
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Reproductive Life Span and Severe Hypoglycemia Risk in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Soyeon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Dong Jin Kwon, Youn-Jee Chung, Jeong Namkung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):578-591. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0135

- 5,976 View
- 230 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Estrogen promotes glucose homeostasis, enhances insulin sensitivity, and maintains counterregulatory responses in recurrent hypoglycemia in women of reproductive age. Postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) might be more vulnerable to severe hypoglycemia (SH) events. However, the relationship between reproductive factors and SH occurrence in T2DM remains unelucidated.
Methods
This study included data on 181,263 women with postmenopausal T2DM who participated in a national health screening program from January 1 to December 31, 2009, obtained using the Korean National Health Insurance System database. Outcome data were obtained until December 31, 2018. Associations between reproductive factors and SH incidence were assessed using Cox proportional hazards models.
Results
During the mean follow-up of 7.9 years, 11,279 (6.22%) postmenopausal women with T2DM experienced SH episodes. A longer reproductive life span (RLS) (≥40 years) was associated with a lower SH risk compared to a shorter RLS (<30 years) (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.74; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.69 to 0.80; P for trend <0.001) after multivariable adjustment. SH risk decreased with every 5-year increment of RLS (with <30 years as a reference [adjusted HR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.86 to 0.95; P=0.0001 for 30−34 years], [adjusted HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.76 to 0.84; P<0.001 for 35−39 years], [adjusted HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.68 to 0.81; P<0.001 for ≥40 years]). The use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) was associated with a lower SH risk than HRT nonuse.
Conclusion
Extended exposure to endogenous ovarian hormone during lifetime may decrease the number of SH events in women with T2DM after menopause. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between serum copper level and reproductive health of Women in the United States: a cross-sectional study
Yi Yuan, Tong-Yu Peng, Guang-Yuan Yu, Zhao Zou, Meng-Ze Wu, Ruofei Zhu, Shuang Wu, Zi Lv, Su-Xin Luo
International Journal of Environmental Health Research.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Reproductive Lifespan and Motor Progression of Parkinson’s Disease
Ruwei Ou, Qianqian Wei, Yanbing Hou, Lingyu Zhang, Kuncheng Liu, Junyu Lin, Tianmi Yang, Jing Yang, Zheng Jiang, Wei Song, Bei Cao, Huifang Shang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(20): 6163. CrossRef - Menopause and development of Alzheimer’s disease: Roles of neural glucose metabolism and Wnt signaling
Paulina Villaseca, Pedro Cisternas, Nibaldo C. Inestrosa
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between serum copper level and reproductive health of Women in the United States: a cross-sectional study
- Drug/Regimen
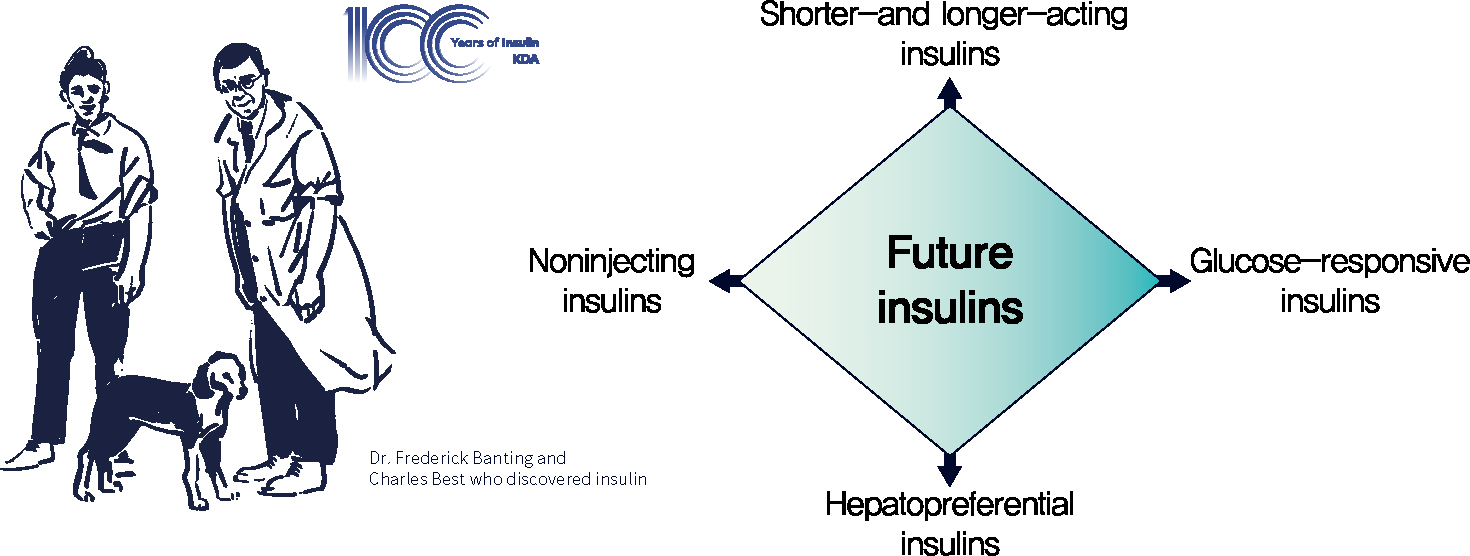
- A Century of Progress in Diabetes Care with Insulin: A History of Innovations and Foundation for the Future
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):629-640. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0163
- 8,582 View
