
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
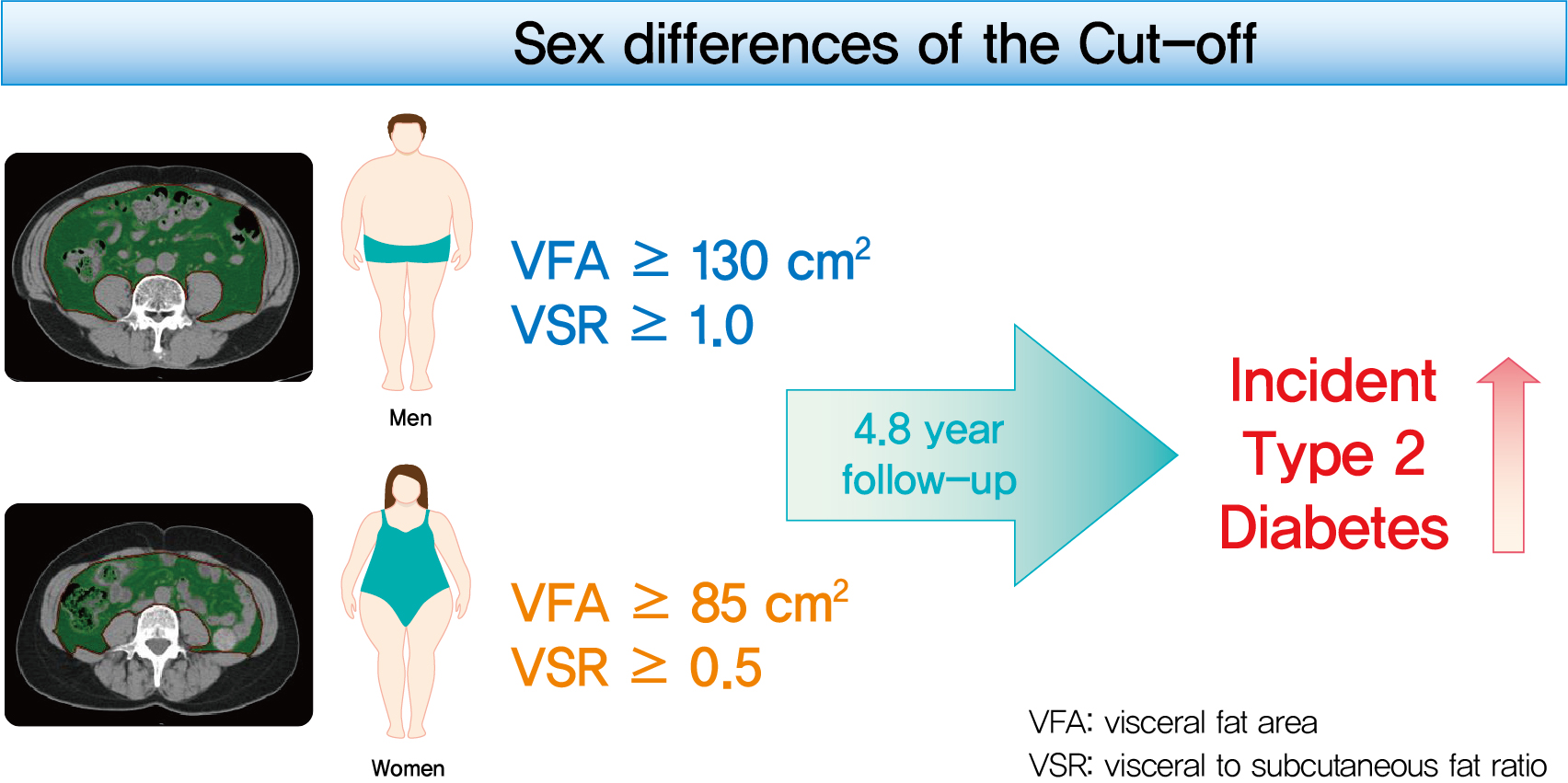
- Sex Differences of Visceral Fat Area and Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Fat Ratio for the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Eun Hee Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Min Jung Lee, Sung-Jin Bae, Jaewon Choe, Chang Hee Jung, Chul-Hee Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):486-498. Published online November 18, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0095
- 9,282 View
- 367 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to determine the optimal cut-off values of visceral fat area (VFA) and visceral-to-subcutaneous fat ratio (VSR) for predicting incident type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
A total of 10,882 individuals (6,835 men; 4,047 women) free of T2DM at baseline aged between 30 and 79 years who underwent abdominal computed tomography scan between 2012 and 2013 as a part of routine health check-ups were included and followed. VFA, subcutaneous fat area, and VSR on L3 vertebral level were measured at baseline.
Results
During a median follow-up of 4.8 years, 730 (8.1% for men; 4.3% for women) incident cases of T2DM were identified. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that the optimal cut-off values of VFA and VSR for predicting incident T2DM were 130.03 cm2 and 1.08 in men, respectively, and 85.7 cm2 and 0.48 in women, respectively. Regardless of sex, higher VFA and VSR were significantly associated with a higher risk of incident T2DM. Compared with the lowest quartiles of VFA and VSR, the highest quartiles had adjusted odds ratios of 2.62 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.73 to 3.97) and 1.55 (95% CI, 1.14 to 2.11) in men, respectively, and 32.49 (95% CI, 7.42 to 142.02) and 11.07 (95% CI, 3.89 to 31.50) in women, respectively.
Conclusion
Higher VFA and VSR at baseline were independent risk factors for the development of T2DM. Sex-specific reference values for visceral fat obesity (VFA ≥130 cm2 or VSR ≥1.0 in men; VFA ≥85 cm2 or VSR ≥0.5 in women) are proposed for the prediction of incident T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Severity of adipose tissue dysfunction is associated with progression of pre-diabetes to type 2 diabetes: the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
Mohammad Jalali, Zahra Bahadoran, Parvin Mirmiran, Fereidoun Azizi, Farhad Hosseinpanah
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Should insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), insulin secretion (HOMA-β), and visceral fat area be considered for improving the performance of diabetes risk prediction models
Huan Hu, Tohru Nakagawa, Toru Honda, Shuichiro Yamamoto, Tetsuya Mizoue
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2024; 12(1): e003680. CrossRef - Adipose organ dysfunction and type 2 diabetes: Role of nitric oxide
Zahra Bahadoran, Parvin Mirmiran, Asghar Ghasemi
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 221: 116043. CrossRef - Prediction of high visceral adipose tissue for sex‐specific community residents in Taiwan
Yu‐Hsuan Chang, Chin‐Sung Chang, Chieh‐Yu Liu, Yin‐Fan Chang, Shiow‐Ching Shun
Nursing & Health Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Guidelines for obesity clinic consultations in primary healthcare clinics
Jee-Hyun Kang, Kyoung-Kon Kim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2024; 67(4): 240. CrossRef - Correlation between fat-to-muscle mass ratio and cognitive impairment in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study
Fan Wu, Yanlan Liu, Chenying Lin, Nahal Haghbin, Longfei Xia, Yaoshuang Li, Tong Chen, Huina Qiu, Weiran Jiang, Jingbo Li, Jingna Lin
BMC Geriatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Body Composition and Metabolic Dysfunction Really Matter for the Achievement of Better Outcomes in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
Mauricio A. Cuello, Fernán Gómez, Ignacio Wichmann, Felipe Suárez, Sumie Kato, Elisa Orlandini, Jorge Brañes, Carolina Ibañez
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1156. CrossRef - MEDICINAL BIOMAGNETISM FOR THE TREATMENT OF OBESITY
Ana Vergínia Campagnollo Bueno, Michelli Gonçalves Seneda, Ângela Mara Rambo, Ana Clara Campagnolo Gonçalves Toledo, Caroline Cabral de Azevedo, Adriane Viapiana Bossa
Health and Society.2023; 3(01): 411. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome in a national population-based cohort of young adults and sex-specific risk for type 2 diabetes
Min-Kyung Lee, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Seo Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Oak-Kee Hong, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The correlation between visceral fat/subcutaneous fat area ratio and monocyte/high-density lipoprotein ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and albuminuria
Haiyan Lin, Jun Zhu, Chen Zheng, Xiaoming Xu, Shandong Ye
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(11): 108521. CrossRef - Effects of the abdominal fat distribution on the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and thyroid hormones among Korean adult males
Hyun-Jin Kim, Byungmi Kim, Seyoung Kim, Hyuktae Kwon, Jae Moon Yun, Belong Cho, Jin-Ho Park
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Visceral Fat Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Obesity
Hong-Kyu Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Hana Park, Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Jaewon Choe
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Visceral adipose tissue reference data computed for GE HealthCare DXA from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data set
Jonathan P. Bennett, Brandon K. Quon, Bo Fan, En Liu, Leila Kazemi, Rosa C. Villegas‐Valle, Raj Ahgun, Xian‐pin Wu, Hou‐De Zhou, Ying Lu, John A. Shepherd
Obesity.2023; 31(12): 2947. CrossRef - Comparison of bioelectrical body and visceral fat indices and anthropometric measures in relation to type 2 diabetes by sex among Chinese adults, a cross-sectional study
Jiangshan He, Binbin Zhang, Yaqi Fan, Yuxue Wang, Mianzhi Zhang, Chunjun Li, Li Zhang, Pei Guo, Minying Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The predictive significance of lipid accumulation products for future diabetes in a non-diabetic population from a gender perspective: an analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics
Jiajun Qiu, Maobin Kuang, Yang Zou, Ruijuan Yang, Qing Shangguan, Dingyang Liu, Guotai Sheng, Wei Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cellular interplay between cardiomyocytes and non-myocytes in diabetic cardiomyopathy
Ren Jie Phang, Rebecca H. Ritchie, Derek J. Hausenloy, Jarmon G. Lees, Shiang Y. Lim
Cardiovascular Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Implication of Sex Differences in Visceral Fat for the Assessment of Incidence Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sang Hyeon Ju, Hyon-Seung Yi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 414. CrossRef - Visceral fat area and body fat percentage measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis correlate with glycometabolism
Shuying Li, Shaoping Li, Jie Ding, Weihong Zhou
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Demographic Specific Abdominal Fat Composition and Distribution Trends in US Adults from 2011 to 2018
Furong Xu, Jacob E. Earp, Bryan J. Blissmer, Ingrid E. Lofgren, Matthew J. Delmonico, Geoffrey W. Greene
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(19): 12103. CrossRef - Visceral Obesity Is a More Important Factor for Colorectal Adenomas than Skeletal Muscle or Body Fat
Ji Yeon Seo, Yoo Min Han, Su Jin Chung, Seon Hee Lim, Jung Ho Bae, Goh Eun Chung
Cancers.2022; 14(21): 5256. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Visceral Obesity and Related Diseases
佳佳 魏
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(12): 11686. CrossRef - Gender differences in the ideal cutoffs of visceral fat area for predicting MAFLD in China
Pingping Yu, Huachao Yang, Xiaoya Qi, Ruixue Bai, Shouqin Zhang, Jianping Gong, Ying Mei, Peng Hu
Lipids in Health and Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Severity of adipose tissue dysfunction is associated with progression of pre-diabetes to type 2 diabetes: the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnant Korean Women Based on Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Thickness as Measured by Ultrasonography
- Sung Hee Yang, Changsoo Kim, Hyun Sook An, Hyun An, Jin Soo Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(6):486-491. Published online September 22, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.486
- 4,769 View
- 55 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study was performed to verify the correlation between abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness (ASFT) measured by ultrasonography (US) during the first trimester of pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) of the second trimester in Korean women and to establish a standard of ASFT for predicting GDM.
Methods A total of 333 singleton pregnant women participated in this study. Their ASFT was measured by US during the 10+6 to 13+6 weeks of pregnancy; then a GDM confirmatory test (100 g oral glucose tolerance test) was conducted during the 24 to 28 week period of pregnancy. Based on the GDM tests, comparative analyses of the ages of the subjects, pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), and weight gain during pregnancy were conducted.
Results The ages of the subjects and weight gains during pregnancy were not correlated to the GDM of the second trimester of pregnancy, but the pre-pregnancy BMIs (22±3.3 kg/m2) and the ASFT (1.9±0.5 cm) measurements between the control group and subjects during the first trimester of pregnancy were found to show significant differences (
P <0.001). The cut-off value of the ASFT for predicting GDM was determined to be 2.4 cm (area under the curve=0.90, sensitivity 75.61%, specificity 91.78%,P <0.001). The odds ratio was 2.91 (95% confidence interval, 1.07 to 7.92;P =0.034), which was higher than the 2.4 cm ASFT.Conclusion It was determined that ASFT as measured by US during the first trimester of pregnancy can be used to predict the risk of developing GDM during the second trimester of pregnancy and for prognosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness combined with a 50-g glucose challenge test at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy in predicting gestational diabetes mellitus
Süleyman Cemil Oğlak, Emine Zeynep Yılmaz, Mehmet Şükrü Budak
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Value of Maternal Upper Abdominal Ad-ipose Thickness in Predicting GDM in Early Pregnancy
娜娜 郭
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(03): 4702. CrossRef - Evaluating the Adipose Tissue Depth as a Predictor Factor for Gestational Diabetes in Later Pregnancy—A Systematic Review
Bianca-Margareta Salmen, Valeria-Anca Pietrosel, Cristiana-Elena Durdu, Teodor Salmen, Cosmina Theodora Diaconu, Ioana-Cristina Bica, Claudia Gabriela Potcovaru, Florentina Gherghiceanu, Roxana-Adriana Stoica, Anca Pantea Stoian
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1492. CrossRef - The Association Between Body Fat Index and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Prospective Cohort Study
Sawanya Benchahong, Prasert Sunsaneevithayakul, Dittakarn Boriboonhirunsarn
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasound evaluation of subcutaneous and visceral abdominal fat as a predictor of gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review
Fernanda Teixeira Benevides, Edward Araujo Júnior, Carla Soraya Costa Maia, Renan Magalhães Montenegro Junior, Francisco Herlânio Costa Carvalho
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine.2022; 35(11): 2216. CrossRef - The Early Sonographic Prediction of Gestational Diabetes in Women From India
Shivani Gupta, Arjun Gupta, C. P. Swarnakar, Monika Rathore, Ramesh Beniwal, Kiran Meena, Anita Simlot, Nidhi Gupta
Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography.2022; 38(1): 18. CrossRef - Can maternal abdominal fat thickness predict antenatal insulin therapy in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus?
Sedat Akgöl, Mehmet Şükrü Budak, Süleyman Cemil Oğlak, Fatma Ölmez, Mehmet Emin Dilek, Serhat Kartal
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2022; 48(3): 634. CrossRef - Prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus by different obesity indices
Zhimin Song, Yan Cheng, Tingting Li, Yongfang Fan, Qingying Zhang, Haidong Cheng
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between maternal adiposity measures and adverse maternal outcomes of pregnancy: Systematic review and meta‐analysis
Nicola Heslehurst, Lem Ngongalah, Theophile Bigirumurame, Giang Nguyen, Adefisayo Odeniyi, Angela Flynn, Vikki Smith, Lisa Crowe, Becky Skidmore, Laura Gaudet, Alexandre Simon, Louise Hayes
Obesity Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of body composition in early pregnancy with gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Fatemeh Alsadat Rahnemaei, Fatemeh Abdi, Reza Pakzad, Seyedeh Hajar Sharami, Fatemeh Mokhtari, Elham Kazemian, Rajakumar Anbazhagan
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0271068. CrossRef - Early Gestational Diabetes Detection Using Neural Network
Tanzina Rahman Hera, Md. Ashikur Rahman Khan, Nishu Nath
WSEAS TRANSACTIONS ON BIOLOGY AND BIOMEDICINE.2021; 18: 1. CrossRef - The association of general obesity, central obesity and visceral body fat with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sura M. Alwash, H. David McIntyre, Abdullah Mamun
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2021; 15(5): 425. CrossRef - Abdominal skin subcutaneous fat thickness over the gestational period in Korean pregnant women: a descriptive observational study
Moon Sook Hwang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(4): 318. CrossRef - Relationship between Maternal Central Obesity and the Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
Da Yao, Qing Chang, Qi-Jun Wu, Shan-Yan Gao, Huan Zhao, Ya-Shu Liu, Yu-Ting Jiang, Yu-Hong Zhao
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Maternal Adipose Tissue Expansion, A Missing Link in the Prediction of Birth Weight Centile
Eleanor M Jarvie, Frances M Stewart, Jane E Ramsay, E Ann Brown, Barbara J Meyer, Gunilla Olivecrona, Bruce A Griffin, Dilys J Freeman
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 105(3): e814. CrossRef - Ultrasound assessment of maternal adipose tissue during 1st trimester screening for aneuploidies and risk of developing gestational diabetes
Francesco D’Ambrosi, Gabriele Rossi, Chiara M. Soldavini, Matteo Di Maso, Ilma F. Carbone, Giulia E. Cetera, Enrico Colosi, Enrico Ferrazzi
Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica.2020; 99(5): 644. CrossRef - Vitamin D Deficiency at Mid-Pregnancy Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Postpartum Glucose Intolerance in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seok Won Park, Yong-Wook Cho, Soo-Kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 97. CrossRef - Fetal pancreatic hyperechogenicity may be an early ultrasonographic sign of gestational diabetes mellitus
Hatice Akkaya, Barış Büke, Gülsüm Uysal
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine.2020; 33(14): 2387. CrossRef The Body Composition in Early Pregnancy is Associated with the Risk of Development of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Late During the Second Trimester
Yanping Liu, Jing Liu, Yinjie Gao, Dan Zheng, Wei Pan, Min Nie, Liangkun Ma
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 2367. CrossRef- New Diagnostic Criteria for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Pregnancy Outcomes in Korea
Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 763. CrossRef - Inter and intra-reliability of ultrasonography for the measurement of abdominal subcutaneous & visceral adipose tissue thickness at 12 weeks gestation
Alexandra Cremona, Kevin Hayes, Clodagh S. O’Gorman, Ciara Ní Laighin, Khadijah I. Ismail, Alan E. Donnelly, Jill Hamilton, Amanda Cotter
BMC Medical Imaging.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness as a simple predictor for gestational diabetes mellitus
Mehmet Sukru Budak, Ilker Kahramanoglu, Salvatore Giovanni Vitale, Sedat Akgol, Mehmet Emin Dilek, Serhat Kartal, Salvatore Caruso, Bekir Kahveci, Mehmet Obut, Muhammed Hanifi Bademkiran, Antonio Cianci
Journal of Perinatal Medicine.2019; 47(6): 605. CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia and Waist Phenotype as Markers in the Prediction of Gestational Diabetes in Iraqi Women
Faris Anwer Rasheed, Raghad Hasan Mshattat, Ulfat Mohammad Alnakkash, Saad Abdulrahma
Research Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2018; 11(1): 25. CrossRef - The importance of treating mild hyperglycemia in pregnant women with diabetes
Kyung-Soo Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 33(6): 1079. CrossRef - Anthropometric and ultrasound measures of maternal adiposity in the first trimester of pregnancy
Narelle Kennedy, Ann Quinton, Michael John Peek, Valeria Lanzarone, Ron Benzie, Ralph Nanan
Australasian Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.2018; 21(3): 147. CrossRef - Simple Screening Using Ultrasonography for Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 438. CrossRef
- Abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness combined with a 50-g glucose challenge test at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy in predicting gestational diabetes mellitus
- The Appropriateness of the Length of Insulin Needles Based on Determination of Skin and Subcutaneous Fat Thickness in the Abdomen and Upper Arm in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Kang Hee Sim, Moon Sook Hwang, Sun Young Kim, Hye Mi Lee, Ji Yeun Chang, Moon Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(2):120-133. Published online April 18, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.2.120
- 5,134 View
- 114 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Longer needle and complicated insulin injection technique such as injecting at a 45-degree angle and making skinfolds may decrease patient compliance to insulin injection therapy. In this light, shorter insulin needles have been recently developed. However, it is necessary to ascertain that such shorter needles are appropriate for Korean patients with diabetes as well.
Methods First, the diverse demographic and diabetic features of 156 Korean adults with diabetes were collected by a questionnaire and a device unit of body fat measurement. The skin and subcutaneous fat thicknesses of each subject were measured by Ultrasound device with a 7- to 12-MHz probe. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance and multiple linear regression.
Results The mean skin thickness was 2.29±0.37 mm in the abdomen and 2.00±0.34 mm in the upper arms, and the mean subcutaneous fat thickness was to 10.15±6.54 mm in the abdomen and 5.50±2.68 mm in the upper arms. Our analysis showed that the factors affecting the skin thickness of the abdomen and upper arms were gender and body mass index (BMI), whereas the factors influencing the subcutaneous fat thickness in the abdomen were gender and BMI, and the factors influencing the subcutaneous fat thickness in the upper arms were gender, BMI, and age. Insulin fluids may not appear to be intradermally injected into the abdomen and upper arms at any needle lengths. The risk of intramuscular injection is likely to increase with longer insulin needles and lower BMI.
Conclusion It is recommended to fully inform the patients about the lengths of needles for insulin injections. As for the recommended needle length, the findings of this study indicate that needles as short as 4 mm are sufficient to deliver insulin for Korean patients with diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inadvertent intramuscular injection risk with subcutaneous insulin injections and risk predictors in adults: a cross-sectional sonographic study
U. A. Liyanage, Y. Mathangasinghe, C. K. Liyanage, E. S. Wijewickrama, D. Mahathanthila, A. J. Dharmawansa, S. Jeyerajesingham, D. S. Warapitiya, M. D. M. S. Wijayabandara, B. C. T. A. N. W. M. R. C. S. Kempitiya, A. Aravinthan, L. M. D. T. Jayasekara, N.
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023; 43(5): 731. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccination and the skin to deltoid muscle distance in adults with diabetes
Marjan Doppen, Ali Mirjalili, Matire Harwood, Allie Eathorne, Irene Braithwaite, Jonathan Bong, Louis Kirton, Ruth Semprini, Mark Weatherall, Alex Semprini, Ciléin Kearns, Melissa Black, Stacey Kung, Michaela Walton, Richard Beasley, Thomas Hills
Vaccine: X.2023; 13: 100248. CrossRef - Integration of capillaric strain sensors toward recognition of human movements
Hudson Gasvoda, Nick Cmager, Rana Altay, Ju Young Lee, I. Emre Araci
Sensors & Diagnostics.2023; 2(1): 212. CrossRef - What variables should inform needle length choice for deltoid intramuscular injection? A systematic review
Ciléin Kearns, Claire Houghton, Emily Dickinson, Lee Hatter, Pepa Bruce, Srinidhi Krishnamoorthy, Mark Weatherall, Thomas Hills, Marjan Doppen, Seyed Ali Mirjalili, Richard Beasley
BMJ Open.2023; 13(1): e063530. CrossRef - Investigation of appropriate needle length considering skin thickness with the real injection posture for insulin injections in diabetic patients
Aya Torii-Goto, Kana Hirai, Yuri Inukai, Yoshimi Hoshina, Kazumi Shiomi, Junko Ito, Masae Yoshikawa
Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Thickness During Pregnancy
Moon Sook Hwang, Eunjeong Song, Jeonghee Ahn, Seungmi Park
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2023; 21(9): 479. CrossRef - Human continuous glucose monitors for measurement of glucose in dairy cows
M.K.H. Byrd, A.G. Arneson, D.R. Soffa, J.W. Stewart, M.L. Rhoads
JDS Communications.2022; 3(1): 78. CrossRef - A finite element model of abdominal human tissue for improving the accuracy in insulin absorption assessment: A feasibility study
Pasquale Arpaia, Davide Cuneo, Sabrina Grassini, Francesca Mancino, Simone Minucci, Nicola Moccaldi, Isabella Sannino
Measurement: Sensors.2021; 18: 100218. CrossRef - Abdominal skin subcutaneous fat thickness over the gestational period in Korean pregnant women: a descriptive observational study
Moon Sook Hwang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(4): 318. CrossRef - User experience for manual injection of 2 mL viscous solutions is enhanced by a new prefillable syringe with a staked 8 mm ultra-thin wall needle
Aurélie Pager, Anne Combedazou, Karen Guerrero, Tzvetelina Tzvetkova-Chevolleau, Didier Morel, Cécile Frolet, Stanislav Glezer
Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery.2020; 17(10): 1485. CrossRef - Evaluating the Impact of Human Factors and Pen Needle Design on Insulin Pen Injection
Christopher Rini, Bruce C. Roberts, Didier Morel, Rick Klug, Benjamin Selvage, Ronald J. Pettis
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2019; 13(3): 533. CrossRef - Subcutaneous Injection of Drugs: Literature Review of Factors Influencing Pain Sensation at the Injection Site
Iris Usach, Rafael Martinez, Teodora Festini, José-Esteban Peris
Advances in Therapy.2019; 36(11): 2986. CrossRef - The Injection Technique Factor: What You Don’t Know or Teach Can Make a Difference
Laurence J. Hirsch, Kenneth W. Strauss
Clinical Diabetes.2019; 37(3): 227. CrossRef - Factors associated with removal difficulties of etonogestrel-containing contraceptive implants (Nexplanon ® )
Julien Chevreau, David Krief, Osama Abou Arab, Mickaël Zitoun, Arthur Foulon, Fabrice Sergent, Jean Gondry
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2018; 224: 81. CrossRef - Insulin Injection Technique in China Compared with the Rest of the World
Zhenqiang Song, Xiaohui Guo, Linong Ji, Xiao Huang, Laurence J. Hirsch, Kenneth W. Strauss
Diabetes Therapy.2018; 9(6): 2357. CrossRef - Ultrasound-guided measurement of skin and subcutaneous tissue thickness in children with diabetes and recommendations for giving insulin injections
Soo Ting Joyce Lim, Yuen Ching Angela Hui, Pei Kwee Lim, Chin Choo Evelyn Lim, Yen Yen Chia, Rashida Farhad Vasanwala
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology.2018; 12: 26. CrossRef - Comment on the New Indian Injection Technique Recommendations: Critical Appraisal of the Real-World Implementation of the Current Guidelines
Felice Strollo, Sandro Gentile
Diabetes Therapy.2017; 8(3): 507. CrossRef - Worldwide Injection Technique Questionnaire Study
Anders H. Frid, Laurence J. Hirsch, Astrid R. Menchior, Didier R. Morel, Kenneth W. Strauss
Mayo Clinic Proceedings.2016; 91(9): 1212. CrossRef - Skin and subcutaneous tissue thickness at insulin injection sites in Chinese diabetes patients: Clinical implications
W. Wang, X. Guo, G. Shen, G. Bai, Z. Wei, J. Liu, L. Hirsch, K. Strauss
Diabetes & Metabolism.2016; 42(5): 374. CrossRef - New Insulin Delivery Recommendations
Anders H. Frid, Gillian Kreugel, Giorgio Grassi, Serge Halimi, Debbie Hicks, Laurence J. Hirsch, Mike J. Smith, Regine Wellhoener, Bruce W. Bode, Irl B. Hirsch, Sanjay Kalra, Linong Ji, Kenneth W. Strauss
Mayo Clinic Proceedings.2016; 91(9): 1231. CrossRef - Le tissu sous-cutané et l’insuline : Une cohabitation délicate Revue de la littérature
K. Strauss, S. Halimi
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2015; 9(5): 504. CrossRef - Subcutaneous Injection Depth Does Not Affect the Pharmacokinetics or Glucodynamics of Insulin Lispro in Normal Weight or Healthy Obese Subjects
Amparo de la Peña, Kwee P. Yeo, Helle Linnebjerg, Edward Catton, Shobha Reddy, Patricia Brown-Augsburger, Linda Morrow, Debra A. Ignaut
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2015; 9(4): 824. CrossRef
- Inadvertent intramuscular injection risk with subcutaneous insulin injections and risk predictors in adults: a cross-sectional sonographic study
- The Relationship between Visceral & Subcutaneous Fat and Small Dense Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Concentration in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Wan Sub Shim, Soo Kyung Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Woo Ahn, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong Soo Cha
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(3):207-216. Published online May 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.3.207
- 2,099 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Visceral obesity is closely associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD). Small dense (sd) LDL is closely associated with CVD. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between visceral and subcutaneous fat accumulation and sd LDL-C concentration. METHODS: 264 type 2 diabetic patients underwent ultrasonography to estimate visceral & subcutaneous fat accumulation and sd LDL-C concentrations were measured. RESULTS: BMI, total cholesterol, sd LDL-C concentration and percentage of sd LDL-C were higher in highest tertile of visceral fat length in male than those in lowest tertile. BMI, total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-C, sd LDL-C concentration and percentage of sd LDL-C were higher in highest tertile of visceral fat length in female than those in lowest tertile. But sd LDL-C concentration and percentage of sd LDL-C were not different among three groups based on the tertile of subcutaneous fat length in male and female. Visceral fat length was correlated with sd LDL-C concentration and percentage of sd LDL-C, total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-C, but negatively with percentage of large buoyant LDL-C and HDL-C after adjustment of age, sex and BMI. Subcutaneous fat length was not correlated with sd LDL-C and percentage of sd LDL-C, total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL-C and LDL-C. CONCLUSION: The association between visceral fat length and sd LDL-C could be a factor that explains the association between visceral obesity and CVD.
- A Case of Failure in Insulin Pump Treatment due to Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Atrophy and Lipohypertrophied Nodules.
- Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Gwanpyo Koh, Seungjoon Oh, Jeong taek Woo, Sung Woon Kim, Jin Woo Kim, Young Seol Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2004;28(6):547-553. Published online December 1, 2004
- 954 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The insulin pump is an effective glycemic control device those function is analogous to the physiologic regulation of insulin in vivo. When sufficient patient education and proper selection of patients is done, the insulin pump is one of the most effective treatment modalities for diabetic patients. However, various side effects and complications might occur during its application. We report here on an unusual case of diabetic ketoacidosis that was caused by acute inflammatory colitis and insulin pump malfunction. Peculiarly, the cause of pump malfunction was far removed from its mechanical problem. We concluded that the cause of the insulin pump malfunction was due to abdominal subcutaneous fat atrophy and the lipohypertrophied nodules of the patient that developed due to the prolonged usage of the insulin pump.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





