
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
- Glimepiride Compared to Liraglutide Increases Plasma Levels of miR-206, miR-182-5p, and miR-766-3p in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Nikolai N. Scherbak, Robert Kruse, Thomas Nyström, Johan Jendle
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):668-681. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0342
- 2,442 View
- 135 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
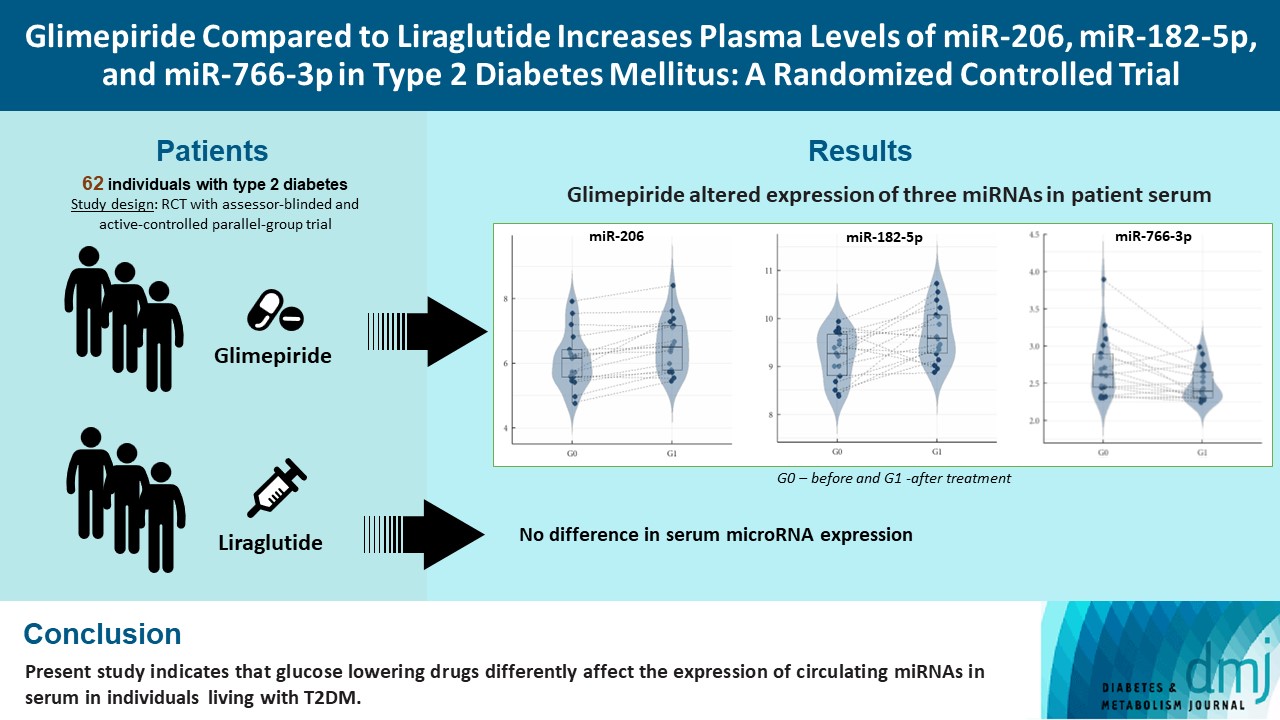
Diabetes is a chronic disease with several long-term complications. Several glucose-lowering drugs are used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), e.g., glimepiride and liraglutide, in which both having different modes of action. Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) are suggested as potential biomarkers that are associated with the disease development and the effects of the treatment. In the current study we evaluated the effect of glimepiride, liraglutide on the expression of the circulating miRNAs.
Methods
The present study is a post hoc trial from a previously randomized control trial comparing liraglutide versus glimepiride both in combination with metformin in subjects with T2DM, and subclinical heart failure. miRNAs were determined in the subjects’ serum samples with next generation sequencing. Expression patterns of the circulating miRNAs were analyzed using bioinformatic univariate and multivariate analyses (clinical trial registration: NCT01425580).
Results
Univariate analyses show that treatment with glimepiride altered expression of three miRNAs in patient serum, miR-206, miR-182-5p, and miR-766-3p. Both miR-182-5p and miR-766-3p were also picked up among the top contributing miRNAs with penalized regularised logistic regressions (Lasso). The highest-ranked miRNAs with respect to Lasso coefficients were miR-3960, miR-31-5p, miR-3613-3p, and miR-378a-3p. Liraglutide treatment did not significantly influence levels of circulating miRNAs.
Conclusion
Present study indicates that glucose-lowering drugs differently affect the expression of circulating miRNAs in serum in individuals with T2DM. More studies are required to investigate possible mechanisms by which glimepiride is affecting the expression of circulating miRNAs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glimepiride Compared to Liraglutide Increases Plasma Levels of miR-206, miR-182-5p, and miR-766-3p in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:668-81)
Nikolai N. Scherbak, Robert Kruse, Thomas Nyström, Johan Jendle
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 882. CrossRef - Glimepiride Compared to Liraglutide Increases Plasma Levels of miR-206, miR-182-5p, and miR-766-3p in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:668-81)
Da Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 879. CrossRef
- Glimepiride Compared to Liraglutide Increases Plasma Levels of miR-206, miR-182-5p, and miR-766-3p in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:668-81)
- Drug/Regimen
- Comparison of Efficacy of Glimepiride, Alogliptin, and Alogliptin-Pioglitazone as the Initial Periods of Therapy in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Open-Label, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study
- Hae Jin Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Kyu Yeon Hur, Soo-Kyung Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Sung Wan Chun, Eun Seok Kang, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):689-700. Published online March 17, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0183
- 5,651 View
- 377 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The choice of an optimal oral hypoglycemic agent in the initial treatment periods for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients remains difficult and deliberate. We compared the efficacy and safety of glimepiride (GLIM), alogliptin (ALO), and alogliptin-pioglitazone (ALO-PIO) in poorly controlled T2DM patients with drug-naïve or metformin failure.
Methods
In this three-arm, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled trial, poorly controlled T2DM patients were randomized to receive GLIM (n=35), ALO (n=31), or ALO-PIO (n=33) therapy for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was change in the mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels at week 24 from baseline. Secondary endpoints were changes in HbA1c level at week 12 from baseline, fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels, lipid profiles at weeks 12 and 24, and parameters of glycemic variability, assessed by continuous glucose monitoring for 24 weeks.
Results
At weeks 12 and 24, the ALO-PIO group showed significant reduction in HbA1c levels compared to the ALO group (–0.96%±0.17% vs. –0.37%±0.17% at week 12; –1.13%±0.19% vs. –0.18%±0.2% at week 24). The ALO-PIO therapy caused greater reduction in FPG levels and significant increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels at weeks 12 and 24 than the ALO therapy. Compared to low-dose GLIM therapy, ALO-PIO therapy showed greater improvement in glycemic variability. The adverse events were similar among the three arms.
Conclusion
ALO-PIO combination therapy during the early period exerts better glycemic control than ALO monotherapy and excellency in glycemic variability than low-dose sulfonylurea therapy in uncontrolled, drug-naïve or metformin failed T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
Fatma Haddad, Ghadeer Dokmak, Maryam Bader, Rafik Karaman
Life.2023; 13(4): 1012. CrossRef - Role of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Antidiabetic Treatment
Ruili Yin, Yongsong Xu, Xin Wang, Longyan Yang, Dong Zhao
Molecules.2022; 27(10): 3055. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
- Comparison of Vildagliptin-Metformin and Glimepiride-Metformin Treatments in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Hyun Jeong Jeon, Tae Keun Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(5):529-535. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.5.529
- 65,535 View
- 96 Download
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The present study investigated the efficacy and safety of vildagliptin-metformin treatment compared to those of glimepiride-metformin treatment for type 2 diabetes.
Methods In a randomized, open-label, comparative study, 106 patients with type 2 diabetes were enrolled. The primary endpoint was a reduction in HbA1c from baseline and secondary endpoints included fasting plasma glucose (FPG) or 2-hour postprandial glucose (2h-PPG) reduction from baseline, as well as HbA1c responder rate and HbA1c reduction according to baseline HbA1c category.
Results Comparable HbA1c reduction was observed with a mean±standard deviation change from baseline to the 32-week endpoint of -0.94±1.15% in the vildagliptin group and -1.00±1.32% in the glimepiride group. A similar reduction in 2h-PPG (vildagliptin group 3.53±4.11 mmol/L vs. the glimepiride group 3.72±4.17 mmol/L) was demonstrated, and the decrements in FPG (vildagliptin group 1.54±2.41 mmol/L vs. glimepiride group 2.16±2.51 mmol/L) were not different between groups. The proportion of patients who achieved an HbA1c less than 7% at week 32 was 50.1% in the vildagliptin group and 56.0% in the glimepiride group. An average body weight gain of 2.53±1.21 kg in the glimepiride group was observed in contrast with the 0.23±0.69 kg weight gain noted in the vildagliptin group. A 10-fold lower incidence of hypoglycemia was demonstrated in the vildagliptin group, in addition to an absence of severe hypoglycemia.
Conclusion Vildagliptin-metformin treatment provided blood glucose control efficacy comparable to that of glimepiride-metformin treatment and resulted in better adverse event profiles with lower risks of hypoglycemia and weight gain.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Randomized, Two-Treatments, Two-Periods, Crossover, Open label, Laboratory-Blind, Single Dose Bioequivalence Study between Vildagliptin/Metformin 50 mg/1000 mg Film Coated Tablets (Sensityn®) and Galvusmet® 50 mg/1000 mg Film Coated Tablets in healthy a
J. Shiekmydeen, T. Siddiqi, K. Chakraborty, S. Khalaf, M. Albarazi, I. Eqtefan, J. Sliva
European Pharmaceutical Journal.2023; 70(2): 1. CrossRef - Bioequivalence Studies of New Generic Formulations of Vildagliptin and Fixed-Drug Combination of Vildagliptin and Metformin Versus Respective Originator Products in Healthy Volunteers
Yvonne Schnaars, Sumedh Gaikwad, Ulrike Gottwald-Hostalek, Ulrike Klingberg, Hari Kiran Chary Vadla, Vamshi Ramana Prathap
Diabetes Therapy.2022; 13(6): 1215. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of dorzagliatin for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
Yunfeng Yu, Xingyu Yang, Keke Tong, Shuang Yin, Gang Hu, Fei Zhang, Pengfei Jiang, Manli Zhou, Weixiong Jian
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Single-Center, Observational, Retrospective Cost-Effective Analysis of Treating Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Addition of DPP4 Inhibitors Versus Intensified Treatment with Conventional Drugs
Akshata Kalyani, Sachin Kuchya, >Prashant Punekar
Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics.2021; 12(3): 125. CrossRef - Comparison of safety and efficacy of glimepiride-metformin and vildagliptin- metformin treatment in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients
Surendra Kumar
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 25(4): 326. CrossRef - Comparative clinical study evaluating the effect of adding Vildagliptin versus Glimepiride to ongoing Metformin therapy on diabetic patients with symptomatic coronary artery disease
Rehab Werida, Mahmoud Kabel, Gamal Omran, Ahmed Shokry, Tarek Mostafa
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 170: 108473. CrossRef - Efficacy of different antidiabetic drugs based on metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A network meta‐analysis involving eight eligible randomized‐controlled trials
Yan Peng, Shu‐Hong Chen, Xiao‐Nan Liu, Qing‐Yun Sun
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(3): 2795. CrossRef - A safety and tolerability profile comparison between dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and sulfonylureas in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Daniela Farah, Graziella Malzoni Leme, Freddy Goldberg Eliaschewitz, Marcelo Cunio Machado Fonseca
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2019; 149: 47. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide monotherapy compared with glimepiride in East‐Asian patients with type 2 diabetes in a multicentre, double‐blind, randomized, parallel‐arm, active comparator, phase III trial
Yu Hong Chen, Chien‐Ning Huang, Young Min Cho, Pengfei Li, Liqun Gu, Feng Wang, Jun Yang, Wei Qing Wang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2018; 20(9): 2121. CrossRef - Cost effectiveness of vildagliptin versus glimepiride as add-on treatment to metformin for the treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2 patients in Greece
Hara Kousoulakou, Magdalini Hatzikou, Varvara Baroutsou, John Yfantopoulos
Cost Effectiveness and Resource Allocation.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The efficacy and safety of adding either vildagliptin or glimepiride to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Gyuri Kim, Sewon Oh, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2017; 18(12): 1179. CrossRef - Predictors of efficacy of GLP-1 agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors: A systematic review
Helene Bihan, Winda L. Ng, Dianna J. Magliano, Jonathan E. Shaw
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2016; 121: 27. CrossRef - New Oral Diabetes Drugs are more effective than Older Agents: Real or a Fraud?
Udaya M Kabadi
Journal of Diabetes, Metabolic Disorders & Control.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic review and meta-analysis of vildagliptin for treatment of type 2 diabetes
Eleni Bekiari, Chrysoula Rizava, Eleni Athanasiadou, Konstantinos Papatheodorou, Aris Liakos, Thomas Karagiannis, Maria Mainou, Maria Rika, Panagiota Boura, Apostolos Tsapas
Endocrine.2016; 52(3): 458. CrossRef - Sulfonylurea Glimepiride: A Proven Cost Effective, Safe and Reliable War Horse in Combating Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes
Udaya M. Kabadi
Journal of Diabetes Mellitus.2015; 05(04): 211. CrossRef - Glycemic effects of vildagliptin and metformin combination therapy in Indian patients with type 2 diabetes: An observational study (印度2型糖尿病患者使用维格列汀与二甲双胍联合治疗对血糖的影响:一项观察性研究)
Sanjay Chatterjee, Sudip Chatterjee
Journal of Diabetes.2014; 6(3): 237. CrossRef - Head‐to‐head comparison of dipeptidyl peptidase‐IV inhibitors and sulfonylureas – a meta‐analysis from randomized clinical trials
Yifei Zhang, Jie Hong, Jie Chi, Weiqiong Gu, Guang Ning, Weiqing Wang
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2014; 30(3): 241. CrossRef - Vildagliptin: A Review of Its Use in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Gillian M. Keating
Drugs.2014; 74(5): 587. CrossRef - Vildagliptin compared to glimepiride on post-prandial lipemia and on insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients
Giuseppe Derosa, Aldo Bonaventura, Lucio Bianchi, Davide Romano, Elena Fogari, Angela D’Angelo, Pamela Maffioli
Metabolism.2014; 63(7): 957. CrossRef - The Placement of DPP-4 Inhibitors in Clinical Practice Recommendations for the Treatment of Types 2 Diabetes
Jaime A. Davidson
Endocrine Practice.2013; 19(6): 1050. CrossRef - Predictive Clinical Parameters and Glycemic Efficacy of Vildagliptin Treatment in Korean Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes
Jin-Sun Chang, Juyoung Shin, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim, Jeong-Ah Shin, Kun-Ho Yoon, Bong-Yun Cha, Ho-Young Son, Jae-Hyoung Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(1): 72. CrossRef - The Efficacy of Vildagliptin in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Jun Sung Moon, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(1): 36. CrossRef - Effect of Vildagliptin on Glucose and Insulin Concentrations During a 24-Hour Period in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Different Ranges of Baseline Hemoglobin A1c Levels
Manuel González-Ortiz, María J. Sánchez-Peña, Luis J. González-Ortiz, José A. Robles-Cervantes, Yessica E. García-Ortega, Esteban A. Gómez-Gaitán, Karina G. Pérez-Rubio, Esperanza Martínez-Abundis
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2013; 15(7): 564. CrossRef - Differential effects of vildagliptin and glimepiride on glucose fluctuations in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus assessed using continuous glucose monitoring
Y. L. He, G. Foteinos, S. Neelakantham, D. Mattapalli, K. Kulmatycki, T. Forst, A. Taylor
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2013; 15(12): 1111. CrossRef - Combination therapy with metformin plus vildagliptin in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Elisa Guarino, Laura Nigi, Aurora Patti, Cecilia Fondelli, Francesco Dotta
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2012; 13(9): 1377. CrossRef
- A Randomized, Two-Treatments, Two-Periods, Crossover, Open label, Laboratory-Blind, Single Dose Bioequivalence Study between Vildagliptin/Metformin 50 mg/1000 mg Film Coated Tablets (Sensityn®) and Galvusmet® 50 mg/1000 mg Film Coated Tablets in healthy a
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Glimepiride, Metformin, and Rosiglitazone Monotherapy in Korean Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetic Patients: The Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Monotherapy Study
- Kun Ho Yoon, Jeong Ah Shin, Hyuk Sang Kwon, Seung Hwan Lee, Kyung Wan Min, Yu Bae Ahn, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sung Woo Park, Kwan Woo Lee, Yeon Ah Sung, Tae Sun Park, Min Seon Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Moon Suk Nam, Hye Soon Kim, Ie Byung Park, Jong Suk Park, Jeong Taek Woo, Ho Young Son
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(1):26-33. Published online February 28, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.1.26
- 55,892 View
- 86 Download
- 31 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Although many anti-diabetic drugs have been used to control hyperglycemia for decades, the efficacy of commonly-used oral glucose-lowering agents in Korean type 2 diabetic patients has yet to be clearly demonstrated.
