
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- The Ratio of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Based on Cystatin C and Creatinine Reflecting Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetic Patients
- Ah Reum Khang, Min Jin Lee, Dongwon Yi, Yang Ho Kang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):415-425. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0177
- 1,864 View
- 114 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
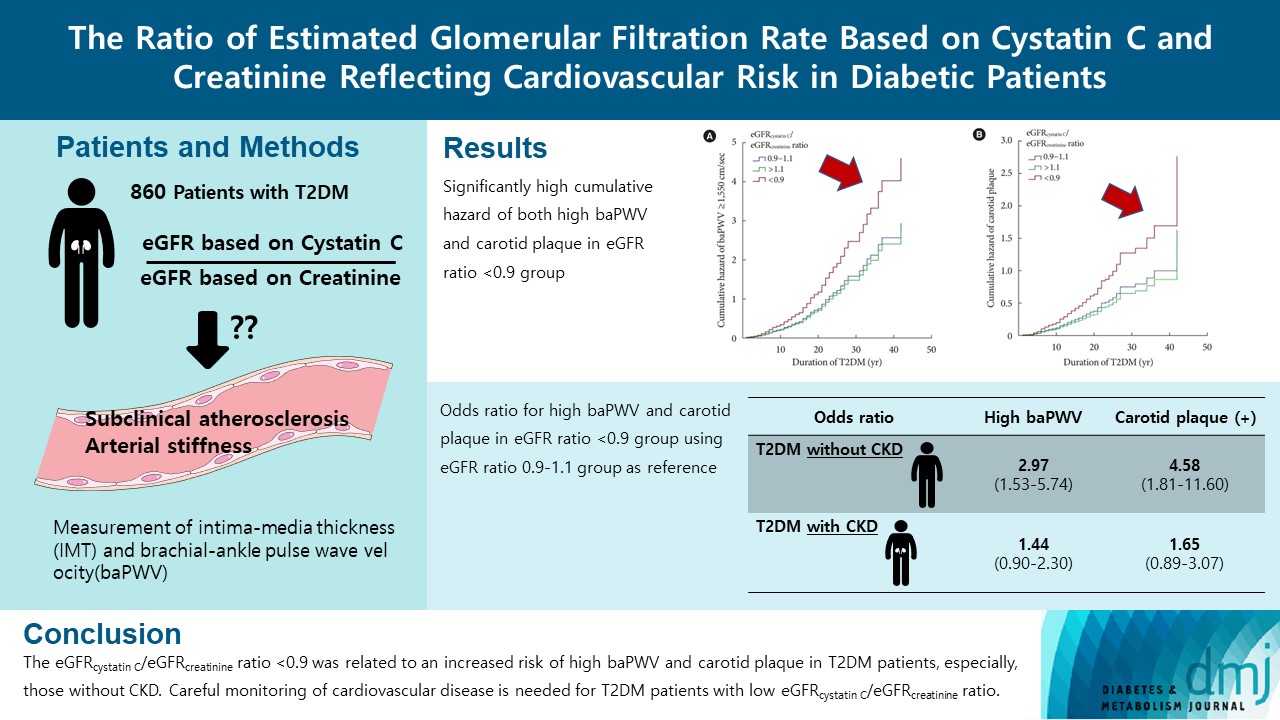
The ratio of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) based on cystatin C and creatinine (eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio) is related to accumulating atherosclerosis-promoting proteins and increased mortality in several cohorts.
Methods
We assessed whether the eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio is a predictor of arterial stiffness and sub-clinical atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, who were followed up during 2008 to 2016. GFR was estimated using an equation based on cystatin C and creatinine.
