
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Others
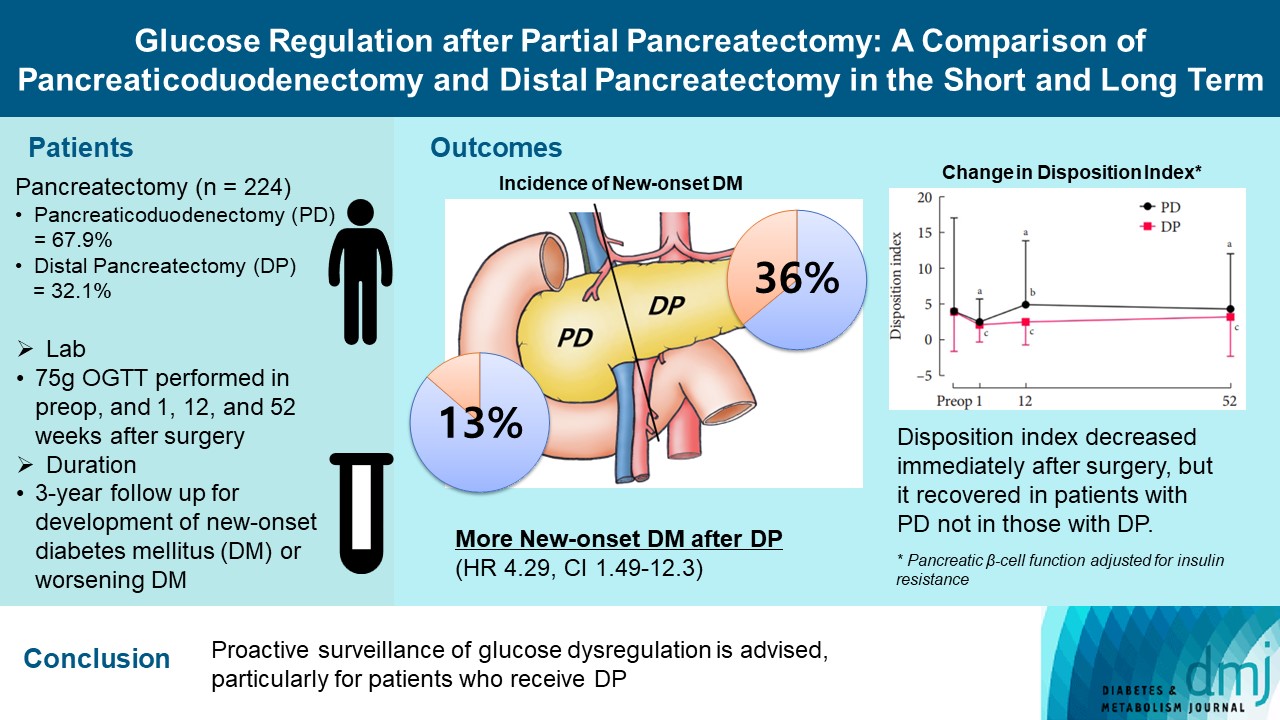
- Glucose Regulation after Partial Pancreatectomy: A Comparison of Pancreaticoduodenectomy and Distal Pancreatectomy in the Short and Long Term
- Jun Suh Lee, Minji Sohn, Kyuho Kim, Yoo-Seok Yoon, Soo Lim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):703-714. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0205
- 1,643 View
- 150 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Long term quality of life is becoming increasingly crucial as survival following partial pancreatectomy rises. The purpose of this study was to investigate the difference in glucose dysregulation after pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) or distal pancreatectomy (DP).
Methods
In this prospective observational study from 2015 to 2018, 224 patients who underwent partial pancreatectomy were selected: 152 (67.9%) received PD and 72 (32.1%) received DP. Comprehensive assessment for glucose regulation, including a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test was conducted preoperatively, and 1, 12, and 52 weeks after surgery. Patients were further monitored up to 3 years to investigate development of new-onset diabetes mellitus (NODM) in patients without diabetes mellitus (DM) at baseline or worsening of glucose regulation (≥1% increase in glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c]) in those with preexisting DM.
Results
The disposition index, an integrated measure of β-cell function, decreased 1 week after surgery in both groups, but it increased more than baseline level in the PD group while its decreased level was maintained in the DP group, resulting in a between-group difference at the 1-year examination (P<0.001). During follow-up, the DP group showed higher incidence of NODM and worsening of glucose regulation than the PD group with hazard ratio (HR) 4.29 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.49 to 12.3) and HR 2.15 (95% CI, 1.09 to 4.24), respectively, in the multivariate analysis including dynamic glycemic excursion profile. In the DP procedure, distal DP and spleen preservation were associated with better glucose regulation. DP had a stronger association with glucose dysregulation than PD.
Conclusion
Proactive surveillance of glucose dysregulation is advised, particularly for patients who receive DP.
- Lifesytle
- Changes in the Quality of Life in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus According to Physician and Patient Behaviors
- Young-Joo Kim, In-Kyung Jeong, Sin-Gon Kim, Dong Hyeok Cho, Chong-Hwa Kim, Chul-Sik Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kyu-Chang Won, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Doo-Man Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):91-102. Published online October 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0251
- 5,885 View
- 95 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetes mellitus (DM) is the most common chronic metabolic disorder with an increasing prevalence worldwide. According to a previous study, physicians' treatment patterns or patients' behaviors change when they become aware of the risk for cardiovascular (CV) disease in patients with DM. However, there exist controversial reports from previous studies in the impact of physicians' behaviors on the patients' quality of life (QoL) improvements. So we investigate the changes in QoL according to physicians and patients' behavioral changes after the awareness of CV risks in patients with type 2 DM.
Methods Data were obtained from a prospective, observational study where 799 patients aged ≥40 years with type 2 DM were recruited at 24 tertiary hospitals in Korea. Changes in physicians' behaviors were defined as changes in the dose/type of antihypertensive, lipid-lowering, and anti-platelet therapies within 6-month after the awareness of CV risks in patients. Changes in patients' behaviors were based on lifestyle modifications. Audit of Diabetes Dependent Quality of Life comprising 19-life-domains was used.
Results The weighted impact score change for local or long-distance journey (
P =0.0049), holidays (P =0.0364), and physical health (P =0.0451) domains significantly differed between the two groups; patients whose physician's behaviors changed showed greater improvement than those whose physician's behaviors did not change.Conclusion This study demonstrates that changes in physicians' behaviors, as a result of perceiving CV risks, improve QoL in some domains of life in DM patients. Physicians should recognize the importance of understanding CV risks and implement appropriate management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spline Longitudinal Multi-response Model for the Detection of Lifestyle-
Based Changes in Blood Glucose of Diabetic Patients
Anna Islamiyati
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 641. CrossRef - Agriophyllum Oligosaccharides Ameliorate Diabetic Insulin Resistance Through INS-R/IRS/Glut4-Mediated Insulin Pathway in db/db Mice and MIN6 Cells
Shuyin Bao, Xiuzhi Wang, Sung Bo Cho, Yan-Ling Wu, Chengxi Wei, Shuying Han, Liming Bao, Qiong Wu, Wuliji Ao, Ji-Xing Nan
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycolipid metabolism and liver transcriptomic analysis of the therapeutic effects of pressed degreased walnut meal extracts on type 2 diabetes mellitus rats
Yulan Li, Dan Chen, Chengmei Xu, Qingyujing Zhao, Yage Ma, Shenglan Zhao, Chaoyin Chen
Food & Function.2020; 11(6): 5538. CrossRef - Cause-of-death statistics in 2018 in the Republic of Korea
Hyun-Young Shin, Jin Kim, Seokmin Lee, Min Sim Park, Sanghee Park, Sun Huh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2020; 63(5): 286. CrossRef
- Spline Longitudinal Multi-response Model for the Detection of Lifestyle-
Based Changes in Blood Glucose of Diabetic Patients
- Clinical Care/Education
- Association of Self-Care Behaviors and Quality of Life among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Chaldoran County, Iran
- Towhid Babazadeh, Mostafa Dianatinasab, Amin Daemi, Hossein Ali Nikbakht, Fatemeh Moradi, Saber Ghaffari-fam
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(6):449-456. Published online December 20, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.449
- 5,133 View
- 89 Download
- 43 Web of Science
- 39 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Self-care of diabetes is an essential part for controlling the disease and improvement of quality of life in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients. This study aimed to analyze the associated factors of quality of life in patients with T2DM in order to design effective interventions.
Methods This cross-sectional study was conducted on 120 T2DM patients referred to health centers of Chaldoran, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran. The quality of life's questionnaires from World Health Organization and the self-care behaviors' questionnaires were used for data collection.
Results The mean age of patients was 46.30% and 53.30% of them were male. Among demographic variables, gender (
P =0.002), age groups (P =0.007), and household monthly income (P =0.009) were significantly associated with total quality of life. Also, self-care nutrition (odds ratio [OR], 1.47;P =0.001), self-management of blood glucose control (OR, 1.29;P =0.002), and self-medication behavior (OR, 1.18;P =0.030) were identified as factors significantly associated with quality of life.Conclusion Self-care behaviors were significantly associated with quality of life; among them, the greatest influence was observed in self-care nutrition behavior. According to the findings of this study, appropriate interventions on self-care behaviors about nutrition can improve the quality of life for T2DM patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of Diabetes Quality of Life Brief Clinical Inventory in Turkish patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Tülay Çevik Saldıran, İlke Kara, Erhan Dinçer, Özgül Öztürk, Rumeysa Çakıcı, Thomas Burroughs
Disability and Rehabilitation.2024; 46(5): 995. CrossRef - The Association between Self-Care Activities and Depression in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Web-Based Survey Study
Sawsan M. Kurdi, Ahmad Alamer, Aya Albaggal, Marwa Alsuwaiket, Fawaz M. Alotaibi, Ibrahim M. Asiri, Dhfer M. Alshayban, Mohammed M. Alsultan, Bashayer Alshehail, Bassem A. Almalki, Dania Hussein, Mansour M. Alotaibi, Osamah M. Alfayez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(2): 419. CrossRef - Role of diabetes health literacy, psychological status, self-care behaviors, and life satisfaction in predicting quality of life in type 2 diabetes
Alireza Jafari, Mahdi Moshki, Mousa Ghelichi-Ghojogh, Mahbobeh Nejatian
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Types of Nursing Intervention on Improving Quality of Life among
Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
Agung Samsu Alam, Amin Samiasih, Mohammad Fatkhul Mubin, Satriya Pranata, Reina Dhamanik
Current Diabetes Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of type 2 diabetes complications and its association with diet knowledge and skills and self‐care barriers in Tabriz, Iran: A cross‐sectional study
Habib Jalilian, Elnaz Javanshir, Leila Torkzadeh, Saeedeh Fehresti, Nazanin Mir, Majid Heidari‐Jamebozorgi, Somayeh Heydari
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Portuguese adaptation of the Chronic Heart Failure Knowledge Questionnaire (KQCHF)
Ana Paula Azzam, Tatiane Fidelis, Andreia Nunes, Rui Valdiviesso, Teresa Limpo, Emília Moreira, José Silva-Cardoso, São Luís Castro
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Hirudotherapy in Alloxan-induced Diabetic Male Rats: Histopathological and Biochemical Changes
Abdolrasoul Namjou, Ebrahim Razavie, Esfandiar Heidarian, Nasser Yazdani, Mahmoud Rafieian-Kopaei
Jundishapur Journal of Natural Pharmaceutical Products.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of Protein By-Products Obtained from Aquatic Organisms as Bioactive Compounds: A Bibliometric Review
Rerisson do Nascimento Alves, José Robenilson Sousa dos Santos, Francisco Lucas Chaves Almeida, Fábio Anderson Pereira da Silva, Íris Braz da Silva Araújo
Food Reviews International.2023; : 1. CrossRef - The relationship between diabetes burden and health-related quality of life in elderly people with diabetes
Gülay Yildirim, Mahruk Rashidi, Funda Karaman, Aslı Genç, Gülşah Ünsal Jafarov, Neşe Kiskaç, İbrahim Ulusoy, Nurten Elki̇n, Sultan Çakmak
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(6): 595. CrossRef - A Cross-sectional Study of Factors Affecting Quality of Life of People with Type 2 Diabetes
Citra Gabriella Mamahit, Kimiko Inaoka, Windy Mariane Virenia Wariki, Erika Ota
Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research.2023; 28(1): 150. CrossRef - Evaluation of Self-Management Behaviors and Its Correlation with the Metabolic Syndrome among the Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients of Northern Saudi Arabia
Aseel Awad Alsaidan, Ashokkumar Thirunavukkarasu, Hassan H. Alhassan, Ibrahim Abdullah Bin Ahmed, Anas Salem Alnasiri, Wejdan Madallah Alhirsan, Nouf Nashmi M. Alazmi, Abdalaziz Khaled Alkhlaf, Jumanah Mohammed Alderbas, Motaz Abdulsalam Alkhaldi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(1): 118. CrossRef - Further Evidence of Psychometric Performance of the Self-care of Diabetes Inventory in Adults With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Maddalena De Maria, Diletta Fabrizi, Michela Luciani, Rosario Caruso, Stefania Di Mauro, Barbara Riegel, Claudio Barbaranelli, Davide Ausili
Annals of Behavioral Medicine.2022; 56(6): 632. CrossRef - The effects of formal nutrition education on anthropometric indices, lipid profile, and glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Seyedeh-Masomeh Derakhshandeh-Rishehri, Motahar Heidari-Beni, Shiva Faghih, Asghar Mirfardi
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(3): 395. CrossRef - The prevalence and predictors of pre-diabetes and diabetes among adults 40–70 years in Kharameh cohort study: A population-based study in Fars province, south of Iran
Masoumeh Ghoddusi Johari, Kimia Jokari, Alireza Mirahmadizadeh, Mozhgan Seif, Abbas Rezaianzadeh
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2022; 21(1): 85. CrossRef - Perception of benefits and barriers associated with dementia prevention behaviors among people with diabetes
Noppamas Pipatpiboon, Nut Koonrungsesomboon, Wachira Suriyawong, Jirapas Sripetchwandee, Sue Turale
Nursing & Health Sciences.2022; 24(1): 274. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Quality of Life in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes of South Benin: A Cross-Sectional Study
Halimatou Alaofè, Waliou Amoussa Hounkpatin, Francois Djrolo, John Ehiri, Cecilia Rosales
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(4): 2360. CrossRef - The relationship between medical comorbidities and health-related quality of life among adults with type 2 diabetes: The experience of different hospitals in southern Bangladesh
Adnan Mannan, Farhana Akter, Naim Uddin Hasan A. Chy, Nazmul Alam, Md. Mashud Rana, Nowshad Asgar Chowdhury, Md. Mahbub Hasan, Mohammad Farris Iman Leong Bin Abdullah
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(5): e0267713. CrossRef - Self-management and self-efficacy of women with gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review
Savvato Karavasileiadou, Wafa Almegewly, Anwar Alanazi, Hanan Alyami, Sofia Chatzimichailidou
Global Health Action.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Family Caregiver Knowledge and Behavior on Elderly Diabetic Patients’ Quality of Life in Northern Thailand
Kitbordin Thongduang, Waraporn Boonchieng, Sineenart Chautrakarn, Parichat Ong-Artborirak
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(16): 10216. CrossRef - Influence of Diabetes Knowledge, Self-Stigma, and Self-Care Behavior on Quality of Life in Patients with Diabetes
Sung Eun Cho, Myoungjin Kwon, Sun Ae Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 1983. CrossRef - A Novel User Utility Score for Diabetes Management Using Tailored Mobile Coaching: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Min-Kyung Lee, Da Young Lee, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2021; 9(2): e17573. CrossRef - Association between self-care management practices and glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Saud Arabia: A cross –sectional study
Abdulaziz Alodhayani, Khalid M. Almutairi, Jason M. Vinluan, Turky H. Almigbal, Wadi B. Alonazi, Mohammed Ali Batais, Muhanna Mohammed Alnassar
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2021; 28(4): 2460. CrossRef - Methodological quality of studies assessing validity and reliability of the European Heart Failure Self-care Behaviour Scale: a systematic review using the COSMIN methodology
Stefan Köberich, Naoko P Kato, Christiane Kugler, Anna Strömberg, Tiny Jaarsma
European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of diabetic retinopathy in Tikur Anbessa Hospital, Ethiopia: a case–control study
Kalid Seid, Temamen Tesfaye, Admasu Belay, Hayat Mohammed
Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Educational Strategies for Secondary Stroke Prevention: An Integrative Literature Review
Dame Elysabeth Tuty Arna Uly Tarihoran, Michelle Honey, Julia Slark
American Journal of Health Education.2021; 52(6): 364. CrossRef - Barriers to Diabetes Patients’ Self-Care Practices in Eastern Ethiopia: A Qualitative Study from the Health Care Providers Perspective
Shiferaw Letta, Fekadu Aga, Tesfaye Assebe Yadeta, Biftu Geda, Yadeta Dessie
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4335. CrossRef - Quality of Life and Self-care Activities in Diabetic Ulcer Patients, Grade 3: Gender Differences
Maria Polikandrioti, Georgios Vasilopoulos, Evangelos Dousis, Georgia Gerogianni, Georgios Panoutsopoulos, Vasileios Dedes, Ioannis Koutelekos
Journal of Caring Sciences.2021; 10(4): 184. CrossRef - Prevalence and predictors of depression in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ravi Kant, Poonam Yadav, Shruti Barnwal, Vishal Dhiman, Bruzily Abraham, Kanchan Gawande
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2021; 10(1): 352. CrossRef - Factors affecting the quality of life in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: a path analysis model
Soheila Ansarzadeh, Leili Salehi, Zohreh Mahmoodi, Abolfazl Mohammadbeigi
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of Fear of Relapse Scale for Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis: Understanding Stressors in Patients
Ali Khatibi, Nahid Moradi, Naghmeh Rahbari, Taranom Salehi, Mohsen Dehghani
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The association of illness perceptions and God locus of health control with self-care behaviours in patients with type 2 diabetes in Saudi Arabia
Mohsen Alyami, Anna Serlachius, Ibrahim Mokhtar, Elizabeth Broadbent
Health Psychology and Behavioral Medicine.2020; 8(1): 329. CrossRef - Self-Care in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
Rebeca Barbosa da Rocha, Cristiano Sales Silva, Vinícius Saura Cardoso
Current Diabetes Reviews.2020; 16(6): 598. CrossRef Adherence to a Health Literacy and Healthy Lifestyle with Improved Blood Pressure Control in Iran
Saber Gaffari-fam, Towhid Babazadeh, Shahram Oliaei, Leila Behboodi, Amin Daemi
Patient Preference and Adherence.2020; Volume 14: 499. CrossRef- Can a modified theory of planned behavior explain the effects of empowerment education for people with type 2 diabetes?
Chung-Ying Lin, Mike K. T. Cheung, Anchor T. F. Hung, Peter K. K. Poon, Sam C. C. Chan, Chetwyn C. H. Chan
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 11: 204201881989752. CrossRef - Impact of health literacy and self-care behaviors on health-related quality of life in Iranians with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study
Saber Gaffari-fam, Yosef Lotfi, Amin Daemi, Towhid Babazadeh, Ehsan Sarbazi, Ghader Dargahi-Abbasabad, Hamed Abri
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Hand Hygiene Practices Among Adults with Diabetes Living in Communities: The 2015 Korea Community Health Survey
Mi Ah Han
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(7): 1279. CrossRef - Predictors of Pap Smear Screening Behavior Among Rural Women in Tabriz, Iran: An Application of Health Belief Model
Towhid Babazadeh , Saber Ghaffari-Fam, Shahram Oliaei, Ehsan Sarbazi, Arash Shirdel , Parvin Mostafa-Gharabaghi, Hosein Azizi
International Journal of Cancer Management.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Prevalence and Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy in Shiraz, Southern Iran
Haleh Ghaem, Nima Daneshi, Shirin Riahi, Mostafa Dianatinasab
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(6): 538. CrossRef - Diabetes Self-Management: A Key to Better Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Diabetes
Maha Al-Khaledi, Hussah Al-Dousari, Shaikhah Al-Dhufairi, Taiba Al-Mousawi, Rehab Al-Azemi, Farah Al-Azimi, Hanan E. Badr
Medical Principles and Practice.2018; 27(4): 323. CrossRef
- Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of Diabetes Quality of Life Brief Clinical Inventory in Turkish patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Clinical Care/Education
- The Role of Negative Affect in the Assessment of Quality of Life among Women with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Nicola R. Gawlik, Malcolm J. Bond
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):130-136. Published online November 7, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.130
- 3,418 View
- 33 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The purpose of this study is to determine the impact of negative affect (defined in terms of lack of optimism, depressogenic attributional style, and hopelessness depression) on the quality of life of women with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Methods Participants (
n =177) completed either an online or paper questionnaire made available to members of Australian diabetes support groups. Measures of optimism, attributional style, hopelessness depression, disease-specific data, and diabetes-related quality of life were sought. Bivariate correlations informed the construction of a structural equation model.Results Participants were 36.3±11.3 years old, with a disease duration of 18.4±11.2 years. Age and recent glycosylated hemoglobin readings were significant contextual variables in the model. All bivariate associations involving the components of negative affect were as hypothesized. That is, poorer quality of life was associated with a greater depressogenic attributional style, higher hopelessness depression, and lower optimism. The structural equation model demonstrated significant direct effects of depressogenic attributional style and hopelessness depression on quality of life, while (lack of) optimism contributed to quality of life indirectly by way of these variables.
Conclusion The recognition of negative affect presentations among patients, and an understanding of its relevance to diabetes-related quality of life, is a valuable tool for the practitioner.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Menopoz dönemindeki diyabetik kadınlarda yaşanılan semptomların yaşam kalitesi parametreleri üzerindeki etkisinin incelenmesi (Prospektif Tek Grup Çalışma)
Ayşegül KOÇ, Betül ÇAKMAK, Birgül GENÇ
Turkish Journal of Diabetes and Obesity.2021; 5(2): 137. CrossRef - Type 1 Diabetes Home Care Project and Educational Consultation
Eun Chong Shin
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(2): 88. CrossRef - Poorer Quality of Life and Treatment Satisfaction is Associated with Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes without Other Advanced Late Complications
Minerva Granado-Casas, Esmeralda Castelblanco, Anna Ramírez-Morros, Mariona Martín, Nuria Alcubierre, Montserrat Martínez-Alonso, Xavier Valldeperas, Alicia Traveset, Esther Rubinat, Ana Lucas-Martin, Marta Hernández, Núria Alonso, Didac Mauricio
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(3): 377. CrossRef - Is Diabetes & Metabolism Journal Eligible to Be Indexed in MEDLINE?
Sun Huh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(6): 472. CrossRef
- Menopoz dönemindeki diyabetik kadınlarda yaşanılan semptomların yaşam kalitesi parametreleri üzerindeki etkisinin incelenmesi (Prospektif Tek Grup Çalışma)
- Factors Associated with Health-Related Quality of Life among Saudi Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Survey
- Ayman A. Al Hayek, Asirvatham A. Robert, Abdulghani Al Saeed, Aus A. Alzaid, Fahad S. Al Sabaan
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(3):220-229. Published online June 17, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.3.220
- 5,189 View
- 111 Download
- 70 Web of Science
- 58 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with high mortality, morbidity, poor general health, and loss of health-related quality of life (HRQOL). The objective of the study was to assess the factors associated with HRQOL among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods This was a cross sectional study conducted among 283 T2DM patients during June 2011 and September 2012 at a major tertiary hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The respondents were purposively and conveniently selected according to their availability during their routine visit to the outpatient clinics and they were interviewed using the Arabic version of the Short-Form 36-item survey (SF-36) to assess the HRQOL.
Results The mean age of the participants was 56.4±13.2 years. Around 63% (178) were males and 37% (105) were females. Glycosylated hemoglobin level was found to be significantly higher among female and HRQOL was higher among male. Respondents who were more than 50 years old had poor HRQOL than less than 50 years age group. Poor economic status, reported diabetic complications and longer duration of diabetes were significantly associated with poor HRQOL. The respondents treated with combination of therapies (oral medication plus insulin) indicated better HRQOL than patients with insulin therapy alone. Multivariate analysis indicated that gender, economic status (except subscale energy), and complications of DM (except subscale energy) as independent risk factor for HRQOL.
Conclusion Gender, economic status, and complication of DM were independent risk factors for majority of the subscales of HRQOL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quality of life, stress, anxiety and depression and associated factors among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Western region Saudi Arabia
Shahad Abduljalil Abualhamael, Mukhtiar Baig, Waleed Alghamdi, Zohair Jamil Gazzaz, Majid Al-Hayani, Abdulrahman Bazi
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life of Adolescents and Children With Type 1 Diabetes in the Jazan Region of Saudi Arabia
Gassem A Gohal, Aqilah Majhali, Esaam Moafa, Sarah H Talebi, Bushra I Maashi, Amani Mutaen, Walaa J Alhamdan, Ibrahim M Dighriri
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life Among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Using the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) in Central Ethiopia: A Multicenter Study
Habtamu Esubalew, Ayele Belachew, Yimer Seid, Habtamu Wondmagegn, Kidus Temesgen, Tsegazeab Ayele
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 1039. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and its determinants among patients with diabetes mellitus: a multicentre cross-sectional study in Northwest Ethiopia
Ashenafi Kibret Sendekie, Ephrem Mebratu Dagnew, Bereket Bahiru Tefera, Eyayaw Ashete Belachew
BMJ Open.2023; 13(1): e068518. CrossRef - Illness Perception and Coping Strategies on the Perceived Quality of Life in Adults with Coronary Heart Diseases: A Model Evaluation
Maedeh Bagheri, Mohammadnaghi Farahani, Hamidreza Hasanabadi, Balal Izanloo
Journal of Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chlorella improves inflammatory profiles and quality of life of prediabetes and diabetes patients
Fernanda Martins, Tamara C. Lopes de Castro, Sara T. Olalla Saad, Rose C. G. Trevisane, Ricardo P. Moreira, Edite Taninaga, Mary L. S. Queiroz, Cristiane Okuda Torello
Fundamental Toxicological Sciences.2023; 10(2): 31. CrossRef - Health-related Quality of Life among Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Southern
Province of Saudi Arabia using WHOQOL-BREF: A Cross-section Study
Areej Homady, Osama Albasheer, Amenah Bajawi, Shatha Hamdi, Aisha Awaf, Tahani Madkhali, Abdallah Sabai, Mohammad R. Zaino, Mohammed Somaili
Current Diabetes Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting Factors of Health-Related Quality of Life Among Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review
Margareta Teli, Ratsiri Thato, Yohanes Andy Rias
SAGE Open Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Diabetic Disease on Health-Related Quality of Life in
Type 2 Diabetic Patients Karbala. Iraq: Across sectional study
Sammar Jassim Mahan, Mohammed Mahmood Mahammad, Hassan Mutrtadha Hassan
Bionatura.2023; 8(CSS 1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of General Health Status in Diabetic Patients Using Short
Form Health Survey (SF-36)
Ali Shlash Al-Ibrahimy, Ihsan Salah Rabea
Current Diabetes Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and Attitudes About Type 2 Diabetes Among Female Nursing Students in Saudi Arabia
Hafsa A. Abdirahman, Tasneem Hassan, Nada A. AbuAlUla, Kathryn H. Jacobsen
World Medical & Health Policy.2022; 14(1): 47. CrossRef - Toward Personalized Hemoglobin A1c Estimation for Type 2 Diabetes
Namho Kim, Da Young Lee, Wonju Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Sung-Min Park
IEEE Sensors Journal.2022; 22(23): 23023. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at a tertiary care hospital in Ethiopia
Girma Tekle Gebremariam, Selam Biratu, Metasebia Alemayehu, Abraham Gebregziabiher Welie, Kebede Beyene, Beate Sander, Gebremedhin Beedemariam Gebretekle, Vijayaprakash Suppiah
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(2): e0264199. CrossRef - The contribution of gastrointestinal microbiota in the existence of type 2 diabetes in Saudi Arabia: Current information and perspectives
Nesreen Aljahdali
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2022; 29(6): 103286. CrossRef - The Health-Related Quality of Life of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Saudi Arabia
Amal Khaleel AbuAlhommos, Amjad Heji Alturaifi, Amnah Mohammed Al-Bin Hamdhah, Hawra Hassan Al-Ramadhan, Zahra Abdullah Al Ali, Hawra Jumah Al Nasser
Patient Preference and Adherence.2022; Volume 16: 1233. CrossRef - Quality of life and factors associated with a good quality of life among diabetes mellitus patients in northern Thailand
Ratipark Tamornpark, Suphaphorn Utsaha, Tawatchai Apidechkul, Dunlayaphap Panklang, Fartima Yeemard, Peeradone Srichan
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycaemic control and its associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes in the Middle East and North Africa: An updated systematic review and meta‐analysis
Odai Hamed Al‐ma'aitah, Daniel Demant, Samantha Jakimowicz, Lin Perry
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(8): 2257. CrossRef - Health‐related quality of life of people with type 2 diabetes and its associated factors at a tertiary care clinic in Ningbo, China: A cross‐sectional study
Naomi Carter, Jialin Li, Miao Xu, Li Li, Xuelan Fan, Shuyan Zhu, Pritpal Chahal, Kaushik Chattopadhyay
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and associated factors among type 2 diabetic adult patients in Debre Markos Referral Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia
Tewodros Eshete Wonde, Tessema Reta Ayene, Nurilign Abebe Moges, Yibelu Bazezew
Heliyon.2022; : e10182. CrossRef - Quality of life among patients with the common chronic disease during COVID-19 pandemic in Northwest Ethiopia: A structural equation modelling
Tadesse Awoke Ayele, Habtewold Shibru Fanta, Malede Mequanent Sisay, Tesfahun Melese Yilma, Melkitu Fentie, Telake Azale, Tariku Belachew, Kegnie Shitu, Tesfa Sewunet Alamneh, Filipe Prazeres
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(12): e0278557. CrossRef - Diabetic foot ulcers: Classification, risk factors and management
Xuan Wang, Chong-Xi Yuan, Bin Xu, Zhi Yu
World Journal of Diabetes.2022; 13(12): 1049. CrossRef - Health‐related quality of life and its predictors among the type 2 diabetes population of Bangladesh: A nation‐wide cross‐sectional study
Lingkan Barua, Mithila Faruque, Hasina Akhter Chowdhury, Palash Chandra Banik, Liaquat Ali
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(2): 277. CrossRef - Assessment of nutritional status and quality of life in individuals with and without diabetes over 65 years of age
Gulseren Pamuk, Gulsah Kaner, Esra Meltem Koc, Tuncay Toşur, Sumeyra Dasdelen, Saliha Aksun, Baris Önder Pamuk
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(1): 141. CrossRef - Function of family of origin and current quality of life: exploring the mediator role of resilience in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes
Guizhi Jia, Xin Li, Yuying Chu, Hongliang Dai
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(2): 346. CrossRef - Self-care activities, glycaemic control and health-related quality of life of patients with type 2 diabetes in a tertiary hospital in Nigeria
Idongesit L. Jackson, Samuel I. Onung, Emmanuel P. Oiwoh
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(1): 137. CrossRef - Quality of life among adult patients living with diabetes in Rwanda: a cross-sectional study in outpatient clinics
Charilaos Lygidakis, Jean Paul Uwizihiwe, Michela Bia, Francois Uwinkindi, Per Kallestrup, Claus Vögele
BMJ Open.2021; 11(2): e043997. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and associated factors among patients with type II diabetes mellitus: A study in the family medicine center (FMC) of Agricultural General Hospital in Hanoi, Vietnam
Nguyen Tran Kien, Nguyen Phuong Hoa, Duong Minh Duc, Johan Wens
Health Psychology Open.2021; 8(1): 205510292199617. CrossRef - Quality of life and adherence to mediterranean diet among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients of a primary health care clinic in Hebron city, Palestine
Manal Badrasawi, May Hamdan, Mohammad Al Tamimi
Mediterranean Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism.2021; 14(3): 255. CrossRef - The TELE-DD project on treatment nonadherence in the population with type 2 diabetes and comorbid depression
Juan Francisco Roy, María Luisa Lozano del Hoyo, Fernando Urcola-Pardo, Alicia Monreal-Bartolomé, Diana Cecilia Gracia Ruiz, María Mercedes Gómez Borao, Ana Belén Artigas Alcázar, José Pedro Martínez Casbas, Alexandra Aceituno Casas, María Teresa Andaluz
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of life among type II diabetic patients attending the primary health centers of King Saud Medical City in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Saleh Alsuwayt, Mohammed Almesned, Shahad Alhajri, Naif Alomari, Razan Alhadlaq, Abdullah Alotaibi
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 10(8): 3040. CrossRef - Influence of Diabetes complications and limitations on health-related quality of life: a study in a southeastern Brazilian city
Cecilia Correa Avila, Margareth Guimarães Lima, Marilisa Berti de Azevedo Barros
Quality of Life Research.2020; 29(2): 473. CrossRef - The impact of diabetes mellitus on health-related quality of life in Saudi Arabia
Diena M. Almasri, Ahmad O. Noor, Ragia H. Ghoneim, Alaa A. Bagalagel, Mansour Almetwazi, Nujud A. Baghlaf, Esraa A. Hamdi
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal.2020; 28(12): 1514. CrossRef - Predictors of health-related quality of life among patients with diabetes on follow-up at Nekemte specialised Hospital, Western Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study
Bikila Regassa Feyisa, Mekdes Tigistu Yilma, Belachew Etana Tolessa
BMJ Open.2020; 10(7): e036106. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study
Dhfer Alshayban, Royes Joseph, Manal S. Fawzy
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(1): e0227573. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Diabetic Foot Ulcer: A Cross-Sectional Study From Saudi Arabia
Mousab Al Ayed, Mutasem Ababneh, Asirvatham Alwin Robert, Nasser Al Misfer, Maria Cruz, Hesiel C Austria, Mohamed Al Dawish
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Study of Health-Related Quality of Life and Healthcare Utilization among Type 2 Diabetic Population in an Urban Area of Eastern Nepal
Sangita Shah, Nilambar Jha, Deepak Kumar Yadav, Prajjwal Pyakurel, Sanjib Kumar Sharma, Suman Bahadur Singh, Alexander Schreiber
International Journal of Endocrinology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Oral Health-related Knowledge and Assessment of Oral Health Status of Diabetic Patients Attending Dental Clinic at College of Dentistry, Hail, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Rashid I Mian, Fawzeyah FH Rashidi, Tahani M Alshammary, Saad Al Zubaidi, Freah Al Shammary, Junaid Amin, Rabia S Khan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2020; 21(1): 78. CrossRef - Prevalence and predictors of depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms among patients with type II diabetes attending primary healthcare centers in the western region of Saudi Arabia: a cross-sectional study
Alhussain Alzahrani, Abdulrahman Alghamdi, Turki Alqarni, Reem Alshareef, Abdullah Alzahrani
International Journal of Mental Health Systems.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-related quality of life among people living with type 2 diabetes: a community based cross-sectional study in rural Nepal
Sailendra Thapa, Prajjwal Pyakurel, Dharani Dhar Baral, Nilambar Jha
BMC Public Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Demographic and clinical predictors of health-related quality of life among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus living in northern Thailand: A cross-sectional study
Saneh Khunkaew, Ritin Fernandez, Jenny Sim
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Health related quality of life (HRQOL) among low socioeconomic population in Malaysia
Sharifa Ezat Wan Puteh, Chamhuri Siwar, Mohd Azlan Shah Zaidi, Hazila Abdul Kadir
BMC Public Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring variables associated with poor health‐related quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes in Jordan
Anan S. Jarab, Eman Alefishat, Tareq L. Mukattash, Abdel Qader Albawab, Rana K. Abu‐Farha, James C. McElnay
Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Services Research.2019; 10(2): 211. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life among adults living with diabetic foot ulcers: a meta-analysis
Saneh Khunkaew, Ritin Fernandez, Jenny Sim
Quality of Life Research.2019; 28(6): 1413. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and its associated factors among adult patients with type II diabetes attending Mizan Tepi University Teaching Hospital, Southwest Ethiopia
Tadesse Gebremedhin, Abdulhalik Workicho, Dessie Abebaw Angaw
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2019; 7(1): e000577. CrossRef - Quality of life of people with diabetes mellitus
Isabela Fernandes de Aguiar Tonetto, Marcelo Henrique Barbosa Baptista, Danielle dos Santos Gomides, Ana Emilia Pace
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the Direct and Indirect Effects of SF-36 Domains Score on Two Main Factors in Diabetic Patients with Path Analysis: Health-Related Quality of Life Study
Paria Dehesh, Tania Dehesh, Mohammad Hossein Gozashti
Romanian Journal of Diabetes Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases.2019; 26(1): 21. CrossRef - General health status in Iranian diabetic patients assessed by short-form-36 questionnaire: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Masoud Behzadifar, Rahim Sohrabi, Roghayeh Mohammadibakhsh, Morteza Salemi, Sharare Taheri Moghadam, Masood Taheri Mirghaedm, Meysam Behzadifar, Hamid Reza Baradaran, Nicola Luigi Bragazzi
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Influencing Pathways to Quality of Life and HbA1c in Patients With Diabetes: A Longitudinal Study That Inform Evidence‐Based Practice
Hui‐Chun Hsu, Yau‐Jiunn Lee, Ruey‐Hsia Wang
Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing.2018; 15(2): 104. CrossRef - Effects of a Psychoeducational Program on Hemoglobin A1c Level and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Jazan, Saudi Arabia
Samy Shaban Mahmoud, Mona Husein EL Mahdy, Mohamed Salih Mahfouz, Ibrahim Saad Nada, Abdulwahab Abdoh Aqeeli, Mohammed Ahmed AL Darbi, Anas Elias Ahmed
BioMed Research International.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - The effects of periodontal treatment on diabetic patients: The DIAPERIO randomized controlled trial
Jean‐Noel Vergnes, Thibault Canceill, Alexia Vinel, Sara Laurencin‐Dalicieux, Françoise Maupas‐Schwalm, Vincent Blasco‐Baqué, Hélène Hanaire, Elise Arrivé, Vincent Rigalleau, Cathy Nabet, Michel Sixou, Pierre Gourdy, Paul Monsarrat
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2018; 45(10): 1150. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and associated factors among patients with diabetes mellitus in Botswana
Godfrey Mutashambara Rwegerera, Thato Moshomo, Marea Gaenamong, Taibat Aderonke Oyewo, Sivasomnath Gollakota, Yordanka Piña Rivera, Anthony Masaka, Brian Godman, Meshack Shimwela, Dereje Habte
Alexandria Journal of Medicine.2018; 54(2): 111. CrossRef - Related factors of quality of life of type 2 diabetes patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiyue Jing, Jiageng Chen, Yanan Dong, Duolan Han, Haozuo Zhao, Xuying Wang, Fei Gao, Changping Li, Zhuang Cui, Yuanyuan Liu, Jun Ma
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Minimally important difference and predictors of change in quality of life in type 2 diabetes: A community‐based survey in China
Xuejing Jin, Gordon G. Liu, Hertzel C. Gerstein, Mitchell A.H. Levine, Haijing Guan, Hongchao Li, Feng Xie
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of long-term multicomponent exercise on health-related quality of life in older adults with type 2 diabetes: evidence from a cohort study
Liliana C. Baptista, Gonçalo Dias, Nelba R. Souza, Manuel T. Veríssimo, Raul A. Martins
Quality of Life Research.2017; 26(8): 2117. CrossRef - Health benefits of Quran memorization for older men
Nazmus Saquib, Juliann Saquib, Abdulrahman Alhadlag, Mohamad Anas Albakour, Bader Aljumah, Mohammed Sughayyir, Ziad Alhomidan, Omar Alminderej, Mohamed Aljaser, Ahmed Mohammed Al-Dhlawiy, Abdulrahman Al-Mazrou
SAGE Open Medicine.2017; 5: 205031211774099. CrossRef - Prevalence of overactive bladder and its impact on quality of life in 1025 patients with type 2 diabetes in mainland China
Dongjuan Xu, Jie Gao, Xiaojuan Wang, Liqun Huang, Kefang Wang
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(8): 1254. CrossRef - Testing whether patients with diabetes and healthy people perceive the meaning of the items in the Persian version of the SF-36 questionnaire similarly: a differential item functioning analysis
Zahra Bagheri, Peyman Jafari, Marzieh Mahmoodi, Mohammad Hossein Dabbaghmanesh
Quality of Life Research.2017; 26(4): 835. CrossRef - Negative effects of diabetes–related distress on health-related quality of life: an evaluation among the adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in three primary healthcare clinics in Malaysia
Boon-How Chew, Sherina Mohd-Sidik, Sazlina Shariff-Ghazali
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Quality of life, stress, anxiety and depression and associated factors among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Western region Saudi Arabia
- Current Status of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Korea: Report of a Hospital-Based Study of Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Korea by the Diabetic Neuropathy Study Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Jong Chul Won, Sang Soo Kim, Kyung Soo Ko, Bong-Yun Cha
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(1):25-31. Published online February 19, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.25
- 3,832 View
- 51 Download
- 28 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is the most common complication associated with diabetes. DPN can present as a loss of sensation, may lead to neuropathic ulcers, and is a leading cause of amputation. Reported estimates of the prevalence of DPN vary due to differences in study populations and diagnostic criteria. Furthermore, the epidemiology and clinical characteristics of DPN in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are not as well understood as those of other complications of diabetes such as retinal and renal disease. Recently, the Diabetic Neuropathy Study Group of the Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) conducted a study investigating the impact of DPN on disease burden and quality of life in patients with T2DM and has published some data that are representative of the nation. This review investigated the prevalence and associated clinical implications of DPN in Korean patients with diabetes based on the KDA study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shear wave elastography of tibial nerve in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy—A cross-sectional study
Dhiri Ranjan Pradhan, Sudhir Saxena, Ravi Kant, Mirtunjai Kumar, Sonal Saran
Skeletal Radiology.2024; 53(3): 547. CrossRef - Association of Sensory Nerve Action Potential Amplitude and Velocity With Type 2 Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Anwar H Siddiqui, Nazia Tauheed, Hamid Ashraf, Jamal Ahmad
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A review on extraction, purification, structural characteristics and bioactivities of polysaccharides from Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce
Xin-Yan Zong, De-Chang Xu, Jun-Yi Yin, Shao-Ping Nie, Ming-Yong Xie
Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre.2022; 27: 100284. CrossRef - Development and characterisation of a rat model that exhibits both metabolic dysfunction and neurodegeneration seen in type 2 diabetes
Katherine Southam, Chantal de Sousa, Abraham Daniel, Bruce V. Taylor, Lisa Foa, Dino Premilovac
The Journal of Physiology.2022; 600(7): 1611. CrossRef - Renal impairment is one of appropriate predictors of future diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a hospital-based 6-year follow-up study
Chi-Sheng Wang, Yen-Wei Pai, Ching-Heng Lin, I-Te Lee, Ming-Hong Chang
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seon Mee Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(4): 222. CrossRef - Compound XiongShao Capsule ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats via inhibiting apoptosis, oxidative - nitrosative stress and advanced glycation end products
Mei-xiang Yu, Bo Lei, Xin Song, Yong-mei Huang, Xiao-qin Ma, Chen-xia Hao, Wan-hua Yang, Man-li Pan
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2021; 268: 113560. CrossRef - Etiology, diagnosis, complications, and treatments of diabetic foot
Dong-Kyo Seo
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2021; 64(8): 523. CrossRef - A nationwide study of patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance with a 10-year follow-up in South Korea
Ka-Won Kang, Ji Eun Song, Byung-Hyun Lee, Min Ji Jeon, Eun Sang Yu, Dae Sik Kim, Se Ryeon Lee, Hwa Jung Sung, Chul Won Choi, Yong Park, Byung Soo Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Acupuncture for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: study protocol for a randomized, placebo-controlled trial
Haiping Deng, Yu Shu, Peiran Lv, Ling Zhao, Ke Cheng, Tingting Zhang, Yi Song, Hua Yang, Hong Tang, Jian Pei, Xueyong Shen
Trials.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Identify the Key Active Ingredients and Pharmacological Mechanisms of Compound XiongShao Capsule in Treating Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy by Network Pharmacology Approach
Meixiang Yu, Xin Song, Wanhua Yang, Ziwei Li, Xiaoqin Ma, Chenxia Hao
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Deep phenotyping neuropathy: An underestimated complication in patients with pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes associated with albuminuria
Stefan Kopf, Jan B. Groener, Zoltan Kender, Thomas Fleming, Sandra Bischoff, Johann Jende, Carsten Schumann, Stefan Ries, Martin Bendszus, Sigrid Schuh-Hofer, Rolf-Detlef Treede, Peter P. Nawroth
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 146: 191. CrossRef - Role of neopterin as a biochemical marker for peripheral neuropathy in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes: Relation to nerve conduction studies
Nancy Samir Elbarbary, Eman Abdel Rahman Ismail, Rana Ahmed El-Hilaly, Fatma Salama Ahmed
International Immunopharmacology.2018; 59: 68. CrossRef - Association between diabetic peripheral neuropathy and heart rate variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes
S.K.M. Azizul Islam, Dongkyu Kim, Young-Sil Lee, Seong-Su Moon
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 140: 18. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seong-Su Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(3): 153. CrossRef - Clinical Importance of Diabetic Neuropathy
Tae Sun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(3): 147. CrossRef - The U-shaped relationship between fibroblast growth factor 21 and microvascular complication in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chan-Hee Jung, Sang-Hee Jung, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chul-Hee Kim, Sung-Koo Kang, Ji-Oh Mok
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(1): 134. CrossRef - Retinal Neurodegeneration Associated With Peripheral Nerve Conduction and Autonomic Nerve Function in Diabetic Patients
Kiyoung Kim, Seung-Young Yu, Hyung Woo Kwak, Eung Suk Kim
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2016; 170: 15. CrossRef - Letter: Cardiovascular Disease Predicts Severe Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:498-506)
Mi-Kyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(1): 83. CrossRef - Associations of serum anti-ganglioside antibodies and inflammatory markers in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Shengjie Ge, Jing Xie, Lequn Zheng, Lijuan Yang, Hong Zhu, Xingbo Cheng, Feixia Shen
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2016; 115: 68. CrossRef - Axonopathy in peripheral neuropathies: Mechanisms and therapeutic approaches for regeneration
Lila M. Landowski, P. James B. Dyck, JaNean Engelstad, Bruce V. Taylor
Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy.2016; 76: 19. CrossRef - Adiponectin gene polymorphisms are associated with increased susceptibility to diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Yao Chen, Jian Wang, Lijing Wang, Peiji Huang, Zeng-Xian Tan, Huai-Jun Liu
Biomarkers.2015; 20(6-7): 474. CrossRef - Effect of Socio-Economic Status on the Prevalence of Diabetes
Yu Jeong Kim, Ja Young Jeon, Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2015; 56(3): 641. CrossRef - Morphologic Changes in Autonomic Nerves in Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy
Heung Yong Jin, Hong Sun Baek, Tae Sun Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(6): 461. CrossRef - Diabetic neuropathy and the sensory apparatus “meissner corpuscle and merkel cellsâ€
Salma Alsunousi, Husnia I. Marrif
Frontiers in Neuroanatomy.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Arterial Stiffness and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Bulent Behlul Altunkeser
Medical Science Monitor.2014; 20: 2074. CrossRef
- Shear wave elastography of tibial nerve in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy—A cross-sectional study
- The Relationship between Diabetes Mellitus and Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Adults: The Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007-2009)
- Yong Jun Choi, Min Suk Lee, So Yeon An, Tae Ho Kim, Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Yoon-Sok Chung, Kwan Woo Lee, Dae Jung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(6):587-594. Published online December 26, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.587
- 4,823 View
- 52 Download
- 45 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetes is a major health problem in Korea. However, interest in the quality of life in patients with diabetes is low. We examined the effects of diabetes on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and compared it with HRQoL in the general Korean population using the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV) (2007-2009).
Methods Using KNHANES IV data, we compared EuroQol (EQ)-5D and EQ-visual analogue scale (VAS) scores after adjusting for sociodemographic and psychosocial factors as well as for comorbidities (hypertension, heart disease, stroke, arthritis, and chronic renal disease). Logistic regressions were used to explore determinants for the lowest quintile HRQoL scales in the diabetes group.
Results The mean age of the 14,441 enrolled subjects (6,129 men and 8,312 women) was 52.5±14.5 years. The mean EQ-5D and EQ-VAS scores were significantly lower in the diabetes group (EQ-5D. 0.87; EQ-VAS, 71.94) than in the non-diabetes group (EQ-5D, 0.94; EQ-VAS, 77.40) (
P <0.001). Self-reported depressive symptom had a significant effect on lowering the EQ-VAS (odds ratio [OR], 1.7; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.1 to 2.6) in the diabetes group. Stress level had a significant effect in lowering both the EQ-5D (OR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.3 to 2.9) and the EQ-VAS (OR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.3 to 2.9). HbA1c, diabetes duration, and treatment modalities had no significant effect on lowering HRQoL.Conclusion Diabetes was clearly associated with impaired HRQoL compared with the non-diabetic population regardless of comorbidities. Therapeutic approaches should focus much more on the subjective perception of health in patients with diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding health‐related quality of life trajectories among older adults with diabetes mellitus: Mixed methods research
Sunhee Park, Taewha Lee
Nursing Open.2023; 10(10): 6945. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Relation between Compliance with Mediterranean Diet and Quality of Life of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Meltem Kudret, Fatma Nişancı Kılınç, Sevilay Karahan
Nutrition and Cancer.2023; 75(2): 562. CrossRef - The status of stigma in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with medication adherence and quality of life in China: A cross-sectional study
Xiaoyan Li, Lingyun Wu, Jie Yun, Qiuhua Sun
Medicine.2023; 102(26): e34242. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Subjective Health Status of Men with Insulin-treated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Secondary Analysis Using Quantile Regression Analysis
Kang Sun Lee, Hyuk Joon Kim, Young Man Kim, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(4): 530. CrossRef - Association of temporomandibular disorders and tinnitus with health‐related quality of life: A cross‐sectional study using the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Geon‐Sik Kong, Sook‐Hyun Lee, Kyoung Sun Park, Jae‐Heung Cho, Koh‐Woon Kim, In‐Hyuk Ha
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2022; 49(3): 283. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at a tertiary care hospital in Ethiopia
Girma Tekle Gebremariam, Selam Biratu, Metasebia Alemayehu, Abraham Gebregziabiher Welie, Kebede Beyene, Beate Sander, Gebremedhin Beedemariam Gebretekle, Vijayaprakash Suppiah
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(2): e0264199. CrossRef - The role of nutritional status in the relationship between diabetes and health-related quality of life
Sohyun Park, Sukyoung Jung, Hyunsook Yoon
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(4): 505. CrossRef - Associations between Food Groups and Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Adults
Shamirah Nabbosa, Sunghee Lee
Nutrients.2022; 14(17): 3643. CrossRef - Quality of life among adult patients living with diabetes in Rwanda: a cross-sectional study in outpatient clinics
Charilaos Lygidakis, Jean Paul Uwizihiwe, Michela Bia, Francois Uwinkindi, Per Kallestrup, Claus Vögele
BMJ Open.2021; 11(2): e043997. CrossRef - THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SELF-MANAGEMENT AND QUALITY OF LIFE AMONG PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Ninik Ambar Sari, Ceria Nurhayati
Nurse and Health: Jurnal Keperawatan.2021; 10(2): 343. CrossRef - Measurement of health-related quality of life in patients with diabetes mellitus using EQ-5D-5L in Hong Kong, China
Eliza Lai yi Wong, Richard Huan Xu, Annie Wai ling Cheung
Quality of Life Research.2020; 29(7): 1913. CrossRef - Non-Exercise Based Estimation of Cardiorespiratory Fitness Mediates Associations between Comorbidities and Health-Related Quality of Life in Older Korean Adults with Diabetes
Inhwan Lee, Shinuk Kim, Hyunsik Kang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(4): 1164. CrossRef - Health related quality of life and healthcare utilization among adults with diabetes and kidney and eye complications in the United States
Abdulkarim M. Meraya, Monira Alwhaibi
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Limitations of Deep Learning Attention Mechanisms in Clinical Research: Empirical Case Study Based on the Korean Diabetic Disease Setting
Junetae Kim, Sangwon Lee, Eugene Hwang, Kwang Sun Ryu, Hanseok Jeong, Jae Wook Lee, Yul Hwangbo, Kui Son Choi, Hyo Soung Cha
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(12): e18418. CrossRef - Predictors of Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Adults with Diabetes Mellitus
Mihyun Jeong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 9058. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status
Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 415. CrossRef - Does ancestry influence health-related quality of life in type 1 diabetes patients? A nationwide study in Brazil
Deborah Conte Santos, Marcela Haas Pizarro, Bianca S. V. Barros, Laura G. Nunes de Melo, Luis Cristovão Porto, Dayse A. Silva, Marilia Brito Gomes
Acta Diabetologica.2018; 55(4): 377. CrossRef - Lipid profiles in adolescents with and without asthma: Korea National Health and nutrition examination survey data
Sun-Hye Ko, Jaewook Jeong, Myong Ki Baeg, Kyung-Do Han, Hwan Soo Kim, Jong-seo Yoon, Hyun Hee Kim, Jin Tack Kim, Yoon Hong Chun
Lipids in Health and Disease.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Health Status of Type 2 Diabetes Outpatients Receiving Care in a Tertiary Hospital in Nigeria
Maxwell Ogochukwu Adibe, Chibueze Anosike, Sunday Odunke Nduka, Abdulmuminu Isah
PharmacoEconomics - Open.2018; 2(3): 337. CrossRef - Association between chronic conditions and health-related quality of life: differences by level of urbanization in Peru
Alvaro Taype-Rondan, Elizabeth Sarah Abbs, Maria Lazo-Porras, William Checkley, Robert H. Gilman, Liam Smeeth, J. Jaime Miranda, Antonio Bernabe-Ortiz
Quality of Life Research.2017; 26(12): 3439. CrossRef - The impact of weight misperception on health-related quality of life in Korean adults (KNHANES 2007–2014): a community-based cross-sectional study
Susan Park, Sejin Lee, Jinseub Hwang, Jin-Won Kwon
BMJ Open.2017; 7(6): e016098. CrossRef - Self-efficacy and self-care behaviours among adults with type 2 diabetes
Melba Sheila D'Souza, Subrahmanya Nairy Karkada, Kader Parahoo, Ramesh Venkatesaperumal, Susan Achora, Arcalyd Rose R. Cayaban
Applied Nursing Research.2017; 36: 25. CrossRef - Factors associated with health-related quality of life in Koreans aged over 50 Years: the fourth and fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Kyoung Min Kwon, Jung Soo Lee, Na Eun Jeon, Yeo Hyung Kim
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of Life in Patients with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
Ho Jin Jung, Ye-Soo Park, Hyoung-Yeon Seo, Jae-Chul Lee, Ki-Chan An, Jin-Hyok Kim, Byung-Joon Shin, Tae Wook Kang, Si Young Park
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2017; 24(3): 187. CrossRef - Health Related Quality of Life among Omani Men and Women with Type 2 Diabetes
Melba Sheila D’Souza, Ramesh Venkatesaperumal, Susan D. Ruppert, Subrahmanya Nairy Karkada, Devakirubai Jacob
Journal of Diabetes Research.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Heavy Alcohol Consumption with Alcoholic Liver Disease Accelerates Sarcopenia in Elderly Korean Males: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2010
Do Seon Song, U Im Chang, Sooa Choi, Yun Duk Jung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yu-Bae Ahn, Jin Mo Yang, Masaki Mogi
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(9): e0163222. CrossRef - Negative effect of a previous diagnosis of diabetes on quality of life in a Japanese population: The Gifu Diabetes Study
Yukiko Nonoyama, Mayumi Yamamoto, Shino Oba, Chisato Nagata, Kazuki Matsui, Jun Takeda
Diabetology International.2016; 7(2): 148. CrossRef - The impact of type 2 diabetes on health related quality of life in Bangladesh: results from a matched study comparing treated cases with non-diabetic controls
Novie Safita, Sheikh Mohammed Shariful Islam, Clara K. Chow, Louis Niessen, Andreas Lechner, Rolf Holle, Michael Laxy
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Utilities for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment-Related Attributes in a South Korean and Taiwanese Population
Narayan Rajan, Kristina S. Boye, Meaghan Gibbs, Yoon Ji Lee, Peter Davey, Mark Ball, Steve M. Babineaux
Value in Health Regional Issues.2016; 9: 67. CrossRef - Knowledge, attitudes, and quality of life of type 2 diabetes patients in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
IbrahimSuliman Al-Aboudi, MohammedAzmi Hassali, AsrulAkmal Shafie
Journal of Pharmacy And Bioallied Sciences.2016; 8(3): 195. CrossRef - Low muscle mass is associated with metabolic syndrome only in nonobese young adults: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2010
Byung Chul Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Sae-Young Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Anwar T. Merchant, Hyeon Woo Yim, Won-Chul Lee, Yong Gyu Park, Yong-Moon Park
Nutrition Research.2015; 35(12): 1070. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Is Associated with Intraocular Pressure Elevation in a Non-Obese Korean Population
Yoon Hong Chun, Kyungdo Han, Shin Hae Park, Kyung-Min Park, Hyeon Woo Yim, Won-Chul Lee, Yong Gyu Park, Yong-Moon Park, Stephen L. Atkin
PLoS ONE.2015; 10(1): e112929. CrossRef - Sarcopenia as a Determinant of Blood Pressure in Older Koreans: Findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) 2008–2010
Kyungdo Han, Yu-Mi Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Seung-Hyun Ko, Seung-Hwan Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Won-Chul Lee, Yong Gyu Park, Mee Kyoung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Yan Li
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(1): e86902. CrossRef - Suicidal ideation and suicide attempts among diabetes mellitus: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV, V) from 2007 to 2012
Jae Ho Chung, Kitae Moon, Do Hyung Kim, Joo-Won Min, Tae Ho Kim, Hee-Jin Hwang
Journal of Psychosomatic Research.2014; 77(6): 457. CrossRef - Diabetes and Depressive Symptoms in Korean Women: The Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010-2011)
Han Na Sung, Hong Seok Chae, Eung Soo Kim, Jong Sung Kim
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2014; 35(3): 127. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Hemorrhoids in Korean Adults: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong-Hyun Lee, Hyo-Eun Kim, Ji-Hun Kang, Jin-Young Shin, Yun-Mi Song
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2014; 35(5): 227. CrossRef - The Health Technology Assessment Environment in Mainland China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan—Implications for the Evaluation of Diabetes Mellitus Therapies
Tessa Kennedy-Martin, Beth D. Mitchell, Kristina S. Boye, Wen Chen, Bradley H. Curtis, Jennifer A. Flynn, Shunya Ikeda, Li Liu, Yen Huei Tarn, Bong-Min Yang, Emmanuel Papadimitropoulos
Value in Health Regional Issues.2014; 3: 108. CrossRef - Can “Healthy” Normal Alanine Aminotransferase Levels Identify the Metabolically Obese Phenotype? Findings from The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2010
Hee Yeon Kim, Chang Wook Kim, Chang Don Lee, Jong Young Choi, Chung-Hwa Park, Si Hyun Bae, Seung Kew Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Yong-Moon Park
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2014; 59(6): 1330. CrossRef - The impact of new screen-detected and previously known type 2 diabetes on health-related quality of life: a population-based study in Qingdao, China
Yanlei Zhang, Jianping Sun, Zengchang Pang, Xiaoyong Wang, Weiguo Gao, Feng Ning, Jie Ren, Anil Kapur, Harri Sintonen, Qing Qiao
Quality of Life Research.2014; 23(8): 2319. CrossRef - Increasing achievement of the target goals for glycemic, blood pressure and lipid control for adults with diagnosed diabetes in Korea
Sung Hoon Yu, Jun Goo Kang, Yoo‐Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Hyung Joon Yoo, Hong Yup Ahn, Sung Woo Park, Cheol‐Young Park
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2013; 4(5): 460. CrossRef - Psychosocial needs of cancer patients and related factors: a multi‐center, cross‐sectional study in Korea
Kyung‐Hyun Choi, Jae‐Hyun Park, Jong‐Hyock Park, Joo‐Sung Park
Psycho-Oncology.2013; 22(5): 1073. CrossRef - Correlates of health-related quality of life in French people with type 2 diabetes
I. Bourdel-Marchasson, C. Druet, C. Helmer, E. Eschwege, P. Lecomte, M. Le-Goff, A.J. Sinclair, A. Fagot-Campagna
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2013; 101(2): 226. CrossRef - Diet Therapy in Patients of Diabetic Nephropathy
Ji-Youn Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2013; 14(1): 27. CrossRef - Health‐related quality of life among Tianjin Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross‐sectional survey
Ji‐Yan Cong, Yue Zhao, Qun‐Yan Xu, Chun‐De Zhong, Qiu‐Ling Xing
Nursing & Health Sciences.2012; 14(4): 528. CrossRef - Effects of Frequency of Follow-Up on Quality of Life of Type 2 Diabetes Patients on Oral Hypoglycemics
Ming Hu, Zhiguang Zhou, Fang Zeng, Zhenqiu Sun
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2012; 14(9): 777. CrossRef
- Understanding health‐related quality of life trajectories among older adults with diabetes mellitus: Mixed methods research
- Comparison of Attitudes Regarding Quality of Life between Insulin-Treated Subjects with Diabetes Mellitus and Healthy Populations
- Fariba Hashemi Hefz Abad, Maryam Shabany Hamedan
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(4):397-403. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.397
- 53,176 View
- 33 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease and one of the main causes of mortality in developing countries. The main objective of treating all chronic diseases, of course, is to improve well-being and attain a satisfactory quality of life (QOL). The major goal of this study is comparison of attitude toward QOL in insulin-dependent subjects with diabetes mellitus and healthy subjects.
Methods In this study, insulin-dependent subjects with diabetes mellitus and healthy subjects were gathered via convenience sampling. The subjects were asked to complete the Hanestad & Albrektsen Attitude to Quality of Life Questionnaire. The questionnaire evaluates five quality of life dimensions-physical, social, mental-emotional, behavioral-activity, and economic-using a scoring system similar to the Likert scale. The Wilcoxon test was used to compare scores between the two groups.
Results The mean total score on attitude toward QOL in the healthy control group was 53.8, and it in the insulin-dependent subjects with diabetes mellitus group was 35.9. The mean total score of attitude toward QOL in the physical dimension, mental-emotional and feelings of well-being dimension, and behavioral-activity dimension were significantly higher in the healthy population than they were in diabetes mellitus groups. Such a difference was not seen in the social and economic dimensions.
Conclusion Since the attitudes of insulin-dependent subjects with diabetes mellitus toward QOL are used as an index of individual and societal health levels, it appears that this group may benefit from education and professional counseling to improve their QOLs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-Related Quality of Life and its Determinants Amongst Women With Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
Alireza Didarloo, Mohammad Alizadeh
Nursing and Midwifery Studies.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between self-reported weight change, educational status, and health-related quality of life in patients with diabetes in Luxembourg
Anastase Tchicaya, Nathalie Lorentz, Stefaan Demarest, Jean Beissel, Daniel R. Wagner
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of life in people with diabetes: a systematic review of studies in Iran
Aliasghar A Kiadaliri, Baharak Najafi, Maryam Mirmalek-Sani
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Heavy burden of non-communicable diseases at early age and gender disparities in an adult population of Burkina Faso: world health survey
Malgorzata Miszkurka, Slim Haddad, Étienne V Langlois, Ellen E Freeman, Seni Kouanda, Maria Victoria Zunzunegui
BMC Public Health.2012;[Epub] CrossRef
- Health-Related Quality of Life and its Determinants Amongst Women With Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
- Self-Management and Health-Related Quality of Life in Adolescent and Adulthood Diabetic Patients.
- Bong Suk Park, Gi Nam Jin, Youn Chung Choi, Ji Hee Chung, Kyoung Hoe Kim, Mi Young Lee, Jang Hyun Koh, Choon Hee Chung
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(3):254-261. Published online May 1, 2005
- 1,135 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The purposes of this study are to analyze the factors that influence selfmanagement and health-related QOL, and to provide useful informations to improve the QOL in adolescent and adult diabetic patients. METHODS: For this study, we interviewed 126 adolescent and adult diabetic patients who visited the Yonsei University Wonju Christian Hospital from March 4th, 2004 to April 5th, 2004. RESULTS: We examined the relationship between the socio-demographic characteristics and the health-related quality of life(QOL). There were statistically significant relationships between the QOL-and employment, years of education, income level and marriage status, but not between the health-related QOL and age and gender. Furthermore, there were no statistically significant relationships between the health-related QOL and smoking or drinking, nor between type 1 and 2 diabetic patients. The health-related QOL was significantly higher for an increased diabetes duration and for a greater number of symptoms, but the QOL was significantly lower in the presence of complications and hospital admission. The health-related QOL was lower when the preprandial blood glucose levels and HbA1c concentrations were higher, but it was higher when the hemoglobin and hematocrit levels were higher. Regarding the treatment methods, the health-related QOL was significantly lower for those patients who took insulin injection. The QOL was higher when the general self-management and diet therapy were well-controlled. Meanwhile, those subjects who had obtained medical informations from doctors, the media(including the internet and TV) and nurses in that order, they selected diet therapy as the hardest factor in the management of their diabetes. CONCLUSION: Adolescent and adult diabetic patients need continuous education and assistance to improve their health-related QOL and to keep from developing complications

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





