
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Complications
- Short-Term Walking Outcomes in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Unilateral Transtibial Amputees
- Dong Gyu Kwak, Jeong-Yong Hur, Jun Sung Moon, Min Cheol Chang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):614-618. Published online November 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0080
- 4,165 View
- 85 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
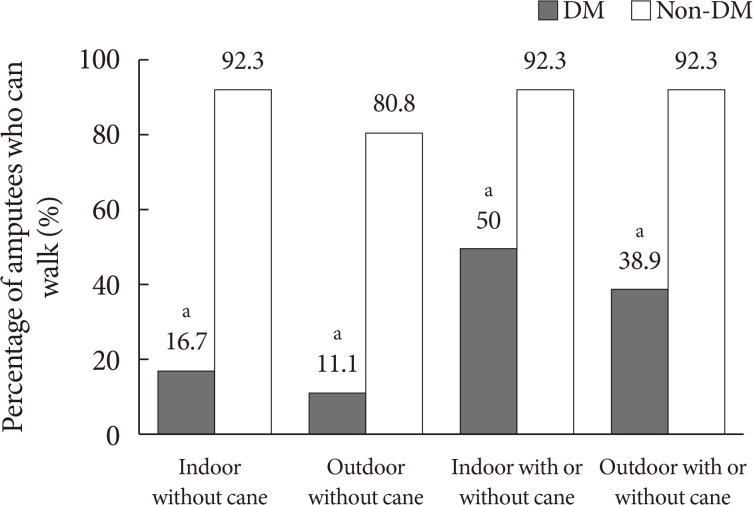
ePub This study compared short-term walking outcomes in diabetic amputees after prosthesis fitting compared to that in non-diabetic amputees. We retrospectively investigated walking outcomes at 3 months after starting gait training with a prosthesis. Forty-four unilateral transtibial amputees with (
n =18) and without diabetes (n =26) were included. At 3 months after gait training with a prosthesis, only 2/18 (11.1%) and 3/18 (16.7%) diabetic amputees were capable of independent outdoor and indoor walking without cane, respectively. However, 21/26 (80.8%) and 24/26 (92.3%) non-diabetic amputees were capable of independent outdoor and indoor walking without cane, respectively. With assistance of cane, most of non-diabetic amputees (n =24, 92.3%) were capable of walking in both outdoor and indoor but only seven (38.9%) and nine (50.0%) diabetic amputees were capable, respectively. Thus, short-term walking outcome were poor in transtibial amputee with diabetes compare to those without diabetes, and these results suggest intensive rehabilitation would be needed to them.
- Complications
- Single Sensor Gait Analysis to Detect Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Proof of Principle Study
- Patrick Esser, Johnny Collett, Kevin Maynard, Dax Steins, Angela Hillier, Jodie Buckingham, Garry D. Tan, Laurie King, Helen Dawes
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(1):82-86. Published online January 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.1.82
- 4,835 View
- 67 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader This study explored the potential utility of gait analysis using a single sensor unit (inertial measurement unit [IMU]) as a simple tool to detect peripheral neuropathy in people with diabetes. Seventeen people (14 men) aged 63±9 years (mean±SD) with diabetic peripheral neuropathy performed a 10-m walk test instrumented with an IMU on the lower back. Compared to a reference healthy control data set (matched by gender, age, and body mass index) both spatiotemporal and gait control variables were different between groups, with walking speed, step time, and SDa (gait control parameter) demonstrating good discriminatory power (receiver operating characteristic area under the curve >0.8). These results provide a proof of principle of this relatively simple approach which, when applied in clinical practice, can detect a signal from those with known diabetes peripheral neuropathy. The technology has the potential to be used both routinely in the clinic and for tele-health applications. Further research should focus on investigating its efficacy as an early indicator of or effectiveness of the management of peripheral neuropathy. This could support the development of interventions to prevent complications such as foot ulceration or Charcot's foot.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Wearable Movement Exploration Device with Machine Learning Algorithm for Screening and Tracking Diabetic Neuropathy—A Cross-Sectional, Diagnostic, Comparative Study
Goran Radunovic, Zoran Velickovic, Slavica Pavlov-Dolijanovic, Sasa Janjic, Biljana Stojic, Irena Jeftovic Velkova, Nikola Suljagic, Ivan Soldatovic
Biosensors.2024; 14(4): 166. CrossRef - Relationship between deep and superficial sensitivity assessments and gait analysis in diabetic foot patients
Mar Sempere‐Bigorra, Lorenzo Brognara, Iván Julian‐Rochina, Antonio Mazzotti, Omar Cauli
International Wound Journal.2023; 20(8): 3023. CrossRef - Intelligent Care Management for Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Scoping Review of Computer Vision and Machine Learning Techniques and Applications
Cynthia Baseman, Maya Fayfman, Marcos C. Schechter, Sarah Ostadabbas, Gabriel Santamarina, Thomas Ploetz, Rosa I. Arriaga
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Survey of the Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy Using Intelligent and Wearable Systems
Muhammad Talha, Maria Kyrarini, Ehsan Ali Buriro
Technologies.2023; 11(6): 163. CrossRef - Gait in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Systematic Review of the
Literature
Julie Soulard, Jacques Vaillant, Nicolas Vuillerme
Current Rheumatology Reviews.2022; 18(2): 117. CrossRef - Implants with Sensing Capabilities
Mladen Veletić, Ehsanul Hoque Apu, Mitar Simić, Jacob Bergsland, Ilangko Balasingham, Christopher H. Contag, Nureddin Ashammakhi
Chemical Reviews.2022; 122(21): 16329. CrossRef - Digital Biomarkers of Gait and Balance in Diabetic Foot, Measurable by Wearable Inertial Measurement Units: A Mini Review
Gu Eon Kang, Angeloh Stout, Ke’Vaughn Waldon, Seungmin Kang, Amanda L. Killeen, Peter A. Crisologo, Michael Siah, Daniel Jupiter, Bijan Najafi, Ashkan Vaziri, Lawrence A. Lavery
Sensors.2022; 22(23): 9278. CrossRef - A Wearable Gait Analysis System Used in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Case–Control Study
Tian Tian, Cheng Wang, Yuan Xu, Yuzhi Bai, Jing Wang, Zhou Long, Xiangdong Wang, Lichun Zhou
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 1799. CrossRef - Wearable Sensor for Assessing Gait and Postural Alterations in Patients with Diabetes: A Scoping Review
Lorenzo Brognara, Antonio Mazzotti, Alberto Di Martino, Cesare Faldini, Omar Cauli
Medicina.2021; 57(11): 1145. CrossRef - The Role of New Technological Opportunities and the Need to Evaluate the Activities Performed in the Prevention of Diabetic Foot with Exercise Therapy
Piergiorgio Francia, Alessandra De Bellis, Giulia Iannone, Rosy Sinopoli, Leonardo Bocchi, Roberto Anichini
Medicines.2021; 8(12): 76. CrossRef - Wearable Health Technology to Quantify the Functional Impact of Peripheral Neuropathy on Mobility in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review
Marta Francisca Corrà, Elke Warmerdam, Nuno Vila-Chã, Walter Maetzler, Luís Maia
Sensors.2020; 20(22): 6627. CrossRef - Functional Balance and Gait Characteristics in Men With Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Emad Al-Yahya, Maha T. Mohammad, Jennifer Muhaidat, Saddam Al Demour, Dania Qutishat, Lara Al-Khlaifat, Rasha Okasheh, Sophie Lawrie, Patrick Esser, Helen Dawes
American Journal of Men's Health.2019; 13(3): 155798831983987. CrossRef - Association between gait and cognition in an elderly population based sample
Vyara Valkanova, Patrick Esser, Naiara Demnitz, Claire E. Sexton, Enikő Zsoldos, Abda Mahmood, Ludovica Griffanti, Mika Kivimäki, Archana Singh-Manoux, Helen Dawes, Klaus P. Ebmeier
Gait & Posture.2018; 65: 240. CrossRef
- Wearable Movement Exploration Device with Machine Learning Algorithm for Screening and Tracking Diabetic Neuropathy—A Cross-Sectional, Diagnostic, Comparative Study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





