
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Genetics
- Association of Combined TCF7L2 and KCNQ1 Gene Polymorphisms with Diabetic Micro- and Macrovascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Rujikorn Rattanatham, Nongnuch Settasatian, Nantarat Komanasin, Upa Kukongviriyapan, Kittisak Sawanyawisuth, Phongsak Intharaphet, Vichai Senthong, Chatri Settasatian
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):578-593. Published online March 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0101
- 5,618 View
- 147 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Vascular complications are the major morbid consequences of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2), potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 1 (KCNQ1), and inwardly-rectifying potassium channel, subfamily J, member 11 gene (KCNJ11) are common T2DM susceptibility genes in various populations. However, the associations between polymorphisms in these genes and diabetic complications are controversial. This study aimed to investigate the effects of combined gene-polymorphisms within TCF7L2, KCNQ1, and KCNJ11 on vascular complications in Thai subjects with T2DM.
Methods
We conducted a case-control study comprising 960 T2DM patients and 740 non-diabetes controls. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in TCF7L2, KCNQ1, and KCNJ11 were genotyped and evaluated for their association with diabetic vascular complications.
Results
The gene variants TCF7L2 rs290487-T, KCNQ1 rs2237892-C, and KCNQ1 rs2237897-C were associated with increased risk of T2DM. TCF7L2 rs7903146-C, TCF7L2 rs290487-C, KCNQ1 rs2237892-T, and KCNQ1 rs2237897-T revealed an association with hypertension. The specific combination of risk-alleles that have effects on T2DM and hypertension, TCF7L2 rs7903146-C, KCNQ1 rs2237892-C, and KCNQ1 rs2237897-T, as genetic risk score (GRS), pronounced significant association with coronary artery disease (CAD), cumulative nephropathy and CAD, and cumulative microvascular and macrovascular complications (respective odds ratios [ORs] with 95% confidence interval [95% CI], comparing between GRS 2–3 and GRS 5–6, were 7.31 [2.03 to 26.35], 3.92 [1.75 to 8.76], and 2.33 [1.13 to 4.79]).
Conclusion
This study demonstrated, for the first time, the effect conferred by specific combined genetic variants in TCF7L2 and KCNQ1 on diabetic vascular complications, predominantly with nephropathy and CAD. Such a specific pattern of gene variant combination may implicate in the progression of T2DM and life-threatening vascular complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genetic Risk Scores Identify People at High Risk of Developing Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review
Aleena Shujaat Ali, Cecilia Pham, Grant Morahan, Elif Ilhan Ekinci
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(5): 1189. CrossRef - Saudi Community-Based Screening Study on Genetic Variants in β-Cell Dysfunction and Its Role in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Amal F. Alshammary, Malak Mohammed Al-Hakeem, Imran Ali Khan
Genes.2023; 14(4): 924. CrossRef - Association between KCNJ11 E23K polymorphism and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A global meta-analysis
Yaxuan Ren, Wenfei Zhu, Jikang Shi, Aiyu Shao, Yi Cheng, Yawen Liu
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(5): 108170. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef - Multiple Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Testing Improves the Prediction of Diabetic Retinopathy Risk with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yu-Ting Hsiao, Feng-Chih Shen, Shao-Wen Weng, Pei-Wen Wang, Yung-Jen Chen, Jong-Jer Lee
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(8): 689. CrossRef - Oxidative Stress Genes in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: Association with Diabetic Kidney Disease
Athanasios Roumeliotis, Stefanos Roumeliotis, Fotis Tsetsos, Marianthi Georgitsi, Panagiotis I. Georgianos, Aikaterini Stamou, Anna Vasilakou, Kalliopi Kotsa, Xanthippi Tsekmekidou, Peristera Paschou, Stylianos Panagoutsos, Vassilios Liakopoulos, Elena Az
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Analysis of the association of polymorphisms of genes markers functions of endothelium and vascular-plate hemostasis with development of diabetic foot syndrome
N. I. Troitskaya, K. G. Shapovalov, V. A. Mudrov
Acta Biomedica Scientifica.2021; 6(4): 18. CrossRef
- Genetic Risk Scores Identify People at High Risk of Developing Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review
- Pathophysiology
- Relationships between Islet-Specific Autoantibody Titers and the Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Yiqian Zhang, Tong Yin, Xinlei Wang, Rongping Zhang, Jie Yuan, Yi Sun, Jing Zong, Shiwei Cui, Yunjuan Gu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):404-416. Published online July 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0239
- 6,388 View
- 161 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Dysimmunity plays a key role in diabetes, especially type 1 diabetes mellitus. Islet-specific autoantibodies (ISAs) have been used as diagnostic markers for different phenotypic classifications of diabetes. This study was aimed to explore the relationships between ISA titers and the clinical characteristics of diabetic patients.
Methods A total of 509 diabetic patients admitted to Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism at the Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University were recruited. Anthropometric parameters, serum biochemical index, glycosylated hemoglobin, urinary microalbumin/creatinine ratio, ISAs, fat mass, and islet β-cell function were measured. Multiple linear regression analysis was performed to identify relationships between ISA titers and clinical characteristics.
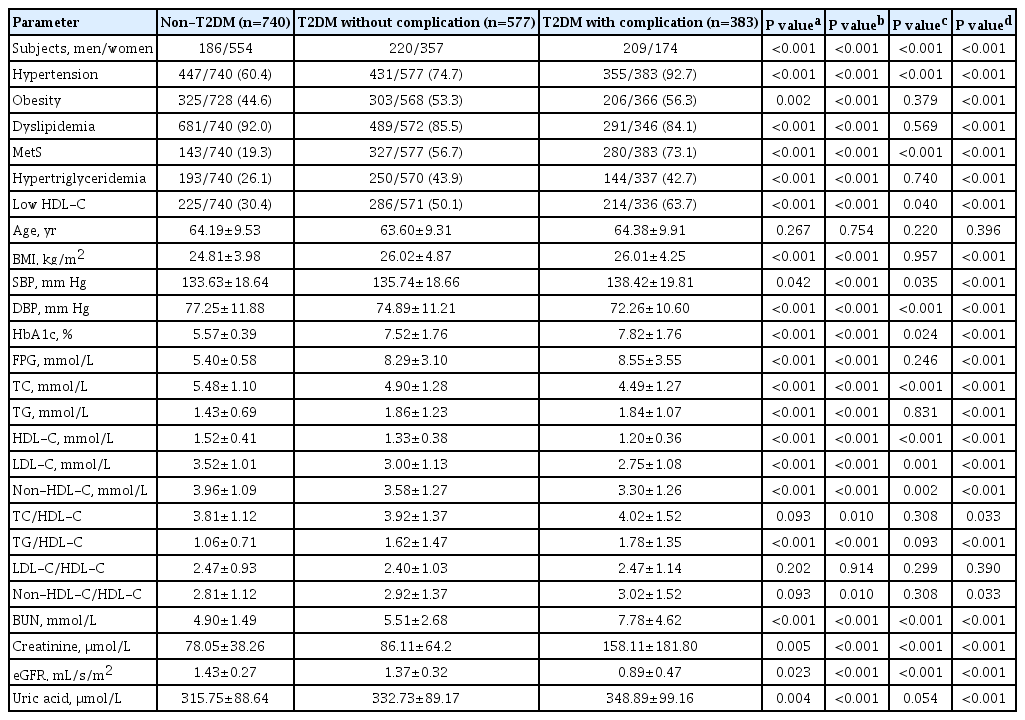
Results Compared with autoantibody negative group, blood pressure, weight, total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), visceral fat mass, fasting C-peptide (FCP), 120 minutes C-peptide (120minCP) and area under C-peptide curve (AUCCP) of patients in either autoantibody positive or glutamate decarboxylase antibody (GADA) positive group were lower. Body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, triglycerides (TGs), body fat mass of patients in either autoantibody positive group were lower than autoantibody negative group. GADA titer negatively correlated with TC, LDL-C, FCP, 120minCP, and AUCCP. The islet cell antibody and insulin autoantibody titers both negatively correlated with body weight, BMI, TC, TG, and LDL-C. After adjusting confounders, multiple linear regression analysis showed that LDL-C and FCP negatively correlated with GADA titer.
Conclusion Diabetic patients with a high ISA titer, especially GADA titer, have worse islet β-cell function, but less abdominal obesity and fewer features of the metabolic syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between β-Cell Autoantibodies and Their Combination with Anthropometric and Metabolic Components and Microvascular Complications in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults
Tomislav Bulum, Marijana Vučić Lovrenčić, Jadranka Knežević Ćuća, Martina Tomić, Sandra Vučković-Rebrina, Lea Duvnjak
Biomedicines.2023; 11(9): 2561. CrossRef - RETRACTED ARTICLE: MiRNA-27a mediates insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 cells through the PPARγ
Yangming Zhuang, Ming Li
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 477(4): 1107. CrossRef - Correlation between Insulin Resistance and Microalbuminuria Creatinine Ratio in Postmenopausal Women
Han Na, Rong Wang, Hai-Long Zheng, Xiao-Pan Chen, Lin-Yang Zheng, Faustino R. Perez-Lopez
International Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - The longitudinal loss of islet autoantibody responses from diagnosis of type 1 diabetes occurs progressively over follow-up and is determined by low autoantibody titres, early-onset, and genetic variants
C L Williams, R Fareed, G L M Mortimer, R J Aitken, I V Wilson, G George, K M Gillespie, A J K Williams, Chitrabhanu Ballav, Atanu Dutta, Michelle Russell-Taylor, Rachel Besser, James Bursell, Shanthi Chandran, Sejal Patel, Anne Smith, Manohara Kenchaiah,
Clinical and Experimental Immunology.2022; 210(2): 151. CrossRef
- Relationship between β-Cell Autoantibodies and Their Combination with Anthropometric and Metabolic Components and Microvascular Complications in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





