
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Article category
- Page Path
- HOME > Article category > Article category
Original Articles
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Alogliptin-Pioglitazone Combination for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Poorly Controlled with Metformin: A Multicenter, Double-Blind Randomized Trial
- Ji-Yeon Park, Joonyub Lee, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kyung Wan Min, Kyung Ah Han, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soo Lim, Young-Hyun Kim, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Mook Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, the Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) study investigators
- Received August 7, 2023 Accepted November 30, 2023 Published online April 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0259 [Epub ahead of print]

- 141 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Guidelines for switching to triple combination therapy directly after monotherapy failure are limited. This study investigated the efficacy, long-term sustainability, and safety of either mono or dual add-on therapy using alogliptin and pioglitazone for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who did not achieve their target glycemic range with metformin monotherapy.
Methods
The Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) was a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial. A total of 214 participants were randomized to receive alogliptin+pioglitazone (Alo+Pio group, n=70), alogliptin (Alo group, n=75), or pioglitazone (Pio group, n=69). The primary outcome was the difference in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels between the three groups at baseline to 24 weeks. For durability, the achievement of HbA1c levels <7% and <6.5% was compared in each group. The number of adverse events was investigated for safety.
Results
After 24 weeks of treatment, the change of HbA1c in the Alo+Pio, Alo, and Pio groups were –1.38%±0.08%, –1.03%±0.08%, and –0.84%±0.08%, respectively. The Alo+Pio group had significantly lower HbA1c levels than the other groups (P=0.0063, P<0.0001) and had a higher proportion of patients with target HbA1c achievement. In addition, insulin sensitivity and β-cell function, lipid profiles, and other metabolic indicators were also improved. There were no significant safety issues in patients treated with triple combination therapy.
Conclusion
Early combination triple therapy showed better efficacy and durability than the single add-on (dual) therapy. Therefore, combination therapy with metformin, alogliptin, and pioglitazone is a valuable early treatment option for T2DM poorly controlled with metformin monotherapy.
- Basic Research
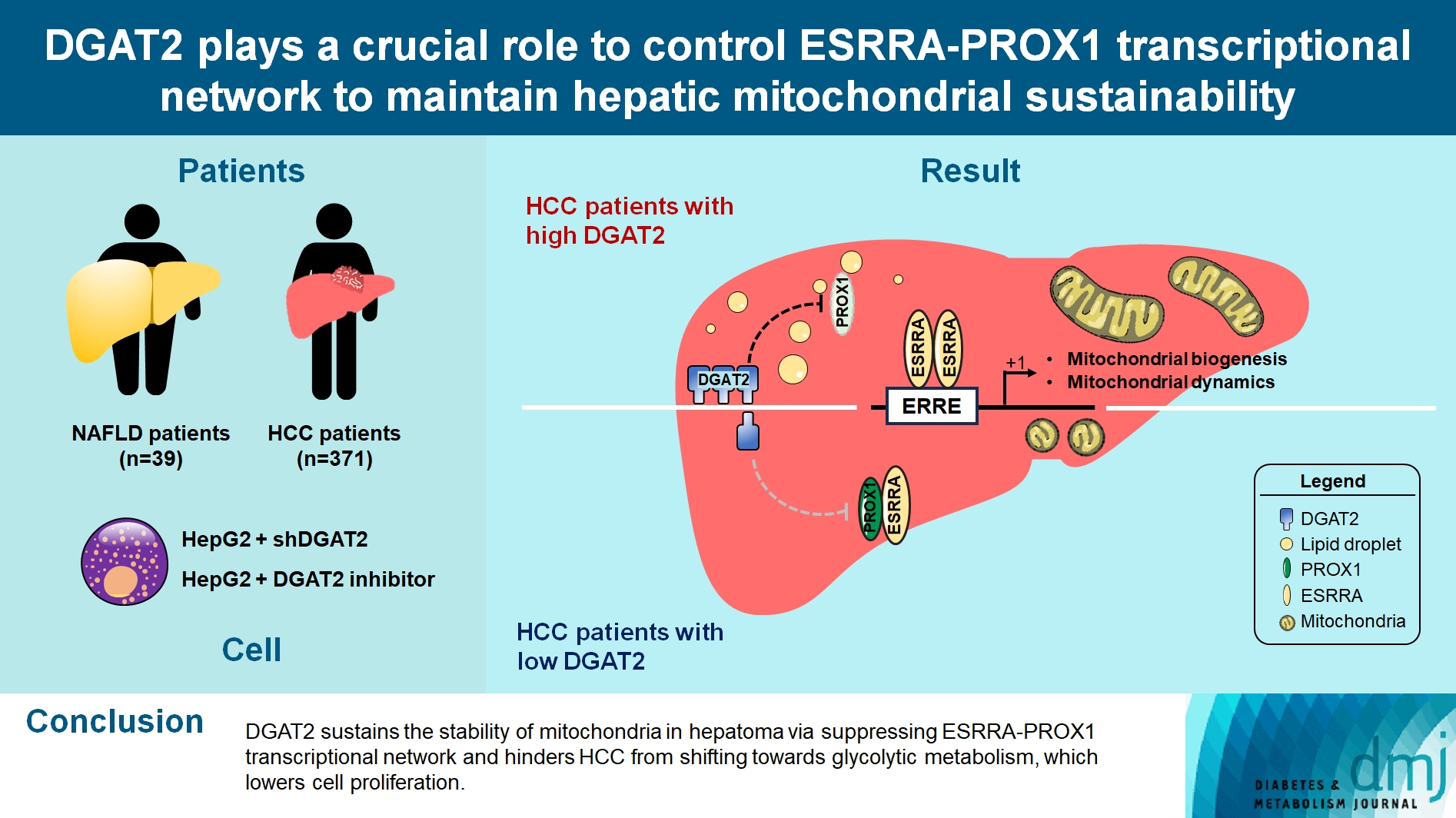
- DGAT2 Plays a Crucial Role to Control ESRRAPROX1 Transcriptional Network to Maintain Hepatic Mitochondrial Sustainability
- Yoseob Lee, Yeseong Hwang, Minki Kim, Hyeonuk Jeon, Seyeon Joo, Sungsoon Fang, Jae-Woo Kim
- Received October 13, 2023 Accepted December 11, 2023 Published online April 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0368 [Epub ahead of print]
- 212 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2) synthesizes triacylglycerol (TG) from diacylglycerol; therefore, DGAT2 is considered as a therapeutic target for steatosis. However, the consequence of inhibiting DGAT2 is not fully investigated due to side effects including lethality and lipotoxicity. In this article, we observed the role of DGAT2 in hepatocarcinoma.
Methods
The role of DGAT2 is analyzed via loss-of-function assay. DGAT2 knockdown (KD) and inhibitor treatment on HepG2 cell line was analyzed. Cumulative analysis of cell metabolism with bioinformatic data were assessed, and further compared with different cohorts of liver cancer patients and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients to elucidate how DGAT2 is regulating cancer metabolism.
Results
Mitochondrial function is suppressed in DGAT2 KD HepG2 cell along with the decreased lipid droplets. In the aspect of the cancer, DGAT2 KD upregulates cell proliferation. Analyzing transcriptome of NAFLD and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients highlights negatively correlating expression patterns of 73 lipid-associated genes including DGAT2. Cancer patients with the lower DGAT2 expression face lower survival rate. DGAT2 KD cell and patients’ transcriptome show downregulation in estrogen- related receptor alpha (ESRRA) via integrated system for motif activity response analysis (ISMARA), with increased dimerization with corepressor prospero homeobox 1 (PROX1).
Conclusion
DGAT2 sustains the stability of mitochondria in hepatoma via suppressing ESRRA-PROX1 transcriptional network and hinders HCC from shifting towards glycolytic metabolism, which lowers cell proliferation.
Review
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
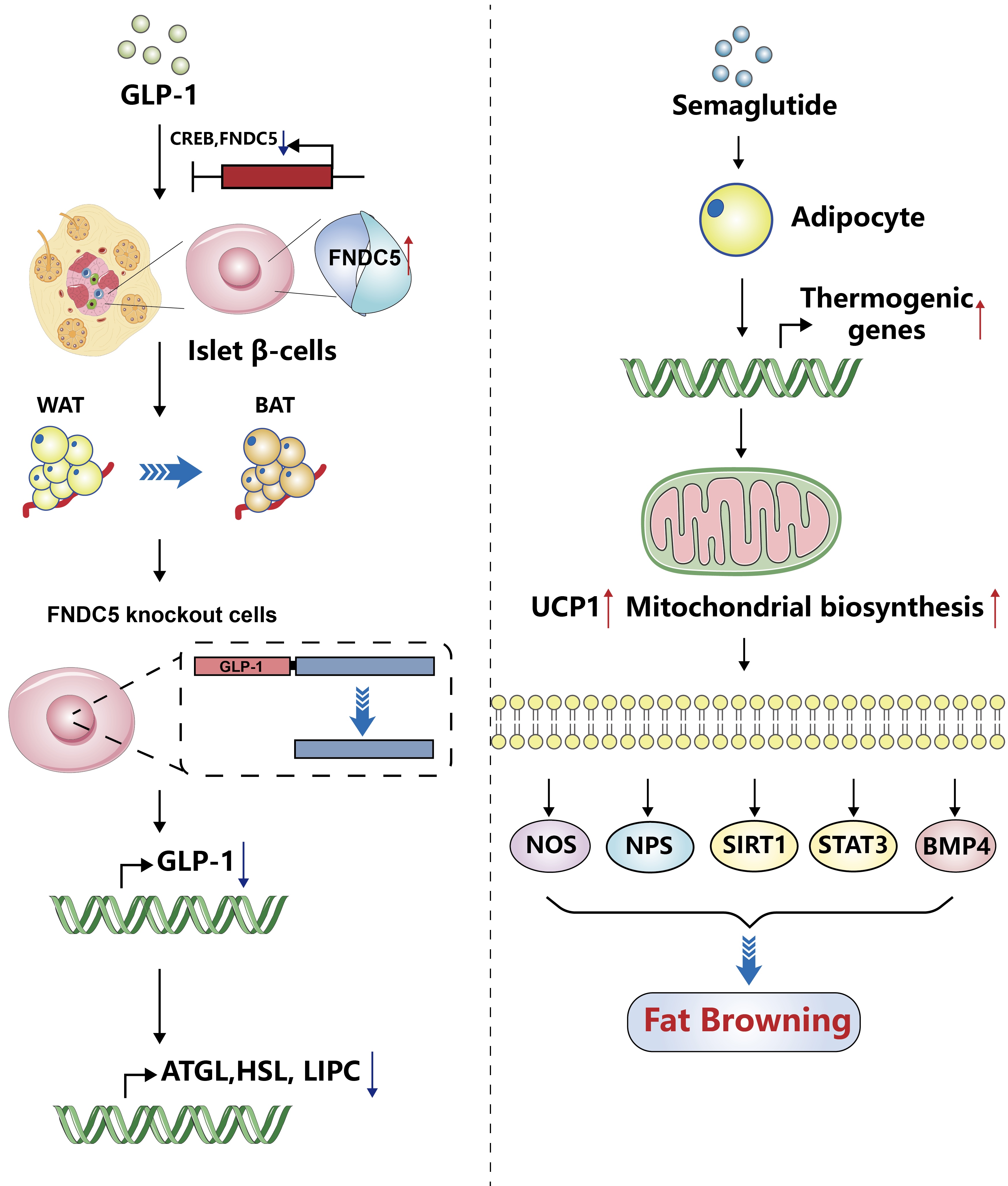
- Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: New Regulator in Lipid Metabolism
- Tong Bu, Ziyan Sun, Yi Pan, Xia Deng, Guoyue Yuan
- Received August 14, 2023 Accepted January 1, 2024 Published online April 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0277 [Epub ahead of print]
- 407 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30-amino acid peptide hormone that is mainly expressed in the intestine and hypothalamus. In recent years, basic and clinical studies have shown that GLP-1 is closely related to lipid metabolism, and it can participate in lipid metabolism by inhibiting fat synthesis, promoting fat differentiation, enhancing cholesterol metabolism, and promoting adipose browning. GLP-1 plays a key role in the occurrence and development of metabolic diseases such as obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and atherosclerosis by regulating lipid metabolism. It is expected to become a new target for the treatment of metabolic disorders. The effects of GLP-1 and dual agonists on lipid metabolism also provide a more complete treatment plan for metabolic diseases. This article reviews the recent research progress of GLP-1 in lipid metabolism.
Original Article
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Biologically Informed Polygenic Scores for Brain Insulin Receptor Network Are Associated with Cardiometabolic Risk Markers and Diabetes in Women
- Jannica S. Selenius, Patricia P. Silveira, Mikaela von Bonsdorff, Jari Lahti, Hannu Koistinen, Riitta Koistinen, Markku Seppälä, Johan G. Eriksson, Niko S. Wasenius
- Received February 10, 2023 Accepted November 25, 2023 Published online March 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0039 [Epub ahead of print]

- 663 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To investigate associations between variations in the co-expression-based brain insulin receptor polygenic score and cardiometabolic risk factors and diabetes mellitus.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 1,573 participants from the Helsinki Birth Cohort Study. Biologically informed expression-based polygenic risk scores for the insulin receptor gene network were calculated for the hippocampal (hePRS-IR) and the mesocorticolimbic (mePRS-IR) regions. Cardiometabolic markers included body composition, waist circumference, circulating lipids, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 and 3 (IGFBP-1 and -3). Glucose and insulin levels were measured during a standardized 2-hour 75 g oral glucose tolerance test and impaired glucose regulation status was defined by the World Health Organization 2019 criteria. Analyzes were adjusted for population stratification, age, smoking, alcohol consumption, socioeconomic status, chronic diseases, birth weight, and leisure-time physical activity.
Results
Multinomial logistic regression indicated that one standard deviation increase in hePRS-IR was associated with increased risk of diabetes mellitus in all participants (adjusted relative risk ratio, 1.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.01 to 1.35). In women, higher hePRS-IR was associated with greater waist circumference and higher body fat percentage, levels of glucose, insulin, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, apolipoprotein B, insulin, and IGFBP-1 (all P≤0.02). The mePRS-IR was associated with decreased IGF-1 level in women (P=0.02). No associations were detected in men and studied outcomes.
Conclusion
hePRS-IR is associated with sex-specific differences in cardiometabolic risk factor profiles including impaired glucose regulation, abnormal metabolic markers, and unfavorable body composition in women.
Editorial
- Enhancing Patient Outcomes: Prioritizing SGLT2is and GLP-1RAs in Diabetes with CVD
- Gwanpyo Koh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):208-212. Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2024.0096
- 628 View
- 101 Download
Response
- Association of Measures of Glucose Metabolism with Colorectal Cancer Risk in Older Chinese: A 13-Year Follow-up of the Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study-Cardiovascular Disease Substudy and Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2024;48:134-45)
- Shu Yi Wang, Lin Xu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):323-324. Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2024.0085
- 377 View
- 10 Download
Editorial
- SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Agonists: A Beacon of Hope for Stroke Prevention in Diabetes
- Jae-Han Jeon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):213-214. Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2024.0079
- 814 View
- 119 Download
Letter
- Association of Measures of Glucose Metabolism with Colorectal Cancer Risk in Older Chinese: A 13-Year Follow-up of the Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study-Cardiovascular Disease Substudy and Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2024;48:134-45)
- Jin Hwa Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):321-322. Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2024.0070
- 411 View
- 13 Download
Review
- Basic Research
- Roles of Histone Deacetylase 4 in the Inflammatory and Metabolic Processes
- Hyunju Kang, Young-Ki Park, Ji-Young Lee, Minkyung Bae
- Received June 5, 2023 Accepted February 7, 2024 Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0174 [Epub ahead of print]

- 619 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4), a class IIa HDAC, has gained attention as a potential therapeutic target in treating inflammatory and metabolic processes based on its essential role in various biological pathways by deacetylating non-histone proteins, including transcription factors. The activity of HDAC4 is regulated at the transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational levels. The functions of HDAC4 are tissue-dependent in response to endogenous and exogenous factors and their substrates. In particular, the association of HDAC4 with non-histone targets, including transcription factors, such as myocyte enhancer factor 2, hypoxia-inducible factor, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, and forkhead box proteins, play a crucial role in regulating inflammatory and metabolic processes. This review summarizes the regulatory modes of HDAC4 activity and its functions in inflammation, insulin signaling and glucose metabolism, and cardiac muscle development.
Original Articles
- Type 1 Diabetes
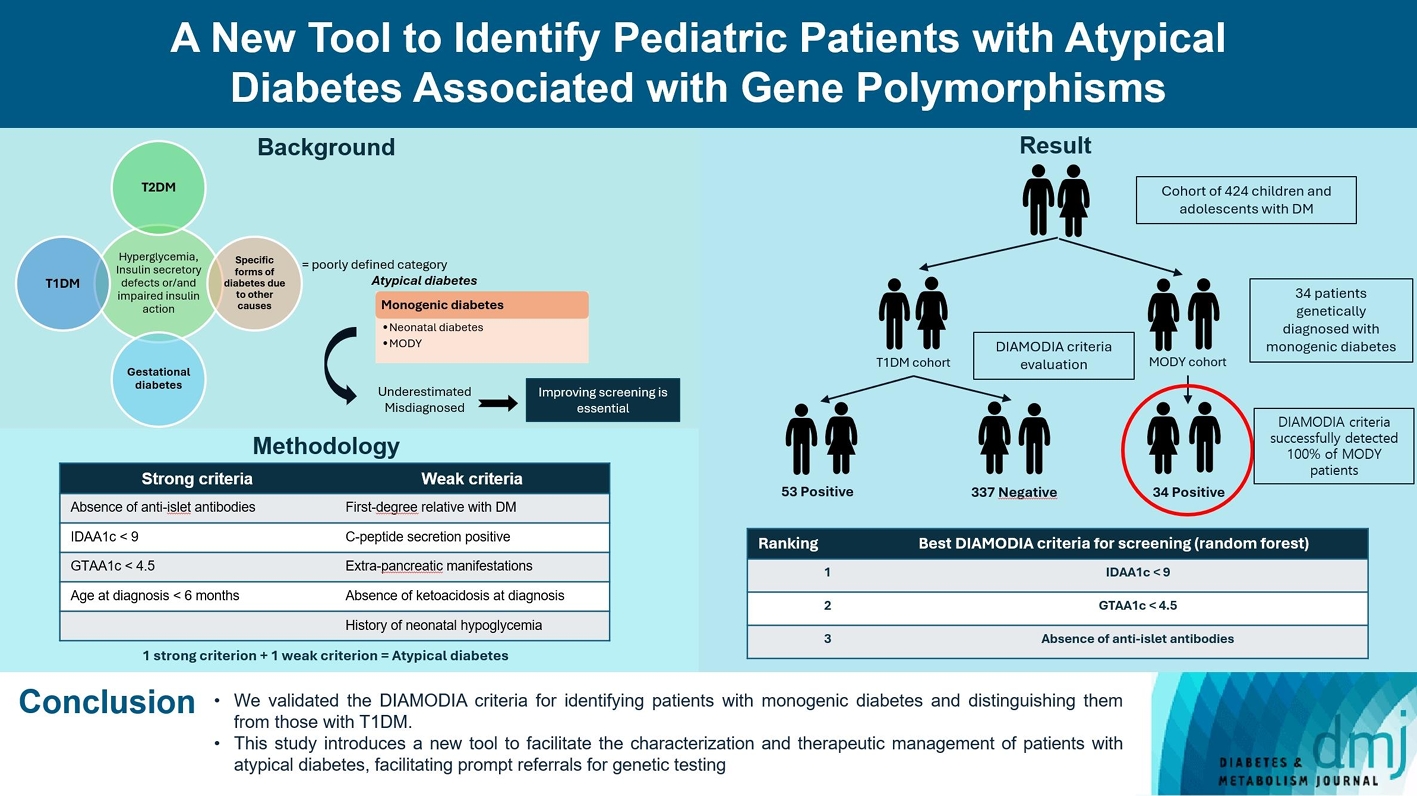
- A New Tool to Identify Pediatric Patients with Atypical Diabetes Associated with Gene Polymorphisms
- Sophie Welsch, Antoine Harvengt, Paola Gallo, Manon Martin, Dominique Beckers, Thierry Mouraux, Nicole Seret, Marie-Christine Lebrethon, Raphaël Helaers, Pascal Brouillard, Miikka Vikkula, Philippe A. Lysy
- Received May 26, 2023 Accepted November 25, 2023 Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0166 [Epub ahead of print]
- 773 View
- 48 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Recent diabetes subclassifications have improved the differentiation between patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus despite several overlapping features, yet without considering genetic forms of diabetes. We sought to facilitate the identification of monogenic diabetes by creating a new tool that we validated in a pediatric maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) cohort.
Methods
We first created the DIAgnose MOnogenic DIAbetes (DIAMODIA) criteria based on the pre-existing, but incomplete, MODY calculator. This new score is composed of four strong and five weak criteria, with patients having to display at least one weak and one strong criterion.
Results
The effectiveness of the DIAMODIA criteria was evaluated in two patient cohorts, the first consisting of patients with confirmed MODY diabetes (n=34) and the second of patients with T1DM (n=390). These DIAMODIA criteria successfully detected 100% of MODY patients. Multiple correspondence analysis performed on the MODY and T1DM cohorts enabled us to differentiate MODY patients from T1DM. The three most relevant variables to distinguish a MODY from T1DM profile were: lower insulin-dose adjusted A1c score ≤9, glycemic target-adjusted A1c score ≤4.5, and absence of three anti-islet cell autoantibodies.
Conclusion
We validated the DIAMODIA criteria, as it effectively identified all monogenic diabetes patients (MODY cohort) and succeeded to differentiate T1DM from MODY patients. The creation of this new and effective tool is likely to facilitate the characterization and therapeutic management of patients with atypical diabetes, and promptly referring them for genetic testing which would markedly improve clinical care and counseling, as well.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
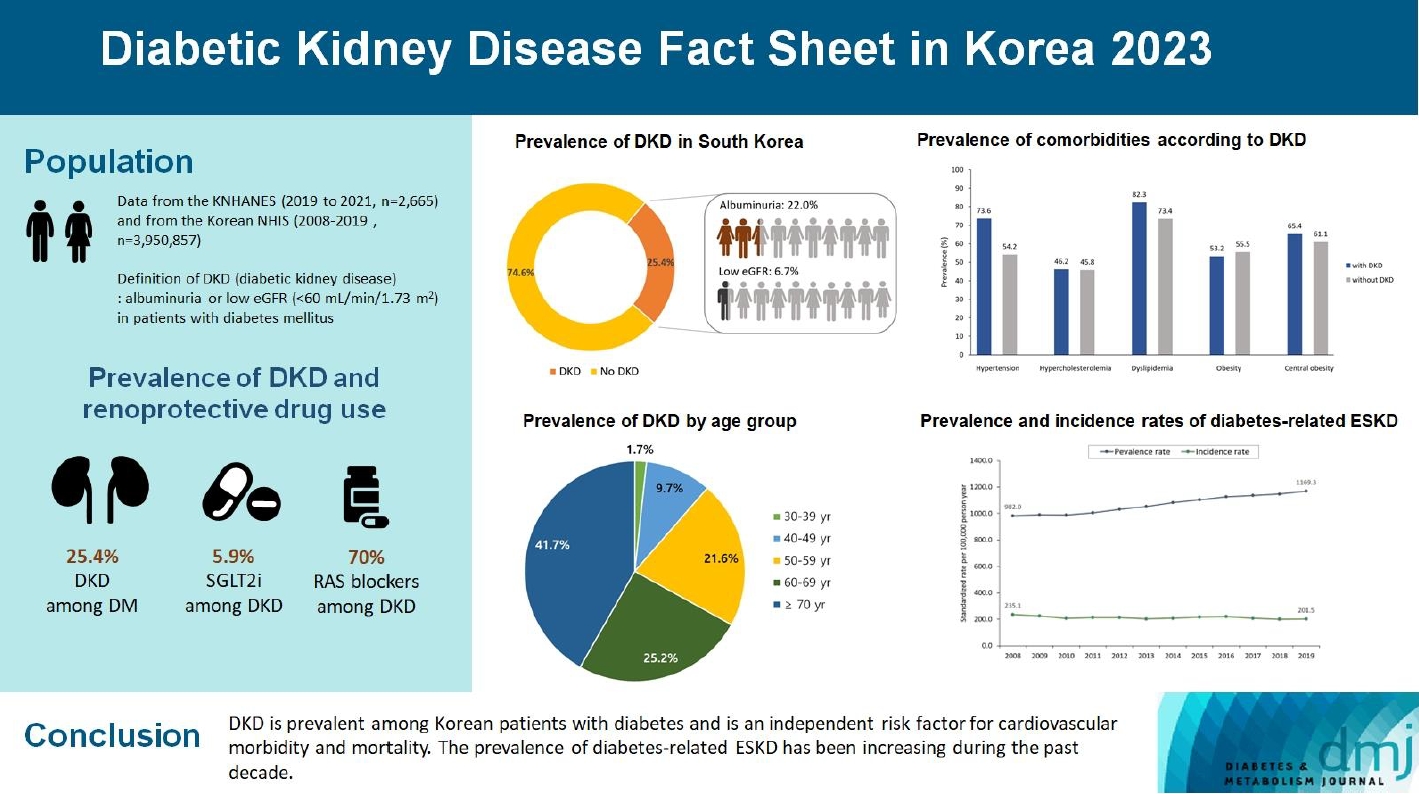
- 2023 Diabetic Kidney Disease Fact Sheet in Korea
- Nam Hoon Kim, Mi-Hae Seo, Jin Hyung Jung, Kyung Do Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Nan Hee Kim, on Behalf of Diabetic Kidney Disease Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Received July 30, 2023 Accepted January 26, 2024 Published online March 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0310 [Epub ahead of print]
- 701 View
- 50 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To investigate the prevalence, incidence, comorbidities, and management status of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) and diabetes-related end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in South Korea.
Methods
We used the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data (2019 to 2021, n=2,665) for the evaluation of prevalence, comorbidities, control rate of glycemia and comorbidities in DKD, and the Korean Health Insurance Service-customized database (2008 to 2019, n=3,950,857) for the evaluation of trends in the incidence and prevalence rate of diabetes-related ESKD, renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockers and sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors use for DKD, and the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and mortality according to DKD stages. DKD was defined as albuminuria or low estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Results
The prevalence of DKD was 25.4% (albuminuria, 22.0%; low eGFR, 6.73%) in patients with diabetes mellitus aged ≥30 years. Patients with DKD had a higher rate of comorbidities, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, and central obesity; however, their control rates were lower than those without DKD. Prescription rate of SGLT2 inhibitors with reduced eGFR increased steadily, reaching 5.94% in 2019. Approximately 70% of DKD patients were treated with RAS blockers. The prevalence rate of diabetesrelated ESKD has been steadily increasing, with a higher rate in older adults. ASCVD and mortality were significantly associated with an in increase in DKD stage.
Conclusion
DKD is prevalent among Korean patients with diabetes and is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, which requiring intensive management of diabetes and comorbidities. The prevalence of diabetes-related ESKD has been increasing, especially in the older adults, during past decade. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endothelial NOX5 Obliterates the Reno-Protective Effect of Nox4 Deletion by Promoting Renal Fibrosis via Activation of EMT and ROS-Sensitive Pathways in Diabetes
Karin A. M. Jandeleit-Dahm, Haritha R. Kankanamalage, Aozhi Dai, Jaroslawna Meister, Sara Lopez-Trevino, Mark E. Cooper, Rhian M. Touyz, Christopher R. J. Kennedy, Jay C. Jha
Antioxidants.2024; 13(4): 396. CrossRef
- Endothelial NOX5 Obliterates the Reno-Protective Effect of Nox4 Deletion by Promoting Renal Fibrosis via Activation of EMT and ROS-Sensitive Pathways in Diabetes
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
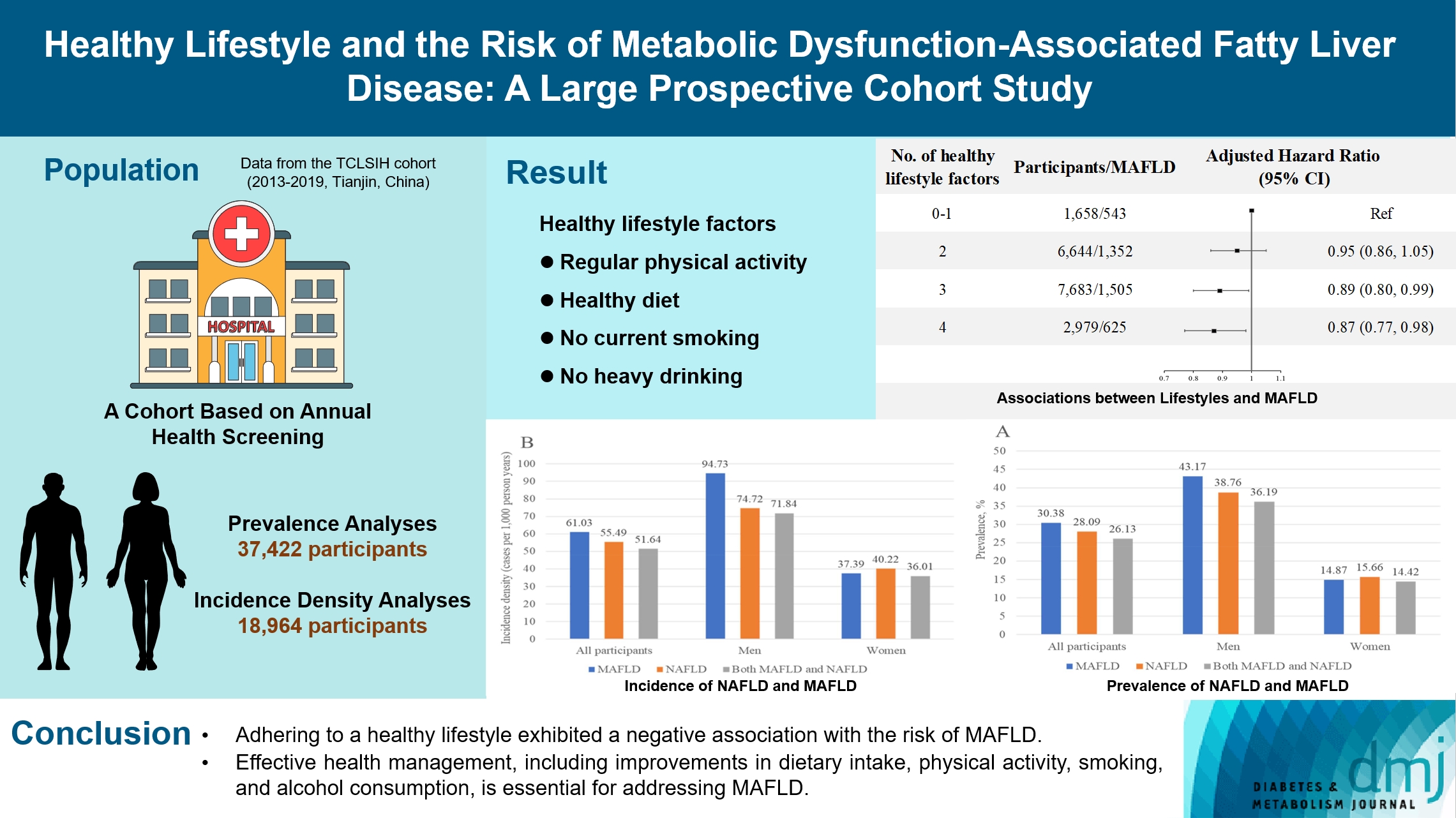
- Healthy Lifestyle and the Risk of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Large Prospective Cohort Study
- Qing Chang, Yixiao Zhang, Tingjing Zhang, Zuyun Liu, Limin Cao, Qing Zhang, Li Liu, Shaomei Sun, Xing Wang, Ming Zhou, Qiyu Jia, Kun Song, Yang Ding, Yuhong Zhao, Kaijun Niu, Yang Xia
- Received April 27, 2023 Accepted November 30, 2023 Published online March 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0133 [Epub ahead of print]
- 538 View
- 41 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The incidence density of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and the effect of a healthy lifestyle on the risk of MAFLD remain unknown. We evaluated the prevalence and incidence density of MAFLD and investigated the association between healthy lifestyle and the risk of MAFLD.
Methods
A cross-sectional analysis was conducted on 37,422 participants to explore the prevalence of MAFLD. A cohort analysis of 18,964 individuals was conducted to identify the incidence of MAFLD, as well as the association between healthy lifestyle and MAFLD. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to calculate the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) with adjustments for confounding factors.
Results
The prevalence of MAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and their comorbidities were 30.38%, 28.09%, and 26.13%, respectively. After approximately 70 thousand person-years of follow-up, the incidence densities of the three conditions were 61.03, 55.49, and 51.64 per 1,000 person-years, respectively. Adherence to an overall healthy lifestyle was associated with a 19% decreased risk of MAFLD (HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.72 to 0.92), and the effects were modified by baseline age, sex, and body mass index (BMI). Subgroup analyses revealed that younger participants, men, and those with a lower BMI experienced more significant beneficial effects from healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion
Our results highlight the beneficial effect of adherence to a healthy lifestyle on the prevention of MAFLD. Health management for improving dietary intake, physical activity, and smoking and drinking habits are critical to improving MAFLD.
Retraction Notice
- A New Concept in Antidiabetic Therapeutics: A Concerted Removal of Labile Iron and Intracellular Deposition of Zinc
- Vladimir Vinokur, Eduard Berenshtein, Mordechai Chevion, Dror Chevion
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):325-325. Published online March 18, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2024.0124
- Retracts: Diabetes Metab J 2024;48(1):59
- 431 View
- 23 Download
Original Article
- Complications
- Glycemic Control and Retinal Microvascular Changes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients without Clinical Retinopathy
- Kangmin Lee, Ga Hye Lee, Seung Eun Lee, Jee Myung Yang, Kunho Bae
- Received May 15, 2023 Accepted December 15, 2023 Published online March 13, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0149 [Epub ahead of print]

- 603 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To investigate the association of glycemic control and retinal microvascular changes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) without diabetic retinopathy (DR).
Methods
This retrospective, observational, cohort study included patients with T2DM without DR. The patients were categorized into intensive control (IC; mean glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] ≤7.0%) and moderate control (MC; mean HbA1c >7.0%) groups. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) and swept-source OCT angiography (OCTA) image parameters were compared between three groups, including healthy controls.
Results
In total, 259 eyes of 259 participants (88 IC, 81 MC, and 90 controls) were included. The foveal avascular zone area was significantly larger in the MC group than IC and control groups (all P<0.05). The IC group had lower vessel density in the superficial retinal layer and deep retinal layer than the controls (all P<0.05). The choriocapillaris (CC) flow deficit (FD) was significantly greater in the MC group than in the IC and control groups (18.2%, 16.7%, and 14.2%, respectively; all P<0.01). In multivariate regression analysis, CC-FD was associated with the mean HbA1c level (P=0.008). There were no significant differences in OCT parameters among the groups.
Conclusion
OCTA revealed that early CC impairment is associated with HbA1c levels; the CC changes precede clinically apparent DR. The OCTA parameters differed among the groups according to the degree of glycemic control. Our results suggest that microvascular changes precede DR and are closely related to glycemic control.
