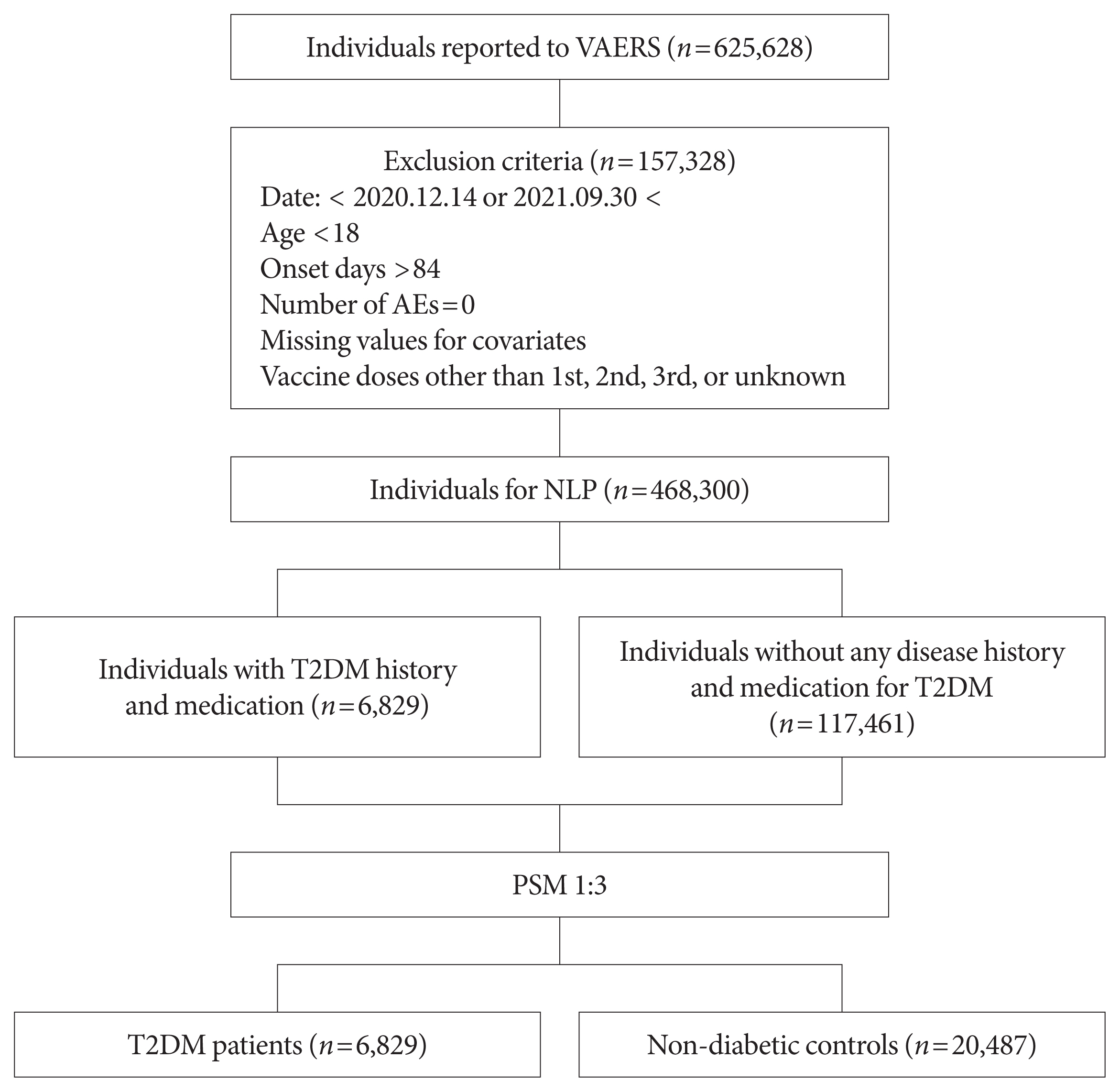
- To compare the risk of AEs after COVID-19 vaccination between patients with T2DM and healthy controls, natural language processing (NLP) was conducted to extract data of patients with a history of T2DM combined with the corresponding medications. The pipeline extracted information about medication (Supplementary Table 2) taken by patients with a history of T2DM according to the FDA and Global Diabetes Community Forum guidelines [11]. Patients without diabetes (controls) were defined as those with no history of disease or medication. The NLP pipeline was developed using Python version 3.7.10 (Python Software Foundation, Wilmington, DE, USA) under the regular expression package ‘re.’ Regular expressions are scripts specialized for processing texts, such as pattern matching and capturing terms [12]. After completing the NLP, we obtained samples resulting in 124,290 reports of individuals (6,829 people with T2DM and 117,461 controls) who experienced at least one AE after COVID-19 vaccination. To validate the accuracy of our NLP work, we compared the results of NLP and manual data extraction in terms of identifying patients with T2DM and their medications. 6,829 and 6,819 key terms for T2DM were identified using NLP and manual extraction, respectively. The concordance rate between the manual extraction and NLP and was 99.85% (6,819/6,829).
- Study population
- This study investigated adults aged 18 years and older who were vaccinated for COVID-19. Initially, data from 468,300 individuals were available. The symptom description from the VAERS data was used to identify T2DM cases. These were matched against non-diabetic controls from the same VAERS data, with matching based on age, sex, and type of vaccine. After applying the NLP extraction algorithm with a history of T2DM combined with the corresponding medications, data of 6,829 people with T2DM and 117,461 controls with AEs were available. Finally, data of 6,829 people with T2DM and 20,487 controls (total 27,316 individuals) with AEs after 1:3 propensity score matching were used for analysis. The flow of our study is summarized in Fig. 1.
- Severe AEs
- We listed 25 severe AEs on the advice of a focus group of three clinical experts. Each was used as the outcome of the analyses. The list of severe AEs was classified using previous studies (Supplementary Table 3) [3,13].
- Statistical analysis
- We first conducted 1:3 propensity score matching for age (categorical, 18–24, 25–39, 40–49, 50–64, 65–74, and ≥75), sex (categorical, male and female), and type of vaccine (JNJ-78436735, mRNA-1273, or BNT162b2). This was to address any selection bias between the T2DM and control groups. The matching resulted in 6,829 patients with T2DM and 20,287 controls. Next, the frequency of each of the 25 severe AEs after COVID-19 vaccination was investigated using the matched data. The chi-squared test and Fisher’s exact test were used for the categorical analyses. Multiple logistic regression analysis was conducted, adjusting for sex, age, sex, onset days, and type of vaccine. Sensitivity analysis was conducted to identify whether the risk of developing severe AEs varied according to vaccine type. The data obtained were subjected to normality testing. A two-sided P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using R version 4.1.0 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
- Data and resource availability
- All of the data used in this study came from the VAERS, which is open to the public. The CDC and the FDA jointly run VAERS: https://vaers.hhs.gov/data/datasets.html.
METHODS
- Compared with the characteristics of data before matching, sex, age group, and vaccine type did not differ significantly after matching between patients with and without T2DM (P>0.05) (Table 1). Of the patients with T2DM, 65.1% were female (male, 34.9%) and over 40% were aged 50 to 65 years. mRNA-1273 (Moderna), BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech), and JNJ-78436735 (Janssen/Johnson and Johnson) were administered in 53.1%, 40.3%, and 6.6%, respectively, of the patients.
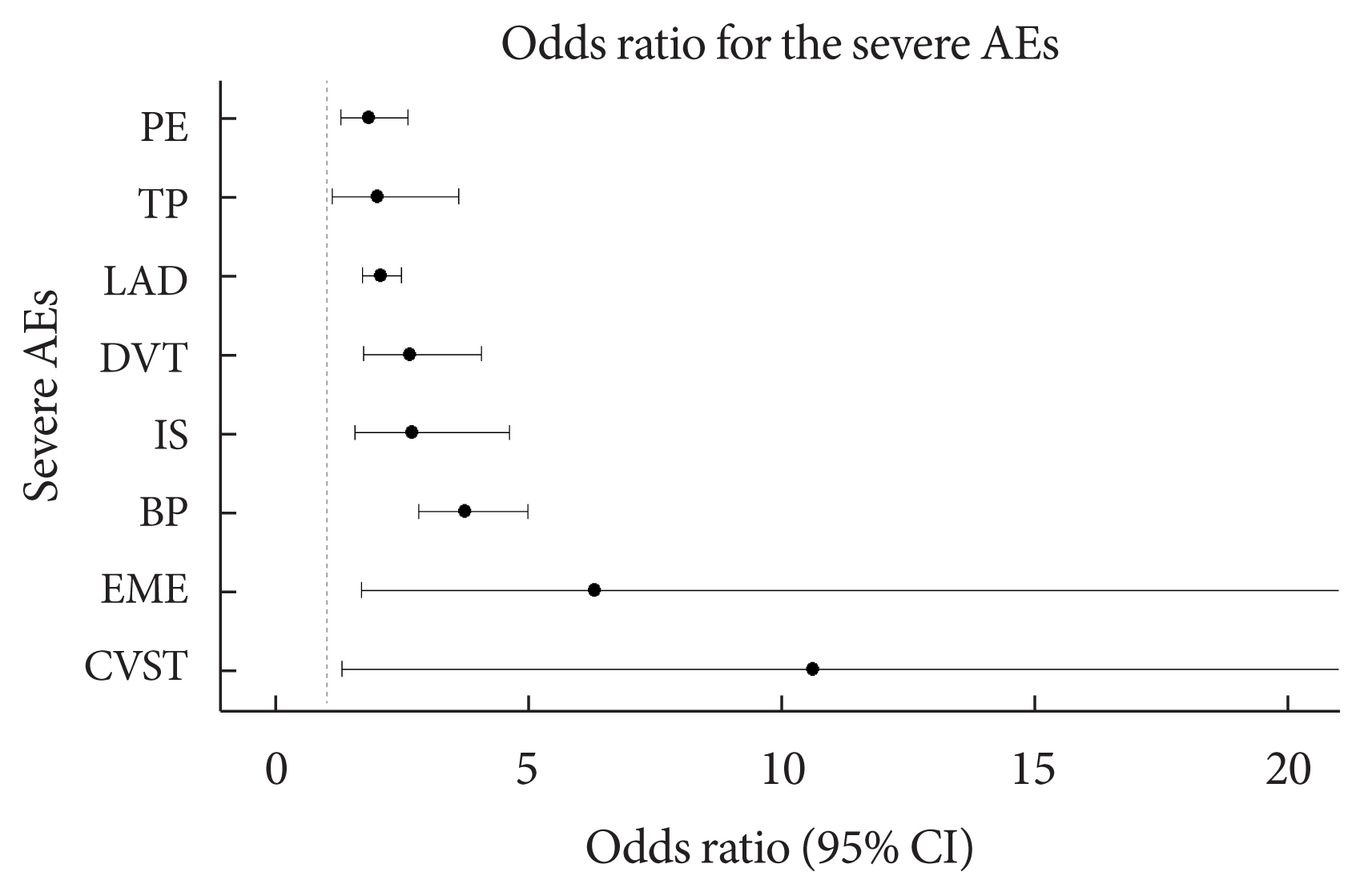
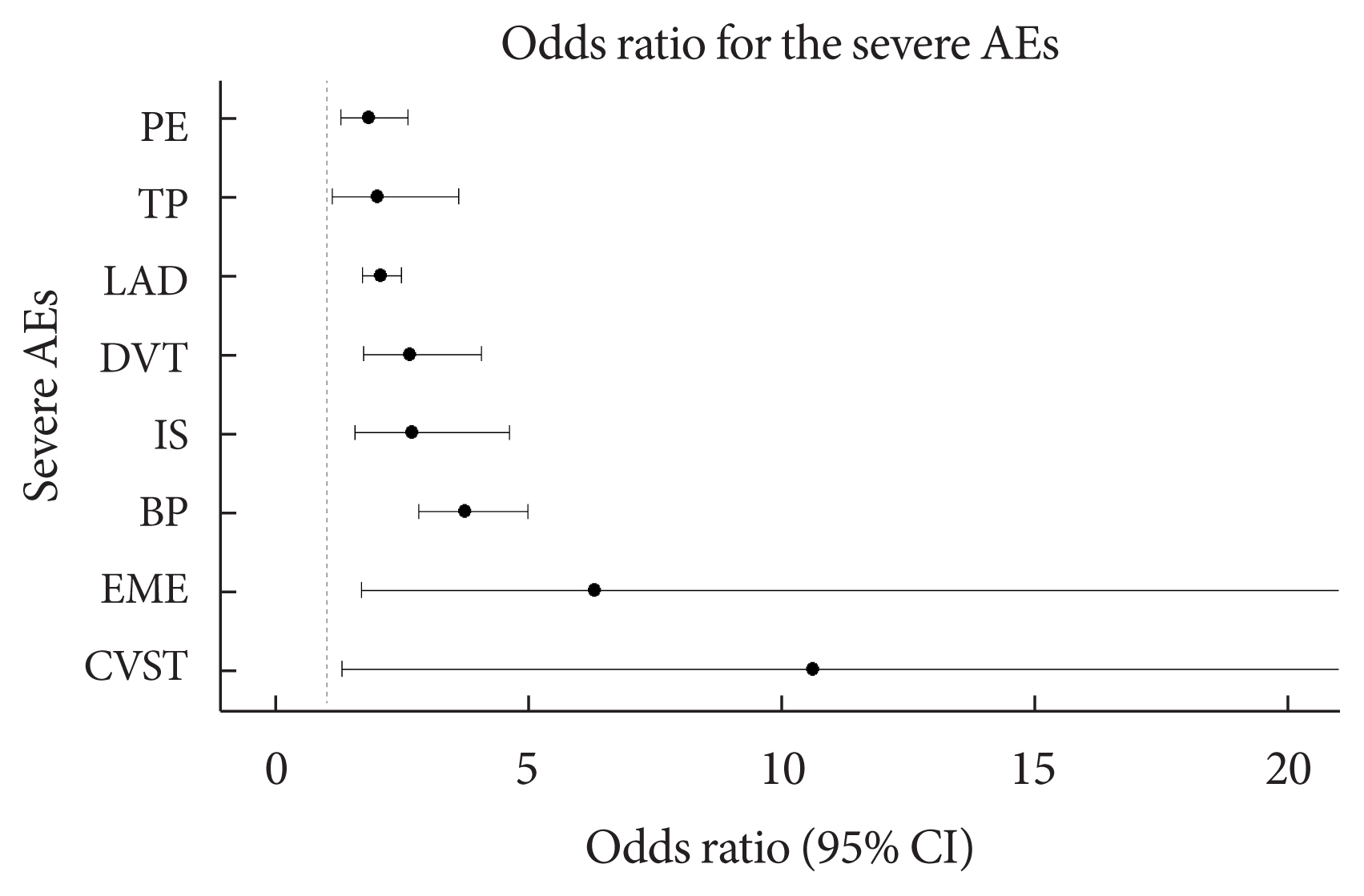
- Table 2 shows the frequency of each of the 25 severe AEs after COVID-19 vaccination with mRNA-1273, BNT162b2, and JNJ-78436735 among the people with and without diabetes. There was a statistically significant difference in the frequency of encephalitis myelitis encephalomyelitis (EME), Bell’s palsy (BP), ischemic stroke (IS), DVT, lymphadenopathy (LAD), thrombocytopenia (TP), and PE (P<0.05). In addition, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) was marginally different between people with and without diabetes (P=0.051). Additionally, we stratified the frequency of AEs among people with and without diabetes by age groups (Supplementary Table 4). For all three vaccination types, the risk of the AEs was higher in patients with T2DM than in the controls (Supplementary Figs. 1–3). After adjusting for sex, age, onset days, and type of vaccine, the eight severe AEs among the 25 severe AEs were significantly associated with T2DM compared with the controls (P<0.05). The severe AEs with the largest differences between the patients with and without T2DM were CVST and EME. The odds of developing CVST and EME were more than 10- and 5-fold higher, respectively, among patients with T2DM compared with the controls. Moreover, BP, IS, DVT, LAD, TP, and PE were more prevalent among patients with T2DM, with odds ratios (ORs) of 3.74, 2.69, 2.65, 2.07, 2.01, and 1.83, respectively (Table 3, Fig. 2).