Results
A total of 860 patients were stratified according to their eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio (i.e., <0.9, 0.9–1.1 [a reference group], and >1.1). Intima-media thickness was comparable among the groups; however, presence of carotid plaque was frequent in the <0.9 group (<0.9 group, 38.3%; 0.9–1.1 group, 21.6% vs. >1.1 group, 17.2%, P<0.001). Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) was faster in the <0.9 group (<0.9 group, 1,656.3±333.0 cm/sec; 0.9–1.1 group, 1,550.5±294.8 cm/sec vs. >1.1 group, 1,494.0±252.2 cm/sec, P<0.001). On comparing the <0.9 group with the 0.9–1.1 group, the multivariate-adjusted odds ratios of prevalence of high baPWV and carotid plaque were 2.54 (P=0.007) and 1.95 (P=0.042), respectively. Cox regression analysis demonstrated near or over 3-fold higher risks of the prevalence of high baPWV and carotid plaque in the <0.9 group without chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Conclusion
We concluded that eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio <0.9 was related to an increased risk of high baPWV and carotid plaque in T2DM patients, especially, those without CKD. Careful monitoring of cardiovascular disease is needed for T2DM patients with low eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intraindividual difference in estimated GFR by creatinine and cystatin C, cognitive trajectories and motoric cognitive risk syndrome
Jinqi Wang, Yueruijing Liu, Rui Jin, Xiaoyu Zhao, Zhiyuan Wu, Ze Han, Zongkai Xu, Xiuhua Guo, Lixin Tao
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2024; 39(5): 860. CrossRef - Research Progress of Creatinine, Cystatin C, and Their Ratio in Renal Diseases
广智 杨
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(04): 976. CrossRef - Muscle mass, creatinine, cystatin C and selective glomerular hypofiltration syndromes
Linnea Malmgren, Anders Grubb
Clinical Kidney Journal.2023; 16(8): 1206. CrossRef - Investigating kidney function changes in young adults with COVID-19: Serum creatinine level, glomerular filtration rate, and biochemical profile analysis
Nikita Matyushin, Dmitriy Ermakov, Inna Vasileva, Roza Vakolyuk, Anastasiya Spaska
Electronic Journal of General Medicine.2023; 20(6): em547. CrossRef
- Intraindividual difference in estimated GFR by creatinine and cystatin C, cognitive trajectories and motoric cognitive risk syndrome
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Normalized Creatinine-to-Cystatin C Ratio and Risk of Diabetes in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
- Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Bo Xie, Yang Yuan, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):476-485. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0074
- 4,774 View
- 205 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
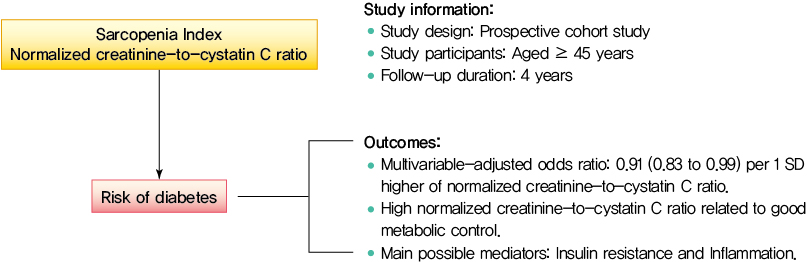
Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio is recently suggested to be a surrogate marker for sarcopenia. However, little is known about its association with diabetes. This study aimed to fill in this gap based on a large-scale prospective cohort.
Methods
A population-based representative sample of 5,055 participants aged ≥45 years from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study was enrolled between 2011 and 2012 and followed at least once during the subsequent surveys at 2013, 2015, or 2018. Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio was calculated and normalized by body weight. Incident diabetes was ascertained by plasma glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, self-reported history, or use of anti-diabetic drugs. Logistic regression analysis and mediation analysis were employed.
Results
During follow-up, 634 participants developed diabetes. The risk of diabetes was gradually and significantly decreased with increased normalized creatinine–cystatin C ratio. The multivariable-adjusted odds ratio for diabetes was 0.91 (95% confidence interval, 0.83 to 0.99) per 1 standard deviation higher of normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio, and this relationship remained significant after controlling for muscle strength. The risk reduction in diabetes was significantly larger in participants with normal-weight and high normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio compared with those with overweight/obesity and high normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio (Pinteraction=0.01). Insulin resistance and inflammation appeared to be key mediators accounting for the observed relationship between normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio and risk of diabetes, with their mediating effect being 93.1% and 22.0%, respectively.
Conclusion
High normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio is associated with reduced risk of diabetes in middle-aged and older adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Muscle Quality in Relation to Prediabetes Phenotypes: A Population-Based Study With Mediation Analysis
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Xiaoying Zhou, Jinshui Xu, Zilin Sun, Haijian Guo, Tongzhi Wu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1151. CrossRef - Sex‐specific associations between skeletal muscle mass and incident diabetes: A population‐based cohort study
Dan Liu, Nan Li, Yiling Zhou, Miye Wang, Peige Song, Changzheng Yuan, Qingyang Shi, Hui Chen, Kaixin Zhou, Huan Wang, Tao Li, Xiong‐Fei Pan, Haoming Tian, Sheyu Li
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(3): 820. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus Should Be Considered While Analysing Sarcopenia-Related Biomarkers
Justyna Rentflejsz, Zyta Beata Wojszel
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(4): 1107. CrossRef - Associations of muscle mass and strength with new-onset diabetes among middle-aged and older adults: evidence from the China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS)
Yun-Yun He, Mei-Ling Jin, Xiang-Yang Fang, Xiao-Juan Wang
Acta Diabetologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The serum creatinine to cystatin C to waist circumference ratios predicts risk for type 2 diabetes: A Chinese cohort study
Yinfei Chen, Weiheng Wen, Zhiliang Mai, Ming Wang, Hong Chen, Jia Sun
Journal of Diabetes.2023; 15(10): 808. CrossRef - Associations of sarcopenia with peak expiratory flow among community-dwelling elderly population: based on the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS)
Yun-Yun He, Mei-Ling Jin, Jing Chang, Xiao-Juan Wang
European Geriatric Medicine.2023; 15(1): 95. CrossRef - Additive impact of diabetes and sarcopenia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A longitudinal nationwide population-based study
Eyun Song, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Ahreum Jang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155678. CrossRef
- Muscle Quality in Relation to Prediabetes Phenotypes: A Population-Based Study With Mediation Analysis
- Clinical Usefulness of Serum Cystatin C as a Marker of Renal Function
- Kwang-Sook Woo, Jae-Lim Choi, Bo-Ram Kim, Ji-Eun Kim, Jin-Yeong Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(4):278-284. Published online August 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.4.278
- 4,204 View
- 47 Download
- 24 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Accurate renal function measurements are important in the diagnosis and treatment of kidney diseases. In contrast to creatinine, the production of serum cystatin C has been extensively reported to be unaffected by body muscle mass, age, gender, and nutritional status.
Methods Our study included 37 samples from diabetic chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients for whom serum creatinine tests had been requested and 40 samples from a healthy populations in Dong-A University Hospital between May 2010 and June 2010. The assay precision (i.e., the coefficient of variation) and the reference range of the serum cystatin C test were evaluated. We compared the estimated glomerular filtration rates (GFRs) based on cystatin C with those based on creatinine. Moreover, we investigated the influences of age, gender, weight, and muscle mass on serum creatinine and serum cystatin C.
Results There was a positive correlation between GFR based on creatinine and that based on cystatin C (
r =0.79,P <0.0001) among the diabetic CKD patients. Serum creatinine and cystatin C were significantly correlated with body weight and muscle mass, but the strengths of these correlations were greater for serum creatinine. The precision study revealed excellent results for both the high and low controls. The 95% reference interval of cystatin C in the healthy population was 0.371 to 1.236 mg/L.Conclusion Based on these results, we conclude that, despite the strong correlation between serum creatinine and cystatin C, cystatin C is less affected by weight and muscle mass and might represent a better alternative for the assessment of renal function.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dyslipidemia and serum cystatin C levels as biomarker of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Tadesse Asmamaw Dejenie, Endeshaw Chekol Abebe, Misganaw Asmamaw Mengstie, Mohammed Abdu Seid, Natnael Atnafu Gebeyehu, Getachew Asmare Adella, Gizchew Ambaw Kassie, Amanuel Yosef Gebrekidan, Molalegn Mesele Gesese, Kirubel Dagnaw Tegegne, Denekew Tenaw A
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum creatinine and type 2 diabetes in the Chinese population: a retrospective cohort study
Rugang Li, Min He, Qilin Yang, Zezhi Liang, Ying li, Ling Huang, Rong Wu, Jieping Huang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Significance of Diabetic Kidney Disease Biomarkers in Predicting Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Jaehyun Bae, Byung-Wan Lee
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1928. CrossRef - Reconsideration of the current models of estimated kidney function‐based drug dose adjustment in older adults: The role of biological age
Radin Alikhani, Manjunath P. Pai
Clinical and Translational Science.2023; 16(11): 2095. CrossRef - The Level of Plasma Cystatin C in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Tuan Nguyen Van, Linh Phan Ha, Diep Pham Thao, Minh Nguyen Thi Binh, Minh Hoang Thi, Thuan Huynh Quang, Lan Thi Phuong Dam
Nephro-Urology Monthly.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of cystatin C in urogenital malignancy
Li Ding, Zijie Liu, Junqi Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of cystatin C-based and creatinine-based glomerular filtration rate in the prediction of postoperative residual hypertension in aldosterone-producing adenoma patients after adrenalectomy
Ching-Way Chen, Cheng-Hsuan Tsai, Chi-Sheng Hung, I-Jung Tsai, Yu-Wei Chiu, Chin-Cheng Chang, Kao-Lang Liu, Shih-Cheng Liao, Vin-Cent Wu, Yen-Hung Lin
Clinica Chimica Acta.2021; 520: 147. CrossRef - Harmonizing acute and chronic kidney disease definition and classification: report of a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Consensus Conference
Norbert H. Lameire, Adeera Levin, John A. Kellum, Michael Cheung, Michel Jadoul, Wolfgang C. Winkelmayer, Paul E. Stevens, Fergus J. Caskey, Chris K.T. Farmer, Alejandro Ferreiro Fuentes, Masafumi Fukagawa, Stuart L. Goldstein, Grace Igiraneza, Andreas Kr
Kidney International.2021; 100(3): 516. CrossRef - Correlation of Serum Cystatin C with Renal Function in Gout Patients with Renal Injury
Yanqun Wu, Shunhua Wang, Xiaoqing Xu
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research.2021; 41(9): 329. CrossRef - Stressors and Resilience: An Integrative Model for Understanding Chronic Kidney Disease
Jacob Hwang, Arvin Jenab
Alternative and Complementary Therapies.2021; 27(6): 267. CrossRef - The role of serum cystatin C in estimation of renal function in survivors of critical illness
Jirarat Eiamcharoenying, Win Kulvichit, Nuttha Lumlertgul, Tawatchai Chaiwatanarat, Sadudee Peerapornratana, Nattachai Srisawat
Journal of Critical Care.2020; 59: 201. CrossRef - Clinician perspectives on inpatient cystatin C utilization: A qualitative case study at Mayo Clinic
James Roland Markos, Karen S. Schaepe, Hilary R. Teaford, Andrew D. Rule, Kianoush B. Kashani, John C. Lieske, Erin F. Barreto, Pierre Delanaye
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(12): e0243618. CrossRef - Influence of Anthropometric Measurements on Serum Creatinine, Urea and eGFR in Healthy Adolescent Subjects
Kavita Rasalkar, Nagaraju Kashamsetty, Bandi Sai Karthik
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2020; 7(36): 1917. CrossRef - Biology and Management of Navel Orangeworm (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in California
Houston Wilson, Charles S Burks, Joshua E Reger, Jacob A Wenger, Kelly Tindall
Journal of Integrated Pest Management.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Low serum creatinine and risk of diabetes: The Japan Epidemiology Collaboration on Occupational Health Study
Huanhuan Hu, Tohru Nakagawa, Toru Honda, Shuichiro Yamamoto, Hiroko Okazaki, Makoto Yamamoto, Toshiaki Miyamoto, Masafumi Eguchi, Takeshi Kochi, Makiko Shimizu, Taizo Murakami, Kentaro Tomita, Takayuki Ogasawara, Naoko Sasaki, Akihiko Uehara, Keisuke Kuwa
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2019; 10(5): 1209. CrossRef - Comparison of monitoring techniques in and near almonds and pistachios under mating disruption treatment for navel orangeworm
C. Burks, B. Higbee, J. Beck
Acta Horticulturae.2018; (1219): 331. CrossRef - Evaluation of creatinine-based and cystatin C-based equations for estimation of glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetic patients
Caroline Pereira Domingueti, Rodrigo Bastos Fóscolo, Ana Cristina Simões e Silva, Luci Maria S. Dusse, Janice Sepúlveda Reis, Maria das Graças Carvalho, Ana Paula Fernandes, Karina Braga Gomes
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 60(2): 108. CrossRef - Diagnostic Accuracy of Serum Cystatin C for the Evaluation of Renal Dysfunction in Diabetic Patients: A Meta‐Analysis
Shi‐kun Yang, Jun Liu, Xian‐ming Zhang, Chun Hu, Wei Zhang, Lin Sun, Hao Zhang
Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis.2016; 20(6): 579. CrossRef - Treatable glomerular hyperfiltration in patients with active acromegaly
Shingo Fujio, Koji Takano, Hiroshi Arimura, Mika Habu, Manoj Bohara, Horofumi Hirano, Ryosuke Hanaya, Yoshihiko Nishio, Chihaya Koriyama, Yasuyuki Kinoshita, Kazunori Arita
European Journal of Endocrinology.2016; 175(4): 325. CrossRef - Glomerular filtration rate assessed by using creatinine and cystatin in patients treated with dabigatran
Gianluca Gessoni, Sara Valverde, Francesca Gessoni, Letizia Valle, Marina Bortolotti, Vincenzo Lidestri, Michele Urso, Roberto Valle
La Rivista Italiana della Medicina di Laboratorio - Italian Journal of Laboratory Medicine.2016; 12(4): 243. CrossRef - СHARACTERISTICS OF THE HEART FATTY ACID-BINDING PROTEIN, INTERLEUKIN-6 AND INTERLEUKIN-8 AS ALTERNATIVE MARKERS OF DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY PROGRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
Yu. A. Ryzhikova, I. N. Vorozhtsova, T. V. Saprina, V. D. Zavadovskaya, A. B. Merinov, I. V. Kulagina
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2015; 14(5): 61. CrossRef - Performance of Cystatin C– and Creatinine-Based Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Equations Depends on Patient Characteristics
Jeffrey W Meeusen, Andrew D Rule, Nikolay Voskoboev, Nikola A Baumann, John C Lieske
Clinical Chemistry.2015; 61(10): 1265. CrossRef - Comparison and evaluation of lupus nephritis response criteria in lupus activity indices and clinical trials
Kristin M Corapi, Mary Anne Dooley, William F Pendergraft
Arthritis Research & Therapy.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Serum Cystatin C as a Marker of Early Renal Impairment in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
Mahmoud Omar, Wael Abdel-Razek, Gamal Abo-Raia, Medhat Assem, Gasser El-Azab
International Journal of Hepatology.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Efficient expression, purification and characterization of native human cystatin C in Escherichia coli periplasm
Yongjun Zhou, Yan Zhou, Jun Li, Jian Chen, Yuqin Yao, Lin Yu, Desheng Peng, Mingrong Wang, Dan Su, Yong He, Lantu Gou
Protein Expression and Purification.2015; 111: 18. CrossRef - Comparison of Carvedilol and Metoprolol for Preventing Contrast-Induced Nephropathy after Coronary Angiography
Mustafa Yılmaz, Alp Aydınalp, Kaan Okyay, Abdullah Tekin, Uğur Abbas Bal, Nilüfer Bayraktar, Aylin Yıldırır, Haldun Müderrisoğlu
Cardiorenal Medicine.2015; 5(3): 199. CrossRef
- Dyslipidemia and serum cystatin C levels as biomarker of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Serum Cystatin C Reflects the Progress of Albuminuria
- Jeong Seon Yoo, Young Mi Lee, Eun Hae Lee, Ji Woon Kim, Shin Young Lee, Ki-Cheon Jeong, Shin Ae Kang, Jong Suk Park, Joo Young Nam, Chul Woo Ahn, Young Duk Song, Kyung Rae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(6):602-609. Published online December 26, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.602
- 4,561 View
- 38 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Research on the relationship between urinary albumin excretion and serum cystatin C in diabetes is restricted to cross-sectional studies. In this study, we investigated how well serial measurements of serum cystatin C level reflect changes in the urinary albumin excretion rate.
Methods We enrolled and retrospectively collected data on 1,058 participants with type 2 diabetes who were older than 18 years and who had more than 3 years of follow-up with serial measurements of albuminuria and serum cystatin C at an outpatient clinic.
Results With the use of a linear mixed model, we found that the albuminuria level for each patient over time corresponded with the annual change in serum cystatin C-based estimated glomerular filtration rate (cysC-eGFR) but did not correspond with the creatinine-based eGFR calculated by the modification of diet in renal disease formula (MDRD-eGFR). The discrepancy in the direction of the trend was smaller with cysC-eGFR than with MDRD-eGFR.
Conclusion Serum cystatin C level reflects the trend in albuminuria level more accurately than serum creatinine level in Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of Cystatin C and Microalbumin as Biomarkers for Nephropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Bhuneshwar Yadav, Shashidhar K.N, Raveesha A, Muninarayana C.
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2021; 10(25): 1866. CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 698. CrossRef - Increase of BACE1, Brain-Renal Risk Factor, Contributes to Kidney Damage in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model
Yan Shi, Feng Gao, Xiaoli Yang, Dongwei Liu, Qiuxia Han, Zhangsuo Liu, Hanyu Zhu, Yong Shen
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2020; 76(1): 237. CrossRef - Diagnostic accuracy of cystitis C and β-2 microglobulin in detection of renal impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes
NourhanA Heiba, ManalS Negm, MaalyM Mabrouk, MohamedH Abou-Freikha
Tanta Medical Journal.2020; 48(2): 91. CrossRef - Lower Leg Fat Depots Are Associated with Albuminuria Independently of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Metabolic Syndrome (Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2008 to 2011)
Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 461. CrossRef - Evaluation of creatinine-based and cystatin C-based equations for estimation of glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetic patients
Caroline Pereira Domingueti, Rodrigo Bastos Fóscolo, Ana Cristina Simões e Silva, Luci Maria S. Dusse, Janice Sepúlveda Reis, Maria das Graças Carvalho, Ana Paula Fernandes, Karina Braga Gomes
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 60(2): 108. CrossRef
- Assessment of Cystatin C and Microalbumin as Biomarkers for Nephropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