- 454 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- The year 2021 marks the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin, which has greatly changed the lives of people with diabetes and become a cornerstone of advances in medical science. A rapid bench-to-bedside application of the lifesaving pancreatic extract and its immediate commercialization was the result of a promising idea, positive drive, perseverance, and collaboration of Banting and colleagues. As one of the very few proteins isolated in a pure form at that time, insulin also played a key role in the development of important methodologies and in the beginning of various fields of modern science. Since its discovery, insulin has evolved continuously to optimize the care of people with diabetes. Since the 1980s, recombinant DNA technology has been employed to engineer insulin analogs by modifying their amino acid sequence, which has resulted in the production of insulins with various profiles that are currently used. However, unmet needs in insulin treatment still exist, and several forms of future insulins are under development. In this review, we discuss the past, present, and future of insulin, including a history of ceaseless innovations and collective intelligence. We believe that this story will be a solid foundation and an unerring guide for the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Antidiabetic Potential of Phytochemicals Found in Vernonia amygdalina
Archna Talwar, Neha Chakraborty, Manaal Zahera, Shruti Anand, Irshad Ahmad, Samra Siddiqui, Avni Nayyar, Ashanul Haque, Mohd Saeed, Ponnurengam Malliappan Sivakumar
Journal of Chemistry.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Insulin’s Legacy: A Century of Breakthroughs and Innovation
Somar Hadid, Emily Zhang, William H. Frishman, Erika Brutsaert
Cardiology in Review.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation on Quality Characteristics and Antidiabetic Properties of Mulberry Leaf Fu Brick Tea
Yuanyuan Shao, Ling Lin, Wei Xu, Zhihua Gong, Jinfeng Li, Jun Zhang, Xinpei Yan, Zhonghua Liu, Wenjun Xiao, Miguel Rebollo-Hernanz
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Prandial Insulins: A Person-Centered Choice
Bhawna Attri, Lakshmi Nagendra, Deep Dutta, Sahana Shetty, Shehla Shaikh, Sanjay Kalra, Saptarshi Bhattacharya
Current Diabetes Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes With Once‐Weekly Insulin Icodec Versus Once‐Daily Insulin Glargine U100 in Insulin‐Naïve and Previously Insulin‐Treated Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta‐Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials
Mushood Ahmed, Aimen Shafiq, Hira Javaid, Hritvik Jain, Abdulqadir J. Nashwan, Qura Tul‐Ain, Jawad Basit
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Konjac Glucomannan: An Emerging Specialty Medical Food to Aid in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yimeng Fang, Jiahui Ma, Pengyu Lei, Lei Wang, Junying Qu, Jing Zhao, Fan Liu, Xiaoqing Yan, Wei Wu, Libo Jin, Hao Ji, Da Sun
Foods.2023; 12(2): 363. CrossRef - Glucose-Responsive Silk Fibroin Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery of Insulin
Guohongfang Tan, Fujian Jiang, Tianshuo Jia, Zhenzhen Qi, Tieling Xing, Subhas C. Kundu, Shenzhou Lu
Biomimetics.2023; 8(1): 50. CrossRef - Network pharmacology-based screening of the active ingredients and mechanisms of Cymbaria daurica against diabetes mellitus
Ruyu Shi, Dongxue Chen, Mingyue Ji, Baochang Zhou, Ziyan Zhang, Chunhong Zhang, Minhui Li
Food Science and Human Wellness.2023; 12(6): 2001. CrossRef - Type 1 Diabetes Overview and Perioperative Management
Grace B. Nelson, Kathryn M. Sumpter
Orthopedic Clinics of North America.2023; 54(3): 287. CrossRef - In Vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): Definitions, Opportunities, and Challenges
Yi-Heng P. Job Zhang, Zhiguang Zhu, Chun You, Lingling Zhang, Kuanqing Liu
Synthetic Biology and Engineering.2023; 1(2): 1. CrossRef - The effect of insulin analogs in people with type 1 diabetes at increased risk of severe hypoglycemia
Sofie Broeng-Mikkelgaard, Julie Maria Bøggild Brøsen, Peter Lommer Kristensen, Birger Thorsteinsson, Ulrik Pedersen-Bjergaard
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Biologic Medications: An Overview of Important Therapies in Children and Adolescents
Melissa S. Tesher
Pediatric Annals.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Sixty-Year Research and Development of Trichosanthin, a Ribosome-Inactivating Protein
Jia-Qi Lu, Kam-Bo Wong, Pang-Chui Shaw
Toxins.2022; 14(3): 178. CrossRef - Extra-Glycemic Effects of Anti-Diabetic Medications: Two Birds with One Stone?
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 415. CrossRef - Les biothérapies en pédiatrie
R. Duclaux-Loras, A. Belot
Perfectionnement en Pédiatrie.2022; 5(3): 193. CrossRef - Dynamic Detection of HbA1c Using a Silicon Nanowire Field Effect Tube Biosensor
Hang Chen, Lijuan Deng, Jialin Sun, Hang Li, Xiaoping Zhu, Tong Wang, Yanfeng Jiang
Biosensors.2022; 12(11): 916. CrossRef
- Antidiabetic Potential of Phytochemicals Found in Vernonia amygdalina
- Clinical Characteristics of Type 2 Diabetes Patients according to Family History of Diabetes
- Seung Uk Jeong, Dong Gu Kang, Dae Ho Lee, Kang Woo Lee, Dong-Mee Lim, Byung Joon Kim, Keun-Yong Park, Hyoun-Jung Chin, Gwanpyo Koh
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(4):222-228. Published online August 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.4.222
- 3,496 View
- 26 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has a strong genetic component, and its prevalence is notably increased in the family members of T2DM patients. However, there are few studies about the family history of T2DM. We carried out this study to assess the influences of family history on clinical characteristics in T2DM patients.
Methods This is a cross-sectional study involving 651 T2DM patients. Patient history and physical examination were performed and fasting blood was taken. If any first degree relative was diabetic, a family history of diabetes was considered to exist.
Results Among the total 621 patients, 38.4% had a family history of diabetes. Patients with a family history had a younger age, higher weight, younger age at diagnosis and higher triglyceride level than did those without a family history. Dyslipidemia medication and metabolic syndrome were more prevalent in familial diabetes. Sex, blood pressure, previous treatment for diabetes, HbA1c, C-peptide, total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol were not different between familial and non-familial diabetes. Upon multiple linear regression analysis, the family history of diabetes remained significantly associated with serum triglyceride level.
Conclusion In T2DM patients with a family history of diabetes, the disease tended to develop earlier. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk factors are more prevalent in familial T2DM than they were in non-familial T2DM. These results support the necessity of earlier screening for diabetes in family members of T2DM patients and more active prevention against cardiovascular disease in T2DM patients with a family history.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- COVID-19-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: Comprehensive Cellular and Molecular Mechanistic Insights
Praise Tatenda Nhau, Mlindeli Gamede, Ntethelelo Sibiya
Pathophysiology.2024; 31(2): 197. CrossRef - Evolutionary algorithm for the optimization of meal intake and insulin administration in patients with type 2 diabetes
Eva Gonzalez-Flo, Elaheh Kheirabadi, Carlos Rodriguez-Caso, Javier Macía
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Cytokines (IL-17 and IL-33), FGF-18, and WNT-5 in the Pathogenesis of Patients with Established Type II Diabetes
Przha Mohammed, Kawa Amin
Journal of Zankoy Sulaimani - Part A.2023; 25(2): 11. CrossRef - Cellular Chitchatting: Exploring the Role of Exosomes as Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Giulia Germena, Laura Cecilia Zelarayán, Rabea Hinkel
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined associations of family history and self-management with age at diagnosis and cardiometabolic risk in 86,931 patients with type 2 diabetes: Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation (JADE) Register from 11 countries
Johnny T. K. Cheung, Eric Lau, Cyrus C. T. Tsui, Edmond L. N. Siu, Naomi K. W. Tse, Nicole Y. L. Hui, Ronald C. W. Ma, Alice P. S. Kong, Amy Fu, Vanessa Lau, Weiping Jia, Wayne H. H. Sheu, Leorino Sobrepena, K. H. Yoon, Alexander T. B. Tan, Yook-Chin Chia
BMC Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Capsaicin, its clinical significance in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy
Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla, Bongani B. Nkambule, Ilenia Cirilli, Fabio Marcheggiani, Sihle E. Mabhida, Khanyisani Ziqubu, Yonela Ntamo, Babalwa Jack, Tawanda M. Nyambuya, Sidney Hanser, Sithandiwe E. Mazibuko-Mbeje
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 153: 113439. CrossRef - Safety profile of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: A brief summary
Annamaria Mascolo, Raffaella Di Napoli, Nunzia Balzano, Donato Cappetta, Konrad Urbanek, Antonella De Angelis, Lucia Scisciola, Irene Di Meo, Maria Giuseppa Sullo, Concetta Rafaniello, Liberata Sportiello
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of triglycerides and waist circumference on insulin resistance and β-cell function in non-diabetic first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes
Fahd Ahmed, Molham AL-Habori, Ebtesam Al-Zabedi, Riyadh Saif-Ali
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Orientin Improves Substrate Utilization and the Expression of Major Genes Involved in Insulin Signaling and Energy Regulation in Cultured Insulin-Resistant Liver Cells
Sithandiwe E. Mazibuko-Mbeje, Sinenhlanhla X. H. Mthembu, Andani Tshiitamune, Ndivhuwo Muvhulawa, Fikile T. Mthiyane, Khanyisani Ziqubu, Christo J. F. Muller, Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla
Molecules.2021; 26(20): 6154. CrossRef - Identification of Pre-Diabetic Biomarkers in the Progression of Diabetes Mellitus
Jae-Ho Lee, Do-Young Kim, Rubee Pantha, Eun-Ho Lee, Jae-Hoon Bae, Eugene Han, Dae-Kyu Song, Taeg Kyu Kwon, Seung-Soon Im
Biomedicines.2021; 10(1): 72. CrossRef - Shared (epi)genomic background connecting neurodegenerative diseases and type 2 diabetes
Valerio Caputo, Andrea Termine, Claudia Strafella, Emiliano Giardina, Raffaella Cascella
World Journal of Diabetes.2020; 11(5): 155. CrossRef - Family history of diabetes in both parents is strongly associated with impaired residual β‐cell function in Japanese type 2 diabetes patients
Minoru Iwata, Yutaka Kamura, Hisae Honoki, Kaori Kobayashi, Manabu Ishiki, Kunimasa Yagi, Yasuo Fukushima, Atsuko Takano, Hiromi Kato, Shihou Murakami, Kiyohiro Higuchi, Chikaaki Kobashi, Kazuhito Fukuda, Yukiko Koshimizu, Kazuyuki Tobe
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2020; 11(3): 564. CrossRef - The relationship between age of onset and risk factors including family history and life style in Korean population with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Jin-Won Noh, Jin Hee Jung, Jeong Eun Park, Jung Hwa Lee, Kang Hee Sim, Jumin Park, Min Hee Kim, Ki-Bong Yoo
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2018; 30(2): 201. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Subjects with Sulfonylurea-Dependent Type 2 Diabetes
Se Hee Min, Soo Heon Kwak, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 509. CrossRef - Nutritional Assessment of Type II Diabetic Patients
El-Sayed H. Bakr
Pakistan Journal of Nutrition.2015; 14(6): 308. CrossRef
- COVID-19-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: Comprehensive Cellular and Molecular Mechanistic Insights
- The Association of Family History of Diabetes and Obesity in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes.
- Wan Sub Shim, Hae Jin Kim, Soo Kyung Kim, Seung Jin Han, Eun Seok Kang, Yu Mie Rhee, Chul Woo Ahn, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong Soo Cha
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(6):540-547. Published online November 1, 2005
- 1,189 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by defects in both insulin secretion and insulin action. Type 2 diabetes has a strong genetic basis, and obesity is also known as a important risk factor for development of diabetes. The relative effects of obesity and family history of diabetes (FHx) to develop diabetes have not been well characterized. The aim of this study was to analyze the relative role of insulin resistance and insulin secretion in the newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients according to the presence of FHx and obesity. METHOD: We evaluated the presence of FHx, fasting and postprandial glucose, C-peptide and insulin in 219 newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients without the history of drug therapy from Jan. 2003 to Oct. 2004. RESULT: The mean age of patients was 54.7+/-10.2(yr) and the mean BMI was 25.5+/-3.0 kg/m2. The patients with FHx develop diabetes earlier than them without FHx. BMI, fasting glucose, postprandial glucose, fasting C-peptide and HOMAIR value were not different between groups. But postprandial C-peptide, fasting insulin, postprandial insulin and HOMAbeta-cell value were significantly lower in patient with FHx than in them without FHx. Interestingly, obese (BMI > or = 25kg/m2) patients with FHx developed diabetes earlier than nonobese (BMI <25kg/m2) patients with FHx. CONCLUSION: Obesity plays an important role in the determination of the earlier onset of diabetes in patients with FHx. Intentional prevention of obesity may be an important means to prevent, at least delay, the onset of diabetes in the subjects with FHx.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





