
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 34(2); 2010 > Article
-
Original ArticleThe Clinical Characteristics of the Newly Diagnosed Early Onset (< 40 Years Old) Diabetes in Outpatients' Clinic
- Kyung-Soo Kim, Hyun-Ju Oh, Ji-Woon Kim, Yeo-Kyung Lee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seok-Won Park, Yoo-Lee Kim, Won-Keun Park, Yong-Wook Cho
-
Korean Diabetes Journal 2010;34(2):119-125.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.2.119
Published online: April 30, 2010
- 4,021 Views
- 42 Download
- 16 Crossref
Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, CHA University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Yong-Wook Cho. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, CHA University College of Medicine, 351 Yatap-dong, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 463-712, Korea. ywcho@cha.ac.kr
Copyright © 2010 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- The prevalence of type 2 diabetes in young adults and adolescents has increased in the last decade according to the increasing obese population. The aim of this study was to examine the clinical characteristics of patients diagnosed with diabetes mellitus before the age of 40 years as compared with patients diagnosed at older ages.
-
Methods
- This was a cross-sectional, retrospective study using data from 350 diabetic patients who were diagnosed with diabetes in an outpatient setting between January 2005 and December 2007. Patients were diagnosed according to the criteria set forth by the American Diabetes Association. We examined the clinical characteristics and laboratory data of the patients through review of medical records and compared the early-onset diabetic patients (< 40 years old) and the usual-onset diabetic patients (≥ 40 years old).
-
Results
- The frequency of early-onset diabetes and usual-onset diabetes were 31.1% (n=109) and 68.9% (n=241), respectively. The early-onset diabetic patients more often had a positive family history of diabetes; higher HbA1c, fasting glucose, and postprandial glucose levels; experienced typical symptoms more frequently; had microalbuminuria more frequently; and required insulin therapy as initial treatment more frequently as compared to usual-onset diabetic patients, and these differences were significant. Conversely, hypertension was significantly more common in the usual-onset diabetic patients.
-
Conclusion
- It could be concluded that we should control early onset diabetes more strictly to prevent its complication because early onset diabetic patients represented more severe hyperglycemia and had more prevalent microalbuminuria.
- Recently, the size of the aging population has increased with the increased life expectancy of the average individual, likely due to the westernization of many aspects of people's lives, and, consequently, the prevalence of diabetes has skyrocketed around the world [1,2]. The prevalence of diabetes in Korea, which was estimated to be less than 1% in 1970, increased dramatically to 7.6% of the total population in 2000 [3], and this trend is likely to continue. Additionally, the mortality rate of patients with diabetes was reported to be only 3 per 100,000 persons in 1979, whereas, in 2002, it was the fourth overall cause of death at 25 per 100,000 persons, following cancer, cerebrovascular disease, and heart disease. Moreover, the fact that diabetes is the number one cause of loss of eyesight, foot amputation (notwithstanding car accidents), and chronic renal failure requiring dialysis, shows its seriousness [4].
- In the past, diabetes was primarily regarded as a chronic disease most commonly affecting the elderly population, but, recently, the prevalence of early-onset (< 40 years of age) diabetes has increased with the growing rate of obesity [5-7]. Considering that the duration of diabetes onset is directly associated with its complications, the occurrence of diabetes in younger individuals has serious ramifications for the health of the population at large. However, it is well known that active blood sugar control through appropriate treatment can reduce the occurrence of the various diabetic complications, especially when the disease is detected early [8-10]. Additionally, the clinical characteristics of early-onset diabetic patients and those of usual-onset (≥ 40 years of age) diabetic patients have been reported to be different [11-13]. Therefore, further elucidation of the unique clinical characteristics of young diabetic patients will provide vital information for a proper diabetes management for them.
- However, there have been only a few researches on distributions of types and the clinical characteristics of early-onset diabetes, and studies comparing early-onset diabetes with usualonset diabetic patients are lacking in the literature. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the clinical characteristics of diabetes patients diagnosed at less than 40 years of age and to compare their clinical manifestation with those of diabetes patients diagnosed at age of 40 or older.
INTRODUCTION
- Subjects
- Study subjects were 350 diabetes patients newly diagnosed based according to criteria recommended by American Diabetes Association [14], selected among the patients who visited the outpatient clinic at endocrinology department of Bundang CHA general hospital from January 2005 to December 2007. Patients were divided into two groups based upon the age at diagnosis: the young group (< 40 years of age) and the older group (≥ 40 years of age). Patients who had previously used insulin preparations, oral hypoglycemic agents, or steroids; those who had received anti-cancer chemotherapy for organ transplantation or a malignant tumor; and those who had undergone pancreatectomy were excluded from the study.
- Methods
- Data were collected by retrospective review of medical records and included the age of onset of diabetes, gender, height, maximal body weight before diabetes onset, body weight at diagnosis, family history of diabetes, typical symptoms of diabetes upon visiting the hospital (polyphagia, polyuria, and weight loss), systolic and diastolic blood pressures, and treatment received during the first three months after diagnosis. A positive family history of diabetes was defined as having at least one 1st-degree or 2nd-degree relative with diabetes. The presence of hypertension was defined as taking antihypertensive agents or a recorded systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mmHg. Body mass index (BMI) (kg/m2) was calculated with patient's weight (kg) divided by height squared (m2). Maximal BMI was calculated using the maximal body weight before diagnosis. Upon diagnosis with diabetes mellitus, blood was drawn to determine the patient's fasting blood glucose (glucose oxidase method), HbA1c (high performance liquid chromatography, Bio-Rad Variant II; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA), insulin (Roche Diagnostic GmbH, Mannheim, Germany), C-peptide (Roche Diagnostic GmbH), total cholesterol, triglycerides, and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Furthermore, 2-hour postprandial serum glucose, insulin, and C-peptide were also measured. Random urine microalbumin and creatinine were measured, and the albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) was calculated. Microalbuminuria was assessed and defined as the presence of 30 mg of albumin/g of creatinine or 30 mg of albumin on 24-hour urine collection. The homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function (HOMA-β) were calculated by using the formula of Matthews et al. [15]: HOMA-IR = fasting insulin (µU/mL) × fasting blood glucose (mmol/L) / 22.5 and HOMA-β = 20 × fasting insulin (µU/mL) / (fasting blood glucose [mmol/L] - 3.5).
- Type 1 diabetes was diagnosed when the fasting C-peptide level was ≤ 0.6 ng/mL or autoantibodies were demonstrated, and type 2 diabetes was diagnosed when the fasting C-peptide level was ≥ 1.2 ng/mL. Cases that could not be classified were defined as "unclassified."
- Statistical analysis
- Statistical analysis was conducted using the SPSS software package (version 11.5; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), and statistical values were presented as mean ± standard deviation. Triglycerides, insulin, C-peptide, HOMA-IR, and HOMA-β were shown with their medians (ranges). Because triglycerides, insulin, C-peptide, HOMA-IR, and HOMA-β showed skewed distributions, they were analyzed after logarithmic transformation. Comparisons of the mean values of continuous variables between the two groups were analyzed by using the independent sample t-test, and discontinuous variables using the chi-squared test. A P-value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
METHODS
- Types of diabetes
- Fasting C-peptide levels of all subjects were measured. Of the 20 patients who had their autoantibody levels measured, only 4 were positive. The number of patients with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and unclassified diabetes were 8 (2.3%), 315 (90.0%), and 27 (7.7%), respectively. Of the 109 patients (31.1%) who were diagnosed at less than 40 years, 6.4% were type 1 diabetes, 85.3% were type 2 diabetes, and 8.3% were unclassified diabetes (Table 1).
- Clinical characteristics of subjects
- Of the total 350 subjects, the mean age of diabetes onset was 47.5 ± 13.5 years, and the mean BMI was 25.1 ± 3.6 kg/m2. Among them, 232 patients (66.3%) were male and 151 patients (43.1%) had a positive family history of diabetes (Table 2).
- Differences in clinical characteristics according to age of onset
- The mean age of the young group and the older group was 31.8 ± 6.4 years was and 54.6 ± 9.3 years, respectively. The rate of males was higher in the young group compared with the older group, and the young group showed more frequent positive family history of diabetes, higher maximal BMI, higher fasting and postprandial glucose levels, higher HbA1c, and higher HOMA-IR compared with the older group. Although there were no differences in BMI, fasting C-peptide, fasting and postprandial insulin, HOMA-β, total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL-C, or LDL-C between the two groups, the older group had a higher frequency of hypertension, higher systolic and diastolic blood pressures, and higher postprandial C-peptide levels. Although urinary albumin excretion was not measured in all subjects, among the 241 patients who were tested for urine albumin, microalbuminuria was found more frequently in the young group compared with older group (Table 2).
- Among the young group, 20.2% had their HbA1c at diagnosis less than 8%, and 33% had those over 12%. In contrast, 36.9% of patients in the older group had their HbA1c at diagnosis less than 8% and 12.4% of patients had those over 12%. Therefore, the average blood glucose tended to be higher in the young group (P for trend < 0.05; Fig. 1). In addition, the younger the age of diabetes onset was, the higher HbA1c at diagnosis was shown (P for trend < 0.05; Fig. 2).
- Differences in symptoms and treatments according to age of onset
- Typical symptoms of diabetes due to hyperglycemia (polyphagia, polyuria, and weight loss) were found in 63.3% of the young group, while they were found only in 29.9% of the older group (P < 0.05). During the first three months after diagnosis, 18.3% of the young group required insulin treatment compared to only 4.1% of patients in the older group (P < 0.05; Fig. 3).
RESULTS
- As the prevalence and incidence of diabetes have skyrocketed around the world as well as in Korea due to lifestyle changes, concern about the disease is greater than ever. Moreover, diabetes, a disease which was previously considered to be a chronic disease frequently found in the elderly, occurs in young adults and even in adolescents with gradual increase of prevalence. Due to a known close correlation between the development of complications and the disease duration, and due to the fact that the HbA1c level will increase gradually despite intensive treatment, determining clinical characteristics of early-onset diabetes patients and treating their disease properly are critical to prevent its complications. However, there have been only a few studies on the investigation of clinical characteristics of diabetes occurring in young adults and adolescents, and comparing their characteristics with those in adults.
- Researches performed in young diabetes patients have reported the prevalence of type 1 and 2 diabetes differently. According to a report published in Korea [16], when 235 diabetes patients diagnosed at less than 35 years of age were classified according to their C-peptide levels, the rates of type 1, type 2, and unclassified diabetes were 13.8%, 80.3%, and 5.9%, respectively. Another study [17] using data from 85 diabetes patients diagnosed at less than 30 years of age, reported that when the type of diabetes was classified according to the fasting C-peptide level, the existence of autoantibodies, and the causes of ketoacidosis, the frequencies of type 1, type 2, and unclassified diabetes were 45.9%, 23.5%, and 25.9%, respectively. The present study found that, among the 109 newly diagnosed patients at less than 40 years of age, the frequencies of type 1, type 2, and unclassified diabetes were 6.4%, 85.3%, and 8.3%, respectively. Possible reasons for this high rate of type 2 diabetes in this early-onset diabetes population could be, i) because this study investigated only outpatients, some patients having type 1 diabetes who initially presented with diabetic ketoacidosis could have been excluded, ii) because autoantibodies of all of the patients were not available, and iii) because the application of relatively higher age cutoff of early-onset diabetes could have led to higher prevalence of type 2 diabetes. The finding that most of the early-onset diabetes patients had type 2 diabetes, not type 1 diabetes, different from our expectation, may suggest that the increasing rate of obesity is having a significant effect on the metabolic status of the younger population.
- Prevalence of diabetes diagnosed at young ages varies according to researchers and regions. A study by Chuang et al. [12] conducted in Asians, reported that the prevalence of diabetes diagnosed at less than 30 years of age varied from 0.4 to 5.6% according to countries, and another study performed in Mexicans showed that the prevalence of diabetes diagnosed at less than 40 years of age was 14% [18]. According to a study by Hillier and Pedula [11], the prevalence of diabetes diagnosed at less than 45 years of age was 11.4%. The present study employed an age cutoff for early-onset diabetes as 40 years of age because this is the age at which diabetes screening was conducted in Korea, and four representative cohort studies on diabetes in Korea reported that its prevalence increases significantly as patients reach the age of 40 and beyond [19]. The prevalence of diabetes diagnosed at less than 40 years of age observed in this study was 31.1%, which was relatively higher than those reported in previous studies, and this discrepancy could be due to the fact that this study examined patients diagnosed with diabetes by their voluntary visit to the hospital, did not use questionnaires or employ the patients' recollections, and excluded patients who had already taken oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin preparations. However, the findings of the present study were consistent with those of previous studies that reported that changes in diet and reduced physical activity have led to a fast-growing obese population and an increase in the prevalence and incidence of diabetes in younger persons [20-22].
- Among persons with a positive family history of diabetes, the disease is known to occur earlier, and obesity has been reported to play a key role in its early onset. Shim et al. [23] reported that diabetes occurred more earlier when persons had a family history of diabetes or a genetic predisposition to beta cell dysfunction along with associated insulin resistance, such as obesity. These results are concordant with those of the present study, which showed that the young group had a higher rate of positive family history of diabetes, higher maximal BMI, and higher HOMA-IR than the older group. However, the finding that no difference in BMI according to age of onset was observed, and that the maximal BMI was higher in the young group compared with the older group, suggests that efforts to reduce body weight and increase exercise to improve insulin sensitivity could decrease the occurrence of diabetes at younger ages because a rapid increase in body weight may lead to or aggravate insulin resistance, and higher insulin resistance could be a factor provoking the development of diabetes.
- In addition, the young group was observed to have higher fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels at diagnosis, higher HbA1c, more typical symptoms of the disease, and more prevalent microalbuminuria than the usual-onset group. Chuang et al. [12] reported that, among type 2 diabetes patients diagnosed at less than 30 years of age, fasting blood glucose and HbA1c at diagnosis were higher than those of type 2 diabetic patients diagnosed at older ages. Park et al. [17] showed in their study performed in diabetes patients aged less than 30 years, that HbA1c levels at diagnosis and in 6.8-year follow-up, were higher than those of older patients with type 2 diabetes measured in other studies, and that the prevalence of complications was relatively higher in young diabetes patients with 32.9% of diabetic retinopathy, 22.4% of neuropathy and 16.4% of proteinuria. In line with the results with previous reports, the higher blood glucose levels in diabetes patients diagnosed at younger age compared with those in older group, could be considered because they had more possibility to visit a hospital due to dietary changes, decreased physical activity, increased work hours, and more confidence in their health. In addition, considering that young diabetes patients had lower postprandial C-peptide levels and higher HOMA-IR, their beta cell function might had been already declined with more serious degree of insulin resistance, causing higher HbA1c levels. Therefore, complications of diabetes could progress faster and more seriously in young diabetes patients, and more efforts for early detection of the disease and for strict blood glucose control are warranted to deal with the future burden of complications in these young patients.
- This study has limitations as a cross-sectional and single center study. In addition, for microalbuminuria measured at diagnosis, there could be a possibility of false positive results caused by high blood sugar. However, our study is meaningful in that we compared various examination results and clinical characteristics at diagnosis according to the age of diabetes onset. Large-scaled, randomized, prospective studies are necessary to determine progressive clinical characteristics including the development of complications and the outcomes of intensive blood sugar control in this patient population.
- These days, the prevalence of young diabetes patients has increased continuously. However, the rate of type 2 diabetes patients, different from our expectation, was high in this early-onset diabetes patients, and these young patients showed more frequent positive family history of diabetes, exhibited more typical symptoms associated with high blood sugar at diagnosis, and more prevalent microalbuminuria. Therefore, active and strict blood sugar control at its early stage is warranted to prevent future diabetic complications.
DISCUSSION
- 1. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004;27:1047-1053. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995-2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care 1998;21:1414-1431. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Kim SM, Lee JS, Lee J, Na JK, Han JH, Yoon DK, Baik SH, Choi DS, Choi KM. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Korea: Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. Diabetes Care 2006;29:226-231. PubMed
- 4. Korea National Statistical Office. Annual report on the cause of death statistics, 2003. 2004. Daejeon: Korea National Statistical Office.
- 5. Mokdad AH, Serdula MK, Dietz WH, Bowman BA, Marks JS, Koplan JP. The spread of the obesity epidemic in the United States, 1991-1998. JAMA 1999;282:1519-1522. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, Nelson DE, Engelgau MM, Vinicor F, Marks JS. Diabetes trends in the U.S.: 1990-1998. Diabetes Care 2000;23:1278-1283. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Rhee BD. Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus among Korean population. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 2003;27:173-178.
- 8. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977-986. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, Hadden D, Turner RC, Holman RR. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ 2000;321:405-412. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Ohkubo Y, Kishikawa H, Araki E, Miyata T, Isami S, Motoyoshi S, Kojima Y, Furuyoshi N, Shichiri M. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a randomized prospective 6-year study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1995;28:103-117. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Hillier TA, Pedula KL. Complications in young adults with early-onset type 2 diabetes: losing the relative protection of youth. Diabetes Care 2003;26:2999-3005. PubMed
- 12. Chuang LM, Soegondo S, Soewondo P, Young-Seol K, Mohamed M, Dalisay E, Go R, Lee W, Tong-Yuan T, Tandhanand S, Nitiyanant W, The-Trach M, Cockram C, Jing-Ping Y. Comparisons of the outcomes on control, type of management and complications status in early onset and late onset type 2 diabetes in Asia. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2006;71:146-155. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Krakoff J, Lindsay RS, Looker HC, Nelson RG, Hanson RL, Knowler WC. Incidence of retinopathy and nephropathy in youth-onset compared with adult-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003;26:76-81. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2008;31(Suppl 1):S55-S60. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985;28:412-419. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Kim HY, Lee CJ, Kang SJ, Hong HK, Baik JM, Oh YB, Jeong DK, Yoo SJ, Kim SM, Kim DS, Kim EJ. A clinical study on Korean 235 diabetes under the age of 35 years. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 1994;18:322-329.
- 17. Park M, Kang YI, Chon S, Oh SJ, Woo JT, Kim SW, Kim JW, Kim YS. The clinical characteristics of young onset diabetes according to etiology based classification. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 2006;30:190-197.Article
- 18. Aguilar-Salinas CA, Rojas R, Gomez-Perez FJ, Garcia E, Valles V, Ríos-Torres JM, Franco A, Olaiz G, Sepülveda J, Rull JA. Prevalence and characteristics of early-onset type 2 diabetes in Mexico. Am J Med 2002;113:569-574. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Oh JY, Lim S, Kim DJ, Kim NH, Moon SD, Jang HC, Cho YM, Song KH, Park KS. The diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in Korea: a pooled analysis of four community-based cohort studies. Diabet Med 2007;24:217-218. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, Zimmet P, Son HY. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet 2006;368:1681-1688. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Ramachandran A, Mary S, Yamuna A, Murugesan N, Snehalatha C. High prevalence of diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors associated with urbanization in India. Diabetes Care 2008;31:893-898. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Gu D, Reynolds K, Duan X, Xin X, Chen J, Wu X, Mo J, Whelton PK, He J. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in the Chinese adult population: International Collaborative Study of Cardiovascular Disease in Asia (InterASIA). Diabetologia 2003;46:1190-1198. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Shim WS, Kim HJ, Kim SK, Han SJ, Kang ES, Rhee YM, Ahn CW, Lim SK, Kim KR, Lee HC, Cha BS. The association of family history of diabetes and obesity in the development of type 2 diabetes. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 2005;29:540-547.
REFERENCES

Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation or number (%).
BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; PP, postprandial.
aEarly-onset, onset at < 40 years of age, bUsual-onset, onset at ≥ 40 years of age, cP < 0.05, early-onset vs usual-onset, dMaximal BMI, calculated using maximal weight, eMicroalbuminuria, albumin/creatinine ratio, ACR ≥ 30 or 30 mg/g of creatinine or mg/day and data are expressed as positive microalbuminuria number/measured microalbuminuria number (%).
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Clinical features of early-onset type 2 diabetes and its association with triglyceride glucose-body mass index: a cross-sectional study
Yanjuan Jiang, Xiaoyang Lai
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical characteristics of patients with early-onset diabetes mellitus: a single-center retrospective study
Wenjing Dong, Saichun Zhang, Shiju Yan, Zhizhuang Zhao, Zengqiang Zhang, Weijun Gu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Chronic Disease and Health Care Utilization Among Young Adults in South Korea
Jongho Park, Yeaeun Kim
Population Health Management.2022; 25(3): 407. CrossRef - Therapeutic potential of dopamine agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Md. Tanvir Kabir, Jannatul Ferdous Mitu, Raushanara Akter, Muhammad Furqan Akhtar, Ammara Saleem, Ahmed Al-Harrasi, Saurabh Bhatia, Md. Sohanur Rahman, Fouad Damiri, Mohammed Berrada, Md. Habibur Rahman
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2022; 29(31): 46385. CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 641. CrossRef - The Difference in Risk Factors Between Adults With Early-Onset (<40 Years Old) Versus Late-Onset (≥40 Years Old) Type 2 Diabetes in a University Hospital From January 2015-December 2017
Marilyn Katrina C Caro, Elaine C Cunanan
Journal of Medicine, University of Santo Tomas.2022; 6(2): 1009. CrossRef - Comparison of clinical features, complication profile, and achievement of guideline targets in early- and late-onset type 2 diabetes patients from North India
Hamid Ashraf, Ahmad Faraz, Jamal Ahmad
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(3): 396. CrossRef - Questionnaire-based Survey of Demographic and Clinical Characteristics, Health Behaviors, and Mental Health of Young Korean Adults with Early-Onset Diabetes
Ji In Park, Hyunjeong Baek, Sang-Wook Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Kee-Ho Song, Ji Hee Yu, Il Sung Nam-Goong, Eun-Hee Cho
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association among Lifestyle Factors, Obesity, C-peptide Secretion, Metabolic Syndrome, and Cardiovascular Risk in Adults with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Study
Sun-Young Kwon, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(2): 125. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes in adolescents and young adults
Nadia Lascar, James Brown, Helen Pattison, Anthony H Barnett, Clifford J Bailey, Srikanth Bellary
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2018; 6(1): 69. CrossRef - The relationship between age of onset and risk factors including family history and life style in Korean population with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Jin-Won Noh, Jin Hee Jung, Jeong Eun Park, Jung Hwa Lee, Kang Hee Sim, Jumin Park, Min Hee Kim, Ki-Bong Yoo
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2018; 30(2): 201. CrossRef - Early-onset diabetes: an epidemic in China
Jiemin Pan, Weiping Jia
Frontiers of Medicine.2018; 12(6): 624. CrossRef - Distinct Predictors and Comorbidities in Early Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Asian Indians
Gadadharan Vijayakumar, Ganapathy K. Sreehari, Aswathi Vijayakumar, Abdul Jaleel
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2017; 15(9): 458. CrossRef - A Predictive Model of Health Outcomes for Young People with Type 2 Diabetes
Sun Young Jung, Sook Ja Lee, Sun Hee Kim, Kyung Mi Jung
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(1): 73. CrossRef - An assessment of the impact of type 2 diabetes on the quality of life based on age at diabetes diagnosis
Jin Ook Chung, Dong Hyeok Cho, Dong Jin Chung, Min Young Chung
Acta Diabetologica.2014; 51(6): 1065. CrossRef - Characteristics, complications and management of a large multiethnic cohort of younger adults with type 2 diabetes
Katrien Benhalima, Soon H. Song, Emma G. Wilmot, Kamlesh Khunti, Laura J. Gray, Ian Lawrence, Melanie Davies
Primary Care Diabetes.2011; 5(4): 245. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA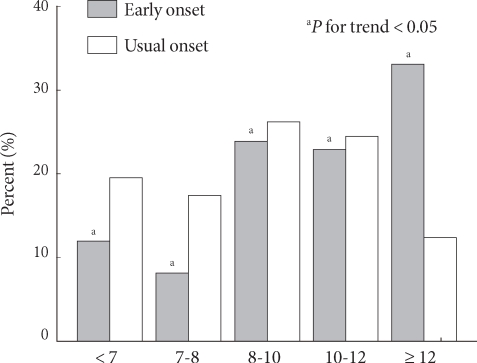



 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite






