
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Sulwon Lecture 2020
- Pathophysiology
- Rho-Kinase as a Therapeutic Target for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases
- Inês Sousa-Lima, Hyun Jeong Kim, John Jones, Young-Bum Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):655-674. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0197
- 5,794 View
- 171 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
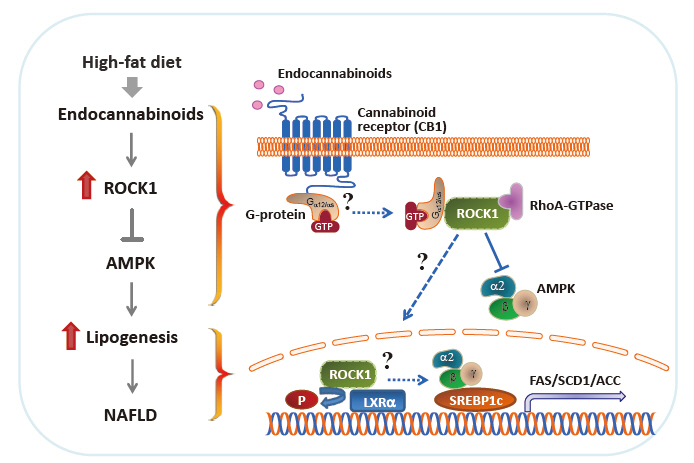
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a major public health problem and the most common form of chronic liver disease, affecting 25% of the global population. Although NAFLD is closely linked with obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus, knowledge on its pathogenesis remains incomplete. Emerging data have underscored the importance of Rho-kinase (Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing kinase [ROCK]) action in the maintenance of normal hepatic lipid homeostasis. In particular, pharmacological blockade of ROCK in hepatocytes or hepatic stellate cells prevents the progression of liver diseases such as NAFLD and fibrosis. Moreover, mice lacking hepatic ROCK1 are protected against obesity-induced fatty liver diseases by suppressing hepatic de novo lipogenesis. Here we review the roles of ROCK as an indispensable regulator of obesity-induced fatty liver disease and highlight the key cellular pathway governing hepatic lipid accumulation, with focus on de novo lipogenesis and its impact on therapeutic potential. Consequently, a comprehensive understanding of the metabolic milieu linking to liver dysfunction triggered by ROCK activation may help identify new targets for treating fatty liver diseases such as NAFLD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- THE ROLE OF N6-METHYLADENOSINE METHYLTRANSFERASE RBM15 IN NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE
Shiqing Li, Shengyi Lian, Wei Cheng, Tao Zhang, Xiaobing Gong
Shock.2024; 61(2): 311. CrossRef - Exploring the potential of drug repurposing for liver diseases: A comprehensive study
Fares E.M. Ali, Mustafa Ahmed Abdel-Reheim, Emad H.M. Hassanein, Mostafa K. Abd El-Aziz, Hanan S. Althagafy, Khalid S.A. Badran
Life Sciences.2024; : 122642. CrossRef - Targeting of G-protein coupled receptor 40 alleviates airway hyperresponsiveness through RhoA/ROCK1 signaling pathway in obese asthmatic mice
Xixi Lin, Like Wang, Xiaojie Lu, Yuanyuan Zhang, Rongying Zheng, Ruijie Chen, Weixi Zhang
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Selectivity matters: selective ROCK2 inhibitor ameliorates established liver fibrosis via targeting inflammation, fibrosis, and metabolism
Alexandra Zanin-Zhorov, Wei Chen, Julien Moretti, Melanie S. Nyuydzefe, Iris Zhorov, Rashmi Munshi, Malavika Ghosh, Cindy Serdjebi, Kelli MacDonald, Bruce R. Blazar, Melissa Palmer, Samuel D. Waksal
Communications Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight Into Rho Kinase Isoforms in Obesity and Energy Homeostasis
Lei Wei, Jianjian Shi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Paeoniflorin alleviates liver injury in hypercholesterolemic rats through the ROCK/AMPK pathway
Tong Liu, Ning Zhang, Lingya Kong, Sijie Chu, Ting Zhang, Guangdi Yan, Donglai Ma, Jun Dai, Zhihong Ma
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fasudil Increased the Sensitivity to Gefitinib in NSCLC by Decreasing Intracellular Lipid Accumulation
Tingting Liao, Jingjing Deng, Wenjuan Chen, Juanjuan Xu, Guanghai Yang, Mei Zhou, Zhilei Lv, Sufei Wang, Siwei Song, Xueyun Tan, Zhengrong Yin, Yumei Li, Yang Jin
Cancers.2022; 14(19): 4709. CrossRef
- THE ROLE OF N6-METHYLADENOSINE METHYLTRANSFERASE RBM15 IN NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE
Original Articles
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Serum Retinol-Binding Protein Levels Are Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Real-World Study
- Zhi-Hui Zhang, Jiang-Feng Ke, Jun-Xi Lu, Yun Liu, Ai-Ping Wang, Lian-Xi Li
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):129-139. Published online August 10, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0222
- 5,590 View
- 182 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
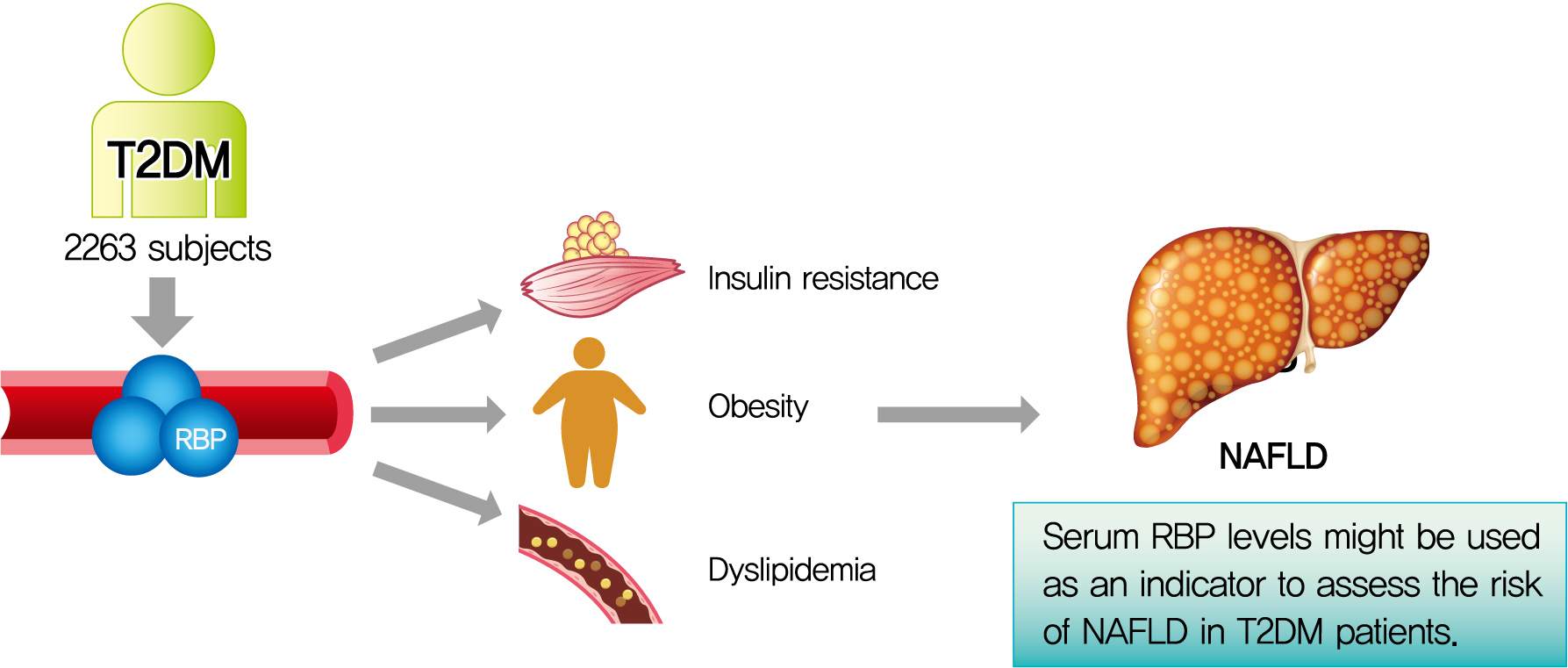
The association of serum retinol-binding protein (RBP) levels with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) remains controversial. Furthermore, few studies have investigated their relationship in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to explore the association between serum RBP levels and NAFLD in Chinese inpatients with T2DM.
Methods
This cross-sectional, real-world study included 2,263 Chinese T2DM inpatients. NAFLD was diagnosed by abdominal ultrasonography. The subjects were divided into four groups based on RBP quartiles, and clinical characteristics were compared among the four groups. The associations of both RBP levels and quartiles with the presence of NAFLD were also analyzed.
Results
After adjustment for sex, age, and diabetes duration, there was a significant increase in the prevalence of NAFLD from the lowest to the highest RBP quartiles (30.4%, 40.0%, 42.4%, and 44.7% for the first, second, third, and fourth quartiles, respectively, P<0.001 for trend). Fully adjusted multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that both increased RBP levels (odds ratio, 1.155; 95% confidence interval, 1.012 to 1.318; P=0.033) and quartiles (P=0.014 for trend) were independently associated with the presence of NAFLD in T2DM patients.
Conclusion
Increased serum RBP levels were independently associated with the presence of NAFLD in Chinese T2DM inpatients. Serum RBP levels may be used as one of the indicators to assess the risk of NAFLD in T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between NAFLD and retinol-binding protein 4 - an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Rui Hu, Xiaoyue Yang, Xiaoyu He, Guangyao Song
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood lactate levels are associated with an increased risk of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes: a real-world study
Yi-Lin Ma, Jiang-Feng Ke, Jun-Wei Wang, Yu-Jie Wang, Man-Rong Xu, Lian-Xi Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High‐normal unconjugated bilirubin is associated with decreased risk of chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes: A real‐world study
Man‐Rong Xu, Chun‐Hua Jin, Jun‐Xi Lu, Mei‐Fang Li, Lian‐Xi Li
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Elina En Li Cho, Chong Zhe Ang, Jingxuan Quek, Clarissa Elysia Fu, Lincoln Kai En Lim, Zane En Qi Heng, Darren Jun Hao Tan, Wen Hui Lim, Jie Ning Yong, Rebecca Zeng, Douglas Chee, Benjamin Nah, Cosmas Rinaldi Adithya Lesmana, Aung Hlaing Bwa, Khin Maung W
Gut.2023; 72(11): 2138. CrossRef - Serum iron is closely associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes: A real-world study
Jun-Wei Wang, Chun-Hua Jin, Jiang-Feng Ke, Yi-Lin Ma, Yu-Jie Wang, Jun-Xi Lu, Mei-Fang Li, Lian-Xi Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Low-normal serum unconjugated bilirubin levels are associated with late but not early carotid atherosclerotic lesions in T2DM subjects
Chun-Hua Jin, Jun-Wei Wang, Jiang-Feng Ke, Jing-Bo Li, Mei-Fang Li, Lian-Xi Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Waist-to-height ratio is a simple and practical alternative to waist circumference to diagnose metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes
Yi-Lin Ma, Chun-Hua Jin, Cui-Chun Zhao, Jiang-Feng Ke, Jun-Wei Wang, Yu-Jie Wang, Jun-Xi Lu, Gao-Zhong Huang, Lian-Xi Li
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - GA/HbA1c ratio is a simple and practical indicator to evaluate the risk of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes: an observational study
Jun-Wei Wang, Chun-Hua Jin, Jiang-Feng Ke, Yi-Lin Ma, Yu-Jie Wang, Jun-Xi Lu, Mei-Fang Li, Lian-Xi Li
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Decreased Serum Osteocalcin is an Independent Risk Factor for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetes
Yu-Jie Wang, Chun-Hua Jin, Jiang-Feng Ke, Jun-Wei Wang, Yi-Lin Ma, Jun-Xi Lu, Mei-Fang Li, Lian-Xi Li
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 3717. CrossRef
- The relationship between NAFLD and retinol-binding protein 4 - an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- Rosiglitazone Activates AMPK and Improves Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in OLETF Rats.
- Eun Hee Cho, Ki Up Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(2):141-148. Published online April 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.2.141
- 1,797 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Insulin resistance is very common in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Glitazones improve insulin sensitivity by acting as a selective agonist of the peroxisome proliferators -activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma), and were shown to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in skeletal muscle and the liver. Glitazones were also shown to reduce hepatic lipogenesis. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the protective mechanism of rosiglitazone on NAFLD is associated with AMPK activation. METHODS: Twelve OLETF rats were divided into 2 groups (control, treatment, n = 6 each). LETO rats served as controls. At 35 weeks of age, treatment group received rosiglitazone 4 mg/kg daily for 3 days. Fasting plasma glucose, insulin, free fatty acid, lactate and triglycerides were measured. Liver tissues from each group were processed for histological and hepatic triglyceride content analysis and western blotting. RESULTS: Fasting plasma glucose, insulin and triglycerides levels were significantly lower in treatment group than in control group. Histologic examination disclosed decreased hepatic steatosis in treatment group. Hepatic triglyceride content was also decreased in treatment group. Sterol regulatory binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and fatty acid synthase (FAS) expression were increased and AMPK phosphorylation was reduced in OLETF rats compared with LETO rats, and these changes were reversed by rosiglitazone treatment. CONCLUSION: Rosiglitazone reduced hepatic steatosis in OLETF rats, and activated AMPK in the liver. These results suggest the role of AMPK activation in the protective action of rosiglitazone on NAFLD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Small Rice Bowl-Based Meal Plan for Energy and Marcronutrient Intake in Korean Men with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study
Hee Jung Ahn, Kyung Ah Han, Jin Young Jang, Jae Hyuk Lee, Kang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(3): 273. CrossRef
- Small Rice Bowl-Based Meal Plan for Energy and Marcronutrient Intake in Korean Men with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





