- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 40(1); 2016 > Article
-
Original ArticleEpidemiology Epidemiology of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea through an Investigation of the National Registration Project of Type 1 Diabetes for the Reimbursement of Glucometer Strips with Additional Analyses Using Claims Data
-
Sun Ok Song1, Young Duk Song1
 , Joo Young Nam1, Kyeong Hye Park1, Ji-Hae Yoon2, Kyung-Mi Son2, Young Ko2, Dong-Ha Lim2
, Joo Young Nam1, Kyeong Hye Park1, Ji-Hae Yoon2, Kyung-Mi Son2, Young Ko2, Dong-Ha Lim2 -
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2016;40(1):35-45.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.1.35
Published online: December 1, 2015
1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
2National Health Insurance Service, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Young Duk Song. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, 100 Ilsan-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang 10444, Korea. ydsyko@gmail.com
• Received: March 10, 2015 • Accepted: June 29, 2015
Copyright © 2016 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- The aim of this study was to estimate the prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) in Korea. In addition, we planned to do a performance analysis of the Registration Project of Type 1 diabetes for the reimbursement of consumable materials.
-
Methods
- To obtain nationwide data on the incidence and prevalence of T1DM, we extracted claims data from July 2011 to August 2013 from the Registration Project of Type 1 diabetes on the reimbursement of consumable materials in the National Health Insurance (NHI) Database. For a more detailed analysis of the T1DM population in Korea, stratification by gender, age, and area was performed, and prevalence and incidence were calculated.
-
Results
- Of the 8,256 subjects enrolled over the 26 months, the male to female ratio was 1 to 1.12, the median age was 37.1 years, and an average of 136 new T1DM patients were registered to the T1DM registry each month, resulting in 1,632 newly diagnosed T1DM patients each year. We found that the incidence rate of new T1DM cases was 3.28 per 100,000 people. The average proportion of T1DM patients compared with each region's population was 0.0125%. The total number of insurance subscribers under the universal compulsory NHI in Korea was 49,662,097, and the total number of diabetes patients, excluding duplication, was 3,762,332.
-
Conclusion
- The prevalence of T1DM over the course of the study was approximately 0.017% to 0.021% of the entire population of Korea, and the annual incidence of T1DM was 3.28:100,000 overall and 3.25:100,000 for Koreans under 20 years old.
- The prevalence of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is thought to be less than 5% of all diabetic patients, but T1DM has a higher prevalence of severe diabetic complications and shorter life spans than those without T1DM [123].
- Insulin therapy, which is continued for the duration of the individual's life, should be started immediately after the onset of T1DM, which lasts a lifetime, causing serious physical, psychological, and economic burdens [4].
- Efforts to cure T1DM have continued steadily and have led to the discovery of insulin, artificial pancreas development, and pancreas/islet transplants, among others. However, successful immune, gene, or stem cell therapy has not been effective in curing T1DM [5]. Therefore, insulin treatment remains the primary and currently available remedy and requires frequent monitoring using a blood glucose meter.
- The prevalence rate of T1DM in the individuals with age 0 to 15 years in Europe and North America is 0.05% to 0.3% [6]. In the United States, the incidence of T1DM was 19.7/100,000 in children less than 10 years old and 18.6/100,000 in individuals over the age of 10 [7]. Another study reported that the number of patients between 0 and 19 years old suffering from diabetes in 2010 was approximately 215,000; approximately one of every 400 to 600 children and adolescents with diabetes is estimated to have T1DM [8]. Data from the International Diabetes Federation in 2010 reported that there were 1.9 billion people between 0 and 14 years of age, 479,600 of whom had T1DM, and that 75,800 people were newly diagnosed with T1DM every year [9].
- There has been a scarcity of reliable epidemiological data on T1DM in Korea. Previously, only a few local epidemiological studies existed. According to the T1DM registration project in Seoul from 1985 to 1988, the incidence of T1DM in school-age children was estimated to be approximately 1.3 people per 100,000 per year [10]. The Korean Pediatric Society found that the average annual incidence of T1DM from 1995 to 2000 was 1.36/100,000 (95% confidence interval, 1.23 to 1.48) and that the incidence of T1DM in Korea had been increasing slightly over the 6-year span [11].
- T1DM is most commonly diagnosed in puberty, but there are also patients diagnosed with T1DM after the age of 20. However, a nationwide incidence rate using large-scale data from all age groups was not available until now. Therefore, we wanted to evaluate the epidemiology of T1DM in our country. In this study, we investigated the prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes between June 2011 and August 2013 in Korea.
INTRODUCTION
- Data source
- In Korea, a universal compulsory National Health Insurance (NHI) program that provides coverage for nearly 100% of the total population was launched by the government in 1989. In 2013, the NHI program covered 97.2% (n=49,989,620) of the population and the Medical Aid system covered the remaining 2.8% (n=1,458,871) of the population [12]. To obtain nationwide data on the incidence and prevalence of T1DM, we extracted claims data from the Type 1 Diabetes Registration Project for the Reimbursement of Consumable Materials, which started on July 1st 2011 by the NHI program.
- The Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) promoted this project nationally to all domestic internal medicine, pediatric, and family medicine doctors; if they examined patients with T1DM, physicians enrolled patients in the registration program. Patients received a financial benefit for subscribing.
