
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
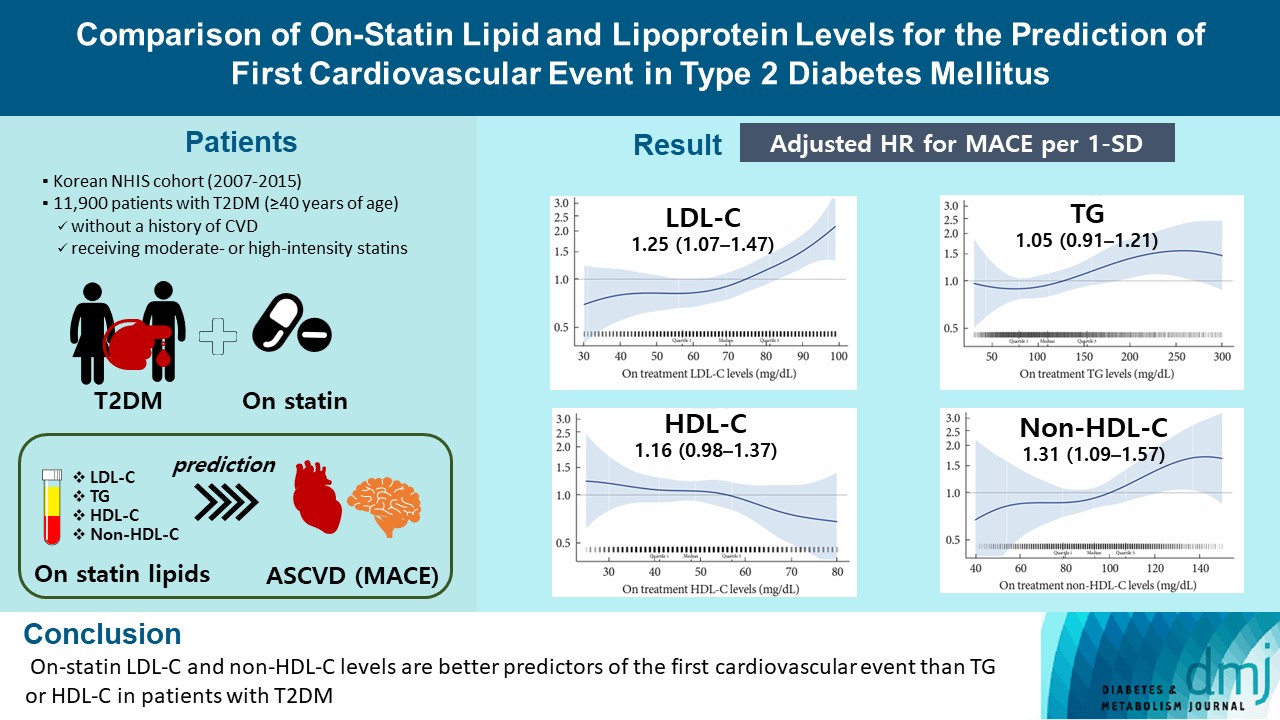
- Comparison of on-Statin Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels for the Prediction of First Cardiovascular Event in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):837-845. Published online August 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0217
- 1,470 View
- 175 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
A substantial cardiovascular disease risk remains even after optimal statin therapy. Comparative predictiveness of major lipid and lipoprotein parameters for cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who are treated with statins is not well documented.
Methods
From the Korean Nationwide Cohort, 11,900 patients with T2DM (≥40 years of age) without a history of cardiovascular disease and receiving moderate- or high-intensity statins were included. The primary outcome was the first occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) including ischemic heart disease, ischemic stroke, and cardiovascular death. The risk of MACE was estimated according to on-statin levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglyceride (TG), highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and non-HDL-C.
Results
MACE occurred in 712 patients during a median follow-up period of 37.9 months (interquartile range, 21.7 to 54.9). Among patients achieving LDL-C levels less than 100 mg/dL, the hazard ratios for MACE per 1-standard deviation change in ontreatment values were 1.25 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.07 to 1.47) for LDL-C, 1.31 (95% CI, 1.09 to 1.57) for non-HDL-C, 1.05 (95% CI, 0.91 to 1.21) for TG, and 1.16 (95% CI, 0.98 to 1.37) for HDL-C, after adjusting for potential confounders and lipid parameters mutually. The predictive ability of on-statin LDL-C and non-HDL-C for MACE was prominent in patients at high cardiovascular risk or those with LDL-C ≥70 mg/dL.
Conclusion
On-statin LDL-C and non-HDL-C levels are better predictors of the first cardiovascular event than TG or HDL-C in patients with T2DM.
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
- Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon, on Behalf of Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline, Korean Diabetes Association and Clinical Practice Guideline Committee, Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):1-9. Published online January 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0448
- 3,601 View
- 379 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
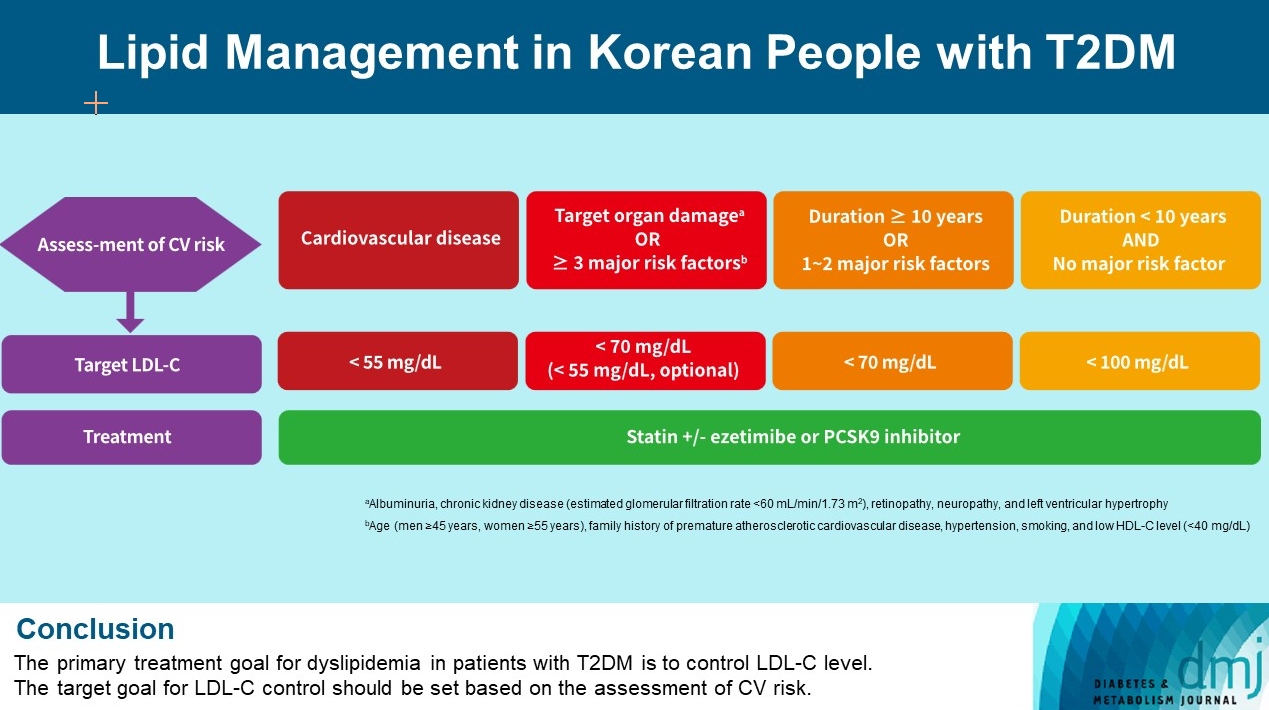
ePub - Dyslipidemia in patients with diabetes is an important treatment target as a modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Although the primary treatment goal for dyslipidemia is to control low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), achieving this goal remains suboptimal according to recent studies. It is important to set the target goal for LDL-C control based on an accurate risk assessment for CVD. Here, we summarize the latest evidence on lipid management in patients with diabetes and present a consensus of the Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis on the treatment goals of LDL-C according to the duration of diabetes, presence of CVD, target organ damage, or major cardiovascular risk factors. In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and CVD, an LDL-C goal of <55 mg/dL and a reduction in LDL-C level by 50% or more from the baseline is recommended. For the primary prevention of CVD in patients with T2DM with a duration of diabetes ≥10 years, major cardiovascular risk factors, or target organ damage, an LDL-C goal of <70 mg/dL is recommended. In patients with T2DM with a duration of diabetes <10 years and no major cardiovascular risk factors, an LDL-C goal of <100 mg/dL is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy.2024; 10(2): 118. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Statin Discontinuation in Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2024; 13(1): 41. CrossRef - Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 184. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 632. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(3): 237. CrossRef
- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
- Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):464-475. Published online March 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0088
- 6,978 View
- 347 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We evaluated the achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) according to up-to-date Korean Diabetes Association (KDA), European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS), and American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines.
Methods
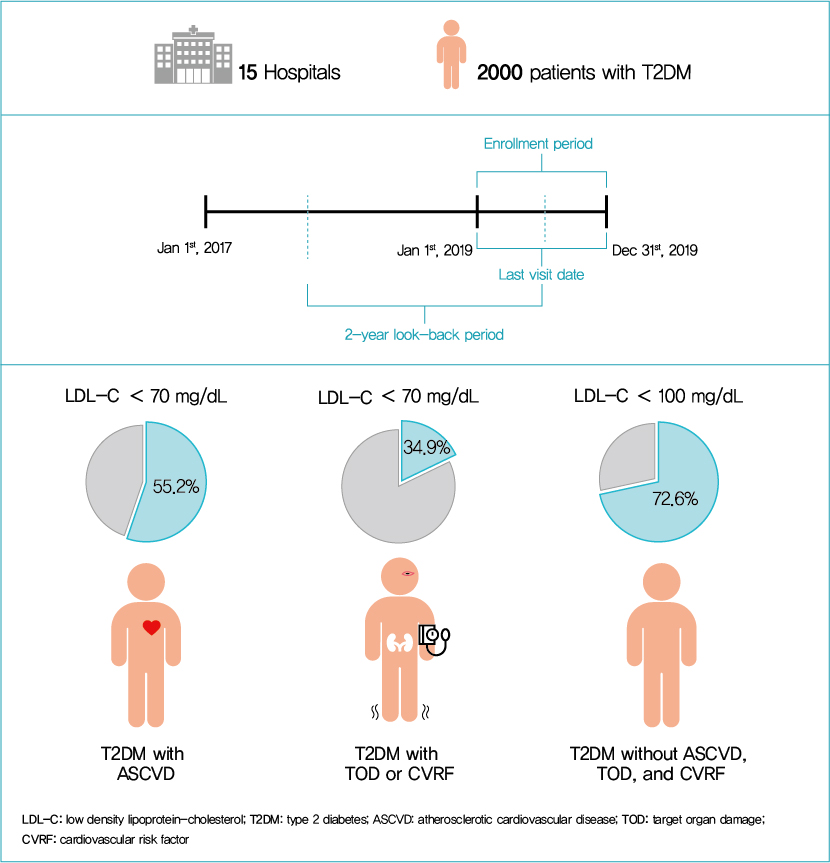
This retrospective cohort study collected electronic medical record data from patients with T2DM (≥20 years) managed by endocrinologists from 15 hospitals in Korea (January to December 2019). Patients were categorized according to guidelines to assess LDL-C target achievement. KDA (2019): Very High-I (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD]) <70 mg/dL; Very High-II (target organ damage [TOD], or cardiovascular risk factors [CVRFs]) <70 mg/dL; high (others) <100 mg/dL. ESC/EAS (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD): <55 mg/dL; Very High-II (TOD or ≥3-CVRF) <55 mg/dL; high (diabetes ≥10 years without TOD plus any CVRF) <70 mg/dL; moderate (diabetes <10 years without CVRF) <100 mg/dL. ADA (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD); Very High-II (age ≥40+ TOD, or any CVRF), for high intensity statin or statin combined with ezetimibe.
Results
Among 2,000 T2DM patients (mean age 62.6 years; male 55.9%; mean glycosylated hemoglobin 7.2%) ASCVD prevalence was 24.7%. Of 1,455 (72.8%) patients treated with statins, 73.9% received monotherapy. According to KDA guidelines, LDL-C target achievement rates were 55.2% in Very High-I and 34.9% in Very High-II patients. With ESC/EAS guidelines, target attainment rates were 26.6% in Very High-I, 15.7% in Very High-II, and 25.9% in high risk patients. Based on ADA guidelines, most patients (78.9%) were very-high risk; however, only 15.5% received high-intensity statin or combination therapy.
Conclusion
According to current dyslipidemia management guidelines, LDL-C goal achievement remains suboptimal in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Hidetaka Hamasaki
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299035. CrossRef - Distinct effects of rosuvastatin and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe on senescence markers of CD8+ T cells in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
Sang-Hyeon Ju, Joung Youl Lim, Minchul Song, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef
- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Mean and Variability of Lipid Measurements and Risk for Development of Subclinical Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction
- Jiyun Park, Mira Kang, Jiyeon Ahn, Min Young Kim, Min Sun Choi, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Jeong Hoon Yang, Sang-Man Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):286-296. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0080
- 5,692 View
- 196 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Subclinical left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is an emerging consequence of increased insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia is one of the few correctable risk factors of LVDD. This study evaluated the role of mean and visit-to-visit variability of lipid measurements in risk of LVDD in a healthy population.
Methods
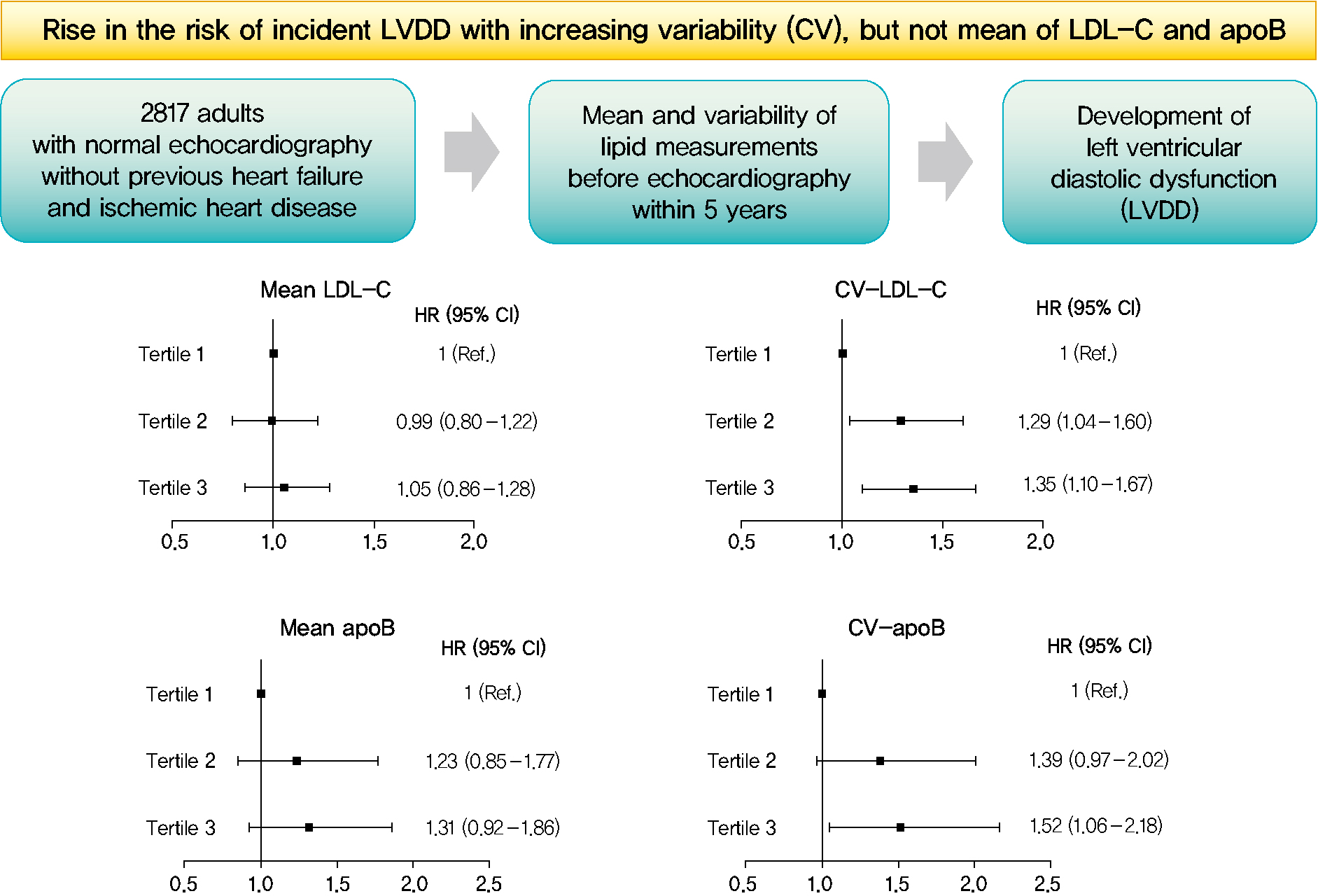
This was a 3.7-year (interquartile range, 2.1 to 4.9) longitudinal cohort study including 2,817 adults (median age 55 years) with left ventricular ejection fraction >50% who underwent an annual or biannual health screening between January 2008 and July 2016. The mean, standard deviation (SD), coefficient of variation (CV), variability independent of the mean (VIM), and average real variability of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), apolipoprotein B (apoB), non-HDL-C, and triglycerides were obtained from three to six measurements during the 5 years preceding the first echocardiogram.
Results
Among the 2,817 patients, 560 (19.9%) developed LVDD. The mean of no component of lipid measurements was associated with risk of LVDD. CV (hazard ratio [HR], 1.35; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.10 to 1.67), SD (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.57), and VIM (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.55) of LDL-C and all the variability parameters of apoB were significantly associated with development of LVDD. The association between CV-LDL and risk of LVDD did not have significant interaction with sex, increasing/decreasing trend at baseline, or use of stain and/or lipid-modifying agents.
Conclusion
The variability of LDL-C and apoB, rather than their mean, was associated with risk for LVDD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Separate and Joint Associations of Remnant Cholesterol Accumulation and Variability With Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Prospective Cohort Study
Jinqi Wang, Rui Jin, Xiaohan Jin, Zhiyuan Wu, Haiping Zhang, Ze Han, Zongkai Xu, Yueruijing Liu, Xiaoyu Zhao, Xiuhua Guo, Lixin Tao
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors: Causative Factor or Epiphenomenon?
Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 257. CrossRef
- Separate and Joint Associations of Remnant Cholesterol Accumulation and Variability With Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Prospective Cohort Study
- Statin Discontinuation after Achieving a Target Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level in Type 2 Diabetic Patients without Cardiovascular Disease: A Randomized Controlled Study
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, Yu-Bae Ahn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(1):64-73. Published online February 19, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.64
- 3,892 View
- 48 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study investigated the rate of relapse of dyslipidemia and the factors which could predict relapse following a short-term statin discontinuation after achieving a target low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level in type 2 diabetic patients without cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Methods Ninety-nine subjects on rosuvastatin treatment and whose LDL-C level was lower than 100 mg/dL were randomly assigned to discontinue or maintain statin treatment at a 2:1 ratio. The subjects were followed-up after 10 weeks. A relapse of dyslipidemia was defined as a reascent of LDL-C level to greater than 100 mg/dL.
Results The statin discontinuation group had a significant rate of relapse compared to the maintenance group (79% vs. 3%, respectively). Pretreatment and baseline lipid levels, their ratios, and hemoglobin A1c level were significantly different between the relapse and nonrelapse groups. The pretreatment and baseline lipid profiles and their ratios were independently associated with relapse. The pretreatment LDL-C level was the most useful parameter for predicting a relapse, with a cutoff of 123 mg/dL. During the follow-up period, no CVD event was noted.
Conclusion The relapse rate of dyslipidemia was high when statins were discontinued in type 2 diabetic patients without CVD. Statin discontinuation should be considered carefully based on the pretreatment lipid profiles of patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardiovascular Outcomes and Mortality Associated With Discontinuing Statins in Older Patients Receiving Polypharmacy
Federico Rea, Annalisa Biffi, Raffaella Ronco, Matteo Franchi, Simona Cammarota, Anna Citarella, Valeria Conti, Amelia Filippelli, Carmine Sellitto, Giovanni Corrao
JAMA Network Open.2021; 4(6): e2113186. CrossRef - Visit-to-visit variability of lipid measurements and the risk of myocardial infarction and all-cause mortality: A prospective cohort study
Xiaoxue Liu, Shouling Wu, Qiaofeng Song, Xizhu Wang
Atherosclerosis.2020; 312: 110. CrossRef - 2018 Guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia
Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyeon Chang Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Young Lee, Byung Jin Kim, Eun Mi Kim, YoonJu Song, Jeong Hyun Lim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Min Kyong Moon, Jin Oh Na, Kwang-Yeol Park, Mi Sun Oh, Sang Youb Han, Junghyun Noh, Kyung Hee Yi, Sang-Hak L
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2019; 34(4): 723. CrossRef - 2018 Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia in Korea
Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyeon Chang Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Young Lee, Byung Jin Kim, Eun Mi Kim, YoonJu Song, Jeong Hyun Lim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Min Kyong Moon, Jin Oh Na, Kwang-Yeol Park, Mi Sun Oh, Sang Youb Han, Junghyun Noh, Kyung Hee Yi, Sang-Hak L
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2019; 8(2): 78. CrossRef - Patterns of statin use and long‐term adherence and persistence among older adults with diabetes
Richard Ofori‐Asenso, Jenni Ilomäki, Mark Tacey, Ella Zomer, Andrea J. Curtis, J. Simon Bell, Sophia Zoungas, Danny Liew
Journal of Diabetes.2018; 10(9): 699. CrossRef - Effect of visit-to-visit LDL-, HDL-, and non-HDL-cholesterol variability on mortality and cardiovascular outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention
Eun Young Lee, Yeoree Yang, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Wook Sung Chung, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kiyuk Chang
Atherosclerosis.2018; 279: 1. CrossRef - Change in ALT levels after administration of HMG‐CoA reductase inhibitors to subjects with pretreatment levels three times the upper normal limit in clinical practice
Hyunah Kim, Hyeseon Lee, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, In Young Choi, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Hun‐Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Therapeutics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Orthodox religious fasting as a medical nutrition therapy for dyslipidemia: where do we stand and how far can we go?
Theocharis Koufakis, Spyridon N Karras, Pantelis Zebekakis, Kalliopi Kotsa
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2018; 72(4): 474. CrossRef - Phenotyping of Korean patients with better-than-expected efficacy of moderate-intensity statins using tensor factorization
Jingyun Choi, Yejin Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, In Young Choi, Hwanjo Yu, Katriina Aalto-Setala
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0197518. CrossRef - Impact of educational outreach intervention on enhancing health care providers' knowledge about statin therapy prescribing in Malaysian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mohamed Hassan Elnaem, Mohamad Haniki Nik Mohamed, Hasniza Zaman Huri, Shah M Azarisman
Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice.2018; 24(3): 521. CrossRef - Use of Moderate‐Intensity Statins for Low‐Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level above 190 mg/dL at Baseline in Koreans
Hun‐Sung Kim, Hyeseon Lee, Sue Hyun Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Sun Jung Baik, Hyunah Kim, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In‐Young Choi, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Ju Han Kim
Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology.2017; 121(4): 272. CrossRef - Cholesterol variability and the risk of mortality, myocardial infarction, and stroke: a nationwide population-based study
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
European Heart Journal.2017; 38(48): 3560. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of the cost-effectiveness of statins according to the baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in Korea
Y. J. Jeong, H. Kim, S. J. Baik, T. M. Kim, S. J. Yang, S.-H. Lee, J.-H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, I. Y. Choi, K.-H. Yoon, H.-S. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2017; 42(3): 292. CrossRef - The differences in the incidence of diabetes mellitus and prediabetes according to the type of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors prescribed in Korean patients
Tong Min Kim, Hyunah Kim, Yoo Jin Jeong, Sun Jung Baik, So Jung Yang, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, In Young Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety.2017; 26(10): 1156. CrossRef - Statin for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(1): 32. CrossRef
- Cardiovascular Outcomes and Mortality Associated With Discontinuing Statins in Older Patients Receiving Polypharmacy

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





