- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 46(1); 2022 > Article
-
Original ArticleComplications Renal Tubular Damage Marker, Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase, as a Predictive Marker of Hepatic Fibrosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
-
Hae Kyung Kim1*
 , Minyoung Lee1*
, Minyoung Lee1* , Yong-ho Lee1,2, Eun Seok Kang1,2, Bong-Soo Cha1,2, Byung-Wan Lee1,2
, Yong-ho Lee1,2, Eun Seok Kang1,2, Bong-Soo Cha1,2, Byung-Wan Lee1,2
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2022;46(1):104-116.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0273
Published online: July 13, 2021
1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Institute of Endocrine Research, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
-
Corresponding author: Byung-Wan Lee
 Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50-1 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Korea E-mail: bwanlee@yuhs.ac
Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50-1 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Korea E-mail: bwanlee@yuhs.ac - *Hae Kyung Kim and Minyoung Lee contributed equally to this study as first authors.
Copyright © 2022 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis is closely associated with the progression of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We investigated whether urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (u-NAG), an early renal tubular damage biomarker in DKD, could be related to the degree of hepatic fibrosis in patients with T2DM.
-
Methods
- A total of 300 patients with T2DM were enrolled in this study. Hepatic steatosis and fibrosis were determined using transient elastography. The levels of urinary biomarkers, including u-NAG, albumin, protein, and creatinine, and glucometabolic parameters were measured.
-
Results
- Based on the median value of the u-NAG to creatinine ratio (u-NCR), subjects were divided into low and high u-NCR groups. The high u-NCR group showed a significantly longer duration of diabetes, worsened hyperglycemia, and a more enhanced hepatic fibrosis index. A higher u-NCR was associated with a greater odds ratio for the risk of higher hepatic fibrosis stage (F2: odds ratio, 1.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04 to 3.82). Also, u-NCR was an independent predictive marker for more advanced hepatic fibrosis, even after adjusting for several confounding factors (β=1.58, P<0.01).
-
Conclusion
- The elevation of u-NAG was independently associated with a higher degree of hepatic fibrosis in patients with T2DM. Considering the common metabolic milieu of renal and hepatic fibrosis in T2DM, the potential use of u-NAG as an effective urinary biomarker reflecting hepatic fibrosis in T2DM needs to be validated in the future.
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with an increased risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [1]. The prevalence of NAFLD is estimated to be 45% to 75% in patients with T2DM, more than two times higher than in the general population [2,3]. Also, the overall prevalence of biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and advanced fibrosis in patients with T2DM is approximately 37.33% and 17.02%, respectively [3]. The coexistence of T2DM and NAFLD significantly increases the risk for the development of NASH and cirrhosis compared to that observed in cases of NAFLD without T2DM [1]. Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is prevalent in approximately 30% to 50% of the population with T2DM [4], and NAFLD is associated with increased incidence and prevalence of nephropathy in T2DM, a phenomenon that is independent of traditional risk factors [5]. This strong relationship between NAFLD and DKD in T2DM may be mediated by the common pathogenic metabolic mechanisms underlying NAFLD and DKD, but the systemic release of several pro-inflammatory mediators in NAFLD may also putatively contribute to their relationship [6].
- Due to the high prevalence of NAFLD and NASH in T2DM patients, an effective and non-invasive biomarker to predict the degree of NAFLD and NASH in T2DM is urgently needed. However, the prevalence of histologically proven NASH in patients with T2DM who exhibit normal liver enzyme levels is 56% [7], suggesting that serum liver enzyme levels are not sufficient to predict the presence of steatohepatitis and fibrosis in patients with T2DM and NAFLD. Considering the close association between NAFLD and DKD, it would be reasonable to investigate whether a urinary biomarker that originally reflects the presence of DKD could simultaneously reflect the development of NASH.
- Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (u-NAG), a well-established renal tubular damage marker, is a potential candidate. NAG is present in the lysosomes of proximal tubule epithelial cells, and its urinary excretion is increased in response to renal proximal tubular cell injury [8]. Since profibrotic changes in renal tubular cells are the cardinal features associated with diabetic nephropathy [8,9], u-NAG levels may reflect the degree of renal fibrosis. Considering that advanced liver fibrosis is independently associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD) among individuals with NAFLD [10], u-NAG, as a potential renal fibrosis marker, may be associated with the degree of NASH and vice versa. Furthermore, the enzymatic activities of serum NAG and u-NAG were elevated in cirrhotic and fibrotic liver disorders, indicating that NAG can be used as a potential systemic biomarker that can identify fibrosis in both the liver and kidney [11,12].
- In this study, we investigated, using transient liver elastography in patients with T2DM, whether u-NAG, an early biomarker of renal tubulopathy, is associated with hepatic fibrosis.
INTRODUCTION
- Study population
- In a retrospective cross-sectional study, we enrolled patients aged ≥19 years with T2DM who had been simultaneously evaluated for transient elastography, FibroScan (Echosens, Paris, France), as well as blood and urinary markers, including u-NAG, albumin, protein, and creatinine at the Severance Hospital between April 2017 and July 2020. T2DM patients were defined as (1) patients taking insulin or an oral hypoglycemic or (2) patients with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5% (47.5 mmol/mol) according to the Korean Diabetes Association clinical practice guidelines [13]. Patients were excluded if they presented any of the following: age <19 years, type 1 diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, hepatic diseases including various forms of hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma, end-stage renal disease (defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] <15 mL/min/1.73 m2), and renal replacement therapy, including renal transplantation and dialysis.
- Demographic data such as age, sex, weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, duration of diabetes, and information about current medications were obtained. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as body weight divided by height squared (kg/m2). Hypertension was defined as a systolic blood pressure of ≥130 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure of ≥85 mm Hg, or the current use of antihypertensive medications according to the guidelines proposed in 2005 by the American Heart Association and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute for Asian populations [14]. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea (approval No. 4-2020-0490); it waived the need for informed consent because of the retrospective nature of the study and the lack of personal information.
- Measurement of blood and urinary parameters
- Following an overnight fast (≥8 hours), morning spot urine samples were collected for measuring u-NAG, albumin, protein, and creatinine levels, and blood samples were collected to measure complete blood count, fasting and postprandial glucose, lipid profile, platelet count, and levels of insulin, C-peptide, HbA1c, glycated albumin, creatinine, albumin, and liver enzymes. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels were calculated using the Friedewald equation in the absence of actual LDL-C measurement [15]. The equation was not used if the patient’s triglyceride level exceeded 400 mg/dL. Pancreatic β-cell function and insulin sensitivity were assessed in non-insulin users using the following indices: homeostasis model assessment-β-cell (HOMA-β)=[20×fasting insulin (μIU/mL)]/[fasting plasma glucose (mmol/L)–3.5] and homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)= [fasting insulin (μIU/mL)×fasting plasma glucose (mmol)]/22.5 [16]. The eGFR was calculated using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation [17]. U-NAG, albumin, and protein levels were adjusted as u-NAG to creatinine ratio (u-NCR), urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (u-ACR), and urinary protein to creatinine ratio (u-PCR), respectively, to minimize the influence of kidney function. Proteinuria was defined as 150 mg/g creatinine, based on the most conservative reported normal value for urinary protein excretion (<150 mg/day) [18]. Albuminuria was defined as 30 mg/g creatinine according to the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes recommendations [19]. CKD was defined as CKD stage 3 (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2). A u-NCR was categorized into two groups: at or below median u-NCR (≤6.77 U/g creatinine) and above the median u-NCR (>6.77 U/g creatinine) as low u-NCR and high u-NCR groups, respectively.
- Measurement of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis
- Transient elastography, FibroScan, was performed by a welltrained physician who was blinded to the participants’ clinical details; the final value was obtained using a standard procedure. Hepatic steatosis was classified into the following stages based on a controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) value (decibels per meter [dB/m]): steatosis stage 0 (S0) <238 dB/m, 238 dB/m≤ steatosis stage 1 (S1) <260 dB/m, 260 dB/m≤ steatosis stage 2 (S2) <293 dB/m, and steatosis stage 3 (S3) ≥293 dB/m [20]. The stages of hepatic fibrosis were further divided based on the liver stiffness measurement (LSM) value (kPa): no fibrosis and mild fibrosis (F0–1) <7 kPa, significant fibrosis (F2) ≥7 kPa, advanced fibrosis (F3) ≥8.7 kPa, and cirrhosis (F4) ≥11.5 kPa [21].
- Using a previously validated fatty liver prediction model, NAFLD was defined as a liver fat score (NLFS) of >–0.64 and Framingham steatosis index (FSI). The fibrosis-4 calculator (FIB-4 index) and NALFD fibrosis score (NFS) were used to determine the extent of hepatic fibrosis, and significant fibrosis was defined as either FIB-4 >2.67, or NFS >0.676, as previously validated [2].
- Statistical analysis
- The data are presented as mean±standard deviation for normally distributed continuous variables and as medians (interquartile range) for non-normally distributed continuous variables. Categorical data are expressed as numbers and percentages. The baseline characteristics of the study population were analyzed based on the u-NCR level using the two-sample Student’s t-test for continuous variables and the chi-square test for categorical variables. A normality test was performed for all the continuous variables. To correct the skewed distributions, non-normally distributed continuous variables, such as u-NCR, u-ACR, and u-PCR were logarithmically transformed before statistical analysis. Outliers of u-NCR ≥23.275 U/g creatinine (n=25) were excluded from the data using Tukey’s fences method [22].
- Correlations between u-NAG and other parameters were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation analysis. Multiple logistic regression analyses were used to determine the independent association between u-NAG and the hepatic fibrosis stages. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis with Youden’s index was conducted to calculate the cut-off value of u-NCR to predict moderate and advanced hepatic fibrosis (stage ≥F2 and F3) [23].
- Stepwise multiple linear regression analyses were performed to evaluate the relationship between LSM and various parameters using u-NCR and u-ACR. Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS statistical software for Windows version 25.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Adjusted odds ratio (aOR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were determined. Statistical significance was set at P<0.05.
METHODS
- Baseline characteristics of the study population according to urinary NAG
- A total of 300 patients (204 men and 96 women) were enrolled in this study. The mean age and median duration of diabetes were 57.1 and 3 years, respectively. The median value of u-NCR was 6.77 U/g creatinine (U/g Cr). The patients were divided into low and high u-NCR groups based on the median u-NCR value (Table 1). The high u-NCR group was characterized by the following: a higher percentage of men, a significantly longer duration of diabetes, and a higher prevalence of hypertension and CKD. Blood pressure, hepatic enzymes, lipid profile except for total cholesterol, and the use of lipid medication did not differ between the two groups. The use of antidiabetic medication, including sulfonylurea and insulin, and antihypertensive medications was more common in the high NCR group than in the low NCR group (Supplementary Table 1). The high NCR group exhibited significantly higher levels of fasting and postprandial glucose, HbA1c, and glycated albumin (all P<0.001), and a significantly lower HOMA-β level (P=0.009). HOMA-IR scores did not differ between the two groups (P=0.097). In the high NCR group, levels of u-ACR, albuminuria, and u-PCR were higher, but eGFR was lower than that in the low NCR group. The higher NCR group had a significantly higher degree of fibrosis as determined by LSM (5.4% vs. 6.3%, P=0.001) and NFS (–1.11 vs. –0.63, P=0.032). Also, more advanced stages of hepatic fibrosis were observed in the high NCR group. However, no significant difference in hepatic steatosis determined by CAP, NLFS, and FSI was observed between the two groups.
- Correlations between urinary NAG and other parameters
- The u-NCR level was positively and significantly correlated with the duration of diabetes and the levels of fasting and postprandial glucose, HbA1c, and glycated albumin (Table 2). Also, the values of u-ACR and u-PCR were positively correlated with that of u-NCR. However, HOMA-β and eGFR were negatively correlated with u-NCR. With respect to hepatic fibrosis indices, the FIB-4 index (r=0.34, P<0.001) and NFS (r=0.35, P<0.001) were positively correlated with u-NCR. However, the hepatic steatosis indices, NLFS and FSI, were not significantly correlated with u-NCR. BMI, waist circumference, and lipid profile, except for total cholesterol, were not associated with u-NCR.
