
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Article by topic
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse > Article by topic
Brief Reports
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Short-Term Effects of the Internet-Based Korea Diabetes Prevention Study: 6-Month Results of a Community-Based Randomized Controlled Trial
- Jin-Hee Lee, Sun-Young Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Chan-Jung Han, Ah Reum Jung, Kook-Rye Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):960-965. Published online March 17, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0225

- 5,344 View
- 151 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- The aims of this study were to determine the short-term effectiveness of an internet-based lifestyle modification (LSM) program in preventing the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in prediabetes patients in community settings. A total of 415 subjects who were diagnosed with prediabetes were randomly assigned to the LSM and standard management (SM) groups. After the 6-month intervention, the LSM group had a statistically significant reduction in body weight, body mass index compared to the SM group participants. In the LSM group, blood glucose levels were significantly decreased after intervention and the clinical improvement effect was evident in the group that achieved the target weight loss of 5% or more of the initial weight for 6 months. Internet-based 6-month-intensive LSM programs conducted by public health center personnel are an effective way to provide lifestyle intervention programs and encourage maintenance of healthy behaviors in subjects with a high risk of T2DM in community settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- U-shaped association between online information exchange and app usage frequency: a large-scale survey of China ‘s online young and middle-aged people with pre diabetes and diabetes
Hanbin Guo, Yibiao Xiao, Canlin Liao, Jiating Sun, Yanchun Xie, Yitong Zheng, Guanhua Fan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovation in diabetes prevention research: The 36-year legacy of China Da Qing diabetes prevention study
Xin Chai, Yachen Wang, Jinping Wang, Qiuhong Gong, Juan Zhang, Ruitai Shao
Chinese Science Bulletin.2023; 68(28-29): 3834. CrossRef - Efficacy of Personalized Diabetes Self-care Using an Electronic Medical Record–Integrated Mobile App in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: 6-Month Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Young Lee, Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Sun-Young Lim, Jin-Hee Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kun-Ho Yoon, Min Kyung Hyun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(7): e37430. CrossRef - Prevention of type 2 diabetes through remotely administered lifestyle programs: A systematic review
Valaree Villegas, Alisha Shah, JoAnn E. Manson, Deirdre K. Tobias
Contemporary Clinical Trials.2022; 119: 106817. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 461. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Seung-Hyun Ko
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 244. CrossRef
- U-shaped association between online information exchange and app usage frequency: a large-scale survey of China ‘s online young and middle-aged people with pre diabetes and diabetes
- Drug/Regimen
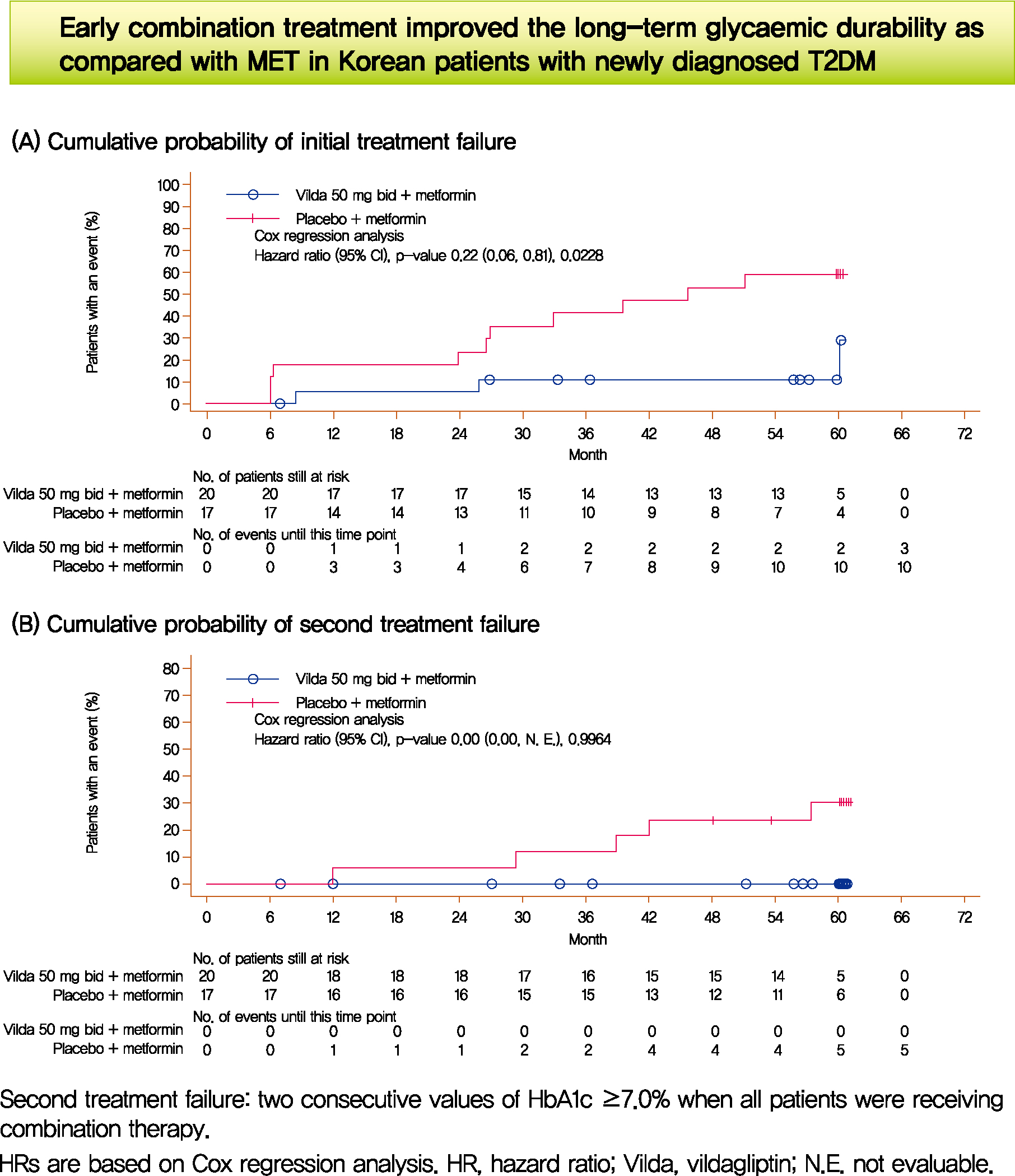
- Long-Term Glycaemic Durability of Early Combination Therapy Strategy versus Metformin Monotherapy in Korean Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Soon-Jib Yoo, Sang-Ah Chang, Tae Seo Sohn, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Jong Min Lee, Sungdae Moon, Pieter Proot, Päivi M Paldánius, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):954-959. Published online November 12, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0173
- 55,006 View
- 367 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- We assessed the glycaemic durability with early combination (EC; vildagliptin+metformin [MET], n=22) versus MET monotherapy (n=17), among newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) enrolled (between 2012 and 2014) in the VERIFY study from Korea (n=39). Primary endpoint was time to initial treatment failure (TF) (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] ≥7.0% at two consecutive scheduled visits after randomization [end of period 1]). Time to second TF was assessed when both groups were receiving and failing on the combination (end of period 2). With EC the risk of initial TF significantly reduced by 78% compared to MET (n=3 [15%] vs. n=10 [58.7%], P=0.0228). No secondary TF occurred in EC group versus five patients (29.4%) in MET. Patients receiving EC treatment achieved consistently lower HbA1c levels. Both treatment approaches were well tolerated with no hypoglycaemic events. In Korean patients with newly diagnosed T2DM, EC treatment significantly and consistently improved the long-term glycaemic durability as compared with MET.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 461. CrossRef
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Short Communication
- Drug/Regimen
- Dulaglutide as an Effective Replacement for Prandial Insulin in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Review
- Hwi Seung Kim, Jiwoo Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):948-953. Published online February 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0180

- 5,711 View
- 231 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Dulaglutide, a weekly injectable glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, has demonstrated effectiveness when combined with basal insulin. We examined whether the efficacy of dulaglutide is comparable to that of prandial insulin in kidney transplant (KT) recipients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) undergoing multiple daily insulin injection (MDI) therapy. Thirty-seven patients, who switched from MDI therapy to basal insulin and dulaglutide, were retrospectively analyzed. Changes in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels, body weight, and basal insulin dose were evaluated over 6 months. Dulaglutide was comparable to three injections of prandial insulin in terms of glycemic control (HbA1c 7.1% vs. 7.0%; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.53 to 0.28; P=0.53). The basal insulin and dulaglutide combination resulted in a reduction in FPG levels by 9.7 mg/dL (95% CI, 2.09 to 41.54; P=0.03), in body weight by 4.9 kg (95% CI, 2.87 to 6.98; P<0.001), and in basal insulin dose by 9.52 IU (95% CI, 5.80 to 3.23; P<0.001). Once-weekly dulaglutide may be an effective alternative for thrice-daily prandial insulin in KT recipients with T2DM currently receiving MDI therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetic Kidney Disease in Post-Kidney Transplant Patients
Ngoc-Yen T. Pham, Diego Cruz, Luis Madera-Marin, Raja Ravender, Pablo Garcia
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(3): 793. CrossRef - Safety and efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Pajaree Krisanapan, Supawadee Suppadungsuk, Kanokporn Sanpawithayakul, Charat Thongprayoon, Pattharawin Pattharanitima, Supawit Tangpanithandee, Michael A Mao, Jing Miao, Wisit Cheungpasitporn
Clinical Kidney Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sweet and simple as syrup: A review and guidance for use of novel antihyperglycemic agents for post‐transplant diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation
S. Elise Lawrence, Mary Moss Chandran, Jeong M. Park, Helen Sweiss, Thomas Jensen, Palak Choksi, Barrett Crowther
Clinical Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Drugs for the Management of Diabetes Kidney Transplant Patients: A Literature Review
Nancy Daniela Valencia-Morales, Beatriz Rodríguez-Cubillo, Rómulo Katsu Loayza-López, Maria Ángeles Moreno de la Higuera, Ana Isabel Sánchez-Fructuoso
Life.2023; 13(6): 1265. CrossRef - Uso de los agonistas del receptor del péptido similar al glucagón tipo 1 en pacientes trasplantados renales
Luis Alberto Vigara, Florentino Villanego, Cristhian Orellana, Myriam Eady, María Gabriela Sánchez, Marta Alonso, María Belén García, José Manuel Amaro, Teresa García, Auxiliadora Mazuecos
Nefrología.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Tolerability and Effectiveness of Switching to Dulaglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled With Insulin Therapy
Youngsook Kim, Ji Hye Huh, Minyoung Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diabetic Kidney Disease in Post-Kidney Transplant Patients
Original Articles
- Basic Research
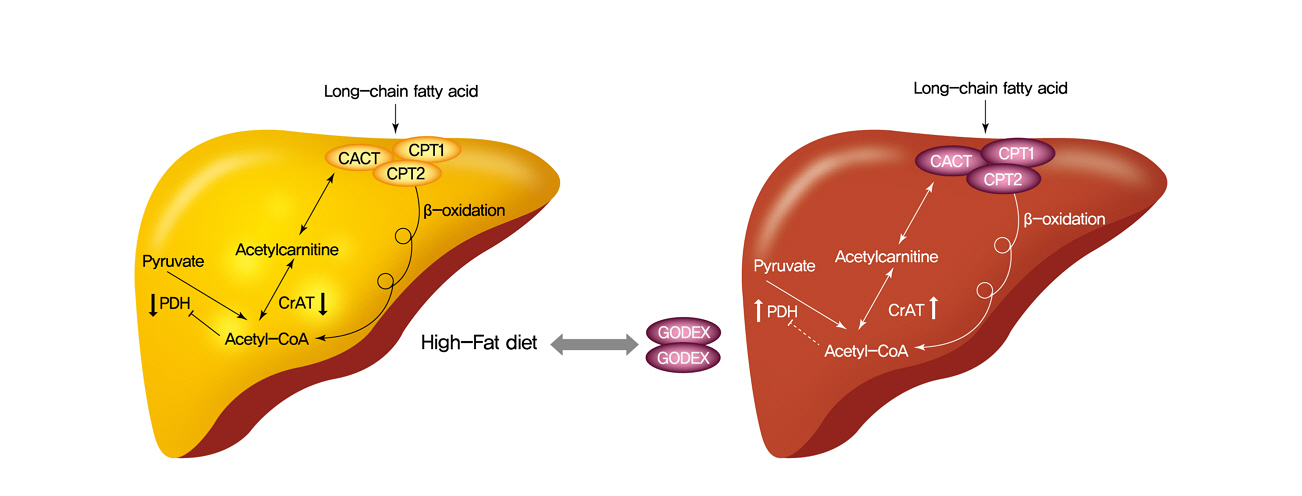
- Carnitine Orotate Complex Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis Through Carnitine Acetyltransferase Pathway
- Jung-Hee Hong, Moon-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):933-947. Published online August 19, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0223
- 5,740 View
- 164 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Carnitine orotate complex (Godex) has been shown to decrease glycated hemoglobin levels and improve steatosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. However, the mechanisms of Godex in glucose metabolism remain unclear.
Methods
Male C57BL/6J mice were divided into four groups: normal-fat diet, high-fat diet, a high-fat diet supplemented with intraperitoneal injection of (500 mg or 2,000 mg/kg/day) Godex for 8 weeks. Computed tomography, indirect calorimetry, and histological analyses including electron microscopy of the liver were performed, and biochemical profiles and oral glucose tolerance test and insulin tolerance test were undertaken. Expressions of genes in the lipid and glucose metabolism, activities of oxidative phosphorylation enzymes, carnitine acetyltransferase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA)/CoA ratio were evaluated.
Results
Godex improved insulin sensitivity and significantly decreased fasting plasma glucose, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance, steatosis, and gluconeogenesis, with a marked increase in fatty acid oxidation as well as better use of glucose in high-fat diet-fed mice. It preserved mitochondrial function and ultrastructure, restored oxidative phosphorylation enzyme activities, decreased acetyl-CoA/CoA ratio, and increased carnitine acetyltransferase content and pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. Carnitine acetyltransferase knockdown partially reversed the effects of Godex in liver and in vitro.
Conclusion
Godex improved insulin resistance and steatosis by regulating carnitine acetyltransferase in liver in high-fat diet-fed mice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of l-Carnitine Supplementation on Liver Enzyme Normalization in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials
Hyunwoo Oh, Chan Hyuk Park, Dae Won Jun
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(7): 1053. CrossRef - Prolonged Use of Carnitine-Orotate Complex (Godex®) Is Associated with Improved Mortality: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Kye-Yeung Park, Sangmo Hong, Kyung-Soo Kim, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(12): 1970. CrossRef - The Role of Carnitine Orotate Complex in Fatty Liver
Hyon-Seung Yi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 866. CrossRef
- Impact of l-Carnitine Supplementation on Liver Enzyme Normalization in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials
- Basic Research
-
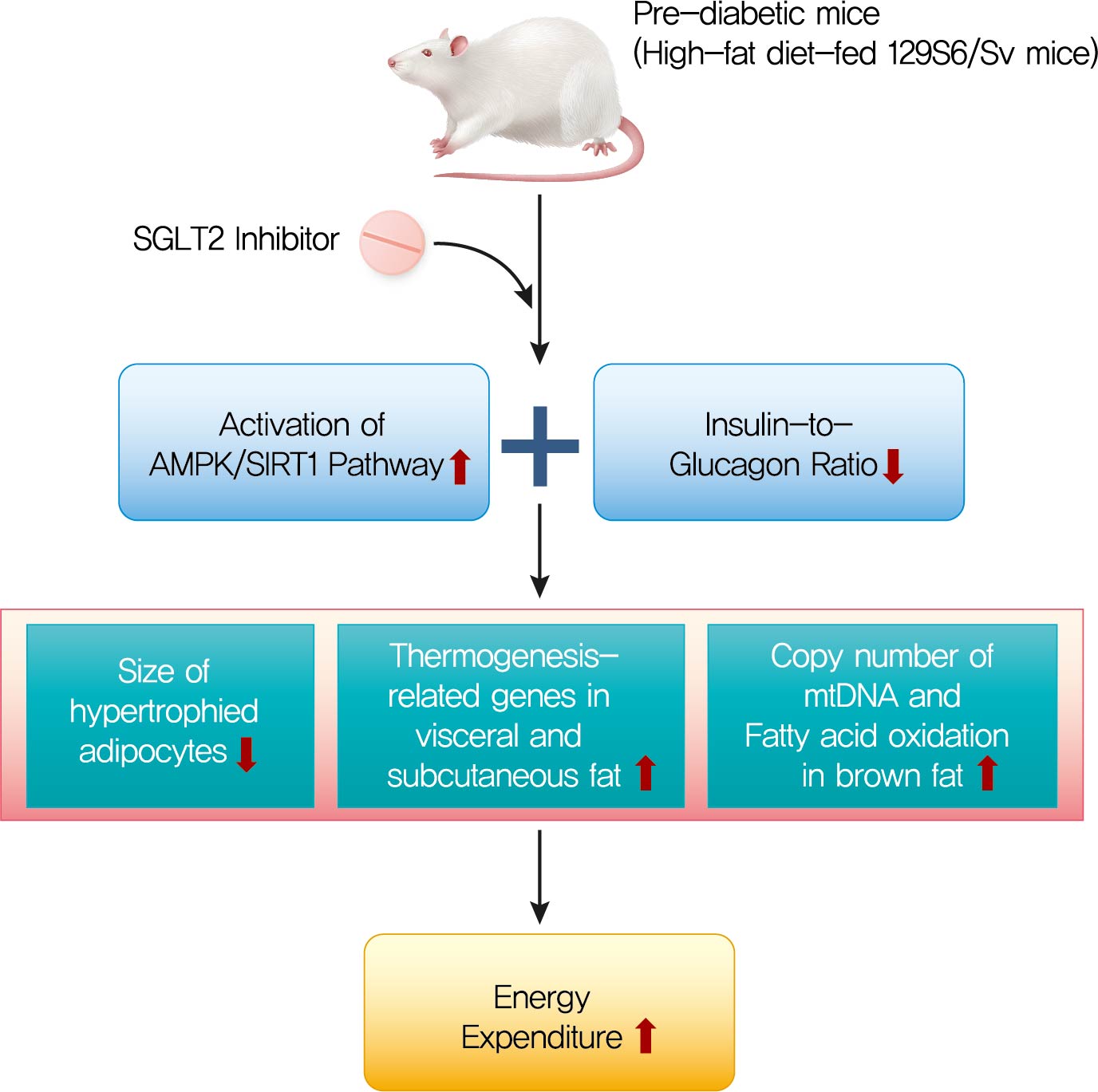
- Ipragliflozin, an SGLT2 Inhibitor, Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Changes by Upregulating Energy Expenditure through Activation of the AMPK/ SIRT1 Pathway
- Ji-Yeon Lee, Minyoung Lee, Ji Young Lee, Jaehyun Bae, Eugene Shin, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):921-932. Published online February 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0187
- 8,417 View
- 410 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are a new class of antidiabetic drugs that exhibit multiple extraglycemic effects. However, there are conflicting results regarding the effects of SGLT2 inhibition on energy expenditure and thermogenesis. Therefore, we investigated the effect of ipragliflozin (a selective SGLT2 inhibitor) on energy metabolism.
Methods
Six-week-old male 129S6/Sv mice with a high propensity for adipose tissue browning were randomly assigned to three groups: normal chow control, 60% high-fat diet (HFD)-fed control, and 60% HFD-fed ipragliflozin-treated groups. The administration of diet and medication was continued for 16 weeks.
Results
The HFD-fed mice became obese and developed hepatic steatosis and adipose tissue hypertrophy, but their random glucose levels were within the normal ranges; these features are similar to the metabolic features of a prediabetic condition. Ipragliflozin treatment markedly attenuated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis and reduced the size of hypertrophied adipocytes to that of smaller adipocytes. In the ipragliflozin treatment group, uncoupling protein 1 (Ucp1) and other thermogenesis-related genes were significantly upregulated in the visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue, and fatty acid oxidation was increased in the brown adipose tissue. These effects were associated with a significant reduction in the insulin-to-glucagon ratio and the activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) pathway in the liver and adipose tissue.
Conclusion
SGLT2 inhibition by ipragliflozin showed beneficial metabolic effects in 129S6/Sv mice with HFD-induced obesity that mimics prediabetic conditions. Our data suggest that SGLT2 inhibitors, through their upregulation of energy expenditure, may have therapeutic potential in prediabetic obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SGLT2 inhibitors and AMPK: The road to cellular housekeeping?
Nasser Safaie, Shahab Masoumi, Shaban Alizadeh, Pourya Mirzajanzadeh, Hamid Reza Nejabati, Mobasher Hajiabbasi, Vahid Alivirdiloo, Neda Chobdari Basmenji, Aysan Derakhshi Radvar, Ziba Majidi, Yousef Faridvand
Cell Biochemistry and Function.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanisms of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure and Their Clinical Value
Yafei Xie, Yujie Wei, Dan Li, Jie Pu, Hong Ding, Xiaowei Zhang
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology.2023; 81(1): 4. CrossRef - Current Treatment Options, Including Diet, Exercise, and Medications
Mazen Noureddin, Manal F. Abdelmalek
Clinics in Liver Disease.2023; 27(2): 397. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibitors and Kidney Diseases: A Clinical Perspective
Panagiotis Theofilis, Rigas G. Kalaitzidis
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 30(23): 2595. CrossRef - Treatment of obesity-related diabetes: significance of thermogenic adipose tissue and targetable receptors
Ruping Pan, Jiadai Liu, Yong Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunomodulatory Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors—Targeting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Aging
Ema Schönberger, Vjera Mihaljević, Kristina Steiner, Sandra Šarić, Tomislav Kurevija, Ljiljana Trtica Majnarić, Ines Bilić Ćurčić, Silvija Canecki-Varžić
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(17): 6671. CrossRef - SGLT‐2 inhibitors enhance the effect of metformin to ameliorate hormonal changes and inflammatory markers in a rat PCOS model
Manal Moustafa Mahmoud, Laila Ahmed Rashed, Somia Abdulatif Soliman, Safaa Mostafa Sayed, Omneya Kamel, Samaa Samir Kamar, Rania El Sayed Hussien
Physiological Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resting energy expenditure based on equation estimation can predict renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and biopsy-proven diabetic kidney disease
Xiang Xiao, Shuming Ji, Junlin Zhang, Deying Kang, Fang Liu
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium-glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Pathological Myocardial
Hypertrophy
Zhicheng Gao, Jiaqi Bao, Yilan Hu, Junjie Tu, Lifang Ye, Lihong Wang
Current Drug Targets.2023; 24(13): 1009. CrossRef - SIRT1 mediates the inhibitory effect of Dapagliflozin on EndMT by inhibiting the acetylation of endothelium Notch1
Weijie Wang, Yilan Li, Yanxiu Zhang, Tao Ye, Kui Wang, Shuijie Li, Yao Zhang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Direct cardio-protection of Dapagliflozin against obesity-related cardiomyopathy via NHE1/MAPK signaling
Ke Lin, Na Yang, Wu Luo, Jin-fu Qian, Wei-wei Zhu, Shi-ju Ye, Chen-xin Yuan, Di-yun Xu, Guang Liang, Wei-jian Huang, Pei-ren Shan
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2022; 43(10): 2624. CrossRef - Pleiotropic effects of SGLT2 inhibitors and heart failure outcomes
Panagiotis Theofilis, Marios Sagris, Evangelos Oikonomou, Alexios S. Antonopoulos, Gerasimos Siasos, Kostas Tsioufis, Dimitris Tousoulis
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 188: 109927. CrossRef - Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in the Regulation of Inflammatory Processes in Animal Models
Sandra Feijóo-Bandín, Alana Aragón-Herrera, Manuel Otero-Santiago, Laura Anido-Varela, Sandra Moraña-Fernández, Estefanía Tarazón, Esther Roselló-Lletí, Manuel Portolés, Oreste Gualillo, José Ramón González-Juanatey, Francisca Lago
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5634. CrossRef - Potential molecular mechanism of action of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in the prevention and management of diabetic retinopathy
Lia Meuthia Zaini, Arief S Kartasasmita, Tjahjono D Gondhowiardjo, Maimun Syukri, Ronny Lesmana
Expert Review of Ophthalmology.2022; 17(3): 199. CrossRef - New insights and advances of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in heart failure
Juexing Li, Lei Zhou, Hui Gong
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Critical Reanalysis of the Mechanisms Underlying the Cardiorenal Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors and Reaffirmation of the Nutrient Deprivation Signaling/Autophagy Hypothesis
Milton Packer
Circulation.2022; 146(18): 1383. CrossRef - Nutraceutical activation of Sirt1: a review
James J DiNicolantonio, Mark F McCarty, James H O'Keefe
Open Heart.2022; 9(2): e002171. CrossRef - Dapagliflozin Restores Impaired Autophagy and Suppresses Inflammation in High Glucose-Treated HK-2 Cells
Jing Xu, Munehiro Kitada, Yoshio Ogura, Haijie Liu, Daisuke Koya
Cells.2021; 10(6): 1457. CrossRef - Could Sodium/Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibitors Have Antiarrhythmic Potential in Atrial Fibrillation? Literature Review and Future Considerations
Dimitrios A. Vrachatis, Konstantinos A. Papathanasiou, Konstantinos E. Iliodromitis, Sotiria G. Giotaki, Charalampos Kossyvakis, Konstantinos Raisakis, Andreas Kaoukis, Vaia Lambadiari, Dimitrios Avramides, Bernhard Reimers, Giulio G. Stefanini, Michael C
Drugs.2021; 81(12): 1381. CrossRef - Differential Pathophysiological Mechanisms in Heart Failure With a Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction in Diabetes
Milton Packer
JACC: Heart Failure.2021; 9(8): 535. CrossRef - Ketone bodies: from enemy to friend and guardian angel
Hubert Kolb, Kerstin Kempf, Martin Röhling, Martina Lenzen-Schulte, Nanette C. Schloot, Stephan Martin
BMC Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- SGLT2 inhibitors and AMPK: The road to cellular housekeeping?
