
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse > Previous issues
- Genetics
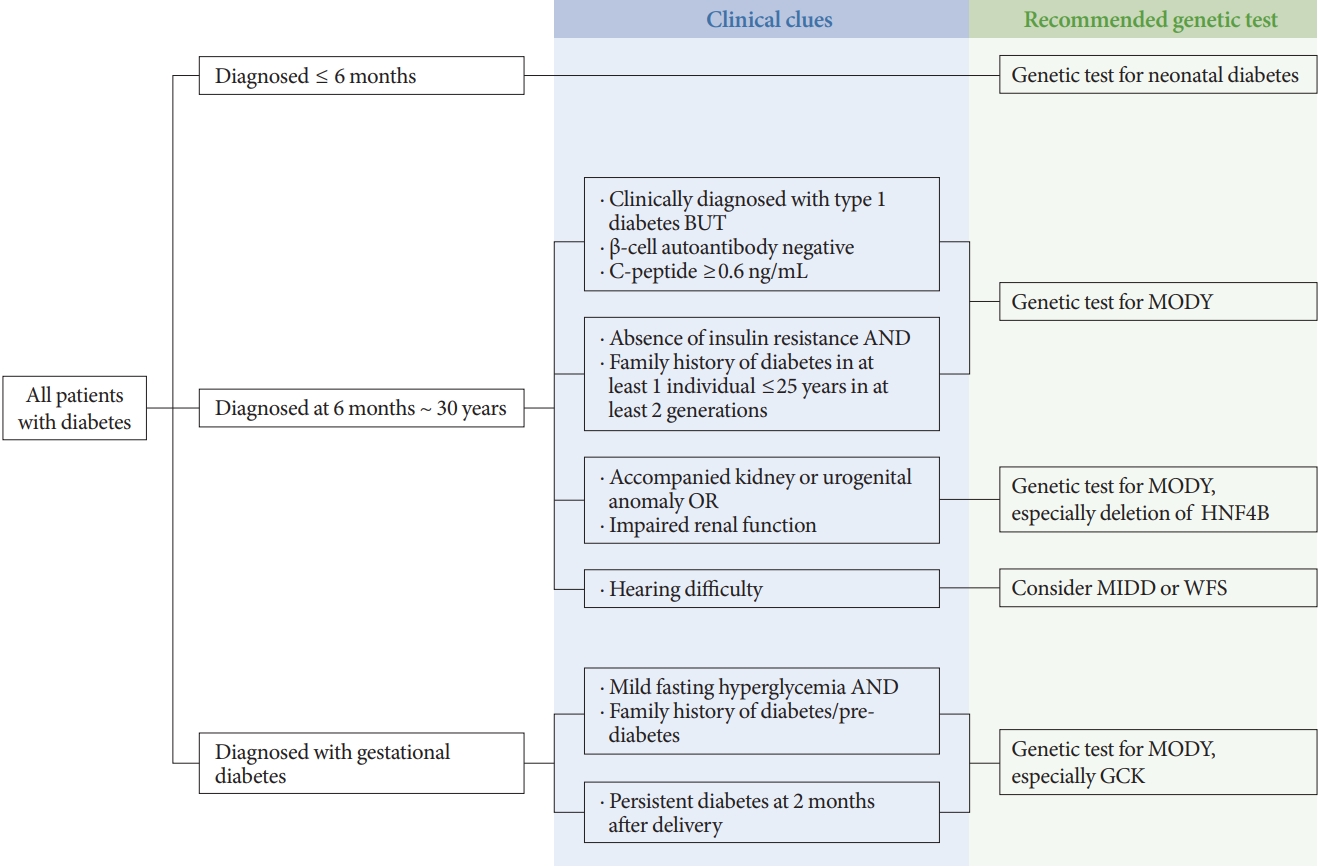
- Update on Monogenic Diabetes in Korea
- Ye Seul Yang, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):627-639. Published online October 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0214
- 6,601 View
- 242 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Monogenic diabetes, including maturity-onset diabetes of the young, neonatal diabetes, and other rare forms of diabetes, results from a single gene mutation. It has been estimated to represent around 1% to 6% of all diabetes. With the advances in genome sequencing technology, it is possible to diagnose more monogenic diabetes cases than ever before. In Korea, 11 studies have identified several monogenic diabetes cases, using Sanger sequencing and whole exome sequencing since 2001. The recent largest study, using targeted exome panel sequencing, found a molecular diagnosis rate of 21.1% for monogenic diabetes in clinically suspected patients. Mutations in glucokinase (GCK), hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α (HNF1A), and HNF4A were most commonly found. Genetic diagnosis of monogenic diabetes is important as it determines the therapeutic approach required for patients and helps to identify affected family members. However, there are still many challenges, which include a lack of simple clinical criterion for selecting patients for genetic testing, difficulties in interpreting the genetic test results, and high costs for genetic testing. In this review, we will discuss the latest updates on monogenic diabetes in Korea, and suggest an algorithm to screen patients for genetic testing. The genetic tests and non-genetic markers for accurate diagnosis of monogenic diabetes will be also reviewed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeted gene panel analysis of Japanese patients with maturity‐onset diabetes of the young‐like diabetes mellitus: Roles of inactivating variants in the ABCC8 and insulin resistance genes
Tohru Yorifuji, Yoh Watanabe, Kana Kitayama, Yuki Yamada, Shinji Higuchi, Jun Mori, Masaru Kato, Toru Takahashi, Tokuko Okuda, Takane Aoyama
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(3): 387. CrossRef - Efficacy of acupuncture on cardiovascular complications in patients with diabetes mellitus in Korea: A nationwide retrospective cohort
Hyejin Jung, Tiana Won, Ga-Yeon Kim, Jowon Jang, Sujung Yeo, Sabina Lim
Journal of Integrative Medicine.2023; 21(2): 176. CrossRef - Identification of rare variants in candidate genes associated with monogenic diabetes in polish mody-x patients
Paulina Jakiel, K. Gadzalska, E. Juścińska, M. Gorządek, T. Płoszaj, S. Skoczylas, M. Borowiec, A. Zmysłowska
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic perspectives on childhood monogenic diabetes: Diagnosis, management, and future directions
Hong-Yan Sun, Xiao-Yan Lin
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(12): 1738. CrossRef - Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)
Seung Shin Park, Soo Heon Kwak
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(3): 157. CrossRef - The Genetic Spectrum of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) in Qatar, a Population-Based Study
Asma A. Elashi, Salman M. Toor, Ilhame Diboun, Yasser Al-Sarraj, Shahrad Taheri, Karsten Suhre, Abdul Badi Abou-Samra, Omar M. E. Albagha
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 24(1): 130. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 277. CrossRef - Sequencing Cell-free Fetal DNA in Pregnant Women With GCK-MODY
Soo Heon Kwak, Camille E Powe, Se Song Jang, Michael J Callahan, Sarah N Bernstein, Seung Mi Lee, Sunyoung Kang, Kyong Soo Park, Hak C Jang, Jose C Florez, Jong-Il Kim, Jong Hee Chae
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(9): 2678. CrossRef - Muscle strength, an independent determinant of glycemic control in older adults with long-standing type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study
Bo Kyung Koo, Seoil Moon, Min Kyong Moon
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A rare, likely pathogenic GCK variant related to maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 2: A case report
Min-Kyung So, Jungwon Huh, Hae Soon Kim
Journal of Genetic Medicine.2021; 18(2): 132. CrossRef
- Targeted gene panel analysis of Japanese patients with maturity‐onset diabetes of the young‐like diabetes mellitus: Roles of inactivating variants in the ABCC8 and insulin resistance genes
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
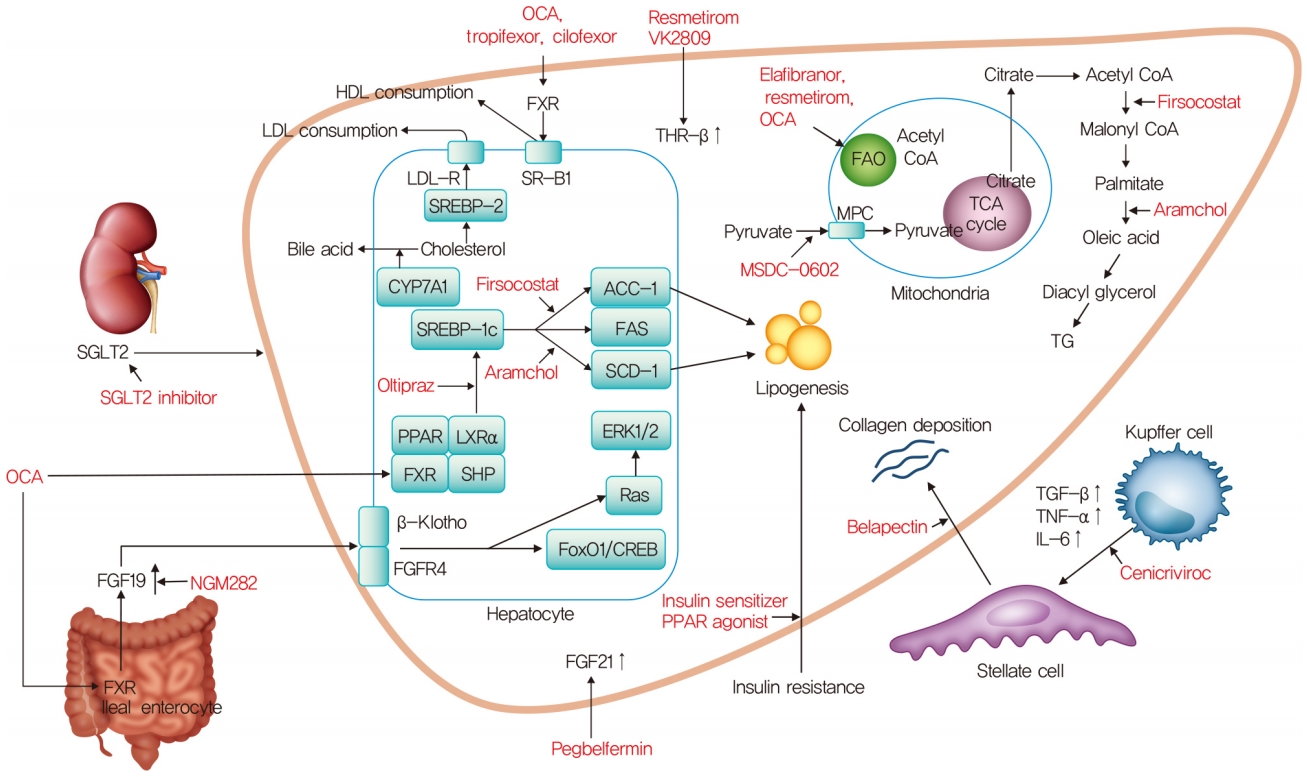
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Drug Revolution Is Coming
- Soung Won Jeong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):640-657. Published online October 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0115
- 11,910 View
- 547 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The worldwide prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is around 25%, and that of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) ranges from 1.5% to 6.45%. Patients with NASH, especially those with fibrosis, are at higher risk for adverse outcomes such as cirrhosis and liver-related mortality. Although vitamin E, pioglitazone, and liraglutide improved liver histology in randomized trials, there are currently no Food and Drug Administration-approved drugs for NASH. Five pharmacologic agents—obeticholic acid, elafibranor, cenicriviroc, resmetirom, and aramchol—are being evaluated in large, histology-based phase 3 trials. Within 2 to 4 years, new and effective drugs for the treatment of NASH are expected. Additionally, many phase 2 trials are ongoing for various agents. Based on the results of phase 2 and 3 trials, combination treatments are also being investigated. Future treatment strategies will comprise drug combinations and precision medicine based on the different phenotypes of NASH and treatment response of the individual patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Progresses on Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Therapeutic Modalities,
and Management of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
Mahdi Barazesh, Sajad Jalili, Morteza Akhzari, Fouzieyeh Faraji, Ebrahim Khorramdin
Current Drug Therapy.2024; 19(1): 20. CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 220. CrossRef - Increased expression of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and O-GlcNAcylation in hepatocytes drives non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hye Jin Chun, Eun Ran Kim, Minyoung Lee, Da Hyun Choi, Soo Hyun Kim, Eugene Shin, Jin-Hong Kim, Jin Won Cho, Dai Hoon Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Metabolism.2023; 145: 155612. CrossRef - Effect of bariatric surgery on NAFLD/NASH: a single-centre observational prospective cohort study
Willy B Theel, Bianca M Boxma-de Klerk, Femme Dirksmeier-Harinck, Elisabeth FC van Rossum, Danny A Kanhai, Jan A Apers, Bas M van Dalen, Robert J De Knegt, Bojou Neecke, Ellen M van der Zwan, Diederick E Grobbee, Thomas Hankemeier, Janneke Wiebolt, Manuel
BMJ Open.2023; 13(7): e070431. CrossRef - Ameliorative role of bioactive phytoconstituents targeting obesity associated NAFLD by modulation of inflammation and lipogenesis pathways: a comprehensive review
Pervej Alom Barbhuiya, Saikat Sen, Manash Pratim Pathak
Phytochemistry Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Inflammatory and fibrotic mechanisms in NAFLD—Implications for new treatment strategies
Youngmin A. Lee, Scott L. Friedman
Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 291(1): 11. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of evogliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: A multicentre, double‐blind, randomized, comparative trial
Eugene Han, Ji Hye Huh, Eun Y. Lee, Ji C. Bae, Sung W. Chun, Sung H. Yu, Soo H. Kwak, Kyong S. Park, Byung‐Wan Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(4): 752. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index is a simple and easy‐to‐calculate marker associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung‐Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2022; 30(6): 1279. CrossRef - Thyroid diseases and new approaches for their treatment
E. A. Fokina, A. O. Shpakov
The Siberian Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2022; 37(3): 90. CrossRef - Gemigliptin Alleviates Succinate-Induced Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation by Ameliorating Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Giang Nguyen, So Young Park, Dinh Vinh Do, Dae-Hee Choi, Eun-Hee Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 918. CrossRef - Inhibition of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 relieves fibrosis through depolarizing of hepatic stellate cell in NASH
Su-Yeon Lee, Sanghwa Kim, Inhee Choi, Yeonhwa Song, Namjeong Kim, Hyung Chul Ryu, Jee Woong Lim, Hyo Jin Kang, Jason Kim, Haeng Ran Seo
Cell Death & Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Lessons on Drug Development: A Literature Review of Challenges Faced in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Clinical Trials
Joel Yeh Siang Chen, Damien Chua, Carissa Odelia Lim, Wan Xi Ho, Nguan Soon Tan
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 24(1): 158. CrossRef - Metabolic Spectrum of Liver Failure in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: From NAFLD to NASH to HCC
Hyunmi Kim, Da Som Lee, Tae Hyeon An, Hyun-Ju Park, Won Kon Kim, Kwang-Hee Bae, Kyoung-Jin Oh
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4495. CrossRef - Allopurinol ameliorates high fructose diet induced hepatic steatosis in diabetic rats through modulation of lipid metabolism, inflammation, and ER stress pathway
In-Jin Cho, Da-Hee Oh, Jin Yoo, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho-Yeon Chung, Soung Won Jeong, Ju-Young Moon, Sang-Ho Lee, Sung-Jig Lim, In-Kyung Jeong
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of intragastric balloon placement in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
João Remí de Freitas Júnior, Igor Braga Ribeiro, Diogo Turiani Hourneaux de Moura, Vitor Massaro Takamatsu Sagae, Gabriel Mayo Vieira de Souza, Guilherme Henrique Peixoto de Oliveira, Sergio A Sánchez-Luna, Thiago Ferreira de Souza, Eduardo Turiani Hourne
World Journal of Hepatology.2021; 13(7): 815. CrossRef - The New Therapeutic Approaches in the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Branka Filipovic, Snezana Lukic, Dragana Mijac, Marija Marjanovic-Haljilji, Marko Vojnovic, Jelena Bogdanovic, Tijana Glisic, Natasa Filipovic, Jamal Al Kiswani, Aleksandra Djokovic, Suncica Kapor, Slobodan Kapor, Zoran Bukumiric, Ana Starcevic
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(24): 13219. CrossRef
- Recent Progresses on Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Therapeutic Modalities,
and Management of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
- Basic Research
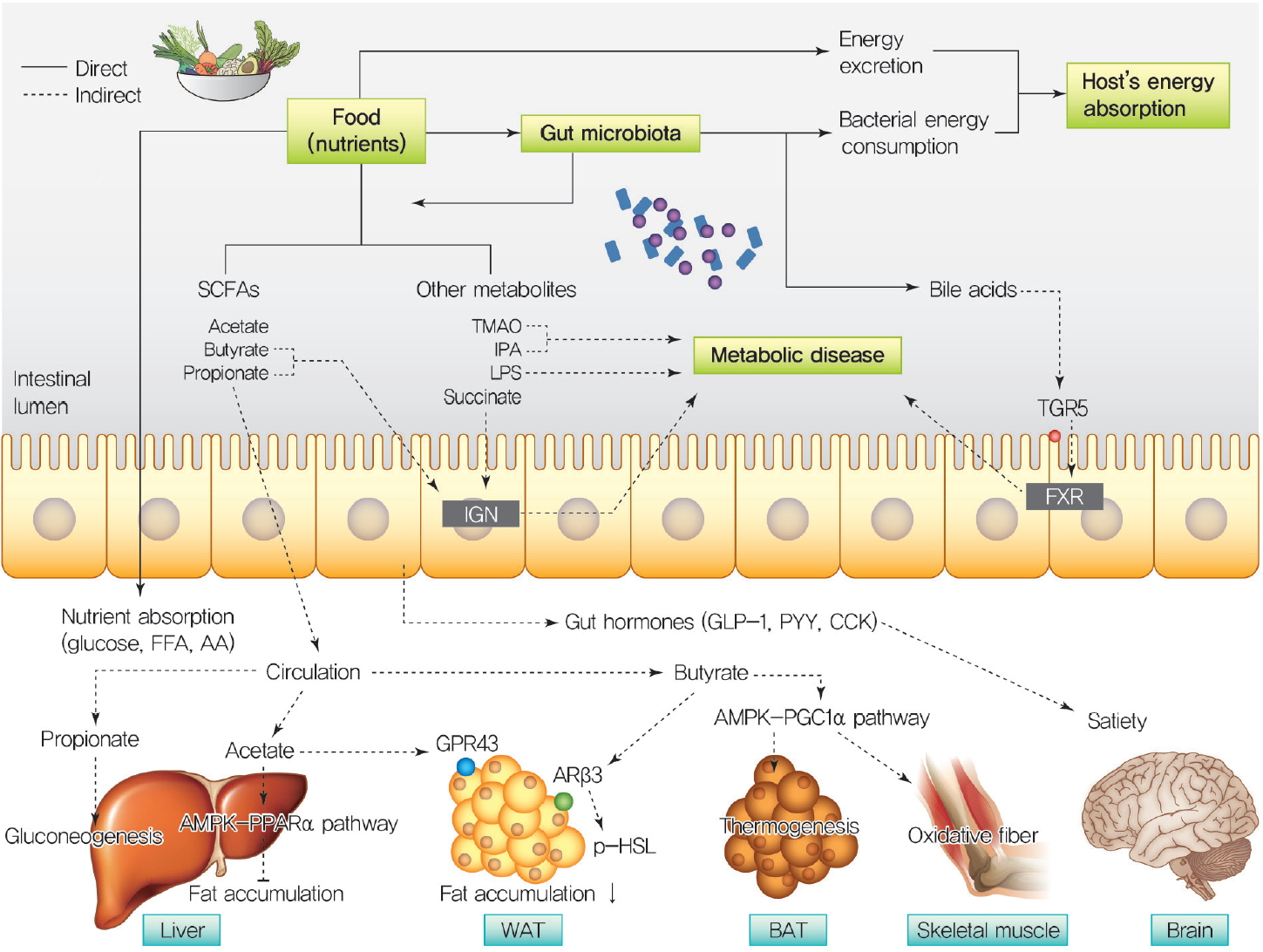
- Revisiting the Bacterial Phylum Composition in Metabolic Diseases Focused on Host Energy Metabolism
- Yeonmi Lee, Hui-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):658-667. Published online July 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0220
- 9,007 View
- 131 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Over a hundred billion bacteria are found in human intestines. This has emerged as an environmental factor in metabolic diseases, such as obesity and related diseases. The majority of these bacteria belong to two dominant phyla,
Bacteroidetes andFirmicutes . Since the ratio ofFirmicutes toBacteroidetes increases in people with obesity and in various animal models, it has been assumed that phylum composition causes the increase in occurrence of metabolic diseases over the past decade. However, this assumption has been challenged by recent studies that have found even an opposite association of phylum composition within metabolic diseases. Moreover, the gut microbiota affects host energy metabolism in various ways including production of metabolites and interaction with host intestinal cells to regulate signaling pathways that affect energy metabolism. However, the direct effect of gut bacteria on host energy intake, such as energy consumption by the bacteria itself and its effects on intestinal energy absorption, has been underestimated. This review aims to discuss whether increased ratio ofFirmicutes toBacteroidetes is associated with the development of metabolic diseases, and whether energy competition between the bacteria and host is a missing part of the mechanism linking gut microbiota to metabolic diseases.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Behavior, intestinal health, and growth of small sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus in different color morphs
Peng Ding, Yushi Yu, Zihe Zhao, Xiang Li, Xiajing Wang, Huiyan Wang, Xiyuan Huang, Jun Ding, Chong Zhao
Marine Environmental Research.2024; 193: 106300. CrossRef - Traditional Chinese Medicine formula Dai-Zong-Fang alleviating hepatic steatosis in db/db mice via gut microbiota modulation
Li-Wei Zhang, Li-Li Zhu, Xiao-Yun Zhu, Shou-Qiang Fu, Xi-Ming Liu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Repeated inoculation with rumen fluid accelerates the rumen bacterial transition with no benefit on production performance in postpartum Holstein dairy cows
Fanlin Kong, Feiran Wang, Yijia Zhang, Shuo Wang, Wei Wang, Shengli Li
Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of oncogenic signatures in the inflammatory colon of C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet
Huawei Zeng, Bryan D. Safratowich, Wen-Hsing Cheng, Michael R. Bukowski
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2023; 111: 109188. CrossRef - Evaluation of the gut microbiome alterations in healthy rats after dietary exposure to different synthetic ZnO nanoparticles
Xinyi Zhu, Henghui Li, Liuzhu Zhou, Huijun Jiang, Minghui Ji, Jin Chen
Life Sciences.2023; 312: 121250. CrossRef - Microplastic-induced gut microbiota and serum metabolic disruption in Sprague-Dawley rats
Nan Zhao, Meirong Zhao, Hangbiao Jin
Environmental Pollution.2023; 320: 121071. CrossRef - Effects of neutral polysaccharide from Platycodon grandiflorum on high-fat diet-induced obesity via the regulation of gut microbiota and metabolites
Jing Song, Qin liu, Mengqi Hao, Xiaohu Zhai, Juan Chen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolite interactions between host and microbiota during health and disease: Which feeds the other?
Yan Zhang, Rui Chen, DuoDuo Zhang, Shuang Qi, Yan Liu
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 160: 114295. CrossRef - Connecting Gut Microbial Diversity with Plasma Metabolome and Fecal Bile Acid Changes Induced by the Antibiotics Tobramycin and Colistin Sulfate
Aishwarya Murali, Varun Giri, Franziska Maria Zickgraf, Philipp Ternes, Hunter James Cameron, Saskia Sperber, Volker Haake, Peter Driemert, Hennicke Kamp, Dorothee Funk-Weyer, Shana J. Sturla, Ivonne M.C.M. Rietjens, Bennard van Ravenzwaay
Chemical Research in Toxicology.2023; 36(4): 598. CrossRef - Short-Term Alternate Feeding between Terrestrially Sourced Oil- and Fish Oil-Based Diets Modulates the Intestinal Microecology of Juvenile Turbot
Xiuhua Ma, Yaoyao Kong, Houguo Xu, Qingzhu Bi, Mengqing Liang, Kangsen Mai, Yanjiao Zhang
Biology.2023; 12(5): 650. CrossRef - Effects and action mechanisms of lotus leaf (Nelumbo nucifera) ethanol extract on gut microbes and obesity in high-fat diet-fed rats
Zhang Yanan, Ma Lu, Zhang Lu, Huo Jinhai, Wang Weiming
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of coffee with different roasting degrees on obesity and related metabolic disorders
Claudia I. Gamboa-Gómez, Laura J. Barragán-Zúñiga, Fernando Guerrero-Romero, Gerardo Martínez-Aguilar, José Luis Gónzalez, Almendra A. Valenzuela-Ramírez, Juan A. Rojas-Contreras, Monica Anese, Maribel Cervantes Flores, Marilisa Alongi
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 111: 105889. CrossRef - Gut Microbiota and Bacterial Translocation in the Pathogenesis of Liver Fibrosis
Roman Maslennikov, Elena Poluektova, Oxana Zolnikova, Alla Sedova, Anastasia Kurbatova, Yulia Shulpekova, Natyia Dzhakhaya, Svetlana Kardasheva, Maria Nadinskaia, Elena Bueverova, Vladimir Nechaev, Anna Karchevskaya, Vladimir Ivashkin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(22): 16502. CrossRef - Eugenol, A Major Component of Clove Oil, Attenuates Adiposity, and Modulates Gut Microbiota in High‐Fat Diet‐Fed Mice
Mengjie Li, Yuhan Zhao, Yanan Wang, Ruixuan Geng, Jingjing Fang, Seong‐Gook Kang, Kunlun Huang, Tao Tong
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Heimao tea polysaccharides ameliorate obesity by enhancing gut microbiota-dependent adipocytes thermogenesis in mice fed with high fat diet
Yu Wang, Ting Li, Yueyue Liu, Chengcheng Yang, Lei Liu, Xiangnan Zhang, Xingbin Yang
Food & Function.2022; 13(24): 13014. CrossRef - The Interplay of Sex Steroids, the Immune Response, and the Intestinal Microbiota
Fernanda Pace, Paula I. Watnick
Trends in Microbiology.2021; 29(9): 849. CrossRef - Heat stress on microbiota composition, barrier integrity, and
nutrient transport in gut, production performance, and its amelioration in farm
animals
Amlan Kumar Patra, Indrajit Kar
Journal of Animal Science and Technology.2021; 63(2): 211. CrossRef - Mechanisms linking gut microbial metabolites to insulin resistance
Hye Rim Jang, Hui-Young Lee
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(6): 730. CrossRef - The impact of gut microbiota metabolites on cellular bioenergetics and cardiometabolic health
Lenka Tomasova, Marian Grman, Karol Ondrias, Marcin Ufnal
Nutrition & Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Behavior, intestinal health, and growth of small sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus in different color morphs
- Early Development of Bidirectional Associations between Sleep Disturbance and Diabetes
- Yongin Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):668-670. Published online October 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0198
- 3,623 View
- 114 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sueño y riesgo cardiometabólico. Revisión narrativa
J. Ildefonzo Arocha Rodulfo, Gestne Aure Fariñez, Fernando Carrera
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis.2024; 36(1): 38. CrossRef - Sleep and cardiometabolic risk. Narrative revision
J. Ildefonzo Arocha Rodulfo, Gestne Aure Fariñez, Fernando Carrera
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis (English Edition).2024; 36(1): 38. CrossRef - Sleep problems and their predictors in community-dwelling older adults with diabetes in India: Evidence from the Longitudinal Ageing Study in India
Vansh Maheshwari, Saurav Basu
Sleep Medicine: X.2024; 7: 100108. CrossRef - Understanding the relationship between sleep and quality of life in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review of the literature
Bróna Laverty, Sreelakshmi Puthezhath Jayanandan, Sinéad Smyth
Journal of Health Psychology.2023; 28(8): 693. CrossRef - Impact of Retirement on Sleep Problems Among Older Workers and Their Partners
Miriam Mutambudzi, Hanna van Solinge, Suzanne Meeks
The Gerontologist.2021; 61(8): 1287. CrossRef
- Sueño y riesgo cardiometabólico. Revisión narrativa
- Technology/Device
- Data Configuration and Publication Trends for the Korean National Health Insurance and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Database
- Hae Kyung Kim, Sun Ok Song, Junghyun Noh, In-Kyung Jeong, Byung-Wan Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):671-678. Published online October 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0207

- 7,193 View
- 243 Download
- 49 Web of Science
- 55 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Big data reports related to diseases and health care for the Korean population have been published since the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) and the Health Insurance Review & Assessment (HIRA) Service provided limited open access to their databases. Here, we reviewed the structure, content, and means of using data from the National Health Insurance (NHI) system for the benefit of Korean researchers and presented the latest publication trends in Korean healthcare data procured from the NHI and HIRA databases.
Methods
Since 2013, researchers have been able to obtain nationwide population-based studies using the NHI and HIRA databases of the insured. We searched publications using the NHI and the HIRA databases between 2013 and 2019 retrieved from PubMed.
Results
The NHI and HIRA databases provide nationwide population-based data. The total number of publications from 2014 to 2019 using NHI and HIRA databases is 2,541 and 655, respectively. A total of 5,465 endocrinology-related studies were performed during 2014 to 2019.
Conclusion
The NHIS and HIRA databases have provided tools for guidelines to approach world-leading population-based epidemiology and disease research. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medical service utilization patterns among adults with insomnia: A retrospective cohort study
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2024; 67: 102325. CrossRef - COVID-19-related cardiovascular disease risk due to weight gain: a nationwide cohort study
Su Kyoung Lee, Yohwan Lim, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
European Journal of Medical Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Kidney Health Plan 2033 in Korea: bridging the gap between the present and the future
Do Hyoung Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Jin Joo Cha, Sua Lee, Hyun Kyung Lee, Jong Wook Choi, Su-Hyun Kim, Sang Youb Han, Cheol Whee Park, Eun Young Lee, Dae Ryong Cha, Sung Gyun Kim, Chun Soo Lim, Sun-Hee Park
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 43(1): 8. CrossRef - Bipolar disorder and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases, heart failure, and all-cause mortality: a population-based matched cohort study in South Korea
You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evidence for the biopsychosocial model of suicide: a review of whole person modeling studies using machine learning
Earvin S. Tio, Melissa C. Misztal, Daniel Felsky
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nationwide Study of the Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis in Korea
Hae In Jung, Dal Ri Nam, Seung-Hun You, Jae-Woo Jung, Kang-Mo Gu, Sun-Young Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative risk factor analysis of prior disease condition and socioeconomic status with the multiple myeloma development: nationwide cohort study
Suein Choi, Eunjin Kim, Jinhee Jung, Sung-Soo Park, Chang-Ki Min, Seunghoon Han
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of physical activity with fractures in kidney transplant recipients: A Korean nationwide cohort study
Sungmi Kim, Jin‐Hyung Jung, Kyungho Lee, Junseok Jeon, Dong Wook Shin, Hye Ryoun Jang, Jung Eun Lee, Kyungdo Han, Wooseong Huh
Clinical Transplantation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Does endometriosis increase the risks of endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer?
Hoon Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Hyeong Sik Ahn
Gynecologic Oncology.2023; 169: 147. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Outcomes according to Comorbidities and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 45. CrossRef - Association between Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Korean Adults: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Junghyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 59. CrossRef - Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Seung-Hwan Lee, Jin Yu, Kyungdo Han, Seung Woo Lee, Sang Youn You, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 129. CrossRef - Genital tract infection and pelvic surgery contribute to the development of endometriosis
Ae Ra Han, Suehyun Lee, Jaehun Cha, Jong-Yeup Kim, Dong-Kyu Kim, Jae Won Han, Chul Jung Kim, Sung Ki Lee
Journal of Reproductive Immunology.2023; 156: 103831. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Comorbidity Differences by Trajectory Groups as a Reference for Identifying Patients at Risk for Late Mortality in Childhood Cancer Survivors: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hyery Kim, Hae Reong Kim, Sung Han Kang, Kyung-Nam Koh, Ho Joon Im, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41203. CrossRef - Investigation of the Relationship Between Psychiatry Visit and Suicide After Deliberate Self-harm: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hye Hyeon Kim, Chanyoung Ko, Ji Ae Park, In Han Song, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41261. CrossRef - Long-term exposure to particulate matter and risk of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia in Korea: a national population-based Cohort Study
Jung-Im Shim, Garam Byun, Jong-Tae T. Lee
Environmental Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Physical Activity With SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Severe Clinical Outcomes Among Patients in South Korea
YoHwan Lim, Myeong Hoon Lee, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
JAMA Network Open.2023; 6(4): e239840. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Nationwide patterns of hydroxychloroquine dosing and monitoring of retinal toxicity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Jae-Eun Lee, Dal Ri Nam, Yoon-Kyoung Sung, Yu Jeong Kim, Sun-Young Jung
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of updated cardiovascular health metrics, including sleep health, with incident diabetes and cardiovascular events in older adults with prediabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Seung Jin Han
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110820. CrossRef - Association of Socioeconomic Status With Long-Term Outcome in Survivors After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: Nationwide Population-Based Longitudinal Study
Kyung Hun Yoo, Yongil Cho, Jaehoon Oh, Juncheol Lee, Byuk Sung Ko, Hyunggoo Kang, Tae Ho Lim, Sang Hwan Lee
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e47156. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Effects of
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum THK-j112 Isolated from
Kimchi against Streptococcus mutans
Du-Na Yu, Eun-Ji Yi, Je-Yong Jung, Tae-Hoo Yi, Moochang Kook
Current Topic in Lactic Acid Bacteria and Probiotics.2023; 9(1): 9. CrossRef - The Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus according to Changes in Obesity Status in Late Middle-Aged Adults: A Nationwide Cohort Study of Korea
Joon Ho Moon, Yeonhoon Jang, Tae Jung Oh, Se Young Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 514. CrossRef - Proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of metachronous gastric cancer after H. pylori eradication in patients who underwent endoscopic resection for gastric neoplasms: A population‐based cohort study
Eun Jeong Gong, Hye‐Kyung Jung, Bora Lee, Jitaek Hong, Jong Wook Kim, Cheol Min Shin, Young Hoon Youn, Kwang Jae Lee
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2023; 58(7): 668. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Lower Extremity Amputation in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Min Jun Seo, Dong Geon Lee, Se Yun Ko, Ga Yeong Song, Geon Yeong Lee, Sung Hwa Kim, Dae Ryong Kang, Jiye Kim, Jun Young Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(17): 5641. CrossRef - Poorer outcomes following COVID-19 infection for patients with depression: A cohort analysis in South Korea
Su Kyoung Lee, Yohwan Lim, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.2023; 52(8): 411. CrossRef - The role of income and frequency of dental visits in the relationship between dental sealant use and resin fillings after extended coverage: a retrospective cohort study
Dong-Hun Han, Hee-Yeon Kang, Jae-In Ryu
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of changes in the hearing aid subsidy on the prevalence of hearing loss in South Korea
Chul Young Yoon, Junhun Lee, Tae Hoon Kong, Young Joon Seo
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Visual Impairment Risk After Alcohol Abstinence in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Open-Angle Glaucoma
Yoon Jeong, Su Hwan Kim, Goneui Kang, Hyung-Jin Yoon, Young Kook Kim, Ahnul Ha
JAMA Network Open.2023; 6(10): e2338526. CrossRef - Impact of statin treatment on cardiovascular risk in patients with type 1 diabetes: a population-based cohort study
Joonsang Yoo, Jimin Jeon, Minyoul Baek, Sun Ok Song, Jinkwon Kim
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Socioeconomic Disparities in the Association Between All-Cause Mortality and Health Check-Up Participation Among Healthy Middle-Aged Workers: A Nationwide Study
Byungyoon Yun, Juyeon Oh, Jaesung Choi, Laura S. Rozek, Heejoo Park, Juho Sim, Yangwook Kim, Jongmin Lee, Jin-Ha Yoon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased Estimated GFR Is Negatively Associated With the Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Severe COVID-19 Within Normal to Mildly Decreased Levels: Nested Case-Control Study
Yohwan Lim, Myeong Hoon Lee, Su Kyoung Lee, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Pregnancy Complications and Low Birth Weight Offsprings in Korean Women With Rheumatic Diseases: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Jin-Su Park, Min Kyung Chung, Hyunsun Lim, Jisoo Lee, Chan Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of variability in body weight and glucose levels with the risk of hip fracture in people with diabetes
Jeongmin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Sang Hyun Park, Mee Kyoung Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Moo-Il Kang, Seung-Hwan Lee
Metabolism.2022; 129: 155135. CrossRef - Travel Time for Dental Care Services Based on Patient Preference in South Korea
Han-A Cho, Bo-Ra Kim, Hosung Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(4): 2051. CrossRef - The Basic Concept of Claim Data-based Research
Su Bee Park, Jae Myung Cha
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2022; 22(1): 70. CrossRef - Trends of severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes in Korea: A longitudinal nationwide cohort study
Jae‐Seung Yun, Kyungdo Han, Seung‐Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(8): 1438. CrossRef - National General Health Screening Program in Korea: history, current status, and future direction
Dong Wook Shin, Juhee Cho, Jae Hyun Park, BeLong Cho
Precision and Future Medicine.2022; 6(1): 9. CrossRef - Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Level and Risk of Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Ji-Yeon Park, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 272. CrossRef - Understanding and Utilizing Claim Data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) and Health Insurance Review & Assessment (HIRA) Database for Research
Dae-Sung Kyoung, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(2): 103. CrossRef - Clinical and Cost-Saving Effects of the Drug Utilization Review Modernization Project in Inpatient and Outpatient Settings in Korea
Dongwon Yoon, Inmyung Song, Ha-Lim Jeon, Sungho Bea, Ahhyung Choi, Hyesung Lee, Ju-Young Shin
Journal of Patient Safety.2022; 18(6): 605. CrossRef - Adherence to healthy lifestyle behaviors as a preventable risk factor for severe hypoglycemia in people with type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal nationwide cohort study
Jae‐Seung Yun, Kyungdo Han, Yong‐Moon Park, Eugene Han, Yong‐ho Lee, Seung‐Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(9): 1533. CrossRef - Analysis of sedation and general anesthesia in patients with special needs in dentistry using the Korean healthcare big data
Jieun Kim, Hyuk Kim, Kwang-Suk Seo, Hyun Jeong Kim
Journal of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.2022; 22(3): 205. CrossRef - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 466. CrossRef - Visual Acuity Outcomes in Diseases Associated with Reduced Visual Acuity: An Analysis of the National Health Insurance Service Database in Korea
Sang-Yeob Kim, Byeong-Yeon Moon, Hyun-Gug Cho, Dong-Sik Yu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(14): 8689. CrossRef - Reproductive Life Span and Severe Hypoglycemia Risk in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soyeon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Dong Jin Kwon, Youn-Jee Chung, Jeong Namkung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 578. CrossRef - Lipid cutoffs for increased cardiovascular disease risk in non-diabetic young people
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 29(14): 1866. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Increasing trends in mortality and costs of infectious diseases in Korea: trends in mortality and costs of infectious diseases
Dahye Baik, Byung-Woo Kim, Moran Ki
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022010. CrossRef - How to Use Health Insurance Data Effectively for Healthcare Research
Ilsu Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(Suppl 2): S31. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol and the risk of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide longitudinal cohort study
Ji Hye Huh, Kyung-do Han, Yun Kyung Cho, Eun Roh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metformin and Cervical Cancer Risk in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
Hyun Min Kim, Min Jin Kang, Sun Ok Song
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 929. CrossRef - Effect of Sex on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease: A Population-Based Study
Kyu Hyang Cho, Sang Won Kim, Jong Won Park, Jun Young Do, Seok Hui Kang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 10(1): 38. CrossRef - Increased Age of Death and Change in Causes of Death Among Persons With Diabetes Mellitus From the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Medical service utilization patterns among adults with insomnia: A retrospective cohort study
- Complications
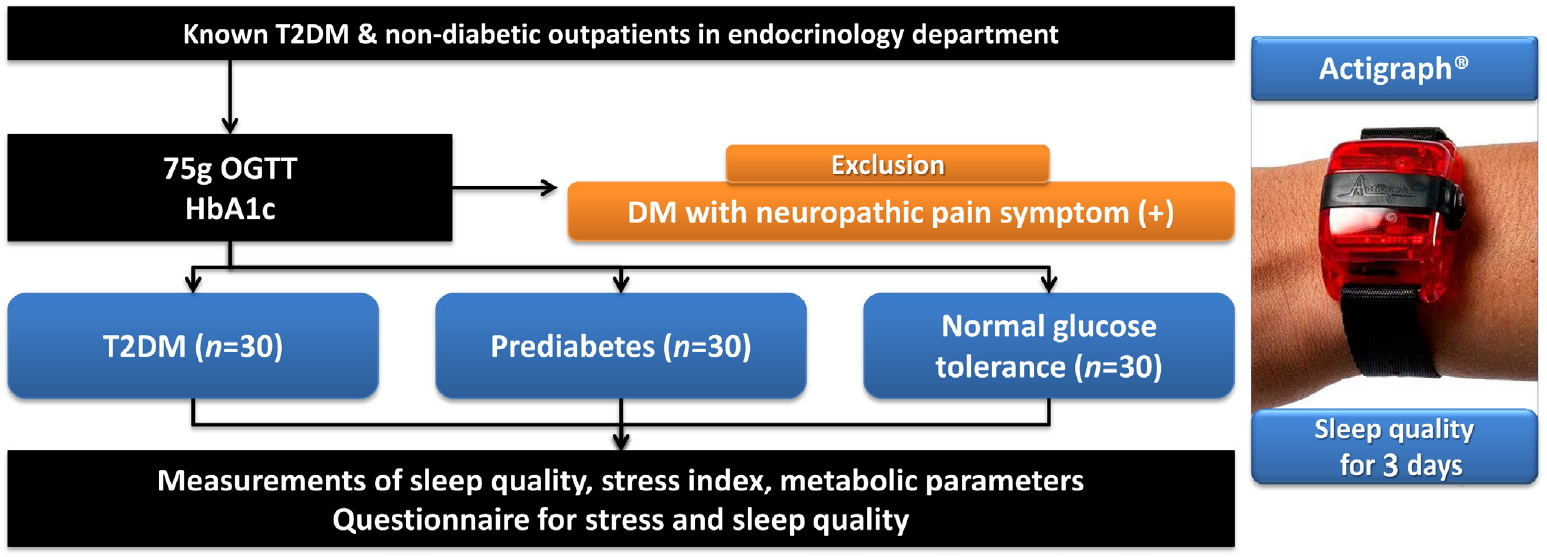
- Deterioration of Sleep Quality According to Glycemic Status
- Myung Haeng Hur, Mi-Kyoung Lee, Kayeon Seong, Jun Hwa Hong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):679-686. Published online April 17, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0125
- 4,875 View
- 113 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a progressive disease with multiple complications. The present study aimed to determine the effects of glycemic status on sleep quality in individuals with T2DM, prediabetes, and normal glucose tolerance (NGT).
Methods A total of 90 participants were categorized into three groups, T2DM (
n =30), prediabetes (n =30), and NGT (n =30). Objective sleep quality was measured with the actigraph wrist-worn device over 3 nights and subjective sleep quality was evaluated with a questionnaire.Results The duration of diabetes in the T2DM group was 2.23 years and the glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels in the T2DM, prediabetes, and NGT groups were 7.83%, 5.80%, and 5.31%, respectively. Sleep efficiency decreased across the T2DM, prediabetes, and NGT groups (86.25%, 87.99%, and 90.22%, respectively;
P =0.047). Additionally, HbA1c levels revealed a significant negative correlation with sleep efficiency (r =−0.348,P =0.001). The sleep quality questionnaire results were similar among the three groups.Conclusion Although the participants in the present study were not necessarily conscious of their sleep disturbances, deterioration in sleep quality progressed according to glycemic status.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factors of non communicable diseases among recently diagnosed diabetic patients in a tertiary care Hospital
Yusra Amin, Sonia Mushtaq, Rukhsana Farooq
Indian Journal of Clinical Anatomy and Physiology.2024; 10(4): 205. CrossRef - Metabolic health tracking using Ultrahuman M1 continuous glucose monitoring platform in non- and pre-diabetic Indians: a multi-armed observational study
Monik Chaudhry, Mohit Kumar, Vatsal Singhal, Bhuvan Srinivasan
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Relation between sleep quality and glycemic control among type 2 diabetic patients
Asmaa Ali Elsayed Ali
Frontiers of Nursing.2023; 10(1): 115. CrossRef - Heart rate variability in different sleep stages is associated with metabolic function and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Wenquan Cheng, Hongsen Chen, Leirong Tian, Zhimin Ma, Xingran Cui
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Diabetic Retinopathy and Insomnia Risk: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Yoo Hyun Um, Tae-Won Kim, Jong-Hyun Jeong, Seung-Chul Hong, Ho-Jun Seo, Kyung-Do Han
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nutritional Biomarkers and Factors Correlated with Poor Sleep Status among Young Females: A Case-Control Study
Sara AL-Musharaf, Lama AlAjllan, Ghadeer Aljuraiban, Munirah AlSuhaibani, Noura Alafif, Syed Danish Hussain
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2898. CrossRef - The impact of sleep disorders on microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (SLEEP T2D): the protocol of a cohort study and feasibility randomised control trial
Christina Antza, Ryan Ottridge, Smitaa Patel, Gemma Slinn, Sarah Tearne, Matthew Nicholls, Brendan Cooper, Asad Ali, Abd A. Tahrani
Pilot and Feasibility Studies.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Development of Bidirectional Associations between Sleep Disturbance and Diabetes
Yongin Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 668. CrossRef
- Risk factors of non communicable diseases among recently diagnosed diabetic patients in a tertiary care Hospital
- Complications
- Association of Snoring with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center Cohort
- So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):687-698. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0128
- 5,245 View
- 108 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
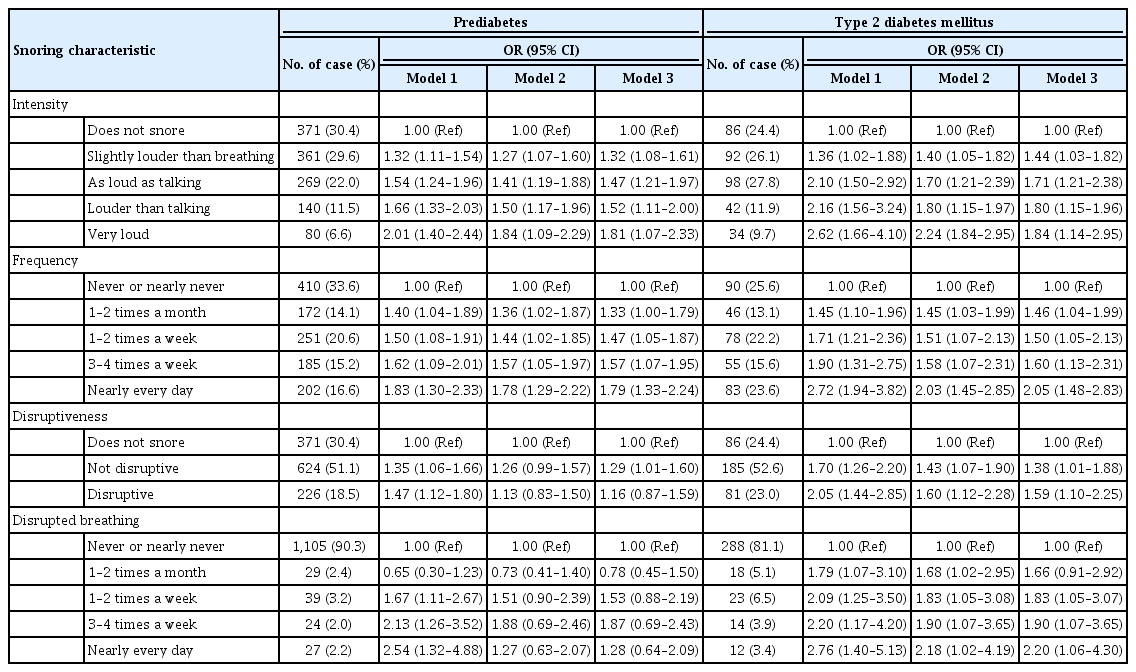
ePub Background Evidence suggests that habitual snoring is an independent risk factor for poor glycemic health. We examined the associations between snoring with prediabetes and diabetes in Korean population.
Methods Self-reported snoring characteristics were collected from 3,948 middle-aged adults without prior cardiovascular diseases. Multivariable linear regression assessed the association of snoring intensity, frequency, disruptiveness, and disrupted breathing with fasting glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level. Then, multinomial regression evaluated how increasing snoring symptoms are associated with the risk for prediabetes and diabetes, adjusting for socioeconomic and behavioral risk factors of diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and other sleep variables.
Results Higher snoring intensity and frequency were positively associated with fasting glucose and HbA1c levels. Participants presenting the most severe snoring were at 1.84 times higher risk (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.09 to 2.29) for prediabetes and 2.24 times higher risk (95% CI, 1.84 to 2.95) for diabetes, compared to non-snorers. Such graded association was also observed amongst the most frequent snorers with higher risk for prediabetes (odds ratio [OR], 1.78; 95% CI, 1.29 to 2.22) and diabetes (OR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.45 to 2.85). Disruptive snoring (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.12 to 2.28) and near-daily disruptive breathing (OR, 2.18; 95% CI, 1.02 to 4.19) were associated with higher odds for diabetes. Such findings remained robust after additional adjustment for sleep duration, excessive daytime sleepiness, unwakefulness, and sleep-deprived driving.
Conclusion Snoring is associated with impaired glucose metabolism even in otherwise metabolically healthy adults. Habitual snorers may require lifestyle modifications and pharmacological treatment to improve glycemic profile.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does seasonality affect snoring? A study based on international data from the past decade
Ping Wang, Cai Chen, Xingwei Wang, Ningling Zhang, Danyang Lv, Wei Li, Fulai Peng, Xiuli Wang
Sleep and Breathing.2023; 27(4): 1297. CrossRef - Association Between Snoring and Diabetes Among Pre- and Postmenopausal Women
Yun Yuan, Fan Zhang, Jingfu Qiu, Liling Chen, Meng Xiao, Wenge Tang, Qinwen Luo, Xianbin Ding, Xiaojun Tang
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 2491. CrossRef - Elevated fasting insulin results in snoring: A view emerged from causal evaluation of glycemic traits and snoring
Minhan Yi, Quanming Fei, Kun Liu, Wangcheng Zhao, Ziliang Chen, Yuan Zhang
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sleeping Duration, Napping and Snoring in Association with Diabetes Control among Patients with Diabetes in Qatar
Hiba Bawadi, Asma Al Sada, Noof Al Mansoori, Sharifa Al Mannai, Aya Hamdan, Zumin Shi, Abdelhamid Kerkadi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4017. CrossRef - Changes in creatinine‐to‐cystatin C ratio over 4 years, risk of diabetes, and cardiometabolic control: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(12): 1025. CrossRef - Association Between Self-Reported Snoring and Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jinsha Ma, Huifang Zhang, Hui Wang, Qian Gao, Heli Sun, Simin He, Lingxian Meng, Tong Wang
Frontiers in Neurology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Development of Bidirectional Associations between Sleep Disturbance and Diabetes
Yongin Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 668. CrossRef
- Does seasonality affect snoring? A study based on international data from the past decade
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- The Association between Pulmonary Functions and Incident Diabetes: Longitudinal Analysis from the Ansung Cohort in Korea
- Hoon Sung Choi, Sung Woo Lee, Jin Taek Kim, Hong Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):699-710. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0109

- 6,131 View
- 104 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background We sought to explore whether reduced pulmonary function is an independent risk factor for incident diabetes in Koreans.
Methods We conducted a prospective cohort study of pulmonary function as a risk factor for incident diabetes using 10-year follow-up data from 3,864 middle-aged adults from the Ansung cohort study in Korea. The incidence of diabetes was assessed using both oral glucose tolerance tests and glycosylated hemoglobin levels.
Results During 37,118 person-years of follow-up, 583 participants developed diabetes (incidence rate: 15.7 per 1,000 person-years). The mean follow-up period was 8.0±3.7 years. Forced vital capacity (FVC; % predicted) and forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1; % predicted) were significantly correlated with incident diabetes in a graded manner after adjustment for sex, age, smoking, exercise, and metabolic parameters. The adjusted hazard ratio (HR) and confidence interval (CI) for diabetes were 1.408 (1.106 to 1.792) and 1.469 (1.137 to 1.897) in the first quartiles of FVC and FEV1, respectively, when compared with the highest quartile. Furthermore, the FVC of the lowest first and second quartiles showed a significantly higher 10-year panel homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance index, with differences of 0.095 (95% CI, 0.010 to 0.018;
P =0.028) and 0.127 (95% CI, 0.044 to 0.210;P =0.003), respectively, when compared to the highest quartiles.Conclusion FVC and FEV1 are independent risk factors for developing diabetes in Koreans. Pulmonary factors are possible risk factors for insulin resistance and diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Validation of the Framingham Diabetes Risk Model Using Community-Based KoGES Data
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park, Young Sun Hong
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Independent and combined associations of multiple-heavy-metal exposure with lung function: a population-based study in US children
Yiting Chen, Anda Zhao, Rong Li, Wenhui Kang, Jinhong Wu, Yong Yin, Shilu Tong, Shenghui Li, Jianyu Chen
Environmental Geochemistry and Health.2023; 45(7): 5213. CrossRef - Role of Pulmonary Function in Predicting New-Onset Cardiometabolic Diseases and Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity
Guochen Li, Yanqiang Lu, Yanan Qiao, Die Hu, Chaofu Ke
Chest.2022; 162(2): 421. CrossRef - Reduced lung function predicts risk of incident type 2 diabetes: insights from a meta-analysis of prospective studies
Yunping Zhou, Fei Meng, Min Wang, Linlin Li, Pengli Yu, Yunxia Jiang
Endocrine Journal.2022; 69(3): 299. CrossRef - Development of Various Diabetes Prediction Models Using Machine Learning Techniques
Juyoung Shin, Jaewon Kim, Chanjung Lee, Joon Young Yoon, Seyeon Kim, Seungjae Song, Hun-Sung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 650. CrossRef - Improving Machine Learning Diabetes Prediction Models for the Utmost Clinical Effectiveness
Juyoung Shin, Joonyub Lee, Taehoon Ko, Kanghyuck Lee, Yera Choi, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(11): 1899. CrossRef - The Association between Pulmonary Functions and Incident Diabetes: Longitudinal Analysis from the Ansung Cohort in Korea (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44: 699-710)
Hoon Sung Choi, Sung Woo Lee, Jin Taek Kim, Hong Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 944. CrossRef - The Association between Pulmonary Functions and Incident Diabetes: Longitudinal Analysis from the Ansung Cohort in Korea (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44: 699-710)
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 940. CrossRef
- Validation of the Framingham Diabetes Risk Model Using Community-Based KoGES Data
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Sex-, Age-, and Metabolic Disorder-Dependent Distributions of Selected Inflammatory Biomarkers among Community-Dwelling Adults
- So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):711-725. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0119
- 5,920 View
- 83 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
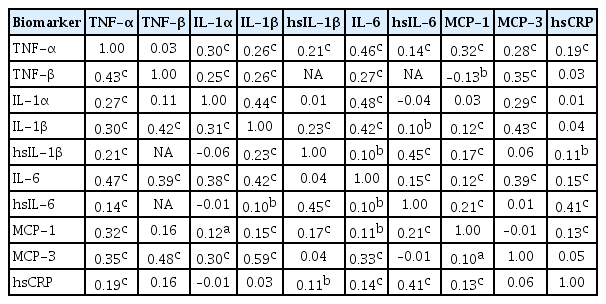
ePub Background Inflammatory cytokines are increasingly utilized to detect high-risk individuals for cardiometabolic diseases. However, with large population and assay methodological heterogeneity, no clear reference currently exists.
Methods Among participants of the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center cohort, of community-dwelling adults aged 30 to 64 without overt cardiovascular diseases, we presented distributions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and -β, interleukin (IL)-1α, -1β, and 6, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 and -3 and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) with and without non-detectable (ND) measurements using multiplex enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Then, we compared each markers by sex, age, and prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, using the Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test.
Results In general, there were inconsistencies in direction and magnitude of differences in distributions by sex, age, and prevalence of cardiometabolic disorders. Overall, the median and the 99th percentiles were higher in men than in women. Older participants had higher TNF-α, high sensitivity IL-6 (hsIL-6), MCP-1, hsCRP, TNF-β, and MCP-3 median, after excluding the NDs. Participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus had higher median for all assayed biomarkers, except for TNF-β, IL-1α, and MCP-3, in which the medians for both groups were 0.00 due to predominant NDs. Compared to normotensive group, participants with hypertension had higher TNF-α, hsIL-6, MCP-1, and hsCRP median. When stratifying by dyslipidemia prevalence, the comparison varied significantly depending on the treatment of NDs.
Conclusion Our findings provide sex-, age-, and disease-specific reference values to improve risk prediction and diagnostic performance for inflammatory diseases in both population- and clinic-based settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterizing CD8+ TEMRA Cells in CP/CPPS Patients: Insights from Targeted Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Functional Investigations
Fei Zhang, Qintao Ge, Jialin Meng, Jia Chen, Chaozhao Liang, Meng Zhang
ImmunoTargets and Therapy.2024; Volume 13: 111. CrossRef - Association between physical activity and inflammatory markers in community-dwelling, middle-aged adults
So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Justin Y. Jeon, Hyeon Chang Kim
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2021; 46(7): 828. CrossRef - The monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio: Sex-specific differences in the tuberculosis disease spectrum, diagnostic indices and defining normal ranges
Thomas S. Buttle, Claire Y. Hummerstone, Thippeswamy Billahalli, Richard J. B. Ward, Korina E. Barnes, Natalie J. Marshall, Viktoria C. Spong, Graham H. Bothamley, Selvakumar Subbian
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0247745. CrossRef
- Characterizing CD8+ TEMRA Cells in CP/CPPS Patients: Insights from Targeted Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Functional Investigations
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- A Comparison of Predictive Performances between Old versus New Criteria in a Risk-Based Screening Strategy for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Subeen Hong, Seung Mi Lee, Soo Heon Kwak, Byoung Jae Kim, Ja Nam Koo, Ig Hwan Oh, Sohee Oh, Sun Min Kim, Sue Shin, Won Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Errol R. Norwitz, Souphaphone Louangsenlath, Chan-Wook Park, Jong Kwan Jun, Joong Shin Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):726-736. Published online April 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0126
- 6,600 View
- 123 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
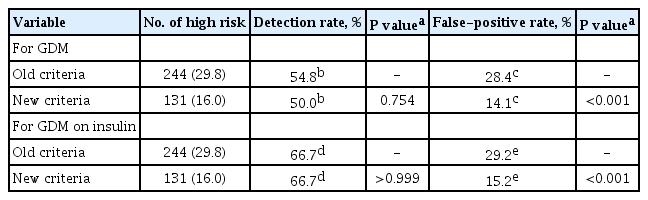
ePub Background The definition of the high-risk group for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) defined by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists was changed from the criteria composed of five historic/demographic factors (old criteria) to the criteria consisting of 11 factors (new criteria) in 2017. To compare the predictive performances between these two sets of criteria.
Methods This is a secondary analysis of a large prospective cohort study of non-diabetic Korean women with singleton pregnancies designed to examine the risk of GDM in women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Maternal fasting blood was taken at 10 to 14 weeks of gestation and measured for glucose and lipid parameters. GDM was diagnosed by the two-step approach.
Results Among 820 women, 42 (5.1%) were diagnosed with GDM. Using the old criteria, 29.8% (
n =244) of women would have been identified as high risk versus 16.0% (n =131) using the new criteria. Of the 42 women who developed GDM, 45.2% (n =19) would have been mislabeled as not high risk by the old criteria versus 50.0% (n =21) using the new criteria (1-sensitivity, 45.2% vs. 50.0%,P >0.05). Among the 778 patients who did not develop GDM, 28.4% (n =221) would have been identified as high risk using the old criteria versus 14.1% (n =110) using the new criteria (1-specificity, 28.4% vs. 14.1%,P <0.001).Conclusion Compared with the old criteria, use of the new criteria would have decreased the number of patients identified as high risk and thus requiring early GDM screening by half (from 244 [29.8%] to 131 [16.0%]).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Seung-Hwan Lee, Jin Yu, Kyungdo Han, Seung Woo Lee, Sang Youn You, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 129. CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Subsequent Development of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes
Seung Mi Lee, Young Mi Jung, Eun Saem Choi, Soo Heon Kwak, Ja Nam Koo, Ig Hwan Oh, Byoung Jae Kim, Sun Min Kim, Sang Youn Kim, Gyoung Min Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Bo Kyung Koo, Sue Shin, Errol R. Norwitz, Chan-Wook Park, Jong Kwan Jun, Won Kim, Joong Shin Park
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 20(11): 2542. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and early prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus using machine learning methods
Seung Mi Lee, Suhyun Hwangbo, Errol R. Norwitz, Ja Nam Koo, Ig Hwan Oh, Eun Saem Choi, Young Mi Jung, Sun Min Kim, Byoung Jae Kim, Sang Youn Kim, Gyoung Min Kim, Won Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Sue Shin, Chan-Wook Park, Taesung Park, Joong Shin Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(1): 105. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-based risk prediction of adverse pregnancy outcomes: Ready for prime time?
Seung Mi Lee, Won Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(1): 47. CrossRef - Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 140. CrossRef - Effect of Different Types of Diagnostic Criteria for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus on Adverse Neonatal Outcomes: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression
Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani, Marzieh Saei Ghare Naz, Razieh Bidhendi-Yarandi, Samira Behboudi-Gandevani
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 605. CrossRef - Development of early prediction model for pregnancy-associated hypertension with graph-based semi-supervised learning
Seung Mi Lee, Yonghyun Nam, Eun Saem Choi, Young Mi Jung, Vivek Sriram, Jacob S. Leiby, Ja Nam Koo, Ig Hwan Oh, Byoung Jae Kim, Sun Min Kim, Sang Youn Kim, Gyoung Min Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Sue Shin, Errol R. Norwitz, Chan-Wook Park, Jong Kwan Jun, Won Kim,
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef - The risk of pregnancy‐associated hypertension in women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Young Mi Jung, Seung Mi Lee, Subeen Hong, Ja Nam Koo, Ig Hwan Oh, Byoung Jae Kim, Sun Min Kim, Sang Youn Kim, Gyoung Min Kim, Sae Kyung Joo, Sue Shin, Errol R. Norwitz, Chan‐Wook Park, Jong Kwan Jun, Won Kim, Joong Shin Park
Liver International.2020; 40(10): 2417. CrossRef
- Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
- COVID-19
-
- Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Sun Joon Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Sung-Rae Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):737-746. Published online October 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0141

- 10,602 View
- 201 Download
- 24 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Inconsistent results have been observed regarding the independent effect of diabetes on the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We conducted a nationwide population-based cohort study to evaluate the relationship between diabetes and COVID-19 severity in South Korea.
Methods
Patients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 aged ≥30 years were enrolled and medical claims data were obtained from the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. Hospitalization, oxygen treatment, ventilator application, and mortality were assessed as severity outcomes. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed after adjusting for age, sex, and comorbidities.
Results
Of 5,307 COVID-19 patients, the mean age was 56.0±14.4 years, 2,043 (38.5%) were male, and 770 (14.5%) had diabetes. The number of patients who were hospitalized, who received oxygen, who required ventilator support, and who died was 4,986 (94.0%), 884 (16.7%), 121 (2.3%), and 211 (4.0%), respectively. The proportion of patients with diabetes in the abovementioned outcome groups was 14.7%, 28.1%, 41.3%, 44.6%, showing an increasing trend according to outcome severity. In multivariate analyses, diabetes was associated with worse outcomes, with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 1.349 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.099 to 1.656; P=0.004) for oxygen treatment, an aOR of 1.930 (95% CI, 1.276 to 2.915; P<0.001) for ventilator use, and an aOR of 2.659 (95% CI, 1.896 to 3.729; P<0.001) for mortality.
Conclusion
Diabetes was associated with worse clinical outcomes in Korean patients with COVID-19, independent of other comorbidities. Therefore, patients with diabetes and COVID-19 should be treated with caution. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of COVID-19 on the Microbiome and Inflammatory Status of Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Gratiela Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, Georgiana Alexandra Grigore, Ilda Czobor Barbu, Mariana-Carmen Chifiriuc, Octavian Savu
Biomedicines.2023; 11(1): 179. CrossRef - Bidirectional Relationship between Glycemic Control and COVID-19 and Perspectives of Islet Organoid Models of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Tongran Zhang, Nannan Wang, Lingqiang Zhu, Lihua Chen, Huisheng Liu
Biomedicines.2023; 11(3): 856. CrossRef - Reasons for Hospitalization Among Australians With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19
Dunya Tomic, Jonathan E. Shaw, Dianna J. Magliano
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels predict outcome in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study
Sylvia Mink, Christoph H. Saely, Andreas Leiherer, Matthias Frick, Thomas Plattner, Heinz Drexel, Peter Fraunberger
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mortality-related risk factors of inpatients with diabetes and COVID-19: A multicenter retrospective study in Belgium
Thomas Servais, France Laurent, Thomas Roland, Camelia Rossi, Elodie De Groote, Valérie Godart, Ernestina Repetto, Michel Ponchon, Pascale Chasseur, Laurent Crenier, Sandrine Van Eeckhoudt, John Yango, Philippe Oriot, Mirela Morisca Gavriliu, Stéphanie Ro
Annales d'Endocrinologie.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Screening, diagnosis and management of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy in clinical practice: International expert consensus recommendations
Dan Ziegler, Solomon Tesfaye, Vincenza Spallone, Irina Gurieva, Juma Al Kaabi, Boris Mankovsky, Emil Martinka, Gabriela Radulian, Khue Thy Nguyen, Alin O Stirban, Tsvetalina Tankova, Tamás Varkonyi, Roy Freeman, Péter Kempler, Andrew JM Boulton
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 186: 109063. CrossRef - The Role of Diabetes and Hyperglycemia on COVID-19 Infection Course—A Narrative Review
Evangelia Tzeravini, Eleftherios Stratigakos, Chris Siafarikas, Anastasios Tentolouris, Nikolaos Tentolouris
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The interrelationship between diabetes mellitus and COVID-19
ThekraAbdulaali Abed, ZainabAdil Ghani Chabuck
Medical Journal of Babylon.2022; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Incidence and Outcomes of COVID-19 Needing Hospital Admission According to Sex: Retrospective Cohort Study Using Hospital Discharge Data in Spain, Year 2020
Jose M. de Miguel-Yanes, Rodrigo Jimenez-Garcia, Javier de Miguel-Diez, Valentin Hernández-Barrera, David Carabantes-Alarcon, Jose J. Zamorano-Leon, Ricardo Omaña-Palanco, Ana Lopez-de-Andres
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2654. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
Jae Hyun Bae, Kyung-Do Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ye Seul Yang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Mook Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 417. CrossRef - The burden and risks of emerging complications of diabetes mellitus
Dunya Tomic, Jonathan E. Shaw, Dianna J. Magliano
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2022; 18(9): 525. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 at Case Hospital, Uganda
Mirriam Apiyo, Ronald Olum, Amina Kabuye, Betty Khainza, Anne M. Amate, Vittal Byabashaija, Derrick Nomujuni, Kato Sebbaale, Peter Senfuka, Simon Kazibwe, Gurav Sharma, Lindsay Davidson, Felix Bongomin, Diamantis Kofteridis
Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Infectious Diseases.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Diabetes, obesity, metabolism, and SARS-CoV-2 infection: the end of the beginning
Daniel J. Drucker
Cell Metabolism.2021; 33(3): 479. CrossRef - Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19
Sang Youl Rhee, Jeongwoo Lee, Hyewon Nam, Dae-Sung Kyoung, Dong Wook Shin, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 251. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccine acceptance among high-risk populations in Uganda
Felix Bongomin, Ronald Olum, Irene Andia-Biraro, Frederick Nelson Nakwagala, Khalid Hudow Hassan, Dianah Rhoda Nassozi, Mark Kaddumukasa, Pauline Byakika-Kibwika, Sarah Kiguli, Bruce J. Kirenga
Therapeutic Advances in Infectious Disease.2021; 8: 204993612110243. CrossRef - Caracterización clínica, según niveles de glucemia, de pacientes hospitalizados por COVID-19: serie de casos
Irene Stulin, Maria Montes de Oca, Gabriela Blanco, Laura Sánchez, Isabel-Carlota Silva, Jennireth Quevedo, Maria Cristina Arvelo, Nathalia Valera, Irene Papa, Hospital Centro Médico de Caracas, Caracas, Venezuela Bacci, Fátima de Abreu, Héctor Villarroel
Investigación Clínica.2021; 62: 27. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 757. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19: Review Article
Mahmoud Nassar, Ahmed Daoud, Nso Nso, Luis Medina, Victoria Ghernautan, Harangad Bhangoo, Andrew Nyein, Mahmoud Mohamed, Ahmed Alqassieh, Karim Soliman, Mostafa Alfishawy, Issac Sachmechi, Anoop Misra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(6): 102268. CrossRef - Dissection of non-pharmaceutical interventions implemented by Iran, South Korea, and Turkey in the fight against COVID-19 pandemic
Mohammad Keykhaei, Sogol Koolaji, Esmaeil Mohammadi, Reyhaneh Kalantar, Sahar Saeedi Moghaddam, Arya Aminorroaya, Shaghayegh Zokaei, Sina Azadnajafabad, Negar Rezaei, Erfan Ghasemi, Nazila Rezaei, Rosa Haghshenas, Yosef Farzi, Sina Rashedi, Bagher Larijan
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(2): 1919. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diabetes Associated Mortality in Patients with COVID-19
Puneeta Gupta, Meeta Gupta, Neena KAtoch, Ketan Garg, Bhawna Garg
International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes, Obesity, and COVID-19
Sang Youl Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(3): 174. CrossRef - Diabetes, hypertension, body mass index, smoking and COVID-19-related mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Yahya Mahamat-Saleh, Thibault Fiolet, Mathieu Edouard Rebeaud, Matthieu Mulot, Anthony Guihur, Douae El Fatouhi, Nasser Laouali, Nathan Peiffer-Smadja, Dagfinn Aune, Gianluca Severi
BMJ Open.2021; 11(10): e052777. CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide-Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:737-46)
Kyuho Kim, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 938. CrossRef
- Impact of COVID-19 on the Microbiome and Inflammatory Status of Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Basic Research
- Effects of Microbiota on the Treatment of Obesity with the Natural Product Celastrol in Rats
- Weiyue Hu, Lingling Wang, Guizhen Du, Quanquan Guan, Tianyu Dong, Ling Song, Yankai Xia, Xinru Wang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):747-763. Published online May 11, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0124
- 9,323 View
- 136 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
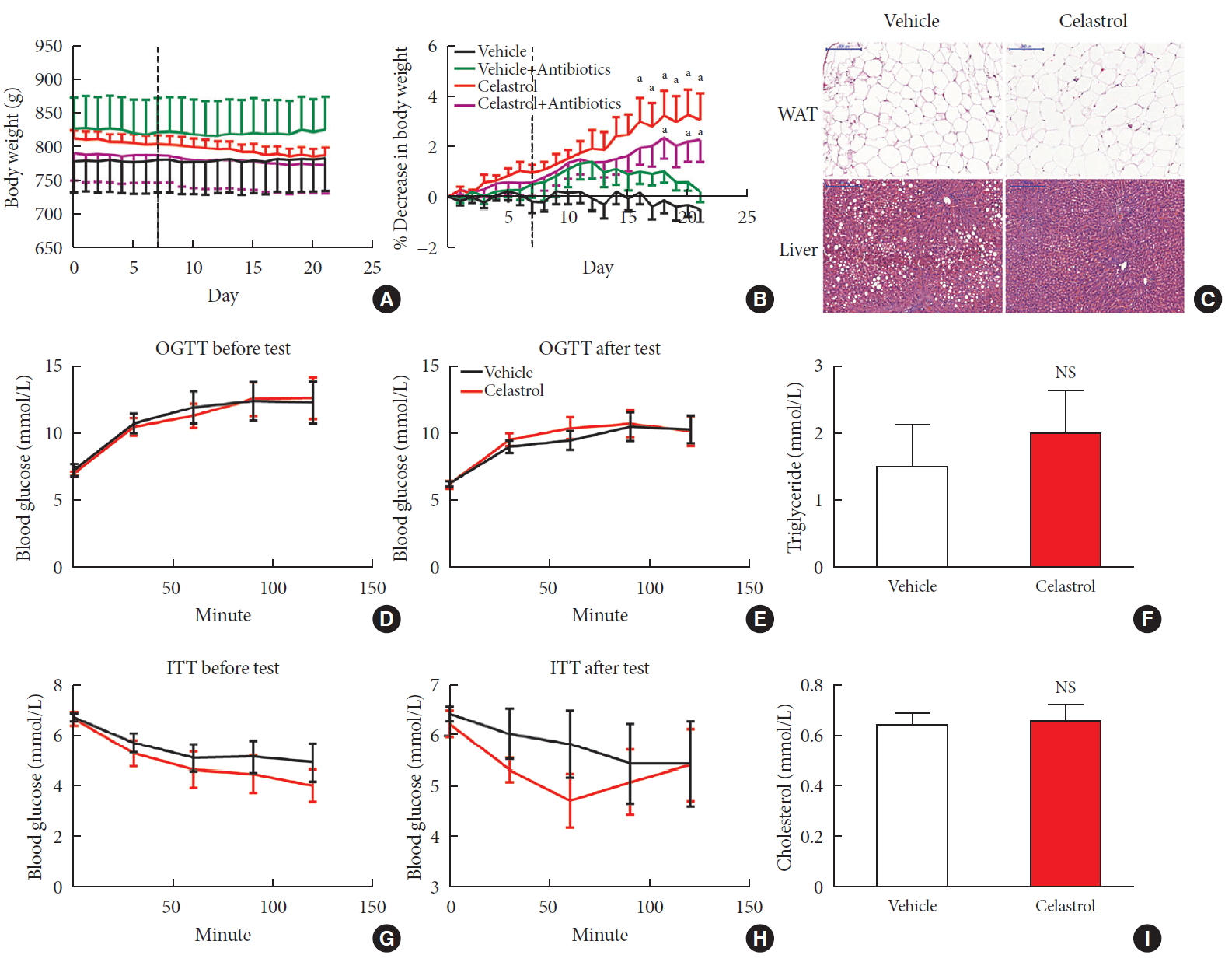
ePub Background Obesity has become one of the most serious issues threatening the health of humankind, and we conducted this study to examine whether and how celastrol protects against obesity.
Methods We fed male Sprague-Dawley rats a high-fat diet and administered celastrol to obese rats for 3 weeks. By recording body weight (BW) and other measures, we identified the effective dose of celastrol for obesity treatment. Feces were collected to perform 16S rRNA sequencing, and hypothalami were extracted for transcriptome sequencing. We then treated leptin knockout rats with celastrol and explored the changes in energy metabolism. Male Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice were used to test the acute toxicity of celastrol.
Results We observed that celastrol reduced BW and promoted energy expenditure at a dose of 500 µg/kg BW but that food intake was not changed after administration. The diversity of the gut microbiota was improved, with an increased ratio of
Bacteroidetes toFirmicutes , and the gut microbiota played an important role in the anti-obesity effects of celastrol. Hypothalamic transcriptome analysis showed a significant enrichment of the leptin signaling pathway, and we found that celastrol significantly enhanced energy expenditure, which was mediated by the leptin signaling pathway. Acute lethal toxicity of celastrol was not observed at doses ranging from 0 to 62.5 mg/kg BW.Conclusion Our study revealed that celastrol decreased the BW of obese rats by enhancing energy expenditure but not by suppressing food intake and that this effect was mediated by the improvement of the gut microbiota and the activation of the hypothalamic leptin signaling pathway.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Natural compounds as obesity pharmacotherapies
Xin‐Yuan Zhao, Ji‐Qiu Wang, G. Gregory Neely, Yan‐Chuan Shi, Qiao‐Ping Wang
Phytotherapy Research.2024; 38(2): 797. CrossRef - Celastrol functions as an emerging manager of lipid metabolism: Mechanism and therapeutic potential
Jia Gu, Ya-Ning Shi, Neng Zhu, Hong-Fang Li, Chan-Juan Zhang, Li Qin
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 164: 114981. CrossRef - Tripterygium hypoglaucum extract ameliorates adjuvant-induced arthritis in mice through the gut microbiota
Jianghui HU, Jimin NI, Junping ZHENG, Yanlei GUO, Yong YANG, Cheng YE, Xiongjie SUN, Hui XIA, Yanju LIU, Hongtao LIU
Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines.2023; 21(10): 730. CrossRef - Health improvements of type 2 diabetic patients through diet and diet plus fecal microbiota transplantation
Lili Su, Zhifan Hong, Tong Zhou, Yuanyuan Jian, Mei Xu, Xuanping Zhang, Xiaoyan Zhu, Jiayin Wang
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Tripterygium hypoglaucum (Levl.) Hutch: A systematic review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicology
Jiangping Wei, Liyun Chen, Sijia Gao, Jirui Wang, Yunhong Wang, Zhiwei Zhang, Yuyu Zhang, Xiaomei Zhang, Yong Yang, Dajian Yang
Pharmacological Research - Modern Chinese Medicine.2022; 3: 100094. CrossRef - Celastrol: An Update on Its Hepatoprotective Properties and the Linked Molecular Mechanisms
Mengzhen Li, Faren Xie, Lu Wang, Guoxue Zhu, Lian-Wen Qi, Shujun Jiang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Celastrol inhibits the proliferation and migration of MCF-7 cells through the leptin-triggered PI3K/AKT pathway
Pingping Chen, Bin Wang, Meng Li, Chunxue Cui, Fei Liu, Yonggang Gao
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2022; 20: 3173. CrossRef - Investigating Celastrol’s Anti-DCM Targets and Mechanisms via Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation
Rui Xi, Yongxin Wan, Lihong Yang, Jingying Zhang, Liu Yang, Shuai Yang, Rui Chai, Fengchen Mu, Qiting Sun, Rui Yan, Zhifang Wu, Sijin Li, Zhijun Liao
BioMed Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Celastrol inhibits TXNIP expression to protect pancreatic β cells in diabetic mice
Si-wei Wang, Tian Lan, Fang Zheng, Hui Huang, Hang-fei Chen, Qi Wu, Feng Zhang
Phytomedicine.2022; 104: 154316. CrossRef - Celastrol: A Promising Agent Fighting against Cardiovascular Diseases
Zhexi Li, Jingyi Zhang, Xulei Duan, Guoan Zhao, Min Zhang
Antioxidants.2022; 11(8): 1597. CrossRef - Celastrol: A lead compound that inhibits SARS‐CoV‐2 replication, the activity of viral and human cysteine proteases, and virus‐induced IL‐6 secretion
Carlos A. Fuzo, Ronaldo B. Martins, Thais F. C. Fraga‐Silva, Martin K. Amstalden, Thais Canassa De Leo, Juliano P. Souza, Thais M. Lima, Lucia H. Faccioli, Débora Noma Okamoto, Maria Aparecida Juliano, Suzelei C. França, Luiz Juliano, Vania L. D. Bonato,
Drug Development Research.2022; 83(7): 1623. CrossRef - In vitro activity of celastrol in combination with thymol against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates
Mahmoud Saad Abdel-Halim, Momen Askoura, Basem Mansour, Galal Yahya, Amira M. El-Ganiny
The Journal of Antibiotics.2022; 75(12): 679. CrossRef - Celastrol alleviates metabolic disturbance in high‐fat diet‐induced obese mice through increasing energy expenditure by ameliorating metabolic inflammation
Xueping Yang, Fan Wu, Lingli Li, Ernest C. Lynch, Linglin Xie, Yan Zhao, Ke Fang, Jingbin Li, Jinlong Luo, Lijun Xu, Xin Zou, Fuer Lu, Guang Chen
Phytotherapy Research.2021; 35(1): 297. CrossRef - Celastrol in metabolic diseases: Progress and application prospects
Shaohua Xu, Yaqian Feng, Weishen He, Wen Xu, Wei Xu, Hongjun Yang, Xianyu Li
Pharmacological Research.2021; 167: 105572. CrossRef - The Anti-Obesity Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Lipid Metabolism
Qijing Fan, Furong Xu, Bin Liang, Xiaoju Zou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Metabolome Mediates the Antiobesity Effect of Celastrol-Induced Gut Microbial Alterations
Shaohua Xu, Liwei Lyu, Huaichang Zhu, Xiaoqiang Huang, Wei Xu, Wen Xu, Yaqian Feng, Yong Fan
Journal of Proteome Research.2021; 20(10): 4840. CrossRef - Interrelated Mechanism by Which the Methide Quinone Celastrol, Obtained from the Roots of Tripterygium wilfordii, Inhibits Main Protease 3CLpro of COVID-19 and Acts as Superoxide Radical Scavenger
Francesco Caruso, Manrose Singh, Stuart Belli, Molly Berinato, Miriam Rossi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(23): 9266. CrossRef
- Natural compounds as obesity pharmacotherapies
- Others
- Can Habitual Exercise Help Reduce Serum Concentrations of Lipophilic Chemical Mixtures? Association between Physical Activity and Persistent Organic Pollutants
- Yu-Mi Lee, Ji-Yeon Shin, Se-A Kim, David R. Jacobs, Duk-Hee Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):764-774. Published online May 11, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0158
- 5,389 View
- 87 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Low-dose persistent organic pollutants (POPs), especially organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), have emerged as a new risk factor of many chronic diseases. As serum concentrations of POPs in humans are mainly determined by both their release from adipose tissue to circulation and their elimination from circulation, management of these internal pathways may be important in controlling the serum concentrations of POPs. As habitual physical activity can increase the elimination of POPs from circulation, we evaluated whether chronic physical activity is related to low serum POP concentrations.
Methods A cross-sectional study of 1,850 healthy adults (age ≥20 years) without cardio-metabolic diseases who participated in the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999 to 2004 was conducted. Information on moderate or vigorous leisure-time physical activity was obtained based on questionnaires. Serum concentrations of OCPs and polychlorinated biphenyls were investigated as typical POPs.
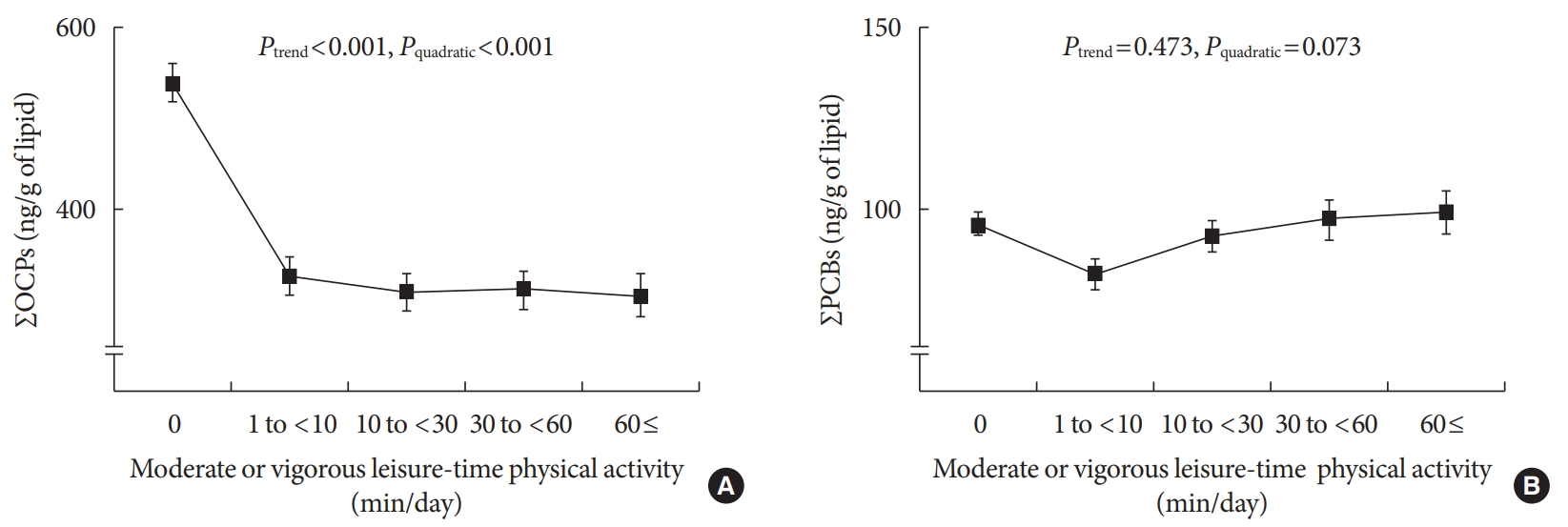
Results Serum concentrations of OCPs among physically active subjects were significantly lower than those among physically inactive subjects (312.8 ng/g lipid vs. 538.0 ng/g lipid,
P <0.001). This difference was maintained after adjustment for potential confounders. When analyses were restricted to physically active subjects, there were small decreases in the serum concentrations of OCPs with increasing duration of physical activity, showing a curvilinear relationship over the whole range of physical activity (P quadratic <0.001). In analyses stratified by age, sex, body mass index, and smoking status, a strong inverse association was similarly observed among all subgroups.Conclusion Physical activity may assist in decreasing serum concentrations of lipophilic chemical mixtures such as OCPs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is Physical Activity an Efficient Strategy to Control the Adverse Effects of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Context of Obesity? A Narrative Review
Quentin A. Serrano, Sébastien Le Garf, Vincent Martin, Serge S. Colson, Nicolas Chevalier
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 883. CrossRef - Physical exercise and persistent organic pollutants
Chang Liu, Hui sheng Hou
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19661. CrossRef - Exposure to a low concentration of mixed organochlorine pesticides impairs glucose metabolism and mitochondrial function in L6 myotubes and zebrafish
Chul-Min Park, Ki-Tae Kim, Dong-Young Rhyu
Journal of Hazardous Materials.2021; 414: 125437. CrossRef - Can Environmental Pollutants Be a Factor Linking Obesity and COVID-19?
Duk-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter to the Editor: Effect of fatty fish or nut consumption on concentrations of persistent organic pollutants in overweight or obese men and women: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Yu-Mi Lee, Duk-Hee Lee
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2020; 30(5): 849. CrossRef - Can habitual exercise really increase serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants?
Yu-Mi Lee, Duk-Hee Lee
Environment International.2020; 140: 105615. CrossRef - Response to correspondence ENVINT_2020_552 “Can habitual exercise really increase serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants?”
Sidsel L. Domazet, Tina K. Jensen, Anders Grøntved
Environment International.2020; 140: 105616. CrossRef
- Is Physical Activity an Efficient Strategy to Control the Adverse Effects of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Context of Obesity? A Narrative Review
- Letter: Differences in Clinical Outcomes between Patients with and without Hypoglycemia during Hospitalization: A Retrospective Study Using Real-World Evidence (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:555-65)
- Sung-Woo Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):775-776. Published online October 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0188
- 4,206 View
- 64 Download
- Letter: Associations among Obesity Degree, Glycemic Status, and Risk of Heart Failure in 9,720,220 Korean Adults (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:592-601)
- Darae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):777-778. Published online October 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0202
- 3,624 View
- 58 Download

 KDA
KDA


 First
First Prev
Prev