Review
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
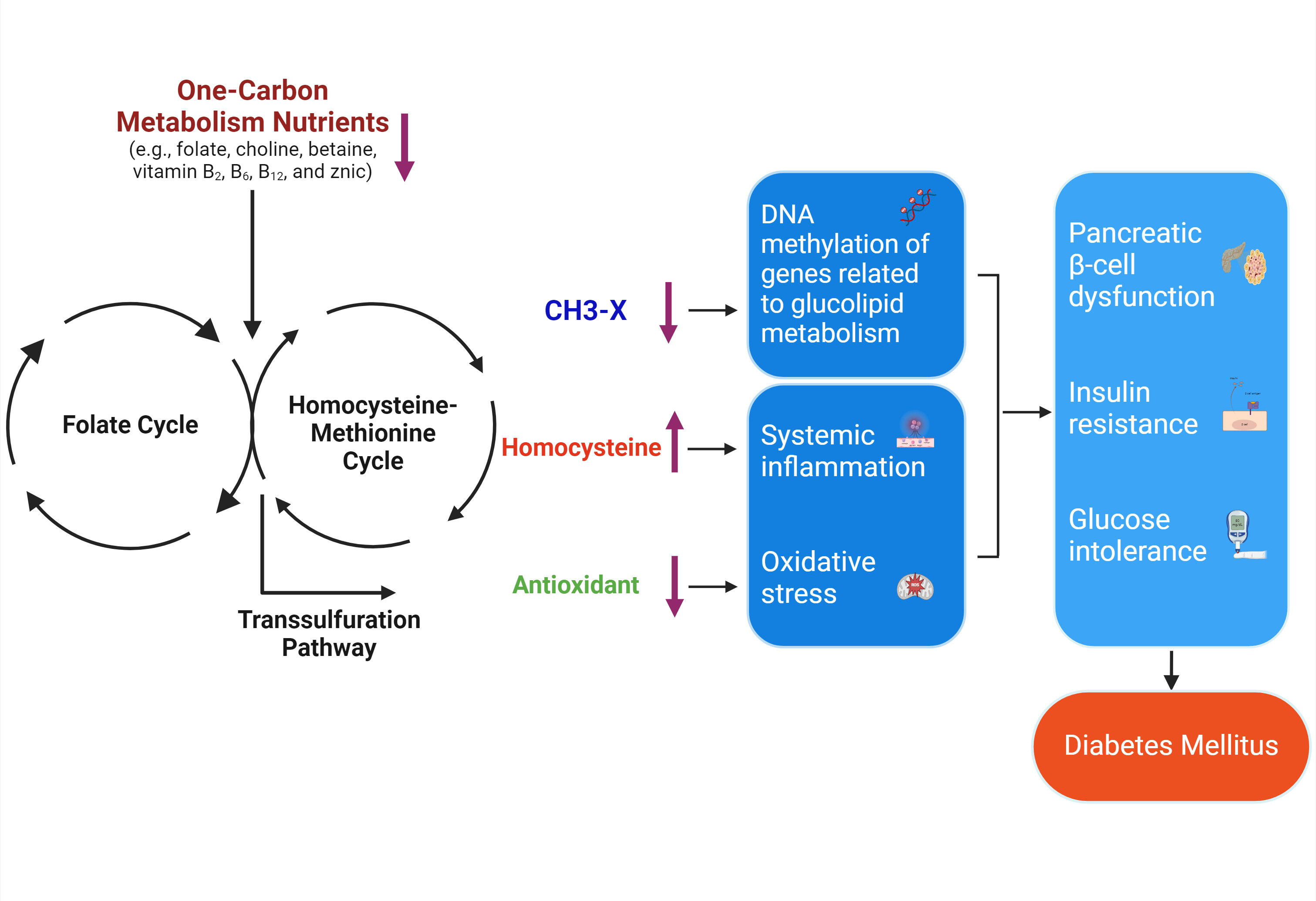
- One-Carbon Metabolism Nutrients, Genetic Variation, and Diabetes Mellitus
- Jie Zhu, Gunjana Saikia, Xiaotao Zhang, Xiaoxi Shen, Ka Kahe
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):170-183. Published online March 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0272
- 1,094 View
- 149 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetes mellitus (DM) affects about 9.3% of the population globally. Hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of DM, owing to its promotion of oxidative stress, β-cell dysfunction, and insulin resistance. HHcy can result from low status of one-carbon metabolism (OCM) nutrients (e.g., folate, choline, betaine, vitamin B6, B12), which work together to degrade homocysteine by methylation. The etiology of HHcy may also involve genetic variation encoding key enzymes in OCM. This review aimed to provide an overview of the existing literature assessing the link between OCM nutrients status, related genetic factors, and incident DM. We also discussed possible mechanisms underlying the role of OCM in DM development and provided recommendations for future research and practice. Even though the available evidence remains inconsistent, some studies support the potential beneficial effects of intakes or blood levels of OCM nutrients on DM development. Moreover, certain variants in OCM-related genes may influence metabolic handling of methyl-donors and presumably incidental DM. Future studies are warranted to establish the causal inference between OCM and DM and examine the interaction of OCM nutrients and genetic factors with DM development, which will inform the personalized recommendations for OCM nutrients intakes on DM prevention.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





