
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 39(2); 2015 > Article
-
Original ArticleClinical Care/Education 1,5-Anhydroglucitol as a Useful Marker for Assessing Short-Term Glycemic Excursions in Type 1 Diabetes
- Hannah Seok1, Ji Hye Huh2, Hyun Min Kim3, Byung-Wan Lee4, Eun Seok Kang4, Hyun Chul Lee4, Bong Soo Cha4
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2015;39(2):164-170.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.2.164
Published online: March 9, 2015
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea.
2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Bong Soo Cha. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 120-752, Korea. bscha@yuhs.ac
Copyright © 2015 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- Type 1 diabetes is associated with more severe glycemic variability and more frequent hypoglycemia than type 2 diabetes. Glycemic variability is associated with poor glycemic control and diabetic complications. In this study, we demonstrate the clinical usefulness of serum 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) for assessing changes in glycemic excursion in type 1 diabetes.
-
Methods
- Seventeen patients with type 1 diabetes were enrolled in this study. A continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) was applied twice at a 2-week interval to evaluate changes in glycemic variability. The changes in serum glycemic assays, including 1,5-AG, glycated albumin and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), were also evaluated.
-
Results
- Most subjects showed severe glycemic excursions, including hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. The change in 1,5-AG level was significantly correlated with changes in the glycemic excursion indices of the standard deviation (SD), mean amplitude of glucose excursion (MAGE), lability index, mean postmeal maximum glucose, and area under the curve for glucose above 180 mg/dL (r=-0.576, -0.613, -0.600, -0.630, and -0.500, respectively; all P<0.05). Changes in glycated albumin were correlated with changes in SD and MAGE (r=0.495 and 0.517, respectively; all P<0.05). However, changes in HbA1c were not correlated with any changes in the CGMS variables.
-
Conclusion
- 1,5-AG may be a useful marker for the assessment of short-term changes in glycemic variability. Furthermore, 1,5-AG may have clinical implications for the evaluation and treatment of glycemic excursions in type 1 diabetes.
- Chronic hyperglycemia is a well-established risk factor for microvascular and macrovascular complications in diabetes [1,2]. Recent studies have reported that glycemic excursions, including both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, are independent risk factors for macrovascular complications [3,4,5].
- Hypoglycemia occurs more frequently in type 1 diabetes than in type 2 diabetes [6]. The titration of insulin doses is indispensable for glycemic control of type 1 diabetes. However, efforts to obtain ideal glycemic control often accompany hypoglycemia, and fear of hypoglycemia often makes glycemic control difficult [7,8]. Therefore, glycemic excursion, including hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, should be evaluated and corrected for proper treatment of type 1 diabetes [9].
- A continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) is currently used to evaluate glycemic excursion, and this is especially useful for type 1 diabetes [10]. Unfortunately, CGMS is expensive and inconvenient because patients must be attached to a needle for several days. Therefore, CGMS is not often used in clinical practice. The serum marker hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is the gold standard for the evaluation of overall glycemic control. However, previous studies have shown that HbA1c levels do not accurately represent glucose fluctuations [5,11]. Therefore, surrogate serum markers that reflect glycemic excursions are needed.
- 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) is naturally occurring in the human body and is structurally similar to glucose [12]. It is filtered in the kidneys and 99.9% is reabsorbed in the renal tubules. Under normal conditions, serum levels of 1,5-AG are constant due to a balance between intake and excretion in renal tubules. When blood glucose is higher than the renal threshold of approximately 180 mg/dL, glucose inhibits renal re-absorption of 1,5-AG and serum 1,5-AG levels [13]. Thus, serum 1,5-AG levels are inversely correlated with hyperglycemia. Interestingly, recent studies have reported that 1,5-AG could reflect glucose excursion over a short term period ranging from 1 to 3 days to several weeks [14,15,16]. However, no previous studies have evaluated whether changes in serum 1,5-AG levels are correlated with changes in glycemic excursions.
- The aim of this study was to evaluate whether 1,5-AG is a useful marker for evaluating short term changes in glycemic excursion. In this study, we examined whether 1,5-AG could be a useful serum assay for assessment and treatment of glycemic excursion in type 1 diabetes.
INTRODUCTION
- Study design and patients
- Seventeen subjects aged 18 to 65 years with type 1 diabetes were recruited at Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea. All subjects were treated with multiple daily injections (MDIs) or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII). The exclusion criteria for this study included severe medical illnesses, pregnancy, anemia, serum creatinine >1.5 mg/dL, or serum albumin <3.5 mg/dL. CGMS was applied to each patient twice with a 2-week interval. The serum glycemic markers were simultaneously measured for the 2-week interval.
- After the first CGMS analysis, the results from CGMS data were analyzed by a single clinician. The patients were subsequently presented with their results and were taught how to manage glucose control via exercise, diet, and adjustment of insulin dosage. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Severance Hospital (4-2011-0144). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
- Continuous glucose monitoring system and data analysis
- A CGMS (Medtronic Minimed, Northridge, CA, USA) was applied to each subject for approximately 72 hours at a 2-week interval. The CGMS sensor measured interstitial tissue fluid glucose every 5 minutes. For calibration, patients were instructed to check their seven-point fingerstick glucose profiles before a meal, 2 hours after a meal, and at bedtime and to enter the data into the CGMS. After 72 hours, the recorded data were downloaded using Medtronic CGMS software. The data recorded during the middle 48 hours were used for analysis in this study. To evaluate glycemic variability, the standard deviation (SD), continuous overall net glycemic action (CONGA), mean amplitude of glycemic excursion (MAGE), lability index (LI), and mean post-meal maximum glucose (MPMG) were calculated using the CGMS data. CONGA-1 was calculated as the SD of the differences between glucose level and the corresponding glucose level measured 1 hour earlier [17]. MAGE was defined as the mean of the absolute difference in peak-to nadir or nadir-to peak direction and was used for assessing intra-day glycemic variability [18]. More than one SD of glycemic excursions were taken into account for MAGE analysis. The LI is calculated by dividing the sum of the square of the difference between successive glucose measurements by the difference in time between measurements [19]. MPMG is the mean of maximal blood glucose levels at 4 hours after consumption of each meal [20]. The area under the curve for a glucose level greater than 180 mg/dL (AUC-180) was measured as the total area of glucose excursions greater than 180 mg/dL [21].
- Measurement of serum glycemic markers
- Serum levels of fasting glucose and postprandial glucose were measured by standard methods. Serum 1,5-AG was measured using an enzymatic assay kit (Kyowa Medex, Tokyo, Japan) and an auto-Hitachi 7600 DDP analyzer (Hitachi High-Technologies Co., Tokyo, Japan) according to the manufacturers' instructions. Serum glycated albumin was measured enzymatically using an albumin-specific proteinase (ketoamine oxidase) and albumin assay reagent (LUCICA GA-L; Asahi Kasei Pharma Co., Tokyo, Japan) with a Hitachi 7699 P-module auto-analyzer (Hitachi Instruments Service, Tokyo, Japan). HbA1c was measured by high-performance liquid chromatography using Variant TM II Turbo (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). The normal ranges are 10.7 to 32.0 µg/mL for 1,5-AG, 11% to 16% for glycated albumin, and 4.0% to 6.0% for HbA1c.
- Statistical analysis
- The data are expressed as the mean with SD or number (proportions). The data changes were established by calculating the differences between the data for a 2-week interval in each subject. Changes of glycemic markers and CGMS variables for a 2-week interval were compared using a nonparametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test. The correlation coefficients were determined using Spearman correlation coefficients. Correlations between changes in glycemic variability indices and changes in serum glycemic markers were analyzed according to baseline mean glucose level (<180 and ≥180 mg/dL). A log transformation was performed for skewed data before further analyses. All statistical analyses were conducted in SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
METHODS
- Baseline characteristics
- The baseline characteristics of the subjects are shown in Table 1. The mean age of the subjects was 49 years, and the mean duration of diabetes was 11.2 years. All subjects were treated with either MDI (88%) or CSII (12%). We collected data at baseline and 2 weeks later. The levels of mean 1,5-AG and mean glycated albumin improved (P=0.017 and P=0.004, respectively). However, there were no differences in mean HbA1c (P=0.077). There were no significant differences between the baseline and CGMS measures after 2 weeks.
- Correlations between changes in serum glycemic assays and changes in CGMS measures
- We then compared the relationship between changes in serum glycemic assays and changes in CGMS variability indices for a 2-week interval (Table 2). The results showed the change in 1,5-AG (Δ1,5-AG) level was significantly correlated with changes in most of the variability indices of CGMS. The Δ1,5-AG was correlated with changes in SD (r=-0.576, P=0.016), MAGE (r=-0.613, P=0.009), LI (r=-0.600, P=0.011), and MPMG (r=-0.630, P=0.007). A change in glycated albumin (Δglycated albumin) was correlated with changes in a several variability indices, including changes in SD (r=0.495, P=0.043) and MAGE (r=0.517, P=0.033). However, changes in HbA1c (ΔHbA1c) did not show a significant correlation with changes in any CGMS variability indices.
- Correlations between changes in serum glycemic assays and changes in CGMS measures according to glycemic control
- To further investigate the clinical usefulness of these findings, the subjects were classified into either the moderate glycemic control group (baseline mean CGMS glucose <180 mg/dL) or the poor glycemic control group (baseline mean CGMS glucose ≥180 mg/dL) (Table 3). In subjects with moderate control (n=11), the Δ1,5-AG showed a significant correlation with changes in CGMS variability indices (mean blood glucose, SD, CONGA-1, MPMG, and AUC-180 [r=-0.609, r=-0.645, r=-0.755, r=-0.764, and r=-0.727, respectively; all P<0.05]). ΔGlycated albumin was only correlated with changes in MAGE (r=0.662, P=0.026). Additionally, ΔHbA1c showed no significant correlation with changes in any CGMS variability indices. Interestingly, in the poor glycemic control group (n=6), Δ1,5-AG, Δglycated albumin, and ΔHbA1c showed no correlations with changes in CGMS glycemic variability indices.
RESULTS
- The Diabetes Control and Complication Trial and the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study demonstrated that chronic hyperglycemia is a risk factor for diabetic complications. Thus, improving glycemic control can reduce diabetic complications [22,23]. Lowering hyperglycemia is currently the main treatment of diabetic patients. However, many recent reports have demonstrated that glycemic variability is associated with diabetic complications independent from hyperglycemia [24,25]. The reason for this finding could be that glycemic variability increases oxidative stress or inflammation, which are both important mediators of hyperglycemia-mediated cellular damage [26,27]. HbA1c is a proper marker for the evaluation of chronic hyperglycemia and is most widely used for determining overall glycemic control in clinical practice. However, it has been reported that HbA1c is not suitable for the evaluation of short-term glycemic control or assessment of glucose fluctuation [23]. In type 1 diabetes, glycemic variability is usually severe and is important. In relatively well-controlled type 1 diabetes, severe glycemic variability and hypoglycemia often occur and are important causes of low treatment compliance [7,28]. Thus, proper assessment of glycemic variability and hypoglycemia is very important for treatment of type 1 diabetes. In our study, patients with type 1 diabetes showed severe glycemic variability. More than half of the subjects showed both severe hypoglycemia (<70 mg/dL) and hyperglycemia (>400 mg/dL) when analyzed with CGMS (data not shown). In this study, 1,5-AG levels in subjects were very low (3.8±2.8 µg/mL) when considering the normal range of 1,5-AG is 10.7 to 32.0 µg/mL. This finding might be suggestive of severe glycemic variability in type 1 diabetes. The mean MPMG (240±39 mg/dL) and mean AUC-180 (23.0±14.6 mg·dL-1·day-1) indicated there was severe postprandial hyperglycemic excursion despite a relatively favorable overall glycemic control of the mean glucose level (166±28 mg/dL). The high mean SD values (63±12 mg/dL) also suggested that there was demonstrable glycemic excursion, including both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
- CGMS is the main method currently used for the evaluation of glycemic variability. Many reports have noted that CGMS could be useful to evaluate the glycemic status and improved glycemic control in type 1 diabetes [11]. Unfortunately, CGMS is not often used in clinical practice because it is expensive and inconvenient. Therefore, there is a need for a simple and convenient method of glycemic variability assessment.
- When using serum glycemic assays to evaluate the improvement or deterioration of glycemic excursion or assessment of a treatment effect on glycemic excursion, the changes in these markers should be associated with changes in glycemic variability. There are no prior studies establishing that changes of serum glycemic assays reflect short term changes in glucose variability.
- In this study, changes in the 1,5-AG level were significantly correlated with changes in CGMS variability indexes, such as SD, MAGE, LI, MPMG, and AUC-180. The changes in glycated albumin showed a partial correlation with changes in the CGMS variability indexes (SD and MAGE). As expected from previous studies, changes in HbA1c did not show a correlation with changes of any variability indexes. There were no gender differences correlated between changes of serum glycemic markers and changes of CGMS variability markers (data not shown). Interestingly, changes in 1,5-AG reflected changes in glycemic variability, especially in patients with a relatively lower mean blood glucose level, but not in cases with higher mean blood glucose levels. This finding is consistent with previous clinical studies showing that 1,5-AG is more useful in evaluating glycemic variability in well- or moderately controlled patients [14,15,20]. The reason for this finding is not yet clear. However, the characteristics of 1,5-AG might provide a possible explanation. In poorly controlled subjects, 1,5-AG levels decrease substantially (nearly an exhausted state). It might take time until the 1,5-AG level is restored. Therefore, changes in the 1,5-AG level could be less apparent in poorly controlled subjects than in well-controlled subjects. This finding might explain the differing results between the well-controlled and poorly controlled subjects in this study. Consistent with our study, Dungan [14] proposed that the 1,5-AG level is appropriate for the evaluation of glycemic variability in well-or moderately controlled patients, which could be appropriate for monitoring short term overall hyperglycemia in poorly controlled patients. Therefore, 1,5-AG could be a useful marker in subjects with severe glycemic excursions despite fair glycemic control.
- This is the first study to demonstrate that 1,5-AG level changes reflect short term changes in glycemic variability. The limitation of this study is the small number of enrolled subjects. Further studies are required to determine which subjects might benefit the most from assessment of 1,5-AG. It is known that the 1,5-AG level could be different in patients with renal impairment, severe liver dysfunction, pregnancy, or persistent glucosuria. Additional studies evaluating the usefulness of 1,5-AG in these patients are needed.
- In conclusion, serum 1,5-AG might be a useful marker for assessing short-term changes in glucose variability in Korean type 1 diabetes, especially in moderately controlled subjects. Furthermore, 1,5-AG levels may be valuable in assessing changes in glycemic variability and could be helpful in achieving better glycemic control with less glycemic excursions.
DISCUSSION
-
Acknowledgements
- This study was supported by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. 2010-0028367).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
NOTES
- 1. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulindependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977-986. ArticlePubMed
- 2. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837-853. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Brownlee M, Hirsch IB. Glycemic variability: a hemoglobin A1c-independent risk factor for diabetic complications. JAMA 2006;295:1707-1708. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Gallagher A, Home PD. The effect of improved post-prandial blood glucose control on post-prandial metabolism and markers of vascular risk in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2005;67:196-203. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Temelkova-Kurktschiev TS, Koehler C, Henkel E, Leonhardt W, Fuecker K, Hanefeld M. Postchallenge plasma glucose and glycemic spikes are more strongly associated with atherosclerosis than fasting glucose or HbA1c level. Diabetes Care 2000;23:1830-1834. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Greven WL, Beulens JW, Biesma DH, Faiz S, de Valk HW. Glycemic variability in inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes on intensive insulin therapy: a cross-sectional, observational study. Diabetes Technol Ther 2010;12:695-699. ArticlePubMed
- 7. UK Hypoglycaemia Study Group. Risk of hypoglycaemia in types 1 and 2 diabetes: effects of treatment modalities and their duration. Diabetologia 2007;50:1140-1147. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Kudva YC, Basu A, Jenkins GD, Pons GM, Vogelsang DA, Rizza RA, Smith SA, Isley WL. Glycemic variation and hypoglycemia in patients with well-controlled type 1 diabetes on a multiple daily insulin injection program with use of glargine and ultralente as basal insulin. Endocr Pract 2007;13:244-250. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Kim JT, Oh TJ, Lee YA, Bae JH, Kim HJ, Jung HS, Cho YM, Park KS, Lim S, Jang HC, Lee HK. Increasing trend in the number of severe hypoglycemia patients in Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:166-172. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Danne T, de Valk HW, Kracht T, Walte K, Geldmacher R, Solter L, von dem Berge W, Welsh ZK, Bugler JR, Lange K, Kordonouri O. Reducing glycaemic variability in type 1 diabetes self-management with a continuous glucose monitoring system based on wired enzyme technology. Diabetologia 2009;52:1496-1503. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. McCall AL, Cox DJ, Crean J, Gloster M, Kovatchev BP. A novel analytical method for assessing glucose variability: using CGMS in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther 2006;8:644-653. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Yamanouchi T, Akanuma Y. Serum 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5 AG): new clinical marker for glycemic control. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1994;24(Suppl):S261-S268. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Dworacka M, Winiarska H, Szymanska M, Kuczynski S, Szczawinska K, Wierusz-Wysocka B. 1,5-anhydro-D-glucitol: a novel marker of glucose excursions. Int J Clin Pract Suppl 2002;129:40-44.
- 14. Dungan KM. 1,5-anhydroglucitol (GlycoMark) as a marker of short-term glycemic control and glycemic excursions. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 2008;8:9-19. ArticlePubMed
- 15. Won JC, Park CY, Park HS, Kim JH, Choi ES, Rhee EJ, Lee WY, Oh KW, Kim SW, Park SW. 1,5-Anhydroglucitol reflects postprandial hyperglycemia and a decreased insulinogenic index, even in subjects with prediabetes and well-controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2009;84:51-57. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Stettler C, Stahl M, Allemann S, Diem P, Schmidlin K, Zwahlen M, Riesen W, Keller U, Christ E. Association of 1,5-anhydroglucitol and 2-h postprandial blood glucose in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2008;31:1534-1535. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 17. McDonnell CM, Donath SM, Vidmar SI, Werther GA, Cameron FJ. A novel approach to continuous glucose analysis utilizing glycemic variation. Diabetes Technol Ther 2005;7:253-263. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Service FJ, Molnar GD, Rosevear JW, Ackerman E, Gatewood LC, Taylor WF. Mean amplitude of glycemic excursions, a measure of diabetic instability. Diabetes 1970;19:644-655. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Ryan EA, Shandro T, Green K, Paty BW, Senior PA, Bigam D, Shapiro AM, Vantyghem MC. Assessment of the severity of hypoglycemia and glycemic lability in type 1 diabetic subjects undergoing islet transplantation. Diabetes 2004;53:955-962. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Dungan KM, Buse JB, Largay J, Kelly MM, Button EA, Kato S, Wittlin S. 1,5-anhydroglucitol and postprandial hyperglycemia as measured by continuous glucose monitoring system in moderately controlled patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1214-1219. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Le Floch JP, Escuyer P, Baudin E, Baudon D, Perlemuter L. Blood glucose area under the curve. Methodological aspects. Diabetes Care 1990;13:172-175. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Writing Team for the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Research Group. Effect of intensive therapy on the microvascular complications of type 1 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2002;287:2563-2569. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Derr R, Garrett E, Stacy GA, Saudek CD. Is HbA(1c) affected by glycemic instability? Diabetes Care 2003;26:2728-2733. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Atkin SL. A1C variability and the risk of microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes: data from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care 2008;31:2198-2202. PubMedPMC
- 25. Zaccardi F, Pitocco D, Ghirlanda G. Glycemic risk factors of diabetic vascular complications: the role of glycemic variability. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2009;25:199-207. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Quagliaro L, Piconi L, Assaloni R, Martinelli L, Motz E, Ceriello A. Intermittent high glucose enhances apoptosis related to oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: the role of protein kinase C and NAD(P)H-oxidase activation. Diabetes 2003;52:2795-2804. PubMed
- 27. Hanefeld M, Fischer S, Julius U, Schulze J, Schwanebeck U, Schmechel H, Ziegelasch HJ, Lindner J. Risk factors for myocardial infarction and death in newly detected NIDDM: the Diabetes Intervention Study, 11-year follow-up. Diabetologia 1996;39:1577-1583. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Ha WC, Oh SJ, Kim JH, Lee JM, Chang SA, Sohn TS, Son HS. Severe hypoglycemia is a serious complication and becoming an economic burden in diabetes. Diabetes Metab J 2012;36:280-284. ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Patient characteristics
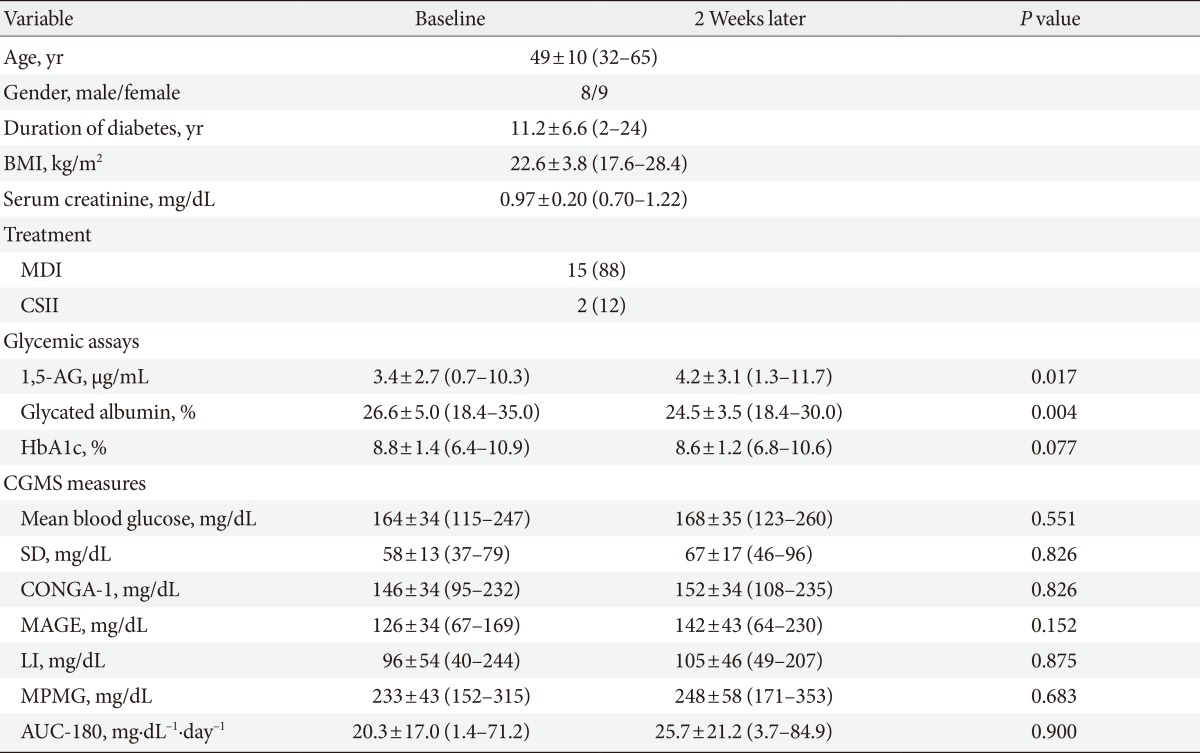
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation (range) or number (%).
BMI, body mass index; MDI, multiple daily injection; CSII, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion; 1,5-AG, 1,5-anhydroglucitol; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; CGMS, continuous glucose monitoring system; SD, standard deviation; CONGA-1, continuous overlapping net glycemic action with 1 hour time intervals; MAGE, mean amplitude of glucose excursion; LI, lability index; MPMG, mean post-meal maximum glucose; AUC-180, area under the curve for glucose above 180 mg/dL.
Correlations between changes of the continuous glucose monitoring system measures and glycemic assays
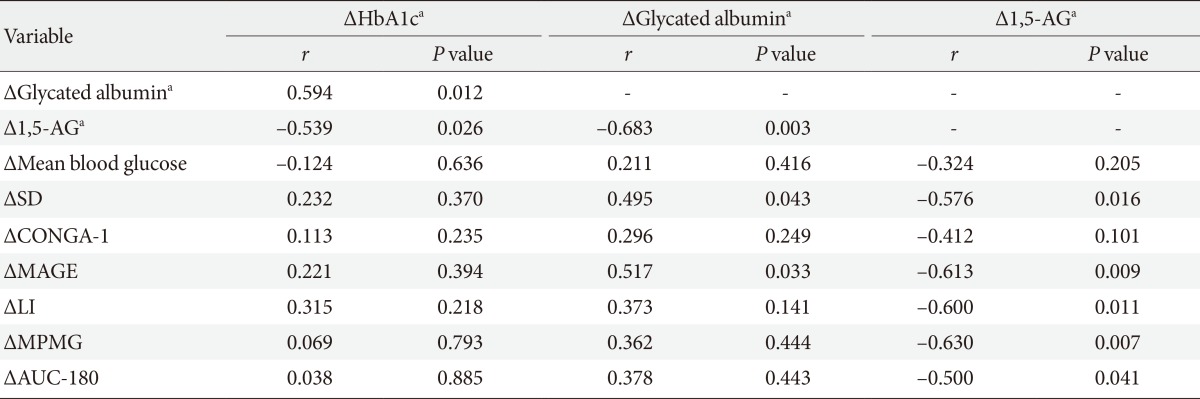
Δ The differences of the variables for the 2-week interval.
HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; 1,5-AG, 1,5-anhydroglucitol; SD, standard deviation; CONGA-1, continuous overlapping net glycemic action with 1 hour time intervals; MAGE, mean amplitude of glucose excursion; LI, lability index; MPMG, mean post-meal maximum glucose; AUC-180, area under the curve for glucose above 180 mg/dL.
aLog transformed.
Correlations between the changes of the continuous glucose monitoring system measures and glycemic assays according to the basal mean glucose level (<180 and ≥180 mg/dL)
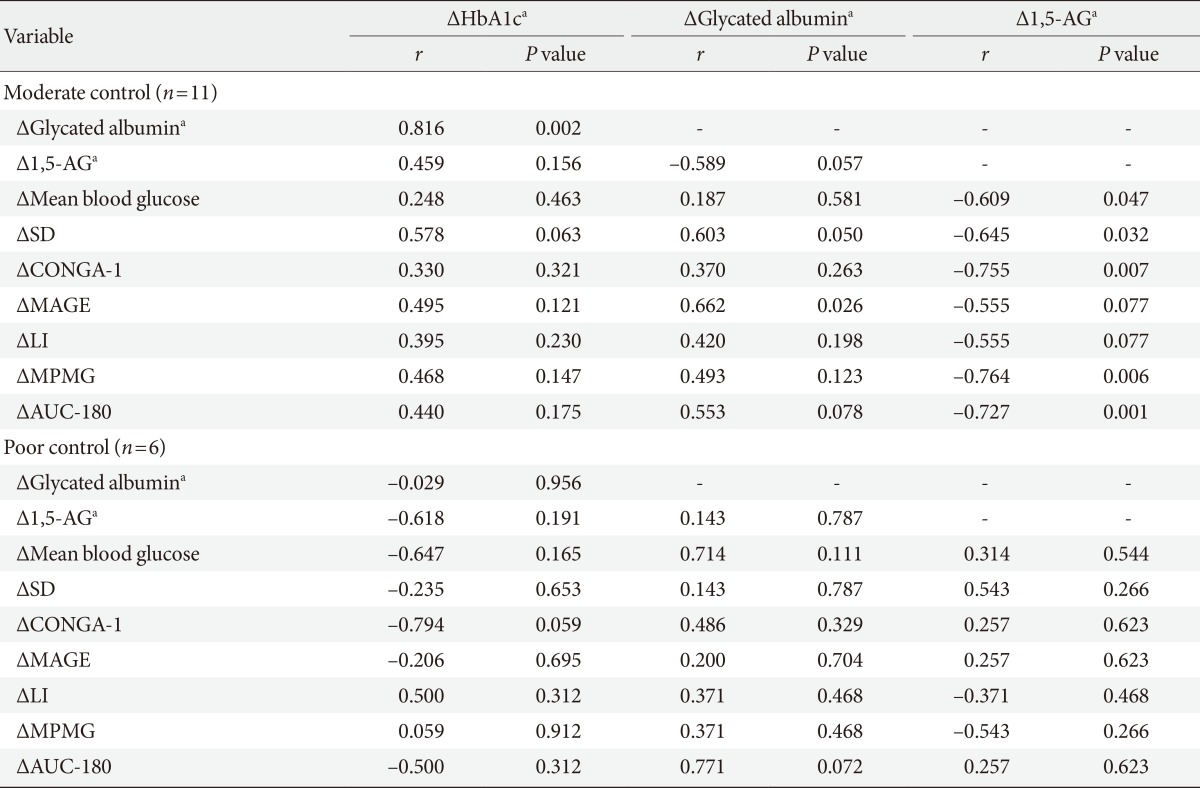
Δ The differences of the variables for the 2-week interval.
HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; 1,5-AG, 1,5-anhydroglucitol; SD, standard deviation; CONGA-1, continuous overlapping net glycemic action with 1 hour time intervals; MAGE, mean amplitude of glucose excursion; LI, lability index; MPMG, mean post-meal maximum glucose; AUC-180, area under the curve for glucose above 180 mg/dL.
aLog transformed.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Glycemic dispersion: a new index for screening high glycemic variability
Rui Shi, Lei Feng, Yan-Mei Liu, Wen-Bo Xu, Bei-Bei Luo, Ling-Tong Tang, Qian-Ye Bi, Hui-Ying Cao
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital Behavior Change Interventions to Reduce Sedentary Behavior and Promote Physical Activity in Adults with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Xiaoyan Zhang, Xue Qiao, Ke Peng, Shan Gao, Yufang Hao
International Journal of Behavioral Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - DBS are suitable for 1,5-anhydroglucitol monitoring in GSD1b and G6PC3-deficient patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors to treat neutropenia
Joseph P. Dewulf, Nathalie Chevalier, Sandrine Marie, Maria Veiga-da-Cunha
Molecular Genetics and Metabolism.2023; 140(3): 107712. CrossRef - The correlation between serum 1, 5-anhydroglucitol and β-cell function in Chinese adults with different glucose metabolism statuses
Yuexing Yuan, Yuanyuan Tan, Yao Wang, Shanhu Qiu, Jiao Yang, Cheng Chen
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HbA1c combined with glycated albumin or 1,5‐anhydroglucitol improves the efficiency of diabetes screening in a Chinese population
Junyi Qian, Cheng Chen, Xiaohang Wang, Yuanyuan Tan, Jiao Yang, Yuexing Yuan, Juan Chen, Haijian Guo, Bei Wang, Zilin Sun, Yao Wang
Diabetic Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of glycemia in chronic kidney disease
Mohamed Hassanein, Tariq Shafi
BMC Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion alters microRNA expression and glycaemic variability in children with type 1 diabetes
Emma S. Scott, Andrzej S. Januszewski, Luke M. Carroll, Gregory R. Fulcher, Mugdha V. Joglekar, Anandwardhan A. Hardikar, Timothy W. Jones, Elizabeth A. Davis, Alicia J. Jenkins
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Red rice koji extract alleviates hyperglycemia by increasing glucose uptake and glucose transporter type 4 levels in skeletal muscle in two diabetic mouse models
Takakazu Yagi, Koji Ataka, Kai-Chun Cheng, Hajime Suzuki, Keizaburo Ogata, Yumiko Yoshizaki, Kazunori Takamine, Ikuo Kato, Shouichi Miyawaki, Akio Inui, Akihiro Asakawa
Food & Nutrition Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - How tightly controlled do fluctuations in blood glucose levels need to be to reduce the risk of developing complications in people with Type 1 diabetes?
R. Livingstone, J. G. Boyle, J. R. Petrie
Diabetic Medicine.2020; 37(4): 513. CrossRef - Resolution on the results of the first working meeting of the scientific advisory board «Actual problems of glycemic variability as a new criterion of glycemic control and safety of diabetes therapy»
Mikhail B. Antsiferov, Gagik R. Galstyan, Alexey V. Zilov, Alexander Y. Mayorov, Tatyana N. Markova, Nikolay A. Demidov, Olga M. Koteshkova, Dmitry N. Laptev, Alisa V. Vitebskaya
Diabetes mellitus.2019; 22(3): 281. CrossRef - Hyperglycemia and Carotenoid Intake Are Associated with Serum Carotenoids in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes
Namrata Sanjeevi, Leah M. Lipsky, Tonja R. Nansel
Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.2019; 119(8): 1340. CrossRef - Correlation of Serum 1,5-AG with Uric Acid in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Different Renal Functions
Kai Zhang, Bizhen Xue, Yuexing Yuan, Yao Wang
International Journal of Endocrinology.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Glycaemic control and glycaemic variability in older people with diabetes
Hermes J Florez
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2018; 6(6): 433. CrossRef - Alternate glycemic markers reflect glycemic variability in continuous glucose monitoring in youth with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes
Christine L. Chan, Laura Pyle, Megan M. Kelsey, Lindsey Newnes, Amy Baumgartner, Philip S. Zeitler, Kristen J. Nadeau
Pediatric Diabetes.2017; 18(7): 629. CrossRef - 1,5-anidroglucitolo: un marcatore non tradizionale di iperglicemia
Gabriella Lavalle, Roberto Testa, Maria Elisabetta Onori, Raffaella Vero, Anna Vero
La Rivista Italiana della Medicina di Laboratorio - Italian Journal of Laboratory Medicine.2017; 13(3-4): 139. CrossRef - Glycemic control and variability in association with body mass index and body composition over 18months in youth with type 1 diabetes
Leah M. Lipsky, Benjamin Gee, Aiyi Liu, Tonja R. Nansel
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2016; 120: 97. CrossRef - How Can We Easily Measure Glycemic Variability in Diabetes Mellitus?
Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(2): 114. CrossRef - Alternative biomarkers for assessing glycemic control in diabetes: fructosamine, glycated albumin, and 1,5-anhydroglucitol
Ji-Eun Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2015; 20(2): 74. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability: How Do We Measure It and Why Is It Important?
Sunghwan Suh, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 273. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite



