
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Complications
- Serum Levels of Adipocyte Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Are Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Preserved Renal Function
- Da Hea Seo, Moonsuk Nam, Mihye Jung, Young Ju Suh, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):875-886. Published online July 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0221
- 5,628 View
- 123 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Recent studies have demonstrated that the levels of adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein (A-FABP) are closely associated with diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study aimed to examine the association between serum A-FABP level and rapid renal function decline in patients with T2DM and preserved renal function.
Methods This was a prospective observational study of 452 patients with T2DM and preserved renal function who had serial measurements of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Rapid renal function decline was defined as an eGFR decline of >4% per year. The association between baseline serum A-FABP level and rapid renal function decline was investigated.
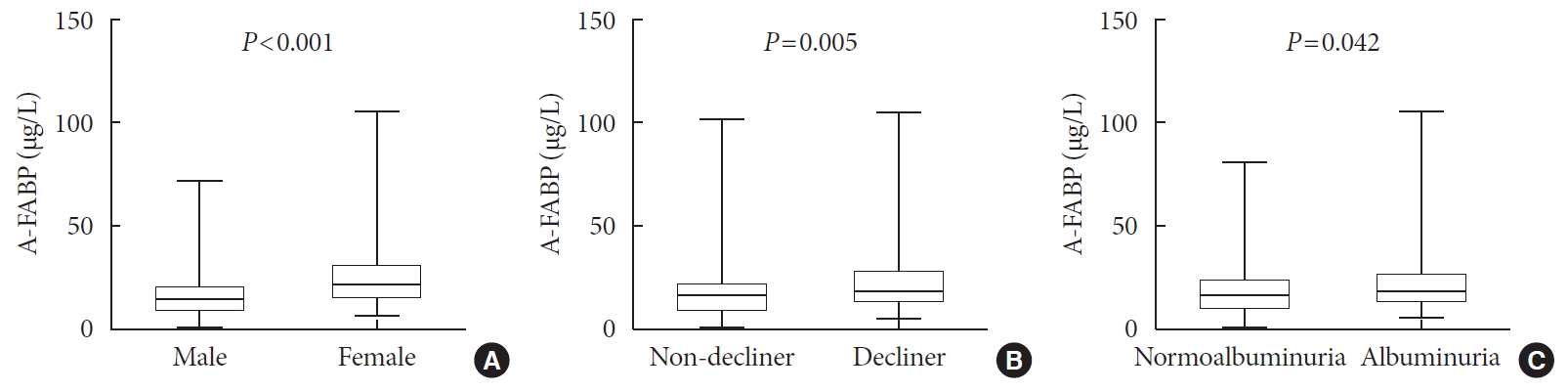
Results Over a median follow-up of 7 years, 82 participants (18.1%) experienced rapid renal function decline. Median A-FABP levels were significantly higher in patients with rapid renal function decline, compared to non-decliners (20.2 ng/mL vs. 17.2 ng/mL,
P =0.005). A higher baseline level of A-FABP was associated with a greater risk of developing rapid renal function decline, independent of age, sex, duration of diabetes, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, history of cardiovascular disease, baseline eGFR, urine albumin creatinine ratio, total cholesterol, glycosylated hemoglobin, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and use of thiazolidinedione, insulin, angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II-receptor blockers and statin (odds ratio, 3.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.53 to 6.29;P =0.002).Conclusion A high level of serum A-FABP is associated with an increased risk of rapid renal function decline in patients with T2DM and preserved renal function. This suggests that A-FABP could play a role in the progression of DKD in the early stages.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 as a biomarker for early detection of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes
Amr M. Shaker, Maggie E. Mohamed, Tarek Ramzy, Mayssa I. Ali
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Circulating thrombospondin-2 level for identifying individuals with rapidly declining kidney function trajectory in type 2 diabetes: a prospective study of the Hong Kong West Diabetes Registry
Chi-Ho Lee, David Tak-Wai Lui, Chloe Yu-Yan Cheung, Carol Ho-Yi Fong, Michele Mae-Ann Yuen, Wing-Sun Chow, Aimin Xu, Karen Siu-Ling Lam
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of inflammatory cytokines and estimated glomerular filtration rate decline in Japanese patients with diabetic kidney disease: a pilot study
Yuka Sugawara, Yosuke Hirakawa, Koki Mise, Kosuke Kashiwabara, Ko Hanai, Satoshi Yamaguchi, Akihiro Katayama, Yasuhiro Onishi, Yui Yoshida, Naoki Kashihara, Yutaka Matsuyama, Tetsuya Babazono, Masaomi Nangaku, Jun Wada
Biomarkers in Medicine.2022; 16(10): 759. CrossRef - The role of statins in patients with early diabetic nephropathy
Xi Zhao, Shu Chun Zhou, Xiu Fang Wang, Hong Wu Liao
Medicine.2022; 101(24): e29099. CrossRef - Serum Adipocyte Fatty-Acid Binding Protein as an Independent Marker of Peripheral Artery Disease in Patients with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Bang-Gee Hsu, Chin-Yee Mah, Du-An Wu, Ming-Chun Chen
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(15): 9459. CrossRef - Fatty acid-binding protein 4 in kidney diseases: From mechanisms to clinics
Weijing Lai, Min Shi, Rongshuang Huang, Ping Fu, Liang Ma
European Journal of Pharmacology.2022; 931: 175224. CrossRef - Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 levels and responses of pancreatic islet β-cells and α-cells in patients with type 2 diabetes
Hong Wang, Jie Cao, Jian-bin Su, Xue-qin Wang, Xing Wang, Dong-mei Zhang, Xiao-hua Wang
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Low-Expression Variant of FABP4 Is Associated With Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes
Emma H. Dahlström, Jani Saksi, Carol Forsblom, Nicoline Uglebjerg, Nina Mars, Lena M. Thorn, Valma Harjutsalo, Peter Rossing, Tarunveer S. Ahluwalia, Perttu J. Lindsberg, Niina Sandholm, Per-Henrik Groop
Diabetes.2021; 70(10): 2391. CrossRef - White adipocyte-targeted dual gene silencing of FABP4/5 for anti-obesity, anti-inflammation and reversal of insulin resistance: Efficacy and comparison of administration routes
Jee Young Chung, Juhyeong Hong, Hyung-Jin Kim, Yoonsung Song, Seok-Beom Yong, Jieun Lee, Yong-Hee Kim
Biomaterials.2021; 279: 121209. CrossRef
- Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 as a biomarker for early detection of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





