- Complications
- The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study
-
Seung Min Chung, Yin Young Lee, Eunyeong Ha, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee, Jian Hur, Kyung Soo Hong, Jong Geol Jang, Hyun Jung Jin, Eun Young Choi, Kyeong-Cheol Shin, Jin Hong Chung, Kwan Ho Lee, June Hong Ahn, Jun Sung Moon
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):405-413. Published online May 21, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0105
-
-
10,206
View
-
143
Download
-
43
Web of Science
-
45
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader
- Background
To determine the role of diabetes mellitus (DM) in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), we explored the clinical characteristics of patients with DM and compared risk factors such as age, glycemic control, and medications to those without DM. MethodsThis was a retrospective cohort study of 117 confirmed patients with COVID-19 which conducted at a tertiary hospital in Daegu, South Korea. The primary outcome was defined as the severe and critical outcome (SCO), of which the composite outcomes of acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, intensive care unit care, and 28-day mortality. We analyzed what clinical features and glycemic control-related factors affect the prognosis of COVID-19 in the DM group. ResultsAfter exclusion, 110 participants were finally included. DM patients (n=29) was older, and showed higher blood pressure compared to non-DM patients. DM group showed higher levels of inflammation-related biomarkers and severity score, and highly progressed to SCO. After adjustment with other risk factors, DM increased the risk of SCO (odds ratio [OR], 10.771; P<0.001). Among the DM patients, SCO was more prevalent in elderly patients of ≥70 years old and age was an independent risk factor for SCO in patients with DM (OR, 1.175; P=0.014), while glycemic control was not. The use of medication did not affect the SCO, but the renin-angiotensin system inhibitors showed protective effects against acute cardiac injury (OR, 0.048; P=0.045). ConclusionThe COVID-19 patients with DM had higher severity and resulted in SCO. Intensive and aggressive monitoring of COVID-19 clinical outcomes in DM group, especially in elderly patients is warranted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Development Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination
Hyeyeon Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Mi Kyoung Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Severity of Symptoms and Mortality in Diabetic Patients with COVID- 19 Infection. Review
Zahraa ALBasry, Abeer Abdulhadi Rashid, Shaymaa Hasan Abbas
Al Mustansiriyah Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2023; 23(1): 91. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Alexander Lang, Nikoletta Christodoulou, Philipp Linnerz, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Manuela Neuenschwander, Janett Barbaresko, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2023; 66(8): 1395. CrossRef - COVID-19 and Cardiovascular Comorbidities
Dirk Müller-Wieland, Nikolaus Marx, Michael Dreher, Katharina Fritzen, Oliver Schnell
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(03): 178. CrossRef - Prevalence and impact of diabetes in hospitalized COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sian A. Bradley, Maciej Banach, Negman Alvarado, Ivica Smokovski, Sonu M. M. Bhaskar
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(2): 144. CrossRef - Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Adithan Ganesh, Michael D. Randall
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2022; 88(6): 2642. CrossRef - Cardioprotective effect of extracellular vesicles derived from ticagrelor-pretreated cardiomyocyte on hyperglycemic cardiomyocytes through alleviation of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Ceylan Verda Bitirim, Zeynep Busra Ozer, Dunya Aydos, Kardelen Genc, Seyma Demirsoy, Kamil Can Akcali, Belma Turan
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of diabetes on COVID‐19 mortality and hospital outcomes from a global perspective: An umbrella systematic review and meta‐analysis
Stavroula Kastora, Manisha Patel, Ben Carter, Mirela Delibegovic, Phyo Kyaw Myint
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycated Albumin and Glycated Albumin/HbA1c Predict the Progression of Coronavirus Disease 2019 from Mild to Severe Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Jeongseon Yoo, Youngah Choi, Shin Ae Park, Ji Yeon Seo, Chul Woo Ahn, Jaehyun Han
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2327. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors and COVID‐19: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis Revealing Critical Bias Across a Body of Observational Research
Jordan Loader, Frances C. Taylor, Erik Lampa, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship of age, sex and prothrombin time related to the severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta analysis
Audrey Fabianisa Mirza, Ceria Halim, Mutiara Indah Sari
F1000Research.2022; 11: 729. CrossRef - Evaluating the effect of COVID-19 on quality measures of patients with type 2 diabetes in two family nurse practitioner–owned clinics
Wendy L. Wright, Patricia A. White, Meredith Welsh, Kelly Cutting
Journal of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners.2022; 34(9): 1090. CrossRef - Early glycaemic variability increases 28-day mortality and prolongs intensive care unit stay in critically ill patients with pneumonia
Seong Ho Kim, Ji Young Kim, Eun Song Kim, Il Rae Park, Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Annals of Medicine.2022; 54(1): 2724. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory drugs and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: Current knowledge and potential effects on early SARS-CoV-2 infection
Iris Louise N. Cabbab, Rafael Vincent M. Manalo
Virus Research.2021; 291: 198190. CrossRef - The Effect of Prior Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor and Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Treatment on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Susceptibility and Outcome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jiuyang Xu, Yaqun Teng, Lianhan Shang, Xiaoying Gu, Guohui Fan, Yijun Chen, Ran Tian, Shuyang Zhang, Bin Cao
Clinical Infectious Diseases.2021; 72(11): e901. CrossRef - Diabetes predicts severity of COVID‐19 infection in a retrospective cohort: A mediatory role of the inflammatory biomarker C‐reactive protein
Huilin Koh, Angela Mei Chung Moh, Ester Yeoh, Yi Lin, Serena Kiat Mun Low, Say Tat Ooi, Seng Kiong Tan, Jaime Hui Xian Lin, Caroline Wei Shan Hoong
Journal of Medical Virology.2021; 93(5): 3023. CrossRef - Susceptibility for Some Infectious Diseases in Patients With Diabetes: The Key Role of Glycemia
Jesús Chávez-Reyes, Carlos E. Escárcega-González, Erika Chavira-Suárez, Angel León-Buitimea, Priscila Vázquez-León, José R. Morones-Ramírez, Carlos M. Villalón, Andrés Quintanar-Stephano, Bruno A. Marichal-Cancino
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes is most important cause for mortality in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Giovanni Corona, Alessandro Pizzocaro, Walter Vena, Giulia Rastrelli, Federico Semeraro, Andrea M Isidori, Rosario Pivonello, Andrea Salonia, Alessandra Sforza, Mario Maggi
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2021; 22(2): 275. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes: Analysis of the scientific production indexed in Scopus
Ibraín Enrique Corrales-Reyes, Frank Hernández-García, Christian R. Mejia
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(3): 765. CrossRef - Impact of diabetes mellitus on in-hospital mortality in adult patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Halla Kaminska, Lukasz Szarpak, Dariusz Kosior, Wojciech Wieczorek, Agnieszka Szarpak, Mahdi Al-Jeabory, Wladyslaw Gawel, Aleksandra Gasecka, Milosz J. Jaguszewski, Przemyslawa Jarosz-Chobot
Acta Diabetologica.2021; 58(8): 1101. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Manuela Neuenschwander, Alexander Lang, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2021; 64(7): 1480. CrossRef - Evolution of a Cohort of COVID-19 Infection Suspects Followed-Up from Primary Health Care
Valle Coronado-Vázquez, Maria del Valle Ramírez-Durán, Juan Gómez-Salgado, María Silvia Dorado-Rabaneda, Elena Benito-Alonso, Marina Holgado-Juan, Cristina Bronchalo-González
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(6): 459. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide 3.0 and 4.5 mg in patients aged younger than 65 and 65 years or older: Post hoc analysis of the AWARD‐11 trial
Juan P. Frias, Enzo Bonora, Luis Nevárez Ruiz, Stanley H. Hsia, Heike Jung, Sohini Raha, David A. Cox, M. Angelyn Bethel, Manige Konig
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(10): 2279. CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Primary Prevention and COVID‐19
Jordan Loader, Erik Lampa, Stefan Gustafsson, Thomas Cars, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive value of HbA1c for in-hospital adverse prognosis in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Zheng Zhu, Yaqian Mao, Gang Chen
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(6): 910. CrossRef - High Fibrosis-4 Index Is Related with Worse Clinical Outcome in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes Mellitus: A Multicenter Observational Study
Sung-Woo Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Jun Sung Moon, Mi Kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 800. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 757. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diabetes Associated Mortality in Patients with COVID-19
Puneeta Gupta, Meeta Gupta, Neena KAtoch, Ketan Garg, Bhawna Garg
International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes, Drug Treatment, and Mortality in COVID-19: A Multinational Retrospective Cohort Study
Jennifer E. Nyland, Nazia T. Raja-Khan, Kerstin Bettermann, Philippe A. Haouzi, Douglas L. Leslie, Jennifer L. Kraschnewski, Leslie J. Parent, Patricia Sue Grigson
Diabetes.2021; 70(12): 2903. CrossRef - Impact of Diabetes on COVID-19 Mortality and Hospital Outcomes, a Global Perspective: An ONTOP Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Stavroula Kastora, Manisha Patel, Ben Carter, Mirela Delibegovic, Phyo Kyaw Myint
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Response: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53)
Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 484. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus is Associated with Severe Infection and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Luxiang Shang, Mengjiao Shao, Qilong Guo, Jia Shi, Yang Zhao, Jiasuoer Xiaokereti, Baopeng Tang
Archives of Medical Research.2020; 51(7): 700. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Mortality Predictors of COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized at Nationally-Designated Treatment Hospitals
Seong-Su Moon, Kwan Lee, Jungi Park, Seongcheol Yun, Yun Sik Lee, Dong Seok Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Mortality Rate and Predictors of Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with Diabetes
Dilaram Acharya, Kwan Lee, Dong Seok Lee, Yun Sik Lee, Seong-Su Moon
Healthcare.2020; 8(3): 338. CrossRef - Letter: The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:405–13)
So-Yeon Kim, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 621. CrossRef - Response: The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:405–13)
Seung Min Chung, June Hong Ahn, Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 625. CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Diabetes in Daegu, South Korea
Mi Kyung Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Sung-Woo Kim, Jun Sung Moon, Nan Hee Cho, Eugene Han, Ji Hong You, Ji Yeon Lee, Miri Hyun, Jae Seok Park, Yong Shik Kwon, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Ki Tae Kwon, Shin Yup Lee, Eon Ju Jeon, Jin-Woo Kim, Hyo-Lim Hong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Chi Yo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 602. CrossRef - Fasting Plasma Glucose Level Independently Predicts the Mortality of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection: A Multicenter, Retrospective Cohort Study
Min Cheol Chang, Jong-Moon Hwang, Jae-Han Jeon, Sang Gyu Kwak, Donghwi Park, Jun Sung Moon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(3): 595. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19
Jeong Hyun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 116. CrossRef - Management of Diabetes in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Prognosis and Practical Issues
Hye Soon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 120. CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Sun Joon Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Sung-Rae Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 737. CrossRef - Adverse impact of renin–angiotensin system blockade on the clinical course in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study
Jeong-Hoon Lim, Jang-Hee Cho, Yena Jeon, Ji Hye Kim, Ga Young Lee, Soojee Jeon, Hee Won Noh, Yong-Hoon Lee, Jaehee Lee, Hyun-Ha Chang, Hee-Yeon Jung, Ji-Young Choi, Sun-Hee Park, Chan-Duck Kim, Yong-Lim Kim, Shin-Woo Kim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes: The Epidemic and the Korean Diabetes Association Perspective
Junghyun Noh, Hyun-Ha Chang, In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 372. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19: Global and regional perspectives
In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon, Moon Kyu Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 166: 108303. CrossRef
- Epidemiology
- The Changes of Trends in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer over a 10-Year Period: Single Center Study
-
Choong Hee Kim, Jun Sung Moon, Seung Min Chung, Eun Jung Kong, Chul Hyun Park, Woo Sung Yoon, Tae Gon Kim, Woong Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(4):308-319. Published online April 27, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0076
-
-
5,009
View
-
66
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader
- Background
This study aims to describe the trends in the severity and treatment modality of patients with diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) at a single tertiary referral center in Korea over the last 10 years and compare the outcomes before and after the introduction of a multidisciplinary diabetic foot team. MethodsIn this retrospective observational study, electronic medical records of patients from years 2002 to 2015 at single tertiary referral center were reviewed. Based on the year of first admission, patients were assigned to a group either before or after the year 2012, the year the diabetes team launched. ResultsOf the 338 patients with DFU, 229 were first admitted until the year 2011 (group A), while 109 were first admitted since the year 2012 (group B). Mean age was higher in group B, and ulcer size was larger than those of group A. Whereas duration of diabetes was longer in group B, glycemic control was improved (mean glycosylated hemoglobin, 9.48% vs. 8.50%). The proportion of minor lower extremity amputation (LEA) was increased, but length of hospital stay was decreased (73.7±79.6 days vs. 39.8±36.9 days). As critical ischemic limb increased, the proportion of major LEA was not decreased. ConclusionImproved glycemic control, multidisciplinary strategies with prompt surgical treatment resulted in reduced length of hospital stay, but these measures did not reduce major LEAs. The increase in critical ischemic limb may have played a role in the unexpected outcome, and may suggest the need for increased vascular intervention strategies in DFU treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Life expectancy of patients with diabetic foot sepsis post-lower extremity amputation at a regional hospital in a South African setting. A retrospective cohort study
Thoriso C. Mokoala, Vhusani Sididzha, Etsumang D. Molefe, Thifhelimbilu E. Luvhengo
The Surgeon.2024; 22(2): e109. CrossRef - Effect of a multidisciplinary team approach in patients with diabetic foot ulcers on major adverse limb events (MALEs): systematic review and meta-analysis for the development of the Italian guidelines for the treatment of diabetic foot syndrome
Marco Meloni, Laura Giurato, Luca Monge, Cesare Miranda, Alessia Scatena, Benedetta Ragghianti, Giovanni Antonio Silverii, Cristiana Vermigli, Alessandro De Cassai, Antonio Volpe, Rodolfo Tramonta, Gerardo Medea, Corrado Bordieri, Marco Falcone, Laura Ste
Acta Diabetologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Percutaneous Endovascular Angioplasty Combined with Negative Pressure Drainage on the “One-Stop” Treatment of Ischemic Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Bo Dong, Xixu Wang, Wei Wang, Biao Hong, Jue Wang, Heng Wang, Yun Gu
Annals of Vascular Surgery.2023; 92: 272. CrossRef - A novel Canadian multidisciplinary acute care pathway for people hospitalised with a diabetic foot ulcer
Abdelrahman Zamzam, Ann‐Marie McLaren, Emily Ram, Muzammil H. Syed, Sreenath Rave, Suzanne H. Lu, Mohammed Al‐Omran, Charles de Mestral
International Wound Journal.2023; 20(8): 3331. CrossRef - Impact of multidisciplinary care of diabetic foot infections for inpatients at Campbelltown Hospital
Timothy Choi, Uchechukwu Levi Osuagwu, Chau Tran, Krupali Bulsari, David Simmons
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multigene Panel Testing in Turkish Hereditary Cancer Syndrome Patients
Esra ARSLAN ATES, Ayberk TURKYILMAZ, Ceren ALAVANDA, Ozlem YILDIRIM, Ahmet Ilter GUNEY
Medeniyet Medical Journal.2022; 37(2): 150. CrossRef - Prediabetes; Prevention and Management
Asad Ali Mughal, Syed Taha Abbas, Huma Asad, Muhammed Zubair, Nasir Ali Khan, Shehla Naseem, Muhammad Zaman Shaikh
Pakistan BioMedical Journal.2022; : 03. CrossRef - A systematic review of multidisciplinary teams to reduce major amputations for patients with diabetic foot ulcers
Jackson Musuuza, Bryn L. Sutherland, Suleyman Kurter, Prakash Balasubramanian, Christie M. Bartels, Meghan B. Brennan
Journal of Vascular Surgery.2020; 71(4): 1433. CrossRef - The Complexity of Diabetic Foot Management: From Common Care to Best Practice. The Italian Expert Opinion by Delphi Survey
Elisabetta Salutini, Enrico Brocco, Roberto Da Ros, Luca Monge, Luigi Uccioli, Roberto Anichini
The International Journal of Lower Extremity Wounds.2020; 19(1): 34. CrossRef - The effect of a multidisciplinary outpatient team approach on outcomes in diabetic foot care: a single center study
Eline Huizing, Michiel A. Schreve, Willemijn Kortmann, Jan P. Bakker, Jean-Paul P. M. de Vries, Çağdaş Ünlü
The Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Characteristics of Diabetic Patients Transferred to Korean Referral Hospitals
-
Min Young Oh, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, In Kyu Lee, Hong Sun Baek, Hyoung Woo Lee, Min Young Chung
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(5):388-394. Published online October 17, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.5.388
-
-
3,570
View
-
26
Download
-
5
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
We evaluated the disease profile and clinical management, including the status of both glycemic control and complications, in patients with diabetes who were transferred to referral hospitals in Korea. MethodsPatients referred to 20 referral hospitals in Gyeongsangnam/Gyeongsangbuk-do and Jeollanam/Jeollabuk-do with at least a 1-year history of diabetes between January and June 2011 were retrospectively reviewed using medical records, laboratory tests, and questionnaires. ResultsA total of 654 patients were enrolled in the study. In total, 437 patients (67%) were transferred from clinics and 197 (30%) patients were transferred from hospitals. A total of 279 patients (43%) visited higher medical institutions without a written medical request. The main reason for the referral was glycemic control in 433 patients (66%). Seventy-three patients (11%) had received more than one session of diabetic education. Only 177 patients (27%) had been routinely self-monitoring blood glucose, and 146 patients (22%) were monitoring hemoglobin A1c. In addition, proper evaluations for diabetic complications were performed for 74 patients (11%). The most common complication was neuropathy (32%) followed by nephropathy (31%). In total, 538 patients (82%) had been taking oral hypoglycemic agents. A relatively large number of patients (44%) had been taking antihypertensive medications. ConclusionWe investigated the clinical characteristics of diabetic patients and identified specific problems in diabetic management prior to the transfer. We also found several problems in the medical system, which were divided into three medical institutions having different roles in Korea. Our findings suggested that the relationships among medical institutions have to be improved, particularly for diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Associations between artificial sweetener intake from cereals, coffee, and tea and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A genetic correlation, mediation, and mendelian randomization analysis
Youqian Zhang, Zitian Tang, Yong Shi, Lin Li, Pratibha V. Nerurkar
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0287496. CrossRef - Transfers between health facilities of people living with diabetes attending primary health care services in the Western Cape Province of South Africa: A retrospective cohort study
Jasantha Odayar, Jody Rusch, Joel A. Dave, Diederick J. Van Der Westhuizen, Elton Mukonda, Maia Lesosky, Landon Myer
Tropical Medicine & International Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The protective role of oily fish intake against type 2 diabetes: insights from a genetic correlation and Mendelian randomization study
Youqian Zhang, Entong Ren, Chunlong Zhang, Yang Wang, Xiaohe Chen, Lin Li
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
Soree Ryang, Sang Soo Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Min Han, Su Kyoung Kwon, Young Il Kim, Il Seong Nam‐Goong, Eun Sook Kim, Mi‐kyung Kim, Chang Won Lee, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Min Jeong Kwon, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(9): 1800. CrossRef - Nonalbumin proteinuria is a simple and practical predictor of the progression of early-stage type 2 diabetic nephropathy
Jong Ho Kim, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Min Jin Lee, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, Sang Heon Song, Yong Ki Kim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(2): 395. CrossRef
- Diabetogenic Effect of Statins: A Double-Edged Sword?
-
Ji Sung Yoon, Hyoung Woo Lee
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(6):415-422. Published online December 12, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.6.415
-
-
3,620
View
-
43
Download
-
16
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
Statins are widely prescribed cholesterol-lowering agents, which have been demonstrated to significantly reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. However, recent trials have reported that statins cause worsening of hyperglycemia and increase the risk of new-onset diabetes. The association between the diabetogenic effect of statins with intensive dose and accompanying major risk factors for diabetes has been demonstrated. However, statins do not appear to have a class effect on insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic patients. Numerous mechanisms have been suggested to explain how statins cause β-cell insulin secretory dysfunction and peripheral insulin resistance leading to incident diabetes. According to findings from an aggregate of large clinical trials, the benefits of statin treatment appear to outweigh the risk of new-onset diabetes. Therefore, it would be inappropriate to discontinue the use of statins for prevention of cardiovascular events because of its potential risk for development of incident diabetes. This review addresses the currently available evidence related to statin use and new-onset diabetes from a clinical perspective. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - High doses of rosuvastatin induce impaired branched‐chain amino acid catabolism and lead to insulin resistance
Xue Bai, Xingzhen Long, Fang Song, Baolin Chen, Changcheng Sheng, Cailin Tang, Li Li, Jiaxing Zhang, Rui Zhang, Jiquan Zhang, Jiali Li
Experimental Physiology.2023; 108(7): 961. CrossRef - Statins and the diabetogenic effect (II)
Nicolae Bacinschi, Ina Guţu, Anastasia Caracaş, Svetlana Latuş, Stela Bacinschi-Gheorghiţă, Aurelia Bacinschi, Dumitru Ştîrba, Olesea Malancea
Farmacist.ro.2022; 5(208): 14. CrossRef - Statins and the diabetogenic effect (I)
Nicolae Bacinschi, Ina Guţu, Anastasia Caracaş, Svetlana Latuş, Stela Bacinschi-Gheorghiţă, Aurelia Bacinschi, Dumitru Ştîrba, Olesea Malancea
Farmacist.ro.2022; 4(207): 16. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of a Fixed-Dose Combination of Candesartan and Rosuvastatin on Blood Pressure and Cholesterol in Patients With Hypertension and Hypercholesterolemia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel Phase III Clinical Study
Kyoung Im Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Yong Hyun Park, Jeong-Cheon Ahn, Sang Hyun Kim, Wook Jin Chung, Weon Kim, Il Suk Sohn, Jin Ho Shin, Yong Jin Kim, Kiyuk Chang, Cheol Woong Yu, Soe Hee Ahn, Seok Yeon Kim, Jae Kean Ryu, Jong Young Lee, Bum Kee Hong, Taek Jong Ho
Clinical Therapeutics.2019; 41(8): 1508. CrossRef - Change in ALT levels after administration of HMG‐CoA reductase inhibitors to subjects with pretreatment levels three times the upper normal limit in clinical practice
Hyunah Kim, Hyeseon Lee, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, In Young Choi, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Hun‐Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Therapeutics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Phenotyping of Korean patients with better-than-expected efficacy of moderate-intensity statins using tensor factorization
Jingyun Choi, Yejin Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, In Young Choi, Hwanjo Yu, Katriina Aalto-Setala
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0197518. CrossRef - Management of patients with statin intolerance
Sabine Fischer, Ulrich Julius
Atherosclerosis Supplements.2017; 30: 33. CrossRef - Use of Moderate‐Intensity Statins for Low‐Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level above 190 mg/dL at Baseline in Koreans
Hun‐Sung Kim, Hyeseon Lee, Sue Hyun Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Sun Jung Baik, Hyunah Kim, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In‐Young Choi, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Ju Han Kim
Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology.2017; 121(4): 272. CrossRef - Uso de estatinas e o risco de Diabetes Mellitus tipo 2: Revisão Baseada na Evidência
Susana Silva, Nuno Monteiro
Revista Brasileira de Medicina de Família e Comunidade.2016; 11(38): 1. CrossRef - Association of statin use and stress-induced hyperglycemia in patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Chen Yan, Ma Qin, Yang S Juan, Li Y Tao, Gao M dong, Zeng Zechun, Yang X Chun, Cong H Liang, Liu Yin, Meng Kang
JRSM Cardiovascular Disease.2016; 5: 204800401663944. CrossRef - Statin‐related aminotransferase elevation according to baseline aminotransferases level in real practice in Korea
H.‐S. Kim, S. H. Lee, H. Kim, S.‐H. Lee, J. H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, S.‐H. Kim, I.‐Y. Choi, K.‐H. Yoon, J. H. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(3): 266. CrossRef - Statins and their increased risk of inducing diabetes
Aris P Agouridis, Michael S Kostapanos, Moses S Elisaf
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2015; 14(12): 1835. CrossRef - Effects ofVacciniumBerries on Serum Lipids: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Yitong Zhu, Ya Miao, Zheying Meng, Yuan Zhong
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Metabolic Syndrome, and Mixed Dyslipidemia: How Similar, How Different, and How to Treat?
Julian Halcox, Anoop Misra
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2015; 13(1): 1. CrossRef - How to balance cardiorenometabolic benefits and risks of statins
Soo Lim, Pyung Chun Oh, Ichiro Sakuma, Kwang Kon Koh
Atherosclerosis.2014; 235(2): 644. CrossRef - Contemporary treatment strategies for Type 2 diabetes-related macrovascular disease
Andrew MN Walker, Richard M Cubbon, Mark T Kearney
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2014; 9(6): 641. CrossRef
- Predicting Mortality of Critically Ill Patients by Blood Glucose Levels
-
Byung Sam Park, Ji Sung Yoon, Jun Sung Moon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(5):385-390. Published online October 17, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.5.385
-
-
3,458
View
-
34
Download
-
10
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
The aim of this study is to observe the outcome of critically ill patients in relation to blood glucose level at admission and to determine the optimal range of blood glucose at admission predicting lower hospital mortality among critically ill patients. MethodsWe conducted a retrospective cohort study of a total 1,224 subjects (males, 798; females, 426) admitted to intensive care unit (ICU) from 1 January 2009 to 31 December 2010. Blood glucose levels at admission were categorized into four groups (group 1, <100 mg/dL; group 2, 100 to 199 mg/dL; group 3, 200 to 299 mg/dL; and group 4, ≥300 mg/dL). ResultsAmong 1,224 patients, 319 patients were already known diabetics, and 296 patients died in ICU. Five hundred fifty-seven subjects received insulin therapy, and 118 received oral hypoglycemic agents. The overall mortality rate was 24.2% (296 patients). The causes of death and mortality rates of diabetic patients were not different from nondiabetic subjects. The mortality curve showed J shape, and there were significant differences in mortality between the groups of blood glucose levels at admission. Group 2 had the lowest mortality rate (P<0.05). ConclusionThese results suggest that serum glucose levels upon admission into ICU is associated with clinical outcomes in ICU patients. Blood glucose level between 100 and 199 mg/dL at the time of ICU admission could predict lower hospital mortality among critically ill patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - HGV4Risk: Hierarchical Global View-guided Sequence Representation Learning for Risk Prediction
Youru Li, Zhenfeng Zhu, Xiaobo Guo, Shaoshuai Li, Yuchen Yang, Yao Zhao
ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data.2024; 18(1): 1. CrossRef - Feature extraction from unequal length heterogeneous EHR time series via dynamic time warping and tensor decomposition
Chi Zhang, Hadi Fanaee-T, Magne Thoresen
Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery.2021; 35(4): 1760. CrossRef - Serum electrolytes levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study
Shridhar Reshma, Sushith Sushith, Mangalore Balakrishna Prathima, D'Sa Janice, Gopal R Madan, Pragathi Gowda, Kiran PK Kumar, Mohandas Rai, Bhuvanesh Sukhlal Kalal
Diabetes mellitus.2020; 23(3): 223. CrossRef - Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality in Severe and Critical COVID-19 Patients in Wuhan, China
Jianfeng Wu, Jianqiang Huang, Guochao Zhu, Yihao Liu, Han Xiao, Qian Zhou, Xiang Si, Hui Yi, Cuiping Wang, Daya Yang, Shuling Chen, Xin Liu, Zelong Liu, Qiongya Wang, Qingquan Lv, Ying Huang, Yang Yu, Xiangdong Guan, Yanbing Li, Krishnarajah Nirantharakum
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 105(12): e4230. CrossRef - Derivation and validation of a new nutritional index for predicting 90 days mortality after ICU admission in a Korean population
Da-Hye Son, Kyung-Sub Kim, Hye-Sun Lee, Ji-Won Lee, Cheung-Soo Shin
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.2020; 119(8): 1283. CrossRef - Acute pancreatic beta cell apoptosis by IL-1β is responsible for postburn hyperglycemia: Evidence from humans and mice
Jun Li, Jie Xu, Xinghua Qin, Hongyan Yang, Juntao Han, Yanhui Jia, Huayu Zhu, Liang Zhu, Jia Li, Wenjun Xie, Dahai Hu, Xing Zhang, Feng Gao
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2019; 1865(2): 275. CrossRef - Determinants of mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: a review
Jana Engelmann, Ulf Manuwald, Constanze Rubach, Joachim Kugler, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Markolf Hanefeld, Ulrike Rothe
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2016; 17(1): 129. CrossRef - The Impact of Measurement Frequency on the Domains of Glycemic Control in the Critically Ill-A Monte Carlo Simulation
James S. Krinsley, David E. Bruns, James C. Boyd
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2015; 9(2): 237. CrossRef - Response: Predicting Mortality of Critically Ill Patients by Blood Glucose Levels (Diabetes Metab J2013;37:385-90)
Byung Sam Park, Ji Sung Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(1): 81. CrossRef - Predicting Mortality of Critically Ill Patients by Blood Glucose Levels (Diabetes Metab J2013;37:385-90)
Hyeong Kyu Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(6): 484. CrossRef
- The Role of Skeletal Muscle in Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
-
Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(4):278-285. Published online August 14, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.4.278
-
-
4,639
View
-
49
Download
-
58
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is closely correlated with abnormal accumulation of visceral fat, but the role of skeletal muscle remains unclear. The aim of this study was to elucidate the role of skeletal muscle in development of NAFLD. MethodsAmong 11,116 subjects (6,242 males), we examined the effects of skeletal muscle mass and visceral fat area (VFA, by bioelectric impedance analysis) on NAFLD using by the fatty liver index (FLI). ResultsOf the total subjects (9,565 total, 5,293 males) included, 1,848 were classified as having NALFD (FLI ≥60). Body mass index, lipid profile, fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, prevalence of type 2 diabetes (DM), hypertension (HTN), and metabolic syndrome were higher in males than females, but FLI showed no significant difference. The low FLI group showed the lowest VFA and highest skeletal muscle mass of all the groups. Skeletal muscle to visceral fat ratio (SVR) and skeletal muscle index had inverse correlations with FLI, when adjusted for age and gender. In multivariate regression analysis, SVR was negatively associated with FLI. Among SVR quartiles, the highest quartile showed very low risk of NAFLD when adjusted for age, gender, lipid profile, DM, HTN, and high sensitivity C-reactive protein from the lowest quartiles (odds ratio, 0.037; 95% confidence interval, 0.029 to 0.049). ConclusionSkeletal muscle mass was inversely associated with visceral fat area, and higher skeletal muscle mass may have a beneficial effect in preventing NAFLD. These results suggest that further studies are needed to ameliorate or slow the progression of sarcopenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease on sarcopenia: evidence from genetic methods
Jiaqin Yuan, Jinglin Zhang, Qiang Luo, Lipeng Peng
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages Intake on Sarcopenic Obesity, Visceral Obesity, and Sarcopenia in Lebanese Patients with MASLD: A Case-Control Study
Maha Hoteit, Myriam Dagher, Nikolaos Tzenios, Najat Al Kaaki, Ghadir Rkein, Abdul Rahman Chahine, Yonna Sacre, Samer Hotayt, Rami Matar, Mahmoud Hallal, Micheal Maitar, Bilal Hotayt
Healthcare.2024; 12(5): 591. CrossRef - Increased visceral fat area to skeletal muscle mass ratio is positively associated with the risk of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in a Chinese population
Chenbing Liu, Nan Li, Di Sheng, Yahong Shao, Lihong Qiu, Chao Shen, Zhong Liu
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Using hyperhomocysteinemia and body composition to predict the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in healthcare workers
Xiaoyan Hao, Honghai He, Liyuan Tao, Peng Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Criteria and Prognostic Relevance of Sarcopenia in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease—A Systematic Review
Claudia-Gabriela Potcovaru, Petruța Violeta Filip, Oana-Maria Neagu, Laura Sorina Diaconu, Teodor Salmen, Delia Cinteză, Anca Pantea Stoian, Florin Bobirca, Mihai Berteanu, Corina Pop
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4713. CrossRef - Association between Muscle Mass Deficits and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Adults with Body Mass Index Less than 23 kg/m2
Mi Young Lee, Hee Jeong Choi, Han Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2023; 13(3): 171. CrossRef - Sex influences the association between appendicular skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Gang Li, Rafael S. Rios, Xin-Xin Wang, Yue Yu, Kenneth I. Zheng, Ou-Yang Huang, Liang-Jie Tang, Hong-Lei Ma, Yi Jin, Giovanni Targher, Christopher D. Byrne, Xiao-Yan Pan, Ming-Hua Zheng
British Journal of Nutrition.2022; 127(11): 1613. CrossRef - 2019 Global NAFLD Prevalence: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Michael H. Le, Yee Hui Yeo, Xiaohe Li, Jie Li, Biyao Zou, Yuankai Wu, Qing Ye, Daniel Q. Huang, Changqing Zhao, Jie Zhang, Chenxi Liu, Na Chang, Feng Xing, Shiping Yan, Zi Hui Wan, Natasha Sook Yee Tang, Maeda Mayumi, Xinting Liu, Chuanli Liu, Fajuan Rui,
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 20(12): 2809. CrossRef - Impact of Sarcopenia and Myosteatosis in Non-Cirrhotic Stages of Liver Diseases: Similarities and Differences across Aetiologies and Possible Therapeutic Strategies
Annalisa Cespiati, Marica Meroni, Rosa Lombardi, Giovanna Oberti, Paola Dongiovanni, Anna Ludovica Fracanzani
Biomedicines.2022; 10(1): 182. CrossRef - Impact of Sarcopenia on the Severity of the Liver Damage in Patients With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Vittoria Zambon Azevedo, Cristina Alina Silaghi, Thomas Maurel, Horatiu Silaghi, Vlad Ratziu, Raluca Pais
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fatty Liver Index and Skeletal Muscle Density
Julie A. Pasco, Sophia X. Sui, Emma C. West, Kara B. Anderson, Pamela Rufus-Membere, Monica C. Tembo, Natalie K. Hyde, Lana J. Williams, Zoe S. J. Liu, Mark A. Kotowicz
Calcified Tissue International.2022; 110(6): 649. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio as a predictor of NAFLD in lean and overweight men and women with effect modification by sex
Yoosun Cho, Yoosoo Chang, Seungho Ryu, Hyun‐Suk Jung, Chan‐won Kim, Hyungseok Oh, Mi Kyung Kim, Won Sohn, Hocheol Shin, Sarah H. Wild, Christopher D. Byrne
Hepatology Communications.2022; 6(9): 2238. CrossRef - Association of Low Skeletal Muscle Mass with the Phenotype of Lean Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Jun-Hyeon Byeon, Min-Kyu Kang, Min-Cheol Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(5): 850. CrossRef - Muscle strength, but not body mass index, is associated with mortality in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
Phunchai Charatcharoenwitthaya, Khemajira Karaketklang, Wichai Aekplakorn
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2022; 13(5): 2393. CrossRef - Effect of progressive resistance training with weight loss compared with weight loss alone on the fatty liver index in older adults with type 2 diabetes: secondary analysis of a 12-month randomized controlled trial
Christine L Freer, Elena S George, Sze-Yen Tan, Gavin Abbott, David W Dunstan, Robin M Daly
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(5): e002950. CrossRef - Muscle Krüppel-like factor 15 regulates lipid flux and systemic metabolic homeostasis
Liyan Fan, David R. Sweet, Domenick A. Prosdocimo, Vinesh Vinayachandran, Ernest R. Chan, Rongli Zhang, Olga Ilkayeva, Yuan Lu, Komal S. Keerthy, Chloe E. Booth, Christopher B. Newgard, Mukesh K. Jain
Journal of Clinical Investigation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - “Bioelectrical impedance analysis in managing sarcopenic obesity in NAFLD”
David J. Hanna, Scott T. Jamieson, Christine S. Lee, Christopher A. Pluskota, Nicole J. Bressler, Peter N. Benotti, Sandeep Khurana, David D. K. Rolston, Christopher D. Still
Obesity Science & Practice.2021; 7(5): 629. CrossRef - Decreased Muscle-to-Fat Mass Ratio Is Associated with Low Muscular Fitness and High Alanine Aminotransferase in Children and Adolescent Boys in Organized Sports Clubs
Kai Ushio, Yukio Mikami, Hiromune Obayashi, Hironori Fujishita, Kouki Fukuhara, Tetsuhiko Sakamitsu, Kazuhiko Hirata, Yasunari Ikuta, Hiroaki Kimura, Nobuo Adachi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(11): 2272. CrossRef - Association of Skeletal Muscle and Adipose Tissue Distribution with Histologic Severity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver
Min-Kyu Kang, Jung-Hun Baek, Young-Oh Kweon, Won-Young Tak, Se-Young Jang, Yu-Rim Lee, Keun Hur, Gyeonghwa Kim, Hye-Won Lee, Man-Hoon Han, Joon-Hyuk Choi, Soo-Young Park, Jung-Gil Park
Diagnostics.2021; 11(6): 1061. CrossRef - Association of Body Composition and Sarcopenia with NASH in Obese Patients
Sophia Marie-Therese Schmitz, Lena Schooren, Andreas Kroh, Alexander Koch, Christine Stier, Ulf Peter Neumann, Tom Florian Ulmer, Patrick Hamid Alizai
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(15): 3445. CrossRef - Patchouli alcohol ameliorates skeletal muscle insulin resistance and NAFLD via AMPK/SIRT1-mediated suppression of inflammation
Do Hyeon Pyun, Tae Jin Kim, Seung Yeon Park, Hyun Jung Lee, A.M. Abd El-Aty, Ji Hoon Jeong, Tae Woo Jung
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2021; 538: 111464. CrossRef - Hepatic Steatosis Contributes to the Development of Muscle Atrophy via Inter-Organ Crosstalk
Kenneth Pasmans, Michiel E. Adriaens, Peter Olinga, Ramon Langen, Sander S. Rensen, Frank G. Schaap, Steven W. M. Olde Damink, Florian Caiment, Luc J. C. van Loon, Ellen E. Blaak, Ruth C. R. Meex
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle mass and cellular membrane integrity assessment in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Iasmin dos Santos Barreto, Raquel Oliveira dos Santos, Raquel Rocha, Claudineia de Souza, Naiade Almeida, Luiza Valois Vieira, Rafael Leiróz, Manoel Sarno, Carla Daltro, Helma Pinchemel Cotrim
Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira.2021; 67(9): 1233. CrossRef - A significant association of non-obese non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with sarcopenic obesity
Kazuhiro Kashiwagi, Michiyo Takayama, Kayoko Fukuhara, Ryoko Shimizu-Hirota, Po-Sung Chu, Nobuhiro Nakamoto, Nagamu Inoue, Yasushi Iwao, Takanori Kanai
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2020; 38: 86. CrossRef - Improvement in Menopause-Associated Hepatic Lipid Metabolic Disorders by Herbal Formula HPC03 on Ovariectomized Rats
BoYoon Chang, Dae Sung Kim, SungYeon Kim
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Sarcopenia is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in men with type 2 diabetes
D.H. Seo, Y.-h. Lee, S.W. Park, Y.J. Choi, B.W. Huh, E. Lee, K.B. Huh, S.H. Kim, B.-S. Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism.2020; 46(5): 362. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and sarcopenia: pathophysiological connections and therapeutic implications
Tiziana Fernández-Mincone, Felipe Contreras-Briceño, Maximiliano Espinosa-Ramírez, Patricio García-Valdés, Antonio López-Fuenzalida, Arnoldo Riquelme, Juan Pablo Arab, Daniel Cabrera, Marco Arrese, Francisco Barrera
Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 14(12): 1141. CrossRef - Association between Atrial Fibrillation and Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Min Kyu Kang, Jung Gil Park, Min Cheol Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2020; 61(10): 860. CrossRef - Relative fat mass at baseline and its early change may be a predictor of incident nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Hwi Young Kim, Su Jung Baik, Hye Ah Lee, Byoung Kwon Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Tae Hun Kim, Kwon Yoo
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Fisetin Alleviates Hepatic and Adipocyte Fibrosis and Insulin Resistance in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Myung-Sook Choi, Ji-Young Choi, Eun-Young Kwon
Journal of Medicinal Food.2020; 23(10): 1019. CrossRef - Relationship between relative skeletal muscle mass and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Changzhou Cai, Xin Song, Yishu Chen, Xueyang Chen, Chaohui Yu
Hepatology International.2020; 14(1): 115. CrossRef - Sarcopenia Is a New Risk Factor of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Min Kyu Kang, Kyeong Ok Kim, Min Cheol Kim, Jung Gil Park, Byung Ik Jang
Digestive Diseases.2020; 38(6): 507. CrossRef - Relationship between Muscle Mass/Strength and Hepatic Fat Content in Post-Menopausal Women
Yajie Zhang, Dajiang Lu, Renwei Wang, Weijie Fu, Shengnian Zhang
Medicina.2019; 55(10): 629. CrossRef - Lower hand grip strength in older adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a nationwide population-based study
Beom-Jun Kim, Seong Hee Ahn, Seung Hun Lee, Seongbin Hong, Mark W. Hamrick, Carlos M. Isales, Jung-Min Koh
Aging.2019; 11(13): 4547. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Nonobese Subjects of African Origin Has Atypical Metabolic Characteristics
Debbie S Thompson, Ingrid A Tennant, Deanne P Soares, Clive Osmond, Chris D Byrne, Terrence E Forrester, Michael S Boyne
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2019; 3(11): 2051. CrossRef - Sarcopenia in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: is it a clinically significant entity?
C. H. De Fré, M. A. De Fré, W. J. Kwanten, B. J. Op de Beeck, L. F. Van Gaal, S. M. Francque
Obesity Reviews.2019; 20(2): 353. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in The Rotterdam Study: About Muscle Mass, Sarcopenia, Fat Mass, and Fat Distribution
Louise Johanna Maria Alferink, Katerina Trajanoska, Nicole Stephanie Erler, Josje Dorothea Schoufour, Robert Jacobus de Knegt, M. Arfan Ikram, Harry Leonardus Antonius Janssen, Oscar H. Franco, Herold J. Metselaar, Fernando Rivadeneira, Sarwa Darwish Mura
Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.2019; 34(7): 1254. CrossRef - Sarcopenia Is Significantly Associated with Presence and Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Goh Eun Chung, Min Joo Kim, Jeong Yoon Yim, Joo Sung Kim, Ji Won Yoon
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2019; 28(2): 129. CrossRef - Association of low skeletal muscle mass with advanced liver fibrosis in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
Min Kyu Kang, Jung Gil Park, Heon Ju Lee, Min Cheol Kim
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2019; 34(9): 1633. CrossRef - Whole‐body vibration for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 6‐month prospective study
Sechang Oh, Natsumi Oshida, Noriko Someya, Tsuyoshi Maruyama, Tomonori Isobe, Yoshikazu Okamoto, Taeho Kim, Bokun Kim, Junichi Shoda
Physiological Reports.2019; 7(9): e14062. CrossRef - L-Lysine Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8 Mice
Tomonori SATO, Nao MURAMATSU, Yoshiaki ITO, Yoshio YAMAMOTO, Takashi NAGASAWA
Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology.2018; 64(3): 192. CrossRef - Short-term treatment with metformin reduces hepatic lipid accumulation but induces liver inflammation in obese mice
Alexandre Abilio de Souza Teixeira, Camila O. Souza, Luana A. Biondo, Loreana Sanches Silveira, Edson A. Lima, Helena A. Batatinha, Adriane Pereira Araujo, Michele Joana Alves, Sandro Massao Hirabara, Rui Curi, José Cesar Rosa Neto
Inflammopharmacology.2018; 26(4): 1103. CrossRef - Vitamin D and Related Deficiencies, Sarcopenia and Visceral Obesity in Obese People with NAFLD
Mihaela Petrova
Gastroenterology & Hepatology: Open Access.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Grip Strength Moderates the Association between Anthropometric and Body Composition Indicators and Liver Fat in Youth with an Excess of Adiposity
Robinson Ramírez-Vélez, Mikel Izquierdo, Jorge Correa-Bautista, Alejandra Tordecilla-Sanders, María Correa-Rodríguez, Jacqueline Schmidt Rio-Valle, Emilio González-Jiménez, Katherine González-Ruíz
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2018; 7(10): 347. CrossRef - Longitudinal Changes in Muscle Mass and Strength, and Bone Mass in Older Adults: Gender-Specific Associations Between Muscle and Bone Losses
Kyoung Min Kim, Soo Lim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Jae Young Lim, Ki Woong Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang
The Journals of Gerontology: Series A.2018; 73(8): 1062. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease connections with fat-free tissues: A focus on bone and skeletal muscle
Eleonora Poggiogalle, Lorenzo Maria Donini, Andrea Lenzi, Claudio Chiesa, Lucia Pacifico
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2017; 23(10): 1747. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Is there a relationship? A systematic review
Cristiane V Tovo, Sabrina A Fernandes, Caroline Buss, Angelo A de Mattos
World Journal of Hepatology.2017; 9(6): 326. CrossRef - Multiple molecular targets in the liver, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in ginger-elicited amelioration of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Chunxia Wang, Robert Batey, Johji Yamahara, Yuhao Li
Journal of Functional Foods.2017; 36: 43. CrossRef - Importance of Lean Muscle Maintenance to Improve Insulin Resistance by Body Weight Reduction in Female Patients with Obesity
Yaeko Fukushima, Satoshi Kurose, Hiromi Shinno, Ha Cao Thu, Nana Takao, Hiromi Tsutsumi, Yutaka Kimura
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(2): 147. CrossRef - Fatty Liver Index Associates with Relative Sarcopenia and GH/ IGF- 1 Status in Obese Subjects
Eleonora Poggiogalle, Carla Lubrano, Lucio Gnessi, Stefania Mariani, Andrea Lenzi, Lorenzo Maria Donini, Rasheed Ahmad
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(1): e0145811. CrossRef - The relationship between hepatic steatosis and skeletal muscle mass index in men with type 2 diabetes
Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Takafumi Osaka, Takuya Fukuda, Muhei Tanaka, Masahiro Yamazaki, Michiaki Fukui
Endocrine Journal.2016; 63(10): 877. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and the cardiometabolic syndrome: A narrative review
G. Bahat, B. İlhan
European Geriatric Medicine.2016; 7(3): 220. CrossRef - Low skeletal muscle mass is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults: the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hee Yeon Kim, Chang Wook Kim, Chung-Hwa Park, Jong Young Choi, Kyungdo Han, Anwar T Merchant, Yong-Moon Park
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2016; 15(1): 39. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk: Pathophysiological mechanisms and implications
Sven M. Francque, Denise van der Graaff, Wilhelmus J. Kwanten
Journal of Hepatology.2016; 65(2): 425. CrossRef - Differences among skeletal muscle mass indices derived from height-, weight-, and body mass index-adjusted models in assessing sarcopenia
Kyoung Min Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(4): 643. CrossRef - Relationship between grip strength and newly diagnosed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a large-scale adult population
Ge Meng, Hongmei Wu, Liyun Fang, Chunlei Li, Fei Yu, Qing Zhang, Li Liu, Huanmin Du, Hongbin Shi, Yang Xia, Xiaoyan Guo, Xing Liu, Xue Bao, Qian Su, Yeqing Gu, Huijun Yang, Bin Yu, Yuntang Wu, Zhong Sun, Kaijun Niu
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Volume-dependent effect of supervised exercise training on fatty liver and visceral adiposity index in subjects with type 2 diabetes The Italian Diabetes Exercise Study (IDES)
Stefano Balducci, Patrizia Cardelli, Luca Pugliese, Valeria D’Errico, Jonida Haxhi, Elena Alessi, Carla Iacobini, Stefano Menini, Lucilla Bollanti, Francesco G. Conti, Antonio Nicolucci, Giuseppe Pugliese
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2015; 109(2): 355. CrossRef - Sarcopenia is a risk factor for elevated aminotransferase in men independently of body mass index, dietary habits, and physical activity
Ki Deok Yoo, Dae Won Jun, Kang Nyeong Lee, Hang Lak Lee, Oh Young Lee, Byung Chul Yoon, Ho Soon Choi
Digestive and Liver Disease.2015; 47(4): 303. CrossRef
- The Relationship between Metformin and Cancer in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
-
Hyun Hee Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Hyoung Woo Lee, Kyu Chang Won
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(2):125-131. Published online April 16, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.2.125
-
-
3,560
View
-
29
Download
-
13
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Recently, several studies reported that the cancer incidence in type 2 diabetes patients is higher than in the general population. Although a number of risks are shared between cancer and diabetes patients, there have been few studies of its correlation. We evaluated the influences of several factors including low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), albuminuria and use of metformin on the risk of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes. MethodsWe enrolled 1,320 patients with at least 5 years of follow-up and 73 patients were diagnosed with cancer during this period. The associations of the risk factors with cancer incidence were evaluated by multiple regression analysis. The subjects were placed into two subgroups based on metformin dosage (<1,000 mg/day, ≥1,000 mg/day) and we compared cancer incidence using analysis of covariance. ResultsLDL-C and albuminuria were not significantly correlated with cancer risk. In contrast, metformin showed a reverse correlation with cancer risk (P=0.006; relative risk, 0.574). In the metformin nonadministration group, smoking, male gender, and high triglyceride levels tended to be contributing factors without statistical significance. Cancer occurence was lower in the low dose metformin group (less than 1,000 mg/day) (P=0.00). ConclusionThese results suggest that the administration of low dose metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes may be associated with a reduced risk of cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Metformin Reduces Tumor Growth in a Murine Flank Schwannoma Model
Sudhir Manickavel, Yolanda Hartman, Andrew Burns, Manuel A. Lora Gonzalez, Jason Warram, Erika Walsh, Jacob B. Hunter, Daniel E. Killeen
Otology & Neurotology.2023; 44(9): 941. CrossRef - Metformin induces TPC-1 cell apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated pathways in vitro and in vivo
Jianwen Ye, Lei Qi, Kunlun Chen, Renfeng Li, Shengping Song, Chuang Zhou, Wenlong Zhai
International Journal of Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Metformin Promotes Apoptosis but Suppresses Autophagy in Glucose-Deprived H4IIE Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Deok-Bae Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(6): 518. CrossRef - Combination Therapy of Metformin and Statin May Decrease Hepatocellular Carcinoma Among Diabetic Patients in Asia
Hsin-Hung Chen, Ming-Chia Lin, Chih-Hsin Muo, Su-Yin Yeh, Fung-Chang Sung, Chia-Hung Kao
Medicine.2015; 94(24): e1013. CrossRef - mitoNEET as a novel drug target for mitochondrial dysfunction
Werner J. Geldenhuys, Thomas C. Leeper, Richard T. Carroll
Drug Discovery Today.2014; 19(10): 1601. CrossRef - Diabetes - Increased Risk for Cancers through Chromosomal Aberrations?
Sudhaa Anand, Badari Nath, Radha Saraswathy
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2014; 15(11): 4571. CrossRef - Oleanolic Acid Induces Metabolic Adaptation in Cancer Cells by Activating the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway
Jia Liu, Lanhong Zheng, Ning Wu, Leina Ma, Jiateng Zhong, Ge Liu, Xiukun Lin
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.2014; 62(24): 5528. CrossRef - Association of Vitamin B12Deficiency and Metformin Use in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Sun-Hye Ko, Sun-Hee Ko, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Hye-Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2014; 29(7): 965. CrossRef - Metformin and Cancer Risk and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Taking into Account Biases and Confounders
Sara Gandini, Matteo Puntoni, Brandy M. Heckman-Stoddard, Barbara K. Dunn, Leslie Ford, Andrea DeCensi, Eva Szabo
Cancer Prevention Research.2014; 7(9): 867. CrossRef - Effects of Metformin on CD133+ Colorectal Cancer Cells in Diabetic Patients
Yanfei Zhang, Meiping Guan, Zongji Zheng, Qian Zhang, Fang Gao, Yaoming Xue, Chunming Liu
PLoS ONE.2013; 8(11): e81264. CrossRef - AACE Comprehensive Diabetes Management Algorithm 2013 Endocrine Practice
Héctor Eloy Tamez-Pérez, Stephanie Lissette Proskauer-Peña, Mayra Ivonne Hernández-Coria
Endocrine Practice.2013; 19(4): 736. CrossRef - Complications of Diabetes Therapy
Sarah D. Corathers, Shawn Peavie, Marzieh Salehi
Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America.2013; 42(4): 947. CrossRef - Metformin and Cancer in Type 2 Diabetes
Hyeong Kyu Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(2): 113. CrossRef
- Diagnostic Accuracy of 64-Slice MDCT Coronary Angiography for the Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
-
Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Ihn-Ho Cho, Hyoung Woo Lee
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(1):54-62. Published online February 15, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.1.54
-
-
3,666
View
-
29
Download
-
13
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
A 64-slice multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) is well known to be a useful noninvasive form of angiography for the general population, but not for certain patients with diabetes. The aim of this study was to investigate the diagnostic accuracy and usefulness of 64-slice MDCT coronary angiography for detecting coronary artery disease in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). MethodsA total of 240 patients were included, 74 of whom had type 2 diabetes (M:F=40:33; 41.8±9.5 years). We compared significant coronary stenosis (>50% luminal narrowing) in MDCT with invasive coronary angiography (ICA) by segment, artery, and patient. We also evaluated the influence of obesity and coronary calcium score on MDCT accuracy. ResultsOf the 4,064 coronary segments studied, 4,062 segments (T2DM=1,109) were assessed quantitatively by both MDCT and ICA, and 706 segments (T2DM=226) were detected as a significant lesion by ICA in all patients. Sensitivity, specificity, as well as positive and negative predictive values for the presence of significant stenosis in T2DM were: by segment, 89.4%, 96.4%, 85.8%, and 97.4%, respectively; by artery (n=222), 95.1%, 92.9%, 94.4%, and 93.8%, respectively; by patients (n=74), 98.4%, 100.0%, 98.4%, and 90.0%, respectively. Regardless of presence of diabetes, there was no significant difference in diagnostic accuracy. Obesity (≥25 kg/m2) and coronary calcium score did not also affect the diagnostic accuracy of MDCT. ConclusionThe 64-slice MDCT coronary angiography was found to have similar diagnostic accuracy with ICA, regardless of diabetes. These results suggest MDCT may be helpful to reduce unnecessary invasive studies for patients with diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Can Radiation Dose Burden of CT Angiography be Reduced While Still Accurately Diagnosing Etiology of Acute Chest Pain?
Sherine M. Sharara, Scott R. Monnin, Manolo Rubio, Rami N. Khouzam, Samar R. Ragheb
Current Problems in Cardiology.2021; 46(4): 100766. CrossRef - Assessment of high sensitivity C-reactive protein and coronary plaque characteristics by computed tomography in patients with and without diabetes mellitus
Hai-Ting Zhou, De-Li Zhao, Guo-Kun Wang, Tian-Zuo Wang, Hong-Wei Liang, Jin-Ling Zhang
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose-Waist Circumference Better Predicts Coronary Calcium Progression Compared with Other Indices of Insulin Resistance: A Longitudinal Observational Study
Yun Kyung Cho, Jiwoo Lee, Hwi Seung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Dong Hyun Yang, Joon-Won Kang, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 10(1): 92. CrossRef - The impact of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome on the progression of coronary artery calcification
Yun Kyung Cho, Yu Mi Kang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jiwoo Lee, Seung Eun Lee, Dong Hyun Yang, Joon-Won Kang, Joong-Yeol Park, Chang Hee Jung, Hong-Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol on Coronary Artery Calcification Progression According to High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels
Da Young Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Se Eun Park, Cheol-young Park, Ki-won Oh, Sung-woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-young Lee
Archives of Medical Research.2017; 48(3): 284. CrossRef - 2013 ACC/AHA Cholesterol Guideline Versus 2004 NCEP ATP III Guideline in the Prediction of Coronary Artery Calcification Progression in a Korean Population
Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Yu Mi Kang, Jenie Yoonoo Hwang, Eun Hee Kim, Dong Hyun Yang, Joon‐Won Kang, Joong‐Yeol Park, Hong‐Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
Journal of the American Heart Association.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging Quality Evaluation of Low Tube Voltage Coronary CT Angiography Using Low Concentration Contrast Medium
Chengzhong Zhang, Yuejun Yu, Zaixian Zhang, Qingguo Wang, Linfeng Zheng, Yan Feng, Zhiguo Zhou, Guixiang Zhang, Kangan Li, Zhuoli Zhang
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(3): e0120539. CrossRef - 2013 ACC/AHA versus 2004 NECP ATP III Guidelines in the Assignment of Statin Treatment in a Korean Population with Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis
Chang Hee Jung, Min Jung Lee, Yu Mi Kang, Dong Hyun Yang, Joon-Won Kang, Eun Hee Kim, Duk-Woo Park, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee, Yingmei Feng
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(9): e0137478. CrossRef - Serum Total Bilirubin Levels Provide Additive Risk Information over the Framingham Risk Score for Identifying Asymptomatic Diabetic Patients at Higher Risk for Coronary Artery Stenosis
Jaechan Leem, Eun Hee Koh, Jung Eun Jang, Chang-Yun Woo, Jin Sun Oh, Min Jung Lee, Joon-Won Kang, Tae-Hwan Lim, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Joong-Yeol Park, Ki-Up Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(5): 414. CrossRef - Association between serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and the progression of coronary artery calcification
Yun Kyung Cho, Yu Mi Kang, Jenie Yoonoo Hwang, Eun Hee Kim, Dong Hyun Yang, Joon-Won Kang, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Atherosclerosis.2015; 243(1): 300. CrossRef - Role of Bilirubin in Diabetic Vascular Complications: Can Bilirubin Predict More than Just Liver Disease?
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(5): 384. CrossRef - The Association of Rate of Weight Gain During Early Adulthood With the Prevalence of Subclinical Coronary Artery Disease in Recently Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes: The MAXWEL-CAD Study
Soo Lim, Sung Hee Choi, Kyoung Min Kim, Sang Il Choi, Eun Ju Chun, Min Joo Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Naveed Sattar
Diabetes Care.2014; 37(9): 2491. CrossRef - Retraction: Diagnostic Accuracy of 64-Slice MDCT Coronary Angiography for the Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Ihn-Ho Cho, Hyoung Woo Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(3): 217. CrossRef
- Understanding the Cardiovascular Effects of Incretin
-
Ji Sung Yoon, Hyoung Woo Lee
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(5):437-443. Published online October 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.5.437
-
-
3,273
View
-
43
Download
-
17
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), a leading cause of death in patients with diabetes mellitus, has several pathogenic mechanisms that are well established. However, the traditional hypoglycemic agents do not have proven positive effects on macrovascular disease. Novel therapeutic agents target the incretin pathway including the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor (GLP-1R) agonists and the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. The glucose-regulatory actions of these agents function by increasing insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon. They also act to increase weight loss not only by inhibiting gastric emptying, but also by reducing appetite. Although GLP-1 and GLP-1R agonists have demonstrated beneficial effects on myocardium and vascular endothelium including coronary and peripheral mouse vessels, they also have anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic actions. These agents also have positive effects on the lipid profile and blood pressure. Although these cardioprotective actions seem to be beyond the effects of glucose control and weight loss, they are mediated through GLP-1R- or GLP-1R-independent actions of cleaved GLP-1 (9-36). Larger randomized controlled trials are necessary to elucidate the clinical promise of these beneficial CVD effects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Cardioprotective Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (9-36) Against Oxidative Injury in H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts: Potential Role of the PI3K/Akt/NOS Pathway
Narawat Nuamnaichati, Warisara Parichatikanond, Supachoke Mangmool
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology.2022; 79(1): e50. CrossRef - Comparisons of pleiotropic effects of SGLT2 inhibition and GLP-1 agonism on cardiac glucose intolerance in heart dysfunction
Belma Turan, Aysegul Durak, Yusuf Olgar, Erkan Tuncay
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 477(11): 2609. CrossRef - Interrelations of components of metabolic syndrome with the level of the hormones involved in regulation of adipose tissue metabolism
A. Y. Babenko, G. A. Matveev, T. I. Alekseenko, I. V. Derevitskii, M. A. Kokina, E. V. Shlyakhto
"Arterial’naya Gipertenziya" ("Arterial Hypertension").2020; 25(6): 639. CrossRef - Attenuation of carotid neointimal formation after direct delivery of a recombinant adenovirus expressing glucagon-like peptide-1 in diabetic rats
Soo Lim, Gha Young Lee, Ho Seon Park, Dong-Hwa Lee, Oh Tae Jung, Kim Kyoung Min, Young-Bum Kim, Hee-Sook Jun, Jang Hak Chul, Kyong Soo Park
Cardiovascular Research.2017; 113(2): 183. CrossRef - Renoprotective Effects of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Sitagliptin: A Review in Type 2 Diabetes
Cristina Mega, Edite Teixeira-de-Lemos, Rosa Fernandes, Flávio Reis
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Letter: Economic Impact of Combining Metformin with Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Diabetic Patients with Renal Impairment in Spanish Patients (Diabetes Metab J2015;39:74-81)
Hannah Seok
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(2): 171. CrossRef - Diuretic and Natriuretic Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Teneligliptin
Masao Moroi, Tetsuya Kubota
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology.2015; 66(2): 159. CrossRef - The Nonglycemic Actions of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors
Na-Hyung Kim, Taeyang Yu, Dae Ho Lee
BioMed Research International.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Tolerability, effectiveness and predictive parameters for the therapeutic usefulness of exenatide in obese, Korean patients with type 2 diabetes
Sun Ok Song, Kwang Joon Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2014; 5(5): 554. CrossRef - The endothelium in diabetes: Its role in insulin access and diabetic complications
Cathryn M. Kolka, Richard N. Bergman
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2013; 14(1): 13. CrossRef - Is GPR119 agonism an appropriate treatment modality for the safe amelioration of metabolic diseases?
Lauren M Cornall, Michael L Mathai, Deanne H Hryciw, Andrew J McAinch
Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs.2013; 22(4): 487. CrossRef - Effects of GLP-1 on Forearm Vasodilator Function and Glucose Disposal During Hyperinsulinemia in the Metabolic Syndrome
Manfredi Tesauro, Francesca Schinzari, Angelo Adamo, Valentina Rovella, Francesca Martini, Nadia Mores, Angela Barini, Dario Pitocco, Giovanni Ghirlanda, Davide Lauro, Umberto Campia, Carmine Cardillo
Diabetes Care.2013; 36(3): 683. CrossRef - Effect of a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitor, Des-Fluoro-Sitagliptin, on Neointimal Formation after Balloon Injury in Rats
Soo Lim, Sung Hee Choi, Hayley Shin, Bong Jun Cho, Ho Seon Park, Byung Yong Ahn, Seon Mee Kang, Ji Won Yoon, Hak Chul Jang, Young-Bum Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Alice Y. W. Chang
PLoS ONE.2012; 7(4): e35007. CrossRef - Glucagon-like peptide 1 and cardiac cell survival
Susana Ravassa, Amaia Zudaire, Javier Díez
Endocrinología y Nutrición (English Edition).2012; 59(9): 561. CrossRef - GLP-1 and cardioprotection: from bench to bedside
S. Ravassa, A. Zudaire, J. Diez
Cardiovascular Research.2012; 94(2): 316. CrossRef - Saxagliptin improves glucose tolerance but not survival in a murine model of dilated cardiomyopathy
Arpita Kalla Vyas, Lauren B. Aerni-Flessner, Maria A. Payne, Attila Kovacs, Patrick Y. Jay, Paul W. Hruz
Cardiovascular Endocrinology.2012; 1(4): 74. CrossRef - Péptido similar al glucagón tipo 1 y supervivencia de la célula cardiaca
Susana Ravassa, Amaia Zudaire, Javier Díez
Endocrinología y Nutrición.2012; 59(9): 561. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Chronic Complications in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on the Korean National Diabetes Program
-
Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Mi Kwang Kwon, Ie Byung Park, Kyu Jeung Ahn, In Ju Kim, Sung-Hoon Kim, Hyoung Woo Lee, Kyung Soo Koh, Doo Man Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Soo Park, Jeong-taek Woo, Young Seol Kim
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(5):504-512. Published online October 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.5.504
-
-
4,561
View
-
39
Download
-
52
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
The Korean National Diabetes Program (KNDP) cohort study is performing an ongoing large-scale prospective multicenter investigation to discover the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in Korean patients. This study was performed to examine the prevalence of chronic complications in patients with type 2 diabetes among those registered in the KNDP cohort within the past 4 years. MethodsThis study was performed between June 2006 and September 2009 at 13 university hospitals and included 4,265 KNDP cohort participants. Among the participants, the crude prevalence of microvascular and macrovascular diseases of those checked for diabetes-related complications was determined, and the adjusted standard prevalence and standardization of the general population prevalence ratio (SPR) was estimated based on the 2005 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) population demographics. ResultsAmong the KNDP registrants, 43.2% had hypertension, 34.8% had dyslipidemia, 10.8% had macrovascular disease, and 16.7% had microvascular disease. The SPR of the KNDP registrants was significantly higher than that of the KNHANES subjects after adjusting for demographics in the KNHANES 2005 population. However, with the exception of cardiovascular disease in females, the standardized prevalence for the most complicated items in the survey was significantly higher than that in the KNHANES subjects. ConclusionThe prevalence of macrovascular disease and peripheral vascular disease were significantly higher in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes than in the normal population. However, no significant difference was noted in the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in females.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye-Sun Park, Yongin Cho, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, So Hun Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and economic impact of changing reimbursement criteria for statin treatment among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea
Siin Kim, Kyungseon Choi, Ji-yool Kim, Hae Sun Suh
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Promising First Cohort Study in Korean Patients with Obesity and Overweight: Gangwon Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Study
Eun-Jung Rhee
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(4): 285. CrossRef - Impact of noncommunicable disease conditions and physical burden on intent to leave midwifery in Hungary
Krisztina Éles Gebriné, Kinga Lampek, Péter Takács, Miklós Zrínyi, Attila Sárváry, Andrea Sárváry
Kontakt.2021; 23(1): 45. CrossRef - Dietary glutamic acid and aspartic acid as biomarkers for predicting diabetic retinopathy
So Young Park, Jieun Kim, Jung Il Son, Sang Youl Rhee, Do-Yeon Kim, Suk Chon, Hyunjung Lim, Jeong-Taek Woo
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 613. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 617. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Prevalence of Comorbidities according to Metformin Use in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Sang Ouk Chin, In Gyoon Ha, Sang Youl Rhee, Su Jin Jeong, Suk Chon, Sung Hoon Kim, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Jeong Taek Woo
International Journal of Endocrinology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Perioperative anesthetic management of patients with diabetes mellitus: focused on blood glucose control
Hyungseok Seo
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2020; 63(9): 526. CrossRef - Predicting Old-age Mortality Using Principal Component Analysis: Results from a National Panel Survey in Korea
Jaeyong Shin, Kwang-Soo Lee, Jae-Hyun Kim
Medicina.2020; 56(7): 360. CrossRef - A relationship between endoscopic findings
and diabetic regulation, and complications in patients with diabetes mellitus
Sevki Konur
Archives of Medical Science – Civilization Diseases.2020; 5(1): 53. CrossRef - Randomized control trial comparing the effect of cilostazol and aspirin on changes in carotid intima-medial thickness
Sangmo Hong, Munsuk Nam, Bertis B. Little, Seihyun Paik, Kwanwoo Lee, Jungtaek Woo, Dooman Kim, Jungoo Kang, Minyoung Chun, Yongsoo Park
Heart and Vessels.2019; 34(11): 1758. CrossRef - Genome‐wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for diabetic nephropathy in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kyung H. Jeong, Jin S. Kim, Jeong‐Taek Woo, Sang Y. Rhee, Yu H. Lee, Yang G. Kim, Ju‐Young Moon, Su K. Kim, Sun W. Kang, Sang H. Lee, Yeong H. Kim
Clinical Genetics.2019; 96(1): 35. CrossRef - Presence of Carotid Plaque Is Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Renal Function
Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim, Joon Ho Song, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Seong Hee Ahn, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim, Moonsuk Nam
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 840. CrossRef - The relationship between demographic and anthropometric characteristics and diabetic complications and number of hospitalizations in hospitalized diabetic patients
Yusuf Kayar, Mehmet Agin
Archives of Medical Science – Civilization Diseases.2019; 4(1): 7. CrossRef - Importance of family history of diabetes in computing a diabetes risk score in Korean prediabetic population
Morena Ustulin, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Kyu Keung Ahn, Ji Eun Lim, Bermseok Oh, Sung-Hoon Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim, Jeong-Taek Woo
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics of frequent emergency department users with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea
Morena Ustulin, Junghoon Woo, Jeong‐taek Woo, Sang Youl Rhee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2018; 9(2): 430. CrossRef - Implementation of the Chronic Disease Care System and its association with health care costs and continuity of care in Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Woorim Kim, Yoon Soo Choy, Sang Ah Lee, Eun-Cheol Park
BMC Health Services Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Long‐term effects on glycaemic control and β‐cell preservation of early intensive treatment in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A multicentre randomized trial
Suk Chon, Sang Youl Rhee, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Soon Jib Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Dae Ho Lee, Young Seol Kim, Jeong‐Taek Woo
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2018; 20(5): 1121. CrossRef - Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index as a Surrogate Marker of Early Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
So Young Park, Sang Ook Chin, Sang Youl Rhee, Seungjoon Oh, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sung Woon Kim, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(4): 285. CrossRef - Metformin reduces the risk of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes
Hae Jin Kim, SooJin Lee, Ki Hong Chun, Ja Young Jeon, Seung Jin Han, Dae Jung Kim, Young Seol Kim, Jeong-Taek Woo, Moon-Suk Nam, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Kwan Woo Lee
Medicine.2018; 97(8): e0036. CrossRef - Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Health Behaviors, Metabolic Control, and Chronic Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
So Hun Kim, Seung Youn Lee, Chei Won Kim, Young Ju Suh, Seongbin Hong, Seong Hee Ahn, Da Hae Seo, Moon-Suk Nam, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 380. CrossRef - Failure of monotherapy in clinical practice in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Korean National Diabetes Program
Ja Young Jeon, Soo Jin Lee, Sieun Lee, Soo Jin Kim, Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Young Seol Kim, Jeong Taek Woo, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Moonsuk Nam, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan‐Woo Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2018; 9(5): 1144. CrossRef - Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease Risk in Korean Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Bo Kyung Koo, Sohee Oh, Yoon Ji Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2018; 7(2): 110. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot
Chang Won Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(3): 168. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and risk factors for retinal diabetic neurodegeneration in type 2 diabetes
Kiyoung Kim, Eung Suk Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Jeong-taek Woo, Seung-Young Yu
Acta Diabetologica.2017; 54(11): 993. CrossRef - Features of Long-Standing Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Study Based on Standardized Clinical Data
Sejeong Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Su Jin Jeong, Kiyoung Kim, Suk Chon, Seung-Young Yu, Jeong-Taek Woo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 393. CrossRef - Clinical heterogeneity of type 1 diabetes (T1D) found in Asia
Yongsoo Park, Kupper A. Wintergerst, Zhiguang Zhou
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Response: Features of Long-Standing Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Study Based on Standardized Clinical Data (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:393-404)
Sang Youl Rhee, Jeong-Taek Woo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 494. CrossRef - Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(5): 845. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia is associated with dementia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: An analysis based on the Korea National Diabetes Program Cohort
Sang Ouk Chin, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Ki Hong Chun, Jeong-taek Woo, Young Seol Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2016; 122: 54. CrossRef - Relationship between fruit and fish intakes and cardiovascular disease risk factors in Korean women with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Based on the 4th and 5th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Ji Soo Oh, Hyesook Kim, Ki Nam Kim, Namsoo Chang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(5): 304. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia and Medical Expenses in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Analysis Based on the Korea National Diabetes Program Cohort
Sang Youl Rhee, Soo Min Hong, Suk Chon, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sung Hoon Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Soo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Jeong-Taek Woo, Young Seol Kim, Zhengdong Zhang
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(2): e0148630. CrossRef - Elevated lipoprotein(a) levels predict cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 10-year prospective cohort study
Tae-Seok Lim, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yu-Bae Ahn, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(6): 1110. CrossRef - Low Economic Status Is Identified as an Emerging Risk Factor for Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Men Aged 30 to 59 Years in Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008 to 2010
Bo Kyung Koo, Sang Wan Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(2): 137. CrossRef - Assessment of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with metformin–sulfonylurea combination: Results of a multicenter, cross‐sectional, observational study in Korea
Sin Gon Kim, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Duk Kyu Kim, Sung Rae Cho, Dong Seop Choi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2015; 6(3): 317. CrossRef - Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Medication-Adherent and -Nonadherent Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the Republic of Korea
So-Yeon An, Hae Jin Kim, Ki Hong Chun, Tae Ho Kim, Ja Young Jeon, Dae Jung Kim, Seung Jin Han, Young Seol Kim, Jeong Taek Woo, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Yongsoo Park, Moonsuk Nam, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan-Woo Lee
Clinical Therapeutics.2014; 36(2): 245. CrossRef - Serum Magnesium Level Is Associated with Type 2 Diabetes in Women with a History of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: The Korea National Diabetes Program Study
Sae Jeong Yang, Soon Young Hwang, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Soo Park, Jeong Taek Woo, Young Seol Kim, Sunmin Park, So-Young Park, Chang Hoon Yim, Hyun Koo Yoon, Sung-Hoon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2014; 29(1): 84. CrossRef - Heart rate variability in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Camila Balsamo Gardim, Bruno Affonso P. de Oliveira, Aline Fernanda B. Bernardo, Rayana Loch Gomes, Francis Lopes Pacagnelli, Roselene Modolo R. Lorençoni, Luiz Carlos M. Vanderlei
Revista Paulista de Pediatria.2014; 32(2): 279. CrossRef - Development of an HbA1c-Based Conversion Equation for Estimating Glycated Albumin in a Korean Population with a Wide Range of Glucose Intolerance
Chang Hee Jung, You-Cheol Hwang, Kwang Joon Kim, Bong Soo Cha, Cheol-Young Park, Won Seon Jeon, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sang Youl Rhee, Jeong-taek Woo, Byung-Wan Lee, Sompop Bencharit
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(4): e95729. CrossRef - It's Still Not Too Late to Make a Change: Current Status of Glycemic Control in Korea
Sang Yong Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(3): 194. CrossRef - Prevalence and factors associated with diabetic retinopathy in a Korean adult population: The 2008–2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ju Yean Yang, Na Kyung Kim, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung Hyun Noh, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Dong-Jun Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2013; 102(3): 218. CrossRef - Increasing achievement of the target goals for glycemic, blood pressure and lipid control for adults with diagnosed diabetes in Korea
Sung Hoon Yu, Jun Goo Kang, Yoo‐Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Hyung Joon Yoo, Hong Yup Ahn, Sung Woo Park, Cheol‐Young Park
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2013; 4(5): 460. CrossRef - Hemoglobin A1c May Be an Inadequate Diagnostic Tool for Diabetes Mellitus in Anemic Subjects
Jung Il Son, Sang Youl Rhee, Jeong-taek Woo, Jin Kyung Hwang, Sang Ouk Chin, Suk Chon, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Woon Kim, Young Seol Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(5): 343. CrossRef - Implication of circulating omentin-1 level on the arterial stiffening in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye Jin Yoo, Soon Young Hwang, Ho Cheol Hong, Hae Yoon Choi, Sae Jeong Yang, Kwan Woo Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Soo Park, Jeong Taek Woo, Young Seol Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik
Endocrine.2013; 44(3): 680. CrossRef - Comparison of Two Creatinine-Based Equations for Predicting Decline in Renal Function in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Nephropathy in a Korean Population
Eun Young Lee, Young-Mi Lee, Kyu Hun Choi, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Beom Seok Kim
International Journal of Endocrinology.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Association between Nutrient Intake and Obesity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients from the Korean National Diabetes Program: A Cross-Sectional Study
So Hun Kim, Seong Bin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Yun Jin Choi, Moonsuk Nam, Hyoung Woo Lee, Ie Byung Park, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Dae Jung Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2012; 27(10): 1188. CrossRef - C1q/TNF-Related Protein-3 (CTRP-3) and Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Concentrations in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Kyung Mook Choi, Soon Young Hwang, Ho Cheol Hong, Sae Jeong Yang, Hae Yoon Choi, Hye Jin Yoo, Kwan Woo Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Soo Park, Jeong Taek Woo, Young Seol Kim, Dong Seop Choi, Byung-Soo Youn, Sei Hyun Baik
Diabetes.2012; 61(11): 2932. CrossRef - Direct Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Related Complications: A Prospective Cohort Study Based on the Korean National Diabetes Program
Tae Ho Kim, Ki Hong Chun, Hae Jin Kim, Seung Jin Han, Dae Jung Kim, Jiyeong Kwak, Young Seol Kim, Jeong Taek Woo, Yongsoo Park, Moonsuk Nam, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Kwan Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2012; 27(8): 876. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Micro- and Macrovascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes in Korea
Jung Hee Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(6): 571. CrossRef - Letter: The Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attending a University Hospital (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:543-50)
Won Jun Kim, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(6): 637. CrossRef - Satisfaction with High Deductible Policies among Patients with Diabetes in the Korean General/University Hospital System
Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Diabetes.2011; 12(4): 179. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Stress in Korean Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using the Problem Areas in Diabetes-Korea Questionnaire
-
Young Sil Eom, Hwa Sun Park, Sei-Hyun Kim, Sun Mee Yang, Moon Suk Nam, Hyoung Woo Lee, Ki Young Lee, Sihoon Lee, Yeun Sun Kim, Ie Byung Park
-
Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(2):182-187. Published online April 30, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.2.182
-
-
4,431
View
-
56
Download
-
16
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
It is known that diabetes and stress are directly or indirectly related, and that it is important to evaluate stress in patients with diabetes. The relationship between Korean diabetics and diabetes-related stress has never been reported. The objective of this study was to develop a stress questionnaire suitable for use with Korean diabetics and to evaluate its utility. MethodsThis study subjects were 307 Korean diabetics, aged 40 to 74 years old, who visited the Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism at Gachon University Gil Hospital, Yeungnam University Medical Center, and Inha University Hospital in Korea between March 2006 and February 2008. We developed a Korean version of Polonsky's Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID) stress questionnaire (PAID-K) and used it to assess degrees of stress in our sample of Korean patients. We evaluated the utility of the questionnaire and analyzed the relationships between clinical characteristics of the study subjects and degrees of stress. ResultsCronbach's alpha for PAID-K was 0.95, and PAID-K scores were significantly correlated with Hypoglycemia Fear Survey scores (r=0.44, P<0.05) and State Trait Anxiety Inventory-6 scores (r=0.21, P<0.05). PAID-K scores were significantly higher in patients with longer durations of diabetes, patients using insulin, and female patients (P=0.02, P=0.038, and P=0.001, respectively). The score also tended to increase as HbA1c levels increased, except for very high HbA1c levels (above 11%) (P for trend<0.05). ConclusionWe developed the PAID-K questionnaire and demonstrated its utility to evaluate levels of stress in diabetic patients in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye-Sun Park, Yongin Cho, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, So Hun Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Distress Measurement Related to Glucose Monitoring of Diabetes Patients
Eujin Choi, Sooyeon Kim, Juhee Cho, Min-Sun Kim, Eun Kyung Kwon, Youngha Kim, Danbee Kang, Sung Yoon Cho
Diabetes Therapy.2023; 14(4): 737. CrossRef - Development and validation of a distress measurement for insulin injections among patients with diabetes
Eujin Choi, Min-Sun Kim, Juhee Cho, Sooyeon Kim, Eun Kyung Kwon, Youngha Kim, Danbee Kang, Sung Yoon Cho
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Experiential Avoidance on the Relationship between Diabetes Distress and Self-Stigma in People with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 in Republic of Korea
Kawoun Seo
Healthcare.2023; 11(20): 2773. CrossRef - Patient-reported outcome measures for assessing health-related quality of life in people with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
Marlous Langendoen-Gort, Lenka Groeneveld, Cecilia A. C. Prinsen, Joline W. Beulens, Petra J. M. Elders, Ilana Halperin, Geetha Mukerji, Caroline B. Terwee, Femke Rutters
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2022; 23(5): 931. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Acceptance Action in the Relationship between Diabetes Distress and Self-stigma among Old Adults with Diabetes in South Korea
Hyesun Kim, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(4): 446. CrossRef - Mobile Healthcare System Provided by Primary Care Physicians Improves Quality of Diabetes Care
Tae Jung Oh, Jie-Eun Lee, Seok Kim, Sooyoung Yoo, Hak Chul Jang
CardioMetabolic Syndrome Journal.2021; 1(1): 88. CrossRef - Measurement Properties of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures for Diabetes: Systematic Review
Priscilla Jia Ling Wee, Yu Heng Kwan, Dionne Hui Fang Loh, Jie Kie Phang, Troy H Puar, Truls Østbye, Julian Thumboo, Sungwon Yoon, Lian Leng Low
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2021; 23(8): e25002. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Acceptance and Action Questionnaire-Stigma (AAQ-S-K)
Hyunjin Lee, Myoungjin Kwon, Kawoun Seo
Healthcare.2021; 9(10): 1355. CrossRef - Adherence to Mediterranean diet and advanced glycation endproducts in patients with diabetes
Marko Grahovac, Marko Kumric, Marino Vilovic, Dinko Martinovic, Ante Kreso, Tina Ticinovic Kurir, Josip Vrdoljak, Karlo Prizmic, Joško Božić
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(11): 1942. CrossRef - The Impact of a Community-Based Food Education Program on Nutrition-Related Knowledge in Middle-Aged and Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Results of a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Carlos Vasconcelos, António Almeida, Maria Cabral, Elisabete Ramos, Romeu Mendes
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(13): 2403. CrossRef - The Effects of the 2030 Diabetes Camp Program on Depression, Anxiety, and Stress in Diabetic Patients
Jin Hee Jung, Jung Hwa Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2019; 20(3): 194. CrossRef - Research of Type 2 Diabetes Patients’ Problem Areas and Affecting Factors
Sebahat Atalikoğlu Başkan, Mehtap Tan
Journal of Diabetes Mellitus.2017; 07(03): 175. CrossRef - Diabetes-related emotional distress instruments: A systematic review of measurement properties
Jiyeon Lee, Eun-Hyun Lee, Chun-Ja Kim, Seung Hei Moon
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(12): 1868. CrossRef - Internet-Based Mentoring Program for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Sun-Hye Ko, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(2): 107. CrossRef - Influence of the Duration of Diabetes on the Outcome of a Diabetes Self-Management Education Program
Seung-Hyun Ko, Sin-Ae Park, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Sun-Hye Ko, Kyung-Mi Shin, Seung-Hwan Lee, Ki-Ho Song, Yong-Moon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(3): 222. CrossRef
|

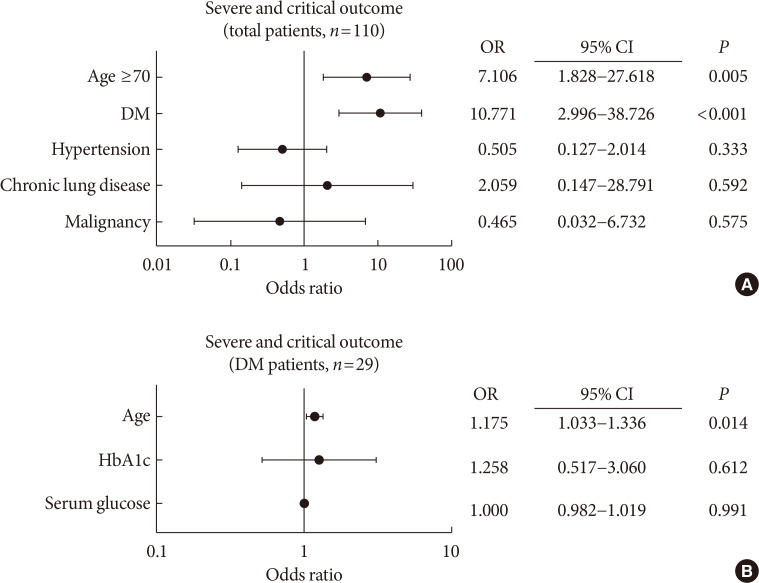

 KDA
KDA