- Basic Research
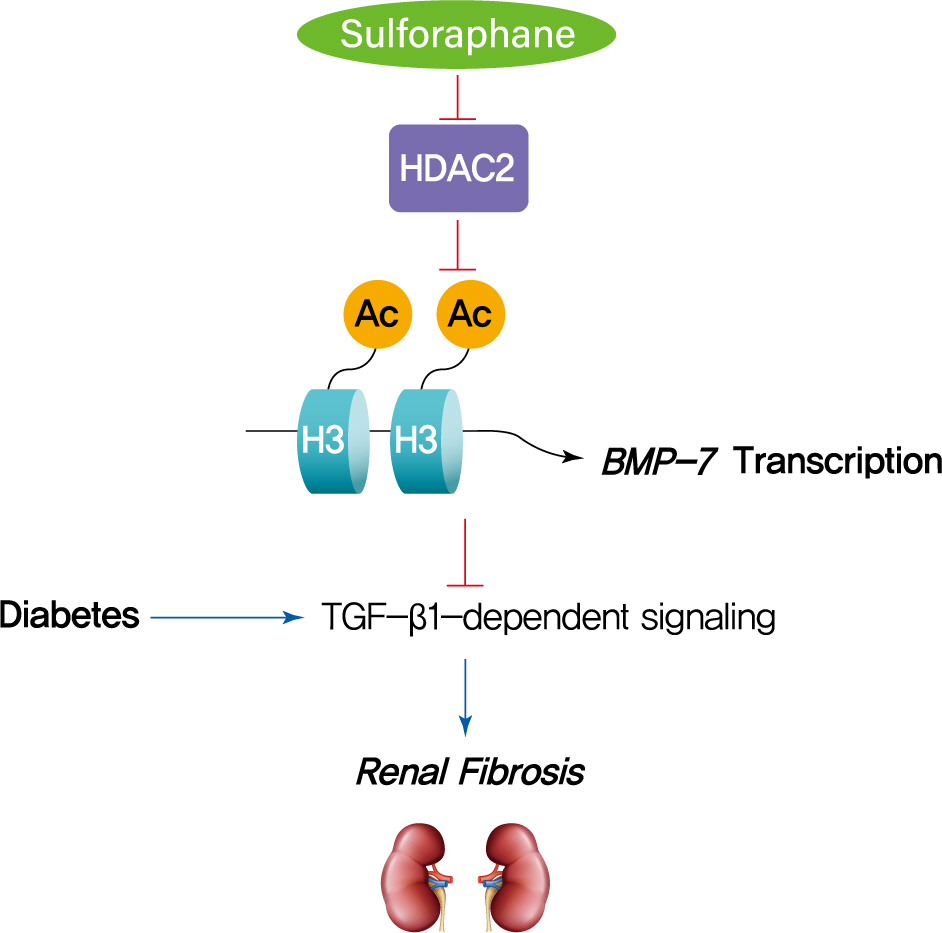
- Sulforaphane Ameliorates Diabetes-Induced Renal Fibrosis through Epigenetic Up-Regulation of BMP-7
- Lili Kong, Hongyue Wang, Chenhao Li, Huiyan Cheng, Yan Cui, Li Liu, Ying Zhao
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):909-920. Published online June 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0168
- 5,318 View
- 141 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
The dietary agent sulforaphane (SFN) has been reported to reduce diabetes-induced renal fibrosis, as well as inhibit histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity. Bone morphologic protein 7 (BMP-7) has been shown to reduce renal fibrosis induced by transforming growth factor-beta1. The aim of this study was to investigate the epigenetic effect of SFN on BMP-7 expression in diabetes-induced renal fibrosis.
Methods
Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice and age-matched controls were subcutaneously injected with SFN or vehicle for 4 months to measure the in vivo effects of SFN on the kidneys. The human renal proximal tubular (HK11) cell line was used to mimic diabetic conditions in vitro. HK11 cells were transfected to over-express HDAC2 and treated with high glucose/palmitate (HG/Pal) to explore the epigenetic modulation of BMP-7 in SFN-mediated protection against HG/Pal-induced renal fibrosis.
Results
SFN significantly attenuated diabetes-induced renal fibrosis in vivo. Among all of the HDACs we detected, HDAC2 activity was markedly elevated in the STZ-induced diabetic kidneys and HG/Pal-treated HK11 cells. SFN inhibited the diabetes-induced increase in HDAC2 activity which was associated with histone acetylation and transcriptional activation of the BMP-7 promoter. HDAC2 over-expression reduced BMP-7 expression and abolished the SFN-mediated protection against HG/Pal-induced fibrosis in vitro.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that the HDAC inhibitor SFN protects against diabetes-induced renal fibrosis through epigenetic up-regulation of BMP-7. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sulforaphane reduces adipose tissue fibrosis via promoting M2 macrophages polarization in HFD fed-mice
Zhenzhen Zhang, Huali Chen, Cheng Pan, Rui Li, Wangsheng Zhao, Tianzeng Song
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119626. CrossRef - Potential of Plant-Derived Compounds in Preventing and Reversing Organ Fibrosis and the Underlying Mechanisms
Patrícia dos Santos Azeredo, Daping Fan, E. Angela Murphy, Wayne E. Carver
Cells.2024; 13(5): 421. CrossRef - Beneficial role of broccoli and its active ingredient, sulforaphane in the treatment of diabetes
Aminu Mohammed, Hafsat Abdullahi Mohammed
Phytomedicine Plus.2023; 3(2): 100431. CrossRef - The Role of Histone Modifications in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Christodoula Kourtidou, Konstantinos Tziomalos
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(6): 6007. CrossRef - Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of NRF2 in Kidney Injury and Diseases
Da-Wei Lin, Yung-Chien Hsu, Cheng-Chih Chang, Ching-Chuan Hsieh, Chun-Liang Lin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6053. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Sulforaphane on Diabetes and Its Complications via Both Nrf2-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms
Minhyuk Kim, Joo Young Lee
Food Supplements and Biomaterials for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sulforaphane exhibits potent renoprotective effects in preclinical models of kidney diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Elisa B. Monteiro, Matheus Ajackson, Milena B. Stockler-Pinto, Fitsum Guebre-Egziabher, Julio B. Daleprane, Christophe O. Soulage
Life Sciences.2023; 322: 121664. CrossRef - Integrated single-cell RNA-seq analysis revealed podocyte injury through activation of the BMP7/AMPK/mTOR mediated autophagy pathway
Hongzhou Lin, Huihui Chen, Rengcheng Qian, Guoqi Tang, Yinjuan Ding, Yalan Jiang, Congde Chen, Dexuan Wang, Maoping Chu, Xiaoling Guo
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2023; 382: 110559. CrossRef - Underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of genistein in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and related complications
Tao Jiang, Yuhe Dong, Wanying Zhu, Tong Wu, Linyan Chen, Yuantong Cao, Xi Yu, Ye Peng, Ling Wang, Ying Xiao, Tian Zhong
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Sulforaphane: A nutraceutical against diabetes-related complications
Sinenhlanhla X.H. Mthembu, Sithandiwe E. Mazibuko-Mbeje, Marakiya T. Moetlediwa, Ndivhuwo Muvhulawa, Sonia Silvestri, Patrick Orlando, Bongani B. Nkambule, Christo J.F. Muller, Duduzile Ndwandwe, Albertus K. Basson, Luca Tiano, Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla
Pharmacological Research.2023; 196: 106918. CrossRef - Nrf2/HO-1 as a therapeutic target in renal fibrosis
Emad H.M. Hassanein, Islam M. Ibrahim, Esraa K. Abd-alhameed, Zeina W. Sharawi, Fatima A. Jaber, Hanan S. Althagafy
Life Sciences.2023; 334: 122209. CrossRef - A mechanistic overview of sulforaphane and its derivatives application in diabetes and its complications
Neda Mohamadi, Vafa Baradaran Rahimi, Mohammad Reza Fadaei, Fatemeh Sharifi, Vahid Reza Askari
Inflammopharmacology.2023; 31(6): 2885. CrossRef - The HDAC2/SP1/miR-205 feedback loop contributes to tubular epithelial cell extracellular matrix production in diabetic kidney disease
Zongji Zheng, Shuting Zhang, Jiaqi Chen, Meina Zou, Yanlin Yang, Wen Lu, Shijing Ren, Xiangyu Wang, Wenhui Dong, Zikun Zhang, Ling Wang, Meiping Guan, Gladys L.Y. Cheing, Yaoming Xue, Yijie Jia
Clinical Science.2022; 136(3): 223. CrossRef - BMP-7 Upregulates Id2 Through the MAPK Signaling Pathway to Improve Diabetic Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis and the Intervention of Oxymatrine
Yawen Xiao, Dan Liang, Zhiyang Li, Zhaowei Feng, Zhiping Yuan, Fan Zhang, Yuanyuan Wang, Yuxia Zhou, Mingjun Shi, Lingling Liu, Ying Xiao, Bing Guo
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HDAC1 Promotes Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by
Inhibiting BMP-7 Transcription Through Histone Deacetylation
Chun Ouyang, Lei Huang, Xiaoqiang Ye, Mingming Ren, Zhen Han
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(10): 660. CrossRef - Class IIa histone deacetylase inhibition ameliorates acute kidney injury by suppressing renal tubular cell apoptosis and enhancing autophagy and proliferation
Jialu Li, Chao Yu, Fengchen Shen, Binbin Cui, Na Liu, Shougang Zhuang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of histone deacetylases and inhibitors in renal fibrosis progression
Jiayu Wang, Jiaxing Li, Xin Zhang, Min Zhang, Xiaopeng Hu, Hang Yin
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The improvement of sulforaphane in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and related complications: A review
Mengjiao Wang, Min Chen, Rui Guo, Yangyang Ding, Haihui Zhang, Yuanqing He
Trends in Food Science & Technology.2022; 129: 397. CrossRef - Defining therapeutic targets for renal fibrosis: Exploiting the biology of pathogenesis
Hao Yan, Jiangxin Xu, Zhifei Xu, Bo Yang, Peihua Luo, Qiaojun He
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 143: 112115. CrossRef
- Sulforaphane reduces adipose tissue fibrosis via promoting M2 macrophages polarization in HFD fed-mice
- Genetics
- The rs2304256 Polymorphism in TYK2 Gene Is Associated with Protection for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Felipe Mateus Pellenz, Cristine Dieter, Guilherme Coutinho Kullmann Duarte, Luís Henrique Canani, Bianca Marmontel de Souza, Daisy Crispim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):899-908. Published online May 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0194
- 4,680 View
- 157 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
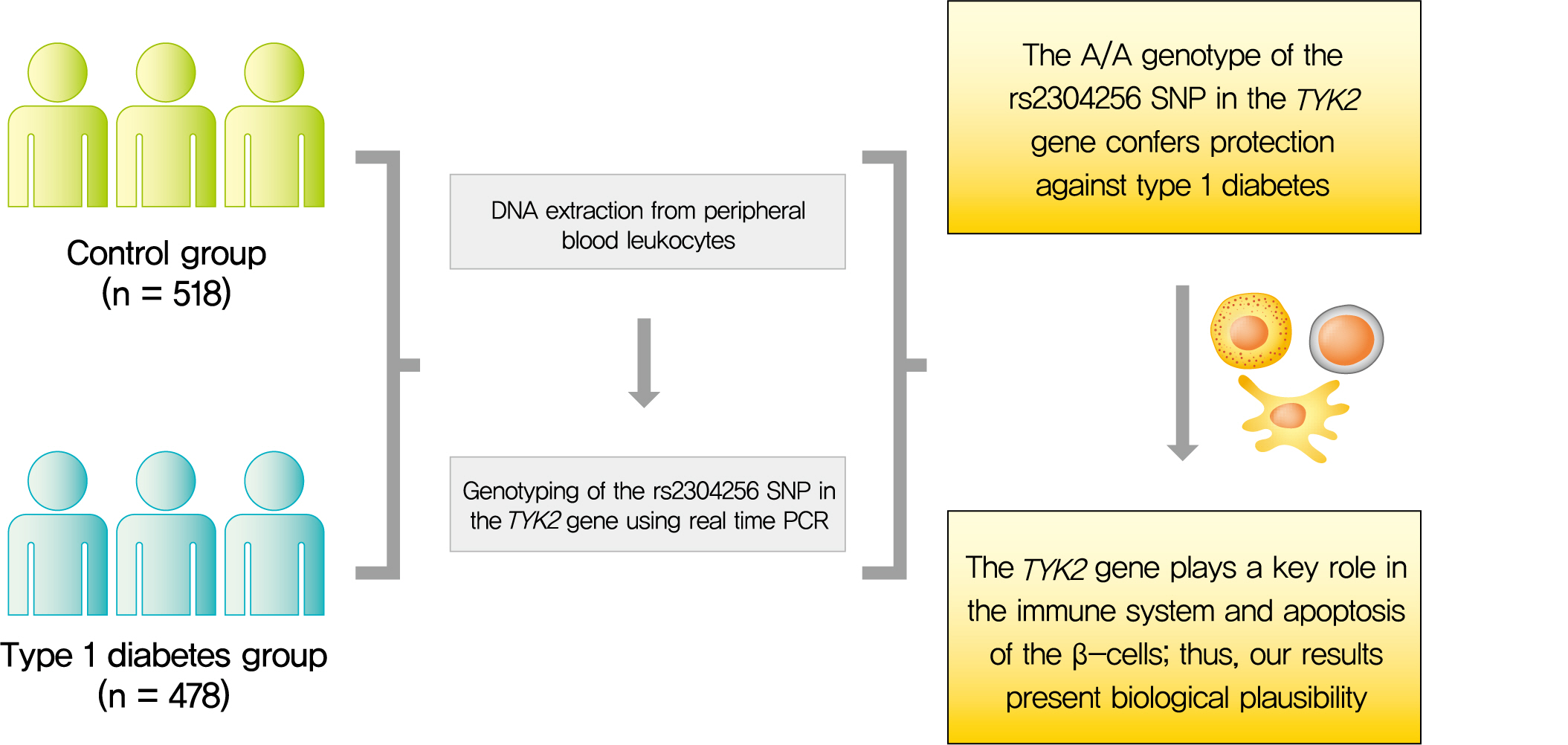
- Background
Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) is a candidate gene for type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) since it plays an important role in regulating apoptotic and pro-inflammatory pathways in pancreatic β-cells through modulation of the type I interferon signaling pathway. The rs2304256 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in TYK2 gene has been associated with protection for different autoimmune diseases. However, to date, only two studies have evaluated the association between this SNP and T1DM, with discordant results. This study thus aimed to investigate the association between the TYK2 rs2304256 SNP and T1DM in a Southern Brazilian population.
Methods
This case-control study comprised 478 patients with T1DM and 518 non-diabetic subjects. The rs2304256 (C/A) SNP was genotyped by real-time polymerase chain reaction technique using TaqMan minor groove binder (MGB) probes.
Results
Genotype and allele frequencies of the rs2304256 SNP differed between T1DM patients and non-diabetic subjects (P<0.0001 and P=0.001, respectively). Furthermore, the A allele was associated with protection against T1DM under recessive (odds ratio [OR], 0.482; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.288 to 0.806) and additive (OR, 0.470; 95% CI, 0.278 to 0.794) inheritance models, adjusting for human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DR/DQ genotypes, gender, and ethnicity.
Conclusion
The A/A genotype of TYK2 rs2304256 SNP is associated with protection against T1DM in a Southern Brazilian population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of genetic variants within TYK2 with pulmonary tuberculosis among Chinese population
Mingwu Zhang, Zhengwei Liu, Yelei Zhu, Kunyang Wu, Lin Zhou, Ying Peng, Junhang Pan, Bin Chen, Xiaomeng Wang, Songhua Chen
Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Host genetic variants associated with COVID-19 reconsidered in a Slovak cohort
Maria Skerenova, Michal Cibulka, Zuzana Dankova, Veronika Holubekova, Zuzana Kolkova, Vincent Lucansky, Dana Dvorska, Andrea Kapinova, Michaela Krivosova, Martin Petras, Eva Baranovicova, Ivana Baranova, Elena Novakova, Peter Liptak, Peter Banovcin, Anna
Advances in Medical Sciences.2024; 69(1): 198. CrossRef
- Associations of genetic variants within TYK2 with pulmonary tuberculosis among Chinese population
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Increased Visit-to-Visit Liver Enzyme Variability Is Associated with Incident Diabetes: A Community-Based 12-Year Prospective Cohort Study
- Kyuhoon Bang, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, You-Cheol Hwang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):890-898. Published online March 17, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0208
- 4,764 View
- 155 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
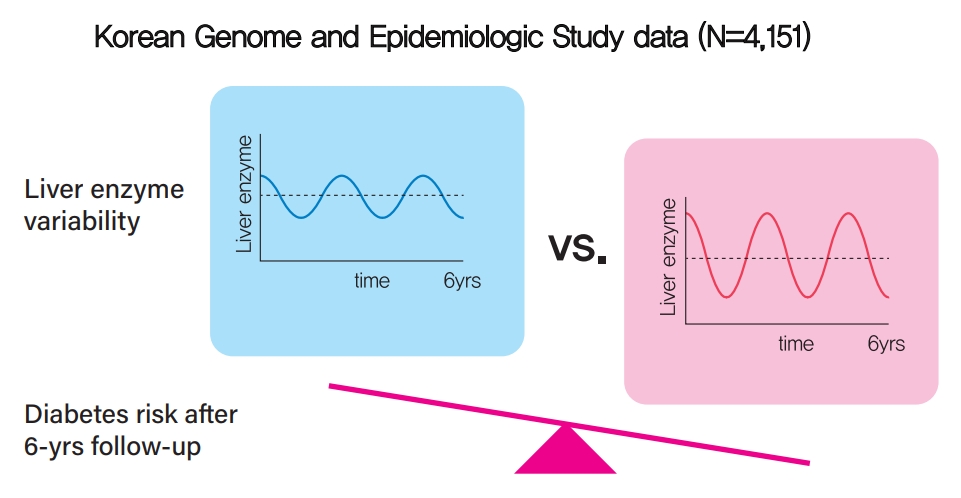
- Background
Fatty liver and/or increased liver enzyme values have been reported to be associated with incident diabetes. We sought to determine whether increased visit-to-visit liver enzyme variability is associated with incident diabetes.
Methods
Study participants were recruited from the Korean Genome and Epidemiologic Study (KoGES). A total of 4,151 people aged 40 to 69 years was recruited and tested every 2 years for up to 12 years. Visit-to-visit aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) variability was evaluated in first the 6-year period through the use of various variability measurements: standard deviation (SD), average successive variability, coefficient of variation (CV), and variation independent of mean (VIM). Oral glucose tolerance test was performed at every visit.
Results
During the 6-year follow‐up appointments, 13.0% (538/4,151) of people developed incident diabetes. Visit-to-visit AST variability was associated with an increased risk of diabetes independent of conventional risk factors for diabetes (hazard ratio per 1-SD increment [95% confidence interval]: 1.06 [1.00 to 1.11], 1.12 [1.04 to 1.21], and 1.13 [1.04 to 1.22] for SD, CV, and VIM, respectively; all P<0.05); however, no such associations were observed in the visit-to-visit ALT variability. According to alcohol consumption status, both AST and ALT variability were independent predictors for incident diabetes in subjects with heavy alcohol consumption; however, neither AST nor ALT variability was associated with diabetes risk in subjects who did not drink alcohol heavily.
Conclusion
Visit-to-visit liver enzyme variability is an independent predictor of incident diabetes. Such association was more evident in those who consumed significant amounts of alcohol.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018
- Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):880-889. Published online July 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0185
- 5,811 View
- 239 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
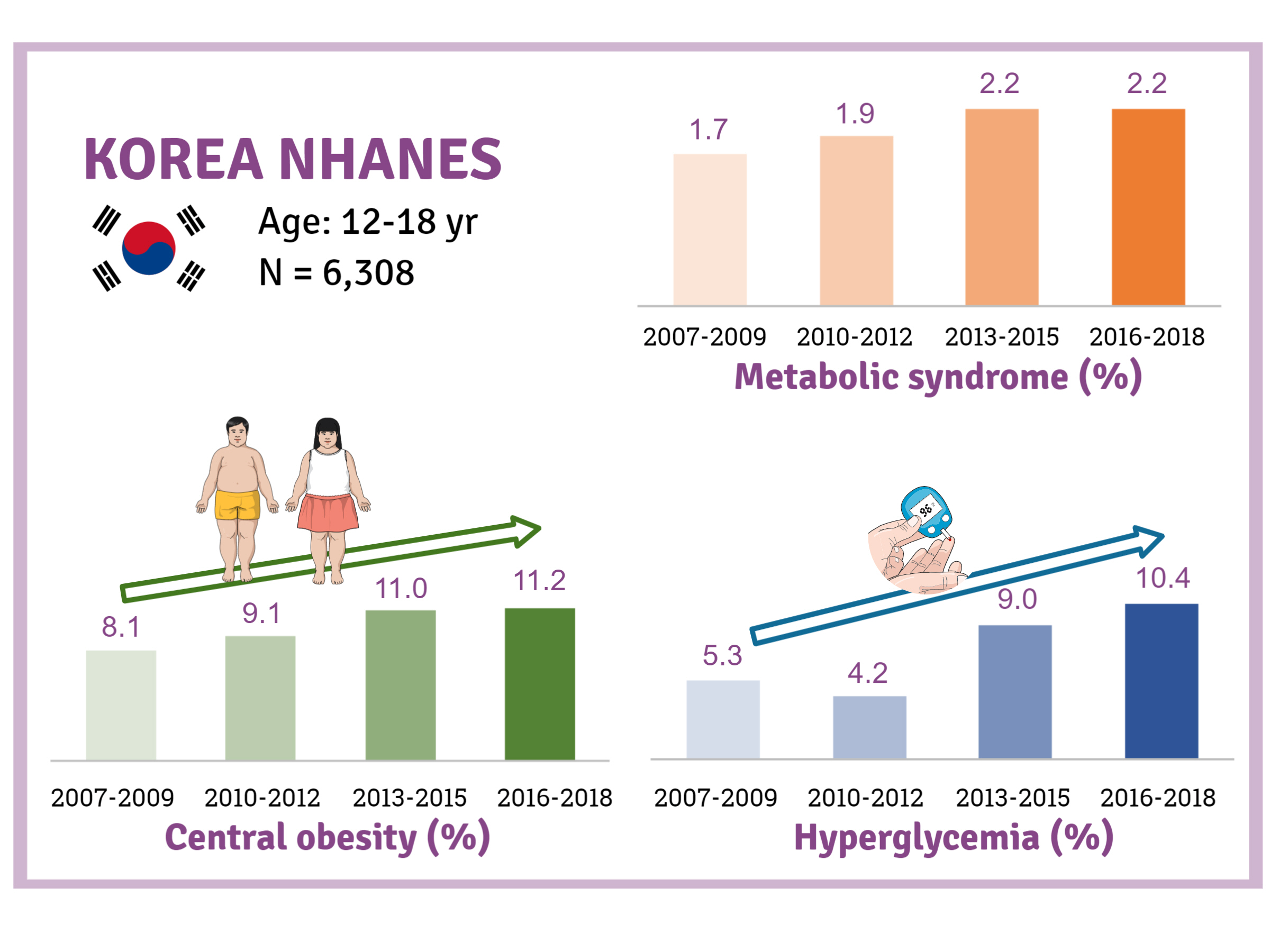
- Background
There is a lack of recent research on the changes in risk factors for metabolic syndrome (MetS) in the Asian pediatric population. We aimed to determine the 12-year trends in the prevalence of MetS and relevant lifestyle factors such as smoking, exercise, and calorie intake among Korean adolescents.
Methods
We investigated trends in MetS and lifestyle factors among 6,308 adolescents aged 12 to 18 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007 to 2018.
Results
The prevalence of MetS was stable from 2007 to 2018 (1.7% to 2.2%). There were significant increases in the prevalence of central obesity (from 8.1% to 11.2%, P=0.012) and hyperglycemia (from 5.3% to 10.4%, P<0.001) and decreases in hypo-high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterolemia (from 22.4% to 14.8%, P<0.001). Total calorie intake and calorie intake from fat significantly increased (P<0.001), whereas calorie intake from carbohydrates significantly decreased (P<0.001) during the study period. The proportions of tobacco smokers and regular walkers significantly decreased from 2007 to 2018. After controlling for all covariates, total calorie intake was positively correlated with waist circumference (P<0.05). HDL-cholesterol was negatively associated with carbohydrate consumption (P<0.01) and positively associated with fat consumption (P<0.001). Regular walking and regular strength training were associated with lower waist circumference (P<0.05). Smoking was associated with lower fasting glucose levels (P<0.01).
Conclusion
Although the prevalence rate of MetS is stable among Korean adolescents, the prevalence of central obesity and hyperglycemia has increased greatly in the recent decade. Public education on proper dietary intake and lifestyle modification is required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Overseas Deployment on Fatty Liver and Metabolic Diseases Among Korean Soldiers
Chang In Han, Jaejun Lee
Military Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impacts of dietary sphingomyelin supplementation on metabolic parameters of healthy adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Chen-Zi Li, Li-Mei Wu, Chen-Xi Zhu, Huan-Yu Du, Guo-Xun Chen, Fang Yang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Thyroid Function and Insulin Resistance Indices in Korean Adolescents: Findings from the 2014–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eunji Mun, Hye Ah Lee, Jung Eun Choi, Rosie Lee, Kyung Hee Kim, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2024; 11(3): 370. CrossRef - Ongoing increasing trends in central precocious puberty incidence among Korean boys and girls from 2008 to 2020
Sinyoung Kang, Mi Jung Park, Jung Min Kim, Jin-Sung Yuk, Shin-Hye Kim, Jun Mori
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0283510. CrossRef - The association between urinary cotinine level and metabolic syndrome profiles among adolescents: findings from the Ewha Birth and growth study
Hyunjin Park, Ui-Jeong Kim, Eun Jeong Choi, Seunghee Jun, Bomi Park, Hye Ah Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hyesook Park
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Based Speech Analysis System for Medical Support
Eui-Sun Kim, Dong Jin Shin, Sung Tae Cho, Kyung Jin Chung
International Neurourology Journal.2023; 27(2): 99. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Increase of Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents in Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the KNHANES
Jung Eun Choi, Hye Ah Lee, Sung Won Park, Jung Won Lee, Ji Hyen Lee, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2023; 10(7): 1105. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children and Adolescents
Ja Hyang Cho
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 103. CrossRef - Temporal Trends of the Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children and Adolescents between 2007 and 2020
Jieun Lee, Sung-Chan Kang, Obin Kwon, Seung-sik Hwang, Jin Soo Moon, Hyun Wook Chae, Jaehyun Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 170. CrossRef - Changes in the Number of Children and Adolescents with Complex Chronic Conditions and Medical Spending: Analyzing National Health Insurance Claims Data from 2011 to 2021
Jeong-Yoon Oh, Su-Jin Cho, Jin-Seon Jung, Jin-Suk Cho, Choon-Seon Park
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2023; 3(2): 155. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 349. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 351. CrossRef - Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hyperte
Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 377. CrossRef - Environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure in relation to metabolic syndrome in US adults
Xue Yang, Qingping Xue, Ying Wen, Yichao Huang, Yi Wang, Gaga Mahai, Tong Yan, Yanjun Liu, Tao Rong, Yixin Wang, Da Chen, Shuqin Zeng, Chun-Xia Yang, Xiong-Fei Pan
Science of The Total Environment.2022; 840: 156673. CrossRef - Commentary on "Single point insulin sensitivity estimator for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese adolescents"
Shin-Hye Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(3): 155. CrossRef
- Impact of Overseas Deployment on Fatty Liver and Metabolic Diseases Among Korean Soldiers
- Complications
- Associations of Plasma Glucagon Levels with Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate, Albuminuria and Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hua-Xing Huang, Liang-Lan Shen, Hai-Yan Huang, Li-Hua Zhao, Feng Xu, Dong-Mei Zhang, Xiu-Lin Zhang, Tong Chen, Xue-Qin Wang, Yan Xie, Jian-Bin Su
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):868-879. Published online March 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0149
- 5,817 View
- 173 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
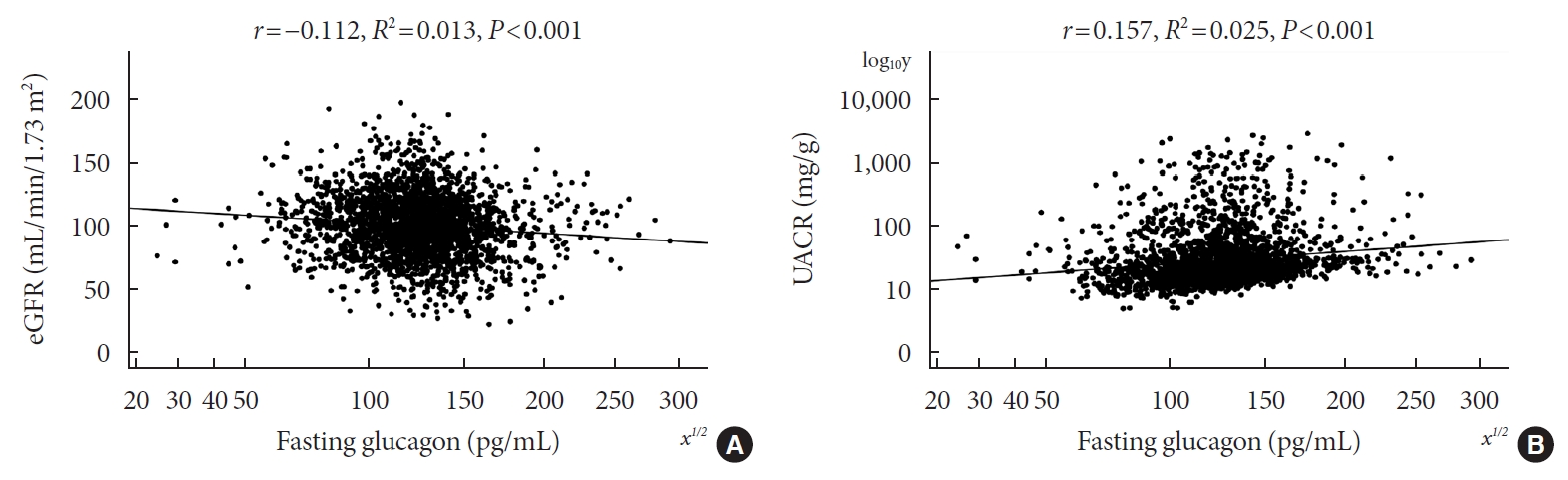
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is characterized by elevated fasting glucagon and impaired suppression of postprandial glucagon secretion, which may participate in diabetic complications. Therefore, we investigated the associations of plasma glucagon with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), albuminuria and diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in T2DM patients.
Methods
Fasting glucagon and postchallenge glucagon (assessed by area under the glucagon curve [AUCgla]) levels were determined during oral glucose tolerance tests. Patients with an eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and/or a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) ≥30 mg/g who presented with diabetic retinopathy were identified as having DKD.
Results
Of the 2,436 recruited patients, fasting glucagon was correlated with eGFR and UACR (r=–0.112 and r=0.157, respectively; P<0.001), and AUCgla was also correlated with eGFR and UACR (r=–0.267 and r=0.234, respectively; P<0.001). Moreover, 31.7% (n=771) presented with DKD; the prevalence of DKD was 27.3%, 27.6%, 32.5%, and 39.2% in the first (Q1), second (Q2), third (Q3), and fourth quartile (Q4) of fasting glucagon, respectively; and the corresponding prevalence for AUCgla was 25.9%, 22.7%, 33.7%, and 44.4%, respectively. Furthermore, after adjusting for other clinical covariates, the adjusted odds ratios (ORs; 95% confidence intervals) for DKD in Q2, Q3, and Q4 versus Q1 of fasting glucagon were 0.946 (0.697 to 1.284), 1.209 (0.895 to 1.634), and 1.521 (1.129 to 2.049), respectively; the corresponding ORs of AUCgla were 0.825 (0.611 to 1.114), 1.323 (0.989 to 1.769), and 2.066 (1.546 to 2.760), respectively. Additionally, when we restricted our analysis in patients with glycosylated hemoglobin <7.0% (n=471), we found fasting glucagon and AUCgla were still independently associated with DKD.
Conclusion
Both increased fasting and postchallenge glucagon levels were independently associated with DKD in T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glucagon in type 2 diabetes: Friend or foe?
Irene Caruso, Nicola Marrano, Giuseppina Biondi, Valentina Annamaria Genchi, Rossella D'Oria, Gian Pio Sorice, Sebastio Perrini, Angelo Cignarelli, Annalisa Natalicchio, Luigi Laviola, Francesco Giorgino
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Glucagon in type 2 diabetes: Friend or foe?
Editorial
- The Role of Carnitine Orotate Complex in Fatty Liver
- Hyon-Seung Yi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):866-867. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0272
- 4,389 View
- 110 Download
Reviews
- Basic Research
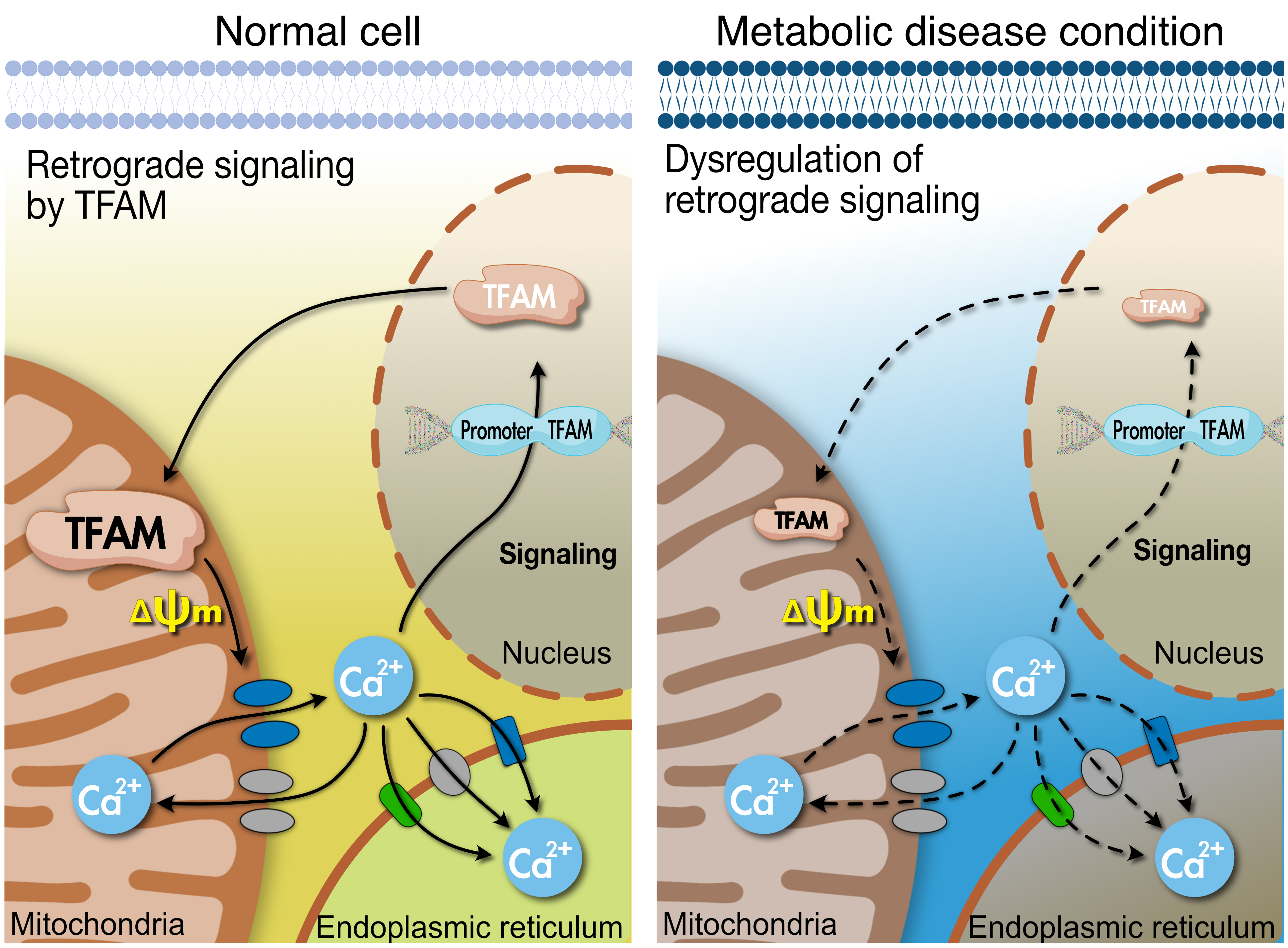
- Mitochondrial TFAM as a Signaling Regulator between Cellular Organelles: A Perspective on Metabolic Diseases
- Jin-Ho Koh, Yong-Woon Kim, Dae-Yun Seo, Tae-Seo Sohn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):853-865. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0138
- 6,585 View
- 274 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Tissues actively involved in energy metabolism are more likely to face metabolic challenges from bioenergetic substrates and are susceptible to mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to metabolic diseases. The mitochondria receive signals regarding the metabolic states in cells and transmit them to the nucleus or endoplasmic reticulum (ER) using calcium (Ca2+) for appropriate responses. Overflux of Ca2+ in the mitochondria or dysregulation of the signaling to the nucleus and ER could increase the incidence of metabolic diseases including insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mitochondrial transcription factor A (Tfam) may regulate Ca2+ flux via changing the mitochondrial membrane potential and signals to other organelles such as the nucleus and ER. Since Tfam is involved in metabolic function in the mitochondria, here, we discuss the contribution of Tfam in coordinating mitochondria-ER activities for Ca2+ flux and describe the mechanisms by which Tfam affects mitochondrial Ca2+ flux in response to metabolic challenges.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeted metabolomics reveals the aberrant energy status in diabetic peripheral neuropathy and the neuroprotective mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine JinMaiTong
Bingjia Zhao, Qian Zhang, Yiqian He, Weifang Cao, Wei Song, Xiaochun Liang
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis.2024; 14(2): 225. CrossRef - Mitochondrial damage‐associated molecular patterns: A new insight into metabolic inflammation in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yan Wang, Jingwu Wang, Si‐Yu Tao, Zhengting Liang, Rong xie, Nan‐nan Liu, Ruxue Deng, Yuelin Zhang, Deqiang Deng, Guangjian Jiang
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Altered Energy Metabolism, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Redox Imbalance Influencing Reproductive Performance in Granulosa Cells and Oocyte During Aging
Hiroshi Kobayashi, Chiharu Yoshimoto, Sho Matsubara, Hiroshi Shigetomi, Shogo Imanaka
Reproductive Sciences.2024; 31(4): 906. CrossRef - When Our Best Friend Becomes Our Worst Enemy: The Mitochondrion in Trauma, Surgery, and Critical Illness
May-Kristin Torp, Kåre-Olav Stensløkken, Jarle Vaage
Journal of Intensive Care Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction and morphological disruption with PT320 delays dopamine degeneration in MitoPark mice
Vicki Wang, Kuan-Yin Tseng, Tung-Tai Kuo, Eagle Yi-Kung Huang, Kuo-Lun Lan, Zi-Rong Chen, Kuo-Hsing Ma, Nigel H. Greig, Jin Jung, Ho-II Choi, Lars Olson, Barry J. Hoffer, Yuan-Hao Chen
Journal of Biomedical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the anti-inflammatory drug celecoxib on cell death signaling in human colon cancer
Ryuto Maruyama, Yuki Kiyohara, Yasuhiro Kudo, Tomoyasu Sugiyama
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2023; 396(6): 1171. CrossRef - gp130 Activates Mitochondrial Dynamics for Hepatocyte Survival in a Model of Steatohepatitis
Daria Shunkina, Anastasia Dakhnevich, Egor Shunkin, Olga Khaziakhmatova, Valeria Shupletsova, Maria Vulf, Alexandra Komar, Elena Kirienkova, Larisa Litvinova
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 396. CrossRef - Pharmacological Activation of Rev-erbα Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by PGC-1α Signaling Pathway
Runmei Zou, Shuo Wang, Hong Cai, Yuwen Wang, Cheng Wang, Vivek Pandey
Cardiovascular Therapeutics.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Protective Effect of Ergothioneine against 7-Ketocholesterol-Induced Mitochondrial Damage in hCMEC/D3 Human Brain Endothelial Cells
Damien Meng-Kiat Leow, Irwin Kee-Mun Cheah, Zachary Wei-Jie Fong, Barry Halliwell, Wei-Yi Ong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(6): 5498. CrossRef - Effect of PPARγ on oxidative stress in diabetes-related dry eye
Jing Wang, Shuangping Chen, Xiuxiu Zhao, Qian Guo, Ruibo Yang, Chen Zhang, Yue Huang, Lechong Ma, Shaozhen Zhao
Experimental Eye Research.2023; 231: 109498. CrossRef - Chiisanoside Mediates the Parkin/ZNF746/PGC-1α Axis by Downregulating MiR-181a to Improve Mitochondrial Biogenesis in 6-OHDA-Caused Neurotoxicity Models In Vitro and In Vivo: Suggestions for Prevention of Parkinson’s Disease
Yu-Ling Hsu, Hui-Jye Chen, Jia-Xin Gao, Ming-Yang Yang, Ru-Huei Fu
Antioxidants.2023; 12(9): 1782. CrossRef - TBBPA causes apoptosis in grass carp hepatocytes involving destroyed ER-mitochondrial function
Dongxu Han, Naixi Yang, Huanyi Liu, Yujie Yao, Shiwen Xu
Chemosphere.2023; 341: 139974. CrossRef - The Protective Mechanism of TFAM on Mitochondrial DNA and its Role in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Ying Song, Wenjun Wang, Beibei Wang, Qiwen Shi
Molecular Neurobiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Dynamics in Leukocytes of Obese Women
Zaida Abad-Jiménez, Teresa Vezza, Sandra López-Domènech, Meylin Fernández-Reyes, Francisco Canet, Carlos Morillas, Segundo Ángel Gómez-Abril, Celia Bañuls, Víctor M. Víctor, Milagros Rocha
Antioxidants.2022; 11(7): 1302. CrossRef - The Effects of Galgunhwanggumhwangryun-tang on Glucose and Energy Metabolism in C2C12 Myotubes
Jihong Oh, Song-Yi Han, Soo Kyoung Lim, Hojun Kim
Journal of Korean Medicine for Obesity Research.2022; 22(2): 93. CrossRef
- Targeted metabolomics reveals the aberrant energy status in diabetic peripheral neuropathy and the neuroprotective mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine JinMaiTong
- Basic Research
- Brown Fat as a Regulator of Systemic Metabolism beyond Thermogenesis
- Okamatsu-Ogura Yuko, Masayuki Saito
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):840-852. Published online June 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0291

- 8,977 View
- 504 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Brown adipose tissue (BAT) is a specialized tissue for nonshivering thermogenesis to dissipate energy as heat. Although BAT research has long been limited mostly in small rodents, the rediscovery of metabolically active BAT in adult humans has dramatically promoted the translational studies on BAT in health and diseases. Moreover, several remarkable advancements have been made in brown fat biology over the past decade: The molecular and functional analyses of inducible thermogenic adipocytes (socalled beige adipocytes) arising from a developmentally different lineage from classical brown adipocytes have been accelerated. In addition to a well-established thermogenic activity of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), several alternative thermogenic mechanisms have been discovered, particularly in beige adipocytes. It has become clear that BAT influences other peripheral tissues and controls their functions and systemic homeostasis of energy and metabolic substrates, suggesting BAT as a metabolic regulator, other than for thermogenesis. This notion is supported by discovering that various paracrine and endocrine factors are secreted from BAT. We review the current understanding of BAT pathophysiology, particularly focusing on its role as a metabolic regulator in small rodents and also in humans.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Brown adipose tissue evaluation using water and triglyceride as indices by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy
Tomomi Iida, Yukio Ueda, Hideo Tsukada, Dai Fukumoto, Takafumi Hamaoka
Journal of Biophotonics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - White-brown adipose tissue interplay in polycystic ovary syndrome: Therapeutic avenues
Khadijeh Abbasi, Reza Zarezadeh, Amir Valizadeh, Amir Mehdizadeh, Hamed Hamishehkar, Mohammad Nouri, Masoud Darabi
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 220: 116012. CrossRef - Brown Adipose Tissue, Batokines, and Bioactive Compounds in Foods: An Update
Fabiane Ferreira Martins, Bruna Cadete Martins, Ananda Vitoria Silva Teixeira, Matheus Ajackson, Vanessa Souza‐Mello, Julio Beltrame Daleprane
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasticity of Adipose Tissues: Interconversion among White, Brown, and Beige Fat and Its Role in Energy Homeostasis
Yanqiu Peng, Lixia Zhao, Min Li, Yunfei Liu, Yuke Shi, Jian Zhang
Biomolecules.2024; 14(4): 483. CrossRef - Thermogenic Brown Fat in Humans: Implications in Energy Homeostasis, Obesity and Metabolic Disorders
Masayuki Saito, Yuko Okamatsu-Ogura
The World Journal of Men's Health.2023; 41(3): 489. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - White adipose tissue undergoes browning during preweaning period in association with microbiota formation in mice
Anju Tsukada, Yuko Okamatsu-Ogura, Emi Futagawa, Yuki Habu, Natsumi Takahashi, Mira Kato-Suzuki, Yuko Kato, Satoshi Ishizuka, Kei Sonoyama, Kazuhiro Kimura
iScience.2023; 26(7): 107239. CrossRef - In situ fluorescence-photoacoustic measurement of the changes of brown adipose tissue in mice under hindlimb unloading
Baojie Gong, Jianxin Tang, Xiaoxiao Jiang, Zhe Zhang, Shiying Li, Hongjun Jin, Liming Nie, Guojia Huang
Journal of Applied Physiology.2023; 135(2): 251. CrossRef - Age-Related Expression Dynamics of Uncoupling Protein 1 in Adipose Tissues of ICR Outbred Mice during Postnatal Ontogenesis
A. V. Yakunenkov, E. I. Elsukova, I. O. Natochy
Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology.2023; 59(4): 1020. CrossRef - UNCOUPLING PROTEIN UCP1 EXPRESSION DYNAMICS IN ADIPOSE TISSUES OF THE OUTBRED ICR MICE IN POSTNATAL ONTOGENESIS
A. V. Yakunenkov, E. I. Elsukova, I. O. Natochy
Журнал эволюционной биохимии и физиологии.2023; 59(4): 255. CrossRef - Antibodies Regulate Dual-Function Enzyme IYD to Induce Functional Synergy between Metabolism and Thermogenesis
Sunghyun Kang, Hwan-Woo Park, Kyung Ho Han
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(14): 7834. CrossRef - Machine learning-featured Secretogranin V is a circulating diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic adenocarcinomas associated with adipopenia
Yunju Jo, Min-Kyung Yeo, Tam Dao, Jeongho Kwon, Hyon‐Seung Yi, Dongryeol Ryu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Possible roles of exercise and apelin against pregnancy complications
Hamed Alizadeh Pahlavani
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationships between the expression of adipose genes and profiles of hospitalized dogs
Yukina Sugiyama, Fumie Shimokawa, Kazutoshi Sugiyama, Takashi Kobayashi, Yusuke Yamashita, Kei Kazama, Ken Onda, Masayuki Funaba, Masaru Murakami
Veterinary Research Communications.2022; 46(4): 1239. CrossRef - Garlic (Allium sativum L.) in diabetes and its complications: Recent advances in mechanisms of action
Yayi Jiang, Rensong Yue, Guojie Liu, Jun Liu, Bo Peng, Maoyi Yang, Lianxue Zhao, Zihan Li
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Fruit of Gardenia jasminoides Induces Mitochondrial Activation and Non-Shivering Thermogenesis through Regulation of PPARγ
Woo Yong Park, Gahee Song, Ja Yeon Park, Kwan-Il Kim, Kwang Seok Ahn, Hyun Jeong Kwak, Jungtae Leem, Jae-Young Um, Jinbong Park
Antioxidants.2021; 10(9): 1418. CrossRef
- Brown adipose tissue evaluation using water and triglyceride as indices by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy
- Technology/Device
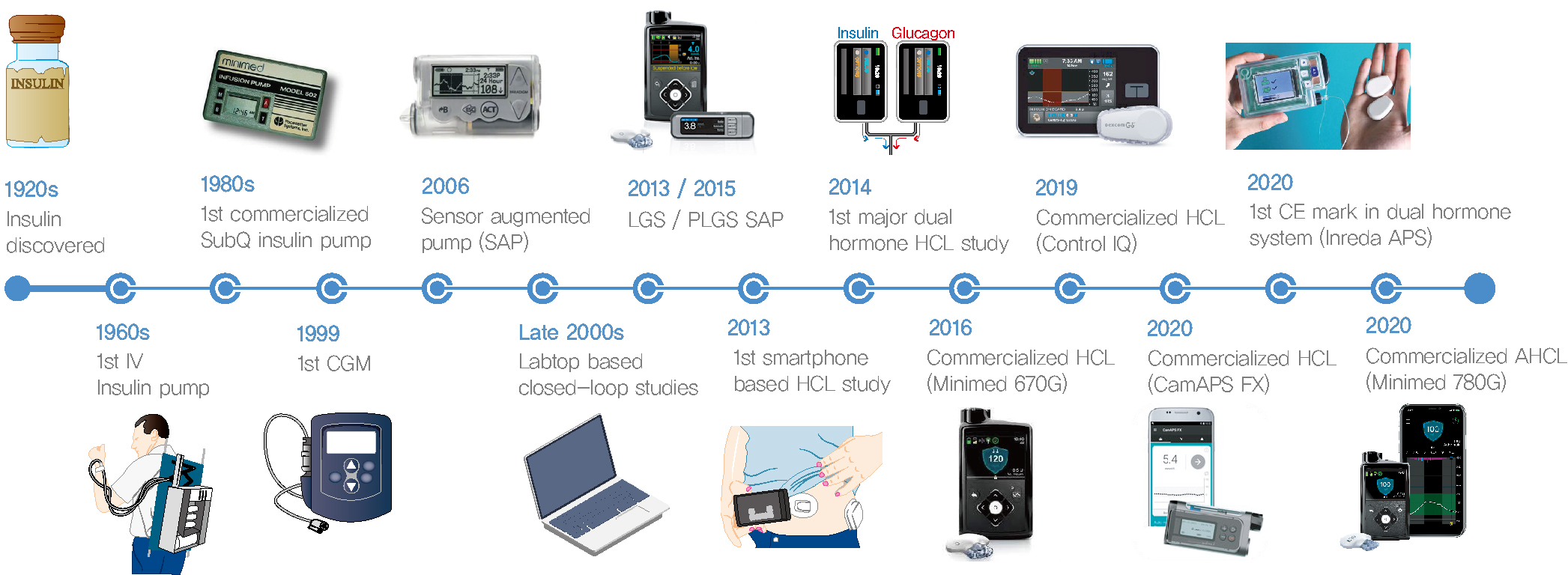
- Current Advances of Artificial Pancreas Systems: A Comprehensive Review of the Clinical Evidence
- Sun Joon Moon, Inha Jung, Cheol-Young Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):813-839. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0177
- 14,308 View
- 794 Download
- 27 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Since Banting and Best isolated insulin in the 1920s, dramatic progress has been made in the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). However, dose titration and timely injection to maintain optimal glycemic control are often challenging for T1DM patients and their families because they require frequent blood glucose checks. In recent years, technological advances in insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring systems have created paradigm shifts in T1DM care that are being extended to develop artificial pancreas systems (APSs). Numerous studies that demonstrate the superiority of glycemic control offered by APSs over those offered by conventional treatment are still being published, and rapid commercialization and use in actual practice have already begun. Given this rapid development, keeping up with the latest knowledge in an organized way is confusing for both patients and medical staff. Herein, we explore the history, clinical evidence, and current state of APSs, focusing on various development groups and the commercialization status. We also discuss APS development in groups outside the usual T1DM patients and the administration of adjunct agents, such as amylin analogues, in APSs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integration of a Safety Module to Prevent Rebound Hypoglycemia in Closed-Loop Artificial Pancreas Systems
María F. Villa-Tamayo, Patricio Colmegna, Marc D. Breton
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024; 18(2): 318. CrossRef - The effects of acute hyperglycaemia on sports and exercise performance in type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Bonar McGuire, Hashim Dadah, Dominic Oliver
Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport.2024; 27(2): 78. CrossRef - A new approach to stabilize diabetes systems with time-varying delays and disturbance rejection
S. Syafiie, Fahd Alharbi, Abdullah Ali Alshehri, Bassam Hasanain
Journal of the Franklin Institute.2024; 361(1): 543. CrossRef - Effects of Low-Dose Glucagon on Subcutaneous Insulin Absorption in Pigs
Ingrid Anna Teigen, Marte Kierulf Åm, Misbah Riaz, Sverre Christian Christiansen, Sven Magnus Carlsen
Current Therapeutic Research.2024; 100: 100736. CrossRef - Robust Online Correlation Method for Identification of a Nonparametric Model of Type 1 Diabetes
Martin Dodek, Eva Miklovičová
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 35899. CrossRef - 100 Years of insulin: A chemical engineering perspective
B. Wayne Bequette
Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering.2023; 40(1): 1. CrossRef - Efficacy of intermittent short‐term use of a real‐time continuous glucose monitoring system in non‐insulin–treated patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial
Sun Joon Moon, Kyung‐Soo Kim, Woo Je Lee, Mi Yeon Lee, Robert Vigersky, Cheol‐Young Park
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(1): 110. CrossRef - Identifiable prediction animal model for the bi-hormonal intraperitoneal artificial pancreas
Karim Davari Benam, Hasti Khoshamadi, Marte Kierulf Åm, Øyvind Stavdahl, Sebastien Gros, Anders Lyngvi Fougner
Journal of Process Control.2023; 121: 13. CrossRef - Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - CGM accuracy: Contrasting CE marking with the governmental controls of the USA (FDA) and Australia (TGA): A narrative review
John S Pemberton, Emma G Wilmot, Katharine Barnard‐Kelly, Lalantha Leelarathna, Nick Oliver, Tabitha Randell, Craig E Taplin, Pratik Choudhary, Peter Adolfsson
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(4): 916. CrossRef - Evaluation of awareness and attitude of paediatric nursing students, nurses, and adolescents regarding type one diabetes advanced devices and virtual nursing
Howaida Moawad Ahmed Ali
Kontakt.2023; 25(2): 100. CrossRef - Predicting the output error of the suboptimal state estimator to improve the performance of the MPC-based artificial pancreas
Martin Dodek, Eva Miklovičová
Control Theory and Technology.2023; 21(4): 541. CrossRef - A Markov Model of Gap Occurrence in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data for Realistic in Silico Clinical Trials
Martina Vettoretti, Martina Drecogna, Simone Del Favero, Andrea Facchinetti, Giovanni Sparacino
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine.2023; 240: 107700. CrossRef - Drug delivery breakthrough technologies – A perspective on clinical and societal impact
Beate Bittner, Manuel Sánchez-Félix, Dennis Lee, Athanas Koynov, Joshua Horvath, Felix Schumacher, Simon Matoori
Journal of Controlled Release.2023; 360: 335. CrossRef - Importance of continuous glucose monitoring in the treatment of diabetes mellitus
Sun Joon Moon, Won-Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 432. CrossRef - Constrained Versus Unconstrained Model Predictive Control for Artificial Pancreas
Chiara Toffanin, Lalo Magni
IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology.2023; 31(5): 2288. CrossRef - Intelligent Insulin vs. Artificial Intelligence for Type 1 Diabetes: Will the Real Winner Please Stand Up?
Valentina Maria Cambuli, Marco Giorgio Baroni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13139. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Efficient Diabetes Care
Gopal Bhagwan Khodve, Sugato Banerjee
Current Diabetes Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The artificial pancreas: two alternative approaches to achieve a fully closed-loop system with optimal glucose control
M. K. Åm, I. A. Teigen, M. Riaz, A. L. Fougner, S. C. Christiansen, S. M. Carlsen
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 47(3): 513. CrossRef - Multivariable Automated Insulin Delivery System for Handling Planned and Spontaneous Physical Activities
Mohammad Reza Askari, Mohammad Ahmadasas, Andrew Shahidehpour, Mudassir Rashid, Laurie Quinn, Minsun Park, Ali Cinar
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023; 17(6): 1456. CrossRef - Advanced Technology (Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop Systems) in Diabetes from the Perspective of Gender Differences
Maria Grazia Nuzzo, Marciano Schettino
Diabetology.2023; 4(4): 519. CrossRef - Artificial Pancreas under a Zone Model Predictive Control based on Gaussian Process models: toward the personalization of the closed loop
Marco Polver, Beatrice Sonzogni, Mirko Mazzoleni, Fabio Previdi, Antonio Ferramosca
IFAC-PapersOnLine.2023; 56(2): 9642. CrossRef - Personalized Constrained MPC for glucose regulation
Chiara Toffanin, Lalo Magni
IFAC-PapersOnLine.2023; 56(2): 9648. CrossRef - Automated Insulin Delivery Systems in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Outpatient Randomized Controlled Trials
Baoqi Zeng, Le Gao, Qingqing Yang, Hao Jia, Feng Sun
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(12): 2300. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dual‐hormone artificial pancreas for glucose control in type 1 diabetes: A meta‐analysis
Baoqi Zeng, Hao Jia, Le Gao, Qingqing Yang, Kai Yu, Feng Sun
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(10): 1967. CrossRef - Dual-Hormone Insulin-and-Pramlintide Artificial Pancreas for Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review
Alezandra Torres-Castaño, Amado Rivero-Santana, Lilisbeth Perestelo-Pérez, Andrea Duarte-Díaz, Analia Abt-Sacks, Vanesa Ramos-García, Yolanda Álvarez-Pérez, Ana M. Wäagner, Mercedes Rigla, Pedro Serrano-Aguilar
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(20): 10262. CrossRef - History of insulin treatment of pediatric patients with diabetes in Korea
Jae Hyun Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 26(4): 237. CrossRef
- Integration of a Safety Module to Prevent Rebound Hypoglycemia in Closed-Loop Artificial Pancreas Systems
- Metabolic risk/Epidemiology
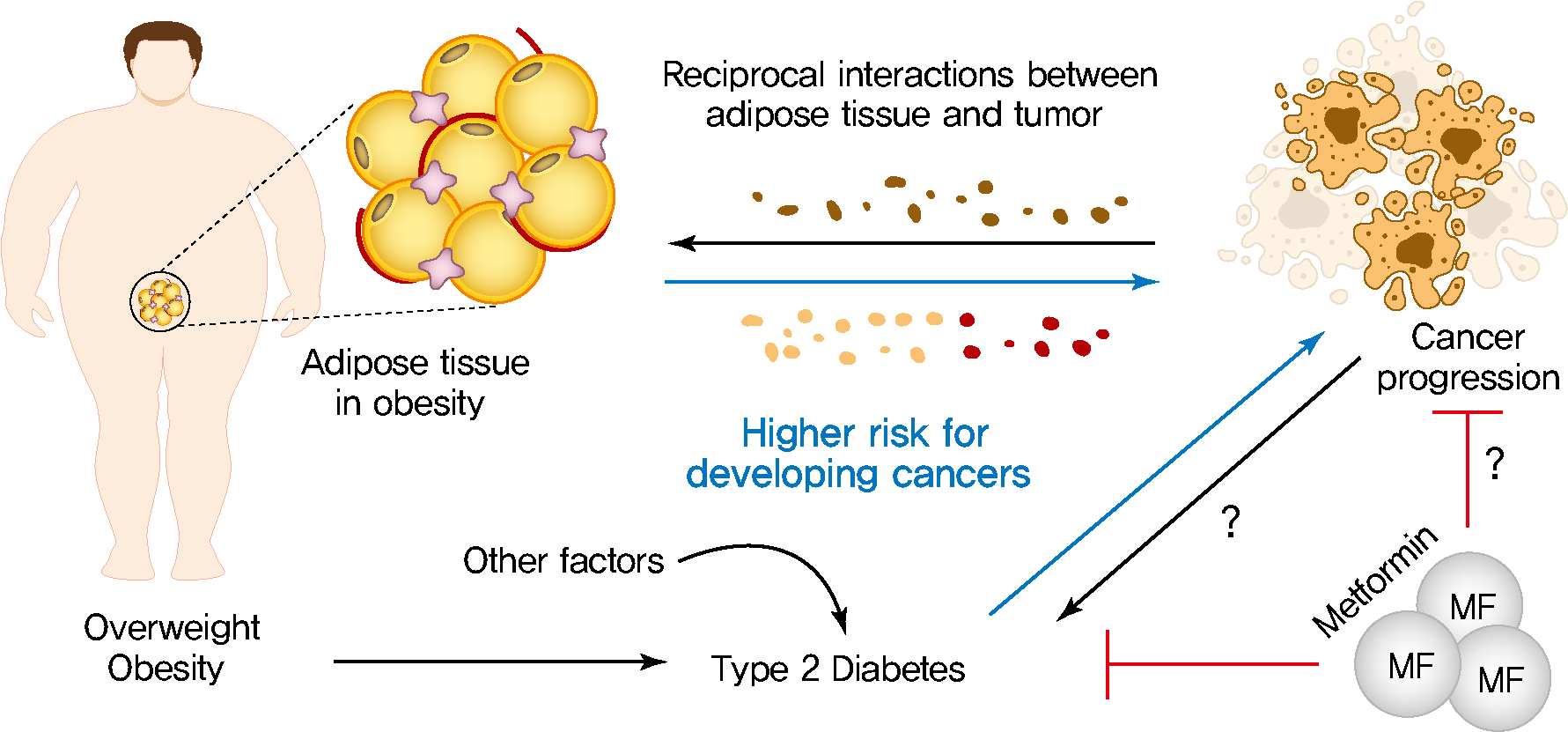
- Obesity, Diabetes, and Increased Cancer Progression
- Dae-Seok Kim, Philipp E. Scherer
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):799-812. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0077
- 13,990 View
- 657 Download
- 70 Web of Science
- 75 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Rates of obesity and diabetes have increased significantly over the past decades and the prevalence is expected to continue to rise further in the coming years. Many observations suggest that obesity and diabetes are associated with an increased risk of developing several types of cancers, including liver, pancreatic, endometrial, colorectal, and post-menopausal breast cancer. The path towards developing obesity and diabetes is affected by multiple factors, including adipokines, inflammatory cytokines, growth hormones, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia. The metabolic abnormalities associated with changes in the levels of these factors in obesity and diabetes have the potential to significantly contribute to the development and progression of cancer through the regulation of distinct signaling pathways. Here, we highlight the cellular and molecular pathways that constitute the links between obesity, diabetes, cancer risk and mortality. This includes a description of the existing evidence supporting the obesity-driven morphological and functional alternations of cancer cells and adipocytes through complex interactions within the tumor microenvironment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triglyceride‐glucose index (TyG index) and endometrial carcinoma risk: A retrospective cohort study
Haimeng Shi, Feifei Guo, Kang Zheng, Rong Li, Huaijun Zhou
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2024; 164(1): 298. CrossRef - Association between total cholesterol levels and all-cause mortality among newly diagnosed patients with cancer
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Adipokines in Tumor Progression and Its Association with Obesity
Jae Won Kim, Jun Hyeok Kim, Yoon Jae Lee
Biomedicines.2024; 12(1): 97. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index is a risk factor for breast cancer in China: a cross-sectional study
Jinghua Zhang, Binbin Yin, Ya Xi, Yongying Bai
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers
Leszek Szablewski
Current Oncology.2024; 31(2): 998. CrossRef - Epigenetic modifications in obesity‐associated diseases
Yiqian Long, Chao Mao, Shuang Liu, Yongguang Tao, Desheng Xiao
MedComm.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Juncture of Diabetes, Cancer, and Observational Population-based Studies: Novel Insights From Canadian Provincial Health Records
Terra Arnason, Kerry Mansell
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of chemotherapy on adipose tissue remodeling: The molecular players involved in this tissue wasting
Samuel Barbosa, Mafalda Barbosa Pedrosa, Rita Ferreira, Daniel Moreira-Gonçalves, Lúcio Lara Santos
Biochimie.2024; 223: 1. CrossRef - Epidemiological and transcriptome data identify shared gene signatures and immune cell infiltration in type 2 diabetes and non-small cell lung cancer
Qian Yuan, Long Li, Liu-shun Wang, Shi-gui Xing
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - THE INFLUENCE OF DIABETES-ASSOCIATED FACTORS OF ONCOGENESIS ON THE RISK OF BREAST AND ENDOMETRIAL CANCER AND ON THE SURVIVAL OF WOMEN WITH THIS CANCER
Tamara S. Vatseba, Liubov K. Sokolova, Vasyl Ye. Neyko, Valentyna V. Dzvonkovska, Oksana V. Muravlova, Volodymyr V. Derpak
Clinical and Preventive Medicine.2024; (2): 99. CrossRef - Associations between diabetes and cancer: A 10-year national population-based retrospective cohort study
Heléna Safadi, Ágnes Balogh, Judit Lám, Attila Nagy, Éva Belicza
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 211: 111665. CrossRef - Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention
Gholamreza Roshandel, Fatemeh Ghasemi-Kebria, Reza Malekzadeh
Cancers.2024; 16(8): 1530. CrossRef - Metabolic Alteration Bridging the Prediabetic State and Colorectal Cancer
Antonino Colloca, Isabella Donisi, Camilla Anastasio, Maria Luisa Balestrieri, Nunzia D’Onofrio
Cells.2024; 13(8): 663. CrossRef - Ultra‐processed food consumption and the risk of pancreatic cancer in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial
Guo‐Chao Zhong, Qian Zhu, Dong Cai, Jie‐Jun Hu, Xin Dai, Jian‐Ping Gong, Wei‐Ping Sun
International Journal of Cancer.2023; 152(5): 835. CrossRef - Advances in “adiponcosis”: Insights in the inner mechanisms at the base of adipose and tumour tissues interplay
Cristina Pagano, Erika di Zazzo, Giorgio Avilia, Beatrice Savarese, Giovanna Navarra, Maria Chiara Proto, Donatella Fiore, Monica Rienzo, Patrizia Gazzerro, Chiara Laezza, Maurizio Bifulco
International Journal of Cancer.2023; 152(12): 2464. CrossRef - Metabolites as signalling molecules
Steven Andrew Baker, Jared Rutter
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology.2023; 24(5): 355. CrossRef - Characterization of neuroendocrine regulation- and metabolism-associated molecular features and prognostic indicators with aid to clinical chemotherapy and immunotherapy of patients with pancreatic cancer
Biao Zhang, Qihang Yuan, Bolin Zhang, Shuang Li, Zhizhou Wang, Hangyu Liu, Fanyue Meng, Xu Chen, Dong Shang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Concentration of Selected Adipokines and Factors Regulating Carbohydrate Metabolism in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer in Respect to Their Body Mass Index
Jarosław Nuszkiewicz, Jolanta Czuczejko, Wiktor Dróżdż, Alina Woźniak, Bogdan Małkowski, Karolina Szewczyk-Golec
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3283. CrossRef - Hormonal Gut–Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3384. CrossRef - A novel five-gene metabolism-related risk signature for predicting prognosis and immune infiltration in endometrial cancer: A TCGA data mining
Huaqing Huang, Xintong Cai, Jiexiang Lin, Qiaoling Wu, Kailin Zhang, Yibin Lin, Bin Liu, Jie Lin
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2023; 155: 106632. CrossRef - Green Antimicrobials as Therapeutic Agents for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Ines D. Teixeira, Eugenia Carvalho, Ermelindo C. Leal
Antibiotics.2023; 12(3): 467. CrossRef - Impact of abdominal obesity on the risk of glioma development in patients with diabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Korea
Hyunji Sang, Yun Kyung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Eun Hee Koh, Sandar Tin Tin
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0283023. CrossRef - Relationship Between Physical Exercise and Cognitive Impairment Among Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: Chain Mediating Roles of Sleep Quality and Depression
Han Zhang, Yefan Zhang, Sen Sheng, Yang Xing, Zhongchen Mou, Yanqiu Zhang, Zhixue Shi, Zhenjie Yu, Qianqian Gao, Weiqin Cai, Qi Jing
Psychology Research and Behavior Management.2023; Volume 16: 817. CrossRef - The Mediterranean Lifestyle to Contrast Low-Grade Inflammation Behavior in Cancer
Rosa Divella, Graziella Marino, Stefania Infusino, Laura Lanotte, Gaia Gadaleta-Caldarola, Gennaro Gadaleta-Caldarola
Nutrients.2023; 15(7): 1667. CrossRef - Distribution of ABO blood groups and Rh factor in benign and malign thyroid nodules
Muzaffer Serdar DENİZ
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2023; 6(2): 462. CrossRef - The Role of Selected Adipocytokines in Ovarian Cancer and Endometrial Cancer
Sebastian Stępień, Paweł Olczyk, Joanna Gola, Katarzyna Komosińska-Vassev, Aleksandra Mielczarek-Palacz
Cells.2023; 12(8): 1118. CrossRef - Coronary Revascularization in Patients With Cancer
Bala Pushparaji, Teodora Donisan, Dinu Valentin Balanescu, Jong Kun Park, Dominique J. Monlezun, Abdelrahman Ali, Ibrahim Halil Inanc, Jaime Caballero, Mehmet Cilingiroglu, Konstantinos Marmagkiolis, Cezar Iliescu
Current Treatment Options in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023; 25(6): 143. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma in a large cohort of type 2 diabetes patients
Carlo B. Giorda, Roberta Picariello, Barbara Tartaglino, Elisa Nada, Giuseppe Costa, Roberta Manti, Luca Monge, Roberto Gnavi
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 200: 110684. CrossRef - Prediction of Hypoglycemia in Diabetic Patients During Colonoscopy
Preparation
Xiaohua Lu, Lingqiao Xie, Wane Zhao, Chuangbiao Zhang, Xixi Luo, Yan Zhou
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2023; 131(05): 274. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - PIK3CA mutation in endometriotic epithelial cells promotes viperin-dependent inflammatory response to insulin
Mike R. Wilson, Shannon Harkins, Jake J. Reske, Rebecca A. Siwicki, Marie Adams, Victoria L. Bae-Jump, Jose M. Teixeira, Ronald L. Chandler
Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Function of MondoA and ChREBP Nutrient—Sensing Factors in Metabolic Disease
Byungyong Ahn
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(10): 8811. CrossRef - Mechanism of Cephalophyllum cephalus Intervention in Diabetes Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology
志梁 范
Hans Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 11(02): 81. CrossRef - Development and validation of a prognostic model based on metabolic risk score to predict overall survival of endometrial cancer in Chinese patients
Xingchen Li, Xiao Yang, Yuan Cheng, Yangyang Dong, Jingyuan Wang, Jianliu Wang
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nε-(1-Carboxymethyl)-L-lysine, an advanced glycation end product, exerts malignancy on chondrosarcoma via the activation of cancer stemness
Ting-Yu Chang, Kuo-Cheng Lan, Chia-Hung Wu, Meei-Ling Sheu, Rong-Sen Yang, Shing-Hwa Liu
Archives of Toxicology.2023; 97(8): 2231. CrossRef - The Link between Diabetes, Pancreatic Tumors, and miRNAs—New Players for Diagnosis and Therapy?
Małgorzata Kozłowska, Agnieszka Śliwińska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(12): 10252. CrossRef - Obesity, diabetes, and cancer: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and potential interventions
Leonardo de Andrade Mesquita, Laura Fink Wayerbacher, Gilberto Schwartsmann, Fernando Gerchman
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Distinct Lipid Phenotype of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) Isolated From Overweight/Obese Endometrial Cancer Patients as Assessed Using Raman Spectroscopy
Tze Hua Yeu, Intan Sofia Omar, S.F. Abdul Sani, Dharini Pathmanathan, Boon Tong Goh, Nithyialakshmi Ravindran, Ik Hui Teo, Yogeeta Gunasagran, Noor Azmi Mat Adenan, Ivy Chung, Amira Hajirah Abd Jamil
Applied Spectroscopy.2023; 77(7): 723. CrossRef - Global, Regional, and National Epidemiology of Diabetes in Children From 1990 to 2019
Kexin Zhang, Chengxia Kan, Fang Han, Jingwen Zhang, Chuanhua Ding, Zhentao Guo, Na Huang, Yang Zhang, Ningning Hou, Xiaodong Sun
JAMA Pediatrics.2023; 177(8): 837. CrossRef - The effects of physical exercise therapy on weight control: its regulation of adipocyte physiology and metabolic capacity
Hyun Jung Park, Sung Ja Rhie, Insop Shim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2023; 19(3): 141. CrossRef - The Ephrin tyrosine kinase a3 (EphA3) is a novel mediator of RAGE-prompted motility of breast cancer cells
Marianna Talia, Francesca Cirillo, Asia Spinelli, Azzurra Zicarelli, Domenica Scordamaglia, Lucia Muglia, Salvatore De Rosis, Damiano Cosimo Rigiracciolo, Gianfranco Filippelli, Ida Daniela Perrotta, Mariano Davoli, Rosanna De Rosa, Rachele Macirella, Elv
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Signal detection in real‐world data and confirmation in clinical trials: Diabetes as a case study for a conversation worth having
Elad Sharon, Megan Othus, Zoe Eloise Quandt
Cancer.2023; 129(18): 2769. CrossRef - Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Obesity in Korean Adults
Jee-Seon Shim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 547. CrossRef - Decoding the role of leptin and adiponectin in obesity-related gastrointestinal cancer
Vanda Marques, Fabiola Arella, Marta B. Afonso, André A. Santos, Cecília M.P. Rodrigues
Clinical Science.2023; 137(15): 1095. CrossRef - Diabetes and two kinds of primary tumors in a patient with thalassemia: a case report and literature review
Xiaoyan Yu, Yi Peng, Tingting Nie, Wenjia Sun, Yajuan Zhou
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Additive impact of diabetes and sarcopenia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A longitudinal nationwide population-based study
Eyun Song, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Ahreum Jang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155678. CrossRef - Obesity and Colorectal Cancer
Jundeok Lee, Su Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 82(2): 63. CrossRef - Cognitive Behavioural Therapies for Weight-Loss in Adults: A Scoping Review Protocol
Laura María Compañ-Gabucio, Diana Mancheño-Bañón, Laura Torres-Collado, Jesús Vioque, Manuela García-de-la-Hera
Healthcare.2023; 11(18): 2473. CrossRef - Saxagliptin, a selective dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, alleviates somatic cell aneugenicity and clastogenicity in diabetic mice
Sabry M. Attia, Sheikh F. Ahmad, Ahmed Nadeem, Mohamed S.M. Attia, Mushtaq A. Ansari, Abdelkader E. Ashour, Norah A. Albekairi, Mohammed A. Al-Hamamah, Ali A. Alshamrani, Saleh A. Bakheet
Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis.2023; 892: 503707. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Linggui Zhugan Decoction in the Treatment of Obesity Based on Network Pharmacology
Chunmei Liu, Li Zhang, Yubin Yang
Science of Advanced Materials.2023; 15(9): 1265. CrossRef - Beyond Body Size: Adiponectin as a Key Player in Obesity-Driven Cancers
Maurizio Capuozzo, Venere Celotto, Loris Landi, Francesco Ferrara, Francesco Sabbatino, Francesco Perri, Marco Cascella, Vincenza Granata, Mariachiara Santorsola, Alessandro Ottaiano
Nutrition and Cancer.2023; 75(10): 1848. CrossRef - Impact of sarcopenic obesity on post-hepatectomy bile leakage for hepatocellular carcinoma
Hikaru Hayashi, Akira Shimizu, Koji Kubota, Tsuyoshi Notake, Hitoshi Masuo, Takahiro Yoshizawa, Kiyotaka Hosoda, Hiroki Sakai, Koya Yasukawa, Yuji Soejima, Ezio Lanza
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(10): e0286353. CrossRef - Colorectal Cancer: From Risk Factors to Oncogenesis
Vlad Alexandru Ionescu, Gina Gheorghe, Nicolae Bacalbasa, Alexandru Laurentiu Chiotoroiu, Camelia Diaconu
Medicina.2023; 59(9): 1646. CrossRef - The impact of poor metabolic health on aggressive breast cancer: adipose tissue and tumor metabolism
Barbara Mensah Sankofi, Estefania Valencia-Rincón, Malika Sekhri, Adriana L. Ponton-Almodovar, Jamie J. Bernard, Elizabeth A. Wellberg
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and growth hormone deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Tingting Kong, Yunpeng Gu, Lei Sun, Run Zhou, Jie Li, Junping Shi
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(10): 959. CrossRef - Impact of Caloric Restriction in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Prospective Case Control Study
Isabella Castellano, Francesco Gallo, Paola Durelli, Taira Monge, Maurizio Fadda, Jasna Metovic, Paola Cassoni, Fulvio Borella, Carlo Raucci, Monica Menischetti, Alessandra Beano, Giuseppe Migliaretti, Concetta Finocchiaro
Nutrients.2023; 15(21): 4677. CrossRef - Metabolomic and lipidomic studies on the intervention of taurochenodeoxycholic acid in mice with hyperlipidemia
Na Cui, Wensen Zhang, Fazhi Su, Zhihong Zhang, Biao Li, Donghui Peng, Yanping Sun, Yuanning Zeng, Bingyou Yang, Haixue Kuang, Qiuhong Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Is MG53 a potential therapeutic target for cancer?
Yunyu Du, Tieying Li, Muqing Yi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood Biomarkers Panels for Screening of Colorectal Cancer and Adenoma on a Machine Learning-Assisted Detection Platform
Hui Wang, Zhiwei Zhou, Haijun Li, Weiguang Xiang, Yilin Lan, Xiaowen Dou, Xiuming Zhang
Cancer Control.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Post-treatment serum triglyceride: An effective biomarker for body fat mass and overall survival in esophageal squamous cell cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy
Jiahua Lyu, Ningjing Yang, Wang Guan, Ling Xiao, Xinyu Nie, Long Liang, Hansong Bai, Churong Li, Hao Kuang, Xiao Wang, Tao Li
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress of MicroRNA-122 in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
路路 潘
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(06): 5706. CrossRef - Cancer and Obesity: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement (CPS) 2022
Ethan Lazarus, Harold Edward Bays
Obesity Pillars.2022; 3: 100026. CrossRef - Obesity Fact Sheet in Korea, 2021: Trends in Obesity Prevalence and Obesity-Related Comorbidity Incidence Stratified by Age from 2009 to 2019
Ye Seul Yang, Byoung-Duck Han, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Jang Won Son
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(2): 169. CrossRef - Fried food consumption and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A large prospective multicenter study
Guo-Chao Zhong, Qian Zhu, Jian-Ping Gong, Dong Cai, Jie-Jun Hu, Xin Dai, Jun-Hua Gong
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intermittent Fasting Is Associated With a Decreased Risk of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Eun Young Choi, Min Kim, Christopher Seungkyu Lee, Suk Ho Byeon, Sung Soo Kim, Minyoung Lee
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2022; 243: 1. CrossRef - Metformin Mitigated Obesity-Driven Cancer Aggressiveness in Tumor-Bearing Mice
Chun-Jung Chen, Chih-Cheng Wu, Cheng-Yi Chang, Jian-Ri Li, Yen-Chuan Ou, Wen-Ying Chen, Su-Lan Liao, Jiaan-Der Wang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(16): 9134. CrossRef - Visceral fat area and body fat percentage measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis correlate with glycometabolism
Shuying Li, Shaoping Li, Jie Ding, Weihong Zhou
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight on the Role of Leptin: A Bridge from Obesity to Breast Cancer
Roberto Buonaiuto, Fabiana Napolitano, Sara Parola, Pietro De Placido, Valeria Forestieri, Giovanna Pecoraro, Alberto Servetto, Luigi Formisano, Pietro Formisano, Mario Giuliano, Grazia Arpino, Sabino De Placido, Carmine De Angelis
Biomolecules.2022; 12(10): 1394. CrossRef - Adipokines as Regulators of Autophagy in Obesity-Linked Cancer
Alin García-Miranda, Alejandra Garcia-Hernandez, Eduardo Castañeda-Saucedo, Napoleon Navarro-Tito, Paola Maycotte
Cells.2022; 11(20): 3230. CrossRef - Roles of hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids in diabetes (HETEs and diabetes)
Linyue Dong, Heyao Wang, Kaixian Chen, Yiming Li
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 156: 113981. CrossRef - Changes in the Fecal Metabolome Accompany an Increase in Aberrant Crypt Foci in the Colon of C57BL/6 Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet
Huawei Zeng, Bryan D. Safratowich, Wen-Hsing Cheng, Andrew D. Magnuson, Matthew J. Picklo
Biomedicines.2022; 10(11): 2891. CrossRef - Targeting Adiponectin in Breast Cancer
Rawan Nehme, Mona Diab-Assaf, Caroline Decombat, Laetitia Delort, Florence Caldefie-Chezet
Biomedicines.2022; 10(11): 2958. CrossRef - Multidisciplinary Progress in Obesity Research
Xiaoqing Lu, Yuxin Jin, Dexin Li, Jingxin Zhang, Jingyan Han, Yin Li
Genes.2022; 13(10): 1772. CrossRef - The association between serum copper and obesity and all-cause mortality: the NHANES 2011–2016
Hongrong Wu, Qingqi Li, Kaifang Zhang, Jianfeng Zhao
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2022; 30(11): 31395. CrossRef - The crosstalk within the breast tumor microenvironment in type II diabetes: Implications for cancer disparities
Christina S. Ennis, Pablo Llevenes, Yuhan Qiu, Ruben Dries, Gerald V. Denis
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Triglyceride‐glucose index (TyG index) and endometrial carcinoma risk: A retrospective cohort study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





