
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Complications
- Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Undiagnosed Diabetic Patients: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Han Na Jang, Min Kyong Moon, Bo Kyung Koo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):620-629. Published online February 23, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0099
- 4,067 View
- 215 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy (DR) in patients with undiagnosed diabetes through a nationwide survey, compared to those with known diabetes.
Methods
Among the participants of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) from 2017 to 2018, individuals aged ≥40 years with diabetes and fundus exam results were enrolled. Sampling weights were applied to represent the entire Korean population. Newly detected diabetes patients through KNHANES were classified under “undiagnosed diabetes.”
Results
Among a total of 9,108 participants aged ≥40 years, 951 were selected for analysis. Of them, 31.3% (standard error, ±2.0%) were classified under “undiagnosed diabetes.” The prevalence of DR in patients with known and undiagnosed diabetes was 24.5%±2.0% and 10.7%±2.2%, respectively (P<0.001). The DR prevalence increased with rising glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels in patients with known and undiagnosed diabetes (P for trend=0.001 in both). Among those with undiagnosed diabetes, the prevalence of DR was 6.9%±2.1%, 8.0%±3.4%, 5.6%±5.7%, 16.7%±9.4%, and 42.6%±14.8% for HbA1c levels of <7.0%, 7.0%–7.9%, 8.0%–8.9%, 9.0%–9.9%, and ≥10.0% respectively. There was no difference in the prevalence of hypertension, dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, or obesity according to the presence or absence of DR.
Conclusion
About one-third of patients with diabetes were unaware of their diabetes, and 10% of them have already developed DR. Considering increasing the prevalence of DR according to HbA1c level was found in patients with undiagnosed diabetes like those with known diabetes, screening and early detection of diabetes and DR are important. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factors of peripheral occlusive arterial disease in patients with diabetic retinopathy due to type 2 diabetes
Milos Maksimovic
Srpski arhiv za celokupno lekarstvo.2024; 152(1-2): 50. CrossRef - Gene Expression Analysis in T2DM and Its Associated Microvascular Diabetic Complications: Focus on Risk Factor and RAAS Pathway
Laxmipriya Jena, Prabhsimran Kaur, Tashvinder Singh, Kangan Sharma, Sushil Kotru, Anjana Munshi
Molecular Neurobiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Asian-Specific Visceral Adiposity Indices Are Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Korean Adults
Jonghwa Jin, Hyein Woo, Youngeun Jang, Won-Ki Lee, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 426. CrossRef - Prevalence of osteosarcopenic obesity and related factors among Iranian older people: Bushehr Elderly Health (BEH) program
Mozhgan Ahmadinezhad, Mohammad Ali Mansournia, Noushin Fahimfar, Gita Shafiee, Iraj Nabipour, Mahnaz Sanjari, Kazem Khalagi, Mohammad Javad Mansourzadeh, Bagher Larijani, Afshin Ostovar
Archives of Osteoporosis.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Risk factors of peripheral occlusive arterial disease in patients with diabetic retinopathy due to type 2 diabetes
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
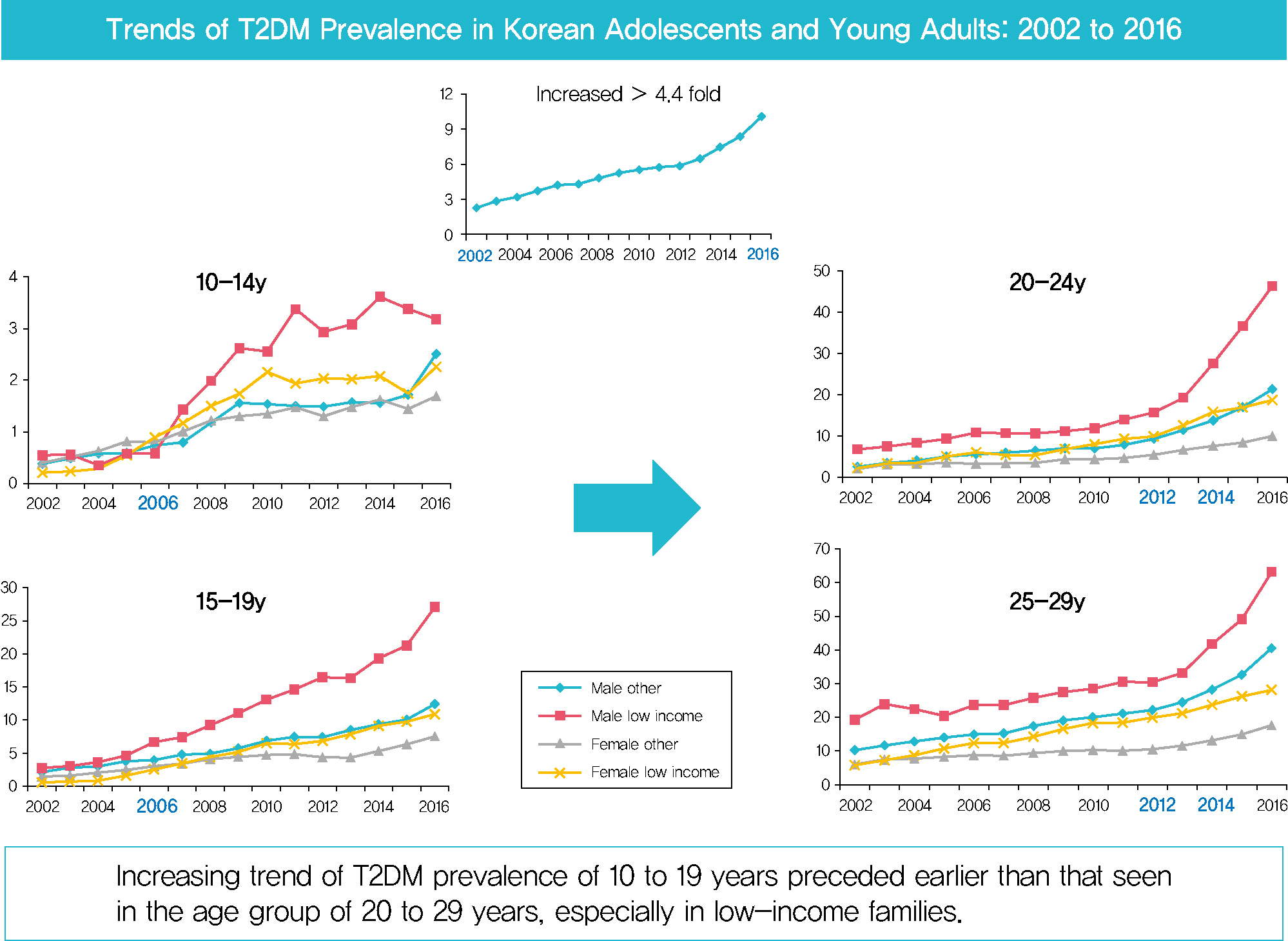
- Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among Korean Children, Adolescents, and Adults Younger than 30 Years: Changes from 2002 to 2016
- Yong Hee Hong, In-Hyuk Chung, Kyungdo Han, Sochung Chung, on Behalf of the Taskforce Team of the Obesity Fact Sheet of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):297-306. Published online October 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0038
- 9,361 View
- 343 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Despite the importance of and social concern regarding prevention of diabetes at younger ages, limited data are available. This study sought to analyze changes in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Koreans younger than 30 years according to sex, age, and level of income.
Methods
The dataset analyzed in this study was derived from health insurance claims recorded in the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database. Participants’ level of income was categorized as low (quintile 1, <20% of insurance premium) or others (quintile 2–5).
Results
In males and females, the prevalence of T2DM per 10,000 people steadily increased from 2.57 in 2002 to 11.41 in 2016, and from 1.96 in 2002 to 8.63 in 2016. The prevalence of T2DM in girls was higher in the age group of 5 to 14 years. Even though the prevalence was higher among those older than 20 years, the increase had started earlier, in the early 2000s, in younger age group. Adolescents aged 10 to 19 years in low-income families showed a remarkable increase in prevalence of T2DM, especially in boys.
Conclusion
The prevalence of T2DM in young Koreans increased more than 4.4-fold from 2002 to 2016, and the increase started in the early 2000s in younger age groups and in low-income families. This is the first study to examine the trend in prevalence of T2DM in children, adolescents, and young adults in Korea. Future studies and collaborations with social support systems to prevent T2DM at an early age group should be performed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
JungMin Choi, Soseul Sung, Sue K. Park, Seyong Park, Hyoyeong Kim, Myeong-Chan Cho, Bryan Williams, Hae-Young Lee
JACC: Asia.2024; 4(4): 265. CrossRef - Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and pathological characteristics of DKD patients with early-onset type 2 diabetes
Liang Wu, Yi-Yang Zhao, Meng-Rui Li, Dong-Yuan Chang, Ming-Hui Zhao, Min Chen
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(8): 108520. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes and Its Association With Psychiatric Disorders in Young Adults in South Korea
Min-Kyung Lee, Su-Young Lee, Seo-Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Hyuk Lee
JAMA Network Open.2023; 6(6): e2319132. CrossRef - Glycemic control and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents during the COVID-19 outbreak
Kyeong Eun Oh, Yu Jin Kim, Ye Rim Oh, Eungu Kang, Hyo-Kyoung Nam, Young-Jun Rhie, Kee-Hyoung Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(4): 275. CrossRef - Position Statement on the Appropriateness and Significance of Adding the Glycated Hemoglobin Test to the National Health Examination
Ji Hye Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Sangjoon Park, Kyunghoon Lee, Jun Goo Kang, Eu Jeong Ku, Su Kyoung Kwon, Won Jun Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Jang Won Son, Young Sil Eom, Kyung Ae Lee, Jeongrim Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Hwa Lee, Jung Hwa Jung, Hochan Cho, Da
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 178. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 349. CrossRef - Prevalence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous federal state in Germany, 2002-2020
C. Baechle, A. Stahl-Pehe, N. Prinz, T. Meissner, C. Kamrath, R.W. Holl, J. Rosenbauer
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 190: 109995. CrossRef - Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Youth
Hwa Young Kim, Jae Hyun Kim
The Ewha Medical Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting High-Risk for Diabetes among Korean Adolescents: An Analysis Using the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2020)
Kyung-Sook Bang, Sang-Youn Jang, Ji-Hye Choe
Children.2022; 9(8): 1249. CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 641. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef
- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
- Lifestyle
- Persistent Anxiety Is Associated with Higher Glycemia Post-Transition to Adult Services in Asian Young Adults with Diabetes
- Ling Zhu, Suresh Rama Chandran, Wee Boon Tan, Xiaohui Xin, Su-Yen Goh, Daphne Su-Lyn Gardner
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):67-76. Published online June 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0226

- 5,331 View
- 104 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
Background There is little longitudinal information on psychological burden and metabolic outcomes in young adults with diabetes (YAD) in Asia. We aimed to evaluate the association between psychological status and glycemia at baseline and 2 years following transition in a cohort of YAD in Singapore.
Methods Subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), aged 17 to 25 years, were recruited from the YAD clinic in Singapore General Hospital. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression and Problem Areas for Diabetes scales were administered at transition (baseline) and at 18 to 24 months. Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) assessed during routine visits was tracked longitudinally.
Results A total of 98 T1DM (74.8%) and 33 T2DM (25.2%) subjects were recruited between January 2011 and November 2017. At baseline, mean HbA1c was 8.6%±1.7%. Only 26.0% achieved HbA1c of ≤7.5% and 16.8% achieved HbA1c of <7%. At baseline, prevalence of anxiety was 29.8%. At 24 months, 14.1% had persistent anxiety. Those with persistent anxiety had the highest mean HbA1c, particularly at 6 months (persistently anxious vs. persistently non-anxious: 9.9%±1.2% vs. 8.2%±1.9%,
P =0.009). At baseline, 9.2% of subjects had depression. This group also had poorer glycemia at baseline (HbA1c of depressed vs non-depressed: 9.6%±2.1% vs. 8.5%±1.6%,P =0.04), which persisted up to 24 months.Conclusion The majority of YAD in Singapore have suboptimal glycemia. Psychological distress is a critical harbinger of poorer metabolic outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Cost-Effectiveness of an Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System Compared to Standard Management of Type 1 Diabetes in a Singapore Setting
Daphne Gardner, Mrinmayee Lakkad, Zhiyu Qiu, Yuta Inoue, Suresh Rama Chandran, Kael Wherry
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye-Sun Park, Yongin Cho, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, So Hun Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Interaction of Glycemia with Anxiety and Depression Is Related to Altered Cerebellar and Cerebral Functional Correlations
Grace E. Shearrer
Brain Sciences.2023; 13(7): 1086. CrossRef - The prevalence of anxiety in adult endocrinology outpatients: A systematic review and meta–analysis
Kelly Ann Kershaw, Ben Storer, Taylor Braund, Cassandra Chakouch, Matthew Coleshill, Sam Haffar, Samuel Harvey, Jill Newby, Gemma Sicouri, Michael Murphy
Psychoneuroendocrinology.2023; 158: 106357. CrossRef - Increased Levels of Serum Glycosylated Hemoglobin are Associated with Depressive Symptoms in a Population with Cancer (≥49 Years): An Antidepressant-Stratified Analysis
Ying Huang, Yilin Xu, Anwen Liu
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2021; Volume 16: 205. CrossRef - The Burden of Type 2 Diabetes and the Value of Achieving Near Normoglycemia from the Patient Perspective
Heather Gelhorn, Zaneta Balantac, Shraddha Shinde, Vivian Thuyanh Thieu, Kristina S. Boye
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(7): 1821. CrossRef
- The Cost-Effectiveness of an Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System Compared to Standard Management of Type 1 Diabetes in a Singapore Setting
- Epidemiology
- Discrepancies between Glycosylated Hemoglobin and Fasting Plasma Glucose for Diagnosing Impaired Fasting Glucose and Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Youth and Young Adults
- Jieun Lee, Young Ah Lee, Jae Hyun Kim, Seong Yong Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):174-182. Published online November 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0046
- 5,107 View
- 73 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been recommended as a diagnostic test for prediabetes and diabetes. Here, we evaluated the level of agreement between diagnoses based on fasting plasma glucose (FPG) versus HbA1c levels and determined optimal HbA1c cutoff values for these diseases in youth and young adults.
Methods The study included 7,332 subjects (
n =4,129, aged 10 to 19 years in youth group; andn =3,203 aged 20 to 29 years in young adult group) from the 2011 to 2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Prediabetes and diabetes were defined as 100 to 125 mg/dL (impaired fasting glucose [IFG]) and ≥126 mg/dL for FPG (diabetes mellitus [DM] by FPG [DMFPG]), and 5.7% to 6.4% and ≥6.5% for HbA1c, respectively.Results In the youth group, 32.5% with IFG had an HbA1c level of 5.7% to 6.4%, and 72.2% with DMFPG had an HbA1c ≥6.5%. In the young adult group, 27.5% with IFG had an HbA1c level of 5.7% to 6.4%, and 66.6% with DMFPG had an HbA1c ≥6.5%. Kappa coefficients for agreement between the FPG and HbA1c results were 0.12 for the youth group and 0.19 for the young adult group. In receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, the optimal HbA1c cutoff for IFG and DMFPG were 5.6% and 5.9% in youths and 5.5% and 5.8% in young adults, respectively.
Conclusion Usefulness of HbA1c for diagnosis of IFG and DMFPG in Koreans aged <30 years remains to be determined due to discrepancies between the results of glucose- and HbA1c-based tests. Additional testing might be warranted at lower HbA1c levels to detect IFG and DMFPG in this age group.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lower Dietary Magnesium Is Associated with a Higher Hemoglobin Glycation Index in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Juan Chen, Song Lin, Xingzhou Wang, Xiwei Wang, Pengxia Gao
Biological Trace Element Research.2024; 202(3): 878. CrossRef - Glycemic traits and colorectal cancer survival in a cohort of South Korean patients: A Mendelian randomization analysis
So Yon Jun, Sooyoung Cho, Min Jung Kim, Ji Won Park, Seung‐Bum Ryoo, Seung Yong Jeong, Kyu Joo Park, Aesun Shin
Cancer Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between HbA1c-derived estimated average glucose and fasting plasma glucose in patients with normal and abnormal hemoglobin patterns
Wilaiwan Sriwimol, Phattanapong Choosongsang, Pensiri Choosongsang, Warakorn Petkliang, Pittaya Treerut
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation.2022; 82(3): 192. CrossRef - Increasing prevalence of fasting hyperglycemia in adolescents aged 10–18 years and its relationship with metabolic indicators: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Study (KNHANES), 2007–2018
Seung Eun Yoo, Ji Hyen Lee, Jung Won Lee, Hye Sook Park, Hye Ah Lee, Hae Soon Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(1): 60. CrossRef - Differences in Clinical Indicators of Diabetes, Hypertension, and Dyslipidemia Among Workers Who Worked Long Hours and Shift Work
EunKyo Kang
Workplace Health & Safety.2021; 69(6): 268. CrossRef - Practice Patterns in the Acceptance of Medically Complex Living Kidney Donors with Obesity, Hypertension, Family History of Kidney Disease, or Donor-Recipient Age Discrepancy
Ziad Arabi, Muhammad Bukhari, Abdullah Hamad, Abdulrahman Altheaby, Saleh Kaysi
Avicenna Journal of Medicine.2021; 11(04): 172. CrossRef - Endocrine comorbidities of pediatric obesity
Jieun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2021; 64(12): 619. CrossRef - Association between handgrip strength and cardiovascular risk factors among Korean adolescents
Kyoung Kon Kim, Kyu Rae Lee, In Cheol Hwang
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 33(9): 1213. CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia is associated with long-term risk of cardiovascular events and specific comorbidity in very high-risk hypertensive patients
O. Ya. Korolyuk, O. M. Radchenko
The Ukrainian Biochemical Journal.2020; 92(2): 8. CrossRef - The Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Weight Loss and Metabolic Changes in Adults with Obesity
Stanisław Głuszek, Arkadiusz Bociek, Edyta Suliga, Jarosław Matykiewicz, Magdalena Kołomańska, Piotr Bryk, Przemysław Znamirowski, Łukasz Nawacki, Martyna Głuszek-Osuch, Iwona Wawrzycka, Dorota Kozieł
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(15): 5342. CrossRef - Peculiarities of Clinical Presentations and Long–Term Complications in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Metabolic Syndrome, depending on their Serum Triglyceride Levels
O. Ya. Korolyuk
Ukraïnsʹkij žurnal medicini, bìologìï ta sportu.2020; 5(1): 125. CrossRef
- Lower Dietary Magnesium Is Associated with a Higher Hemoglobin Glycation Index in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





