
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
- Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):3-14. Published online January 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0335
- 14,617 View
- 890 Download
- 54 Web of Science
- 61 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
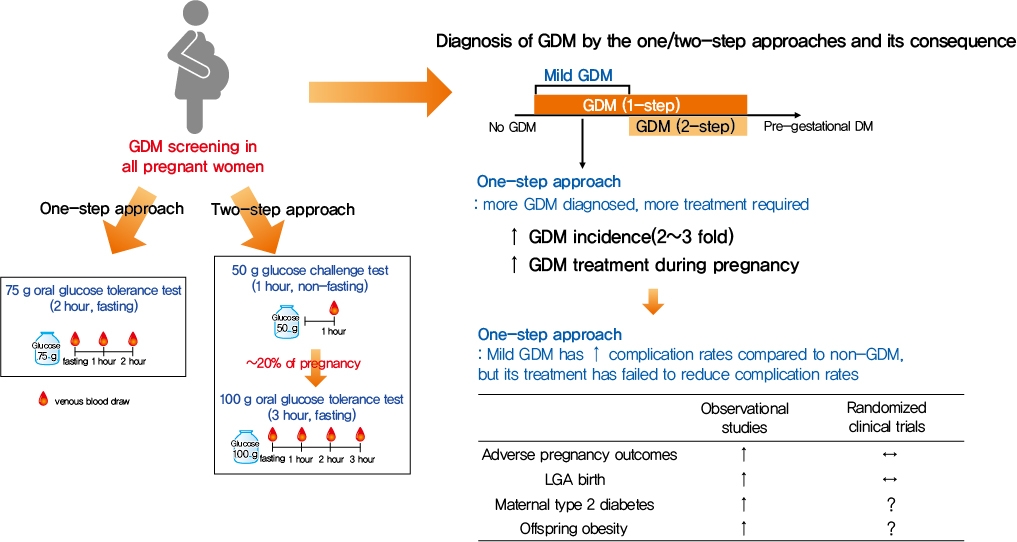
- Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is the most common complication during pregnancy and is defined as any degree of glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy. GDM is associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes and long-term offspring and maternal complications. For GDM screening and diagnosis, a two-step approach (1-hour 50 g glucose challenge test followed by 3-hour 100 g oral glucose tolerance test) has been widely used. After the Hyperglycemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcome study implemented a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test in all pregnant women, a one-step approach was recommended as an option for the diagnosis of GDM after 2010. The one-step approach has more than doubled the incidence of GDM, but its clinical benefit in reducing adverse pregnancy outcomes remains controversial. Long-term complications of mothers with GDM include type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease, and complications of their offspring include childhood obesity and glucose intolerance. The diagnostic criteria of GDM should properly classify women at risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes and long-term complications. The present review summarizes the strengths and weaknesses of the one-step and two-step approaches for the diagnosis of GDM based on recent randomized controlled trials and observational studies. We also describe the long-term maternal and offspring complications of GDM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prophylactic administration of metformin reduces gestational diabetes mellitus incidence in the high-risk populations: a meta-analysis
Hui Yu, Jinling Sun, Honglei Hu
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2024; 193(1): 199. CrossRef - Association of dietary inflammatory index with risk of gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Li Hong, Liyuan Zhu, Jinru Zhang, Yueqi Fu, Xiaoyan Qi, Mei Zhao
British Journal of Nutrition.2024; 131(1): 54. CrossRef - Ferritin and iron supplements in gestational diabetes mellitus: less or more?
Tianlian Li, Jingfan Zhang, Ping Li
European Journal of Nutrition.2024; 63(1): 67. CrossRef - Comparing the screening methods for gestational diabetes mellitus before and during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A systematic review
Xingge Sun, Clare McKeaveney, Helen Noble, Hannah O’Hara, Oliver Perra
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024; 15(4): 500. CrossRef - Protective Effects of Paeoniflorin Against Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rats with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus via Inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK Signaling Pathway
Cheng kun Yuan, Yan Gao, Jinglu Yu, Limin Peng
Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - METTL14‐mediated lncRNA XIST silencing alleviates GDM progression by facilitating trophoblast cell proliferation and migration via the miR‐497‐5p/FOXO1 axis
Yanchuan Li, Yanfeng Liu, Xiao Yao, Haili Wang, Ziyun Shi, Meiqing He
Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity in pregnant women: Application value of simple indices
Shuying Ren, Dan Wu, Ping Li
Clinica Chimica Acta.2024; 554: 117753. CrossRef - ATP5me alleviates high glucose-induced myocardial cell injury
Qingsha Hou, Fang Yan, Xiuling Li, Huanling Liu, Xiang Yang, Xudong Dong
International Immunopharmacology.2024; 129: 111626. CrossRef - Aberrant NK cell profile in gestational diabetes mellitus with fetal growth restriction
Yujing Xiong, Yazhen Wang, Mengqi Wu, Shuqiang Chen, Hui Lei, Hui Mu, Haikun Yu, Yongli Hou, Kang Tang, Xutao Chen, Jie Dong, Xiaohong Wang, Lihua Chen
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal Diabetes and Risk of Hypospadias: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
Zhiyuan Liu, Chengjun Yu, Shuhan Yang, Jin Luo, Jie Zhang, Xiao Wang, Chun Wei, Qinlin Shi, Yi Hua, Xing Liu, Guanghui Wei
Urologia Internationalis.2024; 108(2): 108. CrossRef - Maternal birth weight as an indicator of early and late gestational diabetes mellitus: The Japan Environment and Children's Study
Kazuma Tagami, Noriyuki Iwama, Hirotaka Hamada, Hasumi Tomita, Rie Kudo, Natsumi Kumagai, Hongxin Wang, Seiya Izumi, Zen Watanabe, Mami Ishikuro, Taku Obara, Nozomi Tatsuta, Hirohito Metoki, Chiharu Ota, Takashi Sugiyama, Shinichi Kuriyama, Takahiro Arima
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Perinatal characteristics and pregnancy outcomes of advanced maternal age women with gestational diabetes mellitus: A retrospective cohort study
Chen Jiang, Haiyan Wen, Tingting Hu, Yanfei Liu, Xiaoqing Dai, Yiming Chen
Health Science Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Phenotypic characterisation of regulatory T cells in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus
Ya-nan Zhang, Qin Wu, Yi-hui Deng
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Healthy behaviors and gestational diabetes mellitus in an Iranian setting: A cross-sectional study
Maryam Zare, Afrouz Mardi, Paria Yeghanenia, Daniel Hackett
Medicine.2024; 103(9): e36431. CrossRef - Post‐load glucose is a stronger predictor of adverse pregnancy outcomes than first‐trimester HbA1c in women without gestational diabetes
Shahin Keshtkar Rajabi, Elham Toghraee, Golnoosh Nejatipour
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index in early pregnancy predicts the risk of gestational diabetes: a prospective cohort study
Yufeng Guo, Junwen Lu, Mailiman Bahani, Guifeng Ding, Lei Wang, Yuxia Zhang, Huanmei Zhang, Chengyao Liu, Lijun Zhou, Xiaolan Liu, Fangshen Li, Xiaoli Wang, Hong Ding
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A study on behavior, diet patterns and physical activity among selected GDM and non-GDM women in south India
S Sindhu, S Uma Mageshwari
Journal of Diabetology.2024; 15(1): 86. CrossRef - The Implication of Diabetes-Specialized Nurses in Aiming for the Better Treatment and Management of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Brief Narrative Review
Yefang Zhu, Hongmei Zhang, Ying Xi, Hongli Zhu, Yan Lu, Xue Luo, Zhangui Tang, Hong Lei
Diabetes Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index: A promising biomarker for predicting risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes in Hangzhou, China
Jinghua Zhang, Binbin Yin, Ya Xi, Yongying Bai
Preventive Medicine Reports.2024; 41: 102683. CrossRef - Associations of education attainment with gestational diabetes mellitus and the mediating effects of obesity: A Mendelian randomization study
Xiaoyan Wang, Ying Lan, Na Li, Jinfeng Gao, Dejiao Meng, Shuchuan Miao
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e29000. CrossRef - Quality assessment of videos on social media platforms related to gestational diabetes mellitus in China: A cross-section study
Qin-Yu Cai, Jing Tang, Si-Zhe Meng, Yi Sun, Xia Lan, Tai-Hang Liu
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e29020. CrossRef - One abnormal value in oral glucose tolerance test during pregnancy and type 2 diabetes risk: Insights from a 5-Year Follow-Up study
Rawia Hussein-Aro, Esther Maor-Sagie, Yoel Toledano, Mordechai Hallak, Rinat Gabbay-Benziv
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 211: 111659. CrossRef - Assessment of the Level of Knowledge About Risk Factors, Prevention, and Treatment of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Community Sample From Saudi Arabia
Suzan A Morsy, Ayat M Tawfik, Samar Y Badayyan, Lameer K Shaikh, Shaden AzizKhan, AlKhansaa A Zakari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic Susceptibility, Mendelian Randomization, and Nomogram Model Construction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Qiulian Liang, Ming Li, Gongchen Huang, Ruiqi Li, Linyuan Qin, Ping Zhong, Xuekun Xing, Xiangyuan Yu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on the regulation of trophoblast activity by abnormally expressed hsa_circ_0024838/miR-543/HIF1A in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus
Qian Liu, Faminzi Li, Juan Gui, Lianzhi Wu
Placenta.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - U-shaped Association Between Folic Acid Supplementation and the Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women
Jiuming Zou, Qiang Fu, Xiaoliu Huang, Zhao Yao, Weiye Wang
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2023; 47(1): 78. CrossRef - Vitamin D Supplementation for the Outcomes of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Neonates: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
Chunfeng Wu, Yang Song, Xueying Wang, Pier P. Sainaghi
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Lipolysis and gestational diabetes mellitus onset: a case-cohort genome-wide association study in Chinese
Miao Zhang, Qing Li, Kai-Lin Wang, Yao Dong, Yu-Tong Mu, Yan-Min Cao, Jin Liu, Zi-Heng Li, Hui-Lu Cui, Hai-Yan Liu, An-Qun Hu, Ying-Jie Zheng
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Interactive effect of prepregnancy overweight/obesity and GDM history on prevalence of GDM in biparous women
Xia Xu, Feipeng Huang, Yanni Guo, Lianghui Zheng, Jianying Yan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Microbiome Changes in Pregnancy Disorders
Luca Giannella, Camilla Grelloni, Dayana Quintili, Alessia Fiorelli, Ramona Montironi, Sonila Alia, Giovanni Delli Carpini, Jacopo Di Giuseppe, Arianna Vignini, Andrea Ciavattini
Antioxidants.2023; 12(2): 463. CrossRef - Effects of early standardized management on the growth trajectory of offspring with gestational diabetes mellitus at 0–5 years old: a preliminary longitudinal study
Bingbing Guo, Jingjing Pei, Yin Xu, Yajie Wang, Xinye Jiang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus using the XG Boost machine learning algorithm
Xiaoqi Hu, Xiaolin Hu, Ya Yu, Jia Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus in Indian women: Insights from a large real-world study over ten years at tertiary care research institute
Sanjay Gupte, Gayatri Venkataraman, Aarti S. Shah, Shalaka Jamenis, Chandrakant Rao, Shweta M. Jangam, Kaveri M. Adki, Onkar C. Swami
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023; 43(4): 511. CrossRef - Gestational diabetes mellitus: state of art
S. A. Pletneva, E. V. Enkova, O. V. Khoperskaya, S. V. Shamarin, V. V. Enkova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; (5): 136. CrossRef - Effect of folic acid supplementation in the association between short sleep duration and gestational diabetes mellitus
Zhen Yang, Sisi Hu, Wei Tong, Zhihao Xu, Xiaoliu Huang, Weiye Wang
Sleep and Breathing.2023; 27(6): 2509. CrossRef - Birth weight and large for gestational age trends in offspring of pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus in southern China, 2012-2021
Li-Rong He, Li Yu, Yong Guo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Root causes of long-term complications of gestational diabetes mellitus: Metabolic disturbances of the host and gut microbiota
Mingjin Tao, Gaochen Lu, Sheng Zhang, Pan Li
Clinica Chimica Acta.2023; 548: 117490. CrossRef - Analysis on Related Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) in Subsequent Pregnancies in Multiparous Women with No History of GDM
文静 张
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(07): 11628. CrossRef - Fetoplacental endothelial dysfunction in gestational diabetes mellitus and maternal obesity: A potential threat for programming cardiovascular disease
Mariana S. Diniz, Ursula Hiden, Inês Falcão-Pires, Paulo J. Oliveira, Luis Sobrevia, Susana P. Pereira
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2023; 1869(8): 166834. CrossRef - Diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes mellitus
Tae Jung Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 414. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia in Children: Major Endocrine-Metabolic Causes and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives
Alessia Quarta, Daniela Iannucci, Miriana Guarino, Annalisa Blasetti, Francesco Chiarelli
Nutrients.2023; 15(16): 3544. CrossRef - Relation between weight gain during pregnancy and postpartum reclassification in gestational diabetes
Sofia Coelho, Marta Canha, Ana Rita Leite, João Sérgio Neves, Ana Isabel Oliveira, Davide Carvalho, Maria do Céu Ameida
Endocrine.2023; 82(2): 296. CrossRef - Nurturing through Nutrition: Exploring the Role of Antioxidants in Maternal Diet during Pregnancy to Mitigate Developmental Programming of Chronic Diseases
Mariana S. Diniz, Carina C. Magalhães, Carolina Tocantins, Luís F. Grilo, José Teixeira, Susana P. Pereira
Nutrients.2023; 15(21): 4623. CrossRef - Blood manganese level and gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yingmei Sun, Yu Zhang
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multiparity increases the risk of diabetes by impairing the proliferative capacity of pancreatic β cells
Joon Ho Moon, Joonyub Lee, Kyun Hoo Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Hyeongseok Kim, Hye-Na Cha, Jungsun Park, Hyeonkyu Lee, So-young Park, Hak Chul Jang, Hail Kim
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2023; 55(10): 2269. CrossRef - Physiological Mechanisms Inherent to Diabetes Involved in the Development of Dementia: Alzheimer’s Disease
Himan Mohamed-Mohamed, Victoria García-Morales, Encarnación María Sánchez Lara, Anabel González-Acedo, Teresa Pardo-Moreno, María Isabel Tovar-Gálvez, Lucía Melguizo-Rodríguez, Juan José Ramos-Rodríguez
Neurology International.2023; 15(4): 1253. CrossRef - Synergistic effect between pre-pregnancy smoking and assisted reproductive technology on gestational diabetes mellitus in twin pregnancies
Lingyu Zhang, Yan Huang, Mingjin Zhang, Yanqi Jin
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 61(2): 205. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Impacts on Maternal Health, Fetal Development, Childhood Outcomes, and Long-Term Treatment Strategies
Vaishnavi S Nakshine, Sangita D Jogdand
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of dietary fiber on preventing gestational diabetes mellitus in an at-risk group of high triglyceride-glucose index women: a randomized controlled trial
Yannan Cao, Jing Sheng, Dongyao Zhang, Li Chen, Ying Jiang, Decui Cheng, Yao Su, Yuexin Yu, Haoyi Jia, Pengyuan He, Li Wang, Xianming Xu
Endocrine.2023; 82(3): 542. CrossRef - Correlation between PAPP-A serum levels in the first trimester of pregnancy with the occurrence of gestational diabetes, a multicenter cohort study
Sedigheh Borna, Masoumeh Ashrafzadeh, Marjan Ghaemi, Nasim Eshraghi, Nafiseh Hivechi, Sedigheh Hantoushzadeh
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic levels during pregnancy: A retrospective analysis
Erika Di Zazzo, Sergio Davinelli, Serena Panichella, Giovanni Scapagnini, Mariano Intrieri, Silvio Garofalo
Open Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in Nutritional Strategies for Gestational Diabetes Management: A Systematic Review of Recent Evidence
Juan Carlos Sánchez-García, Ines Saraceno López-Palop, Beatriz Piqueras-Sola, Jonathan Cortés-Martín, Elena Mellado-García, Inmaculada Muñóz Sánchez, Raquel Rodríguez-Blanque
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(1): 37. CrossRef - Comparative efficacy and safety of glyburide, metformin, and insulin in treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus
Jing Lin, Rong-zu Tu, Xun-yu Hong
Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Stacking Ensemble Method for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prediction in Chinese Pregnant Women: A Prospective Cohort Study
Ruiyi Liu, Yongle Zhan, Xuan Liu, Yifang Zhang, Luting Gui, Yimin Qu, Hairong Nan, Yu Jiang, Mehdi Gheisari
Journal of Healthcare Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Secular increase in the prevalence of gestational diabetes and its associated adverse pregnancy outcomes from 2014 to 2021 in Hebei province, China
Mei-Ling Tian, Li-Yan Du, Guo-Juan Ma, Ting Zhang, Xu-Yuan Ma, Ying-Kui Zhang, Zeng-Jun Tang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Aquaporin-8 overexpression is involved in vascular structure and function changes in placentas of gestational diabetes mellitus patients
Yanxing Shan, Jiawen Cui, Xinyi Kang, Weichun Tang, Yiling Lu, Ying Gao, Liping Chen
Open Life Sciences.2022; 17(1): 1473. CrossRef - Vitamin D status and levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in newborns born to mothers with endocrine diseases
N. E. Verisokina, L. Ya. Klimov, I. N. Zakharova, A. L. Zaplatnikov, V. V. Zubkov, A. A. Momotova, V. A. Kuryaninova, R. A. Atanesyan, T. V. Zhelezniakova, M. A. Petrosyan, D. V. Bobryshev, D. A. Volkov, Z. A. Magomadova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (19): 9. CrossRef - IL-6 and IL-8: An Overview of Their Roles in Healthy and Pathological Pregnancies
Aleksandra Vilotić, Mirjana Nacka-Aleksić, Andrea Pirković, Žanka Bojić-Trbojević, Dragana Dekanski, Milica Jovanović Krivokuća
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(23): 14574. CrossRef - Higher Muscle Mass Protects Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus from Progression to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yujin Shin, Joon Ho Moon, Tae Jung Oh, Chang Ho Ahn, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 890. CrossRef - Identification of human placenta-derived circular RNAs and autophagy related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in gestational diabetes mellitus
Yindi Bao, Jun Zhang, Yi Liu, Lianzhi Wu, Jing Yang
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Dietary Polyphenols in Pregnancy and Pregnancy-Related Disorders
Mirjana Nacka-Aleksić, Andrea Pirković, Aleksandra Vilotić, Žanka Bojić-Trbojević, Milica Jovanović Krivokuća, Francesca Giampieri, Maurizio Battino, Dragana Dekanski
Nutrients.2022; 14(24): 5246. CrossRef
- Prophylactic administration of metformin reduces gestational diabetes mellitus incidence in the high-risk populations: a meta-analysis
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Influence of Pre-Pregnancy Underweight Body Mass Index on Fetal Abdominal Circumference, Estimated Weight, and Pregnancy Outcomes in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Minji Kim, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Suk-Joo Choi, Soo-Young Oh, Cheong-Rae Roh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):499-505. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0059

- 5,025 View
- 201 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This study aimed to determine the influence of pre-pregnancy body mass index on pregnancy outcomes in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), comparing underweight patients with GDM with normal weight patients with GDM. Maternal baseline characteristics, ultrasonographic results, and pregnancy and neonatal outcomes were reviewed in 946 women with GDM with singleton pregnancies. Underweight patients with GDM showed a benign course in most aspects during pregnancy, except for developing a higher risk of giving birth to small for gestational age neonates. Underweight women with GDM required less insulin treatment, had a higher rate of vaginal delivery, and had a lower rate of cesarean delivery. In addition, their neonates were more likely to have fetal abdominal circumference and estimated fetal weight below the 10th percentile both at the time of GDM diagnosis and before delivery. Notably, their risk for preeclampsia and macrosomia were lower. Collectively, our data suggest that underweight women with GDM may require a different approach in terms of diagnosis and management throughout their pregnancy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Challenges in the management of gestational diabetes mellitus in anorexia nervosa
Rija Siddiqui, Carrie J McAdams
Psychiatry Research Case Reports.2024; 3(1): 100215. CrossRef - Obesity Is Associated With Higher Risk of Adverse Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes Than Supervised Gestational Diabetes
Namju Seo, You Min Lee, Ye-jin Kim, Ji-hee Sung, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Suk-Joo Choi, Cheong-Rae Roh, Soo-young Oh
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal pre-pregnancy obesity modifies the association between first-trimester thyroid hormone sensitivity and gestational Diabetes Mellitus: a retrospective study from Northern China
Honglin Sun, Yibo Zhou, Jia Liu, Ying Wang, Guang Wang
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Challenges in the management of gestational diabetes mellitus in anorexia nervosa
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Glucose Effectiveness from Short Insulin-Modified IVGTT and Its Application to the Study of Women with Previous Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Micaela Morettini, Carlo Castriota, Christian Göbl, Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, Giovanni Pacini, Laura Burattini, Andrea Tura
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):286-294. Published online January 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0016
- 4,922 View
- 82 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study aimed to design a simple surrogate marker (i.e., predictor) of the minimal model glucose effectiveness (SG), namely calculated SG (CSG), from a short insulin-modified intravenous glucose tolerance test (IM-IVGTT), and then to apply it to study women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus (pGDM).
Methods CSG was designed using the stepwise model selection approach on a population of subjects (
n =181) ranging from normal tolerance to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). CSG was then tested on a population of women with pGDM (n =57). Each subject underwent a 3-hour IM-IVGTT; women with pGDM were observed early postpartum and after a follow-up period of up to 7 years and classified as progressors (PROG) or non-progressors (NONPROG) to T2DM. The minimal model analysis provided a reference SG.Results CSG was described as CSG=1.06×10−2+5.71×10−2×KG/Gpeak, KG being the mean slope (absolute value) of loge glucose in 10–25- and 25–50-minute intervals, and Gpeak being the maximum of the glucose curve. Good agreement between CSG and SG in the general population and in the pGDM group, both at baseline and follow-up (even in PROG and NONPROG subgroups), was shown by the Bland-Altman plots (<5% observations outside limits of agreement), and by the test for equivalence (equivalence margin not higher than one standard deviation). At baseline, the PROG subgroup showed significantly lower SG and CSG values compared to the NONPROG subgroup (
P <0.03).Conclusion CSG is a valid SG predictor. In the pGDM group, glucose effectiveness appeared to be impaired in women progressing to T2DM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 140. CrossRef - Unraveling the Factors Determining Development of Type 2 Diabetes in Women With a History of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Through Machine-Learning Techniques
Ludovica Ilari, Agnese Piersanti, Christian Göbl, Laura Burattini, Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, Andrea Tura, Micaela Morettini
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef
- Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Clinical Care/Education
- Pregnancy Outcomes of Women Additionally Diagnosed as Gestational Diabetes by the International Association of the Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Criteria
- Min Hyoung Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung-Hoon Kim, Joon Seok Hong, Hye Rim Chung, Sung Hee Choi, Moon Young Kim, Hak C. Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):766-775. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0192
- 5,967 View
- 89 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated the pregnancy outcomes in women who were diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) by the International Association of the Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups (IADPSG) criteria but not by the Carpenter-Coustan (CC) criteria.
Methods A total of 8,735 Korean pregnant women were identified at two hospitals between 2014 and 2016. Among them, 2,038 women participated in the prospective cohort to investigate pregnancy outcomes. Diagnosis of GDM was made via two-step approach with 50-g glucose challenge test for screening followed by diagnostic 2-hour 75-g oral glucose tolerance test. Women were divided into three groups: non-GDM, GDM diagnosed exclusively by the IADPSG criteria, and GDM diagnosed by the CC criteria.
Results The incidence of GDM was 2.1% according to the CC criteria, and 4.1% by the IADPSG criteria. Women diagnosed with GDM by the IADPSG criteria had a higher body mass index (22.0±3.1 kg/m2 vs. 21.0±2.8 kg/m2,
P <0.001) and an increased risk of preeclampsia (odds ratio [OR], 6.90; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.84 to 25.87;P =0.004) compared to non-GDM women. Compared to neonates of the non-GDM group, those of the IADPSG GDM group had an increased risk of being large for gestational age (OR, 2.39; 95% CI, 1.50 to 3.81;P <0.001), macrosomia (OR, 2.53; 95% CI, 1.26 to 5.10;P =0.009), and neonatal hypoglycemia (OR, 3.84; 95% CI, 1.01 to 14.74;P =0.049); they were also at an increased risk of requiring phototherapy (OR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.07 to 2.31;P =0.022) compared to the non-GDM group.Conclusion The IADPSG criteria increased the incidence of GDM by nearly three-fold, and women diagnosed with GDM by the IADPSG criteria had an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes in twin and singleton pregnancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Elena Greco, Maria Calanducci, Kypros H. Nicolaides, Eleanor V.H. Barry, Mohammed S.B. Huda, Stamatina Iliodromiti
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2024; 230(2): 213. CrossRef - Neonatal outcomes according to different glucose threshold values in gestational diabetes: a register-based study
Kaisa Kariniemi, Marja Vääräsmäki, Tuija Männistö, Sanna Mustaniemi, Eero Kajantie, Sanna Eteläinen, Elina Keikkala, Anneli Pouta, Risto Kaaja, Johan G Eriksson, Hannele Laivuori, Mika Gissler
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pregnancy complications in women with pregestational and gestational diabetes mellitus
Lukas Reitzle, Christin Heidemann, Jens Baumert, Matthias Kaltheuner, Heinke Adamczewski, Andrea Icks, Christa Scheidt-Nave
Deutsches Ärzteblatt international.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Seung-Hwan Lee, Jin Yu, Kyungdo Han, Seung Woo Lee, Sang Youn You, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 129. CrossRef - Treatment of women with mild gestational diabetes mellitus decreases the risk of adverse perinatal outcomes
Fanny Goyette, Bi Lan Wo, Marie-Hélène Iglesias, Evelyne Rey, Ariane Godbout
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101458. CrossRef - Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies associated with single versus double abnormal values in 100 gr glucose tolerance test
Mohammadali Shahriari, Ali Shahriari, Maryam Khooshideh, Anahita Dehghaninezhad, Arezoo Maleki-Hajiagha, Rana Karimi
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023; 22(2): 1347. CrossRef - Diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes mellitus
Tae Jung Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 414. CrossRef - Update on gestational diabetes and adverse pregnancy outcomes
Bryan Ugwudike, ManHo Kwok
Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology.2023; 35(5): 453. CrossRef - Effects of early standardized management on the growth trajectory of offspring with gestational diabetes mellitus at 0–5 years old: a preliminary longitudinal study
Bingbing Guo, Jingjing Pei, Yin Xu, Yajie Wang, Xinye Jiang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Can Triglyceride/Glucose Index (TyG) and Triglyceride/HDL-Cholesterol Ratio (TG/HDL-c) Predict Gestational Diabetes Mellitus?
Seval YILMAZ ERGANİ, Tolgay Tuyan İLHAN, Betül TOKGÖZ, Burak BAYRAKTAR, Mevlüt BUCAK, Müjde Can İBANOĞLU, Kadriye YAKUT YÜCEL, Kadriye ERDOĞAN, Cantekin İSKENDER, Yaprak ÜSTÜN
Ankara Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi Tıp Dergisi.2023; 56(2): 117. CrossRef - Risk factors for postpartum urinary incontinence: The impact of early-onset and late-onset Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a nested case-control study
Carlos I. Sartorão Filho, Fabiane A. Pinheiro, Luiz Takano, Caroline B. Prudêncio, Sthefanie K. Nunes, Hallur RLS, Iracema M.P. Calderon, Angélica M.P. Barbosa, Marilza V.C. Rudge
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2023; 290: 5. CrossRef - Review of the Screening Guidelines for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: How to Choose Wisely
Ravleen Kaur Bakshi, Akshay Kumar, Vandana Gupta, A.G. Radhika, Puneet Misra, Pankaj Bhardwaj
Indian Journal of Community Medicine.2023; 48(6): 828. CrossRef - Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 140. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Risk and Risk Factors for Postpartum Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Women with Gestational Diabetes: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
Mi Jin Choi, Jimi Choi, Chae Weon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 112. CrossRef - Gestational diabetes mellitus: current screening problems
N. I. Volkova, S. O. Panenko
Diabetes mellitus.2022; 25(1): 72. CrossRef - Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse pregnancy outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis
Wenrui Ye, Cong Luo, Jing Huang, Chenglong Li, Zhixiong Liu, Fangkun Liu
BMJ.2022; : e067946. CrossRef - Effect of Different Types of Diagnostic Criteria for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus on Adverse Neonatal Outcomes: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression
Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani, Marzieh Saei Ghare Naz, Razieh Bidhendi-Yarandi, Samira Behboudi-Gandevani
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 605. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Jung A Kim, Jinsil Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, You-Bin Lee, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108533. CrossRef - Effect of the IADPSG screening strategy for gestational diabetes on perinatal outcomes in Switzerland
Evelyne M. Aubry, Luigi Raio, Stephan Oelhafen
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 175: 108830. CrossRef - Estimated impact of introduction of new diagnostic criteria for gestational diabetes mellitus
Leon de Wit, Anna B Zijlmans, Doortje Rademaker, Christiana A Naaktgeboren, J Hans DeVries, Arie Franx, Rebecca C Painter, Bas B van Rijn
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(6): 868. CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef - Fetal Abdominal Obesity Detected At 24 to 28 Weeks of Gestation Persists Until Delivery Despite Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Wonjin Kim, Soo Kyung Park, Yoo Lee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 547. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the risk of insulin-requiring gestational diabetes
Sang Youn You, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hawn Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal Hyperglycemia during Pregnancy Increases Adiposity of Offspring
Hye Rim Chung, Joon Ho Moon, Jung Sub Lim, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Joon-Seok Hong, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 730. CrossRef - Prepregnancy smoking and the risk of gestational diabetes requiring insulin therapy
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Sang Youn You, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnosis and Glycemic Control
Tae Jung Oh, Hak Chul Jang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(2): 69. CrossRef - New Diagnostic Criteria for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Pregnancy Outcomes in Korea
Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 763. CrossRef
- Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes in twin and singleton pregnancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Progression to Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnant Women with One Abnormal Value in Repeated Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests
- Sunyoung Kang, Min Hyoung Kim, Moon Young Kim, Joon-Seok Hong, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak C. Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):607-614. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0159
- 5,884 View
- 103 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Women with one abnormal value (OAV) in a 100 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) during pregnancy are reported to have an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes. However, there is limited data about whether women with OAV will progress to gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) when the OGTT is repeated.
Methods To identify clinical and metabolic predictors for GDM in women with OAV, we conducted a retrospective study and identified women with OAV in the OGTT done at 24 to 30 weeks gestational age (GA) and repeated the second OGTT between 32 and 34 weeks of GA.
Results Among 137 women with OAV in the initial OGTT, 58 (42.3%) had normal, 40 (29.2%) had OAV and 39 (28.5%) had GDM in the second OGTT. Maternal age, prepregnancy body mass index, weight gain from prepregnancy to the second OGTT, GA at the time of the OGTT, and parity were similar among normal, OAV, and GDM groups. Plasma glucose levels in screening tests were different (151.8±15.7, 155.8±14.6, 162.5±20.3 mg/dL,
P <0.05), but fasting, 1-, 2-, and 3-hour glucose levels in the initial OGTT were not. Compared to women with screen negative, women with untreated OAV had a higher frequency of macrosomia.Conclusion We demonstrated that women with OAV in the initial OGTT significantly progressed to GDM in the second OGTT. Clinical parameters predicting progression to GDM were not found. Repeating the OGTT in women with OAV in the initial test may be helpful to detect GDM progression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies associated with single versus double abnormal values in 100 gr glucose tolerance test
Mohammadali Shahriari, Ali Shahriari, Maryam Khooshideh, Anahita Dehghaninezhad, Arezoo Maleki-Hajiagha, Rana Karimi
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023; 22(2): 1347. CrossRef - One abnormal value or vomiting after oral glucose tolerance test in pregnancy: incidence and impact on maternal-fetal outcomes
Humberto Navarro-Martinez, Juana-Antonia Flores-Le Roux, Gemma Llauradó, Lucia Gortazar, Antonio Payà, Laura Mañé, Juan Pedro-Botet, David Benaiges
Gynecological Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the gut microflora in women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Xuping Wang, Bingfeng Bian, Fuman Du, Chaofeng Xiang, Yu Liu, Na Li, Binhong Duan
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between gestational impaired glucose tolerance and hyperglycemic markers: A prospective study
Ohad Gluck, Hadas Ganer Herman, Nataly Fainstein, Neri Katz, Jacob Bar, Michal Kovo
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2022; 156(1): 82. CrossRef - Association of abnormal-glucose tolerance during pregnancy with exposure to PM2.5 components and sources
Dejian Mai, Chengfang Xu, Weiwei Lin, Dingli Yue, Shaojie Fu, Jianqing Lin, Luan Yuan, Yan Zhao, Yuhong Zhai, Huiying Mai, Xiaoling Zeng, Tingwu Jiang, Xuejiao Li, Jiajia Dai, Boning You, Qin Xiao, Qing Wei, Qiansheng Hu
Environmental Pollution.2022; 292: 118468. CrossRef - Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 140. CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnosis and Glycemic Control
Tae Jung Oh, Hak Chul Jang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(2): 69. CrossRef - Health literacy and diabetes control in pregnant women
Azar Pirdehghan, Mohammad Eslahchi, Farzaneh Esna-Ashari, Shiva Borzouei
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2020; 9(2): 1048. CrossRef
- Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies associated with single versus double abnormal values in 100 gr glucose tolerance test
- Epidemiology
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Testing Allows Better Prediction of Diabetes in Women with a History of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Tae Jung Oh, Yeong Gi Kim, Sunyoung Kang, Joon Ho Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak C. Jang, Joon-Seok Hong, Nam H. Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):342-349. Published online December 7, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0086
- 4,684 View
- 59 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We aimed to identify the postpartum metabolic factors that were associated with the development of diabetes in women with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). In addition, we examined the role of the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in the prediction of future diabetes.
Methods We conducted a prospective study of 179 subjects who previously had GDM but did not have diabetes at 2 months postpartum. The initial postpartum examination including a 75-g OGTT and the frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test (FSIVGTT) was performed 12 months after delivery, and annual follow-up visits were made thereafter.
Results The insulinogenic index (IGI30) obtained from the OGTT was significantly correlated with the acute insulin response to glucose (AIRg) obtained from the FSIVGTT. The disposition indices obtained from the OGTT and FSIVGTT were also significantly correlated. Women who progressed to diabetes had a lower insulin secretory capacity including IGI30, AIRg, and disposition indices obtained from the FSIVGTT and OGTT compared with those who did not. However, the insulin sensitivity indices obtained from the OGTT and FSIVGTT did not differ between the two groups. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the 2-hour glucose and disposition index obtained from the FSIVGTT were significant postpartum metabolic risk factors for the development of diabetes.
Conclusion We identified a crucial role of β-cell dysfunction in the development of diabetes in Korean women with previous GDM. The 2-hour glucose result from the OGTT is an independent predictor of future diabetes. Therefore, the OGTT is crucial for better prediction of future diabetes in Korean women with previous GDM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes mellitus
Tae Jung Oh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 414. CrossRef - Risk factors for women with gestational diabetes mellitus developing type 2 diabetes and the impact on children's health
Yi‐Ling Chiou, Chich‐Hsiu Hung, Ching‐Yun Yu, Te‐Fu Chan, Ming‐Gwo Liu
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2022; 31(7-8): 1005. CrossRef - Postprandial Free Fatty Acids at Mid-Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Large-for-Gestational-Age Newborns in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
So-Yeon Kim, Young Shin Song, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 140. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Higher Muscle Mass Protects Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus from Progression to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yujin Shin, Joon Ho Moon, Tae Jung Oh, Chang Ho Ahn, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 890. CrossRef - Pancreatic fat accumulation is associated with decreased β‐cell function and deterioration in glucose tolerance in Korean adults
Sang Ouk Chin, You‐Cheol Hwang, In‐Jin Cho, In‐Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef - Bihormonal dysregulation of insulin and glucagon contributes to glucose intolerance development at one year post-delivery in women with gestational diabetes: a prospective cohort study using an early postpartum 75-g glucose tolerance test
Riyoko Shigeno, Ichiro Horie, Masaki Miwa, Ayako Ito, Ai Haraguchi, Shoko Natsuda, Satoru Akazawa, Ai Nagata, Yuri Hasegawa, Shoko Miura, Kiyonori Miura, Atsushi Kawakami, Norio Abiru
Endocrine Journal.2021; 68(8): 919. CrossRef - Risk factors during the early postpartum period for type 2 diabetes mellitus in women with gestational diabetes
Maki Kawasaki, Naoko Arata, Naoko Sakamoto, Anna Osamura, Siori Sato, Yoshihiro Ogawa, Ichiro Yasuhi, Masako Waguri, Yuji Hiramatsu
Endocrine Journal.2020; 67(4): 427. CrossRef - Cod-Liver Oil Improves Metabolic Indices and hs-CRP Levels in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
Shuli Yang, Ruixin Lin, Lihui Si, Zhuo Li, Wenwen Jian, Qing Yu, Yan Jia
Journal of Diabetes Research.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef
- Diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes mellitus
- Epidemiology
- Predictors of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Japanese Americans with Normal Fasting Glucose Level
- You-Cheol Hwang, Wilfred Y. Fujimoto, Steven E. Kahn, Donna L. Leonetti, Edward J. Boyko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):198-206. Published online April 25, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0100
- 3,244 View
- 29 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Little is known about the natural course of normal fasting glucose (NFG) in Asians and the risk factors for future diabetes.
Methods A total of 370 Japanese Americans (163 men, 207 women) with NFG levels and no history of diabetes, aged 34 to 75 years, were enrolled. Oral glucose tolerance tests were performed at baseline, 2.5, 5, and 10 years after enrollment.
Results During 10 years of follow-up, 16.1% of participants met criteria for diabetes diagnosis, and 39.6% of subjects still had NFG levels at the time of diabetes diagnosis. During 5 years of follow-up, age (odds ratio [OR], 1.05; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 1.10;
P =0.026) and family history of diabetes (OR, 3.24; 95% CI, 1.42 to 7.40;P =0.005) were independently associated with future diabetes diagnosis; however, fasting glucose level was not an independent predictor. During 10 years of follow-up, family history of diabetes (OR, 2.76; 95% CI, 1.37 to 5.54;P =0.004), fasting insulin level (OR, 1.01; 95% CI, 1.00 to 1.02;P =0.037), and fasting glucose level (OR, 3.69; 95% CI, 1.13 to 12.01;P =0.030) were associated with diabetes diagnosis independent of conventional risk factors for diabetes.Conclusion A substantial number of subjects with NFG at baseline still remained in the NFG range at the time of diabetes diagnosis. A family history of diabetes and fasting insulin and glucose levels were associated with diabetes diagnosis during 10 years of follow-up; however, fasting glucose level was not associated with diabetes risk within the relatively short-term follow-up period of 5 years in subjects with NFG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- J-shape relationship between normal fasting plasma glucose and risk of type 2 diabetes in the general population: results from two cohort studies
Linfeng He, Wenbin Zheng, Zeyu Li, Lu Chen, Wen Kong, Tianshu Zeng
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fasting plasma glucose and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a group of Chinese people with normoglycemia and without obesity
Ziqiong Wang, Zheng Liu, Sen He
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(7): 601. CrossRef - Hidden Risks behind Normal Fasting Glucose: Is It Significant?
Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 196. CrossRef
- J-shape relationship between normal fasting plasma glucose and risk of type 2 diabetes in the general population: results from two cohort studies
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- The Effect of Regular Exercise on Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Kimberley L. Way, Daniel A. Hackett, Michael K. Baker, Nathan A. Johnson
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(4):253-271. Published online August 2, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.4.253
- 10,257 View
- 225 Download
- 113 Web of Science
- 110 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of regular exercise training on insulin sensitivity in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) using the pooled data available from randomised controlled trials. In addition, we sought to determine whether short-term periods of physical inactivity diminish the exercise-induced improvement in insulin sensitivity. Eligible trials included exercise interventions that involved ≥3 exercise sessions, and reported a dynamic measurement of insulin sensitivity. There was a significant pooled effect size (ES) for the effect of exercise on insulin sensitivity (ES, –0.588; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.816 to –0.359;
P <0.001). Of the 14 studies included for meta-analyses, nine studies reported the time of data collection from the last exercise bout. There was a significant improvement in insulin sensitivity in favour of exercise versus control between 48 and 72 hours after exercise (ES, –0.702; 95% CI, –1.392 to –0.012;P =0.046); and this persisted when insulin sensitivity was measured more than 72 hours after the last exercise session (ES, –0.890; 95% CI, –1.675 to –0.105;P =0.026). Regular exercise has a significant benefit on insulin sensitivity in adults with T2DM and this may persist beyond 72 hours after the last exercise session.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exercise Increasing Health-Related Quality of Life in Type 2 Diabetics: A Meta-Analysis
Sohrab Amiri, Mina Fathi-Ashtiani
Physical & Occupational Therapy In Geriatrics.2023; 41(3): 383. CrossRef - Early intervention and intensive management of patients with diabetes, cardiorenal, and metabolic diseases
Yehuda Handelsman, Javed Butler, George L. Bakris, Ralph A. DeFronzo, Gregg C. Fonarow, Jennifer B. Green, George Grunberger, James L. Januzzi, Samuel Klein, Pamela R. Kushner, Darren K. McGuire, Erin D. Michos, Javier Morales, Richard E. Pratley, Matthew
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(2): 108389. CrossRef - Frequency, intensity and duration of muscle strengthening activity and associations with mental health
Stephen Shannon, Mark Shevlin, Noel Brick, Gavin Breslin
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 325: 41. CrossRef - The effects of swimming exercise and detraining on hemorheological parameters and oxidative stress in rats with metabolic syndrome
Busra Emik-Ozdemir, Melek Tunc-Ata, Yasin Ozdemir, Ozgen Kilic-Erkek, Hande Senol, Vural Kucukatay, Melek Bor-Kucukatay
Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme.2023; 37(2): 94. CrossRef - Exercise and heart disease
Nick Gardner, Christopher Beck
InnovAiT: Education and inspiration for general practice.2023; 16(7): 337. CrossRef - Dietary weight loss-induced improvements in metabolic function are enhanced by exercise in people with obesity and prediabetes
Joseph W. Beals, Brandon D. Kayser, Gordon I. Smith, George G. Schweitzer, Kyleigh Kirbach, Monica L. Kearney, Jun Yoshino, Gibraan Rahman, Rob Knight, Bruce W. Patterson, Samuel Klein
Nature Metabolism.2023; 5(7): 1221. CrossRef - Investigating the Effect of Aerobic and Resistance Training on Insulin Resistance and Some Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Systematic Review
Peyman Kaikhosro Doulatyari, Mehran Ghahramani, Kosar Mozaffari
Journal of Clinical Research in Paramedical Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Recommendations from Diabetes UK's 2022 diabetes and physical activity workshop
Anna Morris, Chris Bright, Matthew Cocks, Neil Gibson, Louise Goff, Colin Greaves, Simon Griffin, Ben Jane, Florence Kinnafick, Paul Robb, Michelle Roberts, David Salman, John Saxton, Adrian Taylor, Daniel West, Thomas Yates, Rob C. Andrews, Jason M. R. G
Diabetic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Physical Exercise on Platelets: Focus on Its Effects in Metabolic Chronic Diseases
Cristina Barale, Elena Melchionda, Giulia Tempesta, Alessandro Morotti, Isabella Russo
Antioxidants.2023; 12(8): 1609. CrossRef - Exercise in the Management of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in Adults: A Position Statement from Exercise and Sport Science Australia
Shelley E. Keating, Angelo Sabag, Kate Hallsworth, Ingrid J. Hickman, Graeme A. Macdonald, Jonathan G. Stine, Jacob George, Nathan A. Johnson
Sports Medicine.2023; 53(12): 2347. CrossRef - Effects of Using the Bioelectrical Impedance Method in Nutritional Guidance for Diabetes
Naoko Nishizaka, Shinichirou Shiozawa, Kohzo Nakayama, Kenichi Hirose
The Japanese Journal of Nutrition and Dietetics.2023; 81(5): 228. CrossRef - Effects of moderate exercise versus light exercise on fasting blood glucose in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Manal Kamel Youssef
Physiotherapy Quarterly.2023; 31(3): 101. CrossRef - The Comparison of High-Intensity Interval Training and Moderate-intensity Continuous Training on Inflammatory and Metabolic Variables in Type 2 Diabetes: Study Protocol for A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Sahar Alizadeh, Nahid Mahdieh, Morteza Lotfi Khachak, Mohsen Avandi, Mehdi Hedayati, Camelia Rambod, Hooman Bakhshandeh
Research in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023; 12(4): 117. CrossRef - Acute exercise improves glucose effectiveness but not insulin sensitivity in paraplegia
Gary J. Farkas, Ann M. Swartz, Ashraf S. Gorgey, Arthur S. Berg, David R. Gater
Disability and Rehabilitation.2022; 44(17): 4656. CrossRef - Cultural validation and language translation of the scientific SCI exercise guidelines for use in Indonesia, Japan, Korea, and Thailand
Yukio Mikami, Damayanti Tinduh, KunHo Lee, Chayaporn Chotiyarnwong, Jan W. van der Scheer, Kyung Su Jung, Hiroshi Shinohara, Inggar Narasinta, Seung Hyun Yoon, Napatpaphan Kanjanapanang, Takafumi Sakai, Martha K. Kusumawardhani, Jinho Park, Pannika Prachg
The Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine.2022; 45(6): 821. CrossRef - Effect of Application of Treadmill Training on Metabolic Control and Vitamin D Level in Saudi Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ahmad El Askary, Alaa Shafie, Mazen Almehmadi, Hatem H. Allam, Lamiaa K. Elsayyad, Asmaa F. Hassan, Bader B. Althobaiti, Mohamed Mansour Khalifa, Tamer Saber, Aisha H. Alharthi, Amal F. Gharib, Deepika Koundal
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Skeletal Muscle Hyperemia: A Potential Bridge Between Post-exercise Hypotension and Glucose Regulation
Thomas K. Pellinger, Chi-An W. Emhoff
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise, Physical Activity, and Cardiometabolic Health
Matthew J. Belanger, Prashant Rao, Jeremy M. Robbins
Cardiology in Review.2022; 30(3): 134. CrossRef - Modeling the effects of physical activity, education, health, and subjective wealth on happiness based on Indonesian national survey data
Bhina Patria
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of time-restricted feeding with different feeding windows on metabolic health: A systematic review of human studies
Zhibo Xie, Zhangyuting He, Yuqian Ye, Yilei Mao
Nutrition.2022; 102: 111764. CrossRef - Effect of Exercise Instructions With Ambulatory Accelerometer in Japanese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: a Randomized Control Trial
Jin Matsushita, Hiroshi Okada, Yuki Okada, Takashi Sekiyama, Hideto Iida, Atsushi Shindo, Hiroaki Murata, Michiaki Fukui
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistance Exercise and Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus
Jin-Hwan Yoon
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(2): 97. CrossRef - Inside the diabetic brain: Insulin resistance and molecular mechanism associated with cognitive impairment and its possible therapeutic strategies
Bhaskar Jyoti Dutta, Shamsher Singh, Sanket Seksaria, Ghanshyam Das Gupta, Amrita Singh
Pharmacological Research.2022; 182: 106358. CrossRef - Endurance Training Improves GLP-1 Sensitivity and Glucose Tolerance in Overweight Women
Thorbjörn Åkerström, Malene N Stolpe, Renate Widmer, Thomas F Dejgaard, Jens M Højberg, Kirsten Møller, Jakob S Hansen, Beckey Trinh, Jens J Holst, Carsten Thomsen, Bente K Pedersen, Helga Ellingsgaard
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing related factors to fasting blood sugar and glycosylated hemoglobin in patients with type 2 diabetes simultaneously by a multivariate longitudinal marginal model
Samaneh Hosseinzadeh, Zahra Khatirnamani, Enayatollah Bakhshi, Alireza Heidari, Arash Naghipour
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adherence to aerobic and muscle-strengthening components of the physical activity guidelines and mental health
Stephen Shannon, Angela Carlin, Catherine Woods, Alan M Nevill, Niamh Murphy, Marie H Murphy
Health Promotion International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical activity interventions for glycaemic control in African adults – A systematic review and meta-analysis
Chythra R. Rao, Baskaran Chandrasekaran, N. Ravishankar, Elizeus Rutebemberwa, David Okello
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(12): 102663. CrossRef - The effect of acute aerobic exercise on central arterial stiffness, wave reflections, and hemodynamics in adults with diabetes: A randomized cross-over design
Kimberley L. Way, Angela S. Lee, Stephen M. Twigg, Nathan A. Johnson
Journal of Sport and Health Science.2021; 10(4): 499. CrossRef - Resistance training attenuates circulating FGF‐21 and myostatin and improves insulin resistance in elderly men with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomised controlled clinical trial
Fatemeh Shabkhiz, Mousa Khalafi, Sara Rosenkranz, Pouran Karimi, Kamilia Moghadami
European Journal of Sport Science.2021; 21(4): 636. CrossRef - The interaction between metformin and physical activity on postprandial glucose and glucose kinetics: a randomised, clinical trial
Nanna S. Pilmark, Mark Lyngbæk, Laura Oberholzer, Ida Elkjær, Christina Petersen-Bønding, Katja Kofoed, Christoph Siebenmann, Katja Kellenberger, Gerrit van Hall, Julie Abildgaard, Helga Ellingsgaard, Carsten Lauridsen, Mathias Ried-Larsen, Bente K. Peder
Diabetologia.2021; 64(2): 397. CrossRef - Effects of structured Aerobic Exercise on selected clinical profiles of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review with meta-analysis
NmachukwuIfeoma Ekechukwu, StellaUdumma Anwara, UkamakaGloria Mgbeojedo, OliveU Chijioke, OkechukwuSteven Onwukwe, UchechukwuAnthonia Ezugwu, EchezonaNelson Dominic Ekechukwu, IjeomaL Okoronkwo
International Journal of Medicine and Health Development.2021; 26(1): 17. CrossRef - Impact of acute exercise on immediate and following early post-exercise FGF-21 concentration in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis
Mousa Khalafi, Karim Azali Alamdari, Michael E. Symonds, Hadi Nobari, Jorge Carlos-Vivas
Hormones.2021; 20(1): 23. CrossRef - Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of cardiovascular diseases in people with type 2 diabetes and prediabetes: a consensus statement jointly from the Japanese Circulation Society and the Japan Diabetes Society
Eiichi Araki, Atsushi Tanaka, Nobuya Inagaki, Hiroshi Ito, Kohjiro Ueki, Toyoaki Murohara, Kenjiro Imai, Masataka Sata, Takehiro Sugiyama, Hideki Ishii, Shunsuke Yamane, Takashi Kadowaki, Issei Komuro, Koichi Node
Diabetology International.2021; 12(1): 1. CrossRef - In silico study to quantify the effect of exercise on surface GLUT4 translocation in diabetes management
Darshna M. Joshi, Jignesh Patel, Hardik Bhatt
Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Stair climbing–descending exercise following meals improves 24-hour glucose excursions in people with type 2 diabetes
Hiroto Honda, Makoto Igaki, Motoaki Komatsu, Shin-ichiro Tanaka, Tetsuo Takaishi, Tatsuya Hayashi
The Journal of Physical Fitness and Sports Medicine.2021; 10(1): 51. CrossRef - Glycemic Control of Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Referral Hospitals of Amhara Region, Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study
Berhanu Elfu Feleke, Teferi Elfu Feleke, Melkamu Beyene Kassahun, Wondemu Gebrekirose Adane, Netsanet Fentahun, Abel Girma, Alamirew Alebachew, Eyaya Misgan, Hanna Demelash Desyibelew, Mulat Tirfie Bayih, Omer Seid, Daniel Diaz
BioMed Research International.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Influences of Recreational Tennis-Playing Exercise Time on Cardiometabolic Health Parameters in Healthy Elderly: The ExAMIN AGE Study
Hsiao-Han Chao, Yi-Hung Liao, Chun-Chung Chou
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(3): 1255. CrossRef - Hyperinsulinemia Induced Altered Insulin Signaling Pathway in Muscle of High Fat- and Carbohydrate-Fed Rats: Effect of Exercise
Anu Joseph, S. Parvathy, Koyikkal Karthikeya Varma, Raffaella Mastrocola
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obese vs. Metabolic syndrome – The crosslink between nutritional exposure to bisphenols and physical exercise
Jessica Jones, Paul Reneau, Julia Matzenbacher dos Santos
Medical Hypotheses.2021; 149: 110542. CrossRef - The effects of different doses of exercise on pancreatic β-cell function in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: study protocol for and rationale behind the “DOSE-EX” multi-arm parallel-group randomised clinical trial
Mark P. P. Lyngbaek, Grit E. Legaard, Sebastian L. Bennetsen, Camilla S. Feineis, Villads Rasmussen, Nana Moegelberg, Cecilie F. Brinkløv, Anette B. Nielsen, Katja S. Kofoed, Carsten A. Lauridsen, Caroline Ewertsen, Henrik E. Poulsen, Robin Christensen, G
Trials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Skeletal Muscle–Adipose Tissue–Tumor Axis: Molecular Mechanisms Linking Exercise Training in Prostate Cancer
Sílvia Rocha-Rodrigues, Andreia Matos, José Afonso, Miguel Mendes-Ferreira, Eduardo Abade, Eduardo Teixeira, Bruno Silva, Eugenia Murawska-Ciałowicz, Maria José Oliveira, Ricardo Ribeiro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4469. CrossRef - Comparison between different types of exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network metanalysis of randomized controlled trials
Edoardo Mannucci, Allegra Bonifazi, Matteo Monami
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2021; 31(7): 1985. CrossRef - Effect of exercise on cardiometabolic health of adults with overweight or obesity: Focus on blood pressure, insulin resistance, and intrahepatic fat—A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Francesca Battista, Andrea Ermolao, Marleen A. van Baak, Kristine Beaulieu, John E. Blundell, Luca Busetto, Eliana V. Carraça, Jorge Encantado, Dror Dicker, Nathalie Farpour‐Lambert, Adriyan Pramono, Alice Bellicha, Jean‐Michel Oppert
Obesity Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Multi-Domain Intervention Trial in Older Adults With Diabetes Mellitus for Prevention of Dementia in Japan: Study Protocol for a Multi-Center, Randomized, 18-Month Controlled Trial
Taiki Sugimoto, Atsushi Araki, Hiroki Fujita, Keiko Honda, Nobuya Inagaki, Takeshi Ishida, Junichi Kato, Minoru Kishi, Kazuki Kobayashi, Kunichi Kouyama, Hisashi Noma, Mitsuru Ohishi, Noriko Satoh-Asahara, Hiroyuki Shimada, Kazuhiro Sugimoto, Susumu Suzuk
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Interactive effects of acute exercise and carbohydrate-energy replacement on insulin sensitivity in healthy adults
Drusus A. Johnson-Bonson, Benjamin J. Narang, Russell G. Davies, Aaron Hengist, Harry A. Smith, Jonathan D. Watkins, Harry Taylor, Jean-Philippe Walhin, Javier T. Gonzalez, James A. Betts
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2021; 46(10): 1207. CrossRef - The importance of physical activity in management of type 2 diabetes and COVID-19
Samuel Seidu, Kamlesh Khunti, Tom Yates, Abdullah Almaqhawi, M.J. Davies, Jack Sargeant
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 12: 204201882110546. CrossRef - Appraisal of Triglyceride-Related Markers as Early Predictors of Metabolic Outcomes in the PREVIEW Lifestyle Intervention: A Controlled Post-hoc Trial
Santiago Navas-Carretero, Rodrigo San-Cristobal, Pia Siig Vestentoft, Jennie C. Brand-Miller, Elli Jalo, Margriet Westerterp-Plantenga, Elizabeth J. Simpson, Teodora Handjieva-Darlenska, Gareth Stratton, Maija Huttunen-Lenz, Tony Lam, Roslyn Muirhead, Sal
Frontiers in Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Remission Following Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients With a Body Mass Index of 27.5–32.5 kg/m2
Ping Luo, Yaoquan Cao, Pengzhou Li, Guohui Wang, Zhi Song, Weizheng Li, Zhihong Su, Hui Zhou, Xianhao Yi, Zhibing Fu, Xulong Sun, Haibo Tang, Beibei Cui, Qianqian Yu, Liyong Zhu, Shaihong Zhu
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Metronidazole as an Adjunct to Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy on Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetics
Ambrina Qureshi, Zeba Haque, Hina Qureshi, Waqas Ahmed Farooqui
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1400. CrossRef - Exercise Training Combined with Calanus Oil Supplementation Improves the Central Cardiodynamic Function in Older Women
Marek Štěpán, Klára Daďová, Miloš Matouš, Eva Krauzová, Lenka Sontáková, Michal Koc, Terje Larsen, Ondrej Kuda, Vladimír Štich, Lenka Rossmeislová, Michaela Šiklová
Nutrients.2021; 14(1): 149. CrossRef - Effectiveness of combined exercise in people with type 2 diabetes and concurrent overweight/obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaoyan Zhao, Qianyu He, Yongmei Zeng, Li Cheng
BMJ Open.2021; 11(10): e046252. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes Remission and Lifestyle Medicine: A Position Statement From the American College of Lifestyle Medicine
John Kelly, Micaela Karlsen, Gregory Steinke
American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2020; 14(4): 406. CrossRef - Combined Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Training Reduces Circulating Apolipoprotein J Levels and Improves Insulin Resistance in Postmenopausal Diabetic Women
Yun Kyung Jeon, Sang Soo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Hyun Jeong Kim, Hyun Jun Kim, Jang Jun Park, Yuen Suk Cho, So Hee Joung, Ji Ryang Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Sang Heon Song, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Young-Bum Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 103. CrossRef - The effect of low-volume high-intensity interval training on cardiovascular health outcomes in type 2 diabetes: A randomised controlled trial
Kimberley L. Way, Angelo Sabag, Rachelle N. Sultana, Michael K. Baker, Shelley E. Keating, Sean Lanting, James Gerofi, Vivienne H. Chuter, Ian D. Caterson, Stephen M. Twigg, Nathan A. Johnson
International Journal of Cardiology.2020; 320: 148. CrossRef - Effects of IL-6 Signaling Pathway Inhibition on Weight and BMI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Olivia Patsalos, Bethan Dalton, Hubertus Himmerich
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(17): 6290. CrossRef - Non-Dietary Factors Associated with Glycemic Status among Adults Diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Malawi
Getrude Mphwanthe, Dave Weatherspoon, Alexander Kalimbira, Lorraine Weatherspoon
Social Work in Public Health.2020; 35(6): 380. CrossRef - The impact of high‐intensity interval training on inflammatory markers in metabolic disorders: A meta‐analysis
Mousa Khalafi, Michael E. Symonds
Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports.2020; 30(11): 2020. CrossRef - Effectiveness of martial arts exercise on anthropometric and body composition parameters of overweight and obese subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Fabricio de Souza, Felipe Nunes Lanzendorf, Márcia Mendonça Marcos de Souza, Fabiana Schuelter-Trevisol, Daisson José Trevisol
BMC Public Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal Human Functioning Requires Exercise Across the Lifespan: Mobility in a 1g Environment Is Intrinsic to the Integrity of Multiple Biological Systems
David A. Hart, Ronald F. Zernicke
Frontiers in Physiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Managing NAFLD in Type 2 Diabetes: The Effect of Lifestyle Interventions, a Narrative Review
Siôn A. Parry, Leanne Hodson
Advances in Therapy.2020; 37(4): 1381. CrossRef - Excess Accumulation of Lipid Impairs Insulin Sensitivity in Skeletal Muscle
Sung Sup Park, Young-Kyo Seo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(6): 1949. CrossRef - The Effect of Resistance Exercise Intensity on Acute Hyperglycemia in Young Adult Males
Evan E. Schick, Luis E. Segura, Shayán Emamjomeh, Joshua A. Cotter
Sports.2020; 8(9): 121. CrossRef - Drop-out ratio between moderate to high-intensity physical exercise treatment by patients with, or at risk of, type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Guillem Jabardo-Camprubí, Rafel Donat-Roca, Mercè Sitjà-Rabert, Raimon Milà-Villarroel, Judit Bort-Roig
Physiology & Behavior.2020; 215: 112786. CrossRef - Effects of an intensive lifestyle intervention on the underlying mechanisms of improved glycaemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a secondary analysis of a randomised clinical trial
Mette Y. Johansen, Kristian Karstoft, Christopher S. MacDonald, Katrine B. Hansen, Helga Ellingsgaard, Bolette Hartmann, Nicolai J. Wewer Albrechtsen, Allan A. Vaag, Jens J. Holst, Bente K. Pedersen, Mathias Ried-Larsen
Diabetologia.2020; 63(11): 2410. CrossRef - The effect of BPA exposure on insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes – The impact of muscle contraction
Madison Wade, Virginia Delawder, Paul Reneau, Julia M. dos Santos
Medical Hypotheses.2020; 140: 109675. CrossRef - Dynamic glucose disposal is driven by reduced endogenous glucose production in response to voluntary wheel running: a stable isotope approach
Timothy D. Allerton, Greg M. Kowalski, Hardy Hang, Jacqueline Stephens
American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 319(1): E2. CrossRef Antidiabetic Effects of Physical Activity: How It Helps to Control Type 2 Diabetes
Addisu Dabi Wake
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 2909. CrossRef- The effect of endurance training with crocin consumption on the levels of MFN2 and DRP1 gene expression and glucose and insulin indices in the muscle tissue of diabetic rats
Abdolnabi Peyravi, Nasrin Yazdanpanahi, Hashem Nayeri, Seyyed Ali Hosseini
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evidence for Training-Induced Changes in miRNA Levels in the Skeletal Muscle of Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sarah Simaitis, Benedikt Schulte-Körne, Thorsten Schiffer, Wilhelm Bloch, Hans-Georg Predel, Klara Brixius, Christian Brinkmann
Frontiers in Physiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic diseases affect male reproduction and induce signatures in gametes that may compromise the offspring health
Sara C Pereira, Luís Crisóstomo, Mário Sousa, Pedro F Oliveira, Marco G Alves, Caroline Burson
Environmental Epigenetics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Different mr-proANP-release in High Volume High Intensity Interval Exercise and Continuous Exercise Regimens with Matched Mean Intensity: A Cross-over Design Study
Julian Eigendorf
Exercise Medicine.2020; 4: 5. CrossRef - Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases in People With Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes ― A Consensus Statement Jointly From the Japanese Circulation Society and the Japan Diabetes Society ―
Eiichi Araki, Atsushi Tanaka, Nobuya Inagaki, Hiroshi Ito, Kohjiro Ueki, Toyoaki Murohara, Kenjiro Imai, Masataka Sata, Takehiro Sugiyama, Hideki Ishii, Shunsuke Yamane, Takashi Kadowaki, Issei Komuro, Koichi Node
Circulation Journal.2020; 85(1): 82. CrossRef - Aerobic training reduces immune cell recruitment and cytokine levels in adipose tissue in obese mice
Débora Romualdo Lacerda, Michele Macedo Moraes, Albená Nunes-Silva, Kátia Anunciação Costa, Débora Fernandes Rodrigues, Josiana Lopes Sabino, Letícia Maria de Souza Cordeiro, Vanessa Pinho, Mauro Martins Teixeira, Samuel Penna Wanner, Danusa Dias Soares,
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2019; 44(5): 512. CrossRef - Pharmacologic and Exercise Considerations in Older Adults With Diabetes
Susan L. Wenker, Denise L. Walbrandt Pigarelli
Topics in Geriatric Rehabilitation.2019; 35(1): 31. CrossRef - Human skeletal muscle macrophages increase following cycle training and are associated with adaptations that may facilitate growth
R. Grace Walton, Kate Kosmac, Jyothi Mula, Christopher S. Fry, Bailey D. Peck, Jason S. Groshong, Brian S. Finlin, Beibei Zhu, Philip A. Kern, Charlotte A. Peterson
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - An evidence‐based approach to developing low‐carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes management: A systematic review of interventions and methods
Jessica Turton, Grant D. Brinkworth, Rowena Field, Helen Parker, Kieron Rooney
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(11): 2513. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effect of insulin sensitivity-enhancing lifestyle- and dietary-related adjuncts on antidepressant treatment response: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Olaitan J. Jeremiah, Gráinne Cousins, Finbarr P. Leacy, Brian P. Kirby, Benedict K. Ryan
Systematic Reviews.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Exercise and Treatment with Liraglutide in Obese Rats by Cafeteria Diet
Daiane Didek, Maiara Mikuska Cordeiro, João Lucas de Paula Xavier, Paulo Roberto Ribeiro, Thiago Rentz, Gilson Cesar Nobre Franco, Carla Cristine Kanunfre, Henriette Rosa de Oliveira Emilio, Dionízia Xavier Scomparin
Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term moderate intensity exercise alleviates myocardial fibrosis in type 2 diabetic rats via inhibitions of oxidative stress and TGF-β1/Smad pathway
Shi-Qiang Wang, Dan Li, Yang Yuan
The Journal of Physiological Sciences.2019; 69(6): 861. CrossRef - Low-Intensity Running and High-Intensity Swimming Exercises Differentially Improve Energy Metabolism in Mice With Mild Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Léo Houdebine, Domenico D’Amico, Jean Bastin, Farah Chali, Céline Desseille, Valentin Rumeau, Judy Soukkari, Carole Oudot, Thaïs Rouquet, Bruno Bariohay, Julien Roux, Delphine Sapaly, Laure Weill, Philippe Lopes, Fatima Djouadi, Cynthia Bezier, Frédéric C
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Moderate-to-Vigorous-Intensity Physical Activity Observed in People With Diabetes-Related Foot Ulcers Over a One-Week Period
Maggie Lee, Jaap J. van Netten, Helen Sheahan, Peter A. Lazzarini
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2019; 13(5): 827. CrossRef - The effect of high Intensity interval training versus moderate intensity continuous training on arterial stiffness and 24 h blood pressure responses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kimberley L. Way, Rachelle N. Sultana, Angelo Sabag, Michael K. Baker, Nathan A. Johnson
Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport.2019; 22(4): 385. CrossRef - PPARG Pro12Ala Ala carriers exhibit greater improvements in peripheral insulin sensitivity in response to 12 weeks of aerobic exercise training
Martin Bæk Blond, Theresia Maria Schnurr, Mads Rosenkilde, Jonas Salling Quist, Anne Sofie Gram, Michala Holm Reichkendler, Pernille Landrock Auerbach, Pernille Nordby, Lene Theil Skovgaard, Rasmus Ribel-Madsen, Johanne Marie Justesen, Tuomas Oskari Kilpe
Physiological Genomics.2019; 51(6): 254. CrossRef - Physical Activity and Sports—Real Health Benefits: A Review with Insight into the Public Health of Sweden
Christer Malm, Johan Jakobsson, Andreas Isaksson
Sports.2019; 7(5): 127. CrossRef - Exercise and Inflammation
Llion Roberts, Katsuhiko Suzuki
Antioxidants.2019; 8(6): 155. CrossRef - Effects of a 12-week moderate-intensity exercise training on blood glucose response in patients with type 2 diabetes
Shang-Lin Chiang, Margaret McLean Heitkemper, Yi-Jen Hung, Wen-Chii Tzeng, Meei-Shyuan Lee, Chia-Huei Lin
Medicine.2019; 98(36): e16860. CrossRef - A influência do exercício físico na captação de glicose independente de insulina
Leonardo Soares de Albuquerque Barros, Camila da Cunha Nunes
HU Revista.2019; 45(1): 59. CrossRef - A pilot randomized controlled trial of 6-week combined exercise program on fasting insulin and fitness levels in individuals with spinal cord injury
Dong-Il Kim, J. Andrew Taylor, Can Ozan Tan, Hyuna Park, Ji Young Kim, Sang-Yong Park, Kyong-Mee Chung, Young-Hee Lee, Bum-Suk Lee, Justin Y. Jeon
European Spine Journal.2019; 28(5): 1082. CrossRef - Association between physical activity and diabetic complications among Bangladeshi type 2 diabetic patients
Mohammad Sadaat Bukht, Kazi Rumana Ahmed, Sahadat Hossain, Parisha Masud, Shuhana Sultana, Rasheda Khanam
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(1): 806. CrossRef - Exercise and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
A. Sampath Kumar, Arun G. Maiya, B.A. Shastry, K. Vaishali, N. Ravishankar, Animesh Hazari, Shubha Gundmi, Radhika Jadhav
Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine.2019; 62(2): 98. CrossRef - Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolomics reveals Huangqiliuyi decoction attenuates abnormal metabolism as a novel therapeutic opportunity for type 2 diabetes
Jiao Xu, Zhe-hui Jiang, Xiu-bo Liu, Yan Ma, Wei Ma, Ling Ma
RSC Advances.2019; 9(68): 39858. CrossRef - Importance of the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation-Indian Diabetes Risk Score (MDRF-IDRS) for mass screening of type 2 diabetes and its complications at primary health care centers of North India
Mohammad Mustufa Khan, Gyanendra Kumar Sonkar, Sangeeta Singh, Satyendra Kumar Sonkar
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2019; 39(3): 419. CrossRef - Sugar in mind: Untangling a sweet and sour relationship beyond type 2 diabetes
Nicolas Cherbuin, Erin I. Walsh
Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology.2019; 54: 100769. CrossRef - Aerobic exercise training may improve nerve function in type 2 diabetes and pre‐diabetes: A systematic review
Yu Gu, Sarah M. Dennis, Matthew C. Kiernan, Alison R. Harmer
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Air Pollution Has a Significant Negative Impact on Intentional Efforts to Lose Weight: A Global Scale Analysis
Morena Ustulin, So Young Park, Sang Ouk Chin, Suk Chon, Jeong-taek Woo, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(4): 320. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological Treatment Options in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus
Arkiath V Raveendran
European Endocrinology.2018; 14(2): 31. CrossRef - Adaptation of Skeletal Muscles to Contractile Activity of Varying Duration and Intensity: The Role of PGC-1α
D. V. Popov
Biochemistry (Moscow).2018; 83(6): 613. CrossRef - High-intensity interval training versus continuous training on physiological and metabolic variables in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis
Angélica Trevisan De Nardi, Tainara Tolves, Thatiane Larissa Lenzi, Luis Ulisses Signori, Antônio Marcos Vargas da Silva
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 137: 149. CrossRef - Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome, Objectively Measured Physical Activity and Exercise Training Interventions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monique Mendelson, Sébastien Bailly, Mathieu Marillier, Patrice Flore, Jean Christian Borel, Isabelle Vivodtzev, Stéphane Doutreleau, Samuel Verges, Renaud Tamisier, Jean-Louis Pépin
Frontiers in Neurology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Affective Adaptation to Repeated SIT and MICT Protocols in Insulin-Resistant Subjects
TIINA SAANIJOKI, LAURI NUMMENMAA, MIKKO KOIVUMÄKI, ELIISA LÖYTTYNIEMI, KARI K. KALLIOKOSKI, JARNA C. HANNUKAINEN
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise.2018; 50(1): 18. CrossRef - Aerobic training improves platelet function in type 2 diabetic patients: role of microRNA-130a and GPIIb
Atousa Akbarinia, Mehdi Kargarfard, Mahmood Naderi
Acta Diabetologica.2018; 55(9): 893. CrossRef - Physical activity: the key to cardiometabolic risk reduction in obstructive sleep apnoea
Monique Mendelson, Patrice Flore
European Respiratory Journal.2018; 52(4): 1801775. CrossRef - Potential effect of exercise in ameliorating insulin resistance at transcriptome level
Zhigang Hu, Lei Zhou, Tingting He
The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The influence of physical activity on risk of cardiovascular disease in people who are obese but metabolically healthy
Shinje Moon, Chang-Myung Oh, Moon-Ki Choi, Yoo-Kyung Park, Sukyung Chun, Minkyung Choi, Jae Myung Yu, Hyung Joon Yoo, Pedro Tauler
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(9): e0185127. CrossRef - Exercise Metabolism in Nonobese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Following the Acute Restoration of Normoglycaemia
Christopher J. Gaffney, Peter Mansell, Francis B. Stephens, Ian A. Macdonald, Kostas Tsintzas
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Glucose effectiveness, but not insulin sensitivity, is improved after short-term interval training in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a controlled, randomised, crossover trial
Kristian Karstoft, Margaret A. Clark, Ida Jakobsen, Sine H. Knudsen, Gerrit van Hall, Bente K. Pedersen, Thomas P. J. Solomon
Diabetologia.2017; 60(12): 2432. CrossRef - Protectin DX ameliorates palmitate- or high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and inflammation through an AMPK-PPARα-dependent pathway in mice
Tae Woo Jung, Hyoung-Chun Kim, A. M. Abd El-Aty, Ji Hoon Jeong
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Arginine and aerobic training prevent endothelial and metabolic alterations in rats at high risk for the development of the metabolic syndrome
Renata F. Medeiros, Thaiane G. Gaique, Thais Bento-Bernardes, Raquel Kindlovits, Tamiris M. B. Gomes, Nadia Alice V. Motta, Fernanda Carla Brito, Caroline Fernandes-Santos, Karen J. Oliveira, Antonio Claudio L. Nóbrega
British Journal of Nutrition.2017; 118(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Related Cognitive Impairment and Dementia
Michele Callisaya, Kazunori Nosaka
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2017; 59(2): 503. CrossRef - Study of Insulin Resistance in Women with Preeclampsia
Amit D Sonagra, Asmabi Makandar, Shivaleela M Biradar, Zahoorunissa Deba
Indian journal of Medical Biochemistry.2017; 21(2): 127. CrossRef
- Exercise Increasing Health-Related Quality of Life in Type 2 Diabetics: A Meta-Analysis
- Others
- Application of the Oral Minimal Model to Korean Subjects with Normal Glucose Tolerance and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Min Hyuk Lim, Tae Jung Oh, Karam Choi, Jung Chan Lee, Young Min Cho, Sungwan Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(4):308-317. Published online June 2, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.4.308
- 4,839 View
- 74 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The oral minimal model is a simple, useful tool for the assessment of β-cell function and insulin sensitivity across the spectrum of glucose tolerance, including normal glucose tolerance (NGT), prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in humans.
Methods Plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide levels were measured during a 180-minute, 75-g oral glucose tolerance test in 24 Korean subjects with NGT (
n =10) and T2DM (n =14). The parameters in the computational model were estimated, and the indexes for insulin sensitivity and β-cell function were compared between the NGT and T2DM groups.Results The insulin sensitivity index was lower in the T2DM group than the NGT group. The basal index of β-cell responsivity, basal hepatic insulin extraction ratio, and post-glucose challenge hepatic insulin extraction ratio were not different between the NGT and T2DM groups. The dynamic, static, and total β-cell responsivity indexes were significantly lower in the T2DM group than the NGT group. The dynamic, static, and total disposition indexes were also significantly lower in the T2DM group than the NGT group.
Conclusion The oral minimal model can be reproducibly applied to evaluate β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in Koreans.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fimasartan increases glucose‐stimulated insulin secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension compared with amlodipine
Ye Seul Yang, Min Hyuk Lim, Seong Ok Lee, Eun Roh, Chang Ho Ahn, Soo Heon Kwak, Young Min Cho, Sungwan Kim, Andrea Mari, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2018; 20(7): 1670. CrossRef - The Cut-off Values of Triglycerides and Glucose Index for Metabolic Syndrome in American and Korean Adolescents
Shinje Moon, Joon-Sung Park, Youhern Ahn
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2017; 32(3): 427. CrossRef
- Fimasartan increases glucose‐stimulated insulin secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension compared with amlodipine
- Clinical Care/Education
- Is an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Still Valid for Diagnosing Diabetes Mellitus?
- Dong-Lim Kim, Sun-Doo Kim, Suk Kyeong Kim, Sooyoun Park, Kee-Ho Song
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(2):118-128. Published online November 20, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.2.118
- 4,768 View
- 67 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We evaluated the diagnostic rate of diabetes using fasting plasma glucose (FPG), 2-hour plasma glucose (2h PG) after 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, and we elucidated the pathophysiologic characteristics and risk factors that give rise to diabetes in patients with prediabetes.
Methods The data of 236 patients who had the OGTT at Konkuk University Hospital were analyzed. Fasting, 30, and 120 minutes blood glucose levels and insulin levels were measured. The diagnostic rate of diabetes was assessed using FPG, 2h PG, and HbA1c levels. The clinical data and insulin resistance and secretion evaluations were compared using indexes according to the fasting glucose level.
Results Among 236 subjects, 97 (41.1%) were diabetics and 102 (43.2%) were prediabetics. The rate of diabetes diagnosis by one of the individual criteria was 56.7%, 53.6%, and 84.5% for FPG, HbA1c, and 2h PG, respectively. When two criteria were used to diagnose diabetes, 72.2% of the diabetic patients were identified by FPG and HbA1c, while 100% were identified by FPG and 2h PG, and 91.7% were identified by 2h PG and HbA1c. The HbA1c cut-off value for 2h PG ≥200 mg/dL was 6.1%, and the FPG cut-off value was 115 mg/dL. In impaired fasting glucose subjects, the HbA1c level, Matsuda index, and insulinogenic index were associated with risk of occurrence of overt diabetes (
P <0.01).Conclusion This study suggests that performing additional OGTT for patients with FPG ≥110 mg/dL or HbA1c ≥6.1% is helpful to reclassify their glucose tolerance status and evaluate their potential for progressing to overt diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of preprandial versus postprandial physical activity on glycaemia: Meta-analysis of human intervention studies
Romy Slebe, Eva Wenker, Linda J. Schoonmade, Emma J. Bouman, Denis P. Blondin, David J.T. Campbell, André C. Carpentier, Joris Hoeks, Parminder Raina, Patrick Schrauwen, Mireille J. Serlie, Dirk Jan Stenvers, Renée de Mutsert, Joline W.J. Beulens, Femke R
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111638. CrossRef - Dysglycaemia prediction using readily available clinical, anthropometric, and biochemical measurements
R. Guizar-Heredia, M. Guevara-Cruz, M. Aguilar-López, L.E. González-Salazar, I. Medina-Vera, L. Arteaga-Sánchez, E. Pichardo-Ontiveros, A.E. Serralde-Zúñiga, A. Diaz-Villaseñor, A. Ávila-Nava, N. Torres, A.R. Tovar
Clinical Nutrition Open Science.2024; 55: 91. CrossRef - Dichotomy in the Impact of Elevated Maternal Glucose Levels on Neonatal Epigenome
Ives Yubin Lim, Xinyi Lin, Ai Ling Teh, Yonghui Wu, Li Chen, Menglan He, Shiao-Yng Chan, Julia L MacIsaac, Jerry K Y Chan, Kok Hian Tan, Mary Foong Fong Chong, Michael S Kobor, Keith M Godfrey, Michael J Meaney, Yung Seng Lee, Johan G Eriksson, Peter D Gl
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(3): e1277. CrossRef - Imaging evaluation of the pancreas in diabetic patients
Ni Zeng, Yi Wang, Yue Cheng, Zixing Huang, Bin Song
Abdominal Radiology.2022; 47(2): 715. CrossRef - The Impact of Financial Incentives on Behavior and Self-Management of Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes: Pre- and Post-Quasiexperimental Study
Dalal Abdulaziz Al Kathiry, Fatima Al Slail, Khaled Al-Surimi, Raghib Abusaris
Global Journal on Quality and Safety in Healthcare.2021; 4(3): 88. CrossRef - Practice Patterns in the Acceptance of Medically Complex Living Kidney Donors with Obesity, Hypertension, Family History of Kidney Disease, or Donor-Recipient Age Discrepancy
Ziad Arabi, Muhammad Bukhari, Abdullah Hamad, Abdulrahman Altheaby, Saleh Kaysi
Avicenna Journal of Medicine.2021; 11(04): 172. CrossRef - Secretagogin is Related to Insulin Secretion but Unrelated to Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Status in Pregnancy
Carola Deischinger, Jürgen Harreiter, Karoline Leitner, Dagmar Bancher-Todesca, Sabina Baumgartner-Parzer, Alexandra Kautzky-Willer
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(7): 2277. CrossRef - Hypoglycemic activity of extracts of Chamaecyparis obtusa var. formosana leaf in rats with hyperglycemia induced by high-fat diets and streptozotocin
Chia-Yun Hsu, Gong-Min Lin, Shang-Tzen Chang
Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine.2020; 10(4): 389. CrossRef - Optimal fasting plasma glucose and haemoglobin A1c levels for screening of prediabetes and diabetes according to 2‐hour plasma glucose in a high‐risk population: The Korean Diabetes Prevention Study
Seon‐Ah Cha, Suk Chon, Jae‐Seung Yun, Sang Youl Rhee, Sun‐Young Lim, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Yu‐Bae Ahn, Seung‐Hyun Ko, Jeong‐Taek Woo, Jin‐Hee Lee
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction of type 2 diabetes mellitus using fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c levels among individuals with impaired fasting plasma glucose: a cross-sectional study in Thailand
Tullaya Sitasuwan, Raweewan Lertwattanarak
BMJ Open.2020; 10(11): e041269. CrossRef - The effect of oral glucose tolerance testing on changes in arterial stiffness and blood pressure in elderly women with hypertension and relationships between the stage of diabetes and physical fitness levels
Jaesong Lee, Wonil Park, Eunsook Sung, Bokbeom Kim, Nahyun Kim, Saejong Park, Chulho Shin, Jonghoon Park
Physical Activity and Nutrition.2020; 24(4): 34. CrossRef - From Pre-Diabetes to Diabetes: Diagnosis, Treatments and Translational Research
Radia Khan, Zoey Chua, Jia Tan, Yingying Yang, Zehuan Liao, Yan Zhao
Medicina.2019; 55(9): 546. CrossRef - Molecular imaging of β-cells: diabetes and beyond
Weijun Wei, Emily B. Ehlerding, Xiaoli Lan, Quan-Yong Luo, Weibo Cai
Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews.2019; 139: 16. CrossRef - HbA1c Cutoff for Prediabetes and Diabetes Based on Oral Glucose Tolerance Test in Obese Children and Adolescents
Hyo-Kyoung Nam, Won Kyoung Cho, Jae Hyun Kim, Young-Jun Rhie, Sochung Chung, Kee-Hyoung Lee, Byung-Kyu Suh
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of glucose metabolism disorders in coronary patients enrolled in cardiac rehabilitation: Is glycated haemoglobin useful? Data from the prospective REHABDIAB study
Sopio Tatulashvili, Bénédicte Patois-Vergès, Amandine Nguyen, Marie-Cécile Blonde, Bruno Vergès
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2018; 25(5): 464. CrossRef - Imaging in pancreatic disease
Julien Dimastromatteo, Teresa Brentnall, Kimberly A. Kelly
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2017; 14(2): 97. CrossRef
- The effect of preprandial versus postprandial physical activity on glycaemia: Meta-analysis of human intervention studies
- Effects of 6-Month Sitagliptin Treatment on Insulin and Glucagon Responses in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hae Kyung Yang, Borami Kang, Seung-Hwan Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Bong-Yun Cha, Jae-Hyoung Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(4):335-341. Published online July 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.4.335
- 3,684 View
- 35 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study aimed to evaluate the effect of sitagliptin, an oral dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, on insulin secretion and glucagon suppression in Korean subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods Twenty-four subjects underwent a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) before and after 6 months of sitagliptin treatment. Sitagliptin, insulin, and sulfonylurea were withdrawn for 3 days before OGTT to eliminate any acute effects on β-cell insulin or α-cell glucagon secretion. Venous samples were drawn five times during each OGTT to measure plasma glucose, insulin, and glucagon. Indices on insulin secretion and resistance were calculated.
Results Early phase insulin secretion, measured by the insulinogenic index significantly increased after 6 months of sitagliptin treatment, especially in the higher baseline body mass index group and higher baseline glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) group. There were no significant differences in the insulin resistance indices before and after sitagliptin treatment. Although no significant differences were observed in the absolute levels of glucagon and the glucagon-to-insulin ratio, there was a significant reduction in the percentile change of glucagon-to-insulin ratio at 30- and 120-minute during the OGTT.
Conclusion Although the HbA1c level did not decrease significantly after 6 months of sitagliptin treatment, an increase in insulin secretion and reduction in early phase postprandial plasma glucagon-to-insulin ratio excursion was confirmed in Korean subjects with type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A genetic variant in GLP1R is associated with response to DPP-4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes
Eugene Han, Hye Sun Park, Obin Kwon, Eun Yeong Choe, Hye Jin Wang, Yong-ho Lee, Sang-Hak Lee, Chul Hoon Kim, Lee-Kyung Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Chul Sik Kim, Eun Seok Kang
Medicine.2016; 95(44): e5155. CrossRef - Effects of sitagliptin on circulating zinc-α2-glycoprotein levels in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients: a randomized trial
Mingyuan Tian, Zerong Liang, Rui Liu, Ke Li, Xinrong Tan, Yong Luo, Mengliu Yang, Harvest F Gu, Hua Liu, Ling Li, Gangyi Yang
European Journal of Endocrinology.2016; 174(2): 147. CrossRef - Effects of Sitagliptin on Insulin and Glucagon Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ji Hyun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 304. CrossRef
- A genetic variant in GLP1R is associated with response to DPP-4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes
- The Insulin Resistance but Not the Insulin Secretion Parameters Have Changed in the Korean Population during the Last Decade
- Hae Kyung Yang, Jin Hee Lee, In-Young Choi, Hyuk Sang Kwon, Jeong Ah Shin, Seung Hee Jeong, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Ho Young Son, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(2):117-125. Published online April 20, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.2.117
- 4,553 View
- 46 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study aimed to compare the patterns of insulin secretion and resistance between Korean subjects in the 1990s and 2000s.
Methods Insulin secretion and resistance indices were calculated from subjects who underwent 75-g oral glucose tolerance tests in the year 1997 to 1999 and 2007 to 2011 at the Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Korea.
Results A total of 578 subjects from the 1990s (mean age, 48.5 years) and 504 subjects from the 2000s (mean age, 50.2 years) were enrolled. Compared with the subjects from the 1990s, those from the 2000s exhibited increased insulin resistance (increased homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance), and reduced insulin sensitivity (reduced Matsuda index and quantitative insulin sensitivity check index), regardless of their glucose tolerance status. However, insulinogenic index did not reveal significant differences between the 2 decades in subjects with or without diabetes. A distinct relationship was confirmed between Matsuda index and total area under the curve (insulin/glucose) in each glucose tolerance group. The mean product of the Matsuda index and the total area under the curve (insulin/glucose) as well as the oral disposition index, was lower in subjects with normal glucose tolerance from the 2000s than in those from the 1990s.
Conclusion After rapid economic growth and changes in lifestyle patterns, insulin resistance has worsened across the glucose tolerance status; however, the insulin secretory function remained unchanged, which resulted in an increase in the susceptibility to the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus among Korean subjects without diabetes. We could not rule out the potential selection bias and therefore, further studies in general Korean population are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Longitudinal Changes in Insulin Resistance, Beta-Cell Function and Glucose Regulation Status in Prediabetes
Chul-Hee Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Eun-Hee Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Jaewon Choe, Joong-Yeol Park
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2018; 355(1): 54. CrossRef - Association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and diabetes-related factors in Korean adults without diabetes: The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010–2012
Hyunah Kim, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Hun-Sung Kim
Primary Care Diabetes.2018; 12(1): 59. CrossRef - Long‐term effects on glycaemic control and β‐cell preservation of early intensive treatment in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A multicentre randomized trial
Suk Chon, Sang Youl Rhee, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Soon Jib Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Dae Ho Lee, Young Seol Kim, Jeong‐Taek Woo
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2018; 20(5): 1121. CrossRef - Four Plasma Glucose and Insulin Responses to a 75 g OGTT in Healthy Young Japanese Women
Kei Takahashi, Hidetaka Nakamura, Hiroshi Sato, Hideto Matsuda, Kazuo Takada, Tomiko Tsuji
Journal of Diabetes Research.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of insulin intensification strategies with insulin lispro low mixture twice daily versus basal insulin glargine and prandial insulin lispro once daily in East Asian and Caucasian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
In‐Kyung Jeong, Choon Hee Chung, Zhiguang Zhou, Jeong Hee Han, Ran Duan, Diana M. Edralin, Angel Rodriguez
Journal of Diabetes.2017; 9(4): 396. CrossRef - Insulin Secretory Capacity and Insulin Resistance in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Jong-Dai Kim, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 354. CrossRef - Antisenescence activity of G9a inhibitor BIX01294 on human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells
Min-Ji AHN, Sin-Gu JEONG, Goang-Won CHO
TURKISH JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY.2016; 40: 443. CrossRef - Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase, an early marker of diabetic kidney disease, might reflect glucose excursion in patients with type 2 diabetes
So Ra Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Sang-Guk Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Jeong-Ho Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Medicine.2016; 95(27): e4114. CrossRef
- Longitudinal Changes in Insulin Resistance, Beta-Cell Function and Glucose Regulation Status in Prediabetes
- Normal Glucose Tolerance with a High 1-Hour Postload Plasma Glucose Level Exhibits Decreased β-Cell Function Similar to Impaired Glucose Tolerance
- Tae Jung Oh, Se Hee Min, Chang Ho Ahn, Eun Ky Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(2):147-153. Published online March 9, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.2.147
- 4,104 View
- 43 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Subjects with normal glucose tolerance (NGT) who have a high 1-hour postload plasma glucose level (≥155 mg/dL; NGT 1 hour-high) have been shown to be at higher risk for type 2 diabetes than subjects with NGT 1 hour-low postload plasma glucose level (<155 mg/dL). We compared β-cell function in subjects with NGT 1 hour-high, NGT 1 hour-low, and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT).
Methods We classified subjects into NGT 1 hour-low (
n =149), NGT 1 hour-high (n =43), and IGT (n =52). The β-cell function was assessed based on insulinogenic index (IGI), oral disposition index (DI), and insulin secretion-sensitivity index-2 (ISSI-2).Results Insulin sensitivity was comparable between the subjects with NGT 1 hour-high and NGT 1 hour-low. The β-cell function with/without adjusting insulin sensitivity was significantly different among the three groups. The IGI (pmol/mmol) was 116.8±107.3 vs. 64.8±47.8 vs. 65.8±80.6 (
P =0.141), oral DI was 3.5±4.2 vs. 1.8±1.4 vs. 1.8±3.1 (P <0.001), and ISSI-2 was 301.2±113.7 vs. 213.2±67.3 vs. 172.5±87.5 (P <0.001) in NGT 1 hour-low, NGT 1 hour-high, and IGT, respectively.Post hoc analyses revealed that oral DI and ISSI-2 were significantly different between NGT 1 hour-low and NGT 1 hour-high but comparable between NGT 1 hour-high and IGT.Conclusion Among Korean subjects with NGT, those who have a higher 1-hour postload glucose level have a compromised insulin-sensitivity adjusted β-cell function to a similar degree as IGT subjects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Pancreatic fat accumulation is associated with decreased β‐cell function and deterioration in glucose tolerance in Korean adults
Sang Ouk Chin, You‐Cheol Hwang, In‐Jin Cho, In‐Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Indirect insulin resistance detection: Current clinical trends and laboratory limitations
Sylwia Placzkowska, Lilla Pawlik-Sobecka, Izabela Kokot, Agnieszka Piwowar
Biomedical Papers.2019; 163(3): 187. CrossRef - Clinical Implications of Using Post-Challenge Plasma Glucose Levels for Early Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Older Individuals
Kyong Hye Joung, Sang Hyun Ju, Ji Min Kim, Sorim Choung, Jae Min Lee, Kang Seo Park, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(2): 147. CrossRef - The 1-h post-load plasma glucose as a novel biomarker for diagnosing dysglycemia
Ram Jagannathan, Martin Buysschaert, José Luis Medina, Karin Katz, Sarah Musleh, Brenda Dorcely, Michael Bergman
Acta Diabetologica.2018; 55(6): 519. CrossRef - Elevated 1‐hour post‐load plasma glucose identifies obese youth with abnormal glucose metabolism and an unfavourable inflammatory profile
Anastasios Serbis, Vasileios Giapros, Anna Challa, Nikolaos Chaliasos, Ekaterini Siomou
Clinical Endocrinology.2018; 89(6): 757. CrossRef - One‐hour postload plasma glucose concentration in people with normal glucose homeostasis predicts future diabetes mellitus: a 12‐year community‐based cohort study
Tae Jung Oh, Soo Lim, Kyoung Min Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, HakChul Jang, Nam H. Cho
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 86(4): 513. CrossRef - An elevated 1-h post- load glucose level during the oral glucose tolerance test detects prediabetes
Martin Buysschaert, Michael Bergman, Donald Yanogo, Ram Jagannathan, Benoit Buysschaert, Vanessa Preumont
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2017; 11(2): 137. CrossRef - Delayed insulin secretion response during an OGTT is associated with an increased risk for incidence of diabetes in NGT subjects
Yun Sun, Junfeng Han, Ziwei Lin, Lige Song, Chen Wang, Weiping Jia
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(8): 1537. CrossRef - Postprandial Hyperglycemia
Tae Jung Oh
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(4): 233. CrossRef - β-Cell Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Normal Glucose-Tolerant Subjects Stratified by 1-Hour Plasma Glucose Values
Miranda M. Priya, Anandakumar Amutha, T.A. Pramodkumar, Harish Ranjani, Saravanan Jebarani, Kuppan Gokulakrishnan, Rajendra Pradeepa, Ranjit Unnikrishnan, Ranjit Mohan Anjana, Viswanathan Mohan
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2016; 18(1): 29. CrossRef - Response: Normal Glucose Tolerance with a High 1-Hour Postload Plasma Glucose Level Exhibits Decreased β-Cell Function Similar to Impaired Glucose Tolerance (Diabetes Metab J2015;39:147-53)
Tae Jung Oh, Se Hee Min, Chang Ho Ahn, Eun Ky Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(3): 270. CrossRef - Letter: Normal Glucose Tolerance with a High 1-Hour Postload Plasma Glucose Level Exhibits Decreased β-Cell Function Similar to Impaired Glucose Tolerance (Diabetes Metab J2015;39:147-53)
Hee Kyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(3): 268. CrossRef
- Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
- The Association of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with 30-Minute Post-Challenge Plasma Glucose Levels in Korean Adults with No History of Type 2 Diabetes
- Eun-Suk Choi, Eun-Jung Rhee, Ji-Hoon Choi, Ji-Cheol Bae, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Won-Jun Kim, Se-Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Yong-Kyun Cho, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Sun-Woo Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(5):287-293. Published online October 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.5.287
- 4,074 View
- 31 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Acute postprandial hyperglycemia is an important affector for atherosclerosis in subjects with glucose intolerance. We analyzed the relationship of brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) with fasting and post-challenge plasma glucose levels according to different time points during oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
Methods In 663 subjects with fasting hyperglycemia, 75 g OGTT were performed to confirm the glucose tolerant status, and fasting, post-challenge 30-minute and 120-minute glucose levels were measured. Anthropometric measurements were done, and fasting lipid profiles were measured. baPWV were measured in all subjects and the relationship between fasting, 30- and 120-minute post-challenge glucose levels and baPWV were analyzed.
Results Among the participants, 62.9% were prediabetes and 31.7% were diabetes. Mean baPWV value was significantly higher in subjects with diabetes compared with prediabetes group. In bivariate correlation analyses, age, blood pressure, total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein cholesterol, 30-minute and 120-minute post-challenge glucose levels showed significant positive correlation with baPWV value. In multiple regression analysis, 30-minute post-challenge glucose level was a weak but significant determinant for mean baPWV value even after adjustment for other confounding variables.
Conclusions Postprandial hyperglycemia, especially 30-minute glucose levels showed significant correlation with baPWV in subjects with fasting hyperglycemia. These results can imply the deleterious effect of acute hyperglycemic excursion on arterial stiffness in subjects with glucose intolerance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- One-Hour Post-Load Plasma Glucose Levels are Associated with Early Arterial Stiffness in Subjects with Different Glucose Tolerance
Rui Wang, Xiao-li Liu, Xiao-jiao Jia, Yan Liu, Qiang Lu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1537. CrossRef - The Temporal Pattern of Arterial Stiffness during Aging: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study
Zhengli Tang, Yuanyuan Lu, Yiming Hao, Robert Morris, Di Kang, Fang Wang, Lin Fan, Weijian Wang, Yiqin Wang, Feng Cheng, Gaetano Santulli
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Newly diagnosed abnormal glucose tolerance determines post-MI prognosis in patients with hospital related hyperglycaemia but without known diabetes
Sudipta Chattopadhyay, Anish George, Joseph John, Thozhukat Sathyapalan
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2020; 34(4): 107518. CrossRef - The effect of oral glucose tolerance testing on changes in arterial stiffness and blood pressure in elderly women with hypertension and relationships between the stage of diabetes and physical fitness levels
Jaesong Lee, Wonil Park, Eunsook Sung, Bokbeom Kim, Nahyun Kim, Saejong Park, Chulho Shin, Jonghoon Park
Physical Activity and Nutrition.2020; 24(4): 34. CrossRef - Two-hour post-challenge glucose is a better predictor of adverse outcome after myocardial infarction than fasting or admission glucose in patients without diabetes
Sudipta Chattopadhyay, Anish George, Joseph John, Thozhukat Sathyapalan
Acta Diabetologica.2018; 55(5): 449. CrossRef - Adjustment of the GRACE score by 2-hour post-load glucose improves prediction of long-term major adverse cardiac events in acute coronary syndrome in patients without known diabetes
Sudipta Chattopadhyay, Anish George, Joseph John, Thozhukat Sathyapalan
European Heart Journal.2018; 39(29): 2740. CrossRef - Investigating the Effect of Glucose on Aortic Pulse Wave Velocity Using Pancreatic Clamping Methodology
Houry Puzantian, Karen Teff, Raymond R. Townsend
Biological Research For Nursing.2015; 17(3): 270. CrossRef - Association between the Postprandial Glucose Levels and Arterial Stiffness Measured According to the Cardio-ankle Vascular Index in Non-diabetic Subjects
Atsuko Tsuboi, Chikako Ito, Rumi Fujikawa, Hideya Yamamoto, Yasuki Kihara
Internal Medicine.2015; 54(16): 1961. CrossRef - Insulin Sensitivity and Beta-Cell Function Are Associated with Arterial Stiffness in Individuals without Hypertension
Chuchen Meng, Min Sun, Zhixiao Wang, Qi Fu, Mengdie Cao, Zhenxin Zhu, Jia Mao, Yun Shi, Wei Tang, Xiaoping Huang, Yu Duan, Tao Yang
Journal of Diabetes Research.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Urinary adiponectin concentration is positively associated with micro- and macro-vascular complications
Won Seon Jeon, Ji Woo Park, Namseok Lee, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Won Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Woo Park, Cheol-Young Park, Byung-Soo Youn
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef
- One-Hour Post-Load Plasma Glucose Levels are Associated with Early Arterial Stiffness in Subjects with Different Glucose Tolerance
- Usefulness of Insulin Sensitivity Indexes derived from Oral Glucose Tolerance Test in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
- Hyo Jeong Kim, Eun Kyung Byun, Jee Young Oh, Yeon Ah Sung, Hye Won Chung
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(4):277-284. Published online July 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.4.277
- 2,019 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Insulin resistance is prevalent in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and it makes them to have high risk for development of type 2 diabetes. Evaluation of insulin sensitivity would be important to predict their risks. Although the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp technique is the gold standard for measuring insulin sensitivity, it is too hard to practice in large epidemiologic studies. The aim of this study is to verify the validity of various insulin sensitivity indexes from oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in women with PCOS. METHODS: We performed euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp (target glucose; 90 mg/dL, insulin ;~1 mU/kg.min) to obtain insulin-mediated glucose disposal rate (M-value) in 62 non-diabetic women with PCOS (BMI < 23 kg/m2; n = 37, BMI > or = 23 kg/m2; n = 25). Homeostasis model assessment [HOMA(IR)], quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI), glucose to insulin ratio (G/I ratio), whole body insulin sensitivity index [ISI(COMP)], metabolic clearance rate of glucose [MCR(est)-OGTT(1,2)], and insulin sensitivity indexes [ISI(est)-OGTT(1,2)] were calculated from plasma glucose and insulin levels from standard 75-g OGTT. The correlations of various insulin sensitivity indexes from OGTT with M-value were evaluated. RESULTS: In lean women with PCOS (BMI < 23 kg/m2, n = 37), ISI(COMP) (r = 0.36, P < 0.05), MCRest-OGTT1 (r = 0.49, P < 0.01), ISI(est)-OGTT(1) (r = 0.50, P < 0.01), MCR(est)-OGTT(2) (r = 0.45, P < 0.01) and ISI(est)-OGTT(2) (r = 0.40, P < 0.05) were significantly correlated with M-value. In overweight and obese women with PCOS (BMI > or = 23 kg/m2, n = 25), HOMA(IR) (r = -0.40, P < 0.05), QUICKI (r = 0.40, P < 0.05), MCR(est)-OGTT(1) (r = 0.76, P < 0.001), ISI(est)-OGTT(1) (r = 0.63, P < 0.001), MCR(est)-OGTT(2) (r = 0.58, P < 0.01) and ISI(est)-OGTT(2) (r = 0.42, P < 0.05) showed significant correlations with M-value. CONCLUSION: MCR(est)-OGTT(1) and ISI(est)-OGTT(1) were the most reliable and easily accessible insulin sensitivity indexes obtained from OGTT for measuring of insulin sensitivity in women with PCOS regardless of obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Insulin resistance in a large cohort of women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a comparison between euglycaemic-hyperinsulinaemic clamp and surrogate indexes
Flavia Tosi, Enzo Bonora, Paolo Moghetti
Human Reproduction.2017; 32(12): 2515. CrossRef
- Insulin resistance in a large cohort of women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a comparison between euglycaemic-hyperinsulinaemic clamp and surrogate indexes

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





