- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 44(2); 2020 > Article
-
Brief ReportComplications Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports
-
Na-young Kim1
 , Eunyeong Ha2
, Eunyeong Ha2 , Jun Sung Moon2, Yong-Hoon Lee3
, Jun Sung Moon2, Yong-Hoon Lee3 , Eun Young Choi2
, Eun Young Choi2
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2020;44(2):349-353.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0091
Published online: April 23, 2020
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
2Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
3Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Yong-Hoon Lee. Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, 130 Dongdeok-ro, Jung-gu, Daegu 41944, Korea. id0121@naver.com
- Corresponding author: Eun Young Choi. Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, 170 Hyeonchung-ro, Nam-gu, Daegu 42415, Korea. letact@yu.ac.kr
- *Na-Young Kim and Eunyeong Ha contributed equally to this study as first authors.
Copyright © 2020 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
- Since the first case was contracted by coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) in Daegu, Korea in February 2020, about 6,800 cases and 130 deaths have been reported on April 9, 2020. Recent studies have reported that patients with diabetes showed higher mortality and they had a worse prognosis than the group without diabetes. In poorly controlled patients with diabetes, acute hyperglycemic crises such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) also might be precipitated by COVID-19. Thus, intensive monitoring and aggressive supportive care should be needed to inadequately controlled patients with diabetes and COVID-19 infection. Here, we report two cases of severe COVID-19 patients with acute hyperglycemic crises in Korea.
- Since the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic began in China, more than 10,500 confirmed cases and about 220 coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19)-related deaths have been reported in Korea (as of April 14, 2020). Daegu City accounts for 78% of confirmed cases and 68% of deaths since the outbreak began in February 2020. Recent studies have shown that advanced age or underlying medical comorbidities, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, are considered as risk factors for severe illness and mortality among patients with COVID-19 [1].
- Acute hyperglycemic crises—Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS)—are the serious acute metabolic complications of diabetes, and commonly precipitated by infection. COVID-19 is also estimated to trigger acute hyperglycemic crises in patients with inadequately controlled patients with diabetes, but the evidence for this association is still limited.
- Here, we described two COVID-19 cases compromised with acute hyperglycemic crises—DKA and HHS—during the outbreak in Daegu, South Korea.
INTRODUCTION
- Electric medical records of index cases were reviewed and cross-checked by two independent physicians. Informed consent was waived because of the retrospective nature of the study and the analysis used anonymous clinical data. This study was approved by Institutional Review Board (YUH IRB 2020-03-057) of Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
METHODS
- Case 1
- A 59-year-old man was admitted to the hospital suffering from general weakness, polydipsia, polyuria, and mild dyspnea for 4 days. He had a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and hypertension but was recently discontinuing oral hypoglycemic agents (OHA); he had managed his blood glucose through diet and exercise only. Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level of the patient was 6.4% when measured 5 months earlier.
- Initial vital signs were blood pressure 151/97 mm Hg, heart rate 104 beats/min, respiratory rate 24 breaths/min, and body temperature 37℃, and oxygen saturation 94% by pulse oximetry on room air. Upon admission, plasma glucose was 655 mg/dL and HbA1c was 11.4%. Blood chemistry revealed blood urea nitrogen 88.4 mg/dL, creatinine 1.97 mg/dL, sodium 139 mEq/L, potassium 6.3 mEq/L, and plasma ketone body 4.9 mmol/L. Arterial blood gas analysis (ABGA) on room air demonstrated a compensated metabolic acidosis.
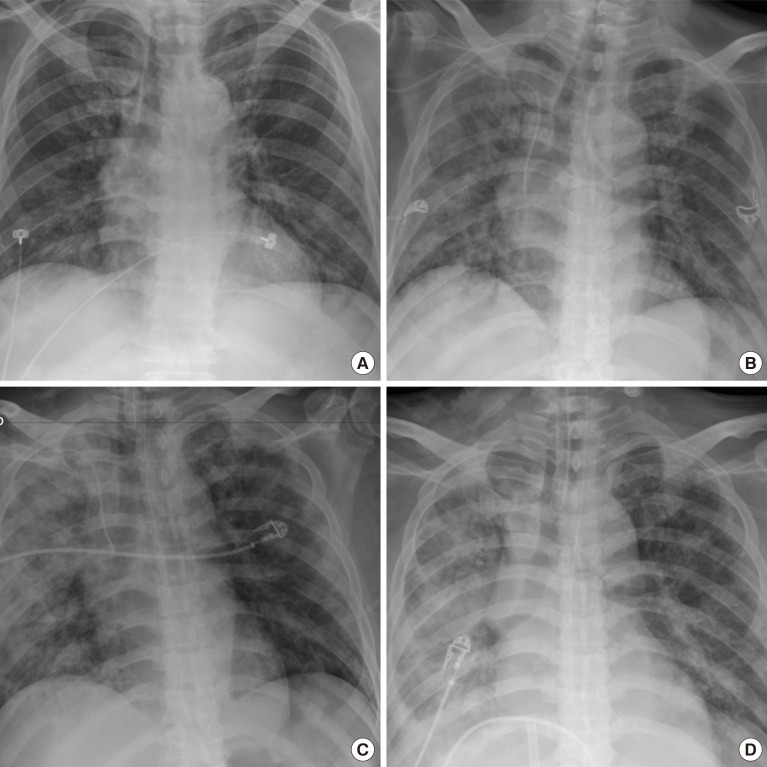
- The patient reportedly had contacted with someone who was diagnosed with COVID-19 22 days prior to his hospital admission. The chest radiograph showed peribronchial ground-glass opacities in both lungs, although there was no obvious flu-like symptom such as cough, sputum, sore throat, or fever (Fig. 1). COVID-19 was confirmed on March 19, 2020, on the basis of real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay that detected SARS-CoV-2. Therefore, anti-viral agents (lopinavir/ritonavir), empirical antibiotics, and symptomatic respiratory treatment for COVID-19 infection as well as treatment for DKA were also performed. The DKA was improved after proper insulin treatment, but the dyspnea and radiologic finding worsened. Mechanical ventilation was initiated on the fourth day of admission. He received intensive treatments such as continuous renal replacement therapy (6th day after admission) and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (13th day after admission).
- On the 14th day of hospitalization, acute myocardial infarction was diagnosed based on the elevation of cardiac enzyme and ST segment on the electrocardiogram, and percutaneous coronary intervention was performed. However, the patient did not recover from respiratory failure and hemodynamic instability and eventually died after 16th day of hospitalization.
- Case 2
- A 72-year-old woman was hospitalized for shortness of breath for 3 days. Before being transferred, the patient was confirmed COVID-19 using RT-PCR test with high oxygen demand. She had a history of T2DM, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, but had stopped taking OHA for several days due to anorexia. Her skin was dry and tough upon physical examination. Her initial vital signs were within normal ranges, but oxygen saturation was 90% in pulse oximetry on 6 L/min of oxygen mask.
- Upon hospital admission, laboratory findings showed increases in plasma levels of glucose (690 mg/dL), effective osmolality (324 mOsm/kg), and HbA1c (12.6%) respectively. Urine and serum ketone body was not detected. ABGA on 6 L/min of oxygen mask showed pH 7.381, HCO3− 18.1 mmol/L, and serum sodium and potassium were within normal range. Her chest radiograph showed multifocal patchy consolidation at both lung fields (Fig. 2).
- Based on the laboratory and imaging results, she was diagnosed with HHS and COVID-19. Treatment was immediately provided with intravenous fluid, regular insulin, anti-viral agents, and empirical antibiotics. Hyperglycemia and dehydration were promptly improved after proper management, but radiologic findings worsened with an increase in oxygen demand. On the second day, invasive mechanical ventilation with prone position was initiated. A tracheostomy was applied on 15th days of hospitalization because the patients was not spontaneously breathing. After 33 days of hospitalization, subsequent COVID-19 tests were all negative but she still needs support from a mechanical ventilator.
RESULTS
- Herein we report two patients with acute hyperglycemia precipitated by COVID-19. One case was in conjunction with DKA and was fatal, and the other had HHS and delayed recovery even after RT-PCR tests were negative. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report of COVID-19 combined with DKA and HHS.
- Emerging information suggests that individuals with diabetes are at increased risk for complications including death among COVID-19 patients. According to a clinical report in China [2] involving 1,099 confirmed COVID-19 patients, diabetes was the second most common comorbidity (16.2%) among severe 173 cases. There are not enough evidences to determine the risk of diabetes for poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients yet, a small study showed that COVID-19 patients with diabetes were not only at higher risk of severe pneumonia but also release excessive inflammatory biomarkers [3]. These results suggest that people with comorbidities, especially with DM, are susceptible to COVID-19 infection.
- It is well known that acute hyperglycemic crises are significantly related to morbidity or death in peoples with diabetes [4]. According to a recent study [5], hospitalization rate and mortality rate per 1,000 diabetes cases due to hyperglycemic crises in the past decade have continued to decline in Korea. Unfortunately, we have experienced the outbreak of COVID-19 limiting the proper use of medical resources in our community. Lessons we learned from these cases are that chronic disease management could be hampered by unexpected the outbreak, and appropriate and aggressive management should be provided in order to improve the prognosis of COVID-19 patients with comorbidities, such as diabetes and hypertension.
- These cases imply that acute hyperglycemic crises can be precipitated by COVID-19 and results in catastrophic outcomes in patients with diabetes and poor glycemic control. Agile policies and strategies for the effective distribution of essential medical resources are necessary to prevent the further loss of life due to the exacerbation of chronic diseases.
DISCUSSION
-
Acknowledgements
- We would like to express our deepest gratitude to all efforts and dedication of the health professionals who have struggled with the COVID-19 in Korea.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
NOTES
- 1. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, Xiang J, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X, Guan L, Wei Y, Li H, Wu X, Xu J, Tu S, Zhang Y, Chen H, Cao B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020;395:1054-1062. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia J, Liu H, Wu Y, Zhang L, Yu Z, Fang M, Yu T, Wang Y, Pan S, Zou X, Yuan S, Shang Y. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med 2020 2 24 [Epub].Article
- 3. Guo W, Li M, Dong Y, Zhou H, Zhang Z, Tian C, Qin R, Wang H, Shen Y, Du K, Zhao L, Fan H, Luo S, Hu D. Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2020 3 31 [Epub].
- 4. Kim KJ, Kwon TY, Yu S, Seo JA, Kim NH, Choi KM, Baik SH, Choi DS, Kim SG, Park Y, Kim NH. Ten-year mortality trends for adults with and without diabetes mellitus in south Korea, 2003 to 2013. Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:394-401. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 5. You JH, Song SO, Park SH, Park KH, Nam JY, Kim DW, Kim HM, Kim DJ, Lee YH, Lee BW. Trends in hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations and in- and out-of-hospital mortality in the last decade based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2019;34:275-281. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
REFERENCES
Case 1. Chest radiographs, at admission (A), 3rd day of hospitalization, peribronchial ground-glass opacities (GGOs) in both lungs (B), 6th day of hospitalization, exacerbation of peribronchial GGOs and nodular opacities in both lungs (C), 15th day of hospitalization (D).

Case 2. Chest radiographs, at admission, atherosclerotic cardiovascular change, increased cardiothoracic ratio and pulmonary vasculature, multifocal patchy consolidation at both lung field (A), 2nd day of hospitalization, minimal improving status of consolidation (B), 20th day of hospitalization, more progression of both lung field consolidation (C), 33rd day of hospitalization, minimal improving status of consolidation (D).
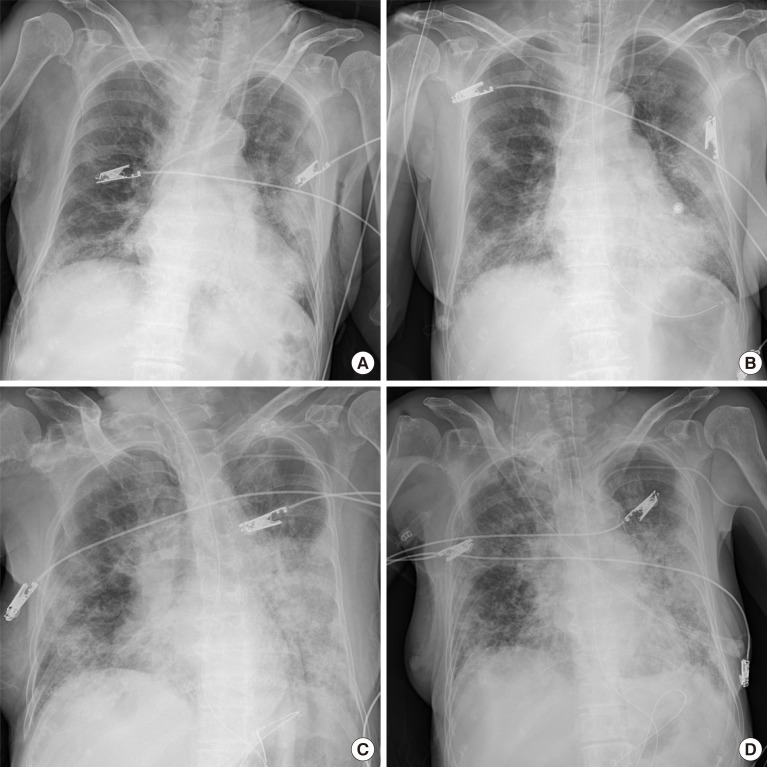
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Clinical Characteristics and Predictors of Mortality in Obese African-Americans with COVID-19: a Single-Center Retrospective Study
Pavani Reddy Garlapati, Suneet Kumar, Meet Patel, Bidyut Sarker, Benjamin Tiongson, Sreedhar Adapa, Sohail Abdul Salim, Mark K. Adler, Vijay Reddy Gayam
Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities.2023; 10(1): 160. CrossRef - Diabetes and the COVID-19 pandemic
Kamlesh Khunti, Jonathan Valabhji, Shivani Misra
Diabetologia.2023; 66(2): 255. CrossRef - Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Development Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination
Hyeyeon Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Mi Kyoung Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID‐19 associated ketosis and diabetic ketoacidosis: A rapid review
Tharun T. Alamuri, Sandhya Mahesh, Kevin Dell'Aquila, Taylor Jan Leong, Rebecca Jennings, Tim Q. Duong
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(7): 1785. CrossRef - Risks associated with acute pancreatitis (AP) with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in COVID-19 patients: a literature review
Sundru Manjulata Devi, Annapurna Pamreddy, Venkata Ramana Narendra
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023; 22(1): 135. CrossRef - A Review of Hyperglycemia in COVID-19
Maryam Zahedi, Saba Kordrostami, Mohammadreza Kalantarhormozi, Marziyeh Bagheri
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A UK nationwide study of adults admitted to hospital with diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state and COVID‐19
Benjamin C. T. Field, Yue Ruan, Kinga A. Várnai, Jim Davies, Robert E. J. Ryder, Rajiv Gandhi, Sophie Harris, Dinesh Nagi, Dipesh Patel, Punith Kempegowda, Sarah H. Wild, Emma G. Wilmot, Kamlesh Khunti, Rustam Rea, Parth Narendran
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(7): 2012. CrossRef - Diabetic Ketoacidosis in COVID-19 Patients: Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes – A Retrospective Study in a Single Tertiary Care Hospital, Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Hana AL Sughaiyer, Abeer AL Haj, Samia Murad Ibrahim Abdulrahman
Dubai Diabetes and Endocrinology Journal.2023; 29(2): 107. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes
Artur Furga
Probacja.2023; 3: 235. CrossRef - COVID-19 SALGININDA DİYABET YÖNETİMİ VE HEMŞİRENİN ROLÜ
Dilek BÜYÜKKAYA BESEN, Merve DERVİŞOĞLU
Gazi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2022; 7(2): 78. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis and COVID-19: what have we learned so far?
Caio Oliveira de Sá-Ferreira, Camila Helena Macedo da Costa, João Campos Wiltgen Guimarães, Nathasha Souza Sampaio, Leticia de Moraes Lopes Silva, Larissa Paula de Mascarenhas, Nicollas Garcia Rodrigues, Talita Labonia dos Santos, Solange Campos, Esther C
American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 322(1): E44. CrossRef - COVID-19 and hyperglycaemic emergencies: perspectives from a developing country
Raisa Bhikoo, Marli Conradie-Smit, Gerhard Van Wyk, Sa’ad Lahri, Elizabeth Du Plessis, Jaco Cilliers, Susan Hugo, Ankia Coetzee
Journal of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Diabetes of South Africa.2022; 27(1): 42. CrossRef - Potential impact of combined influenza and pneumococcal vaccines on the severity of respiratory illness in COVID-19 infection among type 2 diabetic patients
Amr Shaaban Hanafy, Waseem M. Seleem, Hany A. Elkattawy
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The COVID-19-diabetes mellitus molecular tetrahedron
Mehdi Mahmudpour, Katayoun Vahdat, Mohsen Keshavarz, Iraj Nabipour
Molecular Biology Reports.2022; 49(5): 4013. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19; A Bidirectional Interplay
Paraskevi Kazakou, Vaia Lambadiari, Ignatios Ikonomidis, Aikaterini Kountouri, Georgios Panagopoulos, Stavros Athanasopoulos, Eleni Korompoki, Ioannis Kalomenidis, Meletios A. Dimopoulos, Asimina Mitrakou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The mechanism underlying extrapulmonary complications of the coronavirus disease 2019 and its therapeutic implication
Qin Ning, Di Wu, Xiaojing Wang, Dong Xi, Tao Chen, Guang Chen, Hongwu Wang, Huiling Lu, Ming Wang, Lin Zhu, Junjian Hu, Tingting Liu, Ke Ma, Meifang Han, Xiaoping Luo
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Challenges in hyperglycemia management in critically ill patients with COVID-19
Rajesh Kethireddy, Darshan Gandhi, Asim Kichloo, Love Patel
World Journal of Critical Care Medicine.2022; 11(4): 219. CrossRef - New-Onset and Persistent Insulin-Dependent Diabetes in Patients With COVID-19: A Peruvian Experience
Anthony Ramos-Yataco, Emanuel A Salcedo Davila, Kelly Meza, Inga Harbuz-Miller
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19: A Narrative Review
Cristina Rey-Reñones, Sara Martinez-Torres, Francisco M. Martín-Luján, Carles Pericas, Ana Redondo, Carles Vilaplana-Carnerero, Angela Dominguez, María Grau
Biomedicines.2022; 10(9): 2089. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 Infections, Impaired Tissue, and Metabolic Health: Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutics
Shailendra Pratap Singh, Aayushi Bhatnagar, Sujeet Kumar Singh, Sanjib K. Patra, Navjot Kanwar, Abhinav Kanwal, Salomon Amar, Ranata Manna
Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 22(16): 2102. CrossRef - Collateral damage due to COVID-19
Farhan Fazal, Nitin Gupta, Wasim Khot, Yogiraj Ray
Tropical Doctor.2021; 51(1): 126. CrossRef - Diabetic emergencies during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A case–control study
M. S. B. Huda, S. Shaho, B. Trivedi, G. Fraterrigo, L. Chandrarajan, P. Zolfaghari, T. M. Dovey, C. G. Garrett, T. A Chowdhury
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis With COVID-19 Infection in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Taking SGLT2 Inhibitors
Rebecca J. Vitale, Yannis K. Valtis, Marie E. McDonnell, Nadine E. Palermo, Naomi D.L. Fisher
AACE Clinical Case Reports.2021; 7(1): 10. CrossRef - Outcomes and Healthcare Provider Perceptions of Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring (rtCGM) in Patients With Diabetes and COVID-19 Admitted to the ICU
Kenneth W. Chow, Danielle J. Kelly, Mary C. Rieff, Patricia A. Skala, Igor Kravets, Marina M. Charitou, Eric J. Morley, Rajarsi Gupta, Joshua D. Miller
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2021; 15(3): 607. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis presented with COVID-19 infection: A rare case report
Deniz Çekiç, Selçuk Yaylacı, Sümeyye Çekiç, Kubilay İşsever, Hamad Dheir, Havva Kocayiğit, Mehmet Halil Öztürk, Oğuz Karabay
Journal of Clinical Medicine of Kazakhstan.2021; 18(1): 79. CrossRef - Renin-angiotensin system modulators and other risk factors in COVID-19 patients with hypertension: a Korean perspective
Hee-Sung Kim, Minseok Kang, Gilwon Kang
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased Incidence of Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis After COVID-19: A Two-Center Retrospective Study in Korea
Min Jeong Han, Jun Ho Heo
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 783. CrossRef - Diabetes, obesity, and insulin resistance in COVID-19: molecular interrelationship and therapeutic implications
Andrey Santos, Daniéla Oliveira Magro, Rosana Evangelista-Poderoso, Mario José Abdalla Saad
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Neuropsychiatric Symptoms of COVID-19 Explained by SARS-CoV-2 Proteins’ Mimicry of Human Protein Interactions
Hale Yapici-Eser, Yunus Emre Koroglu, Ozgur Oztop-Cakmak, Ozlem Keskin, Attila Gursoy, Yasemin Gursoy-Ozdemir
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 and Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Report of Eight Cases
Balraj Singh, Prem Patel , Parminder Kaur , Nicole Majachani, Michael Maroules
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning Applied to Clinical Laboratory Data in Spain for COVID-19 Outcome Prediction: Model Development and Validation
Juan L Domínguez-Olmedo, Álvaro Gragera-Martínez, Jacinto Mata, Victoria Pachón Álvarez
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2021; 23(4): e26211. CrossRef - Effect of COVID-19 on management of type 1 diabetes: Pushing the boundaries of telemedical healthcare
Ines Bilic Curcic, Maja Cigrovski Berkovic, Tomislav Kizivat, Silvija Canecki Varzic, Robert Smolic, Martina Smolic
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(6): 780. CrossRef - COVID-19 and Diabetes: Understanding the Interrelationship and Risks for a Severe Course
Cyril P. Landstra, Eelco J. P. de Koning
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-World Studies Support Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Independently of Treatment Regimen
James R. Gavin, Clifford J. Bailey
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021; 23(S3): S-19. CrossRef - Evaluation of Characteristics and Outcomes for Patients with Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) With and Without COVID-19 in Elmhurst Queens During Similar Three-Month Periods in 2019 and 2020
Urja Patel, Linda Deluxe, Carlos Salama, Aaron Ross Jimenez, Adrian Whiting, Cedrick Lubin, Nancy Tarlin
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporal trends in emergency admissions for diabetic ketoacidosis in people with diabetes in England before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a population-based study
Shivani Misra, Emma Barron, Eszter Vamos, Stephen Thomas, Ketan Dhatariya, Partha Kar, Bob Young, Kamlesh Khunti, Jonathan Valabhji
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2021; 9(10): 671. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and COVID-19: Understanding the association in light of current evidence
Saikat Sen, Raja Chakraborty, Pratap Kalita, Manash Pratim Pathak
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(28): 8327. CrossRef - Follow-Up Study of the Cardiopulmonary and Psychological Outcomes of COVID-19 Survivors Six Months After Discharge in Sichuan, China
Shuiping Dai, Bennan Zhao, Dafeng Liu, Yongzhao Zhou, Yaling Liu, Lijuan Lan, Yalun Li, Wenxin Luo, Yilan Zeng, Weimin Li
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 7207. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis in patients with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Saad Alhumaid, Abbas Al Mutair, Zainab Al Alawi, Ali A. Rabaan, Mohammed A. Alomari, Sadiq A. Al Salman, Ahmed S. Al-Alawi, Mohammed H. Al Hassan, Hesham Alhamad, Mustafa A. Al-kamees, Fawzi M. Almousa, Hani N. Mufti, Ali M. Alwesabai, Kuldeep Dhama, Jaff
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - In-hospital clinical complications of COVID-19: a brief overview
Kevin John John, Jemimah Nayar, Ajay Kumar Mishra, Vijairam Selvaraj, Mohammad Saud Khan, Amos Lal
Future Virology.2021; 16(11): 717. CrossRef - Combined Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome and Diabetic Ketoacidosis Associated with COVID-19 in a Pediatric Patient
Yu Shan Tseng, Bradley Tilford, Usha Sethuraman, Katherine Cashen, Mehmet Doganay
Case Reports in Critical Care.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Toddler With New Onset Diabetes and Atypical Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome in the Setting of COVID-19
Faraz Alizadeh, Amanda O’Halloran, Areej Alghamdi, Charlotte Chen, Maria Trissal, Avram Traum, Danielle DeCourcey
Pediatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Complicated Case of COVID-19 and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome in an Adolescent Male
Anisha Gohil, Stefan Malin, Kamal Abulebda, Tamara S. Hannon
Hormone Research in Paediatrics.2021; 94(1-2): 71. CrossRef - COVID-19 in People with Diabetes: Perspectives from Saudi Arabia
Asirvatham Alwin Robert, Mohamed Abdulaziz Al Dawish
Current Diabetes Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Case of COVID-19 with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Cardiogenic Shock
Hong Nyun Kim, Jang Hoon Lee, Hun Sik Park, Dong Heon Yang, Se Yong Jang, Myung Hwan Bae, Yongkeun Cho, Shung Chull Chae, Yong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical profile and outcomes in COVID-19 patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: A systematic review of literature
Rimesh Pal, Mainak Banerjee, Urmila Yadav, Sukrita Bhattacharjee
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(6): 1563. CrossRef - Diabetic Ketoacidosis in COVID-19: Unique Concerns and Considerations
Nadine E Palermo, Archana R Sadhu, Marie E McDonnell
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 105(8): 2819. CrossRef - A Case of Combined Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State in a Patient With COVID-19
Shemitha Rafique, Fahad W Ahmed
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef COVID’s Razor: RAS Imbalance, the Common Denominator Across Disparate, Unexpected Aspects of COVID-19
Maureen Czick, Christine Shapter, Robert Shapter
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 3169. CrossRef- Letter: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 480. CrossRef - COVID-19 in people with diabetes: understanding the reasons for worse outcomes
Matteo Apicella, Maria Cristina Campopiano, Michele Mantuano, Laura Mazoni, Alberto Coppelli, Stefano Del Prato
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2020; 8(9): 782. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19: Global and regional perspectives
In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon, Moon Kyu Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 166: 108303. CrossRef - Hyperglycemia, Hypertriglyceridemia, and Acute Pancreatitis in COVID-19 Infection
Chiranjeevi Gadiparthi, Mehak Bassi, Balaji Yegneswaran, Sammy Ho, Capecomorin S. Pitchumoni
Pancreas.2020; 49(7): e62. CrossRef - Response: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53)
Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 484. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis precipitated by COVID-19: A report of two cases and review of literature
Pavan Kumar Reddy, Mohammad Shafi Kuchay, Yatin Mehta, Sunil Kumar Mishra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(5): 1459. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes: What have we learned so far?
Nida Taher, Mohammed SB Huda, Tahseen A Chowdhury
Clinical Medicine.2020; 20(4): e87. CrossRef - High dose ascorbic acid treatment in COVID-19 patients raised some problems in clinical chemistry testing
Fatih Yesildal, Ferruh Kemal Isman
Turkish Journal of Biochemistry.2020; 45(5): 491. CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes: The Epidemic and the Korean Diabetes Association Perspective
Junghyun Noh, Hyun-Ha Chang, In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 372. CrossRef - Practical considerations for pregnant women with diabetes and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection
Glenn P. Boyles, Stephen Thung, Steven G. Gabbe, Mark B. Landon, Maged M. Costantine
American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology MFM.2020; 2(4): 100210. CrossRef - Protracted ketonaemia in hyperglycaemic emergencies in COVID-19: a retrospective case series
Eleni Armeni, Umaira Aziz, Sulmaaz Qamar, Sadia Nasir, Chidambaram Nethaji, Rupert Negus, Nicholas Murch, Huw Clarke Beynon, Pierre Bouloux, Miranda Rosenthal, Sidrah Khan, Ahmed Yousseif, Ravi Menon, Efthimia Karra
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2020; 8(8): 660. CrossRef - Development of a tablet PC-based portable device for colorimetric determination of assays including COVID-19 and other pathogenic microorganisms
Woo Sik Yoo, Hyung Soo Han, Jung Gon Kim, Kitaek Kang, Hyo-Sung Jeon, Jin-Young Moon, Hyeonmi Park
RSC Advances.2020; 10(54): 32946. CrossRef - Machine Learning to Predict Mortality and Critical Events in a Cohort of Patients With COVID-19 in New York City: Model Development and Validation
Akhil Vaid, Sulaiman Somani, Adam J Russak, Jessica K De Freitas, Fayzan F Chaudhry, Ishan Paranjpe, Kipp W Johnson, Samuel J Lee, Riccardo Miotto, Felix Richter, Shan Zhao, Noam D Beckmann, Nidhi Naik, Arash Kia, Prem Timsina, Anuradha Lala, Manish Paran
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(11): e24018. CrossRef - COVID-19: the endocrine opportunity in a pandemic
Subhankar Chatterjee, Ritwik Ghosh, Payel Biswas, Souvik Dubey, Rishi T. Guria, Chandra B. Sharma, Sanjay Kalra
Minerva Endocrinologica.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Diabetes in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Prognosis and Practical Issues
Hye Soon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 120. CrossRef - Short term follow-up of patients presenting with acute onset diabetes and diabetic ketoacidosis during an episode of COVID-19
Mohammad Shafi Kuchay, Pavan Kumar Reddy, Sakshi Gagneja, Anu Mathew, Sunil Kumar Mishra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(6): 2039. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis precipitated by Coronavirus disease 2019 infection: Case series
Ibrahim Alsadhan, Shahad Alruwashid, Maram Alhamad, Sarah Alajmi, Sara Alshehri, Eman Alfadhli, Aishah Ekhzaimy
Current Therapeutic Research.2020; 93: 100609. CrossRef - Determinants of survival after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in Mexican outpatients and hospitalised patients
F.-J. Prado-Galbarro, C. Sanchez-Piedra, A.E. Gamiño-Arroyo, C. Cruz-Cruz
Public Health.2020; 189: 66. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Are Expressed in the Microvasculature and Ducts of Human Pancreas but Are Not Enriched in β Cells
Katie C. Coate, Jeeyeon Cha, Shristi Shrestha, Wenliang Wang, Luciana Mateus Gonçalves, Joana Almaça, Meghan E. Kapp, Maria Fasolino, Ashleigh Morgan, Chunhua Dai, Diane C. Saunders, Rita Bottino, Radhika Aramandla, Regina Jenkins, Roland Stein, Klaus H.
Cell Metabolism.2020; 32(6): 1028. CrossRef - Caring for Hospitalized Patients with Diabetes Mellitus, Hyperglycemia, and COVID-19: Bridging the Remaining Knowledge Gaps
Amisha Wallia, Grace Prince, Emilie Touma, Malek El Muayed, Jane Jeffrie Seley
Current Diabetes Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Recovery From Acute Kidney Injury With Diabetic Ketoacidosis Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report and Literature Review
Chang Xu, Umer Zia
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Outbreak of COVID-19 and Diabetes in Korea: “We Will Find a Way as We Have Always Done”
Kyu Chang Won, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 211. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite