
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review
- Basic Research
- The Link between Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Sarcopenia: An Update Focusing on the Role of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4
- Min-Ji Kim, Ibotombi Singh Sinam, Zerwa Siddique, Jae-Han Jeon, In-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):153-163. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0305
- 4,947 View
- 372 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
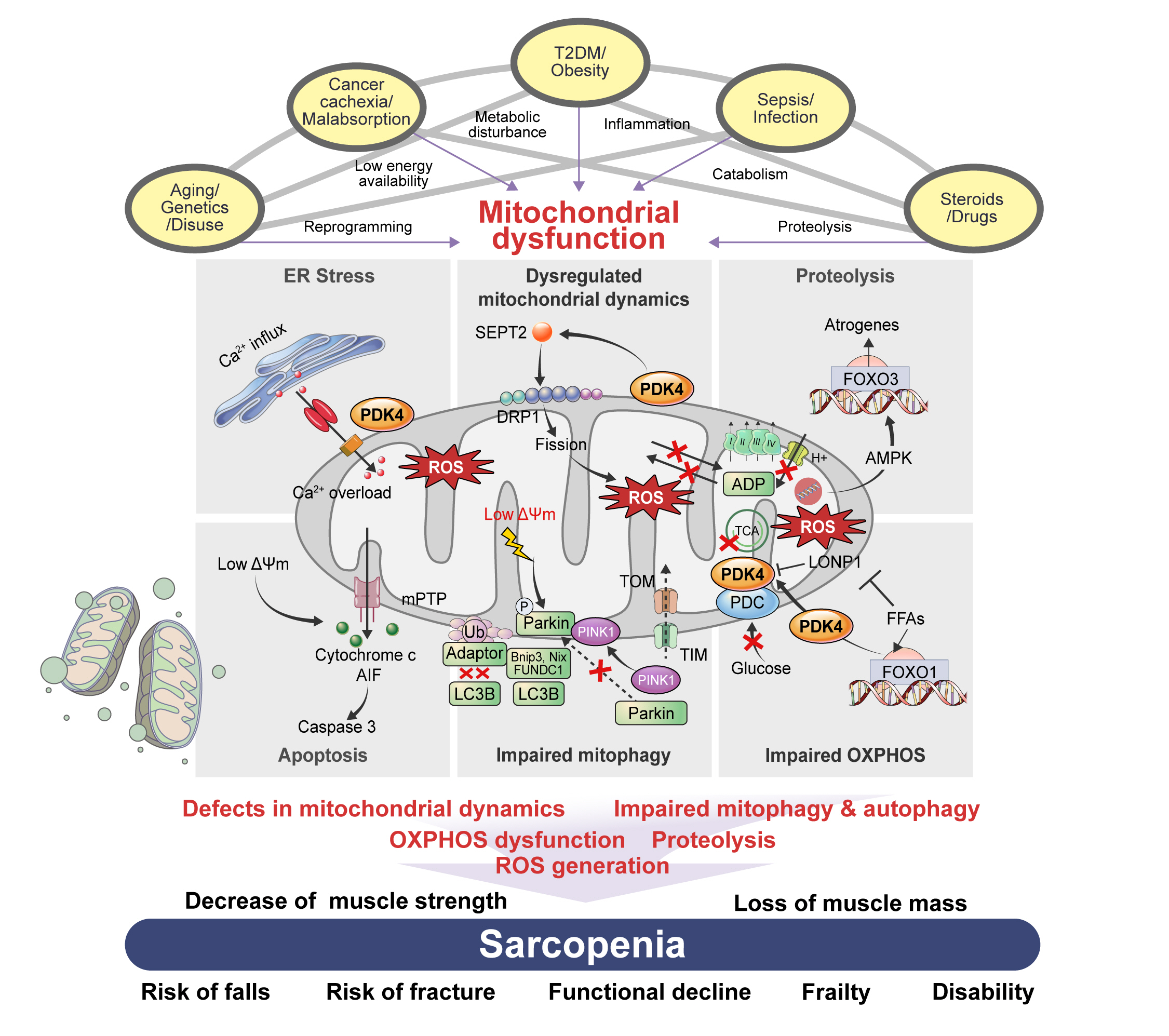
ePub - Sarcopenia, defined as a progressive loss of muscle mass and function, is typified by mitochondrial dysfunction and loss of mitochondrial resilience. Sarcopenia is associated not only with aging, but also with various metabolic diseases characterized by mitochondrial dyshomeostasis. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases (PDKs) are mitochondrial enzymes that inhibit the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which controls pyruvate entry into the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the subsequent adenosine triphosphate production required for normal cellular activities. PDK4 is upregulated in mitochondrial dysfunction-related metabolic diseases, especially pathologic muscle conditions associated with enhanced muscle proteolysis and aberrant myogenesis. Increases in PDK4 are associated with perturbation of mitochondria-associated membranes and mitochondrial quality control, which are emerging as a central mechanism in the pathogenesis of metabolic disease-associated muscle atrophy. Here, we review how mitochondrial dysfunction affects sarcopenia, focusing on the role of PDK4 in mitochondrial homeostasis. We discuss the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of PDK4 on mitochondrial dysfunction in sarcopenia and show that targeting mitochondria could be a therapeutic target for treating sarcopenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis, activatory effects, molecular docking and ADME studies as rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase activators of ureido phenyl substituted 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives
Mustafa Oğuzhan Kaya, Tuna Demirci, Ümit Çalışır, Oğuzhan Özdemir, Yeşim Kaya, Mustafa Arslan
Research on Chemical Intermediates.2024; 50(1): 437. CrossRef - Unraveling the causes of sarcopenia: Roles of neuromuscular junction impairment and mitochondrial dysfunction
Yanmei Miao, Leiyu Xie, Jiamei Song, Xing Cai, Jinghe Yang, Xinglong Ma, Shaolin Chen, Peng Xie
Physiological Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic clues to aging: exploring the role of circulating metabolites in frailty, sarcopenia and vascular aging related traits and diseases
Zonghao Qian, Yuzhen Huang, Yucong Zhang, Ni Yang, Ziwei Fang, Cuntai Zhang, Le Zhang
Frontiers in Genetics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4 Protects Cardiomyocytes from lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mitochondrial Damage by Reducing Lactate Accumulation
Tangtian Chen, Qiumin Xie, Bin Tan, Qin Yi, Han Xiang, Rui Wang, Qin Zhou, Bolin He, Jie Tian, Jing Zhu, Hao Xu
Inflammation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of resistance training plus enriched probiotic supplement on sestrin2, oxidative stress, and mitophagy markers in elderly male Wistar rats
Majid Mohabbat, Hamid Arazi
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between single-muscle evaluation and cross-sectional area muscle evaluation for predicting the prognosis in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study
Hirotaka Takayama, Takuya Yoshimura, Hajime Suzuki, Yuka Hirano, Masahiro Tezuka, Takayuki Ishida, Kiyohide Ishihata, Marie Amitani, Haruka Amitani, Yasunori Nakamura, Yasushi Imamura, Akio Inui, Norifumi Nakamura
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Neuroprotective Effects and Therapeutic Potential of Dichloroacetate: Targeting Metabolic Disorders in Nervous System Diseases
Yue Zhang, Meiyan Sun, Hongxiang Zhao, Zhengyan Wang, Yanan Shi, Jianxin Dong, Kaifang Wang, Xi Wang, Xingyue Li, Haiyan Qi, Xiaoyong Zhao
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2023; Volume 18: 7559. CrossRef
- Synthesis, activatory effects, molecular docking and ADME studies as rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase activators of ureido phenyl substituted 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives
Original Article
- Complication
- Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis
- Tianqi Zhang, Marnie Shaw, Nicolas Cherbuin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):781-802. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0189
- 6,538 View
- 298 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is known to be associated with cognitive decline and brain structural changes. This study systematically reviews and estimates human brain volumetric differences and atrophy associated with T2DM.
Methods
PubMed, PsycInfo and Cochrane Library were searched for brain imaging studies reporting on brain volume differences between individuals with T2DM and healthy controls. Data were examined using meta-analysis, and association between age, sex, diabetes characteristics and brain volumes were tested using meta-regression.
Results
A total of 14,605 entries were identified; after title, abstract and full-text screening applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, 64 studies were included and 42 studies with compatible data contributed to the meta-analysis (n=31,630; mean age 71.0 years; 44.4% male; 26,942 control; 4,688 diabetes). Individuals with T2DM had significantly smaller total brain volume, total grey matter volume, total white matter volume and hippocampal volume (approximately 1% to 4%); meta-analyses of smaller samples focusing on other brain regions and brain atrophy rate in longitudinal investigations also indicated smaller brain volumes and greater brain atrophy associated with T2DM. Meta-regression suggests that diabetes-related brain volume differences start occurring in early adulthood, decreases with age and increases with diabetes duration.
Conclusion
T2DM is associated with smaller total and regional brain volume and greater atrophy over time. These effects are substantial and highlight an urgent need to develop interventions to reduce the risk of T2DM for brain health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes, antidiabetic medications and risk of dementia: A systematic umbrella review and meta‐analysis
Alvin Kuate Defo, Veselko Bakula, Alessandro Pisaturo, Christopher Labos, Simon S. Wing, Stella S. Daskalopoulou
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 441. CrossRef - Cognitive deficits among people with schizophrenia and prediabetes or diabetes
Alexander Panickacheril John, Thynn Mya, Darren Haywood
Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica.2024; 149(1): 65. CrossRef - The association of glucose metabolism measures and diabetes status with Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers of amyloid and tau: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Veerle van Gils, Marianna Rizzo, Jade Côté, Wolfgang Viechtbauer, Giuseppe Fanelli, Jordi Salas-Salvadó, Theresa Wimberley, Mònica Bulló, Fernando Fernandez-Aranda, Søren Dalsgaard, Pieter Jelle Visser, Willemijn J. Jansen, Stephanie J.B. Vos
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2024; 159: 105604. CrossRef - ECHDC3 Variant Regulates the Right Hippocampal Microstructural Integrity and Verbal Memory in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Qiyu Zhao, Xin Du, Feng Liu, Yang Zhang, Wen Qin, Quan Zhang
Neuroscience.2024; 538: 30. CrossRef - The hemodynamic response function as a type 2 diabetes biomarker: a data-driven approach
Pedro Guimarães, Pedro Serranho, João V. Duarte, Joana Crisóstomo, Carolina Moreno, Leonor Gomes, Rui Bernardes, Miguel Castelo-Branco
Frontiers in Neuroinformatics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - What have clinical trials taught us about brain health?
Keon-Joo Lee, Hee-Joon Bae
Cerebral Circulation - Cognition and Behavior.2024; 6: 100199. CrossRef - Understanding the relationship between type-2 diabetes, MRI markers of neurodegeneration and small vessel disease, and dementia risk: a mediation analysis
Leslie Grasset, Eric Frison, Catherine Helmer, Gwénaëlle Catheline, Geneviève Chêne, Carole Dufouil
European Journal of Epidemiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Vulnerability of the Hippocampus to Insults: Links to Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction
Terry L. Davidson, Richard J. Stevenson
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 1991. CrossRef - The gut microbiota‐astrocyte axis: Implications for type 2 diabetic cognitive dysfunction
Zi‐Han Li, Ya‐Yi Jiang, Cai‐Yi Long, Qian Peng, Ren‐Song Yue
CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics.2023; 29(S1): 59. CrossRef - NHANES 2011–2014 Reveals Decreased Cognitive Performance in U.S. Older Adults with Metabolic Syndrome Combinations
Edgar Díaz-Camargo, Juan Hernández-Lalinde, María Sánchez-Rubio, Yudy Chaparro-Suárez, Liseth Álvarez-Caicedo, Alexandra Fierro-Zarate, Marbel Gravini-Donado, Henry García-Pacheco, Joselyn Rojas-Quintero, Valmore Bermúdez
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(7): 5257. CrossRef - People with Diabetes Have Poorer Self-Rated Health (SRH) and Diabetes Moderates the Association between Age and SRH
Weixi Kang, Antonio Malvaso
Diseases.2023; 11(2): 73. CrossRef - Cognitive dysfunction in diabetes: abnormal glucose metabolic regulation in the brain
Shan Zhang, Yueying Zhang, Zhige Wen, YaNan Yang, Tianjie Bu, Xiangwei Bu, Qing Ni
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The psychological basis of hunger and its dysfunctions
Richard J Stevenson
Nutrition Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of Glucose Metabolism Status with Brain Macrostructure and Microstructure: Findings from the UK Biobank
Ruyi Li, Tingting Geng, Lin Li, Qi Lu, Rui Li, Xue Chen, Yunjing Ou, Sen Liu, Xiaoyu Lin, Qingying Tian, Zixin Qiu, Kai Zhu, Ziyue Tang, Kun Yang, An Pan, Gang Liu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e234. CrossRef - Association Between Frequency of Social Contact and Brain Atrophy in Community-Dwelling Older People Without Dementia
Naoki Hirabayashi, Takanori Honda, Jun Hata, Yoshihiko Furuta, Mao Shibata, Tomoyuki Ohara, Yasuko Tatewaki, Yasuyuki Taki, Shigeyuki Nakaji, Tetsuya Maeda, Kenjiro Ono, Masaru Mimura, Kenji Nakashima, Jun-ichi Iga, Minoru Takebayashi, Toshiharu Ninomiya,
Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A diagnosis model for brain atrophy using deep learning and MRI of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Saba Raoof Syed, Saleem Durai M. A.
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes: a tipping point in neurodegenerative diseases
Jose A. Santiago, Mridula Karthikeyan, Madison Lackey, Diana Villavicencio, Judith A. Potashkin
Trends in Molecular Medicine.2023; 29(12): 1029. CrossRef - Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:781-802)
Tianqi Zhang, Marnie Shaw, Nicolas Cherbuin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 815. CrossRef - Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:781-802)
Se Hee Min
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 813. CrossRef - MORPHOFUNCTIONAL CHANGES OF THE BRAIN IN DIABETES MELLITUS
A. V. Smirnov, A. I Bisinbekova, T. I Faibisovich
Journal of Volgograd State Medical University.2022; 19(3): 3. CrossRef
- Diabetes, antidiabetic medications and risk of dementia: A systematic umbrella review and meta‐analysis
Case Report
- A Case of Failure in Insulin Pump Treatment due to Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Atrophy and Lipohypertrophied Nodules.
- Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Gwanpyo Koh, Seungjoon Oh, Jeong taek Woo, Sung Woon Kim, Jin Woo Kim, Young Seol Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2004;28(6):547-553. Published online December 1, 2004
- 960 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The insulin pump is an effective glycemic control device those function is analogous to the physiologic regulation of insulin in vivo. When sufficient patient education and proper selection of patients is done, the insulin pump is one of the most effective treatment modalities for diabetic patients. However, various side effects and complications might occur during its application. We report here on an unusual case of diabetic ketoacidosis that was caused by acute inflammatory colitis and insulin pump malfunction. Peculiarly, the cause of pump malfunction was far removed from its mechanical problem. We concluded that the cause of the insulin pump malfunction was due to abdominal subcutaneous fat atrophy and the lipohypertrophied nodules of the patient that developed due to the prolonged usage of the insulin pump.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





