
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse > Previous issues
Review
- Pathophysiology
- Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hyun-Jin Kim, Kwang-il Kim, on Behalf of the Policy Committee of Korean Society of Hypertension
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):667-674. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0215

- 6,126 View
- 504 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The prevalence of diabetes mellitus continues to increase worldwide, and it is a well-established cardiovascular risk factor. Hypertension is also an important cardiovascular risk factor to be controlled and is common among patients with diabetes mellitus. Optimal blood pressure (BP) goals have been the subject of great debate in the management of hypertension among patients with diabetes mellitus. This review provides detailed results from randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses of clinical outcomes according to the target BP in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In addition, the target BP in patients with diabetes mellitus recommended by different guidelines was summarized and presented. A target BP of <140/90 mm Hg is recommended for patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus, and BP should be controlled to <130/80 mm Hg in patients with diabetes mellitus who have high-risk clinical features. We hope that this review will be helpful to clinicians and patients by promoting the understanding and appropriate application of BP control in the comprehensive management of patients with diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent evidence on target blood pressure in patients with hypertension
Hack-Lyoung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 17. CrossRef - Using Generative AI to Improve the Performance and Interpretability of Rule-Based Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Leon Kopitar, Iztok Fister, Gregor Stiglic
Information.2024; 15(3): 162. CrossRef - Additive interaction of family medical history of diabetes with hypertension on the diagnosis of diabetes among older adults in India: longitudinal ageing study in India
Waquar Ahmed
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging roles of interferon-stimulated gene-15 in age-related telomere attrition, the DNA damage response, and cardiovascular disease
María González-Amor, Beatriz Dorado, Vicente Andrés
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Diabetes and Voluntary Exercise on IgA Concentration and Polymeric Immunoglobulin Receptor Expression in the Submandibular Gland of Rats
Jaebum Park, Yuko Yamamoto, Kouki Hidaka, Satoko Wada-Takahashi, Shun-suke Takahashi, Toshiya Morozumi, Nobuhisa Kubota, Makiko Saita, Juri Saruta, Wakako Sakaguchi, Masahiro To, Tomoko Shimizu, Yuko Mikuni-Takagaki, Keiichi Tsukinoki
Medicina.2023; 59(4): 789. CrossRef - A diabetes update
Zachary Bloomgarden
Journal of Diabetes.2023; 15(7): 542. CrossRef - CARDIOPROTECTIVE AND METABOLIC EFFECTS OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE THERAPY IN PATIENTS WITH SUCH COMORBIDITIES AS ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION, TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS, AND OBESITY
I. P. Dunaieva, N. O. Kravchun, І. A. Ilchenko
Bulletin of Problems Biology and Medicine.2023; 1(2): 211. CrossRef - Hypertensive Heart Failure
Filippos Triposkiadis, Pantelis Sarafidis, Alexandros Briasoulis, Dimitrios E. Magouliotis, Thanos Athanasiou, John Skoularigis, Andrew Xanthopoulos
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(15): 5090. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef
- Recent evidence on target blood pressure in patients with hypertension
Editorial
- Asymptomatic Hypoglycemia after Metabolic Surgery: New Insights from Perioperative Continuous Glucose Monitoring
- Sang-Man Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):675-676. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0307
- 2,014 View
- 173 Download
Original Articles
- Basic Research
- Differentiation of Microencapsulated Neonatal Porcine Pancreatic Cell Clusters in Vitro Improves Transplant Efficacy in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Mice
- Gyeong-Jin Cheon, Heon-Seok Park, Eun-Young Lee, Min Jung Kim, Young-Hye You, Marie Rhee, Ji-Won Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):677-688. Published online February 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0202
- 4,517 View
- 252 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Neonatal porcine pancreatic cell clusters (NPCCs) have been proposed as an alternative source of β cells for islet transplantation because of their low cost and growth potential after transplantation. However, the delayed glucose lowering effect due to the immaturity of NPCCs and immunologic rejection remain as a barrier to NPCC’s clinical application. Here, we demonstrate accelerated differentiation and immune-tolerant NPCCs by in vitro chemical treatment and microencapsulation.
Methods
NPCCs isolated from 3-day-old piglets were cultured in F-10 media and then microencapsulated with alginate on day 5. Differentiation of NPCCs is facilitated by media supplemented with activin receptor-like kinase 5 inhibitor II, triiodothyronine and exendin-4 for 2 weeks. Marginal number of microencapsulated NPCCs to cure diabetes with and without differentiation were transplanted into diabetic mice and observed for 8 weeks.
Results
The proportion of insulin-positive cells and insulin mRNA levels of NPCCs were significantly increased in vitro in the differentiated group compared with the undifferentiated group. Blood glucose levels decreased eventually after transplantation of microencapsulated NPCCs in diabetic mice and normalized after 7 weeks in the differentiated group. In addition, the differentiated group showed nearly normal glucose tolerance at 8 weeks after transplantation. In contrast, neither blood glucose levels nor glucose tolerance were improved in the undifferentiated group. Retrieved graft in the differentiated group showed greater insulin response to high glucose compared with the undifferentiated group.
Conclusion
in vitro differentiation of microencapsulated immature NPCCs increased the proportion of insulin-positive cells and improved transplant efficacy in diabetic mice without immune rejection. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dual-targeted nano-encapsulation of neonatal porcine islet-like cell clusters with triiodothyronine-loaded bifunctional polymersomes
Sang Hoon Lee, Minse Kim, Eun-Jin Lee, Sun Mi Ahn, Yu-Rim Ahn, Jaewon Choi, Jung-Taek Kang, Hyun-Ouk Kim
Discover Nano.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Long‐term efficacy of encapsulated xenogeneic islet transplantation: Impact of encapsulation techniques and donor genetic traits
Heon‐Seok Park, Eun Young Lee, Young‐Hye You, Marie Rhee, Jong‐Min Kim, Seong‐Soo Hwang, Poong‐Yeon Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Dual-targeted nano-encapsulation of neonatal porcine islet-like cell clusters with triiodothyronine-loaded bifunctional polymersomes
- Drug/Regimen
- Comparison of Efficacy of Glimepiride, Alogliptin, and Alogliptin-Pioglitazone as the Initial Periods of Therapy in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Open-Label, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study
- Hae Jin Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Kyu Yeon Hur, Soo-Kyung Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Sung Wan Chun, Eun Seok Kang, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):689-700. Published online March 17, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0183
- 5,648 View
- 377 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The choice of an optimal oral hypoglycemic agent in the initial treatment periods for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients remains difficult and deliberate. We compared the efficacy and safety of glimepiride (GLIM), alogliptin (ALO), and alogliptin-pioglitazone (ALO-PIO) in poorly controlled T2DM patients with drug-naïve or metformin failure.
Methods
In this three-arm, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled trial, poorly controlled T2DM patients were randomized to receive GLIM (n=35), ALO (n=31), or ALO-PIO (n=33) therapy for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was change in the mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels at week 24 from baseline. Secondary endpoints were changes in HbA1c level at week 12 from baseline, fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels, lipid profiles at weeks 12 and 24, and parameters of glycemic variability, assessed by continuous glucose monitoring for 24 weeks.
Results
At weeks 12 and 24, the ALO-PIO group showed significant reduction in HbA1c levels compared to the ALO group (–0.96%±0.17% vs. –0.37%±0.17% at week 12; –1.13%±0.19% vs. –0.18%±0.2% at week 24). The ALO-PIO therapy caused greater reduction in FPG levels and significant increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels at weeks 12 and 24 than the ALO therapy. Compared to low-dose GLIM therapy, ALO-PIO therapy showed greater improvement in glycemic variability. The adverse events were similar among the three arms.
Conclusion
ALO-PIO combination therapy during the early period exerts better glycemic control than ALO monotherapy and excellency in glycemic variability than low-dose sulfonylurea therapy in uncontrolled, drug-naïve or metformin failed T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
Fatma Haddad, Ghadeer Dokmak, Maryam Bader, Rafik Karaman
Life.2023; 13(4): 1012. CrossRef - Role of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Antidiabetic Treatment
Ruili Yin, Yongsong Xu, Xin Wang, Longyan Yang, Dong Zhao
Molecules.2022; 27(10): 3055. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
- Drug/Regimen
- Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
- Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):701-712. Published online June 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0002

- 4,917 View
- 319 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate prescription trends and clinical factors of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) use according to the presence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or heart failure (HF) in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Prescription patterns of SGLT2i use between 2015 and 2019 were determined using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database of claims.
Results
Of all patients with T2DM (n=4,736,493), the annual prescription rate of SGLT2i increased every year in patients with ASCVD (from 2.2% to 10.7%) or HF (from 2.0% to 11.1%). After the first hospitalization for ASCVD (n=518,572), 13.7% (n=71,259) of patients initiated SGLT2i with a median of 10.6 months. After hospitalization for HF (n=372,853), 11.2% (n=41,717) of patients initiated SGLT2i after a median of 8.8 months. In multivariate regression for hospitalization, older age (per 10 years, odds ratio [OR], 0.57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.56 to 0.57), lower household income (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.92 to 0.95), rural residents (OR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.93 to 0.97), and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) users (OR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.81 to 0.84) were associated with lesser initiation of SGLT2i in ASCVD. Additionally, female gender (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.95 to 0.99) was associated with lesser initiation of SGLT2i in HF.
Conclusion
The prescription rate of SGLT2i increased gradually up to 2019 but was suboptimal in patients with ASCVD or HF. After the first hospitalization for ASCVD or HF, older age, female gender, low household income, rural residents, and DPP-4i users were less likely to initiate SGLT2i. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024; 15(3): 285. CrossRef - Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Hospital Readmissions for Fluid Overload among Individuals with Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease: Risk Factors and Multivariable Prediction Models
Jiashen Cai, Dorothy Huang, Hanis Binte Abdul Kadir, Zhihua Huang, Li Choo Ng, Andrew Ang, Ngiap Chuan Tan, Yong Mong Bee, Wei Yi Tay, Chieh Suai Tan, Cynthia C. Lim
Nephron.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Prescribing patterns of SGLT-2 inhibitors for patients with heart failure: A two-center analysis
Teja Chakrala, Roshni O. Prakash, Justin Kim, Hanzhi Gao, Umar Ghaffar, Jaymin Patel, Alex Parker, Bhagwan Dass
American Heart Journal Plus: Cardiology Research and Practice.2023; 28: 100286. CrossRef - Risk of developing chronic kidney disease in young-onset Type 2 diabetes in Korea
Joonyub Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae Hyoung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Yeoree Yang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of SGLT2 inhibitors with DPP-4 inhibitors combined with metformin in patients with acute myocardial infarction and diabetes mellitus
Young Sang Lyu, Seok Oh, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Myung Ho Jeong
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 759. CrossRef
- Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations
- Technology/Device
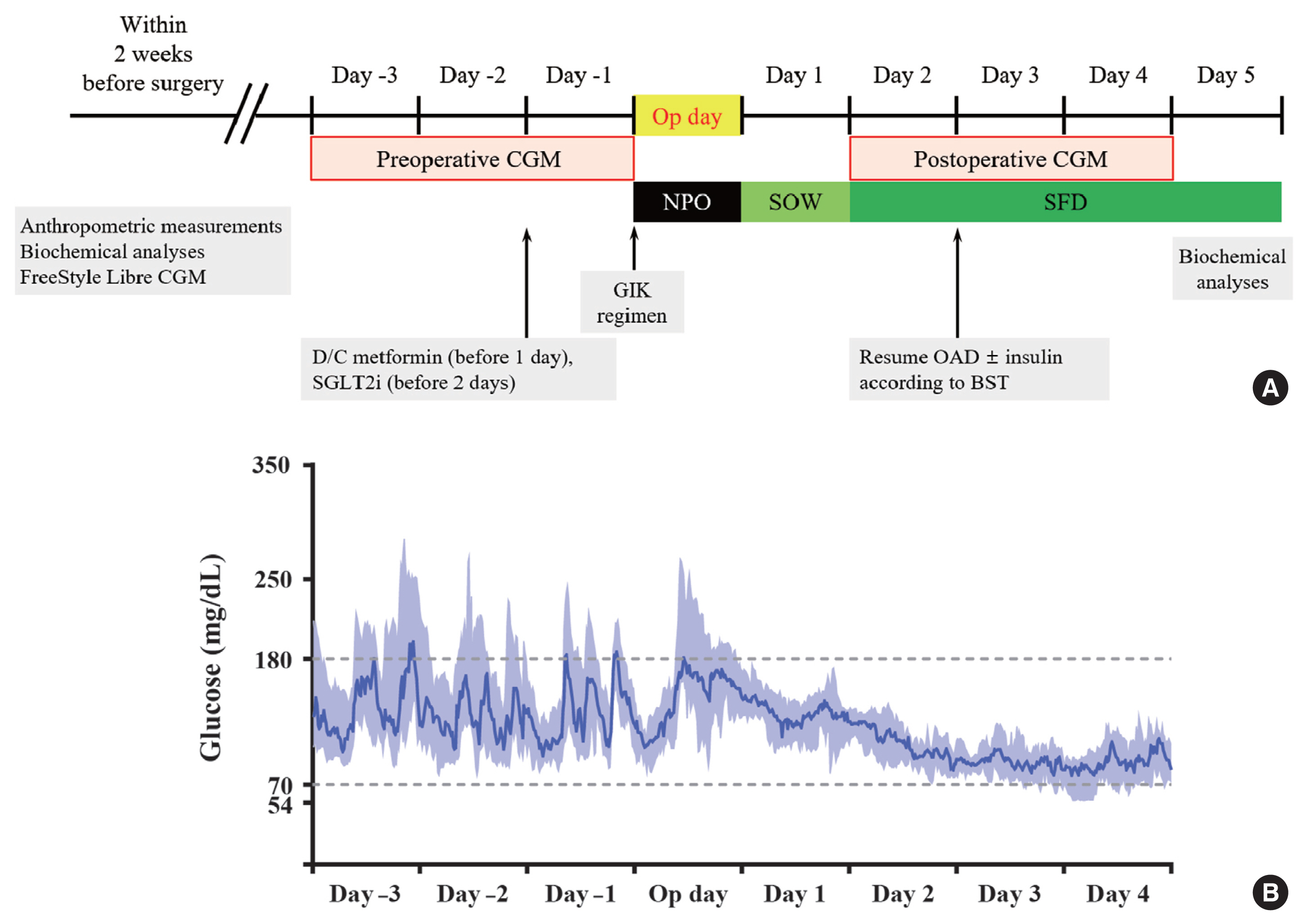
- Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery
- Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Young Suk Park, Tae Jung Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):713-721. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0164
- 4,786 View
- 317 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has been widely used in the management of diabetes. However, the usefulness and detailed data during perioperative status were not well studied. In this study, we described the immediate changes of glucose profiles after metabolic surgery using intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM) in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This was a prospective, single-center, single-arm study including 20 participants with T2DM. The isCGM (FreeStyle Libre CGM) implantation was performed within 2 weeks before surgery. We compared CGM metrics of 3 days before surgery and 3 days after surgery, and performed the correlation analyses with clinical variables.
Results
The mean glucose significantly decreased after surgery (147.0±40.4 to 95.5±17.1 mg/dL, P<0.001). Time in range (TIR; 70 to 180 mg/dL) did not significantly change after surgery in total. However, it was significantly increased in a subgroup of individuals with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥8.0%. Time above range (>250 or 180 mg/dL) was significantly decreased in total. In contrast, time below range (<70 or 54 mg/dL) was significantly increased in total and especially in a subgroup of individuals with HbA1c <8.0% after surgery. The coefficient of variation significantly decreased after surgery. Higher baseline HbA1c was correlated with greater improvement in TIR (rho=0.607, P=0.005).
Conclusion
The isCGM identified improvement of mean glucose and glycemic variability, and increase of hypoglycemia after metabolic surgery, but TIR was not significantly changed after surgery. We detected an increase of TIR only in individuals with HbA1c ≥8.0%. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Ji Soo Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Kyung-Il Park, Seung-Won Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 312. CrossRef - Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients Following Bariatric Surgery: A Scoping Review
Yang Yu, Susan W. Groth
Obesity Surgery.2023; 33(8): 2573. CrossRef - Asymptomatic Hypoglycemia after Metabolic Surgery: New Insights from Perioperative Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Sang-Man Jin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 675. CrossRef
- Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, and All-Cause Mortality according to Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level in the Elderly, a Nationwide Study
- You-Bin Lee, Minji Koo, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Jung A Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):722-732. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0225
- 6,974 View
- 331 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We assessed the myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and all-cause death risks during follow-up according to the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels among older adults.
Methods
The Korean National Health Insurance Service datasets (2002 to 2020) were used for this population-based cohort study. The hazards of MI, stroke, and all-cause mortality during follow-up were analyzed according to LDL-C level in individuals aged ≥65 years without baseline cardiovascular diseases (n=1,391,616).
Results
During a mean 7.55 years, 52,753 MIs developed; 84,224 strokes occurred over a mean 7.47 years. After a mean 8.50 years, 233,963 died. A decrease in LDL-C was associated with lower hazards of MI and stroke. The decreased hazard of stroke in lower LDL-C was more pronounced in statin users, and individuals with diabetes or obesity. The hazard of all-cause death during follow-up showed an inverted J-shaped pattern according to the LDL-C levels. However, the paradoxically increased hazard of mortality during follow-up in lower LDL-C was attenuated in statin users and individuals with diabetes, hypertension, or obesity. In statin users, lower LDL-C was associated with a decreased hazard of mortality during follow-up.
Conclusion
Among the elderly, lower LDL-C was associated with decreased risks of MI and stroke. Lower LDL-C achieved by statins in the elderly was associated with a decreased risk of all-cause death during follow-up, suggesting that LDL-C paradox for the premature death risk in the elderly should not be applied to statin users. Intensive statin therapy should not be hesitated for older adults with cardiovascular risk factors including diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combination of low- or moderate-intensity statin and ezetimibe vs. high-intensity statin monotherapy on primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and all-cause death: a propensity-matched nationwide cohort study
Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, You-Cheol Hwang
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol With All-cause and Cause-specific Mortality in Older Adults in China
Wenqing Ni, Yuebin Lv, Xueli Yuan, Yan Zhang, Hongmin Zhang, Yijing Zheng, Xiaoming Shi, Jian Xu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and all-cause or cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective study
Chin-Huan Chang, Shu-Tin Yeh, Seng-Wei Ooi, Chung-Yi Li, Hua-Fen Chen
PeerJ.2023; 11: e14609. CrossRef - ERCC1 polymorphism and its expression associated with ischemic stroke in Chinese population
Xiao-Dong Deng, Jian-Lin Ke, Tai-Yu Chen, Qin Gao, Zhuo-Lin Zhao, Wei Zhang, Huan Liu, Ming-Liang Xiang, Li-Zhen Wang, Ying Ma, Yun Liu
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 517. CrossRef - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 759. CrossRef
- Combination of low- or moderate-intensity statin and ezetimibe vs. high-intensity statin monotherapy on primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and all-cause death: a propensity-matched nationwide cohort study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Impact of Older Age Adiposity on Incident Diabetes: A Community-Based Cohort Study in China
- Anthony Chen, Weiju Zhou, Jian Hou, Alan Nevill, Yuanlin Ding, Yuhui Wan, Rebecca Jester, Xia Qin, Zhi Hu, Ruoling Chen
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):733-746. Published online April 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0215
- 3,999 View
- 197 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Obesity classifications vary globally and the impact of older age adiposity on incident diabetes has not been well-studied.
Methods
We examined a random sample of 2,809 participants aged ≥60 years in China, who were free of diabetes at baseline and were followed up for up to 10 years to document diabetes (n=178). The incidence of diabetes was assessed in relation to different cut-off points of body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC) in multiple adjusted Cox regression models.
Results
The diabetic risk in the cohort increased linearly with the continuous and quartile variables of BMI and WC. The BMI-World Health Organization (WHO) and BMI-China criteria analysis did not show such a linear relationship, however, the BMI-Asian/Hong Kong criteria did; adjusted hazards ratio (HR) was 0.42 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.20 to 0.90) in BMI <20 kg/m2, 1.46 (95% CI, 0.99 to 2.14) in 23–≤26 kg/m2, and 1.63 (95% CI, 1.09 to 2.45) in ≥26 kg/m2. The WC-China criteria revealed a slightly better prediction of diabetes (adjusted HRs were 1.79 [95% CI, 1.21 to 2.66] and 1.87 [95% CI, 1.22 to 2.88] in central obese action levels 1 and 2) than the WC-WHO. The combination of the BMI-Asian/Hong Kong with WC-China demonstrated the strongest prediction. There were no gender differences in the impact of adiposity on diabetes.
Conclusion
In older Chinese, BMI-Asian/Hong Kong criteria is a better predictor of diabetes than other BMI criterion. Its combination with WC-China improved the prediction of adiposity to diabetes, which would help manage bodyweight in older age to reduce the risk of diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of air pollution with dementia: a systematic review with meta-analysis including new cohort data from China
Jie Tang, Anthony Chen, Fan He, Martin Shipley, Alan Nevill, Hugh Coe, Zhi Hu, Tao Zhang, Haidong Kan, Eric Brunner, Xuguang Tao, Ruoling Chen
Environmental Research.2023; 223: 115048. CrossRef - Impact of fish consumption on all-cause mortality in older people with and without dementia: a community-based cohort study
Aishat T. Bakre, Anthony Chen, Xuguang Tao, Jian Hou, Yuyou Yao, Alain Nevill, James J. Tang, Sabine Rohrmann, Jindong Ni, Zhi Hu, John Copeland, Ruoling Chen
European Journal of Nutrition.2022; 61(7): 3785. CrossRef
- Association of air pollution with dementia: a systematic review with meta-analysis including new cohort data from China
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Associations between Weight-Adjusted Waist Index and Abdominal Fat and Muscle Mass: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
- Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Chantal A. Vella, Michael H. Criqui, Matthew A. Allison, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):747-755. Published online March 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0294
- 5,471 View
- 255 Download
- 30 Web of Science
- 35 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The weight-adjusted waist index (WWI) reflected body compositional changes with aging. This study was to investigate the association of WWI with abdominal fat and muscle mass in a diverse race/ethnic population.
Methods
Computed tomography (CT) data from 1,946 participants for abdominal fat and muscle areas from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (785 Whites, 252 Asians, 406 African American, and 503 Hispanics) were used. Among them, 595 participants underwent repeated CT. The WWI was calculated as waist circumference (cm) divided by the square root of body weight (kg). The associations of WWI with abdominal fat and muscle measures were examined, and longitudinal changes in abdominal composition measures were compared.
Results
In all race/ethnic groups, WWI was positively correlated with total abdominal fat area (TFA), subcutaneous fat area, and visceral fat area, but negatively correlated with total abdominal muscle area (TMA) and abdominal muscle radiodensity (P<0.001 for all). WWI showed a linear increase with aging regardless of race and there were no significant differences in the WWI distribution between Whites, Asians, and African Americans. In longitudinal analyses, over 38.6 months of follow-up, all abdominal fat measures increased but muscle measures decreased, along with increase in WWI. The more the WWI increased, the more the TFA increased and the more the TMA decreased.
Conclusion
WWI showed positive associations with abdominal fat mass and negative associations with abdominal muscle mass, which likely reflects the abdominal compositional changes with aging in a multi-ethnic population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and depression: Results from NHANES 2005–2018
Meng Li, Xue Yu, Wenhui Zhang, Jiahui Yin, Lu Zhang, Guoshuai Luo, Yuanxiang Liu, Jiguo Yang
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 347: 299. CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and gallstones: an analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Si-Hua Wen, Xin Tang, Tao Tang, Zheng-Rong Ye
BMC Gastroenterology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted waist index and myopia in adolescents and young adults: results from NHANES 1999–2008
Xu Han Shi, Li Dong, Rui Heng Zhang, Wen Bin Wei
BMC Ophthalmology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between the weight-adjusted waist index and the odds of type 2 diabetes mellitus in United States adults: a cross-sectional study
Dongdong Zheng, Suzhen Zhao, Dan Luo, Feng Lu, Zhishen Ruan, Xiaokang Dong, Wenjing Chen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Weight-Adjusted Waist Index and depressive symptoms: A nationally representative cross-sectional study from NHANES 2005 to 2018
Hangyu Liu, Jin Zhi, Chuzhao Zhang, Shiyi Huang, Yang Ma, Dandan Luo, Lungang Shi
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 350: 49. CrossRef - Relationship between cognitive function and weight-adjusted waist index in people ≥ 60 years old in NHANES 2011–2014
Xue-li Wang, Hong-lin Feng, Xiao-zhuo Xu, Jing Liu, Xu Han
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted waist index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based study
Changhui Yu, Shiming He, Maobin Kuang, Chao Wang, Xin Huang, Guotai Sheng, Yang Zou
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted waist index and serum total testosterone in males aged 6–19 years in the United States: Data from NHANES 2013–2016
Zhifei Wu, Lingling Bao, Haiyan Wang, Jiajing Zheng, Yu Chen, Wenjuan Wang, Dongkai Qiu
Heliyon.2024; 10(6): e27520. CrossRef - Associations of weight-adjusted-waist index and depression with secondary infertility
Fei Sun, Min Liu, Shanshan Hu, Ruijie Xie, Huijuan Chen, Zhaona Sun, Huiya Bi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and depression in US adults: A cross-sectional study
Yun Shen, Yahui Wu, Panru Luo, Minghan Fu, Kai Zhu, Jinsheng Wang
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 355: 299. CrossRef - Age differences in the association of body mass index-defined obesity with abdominal aortic calcification
Tangmeng Guo, Lili Huang, Zhijian Luo, Huabo Zheng, Shengshuai Shan, Bei Cheng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between weight-adjusted-waist index and diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Zhaoxiang Wang, Xuejing Shao, Wei Xu, Bingshuang Xue, Shao Zhong, Qichao Yang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of existing anthropometric indices for screening sarcopenic obesity in older adults
Jin Eui Kim, Jimi Choi, Miji Kim, Chang Won Won
British Journal of Nutrition.2023; 129(5): 875. CrossRef - Relationship Between Weight-Adjusted Waist Index and Osteoporosis in the Senile in the United States from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2017-2020
Yuxiang Lin, Zijie Liang, Anxin Zhang, Nuo Xu, Xuewen Pei, Nanbu Wang, Liang Zheng, Danghan Xu
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2023; 26(2): 101361. CrossRef - The association of asthma duration with body mass index and Weight-Adjusted-Waist index in a nationwide study of the U.S. adults
Xiaoxiao Han, Xiaofang He, Gui Hao, Lifang Cao, Yinliang Qi, Kexing Han
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between weight-adjusted-waist index and erectile dysfunction in the United State: results from NHANES 2001-2004
Shangqi Cao, Xu Hu, Yanxiang Shao, Yaohui Wang, Yaxiong Tang, Shangqing Ren, Xiang Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and total bone mineral density in adolescents: NHANES 2011–2018
Xiaohua Wang, Shuo Yang, Gansheng He, Lin Xie
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Asthma prevalence is increased in patients with high metabolism scores for visceral fat: study reports from the US
Qiushi Liu, Xiaoxiao Han, Yan Chen, Ying Gao, Wei Yang, Lewei Huang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Positive association between weight-adjusted-waist index and dementia in the Chinese population with hypertension: a cross-sectional study
Wei Zhou, Yanyou Xie, Lingling Yu, Chao Yu, Huihui Bao, Xiaoshu Cheng
BMC Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between weight-adjusted waist index and bone mineral density: results of a nationwide survey
Ya Zhang, Haiyang Wu, Cheng Li, Changxiong Liu, Mingjiang Liu, Xiaozhu Liu, Qiming Yin, Xianzhe Li, Ruijie Xie
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of weight-adjusted-waist index with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES
Qinggang Hu, Kexing Han, Jiapei Shen, Weijie Sun, Long Gao, Yufeng Gao
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight‐adjusted waist as an integrated index for fat, muscle and bone health in adults
Kyoung Jin Kim, Serhim Son, Kyeong Jin Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(5): 2196. CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and female infertility: a population-based study
Zujun Wen, Xiang Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and risk of cardiovascular diseases in United States adults: a cross-sectional study
Haiyang Fang, Feng Xie, Kai Li, Meng Li, Yanqing Wu
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between the weight-adjusted waist index and stroke: a cross-sectional study
Jiayi Ye, Yanjie Hu, Xinrong Chen, Zhe Yin, Xingzhu Yuan, Liping Huang, Ka Li
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and chronic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study
Xiaowan Li, Lanyu Wang, Hongyi Zhou, Hongyang Xu
BMC Nephrology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sex Differences in the Association of Weight-Adjusted-Waist Index with Sarcopenic Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Study of Hemodialysis Patients
Maolu Tian, Qin Lan, Fangfang Yu, Pinghong He, Shanshan Hu, Yan Zha
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2023; 21(10): 596. CrossRef - Lean or Non-obese Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Are They Really Lean?