- Risk of hepatic steatosis/fibrosis stages according to urinary NAG
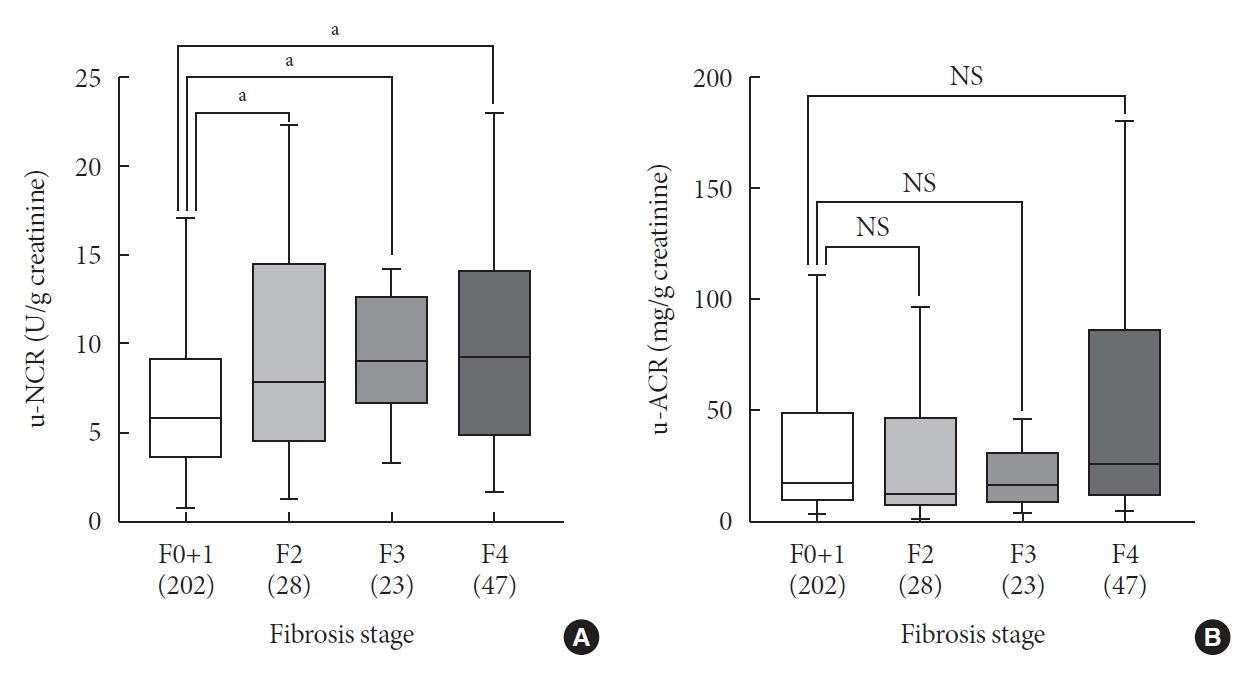
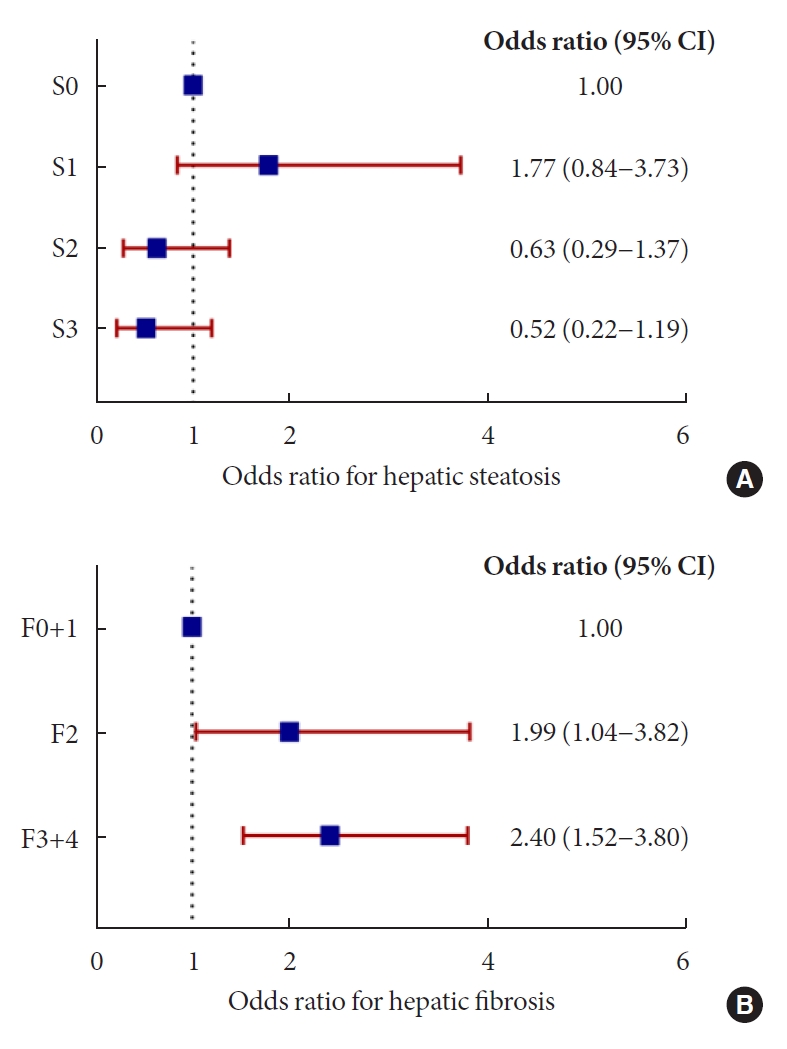
- The association between u-NAG and the stages of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in relation to potential confounders was analyzed using logistic regression analysis. Insulin non-users (n=249) were analyzed to include HOMA indices because of their significance in previous correlation results and clinical settings (Supplementary Tables 2 and 3). Even after adjusting for multiple confounding parameters including demographic factors, the consumption of hypertension and lipid medication, metabolic parameters, and glycemic parameters in Model 4, a higher u-NCR was associated with a greater odds ratio for the risk of higher stage hepatic fibrosis, as the fibrosis stage increased (F2 [OR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.04 to 3.82; P=0.039], F3 and F4 [OR, 2.40; 95% CI, 1.52 to 3.80; P<0.001]) (Fig. 1B, Supplementary Table 3). However, no significant association was observed between u-NCR and any stage of hepatic steatosis (Fig. 1A, Supplementary Table 2). When the median value of u-NCR in each hepatic fibrosis stage was compared (Fig. 2A), u-NCR in the F4 stage showed the highest value across the fibrosis stages compared with those observed in the F0 and F1 stages (9.4 [5.04 to 14.3] vs. 5.9 [3.8 to 9.3], P=0.001); u-ACR did not exhibit a significant trend across the stages of hepatic fibrosis (Fig. 2B). Similar results were obtained when the total population including insulin users (n=300) was analyzed (Supplementary Tables 4 and 5). In this analysis, HOMA indices were excluded owing to the inclusion of insulin users.
- The cut-off values of u-NCR showed the best equilibrium between sensitivity and specificity at 6.31 and 7.84 U/g creatinine to predict the hepatic fibrosis stage above F2 and F3, respectively. The area under the ROC curve values using each cut-off value for F2 and F3 were 0.654 and 0.651, respectively.
- Multiple linear regression analysis of factors affecting the liver stiffness measurement
- To determine the predictive factors for hepatic fibrosis, multiple linear regression analysis was performed with non-insulin users (n=249) (Table 3). Age, sex, BMI, duration of diabetes, history of hypertension, use of lipid medication, HOMA-IR, HOMA-β, u-NCR, and levels of triglyceride, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and HbA1c, were included as independent determinants. In Model 1, when age, sex, BMI, and duration of diabetes were adjusted, u-NCR was identified as a significant independent factor for LSM (standardized β [STD β]=1.58, P<0.001). Hypertension, lipid medication, and metabolic parameters such as triglyceride and ALT levels and HOMA-IR were included in Models 2 and 3, showing that u-NCR was independently associated with LSM. After Model 4 was further adjusted for glycemic factors, including HbA1c level and HOMA-β, u-NCR remained a significant coefficient value for a higher degree of hepatic fibrosis across the models (STD β=1.58, P<0.001). Similar results were obtained when the total population including insulin users (n=300) was analyzed (Supplementary Table 6). In this analysis, HOMA indices were excluded owing to the inclusion of insulin users. The efficacy of u-ACR as a predictive marker for hepatic fibrosis was also investigated and compared with that of u-NCR (Supplementary Tables 7 and 8). U-ACR was not associated with LSM in Model 4 in both non-insulin users and the total population, including insulin users (STD β=0.21, P=0.33 and STD β=0.17, P=0.43).
RESULTS
- Accumulating evidence suggests that the development and progression of NAFLD in T2DM could be associated with DKD characterized by glomerular and tubular damage [5,6,24]. Among the various urinary proteins involved in DKD, urinary albumin primarily constitutes proteinuria, but various non-albumin proteins are also pathophysiologically filtered or secreted. Among the renal tubular secretory proteins, NAG is a well-established renal tubular damage marker [25]. We assumed that systemic inflammation and oxidative stress in the metabolic milieu of T2DM may simultaneously induce both hepatic parenchymal and renal tubular fibrosis and that u-NAG may also be proportionally elevated due to hepatic fibrosis in response to renal fibrosis. Based on this hypothesis, we investigated the relationship between renal tubular damage and hepatic fibrosis in patients with T2DM by measuring u-NAG and liver fibrosis using transient elastography and demonstrated that the increase in u-NAG was significantly associated with a higher degree of hepatic fibrosis in patients with T2DM (Fig. 3). This study has three main findings. First, an increased level of u-NAG is associated with nephropathic indices, poor glycemic control, and the use of antihypertensive medication. Second, even before the development of overt albuminuria, increased u-NAG level is associated with an increased risk for a higher degree of hepatic fibrosis in patients with T2DM. Third, the degree of hepatic steatosis is not associated with the levels of u-NAG and albuminuria in patients with T2DM.
- Serum and urinary levels of NAG may be distinguished due to their different origins. NAG, a lysosomal enzyme, is located in the intracellular lesions of several cells, including renal tubular cells [26]. In addition to the urine, NAG is also present in serum, and serum NAG is mainly secreted from the liver [26]. Therefore, increased serum NAG levels may be associated with hepatic damage, including fibrosis. In the present study, increased urinary excretion of NAG may have directly resulted from damage to renal tubular cells rather than an increased glomerular filtration of serum NAG considering its relatively high molecular weight (>130 kDa) [27]. However, despite their different sources, the urinary concentration of NAG may be closely associated with the serum concentration potentially due to the common metabolic and systemic milieu [28,29]. For example, both serum and urinary concentrations of NAG increased during endotoxemia in vivo [28], possibly by the simultaneous damage to the liver and kidney. Also, serum and urinary concentrations of NAG were commonly elevated in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and microangiopathy [29]. In the present study, the high u-NCR group had a longer duration of diabetes and worsened hyperglycemia compared to the low u-NCR group. Thus, both kidney and liver of the subjects from the high u-NCR group may have been chronically exposed to systemic metabolic stress, and these common pathophysiological mechanisms may have resulted in a simultaneous elevation of NAG in both urine and serum. As the serum NAG concentration was not measured, we could not demonstrate a correlation between serum and u-NAG concentrations. Further studies with a complete measurement of serum and u-NAG should be performed to validate their significant associations.
- An association between non-albumin proteinuria (NAP) and indices of hepatic fibrosis was previously tested and showed a significant correlation [30]. NAP is mainly related to renal tubular damage [31], and it encompasses a variety of proteins such as α-1 microglobulin, β-2 macroglobulin, cystatin C, kidney injury molecule-1, and NAG [31,32]. Therefore, a definite protein that contributed to the level of NAP in association with hepatic fibrosis could not be identified in the previous study [30]. We selected a specific urinary biomarker, NAG, among several components of NAP, to investigate its association with hepatic fibrosis. To our knowledge, this is the first study to analyze the association between this specific renal tubular marker, NAG, and the degree of hepatic fibrosis. Furthermore, the current data make a distinct point compared with the previous study [30], given the use of a different modality to determine NAFLD. Instead of using hepatic fibrosis indices [30], NAFLD was determined using FibroScan, one of the most widely used and well-validated non-invasive methods to assess hepatic fibrosis [33]. The diagnostic accuracy of FibroScan for hepatic fibrosis is superior to that of fibrosis indices [34]. In the present study, we supported our thesis based on compelling evidence generated by FibroScan.
- In another previous report [12], the urinary activity of NAG was elevated in patients with liver cirrhosis in Child-Pugh class C compared with class A and B. However, our data differ from the previous data due to the different characteristics of the study subjects. Patients with diverse liver etiologies but with the fibrosis stage restricted to liver cirrhosis were included in the previous study [12]. In our study, patients with a varying spectrum of hepatic fibrosis attributed to NAFLD were enrolled. Owing to a unified liver etiology with NALFD and a diverse range of hepatic fibrosis, a quantitative association between urinary NAG and hepatic fibrosis in a comprehensive range of NAFLD could be investigated in this study. As a result, a higher u-NAG level was associated with an increased risk of hepatic fibrosis, particularly advanced fibrosis. In contrast, u-NAG was not associated with hepatic steatosis determined using indices or transient elastography. In short, u-NAG may be associated with the development and progression of hepatic fibrosis rather than hepatic steatosis. Our data suggests that a concrete urinary biomarker, NAG, could be used to predict and detect NAFLD in reversible stages. Although further validation studies should be conducted, the adoption of our findings in the clinical field would contribute to a decrease in NAFLD-related mortality and morbidity by early detection and monitoring of progress during NAFLD treatment.
- U-NAG constitutes isolated NAP which is related to renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis [35]. In a previous study [36], u-NAG level was proportional to urinary NAP levels increased in T2DM patients with DKD even before onset of overt albuminuria. Therefore, u-NAG along with NAP could be used as early biomarkers of DKD in patients with T2DM in normoalbuminuric stage. Early DKD with renal tubulopathy is aggravated in systemic response to uncontrolled hyperglycemia, resulting in pro-inflammatory changes and oxidative stress in the whole body [25,30,36]. Considering the localized effect of hyperglycemia on the kidney, increased glucose reabsorption in the proximal tubule causes tubulointerstitial hypoxia, oxidative stress, and fibrosis as well [37,38]. In the current study, increased u-NAG levels were observed in patients with poorly controlled diabetes, β-cell dysfunction, and long-standing diabetes. Thus, chronically enhanced systemic inflammation due to hyperglycemia and insulin depletion in patients increased NAG levels may have resulted in increased pro-inflammatory cytokine production and oxidative stress that consequently induced hepatic fibrosis [30,39]. According to the two-hit theory of NASH, the progression to hepatic fibrosis involves triglyceride deposition in hepatocytes, followed by the formation of reactive oxygen species and free radicals [30,39]. Such development of liver fibrosis may have caused systemic release of proinflammatory mediators that augmented u-NAG elevation in return. Given the correlation of u-NAG with glucometabolic parameters, including HbA1c, HOMA-β, and duration of diabetes that reflect the deterioration of hyperglycemia-associated chronic systemic inflammation, we postulate that u-NAG might have the potential to be a novel biomarker effectively reflecting both renal and hepatic fibrosis. Further investigations with a prospective design for detailed mechanisms about the association between u-NAG levels and fibrotic burden in the kidney and liver are warranted in the future.
- Concerning the association between urinary albumin and NAFLD, albuminuria is related to insulin resistance that underlies the mechanism of metabolic syndrome and plays a role in the development of NAFLD [30,40]. However, in this study, the level of albuminuria was not associated with the degree of hepatic steatosis or fibrosis. These results could be explained by the characteristics of study population. The study subjects had normal kidney function with a mean eGFR of 92.1 mL/min/1.73 m2. Also, the median u-ACR was 12.5 mg/g creatinine (5.7 to 45.7), and albuminuria was prevalent in 32.3% of the total subjects. Thus, the study population had a normal or relatively minimal albuminuria that might have mitigated the association between u-ACR and NAFLD. Meanwhile, u-NAG still significantly reflected the degree of hepatic fibrosis even when albuminuria had not been fully developed in the present study.
- The current study has several limitations. First, a causal relationship between increased u-NAG and hepatic fibrosis could not be determined due to the cross-sectional study design. Long-term, large prospective studies are needed to validate the relationship between elevated u-NAG levels and hepatic fibrosis in the future. Second, liver biopsy data were absent in the current study, although it is the gold standard for diagnosing and predicting the progression of NAFLD by detecting inflammation and the ballooning degeneration of hepatocytes [41,42]. The lack of biopsy data in the current study poses a potential pitfall for underestimating the severity and progression of NAFLD [42]. Third, we could not investigate the self-reported history of alcohol consumption, and patients with a history of alcohol-related liver disease were identified using the International Classification of Diseases Clinical Modification code. Thus, confounding by alcohol consumption remains when interpreting the analyses for the association between u-NAG and hepatic fibrosis.
- To our knowledge, this is the first study demonstrating that increased u-NAG levels are independently associated with an increased risk for a higher degree of hepatic fibrosis in patients with T2DM, even before the development of albuminuria. Enhanced systemic pro-inflammatory response and oxidative stress caused by uncontrolled hyperglycemia may have created a common milieu that explains the quantitative association between u-NAG levels and the degree of hepatic fibrosis. The potential use of u-NAG as an effective clinical biomarker of hepatic fibrosis in T2DM needs to be validated in the future.
DISCUSSION
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Table 2.
Supplementary Table 3.
Supplementary Table 4.
Supplementary Table 5.
Supplementary Table 6.
Supplementary Table 7.
Supplementary Table 8.
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: B.W.L
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: H.K.K., M.L., B.W.L.
Drafting the work or revising: H.K.K, M.L., Y.L., E.S.K., B.S.C., B.W.L.
Final approval of the manuscript: B.W.L.
-
FUNDING
This work was supported by the Technology Innovation Program funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea) (20004103) and by Severance Hospital Research Fund for Clinical excellence (SHRC C 2019-0032).
NOTES
-
Acknowledgements
- This study was supported by the ‘SENTINEL (Severance ENdocrinology daTa scIeNcE pLatform)’ program funded by the 2020 Research fund of Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea and Sung-Kil Lim Research Award (4-2018-1215; DUCD000002) in statistical analyses.
- The authors thank Medical Illustration & Design, part of the Medical Research Support Services of Yonsei University College of Medicine, for all artistic support related to this work.

| Characteristic | Total (n=300) | Low u-NCR (≤6.77 U/g Cr) (n=150) | High u-NCR (>6.77 U/g Cr) (n=150) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | |||||
| Age, yr | 57.1±13.5 | 56.4±13.8 | 57.7±13.2 | 0.410 | |
| Male sex | 204 (68) | 115 (76.7) | 89 (59.3) | 0.001a | |
| Hypertension | 150 (50) | 75 (50) | 99 (66) | 0.005a | |
| Lipid medication | 150 (50) | 82 (54.7) | 82 (54.7) | 0.990 | |
| Duration of diabetes, yr | 3 (0 to 10) | 3 (0 to 8) | 4 (0 to 11) | 0.050a | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26.7±–3.9 | 26.5±3.5 | 26.9±4.3 | 0.470 | |
| Waist circumference, cm | 93.1±10.1 | 92.9±9.2 | 93.4±11.0 | 0.660 | |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 128.3±16.1 | 126.4±15.2 | 130±16.9 | 0.050 | |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 80±13.0 | 79.5±12.2 | 80.6±13.7 | 0.470 | |
| Biochemistry profile | |||||
| AST, IU/L | 27 (19 to 39) | 26 (19 to 36) | 27 (18 to 42) | 0.690 | |
| ALT, IU/L | 27 (19 to 47) | 27 (20 to 49) | 26 (17 to 45) | 0.260 | |
| Albumin, mg/dL | 4.4±0.39 | 4.5±0.31 | 4.3±0.44 | <0.001a | |
| Platelet, 103/μL | 240±75 | 240±68 | 241±51 | 0.940 | |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 164 (135 to 195) | 155 (131 to 192) | 169 (141 to 202) | 0.036a | |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 134 (98 to 194) | 131 (98 to 186) | 137 (99 to 215) | 0.470 | |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 44 (36 to 53) | 44 (38 to 52) | 44 (35 to 54) | 0.620 | |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 89 (63 to 115) | 86 (57 to 113) | 91 (68 to 117) | 0.130 | |
| Glycemic parameter | |||||
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 145±58 | 128±31 | 167±71 | <0.001a | |
| Postprandial glucose, mg/dL | 214±79 | 184±53 | 245±90 | <0.001a | |
| HbA1c, % | 7.7±1.8 | 7.2±1.4 | 8.3±1.9 | <0.001a | |
| Glycated albumin, % | 17 (15 to 22) | 16 (14 to 18) | 20 (17 to 25) | <0.001a | |
| Homeostasis model assessment (insulin non-user n=249) | 133 (56.4) | 116 (46.6) | |||
| HOMA-β | 54.9 (30.7 to 98.0) | 61.5 (38 to 105) | 46 (25.2 to 96.3) | 0.009a | |
| HOMA-IR | 3.4 (2.1 to 6.3) | 3.2 (2.0 to 5.7) | 3.9 (2.2 to 6.6) | 0.097 | |
| Nephropathic indices | |||||
| CKD (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 150 (50) | 4 (2.7) | 17 (11.3) | 0.003a | |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.68 to 0.96) | 0.8 (0.69 to 0.95) | 0.8 (0.66 to 0.96) | 0.900 | |
| eGFR CKD-EPI, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 93.2±19.6 | 96.9±17.2 | 89.6±21.2 | 0.001a | |
| u-NCR, U/g creatinine | 6.8 (4.2 to 10.8) | 4.2 (3.1 to 5.6) | 10.8 (8.4 to 14.4) | <0.001a | |
| u-ACR, mg/g creatinine | 12.5 (5.7 to 45.7) | 8.8 (4.5 to 25.8) | 22.1 (8.5 to 89.7) | <0.001a | |
| Albuminuria (≥30 mg/g creatinine) | 97 (32.3) | 34 (22.7) | 63 (42.0) | <0.001a | |
| u-PCR, mg/g creatinine | 100 (70 to 190) | 80 (60 to 125) | 130 (90 to 283) | <0.001a | |
| Indices of hepatic steatosis | |||||
| CAP, dB/m | 292 (254 to 325) | 292 (257 to 319) | 293 (251 to 336) | 0.710 | |
| NLFS | 0.85 (–0.22 to 2.17) | 0.89 (–0.25 to 2.12) | 0.75 (–0.22 to 2.33) | 0.900 | |
| NLFS >–0.64 | 240 (80.8) | 120 (80.5) | 120 (81.1) | 0.910 | |
| FSI | 0.60 (–0.08 to 1.59) | 0.65 (–0.08 to 1.5) | 0.57 (–0.09 to 1.64) | 0.830 | |
| Indices of hepatic fibrosis | |||||
| LSM, kPa | 6.0 (4.6 to 8.3) | 5.4 (4.5 to 6.7) | 6.3 (4.9 to 10.2) | 0.001a | |
| FIB-4 index | 1.24 (0.83 to 1.89) | 1.15 (0.81 to 1.65) | 1.39 (0.86 to 2.0) | 0.055 | |
| FIB-4 index >2.67 | 39 (13) | 19 (12.7) | 20 (13.3) | 0.86 | |
| NFS | –0.85 (–1.73 to –0.03) | –1.11 (–1.81 to –0.12) | –0.63 (–1.6 to 0.14) | 0.032a | |
| NFS >0.676 | 36 (12) | 17 (11.3) | 19 (12.7) | 0.720 | |
| Hepatic fibrosis stage | |||||
| F0–1 (<7 kPa) | 202 (67.3) | 116 (77.3) | 86 (57.3) | 0.001a | |
| F2 (≥7 kPa) | 28 (9.3) | 11 (7.3) | 17 (11.3) | ||
| F3 (≥8.7 kPa) | 23 (7.7) | 5 (3.3) | 18 (12.0) | ||
| F4 (≥11.5 kPa) | 47 (15.7) | 18 (12) | 29 (19.3) | ||
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation, number (%), or median (interquartile range).
u-NCR, urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase to creatinine ratio; Cr, creatinine; BMI, body mass index; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment-β; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; CKD, chronic kidney disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; CKD-EPI, chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration; u-ACR, urinary albumin to creatinine ratio; u-PCR, urinary protein to creatinine ratio; CAP, controlled attenuation parameter; NLFS, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) liver fat score; FSI, Framingham steatosis index; LSM, liver stiffness measurement; FIB-4, Fibrosis-4-calculator; NFS, NAFLD fibrosis score; F0–1, no fibrosis and mild fibrosis; F2, significant fibrosis.
a Statistical significance at P<0.05.
| Variable |
u-NCRa |
|
|---|---|---|
| r | P value | |
| Demographics | ||
| Age, yr | 0.069 | 0.230 |
| Duration of diabetes, yr | 0.130 | 0.032b |
| BMI, kg/m2 | –0.039 | 0.510 |
| Waist circumference, cm | –0.037 | 0.520 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 0.062 | 0.280 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 0.008 | 0.890 |
| Biochemistry profile | ||
| AST, IU/L | 0.046 | 0.240 |
| ALT, IU/L | –0.010 | 0.800 |
| Albumin, mg/dL | –0.30 | <0.001b |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 0.090 | 0.017b |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 0.001 | 0.980 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | –0.006 | 0.870 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 0.073 | 0.059 |
| Glycemic parameters | ||
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 0.380 | <0.001b |
| Postprandial glucose, mg/dL | 0.440 | <0.001b |
| HbA1c, % | 0.370 | <0.001b |
| Glycated albumin, % | 0.360 | <0.001b |
| HOMA-β (insulin non-user n=249) | –0.150 | 0.021b |
| HOMA-IR (insulin non-user n=249) | 0.087 | 0.170 |
| Nephropathic indices | ||
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.015 | 0.710 |
| eGFR CKD-EPI, mL/min/1.73 m2 | –0.22 | <0.001b |
| u-ACR, mg/g creatinine | 0.230 | <0.001b |
| u-PCR, mg/g creatinine | 0.320 | <0.001b |
| Index of hepatic steatosis | ||
| NLFS | 0.001 | 0.990 |
| FSI | –0.01 | 0.810 |
| Index of hepatic fibrosis | ||
| FIB-4 index | 0.340 | <0.001b |
| NFS | 0.350 | <0.001b |
u-NCR, urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase to creatinine ratio; BMI, body mass index; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment-β; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; CKD-EPI, chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration; u-ACR, urinary albumin to creatinine ratio; u-PCR, urinary protein to creatinine ratio; NLFS, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) liver fat score; FSI, Framingham steatosis index; FIB-4, fibrosis-4-calculator; NFS, NAFLD fibrosis score.
a Statistical significance at P<0.05,
b Log transformed form.
| Variable |
Model 1 |
Model 2 |
Model 3 |
Model 4 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STD β | P value | STD β | P value | STD β | P value | STD β | P value | |
| u-NCR, U/g Cra | 1.58 | <0.001b | 1.41 | 0.001b | 0.130 | 0.002b | 1.58 | <0.001b |
| Age, yr | 0.027 | 0.250 | 0.018 | 0.422 | 0.014 | 0.560 | 0.005 | 0.811 |
| Male sex | –0.46 | 0.481 | –0.520 | 0.421 | –0.180 | 0.781 | –0.046 | 0.942 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 0.21 | 0.009b | 0.211 | 0.011b | 0.150 | 0.101 | 0.130 | 0.160b |
| Duration of diabetes, yr | –0.058 | 0.140 | –0.04 | 0.320 | –0.027 | 0.510 | –0.004 | 0.920 |
| Hypertension | 0.970 | 0.140 | 1.03 | 0.130 | 0.970 | 0.131 | ||
| Lipid medication | –1.74 | 0.007b | –1.69 | 0.009b | –1.68 | 0.007b | ||
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | –0.006 | 0.089 | –0.005 | 0.132 | ||||
| ALT, IU/L | 0.010 | 0.300 | 0.011 | 0.243 | ||||
| HOMA-IR, % | 0.130 | 0.096 | 0.0001 | 0.990 | ||||
| HbA1c, % | 0.141 | 0.550 | ||||||
| HOMA-β | 0.017 | 0.011b | ||||||
Model 1 was adjusted for age, male sex, BMI, and duration of diabetes; Model 2 adjusted for Model 1 parameters plus hypertension, lipid medication; Model 3 adjusted for Model 2 parameters plus triglyceride, ALT, HOMA-IR; Model 4 adjusted for Model 3 parameters plus HbA1c, HOMA-β.
u-NCR, urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase to creatinine ratio; STD, standardized; BMI, body mass index; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment-β.
a Statistical significance at P<0.05,
b Log transformed form.
- 1. Lee BW, Lee YH, Park CY, Rhee EJ, Lee WY, Kim NH, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a position statement of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:382-401.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 2. Lee YH, Cho Y, Lee BW, Park CY, Lee DH, Cha BS, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in diabetes. Part I: epidemiology and diagnosis. Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:31-45.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Younossi ZM, Golabi P, de Avila L, Paik JM, Srishord M, Fukui N, et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol 2019;71:793-801.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Gheith O, Farouk N, Nampoory N, Halim MA, Al-Otaibi T. Diabetic kidney disease: world wide difference of prevalence and risk factors. J Nephropharmacol 2015;5:49-56.PubMedPMC
- 5. Targher G, Bertolini L, Rodella S, Zoppini G, Lippi G, Day C, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is independently associated with an increased prevalence of chronic kidney disease and proliferative/laser-treated retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2008;51:444-50.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Targher G, Chonchol M, Zoppini G, Abaterusso C, Bonora E. Risk of chronic kidney disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: is there a link? J Hepatol 2011;54:1020-9.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Portillo-Sanchez P, Bril F, Maximos M, Lomonaco R, Biernacki D, Orsak B, et al. High prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and normal plasma aminotransferase levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015;100:2231-8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 8. Kim SR, Lee YH, Lee SG, Kang ES, Cha BS, Lee BW. The renal tubular damage marker urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase may be more closely associated with early detection of atherosclerosis than the glomerular damage marker albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2017;16:16.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 9. Simonson MS. Phenotypic transitions and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 2007;71:846-54.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Wijarnpreecha K, Thongprayoon C, Scribani M, Ungprasert P, Cheungpasitporn W. Noninvasive fibrosis markers and chronic kidney disease among adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver in USA. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;30:404-10.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Gressner AM, Roebruck P. Predictive values of serum N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase for fibrotic liver disorders: correlation with monoamine oxidase activity. Clin Chim Acta 1982;124:315-26.PubMed
- 12. Amakasu H, Kanno A, Abe M, Sato K, Goto Y. Urinary N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase activity in liver cirrhosis with renal impairment. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi 1991;88:51-6.PubMed
- 13. Kim MK, Ko SH, Kim BY, Kang ES, Noh J, Kim SK, et al. 2019 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:398-406.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005;112:2735-52.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 1972;18:499-502.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985;28:412-9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Jeong TD, Lee W, Yun YM, Chun S, Song J, Min WK. Development and validation of the Korean version of CKD-EPI equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Clin Biochem 2016;49:713-9.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Shaw AB, Risdon P, Lewis-Jackson JD. Protein creatinine index and Albustix in assessment of proteinuria. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983;287:929-32.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 19. Levey AS, Eckardt KU, Tsukamoto Y, Levin A, Coresh J, Rossert J, et al. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int 2005;67:2089-100.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Sasso M, Beaugrand M, de Ledinghen V, Douvin C, Marcellin P, Poupon R, et al. Controlled attenuation parameter (CAP): a novel VCTE™ guided ultrasonic attenuation measurement for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis: preliminary study and validation in a cohort of patients with chronic liver disease from various causes. Ultrasound Med Biol 2010;36:1825-35.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Wong VW, Vergniol J, Wong GL, Foucher J, Chan HL, Le Bail B, et al. Diagnosis of fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness measurement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2010;51:454-62.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Johansen MB, Christensen PA. A simple transformation independent method for outlier definition. Clin Chem Lab Med 2018;56:1524-32.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Greiner M, Pfeiffer D, Smith RD. Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Prev Vet Med 2000;45:23-41.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Byrne CD, Targher G. NAFLD as a driver of chronic kidney disease. J Hepatol 2020;72:785-801.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Kim SR, Lee YH, Lee SG, Kang ES, Cha BS, Kim JH, et al. Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase, an early marker of diabetic kidney disease, might reflect glucose excursion in patients with type 2 diabetes. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e4114.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Severini G, Aliberti LM, Koch M, Capurso L, Tarquini M. Clinical evaluation of serum N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase as a liver function test. Biochem Med Metab Biol 1990;44:247-51.PubMed
- 27. Zeni L, Norden AG, Cancarini G, Unwin RJ. A more tubulocentric view of diabetic kidney disease. J Nephrol 2017;30:701-17.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 28. Martinovic S, Filipovic N, Hadzic N, Pikula B. N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase as an early marker and indicator of the extent of kidney and liver lesions in endotoxemia and endotoxic shock. Acta Med Iugosl 1991;45:111-21.PubMed
- 29. Skrha J, Perusicova J, Stolba P, Stibor V, Pav J. Comparison of N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase and albuminuria with clinical finding of microangiopathy in type I diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta 1987;166:135-41.PubMed
- 30. Han E, Cho Y, Kim KW, Lee YH, Kang ES, Cha BS, et al. Hepatic fibrosis is associated with total proteinuria in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e21038.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Kim SS, Song SH, Kim IJ, Jeon YK, Kim BH, Kwak IS, et al. Urinary cystatin C and tubular proteinuria predict progression of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care 2013;36:656-61.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 32. Silva R, Meng C, Coentrao L. Diabetic nephropathy and its two phenotypes: the proteinuric and non-proteinuric. Port J Nephrol Hypertens 2017;31:122-31.
- 33. Fallatah HI. Noninvasive biomarkers of liver fibrosis: an overview. Adv Hepatol 2014;2014:357287.ArticlePDF
- 34. Sumida Y, Nakajima A, Itoh Y. Limitations of liver biopsy and non-invasive diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:475-85.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Smith ER, Cai MM, McMahon LP, Wright DA, Holt SG. The value of simultaneous measurements of urinary albumin and total protein in proteinuric patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012;27:1534-41.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Han E, Kim MK, Lee YH, Kim HS, Lee BW. Association between nonalbumin proteinuria and renal tubular damage of N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase and its clinical relevance in patients with type 2 diabetes without albuminuria. J Diabetes Complications 2019;33:255-60.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Miranda-Diaz AG, Pazarin-Villasenor L, Yanowsky-Escatell FG, Andrade-Sierra J. Oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy with early chronic kidney disease. J Diabetes Res 2016;2016:7047238.PubMedPMC
- 38. Slyne J, Slattery C, McMorrow T, Ryan MP. New developments concerning the proximal tubule in diabetic nephropathy: in vitro models and mechanisms. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2015;30 Suppl 4:iv60-7.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Day CP, James OF. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 1998;114:842-5.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Wijarnpreecha K, Thongprayoon C, Boonpheng B, Panjawatanan P, Sharma K, Ungprasert P, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and albuminuria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;30:986-94.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Brown GT, Kleiner DE. Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Metabolism 2016;65:1080-6.ArticlePubMed
- 42. Chang PE, Goh GB, Ngu JH, Tan HK, Tan CK. Clinical applications, limitations and future role of transient elastography in the management of liver disease. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2016;7:91-106.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Intermittent fasting plus early time-restricted eating versus calorie restriction and standard care in adults at risk of type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial
Xiao Tong Teong, Kai Liu, Andrew D. Vincent, Julien Bensalem, Bo Liu, Kathryn J. Hattersley, Lijun Zhao, Christine Feinle-Bisset, Timothy J. Sargeant, Gary A. Wittert, Amy T. Hutchison, Leonie K. Heilbronn
Nature Medicine.2023; 29(4): 963. CrossRef - Significance of Diabetic Kidney Disease Biomarkers in Predicting Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Jaehyun Bae, Byung-Wan Lee
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1928. CrossRef - Abdominal adipose tissue and type 2 diabetic kidney disease: adipose radiology assessment, impact, and mechanisms
Fei Lu, Jinlei Fan, Fangxuan Li, Lijing Liu, Zhiyu Chen, Ziyu Tian, Liping Zuo, Dexin Yu
Abdominal Radiology.2023; 49(2): 560. CrossRef - β‐Amyrin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in mice and regulates the miR‐181b‐5p/HMGB2 axis in high glucose‐stimulated HK‐2 cells
Wenhua Xu, Hongwu Zhang, Qinfeng Zhang, Jialan Xu
Environmental Toxicology.2022; 37(3): 637. CrossRef - High Glycated Hemoglobin Instead of High Body Mass Index Might Increase the Urine N-Acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase Con-Centration in Children and Adolescents with Diabetes Mellitus
Jin-Soon Suh, Kyoung Soon Cho, Seul Ki Kim, Shin-Hee Kim, Won Kyoung Cho, Min Ho Jung, Moon Bae Ahn
Life.2022; 12(6): 879. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite