
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Basic research
- Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4 Inhibition Is Important in Prevention of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Mice
- Ah Reum Khang, Dong Hun Kim, Min-Ji Kim, Chang Joo Oh, Jae-Han Jeon, Sung Hee Choi, In-Kyu Lee
- Received June 22, 2023 Accepted July 13, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0196 [Epub ahead of print]
- 930 View
- 80 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
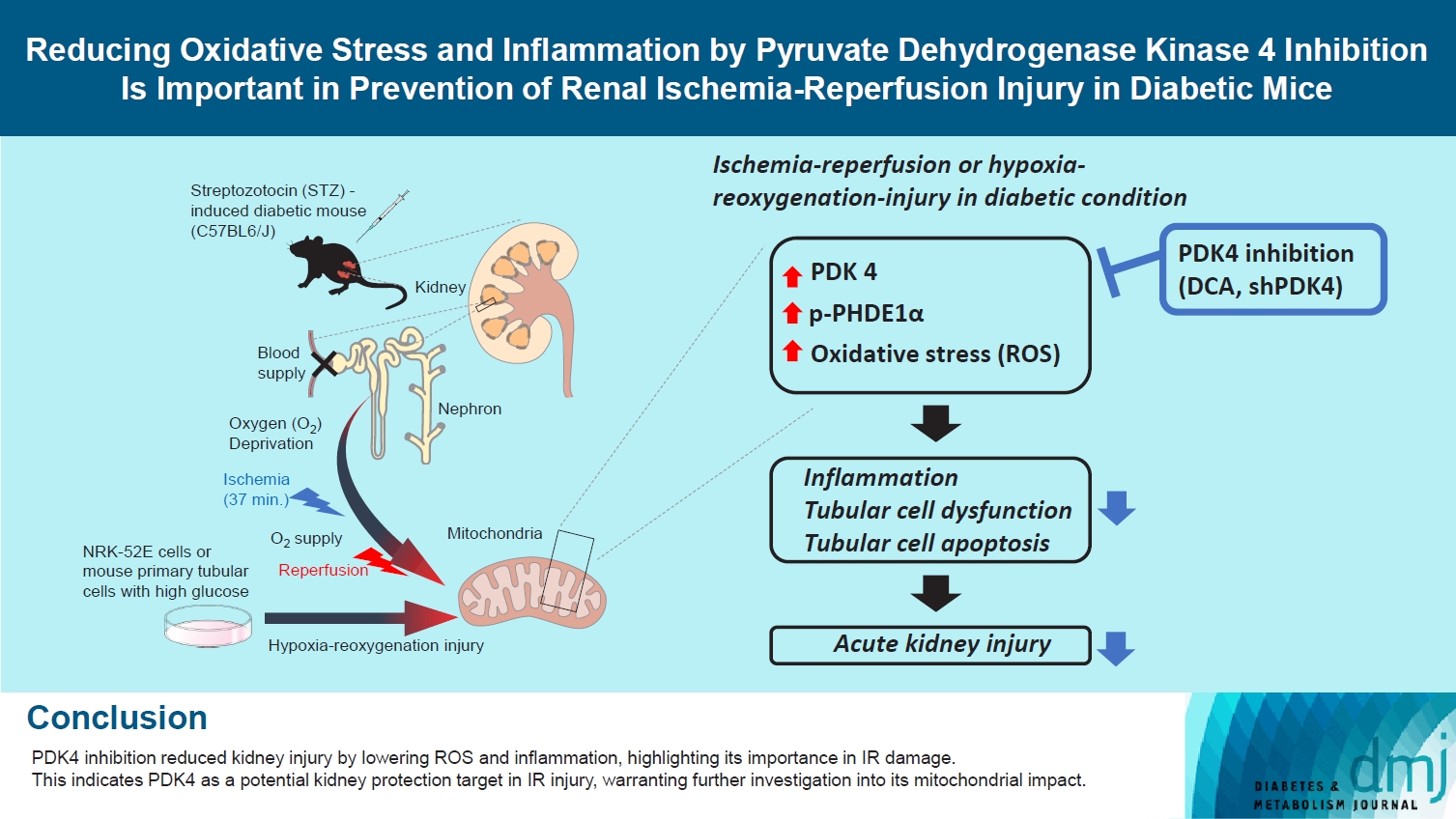
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammation are reported to have a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury, a leading cause of acute kidney injury. The present study investigated the role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) in ROS production and inflammation following IR injury.
Methods
We used a streptozotocin-induced diabetic C57BL6/J mouse model, which was subjected to IR by clamping both renal pedicles. Cellular apoptosis and inflammatory markers were evaluated in NRK-52E cells and mouse primary tubular cells after hypoxia and reoxygenation using a hypoxia work station.
Results
Following IR injury in diabetic mice, the expression of PDK4, rather than the other PDK isoforms, was induced with a marked increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase E1α (PDHE1α) phosphorylation. This was accompanied by a pronounced ROS activation, as well as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) production. Notably, sodium dichloroacetate (DCA) attenuated renal IR injury-induced apoptosis which can be attributed to reducing PDK4 expression and PDHE1α phosphorylation levels. DCA or shPdk4 treatment reduced oxidative stress and decreased TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and MCP-1 production after IR or hypoxia-reoxygenation injury.
Conclusion
PDK4 inhibition alleviated renal injury with decreased ROS production and inflammation, supporting a critical role for PDK4 in IR mediated damage. This result indicates another potential target for reno-protection during IR injury; accordingly, the role of PDK4 inhibition needs to be comprehensively elucidated in terms of mitochondrial function during renal IR injury.
- Others
- Risk Prediction and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in People Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ying-Guat Ooi, Tharsini Sarvanandan, Nicholas Ken Yoong Hee, Quan-Hziung Lim, Sharmila S. Paramasivam, Jeyakantha Ratnasingam, Shireene R. Vethakkan, Soo-Kun Lim, Lee-Ling Lim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):196-207. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0244
- 2,270 View
- 418 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
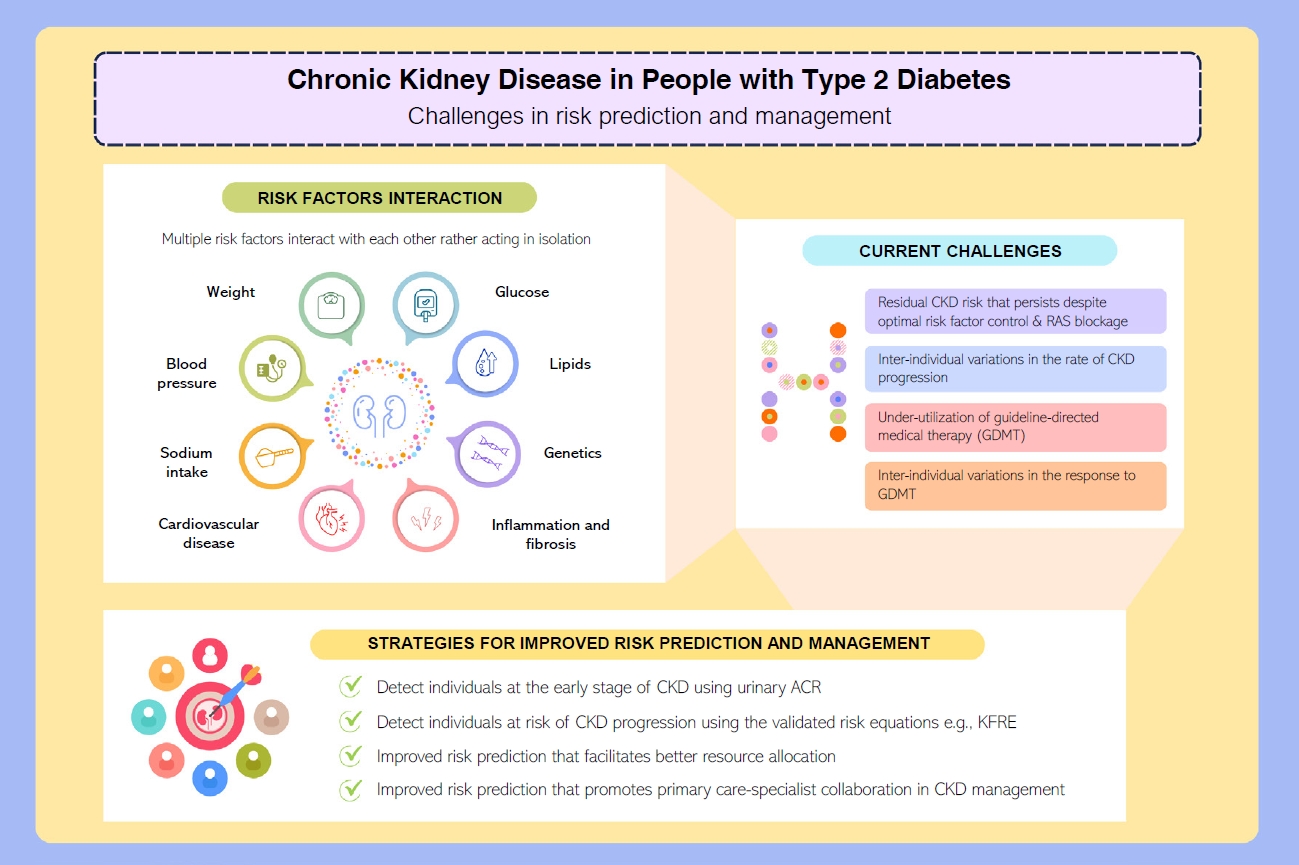
ePub - People with type 2 diabetes mellitus have increased risk of chronic kidney disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Improved care delivery and implementation of guideline-directed medical therapy have contributed to the declining incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in high-income countries. By contrast, the global incidence of chronic kidney disease and associated mortality is either plateaued or increased, leading to escalating direct and indirect medical costs. Given limited resources, better risk stratification approaches to identify people at risk of rapid progression to end-stage kidney disease can reduce therapeutic inertia, facilitate timely interventions and identify the need for early nephrologist referral. Among people with chronic kidney disease G3a and beyond, the kidney failure risk equations (KFRE) have been externally validated and outperformed other risk prediction models. The KFRE can also guide the timing of preparation for kidney replacement therapy with improved healthcare resources planning and may prevent multiple complications and premature mortality among people with chronic kidney disease with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. The present review summarizes the evidence of KFRE to date and call for future research to validate and evaluate its impact on cardiovascular and mortality outcomes, as well as healthcare resource utilization in multiethnic populations and different healthcare settings.
- Drug/Regimen
- Abrupt Decline in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate after Initiating Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Predicts Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Min-Hsiang Chuang, Yu-Shuo Tang, Jui-Yi Chen, Heng-Chih Pan, Hung-Wei Liao, Wen-Kai Chu, Chung-Yi Cheng, Vin-Cent Wu, Michael Heung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):242-252. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0201
- 1,990 View
- 260 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
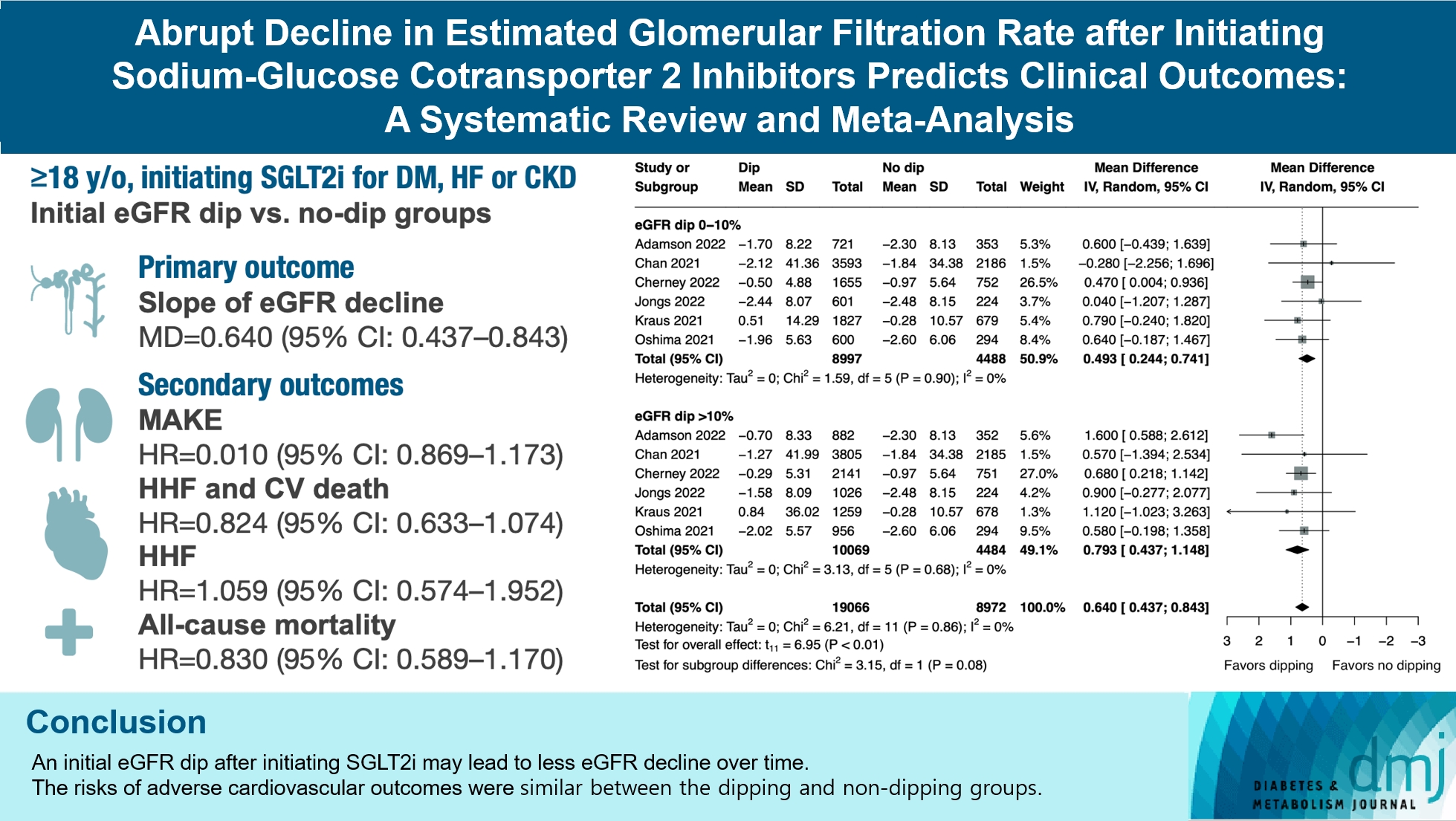
The initiation of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) typically leads to a reversible initial dip in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). The implications of this phenomenon on clinical outcomes are not well-defined.
Methods
We searched MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane Library from inception to March 23, 2023 to identify randomized controlled trials and cohort studies comparing kidney and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with and without initial eGFR dip after initiating SGLT2i. Pooled estimates were calculated using random-effect meta-analysis.
Results
We included seven studies in our analysis, which revealed that an initial eGFR dip following the initiation of SGLT2i was associated with less annual eGFR decline (mean difference, 0.64; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.437 to 0.843) regardless of baseline eGFR. The risk of major adverse kidney events was similar between the non-dipping and dipping groups but reduced in patients with a ≤10% eGFR dip (hazard ratio [HR], 0.915; 95% CI, 0.865 to 0.967). No significant differences were observed in the composite of hospitalized heart failure and cardiovascular death (HR, 0.824; 95% CI, 0.633 to 1.074), hospitalized heart failure (HR, 1.059; 95% CI, 0.574 to 1.952), or all-cause mortality (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.589 to 1.170). The risk of serious adverse events (AEs), discontinuation of SGLT2i due to AEs, kidney-related AEs, and volume depletion were similar between the two groups. Patients with >10% eGFR dip had increased risk of hyperkalemia compared to the non-dipping group.
Conclusion
Initial eGFR dip after initiating SGLT2i might be associated with less annual eGFR decline. There were no significant disparities in the risks of adverse cardiovascular outcomes between the dipping and non-dipping groups.
- Complications
- Dyslipidemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Updated Overview
- Sang Heon Suh, Soo Wan Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):612-629. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0067
- 3,415 View
- 440 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
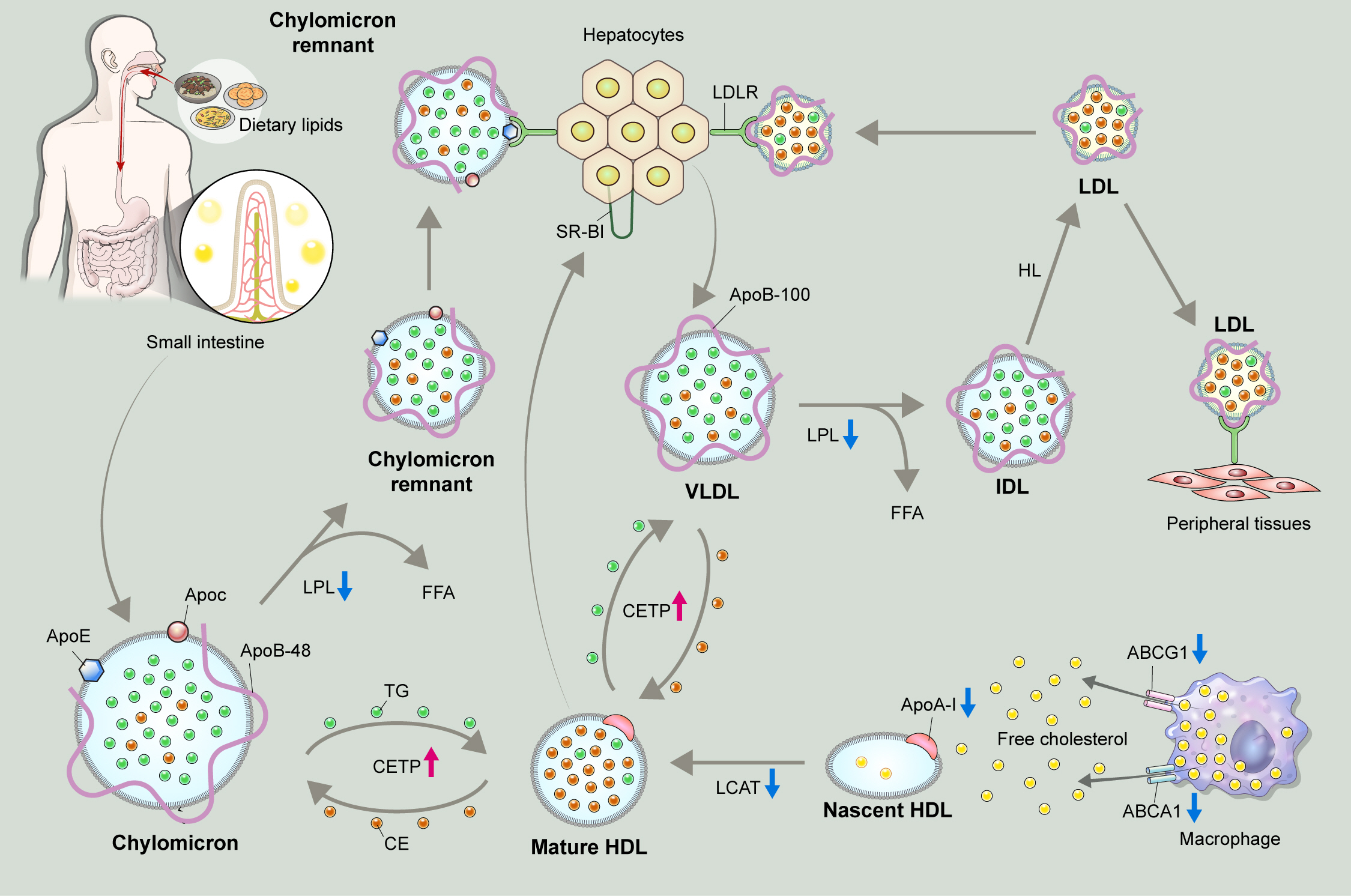
ePub - Dyslipidemia is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor. Whereas the recommendations for the treatment target of dyslipidemia in the general population are being more and more rigorous, the 2013 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes clinical practice guideline for lipid management in chronic kidney disease (CKD) presented a relatively conservative approach with respect to the indication of lipid lowering therapy and therapeutic monitoring among the patients with CKD. This may be largely attributed to the lack of high-quality evidence derived from CKD population, among whom the overall feature of dyslipidemia is considerably distinctive to that of general population. In this review article, we cover the characteristic features of dyslipidemia and impact of dyslipidemia on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CKD. We also review the current evidence on lipid lowering therapy to modify the risk of cardiovascular events in this population. We finally discuss the association between dyslipidemia and CKD progression and the potential strategy to delay the progression of CKD in relation to lipid lowering therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Statin Therapy and Lipid Indices in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic
Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Control Trials
Jafar Karami, Bahman Razi, Danyal Imani, Saeed Aslani, Mahdi Pakjoo, Mahdieh Fasihi, Keyhan Mohammadi, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2024; 30(5): 362. CrossRef
- Statin Therapy and Lipid Indices in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic
Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Control Trials
- Complications
- Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of End-Stage Kidney Disease in South Korea
- Min-Jeong Lee, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Inwhee Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):933-937. Published online December 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0156
- 5,915 View
- 240 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Knowledge of the epidemiologic characteristics of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) patients is essential. The trends in the prevalence, incidence, and mortality rates of ESKD were analyzed retrospectively using the Korean National Health Insurance ServiceNational Sample Cohort database between 2006 and 2015. From 2006 to 2015, the incidence of ESKD decreased from 28.6 to 24.0 per 100,000 people and showed a decreasing pattern with or without diabetes mellitus. However, the incidence of those aged ≥75 years increased, as did the mean age at the onset of ESKD. From 2007 to 2015, the prevalence of ESKD increased in all age groups, but particularly in those aged ≥75 years. The prevalence of ESKD differed by sex and diabetes mellitus status and this gap widened over time. Mortality rates in ESKD patients remained relatively constant throughout the study period. However, mortality rates in ESKD without diabetes decreased over the same period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Kidney Health Plan 2033 in Korea: bridging the gap between the present and the future
Do Hyoung Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Jin Joo Cha, Sua Lee, Hyun Kyung Lee, Jong Wook Choi, Su-Hyun Kim, Sang Youb Han, Cheol Whee Park, Eun Young Lee, Dae Ryong Cha, Sung Gyun Kim, Chun Soo Lim, Sun-Hee Park
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 43(1): 8. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol is an independent risk factor for the incidence of chronic kidney disease in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population-based study
Soo Yeon Jang, Minwoong Kang, Eyun Song, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111639. CrossRef - Effects of Kt/Vurea on outcomes according to age in patients on maintenance hemodialysis
Junseok Jeon, Gui Ok Kim, Bo Yeon Kim, Eun Jung Son, Jun Young Do, Jung Eun Lee, Seok Hui Kang
Clinical Kidney Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Waist circumference and end‐stage renal disease based on glycaemic status: National Health Insurance Service data 2009–2018
Yun Kyung Cho, Ji Hye Huh, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Kyung‐do Han, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung‐Hee Ihm
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(1): 585. CrossRef - Usefulness of continuous glucose monitoring of blood glucose control in patients with diabetes undergoing hemodialysis: A pilot study
Sua Lee, Soyoung Lee, Kyeong Min Kim, Jong Ho Shin
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between N-Terminal Prohormone Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Decreased Skeletal Muscle Mass in a Healthy Adult Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
Tae Kyung Yoo, Marie Yung-Chen Wu, Moon Soo Kim, Mi-Yeon Lee, Yong-Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Chul-Hyun Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 269. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Epigenome-wide association study of diabetic chronic kidney disease progression in the Korean population: the KNOW-CKD study
Hye Youn Sung, Sangjun Lee, Miyeun Han, Woo Ju An, Hyunjin Ryu, Eunjeong Kang, Yong Seek Park, Seung Eun Lee, Curie Ahn, Kook-Hwan Oh, Sue K. Park, Jung-Hyuck Ahn
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Dapagliflozin in Asian Patients With Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction in DAPA-HF
Kieran F. Docherty, Inder S. Anand, Chern-En Chiang, Vijay K. Chopra, Akshay S. Desai, Masafumi Kitakaze, Subodh Verma, Pham N. Vinh, Silvio E. Inzucchi, Lars Køber, Mikhail N. Kosiborod, Felipe A. Martinez, Olof Bengtsson, Piotr Ponikowski, Marc S. Sabat
JACC: Asia.2022; 2(2): 139. CrossRef - Glomerular filtration rate as a kidney outcome of diabetic kidney disease: a focus on new antidiabetic drugs
Hyo Jin Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Sang Heon Song
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(3): 502. CrossRef - The risk of Parkinson's disease according to diabetic kidney disease status in a Korean population
Seung Eun Lee, Juhwan Yoo, Han Seok Choi, Kyungdo Han, Kyoung-Ah Kim
Parkinsonism & Related Disorders.2022; 100: 13. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - The Incidence and Risk Factors of Renal Insufficiency among Korean HIV infected Patients: The Korea HIV/AIDS Cohort Study
Jun Hyoung Kim, Heeseon Jang, Jung Ho Kim, Joon Young Song, Shin-Woo Kim, Sang Il Kim, Bo Youl Choi, Jun Yong Choi
Infection & Chemotherapy.2022; 54(3): 534. CrossRef - Sex difference in the association among nutrition, muscle mass, and strength in peritoneal dialysis patients
Jun Young Do, Seok Hui Kang
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Additive interaction of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease in cancer patient mortality risk
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Kidney Health Plan 2033 in Korea: bridging the gap between the present and the future
- Drug/Regimen
- Evogliptin, a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, Attenuates Renal Fibrosis Caused by Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction in Mice
- Mi-Jin Kim, Na-young Kim, Yun-A Jung, Seunghyeong Lee, Gwon-Soo Jung, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Sungwoo Lee, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):186-192. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0271
- 5,723 View
- 97 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Renal fibrosis is considered to be the final common outcome of chronic kidney disease. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors have demonstrated protective effects against diabetic kidney disease. However, the anti-fibrotic effect of evogliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, has not been studied. Here, we report the beneficial effects of evogliptin on unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)-induced renal fibrosis in mice. Evogliptin attenuated UUO-induced renal atrophy and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Immunohistochemistry and Western blotting demonstrated that evogliptin treatment inhibits pro-fibrotic gene expressions and extracellular matrix production.
In vitro findings showed that the beneficial effects of evogliptin on renal fibrosis are mediated by inhibition of the transforming growth factor-β/Smad3 signaling pathway. The present study demonstrates that evogliptin is protective against UUO-induced renal fibrosis, suggesting that its clinical applications could extend to the treatment of kidney disease of non-diabetic origin.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis
Birte Ohm, Isabelle Moneke, Wolfgang Jungraithmayr
British Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 180(22): 2846. CrossRef - Linagliptin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis in systemic sclerosis mouse model via inhibition of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Biwei Pei, Na Zhang, Tingting Pang, Gengyun Sun
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 477(4): 995. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - Evogliptin Directly Inhibits Inflammatory and Fibrotic Signaling in Isolated Liver Cells
Hye-Young Seo, So-Hee Lee, Eugene Han, Jae Seok Hwang, Sol Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(19): 11636. CrossRef - Optimization and validation of a fluorogenic dipeptidyl peptidase 4 enzymatic assay in human plasma
Hyunyee Yoon, Su Hee Cho, Yu Rim Seo, Kyung-Sang Yu, Sung Sup Park, Moon Jung Song
Analytical Biochemistry.2021; 612: 113952. CrossRef - Use of Anti-Diabetic Agents in Non-Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Bench to Bedside
Sungjin Chung, Gheun-Ho Kim
Life.2021; 11(5): 389. CrossRef - Targeting Dermal Fibroblast Subtypes in Antifibrotic Therapy: Surface Marker as a Cellular Identity or a Functional Entity?
Xin Huang, Yimin Khoong, Chengyao Han, Dai Su, Hao Ma, Shuchen Gu, Qingfeng Li, Tao Zan
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of evogliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, active‐controlled, randomized, double‐blind study with open‐label extension (the EVERGREEN study)
Gyuri Kim, Soo Lim, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Ie B. Park, Kyu J. Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park, Su K. Kwon, Hye S. Kim, Seok W. Park, Sin G. Kim, Min K. Moon, Eun S. Kim, Choon H. Chung, Kang S. Park, Mikyung Kim, Dong J. Chung, Chang B. Lee, Tae H. Kim, Moon‐Kyu Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(9): 1527. CrossRef Effect of Switching from Linagliptin to Teneligliptin Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eugene Han, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4113. CrossRef- Efficacy and safety of novel dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitor evogliptin in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Aishwarya Krishnamurthy, LokeshKumar Sharma, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 24(5): 434. CrossRef
- Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis
- Basic Research
- Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Attenuates Diabetes-Induced Renal Fibrosis by Negatively Regulating TGF-β-p53-Smad2/3-Mediated Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via Activation of AKT
- Sundong Lin, Lechu Yu, Yongqing Ni, Lulu He, Xiaolu Weng, Xuemian Lu, Chi Zhang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):158-172. Published online October 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0235
- 5,856 View
- 114 Download
- 38 Web of Science
- 34 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is required for renal fibrosis, which is a characteristic of diabetic nephropathy (DN). Our previous study demonstrated that fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) prevented DN associated with the suppressing renal connective tissue growth factor expression, a key marker of renal fibrosis. Therefore, the effects of FGF21 on renal fibrosis in a DN mouse model and the underlying mechanisms were investigated in this study.
Methods Type 1 diabetes mellitus was induced in C57BL/6J mice by intraperitoneal injections of multiple low doses of streptozotocin. Then, diabetic and non-diabetic mice were treated with or without FGF21 in the presence of pifithrin-α (p53 inhibitor) or 10-[4′-(N,N-Diethylamino)butyl]-2-chlorophenoxazine hydrochloride (10-DEBC) hydrochloride (Akt inhibitor) for 4 months.
Results DN was diagnosed by renal dysfunction, hypertrophy, tubulointerstitial lesions, and glomerulosclerosis associated with severe fibrosis, all of which were prevented by FGF21. FGF21 also suppressed the diabetes-induced renal EMT in DN mice by negatively regulating transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β)-induced nuclear translocation of Smad2/3, which is required for the transcription of multiple fibrotic genes. The mechanistic studies showed that FGF21 attenuated nuclear translocation of Smad2/3 by inhibiting renal activity of its conjugated protein p53, which carries Smad2/3 into the nucleus. Moreover pifithrin-α inhibited the FGF21-induced preventive effects on the renal EMT and subsequent renal fibrosis in DN mice. In addition, 10-DEBC also blocked FGF21-induced inhibition of renal p53 activity by phosphorylation of mouse double minute-2 homolog (MDM2).
Conclusion FGF21 prevents renal fibrosis via negative regulation of the TGF-β/Smad2/3-mediated EMT process by activation of the Akt/MDM2/p53 signaling pathway.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Epithelial–mesenchymal plasticity in kidney fibrosis
Sudarat Hadpech, Visith Thongboonkerd
genesis.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Wenhui Zhong, Yuheng Jiang, Huizhen Wang, Xiang Luo, Tao Zeng, Huimi Huang, Ling Xiao, Nan Jia, Aiqing Li
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119620. CrossRef - Platelet concentrates may affect the formation of pathological scars by regulating epithelial to mesenchymal transition
Ju Tian, Dandan Shi, Chenyan Long, Jing Ding, Huimin You, Xiaoying He, Biao Cheng
Medical Hypotheses.2024; 182: 111227. CrossRef - Cadherin-responsive hydrogel combined with dental pulp stem cells and fibroblast growth factor 21 promotes diabetic scald repair via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and necroptosis
Wenjie Lu, Juan Zhao, Xiong Cai, Yutian Wang, Wenwei Lin, Yaoping Fang, Yunyang Wang, Jinglei Ao, Jiahui Shou, Jiake Xu, Sipin Zhu
Materials Today Bio.2024; 24: 100919. CrossRef - Sodium butyrate ameliorated diabetic nephropathy-associated tubulointerstitial inflammation by modulating the tight junctions of renal tubular epithelial cells
Tingting Yang, Lin Li, Cai Heng, Pian Sha, Yiying Wang, Jiaming Shen, Zhenzhou Jiang, Sitong Qian, Chujing Wei, Hao Yang, Xia Zhu, Tao Wang, Mengying Wu, Jianyun Wang, Qian Lu, Xiaoxing Yin
Food & Function.2024; 15(5): 2628. CrossRef - Urinary Excretion of Biomolecules Related to Cell Cycle, Proliferation, and Autophagy in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Anton I. Korbut, Vyacheslav V. Romanov, Vadim V. Klimontov
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 487. CrossRef - FGF21 Inhibits Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-induced Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury by Regulating the PPARγ/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Ruixue Li, Xi Liu
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in the Treatment of Kidney Disorders using Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Shivam Rajput, Rishabha Malviya, Prerna Uniyal
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2024; 30(11): 825. CrossRef - Timosaponin BII inhibits TGF‐β mediated epithelial‐mesenchymal transition through Smad‐dependent pathway during pulmonary fibrosis
Dali Ding, Xuebin Shen, Lizhen Yu, Yueyue Zheng, Yao Liu, Wei Wang, Li Liu, Zitong Zhao, Sihui Nian, Limin Liu
Phytotherapy Research.2023; 37(7): 2787. CrossRef - Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) endocrines et fibrogenèse pulmonaire
M. Ghanem, A. Mailleux, B. Crestani
Revue des Maladies Respiratoires.2023; 40(3): 239. CrossRef - Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in Kidney Diseases: Potential and Challenges
Fukun Chen, NaNa Chen, Chunjuan Xia, Hongyue Wang, Lishi Shao, Chen Zhou, Jiaping Wang
Cell Transplantation.2023; 32: 096368972311642. CrossRef - MicroRNA functional metal-organic framework nanocomposite for efficient inhibition of drug-resistant breast cancer cells
Yuxin Shen, Yao Zhang, Xiyue Gao, Mengdi Shang, Yanfei Cai, Zhaoqi Yang
Emergent Materials.2023; 6(5): 1537. CrossRef - Downregulation of a potential therapeutic target NPAS2, regulated by p53, alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via suppressing HES1
Yingying Chen, Zhong He, Bo Zhao, Rui Zheng
Cellular Signalling.2023; 109: 110795. CrossRef - KLF5/MDM2 Axis Modulates Oxidative Stress and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Lens Epithelial Cells: The Role in Diabetic Cataract
Xiao Li, Doudou Chen, Bowen Ouyang, Shengnan Wang, Yawei Li, Li Li, Siquan Zhu, Guangying Zheng
Laboratory Investigation.2023; 103(11): 100226. CrossRef - MAP3K19 Promotes the Progression of Tuberculosis-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Through Activation of the TGF-β/Smad2 Signaling Pathway
Yu Xia, Haiyue Wang, Meihua Shao, Xuemei Liu, Feng Sun
Molecular Biotechnology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus intestinal damp-heat syndrome and the therapeutic effect of Gegen Qinlian Decoction from the perspective of exosomal miRNA
LiSha He, Tingting Bao, Yingying Yang, Han Wang, Chengjuan Gu, Jia Chen, Tiangang Zhai, Xinhui He, Mengyi Wu, Linhua Zhao, Xiaolin Tong
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2022; 285: 114786. CrossRef - Cardamomin protects from diabetes-induced kidney damage through modulating PI3K/AKT and JAK/STAT signaling pathways in rats
Chan Gao, Xiao Fei, Ming Wang, Qi Chen, Ning Zhao
International Immunopharmacology.2022; 107: 108610. CrossRef - Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Predicts Short-Term Prognosis in Patients With Acute Heart Failure: A Prospective Cohort Study
Guihai Wu, Shenglin Wu, Jingyi Yan, Shanshan Gao, Jinxiu Zhu, Minghui Yue, Zexin Li, Xuerui Tan
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Fibrotic Diseases
Min-Qi Jia, Cha-Xiang Guan, Jia-Hao Tao, Yong Zhou, Liang-Jun Yan
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Circ_FOXP1 promotes the growth and survival of high glucose-treated human trophoblast cells through the regulation of miR-508-3p/SMAD family member 2 pathway
Mingqun Li, Yuqin Huang, Hongli Xi, Wei Zhang, Ziwu Xiang, Lingyun Wang, Xuanyu Li, Hongyan Guo
Endocrine Journal.2022; 69(9): 1067. CrossRef - Fibroblast growth factor 21 attenuates the progression of hyperuricemic nephropathy through inhibiting inflammation, fibrosis and oxidative stress
Xinghao Jiang, Qing Wu, Yeboah Kwaku Opoku, Yimeng Zou, Dan Wang, Changhui Hu, Guiping Ren
Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology.2022; 131(6): 474. CrossRef - Myokines: Novel therapeutic targets for diabetic nephropathy
Ming Yang, Shilu Luo, Jinfei Yang, Wei Chen, Liyu He, Di Liu, Li Zhao, Xi Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dojuksan ameliorates tubulointerstitial fibrosis through irisin-mediated muscle-kidney crosstalk
Songling Jiang, Dal-Seok Oh, Debra Dorotea, Eunjung Son, Dong-Seon Kim, Hunjoo Ha
Phytomedicine.2021; 80: 153393. CrossRef - Chromatin accessibility of kidney tubular cells under stress reveals key transcription factor mediating acute and chronic kidney disease
Yuexian Xing, Qi Wang, Jing Zhang, Wenju Li, Aiping Duan, Jingping Yang, Zhihong Liu
The FEBS Journal.2021; 288(18): 5446. CrossRef - Small molecules against the origin and activation of myofibroblast for renal interstitial fibrosis therapy
Ya-long Feng, Wen-bo Wang, Yue Ning, Hua Chen, Pei Liu
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 139: 111386. CrossRef - FGF21 prevents low-protein diet-induced renal inflammation in aged mice
Han Fang, Sujoy Ghosh, Landon C. Sims, Kirsten P. Stone, Cristal M. Hill, Denisha Spires, Daria V. Ilatovskaya, Christopher D. Morrison, Thomas W. Gettys, Krisztian Stadler
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2021; 321(3): F356. CrossRef - IFN-α-2b Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblasts via the TGFβ/Smad Signaling Pathway to Reduce Postoperative Epidural Fibrosis
Zhendong Liu, Hui Chen, Zhehao Fan, Jihang Dai, Yu Sun, Lianqi Yan, Rui Wang, Xiaolei Li, Jingcheng Wang
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research.2021; 41(8): 271. CrossRef - FOXN3 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion via modulating the AKT/MDM2/p53 axis in human glioma
Chaojia Wang, Hanjun Tu, Ling Yang, Chunming Ma, Juntao Hu, Jie Luo, Hui Wang
Aging.2021; 13(17): 21587. CrossRef - Regulation and Potential Biological Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Chronic Kidney Disease
Xue Zhou, Yuefeng Zhang, Ning Wang
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Multiple Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factor in Diabetic Nephropathy
Junyu Deng, Ye Liu, Yiqiu Liu, Wei Li, Xuqiang Nie
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 5273. CrossRef - Exercise Training Alleviates Cardiac Fibrosis through Increasing Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and Regulating TGF-β1-Smad2/3-MMP2/9 Signaling in Mice with Myocardial Infarction
Yixuan Ma, Yixin Kuang, Wenyan Bo, Qiaoqin Liang, Wenfei Zhu, Mengxin Cai, Zhenjun Tian
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(22): 12341. CrossRef - Snai1-induced partial epithelial–mesenchymal transition orchestrates p53–p21-mediated G2/M arrest in the progression of renal fibrosis via NF-κB-mediated inflammation
Ruochen Qi, Jiyan Wang, Yamei Jiang, Yue Qiu, Ming Xu, Ruiming Rong, Tongyu Zhu
Cell Death & Disease.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Destruction of the blood-retina barrier in diabetic retinopathy depends on angiotensin-converting enzyme-mediated TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway activation
Ping Sun, Ning Xu, Yan Li, Yang Han
International Immunopharmacology.2020; 85: 106686. CrossRef Chrysophanol Inhibits the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy via Inactivation of TGF-β Pathway
Chuan Guo, Yarong Wang, Yuanlin Piao, Xiangrong Rao, Dehai Yin
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2020; Volume 14: 4951. CrossRef
- Epithelial–mesenchymal plasticity in kidney fibrosis
- Complications
- Gemigliptin Attenuates Renal Fibrosis Through Down-Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome
- Jung Beom Seo, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Hye-In Woo, Yun-A Jung, Sungwoo Lee, Seunghyeong Lee, Mihyang Park, In-Kyu Lee, Gwon-Soo Jung, Keun-Gyu Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):830-839. Published online March 5, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0181
- 5,498 View
- 128 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The hypoglycemic drugs dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors have proven protective effects on diabetic kidney disease, including renal fibrosis. Although NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation is known to play an important role in the progression of renal fibrosis, the impact of DPP-4 inhibition on NLRP3-mediated inflammation while ameliorating renal fibrosis has not been fully elucidated. Here, we report that the renoprotective effect of gemigliptin is associated with a reduction in NLRP3-mediated inflammation in a murine model of renal fibrosis.
Methods We examined the effects of gemigliptin on renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced in mice by unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Using immunohistochemical and Western blot analysis, we quantitated components of the NLRP3 inflammasome in kidneys with and without gemigliptin treatment, and
in vitro in human kidney tubular epithelial human renal proximal tubule cells (HK-2) cells, we further analyzed the effect of gemigliptin on transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-stimulated production of profibrotic proteins.Results Immunohistological examination revealed that gemigliptin ameliorated UUO-induced tubular atrophy and renal fibrosis. Gemigliptin-treated kidneys showed a reduction in levels of NLRP3, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain (ASC), caspase-1, and interleukin-1β, which had all been markedly increased by UUO. In line with the
in vivo Conclusion The present study shows that activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to UUO-induced renal fibrosis and the renoprotective effect of gemigliptin is associated with attenuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Novel pharmacological interventions for diabetic kidney disease
Seng Kiong Tan, Jairo A. Pinzon-Cortes, Mark E. Cooper
Current Opinion in Nephrology & Hypertension.2024; 33(1): 13. CrossRef - Integrated analysis reveals crosstalk between pyroptosis and immune regulation in renal fibrosis
Fengxia Bai, Longchao Han, Jifeng Yang, Yuxiu Liu, Xiangmeng Li, Yaqin Wang, Ruijian Jiang, Zhaomu Zeng, Yan Gao, Haisong Zhang
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and polystyrene microplastics co-exposure caused oxidative stress to activate NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway aggravated pyroptosis and inflammation in mouse kidney
Shanshan Li, Xuedie Gu, Muyue Zhang, Qihang Jiang, Tong Xu
Science of The Total Environment.2024; 926: 171817. CrossRef - Fluorofenidone attenuates renal fibrosis by inhibiting lysosomal cathepsin‑mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Linfeng Zheng, Wenjuan Mei, Jing Zhou, Xin Wei, Zhijuan Huang, Xiaozhen Lin, Li Zhang, Wei Liu, Qian Wu, Jinhong Li, Yan Yan
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - HIF1α-BNIP3-mediated mitophagy protects against renal fibrosis by decreasing ROS and inhibiting activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
Jialin Li, Qisheng Lin, Xinghua Shao, Shu Li, Xuying Zhu, Jingkui Wu, Shan Mou, Leyi Gu, Qin Wang, Minfang Zhang, Kaiqi Zhang, Jiayue Lu, Zhaohui Ni
Cell Death & Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pyroptosis in renal inflammation and fibrosis: current knowledge and clinical significance
Ya Liu, Haibo Lei, Wenyou Zhang, Qichang Xing, Renzhu Liu, Shiwei Wu, Zheng Liu, Qingzi Yan, Wencan Li, Xiang Liu, Yixiang Hu
Cell Death & Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Tubular injury in diabetic kidney disease: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic perspectives
Yu Wang, Mingyue Jin, Chak Kwong Cheng, Qiang Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hederagenin inhibits high glucose‐induced fibrosis in human renal cells by suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome activation through reducing cathepsin B expression
Guohua Yang, Wang Yang, Hairong Jiang, Qing Yi, Wei Ma
Chemical Biology & Drug Design.2023; 102(6): 1409. CrossRef - Obstructive nephropathy and molecular pathophysiology of renal interstitial fibrosis
Rikke Nørregaard, Henricus A. M. Mutsaers, Jørgen Frøkiær, Tae-Hwan Kwon
Physiological Reviews.2023; 103(4): 2847. CrossRef - Adenine model of chronic renal failure in rats to determine whether MCC950, an NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor, is a renopreventive
Mahmoud S. Sabra, Fahmy K. Hemida, Essmat A. H. Allam
BMC Nephrology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gut microbiota dysbiosis promotes age-related atrial fibrillation by lipopolysaccharide and glucose-induced activation of NLRP3-inflammasome
Yun Zhang, Song Zhang, Bolin Li, Yingchun Luo, Yongtai Gong, Xuexin Jin, Jiawei Zhang, Yun Zhou, Xiaozhen Zhuo, Zixi Wang, Xinbo Zhao, Xuejie Han, Yunlong Gao, Hui Yu, Desen Liang, Shiqi Zhao, Danghui Sun, Dingyu Wang, Wei Xu, Guangjin Qu, Wanlan Bo, Dan
Cardiovascular Research.2022; 118(3): 785. CrossRef - The NLRP3 inflammasome in fibrosis and aging: The known unknowns
Yanqing Liu, Xuezeng Xu, Wangrui Lei, Yuxuan Hou, Yan Zhang, Ran Tang, Zhi Yang, Ye Tian, Yanli Zhu, Changyu Wang, Chao Deng, Shaofei Zhang, Yang Yang
Ageing Research Reviews.2022; 79: 101638. CrossRef - Research progress of endothelial‐mesenchymal transition in diabetic kidney disease
Ying Chen, Hang Zou, Hongwei Lu, Hong Xiang, Shuhua Chen
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine.2022; 26(12): 3313. CrossRef - Exploring the mechanism of Shendi Bushen capsule in anti-renal fibrosis using metabolomics theory and network analysis
Tianwei Meng, Hong Chang, Hongyu Meng
Molecular Omics.2022; 18(9): 873. CrossRef - Gemigliptin suppresses salivary dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
Wan Seok Kang, Woo Kwon Jung, Su-Bin Park, Hyung Rae Kim, Junghyun Kim
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 137: 111297. CrossRef - Long‐Term Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibition Worsens Hypertension and Renal and Cardiac Abnormalities in Obese Spontaneously Hypertensive Heart Failure Rats
Edwin K. Jackson, Zaichuan Mi, Delbert G. Gillespie, Dongmei Cheng, Stevan P. Tofovic
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Disulfiram inhibits inflammation and fibrosis in a rat unilateral ureteral obstruction model by inhibiting gasdermin D cleavage and pyroptosis
Yu Zhang, Ruicheng Zhang, Xiaohu Han
Inflammation Research.2021; 70(5): 543. CrossRef - Inflammasome as an Effective Platform for Fibrosis Therapy
Ting-Ting Chen, Feng Xiao, Nan Li, Shan Shan, Meng Qi, Zi-Ying Wang, Sheng-Nan Zhang, Wei Wei, Wu-Yi Sun
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 1575. CrossRef - Targeting Dermal Fibroblast Subtypes in Antifibrotic Therapy: Surface Marker as a Cellular Identity or a Functional Entity?
Xin Huang, Yimin Khoong, Chengyao Han, Dai Su, Hao Ma, Shuchen Gu, Qingfeng Li, Tao Zan
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Linagliptin Protects against Endotoxin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats by Decreasing Inflammatory Cytokines and Reactive Oxygen Species
Tsung-Jui Wu, Yi-Jen Hsieh, Chia-Wen Lu, Chung-Jen Lee, Bang-Gee Hsu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(20): 11190. CrossRef - Psidium guajava Flavonoids Prevent NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Alleviate the Pancreatic Fibrosis in a Chronic Pancreatitis Mouse Model
Guixian Zhang, Liming Tang, Hongbin Liu, Dawei Liu, Manxue Wang, Jun Cai, Weijun Liu, Wei Nie, Yi Zhang, Xiaomeng Yu
The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.2021; 49(08): 2001. CrossRef - Effect and Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome During Renal Fibrosis
Hong Zhang, Zhengchao Wang
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Zhen-Wu-Tang Protects IgA Nephropathy in Rats by Regulating Exosomes to Inhibit NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway
Honglian Li, Ruirui Lu, Yu Pang, Jicheng Li, Yiwen Cao, Hongxin Fu, Guoxing Fang, Qiuhe Chen, Bihao Liu, Junbiao Wu, Yuan Zhou, Jiuyao Zhou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Protective effect of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on diaphragm muscle fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
Rui Yang, Qiang Jia, Yan Li, Shomaila Mehmood
Experimental Biology and Medicine.2020; 245(14): 1280. CrossRef
- Novel pharmacological interventions for diabetic kidney disease
- Complication
- Soluble Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Levels Are Associated with Decreased Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Eun-Hee Cho, Sang-Wook Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):97-104. Published online October 8, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0030
- 4,336 View
- 52 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) is strongly expressed in the kidney, and soluble levels of this protein are used as a marker in various chronic inflammatory diseases, including diabetes, coronary artery disease, and cancer. This study examined the association between the serum soluble DPP-4 levels and renal function or cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods In this retrospective analysis, soluble DPP-4 levels were measured in preserved sera from 140 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who had participated in our previous coronary artery calcium (CAC) score study.
Results The mean±standard deviation soluble DPP-4 levels in our study sample were 645±152 ng/mL. Univariate analyses revealed significant correlations of soluble DPP-4 levels with the total cholesterol (
r =0.214,P =0.019) and serum creatinine levels (r =−0.315,P <0.001) and the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR; estimated using the modification of diet in renal disease equation) (r =0.303,P =0.001). The associations of soluble DPP-4 levels with serum creatinine and GFR remained significant after adjusting for age, body mass index, and duration of diabetes. However, no associations were observed between soluble DPP-4 levels and the body mass index, waist circumference, or CAC score.Conclusion These data suggest the potential use of serum soluble DPP-4 levels as a future biomarker of deteriorated renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sitagliptin Mitigates Diabetic Nephropathy in a Rat Model of Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes: Possible Role of PTP1B/JAK-STAT Pathway
Sarah M. AL-Qabbaa, Samaher I. Qaboli, Tahani K. Alshammari, Maha A. Alamin, Haya M. Alrajeh, Lama A. Almuthnabi, Rana R. Alotaibi, Asma S. Alonazi, Anfal F. Bin Dayel, Nawal M. Alrasheed, Nouf M. Alrasheed
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6532. CrossRef - Evaluation of the efficacy of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 enzyme and selenium element in people with kidney failure in Kirkuk governorate
Ibrahim Abdullah Ali Al-Jubouri, Nadia Ahmed Saleh Al-Jubouri
Materials Today: Proceedings.2022; 60: 795. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Effects of Incretin-Based Therapies: Integrating Mechanisms With Cardiovascular Outcome Trials
John R. Ussher, Amanda A. Greenwell, My-Anh Nguyen, Erin E. Mulvihill
Diabetes.2022; 71(2): 173. CrossRef - Computer-Aided Screening of Phytoconstituents from Ocimum tenuiflorum against Diabetes Mellitus Targeting DPP4 Inhibition: A Combination of Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, and Pharmacokinetics Approaches
Harshit Sajal, Shashank M. Patil, Ranjith Raj, Abdullah M. Shbeer, Mohammed Ageel, Ramith Ramu
Molecules.2022; 27(16): 5133. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - An update on the interaction between COVID-19, vaccines, and diabetic kidney disease
Yang Yang, Shubiao Zou, Gaosi Xu
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Lobeglitazone Versus Pioglitazone on Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(1): 171. CrossRef - Renoprotective Effects of DPP-4 Inhibitors
Daiji Kawanami, Yuichi Takashi, Hiroyuki Takahashi, Ryoko Motonaga, Makito Tanabe
Antioxidants.2021; 10(2): 246. CrossRef - Serum levels of soluble dipeptidyl peptidase-4 in type 2 diabetes are associated with severity of liver fibrosis evaluated by transient elastography (FibroScan) and the FAST (FibroScan-AST) score, a novel index of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with signif
Masaaki Sagara, Toshie Iijima, Masato Kase, Kanako Kato, Shintaro Sakurai, Takuya Tomaru, Teruo Jojima, Isao Usui, Yoshimasa Aso
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(5): 107885. CrossRef - Distinctive CD26 Expression on CD4 T-Cell Subsets
Oscar J. Cordero, Carlos Rafael-Vidal, Rubén Varela-Calviño, Cristina Calviño-Sampedro, Beatriz Malvar-Fernández, Samuel García, Juan E. Viñuela, José M. Pego-Reigosa
Biomolecules.2021; 11(10): 1446. CrossRef - The Long-Term Study of Urinary Biomarkers of Renal Injury in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Sebastián Montoro-Molina, Andrés Quesada, Francisco O’Valle, Natividad Martín Morales, María del Carmen de Gracia, Isabel Rodríguez-Gómez, Antonio Osuna, Rosemary Wangensteen, Félix Vargas
Kidney and Blood Pressure Research.2021; 46(4): 502. CrossRef - Serum Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 level is related to adiposity in type 1 diabetic adolescents
Amany Ibrahim, Shaimaa Salah, Mona Attia, Hanan Madani, Samah Ahmad, Noha Arafa, Hend Soliman
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(4): 609. CrossRef - Phase I study of YS110, a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody to CD26, in Japanese patients with advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma
Masayuki Takeda, Yuichiro Ohe, Hidehito Horinouchi, Toyoaki Hida, Junichi Shimizu, Takashi Seto, Kaname Nosaki, Takumi Kishimoto, Itaru Miyashita, Masayuki Yamada, Yutaro Kaneko, Chikao Morimoto, Kazuhiko Nakagawa
Lung Cancer.2019; 137: 64. CrossRef
- Sitagliptin Mitigates Diabetic Nephropathy in a Rat Model of Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes: Possible Role of PTP1B/JAK-STAT Pathway
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Associations between Body Mass Index and Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: Findings from the Northeast of Thailand
- Sojib Bin Zaman, Naznin Hossain, Muntasirur Rahman
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(4):330-337. Published online August 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0052
- 3,891 View
- 55 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has emerged as a public health burden globally. Obesity and long-term hyperglycaemia can initiate the renal vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study aimed to investigate the association of body mass index (BMI) with the CKD in patients with T2DM.
Methods This study has used retrospective medical records, biochemical reports, and anthropometric measurements of 3,580 T2DM patients which were collected between January to December 2015 from a district hospital in Thailand. CKD was defined according to the measurement of estimated glomerular filtration rate (<60 mL/min/1.73 m2). Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to explore the association between BMI and CKD in patients with T2DM.
Results The mean age of the participants was 60.86±9.67 years, 53.68% had poor glycaemic control, and 45.21% were overweight. About one-in-four (23.26%) T2DM patients had CKD. The mean BMI of non-CKD group was slightly higher (25.30 kg/m2 vs. 24.30 kg/m2) when compared with CKD patients. Multivariable analysis showed that older age, female sex, hypertension, and microalbuminuria were associated with the presence of CKD. No association was observed between CKD and poorly controlled glycosylated hemoglobin or hypercholesterolemia. Adjusted analysis further showed overweight and obesity were negatively associated with CKD (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 0.73; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.58 to 0.93) and (AOR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.35 to 0.81), respectively.
Conclusion The negative association of BMI with CKD could reflect the reverse causality. Lower BMI might not lead a diabetic patient to develop CKD, but there are possibilities that CKD leads the patient to experience reduced BMI.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and predictors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients worldwide, systematic review and meta-analysis
Eneyew Talie Fenta, Habitu Birhan Eshetu, Natnael Kebede, Eyob Ketema Bogale, Amare Zewdie, Tadele Derbew Kassie, Tadele Fentabil Anagaw, Elyas Melaku Mazengia, Sintayehu Shiferaw Gelaw
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Profile of Obesity and Comorbidities and their Correlation among Hemodialysis Patients, Elbasan
Brunilda Elezi, Skender Topi, Erjona Abazaj
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(E): 225. CrossRef - Association of eNOS and MCP-1 Genetic Variants with Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Nephropathy Susceptibility: A Case–Control and Meta-Analysis Study
Priyanka Raina, Ruhi Sikka, Himanshu Gupta, Kawaljit Matharoo, Surinder Kumar Bali, Virinder Singh, AJS Bhanwer
Biochemical Genetics.2021; 59(4): 966. CrossRef - New Pandemic: Obesity and Associated Nephropathy
Isha Sharma, Yingjun Liao, Xiaoping Zheng, Yashpal S. Kanwar
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between obesity, weight change and decreased renal function in Korean type 2 diabetic patients: a longitudinal follow-up study
Bo-Yeon Kim, Dug-Hyun Choi, Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The burden of chronic kidney disease among people with diabetes by insurance schemes: Findings from a primary referral hospital in Thailand
Sojib Bin Zaman, Rajat Das Gupta, Putthikrai Pramual, Raihan Kabir Khan, Chinakorn Sujimongkol, Naznin Hossain, Mohammad Rifat Haider, Md. Nazmul Karim, Gulam Muhammed Kibria, Sheikh Mohammdad Shariful Islam
Diabetes Epidemiology and Management.2021; 4: 100026. CrossRef - Association between body mass index and estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka
M. R. D. L. Kulathunga, M. A. A. Wijayawardena, Ravi Naidu, S. J. Wimalawansa, A. W. Wijeratne
Environmental Geochemistry and Health.2020; 42(9): 2645. CrossRef - The prevalence of diabetic chronic kidney disease in adult Greek subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A series from hospital-based diabetes clinics
Ilias N. Migdalis, Nikolaos Papanas, Athanasios E. Raptis, Ioannis M. Ioannidis, Alexios E. Sotiropoulos, George D. Dimitriadis
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 166: 108243. CrossRef - Underweight Increases the Risk of End-Stage Renal Diseases for Type 2 Diabetes in Korean Population: Data From the National Health Insurance Service Health Checkups 2009–2017
Yang-Hyun Kim, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Kyung-do Han, Sung-Hee Ihm, Kyung-Hwan Cho, Yong-Gyu Park
Diabetes Care.2020; 43(5): 1118. CrossRef - Prevalence and risk factors of chronic kidney disease among Palestinian type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study
Zaher Nazzal, Zakaria Hamdan, Dunia Masri, Oday Abu-Kaf, Mohammad Hamad
BMC Nephrology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Variability in Blood Pressure, Glucose, and Cholesterol Concentrations, and Body Mass Index on End-Stage Renal Disease in the General Population of Korea
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(5): 755. CrossRef
- Prevalence and predictors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients worldwide, systematic review and meta-analysis
- Complications
- Glycated Albumin Is a More Useful Glycation Index than HbA1c for Reflecting Renal Tubulopathy in Subjects with Early Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Ji Hye Huh, Minyoung Lee, So Young Park, Jae Hyeon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):215-223. Published online May 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0091
- 4,491 View
- 52 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study was to investigate which glycemic parameters better reflect urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (uNAG) abnormality, a marker for renal tubulopathy, in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) subjects with normoalbuminuria and a normal estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
Methods We classified 1,061 participants with T2DM into two groups according to uNAG level—normal vs. high (>5.8 U/g creatinine)—and measured their biochemical parameters.
Results Subjects with high uNAG level had significantly higher levels of fasting and stimulated glucose, glycated albumin (GA), and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and lower levels of homeostasis model assessment of β-cell compared with subjects with normal uNAG level. Multiple linear regression analyses showed that uNAG was significantly associated with GA (standardized β coefficient [β]=0.213,
P =0.016), but not with HbA1c (β=−0.137,P =0.096) or stimulated glucose (β=0.095,P =0.140) after adjusting confounding factors. In receiver operating characteristic analysis, the value of the area under the curve (AUC) for renal tubular injury of GA was significantly higher (AUC=0.634; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.646 to 0.899) than those for HbA1c (AUC=0.598; 95% CI, 0.553 to 0.640), stimulated glucose (AUC=0.594; 95% CI, 0.552 to 0.636), or fasting glucose (AUC=0.558; 95% CI, 0.515 to 0.600). The optimal GA cutoff point for renal tubular damage was 17.55% (sensitivity 59%, specificity 62%).Conclusion GA is a more useful glycation index than HbA1c for reflecting renal tubulopathy in subjects with T2DM with normoalbuminuria and normal eGFR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Improves Renal Tubular Damage in Mice with Diabetic Kidney Disease
Ran Li, Dunmin She, Zhengqin Ye, Ping Fang, Guannan Zong, Yong Zhao, Kerong Hu, Liya Zhang, Sha Lei, Keqin Zhang, Ying Xue
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1331. CrossRef - Use of glycated albumin for the identification of diabetes in subjects from northeast China
Guo-Yan Li, Hao-Yu Li, Qiang Li
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(2): 149. CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease, Cardiovascular Disease and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A New Triumvirate?
Carolina M. Perdomo, Nuria Garcia-Fernandez, Javier Escalada
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(9): 2040. CrossRef - Empagliflozin reduces high glucose-induced oxidative stress and miR-21-dependent TRAF3IP2 induction and RECK suppression, and inhibits human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Nitin A. Das, Andrea J. Carpenter, Anthony Belenchia, Annayya R. Aroor, Makoto Noda, Ulrich Siebenlist, Bysani Chandrasekar, Vincent G. DeMarco
Cellular Signalling.2020; 68: 109506. CrossRef - Glycated Plasma Proteins as More Sensitive Markers for Glycemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes
Lina Zhang, Qibin Zhang
PROTEOMICS – Clinical Applications.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycated albumin and its variability: Clinical significance, research progress and overall review
Dongjun Dai, Yifei Mo, Jian Zhou
Obesity Medicine.2020; 19: 100256. CrossRef - Hepatic fibrosis is associated with total proteinuria in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes
Eugene Han, Yongin Cho, Kyung-won Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-wan Lee
Medicine.2020; 99(33): e21038. CrossRef - Increasing waist circumference is associated with decreased levels of glycated albumin
Yiting Xu, Xiaojing Ma, Yun Shen, Yufei Wang, Jian Zhou, Yuqian Bao
Clinica Chimica Acta.2019; 495: 118. CrossRef - Glucometabolic characteristics and higher vascular complication risk in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes with non-albumin proteinuria
Yongin Cho, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-soo Cha, Byung-wan Lee
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(8): 585. CrossRef - Association of urinary acidification function with the progression of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Huanhuan Zhu, Xi Liu, Chengning Zhang, Qing Li, Xiaofei An, Simeng Liu, Lin Wu, Bo Zhang, Yanggang Yuan, Changying Xing
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(11): 107419. CrossRef
- Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Improves Renal Tubular Damage in Mice with Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Others
- The Effect of Glycemic Status on Kidney Stone Disease in Patients with Prediabetes
- Tzu-Hsien Lien, Jin-Shang Wu, Yi-Ching Yang, Zih-Jie Sun, Chih-Jen Chang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(2):161-166. Published online April 25, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.2.161
- 2,982 View
- 29 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background While the evidence supporting a positive association between diabetes mellitus and kidney stone disease (KSD) is solid, studies examining the association between impaired fasting glucose (IFG) and KSD show inconsistent results. Currently, there are no studies examining the relationship between impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and KSD. The objective of this study is to investigate the effects of different glycemic statuses on KSD. The results may help to motivate patients with diabetes to conform to treatment regimens.
Methods We conducted a cross sectional study of a population that underwent health check-ups between January 2000 and August 2009 at the Health Evaluation Center of National Cheng Kung University Hospital. A total of 14,186 subjects were enrolled. The following categories of glycemic status were used according to the criteria of the 2009 American Diabetes Association: normal glucose tolerance, isolated IGT, isolated IFG, combined IFG/IGT, and diabetes. The existence of KSD was evaluated using renal ultrasonography, and the presence of any hyperechoic structures causing acoustic shadowing was considered to be indicative of KSD.
Results The prevalence of KSD was 7.4% (712/9,621), 9.3% (163/1,755), 10.8% (78/719), 12.0% (66/548), and 11.3% (174/1,543) in subjects with NGT, isolated IGT, isolated IFG, combined IFG/IGT, and diabetes, respectively. Isolated IFG, combined IFG/IGT, and diabetes were associated with KSD after adjusting for other clinical variables, but isolated IGT was not. Age (41 to 64 years vs. ≤40 years, ≥65 years vs. ≤40 years), male gender, hypertension, and hyperuricemia were also independently associated with KSD.
Conclusion Isolated IFG, combined IFG/IGT, and diabetes, but not isolated IGT, were associated with a higher risk of KSD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Related Risk Factor Analysis for Upper Urinary Tract Stones in Patients with Abnormal Glucose Metabolism
泽伟 于
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(02): 749. CrossRef - Nephrolithiasis: A Red Flag for Cardiovascular Risk
Alessia Gambaro, Gianmarco Lombardi, Chiara Caletti, Flavio Luciano Ribichini, Pietro Manuel Ferraro, Giovanni Gambaro
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(19): 5512. CrossRef - Association between metabolic syndrome components and the risk of developing nephrolithiasis: A systematic review and bayesian meta-analysis
Ilham Akbar Rahman, Ilham Fauzan Nusaly, Syakri Syahrir, Harry Nusaly, Makbul Aman Mansyur
F1000Research.2021; 10: 104. CrossRef - Glycemic Status, Insulin Resistance, and the Risk of Nephrolithiasis: A Cohort Study
Seolhye Kim, Yoosoo Chang, Hyun-Suk Jung, Young Youl Hyun, Kyu-Beck Lee, Kwan Joong Joo, Heung Jae Park, Young-Sam Cho, Hyeonyoung Ko, Eunju Sung, Hocheol Shin, Seungho Ryu
American Journal of Kidney Diseases.2020; 76(5): 658. CrossRef - Associations between nephrolithiasis and diabetes mellitus, hypertension and gallstones: A meta‐analysis of cohort studies
Bing‐Biao Lin, Rong‐Hua Huang, Bing‐Liang Lin, Ying‐Kai Hong, Ming‐En Lin, Xue‐Jun He
Nephrology.2020; 25(9): 691. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Urolithiasis (Review)
В. А. Слободянюк
Health of Man.2020; (1): 75. CrossRef - Re: Evidence of Disordered Calcium Metabolism in Adolescent Girls with Type 1 Diabetes: An Observational Study Using a Dual-Stable Calcium Isotope Technique
Dean G. Assimos
Journal of Urology.2018; 199(2): 335. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and uric acid nephrolithiasis: insulin resistance in focus
Leonardo Spatola, Pietro Manuel Ferraro, Giovanni Gambaro, Salvatore Badalamenti, Marco Dauriz
Metabolism.2018; 83: 225. CrossRef - Kidney stones diseases and glycaemic statuses: focus on the latest clinical evidences
Leonardo Spatola, Claudio Angelini, Salvatore Badalamenti, Silvio Maringhini, Giovanni Gambaro
Urolithiasis.2017; 45(5): 457. CrossRef
- Related Risk Factor Analysis for Upper Urinary Tract Stones in Patients with Abnormal Glucose Metabolism
- Chronic Kidney Disease and Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Chinese with Type 2 Diabetes
- Qing-Lin Lou, Xiao-Jun Ouyang, Liu-Bao Gu, Yong-Zhen Mo, Ronald Ma, Jennifer Nan, Alice Kong, Wing-Yee So, Gary Ko, Juliana Chan, Chun-Chung Chow, Rong-Wen Bian
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(6):433-442. Published online December 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.6.433
- 3,898 View
- 42 Download
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background To determine the frequency of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and its associated risk factors in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients, we conducted a cross-sectional study in Nanjing, China, in the period between January 2008 and December 2009.
Methods Patients with type 2 diabetes under the care by Jiangsu Province Official Hospital, Nanjing, China were invited for assessment. CKD was defined as the presence of albuminuria or estimated glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Albuminuria was defined as urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio ≥30 mg/g.
Results We recruited 1,521 urban Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes (mean age, 63.9±12.0 years). The frequency of CKD and albuminuria was 31.0% and 28.9%, respectively. After adjusted by age and sex, hypertension, anemia and duration of diabetes were significantly associated with CKD with odds ratio (95% confidence interval) being 1.93 (1.28 to 2.93), 1.70 (1.09 to 2.64), and 1.03 (1.00 to 1.06), respectively.
Conclusion In conclusion, CKD was common in the urban Nanjing Chinese with type 2 diabetes. Strategies to prevent or delay progression of kidney disease in diabetes should be carried out at the early disease course of type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations between dietary patterns and renal impairment in individuals with diabetes: a cross‐sectional study
Ziling Ding, Xingzhe Wu, Chao Liu, Ruixue Ying, Yi Zhang, Shiqi Zhang, Qiu Zhang, Honglin Hu, Fang Dai
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2024; 37(1): 193. CrossRef - A Randomised Controlled Study of Can Ling Bai Shu San Combined with Guizhi Fuling Pills and Dagliflozin in the Treatment of Proteinuria in Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy Stage IV
杰 张
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(01): 1829. CrossRef - Factors influencing optimal diabetes care and clinical outcomes in Thai patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a multilevel modelling analysis
Apinya Surawit, Tanyaporn Pongkunakorn, Thamonwan Manosan, Pichanun Mongkolsucharitkul, Parinya Chamnan, Krishna Suvarnabhumi, Thanapat Puangpet, Sophida Suta, Sureeporn Pumeiam, Bonggochpass Pinsawas, Suphawan Ophakas, Sananon Pisitpornsuk, Chalita Utchi
BMJ Open.2024; 14(5): e079415. CrossRef - Evaluation of Renal Impairment in Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease by Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine
Yi-lun Qu, Zhe-yi Dong, Hai-mei Cheng, Qian Liu, Qian Wang, Hong-tao Yang, Yong-hui Mao, Ji-jun Li, Hong-fang Liu, Yan-qiu Geng, Wen Huang, Wen-hu Liu, Hui-di Xie, Fei Peng, Shuang Li, Shuang-shuang Jiang, Wei-zhen Li, Shu-wei Duan, Zhe Feng, Wei-guang Zh
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine.2023; 29(4): 308. CrossRef - Extracellular status of thrombospondin-2 in type 2 diabetes mellitus and utility as a biomarker in the determination of early diabetic kidney disease
Zhenzhen Lin, Didong Zhang, Xinxin Zhang, Wanxie Guo, Wenjun Wang, Yingchao Zhang, Zhen Liu, Yanxue Bi, Maolan Wu, Zhuofeng Lin, Xuemian Lu
BMC Nephrology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Lipocalin-2 Levels Are Increased and Independently Associated With Early-Stage Renal Damage and Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque in Patients With T2DM
Jing Gan, Yu Zheng, Qiongli Yu, Yingchao Zhang, Wei Xie, Yaru Shi, Ning Yu, Yu Yan, Zhuofeng Lin, Hong Yang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Prevalence, Progress and Risk Factor Control of Chronic Kidney Disease in Chinese Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Primary Care
Lingwang An, Qiuzhi Yu, Hong Tang, Xianglan Li, Dandan Wang, Qi Tang, Haiyang Xing, Yali He, Xiaona Zhao, Shuhui Zhao, Yaujiunn Lee, Juming Lu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydration status according to impedance vectors and its association with clinical and biochemical outcomes and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease
Paola Vanessa Miranda Alatriste, Eloísa Colin Ramírez, Ximena Atilano Carsi, Cristino Cruz-Rivera, Ángeles Espinosa-Cuevas
Nutrición Hospitalaria.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Prevalence of Diabetic Microvascular Complications in China and the USA
Yu Kuei Lin, Bixia Gao, Lili Liu, Lynn Ang, Kara Mizokami-Stout, Rodica Pop-Busui, Luxia Zhang
Current Diabetes Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Reno-protective potential of sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: Summary evidence from clinical and real-world data
Niti Mittal, Vikas Sehray, Rakesh Mittal, Surjit Singh
European Journal of Pharmacology.2021; 907: 174320. CrossRef - Association between Renal Podocalyxin Expression and Renal Dysfunction in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: A Single-Center, Retrospective Case-Control Study
Rongzhen Wang, Can Yao, Feng Liu
BioMed Research International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Renoprotection with SGLT2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes over a spectrum of cardiovascular and renal risk
Francesco Giorgino, Jiten Vora, Peter Fenici, Anna Solini
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of diabetic nephropathy among Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and different categories of their estimated glomerular filtration rate based on the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation in primary car
Ka Yee Mok, Pang Fai Chan, Loretta K. P. Lai, Kai Lim Chow, David V. K. Chao
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2019; 18(2): 281. CrossRef - The association between serum uric acid to creatinine ratio and renal disease progression in type 2 diabetic patients in Chinese communities
Yao Chunlei, Gu Liubao, Wang Tao, Xing Changying
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(7): 473. CrossRef - Risk factors of chronic kidney diseases in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes
Lin Yang, Tsun Kit Chu, Jinxiao Lian, Cheuk Wai Lo, Pak Ki Lau, Hairong Nan, Jun Liang
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Any grade of relative overhydration is associated with long-term mortality in patients with Stages 4 and 5 non-dialysis chronic kidney disease
Almudena Vega, Soraya Abad, Nicolás Macías, Inés Aragoncillo, Ana García-Prieto, Tania Linares, Esther Torres, Andrés Hernández, José Luño
Clinical Kidney Journal.2018; 11(3): 372. CrossRef - The impact of the quality of care and other factors on progression of chronic kidney disease in Thai patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A nationwide cohort study
Paithoon Sonthon, Supannee Promthet, Siribha Changsirikulchai, Ram Rangsin, Bandit Thinkhamrop, Suthee Rattanamongkolgul, Cameron P. Hurst, Cheng Hu
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(7): e0180977. CrossRef - Association of Chronic Kidney Disease with Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke Risks in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Xue Sun, Jie He, Xiao-Li Ji, Yi-Ming Zhao, Han-Yu Lou, Xiao-Xiao Song, Li-Zhen Shan, Ying-Xiu Kang, Wen-Heng Zeng, Xiao-Hong Pang, Song-Zhao Zhang, Yue Ding, Yue-Zhong Ren, Peng-Fei Shan
Chinese Medical Journal.2017; 130(1): 57. CrossRef - Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated factors in Chinese individuals with type 2 diabetes: Cross-sectional study
Kaifeng Guo, Lei Zhang, Fangya Zhao, Junxi Lu, Pan Pan, Haoyong Yu, Yuqian Bao, Haibing Chen, Weiping Jia
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(5): 803. CrossRef - The association between abnormal heart rate variability and new onset of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A ten-year follow-up study
Jae-Seung Yun, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Hyung-Wook Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2015; 108(1): 31. CrossRef - Association of elevated glycosylated hemoglobin A1c with hyperfiltration in a middle-aged and elderly Chinese population with prediabetes or newly diagnosed diabetes: a cross-sectional study
Wen Hu, Hairong Hao, Weinan Yu, Xiaojuan Wu, Hongwen Zhou
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Serena KM Low, Chee Fang Sum, Lee Ying Yeoh, Subramaniam Tavintharan, Xiao Wei Ng, Simon BM Lee, Wern Ee Tang, Su Chi Lim
Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.2015; 44(5): 164. CrossRef - Low Ankle-Brachial Index Is Associated with Early-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetic Patients Independent of Albuminuria
Xuehong Dong, Dingting Wu, Chengfang Jia, Yu Ruan, Xiaocheng Feng, Guoxing Wang, Jun Liu, Yi Shen, Hong Li, Lianxi Li, Karin Jandeleit-Dahm
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(10): e109641. CrossRef - Health Behaviors and Risk Factors Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Korean Patients with Diabetes: The Fourth Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey
Suk Jeong Lee, Chae Weon Chung
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(1): 8. CrossRef - Urinary miR-29 Correlates with Albuminuria and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Hui Peng, Meirong Zhong, Wenbo Zhao, Cheng Wang, Jun Zhang, Xun Liu, Yuanqing Li, Sujay Dutta Paudel, Qianqian Wang, Tanqi Lou, Emmanuel A. Burdmann
PLoS ONE.2013; 8(12): e82607. CrossRef - Diabetes and its comorbidities—where East meets West
Alice P. S. Kong, Gang Xu, Nicola Brown, Wing-Yee So, Ronald C. W. Ma, Juliana C. N. Chan
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2013; 9(9): 537. CrossRef
- Associations between dietary patterns and renal impairment in individuals with diabetes: a cross‐sectional study
- Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Levels in Comparison with Glomerular Filtration Rate for Evaluation of Renal Function in Patients with Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease
- Kwang-Sook Woo, Jae-Lim Choi, Bo-Ram Kim, Ji-Eun Kim, Won-Suk An, Jin-Yeong Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(4):307-313. Published online August 20, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.4.307
- 4,160 View
- 27 Download
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is a promising biomarker of acute kidney injury. There is a growing body of evidence suggesting that NGAL is also a marker of kidney disease and severity in chronic kidney disease (CKD). We studied the utility of urinary NGAL in more accurately predicting renal function in patients with diabetic CKD.
Methods We studied possible relationships between urinary NGAL, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and proteinuria in diabetic CKD patients and in healthy populations.
Results Urinary NGAL levels were significantly higher in CKD patients than in healthy controls (96.0 [2.7 to 975.2] ng/mL vs. 18.8 [1.3 to 81.9] ng/mL,
P =0.02), and the GFR was lower among CKD patients (49.3 [13.1 to 78.3] mL/min/1.73 m2 vs. 85.6 [72 to 106.7] mL/min/1.73 m2,P <0.0001). The urinary NGAL level showed a significant inverse correlation with GFR (r =-0.5634,P <0.0001). The correlation analyses between urinary protein level and urinary NGAL levels and GFR were as follows: urine protein and urinary NGAL (r =0.3009,P =0.0256), urine protein and GFR (r =-0.6245,P <0.0001), urine microalbumin and urinary NGAL (r =0.1794,P =0.2275), and urine microalbumin and GFR (r =-0.5190,P =0.0002).Conclusion From these results, we concluded that urinary NGAL is a reliable marker of renal function in diabetic CKD patients. However, urinary NGAL did not provide more accurate information regarding renal function than GFR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nanoparticle-antibody conjugate-based immunoassays for detection of CKD-associated biomarkers
Monika Chhillar, Deepak kukkar, Preeti Kukkar, Ki-Hyun Kim
TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry.2023; 158: 116857. CrossRef - Fecal and Urinary Adipokines as Disease Biomarkers
Hauke C. Tews, Tanja Elger, Thomas Grewal, Simon Weidlich, Francesco Vitali, Christa Buechler
Biomedicines.2023; 11(4): 1186. CrossRef - Application of SERS-based nanobiosensors to metabolite biomarkers of CKD
Deepak Kukkar, Monika Chhillar, Ki-Hyun Kim
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2023; 232: 115311. CrossRef - A New Clinical Utility for Tubular Markers to Identify Kidney Responders to Saxagliptin Treatment in Adults With Diabetic Nephropathy
Marwa Mohsen, Ahmed A. Elberry, Alaa Mohamed Rabea, Doaa Mahmoud Khalil, Mohamed E.A. Abdelrahim, Raghda R.S. Hussein
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2022; 46(2): 134. CrossRef - Serum Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin in Patients with Toxic Nephropathies. Prospective Study
Lyudmila A. Demidchik, Valentina V. Lee, Dmitriy A. Klyuyev, Ryszhan Y. Bakirova, Vilen B. Molotov-Luchanskiy, Yelena V. Pozdnyakova, Irina V. Beinikova, Semyon S. Bobyrev
Annals of the Russian academy of medical sciences.2021; 76(2): 142. CrossRef - Assessment of Renal Function Status in Steady-State Sickle Cell Anaemic Children Using Urine Human Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Albumin:Creatinine Ratio
Olatubosun Oladipupo Olawale, Abiodun Folasade Adekanmbi, Ayobola Abimbola Sonuga, Oyebola Oluwagbemiga Sonuga, Samuel Olufemi Akodu, Morufat Mojisola Ogundeyi
Medical Principles and Practice.2021; 30(6): 557. CrossRef - Association of neutrophil-gelatinase-associated lipocalin with microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study
Erhan Aslanhan, David Ojalvo, Ekmek Burak Özsenel, Sema Ucak Basat, Fatih Borlu
Cardiovascular Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 8(3): 82. CrossRef - MicroRNA as novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets in diabetic kidney disease: An update
Qinghua Cao, Xin‐Ming Chen, Chunling Huang, Carol A. Pollock
FASEB BioAdvances.2019; 1(6): 375. CrossRef - Potential serum biomarkers for early detection of diabetic nephropathy
Tarek Kamal Motawi, Nagwa Ibrahim Shehata, Mahmoud Mohamed ElNokeety, Yasmin Farid El-Emady
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 136: 150. CrossRef - Modern methods of diagnosing chronic kidney disease in patients with diabetes mellitus
Tatiana N. Markova, Viktoriia V. Sadovskaya, Marina Y. Bespyatova
Diabetes mellitus.2018; 20(6): 454. CrossRef - Evaluation value of neutrophil gelatinase‐associated lipocalin for the renal dysfunction of patients with chronic kidney disease: A meta‐analysis
Lulu Guo, Yaya Zhao, Zhenzhu Yong, Weihong Zhao
AGING MEDICINE.2018; 1(2): 185. CrossRef - Urinary Tubular Injury Biomarkers Are Associated With ESRD and Death in the REGARDS Study
Ruth F. Dubin, Suzanne Judd, Rebecca Scherzer, Michael Shlipak, David G. Warnock, Mary Cushman, Mark Sarnak, Chirag Parikh, Michael Bennett, Neil Powe, Carmen A. Peralta
Kidney International Reports.2018; 3(5): 1183. CrossRef - Add-on plasmonic patch as a universal fluorescence enhancer
Jingyi Luan, Jeremiah J. Morrissey, Zheyu Wang, Hamed Gholami Derami, Keng-Ku Liu, Sisi Cao, Qisheng Jiang, Congzhou Wang, Evan D. Kharasch, Rajesh R. Naik, Srikanth Singamaneni
Light: Science & Applications.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum NGAL and Cystatin C Comparison With Urinary Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio and Inflammatory Biomarkers as Early Predictors of Renal Dysfunction in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Marcelo R. Bacci, Ethel Z. Chehter, Ligia A. Azzalis, Beatriz Costa de Aguiar Alves, Fernando L.A. Fonseca
Kidney International Reports.2017; 2(2): 152. CrossRef - Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin to predict renal response after induction therapy in active lupus nephritis
Bancha Satirapoj, Chagriya Kitiyakara, Asada Leelahavanichkul, Yingyos Avihingsanon, Ouppatham Supasyndh
BMC Nephrology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) and Retinol-Binding Protein 4 (RBP4) in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Nephropathy
Mohamed H. Mahfouz, Adel M. Assiri, Mohammed H. Mukhtar
Biomarker Insights.2016; 11: BMI.S33191. CrossRef - Intra-abdominal Hypertension and Postoperative Kidney Dysfunction in Cardiac Surgery Patients
Michael A. Mazzeffi, Patrick Stafford, Karin Wallace, Wendy Bernstein, Seema Deshpande, Patrick Odonkor, Ashanpreet Grewal, Erik Strauss, Latoya Stubbs, James Gammie, Peter Rock
Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia.2016; 30(6): 1571. CrossRef - Effects of Therapy on Urine Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Nondiabetic Glomerular Diseases with Proteinuria
Amnuay Sirisopha, Somlak Vanavanan, Anchalee Chittamma, Bunyong Phakdeekitcharoen, Ammarin Thakkinstian, Amornpan Lertrit, Nuankanya Sathirapongsasuti, Chagriya Kitiyakara
International Journal of Nephrology.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Novel urinary biomarkers in pre-diabetic nephropathy
Vikas Garg, Manish Kumar, Himansu Sekhar Mahapatra, Anubhuti Chitkara, Adesh Kumar Gadpayle, Venketansan Sekhar
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology.2015; 19(5): 895. CrossRef - High expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in the kidney proximal tubules of diabetic rats
Fenghua Liu, Huayu Yang, Haiping Chen, Mi Zhang, Qing Ma
Advances in Medical Sciences.2015; 60(1): 133. CrossRef - Anti-albuminuric effects of spironolactone in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial
Sawako Kato, Shoichi Maruyama, Hirofumi Makino, Jun Wada, Daisuke Ogawa, Takashi Uzu, Hisazumi Araki, Daisuke Koya, Keizo Kanasaki, Yutaka Oiso, Motomitsu Goto, Akira Nishiyama, Hiroyuki Kobori, Enyu Imai, Masahiko Ando, Seiichi Matsuo
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology.2015; 19(6): 1098. CrossRef - The inflammation–lipocalin 2 axis may contribute to the development of chronic kidney disease
Atsushi Hashikata, Akiko Yamashita, Shigeki Suzuki, Shintaro Nagayasu, Takanori Shinjo, Ataru Taniguchi, Mitsuo Fukushima, Yoshikatsu Nakai, Kazuko Nin, Naoya Watanabe, Tomoichiro Asano, Yoshimitsu Abiko, Akifumi Kushiyama, Shoichiro Nagasaka, Fusanori Ni
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2014; 29(3): 611. CrossRef - Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin as a Marker of Tubular Damage in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with and without Albuminuria
Abeer A. Al-Refai, Safaa I. Tayel, Ahmed Ragheb, Ashraf G. Dala, Ahmed Zahran
Open Journal of Nephrology.2014; 04(01): 37. CrossRef - Importance of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Differential Diagnosis of Acute and Chronic Renal Failure
Seda Ozkan, Polat Durukan, Cemil Kavalci, Ali Duman, Mustafa Burak Sayhan, Omer Salt, Afsin Ipekci
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined biomarkers evaluation for diagnosing kidney injury in preeclampsia
Jing Xiao, Jianying Niu, Xianwu Ye, Qianqian Yu, Yong Gu
Hypertension in Pregnancy.2013; 32(4): 439. CrossRef
- Nanoparticle-antibody conjugate-based immunoassays for detection of CKD-associated biomarkers
- Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α in Diabetic Nephropathy
- Sungjin Chung, Cheol Whee Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(4):327-336. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.327
- 65,535 View
- 47 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader With a developing worldwide epidemic of diabetes mellitus, the renal complications associated with diabetes have become a serious health concern. Primary therapy for treating diabetic nephropathy is a multifactorial process. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) agonists have been used primarily in clinical practice for the treatment of dyslipidemia and insulin resistance. Given that PPARα expression and regulation of metabolic pathways are involved in oxidative stress, inflammation, blood pressure regulation, and the renin-angiotensin aldosterone system, PPARα likely influences the development and pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy via indirect effects on glucose and lipid homeostasis and also by direct action on the kidneys. These findings suggest that PPARα may become an important therapeutic target for treating diabetic renal complications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Proteome of Circulating Large Extracellular Vesicles in Diabetes and Hypertension
Akram Abolbaghaei, Maddison Turner, Jean-François Thibodeau, Chet E. Holterman, Christopher R. J. Kennedy, Dylan Burger
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(5): 4930. CrossRef - Metformin mitigates renal dysfunction in obese insulin-resistant rats via activation of the AMPK/PPARα pathway
Laongdao Thongnak, Nattavadee Pengrattanachot, Sasivimon Promsan, Nichakorn Phengpol, Prempree Sutthasupha, Krit Jaikumkao, Anusorn Lungkaphin
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2023; 46(5): 408. CrossRef - A comprehensive insight into the molecular and cellular mechanisms of the effects of Propolis on preserving renal function: a systematic review
Paniz Anvarifard, Maryam Anbari, Alireza Ostadrahimi, Mohammadreza Ardalan, Zohreh Ghoreishi
Nutrition & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - APX-115, a pan-NADPH oxidase inhibitor, protects development of diabetic nephropathy in podocyte specific NOX5 transgenic mice
Eun Soo Lee, Hong Min Kim, Sun Hee Lee, Kyung Bong Ha, Yoon Soo Bae, Soo Jin Lee, Sung Hwan Moon, Eun Young Lee, Ji-Hye Lee, Choon Hee Chung
Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2020; 161: 92. CrossRef - Fenofibrate decreased microalbuminuria in the type 2 diabetes patients with hypertriglyceridemia
Xiaomeng Sun, Jia Liu, Guang Wang
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - AMPK allostery: A therapeutic target for the management/treatment of diabetic nephropathy
Kehinde Sulaimon Ayinde, Olamide Tosin Olaoba, Boyenle Ibrahim, Du Lei, Qian Lu, Xiaoxing Yin, Temitope Isaac Adelusi
Life Sciences.2020; 261: 118455. CrossRef - Greater efficacy of atorvastatin versus a non-statin lipid-lowering agent against renal injury: potential role as a histone deacetylase inhibitor
Ravi Shankar Singh, Dharmendra Kumar Chaudhary, Aradhana Mohan, Praveen Kumar, Chandra Prakash Chaturvedi, Carolyn M. Ecelbarger, Madan M. Godbole, Swasti Tiwari
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Upregulation of SIRT1-AMPK by thymoquinone in hepatic stellate cells ameliorates liver injury
Yong Yang, Ting Bai, You-Li Yao, De-Quan Zhang, Yan-Ling Wu, Li-Hua Lian, Ji-Xing Nan
Toxicology Letters.2016; 262: 80. CrossRef - Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α-dependent renoprotection of murine kidney by irbesartan
Makoto Harada, Yuji Kamijo, Takero Nakajima, Koji Hashimoto, Yosuke Yamada, Hisashi Shimojo, Frank J. Gonzalez, Toshifumi Aoyama
Clinical Science.2016; 130(21): 1969. CrossRef - Anthocyanin-rich Seoritae extract ameliorates renal lipotoxicity via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in diabetic mice
Eun Sil Koh, Ji Hee Lim, Min Young Kim, Sungjin Chung, Seok Joon Shin, Bum Soon Choi, Hye Won Kim, Seong Yeon Hwang, Sae Woong Kim, Cheol Whee Park, Yoon Sik Chang
Journal of Translational Medicine.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Epidemiology to Clinical Perspectives
Cheol Whee Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(4): 252. CrossRef - Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists in a battle against the aging kidney
Marijn M. Speeckaert, Céline Vanfraechem, Reinhart Speeckaert, Joris R. Delanghe
Ageing Research Reviews.2014; 14: 1. CrossRef - Fenofibrate and dipyridamole treatments in low-doses either alone or in combination blunted the development of nephropathy in diabetic rats
Pitchai Balakumar, Rajavel Varatharajan, Ying Hui Nyo, Raja Renushia, Devarajan Raaginey, Ann Nah Oh, Shaikh Sohrab Akhtar, Mani Rupeshkumar, Karupiah Sundram, Sokkalingam A. Dhanaraj
Pharmacological Research.2014; 90: 36. CrossRef - Differential effects of low-dose fenofibrate treatment in diabetic rats with early onset nephropathy and established nephropathy
Supriya Kadian, Nanjaian Mahadevan, Pitchai Balakumar
European Journal of Pharmacology.2013; 698(1-3): 388. CrossRef - Age-Associated Molecular Changes in the Kidney in Aged Mice
Ji Hee Lim, Eun Nim Kim, Min Young Kim, Sungjin Chung, Seok Joon Shin, Hyung Wook Kim, Chul Woo Yang, Yong-Soo Kim, Yoon Sik Chang, Cheol Whee Park, Bum Soon Choi
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2012; 2012: 1. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Obesity, the Metabolic Syndrome, and Chronic Kidney Disease
Rikki M. Tanner, Todd M. Brown, Paul Muntner
Current Hypertension Reports.2012; 14(2): 152. CrossRef
- The Proteome of Circulating Large Extracellular Vesicles in Diabetes and Hypertension

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