- The data extraction date was August 30, 2013. We selected patients who were coded as having a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus (DM) according to diagnostic codes (as defined in The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification, ICD-10-CM code). The specific codes used were E10 for T1DM, E11 for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), E12 for malnutrition related DM, E13 for other specific types of DM, and E14 for an unknown type of DM. The category "DM type others" included both the E13 and E14 codes. From the total number of diabetes patients, we estimated the prevalence and incidence of T1DM and its features. We assumed that their ages at the time of registration and at their diagnostic confirmation were the following:
- Age at the time of registration=current age-elapsed year from registration in the project
- Age at the diagnosis confirmation date=current age-elapsed year from diagnostic confirmation date
- To conduct a detailed analysis of the T1DM population in Korea, we stratified by gender, age, and area and calculated the prevalence and incidence. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital (IRB number: 2013-092).
- Registration conditions of the type 1 diabetes registry
- The Registration Requirements of the National Registration Project of Type 1 Diabetes for the reimbursement of consumable diabetes-related supplies had several criteria. Individuals were eligible if they needed insulin for diabetes treatment and had any conditions that showed insulin deficiency or presence of autoimmunity, such as basal C-peptide levels below 0.6 ng/mL, stimulated C-peptide levels below 1.8 ng/mL, urine C-peptide levels below 30 µg for 24 hours, a history of diabetic ketoacidosis at their first diagnosis of DM, or the presence of autoantibodies (Ab) to pancreatic β-cells including glutamic acid-decarboxylase (GAD) Ab. Individual data were reviewed and confirmed by the primary physician and sent to the NHIS local office. Because the Type 1 Diabetes Registration Project for the Reimbursement of Consumable Materials is not a mandatory program, individuals who satisfied the inclusion criteria became affiliated when they were willing to become a member of the registry. The recipients were reimbursed in cash after receipts showing individual medical expenses for glucometer strips were submitted to the insurance claims office.
- Prevalence and incidence
- We stratified by gender and age group (0 to 19, 20 to 39, 40 to 59, 60 to 79, and 80 years or older) to conduct a detailed analysis of the T1DM population in Korea. In addition, registrants were categorized by region and month of registration. Limited-duration prevalence was calculated using the total number of registrants divided by the total insurance policy holder population during the same period. Regional prevalence was calculated by dividing the regionally registered study population by the overall population of each region.
- We conducted additional analyses on the prevalence of T1DM using ICD-10 diagnostic codes from the Korean NHI claims database. We extracted the total number of NHI applicants and the total number of diabetes cases during the 26-month period. All diabetes patients from the claims data were divided into four classifications: T1DM (E1000-E1090), T2DM (E1100-E1190), DM-related malnutrition (E1200-E1290), and other type of DM (E1300-E1490). The actual total number of diabetic patients was determined after eliminating duplications of diagnostic codes in the claiming process.
- We classified diabetic patients according to their requested diagnostic codes and their insulin prescription/oral medication prescription status (i.e., did not receive any prescriptions, received one or more prescriptions for insulin but not oral hypoglycemic agents [OHAs], received one or more prescriptions for OHA but not insulin, or received both insulin and OHA).
- The incidence was estimated from the data after the monthly registration rate was averaged. Incidence rates were calculated as the incidence per calendar year per 100,000 population at risk without adjustment for under-reporting.
- Statistical analysis
- All statistical analyses were performed with PASW version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Data are presented as the mean±standard deviation for continuous variables and discrete variables were expressed as percentages. Comparisons of the prevalence between regions were performed using a chi-square test. Data with a P<0.05 were considered significant.
METHODS
- Baseline characteristics of the enrolled subjects with type 1 diabetes
- A total of 8,256 Korean subjects with T1DM who satisfied the registration conditions were registered during the 26-month period. Among the 8,256 subjects, the mean age at the sampling time point was 35.1±18.4 years old, 3,899 (47.2%) were male and 4,357 (52.8%) were female, and the male to female ratio was 1:1.12. The minimum age was 0 and the maximum age was 89. Registrants were grouped into classes by age at the time of enrollment into the Korean T1DM registry; 2,346 registrants (28.4%) were under 20 years old (114 were 0 to 4 years old, 394 in the 10 to 14 age bracket, and 998 in the 15 to 19 age bracket), 5,910 T1DM patients (71.6%) were over 20 years old, and 96.2% of all subjects were under 69 years of age. According to the age at the time of registration, the age range with the largest number of registrants was 15 to 19, and the number of registrants older than 35 years tended to gradually decrease. The number of registrants older than 85 years was four (Fig. 1).
- Registration eligibility requirements of Korean Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Registry
- All registered subjects with type 1 diabetes used insulin, a mandatory requirement. Of the other optional conditions, 6,020 (72.9%) had a baseline C-peptide level <0.6 ng/mL, 664 (8%) had a stimulated C-peptide level <1.8 ng/mL, 802 (7.9%) had a 24-hour urine C-peptide <30 µg/day, 1,649 (20%) had an initial diagnosis of diabetes with a history of diabetic ketoacidosis, and 1,873 (22.7%) had positive tests for GAD Ab or other Ab (Supplementary Fig. 1).
- Regional distribution of registrants with type 1 diabetes
- Gyeonggi (a local province) had the largest number of registrants with 2,334, followed by Seoul (the capital city) with 2,056, Busan with 641, Jeju with 146, and Sejong with five registrants. The registration rate in the Korean Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Registry was significantly higher in the Jeju region (the biggest island) at 0.026% compared with the other local populations, which averaged 0.0125% (P<0.05) (Fig. 2).
- Monthly enrollment in the Type 1 Diabetes Registry and the number of issued prescriptions for blood glucose test strips
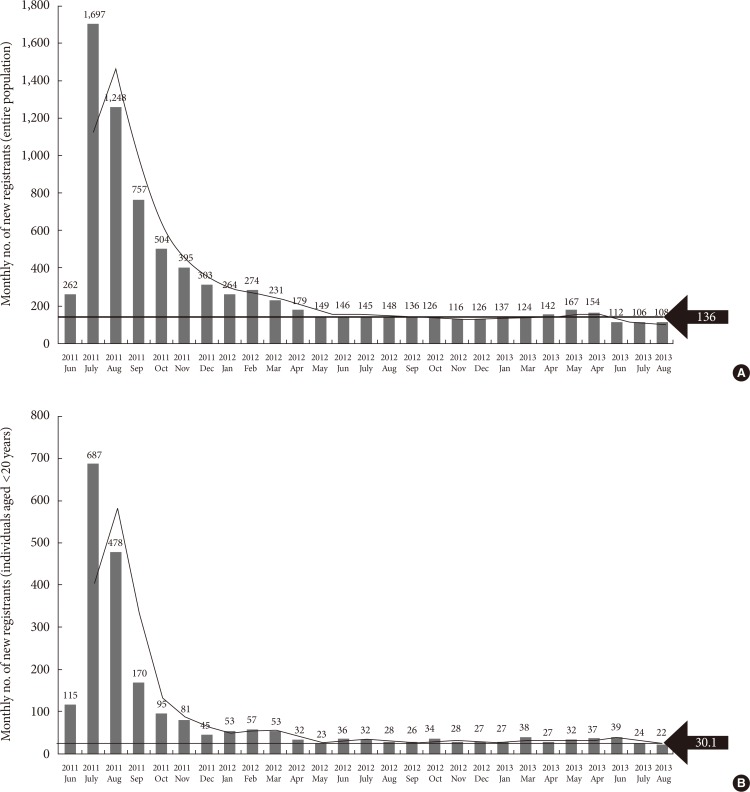
- Registration in the T1DM registry started June 1, 2011. In the first month, 262 people registered, 1,697 enrolled in July, and 757 in September 2011. After September, the average monthly enrollment dropped to 136 (Fig. 3A). A total of 2,346 registrants less than 20 years old during the study period were recruited. Young patients with type 1 diabetes showed a similar pattern of registration as the other ages; the enrollment decreased gradually after July 2011. The monthly average number of registrants was 30.07 after 12 months.
- The monthly number of issued prescriptions for blood glucose test strips increased gradually from 497 initially to more than 1,000 after the first year. However, registered individuals who had never received prescriptions for blood glucose test strips after their enrollments accounted for 15.2% (n=1,255) of the study population. Constant test strip users who had prescriptions for the product and had received the prescription three times or more accounted for 51.9% (n=4,290) of the patients, and 27.3% (n=2,251) of the registry received prescriptions six or more times (Supplementary Fig. 2).
- Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes
- As depicted in Fig. 3A, the present study's data show that the prevalence of T1DM was 1.66 diagnosed per 10,000 policyholders for the 49,662,097 policyholders. An average of 136 new T1DM patients were diagnosed each month, resulting in 1,632 (136×12 months) newly registered T1DM patients each year (Fig. 3A). The incidence of new T1DM cases overall was 3.28 per 100,000 people.
- The prevalence of T1DM in those under 20 years old was 2.11 per 10,000 for the 11,106,122 of policyholders under 20 year-old in Korea. Additionally, the average number of monthly diagnoses and annual enrollments for those under 20 years old was 30.07 and 360.9, respectively. The incidence of T1DM in those under 20 years old was 3.25 per 100,000 of insurance subscribers under 20 year-old (Fig. 3B).
- Further analysis was performed using claims data (Supplementary Table 1). Over the 26-month period during which the study took place, the total number of diagnosed diabetes patients in Korea was 3,762,332, and the number of NHI applicants was 49,662,097. Diabetes claims were divided into the following types: T1DM, 227,280 cases; T2DM, 3,224,091; DM-related malnutrition, 8,573; and other types of DM, 1,190,405. The difference between the sum of the above-mentioned numbers and the total number of diabetic patients was a result of duplication in the reporting process. At least 897,017 patients had their conditions reported using two or more diagnostic codes types. Moreover, there were great differences between the number of diagnoses (8,256) and the number of DM claims (227,280). One must assume, then, that the data for T1DM claim-code use represented the maximum number of potential cases, including T1DM misdiagnoses. This study's authors did try to preclude errors arising from T1DM misdiagnosis by classifying the sampled patients according to whether a type 1 code was requested, the number of insulin prescriptions, and the type of drugs prescribed. This third group was further subdivided into the following four groups: (1) those who received no prescription, (2) those who received one or more prescriptions for insulin but not for OHAs, (3) those who received one or more prescriptions for OHA but not insulin, and (4) those who received both insulin and OHAs. As shown in Supplementary Table 1, 37,947 patients fell under the "type 1 code only" classification; 44,747 had insulin prescriptions filled at least three times; 45,077 received one or more prescriptions for insulin but not for OHAs; and 43,097 received both insulin and OHAs.
- T1DM claims data were classified into three categories (Supplementary Table 1). According to the disease-classification code symbols used, there were only 37,947 patients for whom the T1DM code was requested and 189,333 patients for whom another DM type's code was requested. Regarding the number of insulin prescriptions, the number of patients who never received an insulin prescription after a T1DM claim was reported was 141,516, while the number of insulin prescriptions received three or more times was 44,747. In relation to prescription drug types, the number of patients for whom a T1DM-code claim was made who did not receive any prescription was 95,400. Consequently, this study's authors estimate that the real number of T1DM cases range from a minimum of 8,256 (those currently in the registry for T1DM) to a maximum of 44,747 (those who received insulin prescriptions three or more times). Moreover, the true prevalence of T1DM over the course of the present study was therefore 0.017% to 0.021% of Korea's entire population (relative to Korea's 49,662,097 health-insurance subscribers), and the percentage relative to Korea's 3,762,332 diabetes patients (all types) was approximately 0.22% to 1.19%.
RESULTS
- The incidence of T1DM varies across countries and by ethnicity; however, the global pattern of the incidence of T1DM has not changed markedly since reports published in the 1970s and 1980s. The overall incidence rates of T1DM have varied from 0.1/100,000 to 36.8/100,000 person-year. Finland and Sardinia have the highest incidence, and Caracas, China, and Venezuela have the lowest incidence rates. This represents a greater than 350-fold variation in the incidence among the populations worldwide [1314].
- Although prevalence rates are difficult to interpret and compare because they are from different time periods and are not standardized, the prevalence of T1DM in children ranges from 0.6 per 1,000 to 2.5 per 1,000, with most estimates clustering approximately 1.7 per 1,000 [113].
- Korean diabetologists have long been interested in the prevalence and incidence of T1DM in Korea [1011151617]. Previous investigations were promoted primarily by the Korean Diabetes Association, union of university hospitals, and local medical institutions to determine the epidemiology of T1DM in Korea. However, only limited results could be achieved due to a small sample size and locality restrictions, meaning the true epidemiology of T1DM in Korea was not known.
- In this study, although T1DM had a higher incidence in younger individuals, it is important to note that more than two-thirds of the population was older than 20 in our study, as T1DM patients are getting older and T1DM is also beginning at older ages. These data illustrated a true cross-sectional distribution of ages in T1DM patients.
- Approximately one year after the start of registration, 136 people registered each month (Fig. 3). If the prior existing T1DM patients were enrolled during the early period, the 136 additional monthly registrations might be assumed to represent newly developed T1DM cases, and the annual incidence of T1DM in Korea would be 1,632 per year. We estimated the incidence of newly diagnosed T1DM to be 3.28/100,000 person-year across all ages and 3.25/100,000 person-year in young ages. Previous studies have reported that the incidence of childhood T1DM was 1/100,000 per year. The difference between the two values may originate from different eligibility criteria for including T1DM patients. In addition, we did not find a seasonal difference in enrollment to the registry, unlike previous studies [101118].
- Previous studies also showed regional differences of incidence [1011151617]; however, the regional distribution of registered patients compared with the population was evenly distributed in this study, except for in Jeju Island. Jeju Island had a significantly higher prevalence of T1DM than other areas. We are not certain whether this was related to the registration process or whether large numbers of patients were recruited. Jeju Island is a suitable area for a prospective cohort study with T1DM because it is very isolated and has a small area and a limited number of hospitals. Positive auto-Ab tests may indicate progression to β-cell loss and occurred in 22.7% of the study population (Supplementary Fig. 1), which was lower than previous reports with a diagnosis of T1DM (GADA 80%, IA-2A 70%, and IAA 60%) perhaps because registrants were not required to satisfy all enrollment criteria. Although type 1 diabetes in childhood often involves a straightforward diagnosis, autoimmune diabetes in adults is poorly defined [19]. We did not evaluate the data on auto-Ab divided into an adult and young age group. This analysis may have shown consistent results with previous studies and further was magnified as autoimmune diabetes in adults.
- There were also issues with misclassification that led to the inclusion of other types of diabetes, such as neonatal diabetes (a type of monogenic diabetes) and insulin dependent T2DM. In addition, each Registry entry depended on the active participation of doctors and on receiving patient consent as in the Diabetes Incidence Study and National Diabetes Register in Sweden [20]. To achieve a reliable and feasible approach to monitoring T1DM in the future, there may need to be changes to the eligibility conditions and the process of registration into the T1DM registry, including an automated, passive system.
- Furthermore, the proportion of patients for whom claims were made using DM codes (according to ICD-10) was approximately 8% of Korea's entire population. There is a possibility that this proportion could include the number of individuals with diabetes, pre-diabetes, and suspected diabetes. Inevitably, the data on T1DM claim codes may also include a number of T1DM misdiagnoses in addition to potential cases. We conducted additional analyses to rectify the discrepancy between the number of T1DM codes from claims data and the number of T1DM cases from the enrollment. The resulting overall percentage relative to the total number of diabetes patients was approximately 0.22% to 1.19%, far below the 5% T1DM prevalence reported by previous studies [21]. Although additional studies are required to determine the causes of this discrepancy, the data from this study suggest that the rate of T1DM cases may have dropped due to the substantial increase in T2DM cases in Korea [22].
- This study has several limitations, including how it does not account for all T1DM cases in Korea. This occurred because not all of the individuals diagnosed with T1DM satisfied the inclusion criteria. Registry depended on the active participation of doctors and on receiving patient consent, as with the Diabetes Incidence Study and National Diabetes Register in Sweden [20]. Second, misclassification may have been a limitation. Based on the registration-eligibility requirements, this study's sample may have included insulin-depleted sufferers of T2DM (especially in older patients), monogenic diabetes, including neonatal diabetes, (especially in younger patients), diabetes-related pancreas resection and disease, and Ketosis-prone T2DM, among others. One feasible approach to obtaining more reliable monitoring in the future is to revise the eligibility requirements and the registration process to incorporate a passive, automated system. However, the present study remains valuable because it is the first Korean study of T1DM to analyze the illness according to regional and age distributions based on nationwide, large-scale data.
- In conclusion, the prevalence of T1DM over the course of the present study was approximately 0.017% to 0.021% of Korea's entire population, which is markedly lower than the 5% prevalence percentage reported by previous studies. Finally, the annual incidence of T1DM during the present study was 3.28/100,000 person-year for Korea' population as a whole and 3.25/100,000 person-year for Koreans under 20 years old.
DISCUSSION
-
Acknowledgements
- This work was supported by a 2013 National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital Research Grant (2013-16).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
NOTES
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Table 1
Supplementary Fig. 1
Supplementary Fig. 2
- 1. DIAMOND Project Group. Incidence and trends of childhood type 1 diabetes worldwide 1990-1999. Diabet Med 2006;23:857-866. ArticlePubMed
- 2. EURODIAB ACE Study Group. Variation and trends in incidence of childhood diabetes in Europe. Lancet 2000;355:873-876. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Green A, Gale EA, Patterson CC. Incidence of childhood-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: the EURODIAB ACE Study. Lancet 1992;339:905-909. ArticlePubMed
- 4. SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group. Liese AD, D'Agostino RB Jr, Hamman RF, Kilgo PD, Lawrence JM, Liu LL, Loots B, Linder B, Marcovina S, Rodriguez B, Standiford D, Williams DE. The burden of diabetes mellitus among US youth: prevalence estimates from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Pediatrics 2006;118:1510-1518. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Reichard P, Nilsson BY, Rosenqvist U. The effect of long-term intensified insulin treatment on the development of microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:304-309. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Patterson CC, Dahlquist GG, Gyurus E, Green A, Soltesz G. EURODIAB Study Group. Incidence trends for childhood type 1 diabetes in Europe during 1989-2003 and predicted new cases 2005-20: a multicentre prospective registration study. Lancet 2009;373:2027-2033. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Mayer-Davis EJ, Bell RA, Dabelea D, D'Agostino R Jr, Imperatore G, Lawrence JM, Liu L, Marcovina S. SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group. The many faces of diabetes in American youth: type 1 and type 2 diabetes in five race and ethnic populations: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care 2009;32(Suppl 2):S99-S101. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 8. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes fact sheet: national estimates and general information on diabetes and prediabetes in the United States, 2011. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2011. p. 201.
- 9. International Diabetes Federation: IDF Diabetes Atlas 6th edition cited 2015 Oct 14. Available from: http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas.
- 10. Ko KW, Yang SW, Cho NH. The incidence of IDDM in Seoul from 1985 to 1988. Diabetes Care 1994;17:1473-1475. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Shin CH. Epidemiologic characteristics of type 1 diabetes in children aged 14 years or under in Korea, 1985-2000. Korean J Pediatr 2008;51:569-575.Article
- 12. Song SO, Jung CH, Song YD, Park CY, Kwon HS, Cha BS, Park JY, Lee KU, Ko KS, Lee BW. Background and data configuration process of a nationwide population-based study using the Korean National Health Insurance system. Diabetes Metab J 2014;38:395-403. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Karvonen M, Viik-Kajander M, Moltchanova E, Libman I, LaPorte R, Tuomilehto J. Diabetes Mondiale (DiaMond) Project Group. Incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes worldwide. Diabetes Care 2000;23:1516-1526. PubMed
- 14. Levy-Marchal C, Patterson CC, Green A. EURODIAB ACE Study Group Europe and Diabetes. Geographical variation of presentation at diagnosis of type I diabetes in children: the EURODIAB study. European and Dibetes. Diabetologia 2001;44(Suppl 3):B75-B80. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Lee HK, Oh YS, Chung YH, Yoo HJ, Shin SH, Son HY, Kim SW, Lee HC, Huh KB, Choi YK. Epidemiological characteristics of ketoacidosis among Korean diabetic patients. J Korean Med Sci 1987;2:7-11. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Rhee BD. Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus among Korean population. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 2003;27:173-178.
- 17. Shin CH. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Korean Pediatr Soc 2002;45:1181-1191.
- 18. Levy-Marchal C, Patterson C, Green A. The EURODIAB ACE Study Group. Variation by age group and seasonality at diagnosis of childhood IDDM in Europe. Diabetologia 1995;38:823-830. PubMed
- 19. Gale EA. Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: a guide for the perplexed. Diabetologia 2005;48:2195-2199. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Rawshani A, Landin-Olsson M, Svensson AM, Nystrom L, Arnqvist HJ, Bolinder J, Gudbjornsdottir S. The incidence of diabetes among 0-34 year olds in Sweden: new data and better methods. Diabetologia 2014;57:1375-1381. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 21. Liu LL, Yi JP, Beyer J, Mayer-Davis EJ, Dolan LM, Dabelea DM, Lawrence JM, Rodriguez BL, Marcovina SM, Waitzfelder BE, Fujimoto WY. SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes in Asian and Pacific Islander U.S. youth: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care 2009;32(Suppl 2):S133-S140. PubMedPMC
- 22. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:303-308. ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
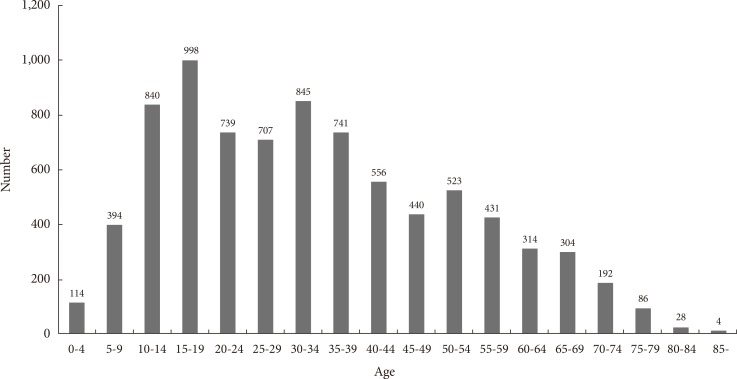
Age at the time of enrollment to the Korean Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Registry. This graph shows the age of registrants at the time of enrollment over 26 months. This is a mixture of incident and prevalent cases.

Fig. 2
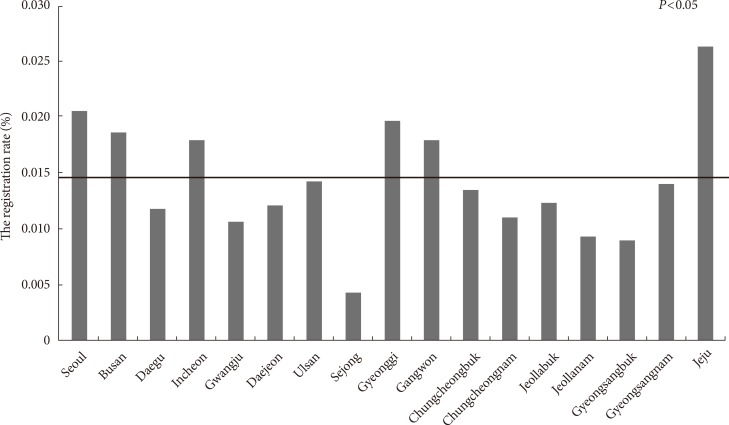
Regional distribution of the registration rate in Korean Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Registry compared with the local population (residence distribution).

Fig. 3

Monthly enrollment after insurance reimbursement project for type 1 diabetes mellitus consumables. (A) Total enrollment in all ages. The number of health insurance subscribers during the study period: 49,662,097; new registrants: 136/month, 1,632/year, 3.29/100,000/year. Black horizontal line: monthly average number of new registrants. (B) Total enrollment of individuals less than 20 years old. The number of health insurance subscribers less than 20 years old during the study period: 11,106,122; new registrants less than 20 years old: 30.07/month, 360.9/year, 3.25/100,000/year. Black horizontal line: monthly average number of new registrants less than 20 years old.

Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Distinct changes to pancreatic volume rather than pancreatic autoantibody positivity: insights into immune checkpoint inhibitors induced diabetes mellitus
Hung-Hui Wei, Ying-Chieh Lai, Gigin Lin, Cheng-Wei Lin, Ya-Chu Chang, John Wen-Cheng Chang, Miaw-Jene Liou, I-Wen Chen
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of genetic variants associated with diabetic kidney disease in multiple Korean cohorts via a genome-wide association study mega-analysis
Heejin Jin, Ye An Kim, Young Lee, Seung-hyun Kwon, Ah Ra Do, Sujin Seo, Sungho Won, Je Hyun Seo
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influenza vaccination trend and related factors among patients with diabetes in Korea: Analysis using a nationwide database
Dong-Hwa Lee, Bumhee Yang, Seonhye Gu, Eung-Gook Kim, Youlim Kim, Hyung Koo Kang, Yeong Hun Choe, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Seungyong Park, Hyun Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 211. CrossRef - Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Se-Won Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 242. CrossRef - Association between long-term air pollution exposure and development of diabetes among community-dwelling adults: Modification of the associations by dietary nutrients
Moon-Kyung Shin, Kyoung-Nam Kim
Environment International.2023; 174: 107908. CrossRef - Structural studies and cell proliferation activity of human Follistatin-like 1 in reducing and non-reducing conditions
S. Shahrbanoo Jafari, Rahman Emamzadeh, Mahboobeh Nazari, Mohamad Reza Ganjalikhany
Process Biochemistry.2023; 130: 245. CrossRef - Exercise Frequency Reduction Is Associated With Higher Risk of Infection in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Nationally Representative Cohort Study
Yohwan Lim, Hye Jun Kim, Sung Soo Yoon, Sang Jun Lee, Myeong Hoon Lee, Hyewon Park, Sun Jae Park, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of statin treatment on cardiovascular risk in patients with type 1 diabetes: a population-based cohort study
Joonsang Yoo, Jimin Jeon, Minyoul Baek, Sun Ok Song, Jinkwon Kim
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and clinical characteristics of fulminant type 1 diabetes mellitus in Korean adults: A multi‐institutional joint research
Sun Ok Song, Jae‐Seung Yun, Seung‐Hyun Ko, Yu‐Bae Ahn, Bo‐Yeon Kim, Chul‐Hee Kim, Ja Young Jeon, Dae Jung Kim, Da Hae Seo, So Hun Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Da Young Lee, Kyung‐Soo Kim, Soo‐Kyung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(1): 47. CrossRef - Epidemiology and phenotypes of diabetes in children and adolescents in non-European-origin populations in or from Western Pacific region
Steven James, Jayanthi Maniam, Pik-To Cheung, Tatsuhiko Urakami, Julia von Oettingen, Supawadee Likitmaskul, Graham Ogle
World Journal of Clinical Pediatrics.2022; 11(2): 173. CrossRef - Weight change and the risk of hip fractures in patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study
S.-W. Lee, K. Han, H.-S. Kwon
Osteoporosis International.2022; 33(8): 1755. CrossRef - Phytochemicals of mustard (Brassica Campestris) leaves tuned the nickel‐cobalt bimetallic oxide properties for enzyme‐free sensing of glucose
Abdul Ghaffar Solangi, Tajness Pirzada, Aqeel Ahmed Shah, Imran Ali Halepoto, Abdul Sattar Chang, Zulifqar Ali Solangi, Muhammad Yameen Solangi, Umair Aftab, Matteo Tonezzer, Aneela Tahira, Ayman Nafady, Shymaa S. Medany, Zafar Hussain Ibupoto
Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society.2022; 69(9): 1608. CrossRef - Low relative hand grip strength is associated with a higher risk for diabetes and impaired fasting glucose among the Korean population
Min Jin Lee, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Yang Ho Kang, Giacomo Pucci
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(10): e0275746. CrossRef - Incidence and risk factors of diabetes mellitus in the Chinese population: a dynamic cohort study
Long Xue, Huiying Wang, YunZhen He, Mengyun Sui, Hongzheng Li, Lin Mei, Xiaohua Ying
BMJ Open.2022; 12(11): e060730. CrossRef - Illness Experiences of Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Ji Eun Kim, Ilaria Campesi
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Association between secondhand smoke exposure and diabetes mellitus in 131 724 Korean never smokers using self‐reported questionnaires and cotinine levels: Gender differences
Byung Jin Kim, Ji Hye Kim, Jeong Gyu Kang, Bum Soo Kim, Jin Ho Kang
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(1): 43. CrossRef - The risk of hip fractures in individuals over 50 years old with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes – A longitudinal nationwide population-based study
Ho Youn Park, Kyoungdo Han, Youngwoo Kim, Yoon Hwan Kim, Yoo Joon Sur
Bone.2021; 142: 115691. CrossRef - Electrochemical performance of the spinel NiCo2O4 based nanostructure synthesized by chemical bath method for glucose detection
Kyu-bong Jang, Kyoung Ryeol Park, Kang Min Kim, Soong-keun Hyun, Chisung Ahn, Jong Cheol Kim, Sung-chul Lim, HyukSu Han, Sungwook Mhin
Applied Surface Science.2021; 545: 148927. CrossRef - Risk Factors of Undiagnosed Diabetes Mellitus among Korean Adults: A National Cross-Sectional Study Using the KNHANES Data
Sangwon Lee, Kwang Sun Ryu, Ha Ye Jin Kang, Na Young You, Kui Son Choi, Yul Hwangbo, Jae Wook Lee, Hyo Soung Cha
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(3): 1195. CrossRef - Increased Incidence of Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis After COVID-19: A Two-Center Retrospective Study in Korea
Min Jeong Han, Jun Ho Heo
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 783. CrossRef - Trends of Diabetes and Prediabetes Prevalence among Korean Adolescents From 2007 to 2018
Ji Hyun Kim, Jung Sub Lim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between domain-specific physical activity and diabetes in Korean adults
Eun-Byeol Lee, Sunghyun Hong, Jihee Min, Dong-Hyuk Park, Wonhee Cho, Sang-Hoon Suh, Hae-Dong Lee, Han-Joo Lee, Heejin Kimm, Sun Ha Jee, Eun Seok Kang, Dong Hoon Lee, Justin Y. Jeon
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prestroke Glucose Control and Functional Outcome in Patients With Acute Large Vessel Occlusive Stroke and Diabetes After Thrombectomy
Jun Young Chang, Wook-Joo Kim, Ji Hyun Kwon, Beom Joon Kim, Joon-Tae Kim, Jun Lee, Jae Kwan Cha, Dae-Hyun Kim, Yong-Jin Cho, Keun-Sik Hong, Soo Joo Lee, Jong-Moo Park, Byung-Chul Lee, Mi Sun Oh, Sang-Hwa Lee, Chulho Kim, Dong-Eog Kim, Kyung Bok Lee, Tae H
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(9): 2140. CrossRef - Diabetes diagnosis from administrative claims and estimation of the true prevalence of diabetes among 4.2 million individuals of the Veneto region (North East Italy)
Enrico Longato, Barbara Di Camillo, Giovanni Sparacino, Claudio Saccavini, Angelo Avogaro, Gian Paolo Fadini
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2020; 30(1): 84. CrossRef - The Combined Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes on the Risk of Colorectal Cancer Depends on Sex: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Hyung Jung Oh, Hye Ah Lee, Chang Mo Moon, Dong-Ryeol Ryu
Yonsei Medical Journal.2020; 61(6): 506. CrossRef - Does Diabetes Increase the Risk of Contracting COVID-19? A Population-Based Study in Korea
Sung-Youn Chun, Dong Wook Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Su Jung Lee, Jung Hyun Chang, Yoon Jung Choi, Seong Woo Kim, Sun Ok Song
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 897. CrossRef - Synthesis of NiCo2O4 Nanostructures and Their Electrochemial Properties for Glucose Detection
Kyu-bong Jang, Kyoung Ryeol Park, Kang Min Kim, Soong-keun Hyun, Jae-eun Jeon, Young Sik Song, Soo-keun Park, Kyoung-il Moon, Chisung Ahn, Sung-chul Lim, Jaewoong Lee, Jong Cheol Kim, HyukSu Han, Sungwook Mhin
Nanomaterials.2020; 11(1): 55. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
Ji Hong You, Sang Ah Lee, Sung-Youn Chun, Sun Ok Song, Byung-Wan Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Edward J. Boyko
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 901. CrossRef - Trends in Hyperglycemic Crisis Hospitalizations and in- and out-of-Hospital Mortality in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data
Ji Hong You, Sun Ok Song, Se Hee Park, Kyoung Hye Park, Joo Young Nam, Dong Wook Kim, Hyun Min Kim, Dong-Jun Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 275. CrossRef - Longitudinal changes in left ventricular structure and function in patients with type 2 diabetes: Normal weight versus overweight/obesity
Seong Hwan Kim, Ki-Chul Sung, Seung Ku Lee, Juri Park, Nan Hee Kim, Sun H Kim, Chol Shin
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2019; 16(5): 450. CrossRef - High Proportion of Adult Cases and Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Population in Korea: A Nationwide Study
You-Bin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Seung-Eun Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(1): 76. CrossRef - Diabetes and the Risk of Infection: A National Cohort Study
Eun Jin Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Young Hwa Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 804. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics of diabetic ketoacidosis in users and non-users of SGLT2 inhibitors
J.Y. Jeon, S.-K. Kim, K.-S. Kim, S.O. Song, J.-S. Yun, B.-Y. Kim, C.-H. Kim, S.O. Park, S. Hong, D.H. Seo, J.A. Seo, J.H. Noh, D.J. Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2019; 45(5): 453. CrossRef - Trends in incidence of total or type 2 diabetes: systematic review
Dianna J Magliano, Rakibul M Islam, Elizabeth L M Barr, Edward W Gregg, Meda E Pavkov, Jessica L Harding, Maryam Tabesh, Digsu N Koye, Jonathan E Shaw
BMJ.2019; : l5003. CrossRef - HDL-Cholesterol, Its Variability, and the Risk of Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Seung-Hwan Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kun-Ho Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 104(11): 5633. CrossRef - Elevated N -acetyl-β- d -glucosaminidase, a urinary tubular damage marker, is a significant predictor of carotid artery atherosclerosis in type 1 diabetes, independent of albuminuria: A cross-sectional study
Minyoung Lee, Namki Hong, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2018; 32(8): 777. CrossRef - House dust mite and Cockroach specific Immunoglobulin E sensitization is associated with diabetes mellitus in the adult Korean population
Mee Kyoung Kim, Jee Sun Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Ki Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Mortality and causes of death in patients with atrial fibrillation: A nationwide population-based study
Euijae Lee, Eue-Keun Choi, Kyung-Do Han, HyunJung Lee, Won-Seok Choe, So-Ryoung Lee, Myung-Jin Cha, Woo-Hyun Lim, Yong-Jin Kim, Seil Oh, Giuseppina Novo
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(12): e0209687. CrossRef - Factors associated with greater benefit of a national reimbursement policy for blood glucose test strips in adult patients with type 1 diabetes: A prospective cohort study
Sang‐Man Jin, Jong Ha Baek, Sunghwan Suh, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Cheol‐Young Park, Hae Kyung Yang, Jae Hyoung Cho, Byung‐Wan Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2018; 9(3): 549. CrossRef - Association of blood pressure components with mortality and cardiovascular events in prehypertensive individuals: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Hyung Jung Oh, Seulbi Lee, Eun-Kyung Lee, Oesook Lee, Eunhee Ha, Eun-Mi Park, Seung-Jung Kim, Duk-Hee Kang, Kyu Bok Choi, Seung Jun Kim, Dong-Ryeol Ryu
Annals of Medicine.2018; 50(5): 443. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Korean Diabetes Risk Score: A 10-Year National Cohort Study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Yong-ho Lee, Sun Ok Song, Jae-woo Lee, Dong Wook Kim, Kyung-hee Cho, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 402. CrossRef - Clinical Utility and Cross-Reactivity of Insulin and C-Peptide Assays by the Lumipulse G1200 System
Jongwon Oh, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hyung-Doo Park
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2018; 38(6): 530. CrossRef - The optimal cut-off of blood pressure related to left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and remodeling in Asian diabetic patients
Ju Young Jung, Sung Keun Park, Jae-Hong Ryoo, Chang-Mo Oh, Jeong Gyu Kang, Kanghee Moon, Keum Ok Lee, Joong-Myung Choi
Journal of Cardiology.2018; 71(1): 16. CrossRef - Association of Body Mass Index with Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and Mortality in People with Diabetes
Dong Hun Lee, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Hyeon Chang Kim, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2018; 27(1): 61. CrossRef - Obesity and Metabolic Unhealthiness Have Different Effects on Colorectal Neoplasms
Sun-Hye Ko, Myong Ki Baeg, Seung Yeon Ko, Hee Sun Jung, Pumsoo Kim, Myung-Gyu Choi
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2017; 102(8): 2762. CrossRef - Alteration of oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines induces apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
Jibin Sha, Bo Sui, Xiaoqing Su, Qingfang Meng, Chenggang Zhang
Molecular Medicine Reports.2017; 16(5): 7715. CrossRef - BMI and All-Cause Mortality in Normoglycemia, Impaired Fasting Glucose, Newly Diagnosed Diabetes, and Prevalent Diabetes: A Cohort Study
Eun Young Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Sang-Wook Yi, Soon-Ae Shin, Jee-Jeon Yi
Diabetes Care.2017; 40(8): 1026. CrossRef - Fasting glucose and risk of colorectal cancer in the Korean Multi-center Cancer Cohort
Hyeree Park, Sooyoung Cho, Hyeongtaek Woo, Sue K. Park, Hai-Rim Shin, Soung-Hoon Chang, Keun-Young Yoo, Aesun Shin, Cheng Hu
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(11): e0188465. CrossRef - Differential association of body mass index on glycemic control in type 1 diabetes
Eun Young Lee, Yong‐ho Lee, Sang‐Man Jin, Hae Kyung Yang, Chang Hee Jung, Cheol‐Young Park, Jae Hyoung Cho, Woo Je Lee, Byung‐Wan Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Stepwise Approach to Problematic Hypoglycemia in Korea: Educational, Technological, and Transplant Interventions
Sang-Man Jin
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 190. CrossRef - Mortality and causes of death in a national sample of type 2 diabetic patients in Korea from 2002 to 2013
Yu Mi Kang, Ye-Jee Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Chang Hee Jung
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite