- Skip Navigation
- Skip to contents

- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 47(1); 2023 > Article
-
ReviewGuideline/Fact Sheet Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
-
Kyu-Sun Lee1*
 , Junghyun Noh2*
, Junghyun Noh2* , Seong-Mi Park3, Kyung Mook Choi4, Seok-Min Kang5, Kyu-Chang Won6, Hyun-Jai Cho1
, Seong-Mi Park3, Kyung Mook Choi4, Seok-Min Kang5, Kyu-Chang Won6, Hyun-Jai Cho1 , Min Kyong Moon7
, Min Kyong Moon7 , The Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association and Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Society of Heart Failure
, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association and Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Society of Heart Failure -
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2023;47(1):10-26.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0420
Published online: January 26, 2023
1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea
3Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
5Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Cardiovascular Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
6Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea
7Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
-
Corresponding authors: Hyun-Jai Cho
 Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, 101 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03080, Korea E-mail: hyunjaicho@snu.ac.k
Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, 101 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03080, Korea E-mail: hyunjaicho@snu.ac.k -
Min Kyong Moon
 Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 20 Boramae-ro 5-gil, Dongjak-gu, Seoul 07061, Korea E-mail: mkmoon@snu.ac.kr
Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 20 Boramae-ro 5-gil, Dongjak-gu, Seoul 07061, Korea E-mail: mkmoon@snu.ac.kr - This manuscript is simultaneously published in the Diabetes & Metabolism Journal and the International Journal of Heart Failure by the Korean Diabetes Association and the Korean Society of Heart Failure.
*Kyu-Sun Lee and Junghyun Noh contributed equally to this study as first authors.
Copyright © 2023 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- ABSTRACT
- Key figure
- INTRODUCTION
- EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PROGNOSIS
- EVALUATION AND DIAGNOSIS OF HF
- TREATMENT ALGORITHM FOR HF IN PATIENTS WITH DM, FOCUSING ON GUIDELINE-DIRECTED MEDICAL THERAPY
- FOLLOW-UP AND MONITORING
- WHEN TO REFER TO HF CARDIOLOGIST
- PHARMACOTHERAPY OF DM IN PATIENTS WITH HF
- CONSENSUS STATEMENT
- SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
- NOTES
- REFERENCES
ABSTRACT
- Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for the development of heart failure. Furthermore, the prognosis of heart failure is worse in patients with diabetes mellitus than in those without it. Therefore, early diagnosis and proper management of heart failure in patients with diabetes mellitus are important. This review discusses the current criteria for diagnosis and screening tools for heart failure and the currently recommended pharmacological therapies for heart failure. We also highlight the effects of anti-diabetic medications on heart failure.
- Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Diagnosis; Heart failure; Therapeutics
- Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome with cardinal symptoms (for example, dyspnea, ankle swelling, and fatigue) and/or signs (for example, elevated jugular venous pressure, pulmonary congestion, lung crackles, and peripheral edema) caused by structural or functional cardiac abnormalities that lead to reduced cardiac output and/or elevated intracardiac pressure [1-3]. Globally, the prevalence of HF and diabetes mellitus (DM) is increasing with the aging of the population [1,4]. Among Korean adults aged 30 years or older, 16.7% (19.2% in men and 14.3% in women) had DM according to the Diabetes Fact Sheet published by the Korean Diabetes Association in 2020 [5]. The prevalence of HF ranges from 1% to 3% in the general adult population in industrialized countries [6]. In Korea, the prevalence of HF has continuously increased from 0.77% in 2002 to 2.24% in 2018 (Fig. 1) [7]. The prevalence of HF according to age and sex also gradually increased between 2002 and 2018 (Supplementary Fig. 1). Obesity and diabetes have been identified as important risk factors for the development and poor prognosis of HF [8]. In this review, we highlight the current criteria for the diagnosis and screening tools for HF and the currently recommended pharmacological therapies for HF. We also discuss the effects of anti-diabetic medications on HF and the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in patients with HF.
INTRODUCTION
- Prevalence of HF in patients with DM
- HF is a common comorbidity and a fatal complication of DM. The prevalence of HF was reported to range from 19% to 26% in patients with DM [9-11]. The hospitalization rates due to HF in the Korean population with DM increased from 72 to 146 and 124 to 161 per 10,000 men and women, respectively, based on data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort from 2006 to 2015 [12].
- The Framingham Heart Study demonstrated an increased risk of HF in patients with DM, a 2-fold higher incidence of HF in men, and five times high for women with DM than in age-matched non-diabetic controls [13]. In observational studies, each 1% increase in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) was associated with a 30% increase in risk of HF in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) [14], and each 1% increase in HbA1c levels was associated with an 8% increase of risk in T2DM, independent of other risk factors, including obesity, smoking, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and coronary heart disease [15]. These results suggest that chronic hyperglycemia is an aggravating factor for HF in patients with both T1DM and T2DM.
- Prevalence of DM in patients with HF
- Although there was heterogeneity between epidemiological studies on HF due to different study populations and different data sources, the prevalence of DM ranged from 20% to 36% in patients with HF in Korea [4]. The prevalence of comorbid DM in patients with HF continuously increased from 2002 to 2018 in Korea [7]. HF-related trials and registries in Western countries have reported that the prevalence of DM ranges from 25% to 45% [16-23].
- Diabetic cardiomyopathy
- In 1972, Rubler et al. [24] proposed the existence of a unique type of cardiomyopathy in patients with DM termed diabetic cardiomyopathy. These patients had congestive HF in the absence of coronary artery disease (CAD), hypertension, valvular heart disease, or alcoholism. This concept was confirmed by the Framingham Heart Study, in which higher rates of HF in women (5-fold) and men (2.4-fold) with DM were shown to be independent of other risk factors, such as age, coronary heart disease, and hypertension [24]. Many epidemiological studies have also confirmed a significantly increased prevalence of ventricular dysfunction in patients with diabetes, independent of the influence of relevant covariates. According to these studies [11,13,24], the American College of Cardiology Foundation [25] and the European Society of Cardiology [26] described diabetic cardiomyopathy as a clinical condition of cardiac dysfunction without atherosclerotic coronary vascular diseases and hypertension in patients with DM.
- The pathophysiology of diabetic cardiomyopathy is complex and not clearly understood. Multiple mechanisms have been suggested to explain diabetic cardiomyopathy development. These include (1) alterations in mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation; (2) impaired mitochondrial Ca2+ handling; (3) cardiac insulin resistance, which causes impaired signaling of insulin receptor substrate, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt), and downstream pathways; (4) activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) in genesis; (5) cardiac autonomic neuropathy; (6) microvascular dysfunction; and (7) inflammatory pathways that result in myocardial fibrosis, stiffness, and hypertrophy [27,28].
- The clinical effects of diabetic cardiomyopathy progress from asymptomatic diastolic dysfunction to systolic dysfunction and symptomatic HF. Many potential novel therapies for diabetic cardiomyopathy, including antioxidants, coenzyme 10, PI3K gamma inhibitors, miRNA-based therapies, and stem cell therapies, are being developed to target the pathophysiology of diabetic cardiomyopathy [29].
- Prognosis of DM in patients with HF
- Patients with HF and DM have worse clinical outcomes, including death, hospitalization, and health-related quality of life, than those without DM [30-33]. DM in patients with HF was associated with a greater relative risk of cardiovascular (CV) death or HF hospitalization, ranging from 1.6- to 2-fold compared to those without DM, regardless of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) [23,34].
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PROGNOSIS
- Screening and diagnosing HF in patients with DM
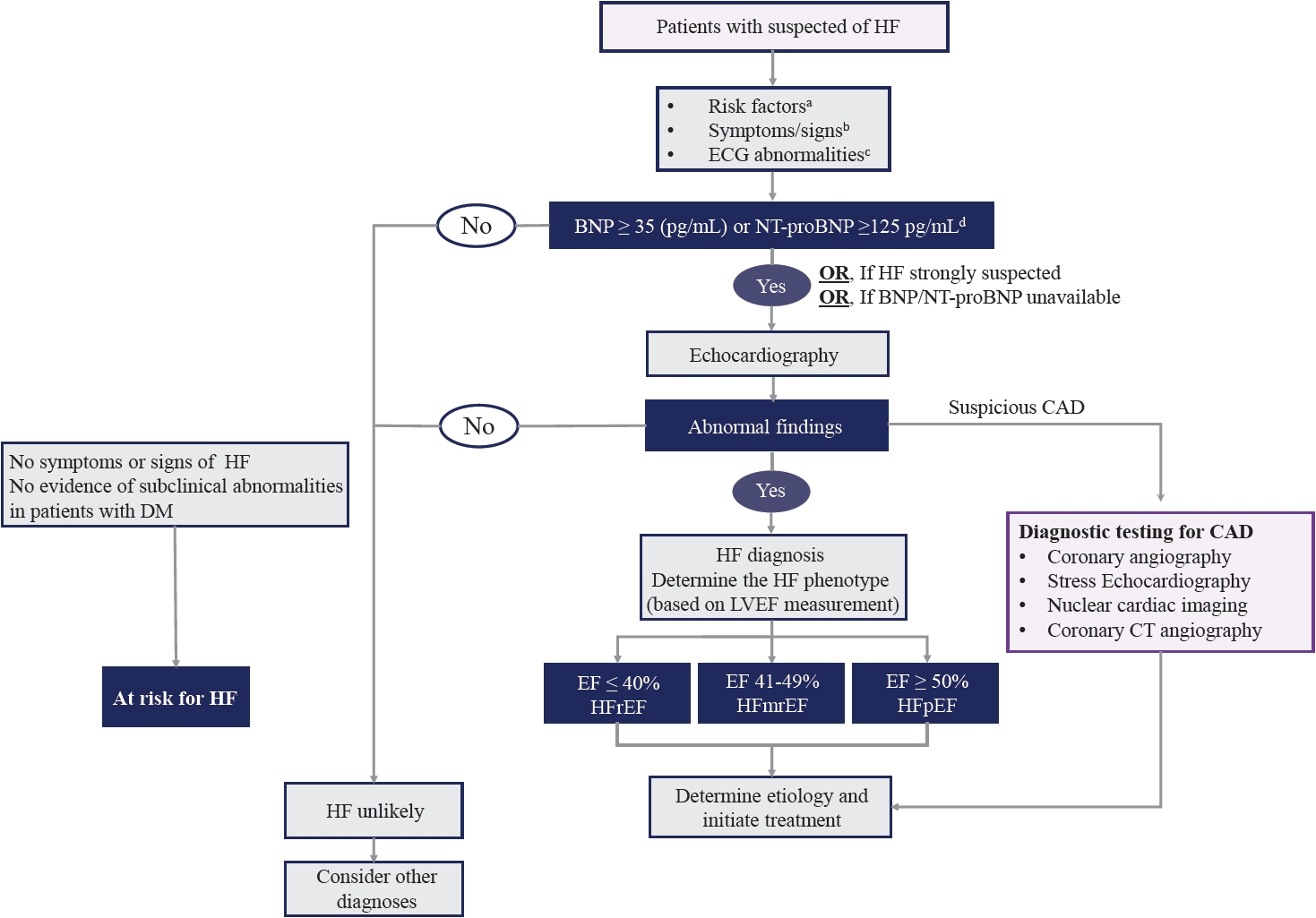
- HF often manifests as the first CV event in patients with DM [35]. Therefore, it is important to evaluate HF in symptomatic patients with DM. The most common and typical symptoms include dyspnea with orthopnea, fatigue, and swelling of the legs or ankles. A careful and detailed history and physical examination are essential for the assessment of HF in symptomatic patients with DM. However, symptoms and signs lack sufficient accuracy to be used alone to diagnose HF [36,37]. In addition to the symptoms and signs, an essential diagnostic work-up includes a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG), chest radiography, and initial laboratory tests. ECG provides important information regarding arrhythmia, heart rate, QRS morphology and duration, and ischemic signs, such as ST-elevation or ST depression. Chest radiography provides information on cardiomegaly, pulmonary congestion, and other lung diseases that can cause dyspnea.
- Initial laboratory testing should include a complete blood count, urinalysis, serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, glucose, fasting lipid profile, liver function tests, iron status profile tests, and thyroid function tests. Among these laboratory tests, troponin-I should be included because it is useful for the detection of acute coronary syndrome.
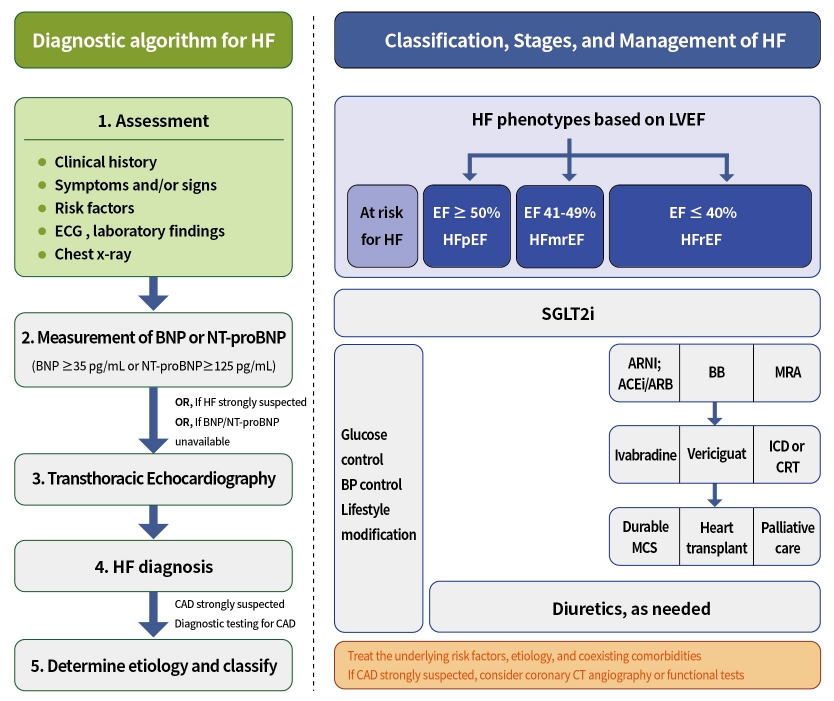
- The measurement of natriuretic peptides (NPs); B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is recommended as an initial diagnostic test in patients with symptoms suggestive of HF, if available. Elevation of the plasma NPs concentration (chronic HF: BNP ≥35 pg/mL or NT-proBNP ≥125 pg/mL; acute HF: BNP ≥100 pg/mL, NT-proBNP ≥300 pg/mL) supports a diagnosis of HF [38].
- Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is recommended as the initial diagnostic test to assess cardiac structure and function after a complete history, physical examination, and laboratory tests, including NPs. The determination of LVEF is a fundamental step in classifying HF (Table 1) and guiding evidence-based pharmacological and device-based therapies.
- In addition to LVEF, evidence supporting increased LV filling pressures (for example, hemodynamic measurement by invasive test or diastolic function on imaging, NP by non-invasive test) is required for HF diagnosis. HF is more likely in patients with a history of myocardial infarction (MI), arterial hypertension, CAD, atrial fibrillation, alcohol misuse, chronic kidney disease, cardiotoxic chemotherapy, and in those with a family history of cardiomyopathy or sudden death [1]. The initial diagnostic tests recommended in the guidelines for the assessment of patients with suspected HF are summarized in Table 2.
- The most common cause and factor related to the development of HF in patients with DM is CAD [39]. Furthermore, DM is a risk factor for CAD. However, diabetic patients present more often with atypical chest pain, or they may have no symptoms even if they have extensive CAD (“silence ischemia”). Therefore, coronary computed tomography angiography or functional stress tests (exercise ECG, stress echocardiography, single photon emission computed tomography, and positron emission tomography) should be considered for the assessment of myocardial ischemia in diabetic patients with typical, atypical cardiac symptoms or abnormal findings on resting ECG even without symptoms. Furthermore, invasive coronary angiography is recommended in patients with angina or may be considered in patients with heart failure reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) with an intermediate to high pre-test probability of CAD and the presence of ischemia in non-invasive stress tests [1,40-42]. The diagnostic algorithm for symptomatic patients with suspected HF and DM is shown in Fig. 2 [43].
- Patients with DM as at-risk for HF or pre-HF
- DM-related pathophysiological factors, such as insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and inflammation, can contribute to the development of structural heart disease and HF via systemic, myocardial, and cellular mechanisms [44]. Therefore, even if patients with DM do not currently have symptoms associated with HF, it is important to recognize patients with DM who are at risk of developing HF; therapeutic strategies to prevent HF in these patients are also important. The HF guidelines emphasize at-risk for HF (stage A) and pre-HF (stage B) [2]. The recent consensus statement of the universal definition and classification of HF classifies patients with DM into stage A category [3]. Even if patients with DM have no symptoms or signs of HF, they are classified as stage B if any of evidence of subclinical abnormalities exists (Supplementary Table 1).
EVALUATION AND DIAGNOSIS OF HF
- Patients at-risk for HF
- The primary treatment goal for patients at risk of HF is to prevent the development of HF. Recent guidelines recommend the following for the primary prevention of HF [2]. (1) In patients with hypertension, blood pressure (<130/80 mm Hg) should be controlled by guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) for hypertension to prevent symptomatic HF. (2) In patients with T2DM and either established CV disease or at high CV risk (Supplementary Table 2), sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors should be used to prevent hospitalization for HF [33-42,44-46]. (3) Healthy lifestyle habits such as regular physical activity, maintaining normal weight, healthy dietary patterns, and avoiding smoking are helpful in reducing the future risk of HF.
- Patients with HFrEF
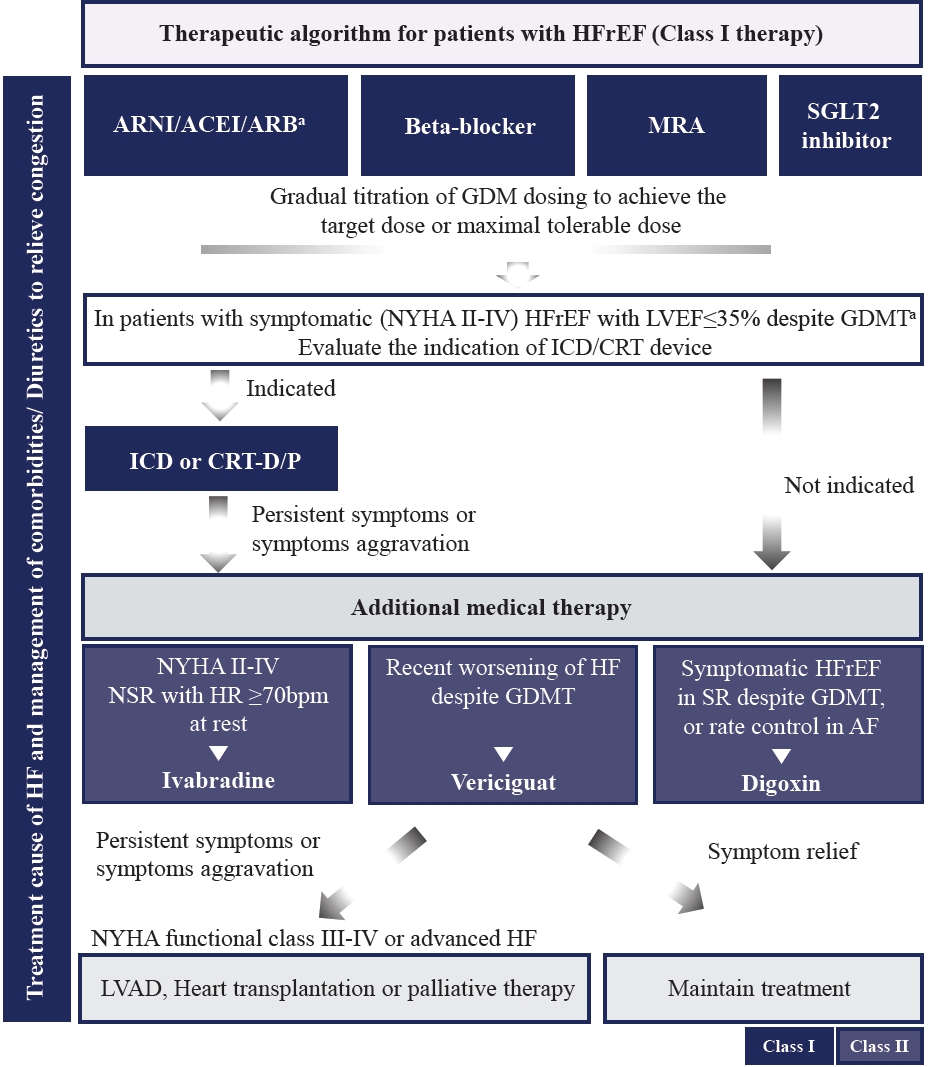
- Recent HF guidelines recommend GDMT medication classes, including RAAS inhibitors (angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor [ARNI], angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor [ACEI], or angiotensin II receptor blocker [ARB]), beta-blocker (BB), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and SGLT2 inhibitors as first-line therapy to reduce CV death and hospitalization in patients with HFrEF and New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II–III symptoms [1,2].
- The quadruple therapy with ARNI, evidence-based BB, MRA, and SGLT2 inhibitors may reduce the risk of death by 73% over 2 years [47]. However, the achievement of the target doses of each drug class before initiating treatment with the next may require 6 months or more. Furthermore, each of these foundational drugs has been shown to reduce morbidity and mortality within 30 days of treatment initiation [48]. Recently, strategies for the initiation and titration of comprehensive disease-modifying therapy have been proposed to obtain the early clinical benefit of each individual therapy (Supplementary Fig. 2) [46,49].
- In recent randomized trials, the proportion of patients with DM varies from 20% to almost 50% [50,51]. However, the benefit of GDMT in patients with HFrEF was observed between those with and without DM. The algorithm for the treatment strategy, including guideline-direct medication and devices in patients with HFrEF, is shown in Fig. 3. Evidence-based doses and contraindications or cautions of disease-modifying drugs for patients with HFrEF are summarized in Table 3, Supplementary Table 3.
- Sacubitril/valsartan, an ARNI, significantly reduced hospitalization for worsening HF, CV mortality, and all-cause mortality in patients with HFrEF compared with enalapril [18]. ARNI also reduces CV death or HF hospitalizations in hospitalized patients due to acute decompensated HF or in ACEI naïve (i.e., de novo) patients with HFrEF [52,53]. Recent evidence suggests that ARNI could reduce the reliance on diuretics in HFrEF patients [54] and promotes reverse cardiac remodeling and improves outcomes in patients with HFrEF [55]. Based on these results, guidelines recommend the use of ARNI in symptomatic patients with HFrEF to reduce the risk of HF hospitalization and death. ARNI is also recommended as a replacement for ACEIs or ARBs in patients with HFrEF to reduce the risk of hospitalization for HF and death (if patients tolerate an ACEI or ARB).
- ACEI is recommended for all patients with HFrEF, unless contraindicated or not tolerated, to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death due to HF. To improve clinical outcomes, ACEIs should be up-titrated to the maximum tolerated recommended doses. ARBs are recommended as a replacement for ACEI or ARNI in patients with HFrEF to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death due to HF (if patients are unable to tolerate an ACEI or ARNI). Only three ARBs (valsartan, candesartan, and losartan) were proven to be beneficial for reducing HF hospitalization or death in large randomized controlled trials (RCTs) [56-59].
- BBs are recommended for all patients with HFrEF to reduce the risk of hospitalization for HF, improve symptoms, and prevent death. BBs should be initiated in a clinically stable, euvolemic status, and from a low dose and gradually titrated to the maximum tolerated dose. Three BBs (bisoprolol, carvedilol, and metoprolol succinate-controlled release/extended release) have been proven to be beneficial for reducing HF hospitalization and mortality in patients with HFrEF [60-62].
- MRA is recommended for all patients with HFrEF to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death due to HF [63]. To improve clinical outcomes, MRA should be up-titrated to the maximum tolerated recommended dose. Patients at risk of renal dysfunction or hyperkalemia require close monitoring of potassium levels and renal function during MRA treatment.
- Dapagliflozin and empagliflozin reduce the risk of CV death or HF hospitalization by approximately 26% and by 25% in patients with symptomatic stable HFrEF [19,51,64]. Furthermore, empagliflozin can reduce the diuretic need in outpatient HF patients [65]. For this CV benefit of SGLT2 inhibitors, dapagliflozin and empagliflozin are recommended for patients with HFrEF to reduce the risk of HF hospitalization and death regardless of diabetes status.
- Patients with HF with improved ejection fraction
- Although there is little data to guide the management of patients with HF with improved ejection fraction (previous LVEF ≤40%, a 10-point increase from baseline LVEF, and a second measurement of LVEF >40%), The Therapy withdrawal in REcovered Dilated cardiomyopathy (TRED-HF) trial demonstrated that withdrawal of GDMT in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy who had recovered their left ventricular (LV) functions resulted in high rate of relapse of HF (44%) within 6 months [66]. Therefore, guidelines recommend that GDMT should be continued to prevent the relapse of HF and LV dysfunction, even in asymptomatic patients.
- Patients with HF with mid-range ejection fraction and HF with preserved ejection fraction
- Until recently, despite the large number of studies performed in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction (HFmrEF), including a significant proportion with diabetes, no current therapies have been proven to reduce CV endpoints except for SGLT2 inhibitors. Two large-scale trials, EMPagliflozin outcomE tRial in Patients With chrOnic heaRt Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction (EMPEROR-preserved) and Dapagliflozin Evaluation to Improve the LIVEs of Patients With PReserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure (DELIVER), assessed the CV effect of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with HFpEF and HFmrEF. These trials have shown that SGLT2 inhibitors (empagliflozin, dapagliflozin) significantly reduced the risk of CV death or hospitalization for worsening HF regardless of diabetic status [67,68].
- Recent prespecified meta-analyses of the several clinical trials testing SGLT2 inhibitors confirmed the robust effect of SGLT2 inhibitors in reducing the risk of CV death and hospitalizations for worsening HF, irrespective of LVEF [69,70]. Taken together, SGLT2 inhibitors will be the foundational therapy to reduce CV death and hospitalization for HF in a broad range of patients with HF, irrespective of diabetes status or LVEF.
- Furthermore, diuretics are recommended to reduce congestion symptoms in these patients. Reducing body weight in obese patients and increasing exercise may further improve symptoms and exercise capacity and should be considered in appropriate patients. It is important to identify and treat the underlying risk factors, etiology, and coexisting comorbidities in HFpEF and HFmrEF (for example, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, and amyloidosis).
TREATMENT ALGORITHM FOR HF IN PATIENTS WITH DM, FOCUSING ON GUIDELINE-DIRECTED MEDICAL THERAPY
General principle of pharmacotherapy
Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers
Beta-blockers
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist
SGLT2 inhibitors
- Patients with chronic HF, even if symptoms are well-controlled and stable, require follow-up to ensure continued optimization of therapy to detect asymptomatic progression of HF. Guidelines recommend follow-up at intervals of no longer than 6 months to check symptoms, heart rate and rhythm, blood pressure, full blood count, electrolytes, and renal function. TTE is also recommended 3 to 6 months after optimizing the GDMT for HFrEF to determine the requirement for the addition of new pharmacological agents and implanted devices. Furthermore, TTE should be repeated in patients with worsening HF. Although measurements of BNP or NT-proBNP provide prognostic information, routine monitoring of NPs is not recommended to adjust GDMT in patients with HF [1,2].
FOLLOW-UP AND MONITORING
- Timely and appropriate referral to HF cardiologists in selected patients is very important to evaluate new-onset HF and optimize treatment strategies to prevent the progression of HF. Table 4 summarizes the clinical cases that should be referred to cardiologists or HF specialists.
WHEN TO REFER TO HF CARDIOLOGIST
- Drug-specific factors to consider when using antihyperglycemic agents in patients with T2DM and HF are described in Table 5.
- SGLT2 inhibitor
- SGLT2 inhibitors reduce blood glucose levels by inhibiting glucose reabsorption in the proximal tubules of the kidneys in patients with T2DM. Clinical trials evaluating the CV outcomes of SGLT2 inhibitors have revealed that SGLT2 inhibitors reduce the risk of HF hospitalization in patients with T2DM [44,45,71]. Furthermore, recent trials have demonstrated that SGLT2 inhibitors have beneficial effects on HF in non-diabetic patients. Study to Evaluate the Effect of Dapagliflozin on the Incidence of Worsening Heart Failure or Cardiovascular Death in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure (DAPA-HF) trial evaluated the effect of dapagliflozin on the risk of worsening HF or death from CV causes in patients with NYHA class II–IV HF and ejection fraction ≤40% [19]. After a median of 18.2 months, dapagliflozin treatment showed a 26% risk reduction in HF hospitalization or CV death (hazard ratio [HR], 0.74; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.65 to 0.85). The beneficial effects of dapagliflozin were similar between patients with and without DM. Similar results were reproduced in the EMPagliflozin outcomE tRial in Patients With chrOnic heaRt Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction (EMPEROR-Reduced) trial [51]. During a median follow-up of 16 months, the primary outcomes of CV death and HF hospitalization were reduced by 25% in the empagliflozin group (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.65 to 0.86). These effects were observed regardless of DM presence. In a retrospective observational study using the National Health Insurance Service claims database in Korea, use of SGLT2 inhibitors was associated with a lower risk of HF compared with use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitors or sulfonylurea (SU) as add-on therapy to metformin in Korean patients with T2DM [72]. Based on these results, SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended as first-line glucose-lowering agents for patients with T2DM with HF, independent of HbA1c.
- SGLT2 inhibitors cause osmotic diuresis by increasing urinary glucose excretion and predisposing patients to dehydration and postural hypotension, especially in older patients or those taking diuretics. The volume depletion caused by SGLT2 inhibitors may lead to renal impairment. Acute kidney injury has been reported in patients treated with SGLT2 inhibitors. Volume status should be assessed, and sufficient water intake should be included in parallel during SGLT2 inhibitor therapy. SGLT2 inhibitors increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) and genital infections, especially in females. Signs and symptoms of UTIs and genital infections should be monitored and treated properly. Ketoacidosis with euglycemia or modestly elevated blood glucose levels (<250 mg/dL) has been reported in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitor therapy [73]. It should be discontinued in situations of prolonged fasting owing to acute illness or before scheduled surgery to avoid the potential risk of diabetic ketoacidosis
- Metformin
- Although metformin has been contraindicated in patients with HF due to the potential risk of lactic acidosis, a recent analysis suggests that metformin has favorable effects in patients with diabetes with HF by improving insulin sensitivity [74]. In a meta-analysis of nine cohort studies, metformin therapy was associated with reduced in all-cause mortality compared to any other antidiabetic therapy: 23% vs. 37% (adjusted odds ratio [OR], 0.80; 95% CI, 0.73 to 0.88) in patients with diabetes with HF [74]. In that study, metformin was not associated with an increased risk of metabolic acidosis. Most evidence supports the safety of metformin in patients with diabetes with HF. However, metformin in patients with acutely decompensated HF, sepsis, or hypoperfusion should be stopped to avoid lactic acidosis.
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are effective for glycemic control and weight loss. In CV outcome trials of GLP-1 RA, some GLP-1 RA showed CV benefits but did not demonstrate the effects on HF in patients with T2DM. The CV outcome trial of liraglutide (Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome Results [LEADER]) revealed a significant reduction in the composite endpoint of death from CV causes, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke in patients with T2DM with an increased CV risk [75]. In Trial to Evaluate Cardiovascular and Other Long-term Outcomes With Semaglutide in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes (SUSTAIN-6) trial, treatment with semaglutide showed a 24% reduction in major adverse CV events [76]. In the Researching Cardiovascular Events With a Weekly Incretin in Diabetes (REWIND) trial, dulaglutide was also associated with a 12% reduction in CV events [77]. However, the risk of hospitalization for HF evaluated as a secondary outcome in these studies did not differ between the treatment and control groups. In a meta-analysis of eight randomized trials, GLP-1 RA reduced the risk of hospitalization for HF by 10% (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.83 to 0.98) [78]. Furthermore, in the Functional Impact of GLP-1 for Heart Failure Treatment (FIGHT) trial with 300 advanced patients with HF (NYHA III–IV) with and without DM, there was no impact of liraglutide on post-hospitalization clinical stability or HF readmission [79]. Thus, GLP-1 RA may be safe for use in patients with HF, although it has not shown beneficial effects.
- Sulfonylureas
- While some observational studies comparing SUs with other anti-diabetic medications showed weak associations between SU treatment and CV risk, the results of RCTs suggest a neutral effect of SUs on adverse CV outcomes. In the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS), no difference was observed between SUs and insulin treatments in HF events in newly diagnosed participants with DM [80]. A meta-analysis of 47 randomized control trials showed neutral outcomes of SUs for CV key outcomes, such as all-cause death, CV death, MI, or stroke [81]. Recently, the Cardiovascular Outcome Study of Linagliptin Versus Glimepiride in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes (CAROLINA) trial showed no difference in CV outcomes, including HF hospitalizations, between treatments with DPP4 inhibitor (linagliptin) and SU (glimepiride) [82]. The suggested potential mechanism of the adverse CV effects of SUs is the inhibition of ischemic conditioning and hypoglycemia. There is no clear evidence of an association between SU use and adverse CV outcomes.
- Insulin
- In observational studies, the prevalence of HF and cardiac mortality risk increased in patients with T2DM receiving insulin treatment [83]. A meta-analysis of patients with HF and DM using dataset of RCTs and population-based cohort studies revealed that insulin use was associated with a higher risk of all-cause mortality (OR, 2.02; 95% CI, 1.87 to 2.19) and rehospitalization for HF (OR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.32 to 1.53) [84]. However, evidence from RCTs has consistently indicated no increase in CV disease risk with insulin use. The Outcome Reduction with Initial Glargine Intervention (ORIGIN) trial evaluated the CV safety of the basal insulin analog glargine in participants with prediabetes or early T2DM and a high CV risk in 6.2 years of follow-up [85]. In this trial, the risks of initial and recurrent HF hospitalizations were similar in the insulin-glargine and standard care groups. In the Trial Comparing Cardiovascular Safety of Insulin Degludec Versus Insulin Glargine in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes at High Risk of Cardiovascular Events (DEVOTE), 4.9% of patients experienced HF hospitalization, and there was no significant difference in the risk of HF hospitalization between treatments [86]. Further studies evaluating the CV safety of insulin therapy in patients with HF are needed.
- DPP4 inhibitors
- Most trials examining the effects of DPP4 inhibitors (alogliptin, sitagliptin, and linagliptin) on CV safety have indicated that DPP4 inhibitor treatment is safe for CV outcomes, including major CV events, CV death, all-cause mortality, and HF hospitalization [87-89]. However, the Does Saxagliptin Reduce the Risk of Cardiovascular Events When Used Alone or Added to Other Diabetes Medications (SAVOR-TIMI 53) trial reported that the risk of HF hospitalization increased in patients with T2DM patients treated with saxagliptin compared to placebo (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.07 to 1.51) [90]. The mechanisms responsible for these observations are not yet fully understood. It is recommended that saxagliptin be used with caution in patients with high CV risk because of the potential risk of HF hospitalization.
- Thiazolidinediones
- Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) can cause fluid retention and weight gain, and may increase the risk of HF. The Rosiglitazone Evaluated for Cardiac Outcomes and Regulation of Glycaemia in Diabetes (RECORD) trial found an increased risk of HF death or hospitalization associated with rosiglitazone (HR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.35 to 3.27) [91]. In the Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication (DREAM) study, rosiglitazone reduced the development of DM and renal disease but increased new-onset HF (HR, 7.03; 95% CI, 1.60 to 30.9) in patients with prediabetes [92]. In the PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events (PROACTIVE) trial, although pioglitazone resulted in a 16% risk reduction in the secondary endpoint of all-cause mortality, non-fatal MI, and stroke (HR, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.72 to 0.98), risk of HF was increased (HR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.10 to 1.80) compared to placebo [93]. TZDs are contraindicated in patients with NYHA class III–IV HF and should be used with caution in patients with signs or symptoms or those at high risk of HF.
- Glycemic target in patients with HF
- While several RCTs have performed addressing the effects of intensive glycemic control on CV end points, optimal glycemic targets in HF patients with DM have not been evaluated yet [94]. Current Korean Diabetes Association guidelines recommend an HbA1c goal of <6.5% for most adults with T2DM but emphasize the individualization based on patient characteristics and comorbidities [95].
PHARMACOTHERAPY OF DM IN PATIENTS WITH HF
- 1. In general, the evaluation and management for heart failure (HF) are similar between people with and without diabetes. Patients with diabetes are at higher risk of HF development and face a poorer prognosis. Therefore, a more comprehensive approach to HF is needed in patients with diabetes.
- 2. The measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP) for the diagnosis or exclusion of HF is recommended in patients with diabetes mellitus presenting with symptoms (dyspnea, chest discomfort, or typical chest pain) and/or signs (pulmonary congestion or peripheral edema).
- 3. Functional stress tests or coronary computed tomography angiography should be considered for the assessment of myocardial ischemia and to determine whether HF originated from coronary artery disease in diabetic patients presenting with symptoms (dyspnea, chest discomfort, or typical chest pain) and/or ischemic signs on electrocardiogram (ST-segment deviations, T-wave inversion, or Q waves).
- 4. Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) should be performed during initial evaluation to assess cardiac structure and function in patients with strongly suspected HF or elevated natriuretic peptide levels (chronic HF: BNP 35 pg/mL or NT-proBNP 125 pg/mL, acute HF: BNP 100 pg/mL, NT-proBNP 300 pg/mL).
- 5. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors, including angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) or angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), beta-blocker (BB), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, are recommended as a first-line therapy to reduce cardiovascular death and hospitalization in patients with heart failure reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and NYHA class II-III symptoms.
- 6. SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction (HFmrEF) regardless of diabetes status for decreasing HF hospitalization and cardiovascular death.
CONSENSUS STATEMENT
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table 2.
Supplementary Table. 3.
Supplementary Fig. 1.
Supplementary Fig. 2.
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Kyu-Chang Won has been publisher of the Diabetes & Metabolism Journal since 2022. Kyung Mook Choi has been editor-inchief of the Diabetes & Metabolism Journal since 2022. They were not involved in the review process of this article. Otherwise, there was no conflict of interest.
-
FUNDING
None
NOTES
-
Acknowledgements
- None

| Diagnostic criteria | HFrEF | HFmrEF | HFpEF |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Symptom±signa | Symptom±signa | Symptom±signa |
| 2 | LVEF ≤40% | LVEF 41%–49% | LVEF ≥50% |
| 3 | - | - | 1. Elevation of natriuretic peptide |
| 2. Objective evidence of cardiac structural and/or functional abnormalities consistent with the presence of LV diastolic dysfunction/or increased LV filling pressure |
HFrEF, heart failure reduced ejection fraction; HFmrEF, heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LV, left ventricular.
a Sings of HF may not be present and/or nonspecific in the early stage of HF (especially in HFpEF) and/or in patients treated with optimal medical treatment, including diuretics.
| Tests | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Natriuretic peptide (BNP or NT-proBNP) | BNP or NT-proBNP is recommended as an initial diagnostic test in patients with symptoms and signs suggestive of HF to rule out the diagnosis of HF. Cutoff value: BNP ≥35 (pg/mL) or NT-proBNP ≥125 pg/mLa |
| ECG | The ECG may reveal abnormalities such as ST elevation, ST depression, atrial fibrillation, Q wave, LV hypertrophy, and a widened QRS complex (for example, LBBB) that increase the likelihood of a diagnosis of HF. |
| Chest X-ray | A chest X-ray is recommended to evaluate the presence or absence of pulmonary congestion and cardiomegaly in patients with suspected HF. |
| Echocardiography | LVEF, chamber size, degree of wall thickness, regional wall motion abnormalities, valvular function, RV function, pulmonary hypertension, and parameters of diastolic function |
| Standard blood tests | CBC, serum urea, electrolytes, creatinine, thyroid, and liver function tests, fasting glucose, HbA1c, lipids, and iron statuses (TSAT and ferritin) |
BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; HF, heart failure; ECG, electrocardiogram; LV, left ventricular; LBBB, left bundle branch block; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; RV, right ventricular; CBC, complete blood count; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; TSAT, transferrin saturation.
a Cutoff values may have lower specificity, especially in older patients or those with atrial fibrillation or chronic kidney disease. Usually, higher cutoff values are recommended for the diagnosis of HF in these patients.
| Starting dose | Target dose | |
|---|---|---|
| ACEI | ||
| Captopril | 6. 25 mg t.i.d. | 50 mg t.i.d. |
| Enalapril | 2.5 mg b.i.d. | 10–20 mg b.i.d. |
| Lisinopril | 2.5–5 mg q.d. | 20–35 mg q.d. |
| Ramipril | 2.5 mg b.i.d. | 5 mg b.i.d. |
| Trandolapril | 0.5 mg q.d. | 4 mg q.d. |
| ARNIa | ||
| Sacubitril/Valsartan | 49/51 mg b.i.d. | 97/103 mg b.i.d. |
| Beta-blockers | ||
| Bisoprolol | 1.25 mg q.d. | 10 mg q.d. |
| Carvedilol | 3.125 mg b.i.d. | 25 mg b.i.d. |
| Metoprolol | 12.5–25 mg q.d. | 200 mg q.d. |
| Nebivolol | 1.25 mg q.d. | 10 mg q.d. |
| MRAs | ||
| Eplerenone | 25 mg q.d. | 50 mg q.d. |
| Spironolactoneb | 25 mg q.d. | 50 mg q.d. |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | ||
| Dapagliflozin | 10 mg q.d. | 10 mg q.d. |
| Empagliflozin | 10 mg q.d. | 10 mg q.d. |
| ARBs | ||
| Candesartan | 4 mg q.d. | 32 mg o.d. |
| Losartan | 50 mg q.d. | 150 mg q.d. |
| Valsartan | 40 mg b.i.d. | 160 mg b.i.d. |
| Other agents | ||
| Ivabradine | 5 mg b.i.d. | 7.5 mg b.i.d. |
| Vericiguat | 2.5 mg q.d. | 10 mg q.d. |
| Digoxin | 62.5 µg q.d. | 250 µg q.d. |
ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; t.i.d., ter in die (three times a day); b.i.d., bis in die (twice daily); q.d., quaque die (once daily); ARNI, angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; SGLT2, sodium-glucose co-transporter 2; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker.
a Sacubitril/valsartan may have an optional lower starting dose of 24/26 mg b.i.d. for patients with a history of symptomatic hypotension,
b Spironolactone has an optional starting dose of 12.5 mg in patients with renal impairment or hyperkalemia.
HF, heart failure; NYHA, New York Heart Association; ICD, implantable cardioverter defibrillation; ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; ARNI, angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor; BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction.
HF, heart failure; ASCVD, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; SGLT2, sodium-glucose co-transporter 2; DKA, diabetic ketoacidosis; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; GI, gastrointestinal; GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; SQ, subcutaneous; DPP4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; SU, sulfonylurea; TZD, thiazolidinedione; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
- 1. McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Bohm M, et al. 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 2021;42:3599-726.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2022;79:e263-421.PubMed
- 3. Bozkurt B, Coats AJ, Tsutsui H, Abdelhamid M, Adamopoulos S, Albert N, et al. Universal definition and classification of heart failure: a report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of the Universal Definition of Heart Failure. J Card Fail 2021;27:P387-413.ArticlePDF
- 4. Park JJ, Choi DJ. Current status of heart failure: global and Korea. Korean J Intern Med 2020;35:487-97.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 5. Bae JH, Han KD, Ko SH, Yang YS, Choi JH, Choi KM, et al. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2021. Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:417-26.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Savarese G, Becher PM, Lund LH, Seferovic P, Rosano GMC, Coats A. Global burden of heart failure: a comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc Res 2022;118:3272-87.ArticlePDF
- 7. Park JJ, Lee CJ, Park SJ, Choi JO, Choi S, Park SM, et al. Heart failure statistics in Korea, 2020: a report from the Korean Society of Heart Failure. Int J Heart Fail 2021;3:224-36.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 8. Jung I, Kwon H, Park SE, Han KD, Park YG, Rhee EJ, et al. Changes in patterns of physical activity and risk of heart failure in newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:327-36.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Ryden L, Armstrong PW, Cleland JG, Horowitz JD, Massie BM, Packer M, et al. Efficacy and safety of high-dose lisinopril in chronic heart failure patients at high cardiovascular risk, including those with diabetes mellitus: results from the ATLAS trial. Eur Heart J 2000;21:1967-78.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Shindler DM, Kostis JB, Yusuf S, Quinones MA, Pitt B, Stewart D, et al. Diabetes mellitus, a predictor of morbidity and mortality in the Studies of Left Ventricular Dysfunction (SOLVD) Trials and Registry. Am J Cardiol 1996;77:1017-20.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Thrainsdottir IS, Aspelund T, Thorgeirsson G, Gudnason V, Hardarson T, Malmberg K, et al. The association between glucose abnormalities and heart failure in the population-based Reykjavik study. Diabetes Care 2005;28:612-6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Park JH, Ha KH, Kim BY, Lee JH, Kim DJ. Trends in cardiovascular complications and mortality among patients with diabetes in South Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:120-4.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Kannel WB, McGee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: the Framingham study. JAMA 1979;241:2035-8.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Lind M, Bounias I, Olsson M, Gudbjornsdottir S, Svensson AM, Rosengren A. Glycaemic control and incidence of heart failure in 20,985 patients with type 1 diabetes: an observational study. Lancet 2011;378:140-6.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, et al. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ 2000;321:405-12.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. SOLVD Investigators, Yusuf S, Pitt B, Davis CE, Hood WB, Cohn JN. Effect of enalapril on survival in patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fractions and congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med 1991;325:293-302.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Zannad F, McMurray JJ, Krum H, van Veldhuisen DJ, Swedberg K, Shi H, et al. Eplerenone in patients with systolic heart failure and mild symptoms. N Engl J Med 2011;364:11-21.ArticlePubMed
- 18. McMurray JJ, Packer M, Desai AS, Gong J, Lefkowitz MP, Rizkala AR, et al. Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure. N Engl J Med 2014;371:993-1004.ArticlePubMed
- 19. McMurray JJ, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Kober L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med 2019;381:1995-2008.PubMed
- 20. Adams KF Jr, Fonarow GC, Emerman CL, LeJemtel TH, Costanzo MR, Abraham WT, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized for heart failure in the United States: rationale, design, and preliminary observations from the first 100,000 cases in the Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry (ADHERE). Am Heart J 2005;149:209-16.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Nieminen MS, Brutsaert D, Dickstein K, Drexler H, Follath F, Harjola VP, et al. EuroHeart Failure Survey II (EHFS II): a survey on hospitalized acute heart failure patients: description of population. Eur Heart J 2006;27:2725-36.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Greenberg BH, Abraham WT, Albert NM, Chiswell K, Clare R, Stough WG, et al. Influence of diabetes on characteristics and outcomes in patients hospitalized with heart failure: a report from the Organized Program to Initiate Lifesaving Treatment in Hospitalized Patients with Heart Failure (OPTIMIZE-HF). Am Heart J 2007;154:277.Article
- 23. MacDonald MR, Petrie MC, Varyani F, Ostergren J, Michelson EL, Young JB, et al. Impact of diabetes on outcomes in patients with low and preserved ejection fraction heart failure: an analysis of the Candesartan in Heart failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM) programme. Eur Heart J 2008;29:1377-85.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral T, Branwood AW, Grishman A. New type of cardiomyopathy associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Cardiol 1972;30:595-602.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Drazner MH, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;62:e147-239.PubMed
- 26. Authors/Task Force Members, Ryden L, Grant PJ, Anker SD, Berne C, Cosentino F, et al. ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD: the Task Force on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and developed in collaboration with the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J 2013;34:3035-87.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Murtaza G, Virk HU, Khalid M, Lavie CJ, Ventura H, Mukherjee D, et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: a comprehensive updated review. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2019;62:315-26.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Lee WS, Kim J. Application of animal models in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:129-45.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 29. Kenny HC, Abel ED. Heart failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circ Res 2019;124:121-41.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Dunlay SM, Givertz MM, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Chan M, Desai AS, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association and the Heart Failure Society of America: this statement does not represent an update of the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA heart failure guideline update. Circulation 2019;140:e294-324.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Park JJ. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of heart failure in diabetes. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:146-57.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 32. Fujita B, Lauten A, Goebel B, Franz M, Fritzenwanger M, Ferrari M, et al. Impact of diabetes mellitus on quality of life in patients with congestive heart failure. Qual Life Res 2012;21:1171-6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 33. Yap J, Tay WT, Teng TK, Anand I, Richards AM, Ling LH, et al. Association of diabetes mellitus on cardiac remodeling, quality of life, and clinical outcomes in heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction. J Am Heart Assoc 2019;8:e013114.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Kristensen SL, Mogensen UM, Jhund PS, Petrie MC, Preiss D, Win S, et al. Clinical and echocardiographic characteristics and cardiovascular outcomes according to diabetes status in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: a report from the I-Preserve Trial (Irbesartan in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction). Circulation 2017;135:724-35.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Birkeland KI, Bodegard J, Eriksson JW, Norhammar A, Haller H, Linssen GC, et al. Heart failure and chronic kidney disease manifestation and mortality risk associations in type 2 diabetes: a large multinational cohort study. Diabetes Obes Metab 2020;22:1607-18.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 36. Oudejans I, Mosterd A, Bloemen JA, Valk MJ, van Velzen E, Wielders JP, et al. Clinical evaluation of geriatric outpatients with suspected heart failure: value of symptoms, signs, and additional tests. Eur J Heart Fail 2011;13:518-27.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Kelder JC, Cramer MJ, van Wijngaarden J, van Tooren R, Mosterd A, Moons KG, et al. The diagnostic value of physical examination and additional testing in primary care patients with suspected heart failure. Circulation 2011;124:2865-73.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Wettersten N. Biomarkers in acute heart failure: diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Int J Heart Fail 2021;3:81-105.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 39. Lee HY. Heart failure and diabetes mellitus: dangerous liaisons. Int J Heart Fail 2022;4:163-74.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 40. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022;45(Suppl 1):S144-74.
- 41. Knuuti J, Wijns W, Saraste A, Capodanno D, Barbato E, Funck-Brentano C, et al. 2019 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J 2020;41:407-77.PubMed
- 42. Sharma A, Coles A, Sekaran NK, Pagidipati NJ, Lu MT, Mark DB, et al. Stress testing versus CT angiography in patients with diabetes and suspected coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;73:893-902.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 43. Korean Society of Heart Failure. 2022 Korean Society of Heart Failure guideline for the management of heart failure. Seoul: Korean Society of Heart Failure; 2022 [cited 2023 Jan 17]. Available from: https://www.kshf.or.kr/news/news_01.php?boardid=ksnotice&mode=view&idx=55.
- 44. Marwick TH, Ritchie R, Shaw JE, Kaye D. Implications of underlying mechanisms for the recognition and management of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018;71:339-51.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2117-28.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2017;377:644-57.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Greene SJ, Butler J, Fonarow GC. Simultaneous or rapid sequence initiation of quadruple medical therapy for heart failure-optimizing therapy with the need for speed. JAMA Cardiol 2021;6:743-4.ArticlePubMed
- 48. Lam PH, Packer M, Fonarow GC, Faselis C, Allman RM, Morgan CJ, et al. Early effects of starting doses of enalapril in patients with chronic heart failure in the SOLVD Treatment Trial. Am J Med 2020;133:e25-31.ArticlePubMed
- 49. McMurray JJ, Packer M. How should we sequence the treatments for heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction?: a redefinition of evidence-based medicine. Circulation 2021;143:875-7.ArticlePubMed
- 50. Shaw JA, Cooper ME. Contemporary management of heart failure in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020;43:2895-903.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 51. Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med 2020;383:1413-24.PubMed
- 52. Velazquez EJ, Morrow DA, DeVore AD, Duffy CI, Ambrosy AP, McCague K, et al. Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition in acute decompensated heart failure. N Engl J Med 2019;380:539-48.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Wachter R, Senni M, Belohlavek J, Straburzynska-Migaj E, Witte KK, Kobalava Z, et al. Initiation of sacubitril/valsartan in haemodynamically stabilised heart failure patients in hospital or early after discharge: primary results of the randomised TRANSITION study. Eur J Heart Fail 2019;21:998-1007.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 54. Kerr B, Pharithi RB, Barrett M, Halley C, Gallagher J, Ledwidge M, et al. Angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors in HFrEF: is this the first disease modifying therapy drug class leading to a substantial reduction in diuretic need? Int J Heart Fail 2021;3:106-16.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 55. Park JJ, Lee SE, Cho HJ, Choi JO, Yoo BS, Kang SM, et al. Real-world usage of sacubitril/valsartan in Korea: a multi-center, retrospective study. Int J Heart Fail 2022;4:193-204.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 56. Cohn JN, Tognoni G; Valsartan Heart Failure Trial Investigators. A randomized trial of the angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan in chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2001;345:1667-75.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Pfeffer MA, Swedberg K, Granger CB, Held P, McMurray JJ, Michelson EL, et al. Effects of candesartan on mortality and morbidity in patients with chronic heart failure: the CHARM-Overall programme. Lancet 2003;362:759-66.ArticlePubMed
- 58. Granger CB, McMurray JJ, Yusuf S, Held P, Michelson EL, Olofsson B, et al. Effects of candesartan in patients with chronic heart failure and reduced left-ventricular systolic function intolerant to angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors: the CHARM-Alternative trial. Lancet 2003;362:772-6.ArticlePubMed
- 59. Konstam MA, Neaton JD, Dickstein K, Drexler H, Komajda M, Martinez FA, et al. Effects of high-dose versus low-dose losartan on clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure (HEAAL study): a randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 2009;374:1840-8.ArticlePubMed
- 60. The Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study II (CIBIS-II): a randomised trial. Lancet 1999;353:9-13.ArticlePubMed
- 61. Packer M, Coats AJ, Fowler MB, Katus HA, Krum H, Mohacsi P, et al. Effect of carvedilol on survival in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1651-8.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Hjalmarson A, Goldstein S, Fagerberg B, Wedel H, Waagstein F, Kjekshus J, et al. Effects of controlled-release metoprolol on total mortality, hospitalizations, and well-being in patients with heart failure: the Metoprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in congestive heart failure (MERIT-HF). MERIT-HF Study Group. JAMA 2000;283:1295-302.ArticlePubMed
- 63. Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme WJ, Cody R, Castaigne A, Perez A, et al. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 1999;341:709-17.ArticlePubMed
- 64. Braunwald E. Gliflozins in the management of cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 2022;386:2024-34.ArticlePubMed
- 65. Kim SJ, Kim BJ, Im SI, Kim HS, Heo JH. Effects of empagliflozin on diuretics reduction in outpatient heart failure patients. Int J Heart Fail 2022;4:183-92.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 66. Halliday BP, Wassall R, Lota AS, Khalique Z, Gregson J, Newsome S, et al. Withdrawal of pharmacological treatment for heart failure in patients with recovered dilated cardiomyopathy (TRED-HF): an open-label, pilot, randomised trial. Lancet 2019;393:61-73.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 67. Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Ferreira JP, Bocchi E, Bohm M, et al. Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med 2021;385:1451-61.PubMed
- 68. Solomon SD, McMurray JJV, Claggett B, de Boer RA, DeMets D, Hernandez AF, et al. Dapagliflozin in heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med 2022;387:1089-98.PubMed
- 69. Jhund PS, Kondo T, Butt JH, Docherty KF, Claggett BL, Desai AS, et al. Dapagliflozin across the range of ejection fraction in patients with heart failure: a patient-level, pooled meta-analysis of DAPA-HF and DELIVER. Nat Med 2022;28:1956-64.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 70. Vaduganathan M, Docherty KF, Claggett BL, Jhund PS, de Boer RA, Hernandez AF, et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients with heart failure: a comprehensive meta-analysis of five randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2022;400:757-67.ArticlePubMed
- 71. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2019;380:347-57.ArticlePubMed
- 72. Jeon JY, Ha KH, Kim DJ. Cardiovascular safety of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors as add-on to metformin monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:505-14.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 73. Donnan JR, Grandy CA, Chibrikov E, Marra CA, Aubrey-Bassler K, Johnston K, et al. Comparative safety of the sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2019;9:e022577.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 74. Eurich DT, Weir DL, Majumdar SR, Tsuyuki RT, Johnson JA, Tjosvold L, et al. Comparative safety and effectiveness of metformin in patients with diabetes mellitus and heart failure: systematic review of observational studies involving 34,000 patients. Circ Heart Fail 2013;6:395-402.PubMed
- 75. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2016;375:311-22.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 76. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jodar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2016;375:1834-44.ArticlePubMed
- 77. Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019;394:121-30.PubMed
- 78. Giugliano D, Scappaticcio L, Longo M, Caruso P, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists and cardiorenal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an updated meta-analysis of eight CVOTs. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2021;20:189.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 79. Margulies KB, Hernandez AF, Redfield MM, Givertz MM, Oliveira GH, Cole R, et al. Effects of liraglutide on clinical stability among patients with advanced heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016;316:500-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 80. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837-53.ArticlePubMed
- 81. Rados DV, Pinto LC, Remonti LR, Leitao CB, Gross JL. Correction: the association between sulfonylurea use and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized clinical trials. PLoS Med 2016;13:e1002091.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 82. Rosenstock J, Kahn SE, Johansen OE, Zinman B, Espeland MA, Woerle HJ, et al. Effect of linagliptin vs glimepiride on major adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: the CAROLINA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019;322:1155-66.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 83. Cooper LB, Mi X, Mentz RJ, Green JB, Anstrom KJ, Hernandez AF, et al. Management of newly treated diabetes in Medicare beneficiaries with and without heart failure. Clin Cardiol 2017;40:38-45.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 84. Cosmi F, Shen L, Magnoli M, Abraham WT, Anand IS, Cleland JG, et al. Treatment with insulin is associated with worse outcome in patients with chronic heart failure and diabetes. Eur J Heart Fail 2018;20:888-95.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 85. Gerstein HC, Jung H, Ryden L, Diaz R, Gilbert RE, Yusuf S, et al. Effect of basal insulin glargine on first and recurrent episodes of heart failure hospitalization: the ORIGIN Trial (Outcome Reduction with Initial Glargine Intervention). Circulation 2018;137:88-90.ArticlePubMed
- 86. Marso SP, McGuire DK, Zinman B, Poulter NR, Emerson SS, Pieber TR, et al. Efficacy and safety of degludec versus glargine in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2017;377:723-32.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 87. White WB, Cannon CP, Heller SR, Nissen SE, Bergenstal RM, Bakris GL, et al. Alogliptin after acute coronary syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2013;369:1327-35.ArticlePubMed
- 88. Green JB, Bethel MA, Armstrong PW, Buse JB, Engel SS, Garg J, et al. Effect of sitagliptin on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015;373:232-42.ArticlePubMed
- 89. Rosenstock J, Perkovic V, Johansen OE, Cooper ME, Kahn SE, Marx N, et al. Effect of linagliptin vs placebo on major cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular and renal risk: the CARMELINA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019;321:69-79.ArticlePubMed
- 90. Scirica BM, Bhatt DL, Braunwald E, Steg PG, Davidson J, Hirshberg B, et al. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 2013;369:1317-26.ArticlePubMed
- 91. Komajda M, McMurray JJ, Beck-Nielsen H, Gomis R, Hanefeld M, Pocock SJ, et al. Heart failure events with rosiglitazone in type 2 diabetes: data from the RECORD clinical trial. Eur Heart J 2010;31:824-31.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 92. DREAM (Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication) Trial Investigators, Gerstein HC, Yusuf S, Bosch J, Pogue J, Sheridan P, et al. Effect of rosiglitazone on the frequency of diabetes in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006;368:1096-105.ArticlePubMed
- 93. Dormandy JA, Charbonnel B, Eckland DJ, Erdmann E, Massi-Benedetti M, Moules IK, et al. Secondary prevention of macrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive Study (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005;366:1279-89.ArticlePubMed
- 94. Shen J, Greenberg BH. Diabetes management in patients with heart failure. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:158-72.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 95. Hur KY, Moon MK, Park JS, Kim SK, Lee SH, Yun JS, et al. 2021 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:461-81.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Effects of Gemigliptin Add-on or Escalation of Metformin Dose on Glycemic Control and Safety in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin and SGLT-2 Inh
Hae Jin Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko, Eun-Jung Rhee, Kyu Yeon Hur, In-Kyung Jeong, Mark Yorek
Journal of Diabetes Research.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects of gemigliptin versus glimepiride on cardiac function in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with metformin: The gemi‐heart study
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Jun Hwa Hong, In‐Chang Hwang, Soo Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(8): 2181. CrossRef - Optimization of guideline-directed medical treatment for heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction
Minjung Bak, Jin-Oh Choi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(5): 595. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite