
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
- Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):3-14. Published online January 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0335
- 14,689 View
- 893 Download
- 54 Web of Science
- 63 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
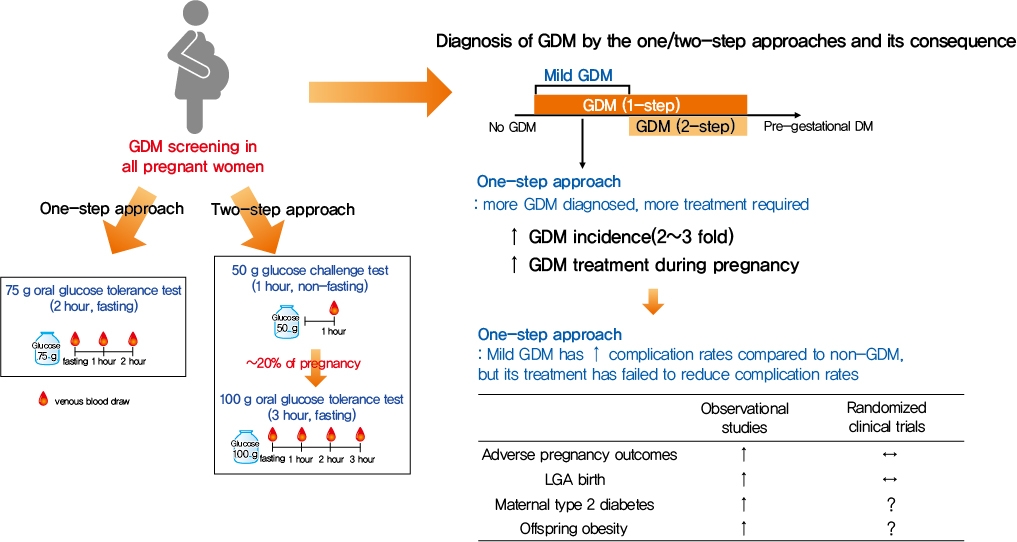
- Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is the most common complication during pregnancy and is defined as any degree of glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy. GDM is associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes and long-term offspring and maternal complications. For GDM screening and diagnosis, a two-step approach (1-hour 50 g glucose challenge test followed by 3-hour 100 g oral glucose tolerance test) has been widely used. After the Hyperglycemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcome study implemented a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test in all pregnant women, a one-step approach was recommended as an option for the diagnosis of GDM after 2010. The one-step approach has more than doubled the incidence of GDM, but its clinical benefit in reducing adverse pregnancy outcomes remains controversial. Long-term complications of mothers with GDM include type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease, and complications of their offspring include childhood obesity and glucose intolerance. The diagnostic criteria of GDM should properly classify women at risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes and long-term complications. The present review summarizes the strengths and weaknesses of the one-step and two-step approaches for the diagnosis of GDM based on recent randomized controlled trials and observational studies. We also describe the long-term maternal and offspring complications of GDM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prophylactic administration of metformin reduces gestational diabetes mellitus incidence in the high-risk populations: a meta-analysis
Hui Yu, Jinling Sun, Honglei Hu
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2024; 193(1): 199. CrossRef - Association of dietary inflammatory index with risk of gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Li Hong, Liyuan Zhu, Jinru Zhang, Yueqi Fu, Xiaoyan Qi, Mei Zhao
British Journal of Nutrition.2024; 131(1): 54. CrossRef - Ferritin and iron supplements in gestational diabetes mellitus: less or more?
Tianlian Li, Jingfan Zhang, Ping Li
European Journal of Nutrition.2024; 63(1): 67. CrossRef - Comparing the screening methods for gestational diabetes mellitus before and during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A systematic review
Xingge Sun, Clare McKeaveney, Helen Noble, Hannah O’Hara, Oliver Perra
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024; 15(4): 500. CrossRef - Protective Effects of Paeoniflorin Against Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rats with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus via Inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK Signaling Pathway
Cheng kun Yuan, Yan Gao, Jinglu Yu, Limin Peng
Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia.2024; 34(3): 536. CrossRef - METTL14‐mediated lncRNA XIST silencing alleviates GDM progression by facilitating trophoblast cell proliferation and migration via the miR‐497‐5p/FOXO1 axis
Yanchuan Li, Yanfeng Liu, Xiao Yao, Haili Wang, Ziyun Shi, Meiqing He
Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity in pregnant women: Application value of simple indices
Shuying Ren, Dan Wu, Ping Li
Clinica Chimica Acta.2024; 554: 117753. CrossRef - ATP5me alleviates high glucose-induced myocardial cell injury
Qingsha Hou, Fang Yan, Xiuling Li, Huanling Liu, Xiang Yang, Xudong Dong
International Immunopharmacology.2024; 129: 111626. CrossRef - Aberrant NK cell profile in gestational diabetes mellitus with fetal growth restriction
Yujing Xiong, Yazhen Wang, Mengqi Wu, Shuqiang Chen, Hui Lei, Hui Mu, Haikun Yu, Yongli Hou, Kang Tang, Xutao Chen, Jie Dong, Xiaohong Wang, Lihua Chen
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal Diabetes and Risk of Hypospadias: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
Zhiyuan Liu, Chengjun Yu, Shuhan Yang, Jin Luo, Jie Zhang, Xiao Wang, Chun Wei, Qinlin Shi, Yi Hua, Xing Liu, Guanghui Wei
Urologia Internationalis.2024; 108(2): 108. CrossRef - Maternal birth weight as an indicator of early and late gestational diabetes mellitus: The Japan Environment and Children's Study
Kazuma Tagami, Noriyuki Iwama, Hirotaka Hamada, Hasumi Tomita, Rie Kudo, Natsumi Kumagai, Hongxin Wang, Seiya Izumi, Zen Watanabe, Mami Ishikuro, Taku Obara, Nozomi Tatsuta, Hirohito Metoki, Chiharu Ota, Takashi Sugiyama, Shinichi Kuriyama, Takahiro Arima
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Perinatal characteristics and pregnancy outcomes of advanced maternal age women with gestational diabetes mellitus: A retrospective cohort study
Chen Jiang, Haiyan Wen, Tingting Hu, Yanfei Liu, Xiaoqing Dai, Yiming Chen
Health Science Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Phenotypic characterisation of regulatory T cells in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus
Ya-nan Zhang, Qin Wu, Yi-hui Deng
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Healthy behaviors and gestational diabetes mellitus in an Iranian setting: A cross-sectional study
Maryam Zare, Afrouz Mardi, Paria Yeghanenia, Daniel Hackett
Medicine.2024; 103(9): e36431. CrossRef - Post‐load glucose is a stronger predictor of adverse pregnancy outcomes than first‐trimester HbA1c in women without gestational diabetes
Shahin Keshtkar Rajabi, Elham Toghraee, Golnoosh Nejatipour
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index in early pregnancy predicts the risk of gestational diabetes: a prospective cohort study
Yufeng Guo, Junwen Lu, Mailiman Bahani, Guifeng Ding, Lei Wang, Yuxia Zhang, Huanmei Zhang, Chengyao Liu, Lijun Zhou, Xiaolan Liu, Fangshen Li, Xiaoli Wang, Hong Ding
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A study on behavior, diet patterns and physical activity among selected GDM and non-GDM women in south India
S Sindhu, S Uma Mageshwari
Journal of Diabetology.2024; 15(1): 86. CrossRef - The Implication of Diabetes-Specialized Nurses in Aiming for the Better Treatment and Management of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Brief Narrative Review
Yefang Zhu, Hongmei Zhang, Ying Xi, Hongli Zhu, Yan Lu, Xue Luo, Zhangui Tang, Hong Lei
Diabetes Therapy.2024; 15(5): 917. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index: A promising biomarker for predicting risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes in Hangzhou, China
Jinghua Zhang, Binbin Yin, Ya Xi, Yongying Bai
Preventive Medicine Reports.2024; 41: 102683. CrossRef - Associations of education attainment with gestational diabetes mellitus and the mediating effects of obesity: A Mendelian randomization study
Xiaoyan Wang, Ying Lan, Na Li, Jinfeng Gao, Dejiao Meng, Shuchuan Miao
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e29000. CrossRef - Quality assessment of videos on social media platforms related to gestational diabetes mellitus in China: A cross-section study
Qin-Yu Cai, Jing Tang, Si-Zhe Meng, Yi Sun, Xia Lan, Tai-Hang Liu
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e29020. CrossRef - One abnormal value in oral glucose tolerance test during pregnancy and type 2 diabetes risk: Insights from a 5-Year Follow-Up study
Rawia Hussein-Aro, Esther Maor-Sagie, Yoel Toledano, Mordechai Hallak, Rinat Gabbay-Benziv
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 211: 111659. CrossRef - Assessment of the Level of Knowledge About Risk Factors, Prevention, and Treatment of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Community Sample From Saudi Arabia
Suzan A Morsy, Ayat M Tawfik, Samar Y Badayyan, Lameer K Shaikh, Shaden AzizKhan, AlKhansaa A Zakari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic Susceptibility, Mendelian Randomization, and Nomogram Model Construction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Qiulian Liang, Ming Li, Gongchen Huang, Ruiqi Li, Linyuan Qin, Ping Zhong, Xuekun Xing, Xiangyuan Yu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on the regulation of trophoblast activity by abnormally expressed hsa_circ_0024838/miR-543/HIF1A in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus
Qian Liu, Faminzi Li, Juan Gui, Lianzhi Wu
Placenta.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between sleep duration during pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yuandong Li, Chao Liang, Cui Wu, Zheng Nan
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Fetal Hemodynamic Parameters in Pregnant Women with Diabetes Mellitus in the Third Trimester of Pregnancy
Dongmei Cai, Su Yan
Heliyon.2024; : e30352. CrossRef - U-shaped Association Between Folic Acid Supplementation and the Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women
Jiuming Zou, Qiang Fu, Xiaoliu Huang, Zhao Yao, Weiye Wang
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2023; 47(1): 78. CrossRef - Vitamin D Supplementation for the Outcomes of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Neonates: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
Chunfeng Wu, Yang Song, Xueying Wang, Pier P. Sainaghi
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Lipolysis and gestational diabetes mellitus onset: a case-cohort genome-wide association study in Chinese
Miao Zhang, Qing Li, Kai-Lin Wang, Yao Dong, Yu-Tong Mu, Yan-Min Cao, Jin Liu, Zi-Heng Li, Hui-Lu Cui, Hai-Yan Liu, An-Qun Hu, Ying-Jie Zheng
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Interactive effect of prepregnancy overweight/obesity and GDM history on prevalence of GDM in biparous women
Xia Xu, Feipeng Huang, Yanni Guo, Lianghui Zheng, Jianying Yan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Microbiome Changes in Pregnancy Disorders
Luca Giannella, Camilla Grelloni, Dayana Quintili, Alessia Fiorelli, Ramona Montironi, Sonila Alia, Giovanni Delli Carpini, Jacopo Di Giuseppe, Arianna Vignini, Andrea Ciavattini
Antioxidants.2023; 12(2): 463. CrossRef - Effects of early standardized management on the growth trajectory of offspring with gestational diabetes mellitus at 0–5 years old: a preliminary longitudinal study
Bingbing Guo, Jingjing Pei, Yin Xu, Yajie Wang, Xinye Jiang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus using the XG Boost machine learning algorithm
Xiaoqi Hu, Xiaolin Hu, Ya Yu, Jia Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus in Indian women: Insights from a large real-world study over ten years at tertiary care research institute
Sanjay Gupte, Gayatri Venkataraman, Aarti S. Shah, Shalaka Jamenis, Chandrakant Rao, Shweta M. Jangam, Kaveri M. Adki, Onkar C. Swami
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023; 43(4): 511. CrossRef - Gestational diabetes mellitus: state of art
S. A. Pletneva, E. V. Enkova, O. V. Khoperskaya, S. V. Shamarin, V. V. Enkova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; (5): 136. CrossRef - Effect of folic acid supplementation in the association between short sleep duration and gestational diabetes mellitus
Zhen Yang, Sisi Hu, Wei Tong, Zhihao Xu, Xiaoliu Huang, Weiye Wang
Sleep and Breathing.2023; 27(6): 2509. CrossRef - Birth weight and large for gestational age trends in offspring of pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus in southern China, 2012-2021
Li-Rong He, Li Yu, Yong Guo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Root causes of long-term complications of gestational diabetes mellitus: Metabolic disturbances of the host and gut microbiota
Mingjin Tao, Gaochen Lu, Sheng Zhang, Pan Li
Clinica Chimica Acta.2023; 548: 117490. CrossRef - Analysis on Related Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) in Subsequent Pregnancies in Multiparous Women with No History of GDM
文静 张
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(07): 11628. CrossRef - Fetoplacental endothelial dysfunction in gestational diabetes mellitus and maternal obesity: A potential threat for programming cardiovascular disease
Mariana S. Diniz, Ursula Hiden, Inês Falcão-Pires, Paulo J. Oliveira, Luis Sobrevia, Susana P. Pereira
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2023; 1869(8): 166834. CrossRef - Diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes mellitus
Tae Jung Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 414. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia in Children: Major Endocrine-Metabolic Causes and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives
Alessia Quarta, Daniela Iannucci, Miriana Guarino, Annalisa Blasetti, Francesco Chiarelli
Nutrients.2023; 15(16): 3544. CrossRef - Relation between weight gain during pregnancy and postpartum reclassification in gestational diabetes
Sofia Coelho, Marta Canha, Ana Rita Leite, João Sérgio Neves, Ana Isabel Oliveira, Davide Carvalho, Maria do Céu Ameida
Endocrine.2023; 82(2): 296. CrossRef - Nurturing through Nutrition: Exploring the Role of Antioxidants in Maternal Diet during Pregnancy to Mitigate Developmental Programming of Chronic Diseases
Mariana S. Diniz, Carina C. Magalhães, Carolina Tocantins, Luís F. Grilo, José Teixeira, Susana P. Pereira
Nutrients.2023; 15(21): 4623. CrossRef - Blood manganese level and gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yingmei Sun, Yu Zhang
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multiparity increases the risk of diabetes by impairing the proliferative capacity of pancreatic β cells
Joon Ho Moon, Joonyub Lee, Kyun Hoo Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Hyeongseok Kim, Hye-Na Cha, Jungsun Park, Hyeonkyu Lee, So-young Park, Hak Chul Jang, Hail Kim
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2023; 55(10): 2269. CrossRef - Physiological Mechanisms Inherent to Diabetes Involved in the Development of Dementia: Alzheimer’s Disease
Himan Mohamed-Mohamed, Victoria García-Morales, Encarnación María Sánchez Lara, Anabel González-Acedo, Teresa Pardo-Moreno, María Isabel Tovar-Gálvez, Lucía Melguizo-Rodríguez, Juan José Ramos-Rodríguez
Neurology International.2023; 15(4): 1253. CrossRef - Synergistic effect between pre-pregnancy smoking and assisted reproductive technology on gestational diabetes mellitus in twin pregnancies
Lingyu Zhang, Yan Huang, Mingjin Zhang, Yanqi Jin
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 61(2): 205. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Impacts on Maternal Health, Fetal Development, Childhood Outcomes, and Long-Term Treatment Strategies
Vaishnavi S Nakshine, Sangita D Jogdand
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of dietary fiber on preventing gestational diabetes mellitus in an at-risk group of high triglyceride-glucose index women: a randomized controlled trial
Yannan Cao, Jing Sheng, Dongyao Zhang, Li Chen, Ying Jiang, Decui Cheng, Yao Su, Yuexin Yu, Haoyi Jia, Pengyuan He, Li Wang, Xianming Xu
Endocrine.2023; 82(3): 542. CrossRef - Correlation between PAPP-A serum levels in the first trimester of pregnancy with the occurrence of gestational diabetes, a multicenter cohort study
Sedigheh Borna, Masoumeh Ashrafzadeh, Marjan Ghaemi, Nasim Eshraghi, Nafiseh Hivechi, Sedigheh Hantoushzadeh
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic levels during pregnancy: A retrospective analysis
Erika Di Zazzo, Sergio Davinelli, Serena Panichella, Giovanni Scapagnini, Mariano Intrieri, Silvio Garofalo
Open Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in Nutritional Strategies for Gestational Diabetes Management: A Systematic Review of Recent Evidence
Juan Carlos Sánchez-García, Ines Saraceno López-Palop, Beatriz Piqueras-Sola, Jonathan Cortés-Martín, Elena Mellado-García, Inmaculada Muñóz Sánchez, Raquel Rodríguez-Blanque
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(1): 37. CrossRef - Comparative efficacy and safety of glyburide, metformin, and insulin in treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus
Jing Lin, Rong-zu Tu, Xun-yu Hong
Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Stacking Ensemble Method for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prediction in Chinese Pregnant Women: A Prospective Cohort Study
Ruiyi Liu, Yongle Zhan, Xuan Liu, Yifang Zhang, Luting Gui, Yimin Qu, Hairong Nan, Yu Jiang, Mehdi Gheisari
Journal of Healthcare Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Secular increase in the prevalence of gestational diabetes and its associated adverse pregnancy outcomes from 2014 to 2021 in Hebei province, China
Mei-Ling Tian, Li-Yan Du, Guo-Juan Ma, Ting Zhang, Xu-Yuan Ma, Ying-Kui Zhang, Zeng-Jun Tang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
Yanxing Shan, Jiawen Cui, Xinyi Kang, Weichun Tang, Yiling Lu, Ying Gao, Liping Chen
Open Life Sciences.2022; 17(1): 1473. CrossRef - Vitamin D status and levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in newborns born to mothers with endocrine diseases
N. E. Verisokina, L. Ya. Klimov, I. N. Zakharova, A. L. Zaplatnikov, V. V. Zubkov, A. A. Momotova, V. A. Kuryaninova, R. A. Atanesyan, T. V. Zhelezniakova, M. A. Petrosyan, D. V. Bobryshev, D. A. Volkov, Z. A. Magomadova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (19): 9. CrossRef - IL-6 and IL-8: An Overview of Their Roles in Healthy and Pathological Pregnancies
Aleksandra Vilotić, Mirjana Nacka-Aleksić, Andrea Pirković, Žanka Bojić-Trbojević, Dragana Dekanski, Milica Jovanović Krivokuća
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(23): 14574. CrossRef - Higher Muscle Mass Protects Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus from Progression to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yujin Shin, Joon Ho Moon, Tae Jung Oh, Chang Ho Ahn, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 890. CrossRef - Identification of human placenta-derived circular RNAs and autophagy related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in gestational diabetes mellitus
Yindi Bao, Jun Zhang, Yi Liu, Lianzhi Wu, Jing Yang
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Dietary Polyphenols in Pregnancy and Pregnancy-Related Disorders
Mirjana Nacka-Aleksić, Andrea Pirković, Aleksandra Vilotić, Žanka Bojić-Trbojević, Milica Jovanović Krivokuća, Francesca Giampieri, Maurizio Battino, Dragana Dekanski
Nutrients.2022; 14(24): 5246. CrossRef
- Prophylactic administration of metformin reduces gestational diabetes mellitus incidence in the high-risk populations: a meta-analysis
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Progression to Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnant Women with One Abnormal Value in Repeated Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests
- Sunyoung Kang, Min Hyoung Kim, Moon Young Kim, Joon-Seok Hong, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak C. Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):607-614. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0159
- 5,889 View
- 103 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Women with one abnormal value (OAV) in a 100 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) during pregnancy are reported to have an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes. However, there is limited data about whether women with OAV will progress to gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) when the OGTT is repeated.
Methods To identify clinical and metabolic predictors for GDM in women with OAV, we conducted a retrospective study and identified women with OAV in the OGTT done at 24 to 30 weeks gestational age (GA) and repeated the second OGTT between 32 and 34 weeks of GA.
Results Among 137 women with OAV in the initial OGTT, 58 (42.3%) had normal, 40 (29.2%) had OAV and 39 (28.5%) had GDM in the second OGTT. Maternal age, prepregnancy body mass index, weight gain from prepregnancy to the second OGTT, GA at the time of the OGTT, and parity were similar among normal, OAV, and GDM groups. Plasma glucose levels in screening tests were different (151.8±15.7, 155.8±14.6, 162.5±20.3 mg/dL,
P <0.05), but fasting, 1-, 2-, and 3-hour glucose levels in the initial OGTT were not. Compared to women with screen negative, women with untreated OAV had a higher frequency of macrosomia.Conclusion We demonstrated that women with OAV in the initial OGTT significantly progressed to GDM in the second OGTT. Clinical parameters predicting progression to GDM were not found. Repeating the OGTT in women with OAV in the initial test may be helpful to detect GDM progression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies associated with single versus double abnormal values in 100 gr glucose tolerance test
Mohammadali Shahriari, Ali Shahriari, Maryam Khooshideh, Anahita Dehghaninezhad, Arezoo Maleki-Hajiagha, Rana Karimi
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023; 22(2): 1347. CrossRef - One abnormal value or vomiting after oral glucose tolerance test in pregnancy: incidence and impact on maternal-fetal outcomes
Humberto Navarro-Martinez, Juana-Antonia Flores-Le Roux, Gemma Llauradó, Lucia Gortazar, Antonio Payà, Laura Mañé, Juan Pedro-Botet, David Benaiges
Gynecological Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the gut microflora in women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Xuping Wang, Bingfeng Bian, Fuman Du, Chaofeng Xiang, Yu Liu, Na Li, Binhong Duan
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between gestational impaired glucose tolerance and hyperglycemic markers: A prospective study
Ohad Gluck, Hadas Ganer Herman, Nataly Fainstein, Neri Katz, Jacob Bar, Michal Kovo
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2022; 156(1): 82. CrossRef - Association of abnormal-glucose tolerance during pregnancy with exposure to PM2.5 components and sources
Dejian Mai, Chengfang Xu, Weiwei Lin, Dingli Yue, Shaojie Fu, Jianqing Lin, Luan Yuan, Yan Zhao, Yuhong Zhai, Huiying Mai, Xiaoling Zeng, Tingwu Jiang, Xuejiao Li, Jiajia Dai, Boning You, Qin Xiao, Qing Wei, Qiansheng Hu
Environmental Pollution.2022; 292: 118468. CrossRef - Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 140. CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnosis and Glycemic Control
Tae Jung Oh, Hak Chul Jang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(2): 69. CrossRef - Health literacy and diabetes control in pregnant women
Azar Pirdehghan, Mohammad Eslahchi, Farzaneh Esna-Ashari, Shiva Borzouei
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2020; 9(2): 1048. CrossRef
- Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies associated with single versus double abnormal values in 100 gr glucose tolerance test
- Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes in Korean Women with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
- Hee-Sook Kim, Hye-Jung Jang, Jeong-Eun Park, Moon-Young Kim, Sun-Young Ko, Sung-Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(4):316-320. Published online August 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.4.316
- 3,348 View
- 35 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The purpose of this study was to evaluate maternal and neonatal outcomes in Korean women with type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Methods We performed a retrospective survey of 163 pregnancies in women with type 1 diabetes (
n =13) and type 2 diabetes (n =150) treated from 2003 to 2010 at Cheil General Hospital & Women's Healthcare Center, Korea. We compared maternal characteristics as well as maternal and neonatal outcomes between groups.Results Differences in glycosylated hemoglobin between type 1 and type 2 diabetes were not significant. Birth weight (3,501±689.6 g vs. 3,366±531.4 g) and rate of major congenital malformations (7.7% vs. 5.6%) were not significantly different. However, women with type 1 diabetes had higher rates of preeclampsia (38.5% vs. 8.2%,
P =0.006), large for gestational age (LGA; 46.2% vs. 20.4%,P =0.004), macrosomia (38.5% vs. 13.4%,P =0.032), and admission for neonatal care (41.7% vs. 14.8%,P =0.03) than women with type 2 diabetes.Conclusion Maternal and neonatal outcomes for women with type 1 diabetes were poorer than for women with type 2 diabetes, especially preeclampsia, LGA, macrosomia and admission to the neonatal intensive care unit.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Type 2 Diabetes on Women’s Health and Well-being During Their Reproductive Years: A Mixed-methods Systematic Review
Aycan Celik, Rita Forde, Simona Racaru, Angus Forbes, Jackie Sturt
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of the electronic nose in predicting preeclampsia in high-risk pregnancies. Pilot study
Karen Beatriz Méndez Rodríguez, Luis Manuel Ramírez Gómez, Leticia Carrizales Yáñez, Rogelio Flores Ramírez, Omar Ornelas-Rebolledo, Jaime Antonio Borjas-García, Francisco Pérez-Vázquez, Maribel Rodríguez Aguilar
Archives of Medical Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Obstetric and neonatal complications among women with autoimmune disease
Andrew Williams, Katherine Grantz, Indulaxmi Seeni, Candace Robledo, Shanshan Li, Marion Ouidir, Carrie Nobles, Pauline Mendola
Journal of Autoimmunity.2019; 103: 102287. CrossRef - Effects of maternal age, parity and pre-pregnancy body mass index on the glucose challenge test and gestational diabetes mellitus
Adel T. Abu-Heija, Majeda R. Al-Bash, Moza A. Al-Kalbani
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences.2017; 12(4): 338. CrossRef - Deficient Vitamin E Uptake During Development Impairs Neural Tube Closure in Mice Lacking Lipoprotein Receptor SR-BI
Nicolás Santander, Carlos Lizama, María José Parga, Alonso Quiroz, Druso Pérez, Guadalupe Echeverría, Lorena Ulloa, Verónica Palma, Attilio Rigotti, Dolores Busso
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Impact of Type 2 Diabetes on Women’s Health and Well-being During Their Reproductive Years: A Mixed-methods Systematic Review
- Pregnancy Outcome in Korean Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosed by the Carpenter-Coustan Criteria.
- Hak Chul Jang, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim, Hong Kyu Lee, Moon Young Kim, Jae Hyug Yang, Son Moon Shin
- Korean Diabetes J. 2004;28(2):122-130. Published online April 1, 2004
- 1,164 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The American Diabetes Association recently proposed the Carpenter-Coustan criteria for the diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus(GDM) based on the results of the Toronto Tri-Hospital Study. The prevalence of GDM in Korean women increased, on average, by 60% when the Carpenter-Coustan criteria were applied. However, the pregnancy outcome of Korean women with GDM with regard to the Carpenter-Coustan criteria tremains to be reported. The pregnancy outcomes of those Korean women with GDM by the Carpenter- Coustan criteria, but not by the NDDG criteria were assessed. METHODS: In this study, a total of 2776 pregnant women underwent universal screening for GDM, between January 1993 and December 1994, as recommended by the Third International Workshop-Conference on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus with minor modifications. The primary pregnancy outcomes were preeclampsia, premature delivery, delivery by C-section, birth weight and LGA infants. RESULTS: Of the 2776 women, 656 screened-positive for GDM. Of these, 37 and 74 had GDM by the Carpenter-Coustan and NDDG criteria, respectively. With increasing glucose intolerance, there was a stepwise increase in premature deliveries, deliveries by C-section and preeclampsia from those screening negative to GDM by the NDDG criteria, with a similar trend for the frequency of LGA infants. The LGA infant screening-negative and positive were 13.5 and 16.1%, but those with a normal glucose tolerance were 27.0 and 33.8% in those screening positive to GDM by the Carpenter-Coustan and NDDG criteria, respectively(P<0.001). CONCLUSION: Our study demonstrated that increasing glucose tolerance was associated with increasing frequencies of adverse pregnancy outcomes in Korean women. The maternally complicated and LGA infants were significantly higher in women with GDM by the Carpenter-Coustan criteria. Thus the Carpenter- Coustan criteria are recommended for the diagnosis of GDM in Korean Women.
- Effect of Self-monitoring of Blood Glucose on Pregnancy Outcome in Women with Mild Gestational Diabetes.
- Hak Chul Jang, Jeong Eun Park, Chang Hoon Yim, Ho Yeun Chung, Ki Ok Han, Hyun Koo Yoon, In Kwon Han, Moon Young Kim, Jae Hyug Yang, Mi Jung Kim, Sun Young Ko, Yeon Kyung Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2001;25(1):93-102. Published online February 1, 2001
- 1,340 View
- 28 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and intensive therapy with insulin demonstrated to have a positive effects in the reduction of the neonatal complications in women with gestational diabetes (GDM). However the utility of SMBG in the mild GDM who does not requiring insulin has not been formally reported. Therefore, to evaluate the effectiveness of SMBG in the management of mild GDM, we compared the pregnancy outcome and the postpartum glucose tolerance of women who monitored their glycemic control by SMBG to those of women who monitored by laboratory glucose test at each office visit during pregnancy. METHODS: We studied 185 women diagnosed as a GDM by NDDG criteria and their fasting glucose concentration < 5.8 mM. All subjects had singleton pregnancy,and no medical diseases that may affect fetal growth, and were certain of gestational age by early ultrasonography. They were treated with an identical GDM management protocol except glucose monitoring. One hundred five women were monitored by laboratory glucose test at each office visit (office group) and 80 women were monitored by SMBG (SMBG group). Pregnancy outcome including rates of cesarian section, obstetric complication, LGA infant and glucose tolerance status at postpartum were compared between two groups. RESULTS: The age, height, prepregnancy weight, weight at delivery and parity were not significantly different between the two groups. Fasting, 1-h, 2-h glucose concentration during the diagnostic test of GDM in SMBG group were similar to those of office group. However, 3-h glucose concentration of office group was 0.3 mM higher than that of SMBG group. The rate of primary cesarian section, preterm labor and pregnancy-induced hypertension of SMBG group were similar to those of office group. The mean postprandial 2-h glucose concentration of office group measured at each office was 0.5 mM higher than that of SMBG group. Although 5% of office group were treated with insulin, 24% of SMBG group were requiring insulin therapy. The birth weight and LGA infant rate of office group were 3403 432 g and 28%, those were heavier and higher than those of SMBG group (3169 447 g, 13.8%). The 90% of office group and 84% of SMBG group were performed 75 g oral glucose tolerance test at postpartum 6-8 weeks. There was no significant difference in rates of diabetes and IGT between office and SMBG group (9.5%, 11.6%; 7.5%, 9.0% respectively). CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrated that SMBG is very seful in early detection of maternal hyperglycemia and lowing the postprandial glucose, as well as reducing the rate of LGA infants in women with mild GDM.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