Methods We evaluated the efficacy of glimepiride, metformin, and rosiglitazone as initial treatment for drug-naïve type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a 48-week, double-blind, randomized controlled study that included 349 Korean patients. Our primary goal was to determine the change in HbA1c levels from baseline to end point. Our secondary goal was to evaluate changes in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels, body weight, frequency of adverse events, and the proportion of participants achieving target HbA1c levels.
Results HbA1c levels decreased from 7.8% to 6.9% in the glimepiride group (
P <0.001), from 7.9% to 7.0% in the metformin group (P <0.001), and from 7.8% to 7.0% (P <0.001) in the rosiglitazone group. Glimepiride and rosiglitazone significantly increased body weight and metformin reduced body weight during the study period. Symptomatic hypoglycemia was more frequent in the glimepiride group and diarrhea was more frequent in the metformin group.Conclusion The efficacy of glimepiride, metformin, and rosiglitazone as antidiabetic monotherapies in drug-naïve Korean type 2 diabetic patients was similar in the three groups, with no statistical difference. This study is the first randomized controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of commonly-used oral hypoglycemic agents in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. An additional subgroup analysis is recommended to obtain more detailed information.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ketogenic Diet Intervention on Metabolic and Psychiatric Health in Bipolar and Schizophrenia: A Pilot Trial
Shebani Sethi, Diane Wakeham, Terence Ketter, Farnaz Hooshmand, Julia Bjornstad, Blair Richards, Eric Westman, Ronald M Krauss, Laura Saslow
Psychiatry Research.2024; 335: 115866. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - The forgotten type 2 diabetes mellitus medicine: rosiglitazone
Bo Xu, Aoxiang Xing, Shuwei Li
Diabetology International.2022; 13(1): 49. CrossRef - Real-world comparison of mono and dual combination therapies of metformin, sulfonylurea, and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors using a common data model
Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Yu Ji Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Eun-Hee Cho, Tae Sun Park
Medicine.2022; 101(8): e28823. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 461. CrossRef - A RANDOMISED, PROSPECTIVE, PARALLELAND OPEN LABEL STUDY TO COMPARE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF METFORMIN PLUS ROSUVASTATIN AND GLIMEPIRIDE PLUS ROSUVASTATIN IN PATIENTS OF COEXISTING NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) AND TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS (T2DM)
Prabhsimran kaur, Gurpreet Kaur Randhawa, Surinder Kumar Salwan
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2021; : 46. CrossRef - Impact of sitagliptin combination therapy and hypoglycemia in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a multi-center retrospective observational cohort study
Tomoyuki Saito, Hirotoshi Ohmura, Shuko Nojiri, Hiroyuki Daida
Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - 2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Bo-Yeon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Junghyun Noh, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seok-O Park, Kyu Yeon Hur, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Kang-Woo Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun-Jung Rhee, SungWan Chun, Sung Hoon Yu
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 398. CrossRef - Oral Hypoglycemic Agents for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Seung-Hyun Ko
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2019; 20(3): 142. CrossRef - Monotherapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Sang Youl Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(1): 15. CrossRef - Failure of monotherapy in clinical practice in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Korean National Diabetes Program
Ja Young Jeon, Soo Jin Lee, Sieun Lee, Soo Jin Kim, Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Young Seol Kim, Jeong Taek Woo, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Moonsuk Nam, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan‐Woo Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2018; 9(5): 1144. CrossRef - Women are less likely than men to achieve optimal glycemic control after 1 year of treatment: A multi-level analysis of a Korean primary care cohort
Seung-Ah Choe, Joo Yeong Kim, Young Sun Ro, Sung-Il Cho, Antonio Palazón-Bru
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(5): e0196719. CrossRef - Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 349. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic Agent Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 337. CrossRef - Monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 959. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic agent therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 2017: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 947. CrossRef - Insulin Secretory Capacity and Insulin Resistance in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Jong-Dai Kim, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 354. CrossRef - Trends of antidiabetic drug use in adult type 2 diabetes in Korea in 2002–2013
Seung-Hyun Ko, Dae-Jung Kim, Jong-Heon Park, Cheol-Young Park, Chang Hee Jung, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Joong-Yeol Park, Kee-Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Ki-Up Lee, Kyung-Soo Ko
Medicine.2016; 95(27): e4018. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Guideline 2015: Oral Hypoglycemic Agents for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Seung-Hyun Ko
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(2): 83. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor, combined with metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 16‐week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled phase III trial
M. K. Kim, E.‐J. Rhee, K. A. Han, A. C. Woo, M.‐K. Lee, B. J. Ku, C. H. Chung, K.‐A. Kim, H. W. Lee, I. B. Park, J. Y. Park, H. C. Chul Jang, K. S. Park, W. I. Jang, B. Y. Cha
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2015; 17(3): 309. CrossRef - Effect of Yanggyuksanhwa-Tang on non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus unresponsive to oral hypoglycemic agents: A case report
Jiman Kim, Seungwon Kwon
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine.2015; 21(2): 157. CrossRef - Efficacy of glimepiride/metformin fixed‐dose combination vs metformin uptitration in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled on low‐dose metformin monotherapy: A randomized, open label, parallel group, multicenter study in Korea
Hye‐soon Kim, Doo‐man Kim, Bong‐soo Cha, Tae Sun Park, Kyoung‐ah Kim, Dong‐lim Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Jeong‐hyun Park, Hak Chul Jang, Dong‐seop Choi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2014; 5(6): 701. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Association between the Use of Oral Anti-hyperglycemic Agents and Hypoglycemia in Japan by Data Mining of the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) Database
Ryogo Umetsu, Yuri Nishibata, Junko Abe, Yukiya Suzuki, Hideaki Hara, Hideko Nagasawa, Yasutomi Kinosada, Mitsuhiro Nakamura
YAKUGAKU ZASSHI.2014; 134(2): 299. CrossRef - Comparative efficacy of glimepiride and metformin in monotherapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Hongmei Zhu, Shuang Zhu, Xiuqian Zhang, Yang Guo, Yunzhen Shi, Zhimin Chen, Siu-wai Leung
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Study of the Effects of a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitor and Sulfonylurea on Glucose Variability in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes with Inadequate Glycemic Control on Metformin
Hun-Sung Kim, Jeong-Ah Shin, Seung-Hwan Lee, Eun-Sook Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Ho-Young Son, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2013; 15(10): 810. CrossRef - Glycemic Effectiveness of Metformin-Based Dual-Combination Therapies with Sulphonylurea, Pioglitazone, or DPP4-Inhibitor in Drug-Naïve Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Young Ki Lee, Sun Ok Song, Kwang Joon Kim, Yongin Cho, Younjeong Choi, Yujung Yun, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun-Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(6): 465. CrossRef - Metformin Based Dual-Combination Therapies in Drug Naïve Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Dong-Lim Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(6): 429. CrossRef - Assessing Relative Bioactivity of Chemical Substances Using Quantitative Molecular Network Topology Analysis
Anna Edberg, Daniel Soeria-Atmadja, Jonas Bergman Laurila, Fredrik Johansson, Mats G. Gustafsson, Ulf Hammerling
Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling.2012; 52(5): 1238. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of ginsam, a vinegar extract from Panax ginseng, in type 2 diabetic patients: Results of a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study
Ji Won Yoon, Seon Mee Kang, Jason L Vassy, Hayley Shin, Yun Hee Lee, Hwa Young Ahn, Sung Hee Choi, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2012; 3(3): 309. CrossRef - What Is the Optimal Monotherapy in Korean Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetic Patients?: The Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Monotherapy Study
Ji Hun Choi, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(1): 23. CrossRef - Predictive characteristics of patients achieving glycaemic control with insulin after sulfonylurea failure
Y.-H. Lee, B.-W. Lee, S. W. Chun, B. S. Cha, H. C. Lee
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2011; 65(10): 1076. CrossRef
- Ketogenic Diet Intervention on Metabolic and Psychiatric Health in Bipolar and Schizophrenia: A Pilot Trial
- Therapeutic Efficacy of Combined Therapy with Once Daily Insulin Glargine and Once Daily Glimepiride in Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Ji Young Park, Hyo Jeong Kim, Bo Kyung Koo, Hyun Jin Kim, Gang Seo Pak, Kyung Ah Han, Kyung Wan Min, Eung Jin Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(5):391-401. Published online September 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.5.391
- 2,262 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Once daily injection and 24 hour lasting glucose lowering effect of insulin glargine had recently changed a perception about the early insulin treatment of type 2 diabetic patients. This study was performed to investigate therapeutic efficacy of combined therapy with insulin glargine and glimepiride in Korean type 2 diabetic patients, who had received oral hypoglycemic agents (OHA) or conventional insulin therapy. METHODS: Total of 192 patients who needed to change the previous therapy because of uncontrolled diabetes or hypoglycemia were included and followed for about 6 months. Two groups of prior treatment modality were analyzed; OHA group (n = 54, 28.1%), conventional insulin therapy group in combination with or without OHA group (n = 138, 71.9%). The primary end point was changes in HbA1c according to baseline characteristics such as prior treatment modality, HbA1C, c-peptide, duration of diabetes mellitus, body mass index and prior used conventional insulin doses. Secondary end point was the dose conversion ratio of insulin glargine to prior used insulin in patients who had one or two insulin therapy. We also evaluated the level of the patients' satisfaction on the glucose lowering effects and the convenience for use of device. RESULTS: The differences of HbA1c according to prior treatment groups were -0.78 +/- 1.76 % in OHA group and 0.07 +/- 1.44 % in conventional insulin group with or without OHA group. The HbA1c improved better when baseline HbA1c was higher than 9%, c-peptide was higher than 0.6 ng/mL, duration of diabetes was shorter than 15 years, BMI was lower than 30 kg/m2 and prior conventional insulin dose was less than 30 IU. However, those effects were attenuated in subjects having duration of diabetes longer than 16 years, BMI higher than 30 kg/m2 and prior insulin dose more than 40 IU. Dose conversion ratio of the insulin glargine to prior insulin was 0.78 +/- 0.30 and showed a tendency to increase in patients who have prior insulin dose more than 40 IU. The scores of the patients' subjective satisfaction on insulin glargine were all high, irrespective of the changes of HbA1c. CONCLUSIONS: Once daily injection of insulin glargine and oral ingestion of glimepiride can be recommended as one of starting insulin regimen for patients who are not adequately controlled by OHA alone or as once daily regimen for whom treated with one or two conventional insulin therapy.
- Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Glimepiride/Metformin Fixed Combination Versus Free Combination in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial.
- Seung Hwan Lee, In Kyu Lee, Sei Hyun Baik, Dong Seop Choi, Kyong Soo Park, Ki Ho Song, Kwan Woo Lee, Bong Soo Cha, Chul Woo Ahn, Hyoung Woo Lee, Choon Hee Chung, Moon Suk Nam, Hong Sun Baek, Yong Ki Kim, Hyo Young Rhim, Ho Young Son
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(6):466-475. Published online November 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.6.466
- 2,305 View
- 34 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Failure to manage diabetes mellitus receiving monotherapy increases as the duration of the disease is protracted, and in many cases it becomes inevitable to introduce combined therapies. However, compliance of the patients tends to decrease. We conducted a clinical study to compare the efficacy and safety of preconstituted and fixed combination therapy of glimepiride plus metformin to those of free combination therapy. METHODS: Two hundred and thirteen patients with type 2 diabetes who had been diagnosed at least six months ago were randomly assigned either to a fixed group or a free group. The initial dosage was chosen according to the previous treatment history and then adjusted every two weeks following a predefined titration algorithm to meet the target mean fasting glucose levels (140 mg/dL). The medications were given for 16 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in HbA1c level from baseline to week 16. Various parameters were checked as secondary outcome measures and safety criteria. RESULTS: HbA1c level of the fixed group and the free group decreased by 1.09% and 1.08%, respectively. The 95% CI of the changes' difference between the two groups (-0.21%, +0.19%) was within the predefined equivalence interval (-0.5%, +0.5%). Secondary outcome measures (the changes of fasting and postprandial plasma glucose level, response rate and compliance) and safety criteria (frequency of hypoglycemia and adverse reactions) were similar between the two groups. CONCLUSION: Fixed combination of glimepiride/metformin is as effective and safe therapy as free combination in type 2 diabetes patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of glimepiride/metformin sustained release once daily vs. glimepiride/metformin twice daily in patients with type 2 diabetes
Y.-C. Hwang, M. Kang, C. W. Ahn, J. S. Park, S. H. Baik, D. J. Chung, H. C. Jang, K.-A. Kim, I.-K. Lee, K. W. Min, M. Nam, T. S. Park, S. M. Son, Y.-A. Sung, J.-T. Woo, K. S. Park, M.-K. Lee
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2013; 67(3): 236. CrossRef - Pharmacokinetic comparison of a new glimepiride 1-mg + metformin 500-mg combination tablet formulation and a glimepiride 2-mg + metformin 500-mg combination tablet formulation: A single-dose, randomized, open-label, two-period, two-way crossover study in
Bo-Hyung Kim, Kwang-Hee Shin, JaeWoo Kim, Kyoung Soo Lim, Kyu-pyo Kim, Jung-Ryul Kim, Joo-Youn Cho, Sang-Goo Shin, In-Jin Jang, Kyung-Sang Yu
Clinical Therapeutics.2009; 31(11): 2755. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of glimepiride/metformin sustained release once daily vs. glimepiride/metformin twice daily in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Efficacy and Safety of Glimepiride: A Novel Sulfonylurea Drug compared with Gliclazide in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: an Open , Randomized Comparative Multi - Center Clinical Study.
- Sung Kwan Hong, Ki Up Lee, Yeon Sang Oh, Ho Young Son, Kwang Won Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Dong Seop Choi, Ie Byung Park, Young Seol Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Hong Kyu Lee, Soon Hyun Shin
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(1):87-97. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,215 View
- 50 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Glimepiride (HOE490, Amaryl (R)) is a new, third generation sulfonylurea, which binds to a different protein of the sulfonylurea receptor than other sulfonylureas. Although there have been many studies proving the efficacy of glimepiride on Caucasian diabetic patients, only a few studies are available on Asian diabetic patients. We performed an open, randomized, comparative multicenter clinical trial to assess the efficacy and safety of glimepiride in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. METHOD: We recruited 262 type 2 cliabetic patients at 12 different university hospitals whose blood glucose was not controlled effectively with diet alone. Patients were randomized to 1~2mg glimepiride or 40~80mg gliclazide depending on the fasting blood glucose level. Doses were increased stepwise, up to 8mg for glimepiride (once-daily) and 320mg for gliclazide (>80 mg as dividedose) respectively, until metabolic control (fasting blood glucose < 7.9 mmol/L) or maximum dose was achieved. The quality of rnetabolic control was assessed by fasting blood glucose and HbA 1c as primary variables. Insulin, C-peptide and weight were monitored as secondary variables. Safety was assessed by obtaining patient history and laboratory values of relevant variables. RESULTS: Of the 262 patients randomized to treatment, 160(61%) patients completed the 18-week study. The rate of successful blood glucose control (3.9

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





