
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Type 1 Diabetes
- A New Tool to Identify Pediatric Patients with Atypical Diabetes Associated with Gene Polymorphisms
- Sophie Welsch, Antoine Harvengt, Paola Gallo, Manon Martin, Dominique Beckers, Thierry Mouraux, Nicole Seret, Marie-Christine Lebrethon, Raphaël Helaers, Pascal Brouillard, Miikka Vikkula, Philippe A. Lysy
- Received May 26, 2023 Accepted November 25, 2023 Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0166 [Epub ahead of print]
- 863 View
- 55 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
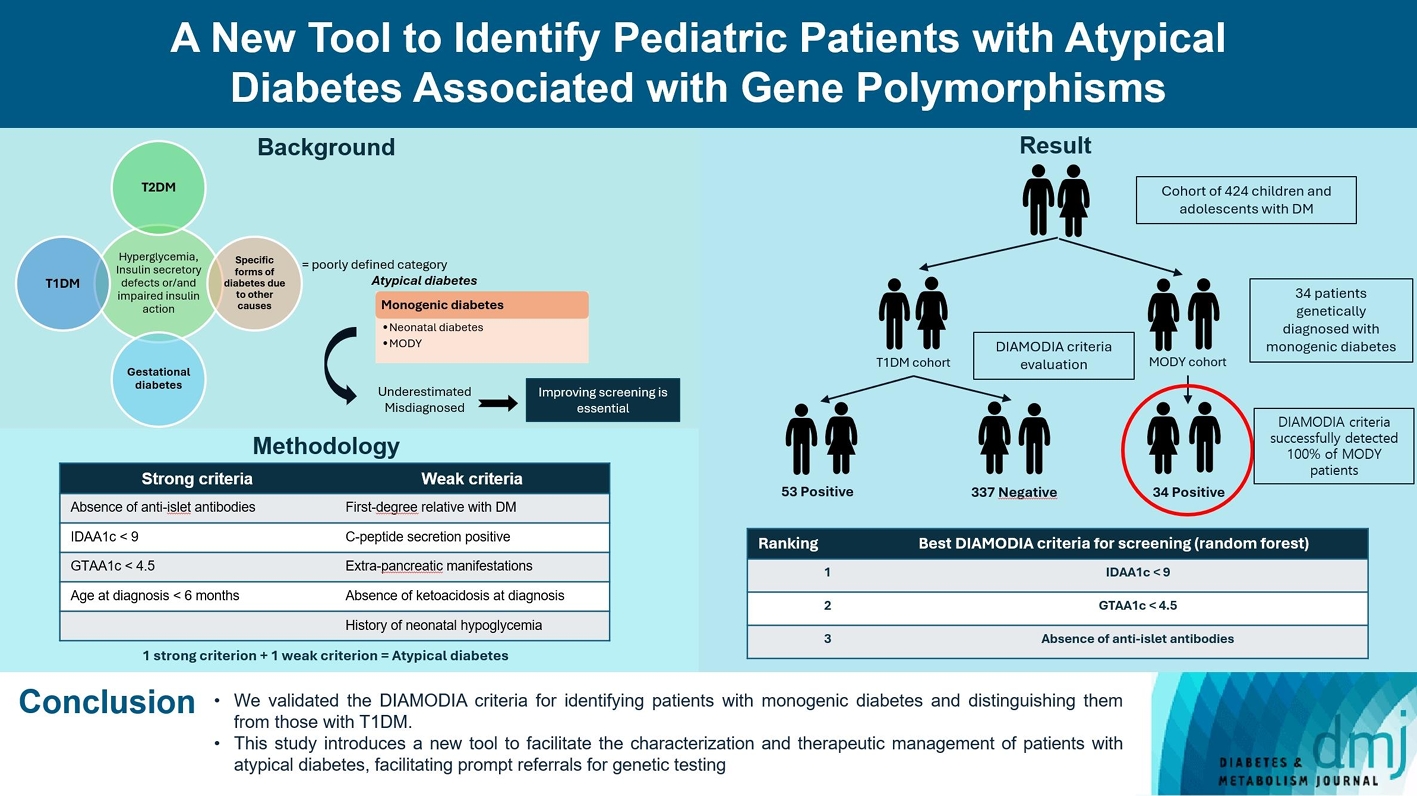
Recent diabetes subclassifications have improved the differentiation between patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus despite several overlapping features, yet without considering genetic forms of diabetes. We sought to facilitate the identification of monogenic diabetes by creating a new tool that we validated in a pediatric maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) cohort.
Methods
We first created the DIAgnose MOnogenic DIAbetes (DIAMODIA) criteria based on the pre-existing, but incomplete, MODY calculator. This new score is composed of four strong and five weak criteria, with patients having to display at least one weak and one strong criterion.
Results
The effectiveness of the DIAMODIA criteria was evaluated in two patient cohorts, the first consisting of patients with confirmed MODY diabetes (n=34) and the second of patients with T1DM (n=390). These DIAMODIA criteria successfully detected 100% of MODY patients. Multiple correspondence analysis performed on the MODY and T1DM cohorts enabled us to differentiate MODY patients from T1DM. The three most relevant variables to distinguish a MODY from T1DM profile were: lower insulin-dose adjusted A1c score ≤9, glycemic target-adjusted A1c score ≤4.5, and absence of three anti-islet cell autoantibodies.
Conclusion
We validated the DIAMODIA criteria, as it effectively identified all monogenic diabetes patients (MODY cohort) and succeeded to differentiate T1DM from MODY patients. The creation of this new and effective tool is likely to facilitate the characterization and therapeutic management of patients with atypical diabetes, and promptly referring them for genetic testing which would markedly improve clinical care and counseling, as well.
- Genetics
- Clinical Characteristics of Diabetes in People with Mitochondrial DNA 3243A>G Mutation in Korea
- Eun Hoo Rho, Sang Ik Baek, Heerah Lee, Moon-Woo Seong, Jong-Hee Chae, Kyong Soo Park, Soo Heon Kwak
- Received March 10, 2023 Accepted July 20, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0078 [Epub ahead of print]
- 534 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
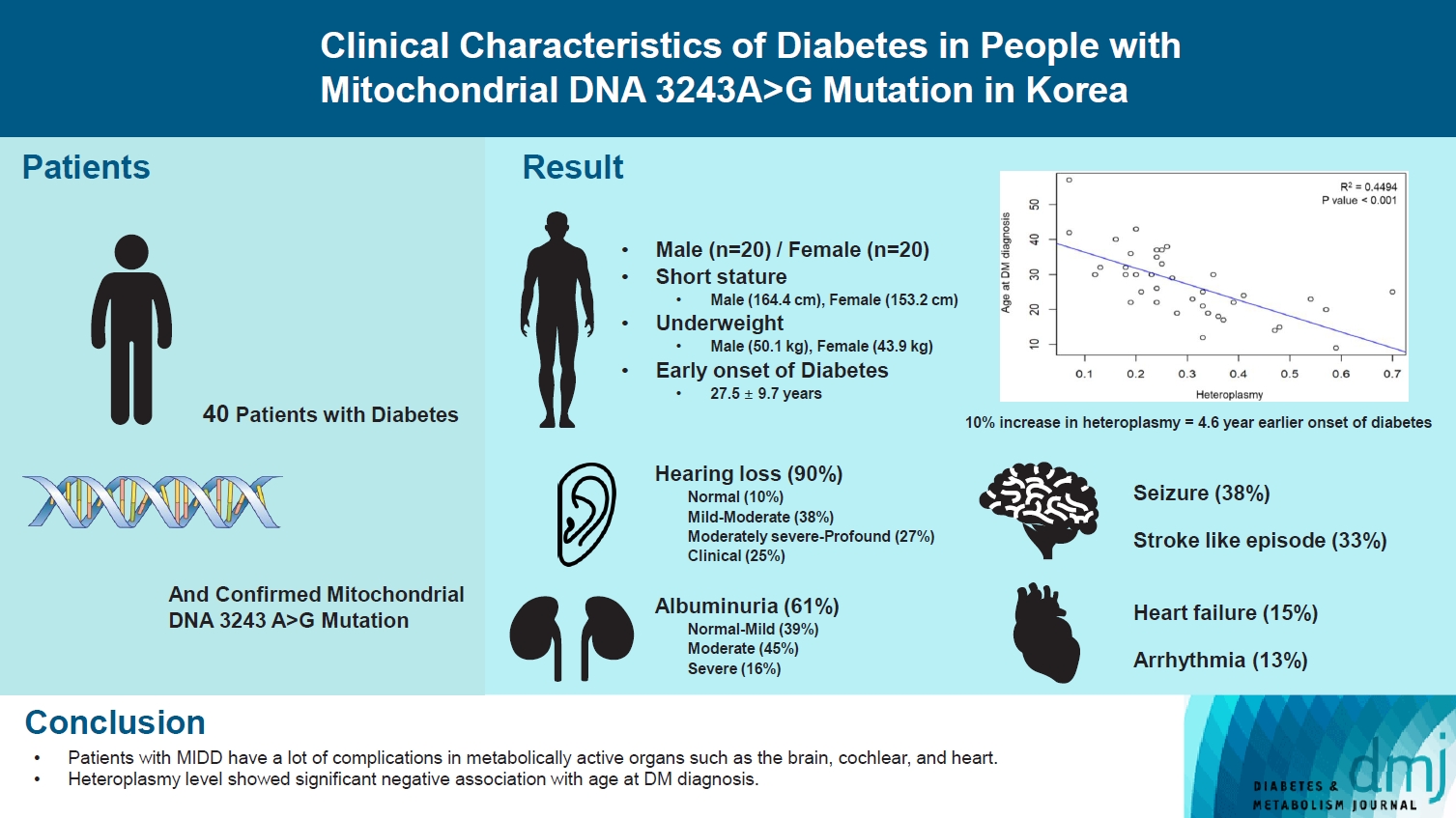
ePub - Maternally inherited diabetes and deafness (MIDD) is a rare mitochondrial disorder primarily resulting from m.3243A>G mutation. The clinical characteristics of MIDD exhibit significant heterogeneity. Our study aims to delineate these characteristics and determine the potential correlation with m.3243A>G heteroplasmy levels. This retrospective, descriptive study encompassed patients with confirmed m.3243A>G mutation and diabetes mellitus at Seoul National University Hospital. Our cohort comprises 40 patients with MIDD, with a mean age at study enrollment of 33.3±12.9 years and an average % of heteroplasmy of 30.0%± 14.6% in the peripheral blood. The most prevalent comorbidity was hearing loss (90%), followed by albuminuria (61%), seizure (38%), and stroke (33%). We observed a significant negative correlation between % of heteroplasmy and age at diabetes diagnosis. These clinical features can aid in the suspicion of MIDD and further consideration of genetic testing for m.3243A>G mutation.
- Complications
- Peripheral Neuropathy Phenotyping in Rat Models of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluating Uptake of the Neurodiab Guidelines and Identifying Future Directions
- Md Jakir Hossain, Michael D. Kendig, Meg E. Letton, Margaret J. Morris, Ria Arnold
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):198-221. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0347
- 5,248 View
- 225 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) affects over half of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, with an urgent need for effective pharmacotherapies. While many rat and mouse models of T2DM exist, the phenotyping of DPN has been challenging with inconsistencies across laboratories. To better characterize DPN in rodents, a consensus guideline was published in 2014 to accelerate the translation of preclinical findings. Here we review DPN phenotyping in rat models of T2DM against the ‘Neurodiab’ criteria to identify uptake of the guidelines and discuss how DPN phenotypes differ between models and according to diabetes duration and sex. A search of PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science databases identified 125 studies, categorised as either diet and/or chemically induced models or transgenic/spontaneous models of T2DM. The use of diet and chemically induced T2DM models has exceeded that of transgenic models in recent years, and the introduction of the Neurodiab guidelines has not appreciably increased the number of studies assessing all key DPN endpoints. Combined high-fat diet and low dose streptozotocin rat models are the most frequently used and well characterised. Overall, we recommend adherence to Neurodiab guidelines for creating better animal models of DPN to accelerate translation and drug development.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SIRT3 alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy by mediating the FoxO3a‐PINK1‐Parkin signaling pathway to activate mitophagy
Jing Yang, Zhuoying Yu, Ye Jiang, Zixian Zhang, Yue Tian, Jie Cai, Min Wei, Yanhan Lyu, Dongsheng Yang, Shixiong Shen, Guo‐Gang Xing, Min Li
CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Compound Qiying Granules alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis
Yan Hu, Chen Chen, Zhengting Liang, Tao Liu, Xiaoling Hu, Guanying Wang, Jinxia Hu, Xiaolin Xie, Zhiyan Liu
Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HCV affects KATP channels through GnT-IVa-mediated N-glycosylation of GLUT2 on the surface of pancreatic β-cells leading to impaired insulin secretion
Ben Niu, Lijing Ma, Lixuan Yao, Yating Zhang, Heng Su
Endocrine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multimodal Comparison of Diabetic Neuropathy in Aged Streptozotocin-Treated Sprague–Dawley and Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats
Annalisa Canta, Valentina A. Carozzi, Alessia Chiorazzi, Cristina Meregalli, Norberto Oggioni, Virginia Rodriguez-Menendez, Barbara Sala, Roberto Cosimo Melcangi, Silvia Giatti, Raffaella Lombardi, Roberto Bianchi, Paola Marmiroli, Guido Cavaletti
Biomedicines.2022; 11(1): 20. CrossRef
- SIRT3 alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy by mediating the FoxO3a‐PINK1‐Parkin signaling pathway to activate mitophagy
- Basic Research
- Sulforaphane Ameliorates Diabetes-Induced Renal Fibrosis through Epigenetic Up-Regulation of BMP-7
- Lili Kong, Hongyue Wang, Chenhao Li, Huiyan Cheng, Yan Cui, Li Liu, Ying Zhao
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):909-920. Published online June 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0168
- 5,443 View
- 141 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
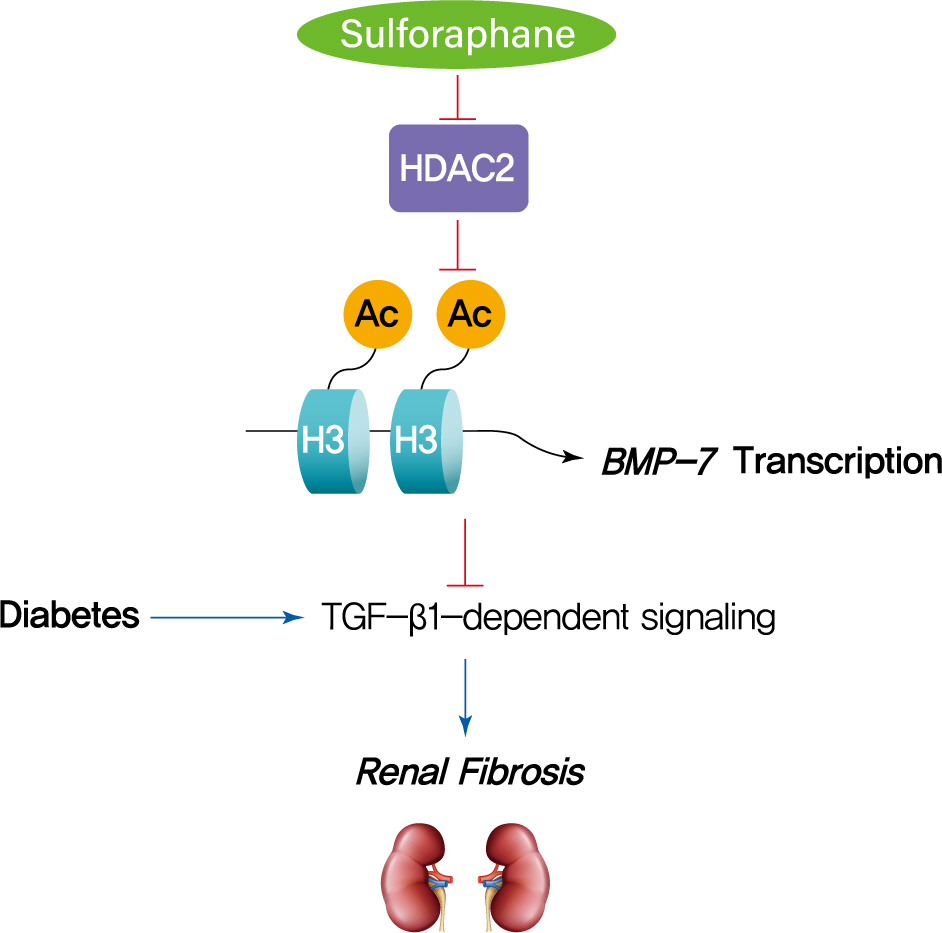
The dietary agent sulforaphane (SFN) has been reported to reduce diabetes-induced renal fibrosis, as well as inhibit histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity. Bone morphologic protein 7 (BMP-7) has been shown to reduce renal fibrosis induced by transforming growth factor-beta1. The aim of this study was to investigate the epigenetic effect of SFN on BMP-7 expression in diabetes-induced renal fibrosis.
Methods
Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice and age-matched controls were subcutaneously injected with SFN or vehicle for 4 months to measure the in vivo effects of SFN on the kidneys. The human renal proximal tubular (HK11) cell line was used to mimic diabetic conditions in vitro. HK11 cells were transfected to over-express HDAC2 and treated with high glucose/palmitate (HG/Pal) to explore the epigenetic modulation of BMP-7 in SFN-mediated protection against HG/Pal-induced renal fibrosis.
Results
SFN significantly attenuated diabetes-induced renal fibrosis in vivo. Among all of the HDACs we detected, HDAC2 activity was markedly elevated in the STZ-induced diabetic kidneys and HG/Pal-treated HK11 cells. SFN inhibited the diabetes-induced increase in HDAC2 activity which was associated with histone acetylation and transcriptional activation of the BMP-7 promoter. HDAC2 over-expression reduced BMP-7 expression and abolished the SFN-mediated protection against HG/Pal-induced fibrosis in vitro.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that the HDAC inhibitor SFN protects against diabetes-induced renal fibrosis through epigenetic up-regulation of BMP-7. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sulforaphane reduces adipose tissue fibrosis via promoting M2 macrophages polarization in HFD fed-mice
Zhenzhen Zhang, Huali Chen, Cheng Pan, Rui Li, Wangsheng Zhao, Tianzeng Song
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119626. CrossRef - Potential of Plant-Derived Compounds in Preventing and Reversing Organ Fibrosis and the Underlying Mechanisms
Patrícia dos Santos Azeredo, Daping Fan, E. Angela Murphy, Wayne E. Carver
Cells.2024; 13(5): 421. CrossRef - Beneficial role of broccoli and its active ingredient, sulforaphane in the treatment of diabetes
Aminu Mohammed, Hafsat Abdullahi Mohammed
Phytomedicine Plus.2023; 3(2): 100431. CrossRef - The Role of Histone Modifications in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Christodoula Kourtidou, Konstantinos Tziomalos
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(6): 6007. CrossRef - Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of NRF2 in Kidney Injury and Diseases
Da-Wei Lin, Yung-Chien Hsu, Cheng-Chih Chang, Ching-Chuan Hsieh, Chun-Liang Lin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6053. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Sulforaphane on Diabetes and Its Complications via Both Nrf2-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms
Minhyuk Kim, Joo Young Lee
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sulforaphane exhibits potent renoprotective effects in preclinical models of kidney diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Elisa B. Monteiro, Matheus Ajackson, Milena B. Stockler-Pinto, Fitsum Guebre-Egziabher, Julio B. Daleprane, Christophe O. Soulage
Life Sciences.2023; 322: 121664. CrossRef - Integrated single-cell RNA-seq analysis revealed podocyte injury through activation of the BMP7/AMPK/mTOR mediated autophagy pathway
Hongzhou Lin, Huihui Chen, Rengcheng Qian, Guoqi Tang, Yinjuan Ding, Yalan Jiang, Congde Chen, Dexuan Wang, Maoping Chu, Xiaoling Guo
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2023; 382: 110559. CrossRef - Underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of genistein in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and related complications
Tao Jiang, Yuhe Dong, Wanying Zhu, Tong Wu, Linyan Chen, Yuantong Cao, Xi Yu, Ye Peng, Ling Wang, Ying Xiao, Tian Zhong
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Sulforaphane: A nutraceutical against diabetes-related complications
Sinenhlanhla X.H. Mthembu, Sithandiwe E. Mazibuko-Mbeje, Marakiya T. Moetlediwa, Ndivhuwo Muvhulawa, Sonia Silvestri, Patrick Orlando, Bongani B. Nkambule, Christo J.F. Muller, Duduzile Ndwandwe, Albertus K. Basson, Luca Tiano, Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla
Pharmacological Research.2023; 196: 106918. CrossRef - Nrf2/HO-1 as a therapeutic target in renal fibrosis
Emad H.M. Hassanein, Islam M. Ibrahim, Esraa K. Abd-alhameed, Zeina W. Sharawi, Fatima A. Jaber, Hanan S. Althagafy
Life Sciences.2023; 334: 122209. CrossRef - A mechanistic overview of sulforaphane and its derivatives application in diabetes and its complications
Neda Mohamadi, Vafa Baradaran Rahimi, Mohammad Reza Fadaei, Fatemeh Sharifi, Vahid Reza Askari
Inflammopharmacology.2023; 31(6): 2885. CrossRef - The HDAC2/SP1/miR-205 feedback loop contributes to tubular epithelial cell extracellular matrix production in diabetic kidney disease
Zongji Zheng, Shuting Zhang, Jiaqi Chen, Meina Zou, Yanlin Yang, Wen Lu, Shijing Ren, Xiangyu Wang, Wenhui Dong, Zikun Zhang, Ling Wang, Meiping Guan, Gladys L.Y. Cheing, Yaoming Xue, Yijie Jia
Clinical Science.2022; 136(3): 223. CrossRef - BMP-7 Upregulates Id2 Through the MAPK Signaling Pathway to Improve Diabetic Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis and the Intervention of Oxymatrine
Yawen Xiao, Dan Liang, Zhiyang Li, Zhaowei Feng, Zhiping Yuan, Fan Zhang, Yuanyuan Wang, Yuxia Zhou, Mingjun Shi, Lingling Liu, Ying Xiao, Bing Guo
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HDAC1 Promotes Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by
Inhibiting BMP-7 Transcription Through Histone Deacetylation
Chun Ouyang, Lei Huang, Xiaoqiang Ye, Mingming Ren, Zhen Han
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(10): 660. CrossRef - Class IIa histone deacetylase inhibition ameliorates acute kidney injury by suppressing renal tubular cell apoptosis and enhancing autophagy and proliferation
Jialu Li, Chao Yu, Fengchen Shen, Binbin Cui, Na Liu, Shougang Zhuang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of histone deacetylases and inhibitors in renal fibrosis progression
Jiayu Wang, Jiaxing Li, Xin Zhang, Min Zhang, Xiaopeng Hu, Hang Yin
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The improvement of sulforaphane in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and related complications: A review
Mengjiao Wang, Min Chen, Rui Guo, Yangyang Ding, Haihui Zhang, Yuanqing He
Trends in Food Science & Technology.2022; 129: 397. CrossRef - Defining therapeutic targets for renal fibrosis: Exploiting the biology of pathogenesis
Hao Yan, Jiangxin Xu, Zhifei Xu, Bo Yang, Peihua Luo, Qiaojun He
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 143: 112115. CrossRef
- Sulforaphane reduces adipose tissue fibrosis via promoting M2 macrophages polarization in HFD fed-mice
- Genetics
- The rs2304256 Polymorphism in TYK2 Gene Is Associated with Protection for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Felipe Mateus Pellenz, Cristine Dieter, Guilherme Coutinho Kullmann Duarte, Luís Henrique Canani, Bianca Marmontel de Souza, Daisy Crispim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):899-908. Published online May 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0194
- 4,773 View
- 157 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
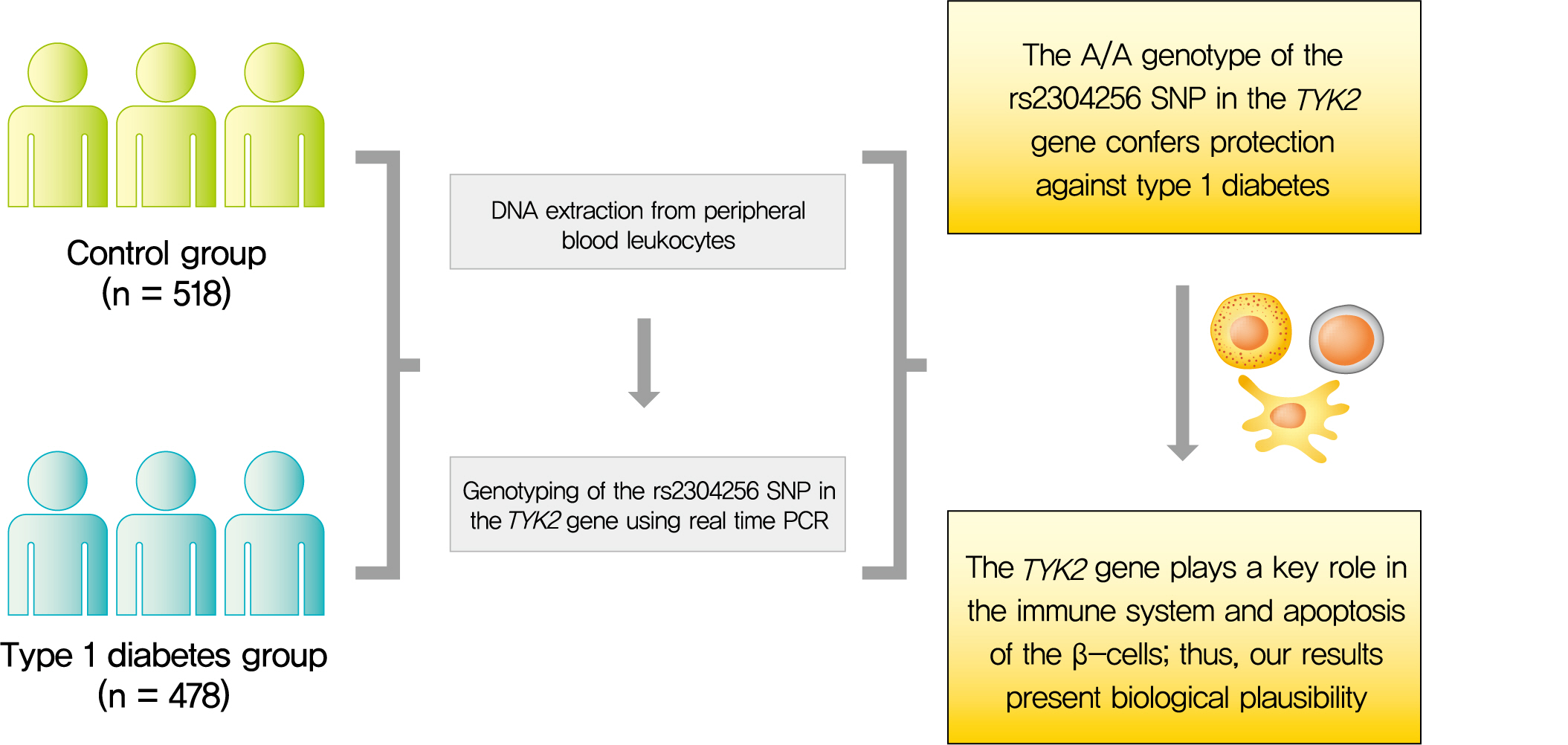
Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) is a candidate gene for type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) since it plays an important role in regulating apoptotic and pro-inflammatory pathways in pancreatic β-cells through modulation of the type I interferon signaling pathway. The rs2304256 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in TYK2 gene has been associated with protection for different autoimmune diseases. However, to date, only two studies have evaluated the association between this SNP and T1DM, with discordant results. This study thus aimed to investigate the association between the TYK2 rs2304256 SNP and T1DM in a Southern Brazilian population.
Methods
This case-control study comprised 478 patients with T1DM and 518 non-diabetic subjects. The rs2304256 (C/A) SNP was genotyped by real-time polymerase chain reaction technique using TaqMan minor groove binder (MGB) probes.
Results
Genotype and allele frequencies of the rs2304256 SNP differed between T1DM patients and non-diabetic subjects (P<0.0001 and P=0.001, respectively). Furthermore, the A allele was associated with protection against T1DM under recessive (odds ratio [OR], 0.482; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.288 to 0.806) and additive (OR, 0.470; 95% CI, 0.278 to 0.794) inheritance models, adjusting for human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DR/DQ genotypes, gender, and ethnicity.
Conclusion
The A/A genotype of TYK2 rs2304256 SNP is associated with protection against T1DM in a Southern Brazilian population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of genetic variants within TYK2 with pulmonary tuberculosis among Chinese population
Mingwu Zhang, Zhengwei Liu, Yelei Zhu, Kunyang Wu, Lin Zhou, Ying Peng, Junhang Pan, Bin Chen, Xiaomeng Wang, Songhua Chen
Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Host genetic variants associated with COVID-19 reconsidered in a Slovak cohort
Maria Skerenova, Michal Cibulka, Zuzana Dankova, Veronika Holubekova, Zuzana Kolkova, Vincent Lucansky, Dana Dvorska, Andrea Kapinova, Michaela Krivosova, Martin Petras, Eva Baranovicova, Ivana Baranova, Elena Novakova, Peter Liptak, Peter Banovcin, Anna
Advances in Medical Sciences.2024; 69(1): 198. CrossRef - Cross-Domain Text Mining of Pathophysiological Processes Associated with Diabetic Kidney Disease
Krutika Patidar, Jennifer H. Deng, Cassie S. Mitchell, Ashlee N. Ford Versypt
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(8): 4503. CrossRef
- Associations of genetic variants within TYK2 with pulmonary tuberculosis among Chinese population
- Genetics
- Association of Combined TCF7L2 and KCNQ1 Gene Polymorphisms with Diabetic Micro- and Macrovascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Rujikorn Rattanatham, Nongnuch Settasatian, Nantarat Komanasin, Upa Kukongviriyapan, Kittisak Sawanyawisuth, Phongsak Intharaphet, Vichai Senthong, Chatri Settasatian
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):578-593. Published online March 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0101
- 5,634 View
- 147 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
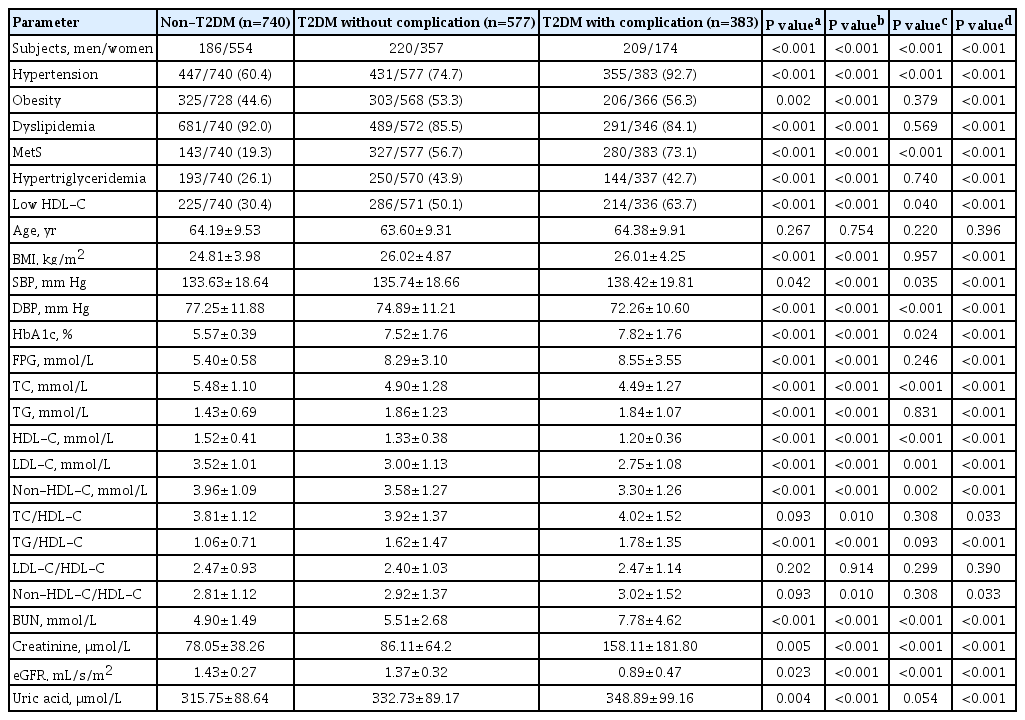
Vascular complications are the major morbid consequences of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2), potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 1 (KCNQ1), and inwardly-rectifying potassium channel, subfamily J, member 11 gene (KCNJ11) are common T2DM susceptibility genes in various populations. However, the associations between polymorphisms in these genes and diabetic complications are controversial. This study aimed to investigate the effects of combined gene-polymorphisms within TCF7L2, KCNQ1, and KCNJ11 on vascular complications in Thai subjects with T2DM.
Methods
We conducted a case-control study comprising 960 T2DM patients and 740 non-diabetes controls. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in TCF7L2, KCNQ1, and KCNJ11 were genotyped and evaluated for their association with diabetic vascular complications.
Results
The gene variants TCF7L2 rs290487-T, KCNQ1 rs2237892-C, and KCNQ1 rs2237897-C were associated with increased risk of T2DM. TCF7L2 rs7903146-C, TCF7L2 rs290487-C, KCNQ1 rs2237892-T, and KCNQ1 rs2237897-T revealed an association with hypertension. The specific combination of risk-alleles that have effects on T2DM and hypertension, TCF7L2 rs7903146-C, KCNQ1 rs2237892-C, and KCNQ1 rs2237897-T, as genetic risk score (GRS), pronounced significant association with coronary artery disease (CAD), cumulative nephropathy and CAD, and cumulative microvascular and macrovascular complications (respective odds ratios [ORs] with 95% confidence interval [95% CI], comparing between GRS 2–3 and GRS 5–6, were 7.31 [2.03 to 26.35], 3.92 [1.75 to 8.76], and 2.33 [1.13 to 4.79]).
Conclusion
This study demonstrated, for the first time, the effect conferred by specific combined genetic variants in TCF7L2 and KCNQ1 on diabetic vascular complications, predominantly with nephropathy and CAD. Such a specific pattern of gene variant combination may implicate in the progression of T2DM and life-threatening vascular complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genetic Risk Scores Identify People at High Risk of Developing Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review
Aleena Shujaat Ali, Cecilia Pham, Grant Morahan, Elif Ilhan Ekinci
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(5): 1189. CrossRef - Saudi Community-Based Screening Study on Genetic Variants in β-Cell Dysfunction and Its Role in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Amal F. Alshammary, Malak Mohammed Al-Hakeem, Imran Ali Khan
Genes.2023; 14(4): 924. CrossRef - Association between KCNJ11 E23K polymorphism and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A global meta-analysis
Yaxuan Ren, Wenfei Zhu, Jikang Shi, Aiyu Shao, Yi Cheng, Yawen Liu
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(5): 108170. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef - Multiple Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Testing Improves the Prediction of Diabetic Retinopathy Risk with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yu-Ting Hsiao, Feng-Chih Shen, Shao-Wen Weng, Pei-Wen Wang, Yung-Jen Chen, Jong-Jer Lee
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(8): 689. CrossRef - Oxidative Stress Genes in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: Association with Diabetic Kidney Disease
Athanasios Roumeliotis, Stefanos Roumeliotis, Fotis Tsetsos, Marianthi Georgitsi, Panagiotis I. Georgianos, Aikaterini Stamou, Anna Vasilakou, Kalliopi Kotsa, Xanthippi Tsekmekidou, Peristera Paschou, Stylianos Panagoutsos, Vassilios Liakopoulos, Elena Az
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Analysis of the association of polymorphisms of genes markers functions of endothelium and vascular-plate hemostasis with development of diabetic foot syndrome
N. I. Troitskaya, K. G. Shapovalov, V. A. Mudrov
Acta Biomedica Scientifica.2021; 6(4): 18. CrossRef
- Genetic Risk Scores Identify People at High Risk of Developing Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review
- Genetics
- Update on Monogenic Diabetes in Korea
- Ye Seul Yang, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):627-639. Published online October 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0214
- 6,646 View
- 243 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
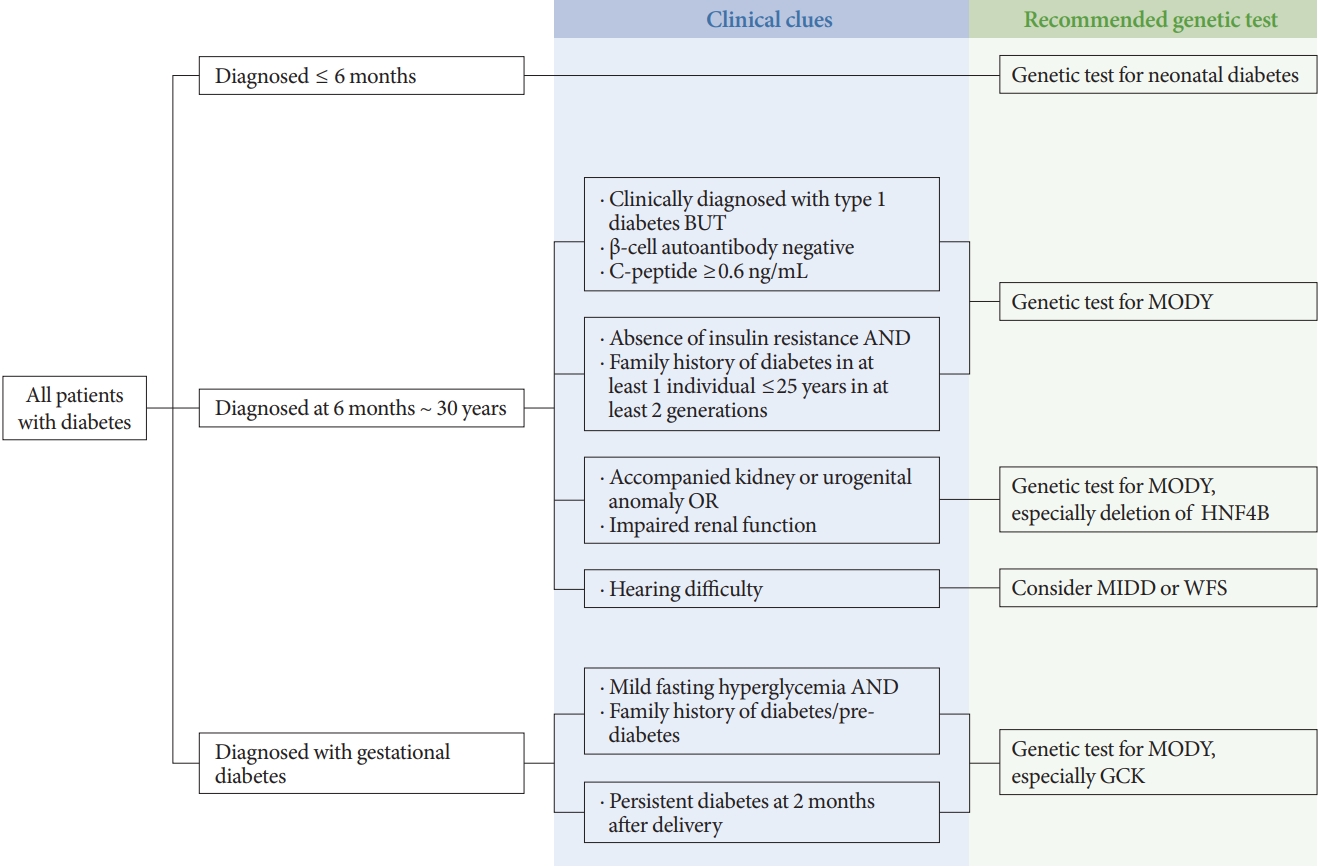
ePub - Monogenic diabetes, including maturity-onset diabetes of the young, neonatal diabetes, and other rare forms of diabetes, results from a single gene mutation. It has been estimated to represent around 1% to 6% of all diabetes. With the advances in genome sequencing technology, it is possible to diagnose more monogenic diabetes cases than ever before. In Korea, 11 studies have identified several monogenic diabetes cases, using Sanger sequencing and whole exome sequencing since 2001. The recent largest study, using targeted exome panel sequencing, found a molecular diagnosis rate of 21.1% for monogenic diabetes in clinically suspected patients. Mutations in glucokinase (GCK), hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α (HNF1A), and HNF4A were most commonly found. Genetic diagnosis of monogenic diabetes is important as it determines the therapeutic approach required for patients and helps to identify affected family members. However, there are still many challenges, which include a lack of simple clinical criterion for selecting patients for genetic testing, difficulties in interpreting the genetic test results, and high costs for genetic testing. In this review, we will discuss the latest updates on monogenic diabetes in Korea, and suggest an algorithm to screen patients for genetic testing. The genetic tests and non-genetic markers for accurate diagnosis of monogenic diabetes will be also reviewed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeted gene panel analysis of Japanese patients with maturity‐onset diabetes of the young‐like diabetes mellitus: Roles of inactivating variants in the ABCC8 and insulin resistance genes
Tohru Yorifuji, Yoh Watanabe, Kana Kitayama, Yuki Yamada, Shinji Higuchi, Jun Mori, Masaru Kato, Toru Takahashi, Tokuko Okuda, Takane Aoyama
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(3): 387. CrossRef - Efficacy of acupuncture on cardiovascular complications in patients with diabetes mellitus in Korea: A nationwide retrospective cohort
Hyejin Jung, Tiana Won, Ga-Yeon Kim, Jowon Jang, Sujung Yeo, Sabina Lim
Journal of Integrative Medicine.2023; 21(2): 176. CrossRef - Identification of rare variants in candidate genes associated with monogenic diabetes in polish mody-x patients
Paulina Jakiel, K. Gadzalska, E. Juścińska, M. Gorządek, T. Płoszaj, S. Skoczylas, M. Borowiec, A. Zmysłowska
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic perspectives on childhood monogenic diabetes: Diagnosis, management, and future directions
Hong-Yan Sun, Xiao-Yan Lin
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(12): 1738. CrossRef - Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)
Seung Shin Park, Soo Heon Kwak
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(3): 157. CrossRef - The Genetic Spectrum of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) in Qatar, a Population-Based Study
Asma A. Elashi, Salman M. Toor, Ilhame Diboun, Yasser Al-Sarraj, Shahrad Taheri, Karsten Suhre, Abdul Badi Abou-Samra, Omar M. E. Albagha
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 24(1): 130. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 277. CrossRef - Sequencing Cell-free Fetal DNA in Pregnant Women With GCK-MODY
Soo Heon Kwak, Camille E Powe, Se Song Jang, Michael J Callahan, Sarah N Bernstein, Seung Mi Lee, Sunyoung Kang, Kyong Soo Park, Hak C Jang, Jose C Florez, Jong-Il Kim, Jong Hee Chae
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(9): 2678. CrossRef - Muscle strength, an independent determinant of glycemic control in older adults with long-standing type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study
Bo Kyung Koo, Seoil Moon, Min Kyong Moon
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A rare, likely pathogenic GCK variant related to maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 2: A case report
Min-Kyung So, Jungwon Huh, Hae Soon Kim
Journal of Genetic Medicine.2021; 18(2): 132. CrossRef
- Targeted gene panel analysis of Japanese patients with maturity‐onset diabetes of the young‐like diabetes mellitus: Roles of inactivating variants in the ABCC8 and insulin resistance genes
- Genetics
- Exome Chip Analysis of 14,026 Koreans Reveals Known and Newly Discovered Genetic Loci Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Seong Beom Cho, Jin Hwa Jang, Myung Guen Chung, Sang Cheol Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):231-240. Published online July 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0163
- 6,247 View
- 195 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
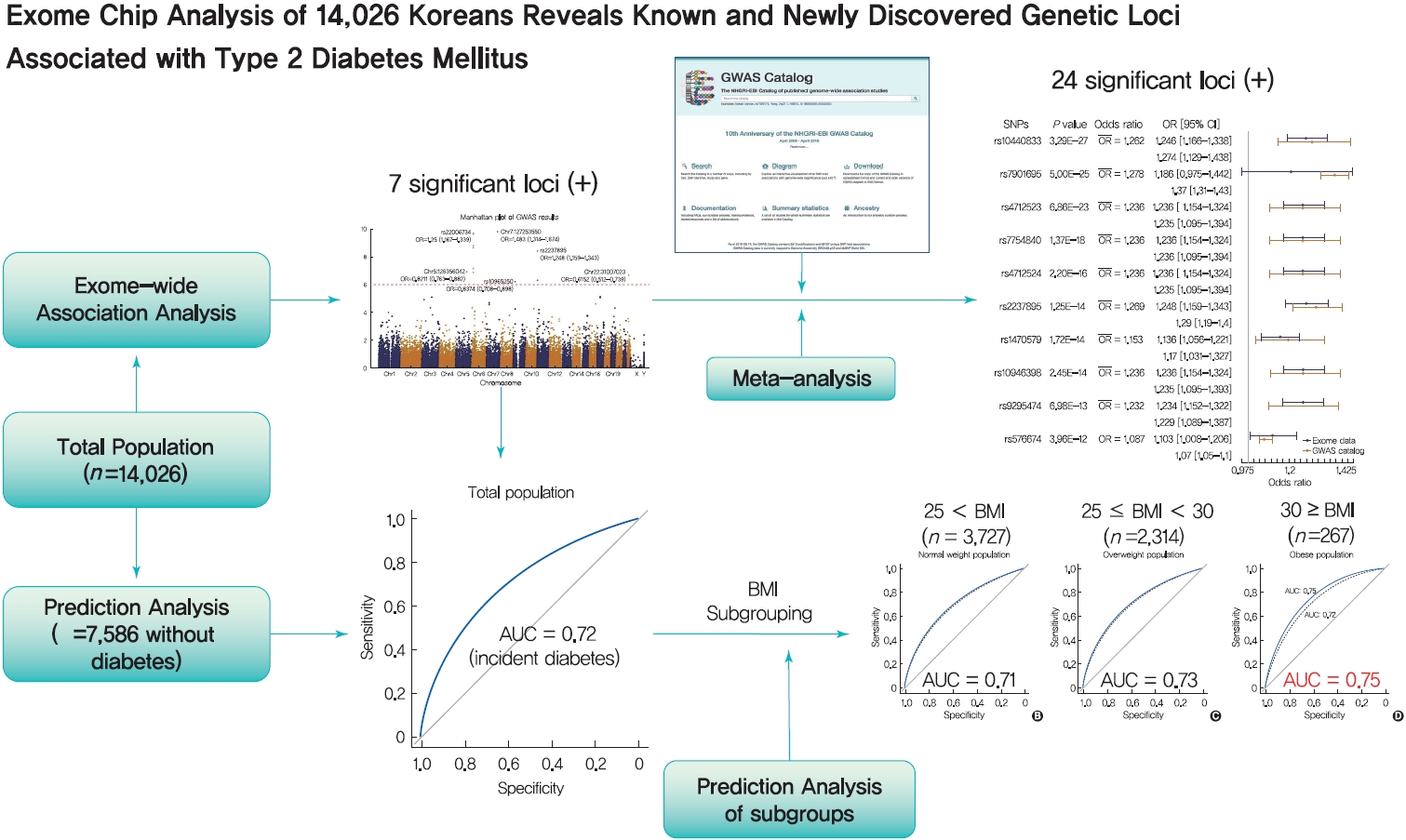
Background Most loci associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) discovered to date are within noncoding regions of unknown functional significance. By contrast, exonic regions have advantages for biological interpretation.
Methods We analyzed the association of exome array data from 14,026 Koreans to identify susceptible exonic loci for T2DM. We used genotype information of 50,543 variants using the Illumina exome array platform.
Results In total, 7 loci were significant with a Bonferroni adjusted
P =1.03×10−6. rs2233580 in paired box gene 4 (PAX4 ) showed the highest odds ratio of 1.48 (P =1.60×10−10). rs11960799 in membrane associated ring-CH-type finger 3 (MARCH3 ) and rs75680863 in transcobalamin 2 (TCN2 ) were newly identified loci. When we built a model to predict the incidence of diabetes with the 7 loci and clinical variables, area under the curve (AUC) of the model improved significantly (AUC=0.72,P <0.05), but marginally in its magnitude, compared with the model using clinical variables (AUC=0.71,P <0.05). When we divided the entire population into three groups—normal body mass index (BMI; <25 kg/m2), overweight (25≤ BMI <30 kg/m2), and obese (BMI ≥30 kg/m2) individuals—the predictive performance of the 7 loci was greatest in the group of obese individuals, where the net reclassification improvement was highly significant (0.51;P =8.00×10−5).Conclusion We found exonic loci having a susceptibility for T2DM. We found that such genetic information is advantageous for predicting T2DM in a subgroup of obese individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Polygenic Risk Score, Lifestyles, and Type 2 Diabetes Risk: A Prospective Chinese Cohort Study
Jia Liu, Lu Wang, Xuan Cui, Qian Shen, Dun Wu, Man Yang, Yunqiu Dong, Yongchao Liu, Hai Chen, Zhijie Yang, Yaqi Liu, Meng Zhu, Hongxia Ma, Guangfu Jin, Yun Qian
Nutrients.2023; 15(9): 2144. CrossRef - Celebrities in the heart, strangers in the pancreatic beta cell: Voltage‐gated potassium channels Kv7.1 and Kv11.1 bridge long QT syndrome with hyperinsulinaemia as well as type 2 diabetes
Anniek F. Lubberding, Christian R. Juhl, Emil Z. Skovhøj, Jørgen K. Kanters, Thomas Mandrup‐Poulsen, Signe S. Torekov
Acta Physiologica.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Substitution of Carbohydrates for Fats and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes among Korean Middle-Aged Adults: Findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Hye-Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Nutrients.2022; 14(3): 654. CrossRef - Ethnic-Specific Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factor PAX4 R192H Is Associated with Attention-Specific Cognitive Impairment in Chinese with Type 2 Diabetes
Su Fen Ang, Serena Low, Tze Pin Ng, Clara S.H. Tan, Keven Ang, Ziliang Lim, Wern Ee Tang, Tavintharan Subramaniam, Chee Fang Sum, Su Chi Lim, Nagaendran Kandiah
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2022; 88(1): 241. CrossRef - TrustGWAS: A full-process workflow for encrypted GWAS using multi-key homomorphic encryption and pseudorandom number perturbation
Meng Yang, Chuwen Zhang, Xiaoji Wang, Xingmin Liu, Shisen Li, Jianye Huang, Zhimin Feng, Xiaohui Sun, Fang Chen, Shuang Yang, Ming Ni, Lin Li, Yanan Cao, Feng Mu
Cell Systems.2022; 13(9): 752. CrossRef - Sex Differences in the Effects of CDKAL1 Variants on Glycemic Control in Diabetic Patients: Findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park, Young Sun Hong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 879. CrossRef
- Polygenic Risk Score, Lifestyles, and Type 2 Diabetes Risk: A Prospective Chinese Cohort Study
- Genetics
- Enhancer-Gene Interaction Analyses Identified the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor as a Susceptibility Gene for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yang Yang, Shi Yao, Jing-Miao Ding, Wei Chen, Yan Guo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):241-250. Published online June 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0204

- 6,050 View
- 104 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Genetic interactions are known to play an important role in the missing heritability problem for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Interactions between enhancers and their target genes play important roles in gene regulation and disease pathogenesis. In the present study, we aimed to identify genetic interactions between enhancers and their target genes associated with T2DM.
Methods We performed genetic interaction analyses of enhancers and protein-coding genes for T2DM in 2,696 T2DM patients and 3,548 controls of European ancestry. A linear regression model was used to identify single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) pairs that could affect the expression of the protein-coding genes. Differential expression analyses were used to identify differentially expressed susceptibility genes in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects.
Results We identified one SNP pair, rs4947941×rs7785013, significantly associated with T2DM (combined
P =4.84×10−10). The SNP rs4947941 was annotated as an enhancer, and rs7785013 was located in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR ) gene. This SNP pair was significantly associated withEGFR expression in the pancreas (P =0.033), and the minor allele “A” of rs7785013 decreasedEGFR gene expression and the risk of T2DM with an increase in the dosage of “T” of rs4947941.EGFR expression was significantly upregulated in T2DM patients, which was consistent with the effect of rs4947941×rs7785013 on T2DM andEGFR expression. A functional validation study using the Mouse Genome Informatics (MGI) database showed thatEGFR was associated with diabetes-relevant phenotypes.Conclusion Genetic interaction analyses of enhancers and protein-coding genes suggested that
EGFR may be a novel susceptibility gene for T2DM.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genome-Wide Epistasis Study of Cerebrospinal Fluid Hyperphosphorylated Tau in ADNI Cohort
Dandan Chen, Jin Li, Hongwei Liu, Xiaolong Liu, Chenghao Zhang, Haoran Luo, Yiming Wei, Yang Xi, Hong Liang, Qiushi Zhang
Genes.2023; 14(7): 1322. CrossRef - Investigation of the mechanism of Shen Qi Wan prescription in the treatment of T2DM via network pharmacology and molecular docking
Piaopiao Zhao, Xiaoxiao Zhang, Yuning Gong, Weihua Li, Zengrui Wu, Yun Tang, Guixia Liu
In Silico Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Raymond C. Harris
Cells.2022; 11(21): 3416. CrossRef - Co-expression Network Revealed Roles of RNA m6A Methylation in Human β-Cell of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Cong Chen, Qing Xiang, Weilin Liu, Shengxiang Liang, Minguang Yang, Jing Tao
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Genome-Wide Epistasis Study of Cerebrospinal Fluid Hyperphosphorylated Tau in ADNI Cohort
- Basic Research
- Role of CRTC2 in Metabolic Homeostasis: Key Regulator of Whole-Body Energy Metabolism?
- Hye-Sook Han, Yongmin Kwon, Seung-Hoi Koo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):498-508. Published online March 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0200
- 6,997 View
- 163 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
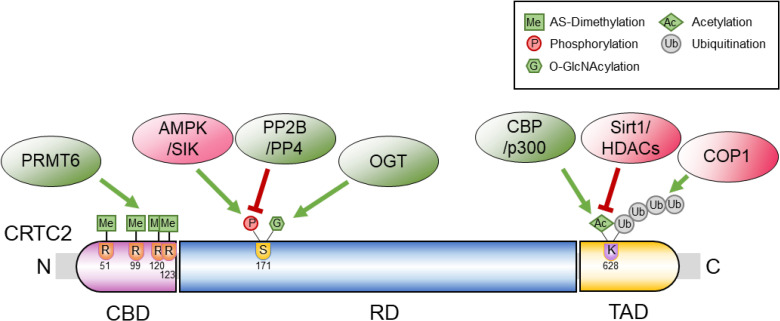
ePub Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling is critical for regulating metabolic homeostasis in mammals. In particular, transcriptional regulation by cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and its coactivator, CREB-regulated transcription coactivator (CRTC), is essential for controlling the expression of critical enzymes in the metabolic process, leading to more chronic changes in metabolic flux. Among the CRTC isoforms, CRTC2 is predominantly expressed in peripheral tissues and has been shown to be associated with various metabolic pathways in tissue-specific manners. While initial reports showed the physiological role of CRTC2 in regulating gluconeogenesis in the liver, recent studies have further delineated the role of this transcriptional coactivator in the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism in various tissues, including the liver, pancreatic islets, endocrine tissues of the small intestines, and adipose tissues. In this review, we discuss recent studies that have utilized knockout mouse models to delineate the role of CRTC2 in the regulation of metabolic homeostasis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integration of genomic and transcriptomic data of inbred mouse models for polygenic obesity and leanness revealed “obese” and “lean” candidate alleles in polyadenylation signals
Martin Šimon, Špela Mikec, Nicholas M. Morton, Santosh S. Atanur, Simon Horvat, Tanja Kunej
Gene Reports.2024; 35: 101903. CrossRef - Mylabris phalerata induces the apoptosis and cell cycle delay in HCC, and potentiates the effect of sorafenib based on the molecular and network pharmacology approach
Young Woo Kim, Seon Been Bak, Su Youn Baek, Il Kon Kim, Won-Yung Lee, Un-Jung Yun, Kwang-Il Park
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology.2023; 19(4): 731. CrossRef - Emerging Role of SMILE in Liver Metabolism
Nanthini Sadasivam, Kamalakannan Radhakrishnan, Hueng-Sik Choi, Don-Kyu Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 2907. CrossRef - PIMT regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice
Bandish Kapadia, Soma Behera, Sireesh T. Kumar, Tapan Shah, Rebecca Kristina Edwin, Phanithi Prakash Babu, Partha Chakrabarti, Kishore V.L. Parsa, Parimal Misra
iScience.2023; 26(3): 106120. CrossRef - Biological functions of CRTC2 and its role in metabolism-related diseases
Hong-Yu Zheng, Yan-Xia Wang, Kun Zhou, Hai-Lin Xie, Zhong Ren, Hui-Ting Liu, Yang-Shao Ou, Zhi-Xiang Zhou, Zhi-Sheng Jiang
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling.2023; 17(3): 495. CrossRef - An insulin-regulated arrestin domain protein controls hepatic glucagon action
Sezin Dagdeviren, Megan F. Hoang, Mohsen Sarikhani, Vanessa Meier, Jake C. Benoit, Marinna C. Okawa, Veronika Y. Melnik, Elisabeth M. Ricci-Blair, Natalie Foot, Randall H. Friedline, Xiaodi Hu, Lauren A. Tauer, Arvind Srinivasan, Maxim B. Prigozhin, Sudha
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2023; 299(8): 105045. CrossRef - The Pleiotropic Face of CREB Family Transcription Factors
Md. Arifur Rahman Chowdhury, Jungeun An, Sangyun Jeong
Molecules and Cells.2023; 46(7): 399. CrossRef - It is a branched road to adipose tissue aging
N. Touitou, B. Lerrer, H. Y. Cohen
Nature Aging.2023; 3(8): 911. CrossRef - Impaired BCAA catabolism in adipose tissues promotes age-associated metabolic derangement
Hye-Sook Han, Eunyong Ahn, Eun Seo Park, Tom Huh, Seri Choi, Yongmin Kwon, Byeong Hun Choi, Jueun Lee, Yoon Ha Choi, Yujin L. Jeong, Gwang Bin Lee, Minji Kim, Je Kyung Seong, Hyun Mu Shin, Hang-Rae Kim, Myeong Hee Moon, Jong Kyoung Kim, Geum-Sook Hwang, S
Nature Aging.2023; 3(8): 982. CrossRef - Exploring the diagnostic value, prognostic value, and biological functions of NPC gene family members in hepatocellular carcinoma based on a multi-omics analysis
Keheng Chen, Xin Zhang, Huixin Peng, Fengdie Huang, Guangyu Sun, Qijiang Xu, Lusheng Liao, Zhiyong Xing, Yanping Zhong, Zhichao Fang, Meihua Liao, Shihua Luo, Wencheng Chen, Mingyou Dong
Functional & Integrative Genomics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNA regulation of AMPK in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Hao Sun, Jongsook Kim Kemper
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2023; 55(9): 1974. CrossRef - Serine active site containing protein 1 depletion alters lipid metabolism and protects against high fat diet-induced obesity in mice
Miaomiao Du, Xueyun Li, Fangyi Xiao, Yinxu Fu, Yu Shi, Sihan Guo, Lifang Chen, Lu Shen, Lan Wang, Huang Cheng, Hao Li, Anran Xie, Yaping Zhou, Kaiqiang Yang, Hezhi Fang, Jianxin Lyu, Qiongya Zhao
Metabolism.2022; 134: 155244. CrossRef - cAMP Signaling in Cancer: A PKA-CREB and EPAC-Centric Approach
Muhammad Bilal Ahmed, Abdullah A. A. Alghamdi, Salman Ul Islam, Joon-Seok Lee, Young-Sup Lee
Cells.2022; 11(13): 2020. CrossRef - Hepatic Sam68 Regulates Systemic Glucose Homeostasis and Insulin Sensitivity
Aijun Qiao, Wenxia Ma, Ying Jiang, Chaoshan Han, Baolong Yan, Junlan Zhou, Gangjian Qin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(19): 11469. CrossRef - The Role of Small Heterodimer Partner-Interacting Leucine Zipper
(SMILE) as a Transcriptional Corepressor in Hepatic Glucose and Lipid
Metabolism
Woo-Ram Park, Byungyoon Choi, Nanthini Sadasivam, Don-Kyu Kim
Trends in Agriculture & Life Sciences.2022; 60: 7. CrossRef - AMPK Localization: A Key to Differential Energy Regulation
Qonita Afinanisa, Min Kyung Cho, Hyun-A Seong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(20): 10921. CrossRef
- Integration of genomic and transcriptomic data of inbred mouse models for polygenic obesity and leanness revealed “obese” and “lean” candidate alleles in polyadenylation signals
- Resistin in Rodents and Humans
- Hyeong Kyu Park, Rexford S. Ahima
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(6):404-414. Published online December 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.6.404
- 5,619 View
- 54 Download
- 122 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Obesity is characterized by excess accumulation of lipids in adipose tissue and other organs, and chronic inflammation associated with insulin resistance and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases are major health concerns. Resistin was first discovered as an adipose-secreted hormone (adipokine) linked to obesity and insulin resistance in rodents. Adipocyte-derived resistin is increased in obese rodents and strongly related to insulin resistance. However, in contrast to rodents, resistin is expressed and secreted from macrophages in humans and is increased in inflammatory conditions. Some studies have also suggested an association between increased resistin levels and insulin resistance, diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Genetic studies have provided additional evidence for a role of resistin in insulin resistance and inflammation. Resistin appears to mediate the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis by promoting endothelial dysfunction, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, arterial inflammation, and formation of foam cells. Indeed, resistin is predictive of atherosclerosis and poor clinical outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease and ischemic stroke. There is also growing evidence that elevated resistin is associated with the development of heart failure. This review will focus on the biology of resistin in rodents and humans, and evidence linking resistin with type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Resistin – A Plausible Therapeutic Target in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis
Manupati Srikanth, Mahaboobkhan Rasool
Immunological Investigations.2024; 53(2): 115. CrossRef - MHO or MUO? White adipose tissue remodeling
Jing Yi Zhao, Li Juan Zhou, Kai Le Ma, Rui Hao, Min Li
Obesity Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin in endocrine pancreas of sheep: Presence and expression related to different diets
Margherita Maranesi, Elisa Palmioli, Cecilia Dall'Aglio, Daniele Marini, Polina Anipchenko, Elena De Felice, Paola Scocco, Francesca Mercati
General and Comparative Endocrinology.2024; 348: 114452. CrossRef - Adipocytokines levels as potential biomarkers for discriminating patients with a diagnosis of depressive disorder from healthy controls
Elżbieta Małujło-Balcerska, Tadeusz Pietras
Journal of Psychiatric Research.2024; 171: 163. CrossRef - Adipokines in atopic dermatitis: the link between obesity and atopic dermatitis
Shiyun Zhang, Bingjie Zhang, Yuehua Liu, Li Li
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Adipokines in the Control of Pituitary Functions
Barbara Kaminska, Beata Kurowicka, Marta Kiezun, Kamil Dobrzyn, Katarzyna Kisielewska, Marlena Gudelska, Grzegorz Kopij, Karolina Szymanska, Barbara Zarzecka, Oguzhan Koker, Ewa Zaobidna, Nina Smolinska, Tadeusz Kaminski
Animals.2024; 14(2): 353. CrossRef - Adipokine imbalance and its role in the pathogenesis of novel coronavirus infection
I. D. Bespalova, U. M. Mitrichenko, V. V. Kalyuzhin, E. S. Koroleva, Yu. I. Koshchavtseva, D. S. Romanov, D. E. Pershina
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2024; 22(4): 164. CrossRef - Association of adipokine levels with obesity in periodontal health and disease: A systematic review with meta‐analysis and meta‐regression
Eswar Kandaswamy, Chun‐Teh Lee, Soumya Bardvalli Gururaj, Sachin Shivanaikar, Vinayak M. Joshi
Journal of Periodontal Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of epicardial adipose tissue in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
O. N. Dzhioeva, Yu. S. Timofeev, V. A. Metelskaya, A. A. Bogdanova, T. Yu. Vedenikin, O. M. Drapkina
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2024; 23(3): 3928. CrossRef - Association of maternal body composition and diet on breast milk hormones and neonatal growth during the first month of lactation
David Ramiro-Cortijo, Pratibha Singh, Gloria Herranz Carrillo, Andrea Gila-Díaz, María A. Martín-Cabrejas, Camilia R. Martin, Silvia M. Arribas
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Upregulation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells resistin gene expression in severe obstructive sleep apnea and obstructive sleep apnea with coexisting type 2 diabetes mellitus
Branislava Rajkov, Marija Zdravković, Ana Ninić, Milica Brajković, Slobodan Klašnja, Vera Gardijan, Lidija Memon, Jelena Munjas, Marija Mihajlović, Vesna Spasojević- Kalimanovska, Vojislav Radosavljević, Miron Sopić
Sleep and Breathing.2023; 27(5): 2031. CrossRef - Fat-to-heart crosstalk in health and disease
Fleur Lodewijks, Timothy A. McKinsey, Emma L. Robinson
Frontiers in Genetics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipokines as Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers for the Severity of COVID-19
Thomas Grewal, Christa Buechler
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1302. CrossRef - Role of adipokines in sarcopenia
Wenhao Lu, Wenjie Feng, Jieyu Lai, Dongliang Yuan, Wenfeng Xiao, Yusheng Li
Chinese Medical Journal.2023; 136(15): 1794. CrossRef - Resistin, TNF-α, and microRNA 124-3p expressions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells are associated with diabetic nephropathy
Amin Monjezi, Azam Khedri, Mehrnoosh Zakerkish, Ghorban Mohammadzadeh
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(1): 62. CrossRef - Resistin in Urine and Breast Milk: Relation to Type of Feeding and Anthropometry at 1-Month
Irena Santosa, Hiromichi Shoji, Kentaro Awata, Yoshiteru Arai, Hiroki Suganuma, Toshiaki Shimizu
Pediatric Reports.2022; 14(1): 86. CrossRef - High Serum Levels of Resistin is Associated With Acute Cerebral Infarction
Kee Ook Lee, Kyung-Yul Lee, Cheol-Young Lee, Ji Hoon Kim, Jaeku Kang, Hoi Young Lee, Sang-Jun Na, Seung-Hun Oh, Ji Hoe Heo
The Neurologist.2022; 27(2): 41. CrossRef - Resistin production does not affect outcomes in a mouse model of acute surgical sepsis
Anthony S. Bonavia, Zissis C. Chroneos, Victor Ruiz-Velasco, Charles H. Lang, Partha Mukhopadhyay
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(3): e0265241. CrossRef - Single-nucleotide polymorphisms as important risk factors of diabetes among Middle East population
Iman Akhlaghipour, Amir Reza Bina, Mohammad Reza Mogharrabi, Ali Fanoodi, Amir Reza Ebrahimian, Soroush Khojasteh Kaffash, Atefeh Babazadeh Baghan, Mohammad Erfan Khorashadizadeh, Negin Taghehchian, Meysam Moghbeli
Human Genomics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Synergistic Effects of Weighted Genetic Risk Scores and Resistin and sST2 Levels on the Prognostication of Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Hsin-Hua Chou, Lung-An Hsu, Jyh-Ming Jimmy Juang, Fu-Tien Chiang, Ming-Sheng Teng, Semon Wu, Yu-Lin Ko
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4292. CrossRef - Hypoxia Increases the Potential for Neutrophil-mediated Endothelial Damage in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Katharine M. Lodge, Arlette Vassallo, Bin Liu, Merete Long, Zhen Tong, Paul R. Newby, Danya Agha-Jaffar, Koralia Paschalaki, Clara E. Green, Kylie B. R. Belchamber, Victoria C. Ridger, Robert A. Stockley, Elizabeth Sapey, Charlotte Summers, Andrew S. Cowb
American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.2022; 205(8): 903. CrossRef - The Role of the Adipokine Resistin in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Klaudia Parafiniuk, Wiktoria Skiba, Anna Pawłowska, Dorota Suszczyk, Aleksandra Maciejczyk, Iwona Wertel
Biomedicines.2022; 10(4): 920. CrossRef - Resistin Modulates Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Uptake in Human Placental Explants via PCSK9
Sonia Nava-Salazar, Arturo Flores-Pliego, Giovanni Pérez-Martínez, Sandra Parra-Hernández, America Vanoye-Carlo, Francisco Ibarguengoitia-Ochoa, Otilia Perichart-Perera, Enrique Reyes-Muñoz, Juan Mario Solis-Paredes, Salvador Espino y Sosa, Guadalupe Estr
Reproductive Sciences.2022; 29(11): 3242. CrossRef - Differential Association of Selected Adipocytokines, Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin, Visfatin and Chemerin, with the Pathogenesis and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: A Case Control Study
Mohammad Muzaffar Mir, Rashid Mir, Mushabab Ayed Abdullah Alghamdi, Javed Iqbal Wani, Zia Ul Sabah, Mohammed Jeelani, Vijaya Marakala, Shahzada Khalid Sohail, Mohamed O’haj, Muffarah Hamid Alharthi, Mohannad Mohammad S. Alamri
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(5): 735. CrossRef - Immune system and sarcopenia: Presented relationship and future perspective
Xuzhi Zhang, Hengzhen Li, Miao He, Jingyu Wang, Yuxiang Wu, Yusheng Li
Experimental Gerontology.2022; 164: 111823. CrossRef - Adipose Tissue Secretion Pattern Influences β-Cell Wellness in the Transition from Obesity to Type 2 Diabetes
Giuseppina Biondi, Nicola Marrano, Anna Borrelli, Martina Rella, Giuseppe Palma, Isabella Calderoni, Edoardo Siciliano, Pasquale Lops, Francesco Giorgino, Annalisa Natalicchio
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5522. CrossRef - Supplemental hydroxychloroquine therapy regulates adipokines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with stable disease
Risa Wakiya, Kiyo Ueeda, Hiromi Shimada, Shusaku Nakashima, Tomohiro Kameda, Nobuyuki Miyatake, Mikiya Kato, Taichi Miyagi, Koichi Sugihara, Mao Mizusaki, Rina Mino, Norimitsu Kadowaki, Hiroaki Dobashi
Clinical Rheumatology.2022; 41(11): 3345. CrossRef - Can soy isoflavones in combination with soy protein change serum concentration of adiponectin and resistin? A systematic review and meta‐analysis on randomized clinical trials
Mitra Hariri, Bahareh Amirkalali, Ensiyeh Mollanoroozy, Ali Gholami
Food Science & Nutrition.2022; 10(12): 4126. CrossRef - Adipokines: Deciphering the cardiovascular signature of adipose tissue
Joseph C. Galley, Shubhnita Singh, Wanessa M.C. Awata, Juliano V. Alves, Thiago Bruder-Nascimento
Biochemical Pharmacology.2022; 206: 115324. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Anti-Obesity Effect of Zeaxanthin and Exercise in HFD-Induced Obese Rats
Mona Al-thepyani, Salha Algarni, Hana Gashlan, Mohamed Elzubier, Lina Baz
Nutrients.2022; 14(23): 4944. CrossRef - Single High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation as an Approach for Reducing Ultramarathon-Induced Inflammation: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
Jan Mieszkowski, Andżelika Borkowska, Błażej Stankiewicz, Andrzej Kochanowicz, Bartłomiej Niespodziński, Marcin Surmiak, Tomasz Waldziński, Rafał Rola, Miroslav Petr, Jędrzej Antosiewicz
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1280. CrossRef - Resistin mitigates stemness and metabolic profile of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via insulin resistance
Komal Rawal, Kishan M. Purohit, Tushar P. Patel, Neeta Karont, Sarita Gupta
Cytokine.2021; 138: 155374. CrossRef - Resistin is co-secreted with adiponectin in white mouse adipocytes
Saliha Musovic, Man Mohan Shrestha, Ali M. Komai, Charlotta S. Olofsson
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2021; 534: 707. CrossRef - Resistin: Potential biomarker and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis
Li Zhou, Jun-Yi Li, Ping-Ping He, Xiao-Hua Yu, Chao-Ke Tang
Clinica Chimica Acta.2021; 512: 84. CrossRef - The circulating levels of CTRP1 and CTRP5 are associated with obesity indices and carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) value in patients with type 2 diabetes: a preliminary study
Ziba Majidi, Solaleh Emamgholipour, Abolfazl Omidifar, Soheil Rahmani Fard, Hossein Poustchi, Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Corylin reduces obesity and insulin resistance and promotes adipose tissue browning through SIRT-1 and β3-AR activation
Chin-Chuan Chen, Chen-Hsin Kuo, Yann-Lii Leu, Shu-Huei Wang
Pharmacological Research.2021; 164: 105291. CrossRef - A Focused Review of the Metabolic Side-Effects of Clozapine
Jessica W. Y. Yuen, David D. Kim, Ric M. Procyshyn, William J. Panenka, William G. Honer, Alasdair M. Barr
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Negative Energy Balance Is Associated with Metabolic Dysfunctions in the Hypothalamus of a Humanized Preclinical Model of Alzheimer’s Disease, the 5XFAD Mouse
Antonio J. López-Gambero, Cristina Rosell-Valle, Dina Medina-Vera, Juan Antonio Navarro, Antonio Vargas, Patricia Rivera, Carlos Sanjuan, Fernando Rodríguez de Fonseca, Juan Suárez
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(10): 5365. CrossRef - Resistin in pregnancy: Analysis of determinants in pairs of umbilical cord blood and maternal serum
Anne Floeck, Nina Ferrari, Christine Joisten, Maria T. Puth, Brigitte Strizek, Ramona Dolscheid-Pommerich, Ulrich Gembruch, Waltraut M. Merz
Cytokine: X.2021; 3(2): 100052. CrossRef - Is resistin the master link between inflammation and inflammation-related chronic diseases?
Mohammed Taouis, Yacir Benomar
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2021; 533: 111341. CrossRef - The dynamics of human bone marrow adipose tissue in response to feeding and fasting
Pouneh K. Fazeli, Miriam A. Bredella, Gisela Pachon-Peña, Wenxiu Zhao, Xun Zhang, Alexander T. Faje, Megi Resulaj, Sai P. Polineni, Tara M. Holmes, Hang Lee, Elizabeth K. O’Donnell, Ormond A. MacDougald, Mark C. Horowitz, Clifford J. Rosen, Anne Klibanski
JCI Insight.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin: A journey from metabolism to cancer
Ankita Deb, Bhavana Deshmukh, Pranay Ramteke, Firoz Khan Bhati, Manoj Kumar Bhat
Translational Oncology.2021; 14(10): 101178. CrossRef - Obesity is the basis of metabolic syndrome
A. F. Verbovoy, N. I. Verbovaya, Yu. A. Dolgikh
Obesity and metabolism.2021; 18(2): 142. CrossRef - Human Milk Metabolic Hormones: Analytical Methods and Current Understanding
Majed A. Suwaydi, Zoya Gridneva, Sharon L. Perrella, Mary E. Wlodek, Ching Tat Lai, Donna T. Geddes
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(16): 8708. CrossRef - Adipokines as Immune Cell Modulators in Multiple Sclerosis
Merel Rijnsburger, Niek Djuric, Inge A. Mulder, Helga E. de Vries
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(19): 10845. CrossRef - The Role of Adipokines in Cardiovascular Pathology
Valery Podzolkov , Anna Pokrovskaya, Ulyana Bazhanova , Tatyana Vargina , Svetlana Anatolievna Knyazeva , Daria Vanina
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(F): 794. CrossRef - Measurement of Plasma Resistin Concentrations in Horses with Metabolic and Inflammatory Disorders
Beatriz Fuentes-Romero, Alberto Muñoz-Prieto, José J. Cerón, María Martín-Cuervo, Manuel Iglesias-García, Escolástico Aguilera-Tejero, Elisa Díez-Castro
Animals.2021; 12(1): 77. CrossRef - EFFECT OF DIET AND EXERCISE-INDUCE WEIGHT LOSS ON LEVEL OF RESISTIN IN PATIENT WITH OBESITY
О. I. Tokarenko, I. O. Andreieva, O. O. Tokarenko, M. M. Surmilo
Modern medical technology.2021; (4): 11. CrossRef - Alteration of gut microbiota affects expression of adiponectin and resistin through modifying DNA methylation in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
Hongyang Yao, Chaonan Fan, Yuanyuan Lu, Xiuqin Fan, Lulu Xia, Ping Li, Rui Wang, Tiantian Tang, Yuanyuan Wang, Kemin Qi
Genes & Nutrition.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin hormone in diabetic kidney disease and its relation to iron status and hepcidin
Zhian Sherzad Hayder, Zrar Saleem Kareem
International Urology and Nephrology.2020; 52(4): 749. CrossRef - Proteoglycans in Obesity-Associated Metabolic Dysfunction and Meta-Inflammation
Ariane R. Pessentheiner, G. Michelle Ducasa, Philip L. S. M. Gordts
Frontiers in Immunology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin Is Increased in Periodontal Cells and Tissues: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Andressa V. B. Nogueira, Marjan Nokhbehsaim, Sema Tekin, Rafael S. de Molon, Luis C. Spolidorio, Svenja Memmert, Anna Damanaki, Andreas Jäger, Sigrun Eick, James Deschner, Joni A. Cirelli
Mediators of Inflammation.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
Alan Chait, Laura J. den Hartigh
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The possible role of endocrine dysfunction of adipose tissue in gestational diabetes mellitus
Patrik Šimják, Kateřina Anderlová, Anna Cinkajzlová, Antonín Pařízek, Michal Kršek, Martin Haluzík
Minerva Endocrinologica.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - High Plasma Resistin Levels Portend the Insulin Resistance-Associated Susceptibility to Early Cognitive Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Chenchen Wang, Xi Huang, Sai Tian, Rong Huang, Dan Guo, Hongyan Lin, Jiaqi Wang, Shaohua Wang
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2020; 75(3): 807. CrossRef - Resistin in metabolism, inflammation, and disease
Deeksha Tripathi, Sashi Kant, Saurabh Pandey, Nasreen Z. Ehtesham
The FEBS Journal.2020; 287(15): 3141. CrossRef - Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases
Lucia Recinella, Giustino Orlando, Claudio Ferrante, Annalisa Chiavaroli, Luigi Brunetti, Sheila Leone
Frontiers in Physiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of CCL18 with Levels of Adi-pokines in the Sera of Patients with Myocardial Infarction in a 6-Month Period: Case Series
Atefeh GamarTalepoor, Ehsan Dowlatshahi, Mehrnoush Doroudchi
Iranian South Medical Journal.2020; 23(3): 222. CrossRef - The Mesentery, Systemic Inflammation, and Crohn’s Disease
Edgardo D Rivera, John Calvin Coffey, Dara Walsh, Eli D Ehrenpreis
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.2019; 25(2): 226. CrossRef - Resistin and adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1 (CAP1) regulate the expression of genes related to insulin resistance in BNL CL.2 mouse liver cells
Dimiter Avtanski, Karin Chen, Leonid Poretsky
Data in Brief.2019; 25: 104112. CrossRef - Proteomic profile of patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing cardiac surgery†
Ilias P Doulamis, George Samanidis, Aspasia Tzani, Asier Antoranz, Anastasios Gkogkos, Panagiotis Konstantopoulos, Vaia Pliaka, Angeliki Minia, Leonidas G Alexopoulos, Despina N Perrea, Konstantinos Perreas
Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery.2019; 28(1): 94. CrossRef - Angiotensin-(1-7), Adipokines and Inflammation
Deborah de Farias Lelis, Daniela Fernanda de Freitas, Amanda Souto Machado, Thaísa Soares Crespo, Sérgio Henrique Sousa Santos
Metabolism.2019; 95: 36. CrossRef - New Insights into Adipokines as Potential Biomarkers for Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Marta Olivera-Santa Catalina, Pedro C. Redondo, Maria P. Granados, Carlos Cantonero, Jose Sanchez-Collado, Letizia Albarran, Jose J. Lopez
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2019; 26(22): 4119. CrossRef - Myokine–adipokine cross-talk: potential mechanisms for the association between plasma irisin and adipokines and cardiometabolic risk factors in Mexican children with obesity and the metabolic syndrome
Adrian M. Gonzalez-Gil, Mariana Peschard-Franco, Elena C. Castillo, Gustavo Gutierrez-DelBosque, Victor Treviño, Christian Silva-Platas, Luisa Perez-Villarreal, Gerardo Garcia-Rivas, Leticia Elizondo-Montemayor
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Life Exposures to Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Relation to Adipokine Hormone Levels at Birth and During Childhood
Colleen Shelly, Philippe Grandjean, Youssef Oulhote, Peter Plomgaard, Ruth Frikke-Schmidt, Flemming Nielsen, Denis Zmirou-Navier, Pal Weihe, Damaskini Valvi
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 104(11): 5338. CrossRef - Overweight and obesity in childhood: Dietary, biochemical, inflammatory and lifestyle risk factors
Samah R. Albataineh, Eman F. Badran, Reema F. Tayyem
Obesity Medicine.2019; 15: 100112. CrossRef - Effects of major adipokines and the −420 C > G resistin gene polymorphism on the long-term outcome of patients with acute ischemic stroke
Stella Bouziana, Konstantinos Tziomalos, Antonis Goulas, Timoleon-Achilleas Vyzantiadis, Maria Papadopoulou, Athanasia Panderi, Apostolos Ι. Ηatzitolios
International Journal of Neuroscience.2019; 129(10): 978. CrossRef - The Complex Interactions Between Obesity, Metabolism and the Brain
Romina María Uranga, Jeffrey Neil Keller
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin: A reappraisal
E. Acquarone, F. Monacelli, R. Borghi, A. Nencioni, P. Odetti
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development.2019; 178: 46. CrossRef - Implications of resistin in type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease: Impairing insulin function and inducing pro‐inflammatory cytokines
Melissa Emamalipour, Khaled Seidi, Ali Jahanban‐Esfahlan, Rana Jahanban‐Esfahlan
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(12): 21758. CrossRef - Serum-based soluble markers differentiate psoriatic arthritis from osteoarthritis
Vinod Chandran, Fatima Abji, Anthony V Perruccio, Rajiv Gandhi, Suzanne Li, Richard J Cook, Dafna D Gladman
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.2019; 78(6): 796. CrossRef - Telmisartan prevents diet-induced obesity and preserves leptin transport across the blood-brain barrier in high-fat diet-fed mice
Franziska Schuster, Gianna Huber, Ines Stölting, Emily E. Wing, Kathrin Saar, Norbert Hübner, William A. Banks, Walter Raasch
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology.2018; 470(11): 1673. CrossRef - Adipokines in human breast milk
Juergen Kratzsch, Yoon Ju Bae, Wieland Kiess
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2018; 32(1): 27. CrossRef - Addressing the Perfect Storm: Biomarkers in Obesity and Pathophysiology of Cardiometabolic Risk
Krasimira Aleksandrova, Dariush Mozaffarian, Tobias Pischon
Clinical Chemistry.2018; 64(1): 142. CrossRef - Adipocytokine Involvement in Innate Immune Mechanisms
Paulina Żelechowska, Elżbieta Kozłowska, Joanna Pastwińska, Justyna Agier, Ewa Brzezińska-Błaszczyk
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research.2018; 38(12): 527. CrossRef - The effect of a garlic supplement on the pro-inflammatory adipocytokines, resistin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and on pain severity, in overweight or obese women with knee osteoarthritis
Sahar Dehghani, Elham Alipoor, Ahmad Salimzadeh, Mehdi Yaseri, Mostafa Hosseini, Christine Feinle-Bisset, Mohammad Javad Hosseinzadeh-Attar
Phytomedicine.2018; 48: 70. CrossRef - Perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) in atherosclerosis: a double-edged sword
Xiao-Yan Qi, Shun-Lin Qu, Wen-Hao Xiong, Oren Rom, Lin Chang, Zhi-Sheng Jiang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Usefulness of the Adipokines as Biomarkers of Ischemic Cardiac Dysfunction
Larisa-Diana Mocan Hognogi, Cerasela-Mihaela Goidescu, Anca-Daniela Farcaş
Disease Markers.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 in patients with liver cirrhosis
Sabrina Krautbauer, Lisa Rein-Fischboeck, Elisabeth M Haberl, Rebekka Pohl, Reiner Wiest, Christa Buechler
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2018; 18(1): 63. CrossRef - Association of Cord Blood Resistin with Neonatal Birth Weight and Gestational Age
Shahnaz Pourarian, Saeed Fotouhikia, Forough Saki
Journal of Comprehensive Pediatrics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Major Adipokines and the −420C>G Resistin Gene Polymorphism as Predictors of Acute Ischemic Stroke Severity and In-Hospital Outcome
Styliani D. Bouziana, Konstantinos Tziomalos, Antonios Goulas, Timoleon-Achilleas Vyzantiadis, Athanasia Panderi, Apostolos Ι. Ηatzitolios
Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases.2018; 27(4): 963. CrossRef - Resistin and NGAL are associated with inflammatory response, endothelial activation and clinical outcomes in sepsis
Stephen P. J. Macdonald, Erika Bosio, Claire Neil, Glenn Arendts, Sally Burrows, Lisa Smart, Simon G. A. Brown, Daniel M. Fatovich
Inflammation Research.2017; 66(7): 611. CrossRef - Reference values for fasting serum resistin in healthy children and adolescents
Ulrik Lausten-Thomsen, Michael Christiansen, Paula Louise Hedley, Tenna Ruest Haarmark Nielsen, Cilius Esmann Fonvig, Oluf Pedersen, Torben Hansen, Jens-Christian Holm
Clinica Chimica Acta.2017; 469: 161. CrossRef - Sarcopenic obesity or obese sarcopenia: A cross talk between age-associated adipose tissue and skeletal muscle inflammation as a main mechanism of the pathogenesis
Alexander Kalinkovich, Gregory Livshits
Ageing Research Reviews.2017; 35: 200. CrossRef - Is There Any Relationship between Plasma 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3, Adipokine Profiles and Excessive Body Weight in Type 2 Diabetic Patients?
Joanna Kocot, Piotr Dziemidok, Małgorzata Kiełczykowska, Jacek Kurzepa, Grzegorz Szcześniak, Irena Musik
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2017; 15(1): 19. CrossRef - Exogenous Adipokine Peptide Resistin Protects Against Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice
Jiangtao Zhu, Di Wu, Chenyu Zhao, Man Luo, Ronald C. Hamdy, Balvin H. L. Chua, Xingshun Xu, Zhigang Miao
Neurochemical Research.2017; 42(10): 2949. CrossRef - Adipokines in Liver Cirrhosis
Christa Buechler, Elisabeth Haberl, Lisa Rein-Fischboeck, Charalampos Aslanidis
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2017; 18(7): 1392. CrossRef - The role of sex steroids in white adipose tissue adipocyte function
A E Newell-Fugate
Reproduction.2017; 153(4): R133. CrossRef - Odanacatib Inhibits Resistin-induced Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy Through the Inactivation of ERK Signaling Pathway
Xian Zheng, Guanchang Cheng, Jianwei Luo, Qunhui Ye, Yongzhi Deng, Lin Wu
International Journal of Pharmacology.2017; 13(2): 212. CrossRef - Linking resistin, inflammation, and cardiometabolic diseases
Hyeong Kyu Park, Mi Kyung Kwak, Hye Jeong Kim, Rexford S. Ahima
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(2): 239. CrossRef - Translating the biology of adipokines in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases: Gaps and open questions
M. Ruscica, A. Baragetti, A.L. Catapano, G.D. Norata
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2017; 27(5): 379. CrossRef - Differences in Mean Levels of Maternal Resistin Serum between Early Onset Preeclampsia (EOPE) and Late Onset Preeclampsia (LOPE)
Yusrawati ., P. Alfajra, R. Machmud
Research Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2016; 10(1): 1. CrossRef - Secret talk between adipose tissue and central nervous system via secreted factors—an emerging frontier in the neurodegenerative research
Avinash Parimisetty, Anne-Claire Dorsemans, Rana Awada, Palaniyandi Ravanan, Nicolas Diotel, Christian Lefebvre d’Hellencourt
Journal of Neuroinflammation.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of adipokines in ischemic stroke risk stratification
Styliani Bouziana, Konstantinos Tziomalos, Antonios Goulas, Apostolos Ι Ηatzitolios
International Journal of Stroke.2016; 11(4): 389. CrossRef - The endocrine function of human placenta: an overview
Mariana A. Costa
Reproductive BioMedicine Online.2016; 32(1): 14. CrossRef - Ursolic acid plays a protective role in obesity-induced cardiovascular diseases
Yu-Ting Lin, Ya-Mei Yu, Weng-Cheng Chang, Su-Yin Chiang, Hsu-Chin Chan, Ming-Fen Lee
Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.2016; 94(6): 627. CrossRef - Determinants of body weight regulation in humans
Milene Moehlecke, Luis Henrique Canani, Lucas Oliveira Junqueira e Silva, Manoel Roberto Maciel Trindade, Rogerio Friedman, Cristiane Bauermann Leitão
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 60(2): 152. CrossRef - Sitagliptin decreases ventricular arrhythmias by attenuated glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)-dependent resistin signalling in infarcted rats
Tsung-Ming Lee, Wei-Ting Chen, Nen-Chung Chang
Bioscience Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Les adipokines : état des lieux et nouveautés
J.-P. Bastard, C. Bastard, S. Fellahi, C. Vatier, J. Capeau, B. Fève
Obésité.2016; 11(3): 181. CrossRef - Factors that promote macrophage homing to adipose tissue in metabolic syndrome
Ishwarlal Jialal, Beverley Adams-Huet, Sridevi Devaraj
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(8): 1434. CrossRef - Uncovering Factors Related to Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function
Aoife M. Curran, Miriam F. Ryan, Elaine Drummond, Eileen R. Gibney, Michael J. Gibney, Helen M. Roche, Lorraine Brennan, Nigel Irwin
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0161350. CrossRef - Resistin’s, obesity and insulin resistance: the continuing disconnect between rodents and humans
X. Huang, Z. Yang
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2016; 39(6): 607. CrossRef - Adipocytokines in renal transplant recipients
Kristof Nagy, Shankar Prasad Nagaraju, Connie M. Rhee, Zoltan Mathe, Miklos Z. Molnar
Clinical Kidney Journal.2016; 9(3): 359. CrossRef - Endocrine alterations from concentric vs. eccentric muscle actions: A brief review
Robert R. Kraemer, V. Daniel Castracane
Metabolism.2015; 64(2): 190. CrossRef - Non-traditional cytokines: How catecholamines and adipokines influence macrophages in immunity, metabolism and the central nervous system
Mark A. Barnes, Monica J. Carson, Meera G. Nair
Cytokine.2015; 72(2): 210. CrossRef - Local and serum levels of adipokines in patients with obesity after periodontal therapy: one‐year follow‐up
Tiago Eduardo Dias Gonçalves, Glaucia Santos Zimmermann, Luciene Cristina Figueiredo, Monique de Carvalho Souza, Daniele Ferreira da Cruz, Marta Ferreira Bastos, Hélio Doyle Pereira da Silva, Poliana Mendes Duarte
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2015; 42(5): 431. CrossRef - Newborn Adipokines and Birth Outcomes
Edwina H. Yeung, Alexander C. McLain, Nancy Anderson, David Lawrence, Nansi S. Boghossian, Charlotte Druschel, Erin Bell
Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology.2015; 29(4): 317. CrossRef - The effect of a preparation of minerals, vitamins and trace elements on the cardiac gene expression pattern in male diabetic rats
Márta Sárközy, Gergő Szűcs, Márton Pipicz, Ágnes Zvara, Katalin Éder, Veronika Fekete, Csilla Szűcs, Judit Bárkányi, Csaba Csonka, László G. Puskás, Csaba Kónya, Péter Ferdinandy, Tamás Csont
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Diet-induced variability of the resistin gene (Retn) transcript level and methylation profile in rats
Joanna Nowacka-Woszuk, Ewa Pruszynska-Oszmalek, Maciej Szydlowski, Slawomir Sadkowski, Izabela Szczerbal
BMC Genetics.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - INFLUENCE OF RESISTIN ON THE COURSE OF ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
A. T. Teplyakov, Sh. D. Akhmedov, T. Ye. Suslova, А. V. Andriyanova, A. V. Kuznetsova, N. V. Protopopova, V. V. Kalyuzhin, O. N. Nasanova
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2015; 14(5): 73. CrossRef - The Effects of a Single Developmentally Entrained Pulse of Testosterone in Female Neonatal Mice on Reproductive and Metabolic Functions in Adult Life
Hyeran Jang, Shalender Bhasin, Tyler Guarneri, Carlo Serra, Mary Schneider, Mi-Jeong Lee, Wen Guo, Susan K. Fried, Karol Pencina, Ravi Jasuja
Endocrinology.2015; 156(10): 3737. CrossRef - The Resin fromProtium heptaphyllumPrevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice: Scientific Evidence and Potential Mechanisms
Karine Maria Martins Bezerra Carvalho, José Delano Barreto Marinho Filho, Tiago Sousa de Melo, Ana Jérsia Araújo, Josiane da Silva Quetz, Maria do Perpétuo Socorro Saldanha da Cunha, Karina Moura de Melo, Armenio Andre de Carvalho Almeida da Silva, Adrian
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Evolution of the Vertebrate Resistin Gene Family
Qingda Hu, Huanran Tan, David M. Irwin, Marc Robinson-Rechavi
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(6): e0130188. CrossRef - Obesity, adipokines and neuroinflammation
Argel Aguilar-Valles, Wataru Inoue, Christoph Rummel, Giamal N. Luheshi
Neuropharmacology.2015; 96: 124. CrossRef - Adipokines at the crossroad between obesity and cardiovascular disease
Filippo Molica, Sandrine Morel, Brenda Kwak, Françoise Rohner-Jeanrenaud, Sabine Steffens
Thrombosis and Haemostasis.2015; 113(03): 553. CrossRef - Resistin – 420 C/G polymorphism and serum resistin level in Iranian patients with gestational diabetes mellitus
Mohammad Ali Takhshid, Zinab Zare
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Ictal adipokines are associated with pain severity and treatment response in episodic migraine
Nu Cindy Chai, Bizu Gelaye, Gretchen E. Tietjen, Paul D. Dash, Barbara A. Gower, Linda W. White, Thomas N. Ward, Ann I. Scher, B. Lee Peterlin
Neurology.2015; 84(14): 1409. CrossRef - Inflammation and insulin/IGF-1 resistance as the possible link between obesity and neurodegeneration
Lindsay J. Spielman, Jonathan P. Little, Andis Klegeris
Journal of Neuroimmunology.2014; 273(1-2): 8. CrossRef - Wild Blueberries (Vaccinium myrtillus) Alleviate Inflammation and Hypertension Associated with Developing Obesity in Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet
Otto T. Mykkänen, Anne Huotari, Karl-Heinz Herzig, Thomas W. Dunlop, Hannu Mykkänen, Pirkka V. Kirjavainen, Michael Müller
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(12): e114790. CrossRef - Role of fat and adipokines in intestinal inflammation
LeaI Kredel, Arvind Batra, Britta Siegmund
Current Opinion in Gastroenterology.2014; 30(6): 559. CrossRef -
13C metabolic flux analysis shows that resistin impairs the metabolic response to insulin in L6E9 myotubes
Shirley Guzmán, Silvia Marin, Anibal Miranda, Vitaly A Selivanov, Josep J Centelles, Romain Harmancey, Fatima Smih, Annie Turkieh, Yves Durocher, Antonio Zorzano, Philippe Rouet, Marta Cascante
BMC Systems Biology.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Bee Pollen Improves Muscle Protein and Energy Metabolism in Malnourished Old Rats through Interfering with the Mtor Signaling Pathway and Mitochondrial Activity
Jérôme Salles, Nicolas Cardinault, Véronique Patrac, Alexandre Berry, Christophe Giraudet, Marie-Laure Collin, Audrey Chanet, Camille Tagliaferri, Philippe Denis, Corinne Pouyet, Yves Boirie, Stéphane Walrand
Nutrients.2014; 6(12): 5500. CrossRef
- Resistin – A Plausible Therapeutic Target in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis
- Association of Estrogen Receptor α Genes
Pvu II andXba I Polymorphisms with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the Inpatient Population of a Hospital in Southern Iran - Farzaneh Mohammadi, Mohammad Pourahmadi, Mohadeseh Mosalanejad, Houshang Jamali, Mohamed Amin Ghobadifar, Saeideh Erfanian
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(4):270-277. Published online August 14, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.4.270
- 3,427 View
- 36 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Estrogen plays a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Very few studies have shown the association between estrogen receptor α (ERα),
Pvu II andXba I gene polymorphisms with T2DM in both men and women. We evaluated the hypothesis thatPvu II andXba I polymorphisms of ERα gene may be associated with T2DM in adult.Methods From spring of 2010 to the fall of 2011, a case-control study was performed at clinical centers of Jahrom University of Medical Sciences. We included 174 patients with T2DM including men and women and 174 age, sex, and body mass index frequency-matched health controls. We analyzed the
Pvu II andXba I polymorphisms of ERα by using the polymerase chain reaction-based restriction fragment length polymorphism method.Results No significant differences between demographic characteristics of control and patients groups were observed. Allele frequencies of both
Pvu II andXba I polymorphisms were significantly different between patients and control subjects (P =0.014 vs.P =0.002, respectively). When the group was separated into women and men, logistic regression analysis of genotype distribution ofPvu II (pp vs. Pp+PP) in both sexes revealed that there was no significant association ofPvu II genotype with men (odds ratio [OR], 1.67; confidence interval [CI], 0.86 to 3.28;P =0.89) and women (OR, 0.96; CI, 0.53 to 1.74;P =0.12).Conclusion Pvu II andXba I polymorphisms in ERα are related with T2DM in the inpatient population.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Single-nucleotide polymorphisms as important risk factors of diabetes among Middle East population
Iman Akhlaghipour, Amir Reza Bina, Mohammad Reza Mogharrabi, Ali Fanoodi, Amir Reza Ebrahimian, Soroush Khojasteh Kaffash, Atefeh Babazadeh Baghan, Mohammad Erfan Khorashadizadeh, Negin Taghehchian, Meysam Moghbeli
Human Genomics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Estrogen receptor 1 gene polymorphisms (PvuII and XbaI) are associated with type 2 diabetes in Palestinian women
Suheir Ereqat, Stéphane Cauchi, Khaled Eweidat, Muawiyah Elqadi, Abedelmajeed Nasereddin
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7164. CrossRef - Association between Genetic Variants and Diabetes Mellitus in Iranian Populations: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies
Mehrnoosh Khodaeian, Samaneh Enayati, Ozra Tabatabaei-Malazy, Mahsa M. Amoli
Journal of Diabetes Research.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Genetic polymorphism of estrogen receptor alpha gene in Egyptian women with type II diabetes mellitus
Tarek M.K. Motawi, Mahmoud A. El-Rehany, Sherine M. Rizk, Maggie M. Ramzy, Doaa M. el-Roby
Meta Gene.2015; 6: 36. CrossRef
- Single-nucleotide polymorphisms as important risk factors of diabetes among Middle East population
- Post-Renal Transplant Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Subjects: Superimposition of Transplant-Related Immunosuppressant Factors on Genetic and Type 2 Diabetic Risk Factors
- Hyun Chul Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(3):199-206. Published online June 14, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.3.199
- 3,612 View
- 31 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Postrenal transplantation diabetes mellitus (PTDM), or new-onset diabetes after organ transplantation, is an important chronic transplant-associated complication. Similar to type 2 diabetes, decreased insulin secretion and increased insulin resistance are important to the pathophysiologic mechanism behind the development of PTDM. However, β-cell dysfunction rather than insulin resistance seems to be a greater contributing factor in the development of PTDM. Increased age, family history of diabetes, ethnicity, genetic variation, obesity, and hepatitis C are partially accountable for an increased underlying risk of PTDM in renal allograft recipients. In addition, the use of and kinds of immunosuppressive agents are key transplant-associated risk factors. Recently, a number of genetic variants or polymorphisms susceptible to immunosuppressants have been reported to be associated with calcineurin inhibition-induced β-cell dysfunction. The identification of high risk factors of PTDM would help prevent PTDM and improve long-term patient outcomes by allowing for personalized immunosuppressant regimens and by managing cardiovascular risk factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors Related to New-Onset Diabetes after Renal Transplantation in Patients of a High Complexity University Hospital in Colombia, 20 Years of Experience
Guillermo E. Guzmán, Angela M. Victoria, Isabella Ramos, Alejandro Maldonado, Eliana Manzi, Juan F. Contreras-Valero, Liliana Mesa, Johanna Schweineberg, Juan G. Posada, Jorge I. Villegas, Luis A. Caicedo, Carlos E. Durán
International Journal of Endocrinology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Synthesis of Fructose Biosensors and Progressing Their Efficiency Using Californium Colloidal Nanoparticles for Detecting Fructose and Triglycerides
Alireza Heidari
Advanced Science, Engineering and Medicine.2020; 12(8): 1002. CrossRef - Comparison of Glucose Tolerance between Kidney Transplant Recipients and Healthy Controls
Hisao Shimada, Junji Uchida, Shunji Nishide, Kazuya Kabei, Akihiro Kosoku, Keiko Maeda, Tomoaki Iwai, Toshihide Naganuma, Yoshiaki Takemoto, Tatsuya Nakatani
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(7): 920. CrossRef - Diabètes post-transplantation rénale
Danièle Dubois-Laforgue
Néphrologie & Thérapeutique.2017; 13: S137. CrossRef - Risk assessment and management of post-transplant diabetes mellitus
Eugene Han, Myoung Soo Kim, Yu Seun Kim, Eun Seok Kang
Metabolism.2016; 65(10): 1559. CrossRef - Renal posttransplantation diabetes mellitus: An overview
Ana Laura Pimentel, Andrea Carla Bauer, Joíza Lins Camargo
Clinica Chimica Acta.2015; 450: 327. CrossRef - HMG CoA Reductase Inhibitor Treatment Induces Dysglycemia in Renal Allograft Recipients
Eun Yeong Choe, Hye Jin Wang, Obin Kwon, Yongin Cho, Kyu Ha Huh, Myoung Soo Kim, Yu Seun Kim, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Eun Seok Kang
Transplantation.2014; 97(4): 419. CrossRef - Statin therapy is associated with the development of new-onset diabetes after transplantation in liver recipients with high fasting plasma glucose levels
Yongin Cho, Min Jung Lee, Eun Yeong Choe, Chang Hee Jung, Dong Jin Joo, Myoung Soo Kim, Bong Soo Cha, Joong-Yeol Park, Eun Seok Kang
Liver Transplantation.2014; 20(5): 557. CrossRef - Post-Transplant Diabetes Mellitus: Is It Associated With Poor Allograft Outcomes in Renal Transplants?
J.Y. Choi, O.J. Kwon
Transplantation Proceedings.2013; 45(8): 2892. CrossRef
- Risk Factors Related to New-Onset Diabetes after Renal Transplantation in Patients of a High Complexity University Hospital in Colombia, 20 Years of Experience
- Challenges in Diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes in Different Populations
- Marian Rewers
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(2):90-97. Published online April 17, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.2.90
- 3,966 View
- 48 Download
- 33 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Diabetes affects today an estimated 366 million people world-wide, including 20 million to 40 million of patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). While T1D accounts for 5% to 20% of those with diabetes, it is associated with higher morbidity, mortality and health care cost than the more prevalent type 2 diabetes. Patients with T1D require exogenous insulin for survival and should be identified as soon as possible after diagnosis to avoid high morbidity due to a delay in insulin treatment. It is also important to present to the patient correct prognosis that differs by the type of diabetes. From the research point of view, correct classification should help to identify the etiologies and to develop specific prevention for T1D. This review summarizes evidence that may be helpful in diagnosing T1D in various ethnic groups. Challenges in interpretation of results commonly used to determine the type of diabetes are highlighted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Corneal Endothelium and Central Corneal Thickness in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Semra Tiryaki Demir, Ahmet Uçar, Gizem Kara Elitok, Sümeyra Keleş Yeşiltaş, Emine Betül Akbaş Özyürek, Saniye Üke Uzun
Hamidiye Medical Journal.2023; 4(1): 50. CrossRef - Analysis of Corneal and Lens Densitometry Changes in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Yusuf Cem Yilmaz, Serife Ciloglu Hayat, Sefik Can Ipek
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2023; 254: 23. CrossRef - Altered Prevalence of Pulp Diagnoses in Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Retrospective Study
Yandy Gonzalez Marrero, Yoshifumi Kobayashi, Mohammad Saqib Ihsan, Lisa A. Pilch, Liyaa Chen, Shuying Jiang, Yi Ye, Daniel H. Fine, Carla Y. Falcon, Paul A. Falcon, Craig S. Hirschberg, Emi Shimizu
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(2): 208. CrossRef - The relationship between GAD65 autoantibody and the risk of T1DM onset
Elham Keshavarzi, Behnoud Baradaran Noveiry, Nima Rezaei
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2022; 21(2): 1935. CrossRef - Ketosis-Prone Type 2 Diabetes (Flatbush Diabetes) in Remission: A Report of Two Cases
Beisi Ji, SumathaChannapatna Suresh, Klynt Bally, Kamrun Naher, Mary A Banerji
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of immune cell components and immune-related gene expression profiles in peripheral blood of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Jian Lin, Yuanhua Lu, Bizhou Wang, Ping Jiao, Jie Ma
Journal of Translational Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of a subgroup of black South Africans with type 1 diabetes who are older at diagnosis but have lower levels of glutamic acid decarboxylase and islet antigen 2 autoantibodies
C. J. Padoa, P. Rheeder, F. J. Pirie, A. A. Motala, J. C. van Dyk, N. J. Crowther
Diabetic Medicine.2020; 37(12): 2067. CrossRef - Evaluation of retinal neurovascular structures by optical coherence tomography and optical coherence tomography angiography in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus without clinical sign of diabetic retinopathy
Semra Tiryaki Demir, Ahmet Ucar, Gizem Kara Elitok, Mehmet Egemen Karatas, Murat Karapapak, Oguz Kaan Kutucu, Saniye Uke Uzun, Dilek Guven
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology.2020; 258(11): 2363. CrossRef - A Genome-Wide Analysis of Long Noncoding RNAs in Circulating Leukocytes and Their Differential Expression in Type 1 Diabetes Patients
Yihan Liu, Xiaoming Du, Jia Cui, Changlong Li, Meng Guo, Jianyi Lv, Xin Liu, Jingtao Dou, Xiaoyan Du, Hongjuan Fang, Zhenwen Chen, Bernd Stratmann
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Uncommon Presentations of Diabetes: Zebras in the Herd
Karen L. Shidler, Lisa R. Letourneau, Lucia M. Novak
Clinical Diabetes.2020; 38(1): 78. CrossRef - Changes in Retinal Microcirculation Precede the Clinical Onset of Diabetic Retinopathy in Children With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Merve Inanc, Kemal Tekin, Hasan Kiziltoprak, Servan Ozalkak, Sibel Doguizi, Zehra Aycan
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2019; 207: 37. CrossRef - Autoimmune signatures for prediction and diagnosis of autoimmune diabetes in Kuwait
Mohamed Jahromi, Fahd Al-Mulla, Ebaa Al-Ozairi
Autoimmunity Reviews.2019; 18(6): 642. CrossRef - Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) and Islet Autoantibodies Are Tools to Characterize Type 1 Diabetes in Arab Countries: Emphasis on Kuwait
Mohamed Jahromi, Ebaa Al-Ozairi
Disease Markers.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Complete loss of insulin secretion capacity in type 1A diabetes patients during long‐term follow up
Sae Uno, Akihisa Imagawa, Junji Kozawa, Kenji Fukui, Hiromi Iwahashi, Iichiro Shimomura
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2018; 9(4): 806. CrossRef - Incidence of type 1 diabetes has doubled in Kuwaiti children 0-14 years over the last 20 years
Azza A. Shaltout, Deborah Wake, Thangavel A. Thanaraj, Dina M. Omar, Dalia Al-AbdulRazzaq, Arshad Channanath, Hessa AlKandari, Majedah Abdulrasoul, Sophie Miller, Nicholas Conway, Jaakko Tuomilehto, Lena Davidsson
Pediatric Diabetes.2017; 18(8): 761. CrossRef - Objective Evaluation of Corneal and Lens Clarity in Children With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Kemal Tekin, Merve Inanc, Erdal Kurnaz, Elvan Bayramoglu, Emre Aydemir, Mustafa Koc, Zehra Aycan
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2017; 179: 190. CrossRef - Differential association of body mass index on glycemic control in type 1 diabetes
Eun Young Lee, Yong‐ho Lee, Sang‐Man Jin, Hae Kyung Yang, Chang Hee Jung, Cheol‐Young Park, Jae Hyoung Cho, Woo Je Lee, Byung‐Wan Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Progress and challenges in macroencapsulation approaches for type 1 diabetes (T1D) treatment: Cells, biomaterials, and devices
Shang Song, Shuvo Roy
Biotechnology and Bioengineering.2016; 113(7): 1381. CrossRef - Covariation of the Incidence of Type 1 Diabetes with Country Characteristics Available in Public Databases
Paula Andrea Diaz-Valencia, Pierre Bougnères, Alain-Jacques Valleron
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(2): e0118298. CrossRef - Glycated albumin and the risk of micro- and macrovascular complications in subjects with Type 1 Diabetes
Hye-jin Yoon, Yong-ho Lee, So Ra Kim, Tyler Hyungtaek Rim, Eun Young Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant protection in girls with type 1 diabetes mellitus during reproductive system development
Lubov I. Kolesnikova, Marina A. Darenskaya, Natalia V. Semenova, Lyudmila A. Grebenkina, Larisa V. Suturina, Marya I. Dolgikh, Svetlana V. Gnusina
Medicina.2015; 51(2): 107. CrossRef - Diagnostic criteria for acute‐onset type 1 diabetes mellitus (2012): Report of the Committee of Japan Diabetes Society on the Research of Fulminant and Acute‐onset Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Eiji Kawasaki, Taro Maruyama, Akihisa Imagawa, Takuya Awata, Hiroshi Ikegami, Yasuko Uchigata, Haruhiko Osawa, Yumiko Kawabata, Tetsuro Kobayashi, Akira Shimada, Ikki Shimizu, Kazuma Takahashi, Masao Nagata, Hideichi Makino, Toshiaki Hanafusa
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2014; 5(1): 115. CrossRef - The Glycated Albumin to Glycated Hemoglobin Ratio Might Not Be Associated with Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Wonjin Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(6): 456. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus associada à desnutrição proteica: realidade ou ficção?
Ana Rita Caldas, André Couto Carvalho, Anabela Giestas, Marta Almeida Ferreira, Cláudia Amaral, Cláudia Freitas, Maria Helena Cardoso
Revista Portuguesa de Endocrinologia, Diabetes e Metabolismo.2014; 9(1): 79. CrossRef - Diagnostic criteria for acute-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus (2012)
Eiji Kawasaki, Taro Maruyama, Akihisa Imagawa, Takuya Awata, Hiroshi Ikegami, Yasuko Uchigata, Haruhiko Osawa, Yumiko Kawabata, Tetsuro Kobayashi, Akira Shimada, Ikki Shimizu, Kazuma Takahashi, Masao Nagata, Hideichi Makino, Toshiaki Hanafusa
Diabetology International.2013; 4(4): 221. CrossRef - Phenylmethimazole Suppresses dsRNA-Induced Cytotoxicity and Inflammatory Cytokines in Murine Pancreatic Beta Cells and Blocks Viral Acceleration of Type 1 Diabetes in NOD Mice
Kelly McCall, Martin Schmerr, Jean Thuma, Calvin James, Maria Courreges, Fabian Benencia, Ramiro Malgor, Frank Schwartz
Molecules.2013; 18(4): 3841. CrossRef - Variation of C peptide decay rate in diabetic patients with positive glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody: better discrimination with initial fasting C peptide
Xia Li, Gan Huang, Jian Lin, Lin Yang, Zhiguang Zhou
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - The Emerging Global Epidemic of Type 1 Diabetes
Jaakko Tuomilehto
Current Diabetes Reports.2013; 13(6): 795. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and insulin independence of Koreans with new‐onset type 2 diabetes presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis
H. Seok, C. H. Jung, S. W. Kim, M. J. Lee, W. J. Lee, J. H. Kim, B‐W. Lee
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2013; 29(6): 507. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and inflammatory pulpal and periapical disease: a review
S. M. F. Lima, D. C. Grisi, E. M. Kogawa, O. L. Franco, V. C. Peixoto, J. F. Gonçalves‐Júnior, M. P. Arruda, T. M. B. Rezende
International Endodontic Journal.2013; 46(8): 700. CrossRef - UM OLHAR SOBRE O DIABETES NA INFÂNCIA E NA JUVENTUDE: NEM TODOS SÃO TIPO 1
Mauren Isfer ANGHEBEM-OLIVEIRA
Infarma - Ciências Farmacêuticas.2013; 25(4): 206. CrossRef - Proteome‐base biomarkers in diabetes mellitus: Progress on biofluids' protein profiling using mass spectrometry
Ana Isabel Padrão, Rita Ferreira, Rui Vitorino, Francisco Amado
PROTEOMICS – Clinical Applications.2012; 6(9-10): 447. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus: formas de presentación clínica y diagnóstico diferencial de la hiperglucemia en la infancia y adolescencia
Ó. Rubio Cabezas, J. Argente
Anales de Pediatría.2012; 77(5): 344.e1. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Corneal Endothelium and Central Corneal Thickness in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
- The Importance of Global Studies of the Genetics of Type 2 Diabetes
- Mark I. McCarthy
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(2):91-100. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.2.91
- 4,142 View
- 29 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Genome wide association analyses have revealed large numbers of common variants influencing predisposition to type 2 diabetes and related phenotypes. These studies have predominantly featured European populations, but are now being extended to samples from a wider range of ethnic groups. The transethnic analysis of association data is already providing insights into the genetic, molecular and biological causes of diabetes, and the relevance of such studies will increase as human discovery genetics increasingly moves towards sequencing-based approaches and a focus on low frequency and rare variants.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Validation and genetic heritability estimation of known type 2 diabetes related variants in the Korean population
Hye-Mi Jang, Mi Yeong Hwang, Bong-Jo Kim, Young Jin Kim
Genomics & Informatics.2021; 19(4): e37. CrossRef - Distinct subtypes of polycystic ovary syndrome with novel genetic associations: An unsupervised, phenotypic clustering analysis
Matthew Dapas, Frederick T. J. Lin, Girish N. Nadkarni, Ryan Sisk, Richard S. Legro, Margrit Urbanek, M. Geoffrey Hayes, Andrea Dunaif, Jenny E. Myers
PLOS Medicine.2020; 17(6): e1003132. CrossRef - Association of a genetic variant of the ZPR1 zinc finger gene with type 2 diabetes mellitus
FUMITAKA TOKORO, REIKO MATSUOKA, SHINTARO ABE, MASAZUMI ARAI, TOSHIYUKI NODA, SACHIRO WATANABE, HIDEKI HORIBE, TETSUO FUJIMAKI, MITSUTOSHI OGURI, KIMIHIKO KATO, SHINYA MINATOGUCHI, YOSHIJI YAMADA
Biomedical Reports.2015; 3(1): 88. CrossRef - Insights into the Genetic Susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes from Genome-Wide Association Studies of Glycaemic Traits
Letizia Marullo, Julia S. El-Sayed Moustafa, Inga Prokopenko
Current Diabetes Reports.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Towards Virtual Knowledge Broker services for semantic integration of life science literature and data sources
Ian Harrow, Wendy Filsell, Peter Woollard, Ian Dix, Michael Braxenthaler, Richard Gedye, David Hoole, Richard Kidd, Jabe Wilson, Dietrich Rebholz-Schuhmann
Drug Discovery Today.2013; 18(9-10): 428. CrossRef - Genome-Wide Association Study for Type 2 Diabetes in Indians Identifies a New Susceptibility Locus at 2q21
Rubina Tabassum, Ganesh Chauhan, Om Prakash Dwivedi, Anubha Mahajan, Alok Jaiswal, Ismeet Kaur, Khushdeep Bandesh, Tejbir Singh, Benan John Mathai, Yogesh Pandey, Manickam Chidambaram, Amitabh Sharma, Sreenivas Chavali, Shantanu Sengupta, Lakshmi Ramakris
Diabetes.2013; 62(3): 977. CrossRef - A replication study of 19 GWAS-validated type 2 diabetes at-risk variants in the Lebanese population
Wassim Y. Almawi, Rita Nemr, Sose H. Keleshian, Akram Echtay, Fabiola Lisa Saldanha, Fatima A. AlDoseri, Eddie Racoubian
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2013; 102(2): 117. CrossRef - Single nucleotide polymorphisms in JAZF1 and BCL11A gene are nominally associated with type 2 diabetes in African-American families from the GENNID study
Kurt A Langberg, Lijun Ma, Neeraj K Sharma, Craig L Hanis, Steven C Elbein, Sandra J Hasstedt, Swapan K Das
Journal of Human Genetics.2012; 57(1): 57. CrossRef - Typ-2-Diabetes-assoziierte Gene
J. Kriebel, H. Grallert, T. Illig
Der Diabetologe.2012; 8(1): 26. CrossRef - Genomweite Assoziationsstudien (GWAS) — Möglichkeiten und Grenzen
Jennifer Kriebel, Thomas Illig, Harald Grallert
BIOspektrum.2012; 18(5): 508. CrossRef - T2DM: Why Epigenetics?
Delphine Fradin, Pierre Bougnères
Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism.2011; 2011: 1. CrossRef
- Validation and genetic heritability estimation of known type 2 diabetes related variants in the Korean population

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