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 980. CrossRef - The association of body mass index and weight waist adjustment index with serum ferritin in a national study of US adults
Hao Han, Ping Ni, Siqi Zhang, Xiaojuan Ji, Mingli Zhu, Wanyu Ma, Hongfeng Ge, Hailiang Chu
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The weight-adjusted-waist index and cognitive impairment among U.S. older adults: a population-based study
Xiao-tong Huang, Xiang Lv, Hong Jiang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between weight-adjusted-waist index and total bone mineral density in adults aged 20-59
Meiqian Guo, Yi Lei, Xueqing Liu, Xiang Li, Yong Xu, Donghui Zheng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between weight-adjusted-waist index and infertility: Results from NHANES 2013 to 2020
Huanxin Zhong, Bin Yu, Fen Zhao, Hongyin Cui, Lifang You, Dao Feng, Yi Lu
Medicine.2023; 102(48): e36388. CrossRef - The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and increased urinary albumin excretion in adults: A population-based study
Zheng Qin, Kaixi Chang, Qinbo Yang, Qiao Yu, Ruoxi Liao, Baihai Su
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between the weight-adjusted-waist index and abdominal aortic calcification in United States adults: Results from the national health and nutrition examination survey 2013–2014
Feng Xie, Yuan Xiao, Xiaozhong Li, Yanqing Wu
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and abdominal aortic calcification in adults aged ≥ 40 years: results from NHANES 2013–2014
Zheng Qin, Dongru Du, Yupei Li, Kaixi Chang, Qinbo Yang, Zhuyun Zhang, Ruoxi Liao, Baihai Su
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and depression: Results from NHANES 2005–2018
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Synergistic Interaction between Hyperuricemia and Abdominal Obesity as a Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome Components in Korean Population
- Min Jin Lee, Ah Reum Khang, Yang Ho Kang, Mi Sook Yun, Dongwon Yi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):756-766. Published online January 20, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0166
- 4,867 View
- 252 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The present study investigated the role of synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity as a risk factor for the components of metabolic syndrome.
Methods
We performed a cross-sectional study using the data of 16,094 individuals from the seventh Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016 to 2018). The adjusted odds ratios of metabolic syndrome and its components were analyzed by multivariate logistic regression analysis. The presence of synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity was evaluated by calculating the additive scales—the relative excess risk due to interaction, attributable proportion due to interaction, and synergy index (SI).
Results
There was a synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity in hypertriglyceridemia (men: SI, 1.39; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 1.98; women: SI, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.02 to 2.69), and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (men: SI, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.41 to 2.91; women: SI, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.05 to 2.95). There was no significant synergistic interaction between hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity for the risk of high blood pressure (men: SI, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.85 to 1.77; women: SI, 1.53; 95% CI, 0.79 to 2.97), and hyperglycemia (men: SI, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.72 to 1.47; women: SI, 1.39; 95% CI, 0.75 to 2.57).
Conclusion
Hyperuricemia and abdominal obesity synergistically increased the risk of hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL-C in both sexes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and factors associated with overweight, obesity and central obesity among adults in Shenmu City, Shaanxi Province, China
Mingxia Liu, Chunjiao Jia, Yaoda Hu, Juan Liu, Lizhen Liu, Shengli Sun, Haiying Wang, Yonglin Liu
Preventive Medicine Reports.2024; 40: 102673. CrossRef - Synergistic interaction between hyperlipidemia and obesity as a risk factor for stress urinary incontinence in Americans
Fangyi Zhu, Mao Chen, Ya Xiao, Xiaoyu Huang, Liying Chen, Li Hong
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of cognitive function in the relationship between surrogate markers of visceral fat and depressive symptoms in general middle-aged and elderly population: A nationwide population-based study
Na Zhang, Jianqian Chao, Xueyu Wu, Hongling Chen, Min Bao
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 338: 581. CrossRef - Biodegradation of Uric Acid by Bacillus paramycoides-YC02
Xiaoyu Cao, Jingyuan Cai, Yu Zhang, Chao Liu, Meijie Song, Qianqian Xu, Yang Liu, Hai Yan
Microorganisms.2023; 11(8): 1989. CrossRef - A predictive model for hyperuricemia among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Urumqi, China
Palizhati Abudureyimu, Yuesheng Pang, Lirun Huang, Qianqian Luo, Xiaozheng Zhang, Yifan Xu, Liang Jiang, Patamu Mohemaiti
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary Ferulic Acid Ameliorates Metabolism Syndrome-Associated Hyperuricemia in Rats via Regulating Uric Acid Synthesis, Glycolipid Metabolism, and Hepatic Injury
Nanhai Zhang, Jingxuan Zhou, Lei Zhao, Ou Wang, Liebing Zhang, Feng Zhou
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prevalence and factors associated with overweight, obesity and central obesity among adults in Shenmu City, Shaanxi Province, China
- Complication
- Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index Variability and Incident Diabetic Microvascular Complications: A Post Hoc Analysis of ACCORD Trial
- Daniel Nyarko Hukportie, Fu-Rong Li, Rui Zhou, Jia-Zhen Zheng, Xiao-Xiang Wu, Xian-Bo Wu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):767-780. Published online May 10, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0258
- 3,769 View
- 220 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Obesity is associated with adverse health events among diabetic patients, however, the relationship between obesity fluctuation and risk of microvascular complications among this specific population is unclear. We aimed to examine the effect of waist circumference (WC) and body mass index (BMI) variability on the risk of diabetic microvascular outcome
Methods
Annually recorded anthropometric data in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) study was used to examine the association of WC and BMI variability defined as variability independent of mean, with the risk of microvascular outcomes, including neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) (Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov., no. NCT00000620).
Results
There were 4,031, 5,369, and 2,601 cases of neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy during a follow-up period of 22,524, 23,941, and 23,850 person-years, respectively. Higher levels of WC and BMI variability were associated with an increased risk of neuropathy. Compared with the lowest quartile, the fully-adjusted HR (95% CI) for the highest quartile of WC and BMI variability for neuropathy risk were 1.21 (1.05 to 1.40) and 1.16 (1.00 to 1.33), respectively. Also, higher quartiles of BMI variability but not WC variability were associated with increased risk of nephropathic events. The fully-adjusted HR (95% CI) for the highest quartile compared with the lowest quartile of BMI variability was 1.31 (1.18 to 1.46). However, the results for retinopathic events were all insignificant.
Conclusion
Among participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus, WC and BMI variability were associated with a higher risk of neuropathic events, whereas BMI variability was associated with an increased risk of nephropathic events. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of body mass index and blood pressure variability with 10-year mortality and renal disease progression in type 2 diabetes
Stephen Fava, Sascha Reiff
Acta Diabetologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index Variability and Incident Diabetic Microvascular Complications: A Post Hoc Analysis of ACCORD Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:767-80)
Yun Kyung Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 147. CrossRef - Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index Variability and Incident Diabetic Microvascular Complications: A Post Hoc Analysis of ACCORD Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:767-80)
Daniel Nyarko Hukportie, Fu-Rong Li, Rui Zhou, Jia-Zhen Zheng, Xiao-Xiang Wu, Xian-Bo Wu
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 150. CrossRef - Weight variability and diabetes complications
Francesco Prattichizzo, Chiara Frigé, Rosalba La Grotta, Antonio Ceriello
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 199: 110646. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy in Latin America (Mexico) and the World: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Oscar Vivanco-Rojas, Sonia López-Letayf, Valentina Londoño-Angarita, Fátima Sofía Magaña-Guerrero, Beatriz Buentello-Volante, Yonathan Garfias
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(20): 6583. CrossRef - Effects of body weight variability on risks of macro- and microvascular outcomes in individuals with type 2 diabetes: The Rio de Janeiro type 2 diabetes cohort
Claudia R.L. Cardoso, Nathalie C. Leite, Gil F. Salles
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 205: 110992. CrossRef - Correlation Between the Variability of Different Obesity Indices and Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study Based on Populations in Taiwan
Zhenzhen Sun, Kun Wang, Chuan Yun, Fang Bai, Xiaodan Yuan, Yaujiunn Lee, Qingqing Lou
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2791. CrossRef - Unraveling shared risk factors for diabetic foot ulcer: a comprehensive Mendelian randomization analysis
Kangli Yin, Tianci Qiao, Yongkang Zhang, Jiarui Liu, Yuzhen Wang, Fei Qi, Junlin Deng, Cheng Zhao, Yongcheng Xu, Yemin Cao
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2023; 11(6): e003523. CrossRef
- Association of body mass index and blood pressure variability with 10-year mortality and renal disease progression in type 2 diabetes
- Complication
- Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis
- Tianqi Zhang, Marnie Shaw, Nicolas Cherbuin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):781-802. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0189
- 6,426 View
- 296 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is known to be associated with cognitive decline and brain structural changes. This study systematically reviews and estimates human brain volumetric differences and atrophy associated with T2DM.
Methods
PubMed, PsycInfo and Cochrane Library were searched for brain imaging studies reporting on brain volume differences between individuals with T2DM and healthy controls. Data were examined using meta-analysis, and association between age, sex, diabetes characteristics and brain volumes were tested using meta-regression.
Results
A total of 14,605 entries were identified; after title, abstract and full-text screening applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, 64 studies were included and 42 studies with compatible data contributed to the meta-analysis (n=31,630; mean age 71.0 years; 44.4% male; 26,942 control; 4,688 diabetes). Individuals with T2DM had significantly smaller total brain volume, total grey matter volume, total white matter volume and hippocampal volume (approximately 1% to 4%); meta-analyses of smaller samples focusing on other brain regions and brain atrophy rate in longitudinal investigations also indicated smaller brain volumes and greater brain atrophy associated with T2DM. Meta-regression suggests that diabetes-related brain volume differences start occurring in early adulthood, decreases with age and increases with diabetes duration.
Conclusion
T2DM is associated with smaller total and regional brain volume and greater atrophy over time. These effects are substantial and highlight an urgent need to develop interventions to reduce the risk of T2DM for brain health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes, antidiabetic medications and risk of dementia: A systematic umbrella review and meta‐analysis
Alvin Kuate Defo, Veselko Bakula, Alessandro Pisaturo, Christopher Labos, Simon S. Wing, Stella S. Daskalopoulou
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 441. CrossRef - Cognitive deficits among people with schizophrenia and prediabetes or diabetes
Alexander Panickacheril John, Thynn Mya, Darren Haywood
Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica.2024; 149(1): 65. CrossRef - The association of glucose metabolism measures and diabetes status with Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers of amyloid and tau: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Veerle van Gils, Marianna Rizzo, Jade Côté, Wolfgang Viechtbauer, Giuseppe Fanelli, Jordi Salas-Salvadó, Theresa Wimberley, Mònica Bulló, Fernando Fernandez-Aranda, Søren Dalsgaard, Pieter Jelle Visser, Willemijn J. Jansen, Stephanie J.B. Vos
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2024; 159: 105604. CrossRef - ECHDC3 Variant Regulates the Right Hippocampal Microstructural Integrity and Verbal Memory in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Qiyu Zhao, Xin Du, Feng Liu, Yang Zhang, Wen Qin, Quan Zhang
Neuroscience.2024; 538: 30. CrossRef - The hemodynamic response function as a type 2 diabetes biomarker: a data-driven approach
Pedro Guimarães, Pedro Serranho, João V. Duarte, Joana Crisóstomo, Carolina Moreno, Leonor Gomes, Rui Bernardes, Miguel Castelo-Branco
Frontiers in Neuroinformatics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - What have clinical trials taught us about brain health?
Keon-Joo Lee, Hee-Joon Bae
Cerebral Circulation - Cognition and Behavior.2024; 6: 100199. CrossRef - Understanding the relationship between type-2 diabetes, MRI markers of neurodegeneration and small vessel disease, and dementia risk: a mediation analysis
Leslie Grasset, Eric Frison, Catherine Helmer, Gwénaëlle Catheline, Geneviève Chêne, Carole Dufouil
European Journal of Epidemiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Vulnerability of the Hippocampus to Insults: Links to Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction
Terry L. Davidson, Richard J. Stevenson
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 1991. CrossRef - The gut microbiota‐astrocyte axis: Implications for type 2 diabetic cognitive dysfunction
Zi‐Han Li, Ya‐Yi Jiang, Cai‐Yi Long, Qian Peng, Ren‐Song Yue
CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics.2023; 29(S1): 59. CrossRef - NHANES 2011–2014 Reveals Decreased Cognitive Performance in U.S. Older Adults with Metabolic Syndrome Combinations
Edgar Díaz-Camargo, Juan Hernández-Lalinde, María Sánchez-Rubio, Yudy Chaparro-Suárez, Liseth Álvarez-Caicedo, Alexandra Fierro-Zarate, Marbel Gravini-Donado, Henry García-Pacheco, Joselyn Rojas-Quintero, Valmore Bermúdez
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(7): 5257. CrossRef - People with Diabetes Have Poorer Self-Rated Health (SRH) and Diabetes Moderates the Association between Age and SRH
Weixi Kang, Antonio Malvaso
Diseases.2023; 11(2): 73. CrossRef - Cognitive dysfunction in diabetes: abnormal glucose metabolic regulation in the brain
Shan Zhang, Yueying Zhang, Zhige Wen, YaNan Yang, Tianjie Bu, Xiangwei Bu, Qing Ni
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The psychological basis of hunger and its dysfunctions
Richard J Stevenson
Nutrition Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of Glucose Metabolism Status with Brain Macrostructure and Microstructure: Findings from the UK Biobank
Ruyi Li, Tingting Geng, Lin Li, Qi Lu, Rui Li, Xue Chen, Yunjing Ou, Sen Liu, Xiaoyu Lin, Qingying Tian, Zixin Qiu, Kai Zhu, Ziyue Tang, Kun Yang, An Pan, Gang Liu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e234. CrossRef - Association Between Frequency of Social Contact and Brain Atrophy in Community-Dwelling Older People Without Dementia
Naoki Hirabayashi, Takanori Honda, Jun Hata, Yoshihiko Furuta, Mao Shibata, Tomoyuki Ohara, Yasuko Tatewaki, Yasuyuki Taki, Shigeyuki Nakaji, Tetsuya Maeda, Kenjiro Ono, Masaru Mimura, Kenji Nakashima, Jun-ichi Iga, Minoru Takebayashi, Toshiharu Ninomiya,
Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A diagnosis model for brain atrophy using deep learning and MRI of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Saba Raoof Syed, Saleem Durai M. A.
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes: a tipping point in neurodegenerative diseases
Jose A. Santiago, Mridula Karthikeyan, Madison Lackey, Diana Villavicencio, Judith A. Potashkin
Trends in Molecular Medicine.2023; 29(12): 1029. CrossRef - Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:781-802)
Tianqi Zhang, Marnie Shaw, Nicolas Cherbuin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 815. CrossRef - Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:781-802)
Se Hee Min
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 813. CrossRef - MORPHOFUNCTIONAL CHANGES OF THE BRAIN IN DIABETES MELLITUS
A. V. Smirnov, A. I Bisinbekova, T. I Faibisovich
Journal of Volgograd State Medical University.2022; 19(3): 3. CrossRef
- Diabetes, antidiabetic medications and risk of dementia: A systematic umbrella review and meta‐analysis
Brief Reports
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Rising Incidence of Diabetes in Young Adults in South Korea: A National Cohort Study
- Hyun Ho Choi, Giwoong Choi, Hojun Yoon, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):803-807. Published online January 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0236
- 65,535 View
- 390 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - We investigated the incidence of diagnosed diabetes in South Korean adults (aged ≥20 years) by analyzing data for the National Health Insurance Service–National Sample Cohort. From 2006 to 2015, the overall incidence rate of diagnosed diabetes decreased by approximately 0.1% per year until 2015. Although, this trend was observed in individuals aged 40 years or over, the rate increased slightly in the 20–29 and 30–39 years age groups, from 0.5 to 0.7 and 2.0 to 2.6 per 1,000 individuals, respectively. The proportion of obese young adults with diabetes increased remarkably, from 51.4% in 2006 to 72.4% in 2015. Thus, young adults need early identification and weight-control strategies to prevent diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cumulative exposure to hypertriglyceridemia and risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Min-Kyung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jong-Dai Kim, Moon Jung Kim, Byungpyo Kim, Jung Heo, Jiyeon Ahn, Seo-Young Sohn, Jae-Hyuk Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111109. CrossRef - Diabetes screening in South Korea: a new estimate of the number needed to screen to detect diabetes
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyung Ae Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(1): 93. CrossRef - Revisiting the Diabetes Crisis in Korea: Call for Urgent Action
Jun Sung Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Position Statement on the Appropriateness and Significance of Adding the Glycated Hemoglobin Test to the National Health Examination
Ji Hye Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Sangjoon Park, Kyunghoon Lee, Jun Goo Kang, Eu Jeong Ku, Su Kyoung Kwon, Won Jun Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Jang Won Son, Young Sil Eom, Kyung Ae Lee, Jeongrim Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Hwa Lee, Jung Hwa Jung, Hochan Cho, Da
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 178. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
Jae Hyun Bae, Kyung-Do Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ye Seul Yang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Mook Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 417. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef - Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 819. CrossRef
- Cumulative exposure to hypertriglyceridemia and risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Trends in the Prevalence of Obesity and Its Phenotypes Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2007 to 2017 in Korea
- Sang Ouk Chin, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):808-812. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0226
- 3,873 View
- 215 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This study used data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV–VII from 2007 to identify the prevalence of obesity and its phenotypes (metabolically unhealthy obesity [MUO] and metabolically healthy obesity [MHO]) and their secular changes. The prevalence of obesity in Korea increased with significant secular changes observed (β=0.326, P trend <0.01) between 2007 and 2017, and especially in men (β=0.682, P trend <0.001) but not in women. The changes in the prevalence of obesity during the study period were different between men and women (P=0.001). The prevalence of MUO significantly increased only in men (β=0.565, P trend <0.01), while that of MHO increased only in women (β=0.179, P<0.05), especially in the younger age group (β=0.308, P<0.01).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hormonal Gut–Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3384. CrossRef - Differences of Regional Fat Distribution Measured by Magnetic Resonance Imaging According to Obese Phenotype in Koreans
Ha-Neul Choi, Hyunjung Lim, Young-Seol Kim, Sang-Youl Rhee, Jung-Eun Yim
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(10): 551. CrossRef
- Hormonal Gut–Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
Letter
- Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:781-802)
- Se Hee Min
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):813-814. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0259
- [Original]
- 2,189 View
- 131 Download

 KDA
KDA


 First
First Prev
Prev