- In the sensitivity analysis, we determined whether the risk of severe AEs varied with COVID-19 vaccine type. To do this, we constructed eight additional multiple logistic regression models after including the interaction term of diabetes and the type of vaccine. Compared with patients with T2DM who were administered the JNJ-78436735 vaccine, those vaccinated with mRNA-1273 had a significantly lower OR of TP (OR, 0.15; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.02 to 0.80), while those vaccinated with BNT162b2 had a significantly higher OR of DVT (OR, 4.69; 95% CI, 1.26 to 18.77). Furthermore, among patients with T2DM who were vaccinated, those who were administered mRNA-1273 had a significantly lower OR of DVT (OR, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.06 to 0.46) and PE (OR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.08 to 0.48) than those vaccinated with BNT162b2 (Table 4).
RESULTS
- In this study, we systemically analyzed 25 severe AEs following the administration of COVID-19 vaccines among patients with T2DM. Compared with the healthy controls, patients with T2DM were more likely to develop eight severe AEs: CVST, EME, BP, IS, DVT, LAD, TP, and PE. In particular, DVT was more prevalent among patients with T2DM vaccinated with BNT162b2, and TP was more common in patients vaccinated with mRNA-1273 than in those vaccinated with JNJ-78436735. Among the two types of mRNA vaccines, mRNA-1273 showed a lower proportion of DVT and PE compared to BNT162b2. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the severe AEs associated with T2DM after COVID-19 vaccination with different types of vaccines.
- Our findings are consistent with those of previous studies that reported a notable class of venous thromboembolism events after COVID-19 vaccination [14]. These events occur when a blood clot breaks off and blocks a vein [15]. COVID-19 vaccination can induce higher viscosity of the blood [16,17], leading to thrombotic complications in the vasculature [18]. In general, patients with T2DM have higher blood viscosity than those without diabetes [19]. Likewise, patients with COVID-19 with comorbidities, such as diabetes, are more vulnerable to thrombotic events [16,20,21]. The release of pro-inflammatory cytokines [22,23], along with hypoxia, immobility, and disseminated vascular coagulation [20,24–27], is intimately linked to the pathophysiology of thrombosis in patients with T2DM with COVID-19. Thromboembolism events among patients with COVID-19 have also shown decreased platelet production and elevated d-dimer levels that hinder blood clotting [28]. This is also marked by higher levels of fibrinogen and interleukin-6 in patients with T2DM than in those without diabetes [22,23].
- Additionally, our findings are consistent with those of a few studies that reported a higher risk of LAD among COVID-19 vaccinated people [29]. The aforementioned mechanisms may also be involved in lymphatic dysfunction in patients with T2DM. Increased metabolic activity can stimulate an immunological response in lymphoid tissues, which may be provisionally associated with greater pro-inflammatory cytokine release and subsequent damage to the lungs [30]. In addition, elevated lymphocyte count and d-dimer levels were associated with in-hospital complications among patients with T2DM infected with SARS-CoV-2 [31].
- Furthermore, COVID-19 patients with comorbidities, such as diabetes, are likely to experience abnormalities in the central nervous system (CNS) or peripheral nervous system (PNS) [21,32,33], which can stimulate the incidence of encephalitis, encephalopathy, or IS. A few case reports also presented the incidence of BP [34] and CVST [35] among patients with diabetes who were infected with SARS-CoV-2. The structure of the spike glycoprotein receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 has a high affinity for angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors in human cells [36]. When virions are attached to the ACE2 receptor distributed on PNS and CNS neurons, they may cause dysfunction in the fibrinolytic system and induce severe neurological side effects, such as cerebral venous thrombosis [37]. A randomized controlled trial has shown that SARS-CoV-2 infection is accompanied by a loss of function and mutations in neurons through the induction of small fiber neuropathy that may promote diabetic neuropathy and diabetic corneas [38]. Patients with diabetes are presumed to be more vulnerable to viral attachment to the ACE2 receptor. In addition, the release of angiotensin 1–7 induces the activation of the sympathetic nervous system. This leads to systemic vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure, which would enhance sympathetic activity through central stimulation [39]. This may contribute to a higher mortality risk and intensive care unit admission rates among patients with diabetes infected with SARS-CoV-2 [33,40].
- Our findings are in line with those of previous studies and case reports showing the heterogeneous risk of AEs according to the type of COVID-19 vaccine. A study reported that occurrence of vaccine-induced immune thrombotic TP may be associated with adenoviral vector-based vaccines [41]. Similarly, the administration of mRNA vaccines is recommended to mitigate the concern over the development of vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia syndrome [42]. We found several case reports of a specific syndrome of thrombosis with TP after vaccination with JNJ-78436735 [43,44]. Additionally, according to a report from the Netherlands Pharmacovigilance Centre Lareb, a government-funded organization that monitors adverse drug reactions, the absolute number of incidents of DVT after COVID-19 vaccination was greater with BNT162b2 than with the adenovirus vector-based vaccine. Furthermore, the number of DVT and PE cases was lower after vaccination with mRNA-1273 than with BNT162b2 [45], which is also consistent with our results.
- This study has some limitations. First, due to the retrospective nature of the study and the absence of sufficient data, we could not fully adjust for all the confounding factors that may be involved in the risk of severe AEs after COVID-19 vaccination. For example, individual health-related characteristics, such as height, weight, current glycemic status, comorbidities, and medications, may also affect the risk of developing severe AEs [46]. Although we controlled for the age and sex of each sample data, a careful interpretation of our study is needed. Second, the characteristics of the VAERS dataset, which consists of self-reported data, are subject to recall bias. Although its policy of requiring vaccine manufacturers and healthcare professionals to report AEs that come to their attention mitigate the concern over neglecting critical AEs in some way [47], dedicated studies with measurement data are warranted to generalize our findings. Third, we could not consider previous vaccinations in our analysis. In other words, because we were unable to distinguish the vaccination series, the AEs associated with the COVID-19 vaccination could have occurred after any series. Future studies that include information about each patient’s previous vaccinations are needed to clearly determine the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine in patients with T2DM.
- In conclusion, patients with T2DM are more likely to experience eight severe AEs after COVID-19 vaccination than those without diabetes. Careful monitoring against severe AEs, such as thrombotic events and neurological dysfunctions, may be warranted in patients with T2DM after COVID-19 vaccination.
DISCUSSION
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Fig. 1.
Supplementary Fig. 2.
Supplementary Fig. 3.
Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Table 2.
Supplementary Table 4.
-
Acknowledgements
- The data were obtained from Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). We thank all of the health care personnel who contributed to the detection, epidemiological investigation, and development of the COVID-19 vaccine.
- Hyun Wook Han are the guarantors of this work and, as such, had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: H.J.K., S.J.L., M.H., H.W.H.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: H.J.K., S.J.L., S.S., J.H.B., G.S., C.W.L., J.H.K., S.R.S., M.H., H.W.H.
Drafting the work or revising: H.J.K., S.J.L.
Final approval of the manuscript: H.J.K., S.J.L., S.S., J.H.B., G.S., C.W.L., J.H.K., S.R.S., M.H., H.W.H.
-
FUNDING
This research was supported by the Bio Industry Technology Development Program (No. 20015086) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry, & Energy (MOTIE, Korea), as well as supported by a grant from the Information and Communications Promotion Fund through the National IT Industry Promotion Agency (NIPA), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), Republic of Korea.
This research was partly supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No.2020-R1F1A1068423, NRF-2019M3C7A1032262), as well as by an Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No.2019-0-00224, AIM: AI based Next-generation Security In-formation Event Management Methodology for Cognitive Intelligence and Secure-Open Framework). This research was partly supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (No. HC20C0118).
NOTES
| Variable | Before matching | After matching | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| T2DM | Non-diabetic | P value | T2DM | Non-diabetic | P value | |
| Number | 6,829 | 117,461 | 6,829 | 20,487 | ||
|
|
||||||
| Sexa | 1.000 | |||||
| Female | 4,443 (65.1) | 78,857 (67.1) | <0.001 | 4,443 (65.1) | 13,329 (65.1) | |
| Male | 2,386 (34.9) | 38,604 (32.9) | 2,386 (34.9) | 7,158 (34.9) | ||
|
|
||||||
| Age, yra | 1.000 | |||||
| 18–24 | 18 (0.3) | 10,520 (9.0) | <0.001 | 18 (0.3) | 54 (0.3) | |
| 25–39 | 377 (5.5) | 30,946 (26.3) | 377 (5.5) | 1,131 (5.5) | ||
| 40–49 | 893 (13.1) | 19,506 (16.6) | 893 (13.1) | 2,679 (13.1) | ||
| 50–64 | 2,811 (41.2) | 28,812 (24.5) | 2,811 (41.2) | 8,433 (41.2) | ||
| 65–74 | 1,852 (27.1) | 15,692 (13.4) | 1,852 (27.1) | 5,556 (27.1) | ||
| ≥75 | 878 (12.9) | 11,985 (10.2) | 878 (12.9) | 2,634 (12.9) | ||
|
|
||||||
| Vaccine typea | 1.000 | |||||
| JNJ-78436735 | 453 (6.6) | 7,326 (6.2) | <0.001 | 453 (6.6) | 1,359 (6.6) | |
| mRNA-1273 | 3,625 (53.1) | 60,298 (51.3) | 3,625 (53.1) | 10,875 (53.1) | ||
| BNT162b2 | 2,751 (40.3) | 49,837 (42.4) | 2,751 (40.3) | 8,253 (40.3) | ||
| Variable | BP (n=201) | DVT (n=89) | LAD (n=509) | PE (n=132) | IS (n=58) | TP (n=47) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM | 3.74 (2.82–4.98)c | 2.65 (1.73–4.07)c | 2.07 (1.72–2.48)c | 1.83 (1.28–2.61)c | 2.69 (1.56–4.61)c | 2.01 (1.11–3.61)a |
| Male sex | 2.34 (1.76–3.11)c | 1.95 (1.27–3.00)b | 0.65 (0.52–0.79)c | 2.01 (1.42–2.87)c | 1.29 (0.76–2.17) | 2.83 (1.57–5.29)c |
| Age | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 1.02 (1.01–1.04)a | 0.97 (0.96–0.97)c | 1.01 (0.99–1.02) | 1.04 (1.02–1.06)c | 1.02 (0.99–1.04) |
| Vaccine type (mRNA-1273) | 1.14 (0.67–2.10) | 0.38 (0.21–0.73)b | 2.24 (1.36–4.05)b | 0.50 (0.31–0.85)b | 0.43 (0.21–1.02)a | 0.38 (0.18–0.88)a |
| Vaccine type (BNT162b2) | 1.03 (0.60–1.91) | 0.44 (0.24–0.87)a | 3.16 (1.91–5.69)c | 0.36 (0.21–0.63)c | 0.38 (0.17–0.94)a | 0.24 (0.10–0.60)b |
The odds ratio was calculated by multiple logistic regression analysis for each severe adverse event after adjusting for sex (reference: female), age, onset days, and vaccine type (reference: JNJ-78436735) as covariates. In the case of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and encephalitis myelitis encephalomyelitis, the frequency of occurrence was very small (10 or less); therefore, the results of logistic regression were not presented in the table.
T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; BP, Bell’s palsy; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; LAD, lymphadenopathy; PE, pulmonary embolism; IS, ischemic stroke; TP, thrombocytopenia.
a P<0.05,
b P<0.01,
c P<0.001.
| Interaction effects | BP | DVT | LAD | PE | IS | TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM×(mRNA-1273) (reference: T2DM× JNJ-78436735) | 1.26 (0.40–3.97) | 0.80 (0.22–2.91) | 1.44 (0.46–5.42) | 0.58 (0.20–1.65) | 1.68 (0.32–10.16) | 0.15 (0.02–0.80)a |
| T2DM×(BNT162b2) (reference: T2DM× JNJ-78436735) | 2.17 (0.67–7.08) | 4.69 (1.26–18.77)a | 1.67 (0.54–6.24) | 2.78 (0.90–8.86) | 2.54 (0.45–16.84) | 0.21 (0.02–1.34) |
| T2DM×(mRNA-1273) (reference: T2DM× BNT162b2) | 0.58 (0.31–1.07) | 0.17 (0.06–0.46)b | 0.87 (0.60–1.25) | 0.21 (0.08–0.48)b | 0.66 (0.19–2.18) | 0.72 (0.17–3.08) |
The odds ratio was calculated by multiple logistic regression analysis for each severe adverse event after adjusting for sex (reference: female), age, onset days, and vaccine type (reference: JNJ-78436735) as covariates. In the case of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and encephalitis myelitis encephalomyelitis, the frequency of occurrence was very small (10 or less, respectively); therefore, the results are not presented in the table.
BP, Bell’s palsy; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; LAD, lymphadenopathy; PE, pulmonary embolism; IS, ischemic stroke; TP, thrombocytopenia; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
a P<0.05,
b P<0.001.
- 1. Cines DB, Bussel JB. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med 2021;384:2254-6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Self WH, Tenforde MW, Rhoads JP, Gaglani M, Ginde AA, Douin DJ, et al. Comparative effectiveness of Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) vaccines in preventing COVID-19 hospitalizations among adults without immunocompromising conditions: United States, March–August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:1337-43.PubMedPMC
- 3. Klein NP, Lewis N, Goddard K, Fireman B, Zerbo O, Hanson KE, et al. Surveillance for adverse events after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination. JAMA 2021;326:1390-9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Amanzio M, Mitsikostas DD, Giovannelli F, Bartoli M, Cipriani GE, Brown WA. Adverse events of active and placebo groups in SARS-CoV-2 vaccine randomized trials: a systematic review. Lancet Reg Health Eur 2022;12:100253.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Targher G, Mantovani A, Wang XB, Yan HD, Sun QF, Pan KH, et al. Patients with diabetes are at higher risk for severe illness from COVID-19. Diabetes Metab 2020;46:335-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Sathish T, Kapoor N, Cao Y, Tapp RJ, Zimmet P. Proportion of newly diagnosed diabetes in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 2021;23:870-4.PubMedPMCPDF
- 7. Huang I, Lim MA, Pranata R. Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Diabetes Metab Syndr 2020;14:395-403.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Al-Maqbali JS, Al Rasbi S, Kashoub MS, Al Hinaai AM, Farhan H, Al Rawahi B, et al. A 59-year-old woman with extensive deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism 7 days following a first dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. Am J Case Rep 2021;22:e932946.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Ahmadi M, Rezaei Z, Shirazi FA, Shafiei M. Guillain–Barre syndrome: a prevalent autoimmune disease during the coronavirus disease-2019 pandemic. Rev Res Med Microbiol 2022;33:e198-211.Article
- 10. Shimabukuro TT, Nguyen M, Martin D, DeStefano F. Safety monitoring in the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). Vaccine 2015;33:4398-405.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 2019;42(Suppl 1):S90-102.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Python Software Foundation. re–Regular expression operations Available from: https://docs.python.org/3/library/re.html (cited 2022 Aug 31).
- 13. Barda N, Dagan N, Ben-Shlomo Y, Kepten E, Waxman J, Ohana R, et al. Safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in a nationwide setting. N Engl J Med 2021;385:1078-90.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Merchant HA. COVID vaccines and thrombotic events: EMA issued warning to patients and healthcare professionals. J Pharm Policy Pract 2021;14:32.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. What is venous thromboembolism? Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/facts.html(cited 2022 Aug 31).
- 16. Sookaromdee P, Wiwanitkit V. Change of safety interval from hyperviscosity problem in COVID-19 vaccine recipient with underlying diabetic problem. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 2021;25:257.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Joob B, Wiwanitkit V. Expected viscosity after COVID-19 vaccination, hyperviscosity and previous COVID-19. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2021;27:10760296211020833.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 18. Mehta J, Singhal S. Hyperviscosity syndrome in plasma cell dyscrasias. Semin Thromb Hemost 2003;29:467-71.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Cho YI, Mooney MP, Cho DJ. Hemorheological disorders in diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2008;2:1130-8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 20. Devi S, Mohakud S, Kar N, Muthuvel D. Deep vein thrombosis with pulmonary thromboembolism in a case of severe COVID-19 pneumonia. BMJ Case Rep 2021;14:e240932.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Khan IH, Savarimuthu S, Leung MS, Harky A. The need to manage the risk of thromboembolism in COVID-19 patients. J Vasc Surg 2020;72:799-804.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Maddaloni E, Buzzetti R. COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: unveiling the interaction of two pandemics. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2020;36:e33213321.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Pal R, Bhansali A. COVID-19, diabetes mellitus and ACE2: the conundrum. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2020;162:108132.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Klok FA, Kruip MJ, van der Meer NJ, Arbous MS, Gommers DA, Kant KM, et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb Res 2020;191:145-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Kahn LS, McIntyre RS, Rafalson L, Berdine DE, Fox CH. Fasting blood glucose and depressive mood among patients with mental illness in a medicaid managed care program. Depress Res Treat 2011;2011:862708.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 26. Atallah B, Mallah SI, AlMahmeed W. Anticoagulation in COVID-19. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 2020;6:260-1.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 27. Yin S, Huang M, Li D, Tang N. Difference of coagulation features between severe pneumonia induced by SARS-CoV2 and non-SARS-CoV2. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2021;51:1107-10.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 28. Xu P, Zhou Q, Xu J. Mechanism of thrombocytopenia in COVID-19 patients. Ann Hematol 2020;99:1205-8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 29. Tu W, Gierada DS, Joe BN. COVID-19 vaccination-related lymphadenopathy: what to be aware of. Radiol Imaging Cancer 2021;3:e210038.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Sampsonas F, Lagadinou M, Karampitsakos T, Solomou E, Doulberis M, Marangos M, et al. Prevalence and significance of mediastinal lymphadenopathy in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus-2 infection. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2021;25:3607-9.PubMed
- 31. Wang Z, Wang Z. Identification of risk factors for in-hospital death of COVID-19 pneumonia: lessions from the early outbreak. BMC Infect Dis 2021;21:113.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 32. Mao L, Jin H, Wang M, Hu Y, Chen S, He Q, et al. Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol 2020;77:683-90.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Karuppan MK, Devadoss D, Nair M, Chand HS, Lakshmana MK. SARS-CoV-2 infection in the central and peripheral nervous system-associated morbidities and their potential mechanism. Mol Neurobiol 2021;58:2465-80.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 34. Afshar ZM, Babazadeh A, Afsharian M, Vaziri S, Ebrahimpour S. Bell’s palsy associated with COVID-19 infection: a case report. Oman Med J 2021;36:e313.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Hughes C, Nichols T, Pike M, Subbe C, Elghenzai S. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis as a presentation of COVID-19. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med 2020;7:001691.PubMedPMC
- 36. Chen Y, Guo Y, Pan Y, Zhao ZJ. Structure analysis of the receptor binding of 2019-nCoV. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020;525:135-40.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Ghosh R, Roy D, Mandal A, Pal SK, Chandra Swaika B, Naga D, et al. Cerebral venous thrombosis in COVID-19. Diabetes Metab Syndr 2021;15:1039-45.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Barros A, Queiruga-Pineiro J, Lozano-Sanroma J, Alcalde I, Gallar J, Fernandez-Vega Cueto L, et al. Small fiber neuropathy in the cornea of COVID-19 patients associated with the generation of ocular surface disease. Ocul Surf 2022;23:40-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Cure E, Cumhur Cure M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers may be harmful in patients with diabetes during COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab Syndr 2020;14:349-50.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 40. Roncon L, Zuin M, Rigatelli G, Zuliani G. Diabetic patients with COVID-19 infection are at higher risk of ICU admission and poor short-term outcome. J Clin Virol 2020;127:104354.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Muir KL, Kallam A, Koepsell SA, Gundabolu K. Thrombotic thrombocytopenia after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination. N Engl J Med 2021;384:1964-5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Warkentin TE, Cuker A. COVID-19 Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/covid-19-vaccine-induced-immune-thrombotic-thrombocytopenia-vitt(cited 2022 Aug 31).
- 43. Takuva S, Takalani A, Garrett N, Goga A, Peter J, Louw V, et al. Thromboembolic events in the South African Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine Study. N Engl J Med 2021;385:570-1.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Kemper M, Berssenbrugge C, Lenz G, Mesters RM. Vaccine-induced pseudothrombocytopenia after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination. Ann Hematol 2022;101:927-8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 45. Netherlands Pharmacovigilance Centre Lareb. Overview of thrombo-embolic events with COVID-19 vaccines Available from: https://www.lareb.nl/media/yhbp4bxl/signal_oe_thromboembolic_events_j07bx_20210426_finalc.pdf(cited 2022 Aug 31).
- 46. El-Sayed MS, Wechie GN, Low CS, Adesanya O, Rao N, Leung VJ. The incidence and duration of COVID-19 vaccine-related reactive lymphadenopathy on 18F-FDG PET-CT. Clin Med (Lond) 2021;21:e633-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 47. Chen G, Li X, Sun M, Zhou Y, Yin M, Zhao B, et al. COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are generally safe in the short term: a vaccine vigilance real-world study says. Front Immunol 2021;12:669010.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Herbal-based therapeutics for diabetic patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection
Yousef Rasmi, Ighli di Bari, Shah Faisal, Munima Haque, Pornanong Aramwit, Aline da Silva, Elmira Roshani Asl
Molecular Biology Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Tuberculosis vaccines update: Is an RNA-based vaccine feasible for tuberculosis?
Sasha E. Larsen, Susan L. Baldwin, Rhea N. Coler
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2023; 130: S47. CrossRef - Neurological Disorders following COVID-19 Vaccination
Ying Yang, Lisu Huang
Vaccines.2023; 11(6): 1114. CrossRef - Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:356-65)
Hye Jun Kim, Sung Ryul Shim, Myunghee Hong, Hyun Wook Han
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 717. CrossRef - Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:356-65)
Jung Hun Ohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 715. CrossRef
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:356-65)
- Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:356-65)
- The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
- Clinical Effects of a Home Care Pilot Program for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Glycemia according to the Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring among Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Real-World Study

 KDA
KDA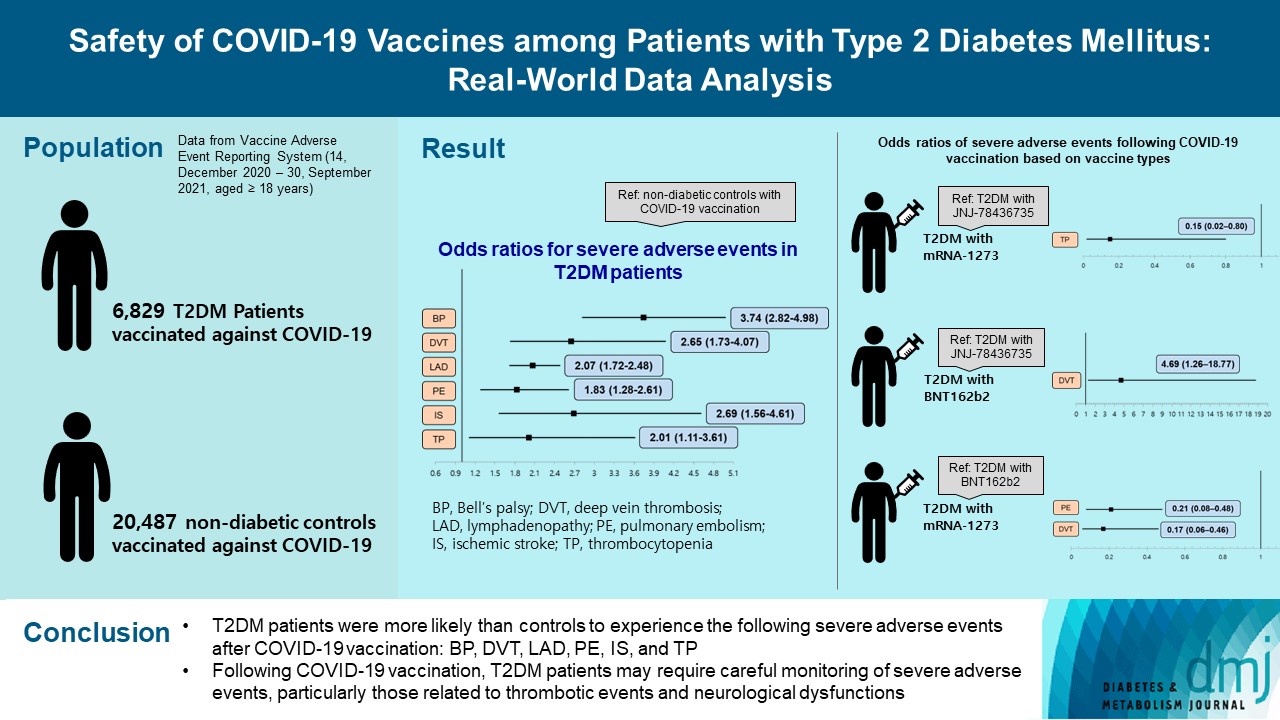
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite